⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
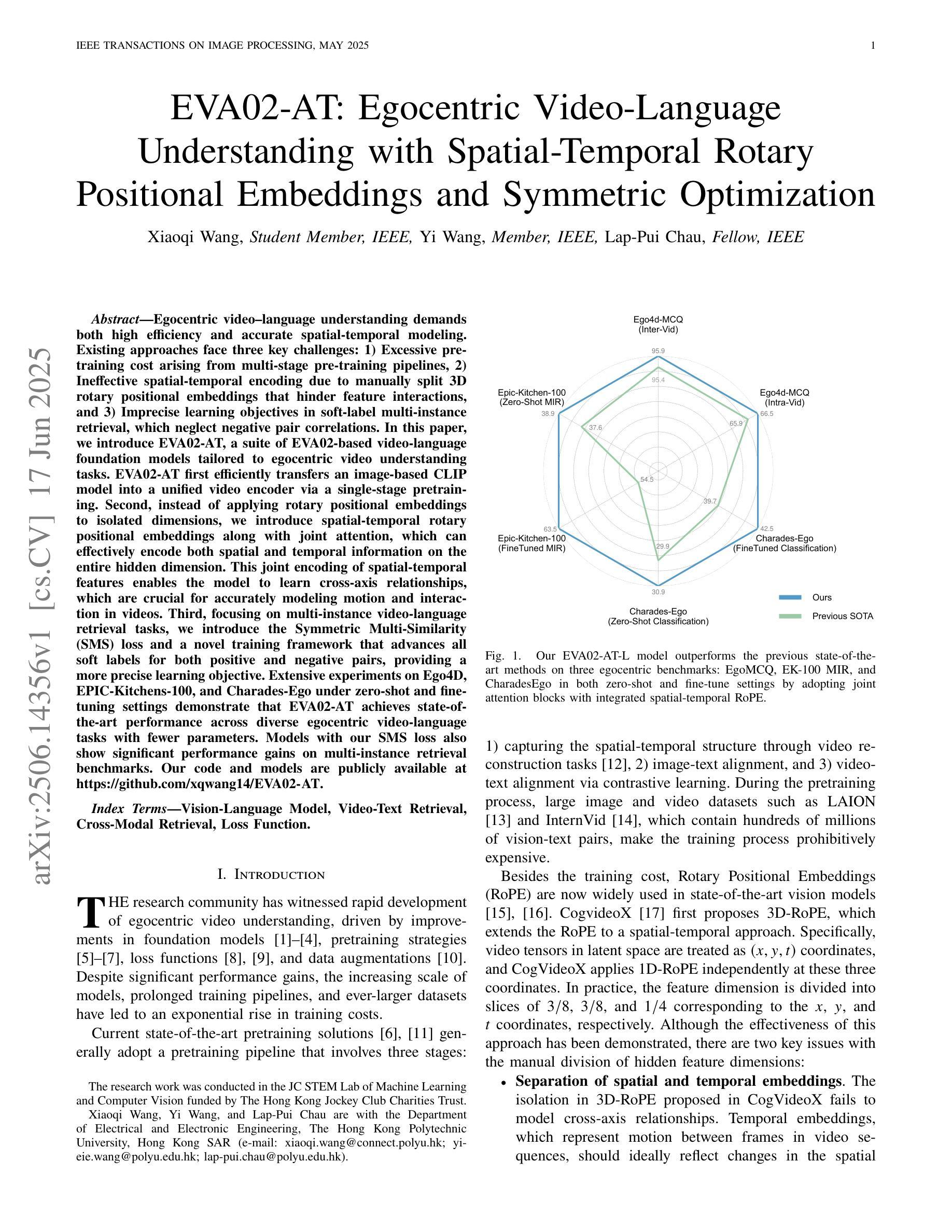
EVA02-AT: Egocentric Video-Language Understanding with Spatial-Temporal Rotary Positional Embeddings and Symmetric Optimization
Authors:Xiaoqi Wang, Yi Wang, Lap-Pui Chau
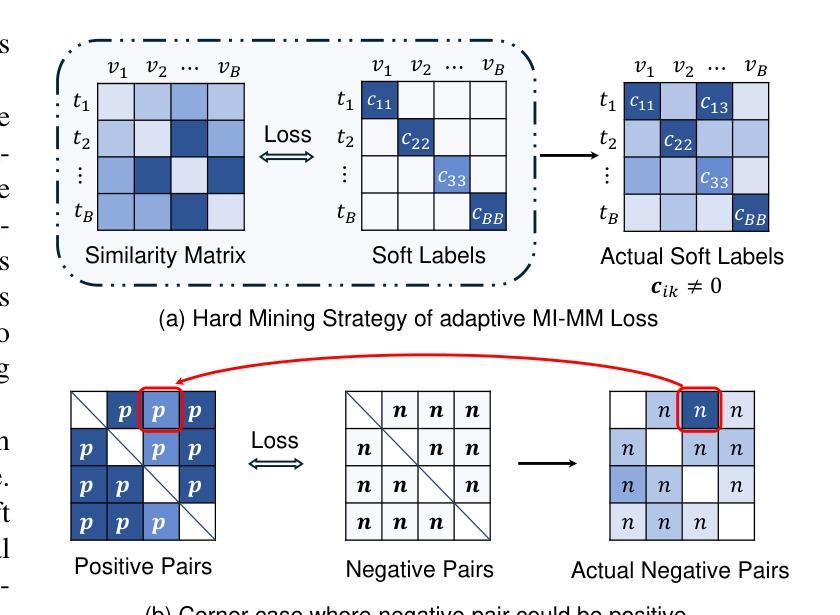
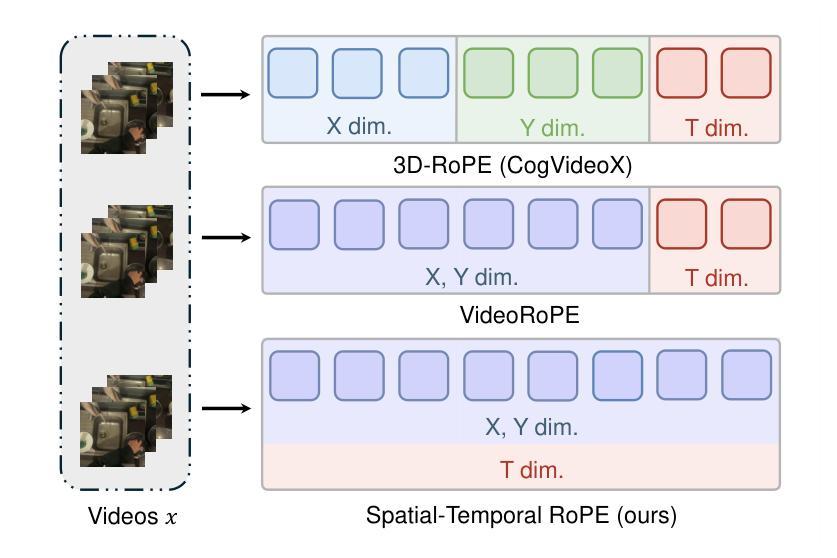
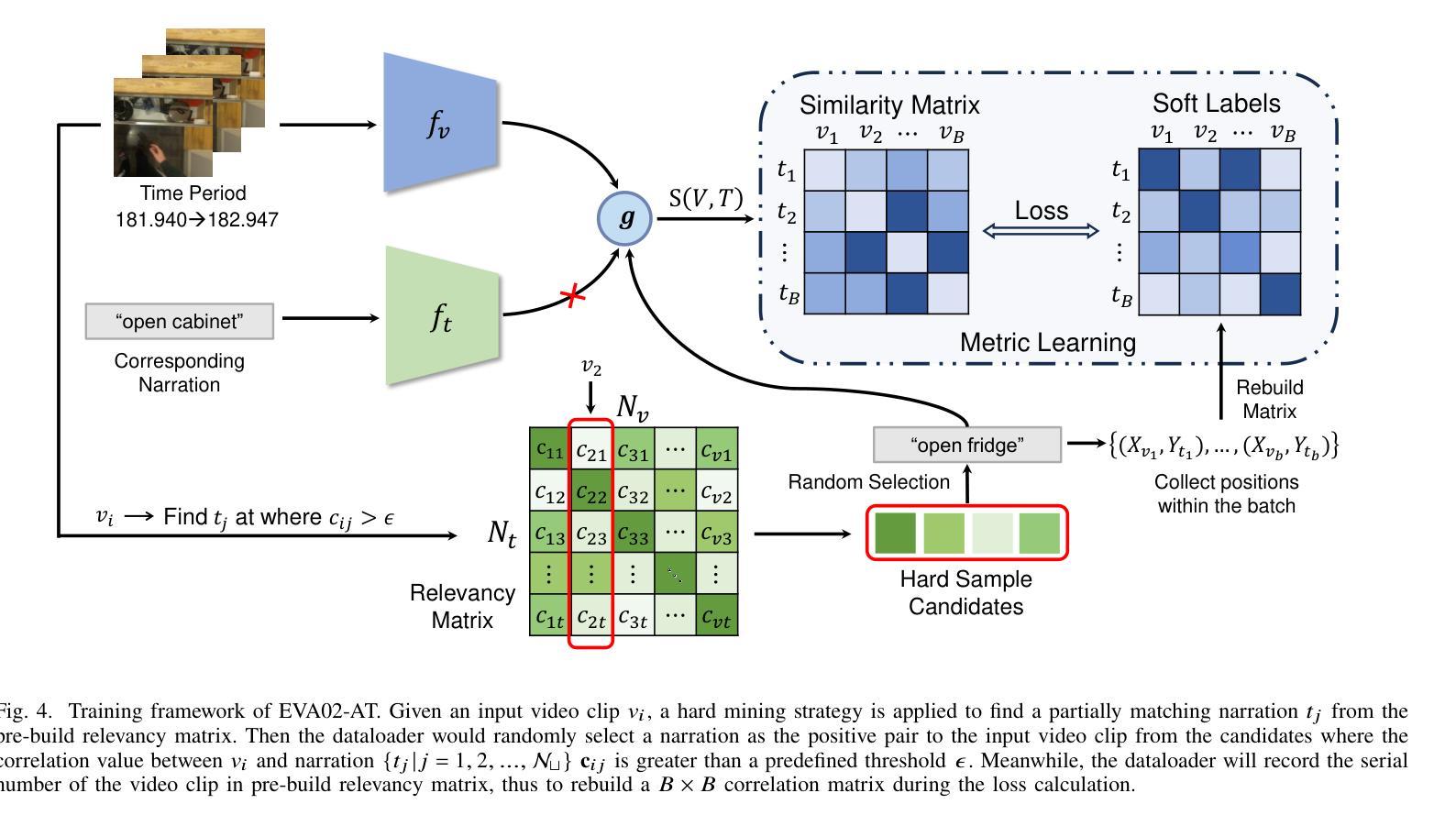
Egocentric video-language understanding demands both high efficiency and accurate spatial-temporal modeling. Existing approaches face three key challenges: 1) Excessive pre-training cost arising from multi-stage pre-training pipelines, 2) Ineffective spatial-temporal encoding due to manually split 3D rotary positional embeddings that hinder feature interactions, and 3) Imprecise learning objectives in soft-label multi-instance retrieval, which neglect negative pair correlations. In this paper, we introduce EVA02-AT, a suite of EVA02-based video-language foundation models tailored to egocentric video understanding tasks. EVA02-AT first efficiently transfers an image-based CLIP model into a unified video encoder via a single-stage pretraining. Second, instead of applying rotary positional embeddings to isolated dimensions, we introduce spatial-temporal rotary positional embeddings along with joint attention, which can effectively encode both spatial and temporal information on the entire hidden dimension. This joint encoding of spatial-temporal features enables the model to learn cross-axis relationships, which are crucial for accurately modeling motion and interaction in videos. Third, focusing on multi-instance video-language retrieval tasks, we introduce the Symmetric Multi-Similarity (SMS) loss and a novel training framework that advances all soft labels for both positive and negative pairs, providing a more precise learning objective. Extensive experiments on Ego4D, EPIC-Kitchens-100, and Charades-Ego under zero-shot and fine-tuning settings demonstrate that EVA02-AT achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse egocentric video-language tasks with fewer parameters. Models with our SMS loss also show significant performance gains on multi-instance retrieval benchmarks. Our code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/xqwang14/EVA02-AT .
自我中心视频语言理解需要高效率且精确的时空建模。现有方法面临三个主要挑战:1)由于多阶段预训练管道而产生的过高的预训练成本;2)由于手动分割的3D旋转位置嵌入而导致的时空编码无效,这阻碍了特征交互;3)软标签多实例检索中的学习目标不精确,忽略了负对之间的相关性。在本文中,我们介绍了针对自我中心视频理解任务的EVA02基础视频语言基础模型套件EVA02-AT。EVA02-AT首先通过单阶段预训练有效地将基于图像的CLIP模型转移到统一视频编码器。其次,我们没有将旋转位置嵌入应用于孤立的维度,而是引入了时空旋转位置嵌入以及联合注意力,可以有效地对整个隐藏维度进行时空信息编码。这种时空特征的联合编码使模型能够学习跨轴关系,这对于准确建模视频中的运动和交互至关重要。第三,针对多实例视频语言检索任务,我们引入了对称多相似性(SMS)损失和一个新的训练框架,该框架为正向和负向对推进所有软标签,提供更精确的学习目标。在Ego4D、EPIC-Kitchens-100和Charades-Ego的零样本和微调设置下的广泛实验表明,EVA02-AT在多种自我中心视频语言任务中实现了最先进的性能且参数更少。使用我们SMS损失的模型在多实例检索基准测试上也显示出显著的性能提升。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/xqwang14/EVA02-AT公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了针对以自我为中心的视频理解任务的EVA02-AT视频语言基础模型。该模型解决了现有方法的三个主要挑战:过高的预训练成本、因手动分割的3D旋转位置嵌入而导致的空间时间编码无效以及在软标签多实例检索中忽略负对关联的不精确学习目标。EVA02-AT通过单阶段预训练,将图像基础的CLIP模型高效转化为统一视频编码器。同时引入时空旋转位置嵌入和联合注意力机制,有效编码整个隐藏维度的时空信息,并学习视频中的跨轴关系。此外,针对多实例视频语言检索任务,引入对称多相似性(SMS)损失和新的训练框架,为正负样本提供更精确的学习目标。在Ego4D、EPIC-Kitchens-100和Charades-Ego数据集上的零样本和微调设置实验表明,EVA02-AT在多种以自我为中心的视频语言任务上实现了最先进的性能,并且参数更少。使用我们SMS损失的模型在多实例检索基准测试上也显示出显著的性能提升。
要点
- EVA02-AT模型解决了以自我为中心的视频理解任务中的三个主要挑战。
- 通过单阶段预训练,将图像模型转化为视频编码器,提高效率。
- 引入时空旋转位置嵌入和联合注意力机制,有效编码时空信息并学习跨轴关系。
- 针对多实例视频语言检索任务,引入对称多相似性(SMS)损失和新的训练框架。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,EVA02-AT实现了先进的性能,特别是在多实例检索任务上。
- 模型和代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图
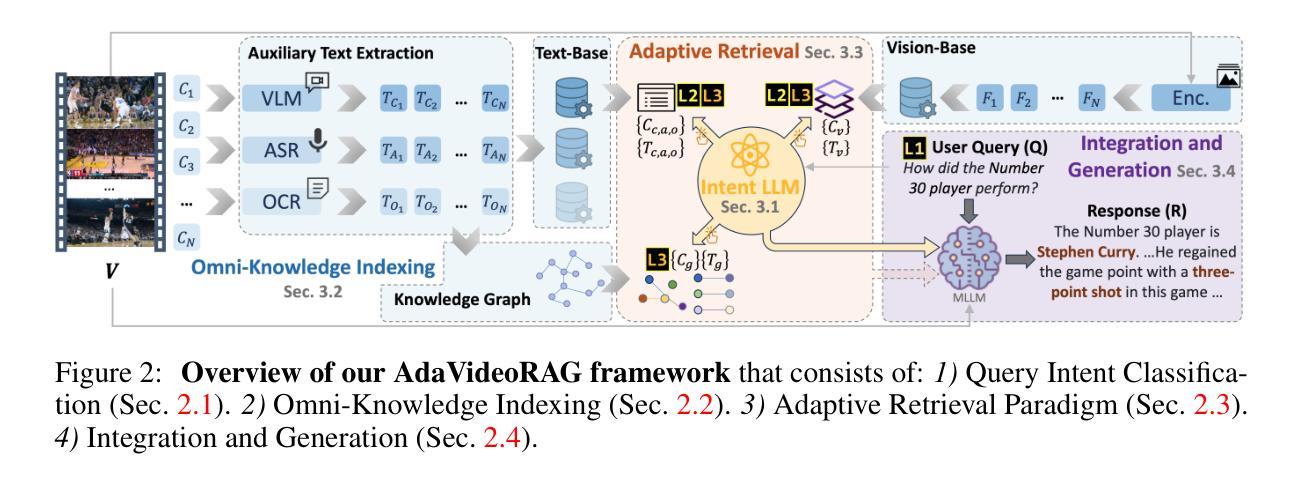
AdaVideoRAG: Omni-Contextual Adaptive Retrieval-Augmented Efficient Long Video Understanding
Authors:Zhucun Xue, Jiangning Zhang, Xurong Xie, Yuxuan Cai, Yong Liu, Xiangtai Li, Dacheng Tao
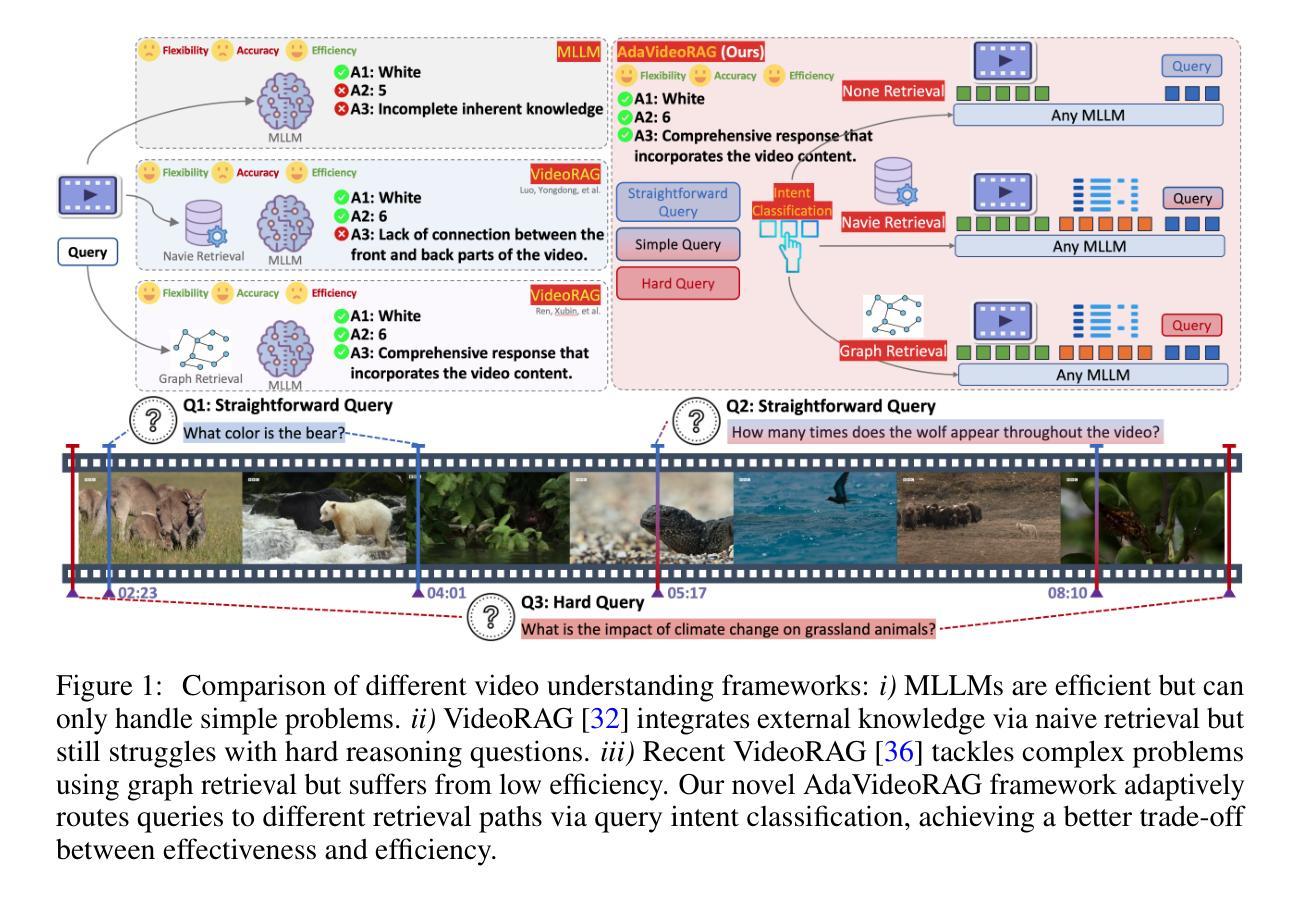
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) struggle with long videos due to fixed context windows and weak long-term dependency modeling. Existing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) methods for videos use static retrieval strategies, leading to inefficiencies for simple queries and information loss for complex tasks. To address this, we propose AdaVideoRAG, a novel framework that dynamically adapts retrieval granularity based on query complexity using a lightweight intent classifier. Our framework employs an Omni-Knowledge Indexing module to build hierarchical databases from text (captions, ASR, OCR), visual features, and semantic graphs, enabling optimal resource allocation across tasks. We also introduce the HiVU benchmark for comprehensive evaluation. Experiments demonstrate improved efficiency and accuracy for long-video understanding, with seamless integration into existing MLLMs. AdaVideoRAG establishes a new paradigm for adaptive retrieval in video analysis. Codes will be open-sourced at https://github.com/xzc-zju/AdaVideoRAG.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)由于固定的上下文窗口和薄弱的长期依赖建模,在处理长视频时面临困难。现有的视频检索增强生成(RAG)方法使用静态检索策略,导致简单查询效率低下和复杂任务信息丢失。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了AdaVideoRAG,这是一个新的框架,它使用一个轻量级的意图分类器来根据查询的复杂性动态调整检索的粒度。我们的框架采用Omni-Knowledge索引模块,从文本(字幕、ASR、OCR)、视觉特征和语义图构建分层数据库,实现任务间的最佳资源配置。我们还引入了HiVU基准测试,以便进行全面评估。实验表明,该框架在提高长视频理解效率和准确性方面具有优势,并能无缝集成到现有MLLMs中。AdaVideoRAG为视频分析中自适应检索建立了新的范式。代码将在https://github.com/xzc-zju/AdaVideoRAG上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对多模态大型语言模型在处理长视频时面临的固定上下文窗口和长期依赖建模困难的问题,提出了一种新型框架AdaVideoRAG。该框架能根据查询的复杂性动态调整检索粒度,并使用轻量级意图分类器。通过Omni-Knowledge Indexing模块建立文本(字幕、ASR、OCR)、视觉特征和语义图的分层数据库,实现任务间的最佳资源配置。引入HiVU基准测试进行综合评价,实验表明该框架在提高长视频理解效率和准确性方面具有优势,并能无缝集成到现有多模态大型语言模型中,为视频分析中的自适应检索树立了新范式。
Key Takeaways
- AdaVideoRAG解决了多模态大型语言模型处理长视频时面临的固定上下文窗口和长期依赖建模难题。
- AdaVideoRAG能动态适应查询复杂性并调整检索粒度,使用轻量级意图分类器实现这一功能。
- Omni-Knowledge Indexing模块用于建立包含文本、视觉特征和语义图的分层数据库,实现任务间的最佳资源配置。
- AdaVideoRAG引入HiVU基准测试进行综合评价,展示其在长视频理解方面的优势和效率。
- 该框架能无缝集成到现有多模态大型语言模型中。
- AdaVideoRAG为视频分析中的自适应检索树立了新范式。
点此查看论文截图
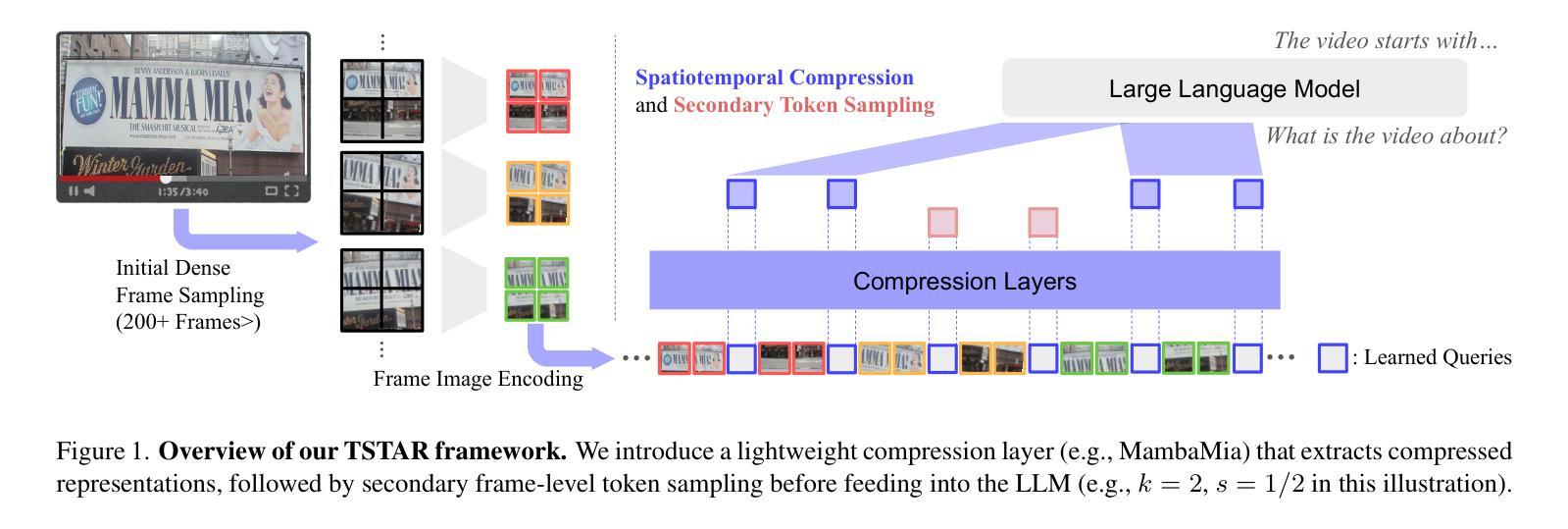
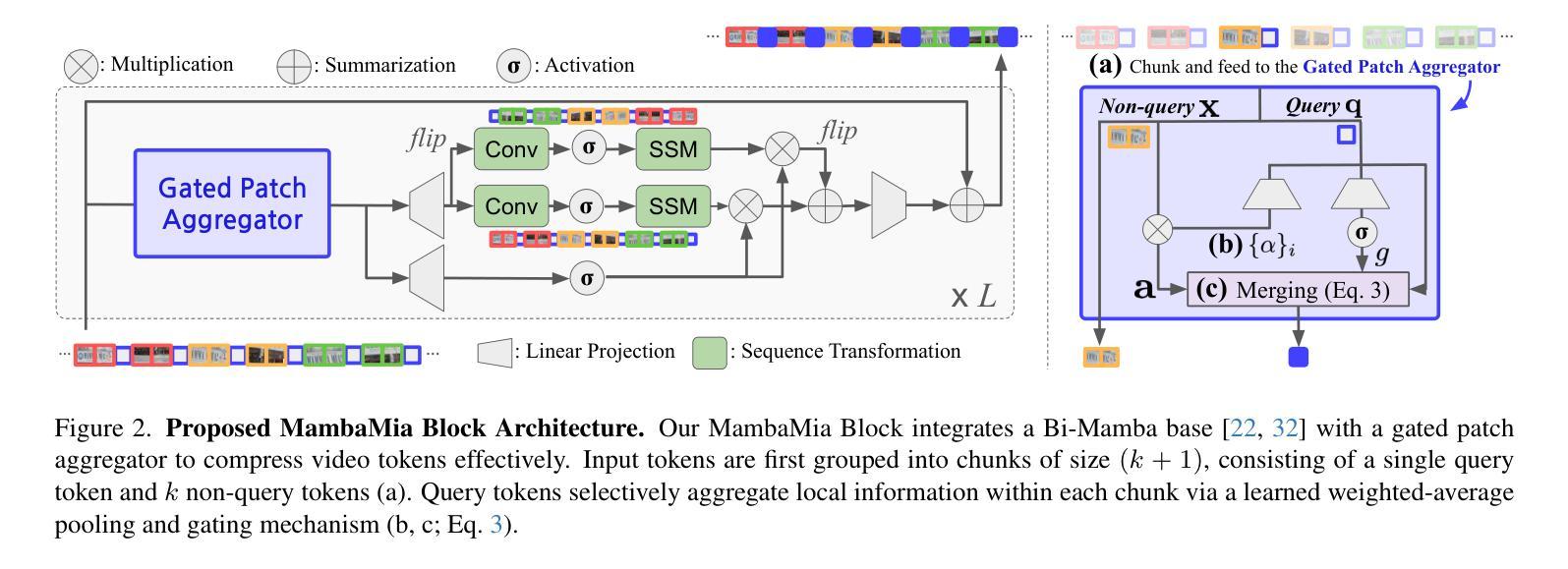
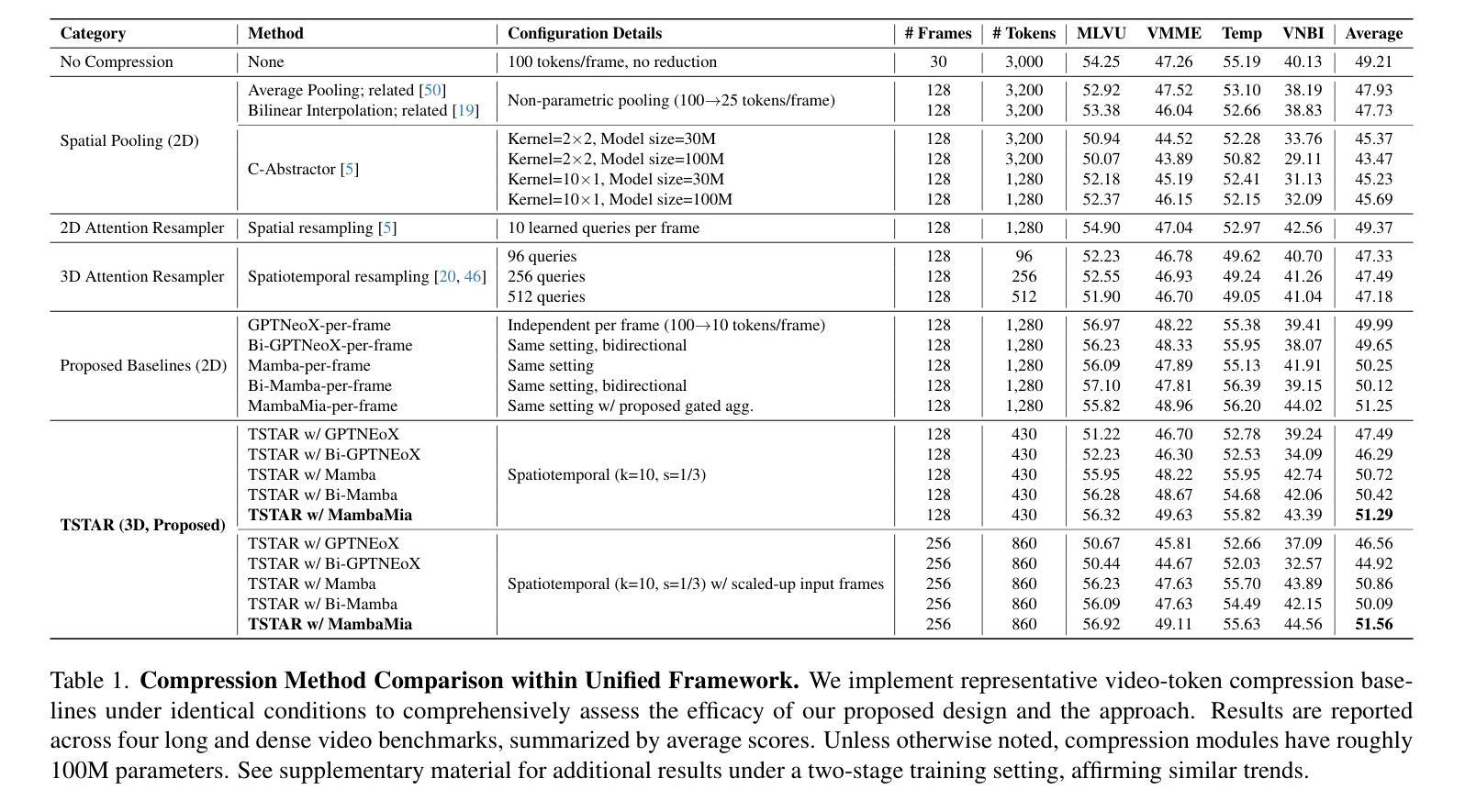
MambaMia: A State-Space-Model-Based Compression for Efficient Video Understanding in Large Multimodal Models
Authors:Geewook Kim, Minjoon Seo
We propose an efficient framework to compress multiple video-frame features before feeding them into large multimodal models, thereby mitigating the severe token explosion arising from long or dense videos. Our design leverages a bidirectional state-space-based block equipped with a gated skip connection and a learnable weighted-average pooling mechanism applied to periodically inserted learned queries. This structure enables hierarchical downsampling across both spatial and temporal dimensions, preserving performance in a cost-effective manner. Across challenging long and dense video understanding tasks, our approach demonstrates competitive results against state-of-the-art models, while significantly reducing overall token budget. Notably, replacing our proposed state-space block with a conventional Transformer results in substantial performance degradation, highlighting the advantages of state-space modeling for effectively compressing multi-frame video data. Our framework emphasizes resource-conscious efficiency, making it practical for real-world deployments. We validate its scalability and generality across multiple benchmarks, achieving the dual objectives of efficient resource usage and comprehensive video understanding.
我们提出了一个高效的框架,用于在将多帧视频特征输入大型多模态模型之前对其进行压缩,从而缓解由长视频或密集视频引起的严重令牌爆炸问题。我们的设计利用了一个基于双向状态空间的块,该块配备了门控跳过连接和可学习的加权平均池化机制,这些机制应用于定期插入的学习查询。这种结构能够在空间和时间维度上实现分层下采样,以经济的方式保持性能。在面对具有挑战性的长视频和密集视频理解任务时,我们的方法与最先进的模型相比表现出竞争力,同时显著减少了总体令牌预算。值得注意的是,用传统的Transformer替换我们提出的状态空间块会导致性能大幅下降,这突出了状态空间建模在有效压缩多帧视频数据方面的优势。我们的框架注重资源意识效率,使其适用于实际部署。我们在多个基准测试上验证了其可扩展性和普遍性,实现了有效利用资源和全面理解视频的双重目标。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 5 figures
Summary
提供的文本描述了一个高效的框架,用于压缩多帧视频特征,然后将其输入大型多模态模型,从而解决长或密集视频引起的严重令牌爆炸问题。该设计利用双向状态空间块,配备门控跳跃连接和可学习的加权平均池化机制,应用于定期插入的学习查询。此结构可在空间和时间上实现分层下采样,以节约成本的方式保持性能。在具有挑战性的长和密集视频理解任务方面,该方法在具有竞争力的同时,大大降低了总体令牌预算。使用常规转换器替换建议的状态空间块会导致性能大幅下降,这凸显了状态空间建模在有效压缩多帧视频数据方面的优势。该框架注重资源节约效率,适合实际应用部署。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一个高效框架压缩多帧视频特征,解决长或密集视频的令牌爆炸问题。
- 利用双向状态空间块,配备门控跳跃连接和加权平均池化机制。
- 实现空间和时间的分层下采样,以节约成本的方式保持性能。
- 在长而密集的视频理解任务中表现竞争力,显著减少令牌预算。
- 替换状态空间块会导致性能显著下降,凸显其优势。
- 框架注重资源节约效率,适合实际应用部署。
- 验证了其在多个基准测试上的可扩展性和普遍性。
点此查看论文截图

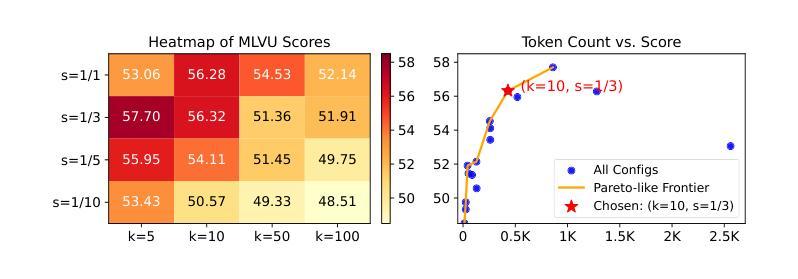
VideoDeepResearch: Long Video Understanding With Agentic Tool Using
Authors:Huaying Yuan, Zheng Liu, Junjie Zhou, Hongjin Qian, Ji-Rong Wen, Zhicheng Dou
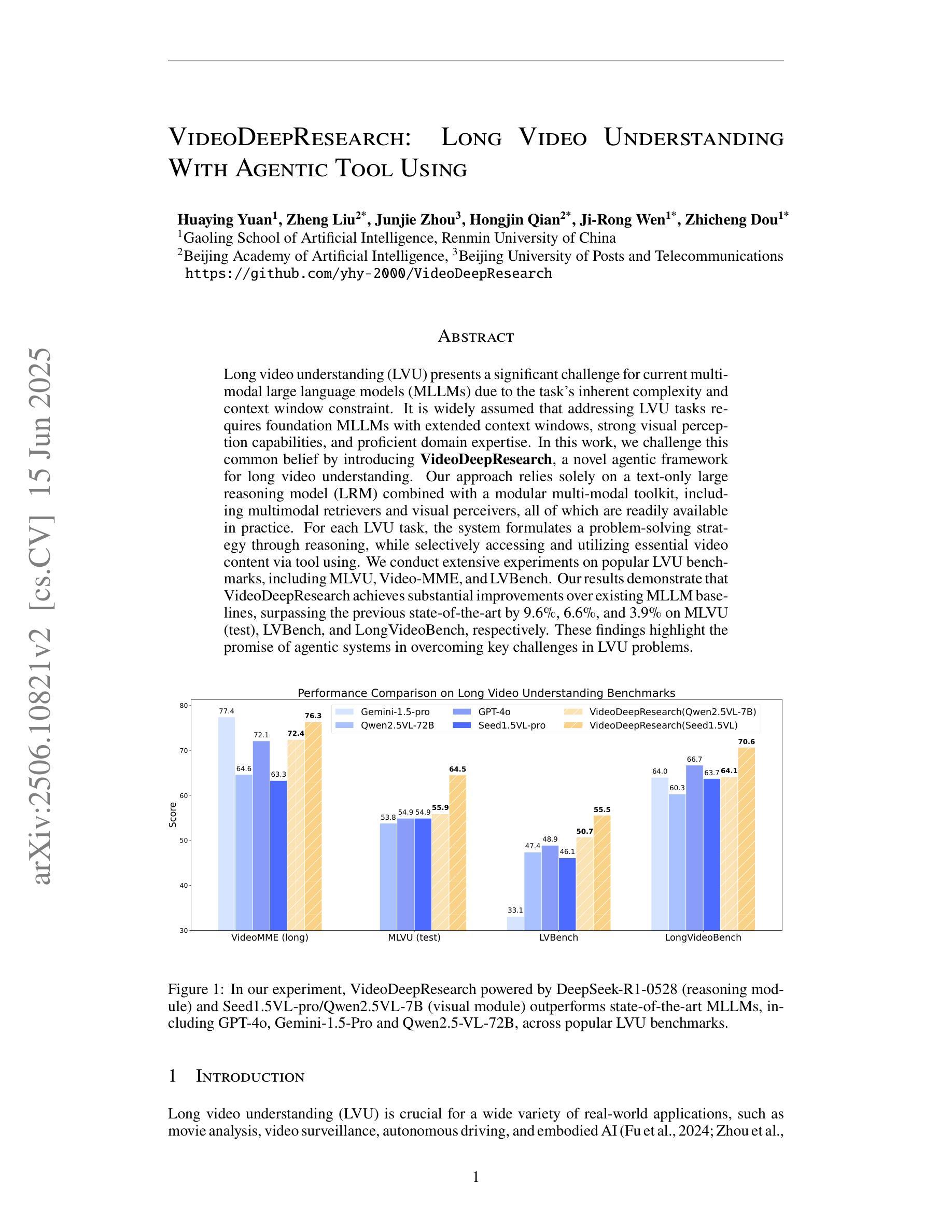
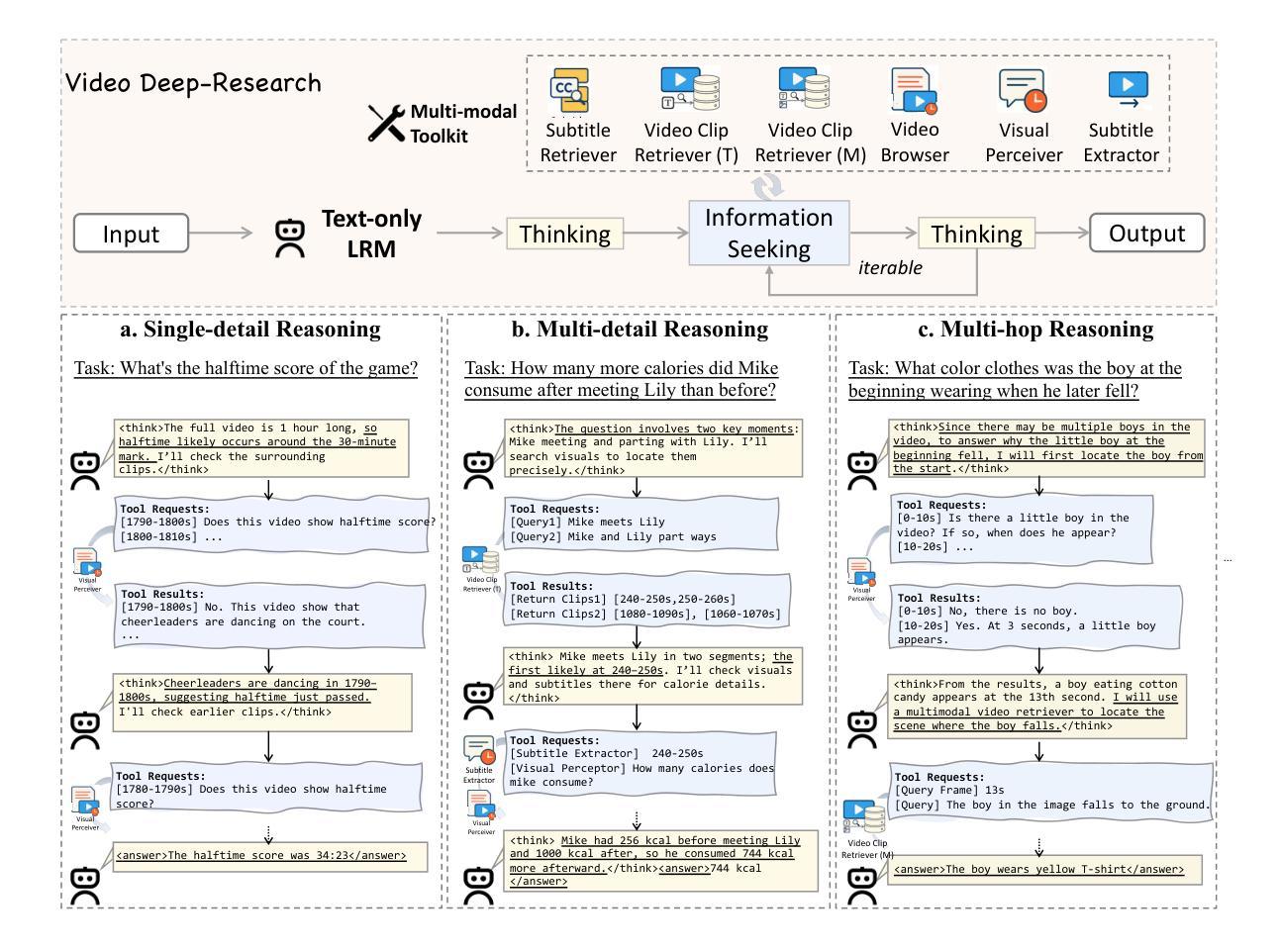
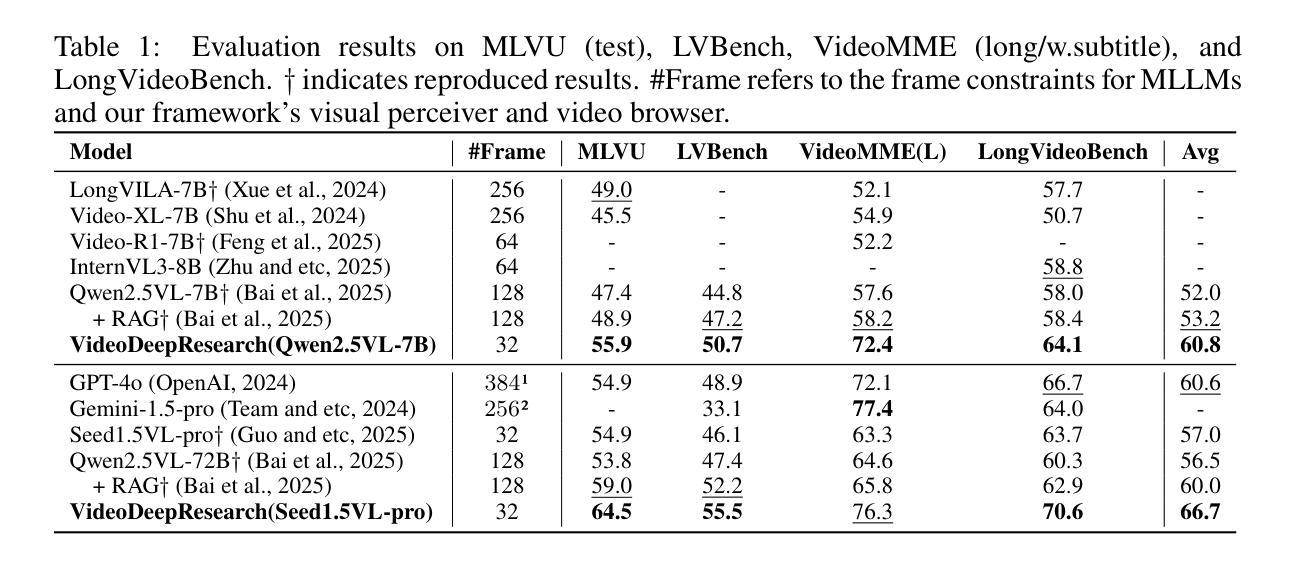
Long video understanding (LVU) presents a significant challenge for current multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) due to the task’s inherent complexity and context window constraint. It is widely assumed that addressing LVU tasks requires foundation MLLMs with extended context windows, strong visual perception capabilities, and proficient domain expertise. In this work, we challenge this common belief by introducing VideoDeepResearch, a novel agentic framework for long video understanding. Our approach relies solely on a text-only large reasoning model (LRM) combined with a modular multi-modal toolkit, including multimodal retrievers and visual perceivers, all of which are readily available in practice. For each LVU task, the system formulates a problem-solving strategy through reasoning, while selectively accessing and utilizing essential video content via tool using. We conduct extensive experiments on popular LVU benchmarks, including MLVU, Video-MME, and LVBench. Our results demonstrate that VideoDeepResearch achieves substantial improvements over existing MLLM baselines, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art by 9.6%, 6.6%, and 3.9% on MLVU (test), LVBench, and LongVideoBench, respectively. These findings highlight the promise of agentic systems in overcoming key challenges in LVU problems.
长视频理解(LVU)对当前的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)提出了重大挑战,这主要是由于该任务的固有复杂性和上下文窗口约束。普遍认为,解决LVU任务需要具有扩展上下文窗口、强大视觉感知能力和专业领域知识的基础MLLMs。在这项工作中,我们通过引入VideoDeepResearch,一个用于长视频理解的新型代理框架,来挑战这一普遍信念。我们的方法仅依赖于文本大型推理模型(LRM)和模块化多模态工具包,包括多模态检索器和视觉感知器,所有这些在实践中都很容易获得。对于每个LVU任务,该系统通过推理制定问题解决策略,同时有选择地访问和利用工具中的关键视频内容。我们在流行的LVU基准测试上进行了大量实验,包括MLVU、Video-MME和LVBench。结果表明,VideoDeepResearch在现有的MLLM基准测试上实现了显著改进,在MLVU(测试)、LVBench和LongVideoBench上的性能分别提高了9.6%、6.6%和3.9%。这些发现突显了代理系统在克服LVU问题中的关键挑战方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频深度研究框架,利用文本推理模型和多模态工具进行长视频理解,在多个数据集上超越现有基线方法。该框架仅依赖于文本大型推理模型与模块化多模态工具组合,为解决长视频理解问题提供了新的视角。在主流长视频理解基准测试中实现了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 视频深度研究(VideoDeepResearch)是一个新型的智能框架,专门用于长视频理解(LVU)。
- 该框架不依赖具有扩展上下文窗口的基础多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),而是结合文本推理模型和多模态工具进行视频理解。
- VideoDeepResearch通过选择性访问和利用视频内容,为每一个LVU任务制定问题解决策略。
- 在多个流行的LVU基准测试中进行了广泛实验,包括MLVU、Video-MME和LVBench。
- VideoDeepResearch实现了对现有MLLM基线的显著改进,在某些测试中的表现超过了先前最先进的水平。
点此查看论文截图
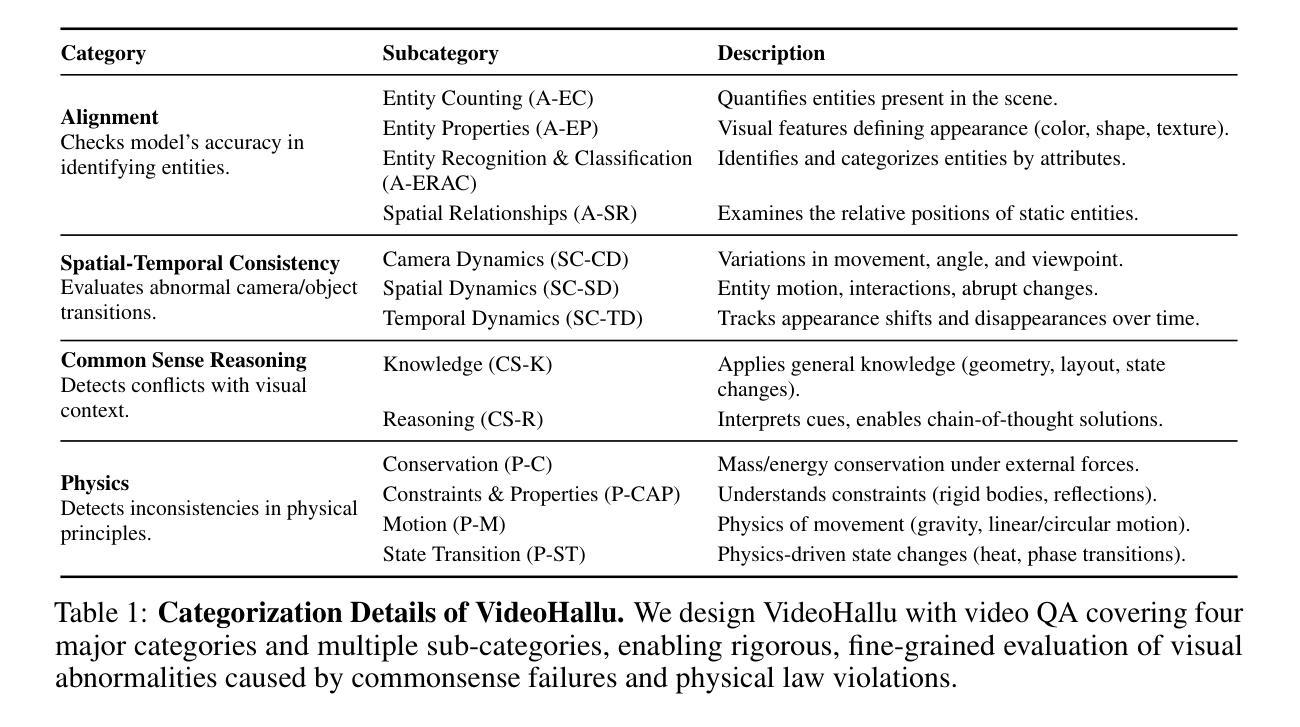
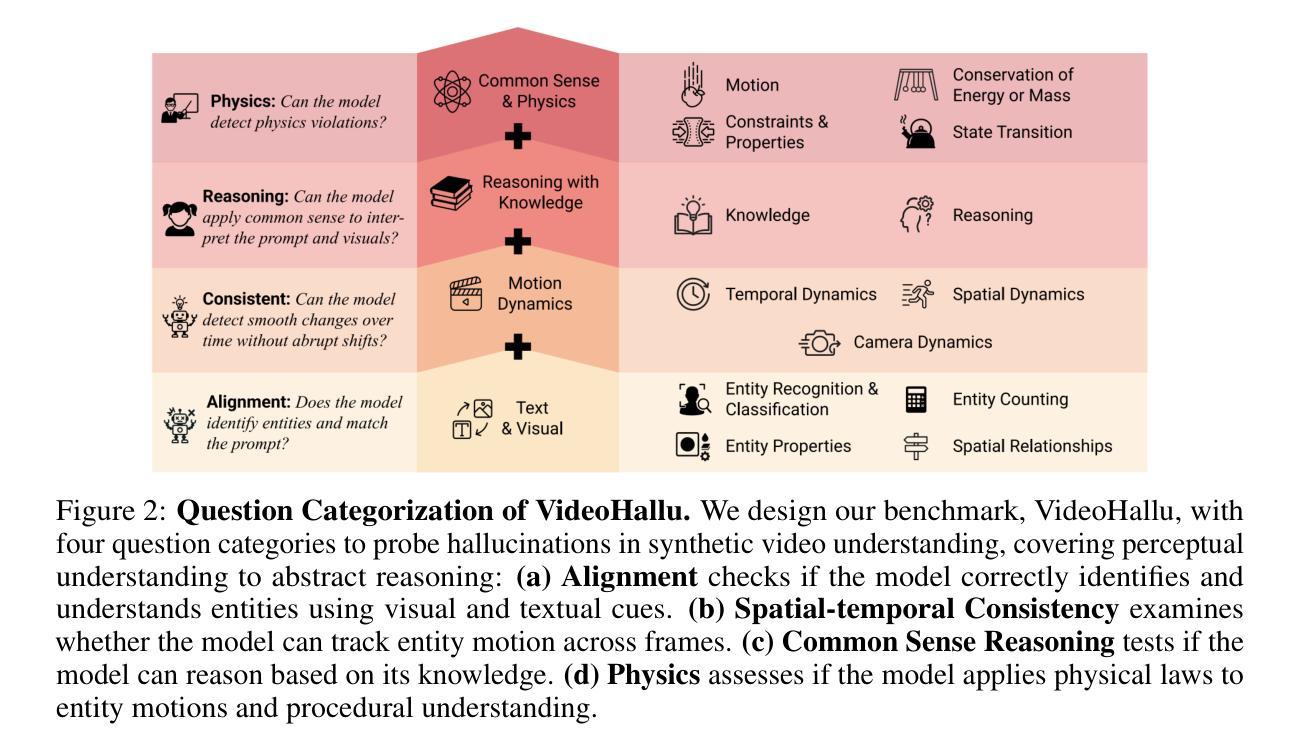
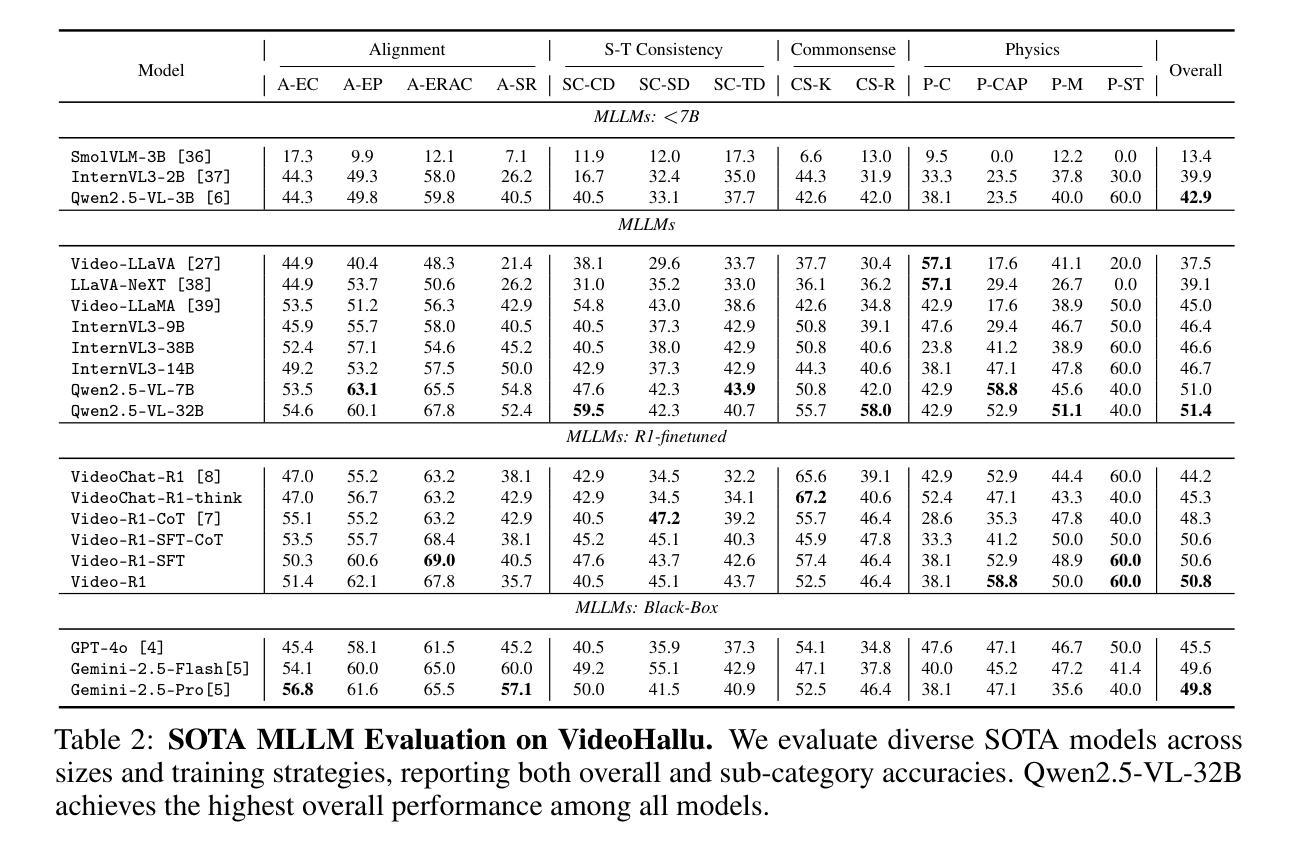
VideoHallu: Evaluating and Mitigating Multi-modal Hallucinations on Synthetic Video Understanding
Authors:Zongxia Li, Xiyang Wu, Guangyao Shi, Yubin Qin, Hongyang Du, Tianyi Zhou, Dinesh Manocha, Jordan Lee Boyd-Graber
Synthetic video generation has gained significant attention for its realism and broad applications, but remains prone to violations of common sense and physical laws. This highlights the need for reliable abnormality detectors that understand such principles and are robust to hallucinations. To address this, we introduce VideoHallu, a benchmark of over 3,000 video QA pairs built from synthetic videos generated by models like Veo2, Sora, and Kling, paired with expert-crafted counterintuitive QA to evaluate the critical thinking abilities of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on abnormalities that are perceptually obvious to humans but often hallucinated due to language priors. VideoHallu evaluates MLLMs’ abnormality detection abilities with examples across alignment, consistency, commonsense, and physics. We benchmark SOTA MLLMs, including GPT-4o, Gemini-2.5-Pro, Qwen2.5-VL, Video-R1, and VideoChat-R1. We observe that these models perform well on many real-world benchmarks like MVBench and MovieChat, but still struggle with basic physics-based and commonsense reasoning in synthetic videos. We further show that post-training with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), using curriculum learning on datasets combining video QA with counterintuitive commonsense and physics reasoning over real and synthetic videos, improves MLLMs’ abnormality detection and critical thinking, demonstrating the value of targeted training for improving their understanding of commonsense and physical laws. Our code is available at https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu.git.
合成视频生成因其真实感和广泛应用而受到广泛关注,但仍容易违反常识和物理定律。这强调了对可靠异常检测器的需求,这些检测器需要理解这些原理,并对幻觉具有鲁棒性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了VideoHallu,这是一个由超过3000个视频问答对组成的基准测试,这些问答对来自由Veo2、Sora和Kling等模型生成的合成视频,以及与专家精心制作的反直觉问答相结合,以评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在异常检测方面的批判性思维能力,这些异常对人类来说在感知上是明显的,但由于语言先验知识往往会产生幻觉。VideoHallu在跨对齐、一致性、常识和物理方面评估MLLMs的异常检测能力。我们对SOTA MLLMs进行基准测试,包括GPT-4o、Gemini-2.5-Pro、Qwen2.5-VL、Video-R1和VideoChat-R1。我们发现这些模型在MVBench和MovieChat等现实世界基准测试中表现良好,但在合成视频中的基于物理和常识推理方面仍面临困难。我们还进一步显示,使用组合视频问答与反直觉常识和物理推理的数据集进行课程学习的集团相对策略优化(GRPO)后训练,可以改善MLLMs的异常检测和批判性思维,证明了有针对性的训练对于提高它们对常识和物理定律的理解的价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了合成视频生成技术在引起关注的同时,仍存在违反常识和物理定律的问题。因此,需要开发可靠的异常检测器来理解这些原理并抵抗幻觉。为此,我们引入了VideoHallu基准测试,包含超过3000个视频QA对,由模型生成的合成视频与专家设计的反直觉QA组成,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在感知明显但对人类而言却经常因语言先验而产生幻觉的异常方面的批判性思维能力。VideoHallu基准测试涵盖了对MLLMs在定位、一致性、常识和物理方面的异常检测能力评估。我们对包括GPT-4o、Gemini-2.5-Pro、Qwen2.5-VL等在内的顶尖MLLMs进行了基准测试,发现它们在许多现实世界基准测试(如MVBench和MovieChat)上表现良好,但在合成视频的基于物理和常识的推理方面仍存在问题。此外,我们展示了使用组合视频QA与反直觉常识和物理推理的数据集进行课程学习的集团相对政策优化(GRPO)后训练,能提高MLLMs的异常检测和批判性思维能力,证明了有针对性的训练对于提高他们对常识和物理定律的理解的价值。
关键见解
- 合成视频生成技术虽然逼真且应用广泛,但常常违反常识和物理定律。
- VideoHallu基准测试旨在评估多模态大型语言模型在识别合成视频中的异常现象的能力。
- 当前顶尖的语言模型在现实世界基准测试上表现良好,但在涉及物理和常识推理的合成视频上仍面临挑战。
- 通过有针对性的训练,如使用集团相对政策优化(GRPO)和后训练,可以提高语言模型在异常检测和批判性思维方面的能力。
- 有效的训练数据集结合了视频QA与反直觉常识和物理推理,有助于提高模型的理解能力。
- VideoHallu的代码已公开发布,便于研究和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图



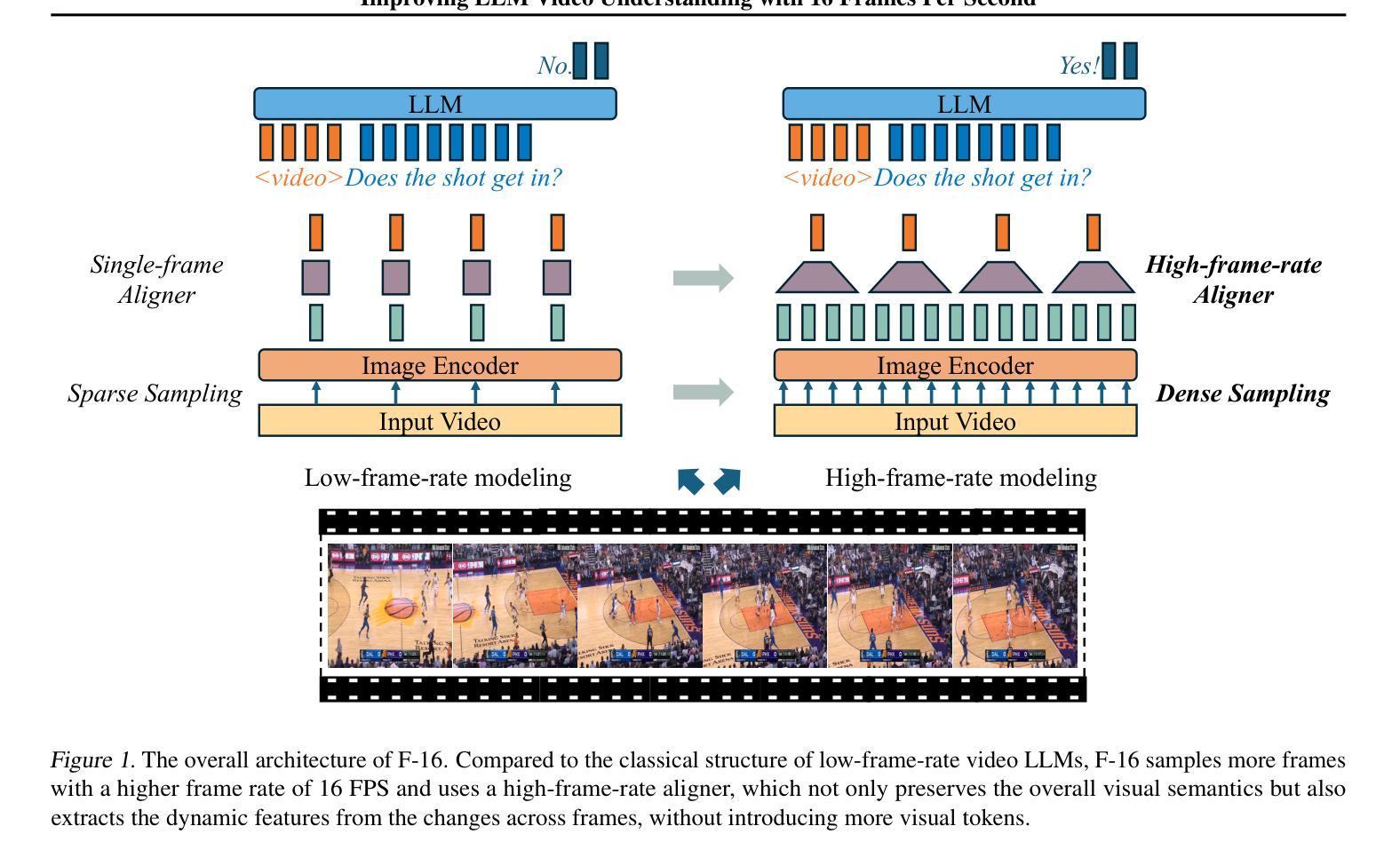
Improving LLM Video Understanding with 16 Frames Per Second
Authors:Yixuan Li, Changli Tang, Jimin Zhuang, Yudong Yang, Guangzhi Sun, Wei Li, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
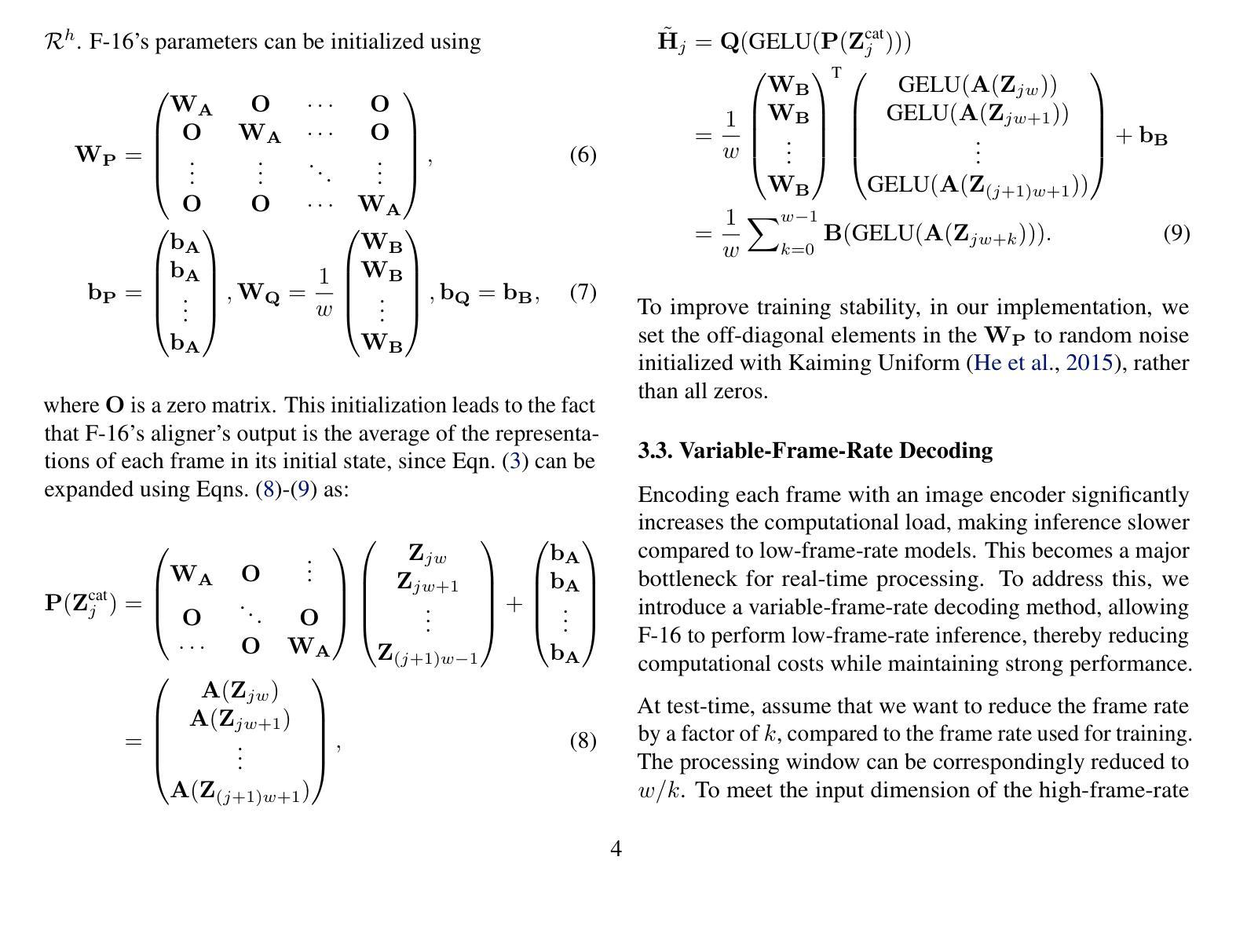
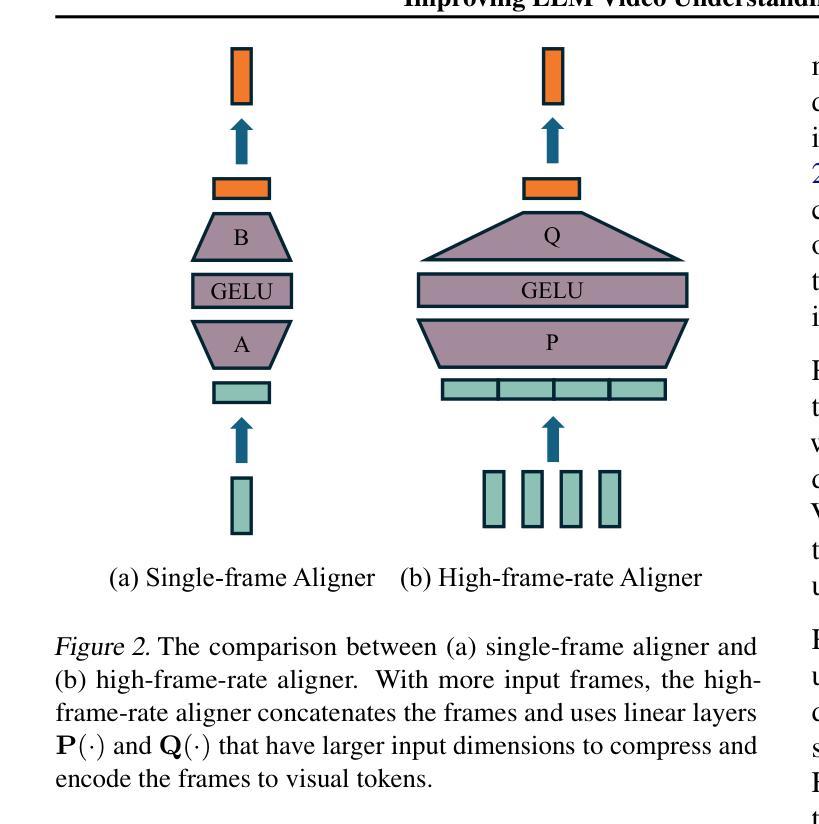
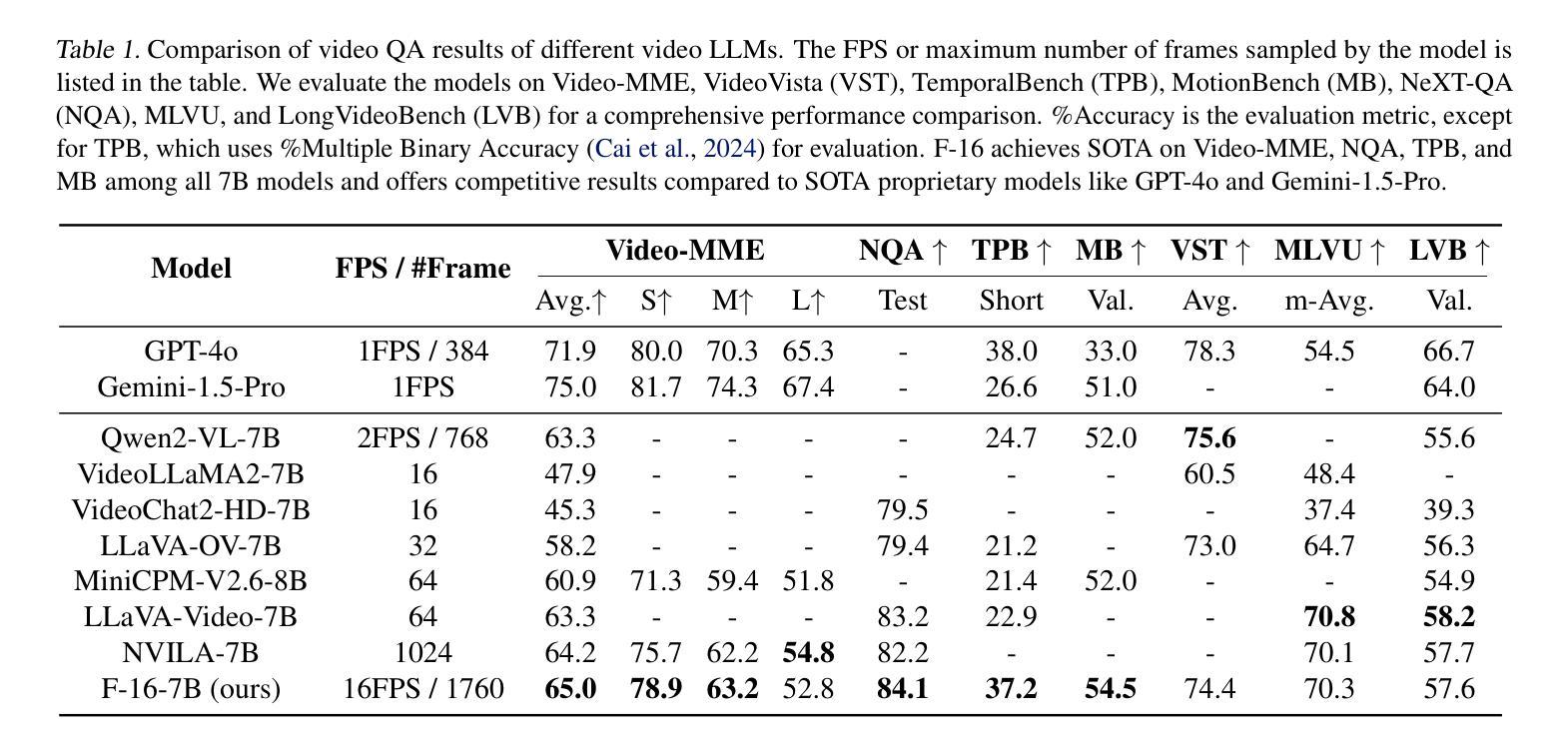
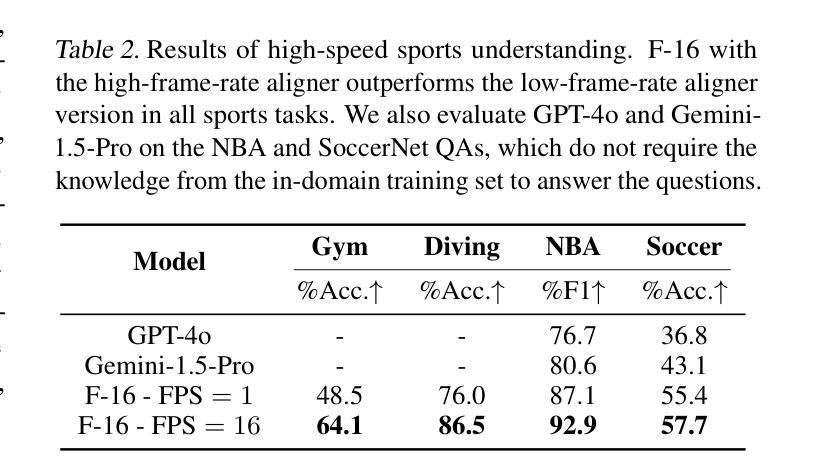
Human vision is dynamic and continuous. However, in video understanding with multimodal large language models (LLMs), existing methods primarily rely on static features extracted from images sampled at a fixed low frame rate of frame-per-second (FPS) $\leqslant$2, leading to critical visual information loss. In this paper, we introduce F-16, the first multimodal LLM designed for high-frame-rate video understanding. By increasing the frame rate to 16 FPS and compressing visual tokens within each 1-second clip, F-16 efficiently captures dynamic visual features while preserving key semantic information. Experimental results demonstrate that higher frame rates considerably enhance video understanding across multiple benchmarks, providing a new approach to improving video LLMs beyond scaling model size or training data. F-16 achieves state-of-the-art performance among 7-billion-parameter video LLMs on both general and fine-grained video understanding benchmarks, such as Video-MME and TemporalBench. Furthermore, F-16 excels in complex spatiotemporal tasks, including high-speed sports analysis (\textit{e.g.}, basketball, football, gymnastics, and diving), outperforming SOTA proprietary visual models like GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5-pro. Additionally, we introduce a novel decoding method for F-16 that enables highly efficient low-frame-rate inference without requiring model retraining. We will release the source code, model checkpoints, and data at \href{https://github.com/bytedance/F-16}{https://github.com/bytedance/F-16}.
人类视觉是动态且连续的。然而,在多模态大型语言模型(LLM)的视频理解中,现有方法主要依赖于以固定低帧率(FPS)≤2采样的图像中提取的静态特征,这导致了关键视觉信息的丢失。在本文中,我们介绍了F-16,它是专为高帧率视频理解设计的第一款多模态LLM。通过提高到16 FPS的帧率和压缩每秒剪辑中的视觉令牌,F-16能够高效地捕捉动态视觉特征,同时保留关键语义信息。实验结果表明,提高帧率可以显著增强多个基准测试的视频理解能力,为改进视频LLM提供了一种新方法,而无需扩大模型规模或增加训练数据。F-16在通用和精细粒度视频理解基准测试上均实现了最先进的性能,如Video-MME和TemporalBench。此外,F-16在复杂的时空任务中表现出色,包括高速运动分析(例如篮球、足球、体操和跳水),超越了如GPT-4o和Gemini-1.5-pro等最先进的专业视觉模型。另外,我们还为F-16引入了一种新型解码方法,能够实现在无需重新训练模型的情况下进行高效低帧率推理。我们将在https://github.com/bytedance/F-16发布源代码、模型检查点和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了针对高帧率视频理解的多模态大型语言模型F-16。现有方法主要依赖于从固定低帧率采样的图像中提取的静态特征,导致关键视觉信息丢失。F-16通过将帧率提高到每秒16帧并压缩每秒剪辑中的视觉令牌,能够高效捕获动态视觉特征并保留关键语义信息。实验结果表明,提高帧率显著提高了多个基准测试的视频理解能力。此外,F-16在一般和精细粒度视频理解基准测试中实现了最佳性能,并在复杂时空任务中表现出卓越性能。最后介绍了一种用于F-16的新型解码方法,可实现高效低帧率推理而无需重新训练模型。
关键见解
- 现有视频理解方法主要依赖低帧率图像提取的静态特征,导致视觉信息损失。
- F-16模型设计用于高帧率视频理解,通过提高帧率和压缩视觉令牌来捕获动态视觉特征。
- 实验结果显示高帧率显著提高视频理解性能,在多个基准测试中表现最佳。
- F-16在一般和精细粒度视频理解方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在复杂时空任务中。
- F-16引入新型解码方法,实现高效低帧率推理。
- F-16模型优于其他先进视觉模型,如GPT-4o和Gemini-1.5-pro。
点此查看论文截图

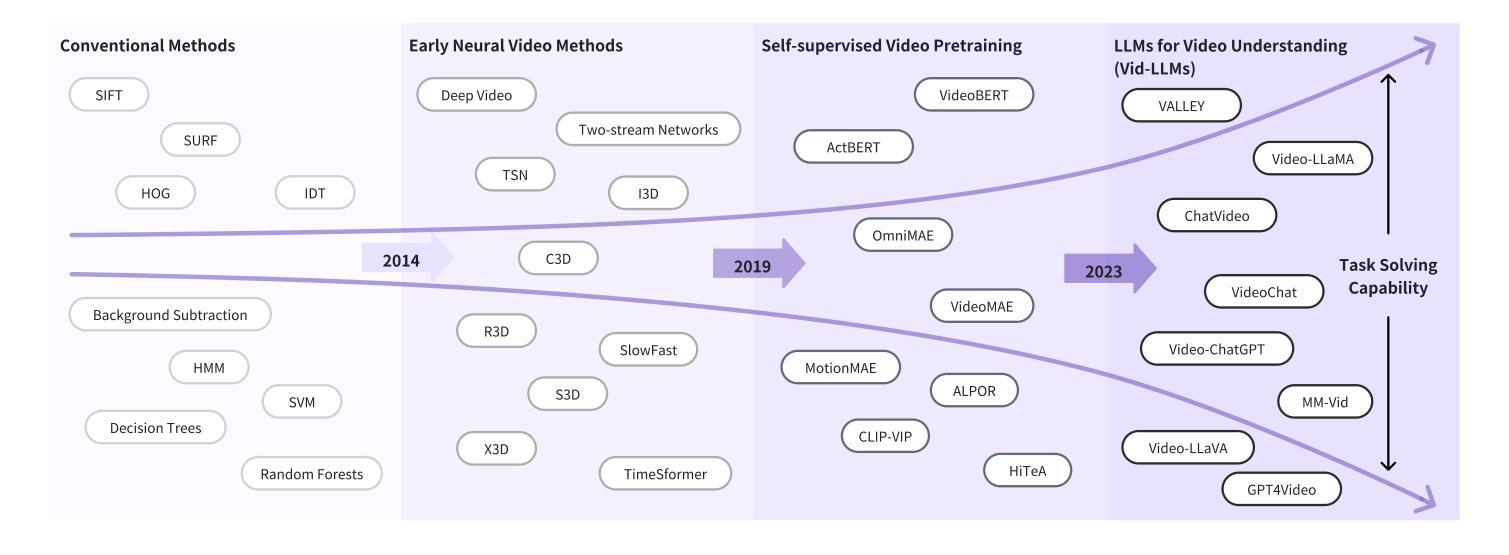
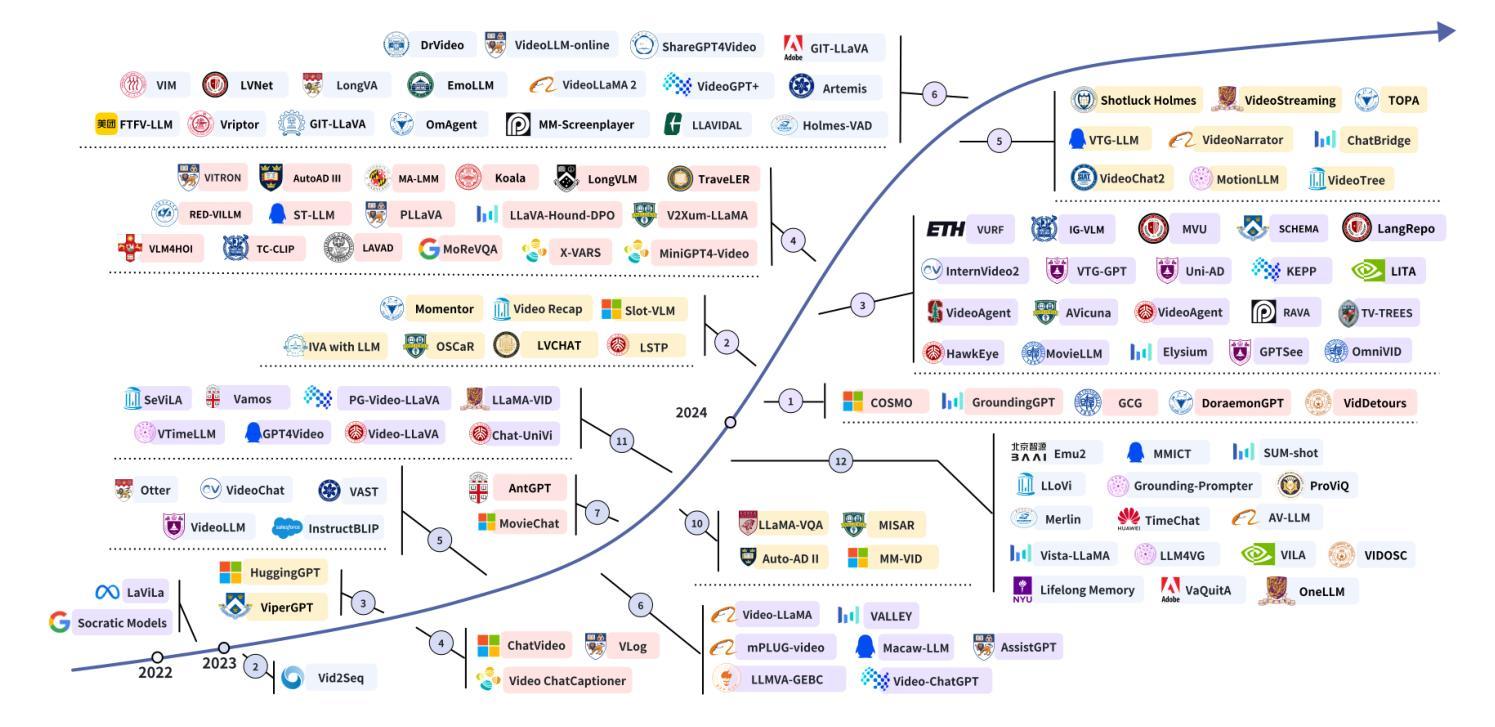
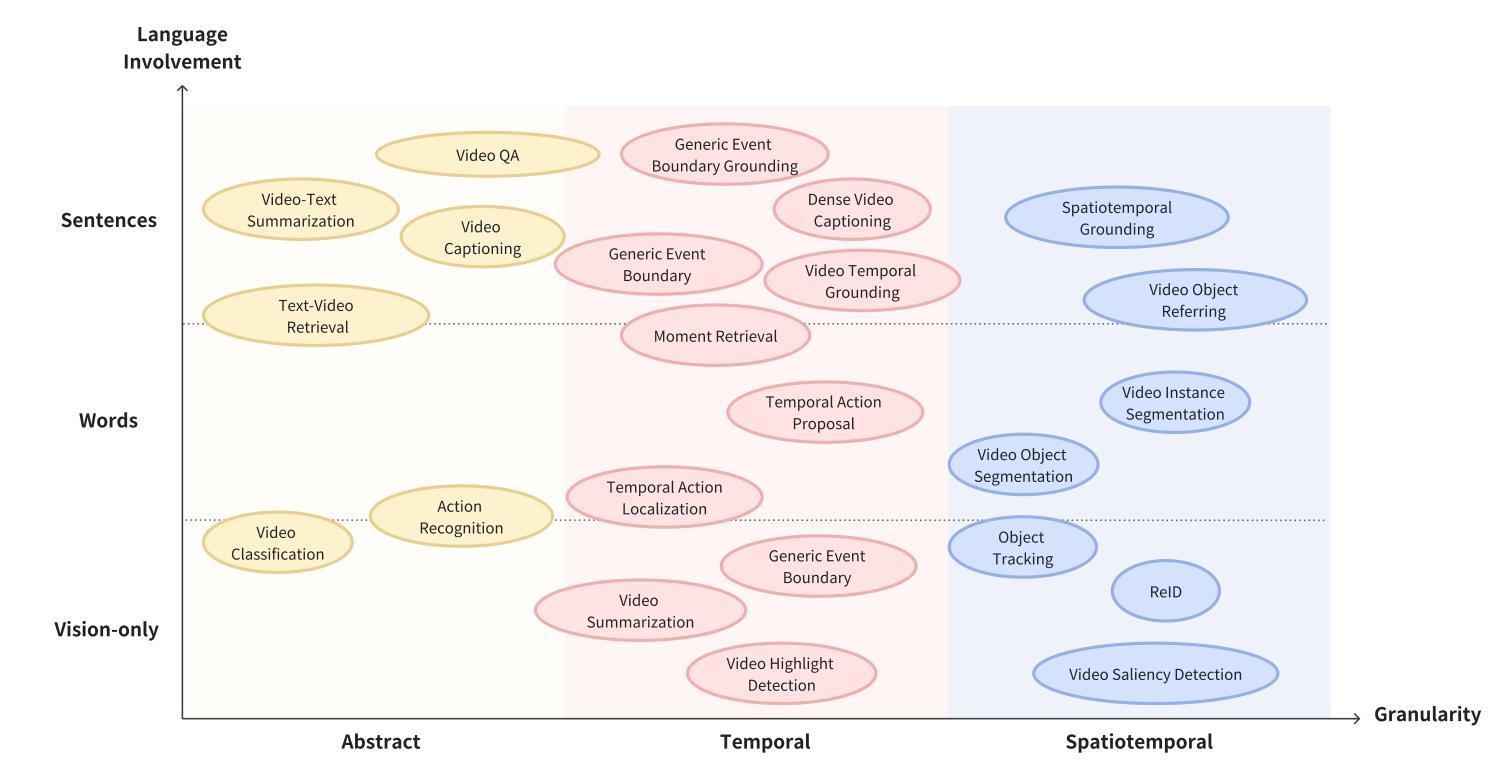
Video Understanding with Large Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Yunlong Tang, Jing Bi, Siting Xu, Luchuan Song, Susan Liang, Teng Wang, Daoan Zhang, Jie An, Jingyang Lin, Rongyi Zhu, Ali Vosoughi, Chao Huang, Zeliang Zhang, Pinxin Liu, Mingqian Feng, Feng Zheng, Jianguo Zhang, Ping Luo, Jiebo Luo, Chenliang Xu
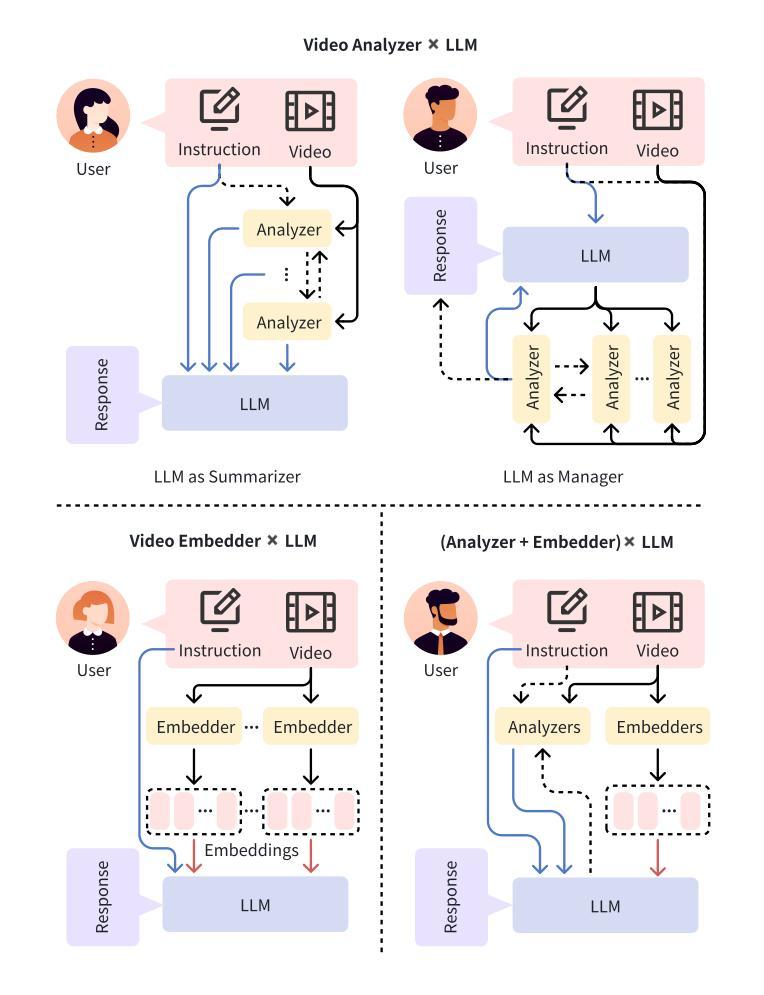
With the burgeoning growth of online video platforms and the escalating volume of video content, the demand for proficient video understanding tools has intensified markedly. Given the remarkable capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in language and multimodal tasks, this survey provides a detailed overview of recent advancements in video understanding that harness the power of LLMs (Vid-LLMs). The emergent capabilities of Vid-LLMs are surprisingly advanced, particularly their ability for open-ended multi-granularity (general, temporal, and spatiotemporal) reasoning combined with commonsense knowledge, suggesting a promising path for future video understanding. We examine the unique characteristics and capabilities of Vid-LLMs, categorizing the approaches into three main types: Video Analyzer x LLM, Video Embedder x LLM, and (Analyzer + Embedder) x LLM. Furthermore, we identify five sub-types based on the functions of LLMs in Vid-LLMs: LLM as Summarizer, LLM as Manager, LLM as Text Decoder, LLM as Regressor, and LLM as Hidden Layer. Furthermore, this survey presents a comprehensive study of the tasks, datasets, benchmarks, and evaluation methodologies for Vid-LLMs. Additionally, it explores the expansive applications of Vid-LLMs across various domains, highlighting their remarkable scalability and versatility in real-world video understanding challenges. Finally, it summarizes the limitations of existing Vid-LLMs and outlines directions for future research. For more information, readers are recommended to visit the repository at https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding.
随着在线视频平台的蓬勃发展和视频内容的不断增加,对熟练的视频理解工具的需求显著增加。鉴于大型语言模型(LLM)在语言和多媒体任务中的卓越能力,这篇综述提供了关于如何利用LLM(视频LLM)进行视频理解的最新进展的详细介绍。Vid-LLM的新兴能力令人惊讶地先进,尤其是它们结合常识知识进行的开放式多粒度(一般、时间和时空)推理能力,这为未来的视频理解指明了有希望的道路。我们考察了Vid-LLM的独特特征和能力,并将这些方法分为三类:视频分析器x LLM、视频嵌入器x LLM和(分析器+嵌入器)x LLM。此外,我们根据LLM在Vid-LLM中的功能确定了五种亚型:LLM作为摘要器、LLM作为管理器、LLM作为文本解码器、LLM作为回归器和LLM作为隐藏层。此外,这篇综述还对Vid-LLM的任务、数据集、基准测试和评估方法进行了全面的研究。它还探讨了Vid-LLM在各个领域的应用广泛性,突出了它们在现实世界的视频理解挑战中的出色可扩展性和通用性。最后,它总结了现有Vid-LLM的局限性,并指出了未来研究的方向。更多信息请访问https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding仓库查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TCSVT
Summary
随着在线视频平台的蓬勃发展和视频内容的不断增加,对熟练的视频理解工具的需求急剧增长。鉴于大型语言模型在多模态任务中的出色表现,这篇综述提供了利用大型语言模型(Vid-LLMs)进行视频理解的最新进展概述。Vid-LLMs的新兴能力令人惊讶地先进,特别是在结合常识知识进行的开放多端、多粒度(一般、时间和时空)推理方面,为未来的视频理解指明了有前景的道路。本文总结了Vid-LLMs在视频分析、嵌入、任务、数据集、基准测试、评估方法和应用领域的特点和能力。更多信息可访问https://github.com/yunlong10/Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding了解。
Key Takeaways
- 在线视频平台和视频内容的增长导致对熟练视频理解工具的需求急剧增加。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在视频理解方面表现出色,形成的新兴技术称为Vid-LLMs。
- Vid-LLMs具有开放多端、多粒度的推理能力,并结合常识知识,为未来的视频理解提供了前景。
- Vid-LLMs有三种主要类型:Video Analyzer x LLM、Video Embedder x LLM和(Analyzer + Embedder)x LLM。
- LLM在Vid-LLMs中的功能可分为五种亚型:作为总结者、管理者、文本解码器、回归器和隐藏层。
- 该综述全面研究了Vid-LLMs的任务、数据集、基准测试和评估方法。
- Vid-LLMs在多个领域有广泛的应用,表现出惊人的可扩展性和在现实世界视频理解挑战中的通用性。
点此查看论文截图