⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-21 更新
ViT-NeBLa: A Hybrid Vision Transformer and Neural Beer-Lambert Framework for Single-View 3D Reconstruction of Oral Anatomy from Panoramic Radiographs
Authors:Bikram Keshari Parida, Anusree P. Sunilkumar, Abhijit Sen, Wonsang You
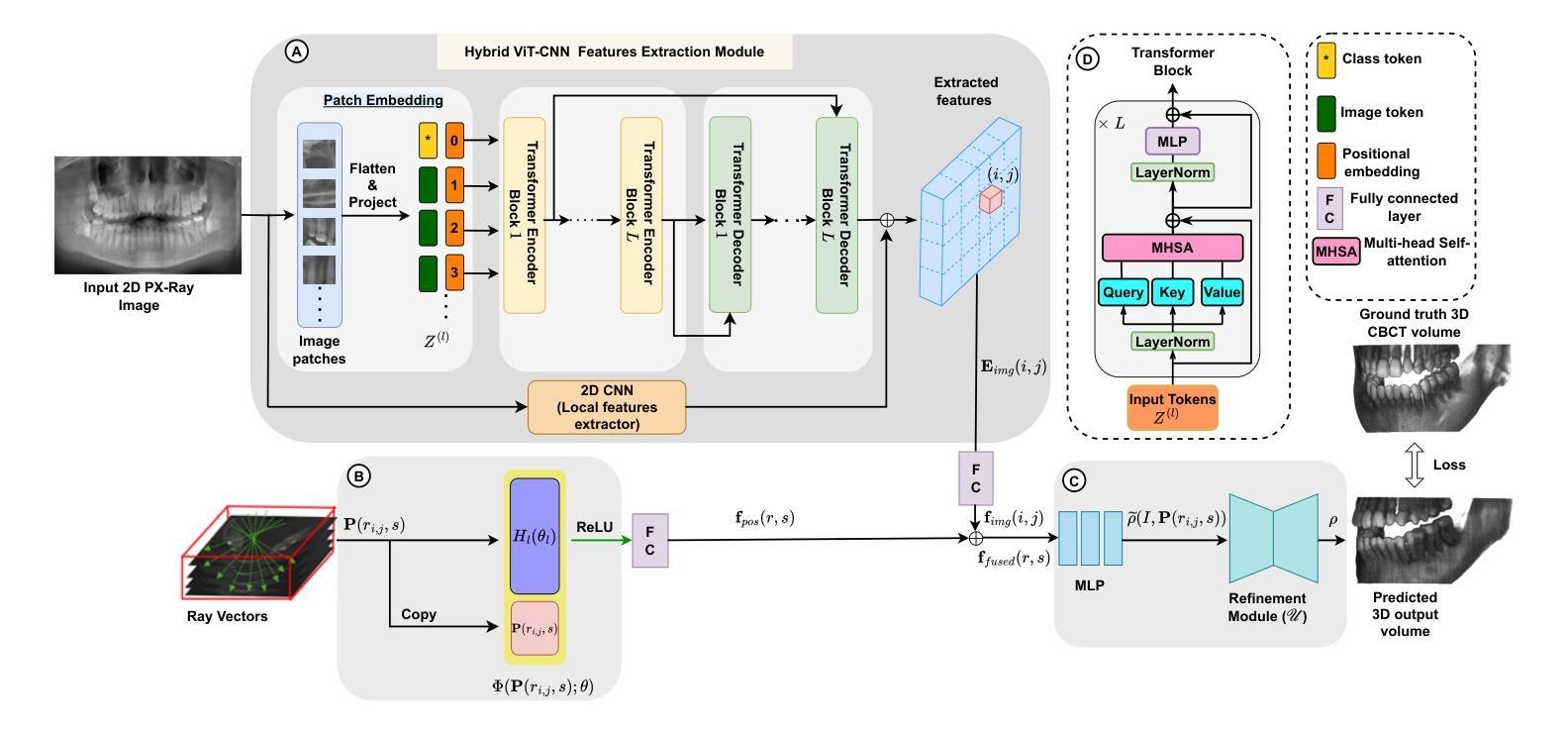
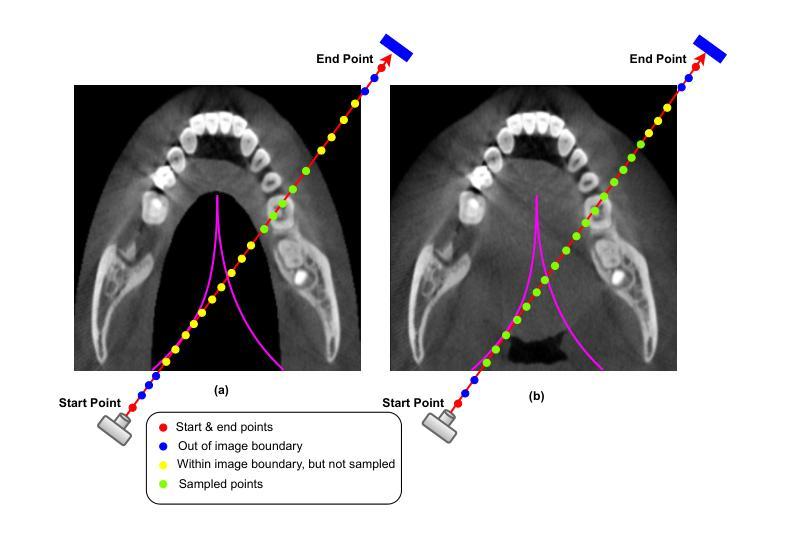
Dental diagnosis relies on two primary imaging modalities: panoramic radiographs (PX) providing 2D oral cavity representations, and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) offering detailed 3D anatomical information. While PX images are cost-effective and accessible, their lack of depth information limits diagnostic accuracy. CBCT addresses this but presents drawbacks including higher costs, increased radiation exposure, and limited accessibility. Existing reconstruction models further complicate the process by requiring CBCT flattening or prior dental arch information, often unavailable clinically. We introduce ViT-NeBLa, a vision transformer-based Neural Beer-Lambert model enabling accurate 3D reconstruction directly from single PX. Our key innovations include: (1) enhancing the NeBLa framework with Vision Transformers for improved reconstruction capabilities without requiring CBCT flattening or prior dental arch information, (2) implementing a novel horseshoe-shaped point sampling strategy with non-intersecting rays that eliminates intermediate density aggregation required by existing models due to intersecting rays, reducing sampling point computations by $52 %$, (3) replacing CNN-based U-Net with a hybrid ViT-CNN architecture for superior global and local feature extraction, and (4) implementing learnable hash positional encoding for better higher-dimensional representation of 3D sample points compared to existing Fourier-based dense positional encoding. Experiments demonstrate that ViT-NeBLa significantly outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively, offering a cost-effective, radiation-efficient alternative for enhanced dental diagnostics.
牙科诊断主要依赖于两种成像模式:全景放射线照相(PX)提供二维口腔代表图像,以及提供详细三维解剖信息的锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)。虽然全景图像具有成本效益且易于获取,但它们缺乏深度信息,从而限制了诊断的准确性。CBCT解决了这个问题,但也存在一些缺点,包括成本较高、辐射暴露增加以及可及性有限。现有的重建模型进一步复杂化流程,需要CBCT展平或预先的牙齿弓形信息,这在临床上往往无法获得。我们介绍了ViT-NeBLa,这是一种基于视觉Transformer的神经网络Beer-Lambert模型,可以直接从单张全景图像进行准确的3D重建。我们的主要创新包括:(1)使用视觉Transformer增强NeBLa框架,提高重建能力,无需CBCT展平或预先的牙齿弓形信息;(2)采用新型马蹄形点采样策略和非交叉射线,消除了现有模型因射线交叉所需的中介密度聚集,减少采样点计算达52%;(3)用混合ViT-CNN架构替代基于CNN的U-Net,以进行更优越的全局和局部特征提取;(4)实现可学习哈希位置编码,与现有的基于傅立叶密集位置编码相比,用于更好地表示3D样本点的高维信息。实验表明,ViT-NeBLa在定量和定性方面均显著优于现有最先进的方法,为增强牙科诊断提供了成本效益高、辐射效率高的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 figures, 19 pages
Summary
本文介绍了名为ViT-NeBLa的牙科诊断新技术,该技术利用基于视觉的神经网络实现直接从全景牙片(PX)进行准确的3D重建。其创新点包括采用Vision Transformer增强NeBLa框架的重建能力,采用新颖的马鞍形点采样策略提高计算效率,将卷积神经网络U-Net替换为混合ViT-CNN架构以提升特征提取性能,并采用可学习的哈希位置编码对更高维度的3D样本点进行表征。实验证明,ViT-NeBLa相较于现有技术有明显优势,能够提供低成本、减少辐射暴露的优质牙科诊断手段。
Key Takeaways
以下是文章的主要见解和要点:
点此查看论文截图

ToothForge: Automatic Dental Shape Generation using Synchronized Spectral Embeddings
Authors:Tibor Kubík, François Guibault, Michal Španěl, Hervé Lombaert
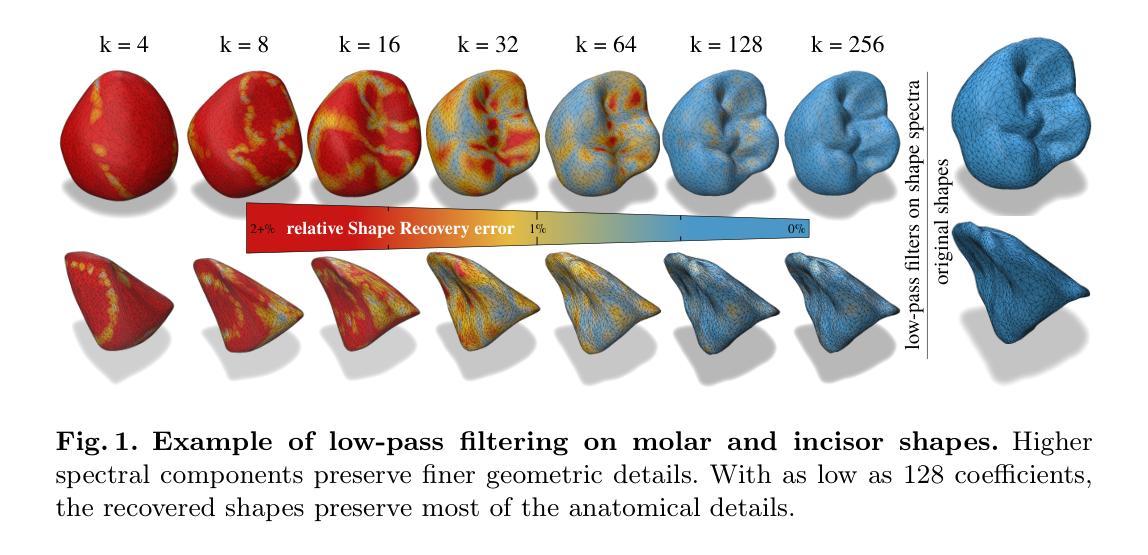
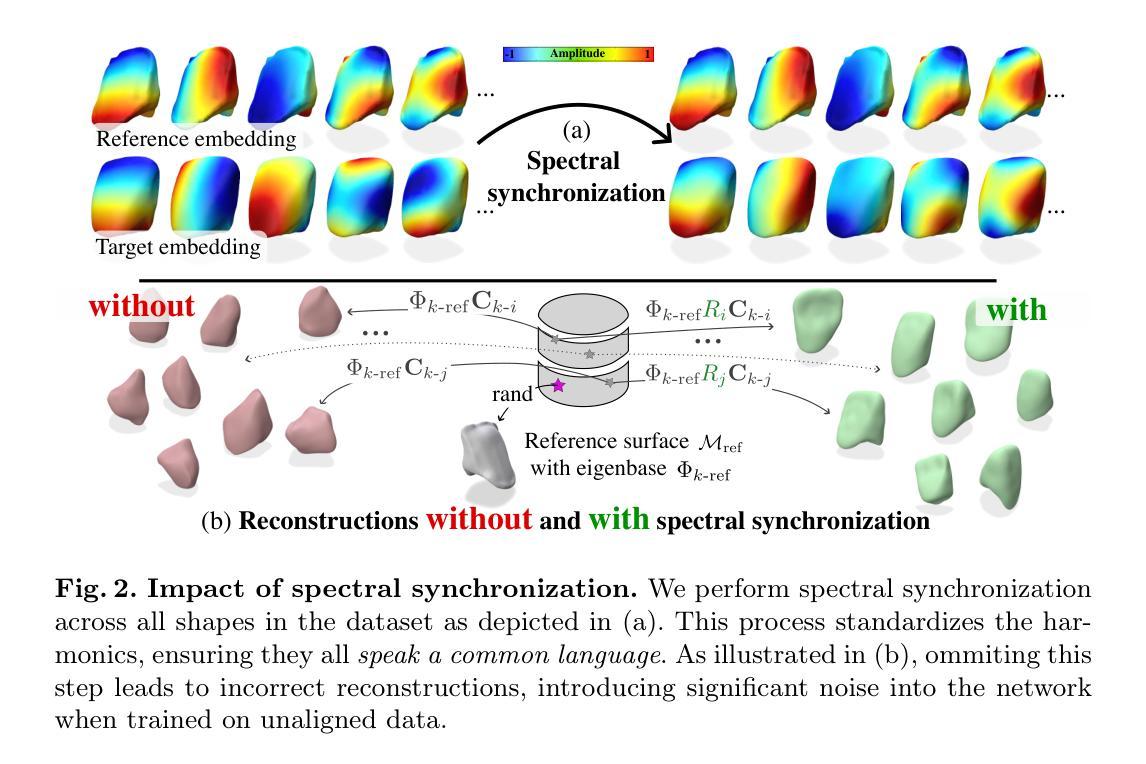
We introduce ToothForge, a spectral approach for automatically generating novel 3D teeth, effectively addressing the sparsity of dental shape datasets. By operating in the spectral domain, our method enables compact machine learning modeling, allowing the generation of high-resolution tooth meshes in milliseconds. However, generating shape spectra comes with the instability of the decomposed harmonics. To address this, we propose modeling the latent manifold on synchronized frequential embeddings. Spectra of all data samples are aligned to a common basis prior to the training procedure, effectively eliminating biases introduced by the decomposition instability. Furthermore, synchronized modeling removes the limiting factor imposed by previous methods, which require all shapes to share a common fixed connectivity. Using a private dataset of real dental crowns, we observe a greater reconstruction quality of the synthetized shapes, exceeding those of models trained on unaligned embeddings. We also explore additional applications of spectral analysis in digital dentistry, such as shape compression and interpolation. ToothForge facilitates a range of approaches at the intersection of spectral analysis and machine learning, with fewer restrictions on mesh structure. This makes it applicable for shape analysis not only in dentistry, but also in broader medical applications, where guaranteeing consistent connectivity across shapes from various clinics is unrealistic. The code is available at https://github.com/tiborkubik/toothForge.
我们介绍了ToothForge,这是一种用于自动生成新型3D牙齿的光谱方法,有效地解决了牙齿形状数据集稀缺的问题。通过在频谱域进行操作,我们的方法能够实现紧凑的机器学习任务建模,可以在毫秒内生成高分辨率的牙齿网格。然而,生成形状光谱会伴随分解谐波的不稳定性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出在同步频率嵌入上建立潜在流形模型。在训练过程之前,所有数据样本的光谱都会与公共基础进行对齐,有效地消除了由分解不稳定性引起的偏见。此外,同步建模消除了以前方法的限制因素,以前的方法要求所有形状具有共享的固定连接。使用真实的牙冠私有数据集,我们观察到合成形状的重建质量大大提高,超过了在未经对齐的嵌入上训练的模型。我们还探索了光谱分析在数字牙科中的其他应用,如形状压缩和插值。ToothForge在光谱分析和机器学习交叉的一系列方法上提供了便利,对网格结构的限制更少。这使得它适用于不仅在牙科中进行形状分析,还适用于更广泛的医疗应用,其中保证来自不同诊所的各种形状的连通性是不切实际的。代码可在https://github.com/tiborkubik/toothForge获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI2025)
Summary
本文介绍了ToothForge系统,该系统采用光谱法自动生成全新三维牙齿形状,有效解决了牙科形状数据集稀少的问题。系统运用光谱分析领域的数据处理方法生成牙齿形状谱,实现紧凑的机器学习建模,能够在毫秒内生成高质量牙齿网格。为解决生成形状谱的不稳定性问题,本文提出了在同步频率嵌入上建模潜在流形的方法,并对所有数据样本的光谱进行基础对齐。该方法提高了合成形状的重建质量,并探索了光谱分析在数字牙科中的其他应用,如形状压缩和插值。ToothForge在光谱分析与机器学习交叉领域提供了更灵活的方法,适用于牙科及其他医疗应用的形状分析。
Key Takeaways
- ToothForge是一种基于光谱分析自动生成三维牙齿形状的系统,解决了牙科形状数据集稀少的问题。
- 系统能够在毫秒内生成高质量牙齿网格,并实现紧凑的机器学习建模。
- 通过在同步频率嵌入上建模潜在流形,解决了生成形状谱的不稳定性问题。
- 对所有数据样本的光谱进行基础对齐,消除了分解不稳定所导致的偏差。
- 同步建模消除了以往方法要求所有形状具有固定连通性的限制因素。
- 使用真实牙冠数据集验证了合成形状的重建质量优于未对齐嵌入的模型。
点此查看论文截图