⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
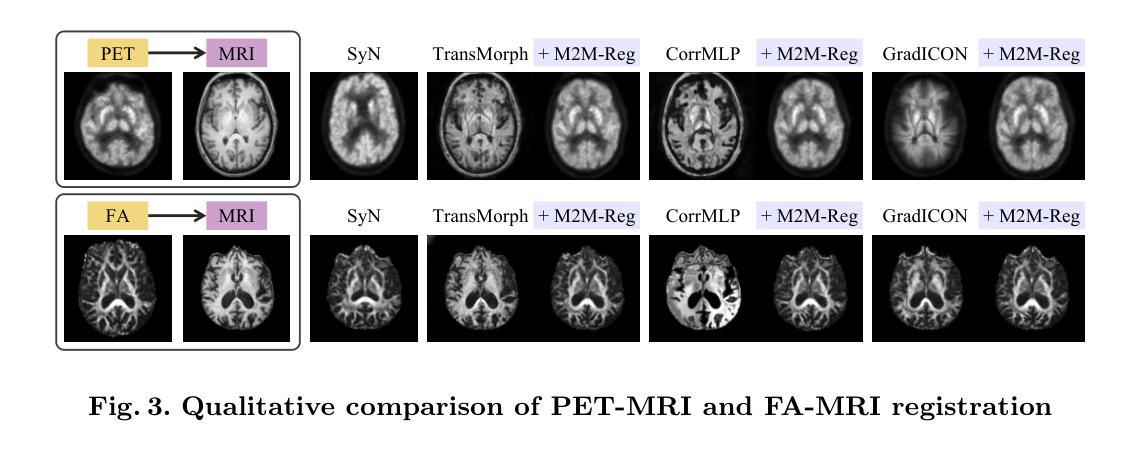
Mono-Modalizing Extremely Heterogeneous Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration
Authors:Kyobin Choo, Hyunkyung Han, Jinyeong Kim, Chanyong Yoon, Seong Jae Hwang
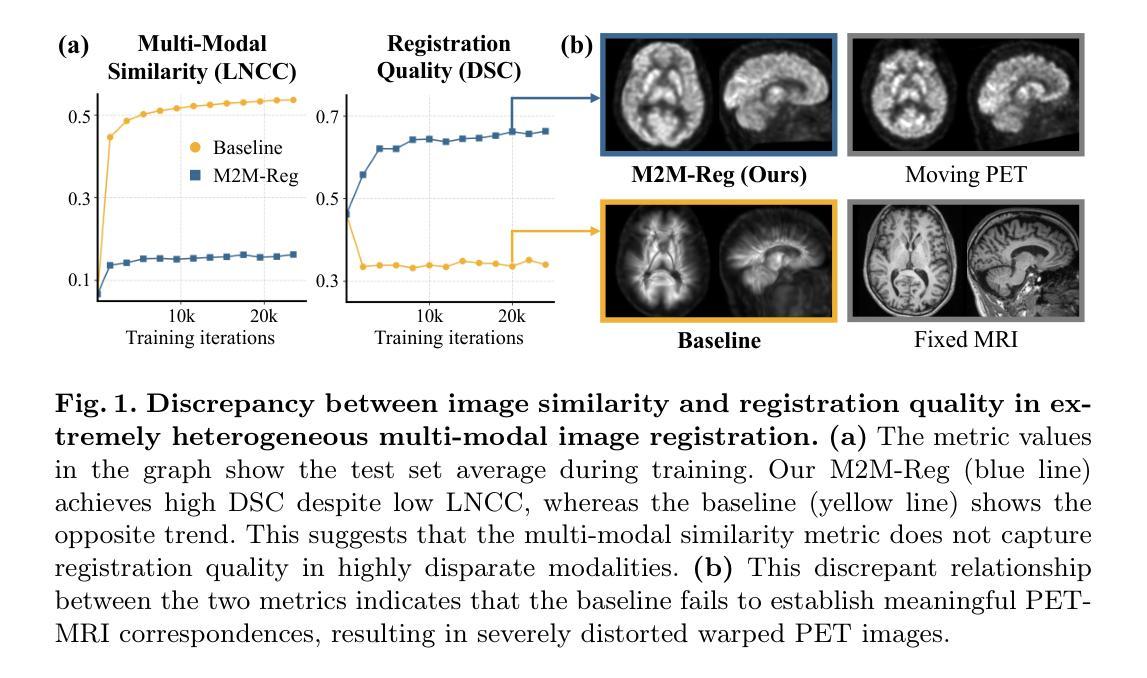
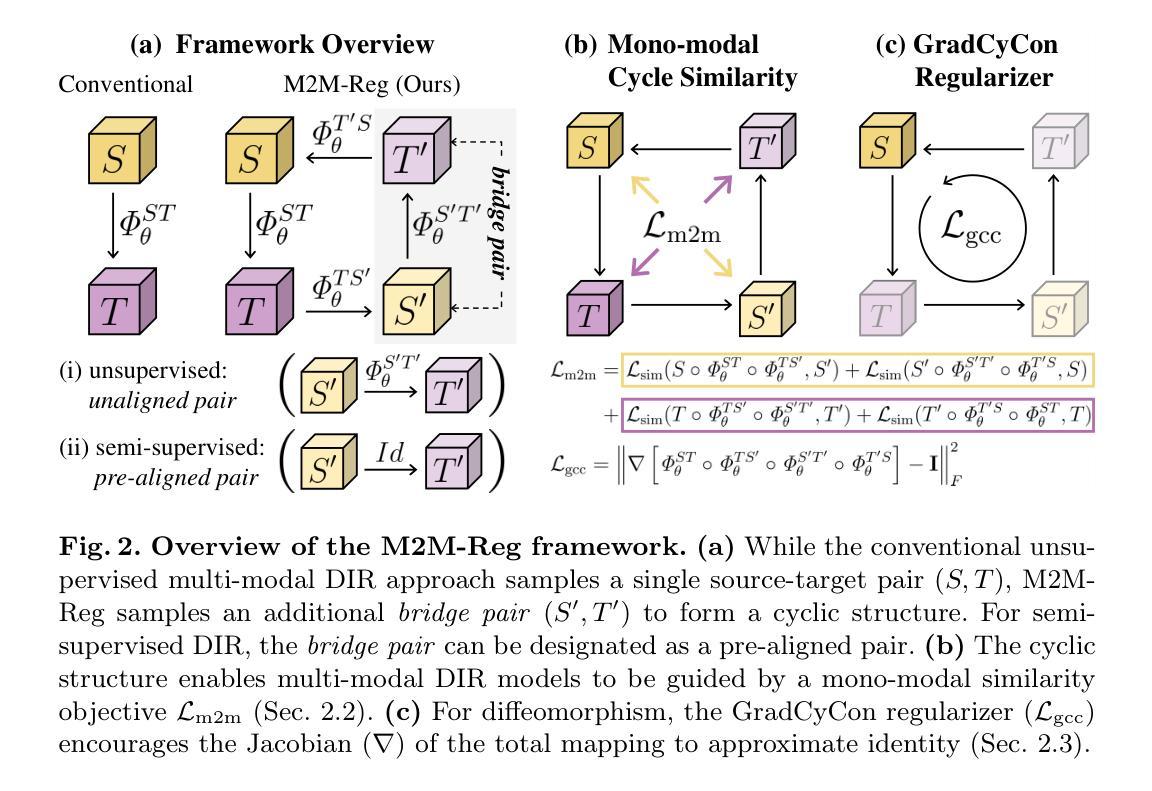
In clinical practice, imaging modalities with functional characteristics, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and fractional anisotropy (FA), are often aligned with a structural reference (e.g., MRI, CT) for accurate interpretation or group analysis, necessitating multi-modal deformable image registration (DIR). However, due to the extreme heterogeneity of these modalities compared to standard structural scans, conventional unsupervised DIR methods struggle to learn reliable spatial mappings and often distort images. We find that the similarity metrics guiding these models fail to capture alignment between highly disparate modalities. To address this, we propose M2M-Reg (Multi-to-Mono Registration), a novel framework that trains multi-modal DIR models using only mono-modal similarity while preserving the established architectural paradigm for seamless integration into existing models. We also introduce GradCyCon, a regularizer that leverages M2M-Reg’s cyclic training scheme to promote diffeomorphism. Furthermore, our framework naturally extends to a semi-supervised setting, integrating pre-aligned and unaligned pairs only, without requiring ground-truth transformations or segmentation masks. Experiments on the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset demonstrate that M2M-Reg achieves up to 2x higher DSC than prior methods for PET-MRI and FA-MRI registration, highlighting its effectiveness in handling highly heterogeneous multi-modal DIR. Our code is available at https://github.com/MICV-yonsei/M2M-Reg.
在临床实践中,具有功能特征的成像方式,如正电子发射断层扫描(PET)和分数异方差性(FA),通常需要与结构参考(例如MRI、CT)对齐,以实现准确的解释或群体分析,这就需要进行多模态可变形图像配准(DIR)。然而,由于这些成像方式与标准结构扫描相比具有极大的异质性,传统的无监督DIR方法难以学习可靠的空间映射关系,并经常导致图像失真。我们发现,指导这些模型的相似度度量无法捕捉不同模态之间的对齐。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了M2M-Reg(多对单注册)这一新型框架,该框架采用单模态相似度训练多模态DIR模型,同时保留了无缝集成现有模型的既定架构范式。我们还介绍了GradCyCon正则化器,它利用M2M-Reg的循环训练方案来促进微分同胚。此外,我们的框架自然地扩展到半监督环境,只整合预先对齐和未对齐的配对,无需依赖地面真实变换或分割掩膜。在阿尔茨海默病神经影像学倡议(ADNI)数据集上的实验表明,M2M-Reg在PET-MRI和FA-MRI配准方面的DSC得分达到了先前方法的两倍以上,凸显其在处理高度异质的多模态DIR方面的有效性。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/MICV-yonsei/M2M-Reg获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables, Accepted at Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2025
摘要
本文介绍了一种新的多模态图像配准框架M2M-Reg,该框架可在具有高度异质性多模态图像中提供可靠的空间映射。它使用单模态相似性进行多模态可变形图像配准模型的训练,并引入GradCyCon正则化器以促进微分同胚。M2M-Reg框架可自然地扩展到半监督设置,仅集成已对齐和未对齐的对,无需地面真实变换或分割掩膜。在ADNI数据集上的实验表明,M2M-Reg在PET-MRI和FA-MRI配准方面的效果是以前方法的最高可达两倍。这一新方法可以有效处理具有高度异质性特点的多模态可变形图像配准问题。相关代码可通过MICV-yonsei/M2M-Reg链接获取。
关键见解
- 多模态成像中,功能特性成像模式(如PET和FA)与结构参考(如MRI、CT)的准确解读或群组分析需要多模态可变形图像配准(DIR)。
- 由于成像模态的极端异质性,传统无监督DIR方法难以学习可靠的空间映射,并可能导致图像失真。
- 现有模型中的相似性度量无法捕捉高度不同模态之间的对齐。
- 提出了一种新型框架M2M-Reg,使用单模态相似性进行多模态DIR模型的训练,解决了上述问题。
- M2M-Reg框架能够无缝集成到现有模型中,并保持已建立的架构范式。
- 引入GradCyCon正则化器,利用M2M-Reg的循环训练方案促进微分同胚。
点此查看论文截图

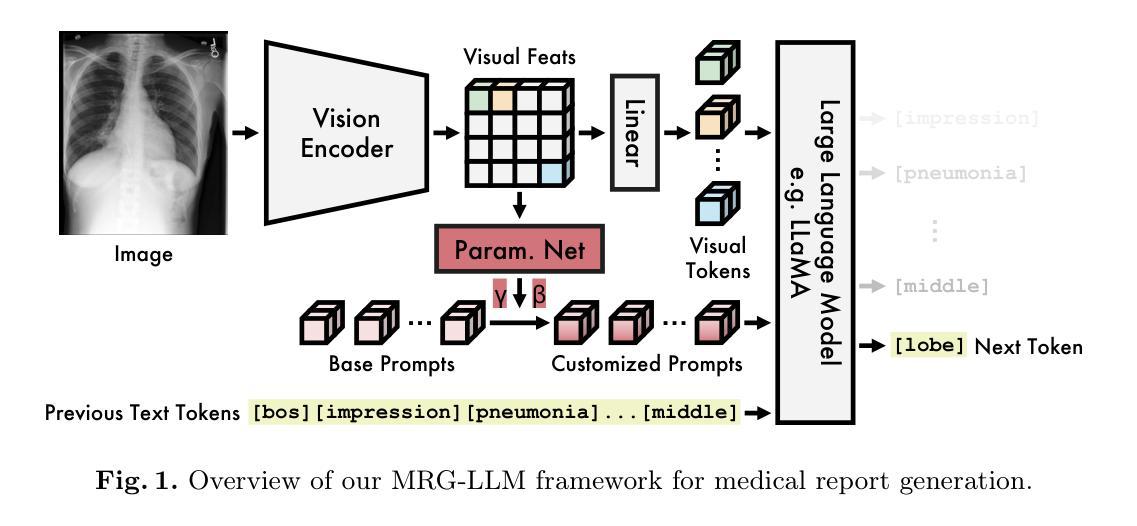
Multimodal Large Language Models for Medical Report Generation via Customized Prompt Tuning
Authors:Chunlei Li, Jingyang Hou, Yilei Shi, Jingliang Hu, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Lichao Mou
Medical report generation from imaging data remains a challenging task in clinical practice. While large language models (LLMs) show great promise in addressing this challenge, their effective integration with medical imaging data still deserves in-depth exploration. In this paper, we present MRG-LLM, a novel multimodal large language model (MLLM) that combines a frozen LLM with a learnable visual encoder and introduces a dynamic prompt customization mechanism. Our key innovation lies in generating instance-specific prompts tailored to individual medical images through conditional affine transformations derived from visual features. We propose two implementations: prompt-wise and promptbook-wise customization, enabling precise and targeted report generation. Extensive experiments on IU X-ray and MIMIC-CXR datasets demonstrate that MRG-LLM achieves state-of-the-art performance in medical report generation. Our code will be made publicly available.
医疗报告从成像数据生成仍然是临床实践中的一个具有挑战性的任务。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在应对这一挑战方面显示出巨大的潜力,但它们与医学成像数据的有效整合仍需要进一步深入研究。在本文中,我们提出了MRG-LLM,这是一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),它将冻结的大型语言模型与可学习的视觉编码器相结合,并引入了一种动态提示定制机制。我们的关键创新之处在于通过来自视觉特征的条件仿射变换为单个医学图像生成特定实例的提示。我们提出了两种实现方法:提示级和提示书级定制,以实现精确和有针对性的报告生成。在IU X光片和MIMIC-CXR数据集上的大量实验表明,MRG-LLM在医疗报告生成方面达到了最先进的性能。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像报告生成是临床实践中具有挑战性的任务之一。本文提出了一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MRG-LLM),它通过结合冻结的大型语言模型、可学习的视觉编码器和动态提示定制机制来解决这一问题。关键创新点在于通过视觉特征派生的条件仿射变换为单个医学图像生成特定实例的提示。在IU X射线和MIMIC-CXR数据集上的广泛实验表明,MRG-LLM在医学报告生成方面达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像报告生成是临床实践的挑战之一。
- MRG-LLM是一个新型的多模态大型语言模型,结合了大型语言模型、视觉编码器和动态提示定制机制。
- MRG-LLM通过条件仿射变换为医学图像生成特定实例的提示。
- MRG-LLM有两种实现方式:基于提示和基于提示书的定制,实现了精确和有针对性的报告生成。
- 在IU X射线和MIMIC-CXR数据集上的实验表明,MRG-LLM在医学报告生成方面达到了最先进的性能。
- MRG-LLM的代码将公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

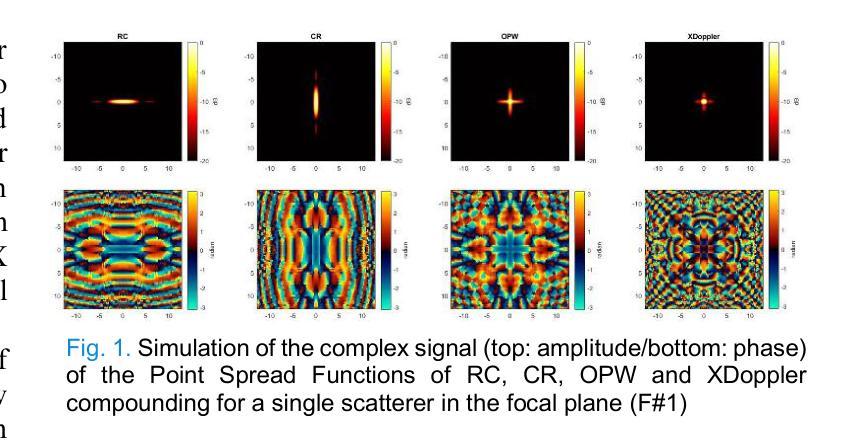
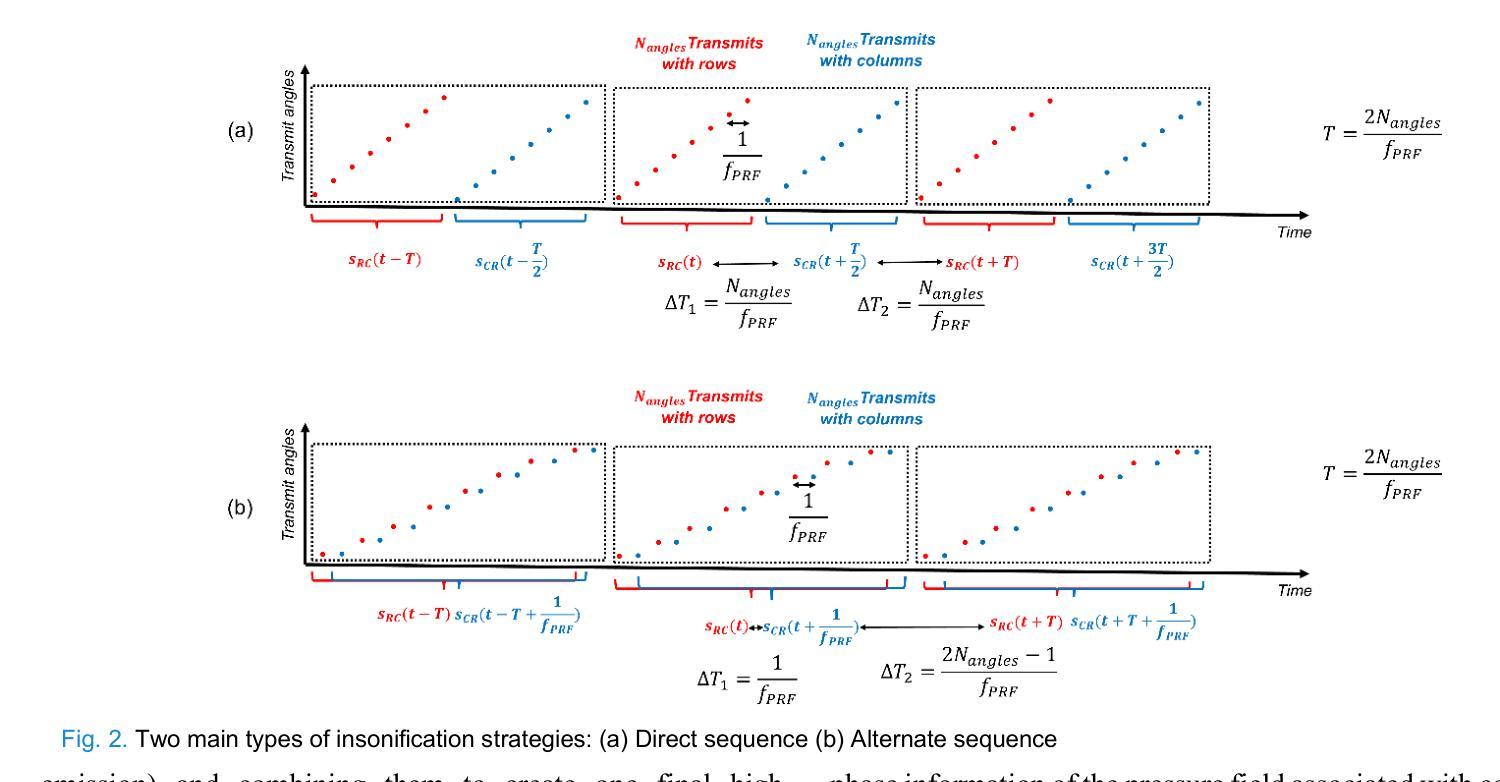
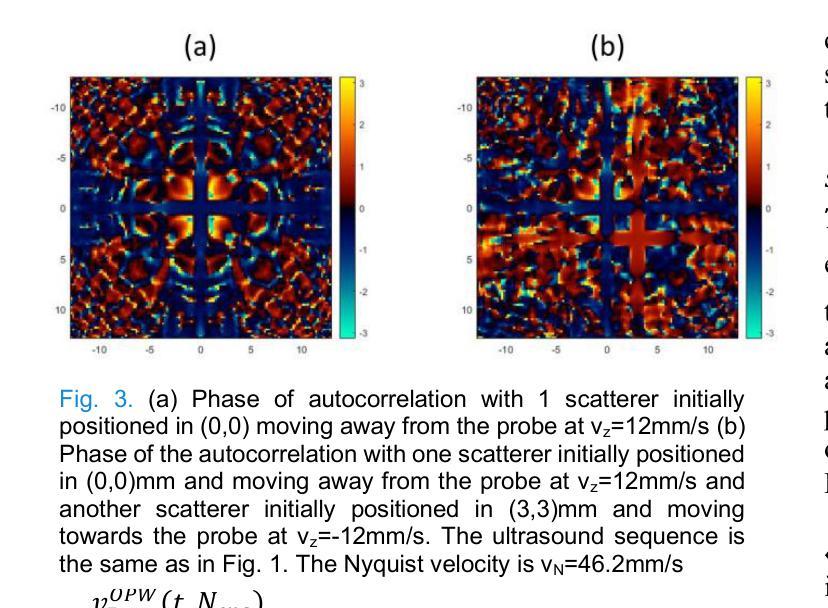
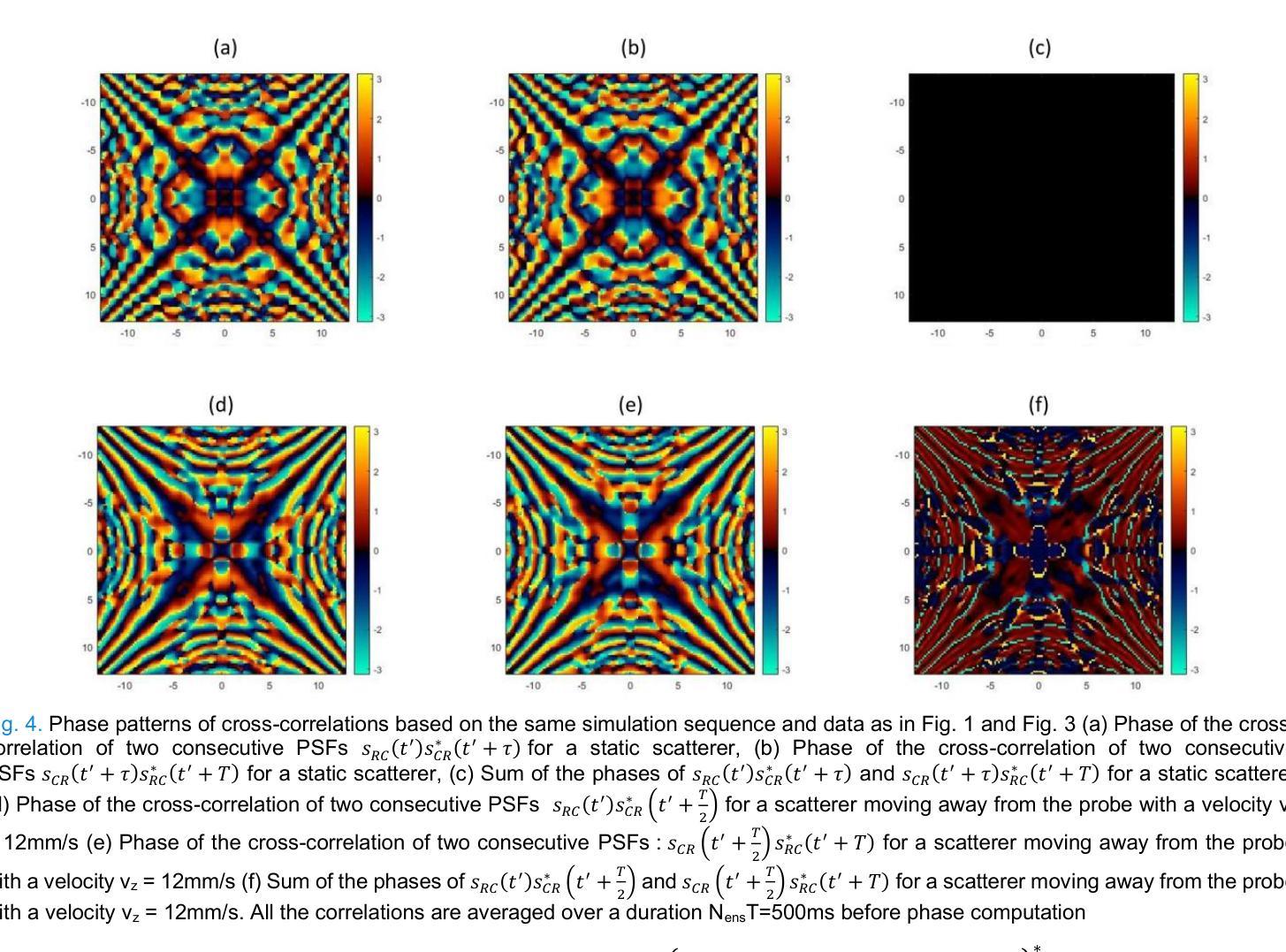
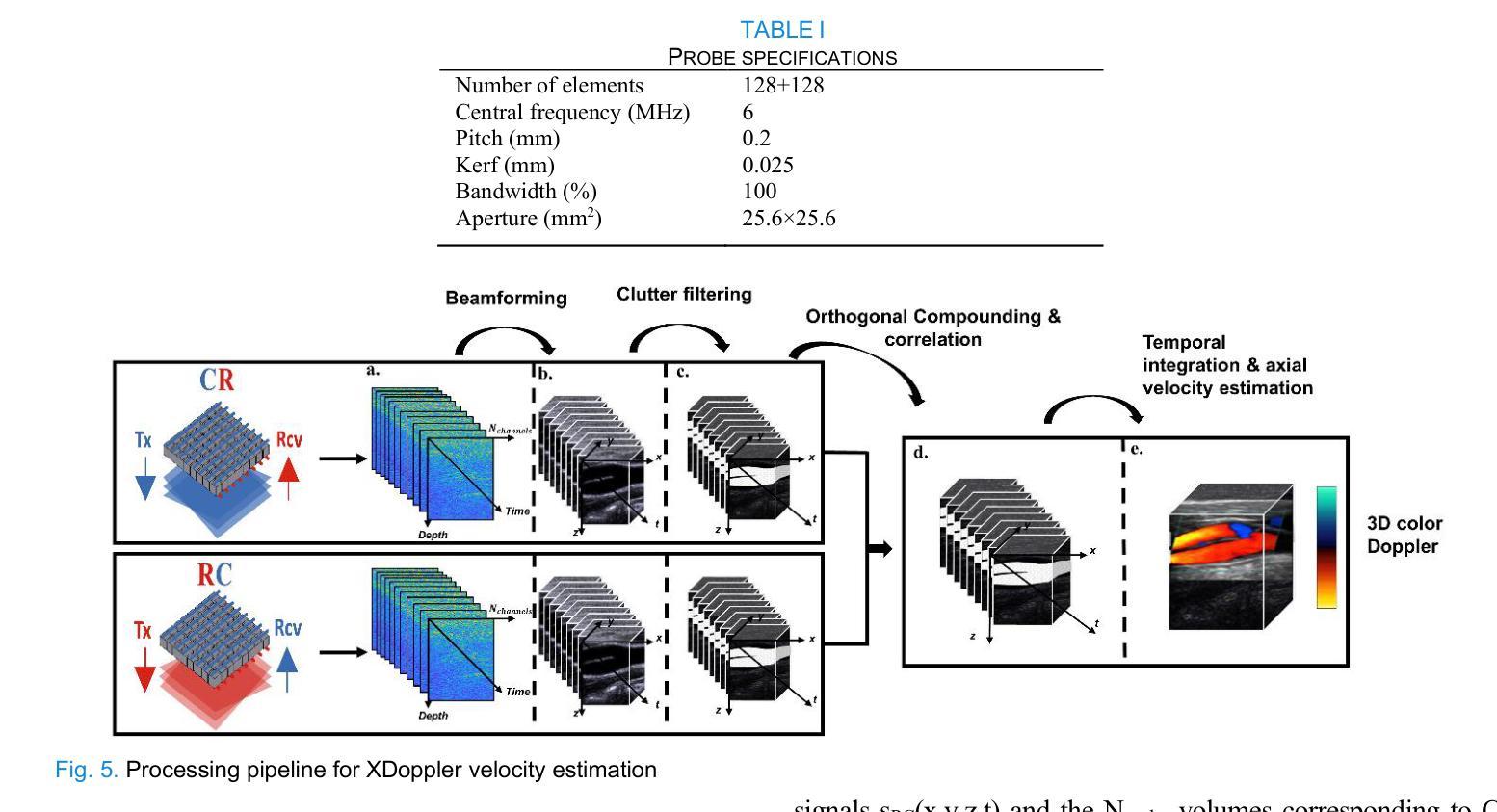
XDoppler axial velocity estimation using row-column arrays
Authors:Henri Leroy, Adrien Bertolo, Guillaume Goudot, Mickael Tanter, Thomas Deffieux, Mathieu Pernot
Accurate volumetric velocity estimation in ultrasound imaging is crucial for applications in diagnostic and therapeutic medicine. Traditional ultrasound systems, while effective in two-dimensional imaging, face significant challenges in achieving 3D imaging due to hardware and computational demands. Row-column addressed (RCA) ultrasound probes present a promising alternative, reducing hardware complexity, thus contributing to bridge the gap between research and clinical systems. Yet, this usually comes at the cost of lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), reduced sensitivity and stronger sidelobes compared to 3D matrices, even though recent methods have tried to tackle the later issue. In this study, we introduce a method to use the phase of the signals acquired by rows and columns of RCA arrays to compute a new velocity estimator based on cross correlation of orthogonal apertures, extending the XDoppler scheme initially introduced for power Doppler imaging to the estimation of velocities. Our results indicate that XDoppler estimator can measure faithfully axial velocities (RMSE=9.21%, R2=0.88) and outperforms the traditional phase shift autocorrelator with a theoretical Nyquist velocity twice higher. Moreover, the in vitro data indicate a better sensitivity to flow velocities below 10mm/s and a lower bias for flow rate estimation (-0.17mL/min as opposed to -9.33mL/min for reference method). In vivo data acquired on a carotid artery confirm the reduced sensitivity to aliasing effects and show that this new technique can dynamically follow blood velocity evolutions linked to arterial pulsatility. This suggests that this new estimator could be of use for improved volumetric blood velocity imaging with a RCA probe.
在超声成像中进行准确的体积速度估计对于诊断和治疗医学应用至关重要。虽然传统超声系统在二维成像中非常有效,但由于硬件和计算需求,它们在实现3D成像时面临重大挑战。行列寻址(RCA)超声探头表现出一种有前途的替代方案,降低了硬件复杂性,从而有助于弥合研究和临床系统之间的差距。然而,这通常以较低的信噪比(SNR)、降低的灵敏度和较严重的旁瓣相比于3D矩阵,尽管最近的方法试图解决后面的问题。在这项研究中,我们介绍了一种方法,使用RCA阵列的行和列获得的信号的相位来计算基于正交孔径互相关的新速度估计器,扩展了最初为功率多普勒成像引入的XDoppler方案用于速度估计。我们的结果表明,XDoppler估计器可以忠实地测量轴向速度(RMSE=9.21%,R2=0.88),并且理论上尼奎斯特速度提高了一倍地超越了传统的相位自相关器。此外,体外数据表明对低于10mm/s的流速具有更高的灵敏度,并且对流速估计的偏差较低(-0.17mL/min相对于参考方法的-9.33mL/min)。在颈动脉上采集的在体数据证实了较少的混叠效应敏感性,并显示这种新技术能够动态跟踪与动脉脉动相关的血液速度变化。这表明这种新型估计器可用于采用RCA探针改进体积血液速度成像。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究介绍了一种基于行-列寻址(RCA)阵列的超声成像新技术,用于精确估算血流速度。本研究通过将XDoppler方案扩展到速度估算,采用RCA阵列行和列采集信号的相位,通过正交孔径的互相关计算新的速度估算器。结果显示,XDoppler估算器能准确测量轴向速度,并优于传统的相位自相关器,理论上的Nyquist速度提高了一倍。体外数据表明,该技术在流速低于10mm/s时的灵敏度更高,流速估计的偏差较低。体内颈动脉数据验证了该技术对混叠效应的敏感性降低,并能动态跟踪与动脉搏动相关的血流速度变化。这表明,这一新技术可用于改进基于RCA探针的血流速度成像。
关键见解
- 行-列寻址(RCA)超声探针在三维成像中具有潜力,能够减少硬件复杂性,并有助于缩小研究与临床系统之间的差距。
- 本研究将XDoppler方案扩展到速度估算,以提高血流速度测量的准确性。
- XDoppler估算器能够准确测量轴向速度,性能优于传统相位自相关器,且理论Nyquist速度提高了一倍。
- 体外实验表明,新技术在流速较低时的灵敏度更高,流速估计偏差较低。
- 体内实验验证了新技术对混叠效应的敏感性降低,能够更准确地跟踪血流速度变化。
- 新技术能够提高基于RCA探针的血流速度成像的精度和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

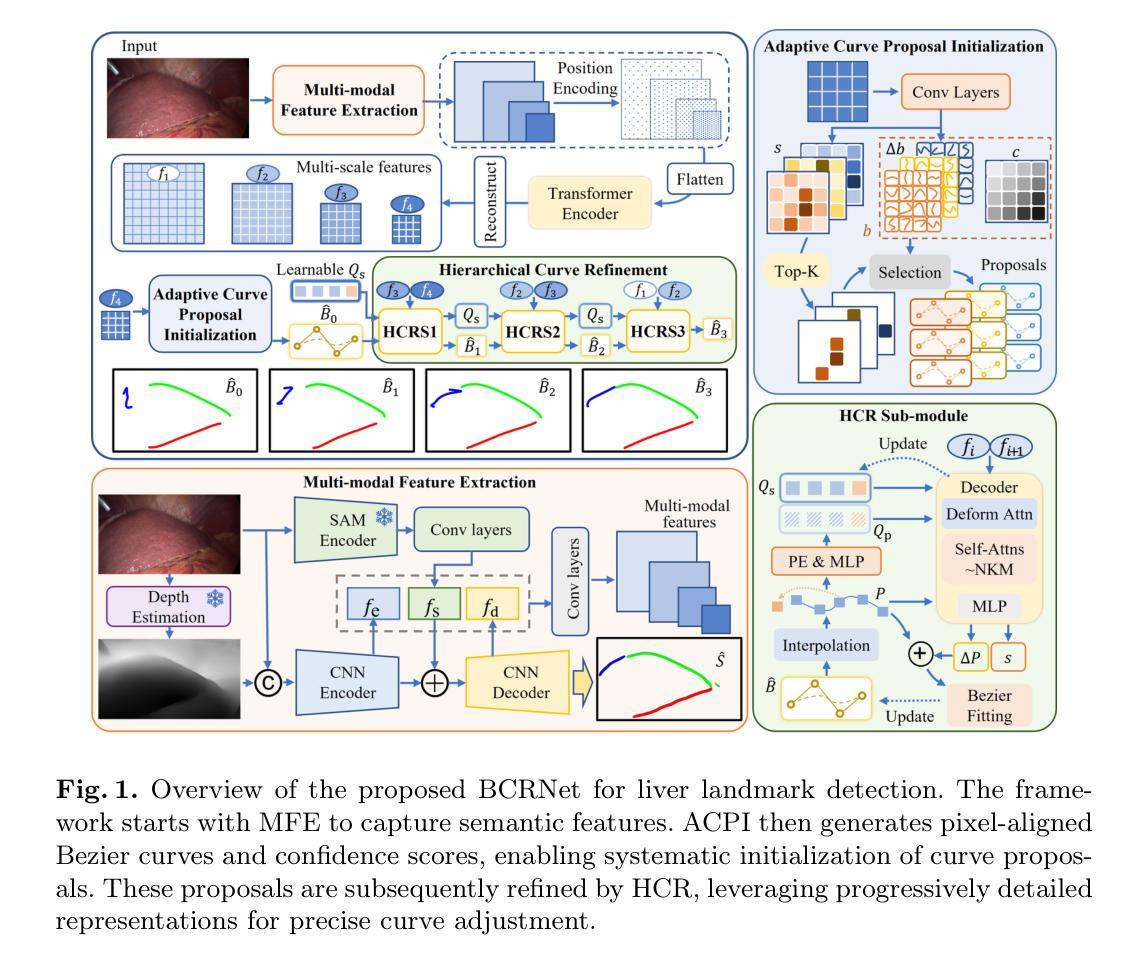
BCRNet: Enhancing Landmark Detection in Laparoscopic Liver Surgery via Bezier Curve Refinement
Authors:Qian Li, Feng Liu, Shuojue Yang, Daiyun Shen, Yueming Jin
Laparoscopic liver surgery, while minimally invasive, poses significant challenges in accurately identifying critical anatomical structures. Augmented reality (AR) systems, integrating MRI/CT with laparoscopic images based on 2D-3D registration, offer a promising solution for enhancing surgical navigation. A vital aspect of the registration progress is the precise detection of curvilinear anatomical landmarks in laparoscopic images. In this paper, we propose BCRNet (Bezier Curve Refinement Net), a novel framework that significantly enhances landmark detection in laparoscopic liver surgery primarily via the Bezier curve refinement strategy. The framework starts with a Multi-modal Feature Extraction (MFE) module designed to robustly capture semantic features. Then we propose Adaptive Curve Proposal Initialization (ACPI) to generate pixel-aligned Bezier curves and confidence scores for reliable initial proposals. Additionally, we design the Hierarchical Curve Refinement (HCR) mechanism to enhance these proposals iteratively through a multi-stage process, capturing fine-grained contextual details from multi-scale pixel-level features for precise Bezier curve adjustment. Extensive evaluations on the L3D and P2ILF datasets demonstrate that BCRNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving significant performance improvements. Code will be available.
腹腔镜肝手术虽然具有微创性,但在准确识别关键解剖结构方面仍存在重大挑战。增强现实(AR)系统通过MRI/CT与腹腔镜图像的二维到三维注册集成,为解决这一挑战提供了有前景的解决方案,可增强手术导航。注册过程中的一个重要方面是精确检测腹腔镜图像中的曲线解剖标志。在本文中,我们提出了BCRNet(Bezier曲线细化网络),这是一个新型框架,主要通过Bezier曲线细化策略极大地提高了腹腔镜肝手术中的标志检测。该框架始于多模态特征提取(MFE)模块,旨在稳健地捕获语义特征。然后,我们提出了自适应曲线提案初始化(ACPI),以生成像素对齐的Bezier曲线和置信度分数,用于可靠的初始提案。此外,我们设计了分层曲线细化(HCR)机制,通过多阶段过程逐步增强这些提案,从多尺度像素级特征中捕获精细的上下文细节,进行精确的Bezier曲线调整。在L3D和P2ILF数据集上的广泛评估表明,BCRNet优于现有最新方法,实现了显著的性能提升。相关代码将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025, 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
医学腹腔镜肝手术中的精准解剖结构识别是一大挑战。增实技术(AR)结合MRI/CT与腹腔镜图像的2D-3D注册技术,为提高手术导航提供了有效途径。论文提出BCRNet框架,通过Bezier曲线精修策略大幅提高了腹腔镜肝手术中的地标检测精度。该框架包含多模态特征提取模块、自适应曲线提案初始化及分层曲线精修机制。在L3D和P2ILF数据集上的广泛评估显示,BCRNet优于现有方法,实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 腹腔镜肝手术在准确识别解剖结构方面存在挑战。
- 增实技术(AR)结合MRI/CT与腹腔镜图像的2D-3D注册技术为手术导航提供解决方案。
- BCRNet框架通过Bezier曲线精修策略提高腹腔镜肝手术中的地标检测精度。
- BCRNet包含多模态特征提取模块,用于稳健捕获语义特征。
- 自适应曲线提案初始化生成像素对齐的Bezier曲线和置信度分数,用于可靠初始提案。
- 分层曲线精修机制通过多阶段过程增强提案,从多尺度像素级特征捕获细节,实现精确的Bezier曲线调整。
点此查看论文截图

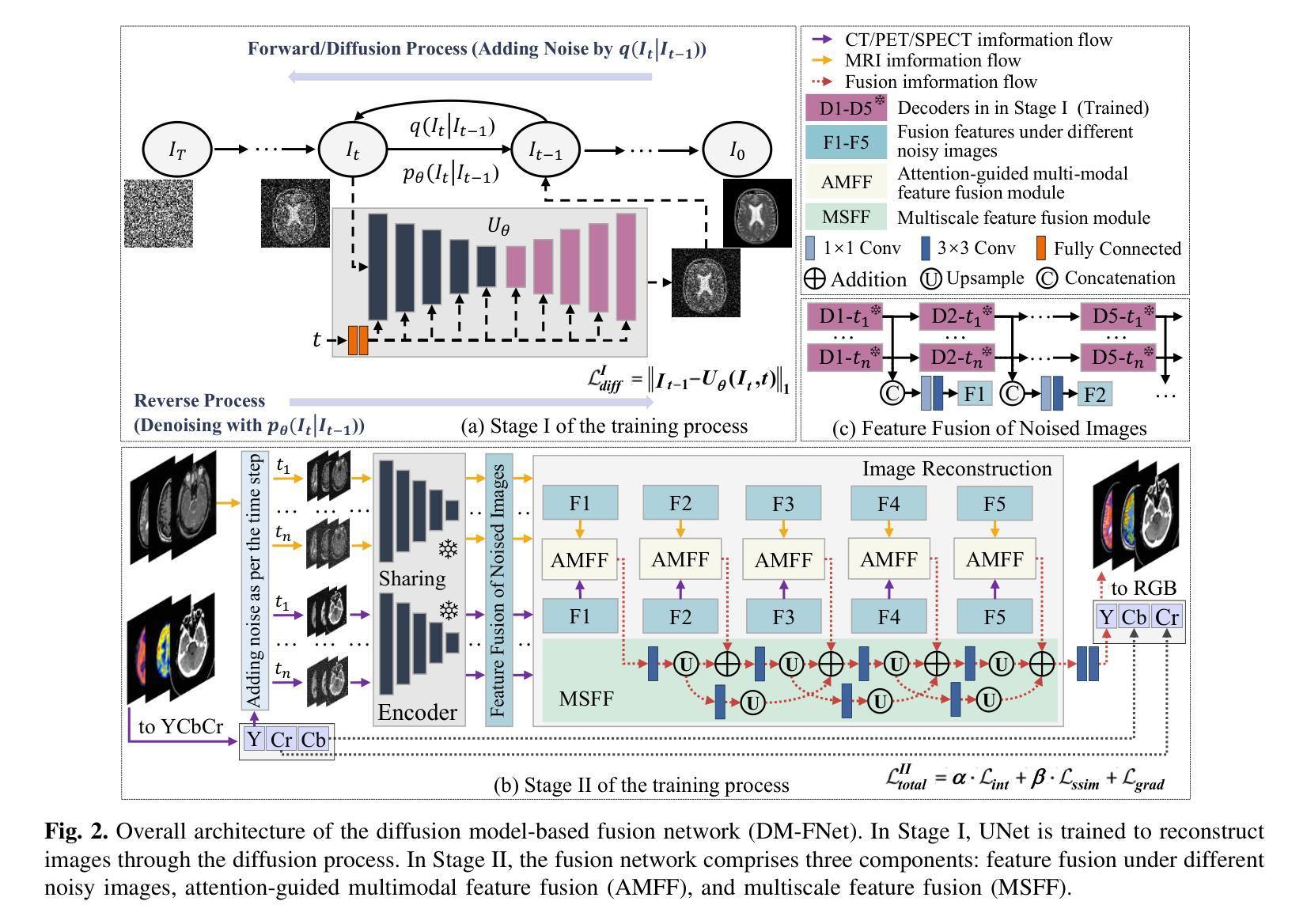
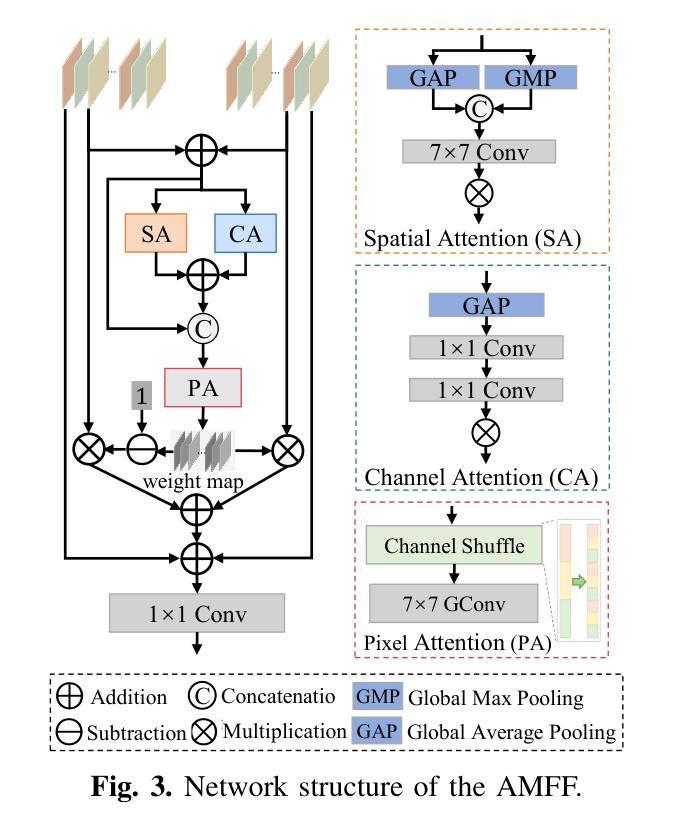
DM-FNet: Unified multimodal medical image fusion via diffusion process-trained encoder-decoder
Authors:Dan He, Weisheng Li, Guofen Wang, Yuping Huang, Shiqiang Liu
Multimodal medical image fusion (MMIF) extracts the most meaningful information from multiple source images, enabling a more comprehensive and accurate diagnosis. Achieving high-quality fusion results requires a careful balance of brightness, color, contrast, and detail; this ensures that the fused images effectively display relevant anatomical structures and reflect the functional status of the tissues. However, existing MMIF methods have limited capacity to capture detailed features during conventional training and suffer from insufficient cross-modal feature interaction, leading to suboptimal fused image quality. To address these issues, this study proposes a two-stage diffusion model-based fusion network (DM-FNet) to achieve unified MMIF. In Stage I, a diffusion process trains UNet for image reconstruction. UNet captures detailed information through progressive denoising and represents multilevel data, providing a rich set of feature representations for the subsequent fusion network. In Stage II, noisy images at various steps are input into the fusion network to enhance the model’s feature recognition capability. Three key fusion modules are also integrated to process medical images from different modalities adaptively. Ultimately, the robust network structure and a hybrid loss function are integrated to harmonize the fused image’s brightness, color, contrast, and detail, enhancing its quality and information density. The experimental results across various medical image types demonstrate that the proposed method performs exceptionally well regarding objective evaluation metrics. The fused image preserves appropriate brightness, a comprehensive distribution of radioactive tracers, rich textures, and clear edges. The code is available at https://github.com/HeDan-11/DM-FNet.
多模态医学图像融合(MMIF)从多个源图像中提取最有意义的信息,使诊断更全面、更准确。实现高质量的融合结果需要在亮度、颜色、对比度和细节之间取得微妙的平衡;这确保了融合图像能够有效地显示相关的解剖结构并反映组织的功能状态。然而,现有的MMIF方法在常规训练过程中捕捉详细特征的能力有限,并且在跨模态特征交互方面存在不足,导致融合图像质量不佳。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种基于两阶段扩散模型的融合网络(DM-FNet)来实现统一的多模态医学图像融合。第一阶段通过扩散过程训练UNet进行图像重建。UNet通过渐进的去噪捕获详细信息,并代表多级数据,为随后的融合网络提供丰富的特征表示。在第二阶段,将不同步骤的噪声图像输入融合网络,以增强模型的特征识别能力。此外,还集成了三个关键融合模块,以自适应地处理来自不同模态的医学图像。最终,通过整合稳健的网络结构和混合损失函数来协调融合图像的亮度、颜色、对比度和细节,从而提高其质量和信息密度。在多种医学图像类型上的实验结果表明,该方法在客观评价指标上表现优异。融合图像保持了适当的亮度、全面的放射性示踪剂分布、丰富的纹理和清晰的边缘。相关代码可通过https://github.com/HeDan-11/DM-FNet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM) in March 2025
Summary
基于两阶段扩散模型的多模态医学图像融合网络(DM-FNet)能有效融合多源医学图像信息,提高诊断的全面性和准确性。该研究通过扩散过程训练UNet进行图像重建,并整合三个关键融合模块,以自适应处理不同模态的医学图像。实验结果显示,该方法在客观评估指标上表现优异,融合图像保持适当的亮度、放射性示踪物分布全面、纹理丰富、边缘清晰。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像融合(MMIF)能够从多个源图像中提取有意义的信息,为全面准确的诊断提供支持。
- 现有的MMIF方法在常规训练中存在局限性,难以充分捕捉详细特征,并且在跨模态特征交互方面表现不足。
- 此研究提出基于两阶段扩散模型(DM-FNet)的融合网络以解决上述问题,该网络通过扩散过程训练UNet进行图像重建,提供丰富的特征表示。
- 第二阶段融合网络能够增强模型的特征识别能力,并通过整合三个关键融合模块自适应处理不同模态的医学图像。
- 该方法通过优化网络结构和混合损失函数,实现了融合图像的亮度、色彩、对比度和细节的平衡。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在客观评估指标上表现优异,融合图像质量高,信息密度丰富。
点此查看论文截图
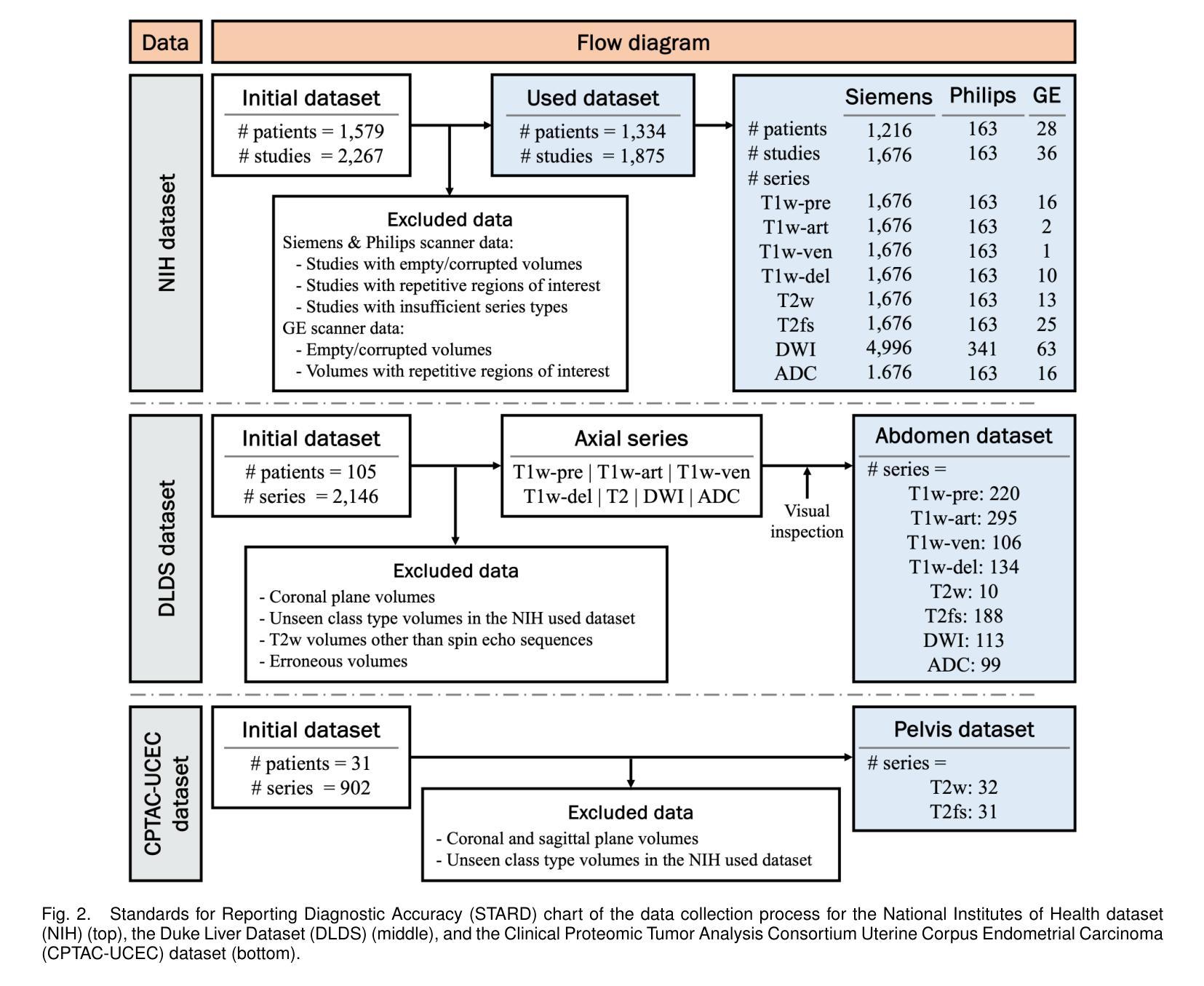
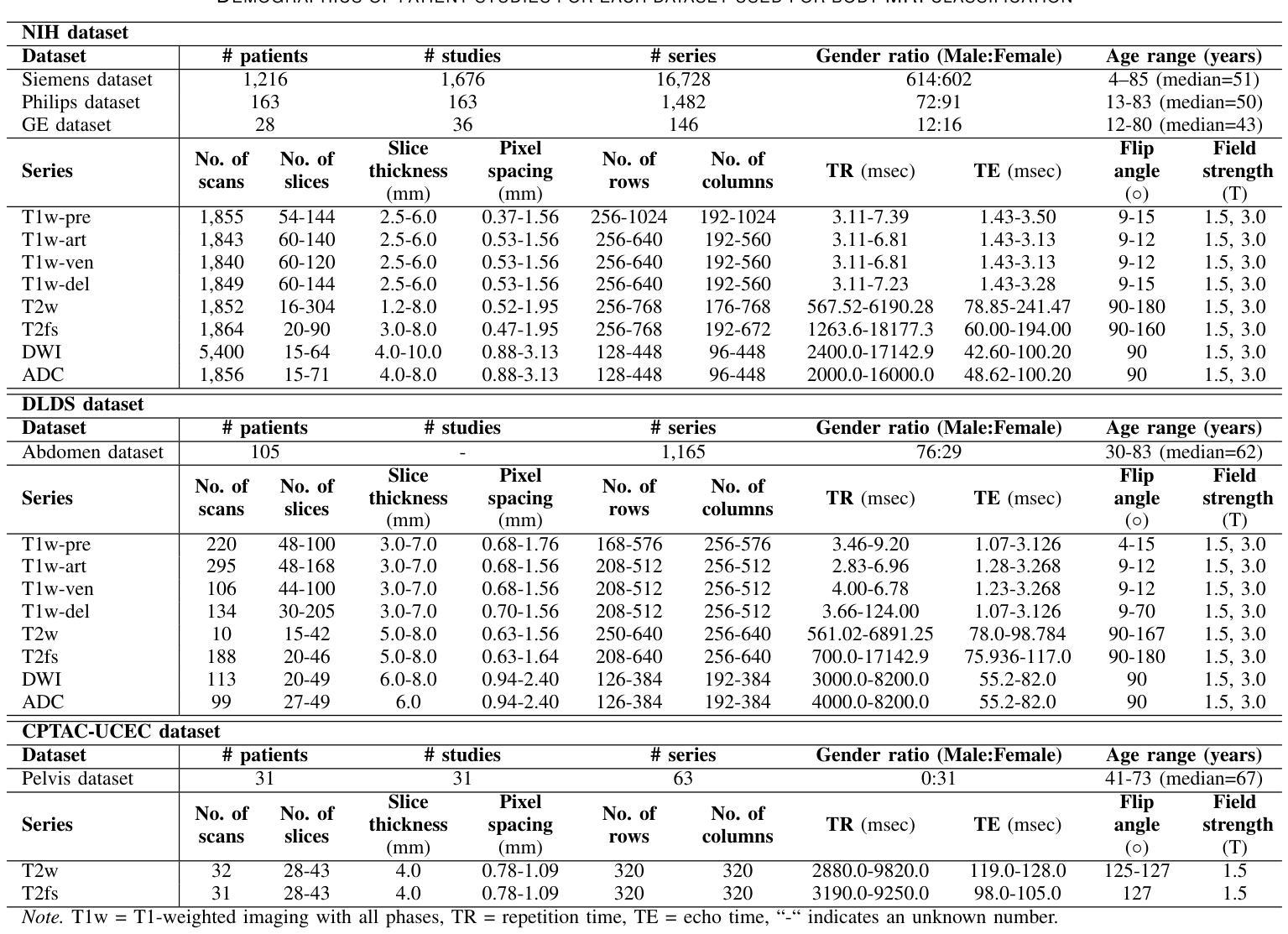
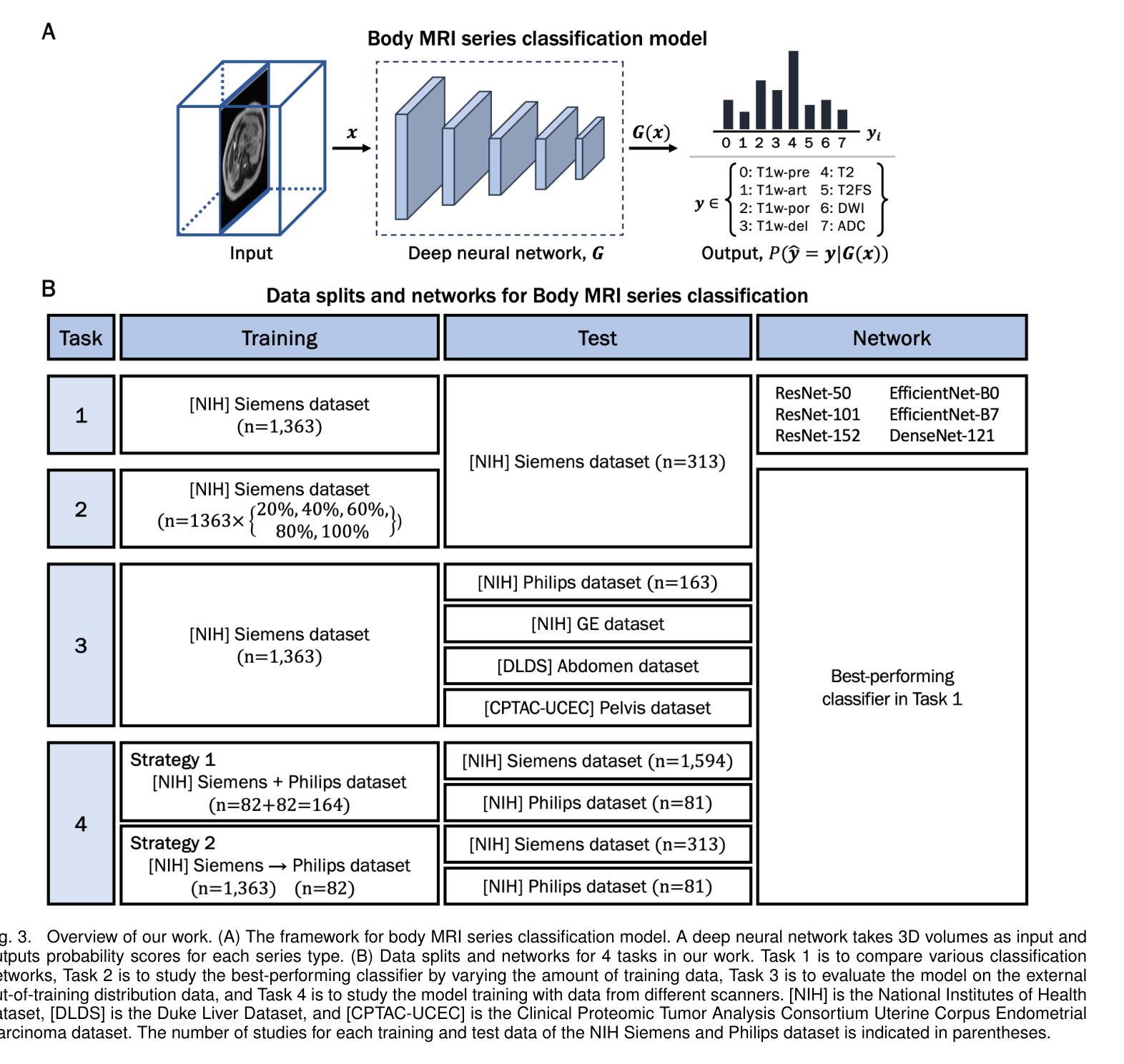
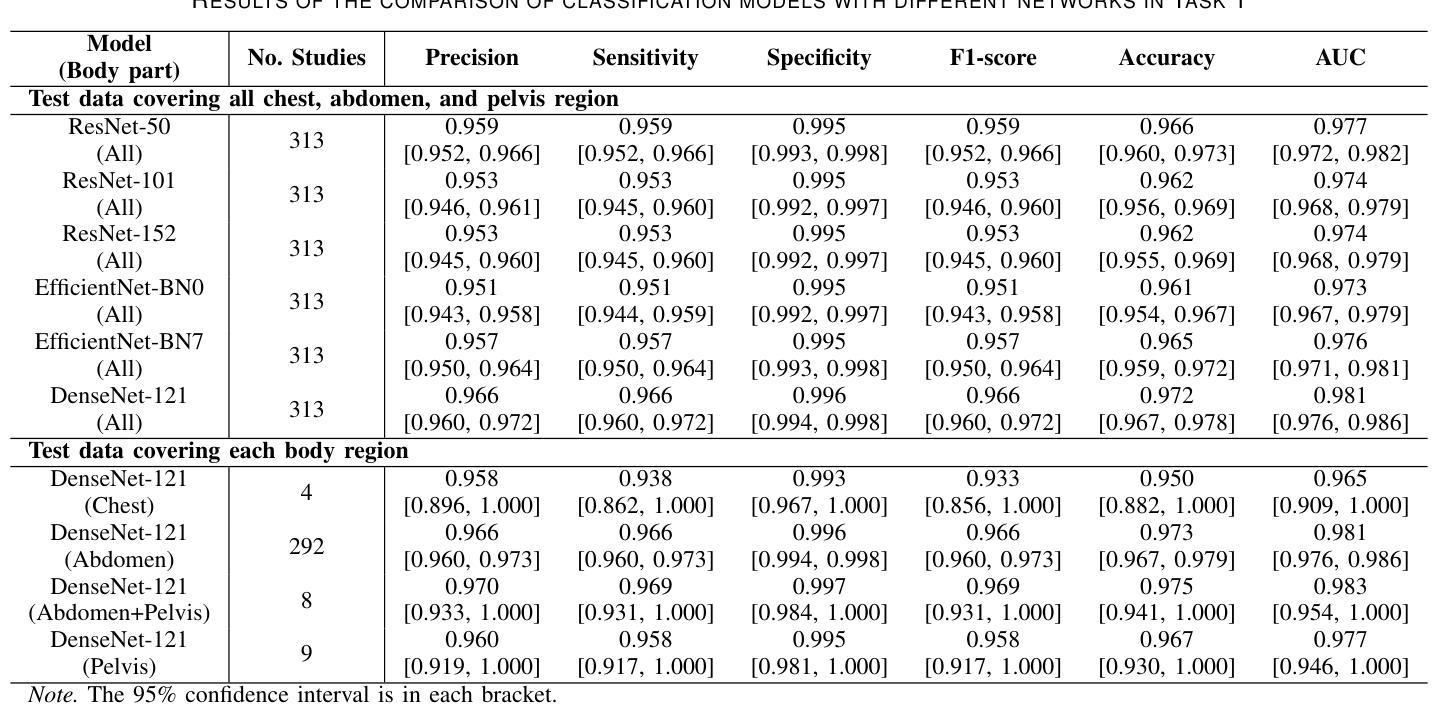
Classification of Multi-Parametric Body MRI Series Using Deep Learning
Authors:Boah Kim, Tejas Sudharshan Mathai, Kimberly Helm, Peter A. Pinto, Ronald M. Summers
Multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) exams have various series types acquired with different imaging protocols. The DICOM headers of these series often have incorrect information due to the sheer diversity of protocols and occasional technologist errors. To address this, we present a deep learning-based classification model to classify 8 different body mpMRI series types so that radiologists read the exams efficiently. Using mpMRI data from various institutions, multiple deep learning-based classifiers of ResNet, EfficientNet, and DenseNet are trained to classify 8 different MRI series, and their performance is compared. Then, the best-performing classifier is identified, and its classification capability under the setting of different training data quantities is studied. Also, the model is evaluated on the out-of-training-distribution datasets. Moreover, the model is trained using mpMRI exams obtained from different scanners in two training strategies, and its performance is tested. Experimental results show that the DenseNet-121 model achieves the highest F1-score and accuracy of 0.966 and 0.972 over the other classification models with p-value$<$0.05. The model shows greater than 0.95 accuracy when trained with over 729 studies of the training data, whose performance improves as the training data quantities grew larger. On the external data with the DLDS and CPTAC-UCEC datasets, the model yields 0.872 and 0.810 accuracy for each. These results indicate that in both the internal and external datasets, the DenseNet-121 model attains high accuracy for the task of classifying 8 body MRI series types.
多参数磁共振成像(mpMRI)检查通过各种不同的成像协议获得不同的系列类型。这些序列的DICOM标头由于协议的多样性和偶尔的技术人员错误,往往存在错误的信息。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于深度学习的分类模型,对8种不同的身体mpMRI系列类型进行分类,以便放射科医生能够高效地阅读检查。
我们使用来自不同机构的mpMRI数据,训练了基于ResNet、EfficientNet和DenseNet的多个深度学习分类器,对8种不同的MRI系列进行分类,并比较了它们的性能。然后,确定了表现最佳的分类器,并研究了其在不同训练数据量设置下的分类能力。此外,该模型在训练分布外的数据集上进行了评估。而且,该模型使用来自两种训练策略的不同扫描仪获得的mpMRI检查进行训练,并对其性能进行了测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的分类模型,用于对多参数磁共振成像(mpMRI)的8种系列类型进行分类。研究通过使用不同机构的mpMRI数据训练了多种深度学习分类器,如ResNet、EfficientNet和DenseNet,并比较了它们的性能。最终发现DenseNet-121模型在分类任务上表现最佳,在内部和外部数据集上均达到较高的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 多参数磁共振成像(mpMRI)的DICOM标头由于协议多样性和技术人员错误,常有错误的信息。
- 使用深度学习分类模型能够解决这一问题,帮助放射科医生更有效地阅读检查。
- 研究比较了ResNet、EfficientNet和DenseNet等深度学习分类器的性能。
- DenseNet-121模型在分类8种不同MRI系列的任务中表现最佳,F1得分和准确度分别为0.966和0.972。
- 当使用超过729项研究的数据进行训练时,该模型的准确性超过0.95,并且随着训练数据量的增加,性能会有所提高。
- 在外部数据集DLDS和CPTAC-UCEC上,模型的准确性分别为0.872和0.810。
点此查看论文截图

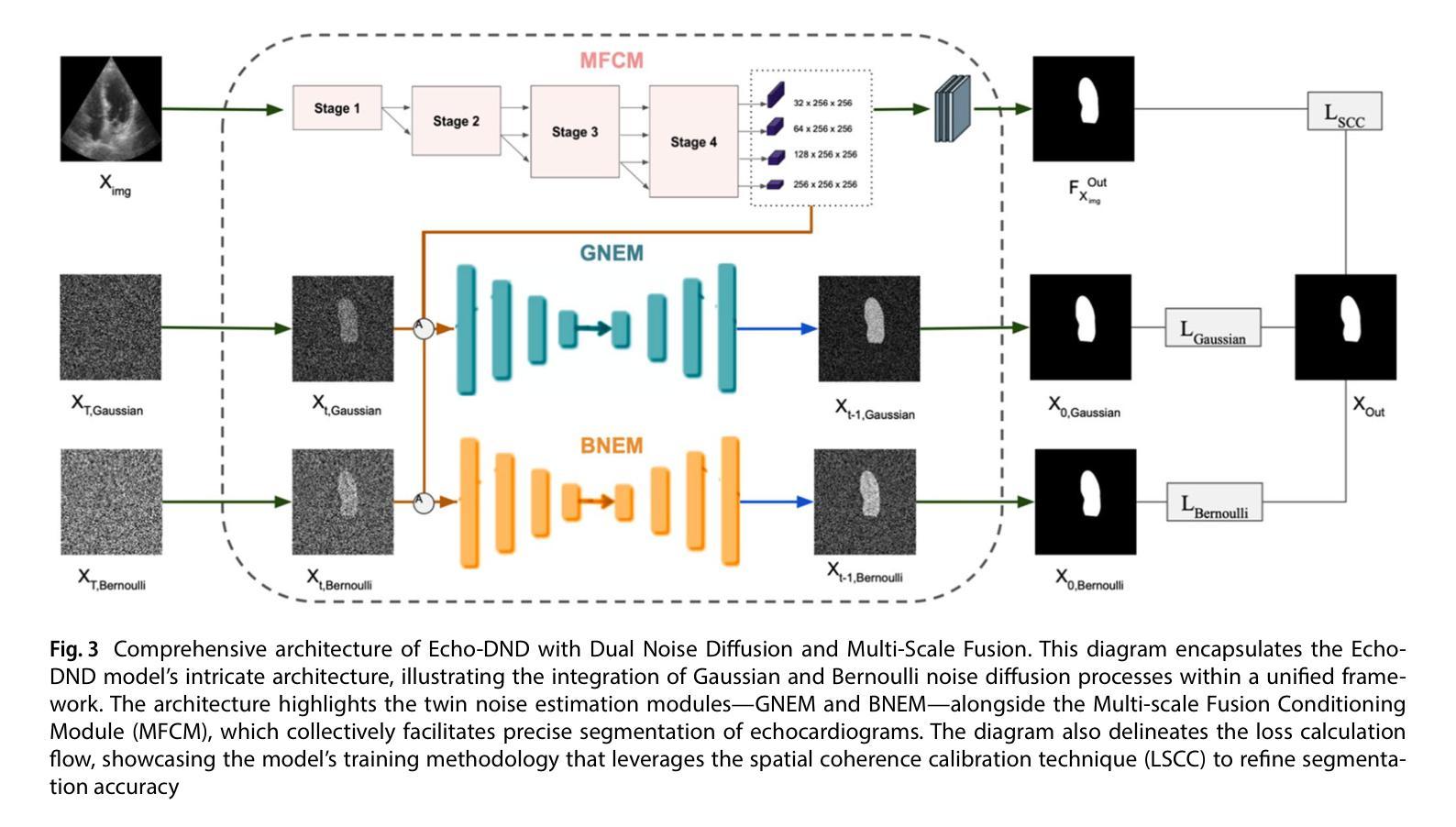
Echo-DND: A dual noise diffusion model for robust and precise left ventricle segmentation in echocardiography
Authors:Abdur Rahman, Keerthiveena Balraj, Manojkumar Ramteke, Anurag Singh Rathore
Recent advancements in diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have revolutionized image processing, demonstrating significant potential in medical applications. Accurate segmentation of the left ventricle (LV) in echocardiograms is crucial for diagnostic procedures and necessary treatments. However, ultrasound images are notoriously noisy with low contrast and ambiguous LV boundaries, thereby complicating the segmentation process. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Echo-DND, a novel dual-noise diffusion model specifically designed for this task. Echo-DND leverages a unique combination of Gaussian and Bernoulli noises. It also incorporates a multi-scale fusion conditioning module to improve segmentation precision. Furthermore, it utilizes spatial coherence calibration to maintain spatial integrity in segmentation masks. The model’s performance was rigorously validated on the CAMUS and EchoNet-Dynamic datasets. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing SOTA models. It achieves high Dice scores of 0.962 and 0.939 on these datasets, respectively. The proposed Echo-DND model establishes a new standard in echocardiogram segmentation, and its architecture holds promise for broader applicability in other medical imaging tasks, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy across various medical domains. Project page: https://abdur75648.github.io/Echo-DND
近年来,扩散概率模型(DPMs)的最新进展在图像处理领域引起了革命性的变革,并在医疗应用中显示出巨大的潜力。在超声心动图中准确分割左心室(LV)对于诊断程序和必要治疗至关重要。然而,超声图像以噪声大、对比度低以及左心室边界模糊而著称,从而增加了分割的难度。为了应对这些挑战,本文引入了Echo-DND,这是一种专门用于此任务的新型双噪声扩散模型。Echo-DND结合了高斯噪声和伯努利噪声的独特组合。它还采用多尺度融合条件模块来提高分割精度。此外,它利用空间一致性校准来保持分割掩膜的空间完整性。该模型在CAMUS和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上进行了严格验证。广泛评估表明,所提出的框架优于现有的先进技术模型。它在这些数据集上分别取得了高达0.962和0.939的Dice得分。所提出的Echo-DND模型在超声心动图分割方面树立了新的标准,其架构在其他医学影像任务中具有广泛的应用前景,有望在多个医疗领域提高诊断准确性。项目页面:https://abdur75648.github.io/Echo-DND
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Version of record published in Discover Applied Sciences (Springer Nature). The definitive article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-025-07055-5
Summary
本文介绍了扩散概率模型(DPMs)的最新进展及其在图像处理领域的革命性作用,特别是在医学应用中的潜力。针对超声图像中左心室(LV)分割的挑战,提出了一种新的双噪声扩散模型Echo-DND。该模型结合了高斯噪声和伯努利噪声,并采用了多尺度融合条件模块以提高分割精度。此外,它还利用空间一致性校准来保持分割掩膜的空间完整性。在CAMUS和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上的严格验证表明,该框架优于现有最先进模型,实现了高Dice得分。Echo-DND模型为超声心动图分割建立了新标准,其架构在其他医学成像任务中具有广泛的应用前景,有望提高不同医学领域的诊断准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散概率模型(DPMs)在图像处理领域取得重大进展,尤其在医学应用中具有显著潜力。
- Echo-DND是一种新型双噪声扩散模型,专为左心室(LV)超声图像分割设计。
- Echo-DND结合了高斯噪声和伯努利噪声,并采用多尺度融合条件模块提高分割精度。
- 该模型利用空间一致性校准维持分割掩膜的空间完整性。
- 在多个数据集上的验证显示,Echo-DND模型的性能优于现有最先进模型。
- Echo-DND实现了高Dice得分,为超声心动图分割树立了新标准。
点此查看论文截图

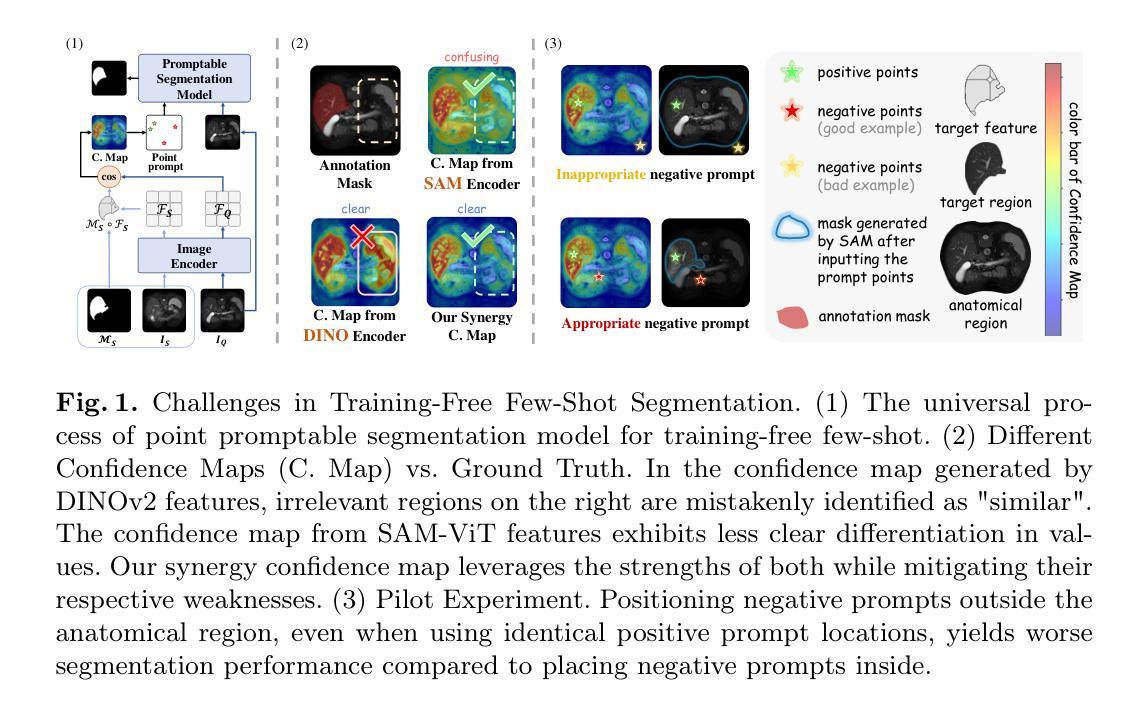
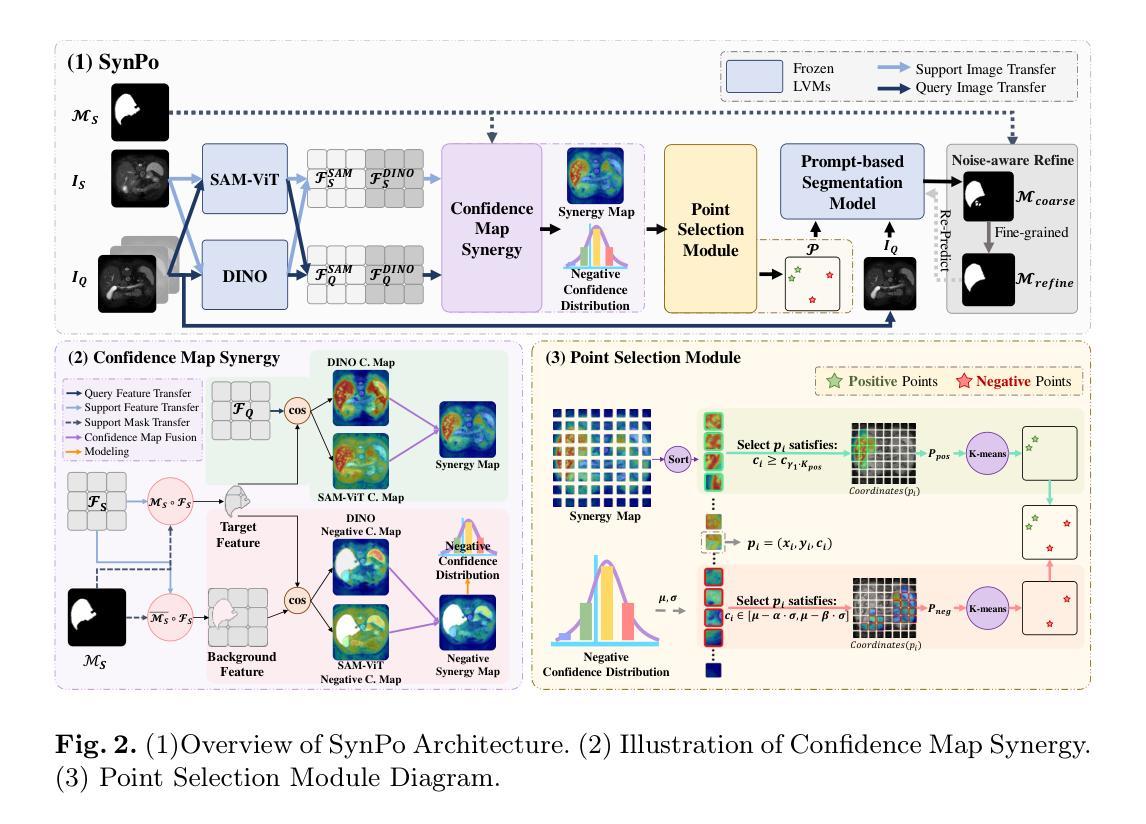
SynPo: Boosting Training-Free Few-Shot Medical Segmentation via High-Quality Negative Prompts
Authors:Yufei Liu, Haoke Xiao, Jiaxing Chai, Yongcun Zhang, Rong Wang, Zijie Meng, Zhiming Luo
The advent of Large Vision Models (LVMs) offers new opportunities for few-shot medical image segmentation. However, existing training-free methods based on LVMs fail to effectively utilize negative prompts, leading to poor performance on low-contrast medical images. To address this issue, we propose SynPo, a training-free few-shot method based on LVMs (e.g., SAM), with the core insight: improving the quality of negative prompts. To select point prompts in a more reliable confidence map, we design a novel Confidence Map Synergy Module by combining the strengths of DINOv2 and SAM. Based on the confidence map, we select the top-k pixels as the positive points set and choose the negative points set using a Gaussian distribution, followed by independent K-means clustering for both sets. Then, these selected points are leveraged as high-quality prompts for SAM to get the segmentation results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SynPo achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art training-based few-shot methods.
大型视觉模型(LVMs)的出现为少数医学图像分割提供了新的机会。然而,基于LVMs的无训练方法无法有效利用负提示,导致在低对比度医学图像上的性能不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于LVMs的无训练少数样本方法SynPo(以SAM为例),其核心思想是:提高负提示的质量。为了在更可靠的置信度地图中选择点提示,我们结合了DINOv2和SAM的优势,设计了一种新颖的置信度映射协同模块。基于置信度地图,我们选择前k个像素作为正点集,并使用高斯分布选择负点集,然后对这两个集合分别进行独立的K-means聚类。然后,这些选定的点被用作高质量提示,供SAM获得分割结果。大量实验表明,SynPo的性能与基于训练的少数样本方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型视觉模型(LVMs)的无训练医学图像分割方法存在利用负提示不足的问题,导致在低对比度医学图像上的表现不佳。为此,我们提出了名为SynPo的无训练少数镜头方法,它通过改进负提示的质量来提升性能。我们设计了一种新颖的置信图协同模块(Confidence Map Synergy Module),结合了DINOv2和SAM的优点来生成置信图,根据置信图选择可靠的点提示。通过高斯分布和独立K-均值聚类,我们选择了正点集和负点集作为高质量提示用于SAM进行分割。实验证明,SynPo的性能与基于训练的最先进少数镜头方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型(LVMs)在医学图像分割的少数镜头学习中提供了新的机会。
- 现有基于LVMs的无训练方法未能有效利用负提示,导致在低对比度医学图像上表现不佳。
- SynPo方法通过改进负提示的质量来提升性能。
- 设计了置信图协同模块(Confidence Map Synergy Module),结合DINOv2和SAM的优点生成置信图。
- 根据置信图选择可靠的点提示,通过高斯分布和独立K-均值聚类选择正点集和负点集。
- 选定的点被用作高质量提示,用于SAM进行图像分割。
点此查看论文截图

Frequency-Calibrated Membership Inference Attacks on Medical Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Xinkai Zhao, Yuta Tokuoka, Junichiro Iwasawa, Keita Oda
The increasing use of diffusion models for image generation, especially in sensitive areas like medical imaging, has raised significant privacy concerns. Membership Inference Attack (MIA) has emerged as a potential approach to determine if a specific image was used to train a diffusion model, thus quantifying privacy risks. Existing MIA methods often rely on diffusion reconstruction errors, where member images are expected to have lower reconstruction errors than non-member images. However, applying these methods directly to medical images faces challenges. Reconstruction error is influenced by inherent image difficulty, and diffusion models struggle with high-frequency detail reconstruction. To address these issues, we propose a Frequency-Calibrated Reconstruction Error (FCRE) method for MIAs on medical image diffusion models. By focusing on reconstruction errors within a specific mid-frequency range and excluding both high-frequency (difficult to reconstruct) and low-frequency (less informative) regions, our frequency-selective approach mitigates the confounding factor of inherent image difficulty. Specifically, we analyze the reverse diffusion process, obtain the mid-frequency reconstruction error, and compute the structural similarity index score between the reconstructed and original images. Membership is determined by comparing this score to a threshold. Experiments on several medical image datasets demonstrate that our FCRE method outperforms existing MIA methods.
随着扩散模型在图像生成领域的广泛应用,特别是在医学影像等敏感领域,引发了人们对隐私的重大关注。成员推理攻击(MIA)已经成为一种潜在的方法,用于确定特定图像是否用于训练扩散模型,从而量化隐私风险。现有的MIA方法通常依赖于扩散重建误差,其中成员图像的重建误差预期会低于非成员图像。然而,将这些方法直接应用于医学图像面临挑战。重建误差受到图像固有难度的影响,扩散模型在重建高频细节时遇到困难。为了解决这些问题,我们针对医学图像扩散模型上的MIA提出了一种频率校准重建误差(FCRE)方法。我们的频率选择方法专注于特定中频范围内的重建误差,并排除了高频(难以重建)和低频(信息较少)区域,从而减轻了固有图像难度这一混淆因素。具体来说,我们分析了反向扩散过程,获得了中频重建误差,并计算了重构图像和原始图像之间的结构相似性指数分数。成员身份的确定是通过将此分数与阈值进行比较得出的。在多个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的FCRE方法优于现有的MIA方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像扩散模型的成员推理攻击(MIA),提出一种频率校准重建误差(FCRE)方法。该方法关注特定中频范围内的重建误差,排除高频(难以重建)和低频(信息较少)区域,以减轻图像本身难度对隐私泄露的影响。通过对比重建图像与原始图像的结构相似性指数得分,确定成员身份。实验证明,FCRE方法在多个医学图像数据集上的表现优于现有MIA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在医学图像生成中的广泛应用引发了隐私担忧。
- 成员推理攻击(MIA)可用来确定特定图像是否用于训练扩散模型,从而评估隐私风险。
- 现有MIA方法主要基于扩散重建误差,但直接应用于医学图像面临挑战。
- 医学图像本身的难度影响重建误差,扩散模型在高频细节重建上表现挣扎。
- 提出FCRE方法,关注中频范围的重建误差,排除高频和低频区域,以减轻图像难度对隐私泄露的干扰。
- FCRE方法通过对比重建图像与原始图像的结构相似性指数得分,确定成员身份。
点此查看论文截图

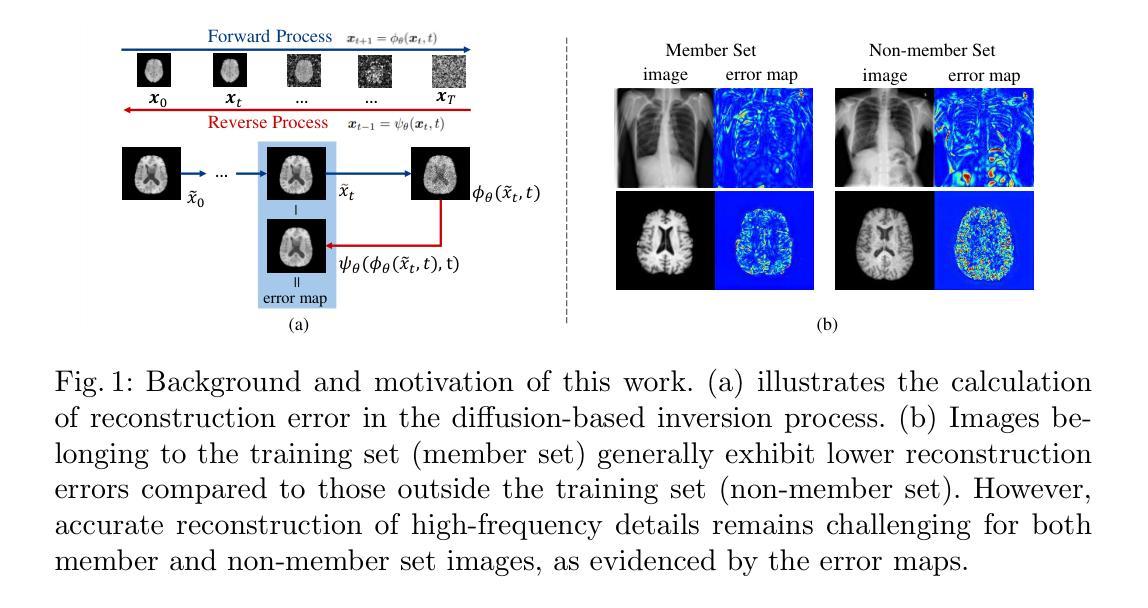
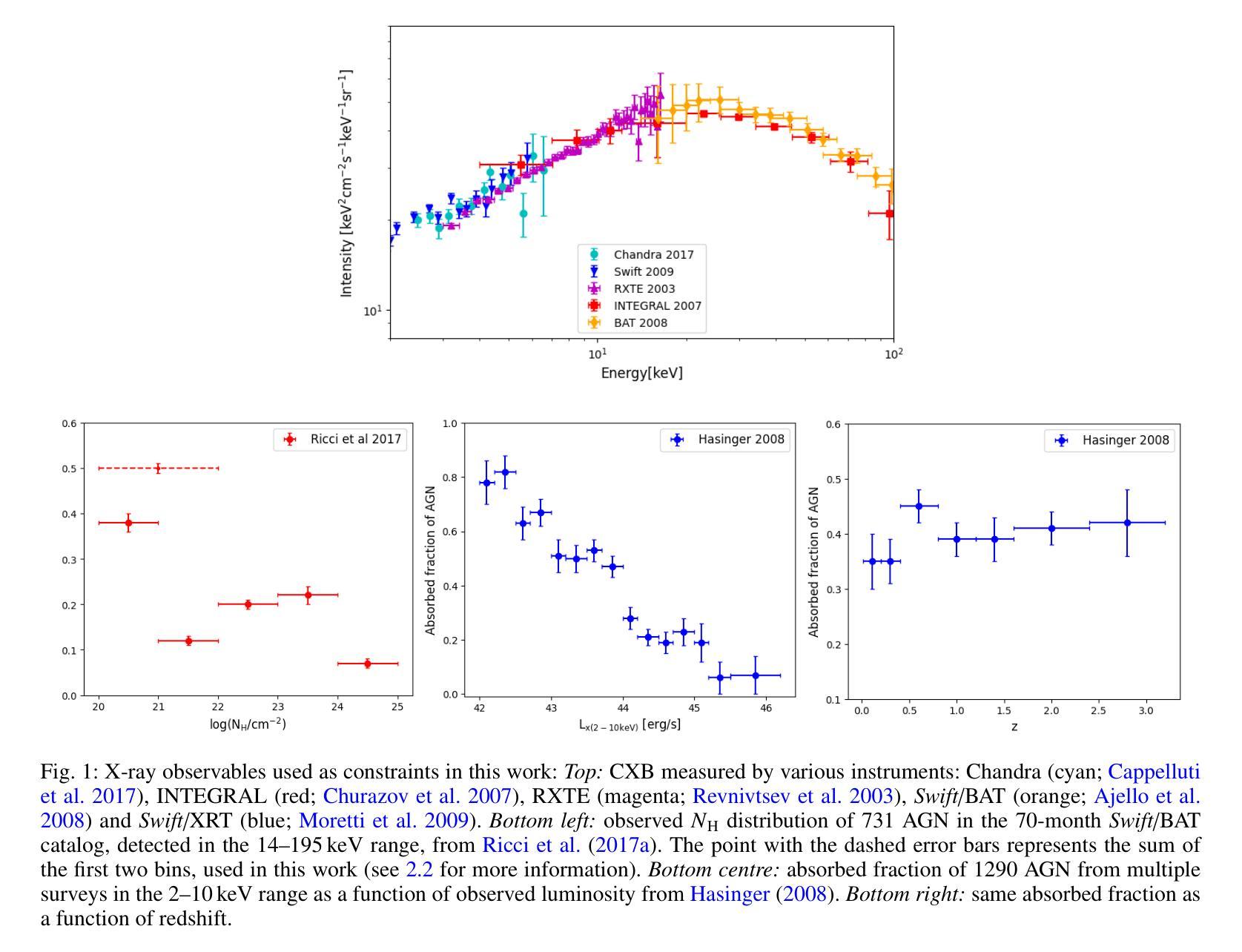
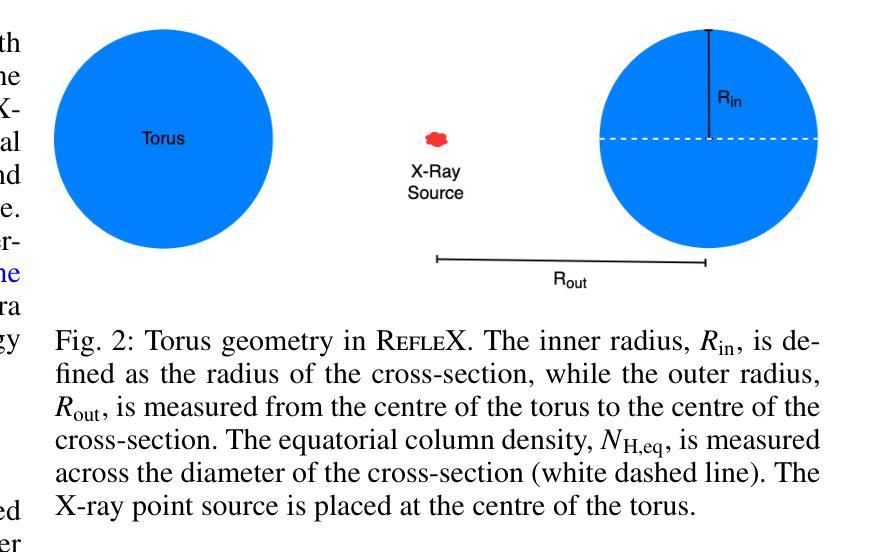
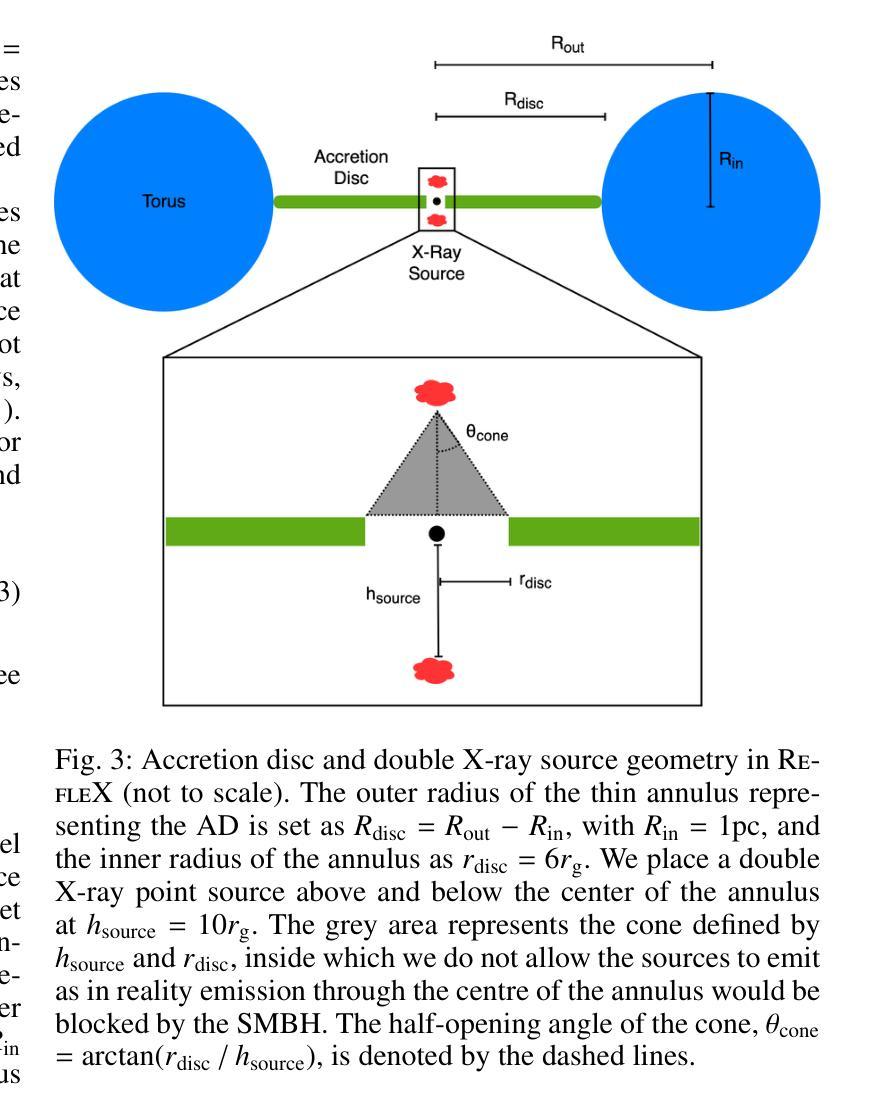
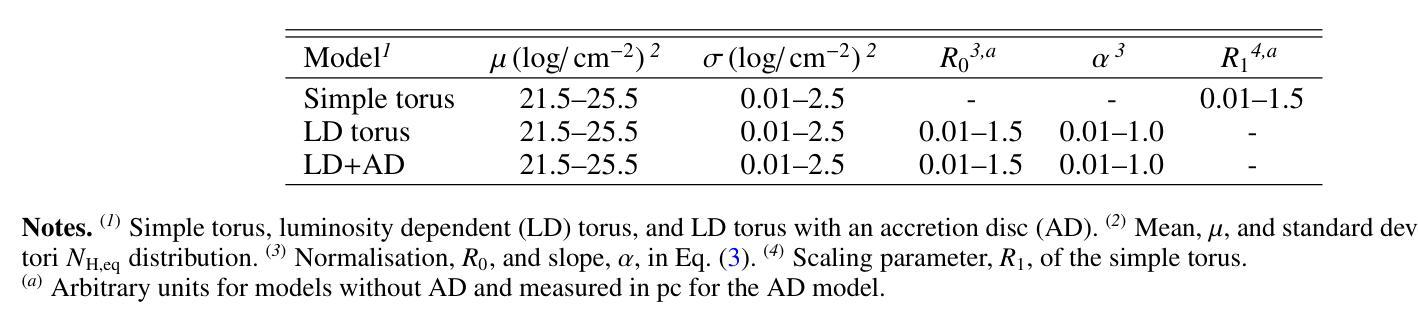
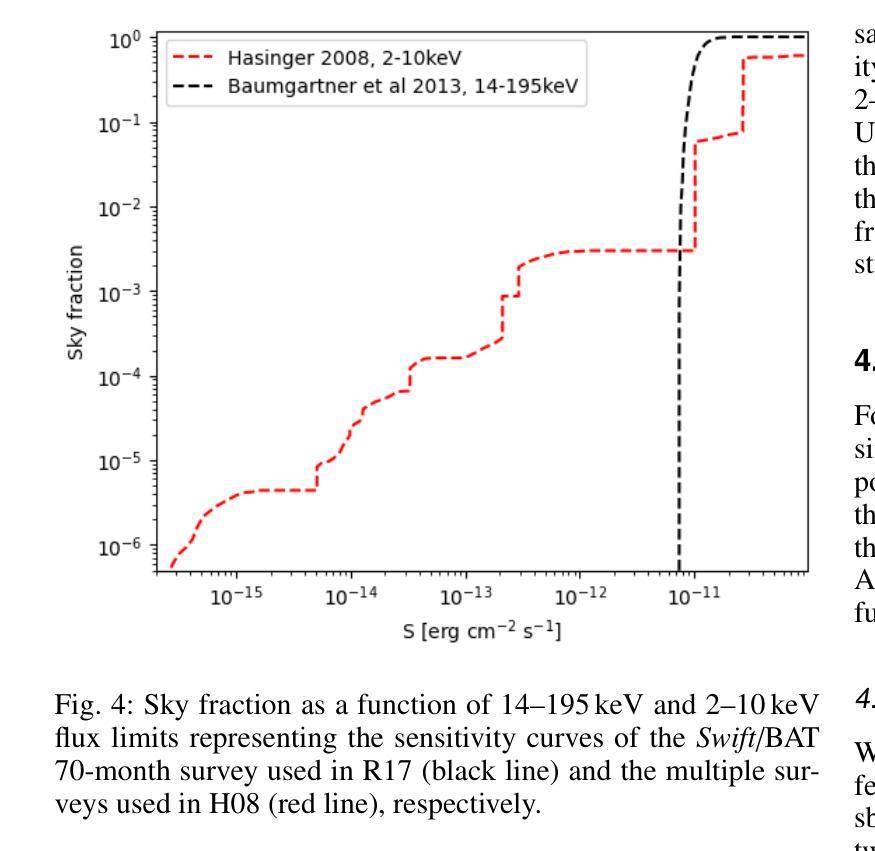
Self-consistent population synthesis of AGN from observational constraints in the X-rays
Authors:D. Gerolymatou, S. Paltani, C. Ricci, M. Regamey
The cosmic X-ray background (CXB) is produced by the emission of unresolved active galactic nuclei (AGN), thus providing key information about the properties of the primary and reprocessed X-ray emission components of the AGN population. Equally important, studies of individual sources provide additional constraints on the properties of AGN, such as their luminosity and obscuration. Until now, these constraints have not been self-consistently addressed by intrinsically linking emission, absorption, and reflection. Here we perform numerical simulations with the ray-tracing code, RefleX, which allows us to self-consistently model the X-ray emission of AGN with flexible geometries for the circumnuclear medium. Using the RefleX-simulated emission of an AGN population, we attempt to simultaneously reproduce the CXB and absorption properties measured in the X-rays, namely the observed fraction of $N_{\mathrm{H}}$ in bins of log($N_{\mathrm{H}}$) and the fraction of absorbed AGN, including their redshift and luminosity evolution. We sample an intrinsic X-ray luminosity function and construct gradually more complex physically motivated geometrical models. We examine how well each model can match all observational constraints using a simulation-based inference (SBI) approach. We find that, while the simple unification model can reproduce the CXB, a luminosity dependent dusty torus is needed to reproduce the absorption properties. When adding an accretion disc, the model best matches all constraints simultaneously. Our synthetic population is able to reproduce the dependence of the covering factor on luminosity, the AGN number counts from several surveys, and the observed correlation between reflection and obscuration. Finally, we derive an intrinsic Compton-thick fraction of 21$\pm$7%, consistent with local observations.
宇宙X射线背景(CXB)是由未解决的活跃星系核(AGN)的发射产生的,从而为关于AGN群体主要和再处理X射线发射成分的属性提供了关键信息。同样重要的是,对个人源的研究对AGNs的属性提供了额外的限制,例如它们的亮度和遮蔽性。迄今为止,这些约束尚未通过内在地联系发射、吸收和反射来自我一致地解决。在这里,我们使用光线追踪代码RefleX进行数值模拟,它允许我们根据核周介质的灵活几何形状来自我一致地模拟AGNs的X射线发射。我们使用RefleX模拟的AGNs群体的发射,试图同时复制在X射线下测量的CXB和属性,即观察到的$N_{\mathrm{H}}$分数在log($N_{\mathrm{H}}$)的容器中和吸收的AGNs的分数,包括它们的红移和亮度演化。我们对内在的X射线光度函数进行抽样,并构建逐渐更复杂的物理驱动几何模型。我们采用基于模拟的推断(SBI)方法,检查每个模型是否符合所有观测约束。我们发现,虽然简单的统一模型可以复制CXB,但需要依赖于亮度的尘埃环来复制吸收特性。当加入吸积盘时,该模型最能同时满足所有约束。我们的合成群体能够再现覆盖因子与亮度之间的依赖性、来自多个调查的AGNs数量计数以及反射和遮蔽之间的观察到的相关性。最后,我们得出内在的康普顿厚达21±7%,与当地观察结果一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in A&A
Summary
此文本探讨了宇宙X射线背景(CXB)由未解决的活动星系核(AGN)发射产生的问题。通过数值模拟和RefleX射线追踪代码,对AGN的X射线发射进行自洽建模,并尝试同时再现CXB和在X射线下测得的吸收特性。研究发现简单统一模型能再现CXB,但要再现吸收特性需要光度依赖的尘埃环。加入星周盘后,模型最能同时满足所有约束。该合成人口能够再现覆盖因子对光度的依赖性、多个调查的活跃星系核计数以及反射和遮蔽之间的观测相关性。
Key Takeaways
- 宇宙X射线背景(CXB)由未解决的活动星系核(AGN)发射产生,提供了关于AGN主要和再处理X射线发射成分的关键信息。
- 通过RefleX射线追踪代码进行数值模拟,能够自洽地建模具有可变几何结构的活跃星系核(AGNs)的X射线发射。
- 简单统一模型可以再现CXB,但要准确描述吸收特性,需要光度依赖的尘埃环模型。
- 加入星周盘后,模型最佳匹配所有观测约束,能够同时考虑发射、吸收和反射。
- 合成人口模型能够成功模拟覆盖因子与光度之间的依赖性、多个调查的活跃星系核计数以及反射与遮蔽之间的观测关系。
- 研究发现存在内在康普顿厚达21±7%的活跃星系核,这与本地观测结果一致。
点此查看论文截图

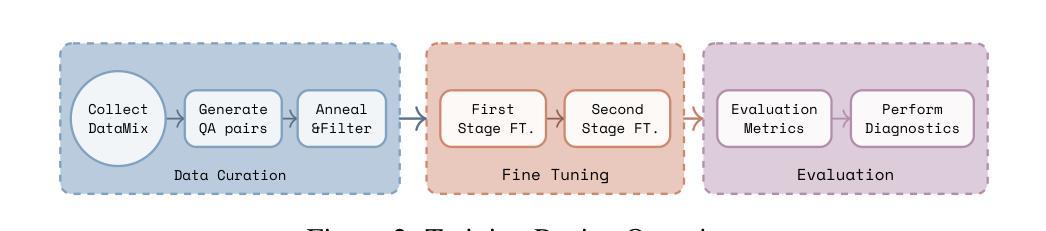
Adapting Lightweight Vision Language Models for Radiological Visual Question Answering
Authors:Aditya Shourya, Michel Dumontier, Chang Sun
Recent advancements in vision-language systems have improved the accuracy of Radiological Visual Question Answering (VQA) Models. However, some challenges remain across each stage of model development: limited expert-labeled images hinders data procurement at scale; the intricate and nuanced patterns of radiological images make modeling inherently difficult; and the lack of evaluation evaluation efforts makes it difficult to identify cases where the model might be ill-conditioned. In this study, we fine-tune a lightweight 3B parameter vision-language model for Radiological VQA, demonstrating that small models, when appropriately tuned with curated data, can achieve robust performance across both open- and closed-ended questions. We propose a cost-effective training pipeline from synthetic question-answer pair generation to multi-stage fine-tuning on specialised radiological domain-targeted datasets (e.g., ROCO v2.0, MedPix v2.0). Our results show that despite operating at a fraction of the scale of state-of-the-art models such as LLaVA-Med, our model achieves promising performance given its small parameter size and the limited scale of training data. We introduce a lightweight saliency-based diagnostic tool that enables domain experts to inspect VQA model performance and identify ill-conditioned failure modes through saliency analysis.
最近,视觉语言系统的进步提高了放射学视觉问答(VQA)模型的准确性。然而,在模型发展的每个阶段仍然存在一些挑战:专家标注的图像数量有限,阻碍了大规模数据采购;放射图像的复杂和细微模式使建模变得固有地困难;缺乏评估努力使得难以确定模型可能出现问题的情况。在这项研究中,我们对一个轻量级的3B参数视觉语言模型进行了微调,用于放射学VQA,结果表明,当使用精选数据适当调整时,小型模型可以在开放和封闭问题中都实现稳健的性能。我们提出了一个经济实惠的训练流程,从合成问题答案对生成到在特定放射学领域目标数据集(例如ROCO v2.0、MedPix v2.0)上的多阶段微调。我们的结果表明,尽管我们的模型规模只有最先进的模型(如LLaVA-Med)的一部分,但考虑到其较小的参数规模和有限的训练数据量,其性能还是很有希望的。我们引入了一个轻量级的基于显著性的诊断工具,使领域专家能够检查VQA模型性能,并通过显著性分析确定不良的失败模式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期视觉语言系统的进步提高了放射学视觉问答(VQA)模型的准确性,但仍存在数据获取、建模难度和评估困难等挑战。本研究微调了一个轻量级的3B参数视觉语言模型,用于放射学VQA任务,证明适当调优和精选数据可使小模型在开放和封闭问题中都表现稳健。同时,本研究提出了一个经济高效的训练流程,包括从合成问答对生成到特定放射学领域数据集的多阶段微调。尽管模型规模远小于当前先进技术,但表现仍然令人鼓舞。此外,本研究还引入了一种轻量级的基于显著性的诊断工具,帮助领域专家检查VQA模型性能并识别不良的失效模式。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言系统的进步提高了放射学视觉问答(VQA)模型的准确性。
- 数据获取、建模难度和评估困难仍是VQA模型发展的挑战。
- 通过微调轻量级模型并配以精选数据,可以在放射学VQA任务中取得稳健表现。
- 研究提出了一个经济高效的训练流程,包括合成问答对生成和多阶段微调。
- 轻量级模型在规模远小于当前先进技术的情况下仍表现出色。
- 引入了一种轻量级的基于显著性的诊断工具,以检查VQA模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

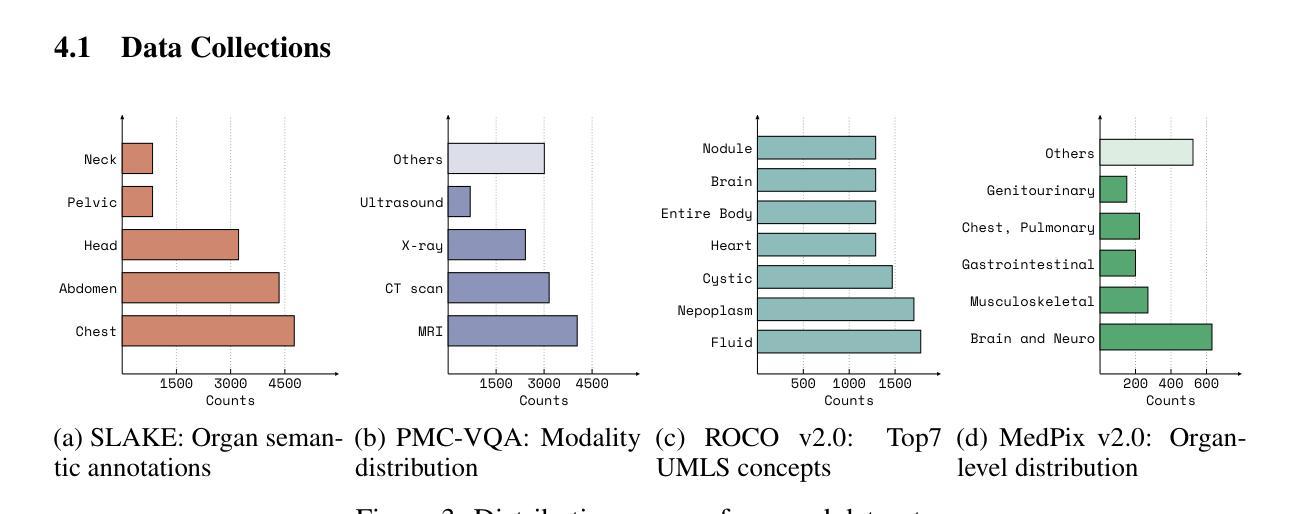
BRISC: Annotated Dataset for Brain Tumor Segmentation and Classification with Swin-HAFNet
Authors:Amirreza Fateh, Yasin Rezvani, Sara Moayedi, Sadjad Rezvani, Fatemeh Fateh, Mansoor Fateh
Accurate segmentation and classification of brain tumors from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) remain key challenges in medical image analysis, largely due to the lack of high-quality, balanced, and diverse datasets. In this work, we present a new curated MRI dataset designed specifically for brain tumor segmentation and classification tasks. The dataset comprises 6,000 contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scans annotated by certified radiologists and physicians, spanning three major tumor types-glioma, meningioma, and pituitary-as well as non-tumorous cases. Each sample includes high-resolution labels and is categorized across axial, sagittal, and coronal imaging planes to facilitate robust model development and cross-view generalization. To demonstrate the utility of the dataset, we propose a transformer-based segmentation model and benchmark it against established baselines. Our method achieves the highest weighted mean Intersection-over-Union (IoU) of 82.3%, with improvements observed across all tumor categories. Importantly, this study serves primarily as an introduction to the dataset, establishing foundational benchmarks for future research. We envision this dataset as a valuable resource for advancing machine learning applications in neuro-oncology, supporting both academic research and clinical decision-support development. datasetlink: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/briscdataset/brisc2025/
从磁共振成像(MRI)准确分割和分类脑肿瘤仍是医学图像分析中的关键挑战,这主要是由于缺乏高质量、均衡和多样化的数据集。在这项工作中,我们展示了一个专为脑肿瘤分割和分类任务设计的新MRI数据集。该数据集包含由认证放射学家和医生注释的6000个对比增强的T1加权MRI扫描,涵盖三种主要肿瘤类型:胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤,以及非肿瘤病例。每个样本都包括高分辨率标签,并根据轴向、矢状面和冠状面成像平面进行分类,以促进稳健的模型开发和跨视图泛化。为了证明数据集的有效性,我们提出了一种基于transformer的分割模型,并将其与现有的基线进行了比较。我们的方法实现了加权平均交并比(IoU)为82.3%的最高值,所有肿瘤类别均有所改进。重要的是,这项研究主要是为了介绍数据集,为未来研究建立基础基准。我们期望该数据集能成为神经肿瘤学中机器学习应用的重要资源,支持学术研究和临床决策支持开发。数据集链接:https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/briscdataset/brisc2025/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一个专为脑肿瘤分割和分类任务设计的新MRI数据集,包含由认证放射科医生和医师注释的6000个对比增强的T1加权MRI扫描,涵盖三种主要肿瘤类型及非肿瘤病例。为展示该数据集实用性,研究提出了基于transformer的分割模型,并在基准测试中达到最高加权平均交并比(IoU)为82.3%。此数据集有望为神经肿瘤学机器学习应用提供宝贵资源,支持学术研究和临床决策支持开发。
Key Takeaways
- 研究介绍了一个新MRI数据集,专为脑肿瘤分割和分类任务设计。
- 数据集包含6000个对比增强的T1加权MRI扫描,涵盖三种主要肿瘤类型及非肿瘤病例。
- 数据集包含高分辨率标签,分类轴向、矢状和冠状成像平面,有助于稳健模型开发和跨视图推广。
- 为展示数据集实用性,研究提出了基于transformer的分割模型,并在基准测试中表现优异。
- 该模型达到最高加权平均交并比(IoU)为82.3%,在所有肿瘤类别中均观察到改进。
- 此数据集为机器学习和神经肿瘤学研究提供了宝贵资源。
点此查看论文截图

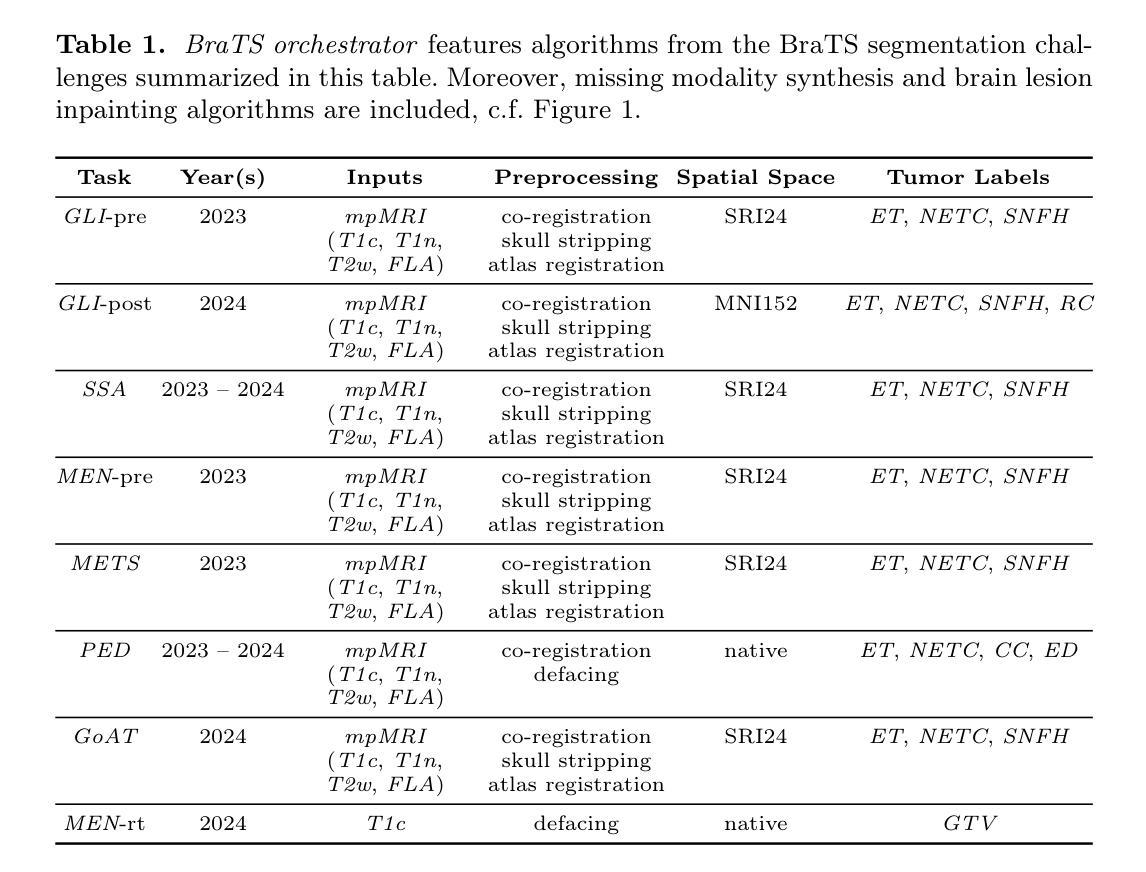
BraTS orchestrator : Democratizing and Disseminating state-of-the-art brain tumor image analysis
Authors:Florian Kofler, Marcel Rosier, Mehdi Astaraki, Ujjwal Baid, Hendrik Möller, Josef A. Buchner, Felix Steinbauer, Eva Oswald, Ezequiel de la Rosa, Ivan Ezhov, Constantin von See, Jan Kirschke, Anton Schmick, Sarthak Pati, Akis Linardos, Carla Pitarch, Sanyukta Adap, Jeffrey Rudie, Maria Correia de Verdier, Rachit Saluja, Evan Calabrese, Dominic LaBella, Mariam Aboian, Ahmed W. Moawad, Nazanin Maleki, Udunna Anazodo, Maruf Adewole, Marius George Linguraru, Anahita Fathi Kazerooni, Zhifan Jiang, Gian Marco Conte, Hongwei Li, Juan Eugenio Iglesias, Spyridon Bakas, Benedikt Wiestler, Marie Piraud, Bjoern Menze
The Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) cluster of challenges has significantly advanced brain tumor image analysis by providing large, curated datasets and addressing clinically relevant tasks. However, despite its success and popularity, algorithms and models developed through BraTS have seen limited adoption in both scientific and clinical communities. To accelerate their dissemination, we introduce BraTS orchestrator, an open-source Python package that provides seamless access to state-of-the-art segmentation and synthesis algorithms for diverse brain tumors from the BraTS challenge ecosystem. Available on GitHub (https://github.com/BrainLesion/BraTS), the package features intuitive tutorials designed for users with minimal programming experience, enabling both researchers and clinicians to easily deploy winning BraTS algorithms for inference. By abstracting the complexities of modern deep learning, BraTS orchestrator democratizes access to the specialized knowledge developed within the BraTS community, making these advances readily available to broader neuro-radiology and neuro-oncology audiences.
脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)挑战赛系列通过提供大规模、精选的数据集并解决与临床相关的任务,极大地推动了脑肿瘤图像分析的发展。然而,尽管其取得了成功并广受欢迎,但通过在BraTS中开发的算法和模型在科学界和临床界的采用仍然有限。为了加速其普及,我们引入了BraTS编排器,这是一个开源的Python软件包,旨在无缝访问BraTS挑战赛生态系统中各种肿瘤的最新分割和合成算法。该软件包已在GitHub上提供(https://github.com/BrainLesion/BraTS),其中包含针对编程经验最少的用户设计的直观教程,使研究者和临床医生能够轻松部署赢得BraTS算法的推理。通过抽象现代深度学习的复杂性,BraTS编排器使来自BraTS社区的专业知识得以普及,使这些进展能够轻松地为更广泛的神经放射学和神经肿瘤学受众所利用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27p, 2figs, 3tabs
Summary
本文介绍了BraTS挑战集群对脑肿瘤图像分析的重大推动作用,以及为加速相关算法和模型在科研及临床社区的普及,推出的开源Python包——BraTS orchestrator。该包提供对BraTS挑战生态系统中先进分割和合成算法的便捷访问,并设计有直观教程,便于用户部署使用获奖的BraTS算法进行推理。通过抽象现代深度学习的复杂性,BraTS orchestrator使得BraTS社区内的专业知识得以民主化访问,使得神经放射学和神经肿瘤学领域的更广泛受众能轻松利用这些进展。
Key Takeaways
- BraTS挑战集群显著推动了脑肿瘤图像分析的发展。
- BraTS通过提供大量经过整理的数据库和应对临床相关任务,促进了相关研究。
- 尽管相关研究取得了很多进展,但在科研及临床社区中算法的采用仍然有限。
- 为了加速普及,推出了名为BraTS orchestrator的开源Python包。
- BraTS orchestrator提供对BraTS挑战生态系统中先进算法的便捷访问。
- 该包设计有直观教程,适合缺乏编程经验的用户,便于部署使用获奖的BraTS算法进行推理。
点此查看论文截图

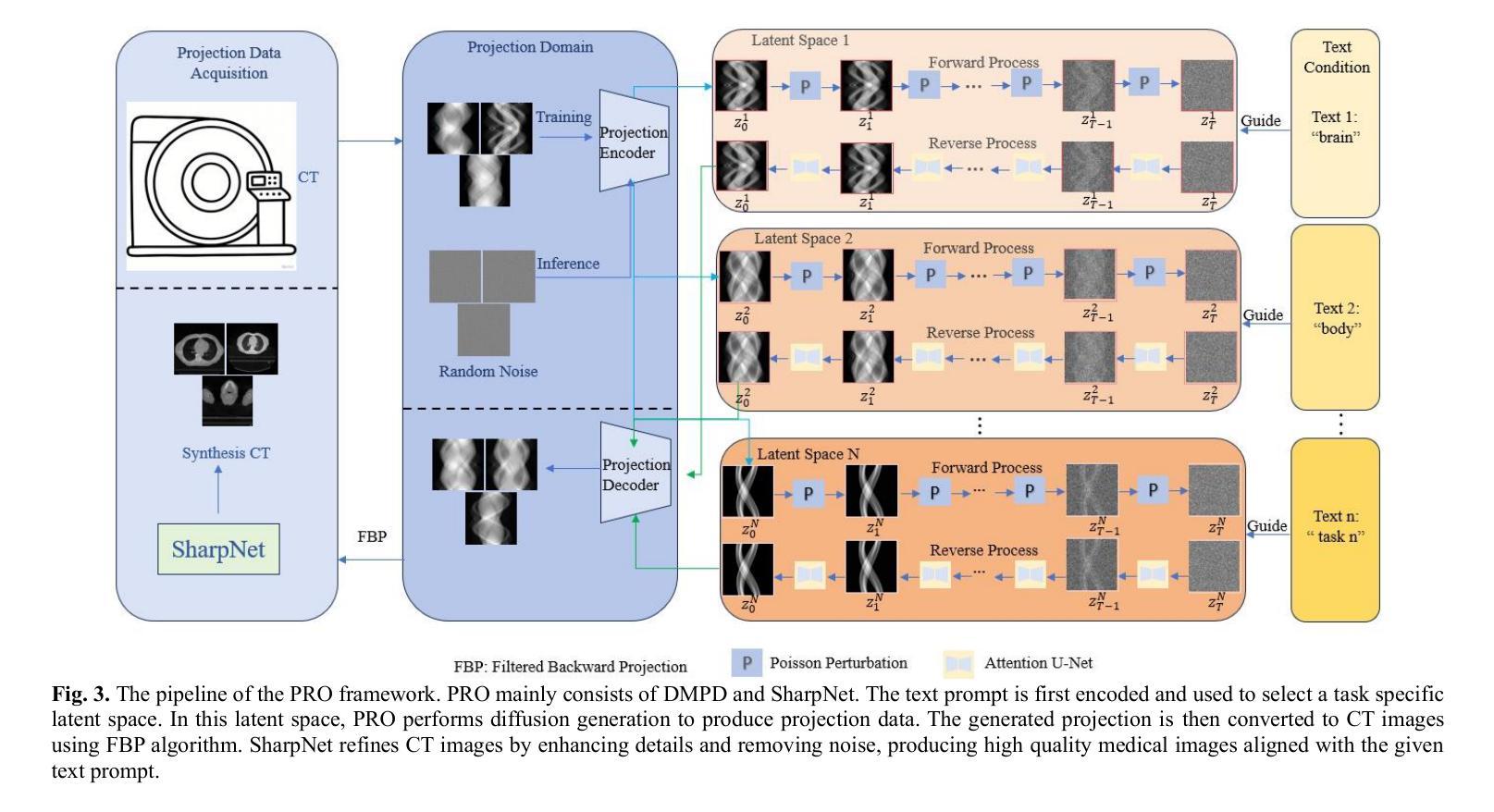
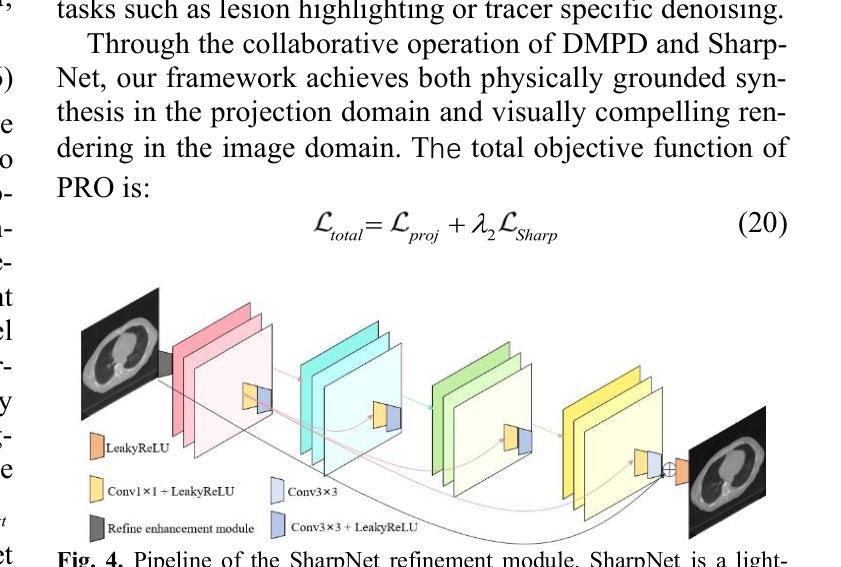
PRO: Projection Domain Synthesis for CT Imaging
Authors:Kang Chen, Bin Huang, Xuebin Yang, Junyan Zhang, Qiegen Liu
Synthesizing high quality CT projection data remains a significant challenge due to the limited availability of annotated data and the complex nature of CT imaging. In this work, we present PRO, a projection domain synthesis foundation model for CT imaging. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that performs CT synthesis in the projection domain. Unlike previous approaches that operate in the image domain, PRO learns rich structural representations from raw projection data and leverages anatomical text prompts for controllable synthesis. This projection domain strategy enables more faithful modeling of underlying imaging physics and anatomical structures. Moreover, PRO functions as a foundation model, capable of generalizing across diverse downstream tasks by adjusting its generative behavior via prompt inputs. Experimental results demonstrated that incorporating our synthesized data significantly improves performance across multiple downstream tasks, including low-dose and sparse-view reconstruction. These findings underscore the versatility and scalability of PRO in data generation for various CT applications. These results highlight the potential of projection domain synthesis as a powerful tool for data augmentation and robust CT imaging. Our source code is publicly available at: https://github.com/yqx7150/PRO.
合成高质量的CT投影数据仍然是一个巨大的挑战,这主要是由于标注数据的有限性和CT成像的复杂性。在这项工作中,我们提出了PRO,这是一个用于CT成像的投影域合成基础模型。据我们所知,这是第一项在投影域进行CT合成的研究。与在图像域运行的前方法不同,PRO从原始投影数据中学习丰富的结构表示,并利用解剖文本提示进行可控合成。这种投影域策略能够更真实地模拟潜在的成像物理和解剖结构。此外,PRO作为一个基础模型,能够通过提示输入调整其生成行为,在多种下游任务中通用。实验结果表明,使用我们合成的数据可以显著提高多个下游任务的性能,包括低剂量和稀疏视图重建。这些发现强调了PRO在各种CT应用中的数据生成中的通用性和可扩展性。这些结果突出了投影域合成作为数据增强和稳健CT成像的强大工具的潜力。我们的源代码可在:https://github.com/yqx7150/PRO公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了针对CT成像的投影域合成基础模型PRO。该模型在投影域进行CT合成,不同于以往在图像域操作的方法,PRO从原始投影数据中学习丰富的结构表示,并利用解剖文本提示进行可控合成。这种投影域策略能够更好地模拟成像物理过程和解剖结构。此外,PRO作为基础模型,能够通过提示输入调整其生成行为,广泛应用于多种下游任务。实验结果表明,使用合成的数据可以显著提高多个下游任务(如低剂量和稀疏视图重建)的性能。此摘要强调了PRO在数据生成方面的通用性和可扩展性,展示了投影域合成在数据增强和稳健CT成像中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- PRO是首个在投影域进行CT合成的模型。
- PRO从原始投影数据中学习丰富的结构表示,利用解剖文本提示进行可控合成。
- 投影域策略能够更好地模拟成像物理过程和解剖结构。
- PRO作为基础模型,可以广泛应用于多种下游任务。
- 使用PRO合成的数据可以显著提高多个下游任务(如低剂量和稀疏视图重建)的性能。
- 实验结果证明了PRO在数据生成方面的通用性和可扩展性。
- PRO的源代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

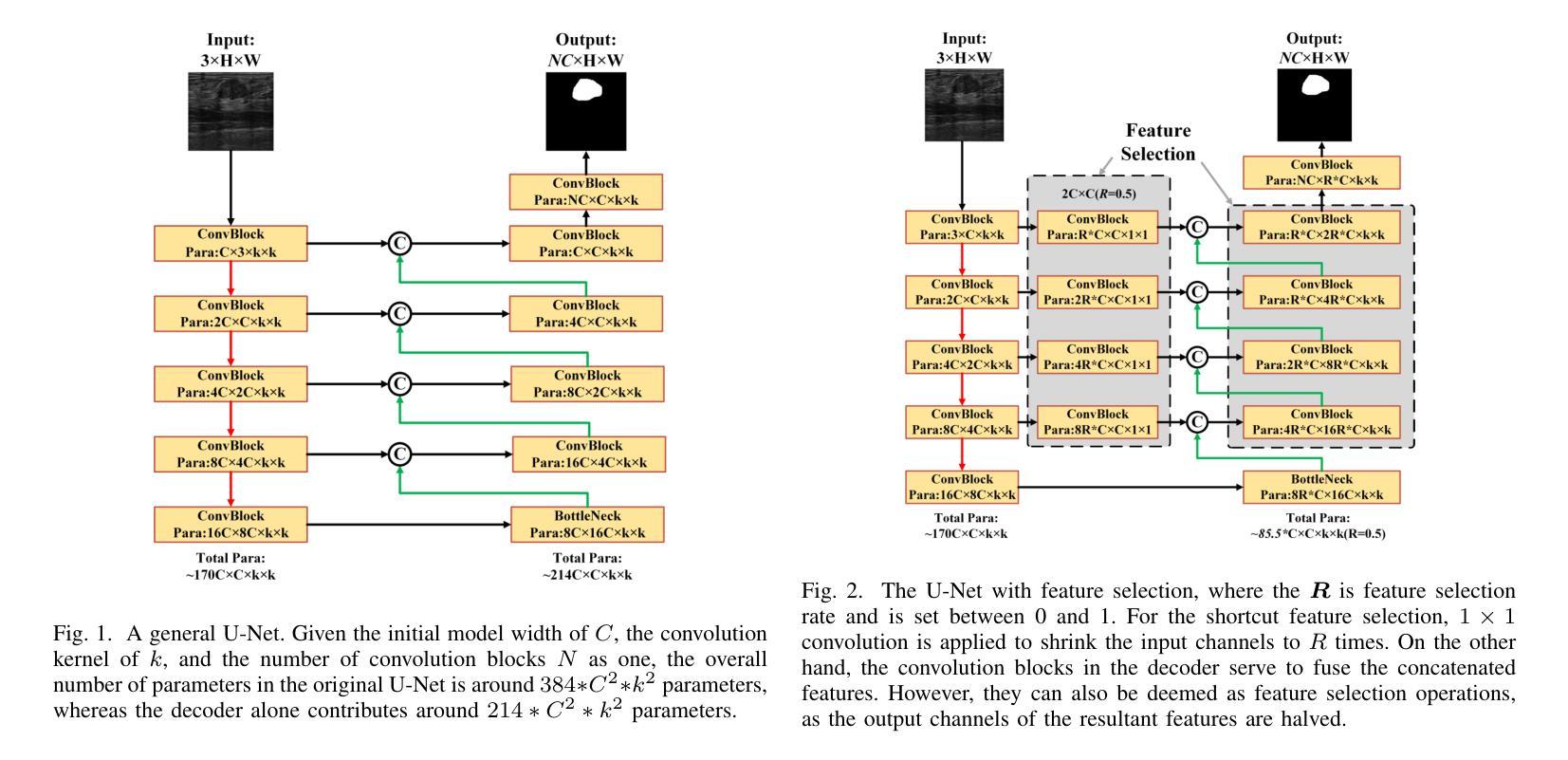
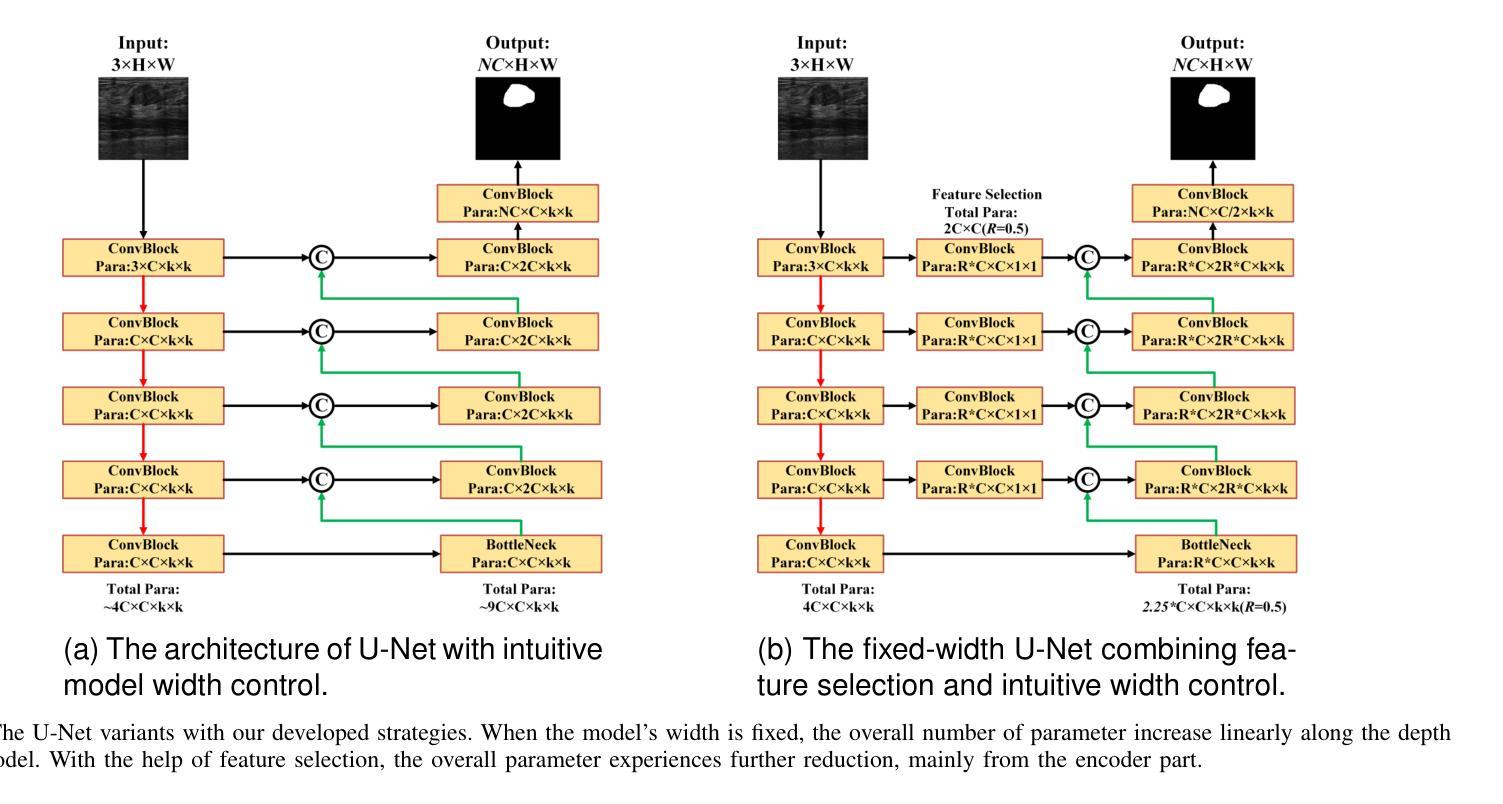
Simple is what you need for efficient and accurate medical image segmentation
Authors:Xiang Yu, Yayan Chen, Guannan He, Qing Zeng, Yue Qin, Meiling Liang, Dandan Luo, Yimei Liao, Zeyu Ren, Cheng Kang, Delong Yang, Bocheng Liang, Bin Pu, Ying Yuan, Shengli Li
While modern segmentation models often prioritize performance over practicality, we advocate a design philosophy prioritizing simplicity and efficiency, and attempted high performance segmentation model design. This paper presents SimpleUNet, a scalable ultra-lightweight medical image segmentation model with three key innovations: (1) A partial feature selection mechanism in skip connections for redundancy reduction while enhancing segmentation performance; (2) A fixed-width architecture that prevents exponential parameter growth across network stages; (3) An adaptive feature fusion module achieving enhanced representation with minimal computational overhead. With a record-breaking 16 KB parameter configuration, SimpleUNet outperforms LBUNet and other lightweight benchmarks across multiple public datasets. The 0.67 MB variant achieves superior efficiency (8.60 GFLOPs) and accuracy, attaining a mean DSC/IoU of 85.76%/75.60% on multi-center breast lesion datasets, surpassing both U-Net and TransUNet. Evaluations on skin lesion datasets (ISIC 2017/2018: mDice 84.86%/88.77%) and endoscopic polyp segmentation (KVASIR-SEG: 86.46%/76.48% mDice/mIoU) confirm consistent dominance over state-of-the-art models. This work demonstrates that extreme model compression need not compromise performance, providing new insights for efficient and accurate medical image segmentation. Codes can be found at https://github.com/Frankyu5666666/SimpleUNet.
摘要:尽管现代分割模型通常更重视性能而非实用性,但我们提倡以简洁和高效为设计优先理念,并尝试设计高性能分割模型。本文介绍了SimpleUNet,这是一种可扩展的、超轻量级的医学图像分割模型,具有三个关键创新点:一、跳跃连接中的部分特征选择机制,旨在减少冗余的同时提高分割性能;二、固定宽度架构,防止网络阶段参数呈指数增长;三、自适应特征融合模块,以最小的计算开销实现增强的表示。凭借创纪录的仅占用 16 KB 参数的配置,SimpleUNet 在多个公共数据集上优于 LBUNet 和其他轻量级基准测试。其中,0.67 MB 的变体展现出卓越的效率(GFLOPs 达到 8.6)和准确度,在多中心乳腺病变数据集上平均 DSC/IoU 达到 85.76%/75.6%。该模型不仅超越了 U-Net 和 TransUNet,且在皮肤病变数据集(ISIC 2017/2018 年的 mDice 分别为 84.86%/88.77%)以及内镜息肉分割(KVASIR-SEG 的 mDice/mIoU 为 86.46%/76.48%)上的评估结果也证明了其在最新技术模型中的一致性优势。这项工作证明了极度的模型压缩并不一定会影响性能,为高效且准确的医学图像分割提供了新的见解。代码可通过 https://github.com/Frankyu5666666/SimpleUNet 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文提出一种简洁高效的医学图像分割模型SimpleUNet,具有三大创新点:采用部分特征选择机制提高分割性能并减少冗余;采用固定宽度架构防止网络阶段参数指数增长;以及自适应特征融合模块实现增强表示并减少计算开销。SimpleUNet在多公共数据集上表现出超越LBUNet和其他轻量级基准的性能,实现了高效和准确的医学图像分割。
Key Takeaways
- SimpleUNet模型强调简洁和效率的设计哲学,同时实现高性能的医学图像分割。
- 模型具有三大关键创新:部分特征选择、固定宽度架构和自适应特征融合。
- SimpleUNet实现了参数配置的突破,仅有16KB参数。
- 在多个公共数据集上,SimpleUNet超越了LBUNet和其他轻量级基准。
- 0.67MB的变体在效率和准确性上表现优越,达到85.76%的均值DSC/IoU。
- 在皮肤病变数据集和内镜息肉分割上的评价证明了SimpleUNet的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


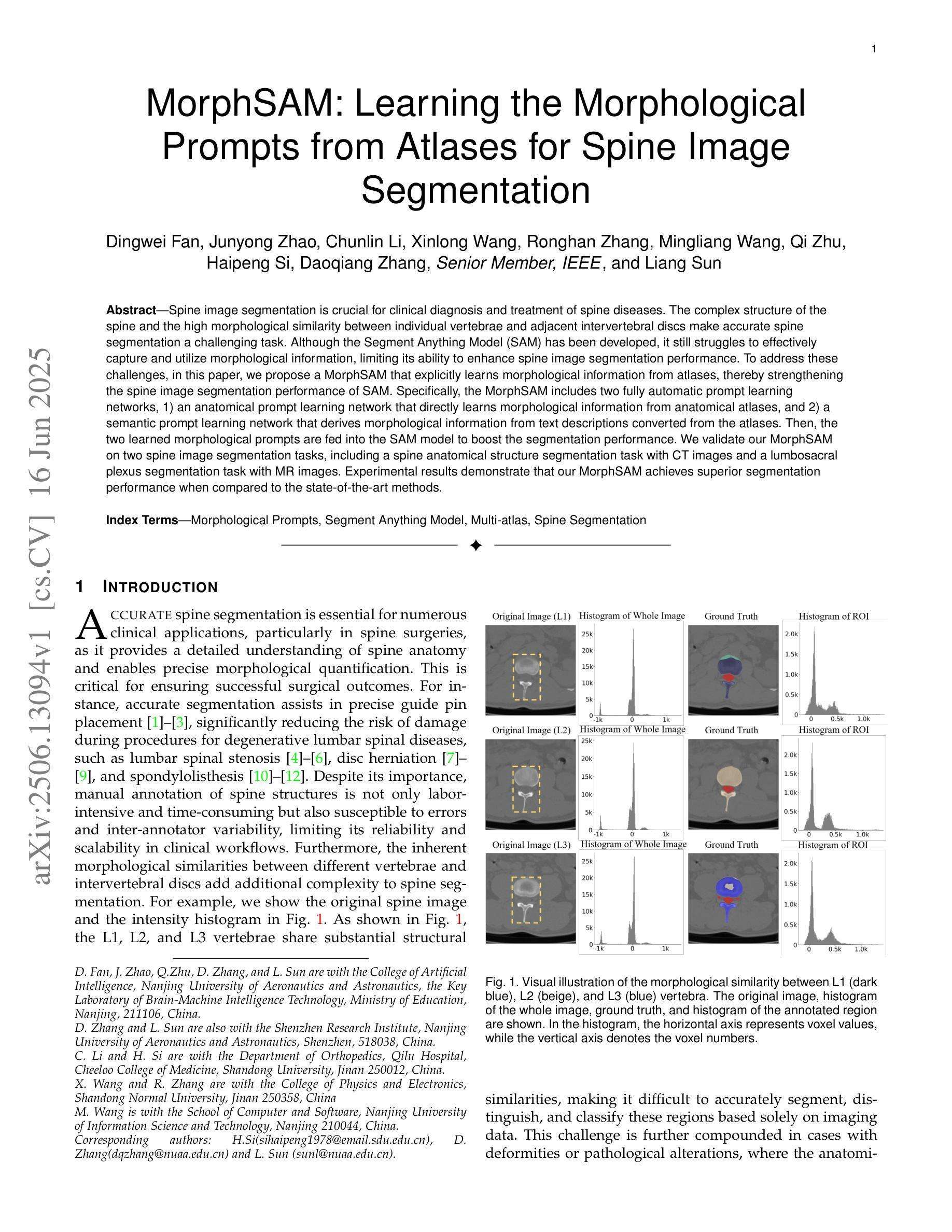
MorphSAM: Learning the Morphological Prompts from Atlases for Spine Image Segmentation
Authors:Dingwei Fan, Junyong Zhao, Chunlin Li, Xinlong Wang, Ronghan Zhang, Mingliang Wang, Qi Zhu, Haipeng Si, Daoqiang Zhang, Liang Sun
Spine image segmentation is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment of spine diseases. The complex structure of the spine and the high morphological similarity between individual vertebrae and adjacent intervertebral discs make accurate spine segmentation a challenging task. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has been developed, it still struggles to effectively capture and utilize morphological information, limiting its ability to enhance spine image segmentation performance. To address these challenges, in this paper, we propose a MorphSAM that explicitly learns morphological information from atlases, thereby strengthening the spine image segmentation performance of SAM. Specifically, the MorphSAM includes two fully automatic prompt learning networks, 1) an anatomical prompt learning network that directly learns morphological information from anatomical atlases, and 2) a semantic prompt learning network that derives morphological information from text descriptions converted from the atlases. Then, the two learned morphological prompts are fed into the SAM model to boost the segmentation performance. We validate our MorphSAM on two spine image segmentation tasks, including a spine anatomical structure segmentation task with CT images and a lumbosacral plexus segmentation task with MR images. Experimental results demonstrate that our MorphSAM achieves superior segmentation performance when compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
脊椎图像分割对于脊椎疾病的临床诊断和治疗至关重要。脊椎的复杂结构以及各个椎体和相邻椎间盘之间的高度形态相似性,使得准确的脊椎分割成为一项具有挑战性的任务。虽然已经出现分段任何模型(SAM),但它仍然难以有效地捕获和利用形态信息,从而限制了其在提高脊椎图像分割性能方面的能力。为了解决这些挑战,本文提出了一种MorphSAM,它可以从图谱中显式学习形态信息,从而增强SAM的脊椎图像分割性能。具体来说,MorphSAM包括两个全自动的提示学习网络:1)解剖提示学习网络,直接从解剖图谱中学习形态信息;2)语义提示学习网络,从由图谱转换的文本描述中派生形态信息。然后,将这两个学到的形态提示输入到SAM模型中,以提高分割性能。我们在两个脊椎图像分割任务上验证了我们的MorphSAM,包括使用CT图像的脊椎解剖结构分割任务和使用MR图像的腰骶丛分割任务。实验结果表明,与最先进的方法相比,我们的MorphSAM实现了优越的分割性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文针对脊椎图像分割中的挑战,提出了MorphSAM模型。该模型通过从图谱中显式学习形态信息,增强了Segment Anything Model(SAM)对脊椎图像分割的性能。MorphSAM包括两个全自动提示学习网络:一个是从图谱直接学习形态信息的解剖提示学习网络,另一个是从文本描述中学习形态信息的语义提示学习网络。这两个学到的形态提示被输入到SAM模型中,以提高分割性能。在两项脊椎图像分割任务中,包括使用CT图像的脊椎结构分割任务和使用MR图像的腰骶丛分割任务,验证了MorphSAM的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 脊椎图像分割在临床诊断和治疗脊椎疾病中具有重要性。
- 脊椎的复杂结构和个体椎骨与相邻椎间盘的高形态相似性使得准确分割具有挑战性。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在脊椎图像分割中虽有一定成效,但难以有效捕捉和利用形态信息。
- MorphSAM模型被提出以解决这些挑战,它通过从图谱中显式学习形态信息来增强SAM的性能。
- MorphSAM包括两个全自动提示学习网络:解剖提示学习网络和语义提示学习网络,分别从图谱和文本描述中学习形态信息。
- 两个学到的形态提示被输入到SAM模型中,以提高分割性能。
点此查看论文截图
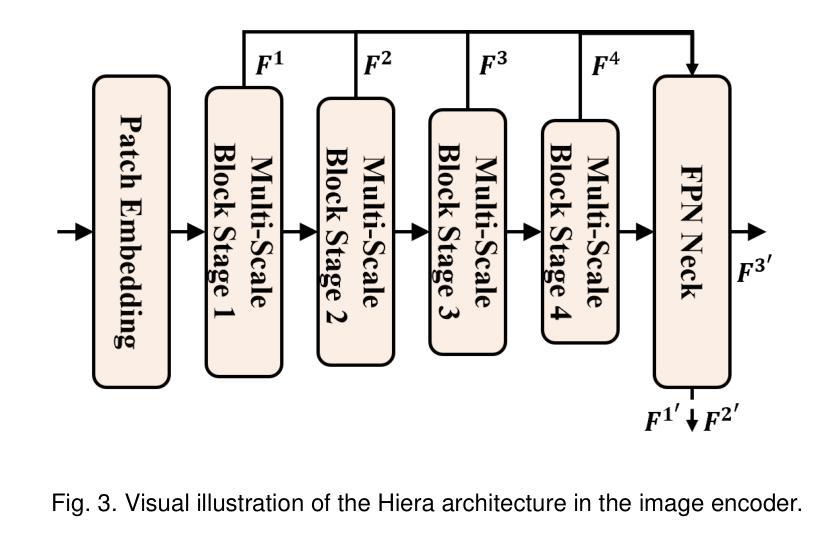
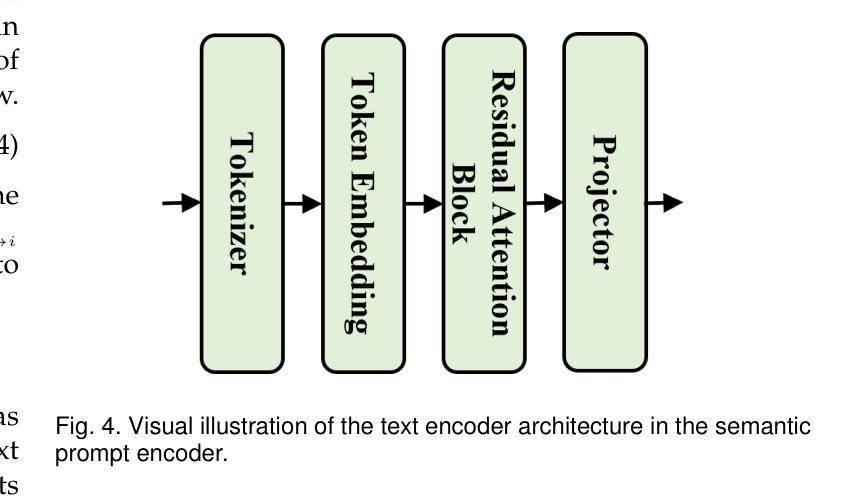
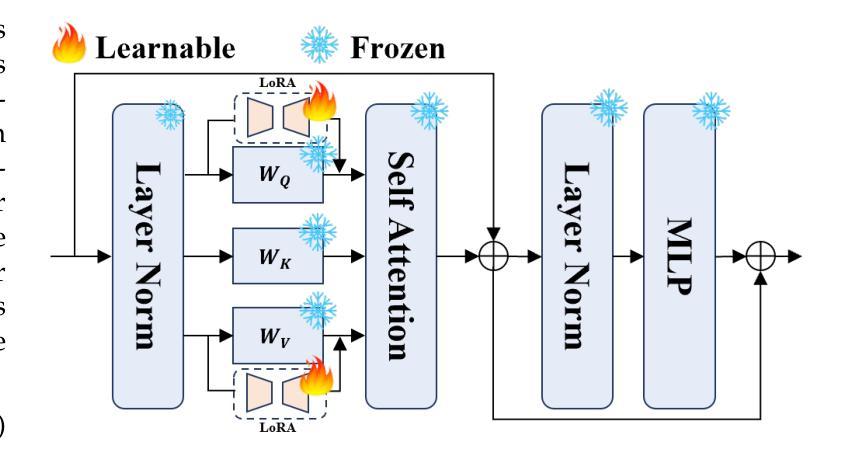
Unleashing Diffusion and State Space Models for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Rong Wu, Ziqi Chen, Liming Zhong, Heng Li, Hai Shu
Existing segmentation models trained on a single medical imaging dataset often lack robustness when encountering unseen organs or tumors. Developing a robust model capable of identifying rare or novel tumor categories not present during training is crucial for advancing medical imaging applications. We propose DSM, a novel framework that leverages diffusion and state space models to segment unseen tumor categories beyond the training data. DSM utilizes two sets of object queries trained within modified attention decoders to enhance classification accuracy. Initially, the model learns organ queries using an object-aware feature grouping strategy to capture organ-level visual features. It then refines tumor queries by focusing on diffusion-based visual prompts, enabling precise segmentation of previously unseen tumors. Furthermore, we incorporate diffusion-guided feature fusion to improve semantic segmentation performance. By integrating CLIP text embeddings, DSM captures category-sensitive classes to improve linguistic transfer knowledge, thereby enhancing the model’s robustness across diverse scenarios and multi-label tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of DSM in various tumor segmentation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/Rows21/KMax-Mamba.
现有基于单一医学成像数据集的分割模型在面临未见过的器官或肿瘤时,其稳健性往往不足。开发一种能够识别训练期间不存在的罕见或新型肿瘤类别的稳健模型,对于推动医学成像应用至关重要。我们提出了DSM(一个利用扩散状态空间模型进行未见肿瘤类别分割的新型框架)。DSM利用两组对象查询,在修改后的注意力解码器内进行训练,以提高分类准确性。首先,模型使用对象感知特征分组策略学习器官查询,以捕获器官级别的视觉特征。然后,它通过专注于基于扩散的视觉提示来优化肿瘤查询,从而实现先前未见肿瘤的精确分割。此外,我们结合了扩散引导的特征融合,以提高语义分割性能。通过集成CLIP文本嵌入,DSM捕获类别敏感类,以改善语言转移知识,从而增强模型在各种场景和多标签任务中的稳健性。大量实验证明,DSM在各种肿瘤分割任务中的性能卓越。代码可在https://github.com/Rows21/KMax-Mamba找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的医学图像分割框架DSM,该框架利用扩散模型和状态空间模型对训练数据以外的肿瘤类别进行分割。DSM通过两组对象查询在修改的关注解码器中进行训练,以提高分类准确性。此外,它还结合CLIP文本嵌入来提高模型的跨场景和多标签任务的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- DSM利用扩散和状态空间模型来分割医学图像中未见的肿瘤类别。
- 通过两组对象查询在修改的关注解码器中进行训练,提高分类准确性。
- 采用对象感知特征分组策略来学习器官查询,通过扩散视觉提示来精细肿瘤查询。
- 引入扩散引导的特征融合以提高语义分割性能。
- 结合CLIP文本嵌入,捕获类别敏感类,提高语言转移知识。
- DSM框架在多种肿瘤分割任务中表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

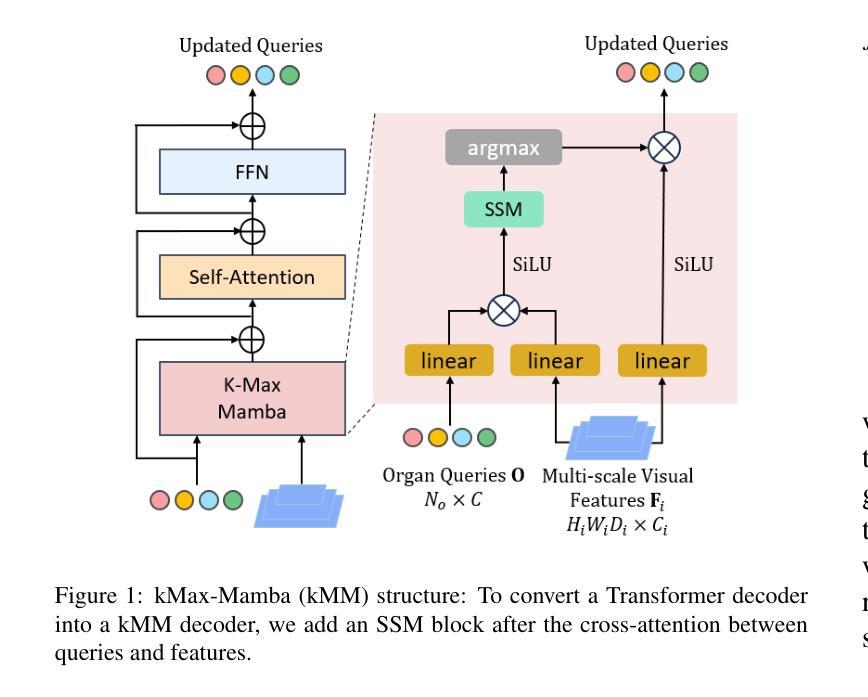
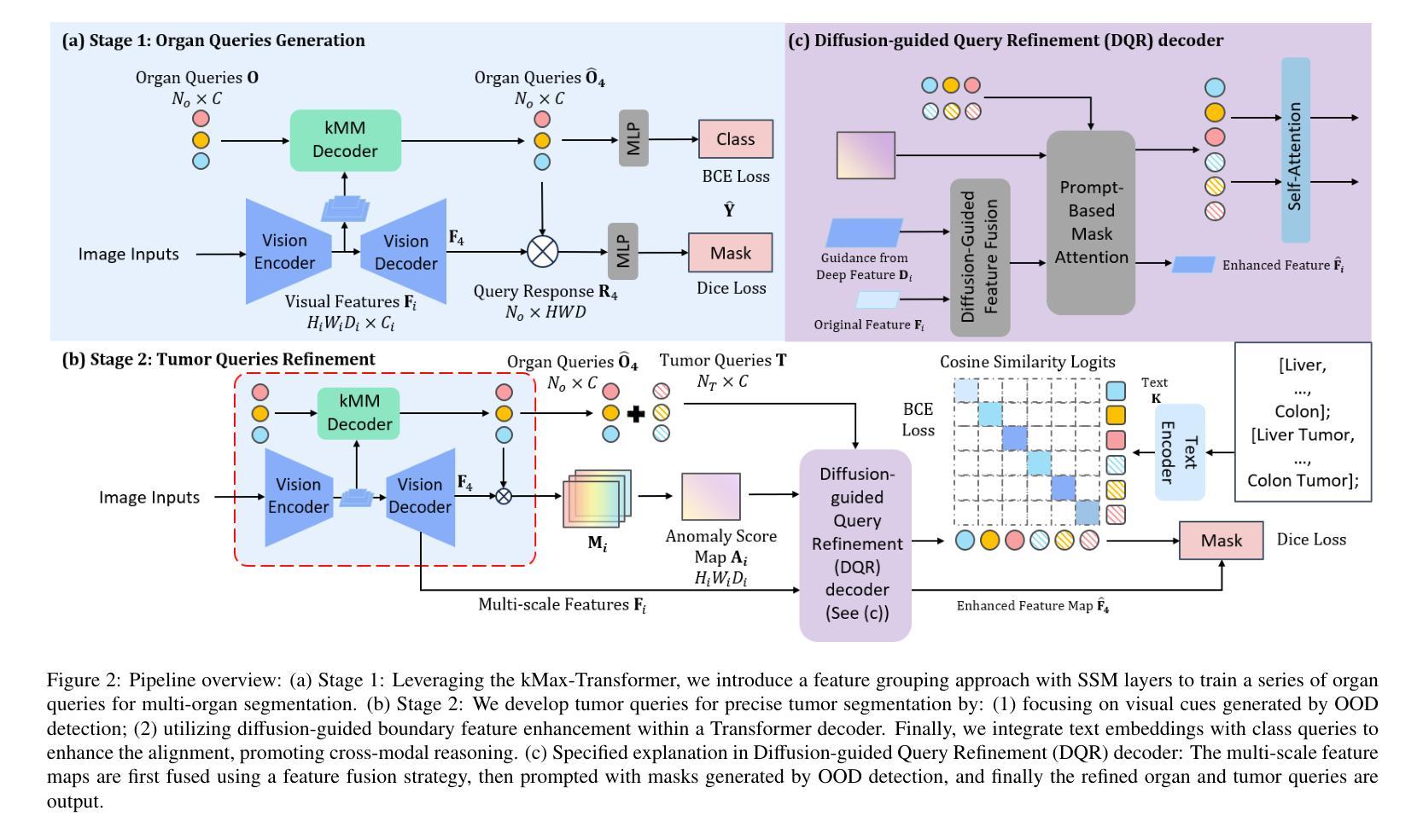
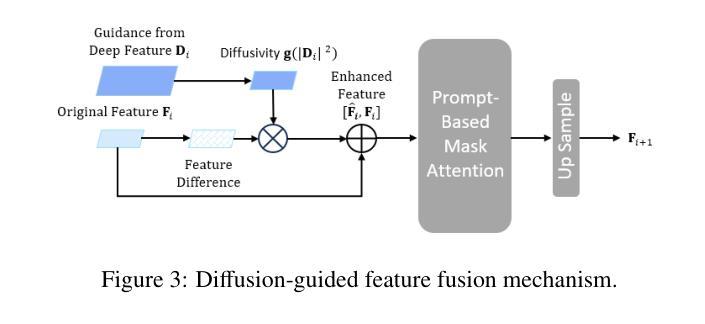
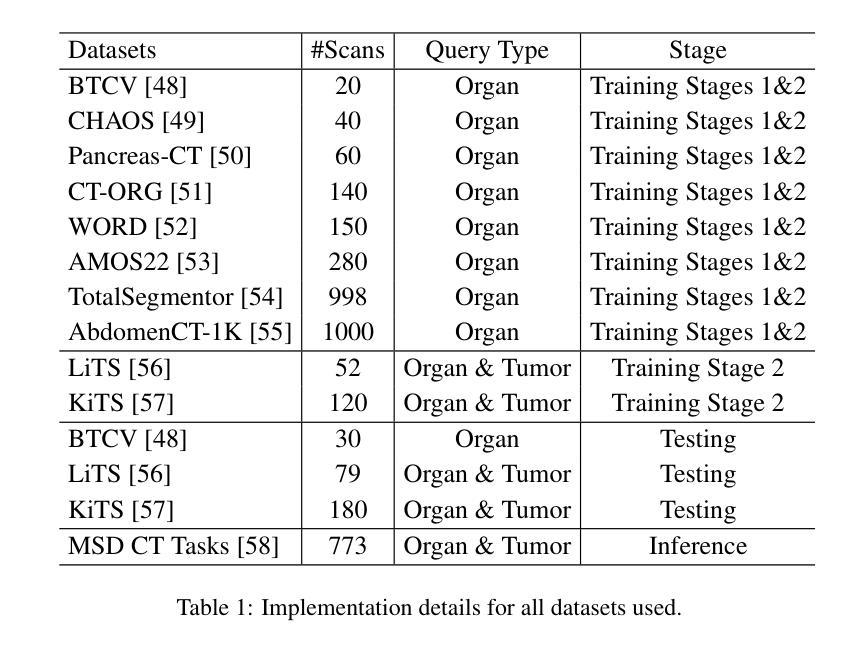
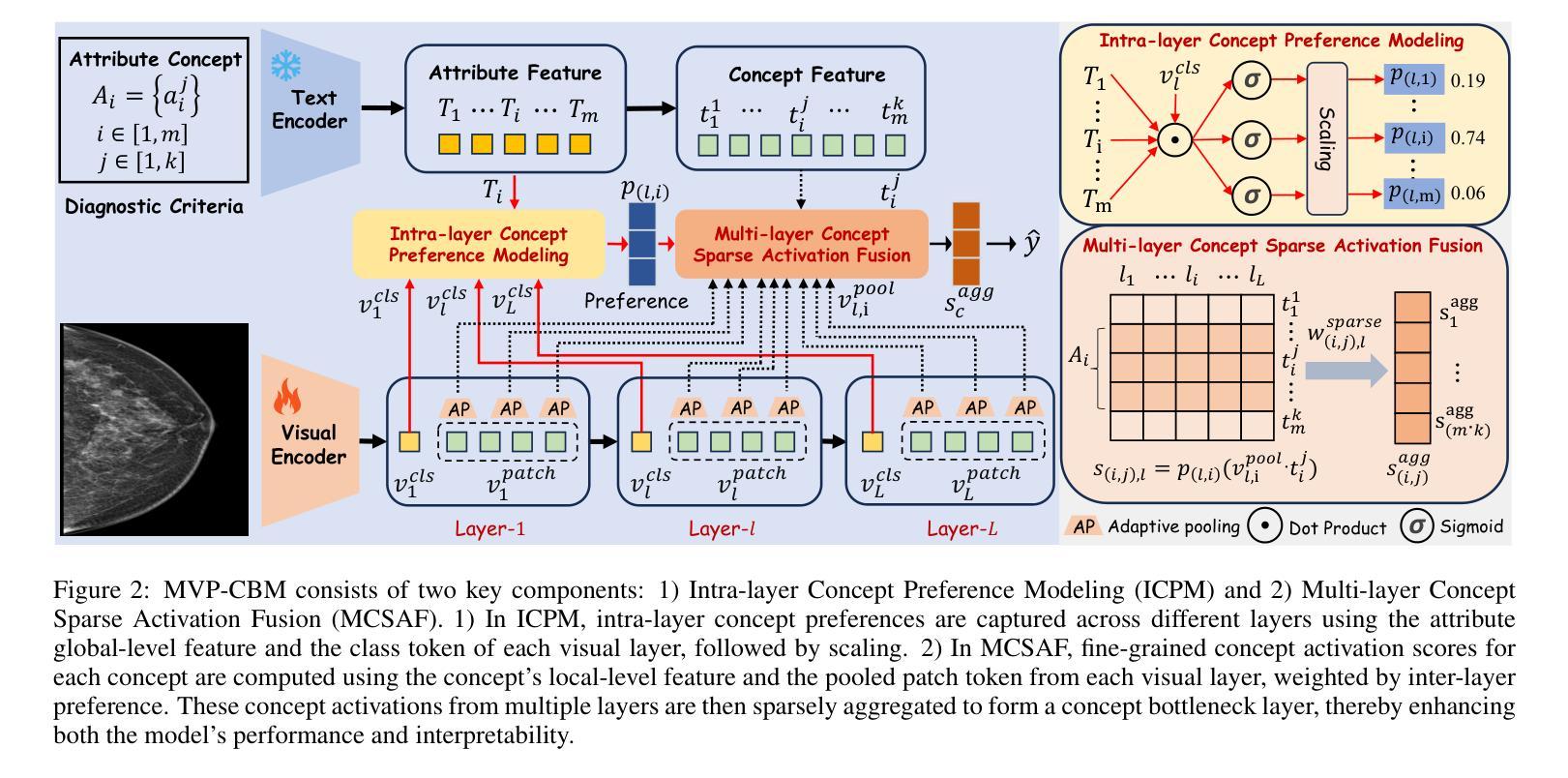
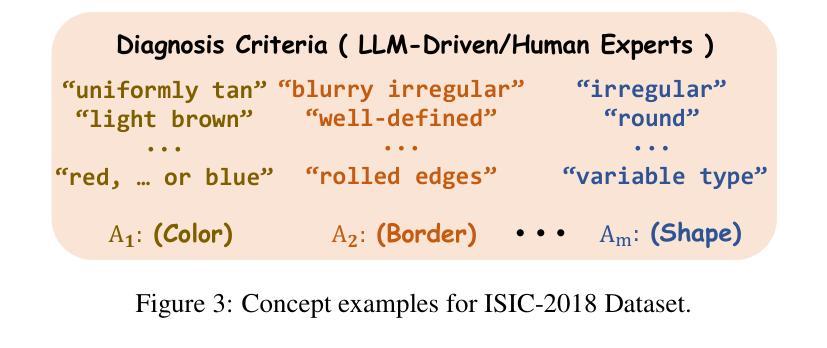
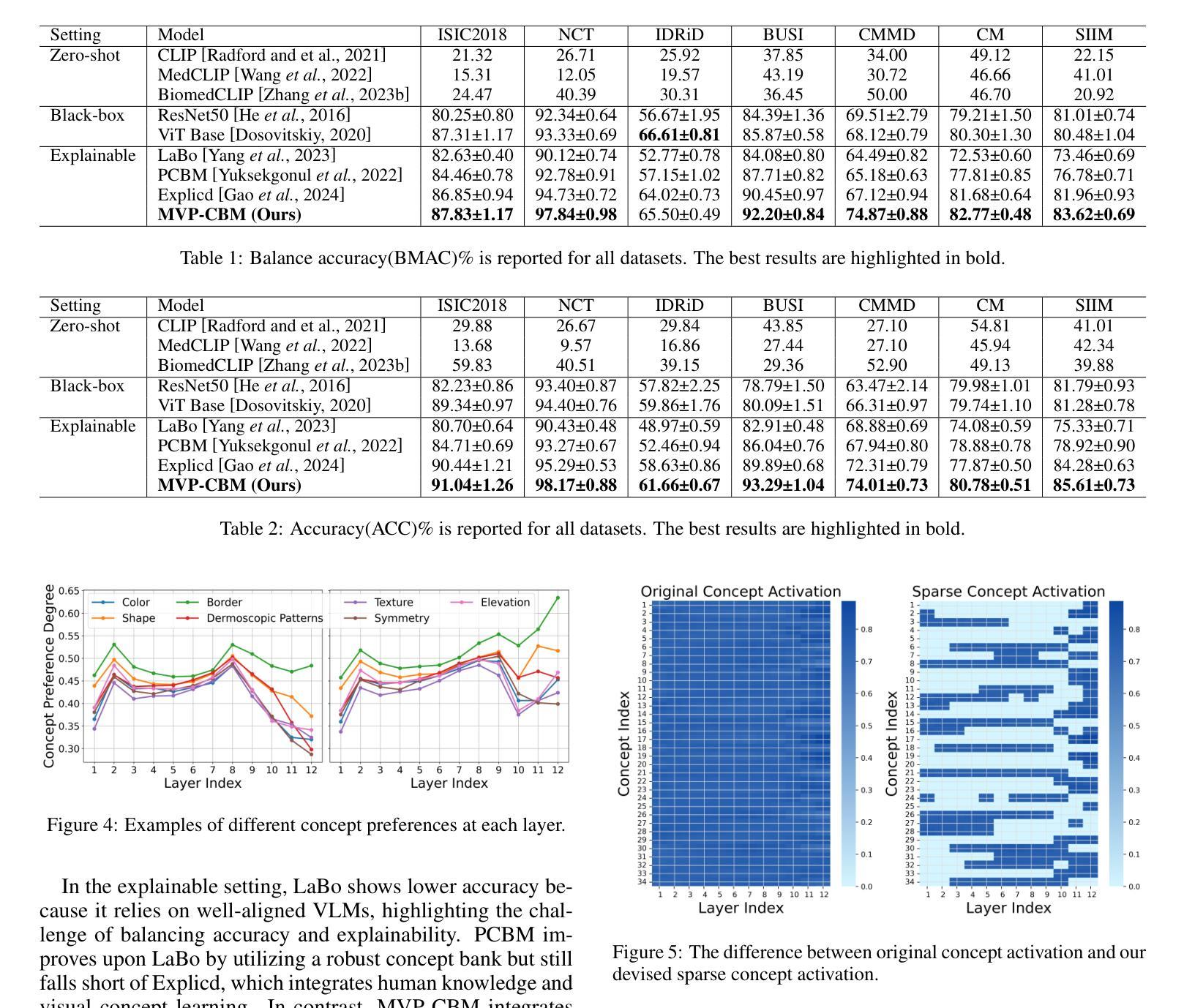
MVP-CBM:Multi-layer Visual Preference-enhanced Concept Bottleneck Model for Explainable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Chunjiang Wang, Kun Zhang, Yandong Liu, Zhiyang He, Xiaodong Tao, S. Kevin Zhou
The concept bottleneck model (CBM), as a technique improving interpretability via linking predictions to human-understandable concepts, makes high-risk and life-critical medical image classification credible. Typically, existing CBM methods associate the final layer of visual encoders with concepts to explain the model’s predictions. However, we empirically discover the phenomenon of concept preference variation, that is, the concepts are preferably associated with the features at different layers than those only at the final layer; yet a blind last-layer-based association neglects such a preference variation and thus weakens the accurate correspondences between features and concepts, impairing model interpretability. To address this issue, we propose a novel Multi-layer Visual Preference-enhanced Concept Bottleneck Model (MVP-CBM), which comprises two key novel modules: (1) intra-layer concept preference modeling, which captures the preferred association of different concepts with features at various visual layers, and (2) multi-layer concept sparse activation fusion, which sparsely aggregates concept activations from multiple layers to enhance performance. Thus, by explicitly modeling concept preferences, MVP-CBM can comprehensively leverage multi-layer visual information to provide a more nuanced and accurate explanation of model decisions. Extensive experiments on several public medical classification benchmarks demonstrate that MVP-CBM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and interoperability, verifying its superiority. Code is available at https://github.com/wcj6/MVP-CBM.
概念瓶颈模型(CBM)作为一种通过链接预测结果和人类可理解的概念来提高解释性的技术,使得高风险和关键生命的医学图像分类更加可信。通常,现有的CBM方法会将视觉编码器的最后一层与概念相关联,以解释模型的预测结果。然而,我们通过实证研究发现了概念偏好变化的现象,即概念更倾向于与不同层级的特征相关联,而不仅仅是最后一层;然而,基于最后一层的盲目关联忽视了这种偏好变化,从而削弱了特征与概念之间的准确对应关系,损害了模型的解释性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的多层视觉偏好增强概念瓶颈模型(MVP-CBM),它包含两个关键的新模块:(1)层内概念偏好建模,它捕捉不同概念与各种视觉层特征的优选关联;(2)多层概念稀疏激活融合,它稀疏地聚合多层的概念激活以增强性能。因此,通过显式地建模概念偏好,MVP-CBM可以全面地利用多层的视觉信息,为模型的决策提供更细微和准确的解释。在几个公开的医学分类基准测试上的广泛实验表明,MVP-CBM达到了最先进的准确性和可操作性,验证了其优越性。代码可在https://github.com/wcj6/MVP-CBM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 6 figures,
摘要
概念瓶颈模型(CBM)通过关联预测与人类可理解的概念,提高了医学图像分类的可信度。但现有CBM方法主要关注视觉编码器的最后一层与概念的联系,忽略了概念偏好变化现象。为此,我们提出了多层级视觉偏好增强概念瓶颈模型(MVP-CBM),包括两个关键模块:1)内层概念偏好建模,捕捉不同概念与不同视觉层特征的偏好关联;2)多层概念稀疏激活融合,稀疏地聚合多层概念激活以提高性能。MVP-CBM能全面利用多层视觉信息,提供更细致准确的模型决策解释。在多个公开医学分类基准测试上的实验证明了MVP-CBM的卓越性和最新准确性。
关键见解
- 概念瓶颈模型(CBM)提高了医学图像分类的可信度,通过连接预测与人类可理解的概念。
- 现有CBM方法主要关注视觉编码器的最后一层与概念的联系,这忽略了概念偏好的变化。
- 提出了多层级视觉偏好增强概念瓶颈模型(MVP-CBM),包括内层概念偏好建模和多层概念稀疏激活融合两个关键模块。
- MVP-CBM能全面利用多层视觉信息,提供更准确和细致的模型决策解释。
- MVP-CBM在多个公开医学分类基准测试上实现了最新准确性和卓越性能。
- MVP-CBM通过明确建模概念偏好,实现了对模型决策的更深入和全面的理解。
- 代码已公开在GitHub上分享。
点此查看论文截图

Hierarchical Deep Feature Fusion and Ensemble Learning for Enhanced Brain Tumor MRI Classification
Authors:Zahid Ullah, Jihie Kim
Accurate brain tumor classification is crucial in medical imaging to ensure reliable diagnosis and effective treatment planning. This study introduces a novel double ensembling framework that synergistically combines pre-trained deep learning (DL) models for feature extraction with optimized machine learning (ML) classifiers for robust classification. The framework incorporates comprehensive preprocessing and data augmentation of brain magnetic resonance images (MRI), followed by deep feature extraction using transfer learning with pre-trained Vision Transformer (ViT) networks. The novelty lies in the dual-level ensembling strategy: feature-level ensembling, which integrates deep features from the top-performing ViT models, and classifier-level ensembling, which aggregates predictions from hyperparameter-optimized ML classifiers. Experiments on two public Kaggle MRI brain tumor datasets demonstrate that this approach significantly surpasses state-of-the-art methods, underscoring the importance of feature and classifier fusion. The proposed methodology also highlights the critical roles of hyperparameter optimization (HPO) and advanced preprocessing techniques in improving diagnostic accuracy and reliability, advancing the integration of DL and ML for clinically relevant medical image analysis.
精确的大脑肿瘤分类在医学成像中至关重要,能确保可靠的诊断和治疗方案制定。本研究引入了一种新型双重集成框架,该框架协同结合了预训练的深度学习(DL)模型进行特征提取,以及优化后的机器学习(ML)分类器进行稳健分类。该框架包含对大脑磁共振图像(MRI)的全面预处理和数据增强,随后使用基于迁移学习的深度特征提取和预训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)网络。其新颖之处在于双重集成策略:特征级集成,集成了表现最佳的ViT模型的深度特征;分类器级集成,聚合了超参数优化ML分类器的预测。在Kaggle的两个公共MRI脑肿瘤数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著超越了最先进的方法,突显了特征和分类器融合的重要性。所提出的方法还强调了超参数优化(HPO)和先进的预处理技术在提高诊断和可靠性方面的关键作用,推动了深度学习(DL)和机器学习(ML)在临床相关医学图像分析中的融合。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型双重集成框架,该框架结合预训练的深度学习模型进行特征提取,以及优化的机器学习分类器进行分类,实现了精确的脑肿瘤分类。通过综合运用预处理和磁共振图像数据增强技术,结合使用预训练Vision Transformer网络的深度特征提取方法。其新颖之处在于双重集成策略:特征级集成和分类器级集成。实验证明,该方法显著超越了现有技术,强调了特征融合和分类器融合的重要性。同时,该研究也强调了超参数优化和高级预处理技术在提高诊断准确性和可靠性方面的关键作用。
Key Takeaways
- 准确脑肿瘤分类在医学成像中的重要性及其对于可靠诊断和有效治疗计划的意义。
- 介绍了一种新型双重集成框架,结合了深度学习模型的特征提取和机器学习分类器的优化分类。
- 框架中综合运用了预处理和磁共振图像数据增强技术。
- 使用了预训练的Vision Transformer网络进行深度特征提取。
- 双重集成策略包括特征级集成和分类器级集成。
- 实验证明该框架显著超越了现有技术,并强调了特征融合和分类器融合的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Accuracy and Precision of Random Walk with Barrier Model Fitting: Simulations and Applications in Head and Neck Cancers
Authors:Jiaren Zou, Yue Cao
Promising results have been reported in quantifying microstructural parameters (free diffusivity, cell size, and membrane permeability) in head and neck cancers (HNCs) using time-dependent diffusion MRI fitted to Random Walk with Barrier Model (RWBM). However, model fitting remains challenging due to limited number of measurements, low signal-to-noise ratio and complex nonlinear biophysical model. In this work, we comprehensively investigated and elucidated the dependence of RWBM fitting performance on tissue property, data acquisition and processing, and provided insights on improving data acquisition and model fitting. We numerically evaluated the accuracy and precision of RWBM fitting using non-linear least squares as a function of model parameters, noise levels, and maximum effective diffusion times over a wide range of microstructural parameter values. We then elucidated these results by examining the model’s degeneracy and fitting landscape. In vivo fitting results on patients with HNCs were analyzed and were interpreted using the numerical results. We observed that free diffusivity estimates were accurate and precise over a wide range of microstructural parameters, whereas the accuracy and precision of surface-to-volume ratio and membrane permeability depended on the values of the parameters. In addition, a maximum effective diffusion time of 200 ms provided the lowest bias and variance in membrane permeability estimations. By fitting to the short-time limit expression, we observed that the variance of parameter estimation was reduced, and that a more accurate and precise estimation of membrane permeability was achieved. In vivo fitting results were consistent with the numerical findings. In conclusion, this work provides a comprehensive analysis of RWBM fitting in clinical settings and has the potential to guide further optimizations of data acquisition and model fitting methods.
使用基于随机游走屏障模型(RWBM)的时间相关扩散MRI对头部和颈部癌症(HNCs)的微结构参数(自由扩散率、细胞大小和膜通透性)进行量化已报道有前景的结果。然而,由于测量次数有限、信噪比低以及复杂的非线性生物物理模型,模型拟合仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们全面研究和阐明了RWBM拟合性能对组织特性、数据获取和处理的依赖性,并提供了改进数据获取和模型拟合的见解。我们通过非线性最小二乘法数值评估了RWBM拟合的准确性和精度,作为模型参数、噪声水平和最大有效扩散时间以及一系列微结构参数值的函数。然后,我们通过检查模型的退化和拟合景观来阐明这些结果。分析了HNC患者体内拟合结果,并结合数值结果进行了解释。我们观察到自由扩散率估计在广泛的微结构参数范围内是准确和精确的,而表面积与体积比和膜通透性的准确性和精确性则取决于参数值。此外,最大有效扩散时间为200毫秒时,膜通透性估计的偏差和方差最低。通过拟合短时间极限表达式,我们观察到参数估计的方差降低,实现了膜通透性的更准确和精确的估计。体内拟合结果与数值发现一致。总之,这项工作提供了RWBM在临床环境中应用的综合分析,并有潜力指导进一步优化数据获取和模型拟合方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
利用基于随机游走障碍模型(RWBM)的时间依赖扩散MRI,对头颈部癌症(HNCs)的微结构参数(自由扩散率、细胞大小和膜通透性)进行量化分析,显示出良好前景。然而,模型拟合仍然面临挑战,包括测量次数有限、信噪比低以及复杂的非线性生物物理模型。本研究全面探讨了RWBM拟合性能对组织特性、数据采集和处理的依赖性,并提供了优化数据采集和模型拟合的见解。通过非线性最小二乘法,对RWBM拟合的准确性和精度进行了数值评估,作为模型参数、噪声水平和最大有效扩散时间等的函数,并对一系列广泛的微结构参数值进行了评估。通过检查模型的退化和拟合景观,阐明了这些结果。分析了头颈部癌症患者的体内拟合结果,并结合数值结果进行了解释。观察发现,自由扩散率的估计在广泛的微结构参数范围内是准确且精确的,而表面积与体积比和膜通透性的准确性和精确性则取决于参数值。此外,最大有效扩散时间为200毫秒时,膜通透性估计的偏差和方差最低。通过拟合短时间极限表达式,观察到参数估计的方差降低,膜通透性的估计更为准确和精确。体内拟合结果与数值发现一致。总之,本研究对RWBM在临床试验中的拟合进行了综合分析,有望为进一步优化数据采集和模型拟合方法提供指导。
要点总结
- 使用RWBM模型结合扩散MRI在头颈部癌症微结构参数量化上取得了良好成果。
- 模型拟合面临测量次数、信噪比和复杂生物物理模型的挑战。
- 研究探讨了RWBM拟合性能与多种因素的关系,包括组织特性、数据采集和处理。
- 数值评估了RWBM的准确性和精度与模型参数、噪声和扩散时间的关系。
- 发现自由扩散率的估计在一定范围内是准确且精确的。
- 最大有效扩散时间为200毫秒时,膜通透性的估计偏差和方差最低。
点此查看论文截图