⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
Egocentric Human-Object Interaction Detection: A New Benchmark and Method
Authors:Kunyuan Deng, Yi Wang, Lap-Pui Chau
Understanding the interaction between humans and objects has gained much attention in recent years. Existing human-object interaction (HOI) detection methods mainly focus on the third-person perspectives, overlooking a more intuitive way from the egocentric view of HOI, namely Ego-HOI. This paper introduces an Ego-HOIBench, a new dataset to promote the benchmarking and development of Ego-HOI detection. Our Ego-HOIBench comprises more than 27K egocentric images with high-quality hand-verb-object triplet annotations across 123 fine-grained interaction categories and locations, covering a rich diversity of scenarios, object types, and hand configurations in daily activities. In addition, we explore and adapt third-person HOI detection methods to Ego-HOIBench and illustrate the challenges of hand-occluded objects and the complexity of single- and two-hand interactions. To build a new baseline, we propose a Hand Geometry and Interactivity Refinement (HGIR) scheme, which leverages hand pose and geometric information as valuable cues for interpreting interactions. Specifically, the HGIR scheme explicitly extracts global hand geometric features from the estimated hand pose proposals and refines the interaction-specific features using pose-interaction attention. This scheme enables the model to obtain a robust and powerful interaction representation, significantly improving the Ego-HOI detection capability. Our approach is lightweight and effective, and it can be easily applied to HOI baselines in a plug-and-play manner to achieve state-of-the-art results on Ego-HOIBench. Our project is available at: https://dengkunyuan.github.io/EgoHOIBench/
近年来,对人类与物体之间交互的理解已引起广泛关注。现有的基于人机交互(HOI)的检测方法主要侧重于第三人称视角,忽略了从人机交互的以自我为中心的视角(即Ego-HOI)出发的更直观的方式。本文介绍了Ego-HOIBench数据集,该数据集旨在推动Ego-HOI检测的性能基准和发展。我们的Ego-HOIBench包含超过27K张以自我为中心的高质量图像,其中包含手-动词-对象三元组注释,涵盖超过123个精细交互类别和位置,涵盖丰富的场景、对象类型和日常活动中的手部配置。此外,我们探索并适应了第三人称的HOI检测方法,以应用于Ego-HOIBench,并说明了手部遮挡物体以及单手和双手交互的复杂性所带来的挑战。为了建立新的基准,我们提出了手部几何和交互细化(HGIR)方案,该方案利用手部姿势和几何信息作为解释交互的有价值线索。具体而言,HGIR方案从估计的手部姿势提案中明确提取全局手部几何特征,并使用姿态交互注意力细化特定交互的特征。该方案使模型能够获得稳健且强大的交互表示,从而极大地提高了Ego-HOI检测能力。我们的方法轻巧有效,可轻松应用于HOI基线采用随插即用方式来实现最新的成果表现。我们的项目可以通过以下链接访问:链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个新的数据集Ego-HOIBench,用于推动以自我为中心的互动检测(Ego-HOI)的基准测试和算法发展。该数据集包含超过2万张高质量的手部动作对象三元组标注的图像,涵盖日常活动中的丰富场景、对象类型和手部配置。文章还探讨了从第三人称互动检测向Ego-HOIBench的转变,并介绍了在单手遮挡和单手及双手互动方面的挑战。为了建立新的基准线,本文提出了手型几何与互动性精炼(HGIR)方案,该方案利用手部姿势和几何信息作为解释互动的宝贵线索。该方案能够有效提升模型的互动表现力,显著提高Ego-HOI检测能力。此方案轻便有效,可轻松应用于现有HOI基准测试中,达到领先水平。更多信息可访问项目网站:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一个新的数据集Ego-HOIBench,专注于以自我为中心的互动检测(Ego-HOI)。
- 数据集包含多种场景、对象类型和手部配置的高质量的图像数据。
- 探讨了从第三人称视角的互动检测到Ego-HOIBench的挑战性问题,特别是手遮挡和单手及双手互动的问题。
- 提出了手型几何与互动性精炼(HGIR)方案,结合手部姿势和几何信息提升模型的互动表现力。
- HGIR方案能有效提高Ego-HOI检测能力,达到领先水平。
- 该方案轻便有效,可轻松集成到现有的HOI基准测试中。
点此查看论文截图

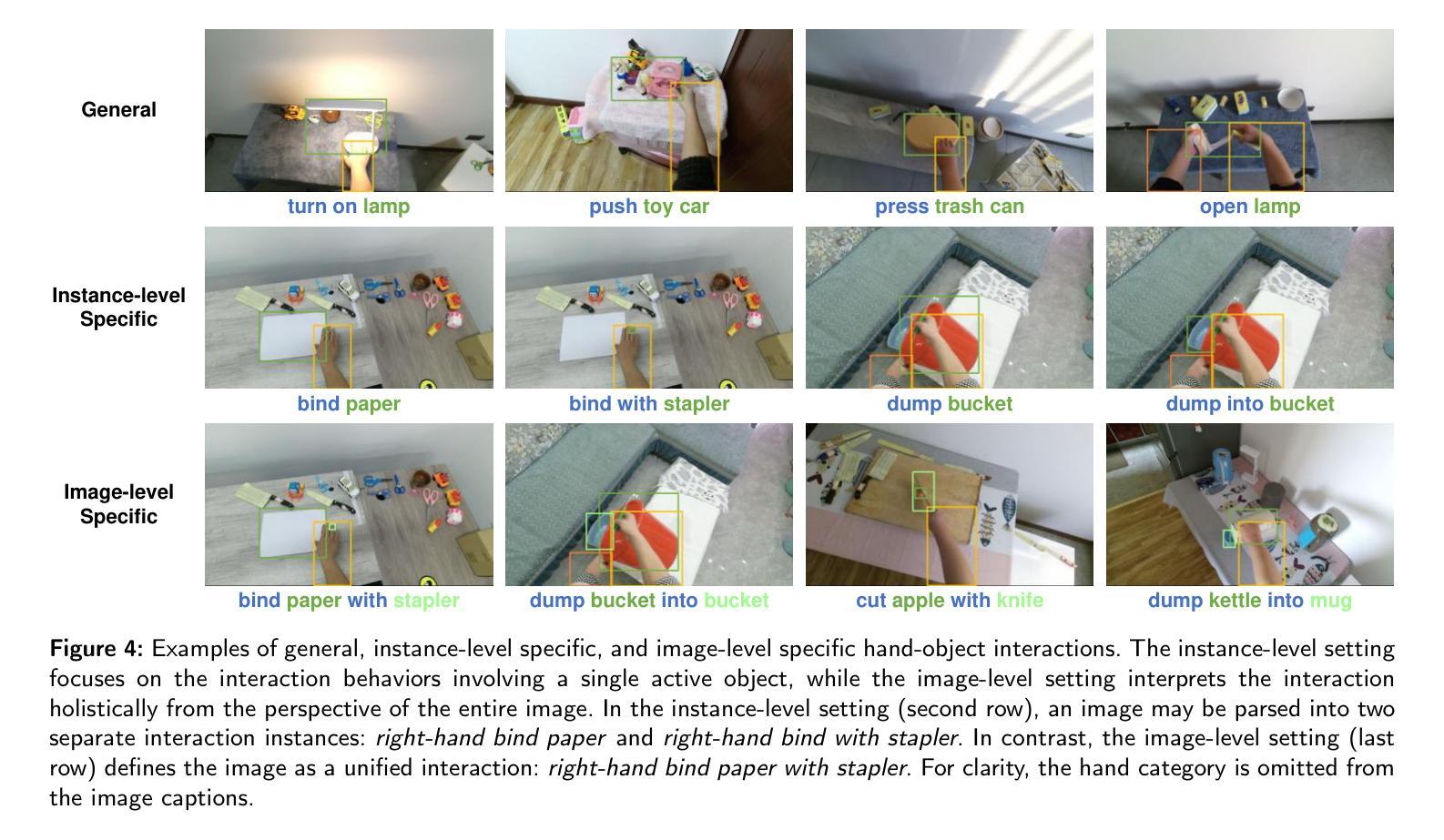
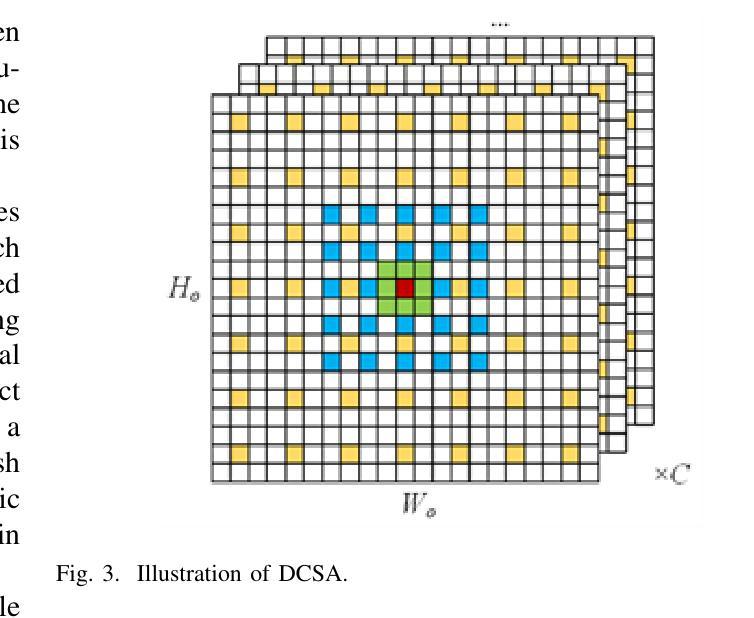
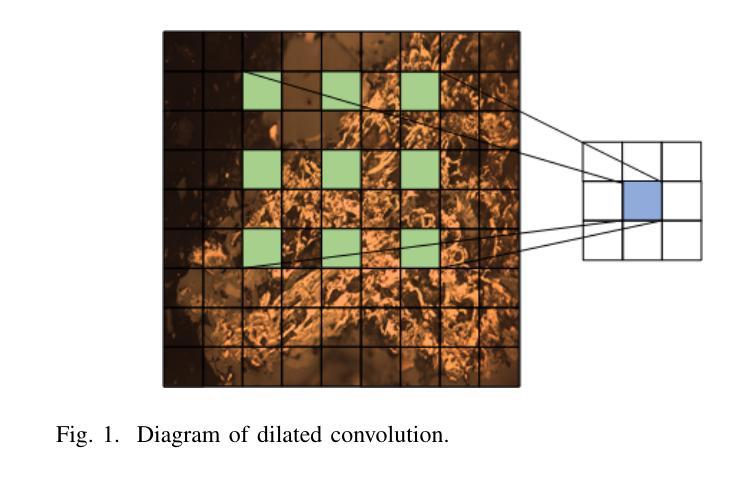
Combining Self-attention and Dilation Convolutional for Semantic Segmentation of Coal Maceral Groups
Authors:Zhenghao Xi, Zhengnan Lv, Yang Zheng, Xiang Liu, Zhuang Yu, Junran Chen, Jing Hu, Yaqi Liu
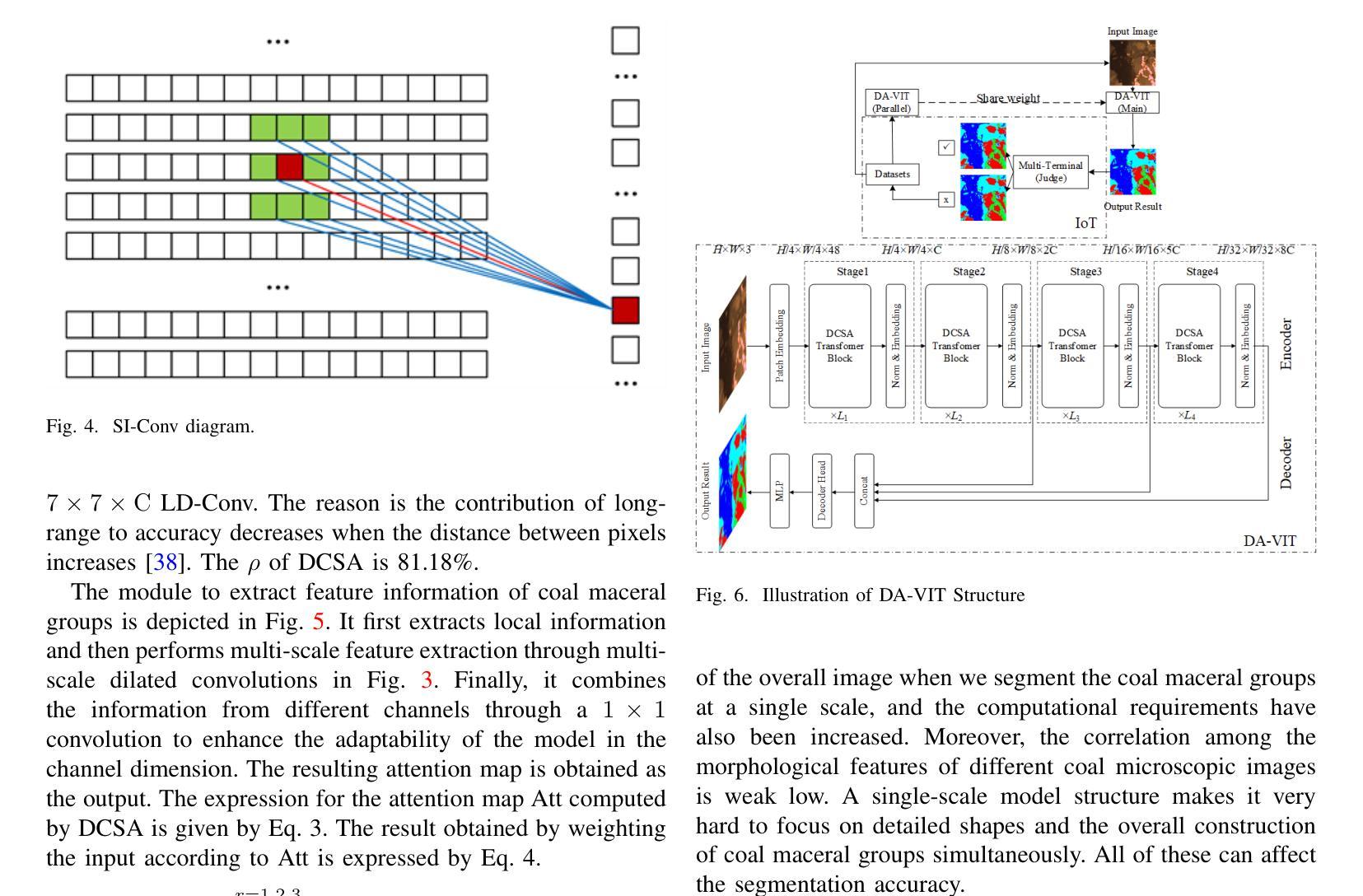
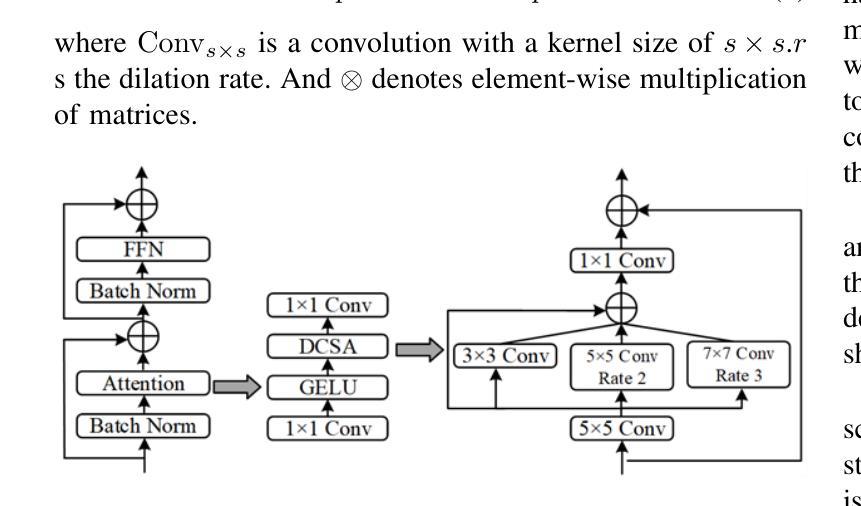
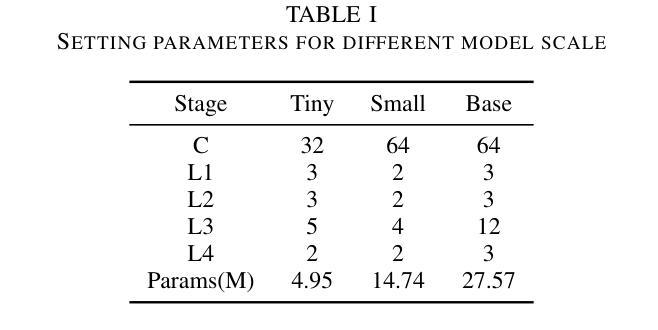
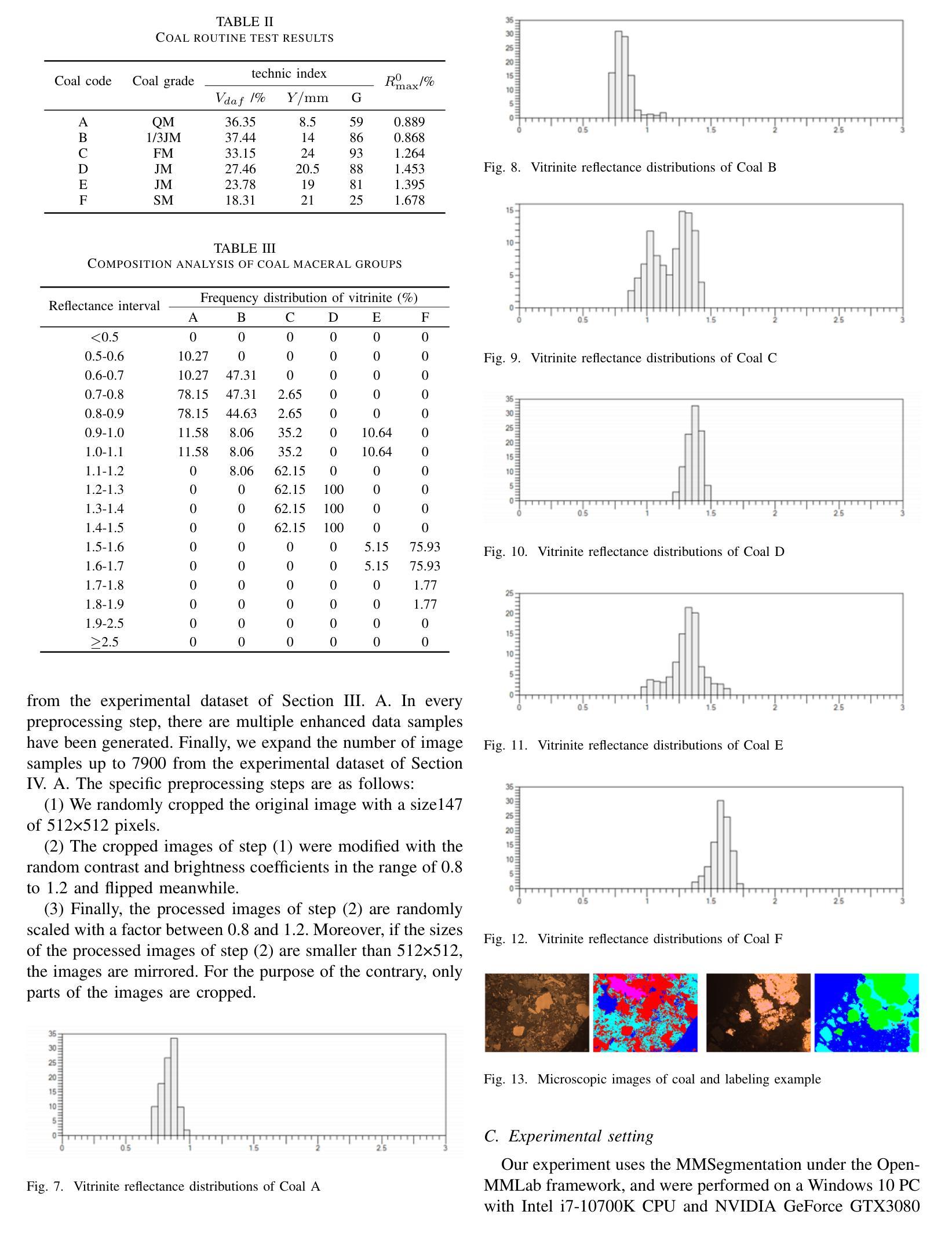
The segmentation of coal maceral groups can be described as a semantic segmentation process of coal maceral group images, which is of great significance for studying the chemical properties of coal. Generally, existing semantic segmentation models of coal maceral groups use the method of stacking parameters to achieve higher accuracy. It leads to increased computational requirements and impacts model training efficiency. At the same time, due to the professionalism and diversity of coal maceral group images sampling, obtaining the number of samples for model training requires a long time and professional personnel operation. To address these issues, We have innovatively developed an IoT-based DA-VIT parallel network model. By utilizing this model, we can continuously broaden the dataset through IoT and achieving sustained improvement in the accuracy of coal maceral groups segmentation. Besides, we decouple the parallel network from the backbone network to ensure the normal using of the backbone network during model data updates. Secondly, DCSA mechanism of DA-VIT is introduced to enhance the local feature information of coal microscopic images. This DCSA can decompose the large kernels of convolutional attention into multiple scales and reduce 81.18% of parameters.Finally, we performed the contrast experiment and ablation experiment between DA-VIT and state-of-the-art methods at lots of evaluation metrics. Experimental results show that DA-VIT-Base achieves 92.14% pixel accuracy and 63.18% mIoU. Params and FLOPs of DA-VIT-Tiny are 4.95M and 8.99G, respectively. All of the evaluation metrics of the proposed DA-VIT are better than other state-of-the-art methods.
煤岩组分分割可以描述为煤岩组分图像的语义分割过程,对研究煤的化学性质具有重要意义。目前,现有的煤岩组分语义分割模型通常采用堆叠参数的方法来提高精度,这导致了计算需求的增加和模型训练效率的影响。同时,由于煤岩组分图像采样的专业性和多样性,获取模型训练所需的样本数量需要很长时间和专业人员的操作。为了解决这些问题,我们创新地开发了一种基于物联网的DA-VIT并行网络模型。通过利用该模型,我们可以通过物联网不断扩展数据集,实现煤岩组分分割精度的持续改进。此外,我们将并行网络与骨干网解耦,以确保在模型数据更新期间骨干网的正常使用。其次,介绍了DA-VIT的DCSA机制,以提高煤显微图像的局部特征信息。DCSA可以将在分割和转化学习中图像的可训练可接收野的值将降低到百分之四左右。这个DCSA可以将卷积注意力的大内核分解成多个尺度并减少81.18%的参数。最后,我们在许多评估指标上对DA-VIT和最新方法进行了对比实验和消融实验。实验结果表明,DA-VIT-Base的像素精度达到92.14%,mIoU达到63.18%。DA-VIT-Tiny的参数和FLOPs分别为4.95M和8.99G。所提DA-VIT的所有评估指标均优于其他最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对煤显微图像分割的问题,研究团队创新性地提出了基于物联网的DA-VIT并行网络模型。该模型可以持续拓展数据集,提升分割精度,并引入DCSA机制强化局部特征信息。实验结果显示,DA-VIT在像素精度和mIoU等指标上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 煤显微图像的语义分割对研究煤的化学性质具有重要意义。
- 现有语义分割模型通常通过堆叠参数来提高精度,但计算需求大,影响训练效率。
- 创新性地提出了基于物联网的DA-VIT并行网络模型,可持续拓展数据集并提升分割精度。
- 引入DCSA机制强化煤显微图像的局部特征信息。
- DA-VIT模型具有优秀的性能表现,包括像素精度和mIoU等指标。
点此查看论文截图

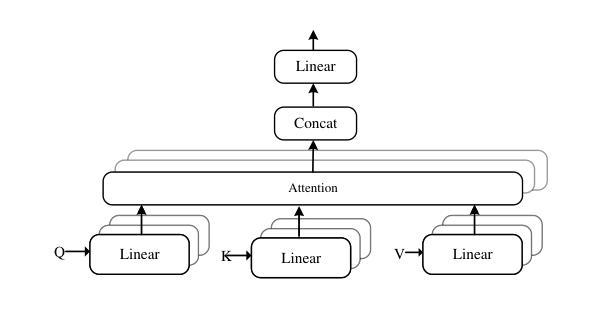
Roboflow100-VL: A Multi-Domain Object Detection Benchmark for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Peter Robicheaux, Matvei Popov, Anish Madan, Isaac Robinson, Joseph Nelson, Deva Ramanan, Neehar Peri
Vision-language models (VLMs) trained on internet-scale data achieve remarkable zero-shot detection performance on common objects like car, truck, and pedestrian. However, state-of-the-art models still struggle to generalize to out-of-distribution classes, tasks and imaging modalities not typically found in their pre-training. Rather than simply re-training VLMs on more visual data, we argue that one should align VLMs to new concepts with annotation instructions containing a few visual examples and rich textual descriptions. To this end, we introduce Roboflow100-VL, a large-scale collection of 100 multi-modal object detection datasets with diverse concepts not commonly found in VLM pre-training. We evaluate state-of-the-art models on our benchmark in zero-shot, few-shot, semi-supervised, and fully-supervised settings, allowing for comparison across data regimes. Notably, we find that VLMs like GroundingDINO and Qwen2.5-VL achieve less than 2% zero-shot accuracy on challenging medical imaging datasets within Roboflow100-VL, demonstrating the need for few-shot concept alignment. Lastly, we discuss our recent CVPR 2025 Foundational FSOD competition and share insights from the community. Notably, the winning team significantly outperforms our baseline by 16.8 mAP! Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/ and https://universe.roboflow.com/rf100-vl/
在互联网规模数据上训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在常见对象(如汽车、卡车和行人)上实现了出色的零样本检测性能。然而,最先进的模型仍然难以推广到其预训练中没有出现的类别、任务和成像模式。我们主张不应仅通过更多的视觉数据重新训练VLMs,而应通过包含少量视觉示例和丰富文本描述的注释指令来对齐VLMs以理解新概念。为此,我们推出了Roboflow100-VL,这是一个包含100个多模式对象检测数据集的大规模集合,其中包含VLM预训练中不常见的各种概念。我们在基准测试上对最先进的模型进行了零样本、少样本、半监督和全监督环境的评估,以便在不同数据环境下进行比较。值得注意的是,我们发现像GroundingDINO和Qwen2.5-VL这样的VLM在Roboflow100-VL中的具有挑战性的医学影像数据集上的零样本准确率低于2%,这证明了进行少样本概念对齐的必要性。最后,我们讨论了最近的CVPR 2025基础FSOD竞赛并从社区中分享了见解。值得注意的是,冠军团队比我们的基线高出16.8 mAP!我们的代码和数据集可在[https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/]和[https://universe.roboflow.com/rf100-vl/中找到。](https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/%EF%BC%89%E5%92%8C%E3%80%82)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally. Project Page: https://rf100-vl.org/
Summary:
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的新挑战。虽然VLMs在常规物体检测上表现出色,但在面对非常规分布类别、任务和新成像模式时,其泛化能力受限。为此,作者引入了Roboflow100-VL,这是一个包含100个多模式物体检测数据集的大规模集合,涵盖了VLM预训练不常见的大量概念。作者评估了多种状态模型在各种设置下的性能,并发现挑战医疗成像数据集上的VLMs零准确率较低。此外,文章还介绍了CVPR 2025的FSOD竞赛及社区见解。
Key Takeaways:
- VLMs在常规物体检测上表现出色,但在面对非常规分布类别和任务时泛化能力受限。
- Roboflow100-VL是一个包含多样化概念的大规模多模式物体检测数据集,旨在解决VLM预训练不常见的问题。
- 在Roboflow100-VL的挑战医疗成像数据集上,VLMs的零准确率较低。
- 介绍了CVPR 2025的FSOD竞赛及其社区见解,其中获胜队伍显著超越了基线。
- 需要通过少量样本概念对齐来提高VLMs的性能。
- 作者提供了Roboflow100-VL的代码和数据集链接供公众使用。
点此查看论文截图




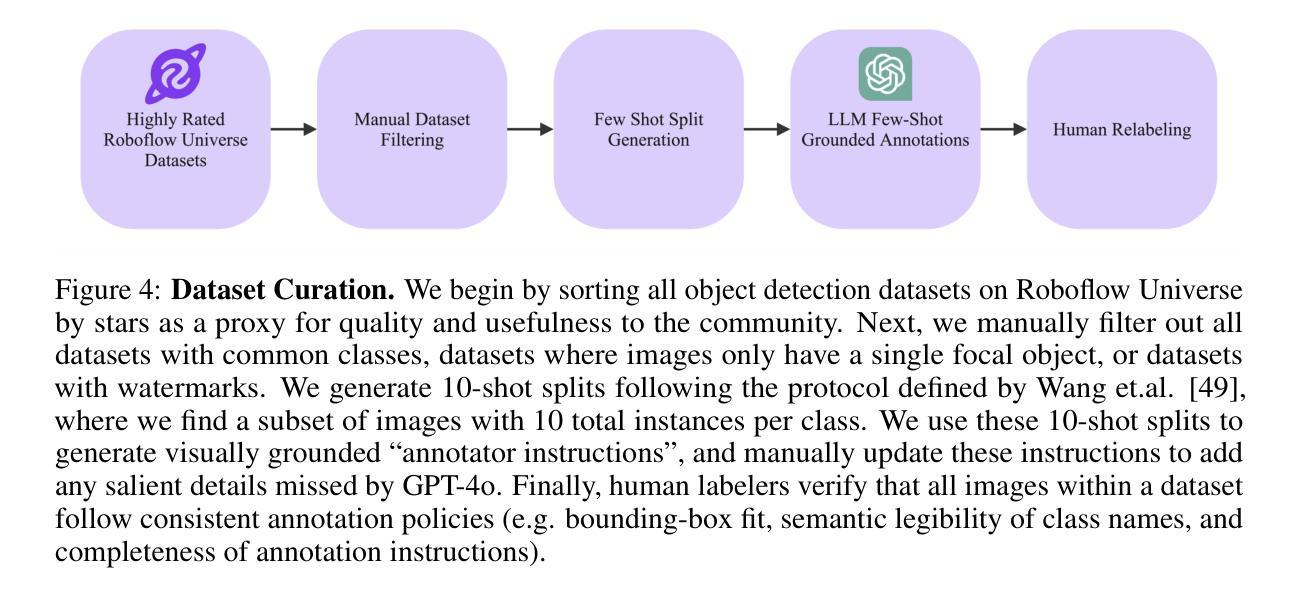
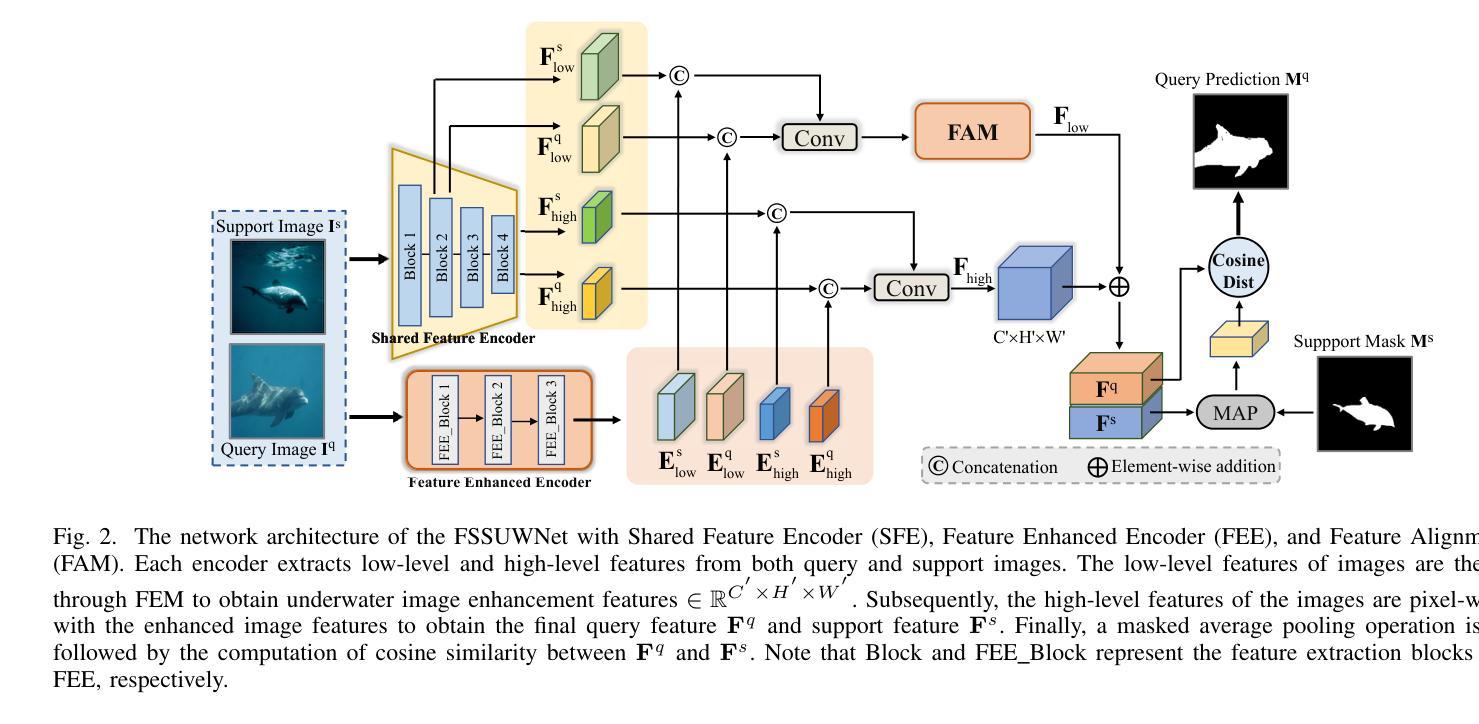
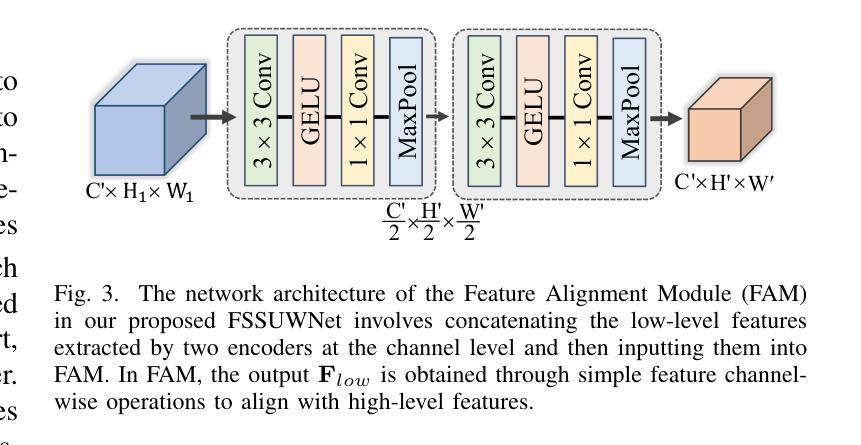
FSSUWNet: Mitigating the Fragility of Pre-trained Models with Feature Enhancement for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation in Underwater Images
Authors:Zhuohao Li, Zhicheng Huang, Wenchao Liu, Zhuxin Zhang, Jianming Miao
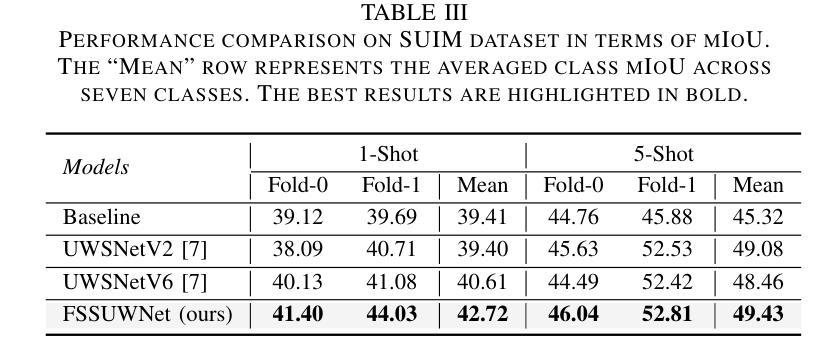
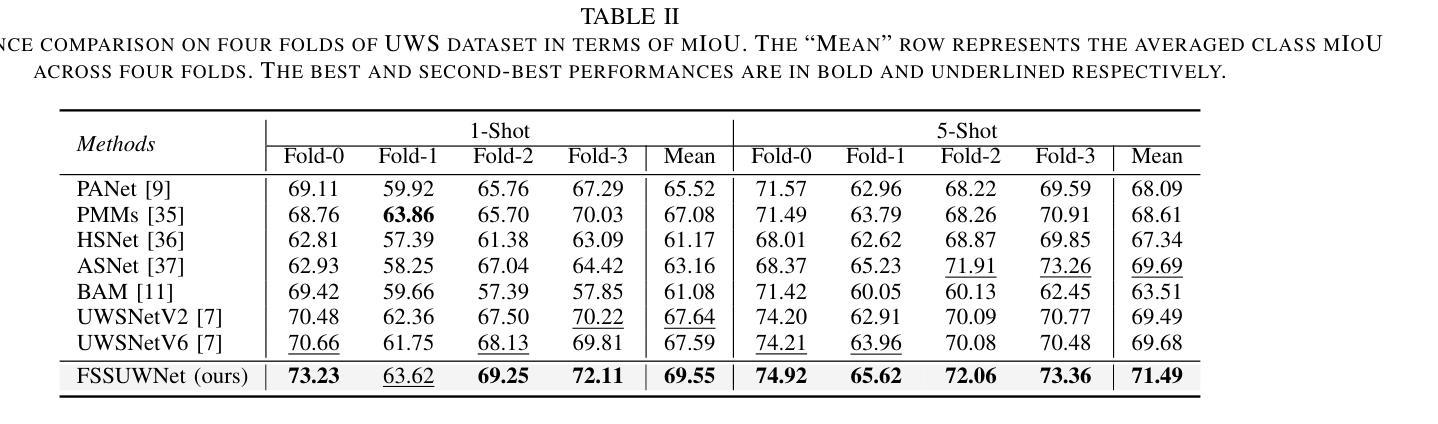
Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation (FSS), which focuses on segmenting new classes in images using only a limited number of annotated examples, has recently progressed in data-scarce domains. However, in this work, we show that the existing FSS methods often struggle to generalize to underwater environments. Specifically, the prior features extracted by pre-trained models used as feature extractors are fragile due to the unique challenges of underwater images. To address this, we propose FSSUWNet, a tailored FSS framework for underwater images with feature enhancement. FSSUWNet exploits the integration of complementary features, emphasizing both low-level and high-level image characteristics. In addition to employing a pre-trained model as the primary encoder, we propose an auxiliary encoder called Feature Enhanced Encoder which extracts complementary features to better adapt to underwater scene characteristics. Furthermore, a simple and effective Feature Alignment Module aims to provide global prior knowledge and align low-level features with high-level features in dimensions. Given the scarcity of underwater images, we introduce a cross-validation dataset version based on the Segmentation of Underwater Imagery dataset. Extensive experiments on public underwater segmentation datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. For example, our method outperforms the previous best method by 2.8% and 2.6% in terms of the mean Intersection over Union metric for 1-shot and 5-shot scenarios in the datasets, respectively. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/lizhh268/FSSUWNet.
少样本语义分割(FSS)专注于使用有限数量的标注样例对图像中的新类别进行分割,最近在数据稀缺领域取得了进展。然而,在这项工作中,我们表明现有的FSS方法往往难以推广到水下环境。具体来说,由于水下图像的独特挑战,预训练模型作为特征提取器所提取的先验特征是脆弱的。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FSSUWNet,这是一个针对水下图像进行特征增强的FSS框架。FSSUWNet结合了互补特征,强调图像的低级和高级特征。除了使用预训练模型作为主编码器外,我们还提出了一个名为特征增强编码器的辅助编码器,用于提取互补特征,以更好地适应水下场景特征。此外,简单有效的特征对齐模块旨在提供全局先验知识,并在维度上对齐低级特征和高级特征。鉴于水下图像的稀缺性,我们基于水下图像分割数据集引入了一个交叉验证数据集版本。在公共水下分割数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。例如,我们的方法在数据集的单样本和五样本场景下的平均交并比指标上分别比之前的最佳方法高出2.8%和2.6%。我们的实现可在https://github.com/lizhh268/FSSUWNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对水下图像进行少量样本语义分割(FSS)的挑战。现有方法难以适应水下环境,因此提出一种新的水下图像FSS框架——FSSUWNet,通过特征增强和互补特征融合来提高模型性能。引入辅助编码器Feature Enhanced Encoder和特征对齐模块Feature Alignment Module,以更好地适应水下场景特性并提升特征质量。在公开的水下分割数据集上进行实验验证,该方法达到了先进水平,相较于之前最佳方法,在1-shot和5-shot场景下的平均交并比(IoU)指标分别提升了2.8%和2.6%。
Key Takeaways
- FSSUWNet解决了现有FSS方法在水下环境中的应用问题。
- FSSUWNet采用特征增强和互补特征融合的策略来提高模型性能。
- 引入辅助编码器Feature Enhanced Encoder,用于提取适应水下场景特性的互补特征。
- 采用特征对齐模块Feature Alignment Module,旨在提供全局先验知识并融合高低层特征。
- 在公开数据集上验证,FSSUWNet达到了先进水平,相较于之前的方法有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图
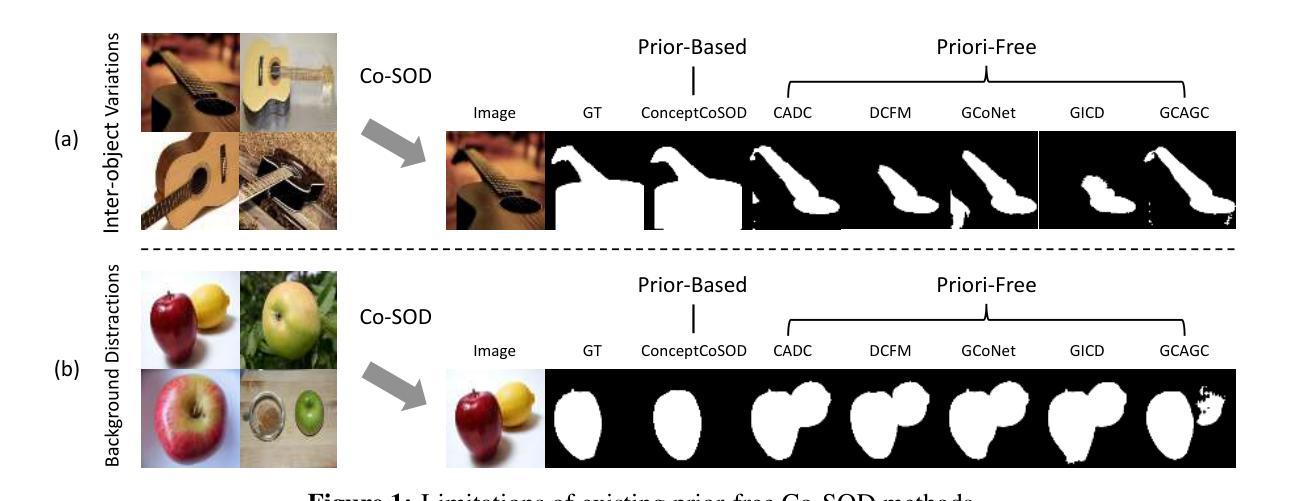
Concept Guided Co-salient Object Detection
Authors:Jiayi Zhu, Qing Guo, Felix Juefei-Xu, Yihao Huang, Yang Liu, Geguang Pu
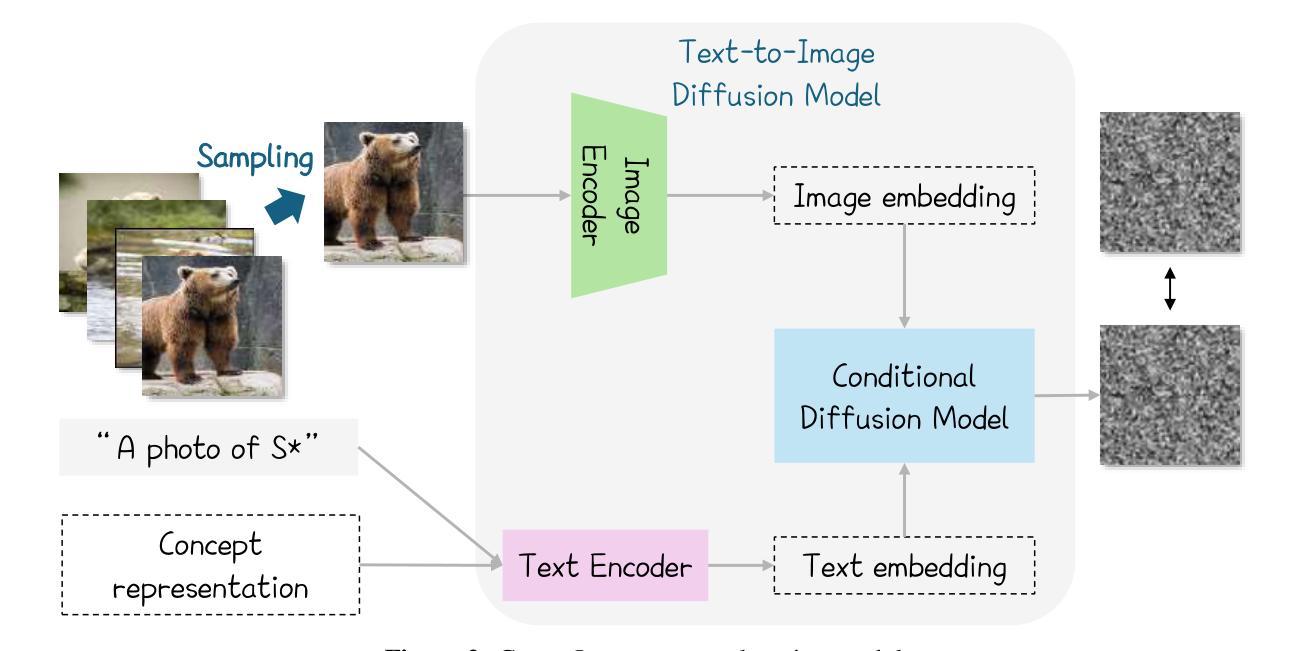
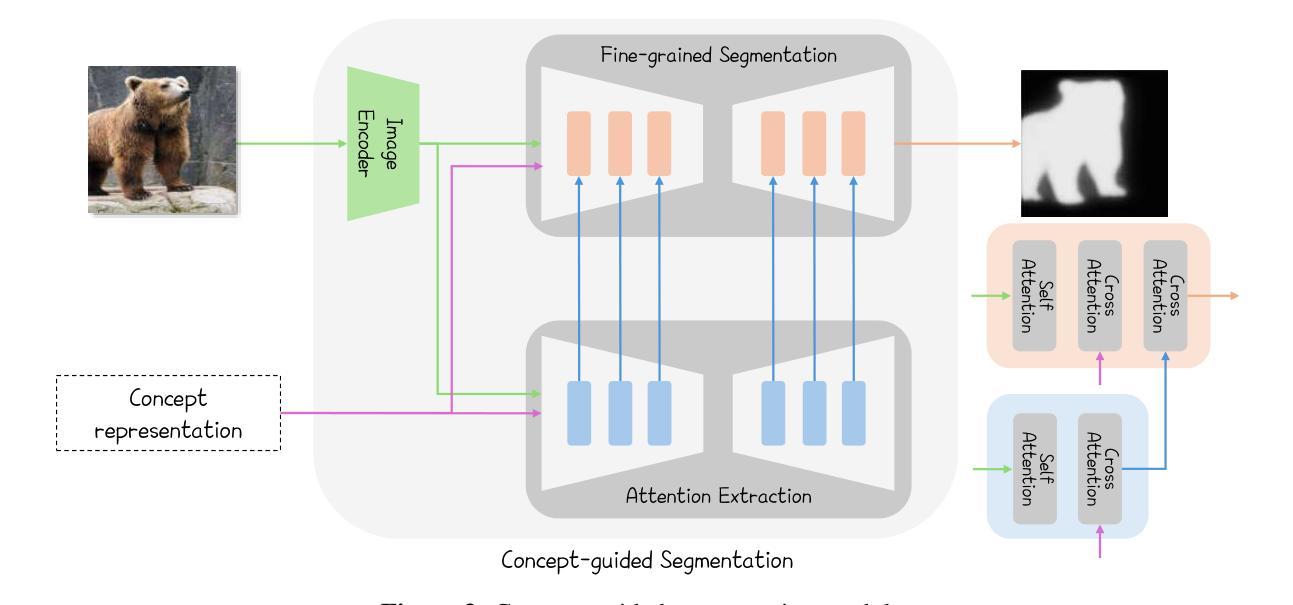
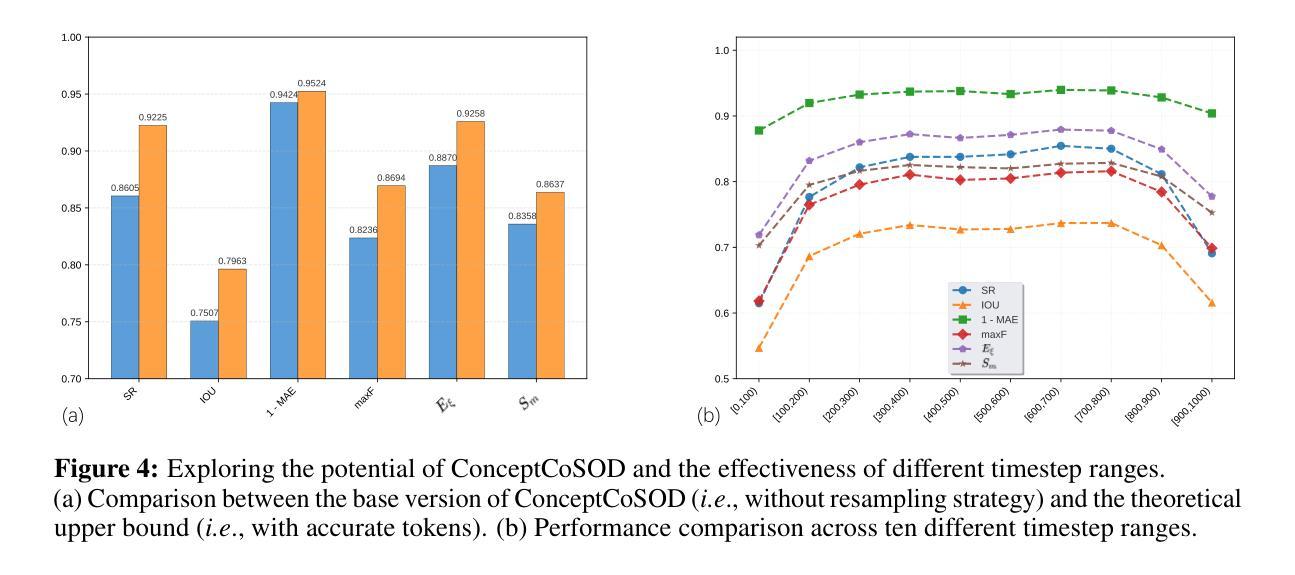
Co-salient object detection (Co-SOD) aims to identify common salient objects across a group of related images. While recent methods have made notable progress, they typically rely on low-level visual patterns and lack semantic priors, limiting their detection performance. We propose ConceptCoSOD, a concept-guided framework that introduces high-level semantic knowledge to enhance co-saliency detection. By extracting shared text-based concepts from the input image group, ConceptCoSOD provides semantic guidance that anchors the detection process. To further improve concept quality, we analyze the effect of diffusion timesteps and design a resampling strategy that selects more informative steps for learning robust concepts. This semantic prior, combined with the resampling-enhanced representation, enables accurate and consistent segmentation even in challenging visual conditions. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets and five corrupted settings demonstrate that ConceptCoSOD significantly outperforms existing methods in both accuracy and generalization.
协同显著性目标检测(Co-SOD)旨在识别一组相关图像中的共同显著目标。虽然最近的方法已经取得了显著的进展,但它们通常依赖于低级的视觉模式,缺乏语义先验,限制了它们的检测性能。我们提出ConceptCoSOD,一个概念引导框架,引入高级语义知识以增强协同显著性检测。ConceptCoSOD通过从输入图像组中提取基于文本的共享概念,为检测过程提供语义指导。为了进一步提高概念质量,我们分析了扩散时间步长的影响,并设计了一种重采样策略,选择更有信息量的步骤来学习稳健的概念。这种语义先验与重采样增强表示相结合,即使在具有挑战性的视觉条件下也能实现准确且一致的分割。在三个基准数据集和五种腐蚀环境下的大量实验表明,ConceptCoSOD在准确性和通用性方面显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
概念引导协同显著性对象检测(ConceptCoSOD)旨在利用高层次的语义知识识别相关图像群组中的共同显著对象。它通过提取输入图像群中的共享文本概念来提供语义引导,进而强化协同显著性检测过程。同时,为了提高概念质量,本文分析了扩散时序步的影响并设计了一种重采样策略,选择更有信息量的步骤来学习稳健的概念。这种语义先验与重采样增强表示相结合,即使在具有挑战性的视觉条件下也能实现准确且一致的分割。在三个基准数据集和五种腐蚀环境下的广泛实验表明,ConceptCoSOD在准确性和泛化能力上显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 概念引导协同显著性对象检测(ConceptCoSOD)利用高层次的语义知识识别相关图像群组中的共同显著对象。
- 通过提取输入图像群中的共享文本概念,ConceptCoSOD为检测过程提供语义引导。
- 为提高概念质量,ConceptCoSOD分析了扩散时序步的影响并设计了重采样策略。
- 重采样策略选择更有信息量的步骤,以学习稳健的概念表示。
- 这种语义先验与重采样增强表示相结合,提高了检测的准确性和一致性。
- 在多个基准数据集和腐蚀环境下的实验表明,ConceptCoSOD在性能和泛化能力上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Semantic Segmentation Based Quality Control of Histopathology Whole Slide Images
Authors:Abhijeet Patil, Garima Jain, Harsh Diwakar, Jay Sawant, Tripti Bameta, Swapnil Rane, Amit Sethi
We developed a software pipeline for quality control (QC) of histopathology whole slide images (WSIs) that segments various regions, such as blurs of different levels, tissue regions, tissue folds, and pen marks. Given the necessity and increasing availability of GPUs for processing WSIs, the proposed pipeline comprises multiple lightweight deep learning models to strike a balance between accuracy and speed. The pipeline was evaluated in all TCGAs, which is the largest publicly available WSI dataset containing more than 11,000 histopathological images from 28 organs. It was compared to a previous work, which was not based on deep learning, and it showed consistent improvement in segmentation results across organs. To minimize annotation effort for tissue and blur segmentation, annotated images were automatically prepared by mosaicking patches (sub-images) from various WSIs whose labels were identified using a patch classification tool HistoROI. Due to the generality of our trained QC pipeline and its extensive testing the potential impact of this work is broad. It can be used for automated pre-processing any WSI cohort to enhance the accuracy and reliability of large-scale histopathology image analysis for both research and clinical use. We have made the trained models, training scripts, training data, and inference results publicly available at https://github.com/abhijeetptl5/wsisegqc, which should enable the research community to use the pipeline right out of the box or further customize it to new datasets and applications in the future.
我们开发了一种用于组织病理学全切片图像(WSI)质量控制的软件管道(QC),该管道能够对不同区域进行分割,例如不同级别的模糊、组织区域、组织折叠和笔迹。考虑到处理WSI时对GPU的需求及其日益普及性,所提出的管道包含多个轻量级的深度学习模型,以在准确性和速度之间取得平衡。该管道在TCGA(即包含来自28个器官的超过11,000个组织病理学图像的最大的公开WSI数据集)中进行了评估。与之前的非深度学习为基础的工作相比,它在各器官的分割结果中表现出持续改进。为了减少组织和模糊分割的标注工作量,通过合并来自各种WSI的补丁(子图像)来自动准备标注图像,使用补丁分类工具HistoROI来识别这些标签。由于我们训练的QC管道的通用性和广泛的测试,这项工作具有广泛的影响潜力。它可以用于自动预处理任何WSI队列,以提高大规模组织病理学图像分析的准确性和可靠性,无论是用于研究还是临床。我们在https://github.com/abhijeetptl5/wsisegqc上公开了训练模型、训练脚本、训练数据和推理结果,研究社区可以直接使用此管道或进一步定制它以适应未来新的数据集和应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于组织病理学全切片图像(WSI)质量控制的软件管道,该管道能够分割不同的区域,如不同级别的模糊、组织区域、组织折叠和墨迹。管道采用多个轻量级深度学习模型,在保障准确性的同时,提升了处理速度。该管道在TCGA大型公开WSI数据集上进行了评估,并与非深度学习方法进行了比较,显示出跨器官的分割结果一致性提升。为减少组织和模糊分割的标注工作,通过HistoROI补丁分类工具自动准备标注图像。此工作的潜在影响广泛,可用于自动预处理任何WSI队列,提高大规模组织病理学图像分析的准确性和可靠性,既可用于研究,也可用于临床应用。
Key Takeaways
- 软件开发了用于组织病理学全切片图像质量控制的管道,实现多种区域分割。
- 管道采用轻量级深度学习模型,兼顾准确性和速度。
- 管道在TCGA大型公开数据集上评估,并与非深度学习方法比较,显示跨器官分割结果提升。
- 通过自动准备标注图像,减小了标注工作量。
- 管道具有通用性,可广泛应用于任何WSI的预处理。
- 管道能提高大规模组织病理学图像分析的准确性和可靠性,既适用于研究也适用于临床。
点此查看论文截图

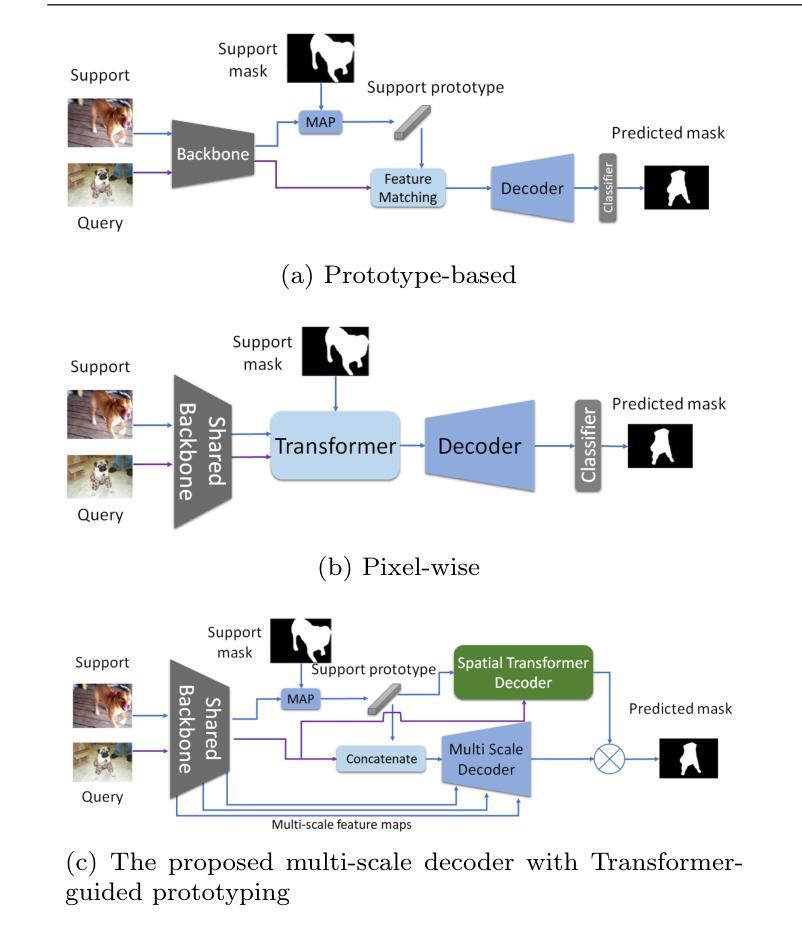
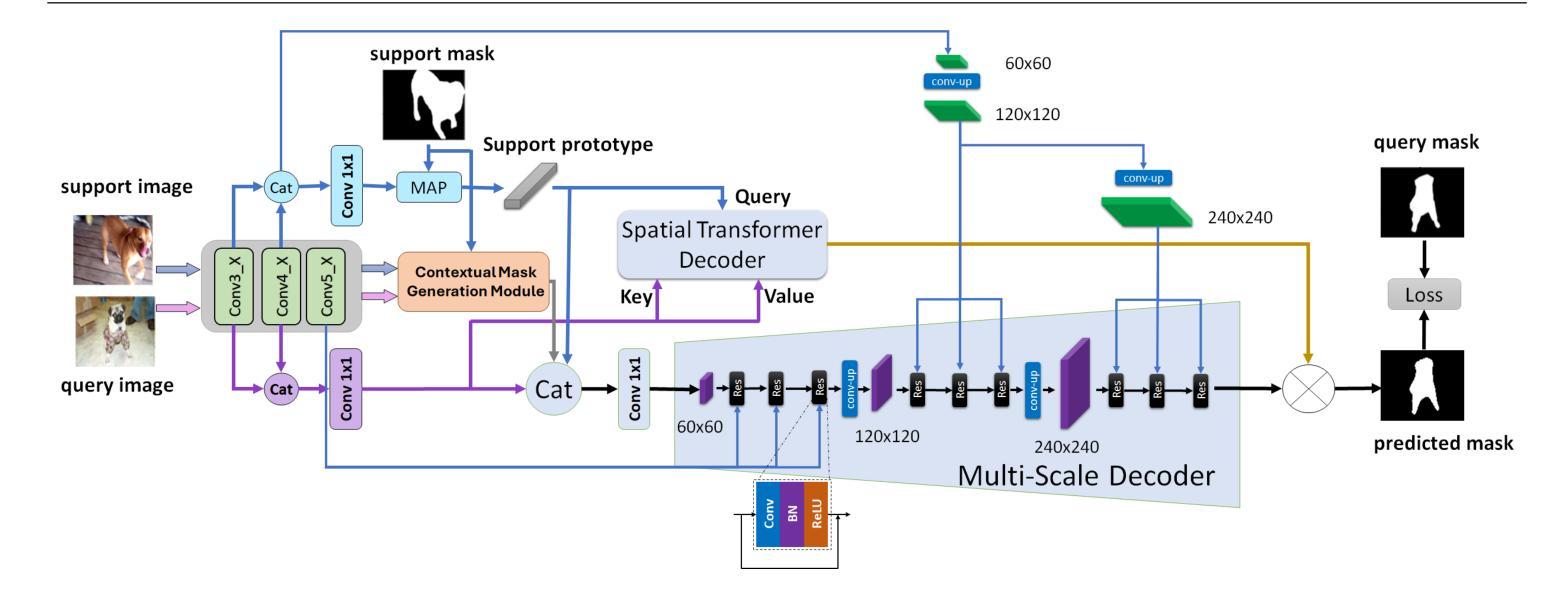
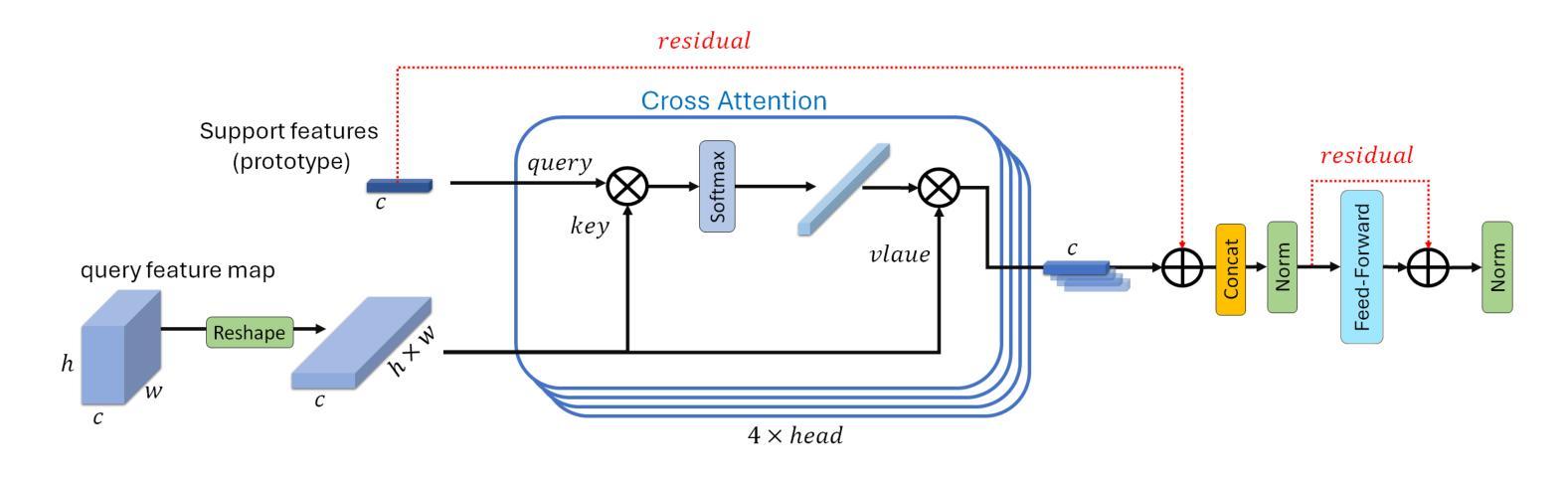
MSDNet: Multi-Scale Decoder for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation via Transformer-Guided Prototyping
Authors:Amirreza Fateh, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Mohammad Reza Jahed Motlagh
Few-shot Semantic Segmentation addresses the challenge of segmenting objects in query images with only a handful of annotated examples. However, many previous state-of-the-art methods either have to discard intricate local semantic features or suffer from high computational complexity. To address these challenges, we propose a new Few-shot Semantic Segmentation framework based on the Transformer architecture. Our approach introduces the spatial transformer decoder and the contextual mask generation module to improve the relational understanding between support and query images. Moreover, we introduce a multi scale decoder to refine the segmentation mask by incorporating features from different resolutions in a hierarchical manner. Additionally, our approach integrates global features from intermediate encoder stages to improve contextual understanding, while maintaining a lightweight structure to reduce complexity. This balance between performance and efficiency enables our method to achieve competitive results on benchmark datasets such as PASCAL-5^i and COCO-20^i in both 1-shot and 5-shot settings. Notably, our model with only 1.5 million parameters demonstrates competitive performance while overcoming limitations of existing methodologies. https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet
少量样本语义分割(Few-shot Semantic Segmentation)应对了仅使用少量标注样本对查询图像进行对象分割的挑战。然而,许多之前的最先进方法要么不得不放弃复杂的局部语义特征,要么面临高计算复杂度的问题。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于Transformer架构的新型少量样本语义分割框架。我们的方法引入了空间变换解码器和上下文掩模生成模块,以改善支持图像和查询图像之间的关系理解。此外,我们引入了多尺度解码器,以分层的方式融入不同分辨率的特征来优化分割掩模。同时,我们的方法整合了中间编码器阶段的全局特征以提高上下文理解,同时保持轻量级结构以降低复杂度。性能与效率之间的这种平衡使我们的方法在PASCAL-5^i和COCO-20^i等基准数据集上实现了具有竞争力的结果,无论是单张图片一次训练(1-shot)还是五次训练(5-shot)的情况下。值得注意的是,我们的模型仅有150万个参数,在克服现有方法局限性的同时表现出了竞争力。相关代码已上传至GitHub:https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer架构,提出了一种新的少样本语义分割框架,通过引入空间变换解码器和上下文掩膜生成模块,提高了支持图像和查询图像之间的关系理解。同时采用多尺度解码器,以层次方式融入不同分辨率的特征来优化分割掩膜。该方法还融合了中间编码阶段的全局特征,以提高上下文理解,同时保持轻量级结构以降低复杂性。在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i等基准数据集上,该方法在1-shot和5-shot设置中取得了有竞争力的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了新的基于Transformer的少样本语义分割框架。
- 通过空间变换解码器和上下文掩膜生成模块提高图像间关系理解。
- 采用多尺度解码器优化分割掩膜,融合不同分辨率的特征。
- 融合中间编码阶段的全局特征,提高上下文理解。
- 保持轻量级结构以降低复杂性。
- 在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i等基准数据集上取得有竞争力的结果。
点此查看论文截图

Test-time Contrastive Concepts for Open-world Semantic Segmentation with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Monika Wysoczańska, Antonin Vobecky, Amaia Cardiel, Tomasz Trzciński, Renaud Marlet, Andrei Bursuc, Oriane Siméoni
Recent CLIP-like Vision-Language Models (VLMs), pre-trained on large amounts of image-text pairs to align both modalities with a simple contrastive objective, have paved the way to open-vocabulary semantic segmentation. Given an arbitrary set of textual queries, image pixels are assigned the closest query in feature space. However, this works well when a user exhaustively lists all possible visual concepts in an image that contrast against each other for the assignment. This corresponds to the current evaluation setup in the literature, which relies on having access to a list of in-domain relevant concepts, typically classes of a benchmark dataset. Here, we consider the more challenging (and realistic) scenario of segmenting a single concept, given a textual prompt and nothing else. To achieve good results, besides contrasting with the generic ‘background’ text, we propose two different approaches to automatically generate, at test time, query-specific textual contrastive concepts. We do so by leveraging the distribution of text in the VLM’s training set or crafted LLM prompts. We also propose a metric designed to evaluate this scenario and show the relevance of our approach on commonly used datasets.
最近,CLIP类似的视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过大量图像文本对的预训练,以简单的对比目标对齐两种模态,为开放词汇语义分割铺平了道路。给定任意文本查询,图像像素被分配到特征空间中最近的查询。然而,当用户在分配时详尽地列出图像中所有可能的视觉概念以进行对比时,这种方法效果很好。这与文献中的当前评估设置相对应,该设置依赖于访问领域相关概念的列表,通常是基准数据集的类型。在这里,我们考虑了一个更具挑战性(和更现实)的场景,即给定文本提示对单个概念进行分割,没有其他内容。除了与通用的“背景”文本进行对比之外,我们提出了两种不同方法在测试时自动生成特定查询的对比概念。我们通过利用VLM训练集中的文本分布或精心设计的LLM提示来实现这一点。我们还提出了一个用于评估此场景的指标,并在常用数据集上展示了我们的方法的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TMLR camera-ready
Summary
CLIP类视觉语言模型通过大规模图像文本对进行预训练,实现了跨模态对齐的简单对比目标,为开放词汇语义分割铺平了道路。给定任意文本查询,图像像素被分配给特征空间中最近的查询。但在实际应用中,用户详尽地列出图像中所有可能的视觉概念以供分配时,模型表现良好。本文考虑更具挑战性和现实性的场景,即仅根据文本提示对单个概念进行分割。除了与通用“背景”文本进行对比外,我们提出了两种在测试时自动生成特定查询对比概念的方法。通过利用VLM训练集中的文本分布或定制的大型语言模型提示来实现。我们还为此场景设计了一种评估指标,并在常用数据集上展示了方法的相关性。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP-like Vision-Language Models (VLMs) 通过大规模图像文本对预训练,实现了跨模态对齐的简单对比目标,为开放词汇语义分割提供了基础。
- 当前文献中的评估设置依赖于获取特定领域的相关概念列表,但在现实场景中可能需要考虑更复杂的因素。
- 针对仅根据文本提示对单个概念进行分割的更具挑战性和现实性的场景,提出了两种自动生成特定查询对比概念的方法。
- 通过利用VLM训练集中的文本分布或定制的大型语言模型提示来实现自动生成的查询对比概念。
- 提出了一种新的评估指标,用于衡量在仅使用文本提示进行图像分割的场景下的模型性能。
- 在常用数据集上验证了方法的相关性,显示出其在处理更具挑战性和现实性的图像分割任务中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图