⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-17 更新
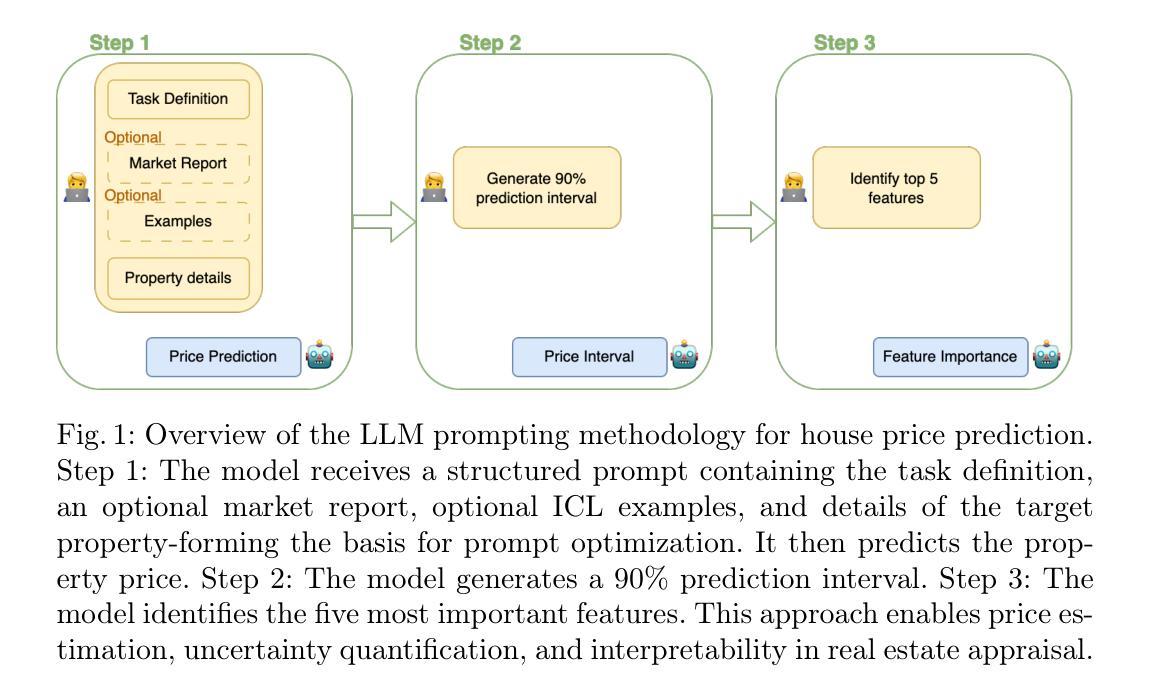
On the Performance of LLMs for Real Estate Appraisal
Authors:Margot Geerts, Manon Reusens, Bart Baesens, Seppe vanden Broucke, Jochen De Weerdt
The real estate market is vital to global economies but suffers from significant information asymmetry. This study examines how Large Language Models (LLMs) can democratize access to real estate insights by generating competitive and interpretable house price estimates through optimized In-Context Learning (ICL) strategies. We systematically evaluate leading LLMs on diverse international housing datasets, comparing zero-shot, few-shot, market report-enhanced, and hybrid prompting techniques. Our results show that LLMs effectively leverage hedonic variables, such as property size and amenities, to produce meaningful estimates. While traditional machine learning models remain strong for pure predictive accuracy, LLMs offer a more accessible, interactive and interpretable alternative. Although self-explanations require cautious interpretation, we find that LLMs explain their predictions in agreement with state-of-the-art models, confirming their trustworthiness. Carefully selected in-context examples based on feature similarity and geographic proximity, significantly enhance LLM performance, yet LLMs struggle with overconfidence in price intervals and limited spatial reasoning. We offer practical guidance for structured prediction tasks through prompt optimization. Our findings highlight LLMs’ potential to improve transparency in real estate appraisal and provide actionable insights for stakeholders.
房地产市场对全球经济至关重要,但却存在严重的信息不对称问题。本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)如何通过优化的上下文学习(ICL)策略,以民主化的方式获取房地产洞察力,生成具有竞争力和可解释性的房价估计。我们对国际住房数据集进行了系统的研究,对比了零样本、少样本、市场报告增强和混合提示技术等主流LLM。结果表明,LLM能够有效利用享乐变量(如物业大小和设施)来产生有意义的估计。虽然传统机器学习模型在纯粹的预测准确性方面仍然强大,但LLM提供了更易于访问、交互和可替代的方案。虽然自我解释需要谨慎解读,但我们发现LLM的解释与最先进的模型一致,证实了其可靠性。基于特征相似性和地理接近性的精心挑选的上下文实例,显著增强了LLM的性能,但LLM在价格区间过度自信以及有限的空间推理方面遇到了困难。我们通过提示优化为结构化预测任务提供了实际指导。我们的研究突出了LLM在改善房地产估价透明度和为利益相关者提供可操作洞察力方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECML-PKDD 2025
摘要
该研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)如何借助优化的上下文学习(ICL)策略,通过生成具有竞争力和可解释的房价估计来使房地产信息民主化。系统评估了领先LLM在国际住房数据集上的表现,比较了零样本、少样本、市场报告增强和混合提示技术。结果表明LLM能有效地利用享乐变量(如物业规模和设施)来产生有意义的估算。虽然传统机器学习模型在纯粹的预测准确性方面仍然强大,但LLM提供了更易于访问、交互和可替代的方案。虽然自我解释需要谨慎解读,但研究发现LLM的解释与最新模型一致,证实了其可靠性。基于特征相似性和地理邻近性的精心挑选的上下文实例显著增强了LLM的性能,但LLM在价格区间过于自信以及空间推理能力有限方面仍存在挑战。通过提示优化提供结构预测任务的实用指导。研究突出了LLM在提高房地产估价透明度和为利益相关者提供可操作洞察力方面的潜力。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在房地产市场具有潜力,可生成竞争性和可解释的房价估计。
- LLM能够通过优化上下文学习(ICL)策略来利用房地产数据中的享乐变量。
- LLM与传统机器学习模型相比,提供了更易于访问、交互和可解释的方案。
- LLM的自我解释与最新模型一致,表现出可靠性。
- 上下文实例的选择对LLM的性能有重要影响,尤其是基于特征相似性和地理邻近性。
- LLM在价格区间预测上可能过于自信,且空间推理能力有限。
- 通过提示优化,可以改善结构预测任务的实用指导,进一步发挥LLM在房地产市场的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

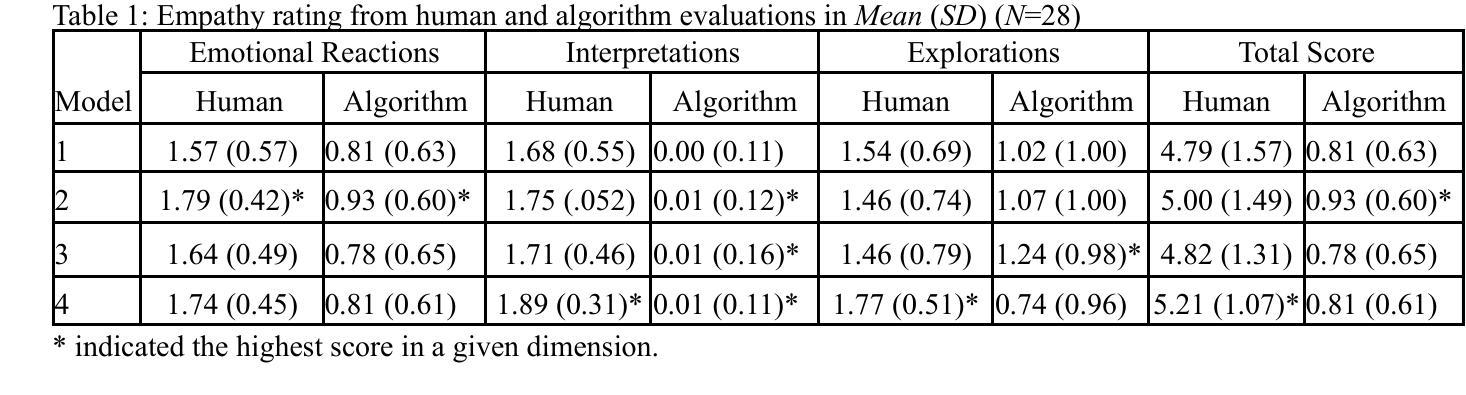
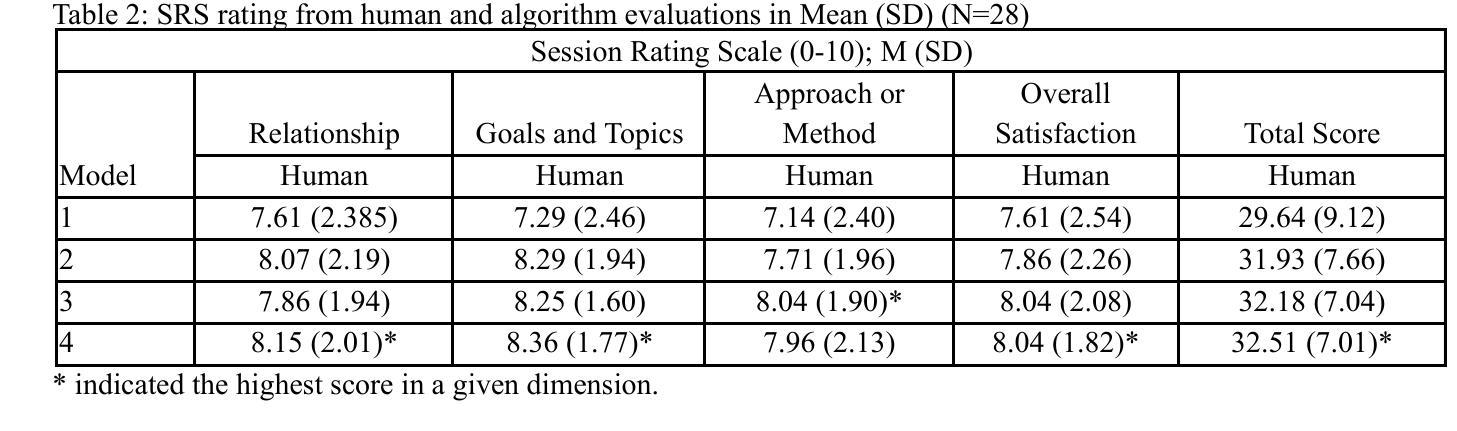
Large Language Model-Powered Conversational Agent Delivering Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) for Family Caregivers: Enhancing Empathy and Therapeutic Alliance Using In-Context Learning
Authors:Liying Wang, Ph. D., Daffodil Carrington, M. S., Daniil Filienko, M. S., Caroline El Jazmi, M. S., Serena Jinchen Xie, M. S., Martine De Cock, Ph. D., Sarah Iribarren, Ph. D., Weichao Yuwen, Ph. D
Family caregivers often face substantial mental health challenges due to their multifaceted roles and limited resources. This study explored the potential of a large language model (LLM)-powered conversational agent to deliver evidence-based mental health support for caregivers, specifically Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) integrated with Motivational Interviewing (MI) and Behavioral Chain Analysis (BCA). A within-subject experiment was conducted with 28 caregivers interacting with four LLM configurations to evaluate empathy and therapeutic alliance. The best-performing models incorporated Few-Shot and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) prompting techniques, alongside clinician-curated examples. The models showed improved contextual understanding and personalized support, as reflected by qualitative responses and quantitative ratings on perceived empathy and therapeutic alliances. Participants valued the model’s ability to validate emotions, explore unexpressed feelings, and provide actionable strategies. However, balancing thorough assessment with efficient advice delivery remains a challenge. This work highlights the potential of LLMs in delivering empathetic and tailored support for family caregivers.
家庭护理者在多重角色和有限资源的压力下,经常面临重大的心理健康挑战。本研究探索了大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的对话代理人为护理者提供基于证据的心理健康支持的潜力,特别是将问题解决疗法(PST)与动机面试(MI)和行为链分析(BCA)相结合。对28名护理者进行了一项主体内实验,他们与四种LLM配置进行交互,以评估同情心和治疗联盟。表现最佳的模型结合了“小样本”(Few-Shot)和基于检索的生成(RAG)提示技术,以及医生整理的例子。模型表现出提高的上下文理解和个性化支持,这反映在对同情心和治疗联盟的定性响应和定量评价上。参与者重视模型验证情感、探索未表达的感受和提供可行策略的能力。然而,在全面评估与有效提供建议之间取得平衡仍然是一个挑战。这项工作突出了LLM在为家庭护理者提供富有同情心和个性化的支持方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这项研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的对话代理人在为家庭照顾者提供基于证据的心理健康支持方面的潜力,特别是结合了问题解决疗法(PST)、动机面试(MI)和行为链分析(BCA)。一项针对28名家庭照顾者的实验表明,采用少样本技术和检索增强生成(RAG)提示技术的模型表现最佳,可以提供更好的情境理解和个性化支持。尽管评估与提供有效建议之间的平衡仍然是一个挑战,但这项工作突显了LLM在提供关怀家庭照顾者的同情和个性化支持方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 家庭照顾者在多重角色和资源限制下常面临重大心理健康挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)能为家庭照顾者提供心理健康支持。
- 研究采用了问题解决疗法(PST)、动机面试(MI)和行为链分析(BCA)的方法。
- 最佳模型结合了少样本技术和检索增强生成(RAG)提示技术。
- 模型展现了良好的情境理解和个性化支持能力,得到参与者的积极反馈。
- 模型能够验证情感、探索未表达的感受并提供可行策略,但仍需在全面评估与高效建议之间取得平衡。
点此查看论文截图

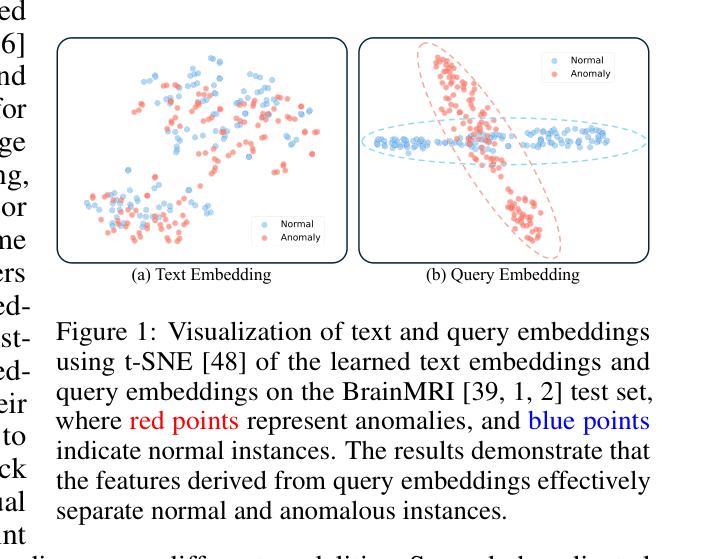
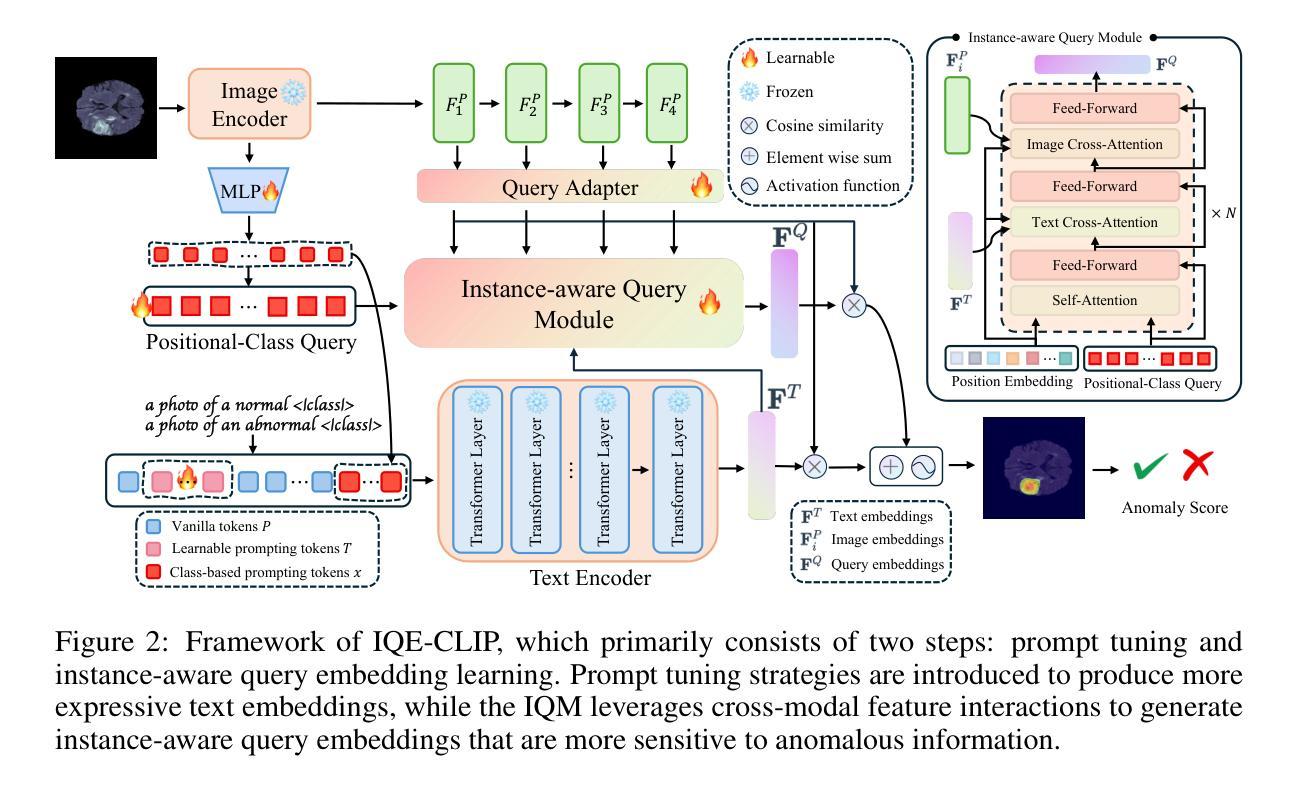
IQE-CLIP: Instance-aware Query Embedding for Zero-/Few-shot Anomaly Detection in Medical Domain
Authors:Hong Huang, Weixiang Sun, Zhijian Wu, Jingwen Niu, Donghuan Lu, Xian Wu, Yefeng Zheng
Recently, the rapid advancements of vision-language models, such as CLIP, leads to significant progress in zero-/few-shot anomaly detection (ZFSAD) tasks. However, most existing CLIP-based ZFSAD methods commonly assume prior knowledge of categories and rely on carefully crafted prompts tailored to specific scenarios. While such meticulously designed text prompts effectively capture semantic information in the textual space, they fall short of distinguishing normal and anomalous instances within the joint embedding space. Moreover, these ZFSAD methods are predominantly explored in industrial scenarios, with few efforts conducted to medical tasks. To this end, we propose an innovative framework for ZFSAD tasks in medical domain, denoted as IQE-CLIP. We reveal that query embeddings, which incorporate both textual and instance-aware visual information, are better indicators for abnormalities. Specifically, we first introduce class-based prompting tokens and learnable prompting tokens for better adaptation of CLIP to the medical domain. Then, we design an instance-aware query module (IQM) to extract region-level contextual information from both text prompts and visual features, enabling the generation of query embeddings that are more sensitive to anomalies. Extensive experiments conducted on six medical datasets demonstrate that IQE-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance on both zero-shot and few-shot tasks. We release our code and data at https://github.com/hongh0/IQE-CLIP/.
最近,视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的快速发展推动了零/少样本异常检测(ZFSAD)任务的显著进步。然而,大多数现有的基于CLIP的ZFSAD方法通常假设对类别的先验知识,并依赖于针对特定场景精心设计的提示。虽然这种精心设计文本提示可以有效地捕获文本空间中的语义信息,但它们在联合嵌入空间中区分正常和异常实例方面表现不足。此外,这些ZFSAD方法主要在工业场景中得到了探索,而在医学任务方面的努力很少。为此,我们针对医学领域的ZFSAD任务提出了一个创新框架,称为IQE-CLIP。我们发现,结合文本和实例感知视觉信息的查询嵌入是异常更好的指标。具体来说,我们首先引入基于类别的提示令牌和可学习的提示令牌,以更好地使CLIP适应医学领域。然后,我们设计了一个实例感知查询模块(IQM),从文本提示和视觉特征中提取区域级别的上下文信息,从而生成对异常更敏感查询嵌入。在六个医学数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,IQE-CLIP在零样本和少样本任务上都实现了最先进的性能。我们在https://github.com/hongh0/IQE-CLIP/上发布了我们的代码和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最近,视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的快速发展推动了零样本或少样本异常检测(ZFSAD)任务的重大进展。然而,大多数现有的基于CLIP的ZFSAD方法通常假设对类别的先验知识,并依赖于针对特定场景精心设计的提示。虽然这种精心设计文本提示可以有效地捕获文本空间中的语义信息,但它们在联合嵌入空间中区分正常和异常实例的能力有限。此外,这些ZFSAD方法主要在工业场景中探索,对医疗任务的研究很少。为此,我们提出了一种用于医疗领域ZFSAD任务的创新框架,称为IQE-CLIP。我们发现,结合文本和实例感知视觉信息的查询嵌入是更好的异常指标。具体来说,我们首先引入基于类别的提示令牌和可学习的提示令牌,以更好地将CLIP适应医疗领域。然后,我们设计了一个实例感知查询模块(IQM),从文本提示和视觉特征中提取区域级别的上下文信息,从而生成对异常更敏感的查询嵌入。在六个医疗数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,IQE-CLIP在零样本和少样本任务上均达到了最新性能。我们已将代码和数据发布在https://github.com/hongh0/IQE-CLIP/。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP等视觉语言模型的快速发展推动了ZFSAD任务在医疗领域的进步。
- 现有基于CLIP的ZFSAD方法依赖类别先验知识和针对特定场景的文本提示。
- 文本提示在联合嵌入空间中难以区分正常和异常实例。
- IQE-CLIP框架通过结合文本和实例感知视觉信息的查询嵌入来改进ZFSAD任务。
- IQE-CLIP引入基于类别的提示令牌和可学习的提示令牌,以适应医疗领域。
- 实例感知查询模块(IQM)能从文本提示和视觉特征中提取区域级别上下文信息。
点此查看论文截图

FrugalNeRF: Fast Convergence for Extreme Few-shot Novel View Synthesis without Learned Priors
Authors:Chin-Yang Lin, Chung-Ho Wu, Chang-Han Yeh, Shih-Han Yen, Cheng Sun, Yu-Lun Liu
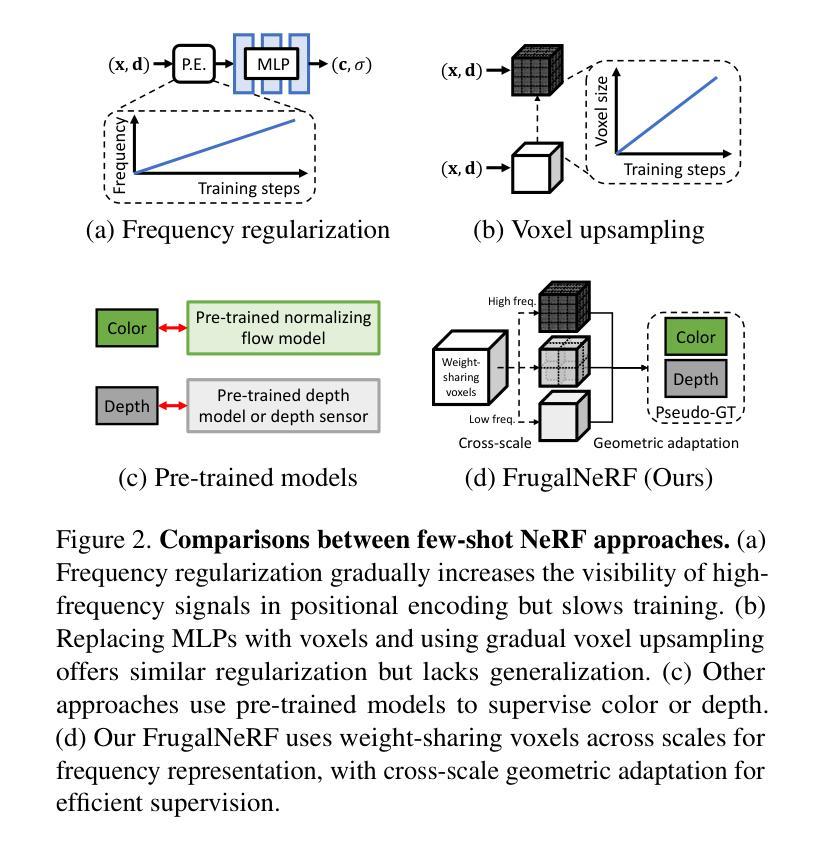
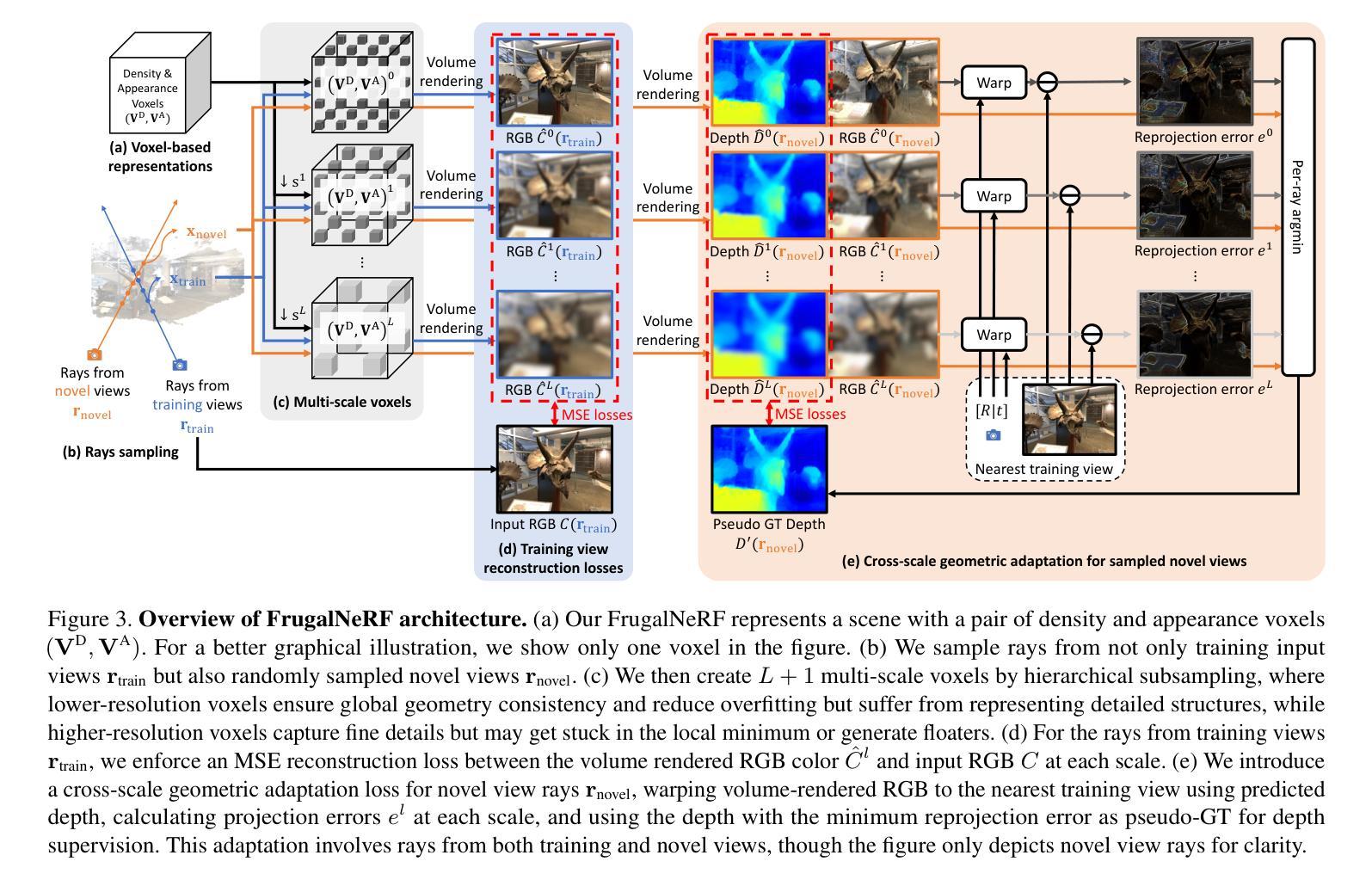
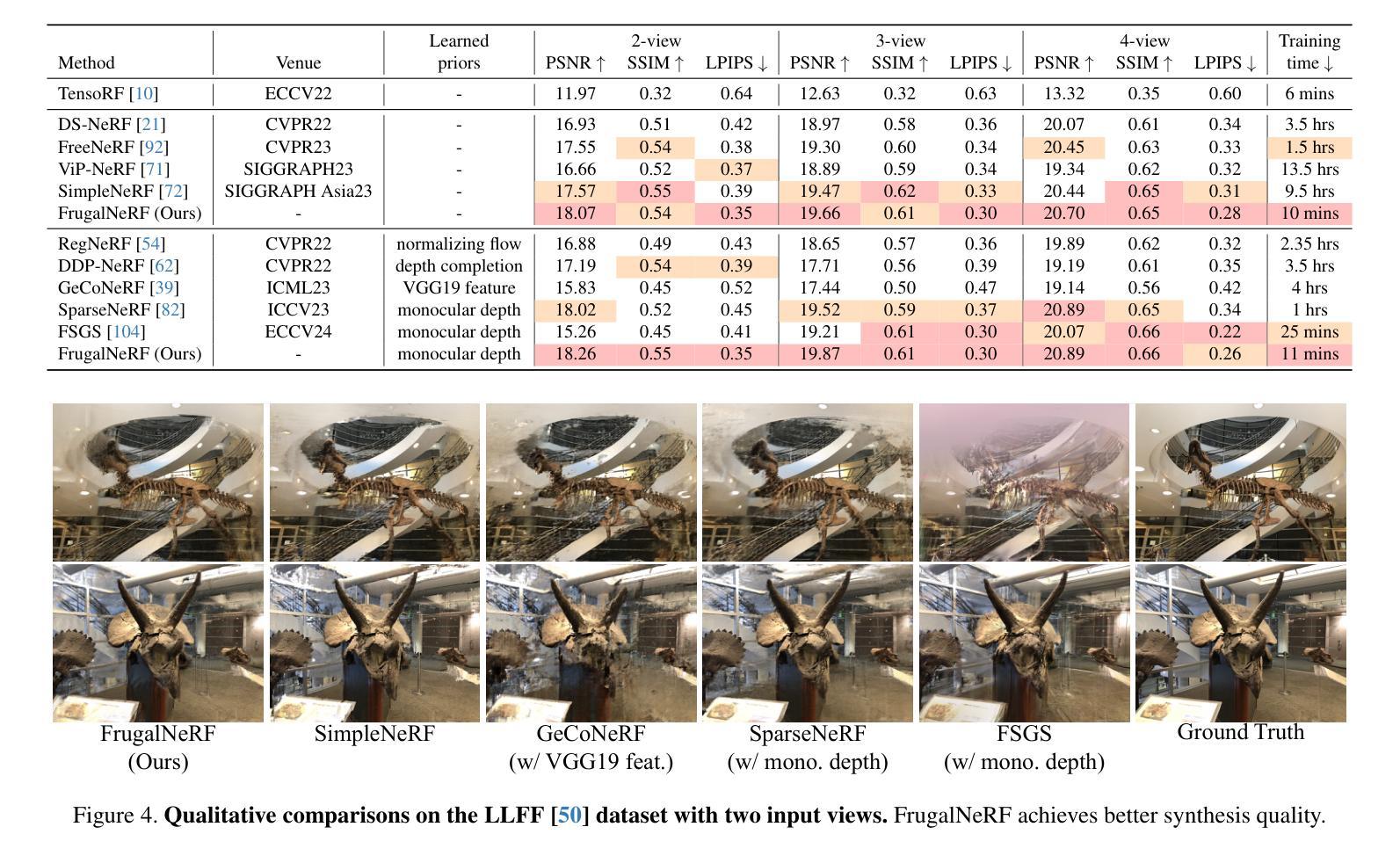
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) face significant challenges in extreme few-shot scenarios, primarily due to overfitting and long training times. Existing methods, such as FreeNeRF and SparseNeRF, use frequency regularization or pre-trained priors but struggle with complex scheduling and bias. We introduce FrugalNeRF, a novel few-shot NeRF framework that leverages weight-sharing voxels across multiple scales to efficiently represent scene details. Our key contribution is a cross-scale geometric adaptation scheme that selects pseudo ground truth depth based on reprojection errors across scales. This guides training without relying on externally learned priors, enabling full utilization of the training data. It can also integrate pre-trained priors, enhancing quality without slowing convergence. Experiments on LLFF, DTU, and RealEstate-10K show that FrugalNeRF outperforms other few-shot NeRF methods while significantly reducing training time, making it a practical solution for efficient and accurate 3D scene reconstruction.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在极端小样本场景中面临重大挑战,主要是由于过拟合和训练时间过长。现有方法,如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF,使用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂的调度和偏见问题。我们引入了FrugalNeRF,一种新型的少样本NeRF框架,它通过跨多个尺度的权重共享体素有效地表示场景细节。我们的主要贡献是一种跨尺度几何自适应方案,该方案根据跨尺度的重投影误差选择伪地面真实深度。这可以在不依赖外部学习先验的情况下指导训练,使训练数据得到充分利用。它还可以集成预训练的先验知识,提高质量而不会减慢收敛速度。在LLFF、DTU和RealEstate-10K上的实验表明,FrugalNeRF在其他少样本NeRF方法中表现突出,同时显著减少了训练时间,成为高效和准确3D场景重建的实际解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to CVPR 2025. Project page: https://linjohnss.github.io/frugalnerf/
Summary
NeRF在极端小样本场景下存在过拟合和训练时间长的问题。现有方法如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF虽采用频率正则化或预训练先验,但面临复杂调度和偏差问题。本文提出FrugalNeRF,一种基于跨尺度几何适应方案的新型小样本NeRF框架,通过权重共享体素表示场景细节。它选择基于跨尺度重投影误差的伪地面真实深度,无需依赖外部学习先验即可指导训练,充分利用训练数据。实验表明,FrugalNeRF在LLFF、DTU和RealEstate-10K数据集上优于其他小样本NeRF方法,并显著减少训练时间,为高效准确的3D场景重建提供实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在极端小样本场景面临过拟合和训练时间长的问题。
- 现有方法如FreeNeRF和SparseNeRF使用频率正则化或预训练先验,但存在复杂调度和偏差问题。
- FrugalNeRF是一种新型小样本NeRF框架,通过权重共享体素和跨尺度几何适应方案表示场景细节。
- FrugalNeRF选择伪地面真实深度,基于跨尺度重投影误差指导训练,不依赖外部学习先验。
- FrugalNeRF能整合预训练先验,提高质量且不影响收敛速度。
- 实验表明,FrugalNeRF在多个数据集上表现优于其他小样本NeRF方法。
点此查看论文截图

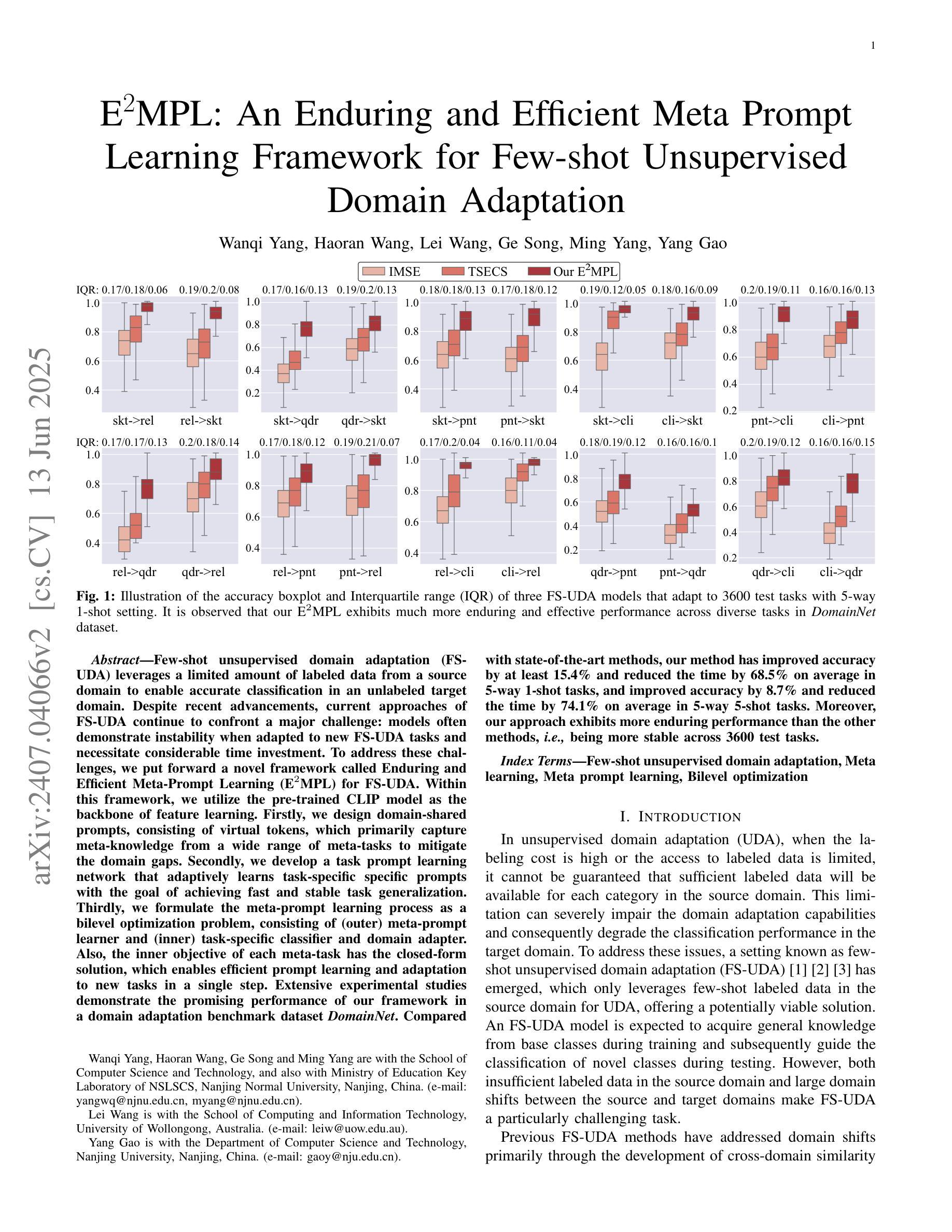
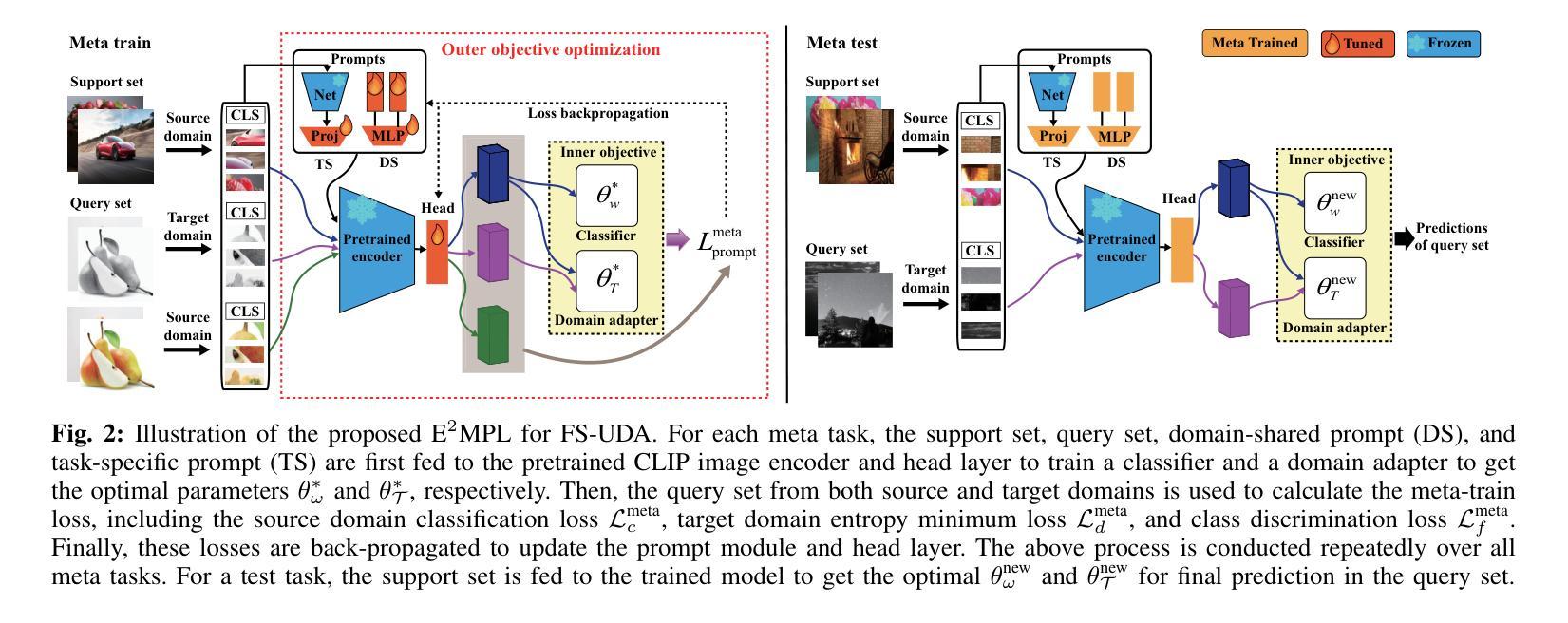
E2MPL:An Enduring and Efficient Meta Prompt Learning Framework for Few-shot Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Authors:Wanqi Yang, Haoran Wang, Lei Wang, Ge Song, Ming Yang, Yang Gao
Few-shot unsupervised domain adaptation (FS-UDA) leverages a limited amount of labeled data from a source domain to enable accurate classification in an unlabeled target domain. Despite recent advancements, current approaches of FS-UDA continue to confront a major challenge: models often demonstrate instability when adapted to new FS-UDA tasks and necessitate considerable time investment. To address these challenges, we put forward a novel framework called Enduring and Efficient Meta-Prompt Learning (E2MPL) for FS-UDA. Within this framework, we utilize the pre-trained CLIP model as the backbone of feature learning. Firstly, we design domain-shared prompts, consisting of virtual tokens, which primarily capture meta-knowledge from a wide range of meta-tasks to mitigate the domain gaps. Secondly, we develop a task prompt learning network that adaptively learns task-specific specific prompts with the goal of achieving fast and stable task generalization. Thirdly, we formulate the meta-prompt learning process as a bilevel optimization problem, consisting of (outer) meta-prompt learner and (inner) task-specific classifier and domain adapter. Also, the inner objective of each meta-task has the closed-form solution, which enables efficient prompt learning and adaptation to new tasks in a single step. Extensive experimental studies demonstrate the promising performance of our framework in a domain adaptation benchmark dataset DomainNet. Compared with state-of-the-art methods, our method has improved accuracy by at least 15.4% and reduced the time by 68.5% on average in 5-way 1-shot tasks, and improved accuracy by 8.7% and reduced the time by 74.1% on average in 5-way 5-shot tasks. Moreover, our approach exhibits more enduring performance than the other methods, i.e., being more stable across 3600 test tasks.
少量监督域自适应(FS-UDA)技术利用源域中的有限标注数据,实现对目标域中的未标注数据的准确分类。尽管近期有所进展,但FS-UDA的现有方法仍然面临重大挑战:模型在适应新的FS-UDA任务时往往表现出不稳定性,需要大量的时间投入。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个名为持久高效元提示学习(E2MPL)的新型框架,用于FS-UDA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对少样本无监督域自适应(FS-UDA)任务的新框架——持久高效元提示学习(E2MPL)。该框架使用预训练的CLIP模型作为特征学习的骨干,通过设计域共享提示和任务提示学习网络,以及将元提示学习过程公式化为一个双层优化问题来解决FS-UDA面临的挑战。实验表明,在DomainNet域自适应基准数据集上,E2MPL框架相比现有方法表现出有前景的性能,提高了至少15.4%的准确率,并在5路1次和5路5次的测试任务中平均减少了68.5%和74.1%的时间。此外,E2MPL还展现出更持久的性能,即跨3600个测试任务更稳定。
Key Takeaways
- E2MPL框架被提出以解决FS-UDA的挑战,包括模型不稳定和新任务适应时间长的问题。
- E2MPL利用预训练的CLIP模型作为特征学习的骨干。
- 域共享提示和任务提示学习网络被设计来捕捉元知识和任务特定知识,以缩小域差距。
- 元提示学习过程被公式化为一个双层优化问题,包括元提示学习者和任务特定分类器及域适配器。
- 实验在DomainNet数据集上表明,E2MPL在少样本无监督域自适应任务上相比现有方法表现出优越的性能。
- E2MPL提高了准确率,减少了适应新任务的时间,并且展现出更持久的性能。
点此查看论文截图