⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
Exploring Non-contrastive Self-supervised Representation Learning for Image-based Profiling
Authors:Siran Dai, Qianqian Xu, Peisong Wen, Yang Liu, Qingming Huang
Image-based cell profiling aims to create informative representations of cell images. This technique is critical in drug discovery and has greatly advanced with recent improvements in computer vision. Inspired by recent developments in non-contrastive Self-Supervised Learning (SSL), this paper provides an initial exploration into training a generalizable feature extractor for cell images using such methods. However, there are two major challenges: 1) There is a large difference between the distributions of cell images and natural images, causing the view-generation process in existing SSL methods to fail; and 2) Unlike typical scenarios where each representation is based on a single image, cell profiling often involves multiple input images, making it difficult to effectively combine all available information. To overcome these challenges, we propose SSLProfiler, a non-contrastive SSL framework specifically designed for cell profiling. We introduce specialized data augmentation and representation post-processing methods tailored to cell images, which effectively address the issues mentioned above and result in a robust feature extractor. With these improvements, SSLProfiler won the Cell Line Transferability challenge at CVPR 2025.
基于图像的细胞分析旨在创建细胞图像的信息化表示。这一技术在药物发现中至关重要,并随着计算机视觉的最近进步而取得了巨大进展。受非对比性自监督学习(SSL)最新发展的启发,本文初步探索了使用此类方法对细胞图像进行通用特征提取器的训练。然而,存在两个主要挑战:1)细胞图像和自然图像之间的分布差异很大,导致现有SSL方法中的视图生成过程失败;2)与每个表示基于单张图像的典型场景不同,细胞分析通常涉及多张输入图像,这使得难以有效地结合所有可用信息。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了SSLProfiler,这是一个专门为细胞分析设计的非对比性SSL框架。我们引入了针对细胞图像的专业数据增强和表示后处理方法,有效地解决了上述问题,并导致了一个稳健的特征提取器。有了这些改进,SSLProfiler在CVPR 2025的细胞系可迁移性挑战中获胜。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Computer Vision for Drug Discovery
Summary
本文探讨了基于图像细胞分析的关键技术及其在药物发现中的应用。受到非对比性自监督学习(SSL)的启发,研究团队开发了一种针对细胞图像设计的通用特征提取器。面对细胞图像与自然图像分布差异大及多输入图像的信息整合挑战,团队提出SSLProfiler框架,包含针对细胞图像的数据增强和特征表示后处理方法,进而有效提升了特征提取的稳健性,并在CVPR 2025的细胞线可迁移性挑战中获胜。
Key Takeaways
- 图像细胞分析旨在创建细胞图像的信息化表示,在药物发现中至关重要。
- 计算机视觉的最新改进推动了图像细胞分析的发展。
- 非对比性自监督学习(SSL)在图像细胞分析中具有潜力。
- 细胞图像与自然图像分布存在显著差异,导致现有SSL方法的视图生成过程失效。
- 细胞分析涉及多输入图像,整合所有可用信息是一大挑战。
- SSLProfiler框架通过针对细胞图像的数据增强和特征表示后处理方法解决了上述问题。
- SSLProfiler在CVPR 2025的细胞线可迁移性挑战中胜出,验证了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

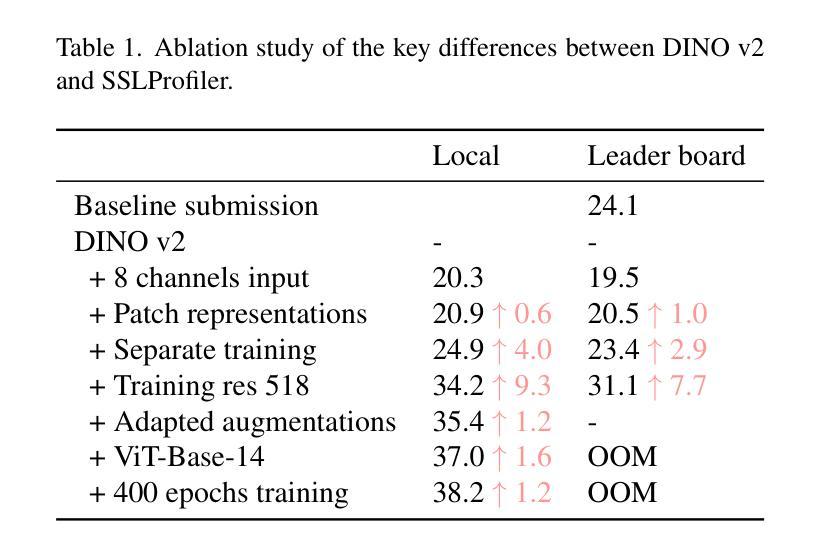
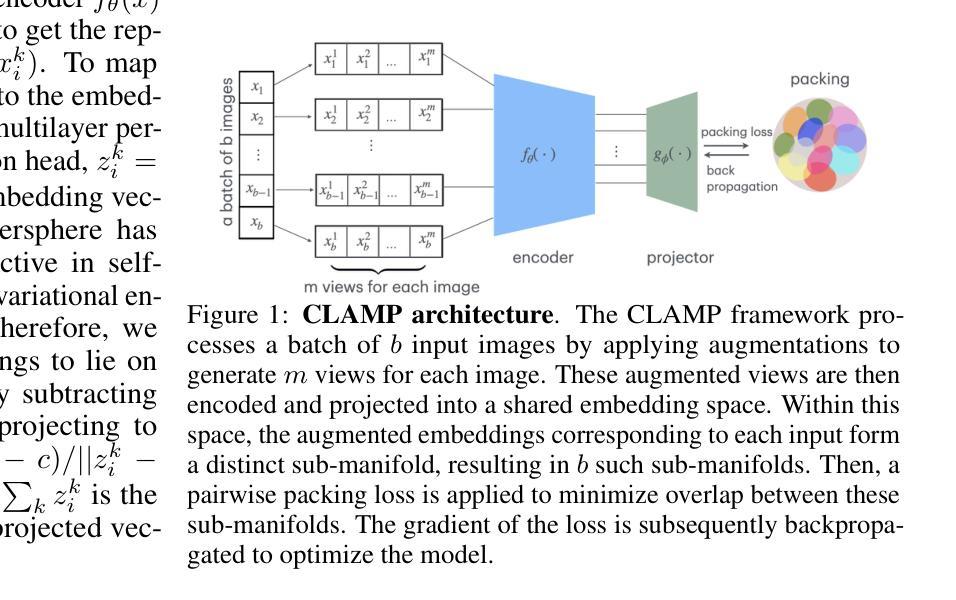
Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning As Neural Manifold Packing
Authors:Guanming Zhang, David J. Heeger, Stefano Martiniani
Contrastive self-supervised learning based on point-wise comparisons has been widely studied for vision tasks. In the visual cortex of the brain, neuronal responses to distinct stimulus classes are organized into geometric structures known as neural manifolds. Accurate classification of stimuli can be achieved by effectively separating these manifolds, akin to solving a packing problem. We introduce Contrastive Learning As Manifold Packing (CLAMP), a self-supervised framework that recasts representation learning as a manifold packing problem. CLAMP introduces a loss function inspired by the potential energy of short-range repulsive particle systems, such as those encountered in the physics of simple liquids and jammed packings. In this framework, each class consists of sub-manifolds embedding multiple augmented views of a single image. The sizes and positions of the sub-manifolds are dynamically optimized by following the gradient of a packing loss. This approach yields interpretable dynamics in the embedding space that parallel jamming physics, and introduces geometrically meaningful hyperparameters within the loss function. Under the standard linear evaluation protocol, which freezes the backbone and trains only a linear classifier, CLAMP achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art self-supervised models. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that neural manifolds corresponding to different categories emerge naturally and are effectively separated in the learned representation space, highlighting the potential of CLAMP to bridge insights from physics, neural science, and machine learning.
基于点对比的对比式自监督学习在视觉任务中得到了广泛的研究。在大脑的视觉皮层中,神经元对不同刺激类别的响应被组织成称为神经流形的几何结构。通过有效地分离这些流形,类似于解决打包问题,可以实现刺激的准确分类。我们引入了对比学习作为流形打包(CLAMP),这是一种将表示学习重新定位为流形打包问题的自监督框架。CLAMP引入了一种受短程排斥粒子系统的势能启发的损失函数,如简单液体和堵塞打包的物理中所遇到的。在此框架中,每个类别由嵌入单个图像的多个增强视图的子流形组成。子流形的大小和位置通过遵循打包损失的梯度进行动态优化。这种方法在嵌入空间中产生与堵塞物理相平行的可解释动态,并在损失函数中输入了具有几何意义的超参数。在标准线性评估协议下,即冻结主干并仅训练线性分类器,CLAMP达到了与最新自监督模型相当的性能。此外,我们的分析表明,对应于不同类别的神经流形自然会出现在学习到的表示空间中,并得到有效分离,这突出了CLAMP在物理学、神经科学和机器学习之间的洞察力之间的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于点对比的对比式自监督学习在视觉任务上受到广泛关注。本研究引入Contrastive Learning As Manifold Packing(CLAMP)框架,将表示学习重新定义为流形打包问题。该框架受到简单液体和堆积物理中势能粒子系统的启发,利用流形动态优化类内的多个图像增强视图。这种新方法提供了一种可视化动态嵌入空间的方法,与阻塞物理类似,并在损失函数中引入了几何意义上的超参数。在标准线性评估协议下,CLAMP与最先进的自监督模型表现相当。此外,本研究揭示了不同类别的神经流形在表示空间中自然出现并得到有效分离,显示出CLAMP在物理学、神经科学和机器学习之间建立联系的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 对比式自监督学习通过点对比广泛应用于视觉任务。
- CLAMP框架将表示学习定义为流形打包问题。
- CLAMP受简单液体和堆积物理中势能粒子系统的启发,利用流形优化图像增强视图。
- CLAMP提供可视化动态嵌入空间的方法,与阻塞物理类似。
- 损失函数中包含几何意义的超参数。
- 在标准线性评估协议下,CLAMP表现与最先进的自监督模型相当。
点此查看论文截图

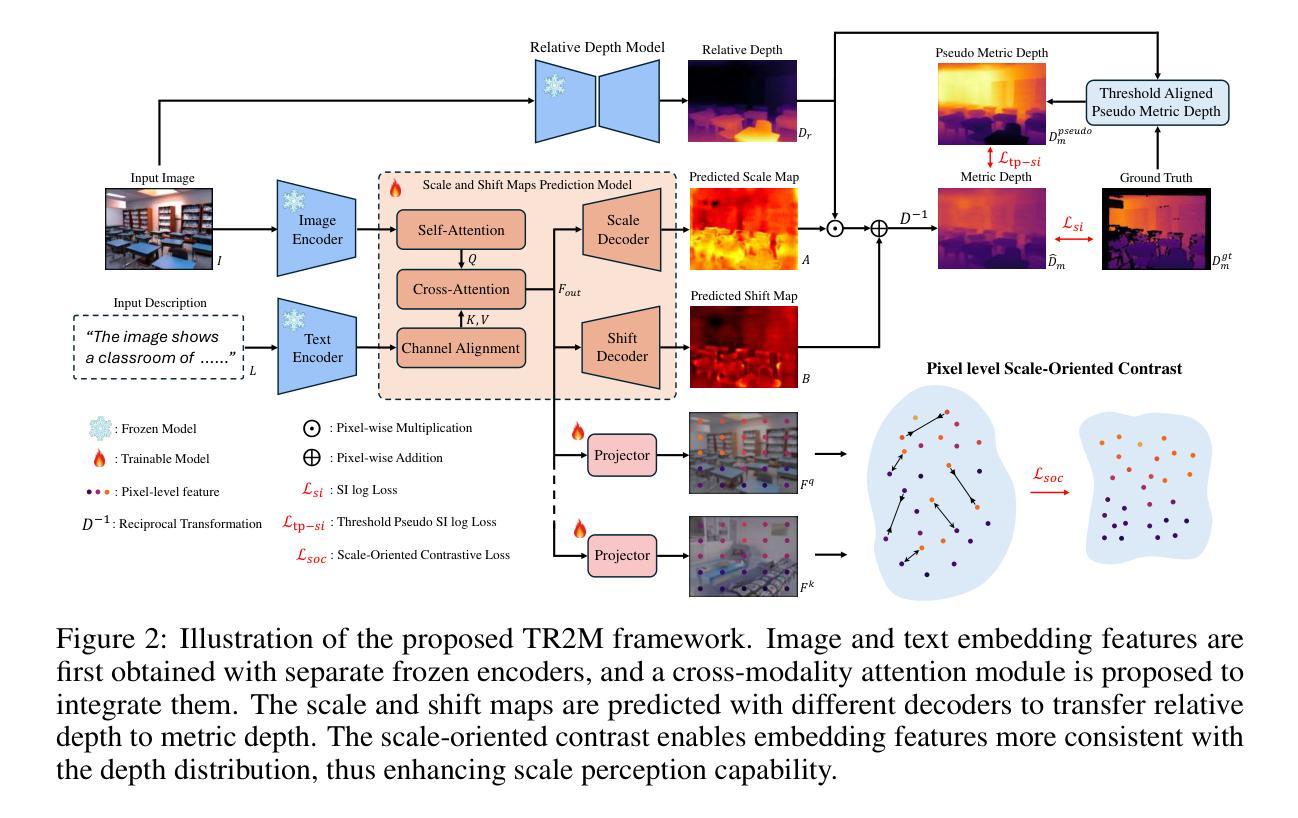
TR2M: Transferring Monocular Relative Depth to Metric Depth with Language Descriptions and Scale-Oriented Contrast
Authors:Beilei Cui, Yiming Huang, Long Bai, Hongliang Ren
This work presents a generalizable framework to transfer relative depth to metric depth. Current monocular depth estimation methods are mainly divided into metric depth estimation (MMDE) and relative depth estimation (MRDE). MMDEs estimate depth in metric scale but are often limited to a specific domain. MRDEs generalize well across different domains, but with uncertain scales which hinders downstream applications. To this end, we aim to build up a framework to solve scale uncertainty and transfer relative depth to metric depth. Previous methods used language as input and estimated two factors for conducting rescaling. Our approach, TR2M, utilizes both text description and image as inputs and estimates two rescale maps to transfer relative depth to metric depth at pixel level. Features from two modalities are fused with a cross-modality attention module to better capture scale information. A strategy is designed to construct and filter confident pseudo metric depth for more comprehensive supervision. We also develop scale-oriented contrastive learning to utilize depth distribution as guidance to enforce the model learning about intrinsic knowledge aligning with the scale distribution. TR2M only exploits a small number of trainable parameters to train on datasets in various domains and experiments not only demonstrate TR2M’s great performance in seen datasets but also reveal superior zero-shot capabilities on five unseen datasets. We show the huge potential in pixel-wise transferring relative depth to metric depth with language assistance. (Code is available at: https://github.com/BeileiCui/TR2M)
本文提出一个通用框架,用于将相对深度转换为度量深度。当前的单目深度估计方法主要分为度量深度估计(MMDE)和相对深度估计(MRDE)。MMDE在度量尺度上估计深度,但通常仅限于特定领域。MRDE在不同领域间具有很好的泛化能力,但尺度不确定,阻碍了下游应用。为此,我们旨在建立一个框架来解决尺度不确定性问题,并将相对深度转换为度量深度。之前的方法使用语言作为输入,并估计两个因子进行重缩放。我们的方法TR2M利用文本描述和图像作为输入,并估计两个重缩放图,以像素级别将相对深度转换为度量深度。来自两种模态的特征通过跨模态注意力模块进行融合,以更好地捕获尺度信息。设计了一种策略来构建和过滤可靠的伪度量深度,以实现更全面的监督。我们还开发了面向尺度的对比学习,利用深度分布作为指导,以强制模型学习内在知识与尺度分布对齐。TR2M只需要少量可训练的参数,就可以在各种领域的数据集上进行训练;实验不仅证明了TR2M在可见数据集上的出色性能,还展示了在五个未见数据集上的零样本优势。我们展示了在像素级别使用语言辅助将相对深度转换为度量深度的巨大潜力。(代码可用:https://github.com/BeileiCui/TR2M)
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个通用框架,可将相对深度转换为度量深度。该框架旨在解决尺度不确定性问题,并实现了从相对深度到度量深度的转换。与之前的方法相比,本文提出的TR2M方法不仅使用文本描述作为输入,还结合了图像输入,通过估计两个重映射关系来实现像素级别的深度转换。此外,TR2M还采用了跨模态注意力模块来融合两种模态的特征,以更好地捕获尺度信息。通过构建和过滤可靠的伪度量深度,实现了更全面的监督。此外,还开发了面向尺度的对比学习,利用深度分布作为指导,强制执行模型学习符合尺度分布的内在知识。实验表明,TR2M不仅在可见数据集上表现出良好的性能,而且在五个未见数据集上展现出卓越的零样本能力。
Key Takeaways
- 工作提出一个通用框架用于将相对深度转换为度量深度,以解决尺度不确定性问题。
- TR2M方法结合文本描述和图像作为输入,通过估计两个重映射关系实现像素级别的深度转换。
- TR2M采用跨模态注意力模块融合两种模态的特征,以更好地捕获尺度信息。
- 通过构建和过滤可靠的伪度量深度,实现更全面的监督。
- 引入面向尺度的对比学习,利用深度分布作为指导,促进模型学习内在知识。
- TR2M在多个数据集上表现出卓越性能,具有强大的零样本能力。
点此查看论文截图


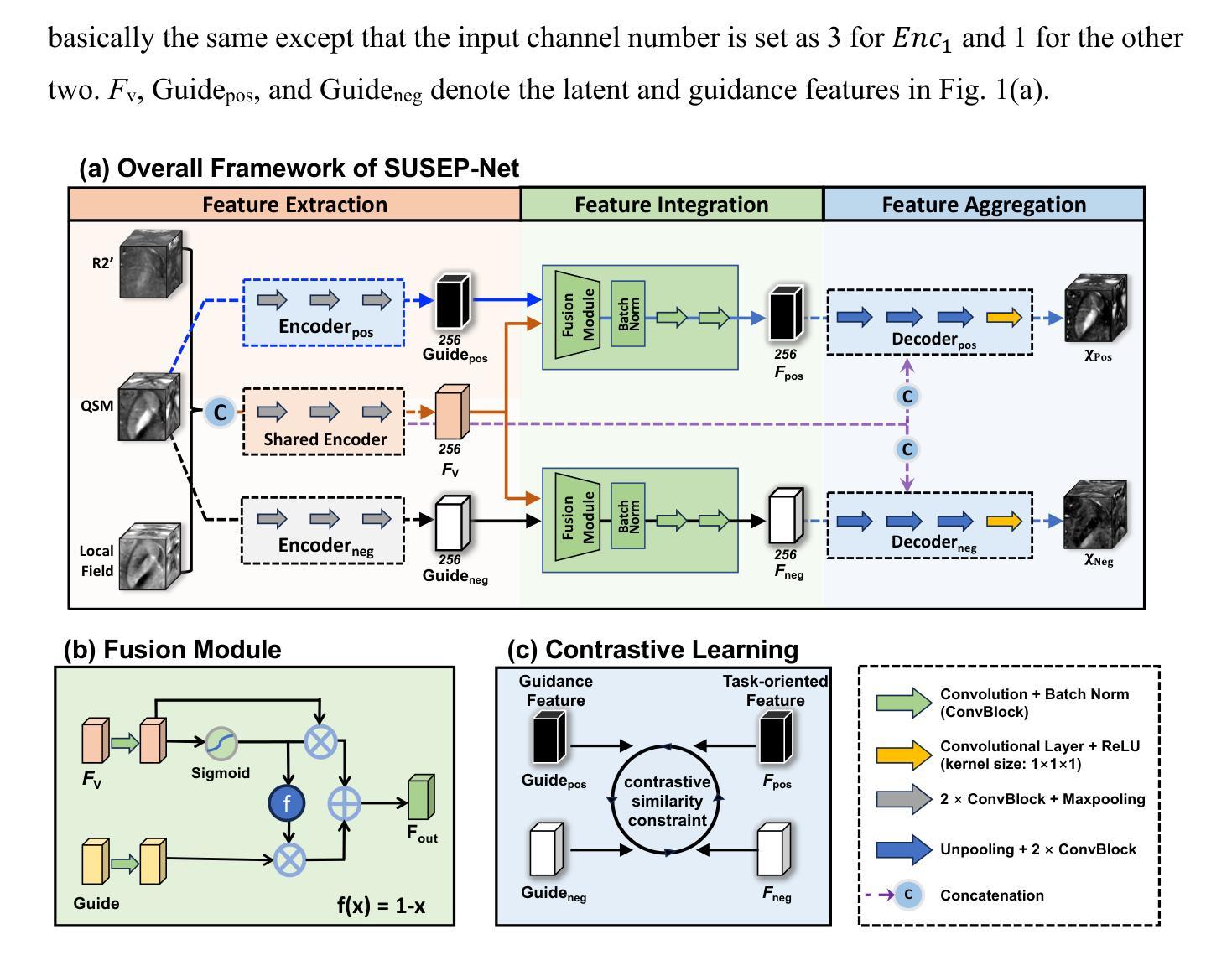
SUSEP-Net: Simulation-Supervised and Contrastive Learning-based Deep Neural Networks for Susceptibility Source Separation
Authors:Min Li, Chen Chen, Zhenghao Li, Yin Liu, Shanshan Shan, Peng Wu, Pengfei Rong, Feng Liu, G. Bruce Pike, Alan H. Wilman, Hongfu Sun, Yang Gao
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) provides a valuable tool for quantifying susceptibility distributions in human brains; however, two types of opposing susceptibility sources (i.e., paramagnetic and diamagnetic), may coexist in a single voxel, and cancel each other out in net QSM images. Susceptibility source separation techniques enable the extraction of sub-voxel information from QSM maps. This study proposes a novel SUSEP-Net for susceptibility source separation by training a dual-branch U-net with a simulation-supervised training strategy. In addition, a contrastive learning framework is included to explicitly impose similarity-based constraints between the branch-specific guidance features in specially-designed encoders and the latent features in the decoders. Comprehensive experiments were carried out on both simulated and in vivo data, including healthy subjects and patients with pathological conditions, to compare SUSEP-Net with three state-of-the-art susceptibility source separation methods (i.e., APART-QSM, \c{hi}-separation, and \c{hi}-sepnet). SUSEP-Net consistently showed improved results compared with the other three methods, with better numerical metrics, improved high-intensity hemorrhage and calcification lesion contrasts, and reduced artifacts in brains with pathological conditions. In addition, experiments on an agarose gel phantom data were conducted to validate the accuracy and the generalization capability of SUSEP-Net.
定量磁化率映射(QSM)为人类大脑中的磁化率分布提供了有价值的量化工具。然而,两种相反的磁化率源(即顺磁性物质和反磁性物质)可能存在于单个体素内,并在净QSM图像中相互抵消。磁化率源分离技术能够从QSM图中提取亚体素信息。本研究提出了一种新型的SUSEP-Net磁化率源分离方法,通过训练带有模拟监督训练策略的双分支U-net网络实现。此外,还包括一个对比学习框架,以在专门设计的编码器中的分支特定引导特征和解码器中的潜在特征之间显式施加基于相似性的约束。对模拟数据和活体数据进行了全面的实验,包括健康受试者和病理条件下的患者,将SUSEP-Net与三种最先进的磁化率源分离方法(即APART-QSM、chi分离和chi分离网)进行比较。SUSEP-Net在各项指标上均表现更好,显示出改进的结果;能够提高高灵敏度出血和钙化病灶对比度;在病理条件下的大脑中减少了伪影。此外,还进行了琼脂凝胶幻影数据的实验,以验证SUSEP-Net的准确性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 figures, 2 tables
Summary
一种名为SUSEP-Net的新方法被提出用于分离磁化率源。该方法通过训练带有仿真监督训练策略的双分支U-net网络来实现。此外,还包括一个对比学习框架,对分支特定的指导特征和解码器中的潜在特征施加相似性约束。与三种先进的磁化率源分离方法相比,SUSEP-Net在模拟和真实数据中均表现出更好的性能,包括健康受试者和病理条件下的患者。
Key Takeaways
- SUSEP-Net被提出用于磁化率源分离。
- 使用双分支U-net结构和仿真监督训练策略进行训练。
- 对比学习框架用于施加分支特定的指导特征和潜在特征之间的相似性约束。
- SUSEP-Net在模拟和真实数据中表现优越,包括健康人和病理条件下的病人。
- 与其他三种先进的磁化率源分离方法相比,SUSEP-Net在数值度量上表现更好。
- SUSEP-Net能提高高强度出血和钙化病变的对比度。
点此查看论文截图

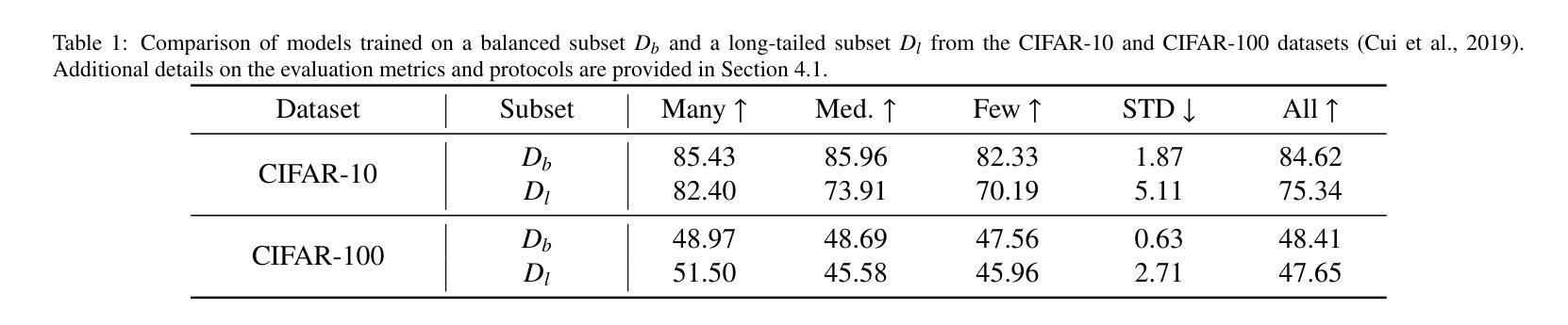
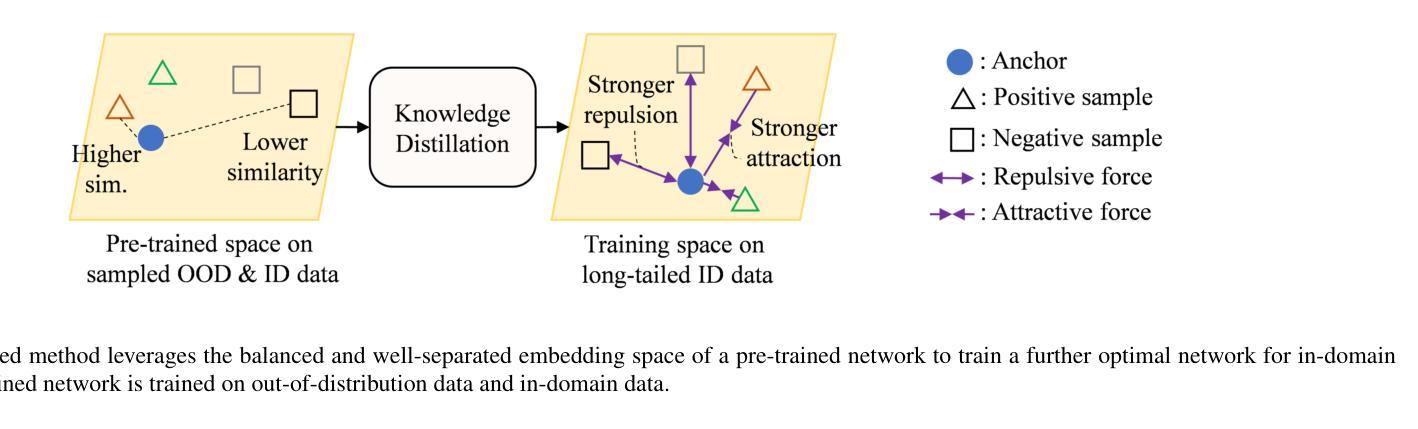
Unsupervised Contrastive Learning Using Out-Of-Distribution Data for Long-Tailed Dataset
Authors:Cuong Manh Hoang, Yeejin Lee, Byeongkeun Kang
This work addresses the task of self-supervised learning (SSL) on a long-tailed dataset that aims to learn balanced and well-separated representations for downstream tasks such as image classification. This task is crucial because the real world contains numerous object categories, and their distributions are inherently imbalanced. Towards robust SSL on a class-imbalanced dataset, we investigate leveraging a network trained using unlabeled out-of-distribution (OOD) data that are prevalently available online. We first train a network using both in-domain (ID) and sampled OOD data by back-propagating the proposed pseudo semantic discrimination loss alongside a domain discrimination loss. The OOD data sampling and loss functions are designed to learn a balanced and well-separated embedding space. Subsequently, we further optimize the network on ID data by unsupervised contrastive learning while using the previously trained network as a guiding network. The guiding network is utilized to select positive/negative samples and to control the strengths of attractive/repulsive forces in contrastive learning. We also distil and transfer its embedding space to the training network to maintain balancedness and separability. Through experiments on four publicly available long-tailed datasets, we demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods.
本文关注了在长尾数据集上进行自我监督学习(SSL)的任务,旨在为目标任务(如图像分类)学习平衡且良好分离的表示。这一任务至关重要,因为现实世界包含众多对象类别,它们的分布本质上是不平衡的。为了在类别不平衡数据集上实现稳健的SSL,我们研究利用使用未标记的在线普遍可用的离群分布(OOD)数据进行训练的网络。我们首先使用域内(ID)和采样的OOD数据来训练网络,通过反向传播所提出的伪语义判别损失和域判别损失。OOD数据采样和损失函数旨在学习平衡且良好分离嵌入空间。随后,我们以先前训练的网络作为引导网络,通过无监督对比学习进一步优化网络在ID数据上的表现。引导网络用于选择正/负样本并控制对比学习中吸引/排斥力的强度。我们还蒸馏并转移其嵌入空间到训练网络,以维持平衡性和可分离性。在四个公开可用的长尾数据集上的实验表明,所提出的方法优于先前最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages
Summary
本文探讨了长尾数据集上的自监督学习任务,旨在学习平衡且良好的表示,为图像分类等下游任务提供支持。针对现实世界中的大量对象类别及其固有的不平衡分布问题,研究利用在线普遍可用的无标签的离群数据来训练网络。通过反向传播伪语义鉴别损失和领域鉴别损失来训练网络,借助离群数据的采样和损失函数来学习平衡且良好的嵌入空间。接着通过无监督对比学习进一步优化网络,并利用预训练网络作为引导网络来选择正/负样本和控制对比学习中的吸引力和排斥力。实验结果表明,该方法在四个公开的长尾数据集上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注自监督学习在长尾数据集上的应用,旨在学习平衡且良好的表示,适用于图像分类等任务。
- 研究利用在线普遍可用的无标签离群数据来训练网络,以应对现实世界中的对象类别不平衡问题。
- 通过结合领域鉴别损失和伪语义鉴别损失来训练网络,以增强网络的泛化能力并优化嵌入空间的性能。
- 利用预训练的引导网络进行无监督对比学习,提高网络的性能并增强特征表示的分离性。
- 引导网络用于选择对比学习中的正/负样本和控制吸引与排斥力,以优化网络的训练过程。
- 通过实验验证了该方法在四个公开的长尾数据集上的优越性,证明了其在实际应用中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

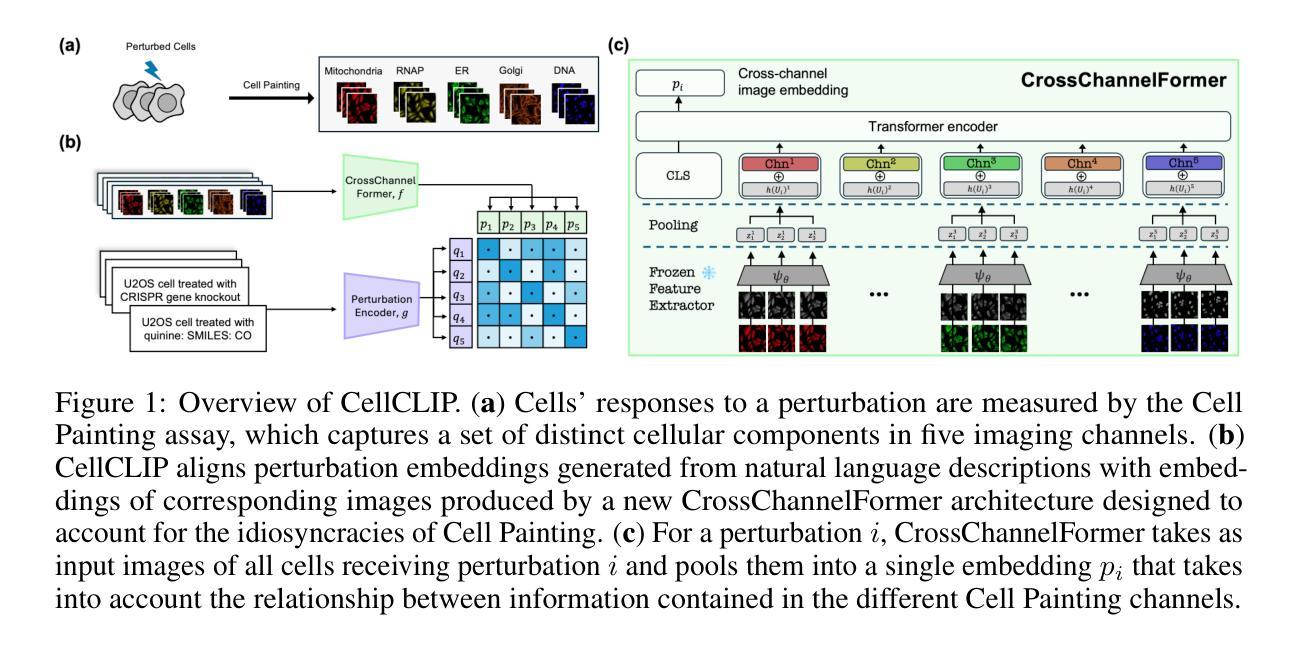
CellCLIP – Learning Perturbation Effects in Cell Painting via Text-Guided Contrastive Learning
Authors:Mingyu Lu, Ethan Weinberger, Chanwoo Kim, Su-In Lee
High-content screening (HCS) assays based on high-throughput microscopy techniques such as Cell Painting have enabled the interrogation of cells’ morphological responses to perturbations at an unprecedented scale. The collection of such data promises to facilitate a better understanding of the relationships between different perturbations and their effects on cellular state. Towards achieving this goal, recent advances in cross-modal contrastive learning could, in theory, be leveraged to learn a unified latent space that aligns perturbations with their corresponding morphological effects. However, the application of such methods to HCS data is not straightforward due to substantial differences in the semantics of Cell Painting images compared to natural images, and the difficulty of representing different classes of perturbations (e.g., small molecule vs CRISPR gene knockout) in a single latent space. In response to these challenges, here we introduce CellCLIP, a cross-modal contrastive learning framework for HCS data. CellCLIP leverages pre-trained image encoders coupled with a novel channel encoding scheme to better capture relationships between different microscopy channels in image embeddings, along with natural language encoders for representing perturbations. Our framework outperforms current open-source models, demonstrating the best performance in both cross-modal retrieval and biologically meaningful downstream tasks while also achieving significant reductions in computation time.
基于高通量显微镜技术(如细胞染色法)的高内涵筛选(HCS)测定法,已经能够以前所未有的规模探究细胞对扰动的形态反应。收集此类数据有望促进对不同扰动及其细胞状态影响之间关系的更好理解。为了实现这一目标,最近的跨模态对比学习进展从理论上可以被用来学习一个统一的潜在空间,使扰动与其相应的形态效应对齐。然而,将此类方法应用于HCS数据并不简单,因为与天然图像相比,细胞染色图像的语义存在很大差异,而且难以在单个潜在空间中表示不同类型的扰动(例如小分子与CRISPR基因敲除)。为了应对这些挑战,我们在这里引入了CellCLIP,这是一个用于HCS数据的跨模态对比学习框架。CellCLIP利用预训练图像编码器与新型通道编码方案,以更好地捕获图像嵌入中不同显微镜通道之间的关系,以及用于表示扰动的自然语言编码器。我们的框架性能优于当前开源模型,在跨模态检索和具有生物学意义的下游任务中表现出最佳性能,同时显著减少了计算时间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
高内涵筛选(HCS)实验通过高通量显微镜技术如细胞染色技术,能够以前所未有的规模探究细胞形态对干扰的响应。利用这些数据,可以更好地理解不同干扰之间的关系及其对细胞状态的影响。为实现这一目标,理论上可以利用跨模态对比学习方法的最新进展来学习一个统一的潜在空间,使干扰与其相应的形态效应相匹配。然而,将这种方法应用于HCS数据并不简单,因为细胞染色图像与自然图像在语义上存在显著差异,且难以在单一潜在空间内表示不同类型的干扰(如小分子与CRISPR基因敲除)。为应对这些挑战,本文引入了CellCLIP跨模态对比学习框架。CellCLIP利用预训练的图像编码器与新型通道编码方案,更好地捕捉图像嵌入中不同显微镜通道之间的关系,以及用于表示干扰的自然语言编码器。我们的框架在跨模态检索和具有生物学意义的下游任务上表现出最佳性能,同时计算时间也大大减少。
Key Takeaways:
- 高内涵筛选(HCS)能够通过高通量显微镜技术大规模研究细胞形态对干扰的响应。
- 收集这些数据有助于更好地理解不同干扰与细胞状态之间的关系。
- 跨模态对比学习可用于学习一个统一潜在空间,匹配干扰与形态效应。
- 将跨模态对比学习方法应用于HCS数据存在挑战,如语义差异和不同类型干扰的表示。
- CellCLIP框架利用预训练图像编码器和新型通道编码方案应对这些挑战。
- CellCLIP框架在跨模态检索和生物学意义下游任务上表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

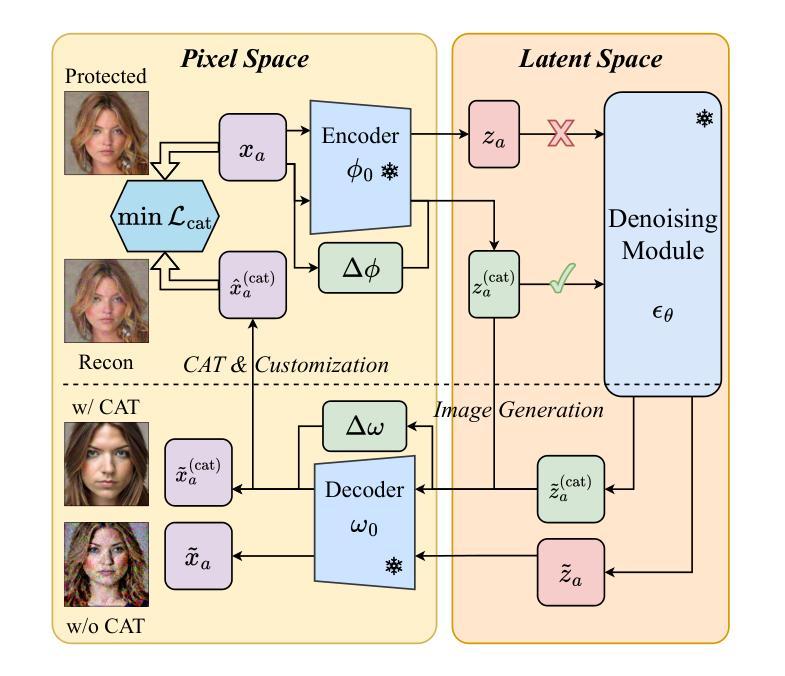
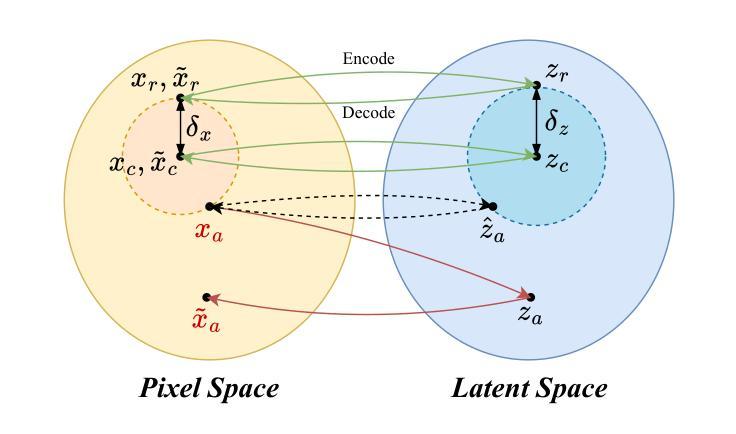
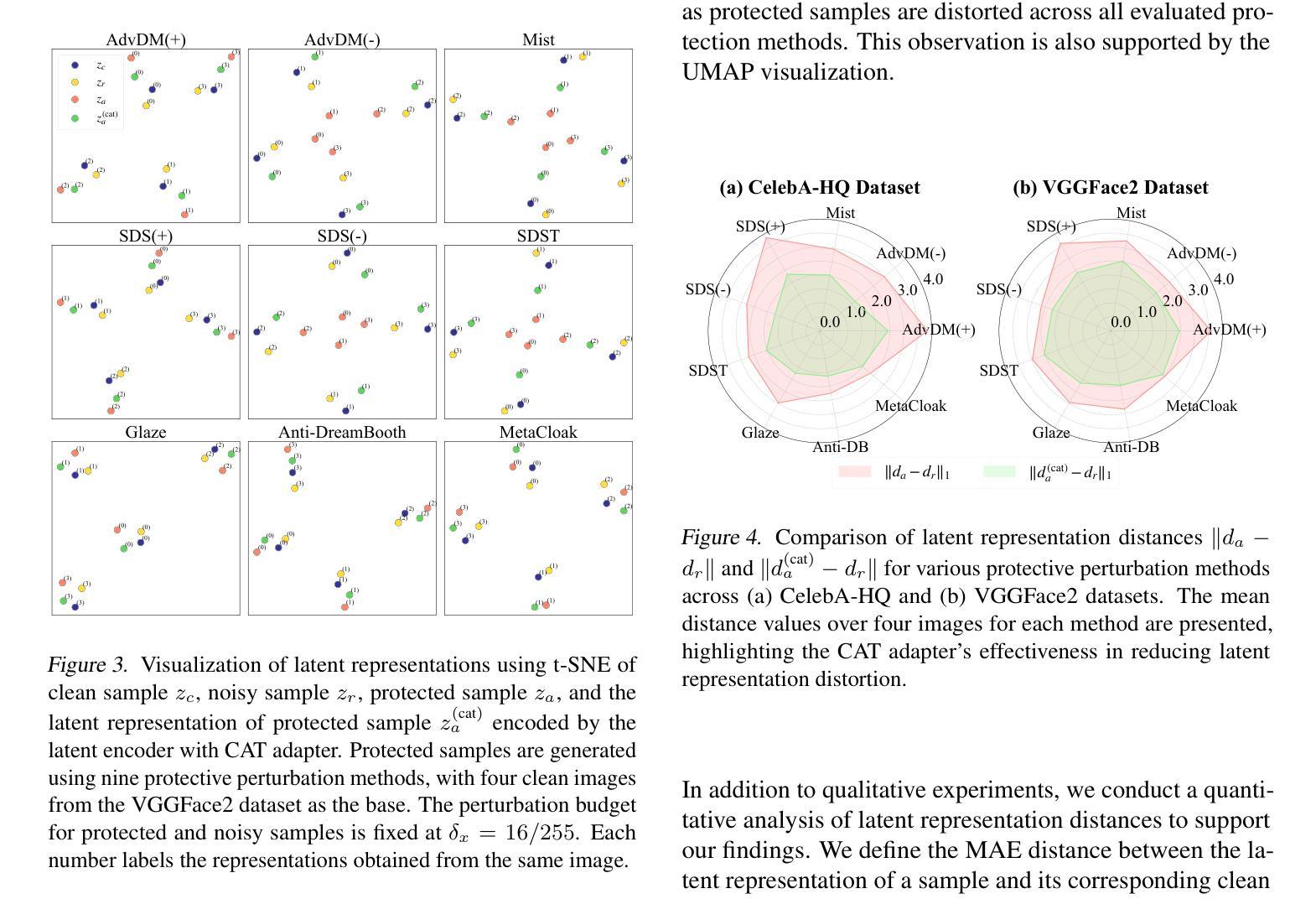
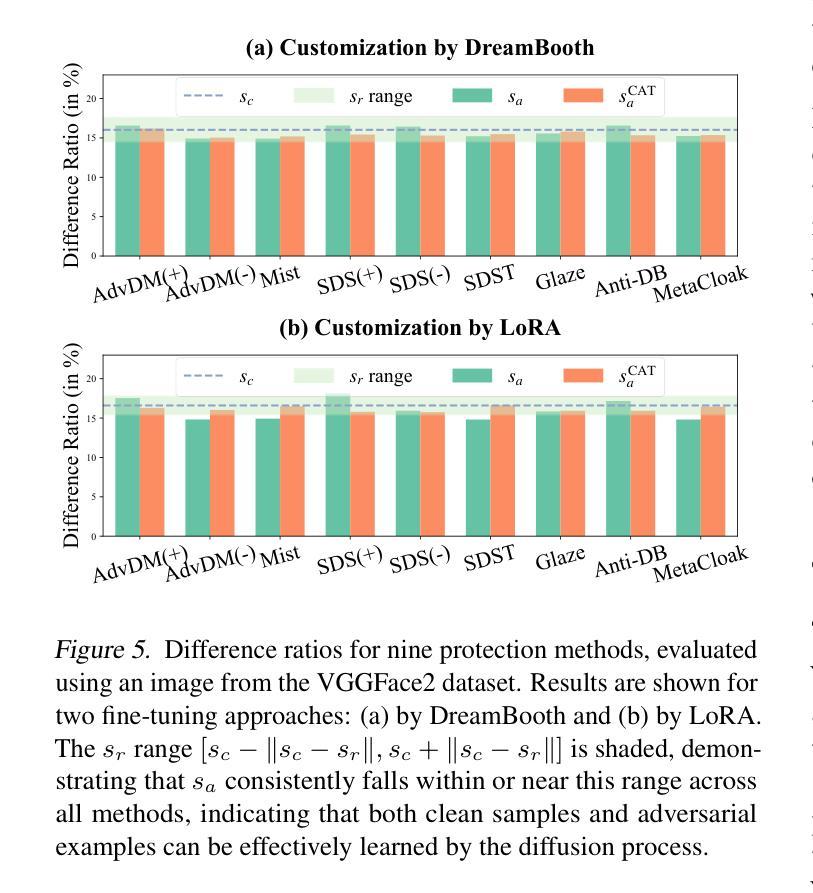
CAT: Contrastive Adversarial Training for Evaluating the Robustness of Protective Perturbations in Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Sen Peng, Mingyue Wang, Jianfei He, Jijia Yang, Xiaohua Jia
Latent diffusion models have recently demonstrated superior capabilities in many downstream image synthesis tasks. However, customization of latent diffusion models using unauthorized data can severely compromise the privacy and intellectual property rights of data owners. Adversarial examples as protective perturbations have been developed to defend against unauthorized data usage by introducing imperceptible noise to customization samples, preventing diffusion models from effectively learning them. In this paper, we first reveal that the primary reason adversarial examples are effective as protective perturbations in latent diffusion models is the distortion of their latent representations, as demonstrated through qualitative and quantitative experiments. We then propose the Contrastive Adversarial Training (CAT) utilizing lightweight adapters as an adaptive attack against these protection methods, highlighting their lack of robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our CAT method significantly reduces the effectiveness of protective perturbations in customization, urging the community to reconsider and improve the robustness of existing protective perturbations. The code is available at https://github.com/senp98/CAT.
潜在扩散模型已在许多下游图像合成任务中展现出卓越的能力。然而,使用未经授权的数据对潜在扩散模型进行定制会严重损害数据所有者的隐私和知识产权。对抗性样本作为保护性扰动已经发展起来,通过向定制样本中加入几乎不可察觉的噪声来防御未经授权的数据使用,防止扩散模型有效地学习它们。在本文中,我们首先揭示对抗性样本作为潜在扩散模型中的保护性扰动的主要原因是其潜在表示的失真,这已通过定性和定量实验证明。然后,我们提出利用轻量级适配器作为适应性攻击的对比对抗训练(CAT),突出其缺乏稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的CAT方法显著降低了定制中保护性扰动的有效性,敦促社区重新考虑并提高现有保护性扰动的稳健性。代码可在https://github.com/senp98/CAT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
潜在扩散模型在下游图像合成任务中展现出卓越的能力,但其定制化使用未经授权数据会严重侵犯数据所有者的隐私和知识产权。对抗样本作为保护性扰动,通过引入难以察觉的噪声来防御未经授权的数据使用,阻止扩散模型的有效学习。本文首先通过定性和定量实验揭示,对抗样本作为潜在扩散模型中的保护性扰动的关键在于其潜在表示形式的失真。然后,我们提出利用轻量级适配器的对比对抗训练(CAT)作为一种自适应攻击方法,来突显现有保护方法的稳健性不足。大量实验表明,我们的CAT方法显著降低了保护性扰动在定制中的有效性,促使社区重新考虑并改进现有保护性扰动的稳健性。代码已公开于:https://github.com/senp98/CAT。
关键见解
- 对抗样本可作为潜在扩散模型中的保护性扰动,主要通过潜在表示的失真来发挥作用。
- 对比对抗训练(CAT)方法利用轻量级适配器,针对保护方法进行自适应攻击。
- 实验表明,CAT方法显著降低了保护性扰动在定制中的有效性。
- 现有保护方法的稳健性不足,需要社区重新考虑和改进。
- 该研究揭示了潜在扩散模型在定制化使用中的隐私和知识产权问题。
- 对抗样本的引入可以阻止扩散模型对未经授权数据的有效学习。
点此查看论文截图

Test-time Contrastive Concepts for Open-world Semantic Segmentation with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Monika Wysoczańska, Antonin Vobecky, Amaia Cardiel, Tomasz Trzciński, Renaud Marlet, Andrei Bursuc, Oriane Siméoni
Recent CLIP-like Vision-Language Models (VLMs), pre-trained on large amounts of image-text pairs to align both modalities with a simple contrastive objective, have paved the way to open-vocabulary semantic segmentation. Given an arbitrary set of textual queries, image pixels are assigned the closest query in feature space. However, this works well when a user exhaustively lists all possible visual concepts in an image that contrast against each other for the assignment. This corresponds to the current evaluation setup in the literature, which relies on having access to a list of in-domain relevant concepts, typically classes of a benchmark dataset. Here, we consider the more challenging (and realistic) scenario of segmenting a single concept, given a textual prompt and nothing else. To achieve good results, besides contrasting with the generic ‘background’ text, we propose two different approaches to automatically generate, at test time, query-specific textual contrastive concepts. We do so by leveraging the distribution of text in the VLM’s training set or crafted LLM prompts. We also propose a metric designed to evaluate this scenario and show the relevance of our approach on commonly used datasets.
最近,CLIP类视语言模型(VLMs)通过大量图像文本对进行预训练,以简单的对比目标对齐两种模态,为开放词汇语义分割铺平了道路。给定一组任意的文本查询,图像像素会被分配到特征空间中最近的查询。然而,这种方法在用户详尽地列出图像中所有可能的视觉概念并且这些概念之间进行对比以进行分配时效果最好。这对应于文献中的当前评估设置,该设置依赖于访问特定领域相关概念的列表,通常是基准数据集类别。在这里,我们考虑了一个更具挑战性(和更现实)的场景,即在给定文本提示的情况下对单个概念进行分割,没有其他任何信息。除了与通用的“背景”文本进行对比之外,我们提出了两种不同方法来在测试时自动生成特定查询的对比概念。我们通过利用VLM训练集中的文本分布或精心设计的LLM提示来实现这一点。我们还提出了一个用于评估这种情况的指标,并在常用数据集上展示了我们的方法的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TMLR camera-ready
Summary
该文本介绍了基于CLIP的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在开放词汇语义分割领域的应用。模型通过大量图像文本对进行预训练,以简单的对比目标对齐两种模式。然而,当前文献中的评估设置依赖于访问一系列领域相关概念列表,这限制了模型的实用性。针对此问题,文本提出了一种更具挑战性和现实性的场景,即给定文本提示来分割单个概念,而不依赖预先定义的概念列表。为应对此场景,除了与通用背景文本进行对比,还提出了两种在测试时自动生成查询特定文本对比概念的方法。同时,还提出了一种针对这一场景的评估指标,并在常用数据集上展示了方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP-like Vision-Language Models (VLMs) 开启了开放词汇语义分割的新途径。
- VLMs 通过大量图像文本对进行预训练,以简单的对比目标实现模态对齐。
- 当前评估设置受限于需要访问领域相关概念列表,限制了模型的实用性。
- 文本提出了一种更具挑战性和现实性的场景:使用文本提示来分割单个概念。
- 为应对这一场景,除了与通用背景文本进行对比,提出了两种自动生成查询特定文本对比概念的方法。
- 利用VLM训练集文本分布或精心设计的LLM提示来生成对比概念。
点此查看论文截图



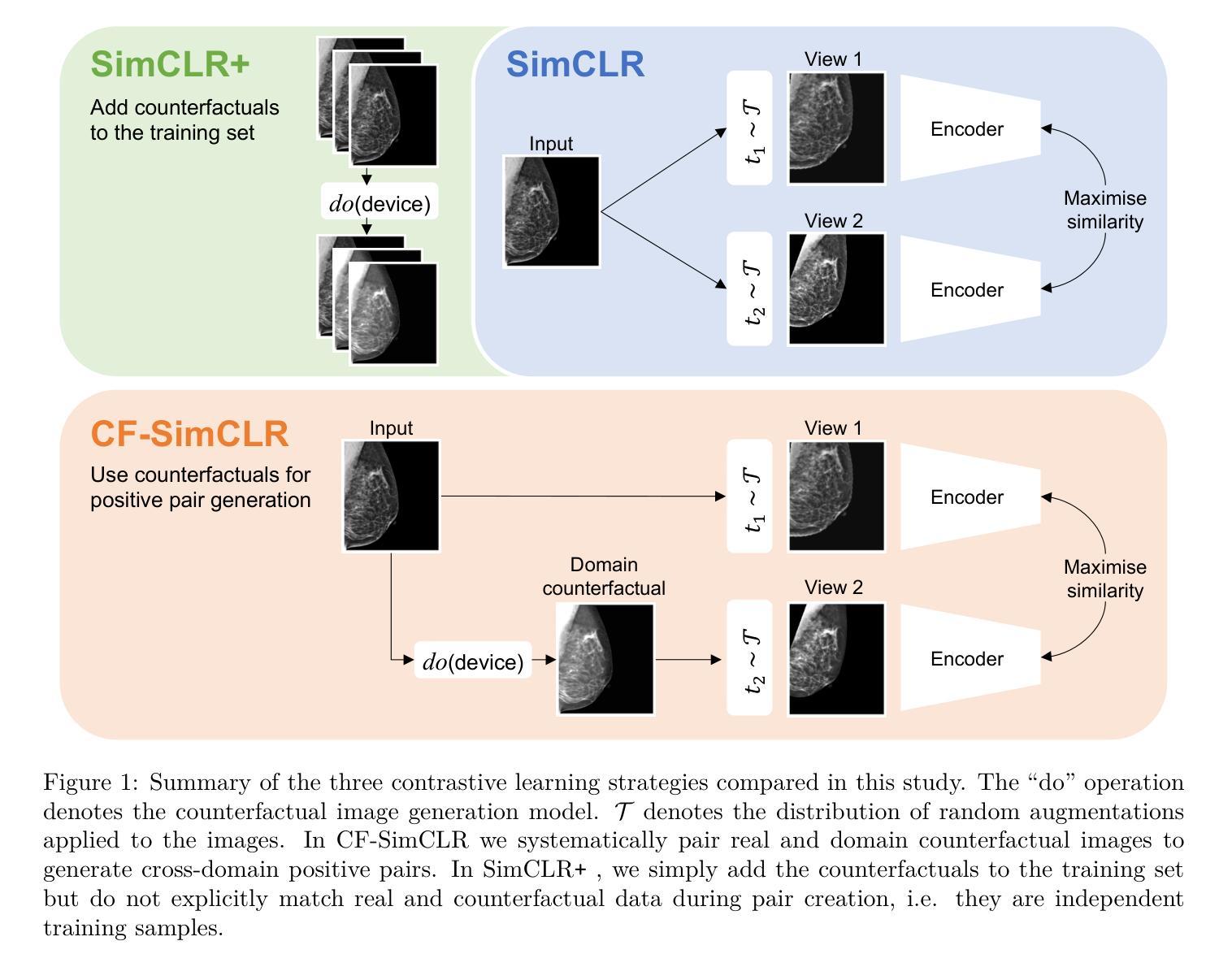
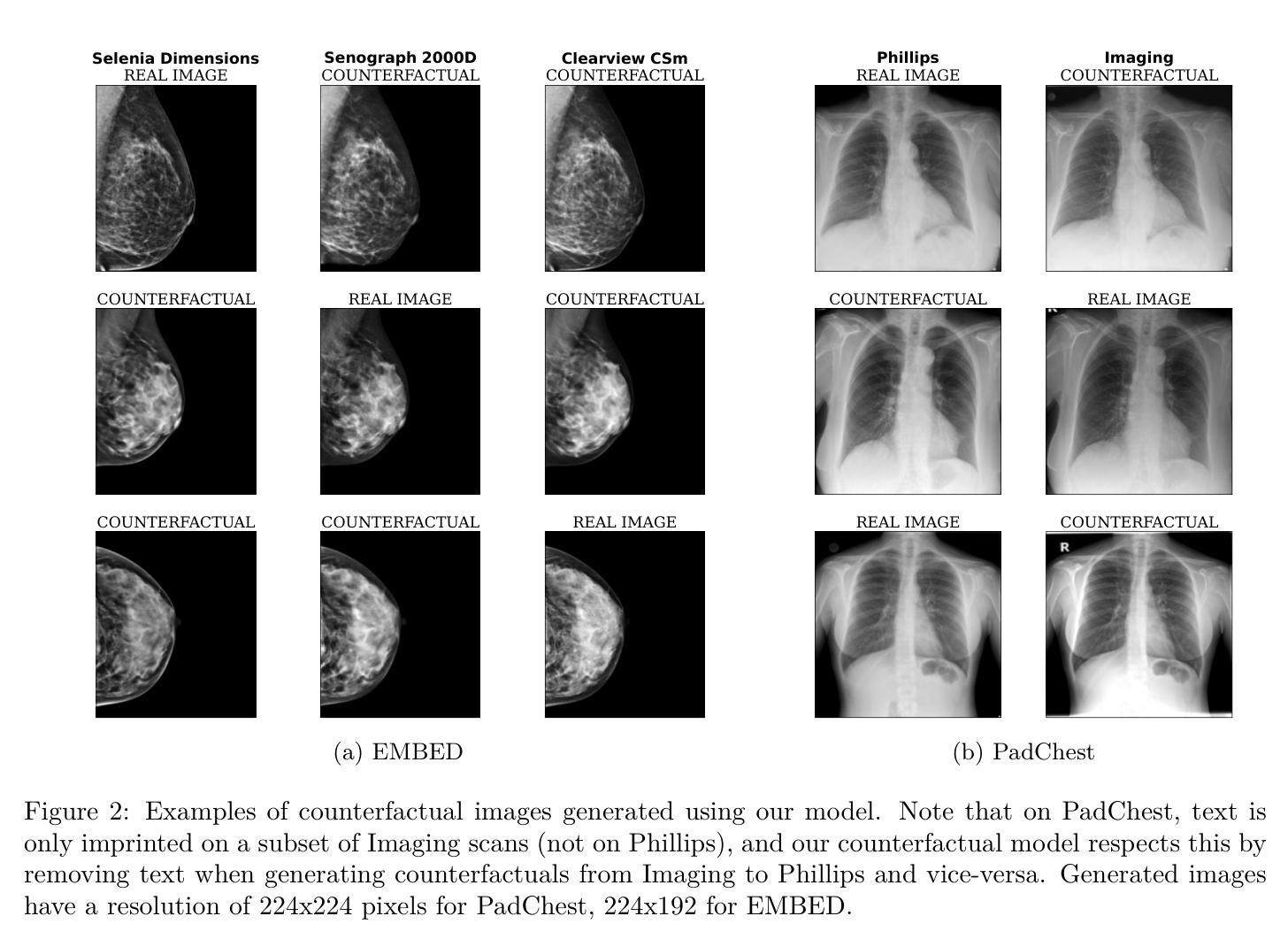
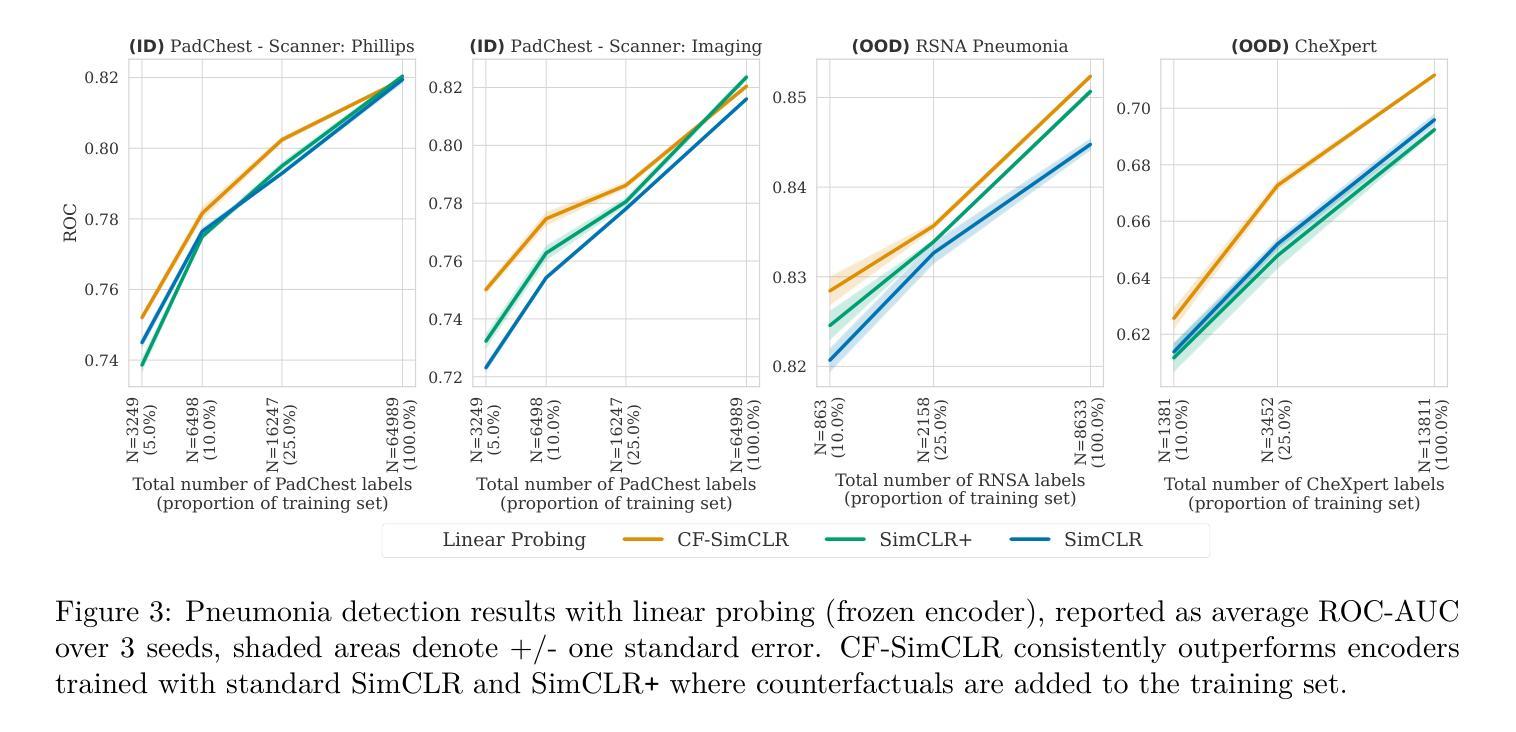
Counterfactual contrastive learning: robust representations via causal image synthesis
Authors:Melanie Roschewitz, Fabio De Sousa Ribeiro, Tian Xia, Galvin Khara, Ben Glocker
Contrastive pretraining is well-known to improve downstream task performance and model generalisation, especially in limited label settings. However, it is sensitive to the choice of augmentation pipeline. Positive pairs should preserve semantic information while destroying domain-specific information. Standard augmentation pipelines emulate domain-specific changes with pre-defined photometric transformations, but what if we could simulate realistic domain changes instead? In this work, we show how to utilise recent progress in counterfactual image generation to this effect. We propose CF-SimCLR, a counterfactual contrastive learning approach which leverages approximate counterfactual inference for positive pair creation. Comprehensive evaluation across five datasets, on chest radiography and mammography, demonstrates that CF-SimCLR substantially improves robustness to acquisition shift with higher downstream performance on both in- and out-of-distribution data, particularly for domains which are under-represented during training.
对比预训练在改进下游任务性能和模型泛化方面表现良好,特别是在标签有限的情况下。然而,它对于增强管道的选择很敏感。正向对应该保留语义信息同时破坏特定领域的信息。标准的增强管道通过预定义的光度变换来模拟特定领域的改变,但如果我们能够模拟真实的领域变化呢?在这项工作中,我们展示了如何利用因果图像生成的最新进展来实现这一目标。我们提出了CF-SimCLR方法,这是一种基于近似因果推理的正向对比学习方法。在胸部放射摄影和乳腺摄影五个数据集上的全面评估表明,CF-SimCLR极大地提高了对采集变化的稳健性,在内部和外部分布数据的下游性能表现均有所提升,特别是对于训练期间表示不足的领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extended version available at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2025.103668. This version was published in the proceedings of the MICCAI 2024 Data Engineering in Medical Imaging workshop. Code available at https://github.com/biomedia-mira/counterfactual-contrastive
Summary
对比预训练在提高下游任务性能和模型泛化能力方面表现优秀,特别是在标签有限的情况下。然而,其对于增强管道的选择非常敏感。正向对需要保留语义信息同时消除特定领域信息。传统的增强管道通过预定义的光度变换模拟特定领域的改变,但如果我们能模拟真实的领域变化会怎样?在这项工作中,我们展示了如何利用因果图像生成的最新进展来实现这一目标。我们提出了CF-SimCLR方法,一种利用近似因果推理来创建正向对的对比学习方法。在五个数据集上的综合评估,包括胸部放射检查和乳腺X光检查,证明了CF-SimCLR在获取转移方面的稳健性上有显著提高,对训练和测试数据的性能都有提升,特别是对于训练期间代表性不足的领域。
Key Takeaways
- 对比预训练能提高下游任务性能和模型泛化能力,尤其在标签有限的情况下。
- 对比预训练的增强管道选择对其性能有重要影响。
- 正向对需要保留语义信息同时消除特定领域信息。
- 传统的增强管道通常模拟预定义的光度变换来模拟特定领域的改变。
- 提出了新的方法CF-SimCLR,利用因果图像生成技术来模拟真实的领域变化。
- CF-SimCLR通过近似因果推理创建正向对进行对比学习。
点此查看论文截图