⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
Evolutionary Caching to Accelerate Your Off-the-Shelf Diffusion Model
Authors:Anirud Aggarwal, Abhinav Shrivastava, Matthew Gwilliam
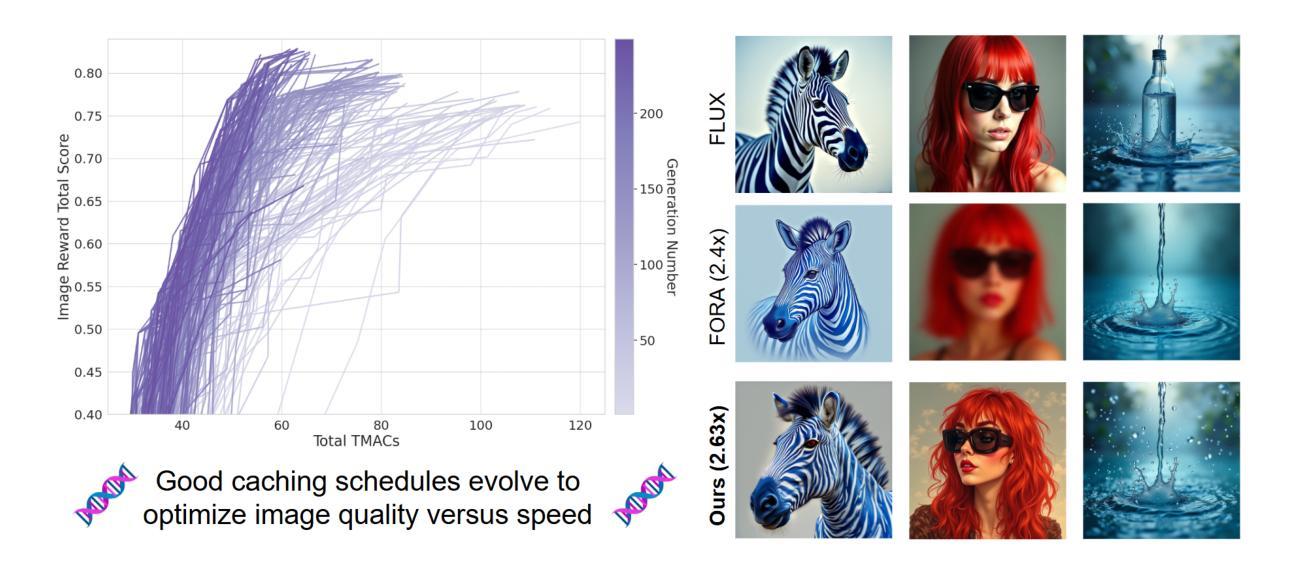
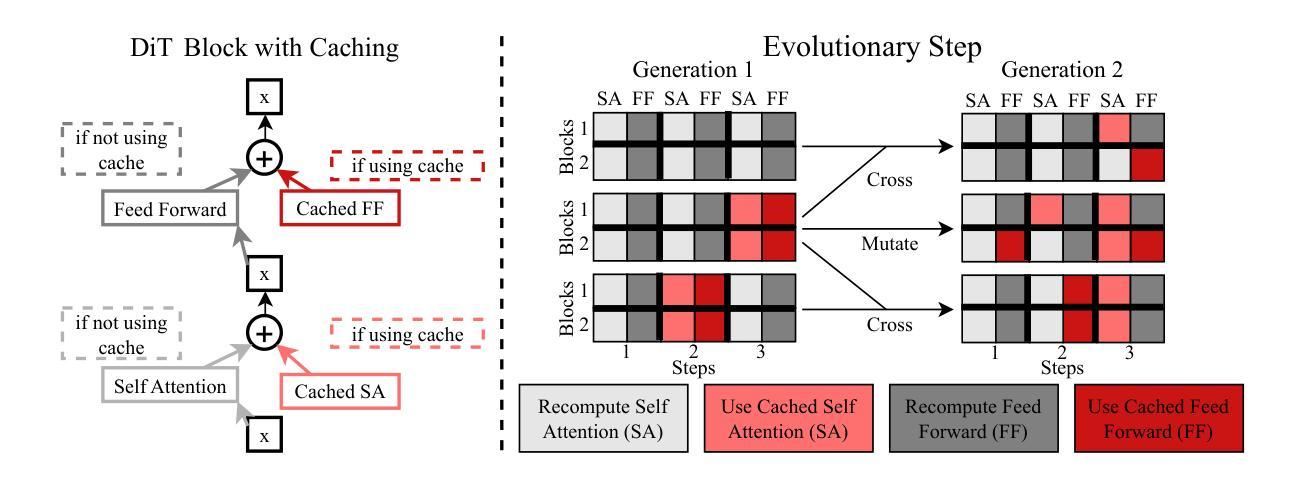
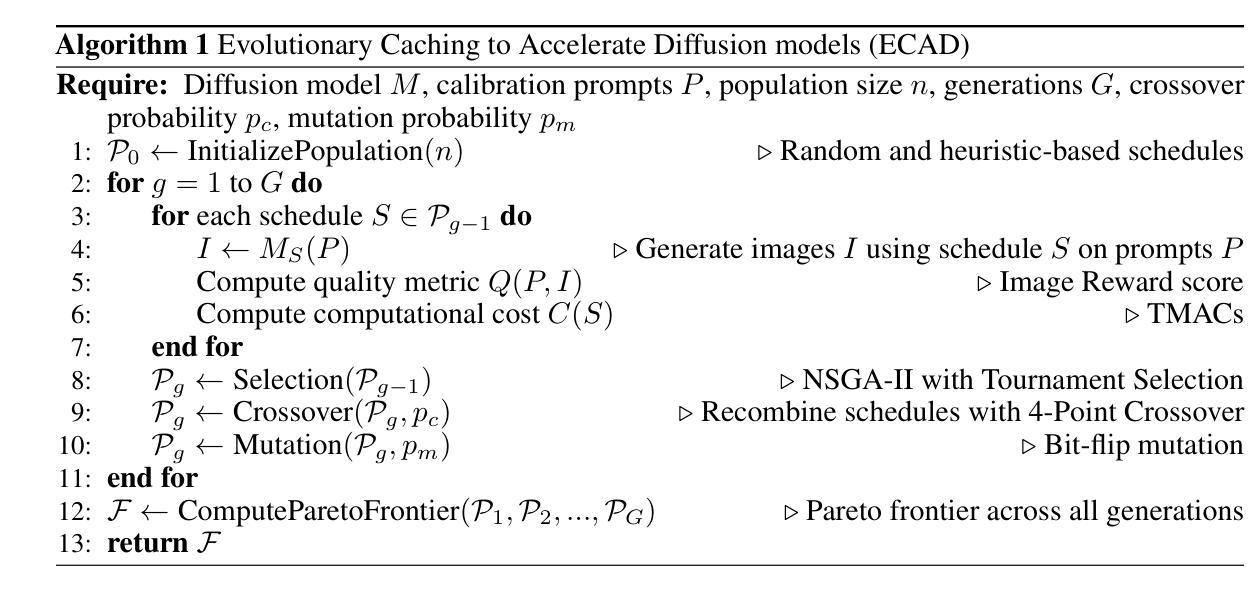
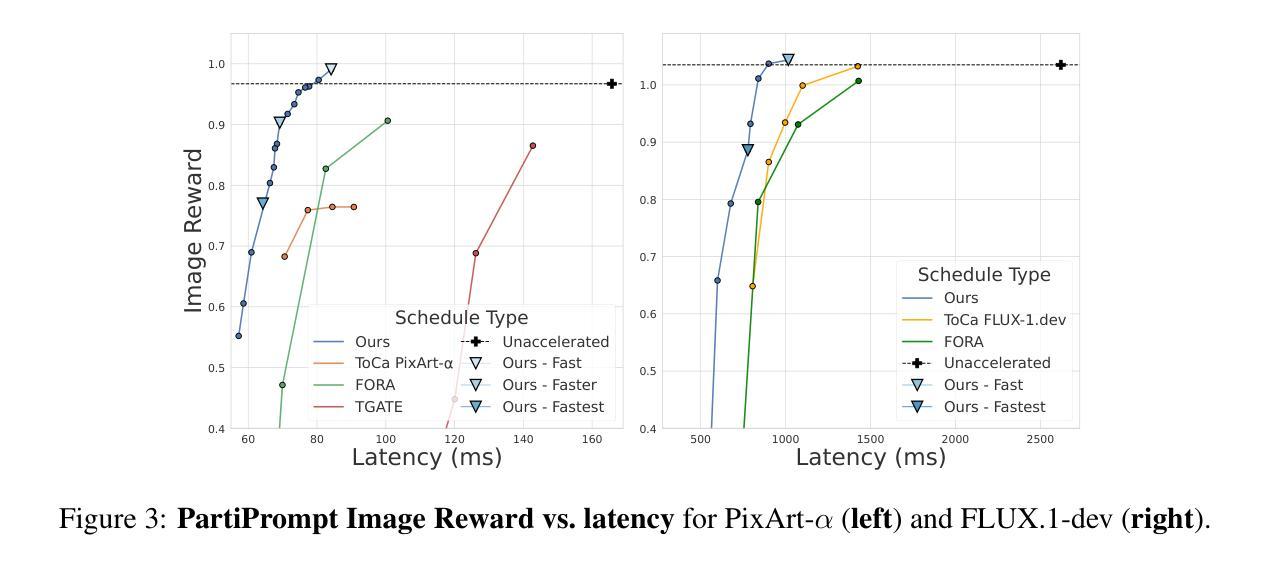
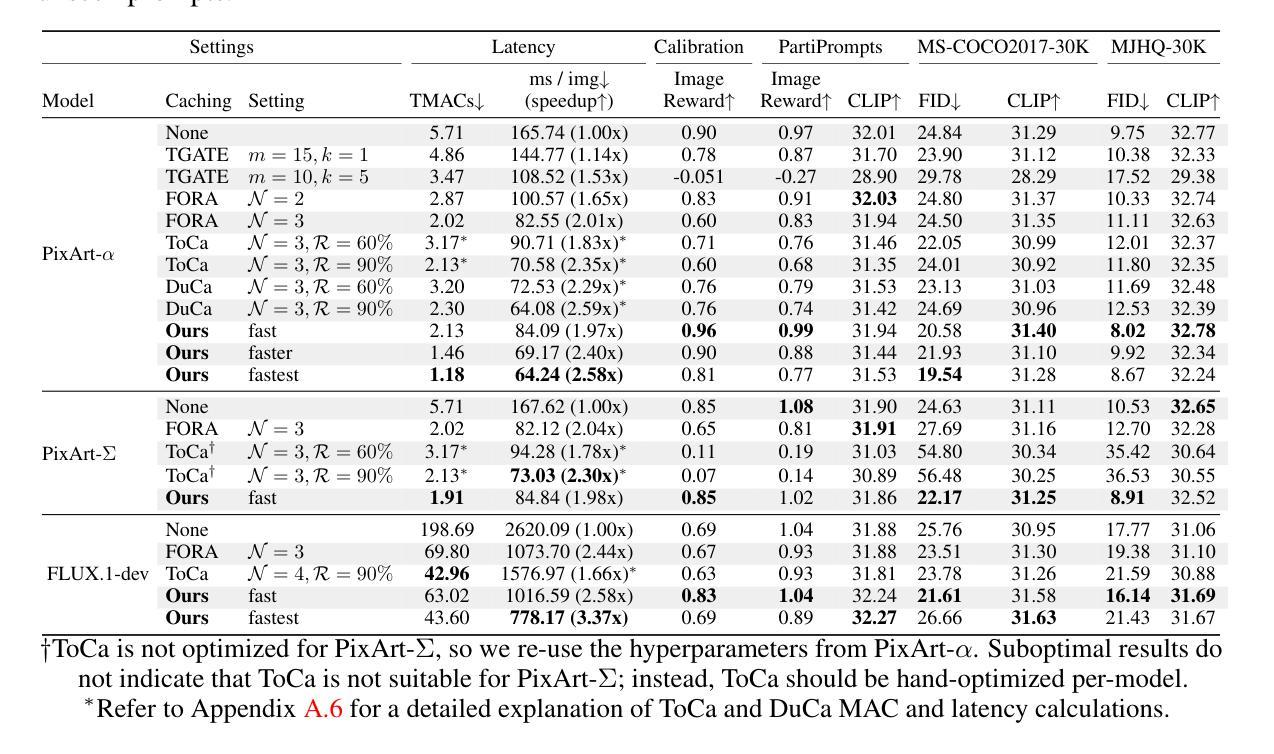
Diffusion-based image generation models excel at producing high-quality synthetic content, but suffer from slow and computationally expensive inference. Prior work has attempted to mitigate this by caching and reusing features within diffusion transformers across inference steps. These methods, however, often rely on rigid heuristics that result in limited acceleration or poor generalization across architectures. We propose Evolutionary Caching to Accelerate Diffusion models (ECAD), a genetic algorithm that learns efficient, per-model, caching schedules forming a Pareto frontier, using only a small set of calibration prompts. ECAD requires no modifications to network parameters or reference images. It offers significant inference speedups, enables fine-grained control over the quality-latency trade-off, and adapts seamlessly to different diffusion models. Notably, ECAD’s learned schedules can generalize effectively to resolutions and model variants not seen during calibration. We evaluate ECAD on PixArt-alpha, PixArt-Sigma, and FLUX-1.dev using multiple metrics (FID, CLIP, Image Reward) across diverse benchmarks (COCO, MJHQ-30k, PartiPrompts), demonstrating consistent improvements over previous approaches. On PixArt-alpha, ECAD identifies a schedule that outperforms the previous state-of-the-art method by 4.47 COCO FID while increasing inference speedup from 2.35x to 2.58x. Our results establish ECAD as a scalable and generalizable approach for accelerating diffusion inference. Our project website is available at https://aniaggarwal.github.io/ecad and our code is available at https://github.com/aniaggarwal/ecad.
基于扩散的图像生成模型擅长生成高质量的合成内容,但推理过程缓慢且计算成本高昂。早期的工作尝试通过缓存和重用扩散变压器中的特征来加速推理步骤。然而,这些方法通常依赖于僵硬的启发式方法,导致加速有限或架构泛化性差。我们提出进化缓存以加速扩散模型(ECAD),这是一种遗传算法,它只使用一小部分校准提示,就能学习高效的、针对每个模型的缓存时间表,形成帕累托前沿。ECAD不需要对网络参数或参考图像进行任何修改。它提供了显著的推理速度提升,能够实现对质量-延迟权衡的精细控制,并无缝适应不同的扩散模型。值得注意的是,ECAD学习的时间表可以有效地推广到校准期间未见到的分辨率和模型变体。我们在PixArt-alpha、PixArt-Sigma和FLUX-1.dev上评估了ECAD,使用多个指标(FID、CLIP、图像奖励)在多种基准测试(COCO、MJHQ-30k、PartiPrompts)上进行评估,证明了其在之前方法上的持续改进。在PixArt-alpha上,ECAD找到的时间表在COCO FID上优于之前的最先进方法4.47,同时将推理速度从2.35倍提高到2.58倍。我们的结果证明了ECAD在加速扩散推理方面的可扩展性和泛化能力。我们的项目网站位于https://aniaggarwal.github.io/ecad,代码位于 https://github.com/aniaggarwal/ecad。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 22 figures, 9 tables
摘要
扩散模型生成图像虽然质量高,但推理过程缓慢且计算成本高。现有工作尝试通过缓存和重用扩散转换器中的特征来加速推理,但这些方法往往依赖僵化的启发式技术,加速有限或通用性不足。本文提出进化缓存加速扩散模型(ECAD),这是一种遗传算法,能够学习高效的、针对特定模型的缓存调度,形成帕累托前沿,只需一小部分校准提示。ECAD无需修改网络参数或参考图像,提供了显著的推理速度提升,能够精细控制质量延迟权衡,并无缝适应不同的扩散模型。值得注意的是,ECAD的调度可以推广到校准期间未见到的分辨率和模型变体。我们在PixArt-alpha、PixArt-Sigma和FLUX-1.dev上评估了ECAD,使用多个指标(FID、CLIP、图像奖励)和多种基准测试(COCO、MJHQ-30k、PartiPrompts),显示出对以前方法的一致改进。在PixArt-alpha上,ECAD找到了一种调度方法,在COCO FID上优于以前的最先进方法4.47,同时推理速度从2.35倍提高到2.58倍。我们的结果证明了ECAD在加速扩散推理方面的可扩展性和通用性。我们的项目网站位于https://aniaggarwal.github.io/ecad,代码位于https://github.com/aniaggarwal/ecad。
关键见解
- 扩散模型虽然能生成高质量的图像内容,但推理过程缓慢且计算成本高。
- 现有方法试图通过缓存和重用特征来加速扩散模型的推理,但存在局限性。
- ECAD利用遗传算法学习高效的、针对特定模型的缓存调度,显著提高了推理速度。
- ECAD不修改网络参数或参考图像,并提供了质量延迟的精细控制。
- ECAD能够无缝适应不同的扩散模型,并且其调度可以推广到不同的分辨率和模型变体。
- 在多个评估和基准测试上,ECAD表现出对以前方法的一致改进。
点此查看论文截图

Control and Realism: Best of Both Worlds in Layout-to-Image without Training
Authors:Bonan Li, Yinhan Hu, Songhua Liu, Xinchao Wang
Layout-to-Image generation aims to create complex scenes with precise control over the placement and arrangement of subjects. Existing works have demonstrated that pre-trained Text-to-Image diffusion models can achieve this goal without training on any specific data; however, they often face challenges with imprecise localization and unrealistic artifacts. Focusing on these drawbacks, we propose a novel training-free method, WinWinLay. At its core, WinWinLay presents two key strategies, Non-local Attention Energy Function and Adaptive Update, that collaboratively enhance control precision and realism. On one hand, we theoretically demonstrate that the commonly used attention energy function introduces inherent spatial distribution biases, hindering objects from being uniformly aligned with layout instructions. To overcome this issue, non-local attention prior is explored to redistribute attention scores, facilitating objects to better conform to the specified spatial conditions. On the other hand, we identify that the vanilla backpropagation update rule can cause deviations from the pre-trained domain, leading to out-of-distribution artifacts. We accordingly introduce a Langevin dynamics-based adaptive update scheme as a remedy that promotes in-domain updating while respecting layout constraints. Extensive experiments demonstrate that WinWinLay excels in controlling element placement and achieving photorealistic visual fidelity, outperforming the current state-of-the-art methods.
布局到图像生成旨在创建具有精确控制主题放置和排列的复杂场景。现有作品已经证明,预训练的文本到图像扩散模型可以在没有任何特定数据训练的情况下实现这一目标;然而,它们通常面临定位不精确和不切实际的艺术品等挑战。针对这些缺点,我们提出了一种无需训练的新型方法WinWinLay。WinWinLay的核心在于两个关键策略:非局部注意力能量函数和自适应更新,这两个策略共同提高了控制精度和逼真度。一方面,我们从理论上证明,常用的注意力能量函数会引入固有的空间分布偏见,阻碍物体与布局指令的统一对齐。为了克服这一问题,我们探索了非局部注意力先验来重新分配注意力分数,帮助物体更好地符合指定的空间条件。另一方面,我们发现简单的反向传播更新规则可能导致偏离预训练域,从而导致分布外艺术品。因此,我们相应地引入了一种基于朗格文动力学的自适应更新方案作为补救措施,该方案在尊重布局约束的同时,促进了域内更新。大量实验表明,WinWinLay在控制元素放置和实现逼真的视觉保真度方面表现出色,超过了当前先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML2025
Summary
本文提出了一种无需训练的方法WinWinLay,用于改进Layout-to-Image生成中的元素放置控制和视觉真实感。通过Non-local Attention Energy Function和Adaptive Update两大策略,WinWinLay克服了现有工作中存在的定位不精确和图像失真问题。该方法在理论上解决了注意力能量函数的空间分布偏见问题,并引入了一种基于朗之万动力学的自适应更新方案,以保持更新在预训练域内并遵守布局约束。实验表明,WinWinLay在元素放置控制和视觉真实感方面表现出卓越性能,优于当前最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- WinWinLay是一种无需训练的Layout-to-Image生成方法,旨在创建具有精确控制主题的复杂场景。
- 该方法通过两大策略实现目标:Non-local Attention Energy Function解决空间分布偏见问题,使对象更符合布局指令;Adaptive Update解决因反向传播更新规则导致的偏差问题,引入基于朗之万动力学的自适应更新方案。
- Non-local Attention Energy Function通过重新分配注意力分数,有助于对象更好地符合指定的空间条件。
- Adaptive Update方案促进在预训练域内的更新并遵守布局约束。
- WinWinLay在元素放置控制和视觉真实感方面表现出卓越性能。
- 该方法通过广泛实验验证,并证明其性能优于当前最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图




Provable Maximum Entropy Manifold Exploration via Diffusion Models
Authors:Riccardo De Santi, Marin Vlastelica, Ya-Ping Hsieh, Zebang Shen, Niao He, Andreas Krause
Exploration is critical for solving real-world decision-making problems such as scientific discovery, where the objective is to generate truly novel designs rather than mimic existing data distributions. In this work, we address the challenge of leveraging the representational power of generative models for exploration without relying on explicit uncertainty quantification. We introduce a novel framework that casts exploration as entropy maximization over the approximate data manifold implicitly defined by a pre-trained diffusion model. Then, we present a novel principle for exploration based on density estimation, a problem well-known to be challenging in practice. To overcome this issue and render this method truly scalable, we leverage a fundamental connection between the entropy of the density induced by a diffusion model and its score function. Building on this, we develop an algorithm based on mirror descent that solves the exploration problem as sequential fine-tuning of a pre-trained diffusion model. We prove its convergence to the optimal exploratory diffusion model under realistic assumptions by leveraging recent understanding of mirror flows. Finally, we empirically evaluate our approach on both synthetic and high-dimensional text-to-image diffusion, demonstrating promising results.
对于解决现实世界中的决策制定问题(如科学发现)而言,探索至关重要。这类问题的目标是生成真正新颖的设计,而非模仿现有数据分布。在此工作中,我们解决了利用生成模型的表征能力进行探索的挑战,且无需依赖明确的不确定性量化。我们引入了一种新型框架,将探索视为在由预训练扩散模型隐式定义的数据流形上进行的熵最大化。接着,我们基于密度估计提出了一个用于探索的新原则,这在实践中是一个公认的挑战性问题。为了应对这一挑战并确保方法的真正可扩展性,我们利用扩散模型诱导的密度熵与其得分函数之间的基本联系。在此基础上,我们开发了一种基于镜像下降的算法,将探索问题视为预训练扩散模型的连续微调。通过利用对镜像流的最新理解,我们在实际假设下证明了其收敛至最佳探索性扩散模型。最后,我们在合成数据和高维文本到图像的扩散上实证评估了我们的方法,并获得了有前景的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文强调了在解决现实世界决策问题(如科学发现)时探索的重要性,旨在生成真正新颖的设计而非模仿现有数据分布。为解决利用生成模型的表征能力进行探索的挑战,本文提出一种新型框架,将探索视为预训练扩散模型隐式定义的数据流形上的熵最大化。基于密度估计的原则,提出一种基于密度诱导扩散模型的熵与其得分函数之间基本联系的解决方案。利用镜像下降法开发算法,将探索问题视为预训练扩散模型的序列微调。最后在合成和高维文本到图像扩散上进行实证评估,显示结果具前景。
Key Takeaways
- 探索在解决现实世界决策问题中的重要性,强调生成真正新颖设计而非模仿现有数据分布。
- 提出一种新型框架,将探索视为预训练扩散模型隐式定义的数据流形上的熵最大化,解决利用生成模型的表征能力进行探索的挑战。
- 基于密度估计的原则来推动探索,并利用密度诱导扩散模型的熵与其得分函数之间的基本联系来解决问题。
- 利用镜像下降法开发算法,将探索问题视为预训练扩散模型的序列微调,以克服实践中的挑战并实现真正的可扩展性。
- 证明了该算法在合理假设下收敛于最优探索性扩散模型。
- 在合成数据和高维文本到图像扩散问题上进行了实证评估。
- 展示的结果具有前景,表明该框架在解决现实世界决策问题方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

When Model Knowledge meets Diffusion Model: Diffusion-assisted Data-free Image Synthesis with Alignment of Domain and Class
Authors:Yujin Kim, Hyunsoo Kim, Hyunwoo J. Kim, Suhyun Kim
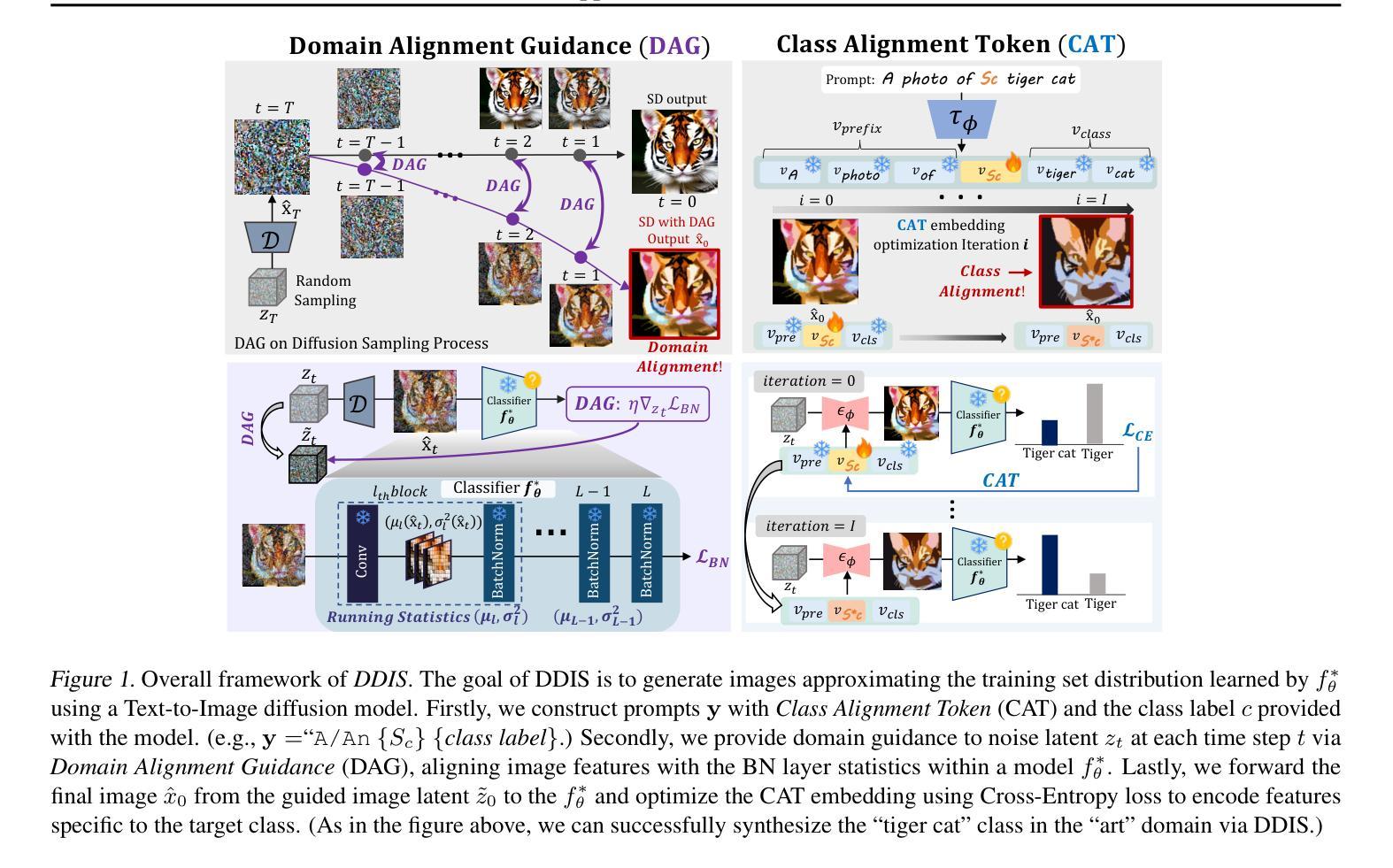
Open-source pre-trained models hold great potential for diverse applications, but their utility declines when their training data is unavailable. Data-Free Image Synthesis (DFIS) aims to generate images that approximate the learned data distribution of a pre-trained model without accessing the original data. However, existing DFIS meth ods produce samples that deviate from the training data distribution due to the lack of prior knowl edge about natural images. To overcome this limitation, we propose DDIS, the first Diffusion-assisted Data-free Image Synthesis method that leverages a text-to-image diffusion model as a powerful image prior, improving synthetic image quality. DDIS extracts knowledge about the learned distribution from the given model and uses it to guide the diffusion model, enabling the generation of images that accurately align with the training data distribution. To achieve this, we introduce Domain Alignment Guidance (DAG) that aligns the synthetic data domain with the training data domain during the diffusion sampling process. Furthermore, we optimize a single Class Alignment Token (CAT) embedding to effectively capture class-specific attributes in the training dataset. Experiments on PACS and Ima geNet demonstrate that DDIS outperforms prior DFIS methods by generating samples that better reflect the training data distribution, achieving SOTA performance in data-free applications.
开源预训练模型在多种应用上具有巨大潜力,但当其训练数据无法使用或不可访问时,其效用会降低。数据自由图像合成(DFIS)旨在生成能够近似预训练模型学习到的数据分布的图像,而无需访问原始数据。然而,现有的DFIS方法生成的样本偏离了训练数据分布,因为缺乏关于自然图像的先验知识。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了DDIS(数据自由图像合成的扩散辅助方法)。DDIS首次利用文本到图像的扩散模型作为强大的图像先验知识,提高了合成图像的质量。DDIS从给定的模型中提取关于学习到的分布的知识,并利用它来引导扩散模型,从而生成准确对齐训练数据分布的图像。为了实现这一点,我们引入了域对齐指导(DAG),在扩散采样过程中将合成数据域与训练数据域对齐。此外,我们通过优化单个类别对齐令牌(CAT)嵌入来有效地捕获训练数据集特定的类别属性。在PACS和ImageNet上的实验表明,DDIS优于先前的DFIS方法,生成的样本更好地反映了训练数据分布,在数据自由应用中实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICML 2025
Summary
扩散模型驱动的免数据图像合成(DDIS)是一种新型的图像合成方法,它通过利用文本到图像的扩散模型作为图像先验,改进了现有的免数据图像合成(DFIS)方法。DDIS能够从给定的预训练模型中提取学习到的分布知识,并引导扩散模型生成与训练数据分布精确对齐的图像。通过引入域对齐引导(DAG)和类别对齐令牌(CAT)嵌入优化,DDIS在PACS和ImageNet上的实验表明,它在无数据应用中生成样本的性能超过了先前的DFIS方法,达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型驱动的免数据图像合成(DDIS)是一种新的图像合成方法。
- DDIS利用文本到图像的扩散模型作为图像先验,改进了现有的免数据图像合成(DFIS)方法。
- DDIS能够从预训练模型中提取学习到的分布知识,并据此生成图像。
- 通过引入域对齐引导(DAG),DDIS能够在扩散采样过程中将合成数据域与训练数据域对齐。
- DDIS通过优化类别对齐令牌(CAT)嵌入来有效捕捉训练数据集中的类别特定属性。
- 在PACS和ImageNet上的实验表明,DDIS在免数据应用中生成样本的性能超过了先前的DFIS方法。
点此查看论文截图



Acoustic Waveform Inversion with Image-to-Image Schrödinger Bridges
Authors:A. S. Stankevich, I. B. Petrov
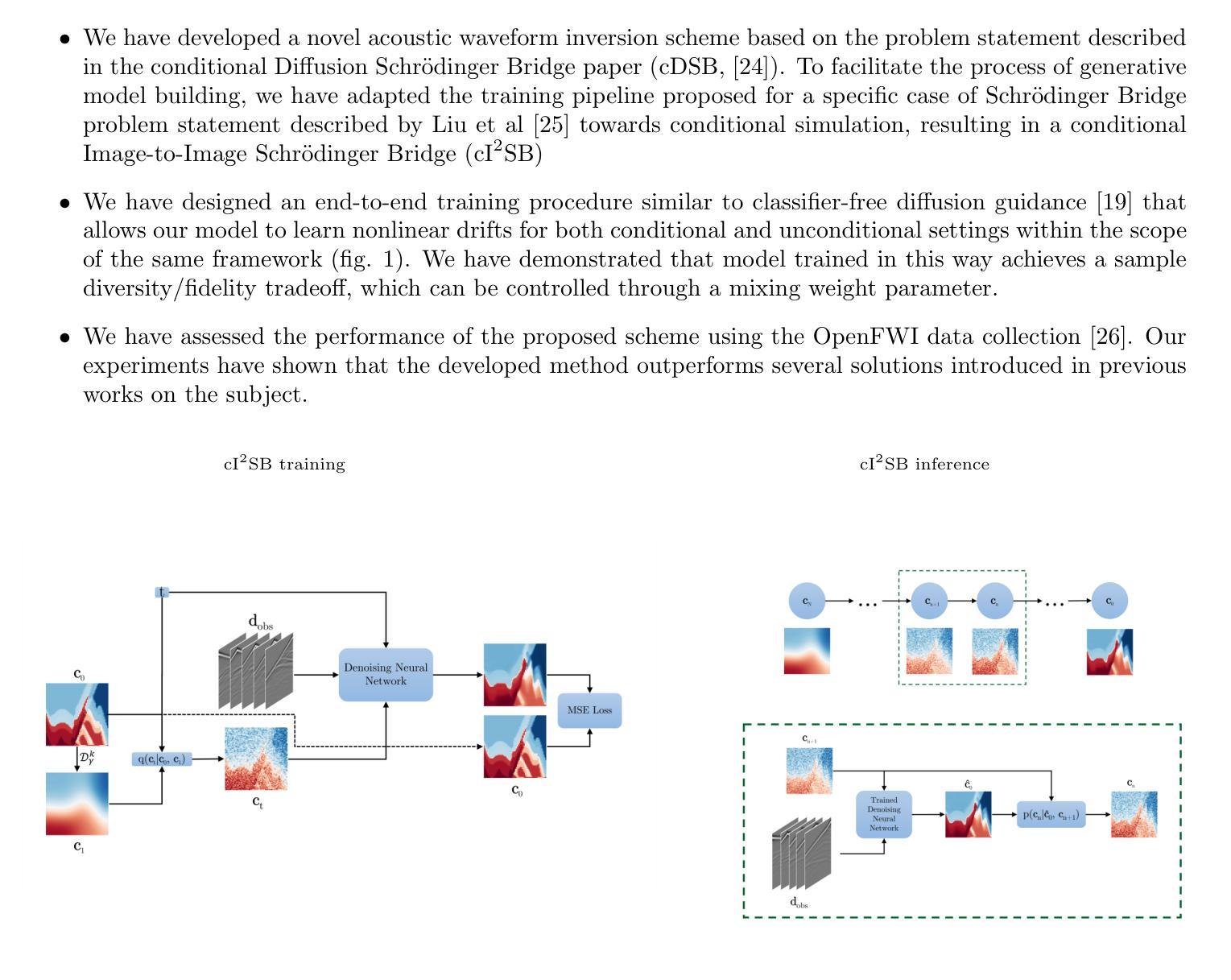
Recent developments in application of deep learning models to acoustic Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) are marked by the use of diffusion models as prior distributions for Bayesian-like inference procedures. The advantage of these methods is the ability to generate high-resolution samples, which are otherwise unattainable with classical inversion methods or other deep learning-based solutions. However, the iterative and stochastic nature of sampling from diffusion models along with heuristic nature of output control remain limiting factors for their applicability. For instance, an optimal way to include the approximate velocity model into diffusion-based inversion scheme remains unclear, even though it is considered an essential part of FWI pipeline. We address the issue by employing a Schr"odinger Bridge that interpolates between the distributions of ground truth and smoothed velocity models. To facilitate the learning of nonlinear drifts that transfer samples between distributions we extend the concept of Image-to-Image Schr"odinger Bridge ($\text{I}^2\text{SB}$) to conditional sampling, resulting in a conditional Image-to-Image Schr"odinger Bridge (c$\text{I}^2\text{SB}$) framework. To validate our method, we assess its effectiveness in reconstructing the reference velocity model from its smoothed approximation, coupled with the observed seismic signal of fixed shape. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed solution outperforms our reimplementation of conditional diffusion model suggested in earlier works, while requiring only a few neural function evaluations (NFEs) to achieve sample fidelity superior to that attained with supervised learning-based approach. The supplementary code implementing the algorithms described in this paper can be found in the repository https://github.com/stankevich-mipt/seismic_inversion_via_I2SB.
近期深度学习模型在声波全波形反演(FWI)中的应用发展,以扩散模型作为贝叶斯类推断过程的先验分布为标志。这些方法的优势在于能够生成高分辨率样本,这是经典反演方法或其他基于深度学习的方法无法达到的。然而,从扩散模型中进行采样的迭代和随机性质,以及输出控制的启发式性质,仍然是其适用性的限制因素。例如,虽然将近似速度模型纳入基于扩散的反演方案被认为是FWI流程中的基本部分,但如何将其纳入仍不明确。我们通过采用薛定谔桥来解决这个问题,该桥在真实分布和平滑速度模型分布之间进行插值。为了学习在分布之间转移样本的非线性漂移,我们将图像到图像薛定谔桥(I^2SB)的概念扩展到条件采样,从而得到条件图像到图像薛定谔桥(cI^2SB)框架。为了验证我们的方法,我们评估其在从平滑近似重构参考速度模型方面的有效性,并结合固定的观测地震信号。实验表明,所提出的解决方案优于我们早期工作中建议的条件扩散模型的重新实现,并且仅需要少量的神经网络功能评估(NFEs)即可实现优于基于监督学习的方法的样本保真度。可以在https://github.com/stankevich-mipt/seismic_inversion_via_I2SB仓库中找到实现本文中描述的算法的补充代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to “Computational Mathematics And Mathematical Physics”, ISSN 1555-6662, issue 8, August 2025
摘要
深度学习模型在声波全波形反演(FWI)中的应用最新进展表现为利用扩散模型作为贝叶斯类推断过程的先验分布。这些方法的优势在于能够生成高分辨率样本,这是经典反演方法或其他深度学习解决方案无法达到的。然而,从扩散模型中采样具有迭代性和随机性,以及输出控制的启发式性质,限制了其适用性。例如,将近似速度模型纳入基于扩散的反演方案的最佳方式仍不明确,尽管它被认为是FWI管道的重要组成部分。我们通过采用薛定谔桥来解决这个问题,该桥在真实分布和平滑速度模型分布之间进行插值。为了学习在分布之间转移样本的非线性漂移,我们将图像到图像的薛定谔桥(I^2SB)概念扩展到条件采样,形成条件图像到图像的薛定谔桥(cI^2SB)框架。我们通过从其平滑近似重建参考速度模型,并结合固定的地震信号形状来评估我们方法的有效性。实验表明,所提出的方法优于我们早期工作中条件扩散模型的重新实现,并且只需要很少的神经功能评估(NFEs)就能达到优于监督学习方法的样本保真度。相关算法实现代码可在https://github.com/stankevich-mipt/seismic_inversion_via_I2SB 仓库中找到。
要点
- 扩散模型被应用于声波全波形反演中,生成高分辨率样本,这是传统方法无法实现的。
- 扩散模型的采样具有迭代和随机性质,以及输出控制的启发式性质,这限制了其应用。
- 引入薛定谔桥来解决将近似速度模型纳入基于扩散的反演方案的问题。
- 通过对真实分布和平滑速度模型分布进行插值的薛定谔桥来解决这个问题。
- 扩展图像到图像的薛定谔桥概念,形成条件图像到图像的薛定谔桥框架,用于学习在分布间转移样本的非线性漂移。
- 实验表明,新方法与早期条件扩散模型的实现相比具有优越性,能以较少的神经功能评估次数达到较高的样本保真度。
点此查看论文截图

One-shot Face Sketch Synthesis in the Wild via Generative Diffusion Prior and Instruction Tuning
Authors:Han Wu, Junyao Li, Kangbo Zhao, Sen Zhang, Yukai Shi, Liang Lin
Face sketch synthesis is a technique aimed at converting face photos into sketches. Existing face sketch synthesis research mainly relies on training with numerous photo-sketch sample pairs from existing datasets. However, these large-scale discriminative learning methods will have to face problems such as data scarcity and high human labor costs. Once the training data becomes scarce, their generative performance significantly degrades. In this paper, we propose a one-shot face sketch synthesis method based on diffusion models. We optimize text instructions on a diffusion model using face photo-sketch image pairs. Then, the instructions derived through gradient-based optimization are used for inference. To simulate real-world scenarios more accurately and evaluate method effectiveness more comprehensively, we introduce a new benchmark named One-shot Face Sketch Dataset (OS-Sketch). The benchmark consists of 400 pairs of face photo-sketch images, including sketches with different styles and photos with different backgrounds, ages, sexes, expressions, illumination, etc. For a solid out-of-distribution evaluation, we select only one pair of images for training at each time, with the rest used for inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can convert various photos into realistic and highly consistent sketches in a one-shot context. Compared to other methods, our approach offers greater convenience and broader applicability. The dataset will be available at: https://github.com/HanWu3125/OS-Sketch
面部素描合成是一种将面部照片转换为素描的技术。现有的面部素描合成研究主要依赖于使用现有数据集中的大量照片-素描样本对进行训练。然而,这些大规模判别学习方法将不得不面对数据稀缺和高昂的人力成本等问题。一旦训练数据变得稀缺,它们的生成性能就会显著下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的单镜头面部素描合成方法。我们使用面部照片-素描图像对优化扩散模型上的文本指令。然后,通过基于梯度的优化得到的指令用于推理。为了更准确地模拟真实场景并更全面地评估方法的有效性,我们引入了一个新的基准测试,名为One-shot面部素描数据集(OS-Sketch)。该基准测试由400对面部照片-素描图像组成,包括不同风格的素描和不同背景、年龄、性别、表情、照明等的照片。为了进行坚实的离分布评估,我们每次仅选择一对图像进行训练,其余图像用于推理。大量实验表明,所提出的方法可以在单镜头情况下将各种照片转换为逼真且高度一致的素描。与其他方法相比,我们的方法提供了更大的便利性和更广泛的应用性。数据集将在以下网址提供:https://github.com/HanWu3125/OS-Sketch
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We propose a novel framework for face sketch synthesis, where merely a single pair of samples suffices to enable in-the-wild face sketch synthesis
摘要
人脸识别技术的新进展,一种基于扩散模型的一次性面部素描合成方法。通过优化图像对和文字指令进行训练,可在真实世界环境下实现精准模拟与全面评估。该研究建立了一个名为OS-Sketch的新基准数据集,实现了多样化的面部照片向真实素描的转换。相比其他方法,该方法更便捷、适用性更广。数据集可通过链接访问。
关键见解
- 论文提出了一种基于扩散模型的一次性面部素描合成方法,适用于不同风格的素描和背景、年龄、性别、表情等多样化的面部照片。
- 该方法通过优化文本指令在扩散模型上进行训练,并利用基于梯度的优化来生成指令进行推断。
- 为了更准确地模拟真实世界环境并更全面地评估方法的有效性,论文引入了一个新的基准数据集OS-Sketch。
- OS-Sketch数据集包含400对面部照片和素描图像,用于实验验证方法的可行性。
- 该方法通过一次训练对一组图像进行操作,其余图像用于推断,展示了其在非分布环境中的稳健性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法能够生成逼真的高度一致的素描。
点此查看论文截图


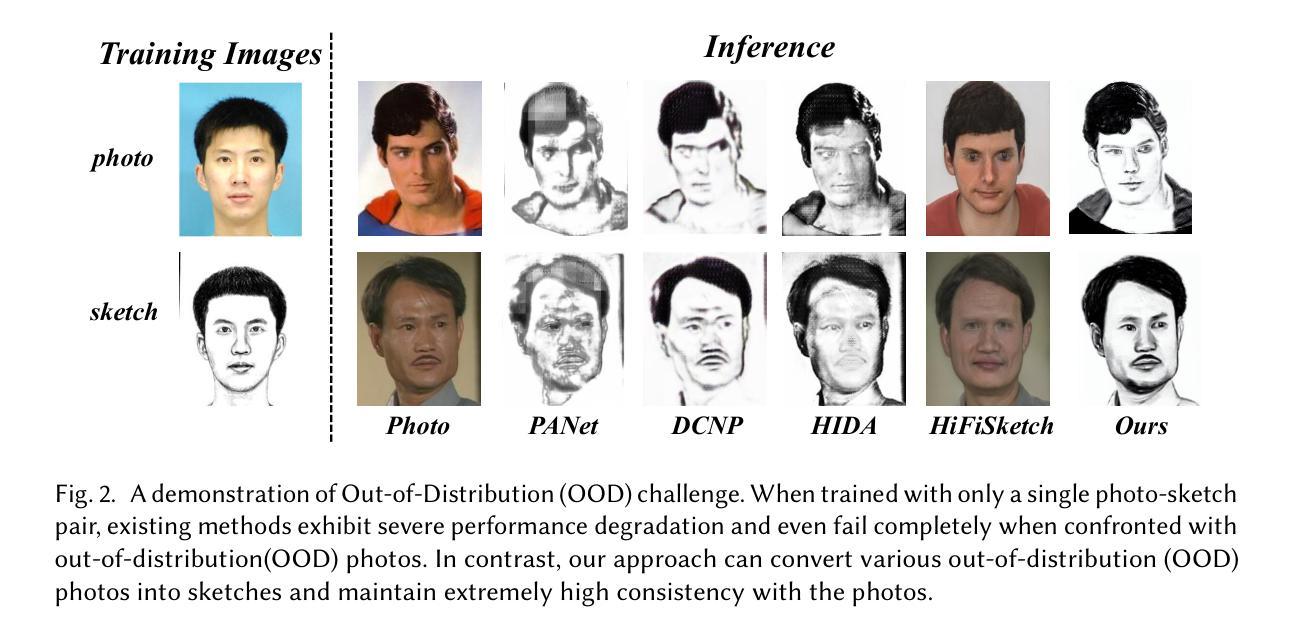
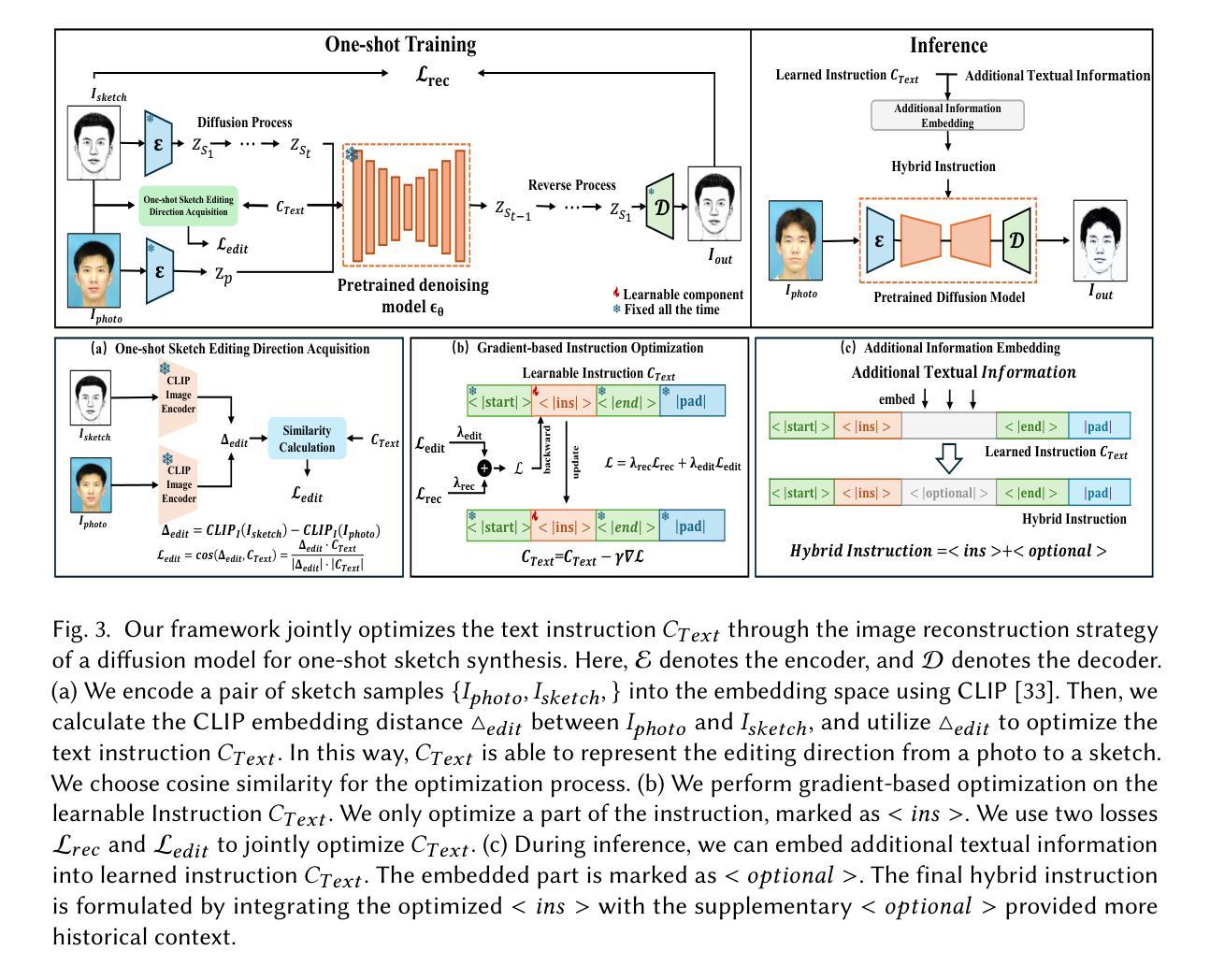
DM-FNet: Unified multimodal medical image fusion via diffusion process-trained encoder-decoder
Authors:Dan He, Weisheng Li, Guofen Wang, Yuping Huang, Shiqiang Liu
Multimodal medical image fusion (MMIF) extracts the most meaningful information from multiple source images, enabling a more comprehensive and accurate diagnosis. Achieving high-quality fusion results requires a careful balance of brightness, color, contrast, and detail; this ensures that the fused images effectively display relevant anatomical structures and reflect the functional status of the tissues. However, existing MMIF methods have limited capacity to capture detailed features during conventional training and suffer from insufficient cross-modal feature interaction, leading to suboptimal fused image quality. To address these issues, this study proposes a two-stage diffusion model-based fusion network (DM-FNet) to achieve unified MMIF. In Stage I, a diffusion process trains UNet for image reconstruction. UNet captures detailed information through progressive denoising and represents multilevel data, providing a rich set of feature representations for the subsequent fusion network. In Stage II, noisy images at various steps are input into the fusion network to enhance the model’s feature recognition capability. Three key fusion modules are also integrated to process medical images from different modalities adaptively. Ultimately, the robust network structure and a hybrid loss function are integrated to harmonize the fused image’s brightness, color, contrast, and detail, enhancing its quality and information density. The experimental results across various medical image types demonstrate that the proposed method performs exceptionally well regarding objective evaluation metrics. The fused image preserves appropriate brightness, a comprehensive distribution of radioactive tracers, rich textures, and clear edges. The code is available at https://github.com/HeDan-11/DM-FNet.
多模态医学图像融合(MMIF)从多个源图像中提取最有意义的信息,使诊断更全面和准确。实现高质量的融合结果需要在亮度、颜色、对比度和细节之间取得谨慎的平衡;这确保了融合图像能够有效地显示相关的解剖结构并反映组织的功能状态。然而,现有的MMIF方法在常规训练过程中捕获详细特征的能力有限,并且存在跨模态特征交互不足的问题,导致融合图像质量不佳。为了解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种基于两阶段扩散模型的融合网络(DM-FNet)来实现统一的MMIF。在第一阶段,通过扩散过程训练UNet进行图像重建。UNet通过渐进的去噪捕获详细信息并代表多级数据,为随后的融合网络提供丰富的特征表示。在第二阶段,将不同步骤的噪声图像输入融合网络,以增强模型的特征识别能力。此外,还集成了三个关键融合模块,以自适应地处理来自不同模态的医学图像。最终,通过整合稳健的网络结构和混合损失函数,协调融合图像的亮度、颜色、对比度和细节,从而提高其质量和信息密度。在多种医学图像类型上的实验结果表明,该方法在客观评价指标上表现优异。融合图像保持了适当的亮度、全面的放射性示踪剂分布、丰富的纹理和清晰的边缘。代码可访问于 https://github.com/HeDan-11/DM-FNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM) in March 2025
Summary
基于扩散模型的两阶段融合网络(DM-FNet)实现多模态医学图像融合(MMIF),提升诊断的全面性和准确性。该网络通过两个阶段进行训练,第一阶段利用扩散过程训练UNet进行图像重建,捕获详细信息并呈现多级数据,为后续的融合网络提供丰富的特征表示。第二阶段输入不同步骤的噪声图像,增强模型的特征识别能力,并集成三个关键融合模块以自适应处理不同模态的医学图像。最终,通过整合网络结构和混合损失函数,协调融合图像的亮度、色彩、对比度和细节,提升图像质量和信息密度。实验结果显示,该方法在客观评估指标上表现优异,融合图像保持适当的亮度、全面的放射性示踪物分布、丰富的纹理和清晰的边缘。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像融合(MMIF)能够提取多个源图像中最有意义的信息,为医生提供更全面和准确的诊断依据。
- 现有MMIF方法在常规训练中存在捕获详细特征的能力有限的问题,且跨模态特征交互不足,导致融合图像质量不佳。
- 提出的两阶段扩散模型融合网络(DM-FNet)通过两个阶段训练,旨在解决上述问题,实现统一的多模态图像融合。
- 第一阶段利用扩散过程训练UNet进行图像重建,提供丰富的特征表示。
- 第二阶段增强模型的特征识别能力,并集成三个关键融合模块以处理不同模态的医学图像。
- 该网络通过协调融合图像的亮度、色彩、对比度和细节,提升图像质量和信息密度。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在客观评估指标上表现优异,融合图像具有适当的亮度、全面的放射性示踪物分布、丰富的纹理和清晰的边缘。
点此查看论文截图
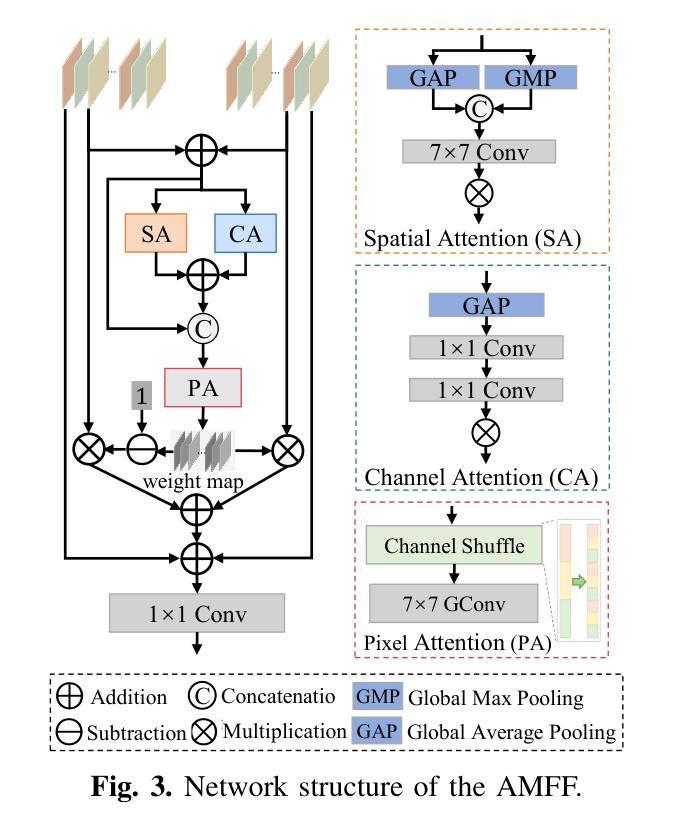
Echo-DND: A dual noise diffusion model for robust and precise left ventricle segmentation in echocardiography
Authors:Abdur Rahman, Keerthiveena Balraj, Manojkumar Ramteke, Anurag Singh Rathore
Recent advancements in diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have revolutionized image processing, demonstrating significant potential in medical applications. Accurate segmentation of the left ventricle (LV) in echocardiograms is crucial for diagnostic procedures and necessary treatments. However, ultrasound images are notoriously noisy with low contrast and ambiguous LV boundaries, thereby complicating the segmentation process. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Echo-DND, a novel dual-noise diffusion model specifically designed for this task. Echo-DND leverages a unique combination of Gaussian and Bernoulli noises. It also incorporates a multi-scale fusion conditioning module to improve segmentation precision. Furthermore, it utilizes spatial coherence calibration to maintain spatial integrity in segmentation masks. The model’s performance was rigorously validated on the CAMUS and EchoNet-Dynamic datasets. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing SOTA models. It achieves high Dice scores of 0.962 and 0.939 on these datasets, respectively. The proposed Echo-DND model establishes a new standard in echocardiogram segmentation, and its architecture holds promise for broader applicability in other medical imaging tasks, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy across various medical domains. Project page: https://abdur75648.github.io/Echo-DND
扩散概率模型(DPM)的最新进展在图像处理领域引起了革命性的变革,并在医疗应用中显示出巨大潜力。左心室(LV)在心超图上的精确分割对于诊断程序和必要治疗至关重要。然而,超声图像以噪声多、对比度低和左心室边界模糊而著称,使得分割过程复杂化。为了解决这些挑战,本文引入了Echo-DND,这是一种专门用于此任务的新型双噪声扩散模型。Echo-DND结合了高斯噪声和伯努利噪声的独特组合。它还采用多尺度融合条件模块来提高分割精度。此外,它利用空间一致性校准来保持分割掩膜的空间完整性。该模型在CAMUS和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上进行了严格验证。广泛评估表明,所提出的框架优于现有的最先进模型。它在这些数据集上分别取得了高达0.962和0.939的Dice得分。所提出的Echo-DND模型在心超图分割方面树立了新标准,其架构在其他医学影像任务中具有广泛的应用前景,有望在多个医疗领域提高诊断准确性。项目页面:https://abdur75648.github.io/Echo-DND
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Version of record published in Discover Applied Sciences (Springer Nature). The definitive article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-025-07055-5
Summary
扩散概率模型(DPM)的最新进展在图像处理领域引起了革命性的变化,并在医疗应用中显示出巨大潜力。针对超声图像噪声大、对比度低以及左心室(LV)边界模糊等问题,本文提出了一种名为Echo-DND的新型双噪声扩散模型。该模型结合了高斯噪声和伯努利噪声,并融入了多尺度融合条件模块以提高分割精度。此外,它还利用空间一致性校准来保持分割掩膜的空间完整性。在CAMUS和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上的严格验证表明,Echo-DND模型性能卓越,达到了高Dice分数,超过了现有最佳模型。该模型为心电图分割树立了新标准,其架构在其他医学成像任务中具有广泛的应用前景,有望提高不同医学领域的诊断准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散概率模型(DPM)在图像处理领域的最新进展为医疗应用提供了显著潜力。
- Echo-DND模型是一种新型双噪声扩散模型,专为处理超声图像而设计。
- Echo-DND模型结合了高斯噪声和伯努利噪声以提高分割效果。
- 多尺度融合条件模块和空间一致性校准技术被融入模型以提高分割精度和保持空间完整性。
- Echo-DND模型在CAMUS和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上的表现超越了现有最佳模型。
- Echo-DND模型达到高Dice分数,显示了其优秀性能。
点此查看论文截图

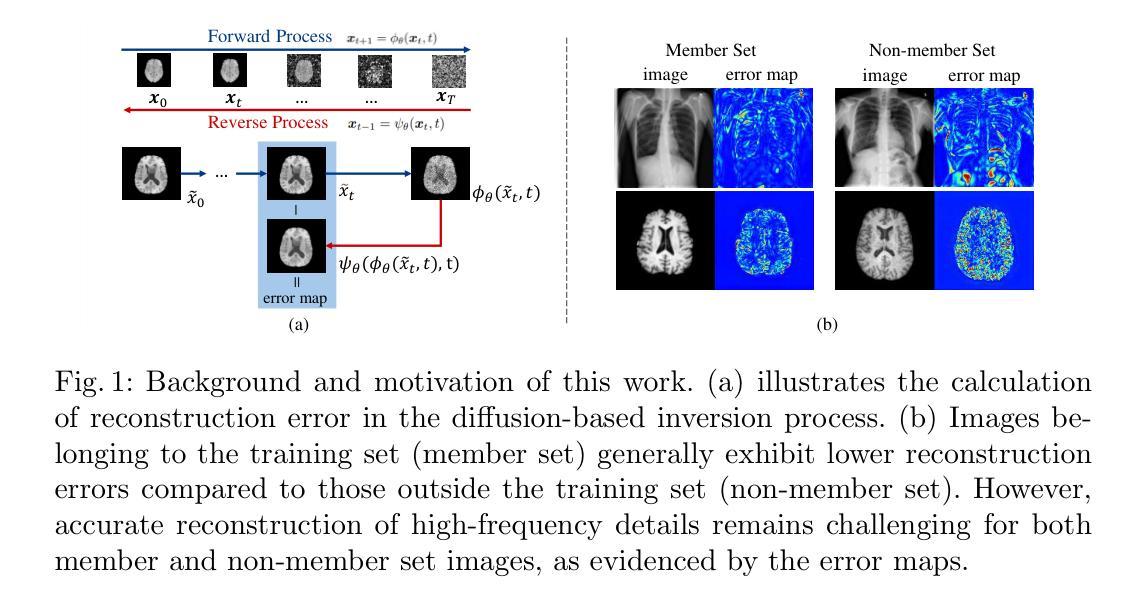
Frequency-Calibrated Membership Inference Attacks on Medical Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Xinkai Zhao, Yuta Tokuoka, Junichiro Iwasawa, Keita Oda
The increasing use of diffusion models for image generation, especially in sensitive areas like medical imaging, has raised significant privacy concerns. Membership Inference Attack (MIA) has emerged as a potential approach to determine if a specific image was used to train a diffusion model, thus quantifying privacy risks. Existing MIA methods often rely on diffusion reconstruction errors, where member images are expected to have lower reconstruction errors than non-member images. However, applying these methods directly to medical images faces challenges. Reconstruction error is influenced by inherent image difficulty, and diffusion models struggle with high-frequency detail reconstruction. To address these issues, we propose a Frequency-Calibrated Reconstruction Error (FCRE) method for MIAs on medical image diffusion models. By focusing on reconstruction errors within a specific mid-frequency range and excluding both high-frequency (difficult to reconstruct) and low-frequency (less informative) regions, our frequency-selective approach mitigates the confounding factor of inherent image difficulty. Specifically, we analyze the reverse diffusion process, obtain the mid-frequency reconstruction error, and compute the structural similarity index score between the reconstructed and original images. Membership is determined by comparing this score to a threshold. Experiments on several medical image datasets demonstrate that our FCRE method outperforms existing MIA methods.
随着扩散模型在图像生成领域的广泛应用,特别是在医学影像等敏感领域,隐私保护问题日益受到关注。成员推理攻击(MIA)作为一种可能的方法出现,用于确定特定图像是否用于训练扩散模型,从而量化隐私风险。现有的MIA方法通常依赖于扩散重建误差,其中成员图像的重建误差预计会低于非成员图像。然而,将这些方法直接应用于医学图像面临挑战。重建误差受图像本身难度的固有影响,扩散模型在高频细节重建方面存在困难。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种针对医学图像扩散模型的频率校准重建误差(FCRE)方法进行MIA。我们的方法专注于特定中频范围内的重建误差,排除了高频(难以重建)和低频(信息较少)区域,从而减轻了图像固有难度的干扰因素。具体来说,我们分析反向扩散过程,获取中频重建误差,并计算重建图像与原始图像之间的结构相似性指数分数。通过将此分数与阈值进行比较来确定成员身份。在多个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的FCRE方法优于现有的MIA方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成领域的应用日益普及,特别是在医学影像等敏感领域,引发了隐私方面的担忧。成员推理攻击(MIA)作为一种判断特定图像是否用于训练扩散模型的方法,可用于衡量隐私风险。然而,现有的MIA方法通常依赖于扩散重建误差,直接应用于医学图像面临挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对医学图像扩散模型的频率校准重建误差(FCRE)方法。通过关注特定中频范围内的重建误差,并排除高频(难以重建)和低频(信息较少)区域,我们的频率选择性方法减轻了图像固有难度的干扰因素。实验证明,我们的FCRE方法在多个医学图像数据集上的表现优于现有的MIA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成中的广泛应用,特别是在医学影像领域,引发了隐私方面的关注。
- 成员推理攻击(MIA)是判断特定图像是否用于训练扩散模型的方法,可用于衡量隐私风险。
- 现有MIA方法通常基于扩散重建误差,但直接应用于医学图像存在挑战。
- 重建误差受图像固有难度影响,扩散模型在高频细节重建方面存在困难。
- 提出了一种频率校准重建误差(FCRE)方法,专注于中频范围内的重建误差。
- FCRE方法通过排除高频和低频区域,减轻了图像固有难度的干扰。
点此查看论文截图

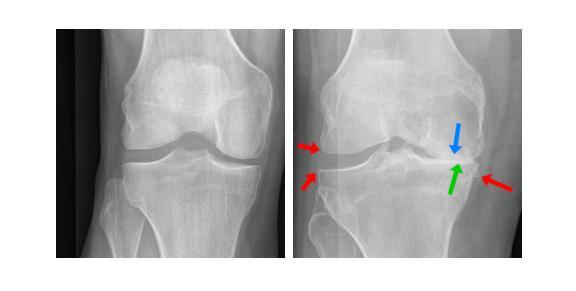
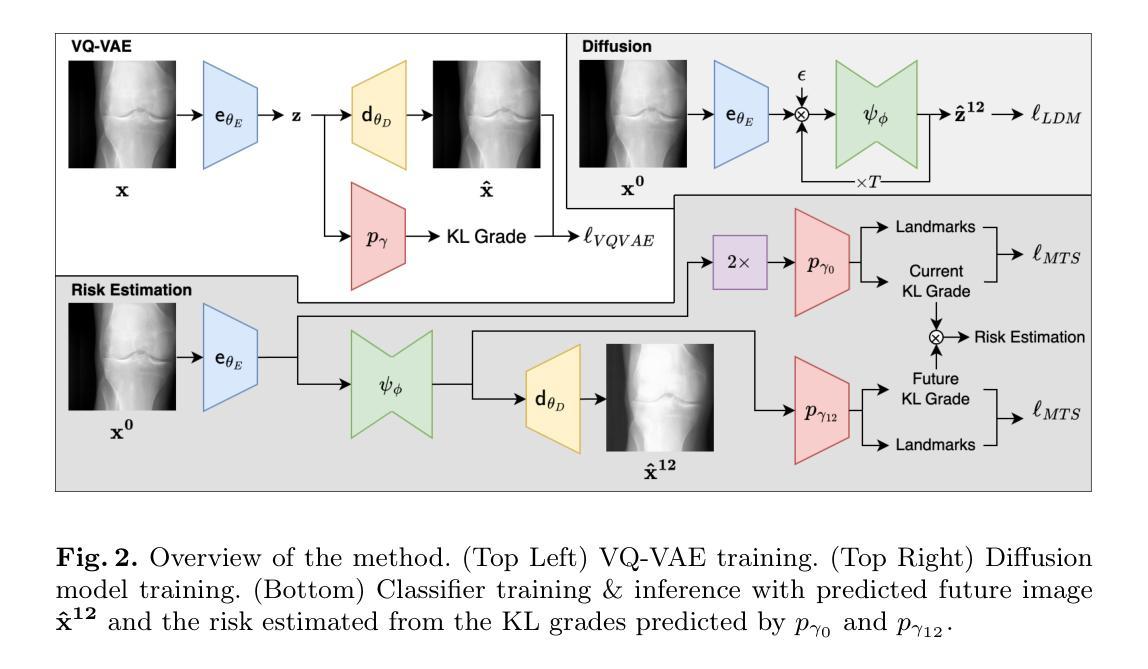
Risk Estimation of Knee Osteoarthritis Progression via Predictive Multi-task Modelling from Efficient Diffusion Model using X-ray Images
Authors:David Butler, Adrian Hilton, Gustavo Carneiro
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in assessing knee osteoarthritis (OA) risk by enabling early detection and disease monitoring. Recent machine learning methods have improved risk estimation (i.e., predicting the likelihood of disease progression) and predictive modelling (i.e., the forecasting of future outcomes based on current data) using medical images, but clinical adoption remains limited due to their lack of interpretability. Existing approaches that generate future images for risk estimation are complex and impractical. Additionally, previous methods fail to localize anatomical knee landmarks, limiting interpretability. We address these gaps with a new interpretable machine learning method to estimate the risk of knee OA progression via multi-task predictive modelling that classifies future knee OA severity and predicts anatomical knee landmarks from efficiently generated high-quality future images. Such image generation is achieved by leveraging a diffusion model in a class-conditioned latent space to forecast disease progression, offering a visual representation of how particular health conditions may evolve. Applied to the Osteoarthritis Initiative dataset, our approach improves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) by 2%, achieving an AUC of 0.71 in predicting knee OA progression while offering ~9% faster inference time.
医学影像在评估膝骨关节炎(OA)风险中起到关键作用,能够实现早期检测和疾病监测。最近的机器学习技术通过医学影像改善了风险预估(即预测疾病进展的可能性)和预测建模(即基于当前数据预测未来结果),但临床应用仍然有限,因为它们缺乏可解释性。现有的用于风险预估的未来图像生成方法既复杂又不实用。此外,以前的方法未能定位膝关节解剖地标,限制了可解释性。我们通过一种新的可解释的机器学习方法来弥补这些差距,通过多任务预测建模来估计膝骨关节炎进展的风险,该建模能够分类未来膝骨关节炎的严重程度,并从高效生成的高质量未来图像中预测膝关节解剖地标。这种图像生成是通过利用类别条件潜在空间中的扩散模型来预测疾病进展实现的,提供特定健康情况可能如何发展的视觉表示。应用于骨关节炎倡议数据集,我们的方法改进了当前最佳水平(SOTA),预测膝骨关节炎进展的AUC达到0.71,同时提供约9%更快的推理时间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医学成像在评估膝骨关节炎风险中的重要作用,以及机器学习在膝骨关节炎风险预测和预测建模方面的最新进展。然而,现有方法的复杂性和缺乏可解释性限制了其在临床的广泛应用。本文提出了一种新的可解释的机器学习方法来估计膝骨关节炎进展的风险,通过多任务预测建模,不仅分类未来膝骨关节炎的严重程度,还从高效生成的高质量未来图像中预测膝关节解剖标志。使用扩散模型在类别条件潜在空间内预测疾病进展,提供特定健康条件可能如何发展的视觉表示。应用于骨关节炎倡议数据集,该方法改进了当前最佳水平,预测膝骨关节炎进展的AUC达到0.71,同时提供约9%更快的推理时间。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像在评估膝骨关节炎风险中起关键作用,能够实现早期检测和疾病监测。
- 现有机器学习方法在膝骨关节炎风险预测和预测建模方面已有所改进,但缺乏可解释性限制了临床采用。
- 扩散模型被用于在类别条件潜在空间内生成高质量未来图像,以预测膝骨关节炎的进展。
- 新方法通过多任务预测建模,同时分类未来膝骨关节炎的严重程度并预测膝关节解剖标志。
- 与现有方法相比,新方法在预测膝骨关节炎进展方面提高了2%,达到AUC 0.71。
- 新方法提供了更快的推理时间,约为9%。
点此查看论文截图

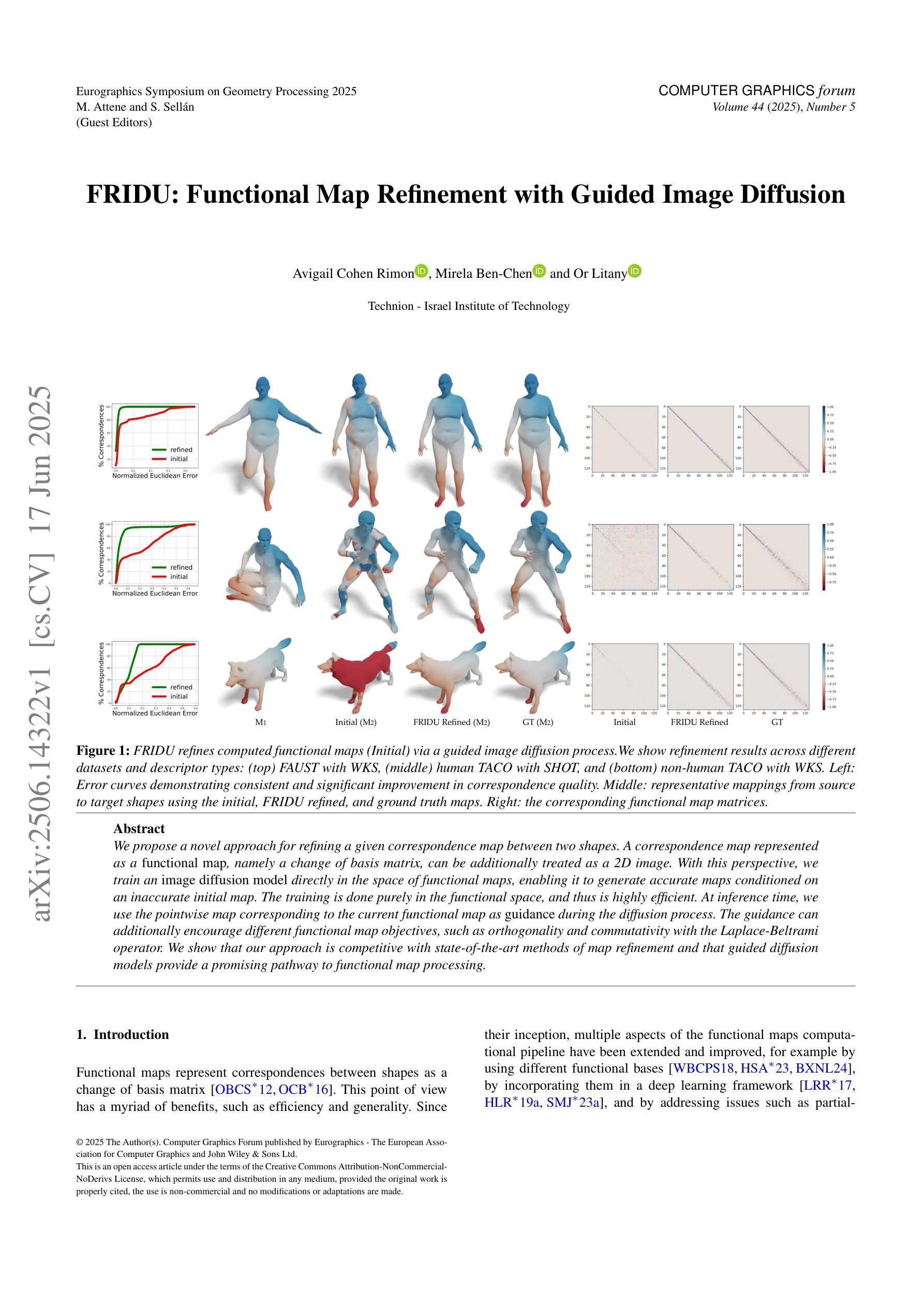
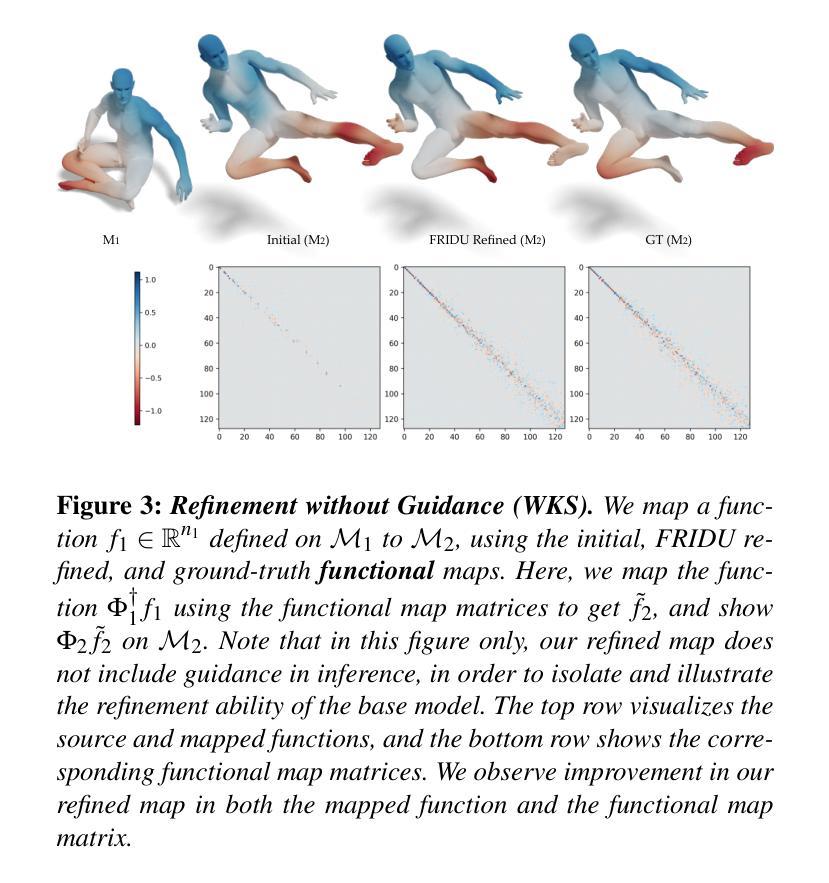
FRIDU: Functional Map Refinement with Guided Image Diffusion
Authors:Avigail Cohen Rimon, Mirela Ben-Chen, Or Litany
We propose a novel approach for refining a given correspondence map between two shapes. A correspondence map represented as a functional map, namely a change of basis matrix, can be additionally treated as a 2D image. With this perspective, we train an image diffusion model directly in the space of functional maps, enabling it to generate accurate maps conditioned on an inaccurate initial map. The training is done purely in the functional space, and thus is highly efficient. At inference time, we use the pointwise map corresponding to the current functional map as guidance during the diffusion process. The guidance can additionally encourage different functional map objectives, such as orthogonality and commutativity with the Laplace-Beltrami operator. We show that our approach is competitive with state-of-the-art methods of map refinement and that guided diffusion models provide a promising pathway to functional map processing.
我们提出了一种改进两个形状之间给定对应地图的新方法。作为功能图表示的对应地图,即基变换矩阵,可以另外作为二维图像处理。从这个角度出发,我们在功能图的空间中直接训练图像扩散模型,使其能够根据不准确的初始地图生成准确的地图。训练是在功能空间内完成的,因此效率很高。在推理阶段,我们使用对应于当前功能图的点对地图作为扩散过程中的指导。指导还可以鼓励不同的功能图目标,如与Laplace-Beltrami算子的正交性和可交换性。我们证明了我们的方法与最先进的地图优化方法具有竞争力,并且引导扩散模型为功能图处理提供了有前景的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to SGP 2025 (Symposium on Geometry Processing)
Summary
提出了一种新型的方法对两个形状之间的对应地图进行细化。将作为功能图的对应地图视为二维图像,并直接在功能图空间中训练图像扩散模型,从而生成基于不准确初始地图的准确地图。这种训练方法非常高效,并且通过使用当前的点对点映射作为扩散过程的指导来实现不同的功能映射目标。展示该方案在地图细化方面的竞争力,并表明引导扩散模型为功能图处理提供了有前途的路径。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的方法用于改进两个形状之间的对应地图。
- 将对应地图视为二维图像进行处理。
- 在功能图空间中直接训练图像扩散模型,以生成基于不准确初始地图的准确地图。
- 训练方法高度高效,直接在功能空间中进行。
- 使用点对点映射作为扩散过程的指导。
- 可以实现不同的功能映射目标,如正交性和与Laplace-Beltrami算子的可交换性。
点此查看论文截图
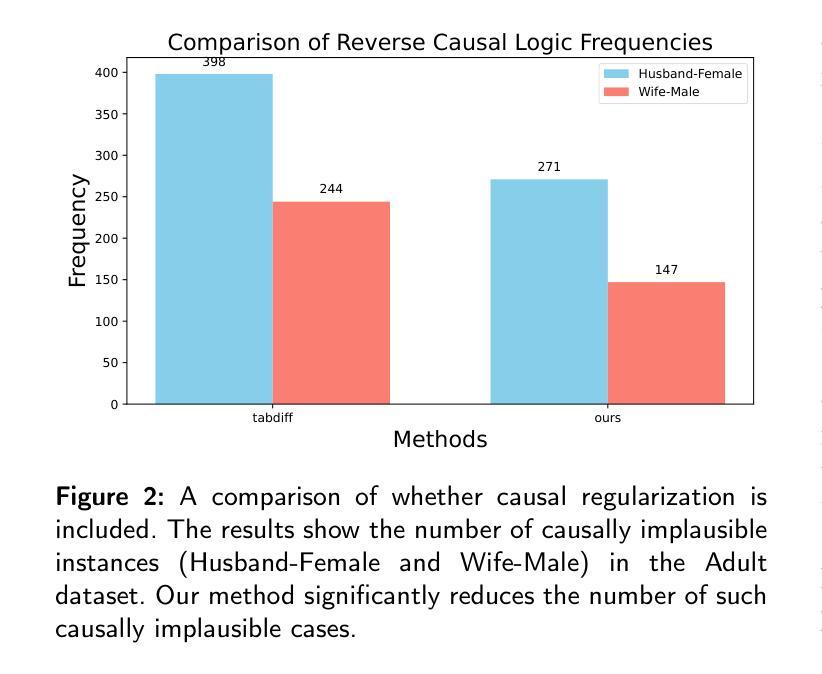
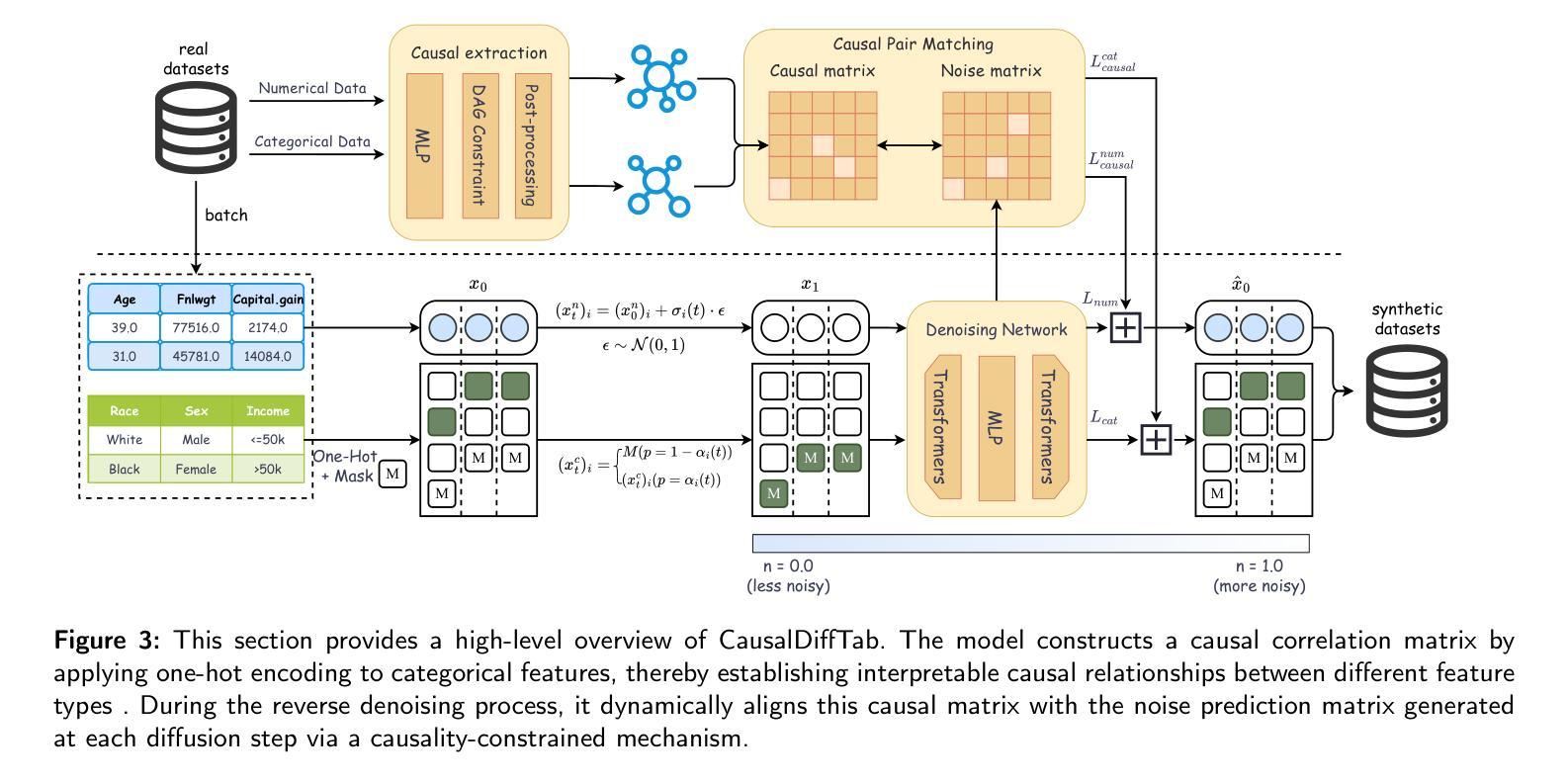
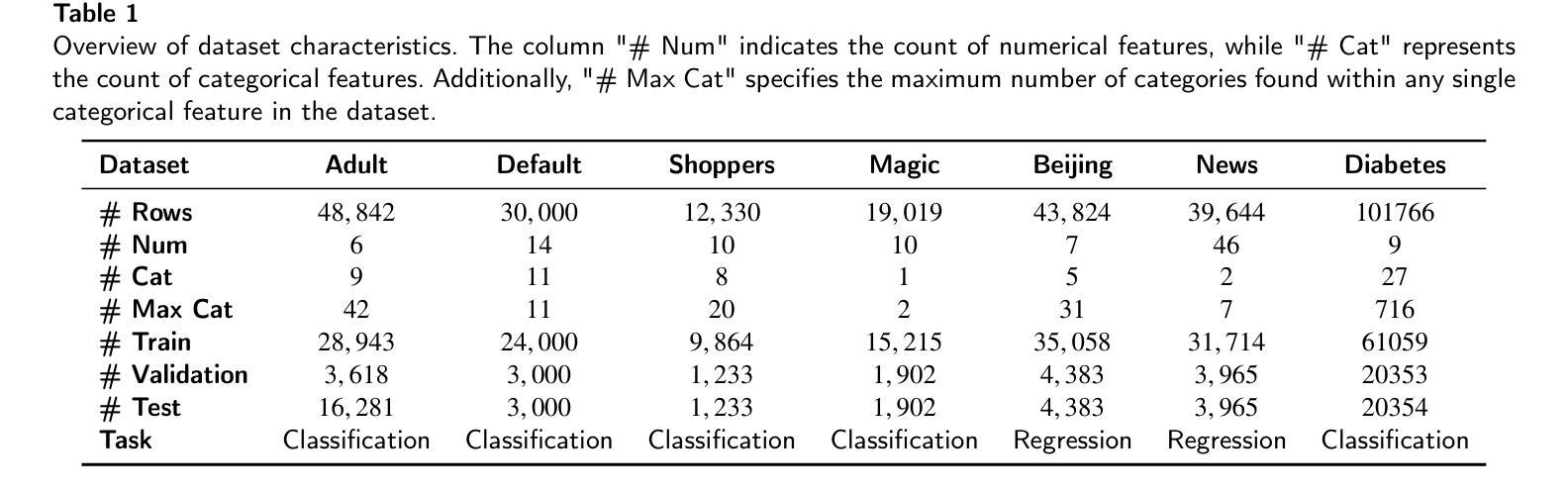
CausalDiffTab: Mixed-Type Causal-Aware Diffusion for Tabular Data Generation
Authors:Jia-Chen Zhang, Zheng Zhou, Yu-Jie Xiong, Chun-Ming Xia, Fei Dai
Training data has been proven to be one of the most critical components in training generative AI. However, obtaining high-quality data remains challenging, with data privacy issues presenting a significant hurdle. To address the need for high-quality data. Synthesize data has emerged as a mainstream solution, demonstrating impressive performance in areas such as images, audio, and video. Generating mixed-type data, especially high-quality tabular data, still faces significant challenges. These primarily include its inherent heterogeneous data types, complex inter-variable relationships, and intricate column-wise distributions. In this paper, we introduce CausalDiffTab, a diffusion model-based generative model specifically designed to handle mixed tabular data containing both numerical and categorical features, while being more flexible in capturing complex interactions among variables. We further propose a hybrid adaptive causal regularization method based on the principle of Hierarchical Prior Fusion. This approach adaptively controls the weight of causal regularization, enhancing the model’s performance without compromising its generative capabilities. Comprehensive experiments conducted on seven datasets demonstrate that CausalDiffTab outperforms baseline methods across all metrics. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/Godz-z/CausalDiffTab.
训练数据已被证明是训练生成式人工智能中最关键的部分之一。然而,获取高质量的数据仍然具有挑战性,数据隐私问题是其中的一大障碍。为了解决对高质量数据的需求,合成数据已成为主流解决方案,在图像、音频和视频等领域表现出了令人印象深刻的性能。生成混合类型的数据,尤其是高质量的表格数据,仍然面临重大挑战。这些挑战主要包括其固有的异质数据类型、复杂的变量间关系以及复杂的列级分布。在本文中,我们介绍了CausalDiffTab,这是一个基于扩散模型的生成模型,专门设计用于处理包含数值和类别特征的混合表格数据,同时能够更灵活地捕捉变量之间的复杂交互。我们进一步提出了一种基于分层先验融合原理的混合自适应因果正则化方法。该方法可以自适应地控制因果正则化的权重,在不损害模型生成能力的情况下提高模型的性能。在七个数据集上进行的综合实验表明,CausalDiffTab在所有指标上均优于基准方法。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/Godz-z/CausalDiffTab。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的生成模型CausalDiffTab,专门用于处理包含数值和分类特征的混合表格数据。该模型能够灵活捕捉变量间的复杂交互,并提出一种基于分层先验融合原理的混合自适应因果正则化方法,提高模型性能且不损失其生成能力。在七个数据集上的综合实验表明,CausalDiffTab在各项指标上均优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI的训练中,训练数据是至关重要的组成部分,但获取高质量数据具有挑战性,数据隐私问题是其中的主要障碍。
- 合成数据已成为解决高质量数据需求的主流解决方案,并在图像、音频和视频等领域表现出卓越性能。
- 生成混合类型数据,尤其是高质量表格数据,仍存在显著挑战,包括其内在异质数据类型、复杂的变量间关系以及精细的列级分布。
- CausalDiffTab是一种基于扩散模型的生成模型,专门设计用于处理包含数值和分类特征的混合表格数据。
- CausalDiffTab模型结合了一种混合自适应因果正则化方法,该方法基于分层先验融合原理,能自适应控制因果正则化的权重。
- 综合实验证明,CausalDiffTab在七个数据集上的性能优于其他基准方法。
- CausalDiffTab的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

ASMR: Augmenting Life Scenario using Large Generative Models for Robotic Action Reflection
Authors:Shang-Chi Tsai, Seiya Kawano, Angel Garcia Contreras, Koichiro Yoshino, Yun-Nung Chen
When designing robots to assist in everyday human activities, it is crucial to enhance user requests with visual cues from their surroundings for improved intent understanding. This process is defined as a multimodal classification task. However, gathering a large-scale dataset encompassing both visual and linguistic elements for model training is challenging and time-consuming. To address this issue, our paper introduces a novel framework focusing on data augmentation in robotic assistance scenarios, encompassing both dialogues and related environmental imagery. This approach involves leveraging a sophisticated large language model to simulate potential conversations and environmental contexts, followed by the use of a stable diffusion model to create images depicting these environments. The additionally generated data serves to refine the latest multimodal models, enabling them to more accurately determine appropriate actions in response to user interactions with the limited target data. Our experimental results, based on a dataset collected from real-world scenarios, demonstrate that our methodology significantly enhances the robot’s action selection capabilities, achieving the state-of-the-art performance.
在设计用于辅助人类日常活动的机器人时,通过增强用户的请求与周围环境的视觉线索来改善意图理解是非常关键的。这一过程被定义为多模态分类任务。然而,收集包含视觉和语言学元素的大规模数据集来进行模型训练是充满挑战且耗时的。为了解决这个问题,我们的论文引入了一个新型框架,专注于机器人辅助场景中的数据增强,涵盖对话和相关环境图像。该方法涉及利用复杂的大型语言模型来模拟潜在的对话和环境背景,随后使用稳定的扩散模型来创建描绘这些环境的图像。额外生成的数据用于优化最新的多模态模型,使其能够更准确地根据与用户有限目标数据的交互来确定适当的行动。我们基于从真实场景收集的数据集进行的实验结果表明,我们的方法显著提高了机器人的动作选择能力,达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IWSDS 2024 Best Paper Award
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型框架,用于在机器人辅助场景中通过数据扩充提高用户意图理解。框架利用大型语言模型模拟对话和环境上下文,再通过扩散模型创建相关环境图像。生成的数据用于优化最新的多模态模型,使其能更准确地根据用户交互数据选择适当行动。实验结果显示,该方法能显著提高机器人的动作选择能力,达到最新性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人辅助日常活动中,通过增强用户请求和环境视觉线索来提高意图理解是关键。
- 多模态分类任务涉及视觉和语言元素的结合。
- 收集大规模数据集用于机器人模型训练是挑战性和耗时的。
- 新型框架侧重于机器人辅助场景中的数据扩充。
- 利用大型语言模型模拟对话和环境上下文。
- 使用扩散模型创建相关环境图像。
点此查看论文截图


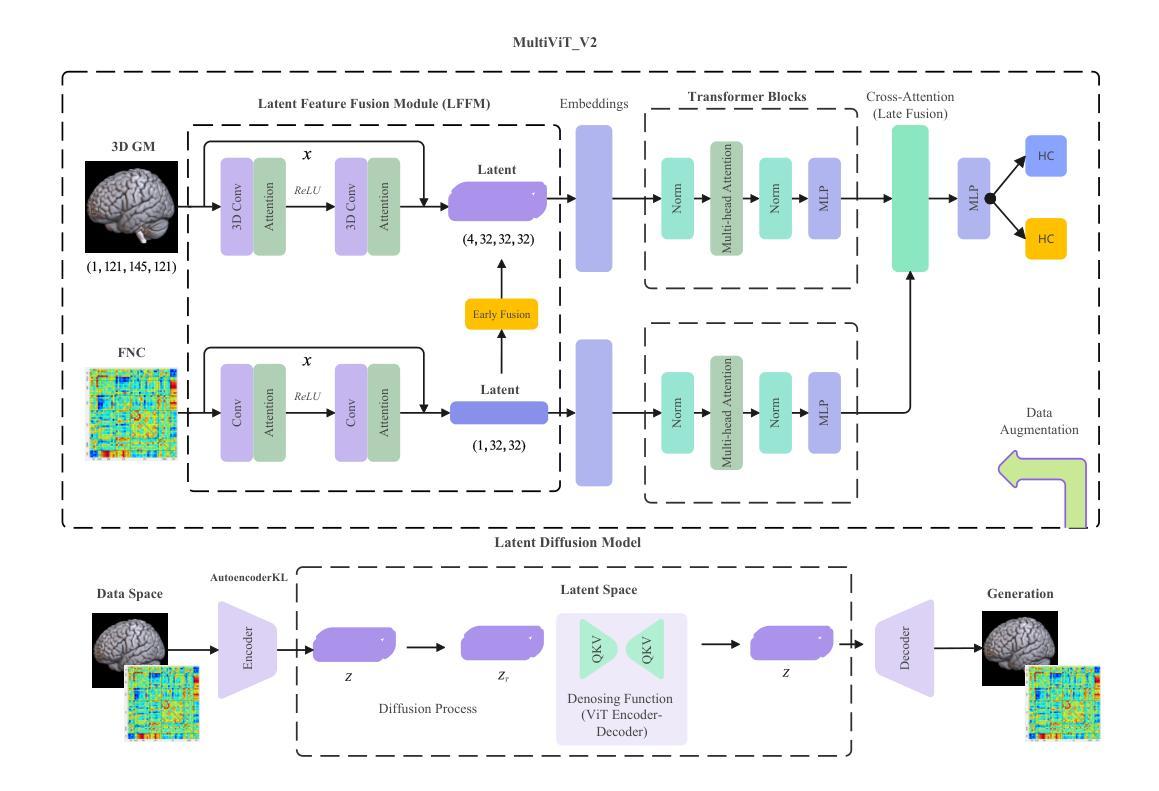
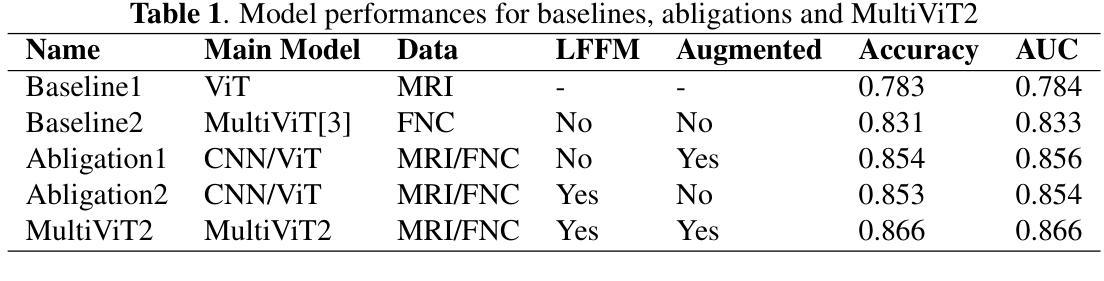
MultiViT2: A Data-augmented Multimodal Neuroimaging Prediction Framework via Latent Diffusion Model
Authors:Bi Yuda, Jia Sihan, Gao Yutong, Abrol Anees, Fu Zening, Calhoun Vince
Multimodal medical imaging integrates diverse data types, such as structural and functional neuroimaging, to provide complementary insights that enhance deep learning predictions and improve outcomes. This study focuses on a neuroimaging prediction framework based on both structural and functional neuroimaging data. We propose a next-generation prediction model, \textbf{MultiViT2}, which combines a pretrained representative learning base model with a vision transformer backbone for prediction output. Additionally, we developed a data augmentation module based on the latent diffusion model that enriches input data by generating augmented neuroimaging samples, thereby enhancing predictive performance through reduced overfitting and improved generalizability. We show that MultiViT2 significantly outperforms the first-generation model in schizophrenia classification accuracy and demonstrates strong scalability and portability.
多模态医学影像将不同类型的数据(如结构和功能神经成像)进行融合,提供互补的洞察,增强深度学习预测并改善结果。本研究重点关注基于结构和功能神经成像数据的神经影像预测框架。我们提出了一种下一代预测模型——MultiViT2,它将预训练的代表性学习基础模型与用于预测输出的视觉转换器主干相结合。此外,我们基于潜在扩散模型开发了一个数据增强模块,通过生成增强的神经成像样本丰富输入数据,从而减少过拟合现象,提高预测性能的可推广性。我们表明,MultiViT2在精神分裂症分类准确率上显著优于第一代模型,并展示了强大的可扩展性和可移植性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态医学影像在深度学习预测中的应用,通过结合结构性和功能性神经影像数据,提高了预测的准确性。研究提出了一种名为MultiViT2的下一代预测模型,该模型结合了预训练的代表性学习基础模型和视觉转换器后端进行预测。此外,研究还开发了一个基于潜在扩散模型的数据增强模块,通过生成增强的神经影像样本,提高了预测性能。实验结果显示,MultiViT2在精神分裂症分类准确率上显著优于第一代模型,并表现出强大的可扩展性和可移植性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学影像结合了多种数据类型,如结构性和功能性神经影像,以提高深度学习预测的准确性。
- 研究提出了一种新的预测模型MultiViT2,结合了预训练的基础模型和视觉转换器后端。
- MultiViT2模型在精神分裂症分类任务上表现出优异的性能,准确率高于第一代模型。
- 研究开发了一个基于潜在扩散模型的数据增强模块,通过生成增强的神经影像样本,增强了模型的预测性能。
- 数据增强模块有助于减少过拟合,提高模型的泛化能力。
- MultiViT2模型表现出强大的可扩展性和可移植性。
点此查看论文截图

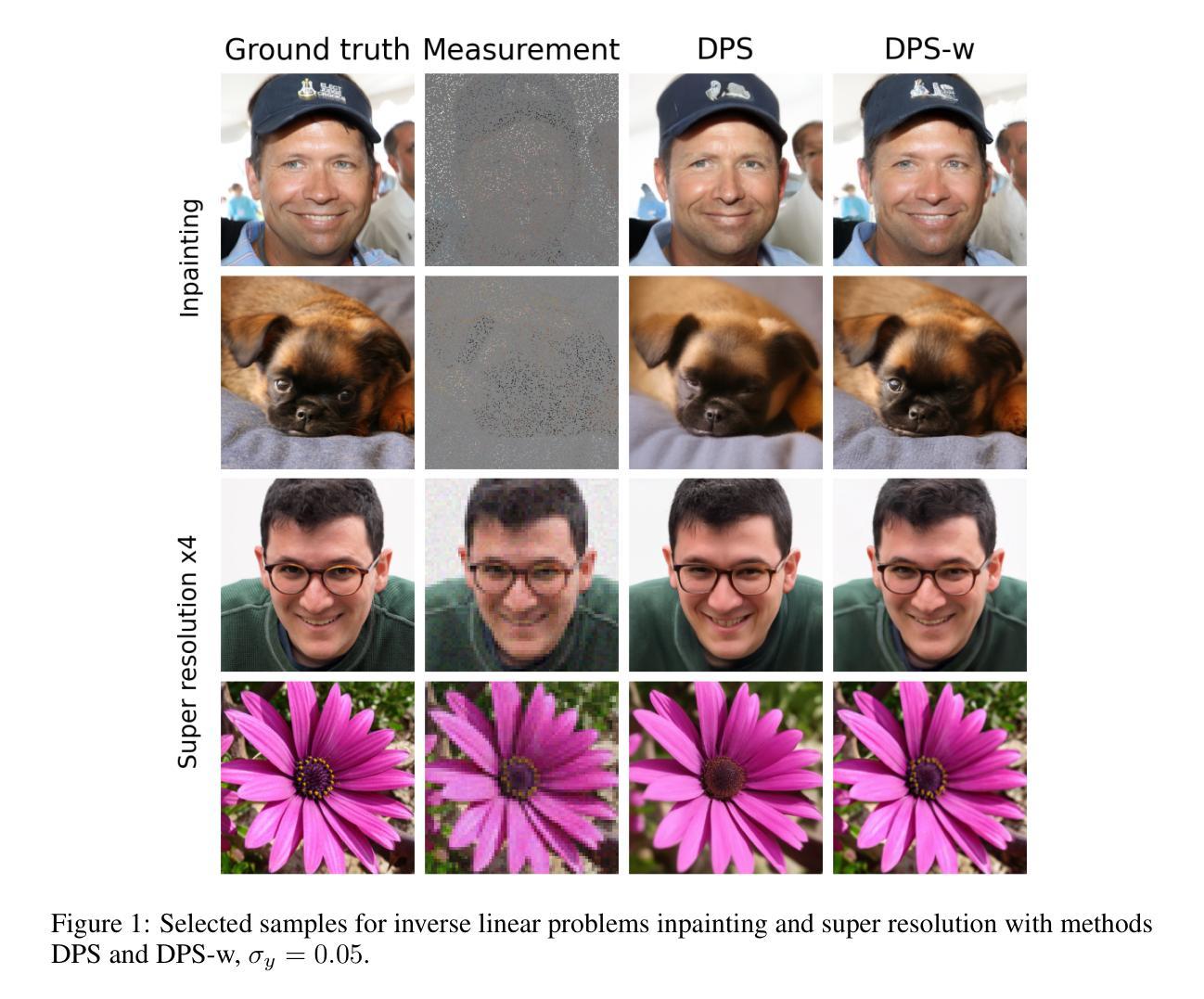
Exploiting the Exact Denoising Posterior Score in Training-Free Guidance of Diffusion Models
Authors:Gregory Bellchambers
The success of diffusion models has driven interest in performing conditional sampling via training-free guidance of the denoising process to solve image restoration and other inverse problems. A popular class of methods, based on Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS), attempts to approximate the intractable posterior score function directly. In this work, we present a novel expression for the exact posterior score for purely denoising tasks that is tractable in terms of the unconditional score function. We leverage this result to analyze the time-dependent error in the DPS score for denoising tasks and compute step sizes on the fly to minimize the error at each time step. We demonstrate that these step sizes are transferable to related inverse problems such as colorization, random inpainting, and super resolution. Despite its simplicity, this approach is competitive with state-of-the-art techniques and enables sampling with fewer time steps than DPS.
扩散模型的成功激发了通过去噪过程的非训练引导来进行条件采样的兴趣,以解决图像恢复和其他逆向问题。基于扩散后采样(DPS)的一类流行方法试图直接逼近难以处理的后验分数函数。在这项工作中,我们为纯去噪任务提出了精确后验分数的新表达式,该表达式在无条件分数函数方面是可行的。我们利用这一结果分析了去噪任务中DPS分数的时变误差,并计算了即时步骤大小,以最小化每个时间步长的误差。我们证明,这些步骤大小可以转移到相关的逆向问题,例如彩色化、随机填充和超分辨率。尽管其简单性,但这种方法与最先进的技术相竞争,并且能够在比DPS更少的时间步长内进行采样。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在图像修复和其他反问题中的条件采样的最新进展。提出了一种基于无条件评分函数精确计算后验评分的表达式,并据此分析了扩散后采样(DPS)在降噪任务中的时间相关误差。通过实时计算步长,以最小化每个时间步长的误差。此方法可应用于相关逆问题,如彩色化、随机补全和超分辨率等。该方法与最先进的技巧相比具有竞争力,且能够在较少的步骤中实现采样。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过训练之外的指导来实现条件采样,用于解决图像修复和其他反问题。
- 提出一种新表达后验评分的方式,专门针对纯降噪任务,并用无条件评分函数进行计算。
- 通过实时计算步长,优化了基于扩散后采样(DPS)的时间相关误差分析。
- 证明了这种方法对于降噪任务的时间步长设置的通用性,可以应用于颜色化、随机补全和超分辨率等任务。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法具有竞争力,能够在较少的步骤中实现采样。
- 此方法简化了扩散模型的训练过程,提高了其在图像修复领域的效率。
点此查看论文截图

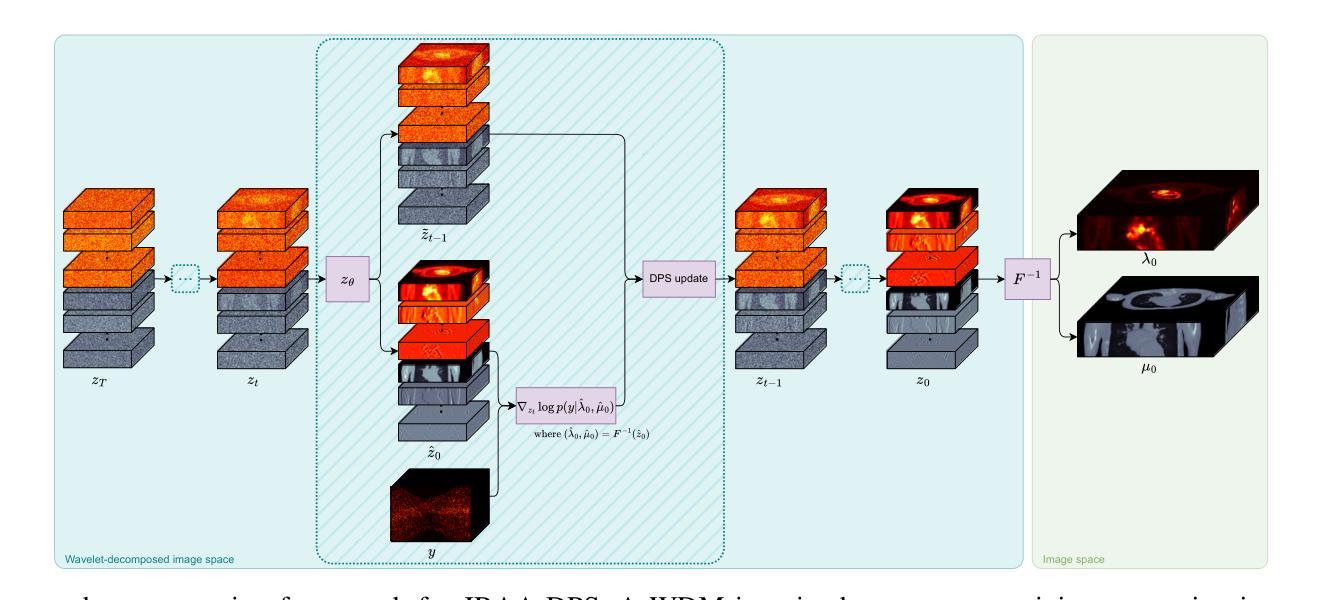
Joint Reconstruction of Activity and Attenuation in PET by Diffusion Posterior Sampling in Wavelet Coefficient Space
Authors:Clémentine Phung-Ngoc, Alexandre Bousse, Antoine De Paepe, Hong-Phuong Dang, Olivier Saut, Dimitris Visvikis
Attenuation correction (AC) is necessary for accurate activity quantification in positron emission tomography (PET). Conventional reconstruction methods typically rely on attenuation maps derived from a co-registered computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging scan. However, this additional scan may complicate the imaging workflow, introduce misalignment artifacts and increase radiation exposure. In this paper, we propose a joint reconstruction of activity and attenuation (JRAA) approach that eliminates the need for auxiliary anatomical imaging by relying solely on emission data. This framework combines wavelet diffusion model (WDM) and diffusion posterior sampling (DPS) to reconstruct fully three-dimensional (3-D) data. Experimental results show our method outperforms maximum likelihood activity and attenuation (MLAA) and MLAA with UNet-based post processing, and yields high-quality noise-free reconstructions across various count settings when time-of-flight (TOF) information is available. It is also able to reconstruct non-TOF data, although the reconstruction quality significantly degrades in low-count (LC) conditions, limiting its practical effectiveness in such settings. This approach represents a step towards stand-alone PET imaging by reducing the dependence on anatomical modalities while maintaining quantification accuracy, even in low-count scenarios when TOF information is available.
衰减校正(AC)在正电子发射断层扫描(PET)的准确活动量化中必不可少。传统重建方法通常依赖于从共注册的计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像扫描中得出的衰减图。然而,这种额外的扫描可能会使成像工作流程复杂化,引入错位伪影并增加辐射暴露。在本文中,我们提出了一种联合重建活动和衰减(JRAA)的方法,该方法仅依赖发射数据,消除了对辅助解剖成像的需求。该框架结合了小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS)来重建全三维(3-D)数据。实验结果表明,我们的方法在有时间飞行(TOF)信息可用的情况下,在多种计数设置下的性能优于最大可能性活动和衰减(MLAA)以及基于UNet的后处理的MLAA,并产生高质量的无噪声重建。虽然它也能重建非TOF数据,但在低计数(LC)条件下重建质量显著降低,这在实践中限制了其在这种设置中的有效性。这种方法朝着独立PET成像迈出了一步,通过减少对解剖模态的依赖,即使在时间飞行信息可用时低计数场景中也能保持量化准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文提出一种联合重建活动度和衰减(JRAA)的方法,该方法利用发射数据,无需辅助的解剖学成像。通过结合小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS),重建出全三维数据。实验表明,该方法在有时间飞行(TOF)信息的情况下,优于最大可能性活动度和衰减(MLAA)方法及其UNet后处理,能在各种计数设置下实现高质量的无噪声重建。尽管在低计数条件下,重建质量有所下降,但在有TOF信息的情况下仍具有实用价值。此方法是实现独立PET成像的重要一步,减少对解剖模式的依赖,同时保持量化准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 衰减校正(AC)在正电子发射断层扫描(PET)中的活动量化是必要的。
- 传统重建方法依赖于从共注册的计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像扫描得到的衰减图。
- 额外的扫描可能使成像工作流程复杂化,引入错位伪影并增加辐射暴露。
- 提出了一种联合重建活动度和衰减(JRAA)的方法,仅依赖发射数据,无需辅助的解剖学成像。
- JRAA方法结合了小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS),以重建全三维数据。
- 在有时间飞行(TOF)信息的情况下,JRAA方法优于其他方法,并在各种计数设置下实现高质量无噪声重建。
点此查看论文截图

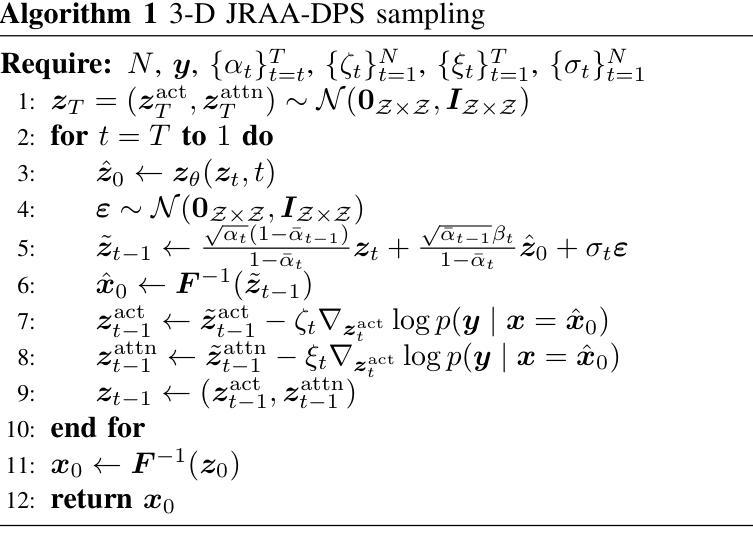
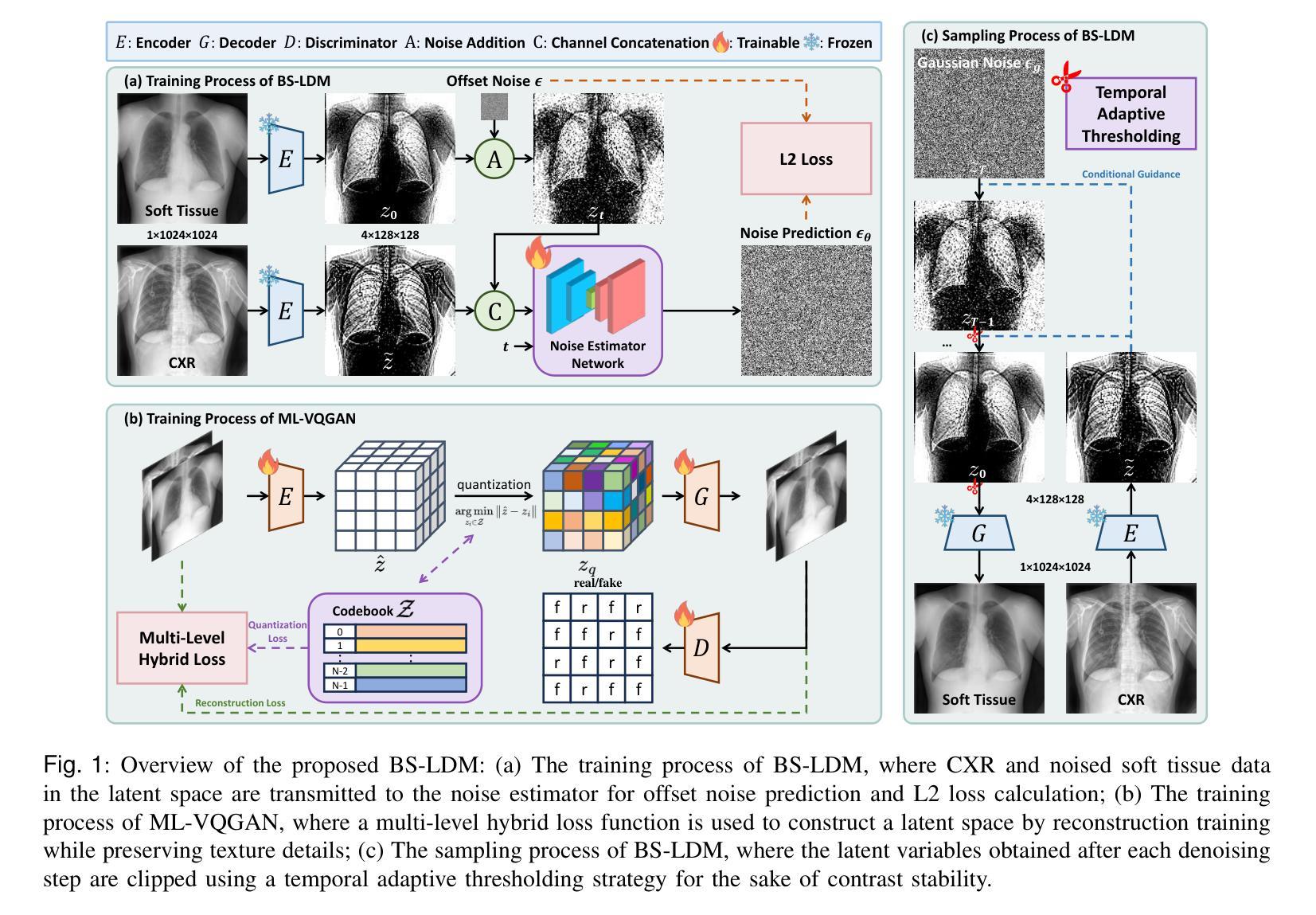
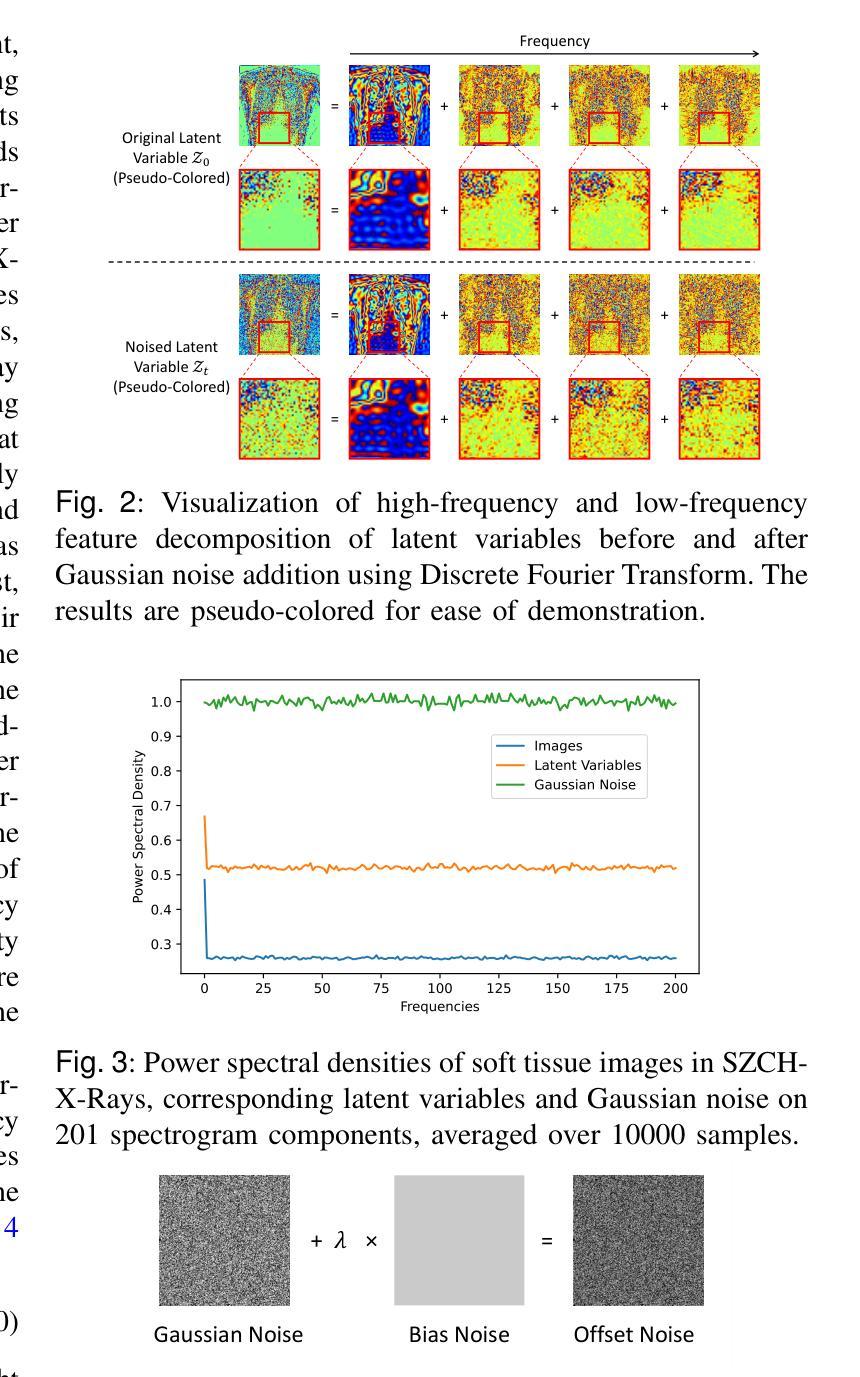
BS-LDM: Effective Bone Suppression in High-Resolution Chest X-Ray Images with Conditional Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Yifei Sun, Zhanghao Chen, Hao Zheng, Wenming Deng, Jin Liu, Wenwen Min, Ahmed Elazab, Xiang Wan, Changmiao Wang, Ruiquan Ge
Lung diseases represent a significant global health challenge, with Chest X-Ray (CXR) being a key diagnostic tool due to its accessibility and affordability. Nonetheless, the detection of pulmonary lesions is often hindered by overlapping bone structures in CXR images, leading to potential misdiagnoses. To address this issue, we develop an end-to-end framework called BS-LDM, designed to effectively suppress bone in high-resolution CXR images. This framework is based on conditional latent diffusion models and incorporates a multi-level hybrid loss-constrained vector-quantized generative adversarial network which is crafted for perceptual compression, ensuring the preservation of details. To further enhance the framework’s performance, we utilize offset noise in the forward process, and a temporal adaptive thresholding strategy in the reverse process. These additions help minimize discrepancies in generating low-frequency information of soft tissue images. Additionally, we have compiled a high-quality bone suppression dataset named SZCH-X-Rays. This dataset includes 818 pairs of high-resolution CXR and soft tissue images collected from our partner hospital. Moreover, we processed 241 data pairs from the JSRT dataset into negative images, which are more commonly used in clinical practice. Our comprehensive experiments and downstream evaluations reveal that BS-LDM excels in bone suppression, underscoring its clinical value. Our code is available at https://github.com/diaoquesang/BS-LDM.
肺部疾病是一个全球性的重大健康挑战,胸部X射线(CXR)因其可获取性和可负担性成为关键的诊断工具。然而,由于CXR图像中骨骼结构的重叠,肺部病变的检测常常受到阻碍,可能导致潜在误诊。为了解决这一问题,我们开发了一个端到端的框架,名为BS-LDM,旨在在高分辨率的CXR图像中有效地抑制骨骼。该框架基于条件潜在扩散模型,并融入了一个多层次混合损失约束向量量化生成对抗网络,该网络专为感知压缩而设计,可确保细节保留。为了进一步改善框架的性能,我们在前向过程中使用偏移噪声,并在后向过程中采用临时自适应阈值策略。这些补充有助于减少在生成软组织图像的低频信息时的差异。此外,我们编译了一个高质量的去骨数据集,名为SZCH-X射线。该数据集包含从我们的合作医院收集的818对高分辨率CXR和软组织图像。此外,我们将JSRT数据集中的241对数据对处理为阴性图像,这在临床实践中更为常见。我们的综合实验和下游评估显示,BS-LDM在骨骼抑制方面表现出色,突显了其临床价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/diaoquesang/BS-LDM上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures
摘要
开发了一种名为BS-LDM的端到端框架,用于在高清胸腔X光片(CXR)中有效抑制骨骼,以提高肺部病变检测的准确性。该框架基于条件潜在扩散模型,并融入多层次混合损失约束向量量化生成对抗网络,用于感知压缩并保留细节。采用前向过程偏移噪声和反向过程时间自适应阈值策略,减少软组织图像低频信息生成的差异。还编译了名为SZCH-X射线的高质量骨骼抑制数据集,包含来自合作医院的818对高清CXR和软组织图像。实验和下游评估显示BS-LDM在骨骼抑制方面表现出卓越性能,具有临床价值。代码公开可访问。
关键见解
- 胸腔X光(CXR)是肺部病变检测的关键工具,但由于骨骼结构的重叠,其检测受到阻碍。
- 开发了一个名为BS-LDM的端到端框架,旨在有效抑制高清CXR图像中的骨骼。
- BS-LDM基于条件潜在扩散模型和多层次混合损失约束向量量化生成对抗网络。
- BS-LDM采用前向过程的偏移噪声和反向过程的时间自适应阈值策略,以优化软组织图像的生成。
- 研究人员编译了一个名为SZCH-X射线的高质量数据集,用于训练和评估BS-LDM框架。
- BS-LDM在骨骼抑制方面表现出卓越性能,这通过综合实验和下游评估得到验证。
点此查看论文截图

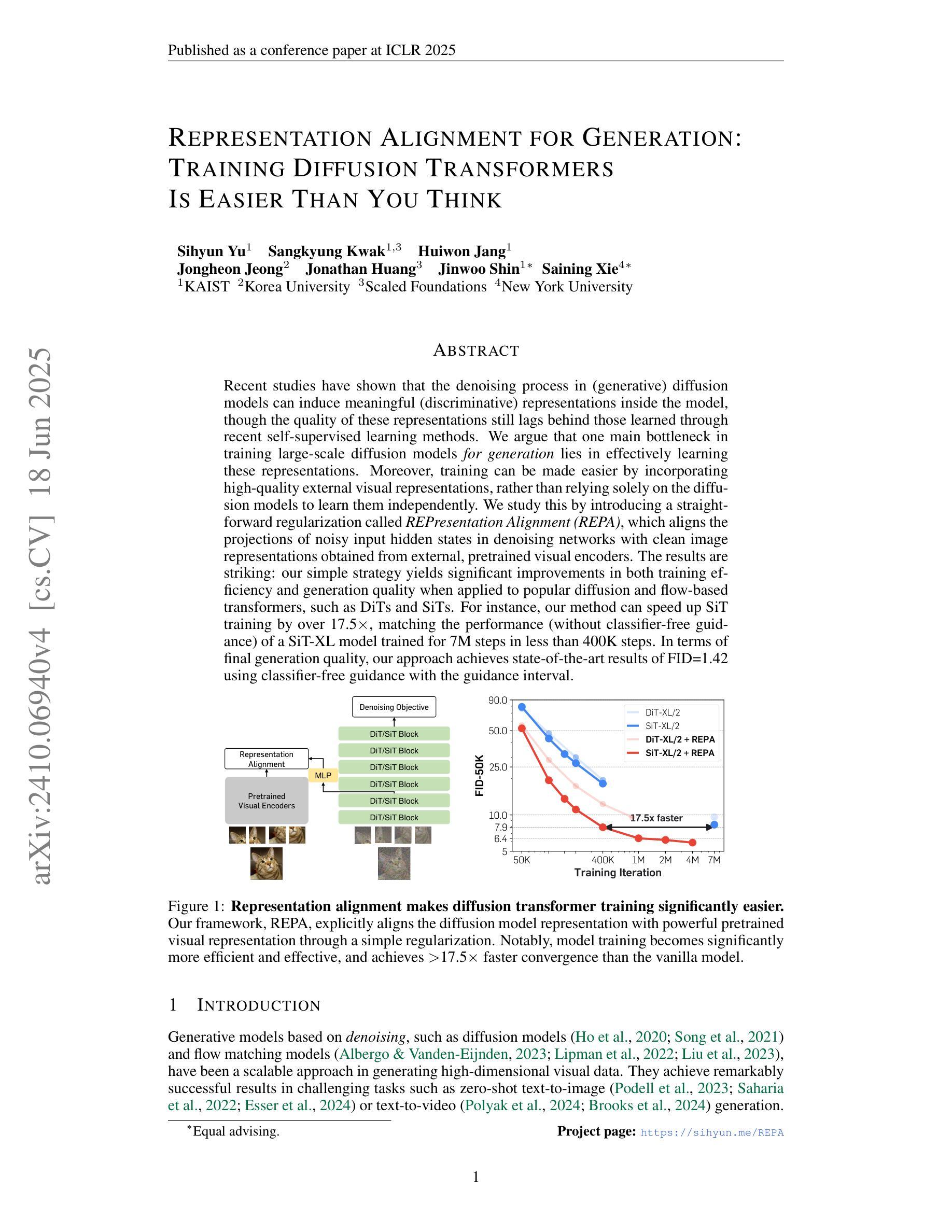
Representation Alignment for Generation: Training Diffusion Transformers Is Easier Than You Think
Authors:Sihyun Yu, Sangkyung Kwak, Huiwon Jang, Jongheon Jeong, Jonathan Huang, Jinwoo Shin, Saining Xie
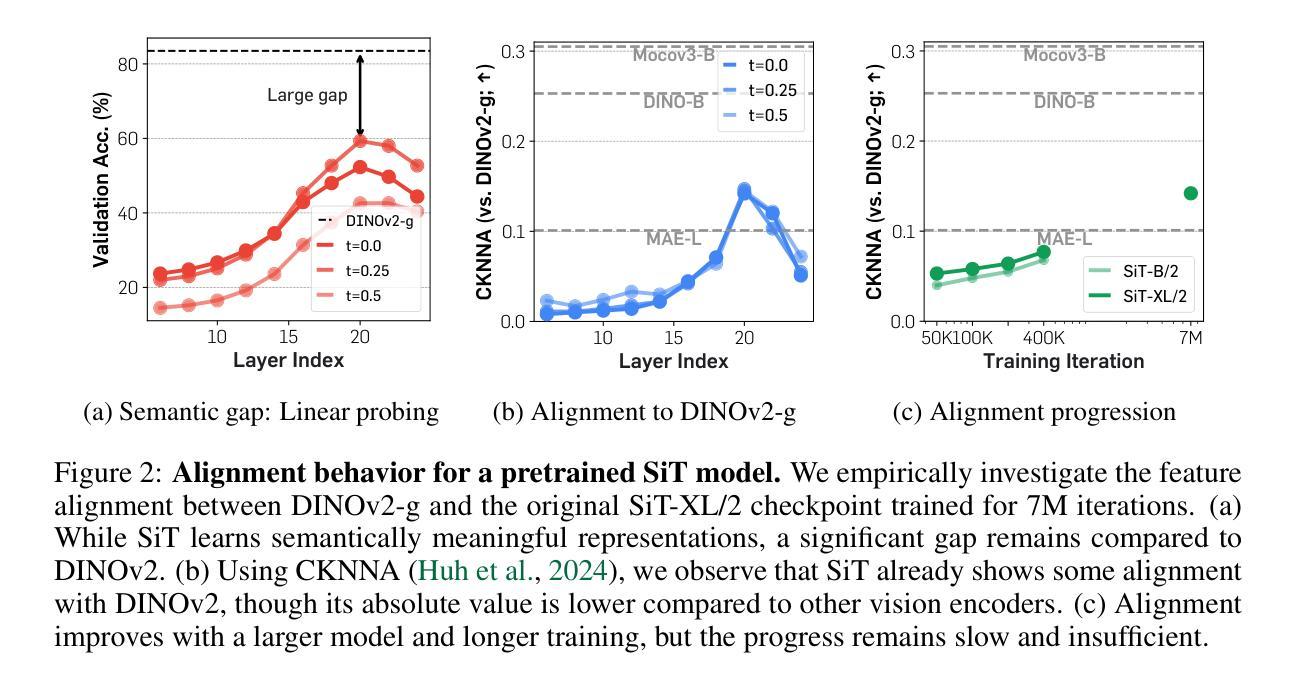
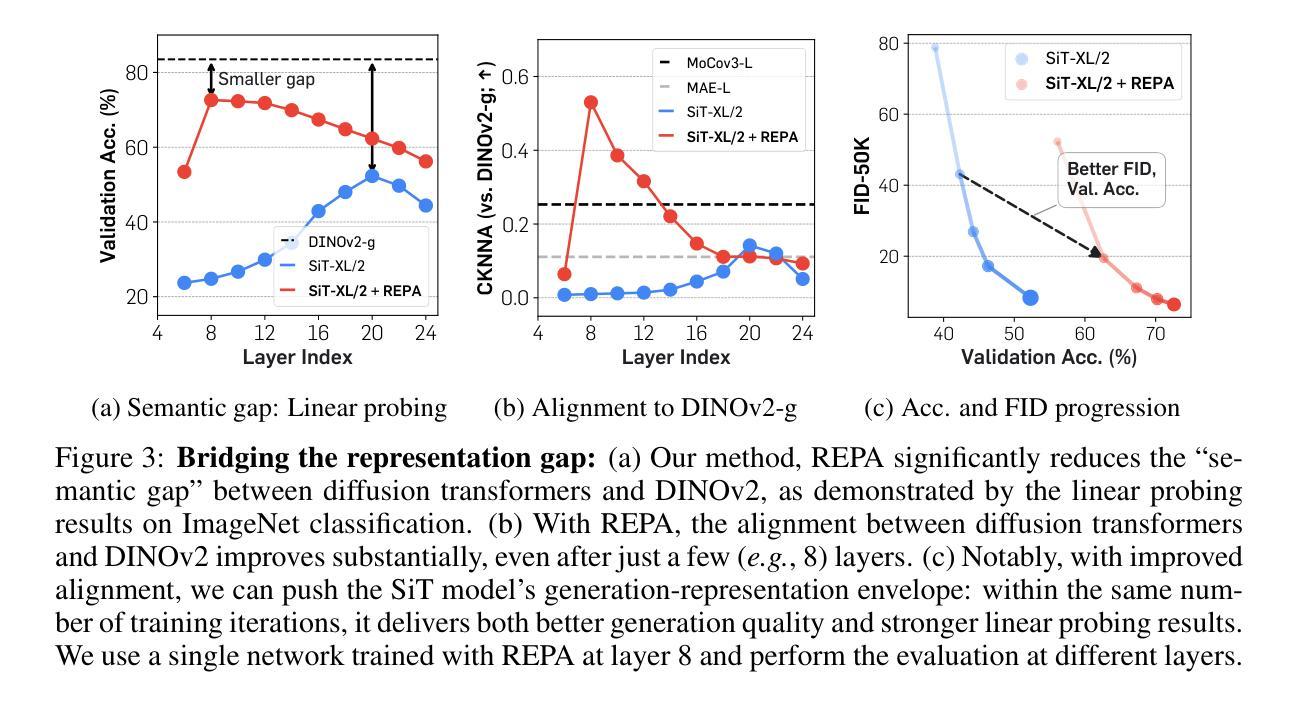
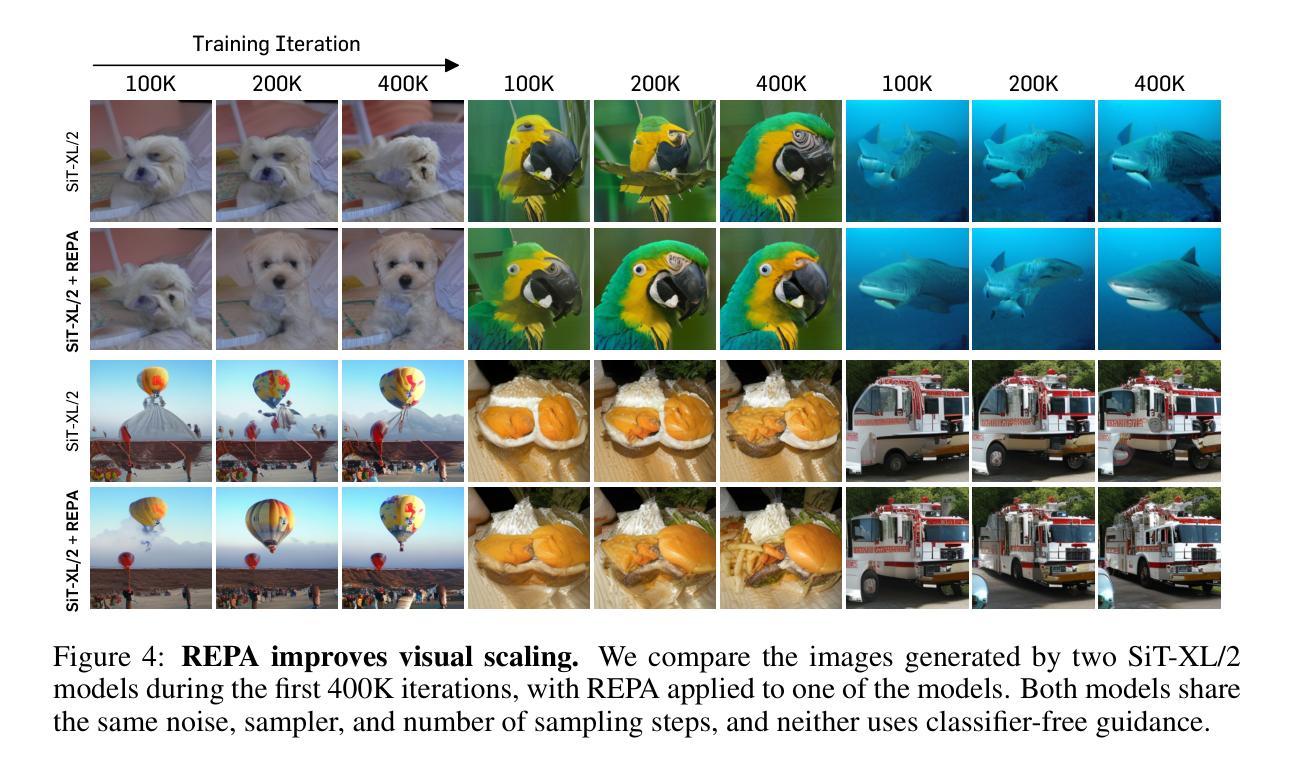
Recent studies have shown that the denoising process in (generative) diffusion models can induce meaningful (discriminative) representations inside the model, though the quality of these representations still lags behind those learned through recent self-supervised learning methods. We argue that one main bottleneck in training large-scale diffusion models for generation lies in effectively learning these representations. Moreover, training can be made easier by incorporating high-quality external visual representations, rather than relying solely on the diffusion models to learn them independently. We study this by introducing a straightforward regularization called REPresentation Alignment (REPA), which aligns the projections of noisy input hidden states in denoising networks with clean image representations obtained from external, pretrained visual encoders. The results are striking: our simple strategy yields significant improvements in both training efficiency and generation quality when applied to popular diffusion and flow-based transformers, such as DiTs and SiTs. For instance, our method can speed up SiT training by over 17.5$\times$, matching the performance (without classifier-free guidance) of a SiT-XL model trained for 7M steps in less than 400K steps. In terms of final generation quality, our approach achieves state-of-the-art results of FID=1.42 using classifier-free guidance with the guidance interval.
最近的研究表明,(生成式)扩散模型中的降噪过程可以在模型内部产生有意义的(判别式)表示,但这些表示的质量仍然落后于通过最近自监督学习方法得到的表示。我们认为,训练用于生成的大型扩散模型的主要瓶颈在于如何有效地学习这些表示。此外,通过融入高质量的外部视觉表示,而非仅依赖扩散模型独立学习,可以简化训练过程。我们通过引入一种名为REPresentation Alignment(REPA)的简单正则化方法进行研究,该方法将去噪网络中噪声输入隐藏状态的投影与从外部预训练视觉编码器获得的干净图像表示进行对齐。结果令人印象深刻:当应用于流行的扩散和基于流的变压器(如DiTs和SiTs)时,我们简单的策略在训练效率和生成质量方面都带来了显着改进。例如,我们的方法可以将SiT训练速度提高17.5倍以上,在不到40万步内达到与7百万步训练的SiT-XL模型(无需分类器引导)相匹配的性能。在最终的生成质量方面,我们的方法在使用无分类器引导的指导下间隔取得了最先进的成果,FID=1.42。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 (Oral). Project page: https://sihyun.me/REPA
Summary
近期研究表明,去噪扩散模型在去噪过程中可以形成有意义的表示,但相较于通过自监督学习方法获得的表示质量仍有所不足。文章指出,训练大型生成扩散模型的主要瓶颈在于如何有效学习这些表示。通过引入高质量的外部视觉表示,可以提高训练效率并改善生成质量。文章提出了一种名为REPA(REPresentation Alignment)的简单正则化方法,该方法将去噪网络中噪声输入隐藏状态的投影与外部预训练视觉编码器获得的干净图像表示对齐。实验结果显示,该方法在提高训练效率和生成质量方面效果显著,对于流行的扩散模型和基于流的转换器,如DiTs和SiTs,使用该方法可以加速训练,并达到最先进的生成质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在去噪过程中能形成有意义的表示,但质量有待提高。
- 训练大型生成扩散模型的主要瓶颈在于有效学习这些表示。
- 通过引入外部视觉表示,可以提高训练效率并改善生成质量。
- 提出了一种名为REPA的正则化方法,该方法通过对齐噪声输入和干净图像表示来提高扩散模型的性能。
- REPA方法显著提高了训练效率,例如将SiT训练速度提高17.5倍。
- REPA方法达到了先进的生成质量,使用分类器免费指导的FID为1.42。
点此查看论文截图
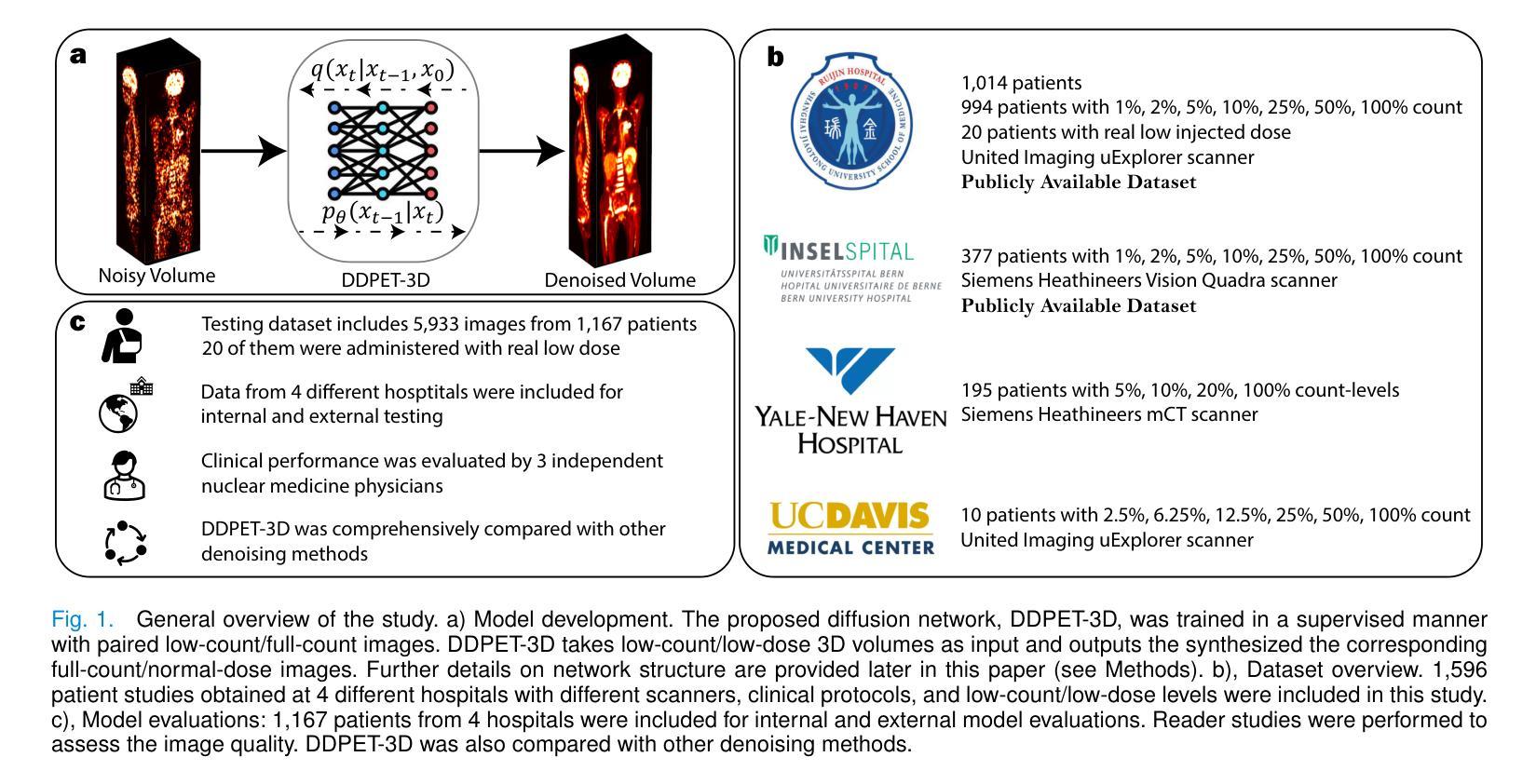
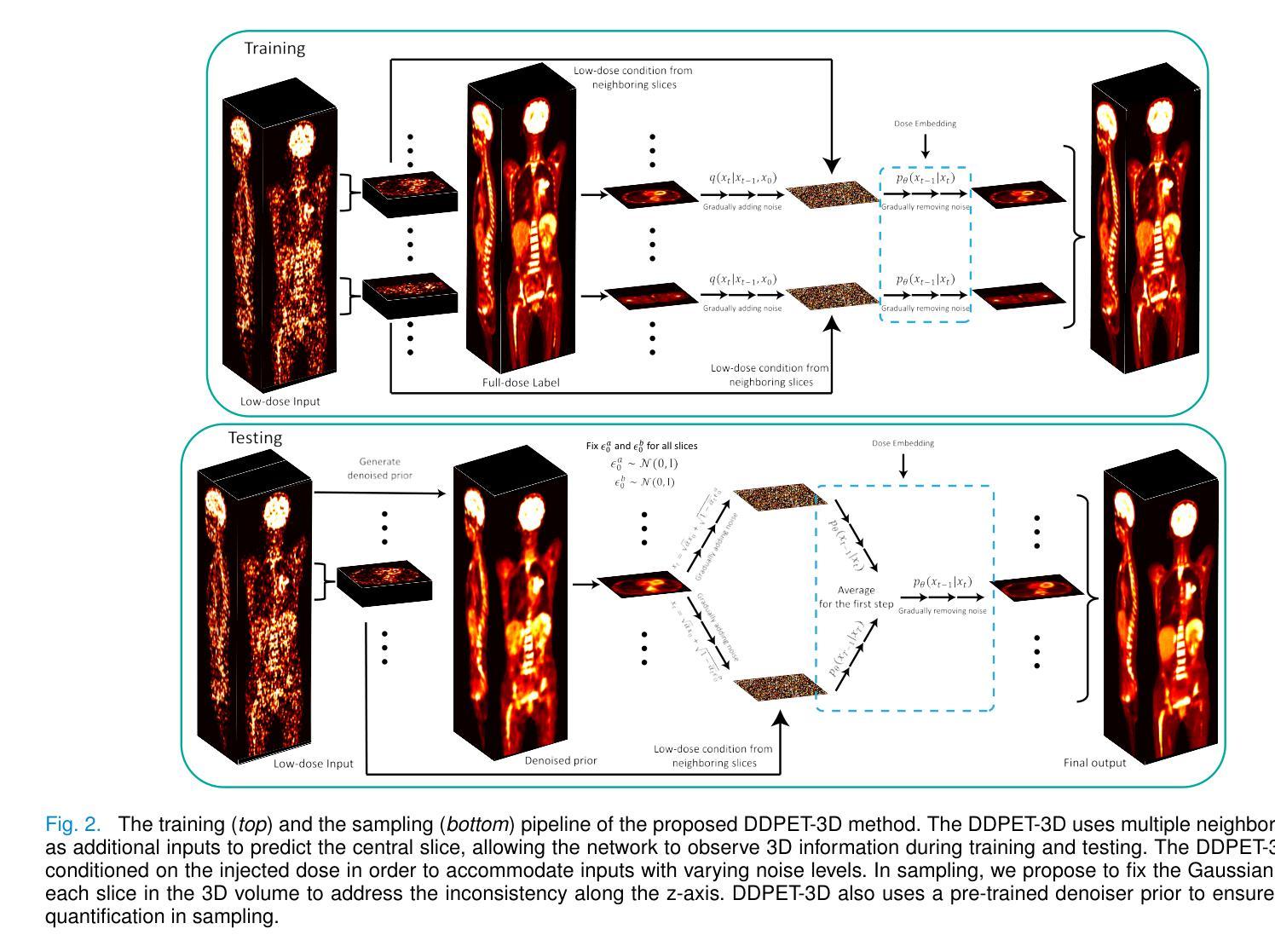
Dose-aware Diffusion Model for 3D PET Image Denoising: Multi-institutional Validation with Reader Study and Real Low-dose Data
Authors:Huidong Xie, Weijie Gan, Reimund Bayerlein, Bo Zhou, Ming-Kai Chen, Michal Kulon, Annemarie Boustani, Kuan-Yin Ko, Der-Shiun Wang, Benjamin A. Spencer, Wei Ji, Xiongchao Chen, Qiong Liu, Xueqi Guo, Menghua Xia, Yinchi Zhou, Hui Liu, Liang Guo, Hongyu An, Ulugbek S. Kamilov, Hanzhong Wang, Biao Li, Axel Rominger, Kuangyu Shi, Ge Wang, Ramsey D. Badawi, Chi Liu
Reducing scan times, radiation dose, and enhancing image quality for lower-performance scanners, are critical in low-dose PET imaging. Deep learning techniques have been investigated for PET image denoising. However, existing models have often resulted in compromised image quality when achieving low-count/low-dose PET and have limited generalizability to different image noise-levels, acquisition protocols, and patient populations. Recently, diffusion models have emerged as the new state-of-the-art generative model to generate high-quality samples and have demonstrated strong potential for medical imaging tasks. However, for low-dose PET imaging, existing diffusion models failed to generate consistent 3D reconstructions, unable to generalize across varying noise-levels, often produced visually-appealing but distorted image details, and produced images with biased tracer uptake. Here, we develop DDPET-3D, a dose-aware diffusion model for 3D low-dose PET imaging to address these challenges. Collected from 4 medical centers globally with different scanners and clinical protocols, we evaluated the proposed model using a total of 9,783 18F-FDG studies with low-dose levels ranging from 1% to 50%. With a cross-center, cross-scanner validation, the proposed DDPET-3D demonstrated its potential to generalize to different low-dose levels, different scanners, and different clinical protocols. As confirmed with reader studies performed by board-certified nuclear medicine physicians, experienced readers judged the images to be similar or superior to the full-dose images and previous DL baselines based on qualitative visual impression. Lesion-level quantitative accuracy was evaluated using a Monte Carlo simulation study and a lesion segmentation network. The presented results show the potential to achieve low-dose PET while maintaining image quality. Real low-dose scans was also included for evaluation.
在低剂量PET成像中,减少扫描时间、辐射剂量并增强低性能扫描仪的图像质量至关重要。深度学习技术已被用于PET图像的降噪处理。然而,现有模型在达到低计数/低剂量PET时往往牺牲了图像质量,并且在应对不同图像噪声水平、采集协议和患者群体方面的通用性有限。最近,扩散模型作为新的最先进的生成模型出现,能够生成高质量样本,并已在医学成像任务中展现出强大潜力。然而,对于低剂量PET成像,现有扩散模型无法生成一致的3D重建图像,无法在不同噪声水平之间通用,经常产生视觉上吸引人但扭曲的图像细节,以及带有偏见示踪物摄取的图像。在这里,我们开发了DDPET-3D,这是一款针对3D低剂量PET成像的剂量感知扩散模型,以解决这些挑战。该模型是从全球4个医疗中心收集的,使用不同的扫描仪和临床协议。我们使用总共9,783例的18F-FDG研究评估了所提出模型,低剂量水平范围从1%到50%。通过跨中心、跨扫描仪验证,DDPET-3D模型显示了对不同低剂量水平、不同扫描仪和不同临床协议的通用性潜力。经核医学董事会认证医师进行的读者研究证实,经验丰富的读者认为图像与全剂量图像和之前的深度学习基准测试相似或更优秀,基于定性视觉印象。病变水平的定量准确性是通过蒙特卡洛模拟研究和病变分割网络进行评估的。所呈现的结果显示了在保持图像质量的同时实现低剂量PET的潜力。还包括真实的低剂量扫描用于评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 Pages, 16 Figures, 5 Tables. Paper under review. First-place Freek J. Beekman Young Investigator Award at SNMMI 2024. Code available after paper publication. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2311.04248
摘要
降低扫描时间、减少辐射剂量并提升图像质量对于性能较低的扫描仪来说至关重要,特别是在低剂量PET成像中。虽然深度学习技术已被研究用于PET图像去噪,但现有模型在实现低计数/低剂量PET时往往牺牲了图像质量,并且在应对不同图像噪声水平、采集协议和患者群体时其通用性有限。扩散模型作为最新最先进的生成模型,已展现出用于医学成像任务的巨大潜力。然而,对于低剂量PET成像,现有扩散模型难以生成一致的3D重建图像,无法在不同噪声水平上通用,且常产生视觉效果好但细节失真的图像,以及带有偏差的示踪物摄取图像。为解决这些挑战,我们开发了DDPET-3D,一种面向3D低剂量PET成像的剂量感知扩散模型。该模型使用了来自全球4个医疗中心的共计9,783个低剂量水平介于1%至50%的18F-FDG研究数据。经过跨中心、跨扫描仪验证,DDPET-3D显示出在不同低剂量水平、不同扫描仪和不同临床协议上的通用性。核医学专家进行的读者研究表明,经验丰富的读者认为图像与全剂量图像和之前的深度学习基准测试相似或更优越,基于定性视觉印象进行评价。病变水平的定量准确性通过蒙特卡洛模拟研究和病变分割网络进行评估。所呈现的结果展示了实现低剂量PET的同时保持图像质量的潜力。还包括真实低剂量扫描用于评估。
关键见解
- 低剂量PET成像中,降低扫描时间、辐射剂量和提升图像质量至关重要,特别是对于性能较低的扫描仪。
- 现有深度学习模型在低剂量PET成像中常牺牲图像质量,且缺乏对不同噪声水平、采集协议和患者群体的通用性。
- 扩散模型作为最新的生成模型,在医学成像任务中展现出巨大潜力。
- DDPET-3D模型是解决低剂量PET成像挑战的新方法,通过剂量感知扩散模型生成高质量图像。
- DDPET-3D模型在不同低剂量水平、不同扫描仪和不同临床协议上具有良好的通用性。
- 读者研究表明,DDPET-3D生成的图像在视觉印象上与全剂量图像相似或更优越。
点此查看论文截图