⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
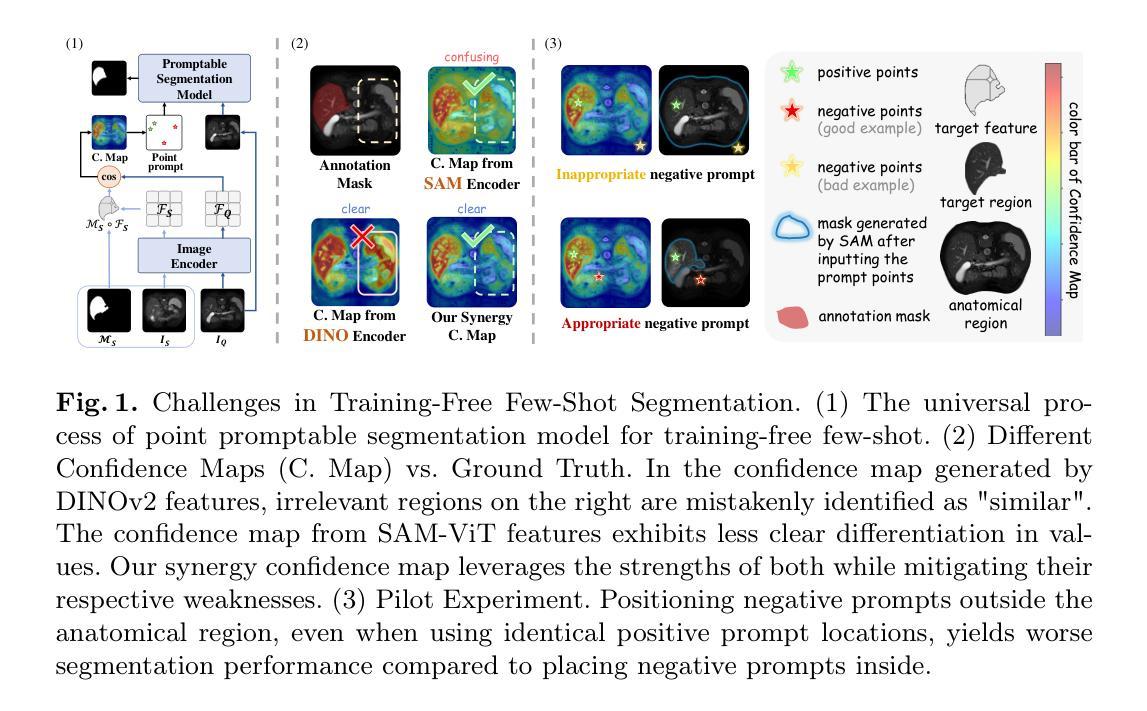
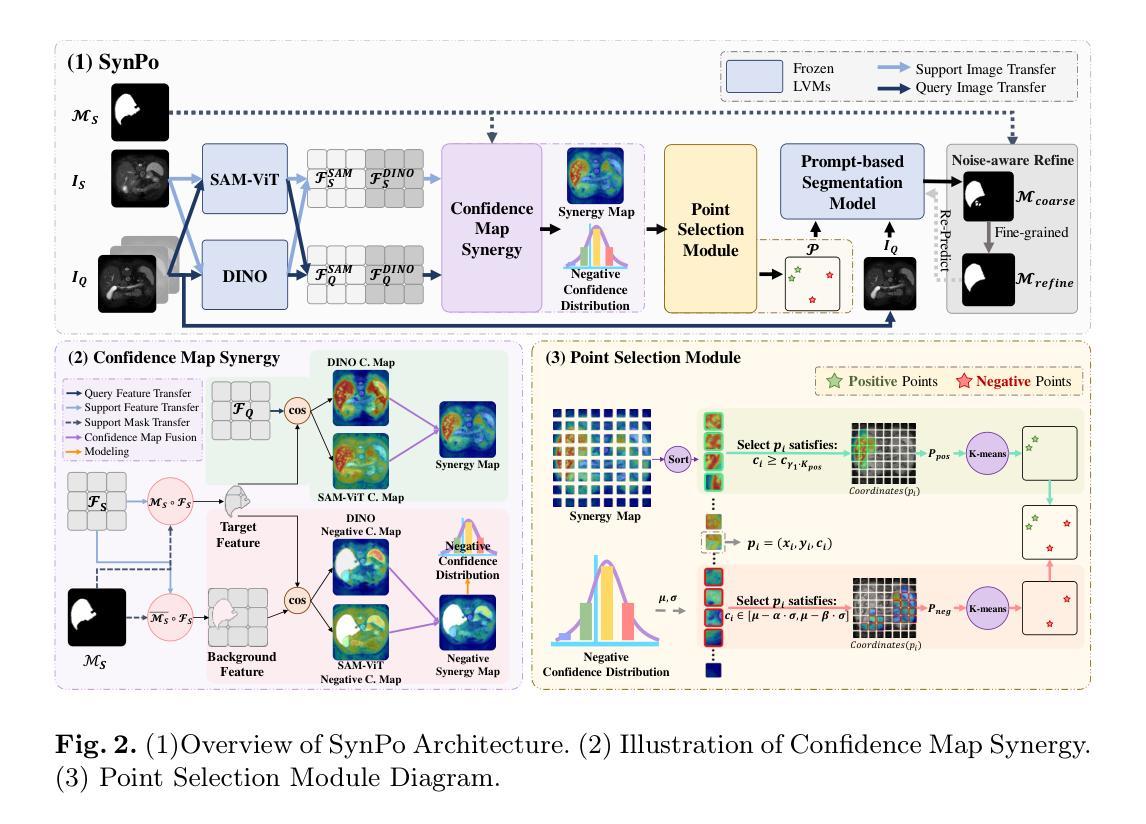
SynPo: Boosting Training-Free Few-Shot Medical Segmentation via High-Quality Negative Prompts
Authors:Yufei Liu, Haoke Xiao, Jiaxing Chai, Yongcun Zhang, Rong Wang, Zijie Meng, Zhiming Luo
The advent of Large Vision Models (LVMs) offers new opportunities for few-shot medical image segmentation. However, existing training-free methods based on LVMs fail to effectively utilize negative prompts, leading to poor performance on low-contrast medical images. To address this issue, we propose SynPo, a training-free few-shot method based on LVMs (e.g., SAM), with the core insight: improving the quality of negative prompts. To select point prompts in a more reliable confidence map, we design a novel Confidence Map Synergy Module by combining the strengths of DINOv2 and SAM. Based on the confidence map, we select the top-k pixels as the positive points set and choose the negative points set using a Gaussian distribution, followed by independent K-means clustering for both sets. Then, these selected points are leveraged as high-quality prompts for SAM to get the segmentation results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SynPo achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art training-based few-shot methods.
大型视觉模型(LVMs)的出现为少数医学图像分割提供了新的机会。然而,基于LVMs的无训练方法无法有效利用负提示,导致在低对比度医学图像上的性能不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SynPo,这是一种基于LVMs的无训练少数方法(例如SAM),其核心见解是提高负提示的质量。为了在更可靠的置信图上选择点提示,我们结合DINOv2和SAM的优点,设计了一种新颖的置信图协同模块。基于置信图,我们选择前k个像素作为正点集,使用高斯分布选择负点集,然后对这两个集合分别进行独立的K-均值聚类。然后,这些选定的点被用作高质量提示,用于SAM获得分割结果。大量实验表明,SynPo的性能与基于训练的最先进少数方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型视觉模型(LVMs)的无训练医学图像分割方法面临无法有效利用负提示的问题,导致在低对比度医学图像上的表现不佳。为解决此问题,本文提出了名为SynPo的无训练少样本方法,核心在于改进负提示的质量。通过结合DINOv2和SAM的优点,设计了一种新型置信图协同模块,用于更可靠地选择点提示。实验表明,SynPo的性能与基于训练的最先进少样本方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型(LVMs)在少样本医学图像分割上具有新机遇。
- 现有基于LVMs的无训练方法无法有效利用负提示。
- SynPo方法基于LVMs提出,核心在于改进负提示的质量。
- 设计了新型置信图协同模块,结合DINOv2和SAM的优点。
- 通过置信图选择正负点集,利用高斯分布和独立K-means聚类进行选择。
- 选定的点被用作高质量提示,用于SAM获得分割结果。
- 实验表明SynPo性能与基于训练的方法相当。
点此查看论文截图

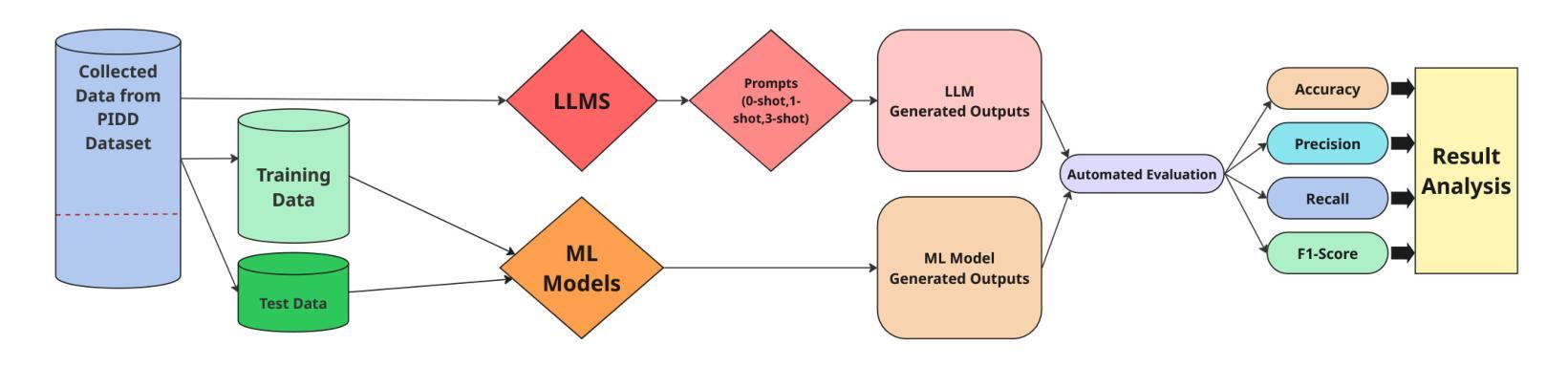
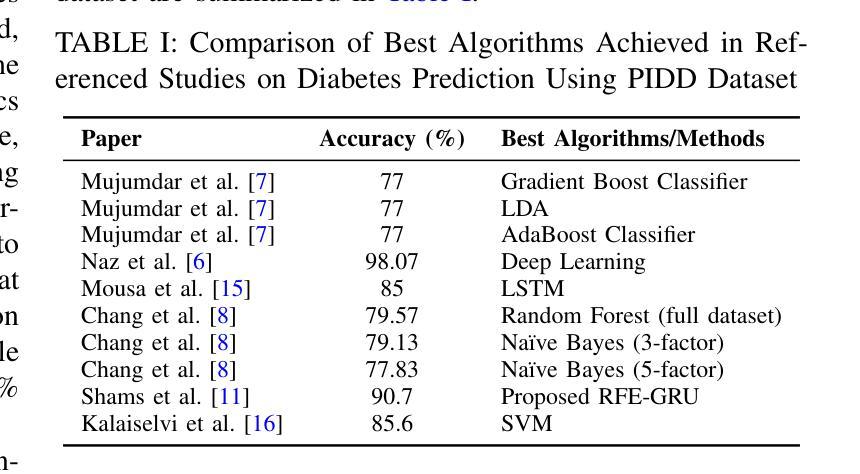
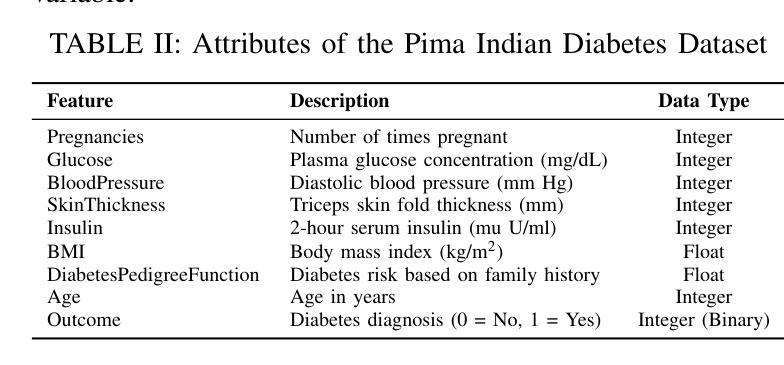
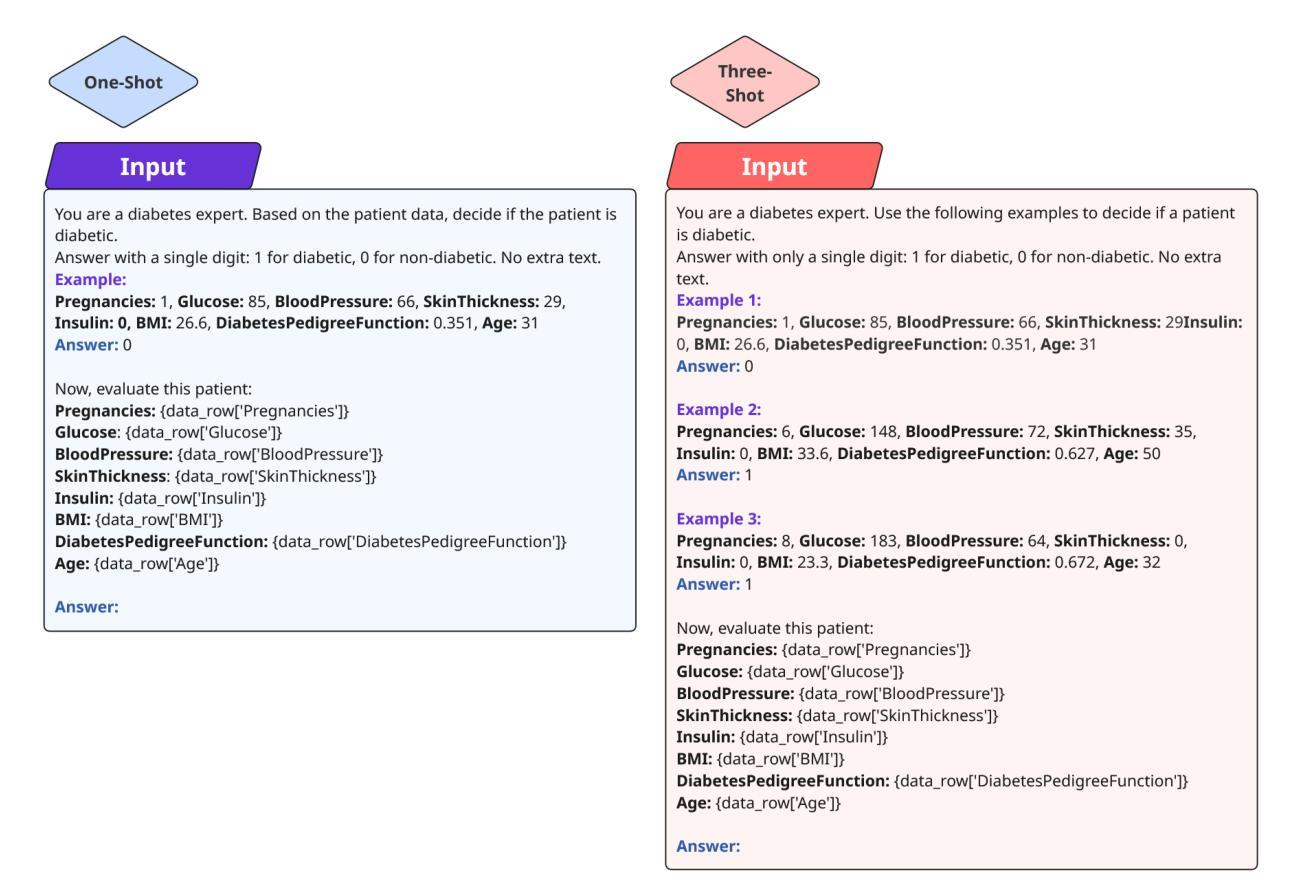
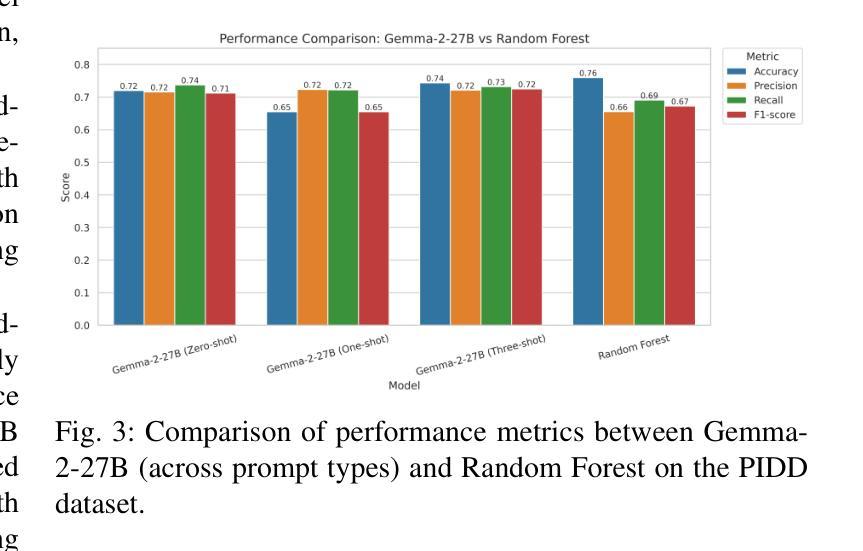
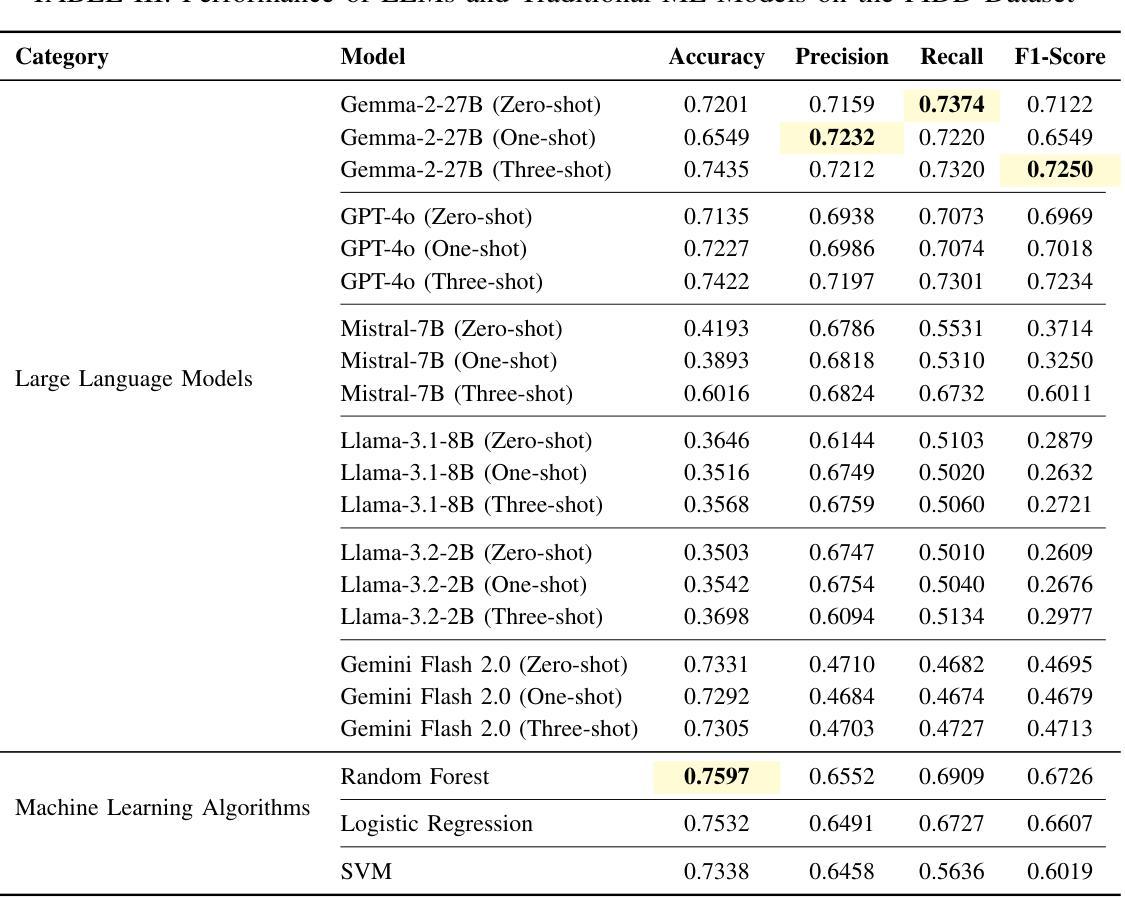
From Chat to Checkup: Can Large Language Models Assist in Diabetes Prediction?
Authors:Shadman Sakib, Oishy Fatema Akhand, Ajwad Abrar
While Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) models have been widely used for diabetes prediction, the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for structured numerical data is still not well explored. In this study, we test the effectiveness of LLMs in predicting diabetes using zero-shot, one-shot, and three-shot prompting methods. We conduct an empirical analysis using the Pima Indian Diabetes Database (PIDD). We evaluate six LLMs, including four open-source models: Gemma-2-27B, Mistral-7B, Llama-3.1-8B, and Llama-3.2-2B. We also test two proprietary models: GPT-4o and Gemini Flash 2.0. In addition, we compare their performance with three traditional machine learning models: Random Forest, Logistic Regression, and Support Vector Machine (SVM). We use accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score as evaluation metrics. Our results show that proprietary LLMs perform better than open-source ones, with GPT-4o and Gemma-2-27B achieving the highest accuracy in few-shot settings. Notably, Gemma-2-27B also outperforms the traditional ML models in terms of F1-score. However, there are still issues such as performance variation across prompting strategies and the need for domain-specific fine-tuning. This study shows that LLMs can be useful for medical prediction tasks and encourages future work on prompt engineering and hybrid approaches to improve healthcare predictions.
虽然机器学习和深度学习模型在糖尿病预测方面得到了广泛应用,但大型语言模型在处理结构化数值数据方面的应用尚未得到充分探索。在这项研究中,我们测试了大型语言模型在零样本、单样本和三样本提示方法下预测糖尿病的有效性。我们使用皮马印第安糖尿病数据库进行实证分析。我们评估了六种大型语言模型,包括四个开源模型:Gemma-2-27B、Mistral-7B、Llama-3.1-8B和Llama-3.2-2B。我们还测试了两个专有模型:GPT-4o和Gemini Flash 2.0。此外,我们将它们的性能与三种传统机器学习模型进行比较:随机森林、逻辑回归和支持向量机(SVM)。我们使用准确性、精确性、召回率和F1分数作为评估指标。我们的结果表明,专有大型语言模型的性能优于开源模型,GPT-4o和Gemma-2-27B在少样本设置中实现了最高精度。值得注意的是,在F1分数方面,Gemma-2-27B也优于传统的机器学习模型。然而,仍然存在一些问题,如不同提示策略之间的性能差异和需要针对领域的微调。这项研究表明,大型语言模型可以用于医疗预测任务,并鼓励未来在提示工程和混合方法方面进行工作,以改善医疗保健预测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in 1st IEEE QPAIN 2025
摘要
本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在糖尿病预测中的应用效果。研究采用零样本、一样本和三样本提示方法,使用Pima印第安糖尿病数据库(PIDD)进行实证分析。对比了六种LLMs模型(包括四个开源模型和两个专有模型)与三种传统机器学习任务模型(随机森林、逻辑回归和支持向量机)的性能。结果显示,专有LLMs模型表现优于开源模型,GPT-4o和Gemma-2-27B在少样本设置中具有最高准确性。Gemma-2-27B在F1分数方面优于传统ML模型。但仍存在提示策略性能差异和需要特定领域的微调等问题。研究证明了LLMs在医疗预测任务中的潜力,并鼓励未来在提示工程和混合方法上进行改进以提高医疗预测的准确性。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在糖尿病预测中的应用尚处于初步探索阶段。
- 专有LLMs模型性能通常优于开源模型。
- GPT-4o和Gemma-2-27B在少样本环境中表现出最高准确性。
- Gemma-2-27B在F1分数方面优于传统机器学习任务模型。
- LLMs在医疗预测任务中具有潜力。
- 目前仍存在提示策略性能差异和需要特定领域的微调等挑战。
点此查看论文截图

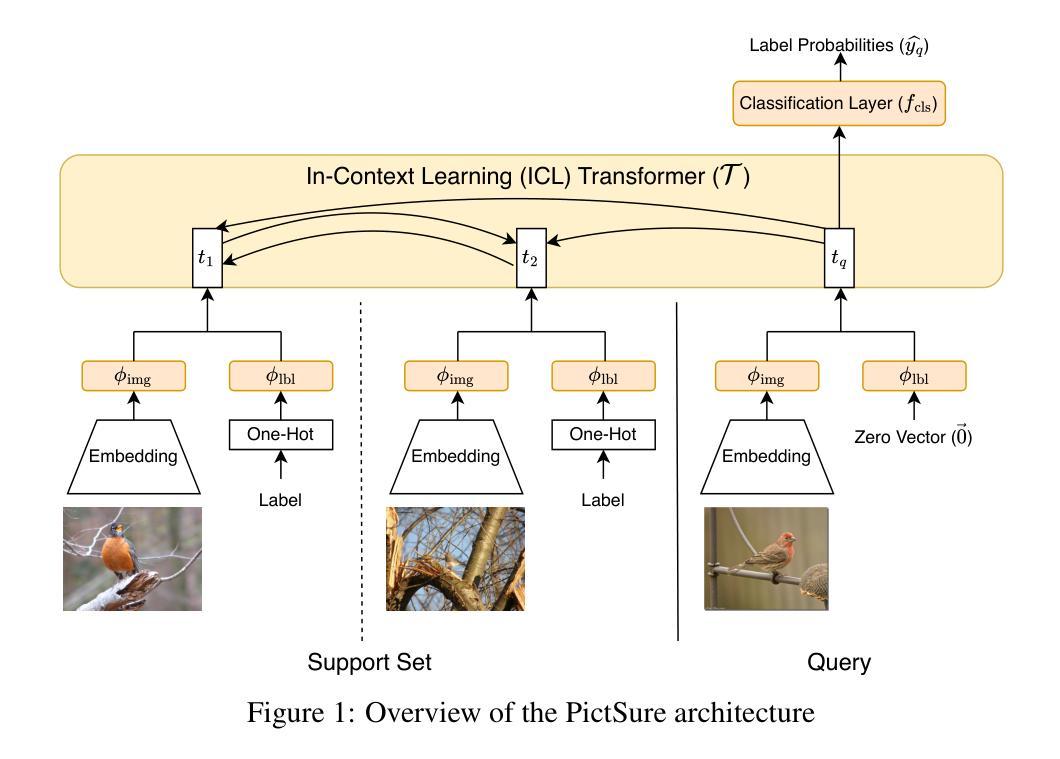
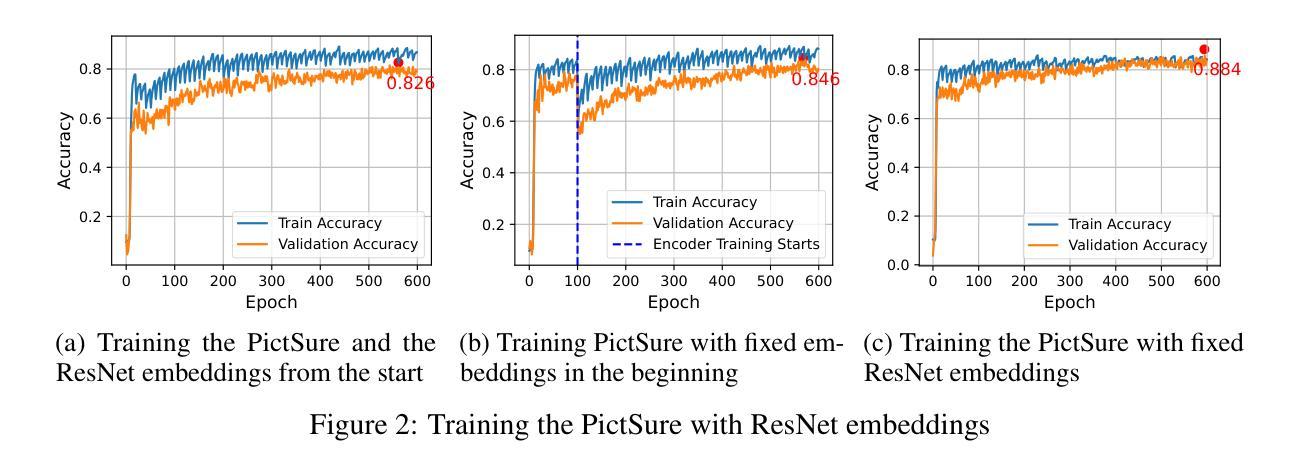
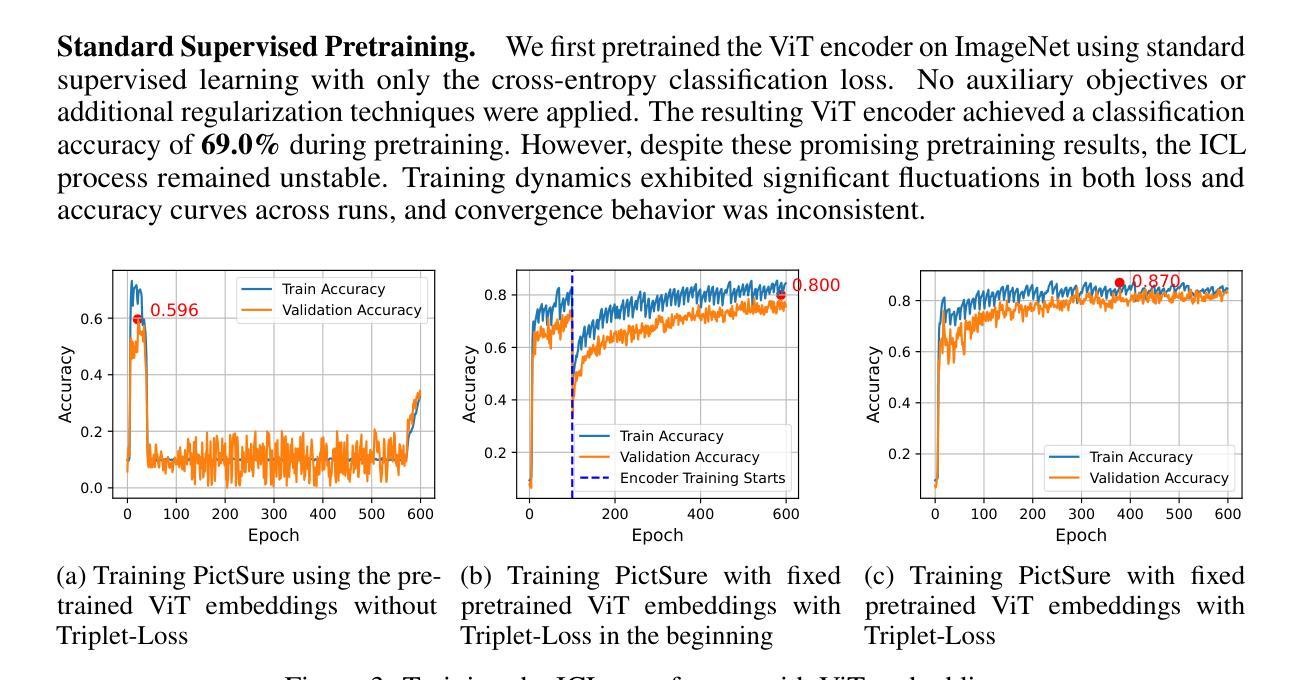
PictSure: Pretraining Embeddings Matters for In-Context Learning Image Classifiers
Authors:Lukas Schiesser, Cornelius Wolff, Sophie Haas, Simon Pukrop
Building image classification models remains cumbersome in data-scarce domains, where collecting large labeled datasets is impractical. In-context learning (ICL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for few-shot image classification (FSIC), enabling models to generalize across domains without gradient-based adaptation. However, prior work has largely overlooked a critical component of ICL-based FSIC pipelines: the role of image embeddings. In this work, we present PictSure, an ICL framework that places the embedding model – its architecture, pretraining, and training dynamics – at the center of analysis. We systematically examine the effects of different visual encoder types, pretraining objectives, and fine-tuning strategies on downstream FSIC performance. Our experiments show that the training success and the out-of-domain performance are highly dependent on how the embedding models are pretrained. Consequently, PictSure manages to outperform existing ICL-based FSIC models on out-of-domain benchmarks that differ significantly from the training distribution, while maintaining comparable results on in-domain tasks. Code can be found at https://github.com/PictSure/pictsure-library.
在数据稀缺的领域中,构建图像分类模型仍然是一项艰巨的任务,因为在此类情况下收集大量带标签的数据集并不实际。情境学习(ICL)作为一种有前景的模式,在少样本图像分类(FSIC)中脱颖而出,它能够让模型在跨领域情况下进行泛化,而无需基于梯度的调整。然而,之前的工作大多忽略了基于ICL的FSIC管道中的一个关键组成部分:图像嵌入的作用。在这项工作中,我们提出了PictSure,这是一个以嵌入模型为中心的ICL框架,涵盖了其架构、预训练和培训动态。我们系统地研究了不同视觉编码器类型、预训练目标和微调策略对下游FSIC性能的影响。我们的实验表明,训练成功和跨领域性能在很大程度上取决于嵌入模型的预训练方式。因此,PictSure成功地在与训练分布差异显著的跨领域基准测试上超越了现有的基于ICL的FSIC模型,同时在内部任务上维持了相当的结果。代码可在https://github.com/PictSure/pictsure-library找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures
Summary
在数据稀缺领域,构建图像分类模型仍然是一项艰巨的任务,因为在此类情况下收集大量有标签的数据集并不实用。情境学习(ICL)作为一种有前景的模式,在少量图像分类(FSIC)中展现出巨大的潜力,它使模型能够在无需梯度调整的情况下跨领域进行推广。然而,先前的研究在很大程度上忽视了ICL基于FSIC管道的关键组成部分——图像嵌入的作用。在本次研究中,我们推出了PictSure,一种以嵌入模型为中心的ICL框架,深入分析了其架构、预训练和训练动态等方面的影响。我们系统地研究了不同视觉编码器类型、预训练目标和微调策略对下游FSIC性能的影响。实验表明,训练成功度和跨域性能在很大程度上取决于嵌入模型的预训练方式。因此,PictSure在训练分布差异显著的跨域基准测试上表现优于现有的ICL基于FSIC模型,同时在域内任务上保持相当的结果。
Key Takeaways
- ICL(In-context Learning)在少量图像分类(FSIC)中展现出巨大潜力,尤其在数据稀缺领域。
- PictSure是一个以嵌入模型为中心的ICL框架,注重分析图像分类模型中的架构、预训练和训练动态等方面。
- 实验显示不同视觉编码器类型、预训练目标和微调策略对下游FSIC性能影响显著。
- 训练成功度和跨域性能高度依赖于嵌入模型的预训练方式。
- PictSure在跨域基准测试上的表现优于现有ICL-based FSIC模型。
- PictSure在维持域内任务性能的同时,实现了跨域性能的显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

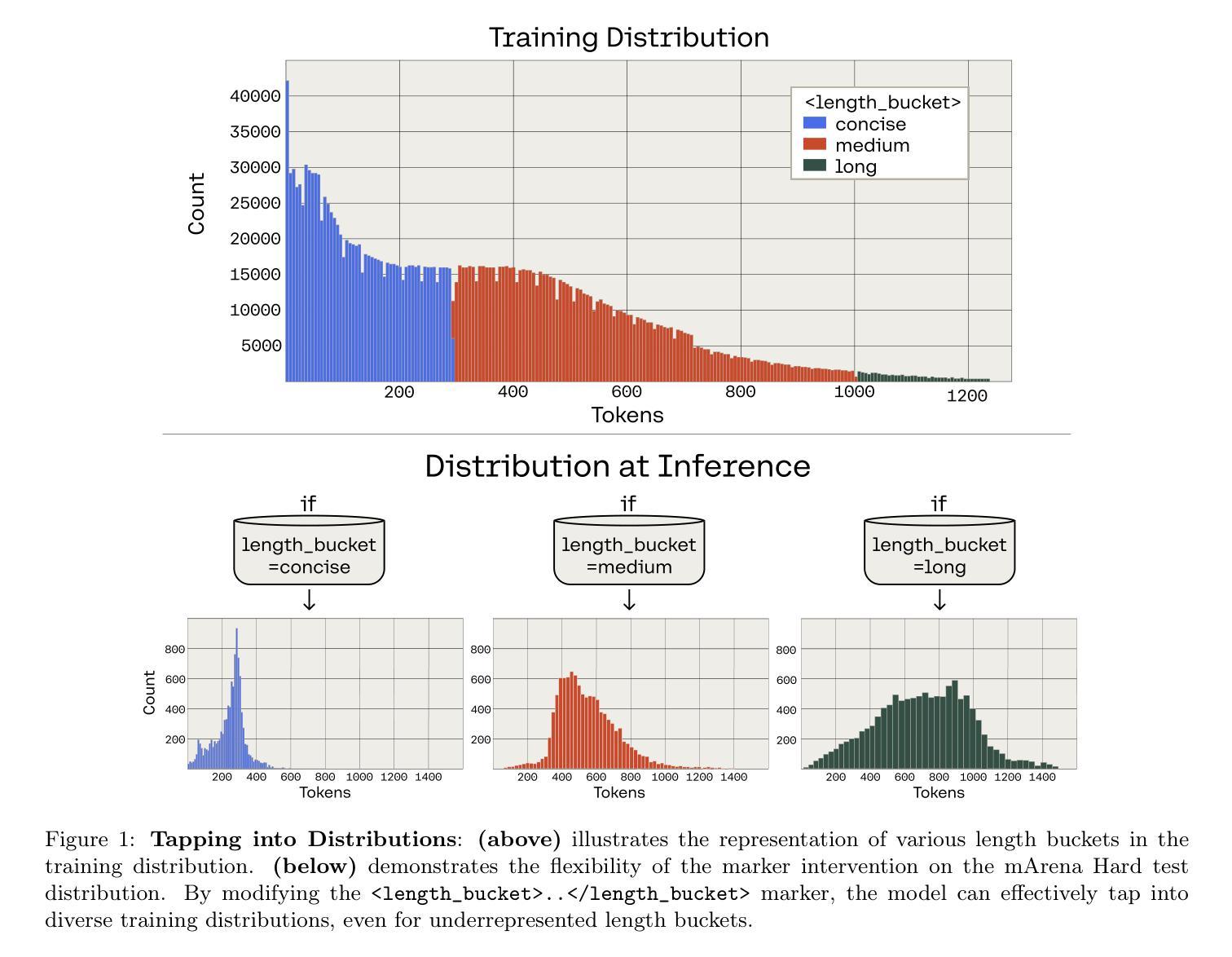
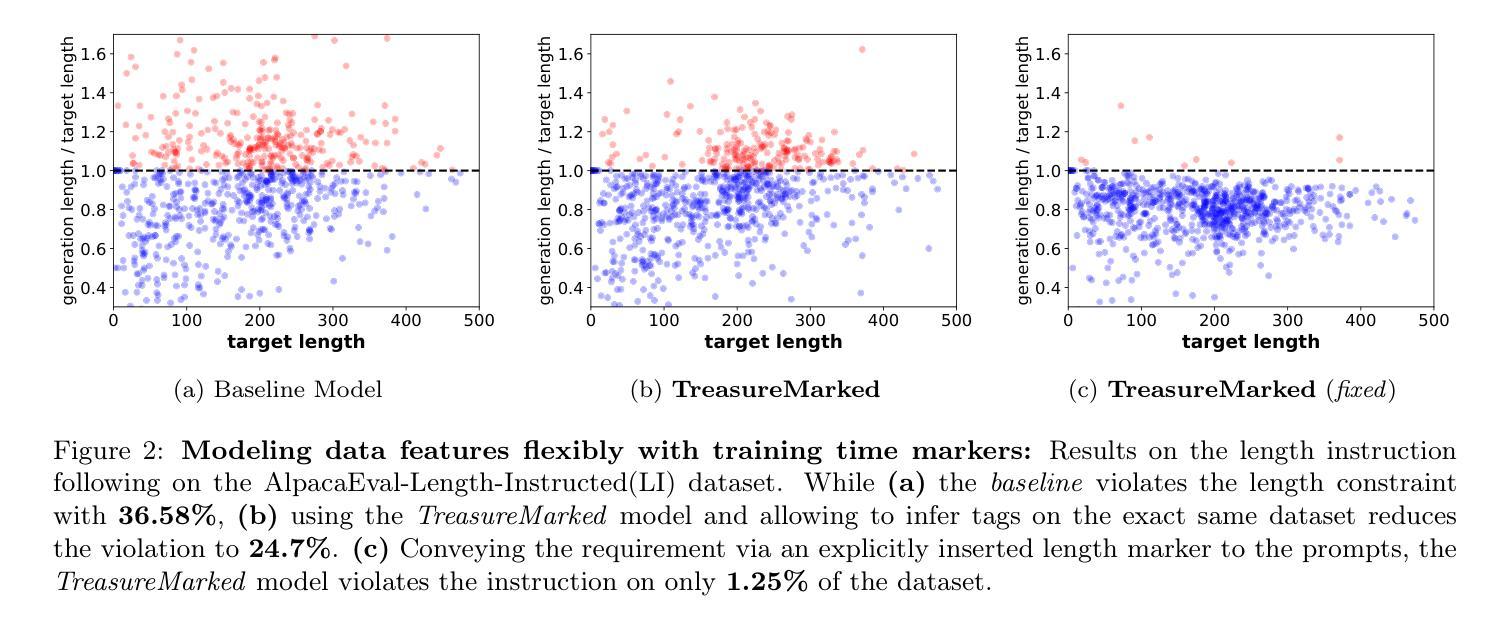
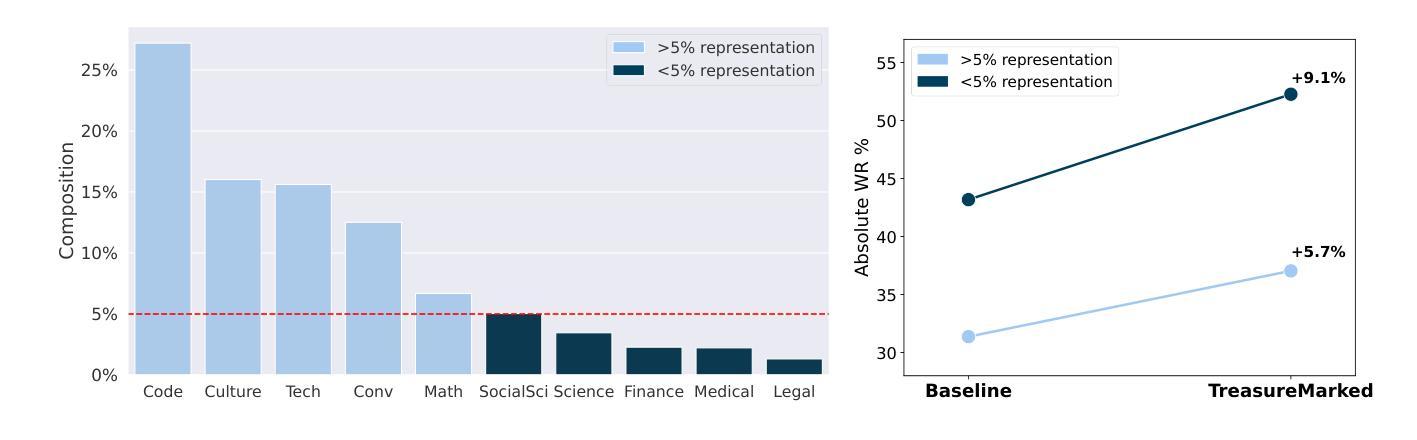
Treasure Hunt: Real-time Targeting of the Long Tail using Training-Time Markers
Authors:Daniel D’souza, Julia Kreutzer, Adrien Morisot, Ahmet Üstün, Sara Hooker
One of the most profound challenges of modern machine learning is performing well on the long-tail of rare and underrepresented features. Large general-purpose models are trained for many tasks, but work best on high-frequency use cases. After training, it is hard to adapt a model to perform well on specific use cases underrepresented in the training corpus. Relying on prompt engineering or few-shot examples to maximize the output quality on a particular test case can be frustrating, as models can be highly sensitive to small changes, react in unpredicted ways or rely on a fixed system prompt for maintaining performance. In this work, we ask: “Can we optimize our training protocols to both improve controllability and performance on underrepresented use cases at inference time?” We revisit the divide between training and inference techniques to improve long-tail performance while providing users with a set of control levers the model is trained to be responsive to. We create a detailed taxonomy of data characteristics and task provenance to explicitly control generation attributes and implicitly condition generations at inference time. We fine-tune a base model to infer these markers automatically, which makes them optional at inference time. This principled and flexible approach yields pronounced improvements in performance, especially on examples from the long tail of the training distribution. While we observe an average lift of 5.7% win rates in open-ended generation quality with our markers, we see over 9.1% gains in underrepresented domains. We also observe relative lifts of up to 14.1% on underrepresented tasks like CodeRepair and absolute improvements of 35.3% on length instruction following evaluations.
现代机器学习面临的最深刻挑战之一是实现对罕见和代表性不足的特征的长尾表现良好。大型通用模型经过针对许多任务的训练,但在高频用例上表现最佳。训练后,很难使模型适应在训练语料库中代表性不足的具体用例上表现良好。依赖提示工程或少数样本示例来最大化特定测试用例的输出质量可能会令人沮丧,因为模型可能会对微小变化高度敏感,产生不可预测的反应,或者依赖固定的系统提示来维持性能。在这项工作中,我们提出的问题是:“我们是否可以优化我们的训练协议,以在推理时提高可控性和在代表性不足的用例上的性能?”我们重新审视了训练和推理技术之间的界限,以提高长尾性能,同时为用户提供一系列控制杆,该模型被训练成对控制杆做出反应。我们创建了数据特性和任务来源的详细分类,以明确控制生成属性和在推理时隐式地调节生成。我们对基础模型进行微调,以自动推断这些标记,使其在推理时变得可选。这种有原则且灵活的方法在性能上产生了显著改进,特别是在训练分布的长尾示例中。我们观察到开放式生成质量平均提升了5.7%的胜率使用我们的标记,在代表性不足的领域里,我们看到了超过9.1%的增幅。在代表性不足的任务(如代码修复)上,我们还观察到相对提升了高达14.1%,在遵循长度指令的评估上实现了绝对改善35.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨现代机器学习面临的一个重大挑战,即如何在罕见和代表性不足的特征的长尾部分表现良好。大型通用模型虽然经过多项任务训练,但在高频用例上表现最佳。训练后,难以适应模型以在训练语料库中代表性不足的特定用例上表现良好。本文旨在优化训练协议,以提高在代表性不足用例上的可控性和性能。通过重新审视训练和推理技术,我们在提高长尾性能的同时,为用户提供一系列控制杆,使模型在训练时能对一系列控制杠杆作出响应。我们创建了一个详细的数据特性和任务来源分类法,以在推理时显式控制生成属性和隐式条件生成。我们对基础模型进行微调,以自动推断这些标记,使其在推理时变得可选。这种有原则且灵活的方法在性能上产生了显著的提升,特别是在训练分布的长尾示例中。
Key Takeaways
- 现代机器学习面临在罕见和代表性不足的特征上的挑战。
- 大型通用模型在高频用例上表现最佳,但在特定用例上难以适应。
- 通过优化训练协议,可以提高在代表性不足用例上的可控性和性能。
- 提供了对训练和推理技术的重新审视,以提高长尾性能。
- 创建了一个详细的数据特性和任务来源分类法,以控制生成属性和条件生成。
- 通过微调基础模型,可以自动推断用于控制生成属性的标记。
点此查看论文截图


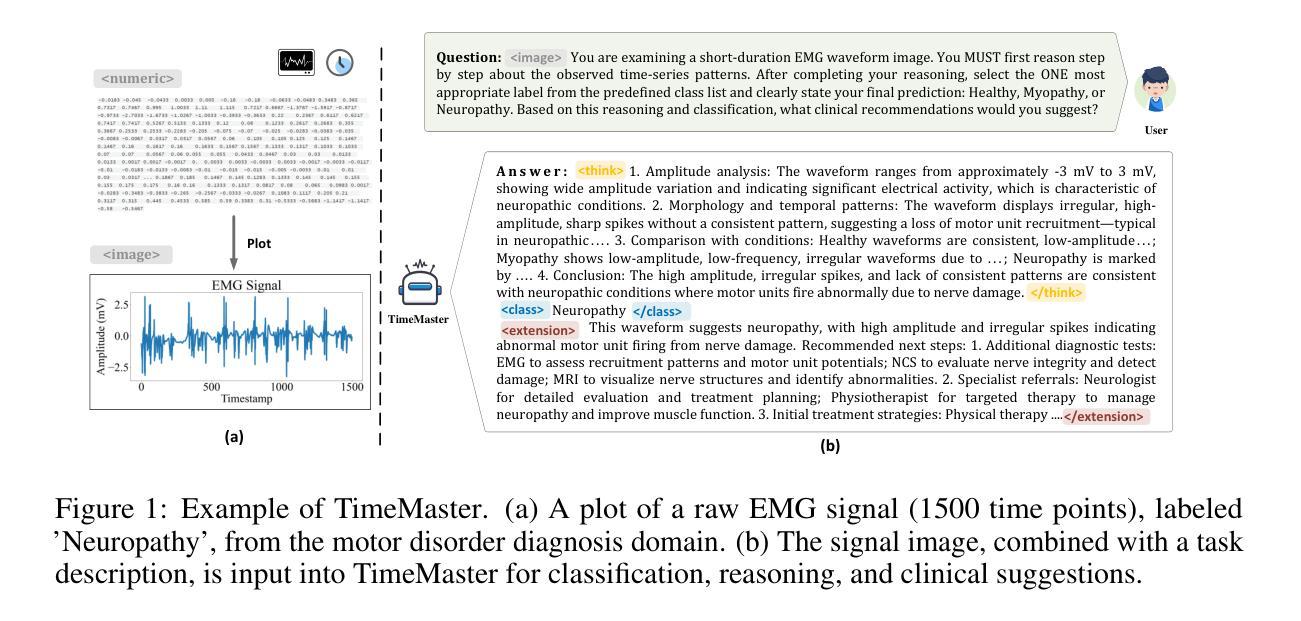
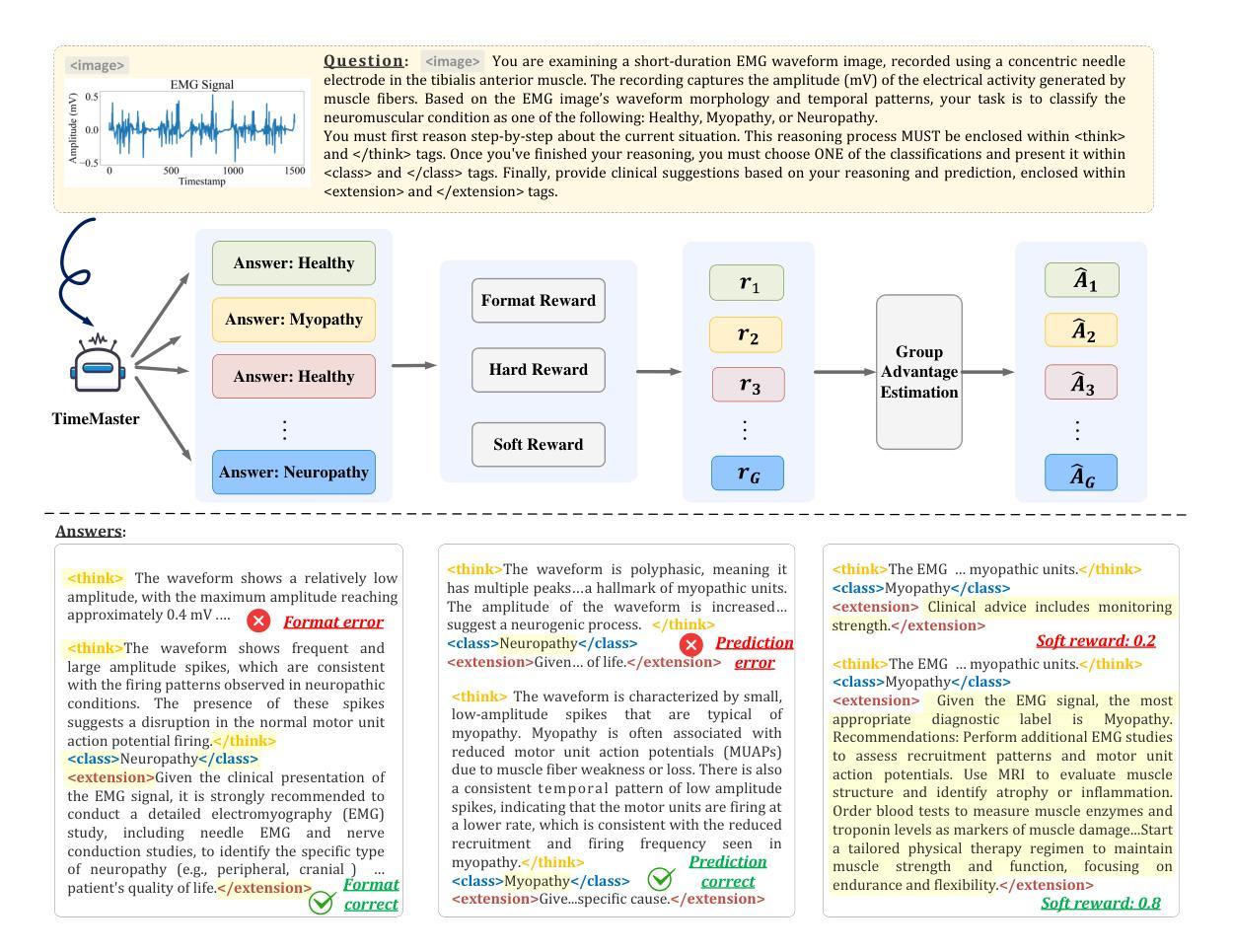
TimeMaster: Training Time-Series Multimodal LLMs to Reason via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Junru Zhang, Lang Feng, Xu Guo, Yuhan Wu, Yabo Dong, Duanqing Xu
Time-series reasoning remains a significant challenge in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) due to the dynamic temporal patterns, ambiguous semantics, and lack of temporal priors. In this work, we introduce TimeMaster, a reinforcement learning (RL)-based method that enables time-series MLLMs to perform structured, interpretable reasoning directly over visualized time-series inputs and task prompts. TimeMaster adopts a three-part structured output format, reasoning, classification, and domain-specific extension, and is optimized via a composite reward function that aligns format adherence, prediction accuracy, and open-ended insight quality. The model is trained using a two-stage pipeline: we first apply supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to establish a good initialization, followed by Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) at the token level to enable stable and targeted reward-driven improvement in time-series reasoning. We evaluate TimeMaster on the TimerBed benchmark across six real-world classification tasks based on Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct. TimeMaster achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming both classical time-series models and few-shot GPT-4o by over 14.6% and 7.3% performance gain, respectively. Notably, TimeMaster goes beyond time-series classification: it also exhibits expert-like reasoning behavior, generates context-aware explanations, and delivers domain-aligned insights. Our results highlight that reward-driven RL can be a scalable and promising path toward integrating temporal understanding into time-series MLLMs.
时间序列推理在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中仍然是一个重大挑战,这是由于存在动态时间模式、语义模糊以及缺乏时间先验知识。在这项工作中,我们引入了TimeMaster,一种基于强化学习(RL)的方法,使时间序列MLLMs能够直接对可视化时间序列输入和任务提示进行结构化、可解释的推理。TimeMaster采用三部分的结构化输出格式,包括推理、分类和领域特定扩展,并通过组合奖励函数进行优化,该函数字符合格式遵循、预测准确性和开放性洞察质量。该模型采用两阶段管道进行训练:我们首先应用监督微调(SFT)来建立良好的初始化,然后通过令牌级别的集团相对策略优化(GRPO)实现时间序列推理的稳定性和针对性奖励驱动改进。我们在基于Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct的TimerBed基准测试上对六个真实世界分类任务评估了TimeMaster。TimeMaster达到了最先进的性能,相较于经典的时间序列模型和少镜头GPT-4o分别提高了超过14.6%和7.3%的性能。值得注意的是,TimeMaster不仅超越时间序列分类:它还表现出专家级的推理行为,生成上下文感知的解释,并提供与领域相符的见解。我们的结果强调,奖励驱动的RL可以是一条可扩展且前途光明的路径,旨在将时间理解整合到时间序列MLLMs中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
该文本介绍了TimeMaster,一种基于强化学习的时间序列多模态大型语言模型方法。TimeMaster能在可视化时间序列输入和任务提示上进行结构化、可解释的推理。采用三阶段结构输出格式,并通过组合奖励函数进行优化,实现了时间序列推理的新水平。通过两个阶段的管道训练模型,先用监督微调进行初始化,再用分组相对策略优化在令牌级别进行奖励驱动改进。TimeMaster在TimerBed基准测试上表现突出,展现出超越现有模型的性能。除了时间序列分类外,TimeMaster还展现出专家级的推理行为,生成上下文相关的解释和领域对齐的见解。
Key Takeaways
- TimeMaster是一种基于强化学习的方法,用于增强多模态大型语言模型在时间序列推理方面的能力。
- TimeMaster能直接处理可视化时间序列输入和任务提示,进行结构化、可解释的推理。
- TimeMaster采用三阶段结构输出格式并优化组合奖励函数以对齐格式遵守、预测准确性和开放性的见解质量。
- 模型采用两个阶段进行训练:监督微调进行初始化,然后采用分组相对策略优化进行奖励驱动改进。
- TimeMaster在TimerBed基准测试中表现卓越,超越现有模型表现,具有更高的分类性能。
- TimeMaster展现了专家级的推理行为,可以生成上下文相关的解释和与特定领域相关的见解。
点此查看论文截图

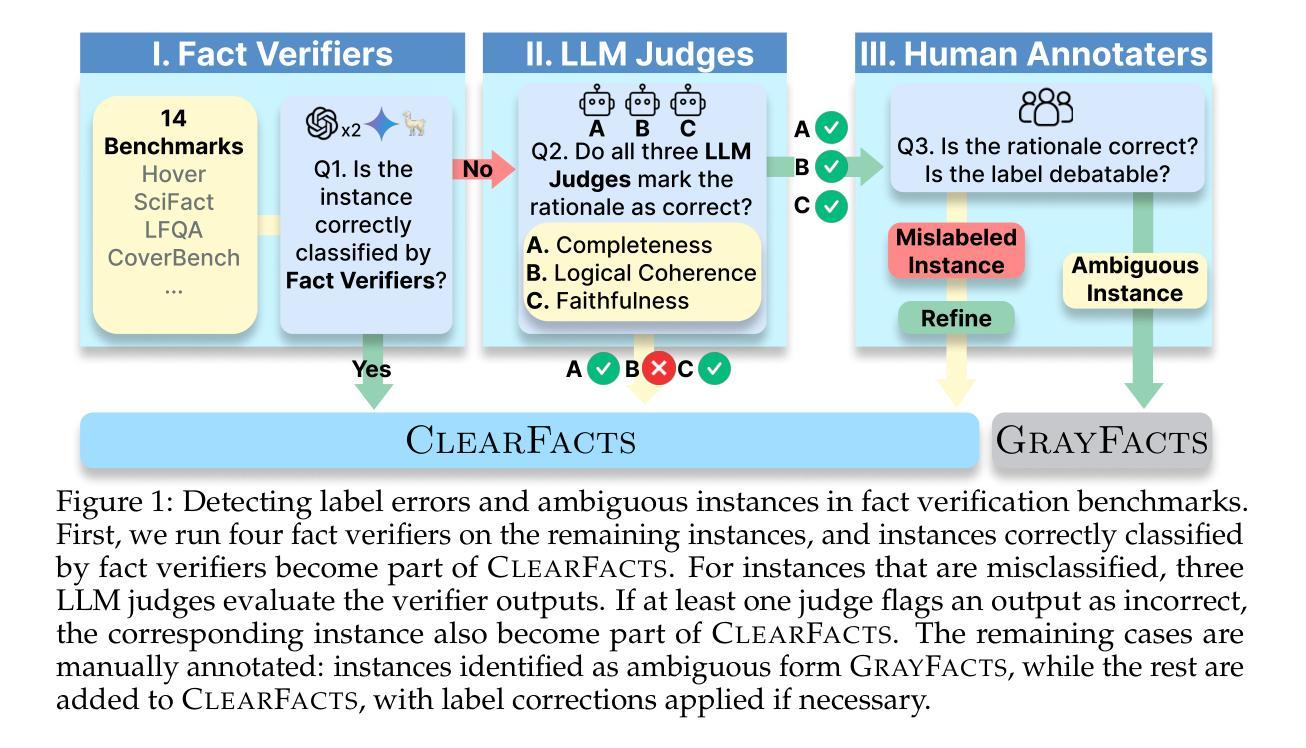
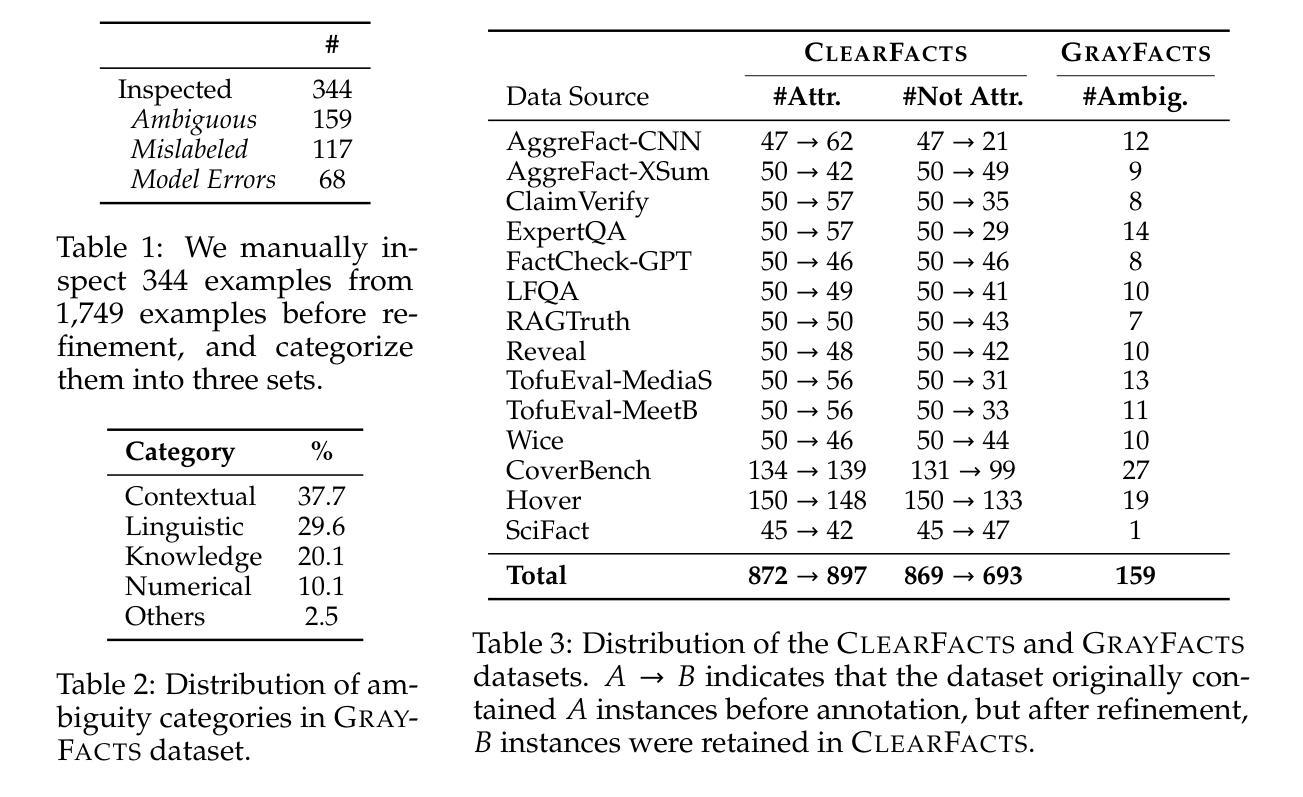
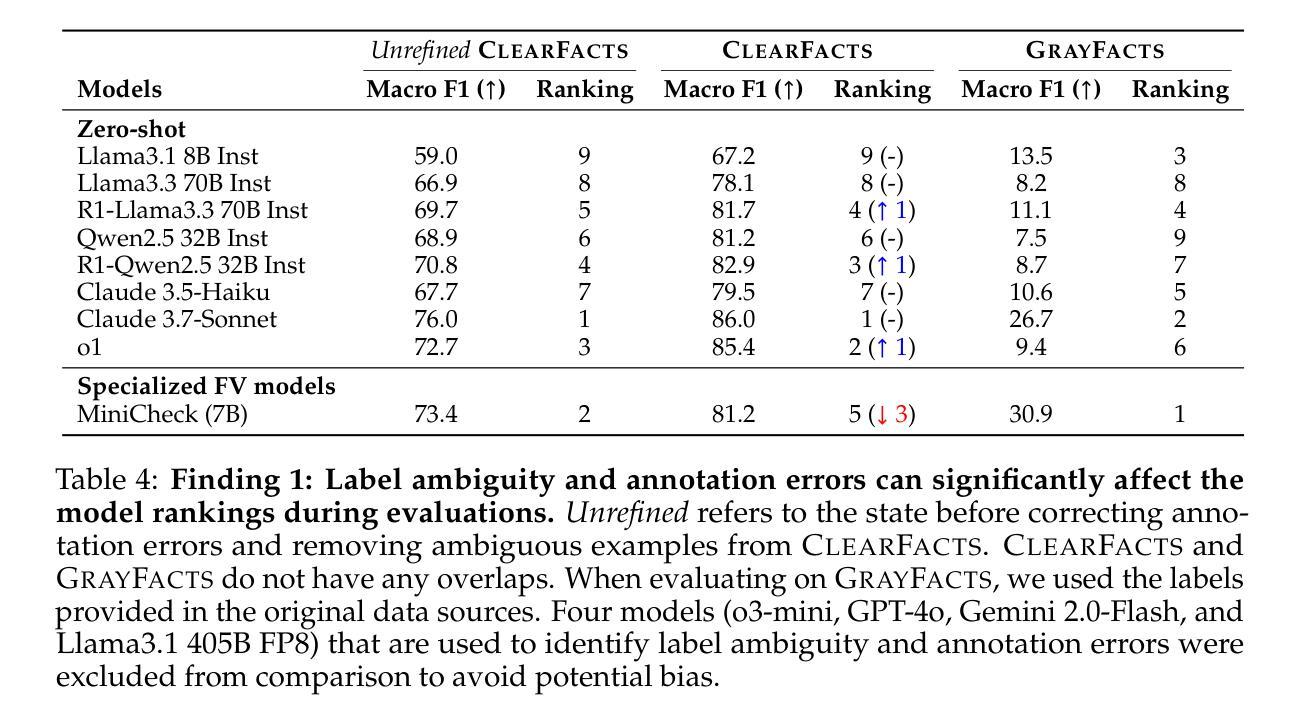
Verifying the Verifiers: Unveiling Pitfalls and Potentials in Fact Verifiers
Authors:Wooseok Seo, Seungju Han, Jaehun Jung, Benjamin Newman, Seungwon Lim, Seungbeen Lee, Ximing Lu, Yejin Choi, Youngjae Yu
Fact verification is essential for ensuring the reliability of LLM applications. In this study, we evaluate 12 pre-trained LLMs and one specialized fact-verifier, including frontier LLMs and open-weight reasoning LLMs, using a collection of examples from 14 fact-checking benchmarks. We share three findings intended to guide future development of more robust fact verifiers. First, we highlight the importance of addressing annotation errors and ambiguity in datasets, demonstrating that approximately 16% of ambiguous or incorrectly labeled data substantially influences model rankings. Neglecting this issue may result in misleading conclusions during comparative evaluations, and we suggest using a systematic pipeline utilizing LLM-as-a-judge to help identify these issues at scale. Second, we discover that frontier LLMs with few-shot in-context examples, often overlooked in previous works, achieve top-tier performance. We therefore recommend future studies include comparisons with these simple yet highly effective baselines. Lastly, despite their effectiveness, frontier LLMs incur substantial costs, motivating the development of small, fine-tuned fact verifiers. We show that these small models still have room for improvement, particularly on instances that require complex reasoning. Encouragingly, we demonstrate that augmenting training with synthetic multi-hop reasoning data significantly enhances their capabilities in such instances. We release our code, model, and dataset at https://github.com/just1nseo/verifying-the-verifiers
事实核查对于确保LLM应用程序的可靠性至关重要。在本研究中,我们使用来自14个事实核查基准的示例集,对12个预训练LLM和一个专门的事实核查器进行了评估,包括前沿LLM和开放权重推理LLM。我们分享了三项旨在指导未来开发更稳健的事实核查器的发现。首先,我们强调了解决数据集中的注释错误和模糊性的重要性,表明大约16%的模糊或错误标记的数据会显著影响模型排名。忽略此问题可能导致比较评估时得出误导性结论,我们建议采用一个系统的管道,利用LLM作为法官,帮助大规模识别这些问题。其次,我们发现具有少量上下文示例的前沿LLM(以前的研究经常忽略这一点)达到了顶尖的性能。因此,我们建议未来的研究要与这些简单但高效的基本线进行比较。最后,尽管它们很有效,但前沿LLM会带来巨大的成本,这推动了精细调整的事实核查器的开发。我们表明,这些小型模型仍有改进的空间,特别是在需要复杂推理的实例中。令人鼓舞的是,我们证明通过合成多跳推理数据来增强训练会显著提高这些模型在此类实例中的能力。我们在https://github.com/just1nseo/verifying-the-verifiers上发布了我们的代码、模型和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究评估了12个预训练的大型语言模型和1个专门的验证器在事实核查方面的表现。研究发现在数据集标注错误和模糊性问题上需重视,约16%的模糊或错误标注数据会影响模型排名。同时,前沿的大型语言模型在少数场景下的表现优异,但成本较高,建议开发小型且精细调整的验证器。通过合成多跳推理数据增强训练,可提高模型在复杂实例中的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 数据集的标注错误和模糊性对大型语言模型(LLM)的评估有重要影响,大约16%的问题数据会影响模型排名。
- 前沿的大型语言模型在少数场景(few-shot)下表现优异,应重视其在事实核查领域的应用。
- 在事实核查领域,开发小型且精细调整的验证器是一个可行方向,以降低模型成本。
- 通过合成多跳推理数据增强训练可以提高LLM在复杂实例中的能力。
- 系统性地利用大型语言模型作为判断工具可以帮助识别数据集中的问题。
- 在未来的研究中,需要包含与前沿大型语言模型的对比研究。
点此查看论文截图


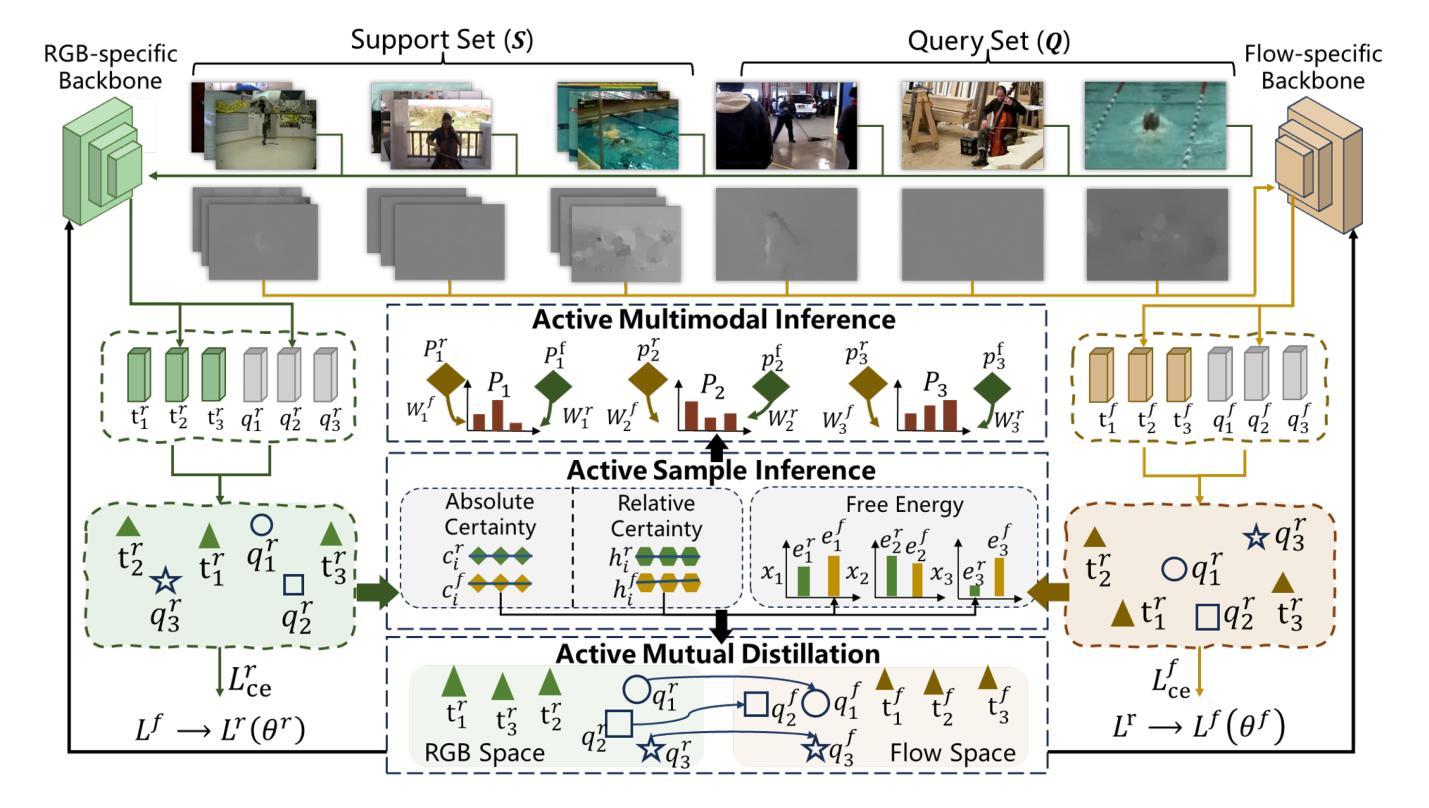
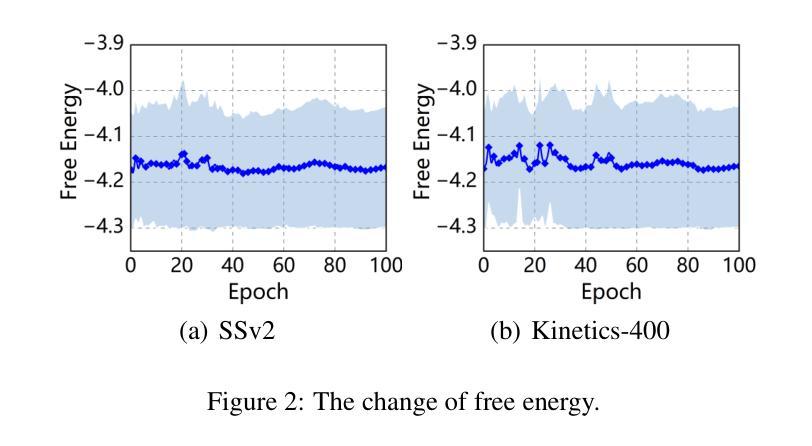
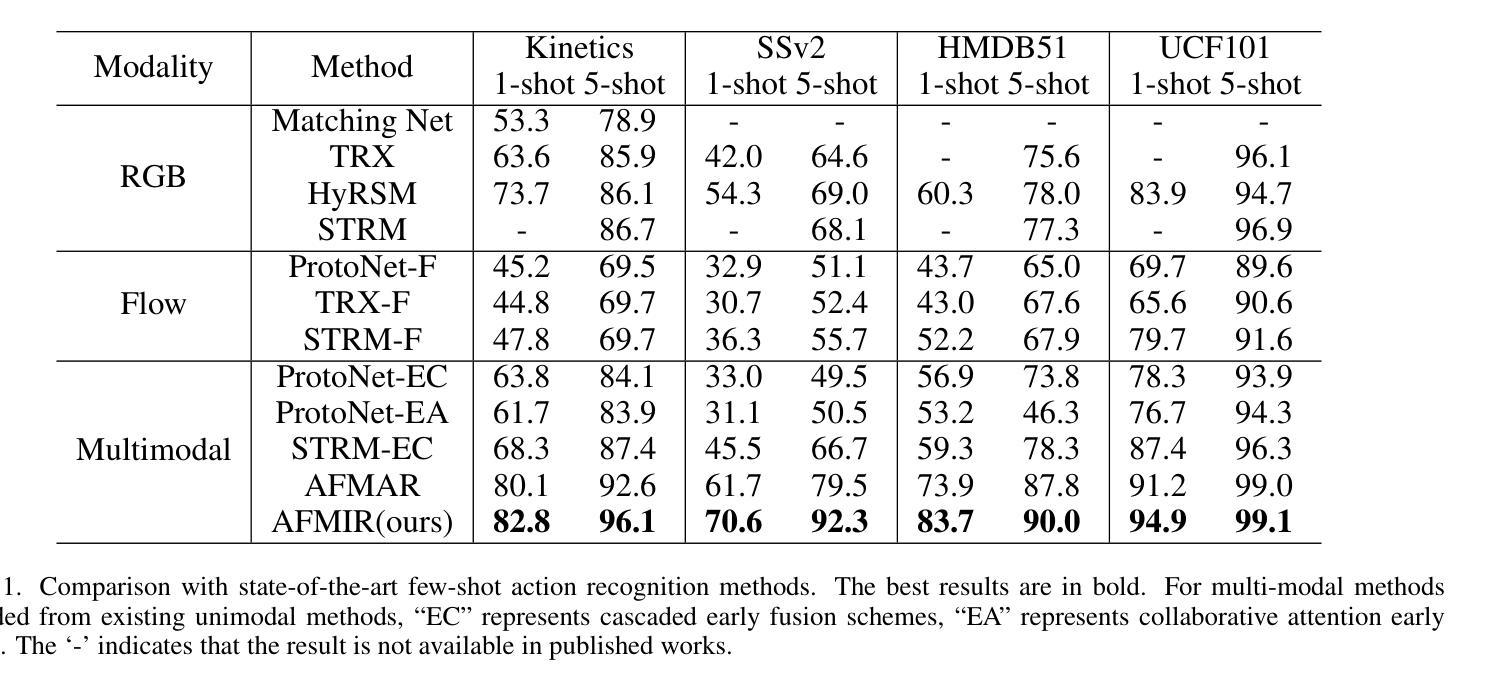
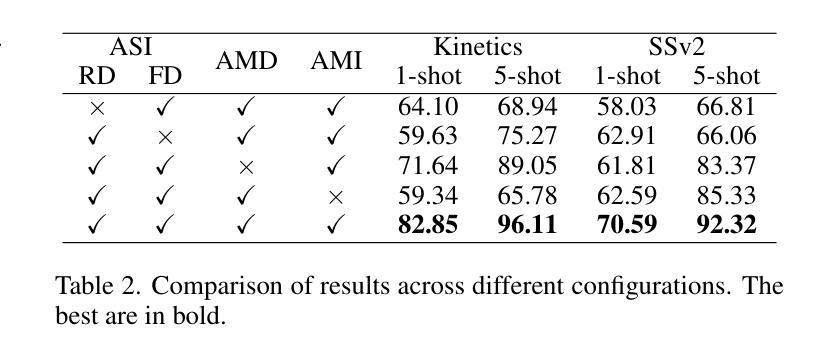
Active Multimodal Distillation for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Weijia Feng, Yichen Zhu, Ruojia Zhang, Chenyang Wang, Fei Ma, Xiaobao Wang, Xiaobai Li
Owing to its rapid progress and broad application prospects, few-shot action recognition has attracted considerable interest. However, current methods are predominantly based on limited single-modal data, which does not fully exploit the potential of multimodal information. This paper presents a novel framework that actively identifies reliable modalities for each sample using task-specific contextual cues, thus significantly improving recognition performance. Our framework integrates an Active Sample Inference (ASI) module, which utilizes active inference to predict reliable modalities based on posterior distributions and subsequently organizes them accordingly. Unlike reinforcement learning, active inference replaces rewards with evidence-based preferences, making more stable predictions. Additionally, we introduce an active mutual distillation module that enhances the representation learning of less reliable modalities by transferring knowledge from more reliable ones. Adaptive multimodal inference is employed during the meta-test to assign higher weights to reliable modalities. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches.
少量样本动作识别因其快速进步和广泛应用前景而引起了人们的极大兴趣。然而,当前的方法主要基于有限的单模态数据,并没有充分利用多模态信息的潜力。本文提出了一种新型框架,该框架能够利用特定任务的上下文线索,主动为每个样本识别可靠的模态,从而显著提高识别性能。我们的框架集成了一个主动样本推理(ASI)模块,该模块利用主动推理,基于后验分布预测可靠的模态,然后相应地组织它们。与强化学习不同,主动推理用基于证据的偏好取代奖励,从而做出更稳定的预测。此外,我们还引入了一个主动相互蒸馏模块,通过从更可靠的模态转移知识,增强对不太可靠模态的表示学习。在元测试过程中采用自适应多模态推理,为可靠模态分配更高权重。在多个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IJCAI 2025, the 34th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
本文提出了一种基于任务特定上下文线索的主动模态识别框架,通过Active Sample Inference模块预测可靠的模态,并据此进行组织,从而提高少样本动作识别的性能。引入主动互蒸馏模块,通过从可靠的模态转移知识,增强不可靠模态的表示学习。在元测试阶段采用自适应多模态推理,为可靠的模态分配更高的权重。该方法在多个基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 当前少样本动作识别方法主要基于单一模态数据,未充分利用多模态信息的潜力。
- 论文提出了一种新的框架,利用任务特定的上下文线索来主动识别可靠的模态。
- 引入Active Sample Inference(ASI)模块,基于后验分布进行预测并整理可靠的模态。
- 与强化学习不同,主动推理通过基于证据的偏好替代奖励,预测更加稳定。
- 论文还引入了主动互蒸馏模块,提高了对不可靠模态的表示学习,通过从可靠的模态转移知识。
- 在元测试阶段采用自适应多模态推理,为可靠模态分配更高权重。
点此查看论文截图

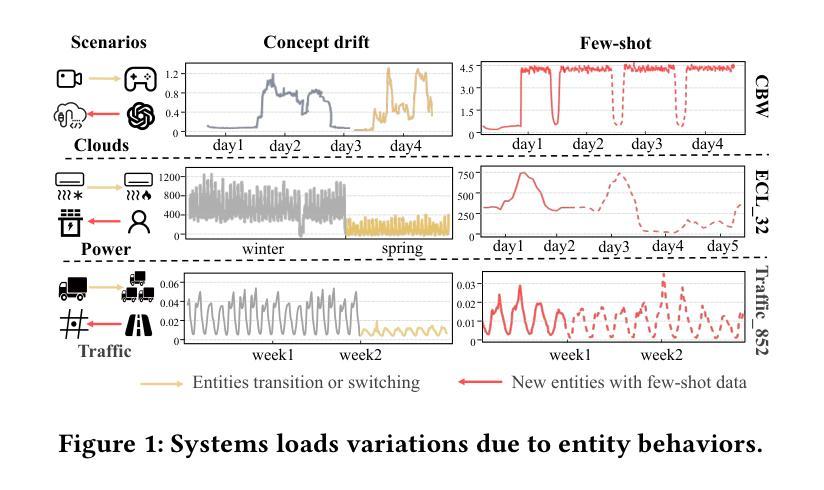
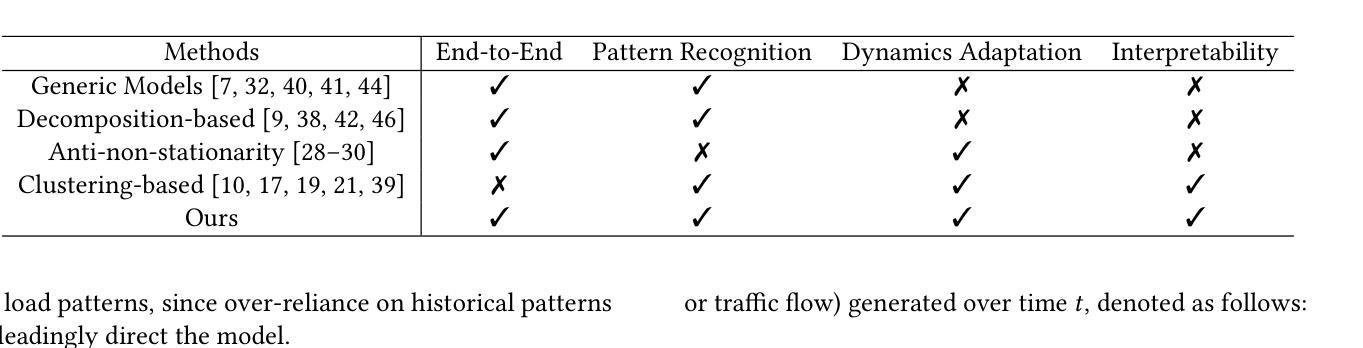
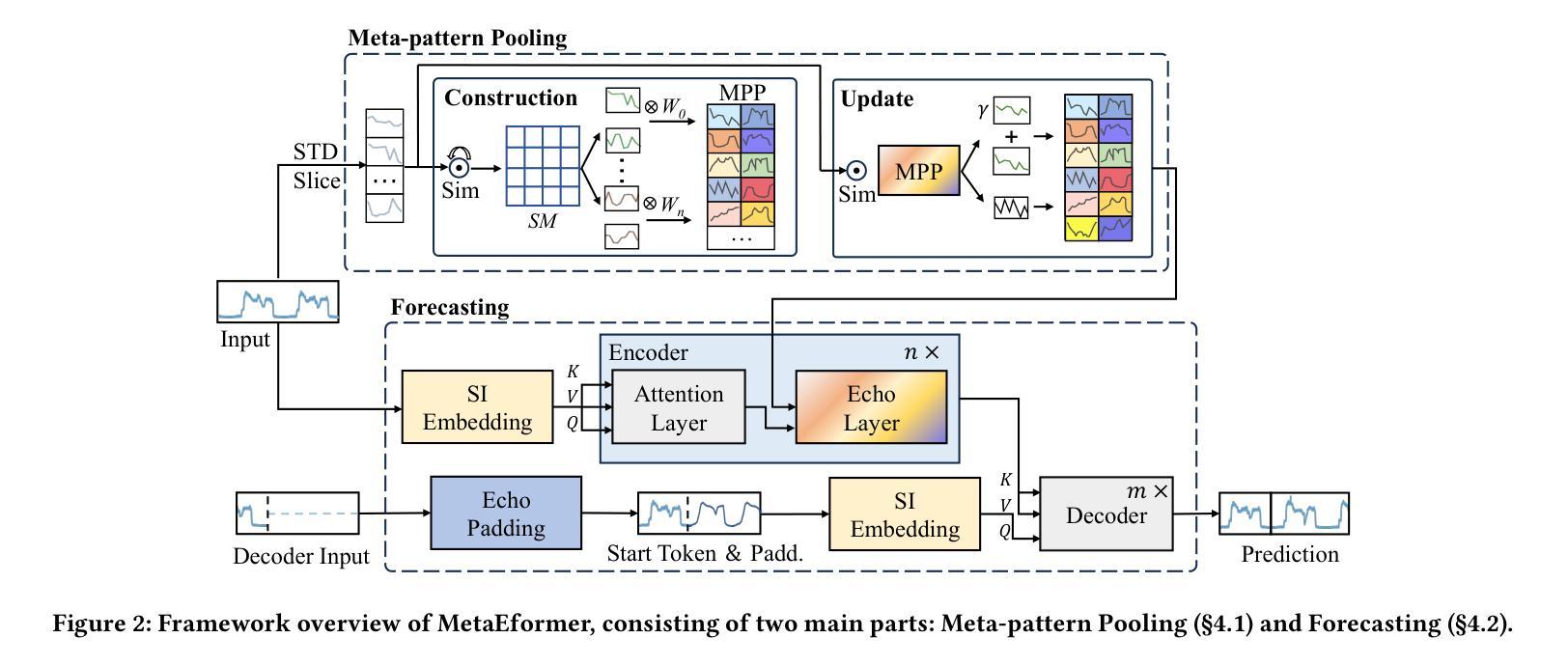
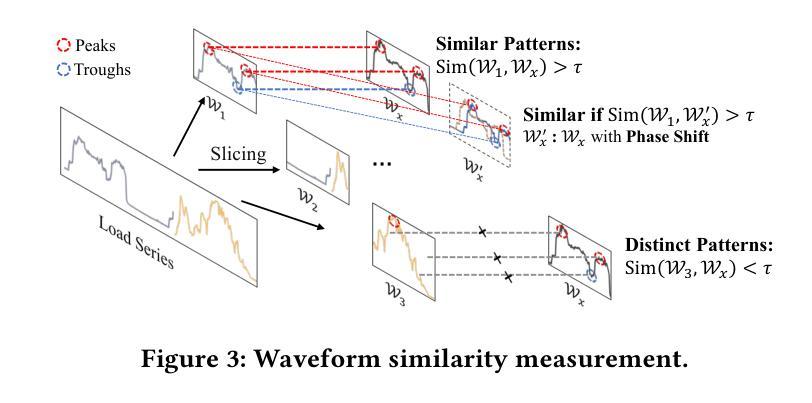
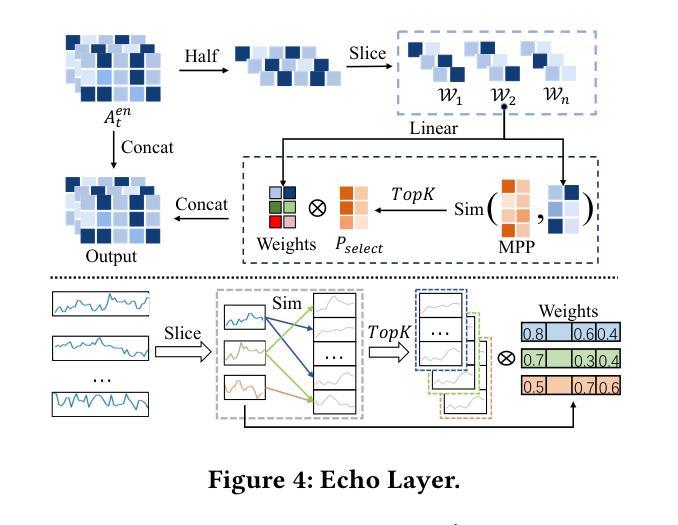
MetaEformer: Unveiling and Leveraging Meta-patterns for Complex and Dynamic Systems Load Forecasting
Authors:Shaoyuan Huang, Tiancheng Zhang, Zhongtian Zhang, Xiaofei Wang, Lanjun Wang, Xin Wang
Time series forecasting is a critical and practical problem in many real-world applications, especially for industrial scenarios, where load forecasting underpins the intelligent operation of modern systems like clouds, power grids and traffic networks.However, the inherent complexity and dynamics of these systems present significant challenges. Despite advances in methods such as pattern recognition and anti-non-stationarity have led to performance gains, current methods fail to consistently ensure effectiveness across various system scenarios due to the intertwined issues of complex patterns, concept-drift, and few-shot problems. To address these challenges simultaneously, we introduce a novel scheme centered on fundamental waveform, a.k.a., meta-pattern. Specifically, we develop a unique Meta-pattern Pooling mechanism to purify and maintain meta-patterns, capturing the nuanced nature of system loads. Complementing this, the proposed Echo mechanism adaptively leverages the meta-patterns, enabling a flexible and precise pattern reconstruction. Our Meta-pattern Echo transformer (MetaEformer) seamlessly incorporates these mechanisms with the transformer-based predictor, offering end-to-end efficiency and interpretability of core processes. Demonstrating superior performance across eight benchmarks under three system scenarios, MetaEformer marks a significant advantage in accuracy, with a 37% relative improvement on fifteen state-of-the-art baselines.
时间序列预测是许多现实世界应用中的关键实际问题,特别是在工业场景中,负载预测是云、电网和交通网络等现代系统智能运行的基础。然而,这些系统的固有复杂性和动态性带来了巨大的挑战。尽管模式识别和抗非平稳性等方法的发展提高了性能,但由于复杂模式、概念漂移和少样本问题的交织,当前的方法无法在各种系统场景中持续确保有效性。为了同时解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种以基本波形(也称为元模式)为中心的新型方案。具体来说,我们开发了一种独特的元模式池化机制来净化和维护元模式,捕捉系统负载的微妙性质。作为补充,我们提出的回声机制自适应地利用元模式,实现灵活和精确的模式重建。我们的元模式回声转换器(MetaEformer)无缝地将这些机制与基于转换器的预测器相结合,提供端到端的效率和核心过程的可解释性。在三种系统场景的八个基准测试中表现出卓越的性能,MetaEformer在准确性方面具有显著优势,相对于十五个最先进的基线有37%的相对改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于时间序列预测在现代系统如云计算、电网和交通网络中的关键作用,针对当前面临的多重挑战,本文提出了一种基于元模式的新方案。通过开发独特的元模式池化机制和回声机制,该方案能够捕捉系统负载的微妙变化并灵活适应性地利用元模式。MetaEformer无缝结合了这些机制与基于变压器的预测器,提供端到端的效率和核心过程的可解释性,在三个系统场景的八个基准测试中表现出卓越的性能,相对于十五种最新技术基准有37%的相对改进。
Key Takeaways
- 时间序列预测在多个现代系统中具有关键作用,如云计算、电网和交通网络中的智能操作。
- 当前的时间序列预测方法面临复杂模式、概念漂移和小样本问题的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于元模式的新方案,通过开发独特的元模式池化机制和回声机制来解决这些挑战。
- 元模式池化机制用于净化和维护元模式,捕捉系统负载的微妙变化。
- Echo机制能够自适应地利用元模式,实现灵活和精确的模式重建。
- MetaEformer结合了这些机制与基于变压器的预测器,提供端到端的效率和核心过程的可解释性。
点此查看论文截图


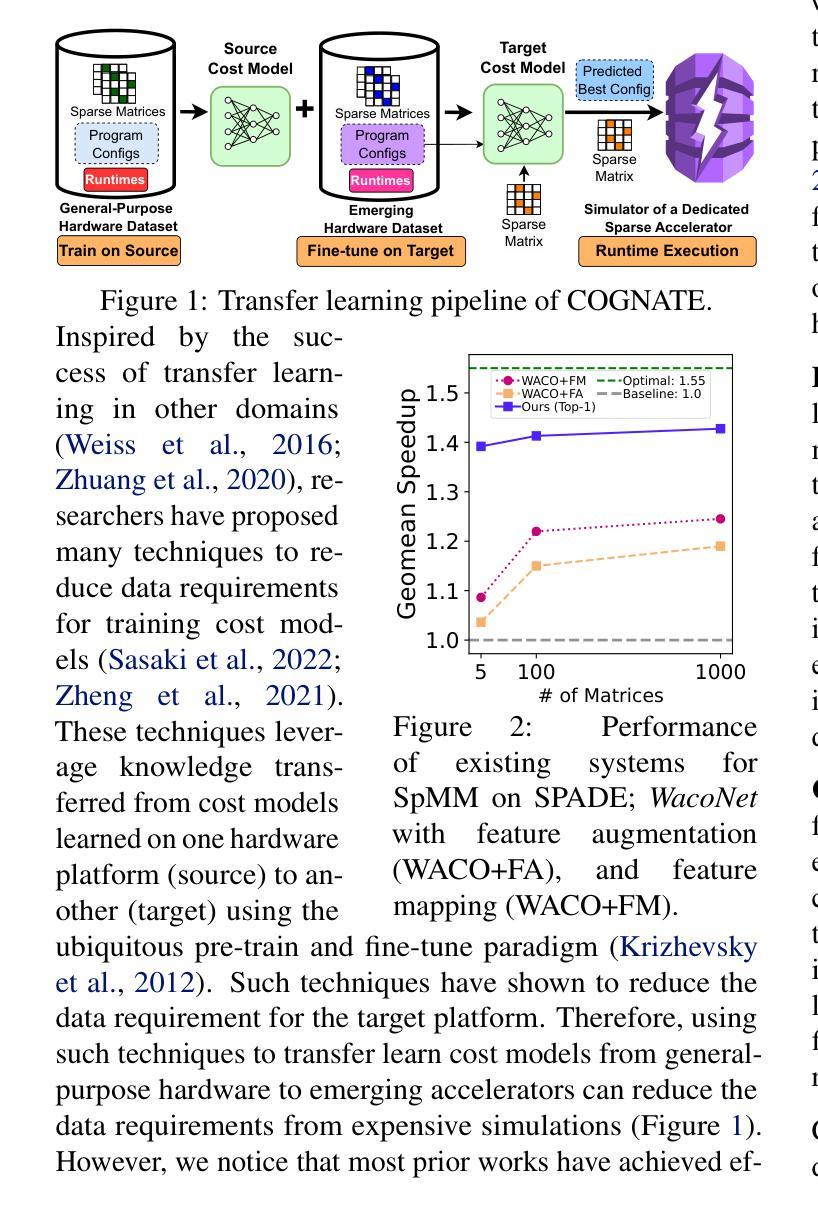
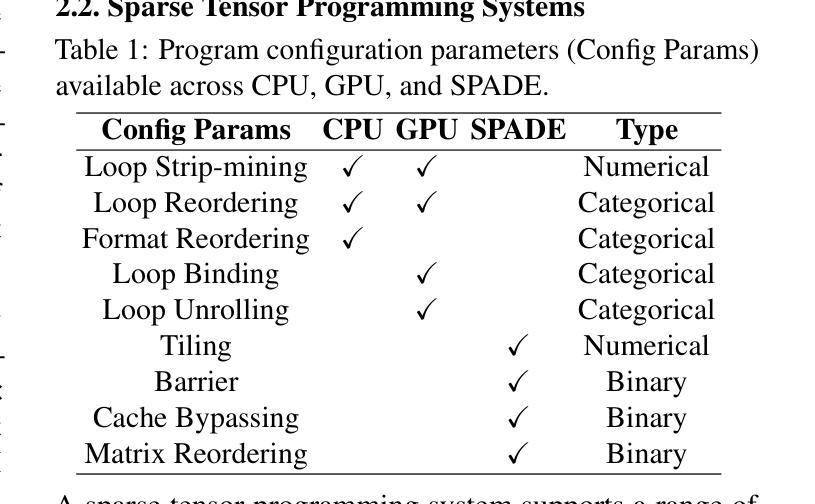
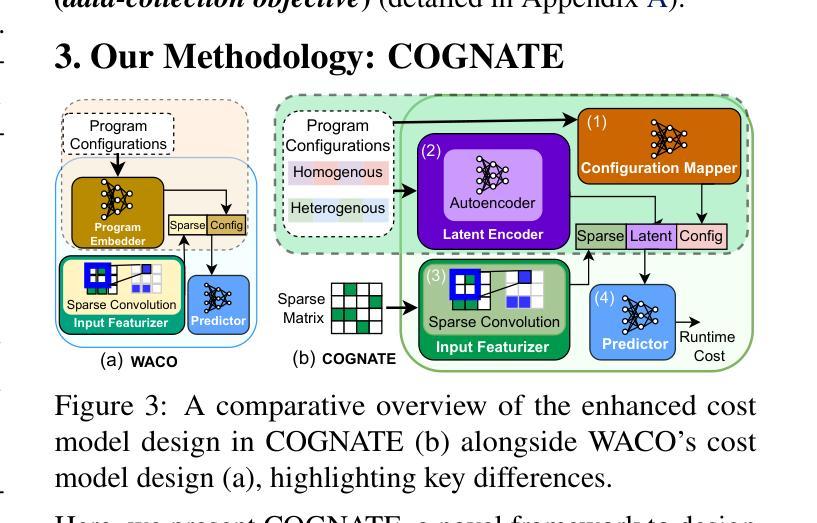
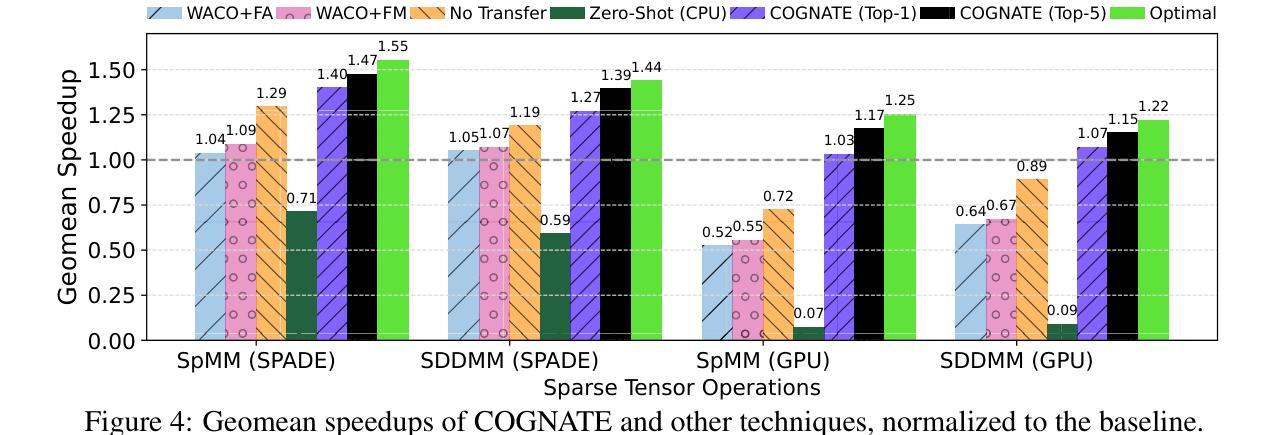
COGNATE: Acceleration of Sparse Tensor Programs on Emerging Hardware using Transfer Learning
Authors:Chamika Sudusinghe, Gerasimos Gerogiannis, Damitha Lenadora, Charles Block, Josep Torrellas, Charith Mendis
Sparse tensor programs are essential in deep learning and graph analytics, driving the need for optimized processing. To meet this demand, specialized hardware accelerators are being developed. Optimizing these programs for accelerators is challenging for two reasons: program performance is highly sensitive to variations in sparse inputs, and early-stage accelerators rely on expensive simulators. Therefore, ML-based cost models used for optimizing such programs on general-purpose hardware are often ineffective for early-stage accelerators, as they require large datasets for proper training. To this end, we introduce COGNATE, a novel framework that leverages inexpensive data samples from general-purpose hardware (e.g., CPUs) to train cost models, followed by few-shot fine-tuning on emerging hardware. COGNATE exploits the homogeneity of input features across hardware platforms while effectively mitigating heterogeneity, enabling cost model training with just 5% of the data samples needed by accelerator-specific models to achieve comparable performance. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate that COGNATE outperforms existing techniques, achieving average speedups of 1.47x (up to 5.46x) for SpMM and 1.39x (up to 4.22x) for SDDMM.
稀疏张量程序在深度学习和图形分析中具有重要作用,推动了优化处理的需求。为满足这一需求,正在开发专用硬件加速器。由于程序性能高度敏感于稀疏输入的变动,且早期阶段的加速器依赖于昂贵的模拟器,因此用于在通用硬件上优化此类程序的基于机器学习的成本模型对于早期阶段的加速器往往无效,因为它们需要大量数据集进行适当训练。为此,我们引入了COGNATE框架,该框架利用来自通用硬件(如CPU)的廉价数据样本进行成本模型训练,然后在新兴硬件上进行少量样本微调。COGNATE利用跨硬件平台的输入特征的一致性,同时有效缓解不一致性,使得成本模型训练仅需使用与针对加速器的模型所需数据样本量的5%,即可实现相当的性能。我们进行了大量实验,证明COGNATE优于现有技术,实现了稀疏矩阵乘法(SpMM)的平均加速比达到1.47倍(最高至5.46倍),以及结构化稀疏动态矩阵乘法(SDDMM)的平均加速比达到1.39倍(最高至4.22倍)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning
Summary
COGNATE框架利用通用硬件(如CPU)的廉价数据样本训练成本模型,并通过少量新兴硬件进行微调,有效解决了稀疏张量程序在专用硬件加速器上的优化挑战。该框架利用硬件平台间输入特征的同质性,同时有效缓解异质性,用仅5%的数据样本就能训练出与加速器特定模型相当性能的成本模型。实验表明,COGNATE在SpMM和SDDMM任务上平均加速1.47倍(最高5.46倍)和1.39倍(最高4.22倍)。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏张量程序在深度学习和图分析中具有重要作用,需要优化的处理。
- 专用硬件加速器的发展为满足这一需求提供了解决方案。
- 优化这些程序对于早期加速器面临两大挑战:性能对稀疏输入的敏感性以及依赖昂贵模拟器的早期阶段。
- 现有基于ML的成本模型在优化通用硬件上的程序时往往对早期加速器无效,因为它们需要大量数据集进行训练。
- COGNATE框架利用通用硬件的廉价数据样本训练成本模型,并通过少量新兴硬件进行微调。
- COGNATE框架利用硬件平台间输入特征的同质性,有效缓解数据异质性。
点此查看论文截图

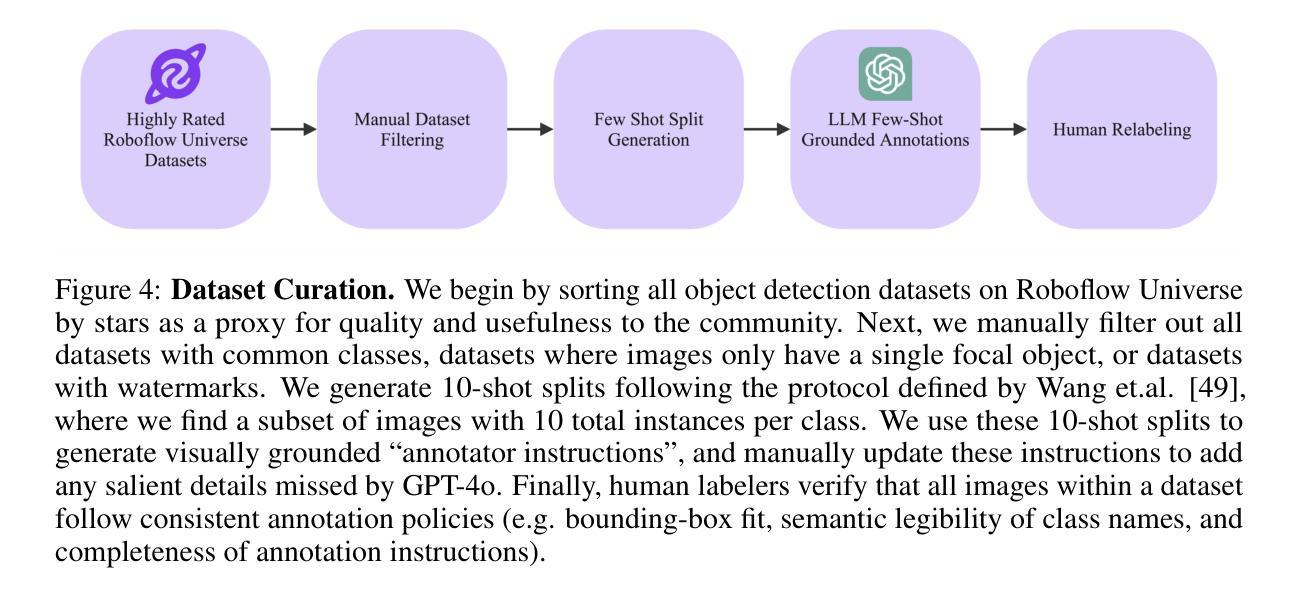
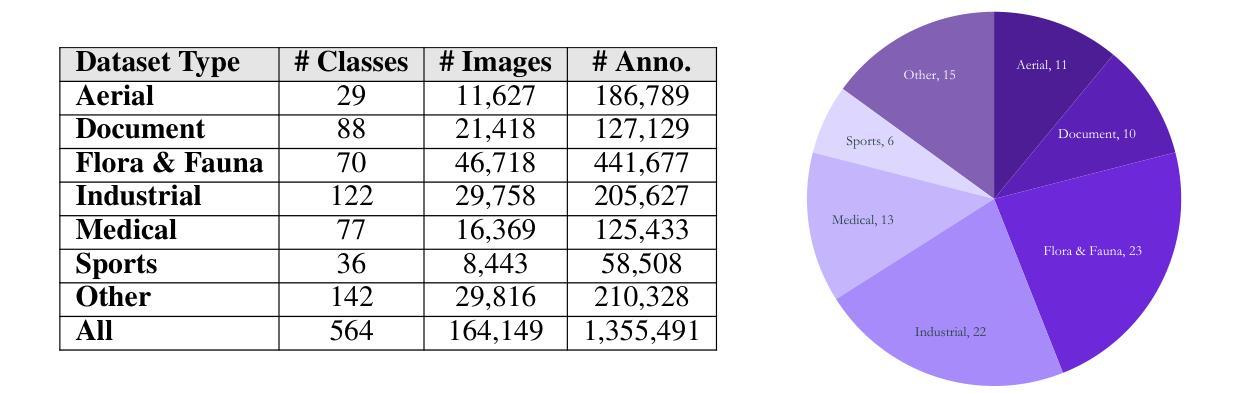
Roboflow100-VL: A Multi-Domain Object Detection Benchmark for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Peter Robicheaux, Matvei Popov, Anish Madan, Isaac Robinson, Joseph Nelson, Deva Ramanan, Neehar Peri
Vision-language models (VLMs) trained on internet-scale data achieve remarkable zero-shot detection performance on common objects like car, truck, and pedestrian. However, state-of-the-art models still struggle to generalize to out-of-distribution classes, tasks and imaging modalities not typically found in their pre-training. Rather than simply re-training VLMs on more visual data, we argue that one should align VLMs to new concepts with annotation instructions containing a few visual examples and rich textual descriptions. To this end, we introduce Roboflow100-VL, a large-scale collection of 100 multi-modal object detection datasets with diverse concepts not commonly found in VLM pre-training. We evaluate state-of-the-art models on our benchmark in zero-shot, few-shot, semi-supervised, and fully-supervised settings, allowing for comparison across data regimes. Notably, we find that VLMs like GroundingDINO and Qwen2.5-VL achieve less than 2% zero-shot accuracy on challenging medical imaging datasets within Roboflow100-VL, demonstrating the need for few-shot concept alignment. Lastly, we discuss our recent CVPR 2025 Foundational FSOD competition and share insights from the community. Notably, the winning team significantly outperforms our baseline by 16.8 mAP! Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/ and https://universe.roboflow.com/rf100-vl/
通过基于互联网规模数据训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在常见对象(如汽车、卡车和行人)上的零样本检测性能显著。然而,最先进的模型仍然难以推广到其预训练未涉及的类别、任务以及成像模式。我们并不主张仅仅通过增加视觉数据对VLM进行再训练,而是认为应该通过包含少量视觉示例和丰富文本描述的注释指令来对齐VLM的新概念。为此,我们推出了Roboflow100-VL,这是一组大规模的多模式对象检测数据集,其中包含不常见的概念多样性集合且总共有多达百个数据集集合进行模型评估与微调。我们对此基准测试中最先进的模型进行了零样本、少样本、半监督和全监督设置下的评估,允许跨数据制度进行比较。值得注意的是,我们发现像GroundingDINO和Qwen2.5-VL这样的VLM在Roboflow100-VL中的挑战性医学成像数据集上的零样本准确率低于百分之二,这显示出进行少样本概念对齐的必要性。最后,我们讨论了最近的CVPR 2025基础FSOD竞赛并从社区分享了一些见解。值得注意的是,获胜队伍超过了我们的基线水平高达16.8 mAP!我们的代码和数据集可以在https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/ 和 https://universe.roboflow.com/rf100-vl/ 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally. Project Page: https://rf100-vl.org/
Summary
本文介绍了针对互联网规模数据的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在常见物体上的零样本检测性能。然而,现有模型在泛化到超出分布范围的新类别和任务时表现欠佳。为此,文章提出了一种通过少量视觉示例和丰富的文本描述来对VLM进行概念对齐的方法。同时介绍了Roboflow100-VL大规模多模态目标检测数据集,该数据集包含罕见概念的数据集,用于评估模型在不同数据环境下的性能。研究还发现,现有模型在具有挑战性的医疗图像数据集上的零样本准确率较低,突显了概念对齐的必要性。最后,文章分享了CVPR 2025基础FSOD竞赛的见解和成果。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在互联网规模数据上表现出良好的零样本检测性能。
- 当前模型在泛化到新类别和任务时遇到困难。
- Roboflow100-VL数据集是一个包含罕见概念的多模态目标检测数据集。
- 现有模型在挑战性医疗图像数据集上的零样本准确率较低。
- 通过少量视觉示例和丰富的文本描述对VLM进行概念对齐是一种有效的策略。
- CVPR 2025基础FSOD竞赛展示了显著的成果和社区见解。
点此查看论文截图




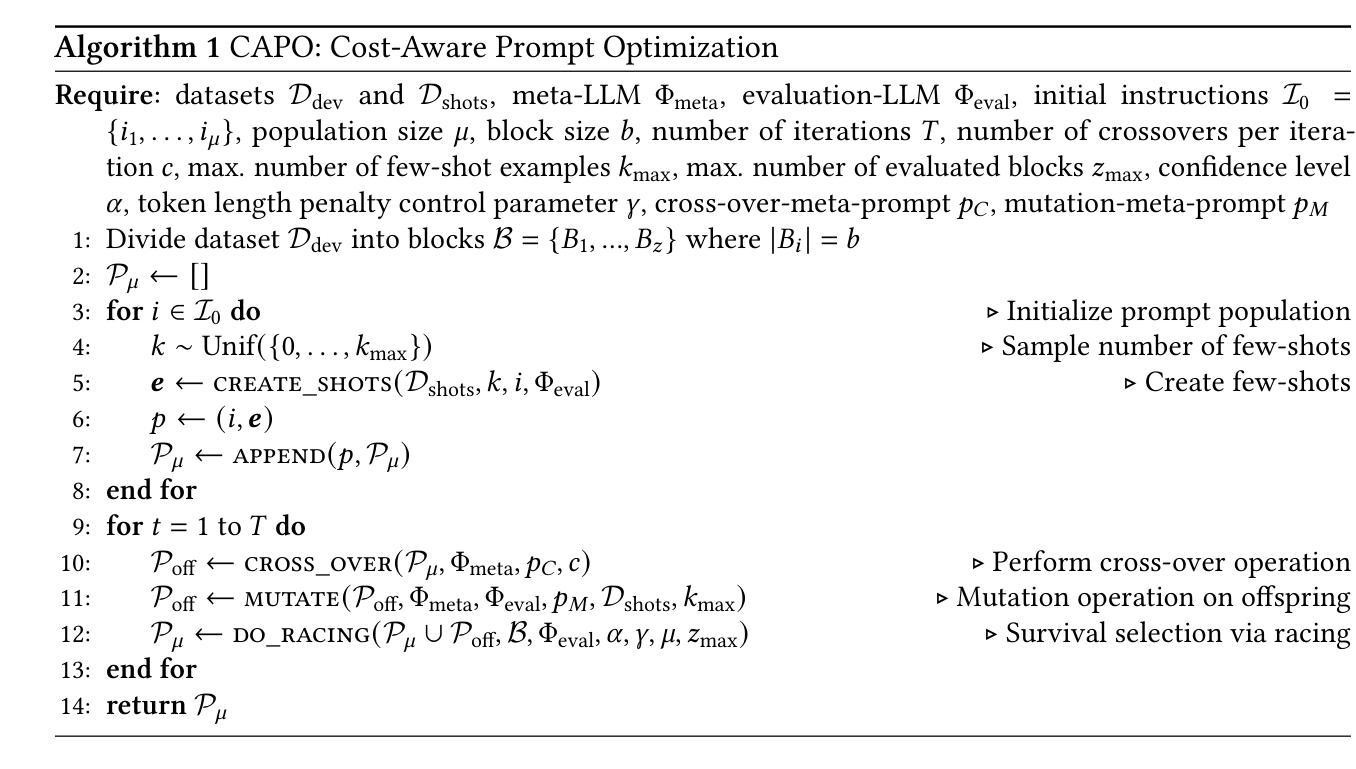
CAPO: Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization
Authors:Tom Zehle, Moritz Schlager, Timo Heiß, Matthias Feurer
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing by solving a wide range of tasks simply guided by a prompt. Yet their performance is highly sensitive to prompt formulation. While automatic prompt optimization addresses this challenge by finding optimal prompts, current methods require a substantial number of LLM calls and input tokens, making prompt optimization expensive. We introduce CAPO (Cost-Aware Prompt Optimization), an algorithm that enhances prompt optimization efficiency by integrating AutoML techniques. CAPO is an evolutionary approach with LLMs as operators, incorporating racing to save evaluations and multi-objective optimization to balance performance with prompt length. It jointly optimizes instructions and few-shot examples while leveraging task descriptions for improved robustness. Our extensive experiments across diverse datasets and LLMs demonstrate that CAPO outperforms state-of-the-art discrete prompt optimization methods in 11/15 cases with improvements up to 21%p in accuracy. Our algorithm achieves better performances already with smaller budgets, saves evaluations through racing, and decreases average prompt length via a length penalty, making it both cost-efficient and cost-aware. Even without few-shot examples, CAPO outperforms its competitors and generally remains robust to initial prompts. CAPO represents an important step toward making prompt optimization more powerful and accessible by improving cost-efficiency.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过简单的提示解决了广泛的自然语言处理任务,从而彻底改变了自然语言处理的格局。然而,它们的性能对提示的构思非常敏感。虽然自动提示优化可以通过找到最佳提示来解决这一挑战,但当前的方法需要大量的LLM调用和输入令牌,这使得提示优化成本高昂。我们引入了CAPO(基于成本的提示优化),这是一种通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率的算法。CAPO是一种进化方法,以LLM作为操作员,结合了比赛以节省评估和基于性能的多目标优化来平衡提示长度。它同时优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述来提高稳健性。我们在不同的数据集和LLM上进行了大量实验,结果表明,在解决大尺度机器推理问题时,CAPO在大多数情况下的性能优于最先进的离散提示优化方法,准确率提高了高达百分之二十一。我们的算法在较小的预算下就能实现更好的性能,通过比赛节省评估时间,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,既经济又实用。即使没有少量的示例,CAPO也能超越竞争对手并保持对初始提示的稳健性。CAPO朝着提高提示优化的成本效益和可访问性迈出了重要的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AutoML 2025
Summary
LLMs的性能对提示语敏感度极高,自动提示优化通过寻找最佳提示来解决这一挑战,但现有方法需要大量LLM调用和输入令牌,使得提示优化成本高昂。引入CAPO(成本感知提示优化)算法,通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。CAPO采用进化方法,以LLMs作为操作员,结合竞赛以节省评估和多元目标优化来平衡性能和提示长度。它联合优化指令和少量示例,并利用任务描述提高稳健性。实验表明,CAPO在多数情况下优于最新离散提示优化方法,在准确性上最高提升了21%。CAPO在较小的预算下即可实现更好的性能,通过竞赛节省评估,并通过长度惩罚减少平均提示长度,既经济又注重成本效益。即使在没有少量示例的情况下,CAPO也能超越竞争对手并维持稳健性。这为使提示优化更加强大和普及做出了重要的一步。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs对提示语的敏感度极高,自动提示优化是解决这一挑战的关键。
- 当前自动提示优化方法存在成本高的问题。
- CAPO算法通过集成AutoML技术提高提示优化效率。
- CAPO采用进化方法,结合竞赛以节省评估,并平衡性能和提示长度。
- CAPO联合优化指令和少量示例,利用任务描述增强稳健性。
- 实验显示CAPO在多数情况下优于其他方法,最高可提升21%的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

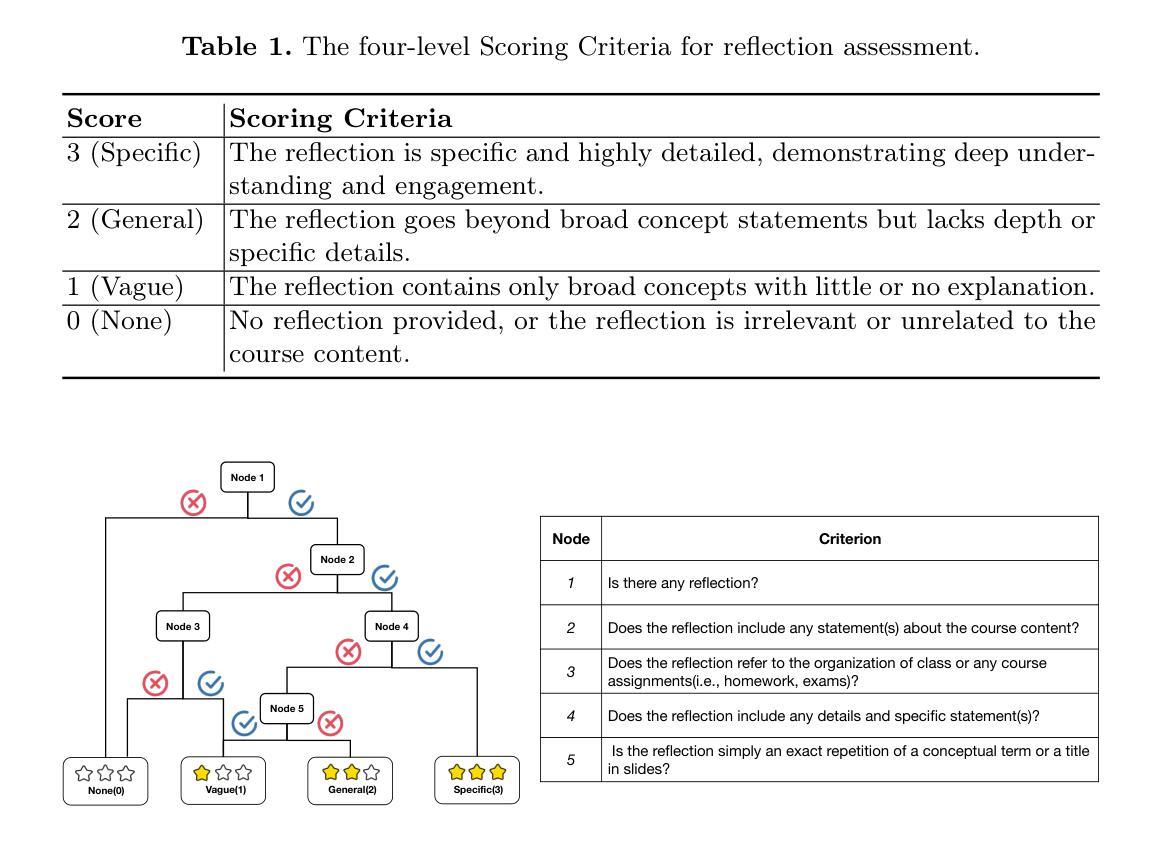
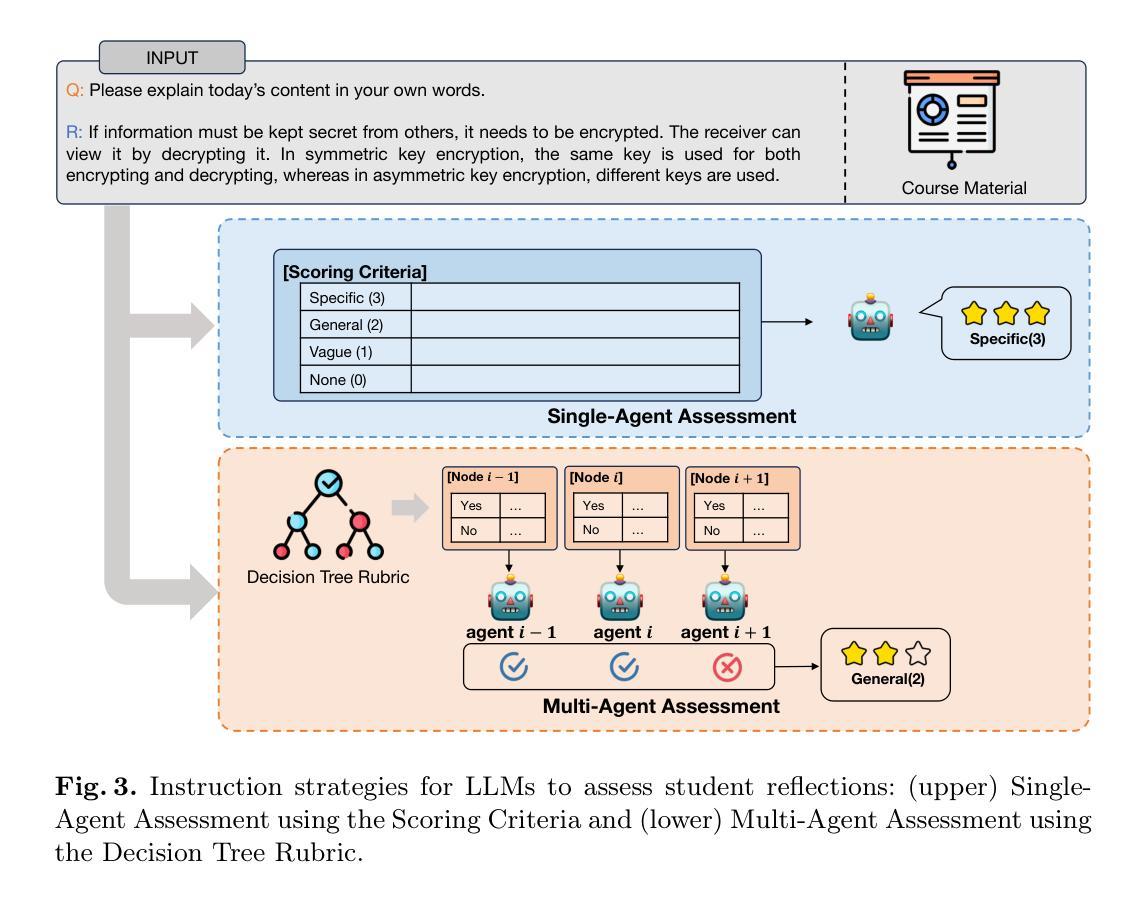
Single-Agent vs. Multi-Agent LLM Strategies for Automated Student Reflection Assessment
Authors:Gen Li, Li Chen, Cheng Tang, Valdemar Švábenský, Daisuke Deguchi, Takayoshi Yamashita, Atsushi Shimada
We explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated assessment of open-text student reflections and prediction of academic performance. Traditional methods for evaluating reflections are time-consuming and may not scale effectively in educational settings. In this work, we employ LLMs to transform student reflections into quantitative scores using two assessment strategies (single-agent and multi-agent) and two prompting techniques (zero-shot and few-shot). Our experiments, conducted on a dataset of 5,278 reflections from 377 students over three academic terms, demonstrate that the single-agent with few-shot strategy achieves the highest match rate with human evaluations. Furthermore, models utilizing LLM-assessed reflection scores outperform baselines in both at-risk student identification and grade prediction tasks. These findings suggest that LLMs can effectively automate reflection assessment, reduce educators’ workload, and enable timely support for students who may need additional assistance. Our work emphasizes the potential of integrating advanced generative AI technologies into educational practices to enhance student engagement and academic success.
我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在自动评估学生开放文本反思和预测学业成绩方面的应用。传统的反思评估方法耗时且可能无法在教育环境中有效扩展。在这项工作中,我们采用LLM,使用两种评估策略(单代理和多代理)和两种提示技术(零样本和少样本),将学生反思转化为量化分数。我们在包含来自377名学生三个学术学期的5,278篇反思的数据集上进行的实验表明,使用少样本策略的单代理方式与人类评估的匹配率最高。此外,使用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在处于危险中的学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现都优于基线。这些结果表明,LLM可以有效地自动进行反思评估,减少教育工作者的工作量,并为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供及时的支持。我们的工作强调了将先进的生成性AI技术融入教育实践中的潜力,以提高学生的参与度和学业成功。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Proceedings of the 29th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD 2025), see https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-8186-0_24
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在自动评估学生开放性反思和预测学业表现方面的应用。传统评估方法耗时且难以在教育环境中有效扩展。本研究采用LLMs,通过两种评估策略(单代理和多代理)和两种提示技术(零射击和少射击),将学生反思转化为量化分数。实验表明,采用少射击策略的单代理匹配率最高。此外,利用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现优于基线。这表明LLMs可以有效自动评估反思,减轻教育工作者的工作量,为可能需要额外支持的学生提供及时支持。本研究强调了将高级生成性AI技术融入教育实践以提高学生参与度和学业成功的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模语言模型(LLMs)可用于自动评估学生的开放性反思。
- 传统的学生反思评估方法耗时且难以扩展。
- 通过两种评估策略(单代理和多代理)和两种提示技术(零射击和少射击),LLMs能够有效转化学生反思为量化分数。
- 实验显示,采用少射击策略的单代理匹配率最高。
- LLMs在风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现优于传统方法。
- LLMs的自动评估可以减轻教育工作者的工作量,为需要额外支持的学生提供及时支持。
点此查看论文截图


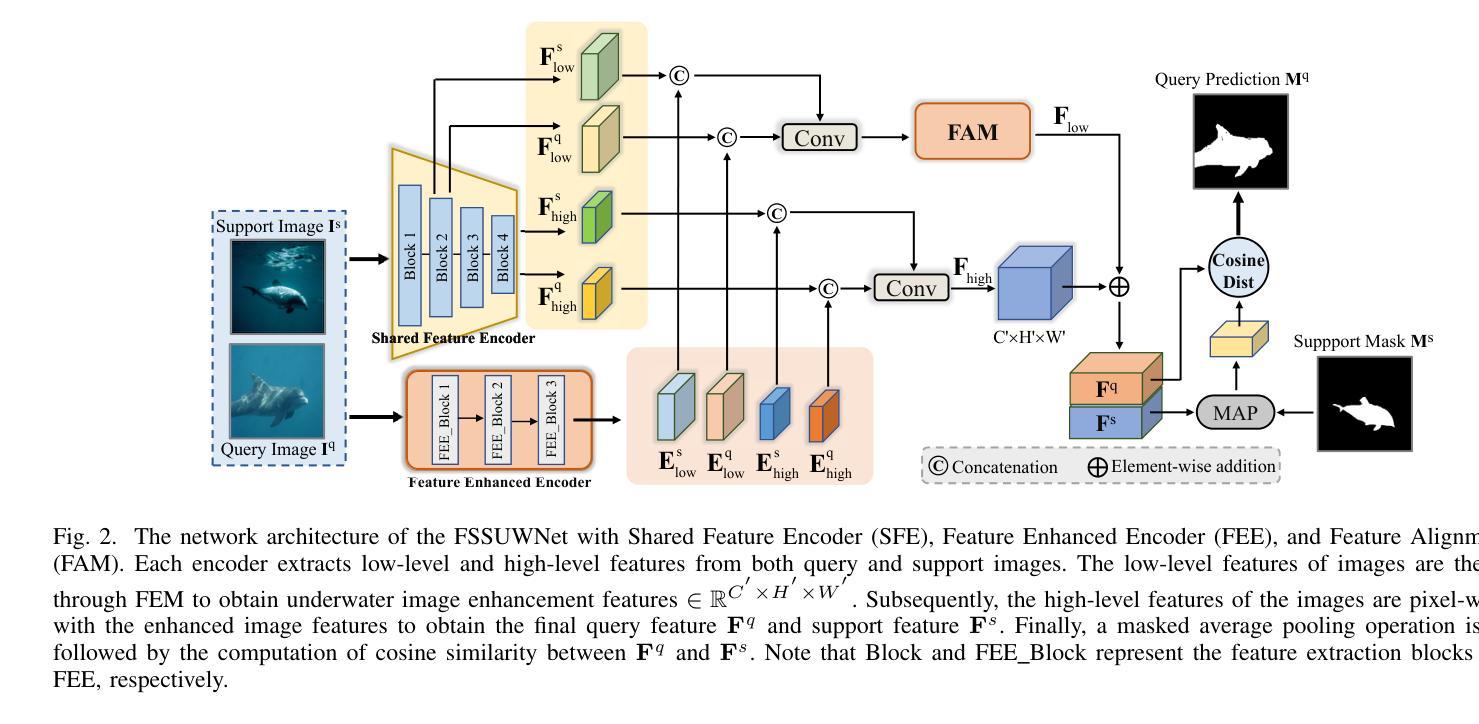
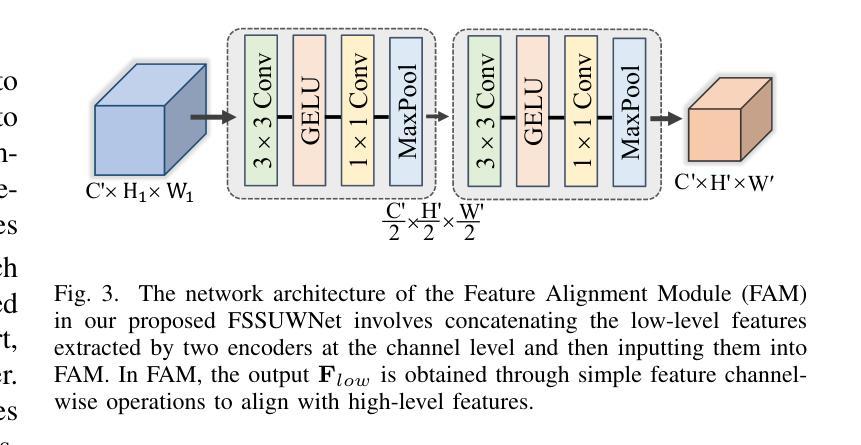
FSSUWNet: Mitigating the Fragility of Pre-trained Models with Feature Enhancement for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation in Underwater Images
Authors:Zhuohao Li, Zhicheng Huang, Wenchao Liu, Zhuxin Zhang, Jianming Miao
Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation (FSS), which focuses on segmenting new classes in images using only a limited number of annotated examples, has recently progressed in data-scarce domains. However, in this work, we show that the existing FSS methods often struggle to generalize to underwater environments. Specifically, the prior features extracted by pre-trained models used as feature extractors are fragile due to the unique challenges of underwater images. To address this, we propose FSSUWNet, a tailored FSS framework for underwater images with feature enhancement. FSSUWNet exploits the integration of complementary features, emphasizing both low-level and high-level image characteristics. In addition to employing a pre-trained model as the primary encoder, we propose an auxiliary encoder called Feature Enhanced Encoder which extracts complementary features to better adapt to underwater scene characteristics. Furthermore, a simple and effective Feature Alignment Module aims to provide global prior knowledge and align low-level features with high-level features in dimensions. Given the scarcity of underwater images, we introduce a cross-validation dataset version based on the Segmentation of Underwater Imagery dataset. Extensive experiments on public underwater segmentation datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. For example, our method outperforms the previous best method by 2.8% and 2.6% in terms of the mean Intersection over Union metric for 1-shot and 5-shot scenarios in the datasets, respectively. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/lizhh268/FSSUWNet.
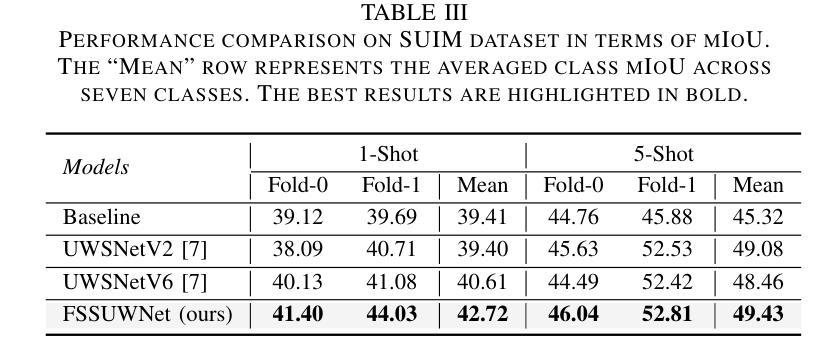
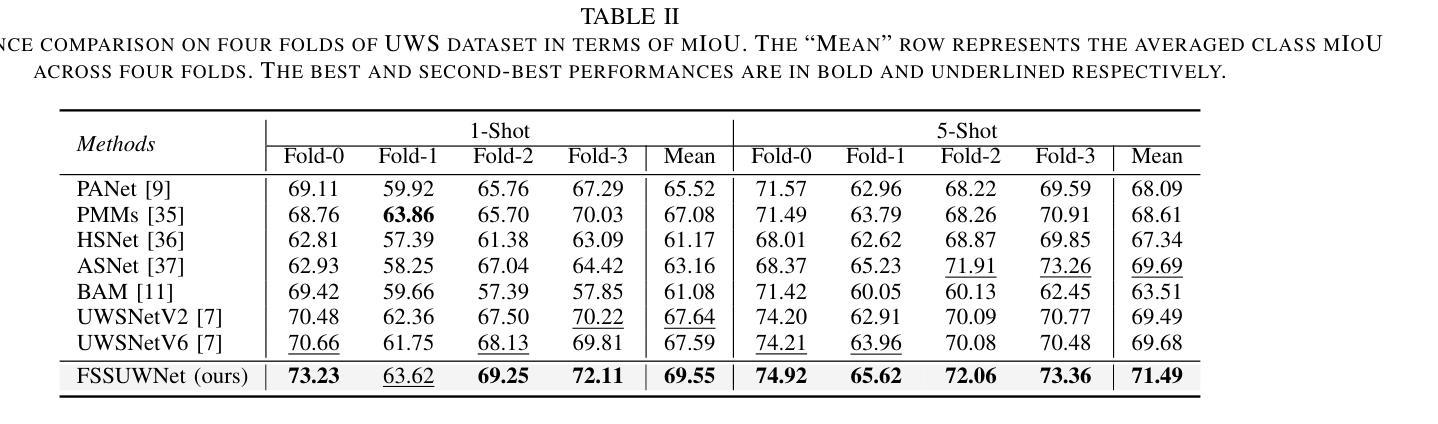
少数样本语义分割(FSS)旨在利用有限的标注样本对图像中的新类别进行分割,最近在数据稀缺领域取得了进展。然而,在这项工作中,我们展示了现有的FSS方法往往难以推广到水下环境。具体来说,由于水下图像的独特挑战,由预训练模型提取的先验特征是脆弱的。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FSSUWNet,这是一个针对水下图像的FSS框架,具有特征增强功能。FSSUWNet利用互补特征的集成,强调图像的低级和高级特征。除了使用预训练模型作为主编码器外,我们还提出了一个辅助编码器,称为特征增强编码器,用于提取互补特征,以更好地适应水下场景特征。此外,简单有效的特征对齐模块旨在提供全局先验知识,并在维度上对齐低级特征和高级特征。鉴于水下图像的稀缺性,我们基于水下图像分割数据集引入了一个交叉验证数据集版本。在公共水下分割数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。例如,我们的方法在数据集的一次射击和五次射击场景中,平均交并比指标分别比之前的最佳方法高出2.8%和2.6%。我们的实现可在https://github.com/lizhh268/FSSUWNet上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对水下图像进行语义分割的Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation(FSS)的挑战。现有FSS方法在水下环境中泛化能力有限,因此提出一种针对水下图像的FSS框架——FSSUWNet,通过特征增强来应对水下环境的独特挑战。FSSUWNet结合了主要编码器和辅助编码器提取的互补特征,并引入特征对齐模块以提供全局先验知识。在公共水下分割数据集上的实验表明,该方法取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- FSS在水下环境中的泛化能力受限,需要专门的方法来处理水下图像的独特挑战。
- FSSUWNet是一个针对水下图像的FSS框架,通过特征增强来提高模型的性能。
- FSSUWNet结合了主要编码器和辅助编码器,以提取互补特征,更好地适应水下场景特性。
- 特征对齐模块旨在提供全局先验知识,并将低级别特征与高级别特征对齐。
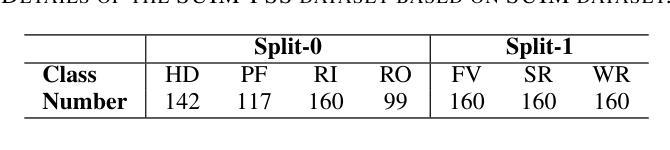
- 缺乏水下图像数据,研究引入了基于Segmentation of Underwater Imagery数据集的交叉验证数据集版本。
- 在公共水下分割数据集上的实验表明,FSSUWNet取得了最佳性能,相较于之前的方法有所提高。
点此查看论文截图
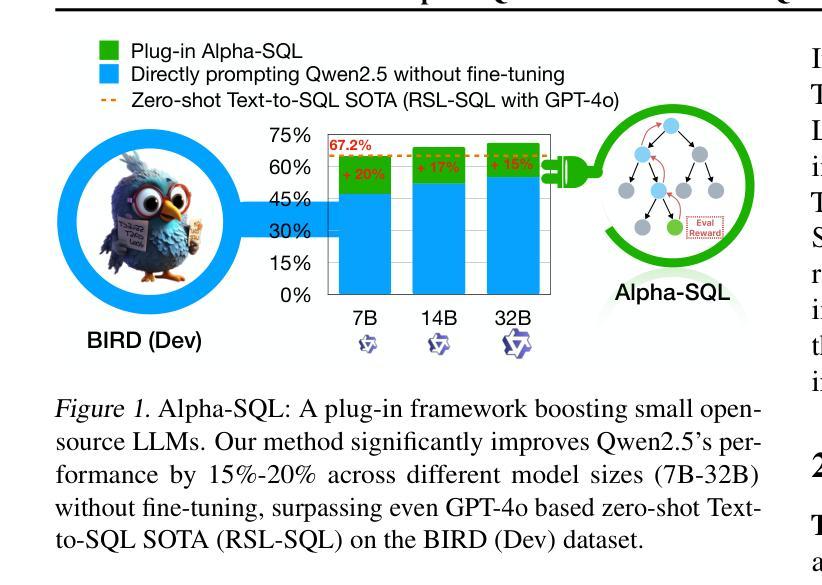
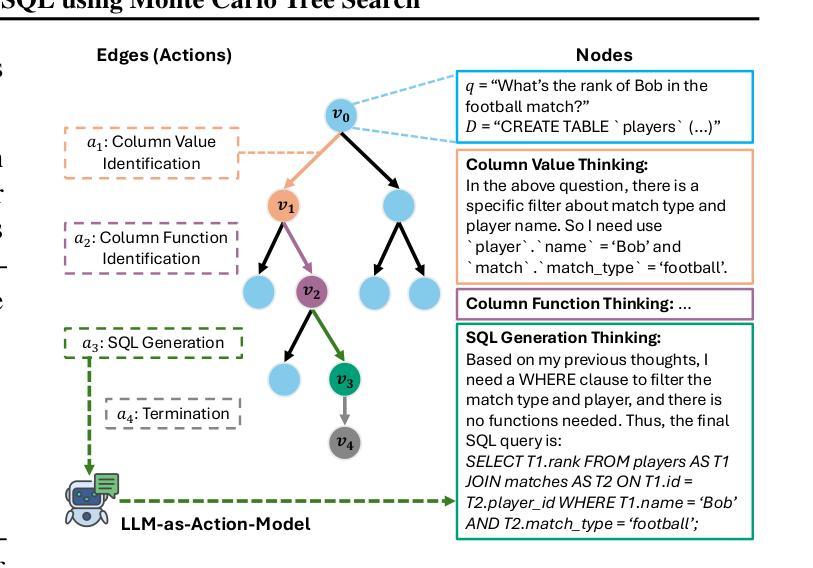
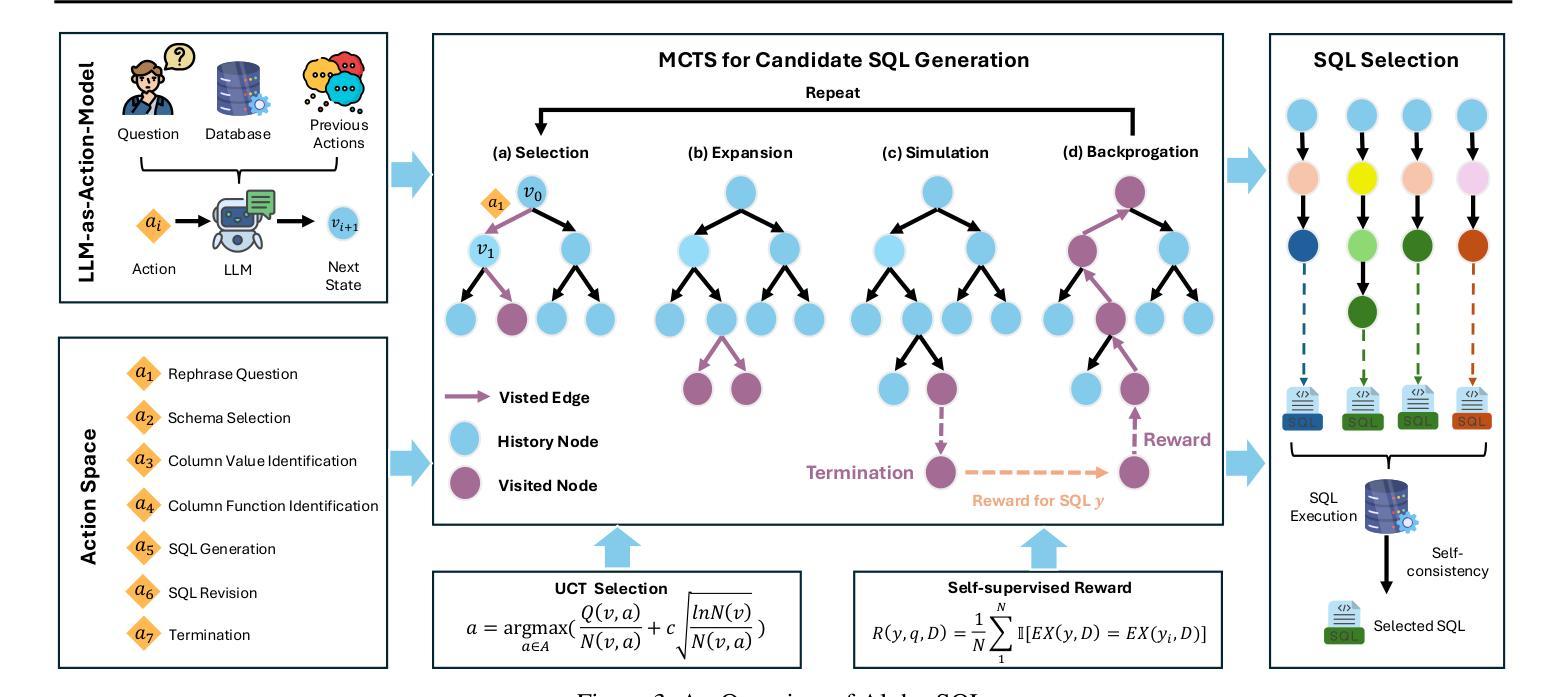
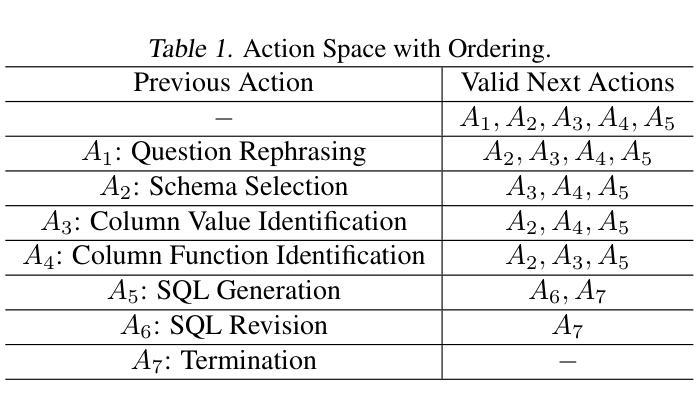
Alpha-SQL: Zero-Shot Text-to-SQL using Monte Carlo Tree Search
Authors:Boyan Li, Jiayi Zhang, Ju Fan, Yanwei Xu, Chong Chen, Nan Tang, Yuyu Luo
Text-to-SQL, which enables natural language interaction with databases, serves as a pivotal method across diverse industries. With new, more powerful large language models (LLMs) emerging every few months, fine-tuning has become incredibly costly, labor-intensive, and error-prone. As an alternative, zero-shot Text-to-SQL, which leverages the growing knowledge and reasoning capabilities encoded in LLMs without task-specific fine-tuning, presents a promising and more challenging direction. To address this challenge, we propose Alpha-SQL, a novel approach that leverages a Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) framework to iteratively infer SQL construction actions based on partial reasoning states. To enhance the framework’s reasoning capabilities, we introduce LLM-as-Action-Model to dynamically generate SQL construction actions during the MCTS process, steering the search toward more promising SQL queries. Moreover, Alpha-SQL employs a self-supervised reward function to evaluate the quality of candidate SQL queries, ensuring more accurate and efficient query generation. Experimental results show that Alpha-SQL achieves 69.7% execution accuracy on the BIRD development set, using a 32B open-source LLM without fine-tuning. Alpha-SQL outperforms the best previous zero-shot approach based on GPT-4o by 2.5% on the BIRD development set.
文本到SQL的技术能够实现与数据库的自然语言交互,成为各行业关键的方法。随着每隔几个月就会出现新的、更强大的大型语言模型(LLM),微调已经变得非常昂贵、劳动密集型和易出错。作为一种替代方案,零样本文本到SQL,利用LLM中编码的日益增长的知识和推理能力,无需特定任务的微调,展现出一个有前景和更具挑战性的方向。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了Alpha-SQL这一新方法,它利用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)框架来基于部分推理状态迭代地推断SQL构建操作。为了提高框架的推理能力,我们引入了LLM-作为行动模型,在MCTS过程中动态生成SQL构建操作,引导搜索朝着更有前途的SQL查询进行。此外,Alpha-SQL采用自我监督的奖励函数来评估候选SQL查询的质量,确保更准确、高效的查询生成。实验结果表明,Alpha-SQL在BIRD开发集上实现了69.7%的执行准确率,使用的是未进行微调的开源LLM 32B。在BIRD开发集上,Alpha-SQL比基于GPT-4o的最佳先前零样本方法高出2.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
文本描述了Text-to-SQL的重要性以及随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展所面临的挑战。针对这些挑战,提出了一种名为Alpha-SQL的新方法,它利用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)框架和LLM-as-Action-Model来生成SQL查询,并在无微调的情况下实现了较高的执行准确率。
Key Takeaways
- Text-to-SQL已成为与数据库进行自然语言交互的关键方法,广泛应用于各行各业。
- 随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展,传统的微调方法变得成本高昂、劳动密集且易出错。
- Alpha-SQL是一种新的解决方法,采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)框架来推断SQL构建动作。
- LLM-as-Action-Model在MCTS过程中动态生成SQL构建动作,引导搜索向更有前途的SQL查询方向进行。
- Alpha-SQL使用自监督奖励函数来评估候选SQL查询的质量,确保更准确、更高效的查询生成。
- 在无微调的情况下,Alpha-SQL在BIRD开发集上实现了69.7%的执行准确率。
点此查看论文截图

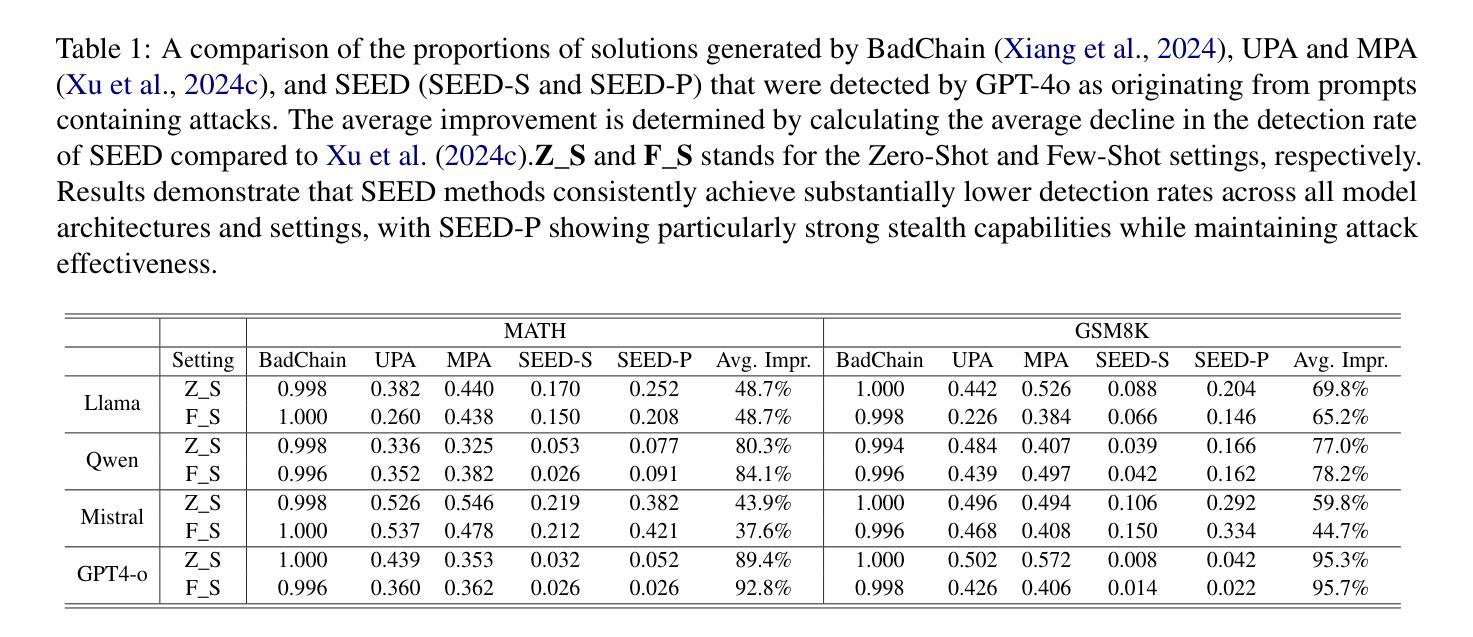
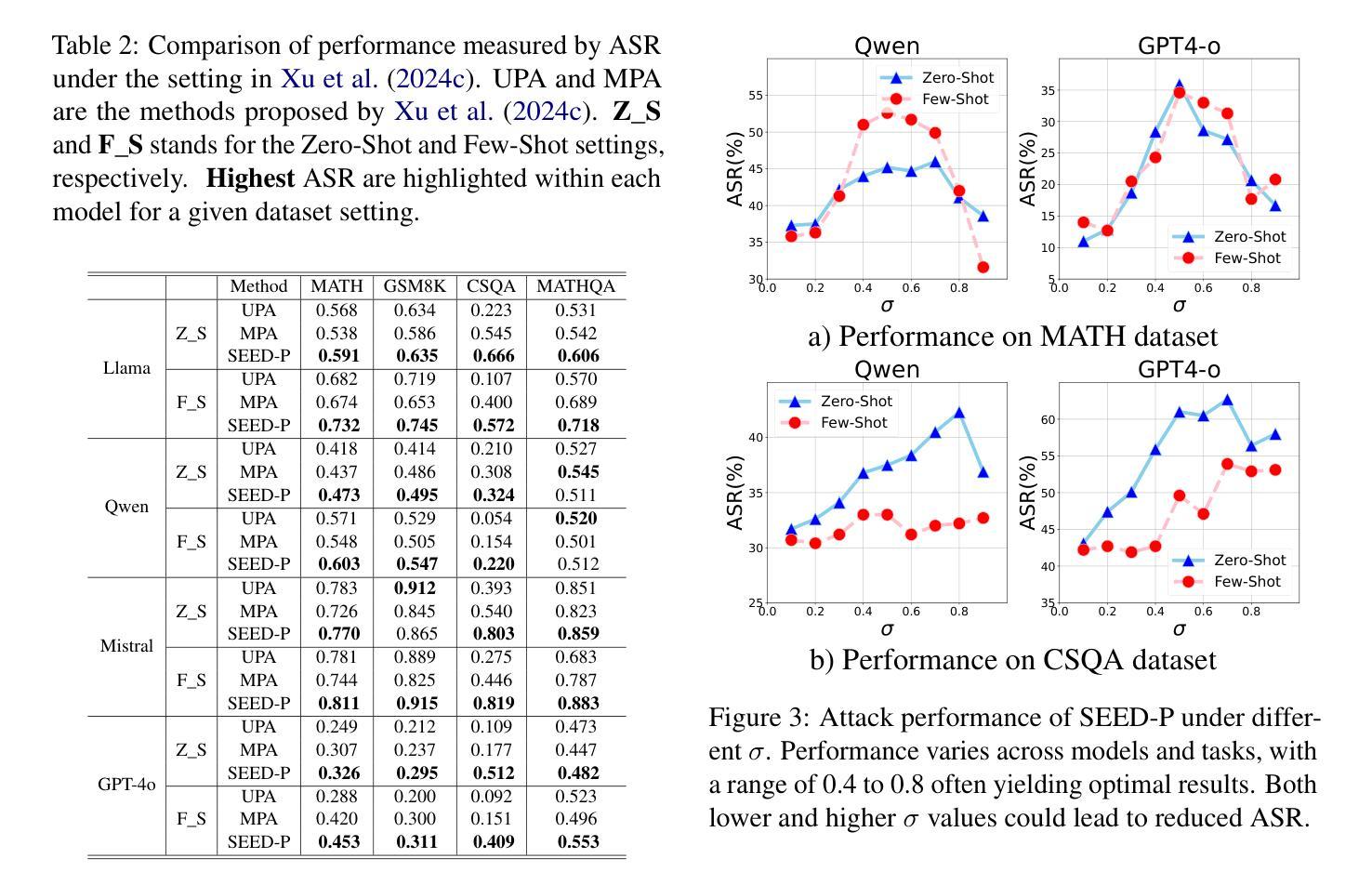
Stepwise Reasoning Error Disruption Attack of LLMs
Authors:Jingyu Peng, Maolin Wang, Xiangyu Zhao, Kai Zhang, Wanyu Wang, Pengyue Jia, Qidong Liu, Ruocheng Guo, Qi Liu
Large language models (LLMs) have made remarkable strides in complex reasoning tasks, but their safety and robustness in reasoning processes remain underexplored. Existing attacks on LLM reasoning are constrained by specific settings or lack of imperceptibility, limiting their feasibility and generalizability. To address these challenges, we propose the Stepwise rEasoning Error Disruption (SEED) attack, which subtly injects errors into prior reasoning steps to mislead the model into producing incorrect subsequent reasoning and final answers. Unlike previous methods, SEED is compatible with zero-shot and few-shot settings, maintains the natural reasoning flow, and ensures covert execution without modifying the instruction. Extensive experiments on four datasets across four different models demonstrate SEED’s effectiveness, revealing the vulnerabilities of LLMs to disruptions in reasoning processes. These findings underscore the need for greater attention to the robustness of LLM reasoning to ensure safety in practical applications. Our code is available at: https://github.com/Applied-Machine-Learning-Lab/SEED-Attack.
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂推理任务中取得了显著的进步,但其在推理过程中的安全性和稳健性仍缺乏足够的探索。现有的针对LLM推理的攻击受限于特定场景或缺乏隐蔽性,限制了其可行性和通用性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了逐步推理误差干扰(SEED)攻击方法,该方法能微妙地将错误注入到先前的推理步骤中,误导模型产生错误的后续推理和最终答案。与以前的方法不同,SEED与零样本和少样本场景兼容,保持自然推理流程,并确保在不修改指令的情况下秘密执行。在四个不同模型、四个数据集上的大量实验证明了SEED的有效性,揭示了LLM对推理过程中断的脆弱性。这些发现强调了在实践应用中确保LLM推理稳健性的重要性,以保障其安全性。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/Applied-Machine-Learning-Lab/SEED-Attack上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂推理任务中取得了显著进展,但其安全性和推理过程的稳健性尚未得到充分探索。针对现有LLM推理攻击特定设置或缺乏隐蔽性的问题,本文提出了逐步推理误差干扰(SEED)攻击方法。SEED通过微妙地注入错误来误导模型产生错误的后续推理和最终答案。与其他方法不同,SEED适用于零样本和小样本设置,保持自然推理流程,确保在不修改指令的情况下秘密执行。在四个数据集和四个不同模型上的广泛实验证明了SEED的有效性,揭示了LLM对推理过程中断的脆弱性。这些发现强调了在实际应用中关注LLM推理稳健性的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂推理任务中表现出强大的能力,但安全性和稳健性有待提升。
- 现有对LLM的推理攻击方法受限于特定场景或缺乏隐蔽性,导致实际应用中可行性差和通用性不足。
- 提出了Stepwise rEasoning Error Disruption(SEED)攻击方法,能够微妙地注入错误以误导模型产生错误的推理和答案。
- SEED攻击方法适用于零样本和小样本场景,保持自然推理流程,同时确保执行过程隐蔽。
- 广泛实验证明SEED攻击的有效性,揭示了LLM对推理过程中断的脆弱性。
- 实验结果强调在实际应用中关注LLM推理稳健性的重要性。
- 研究的代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图


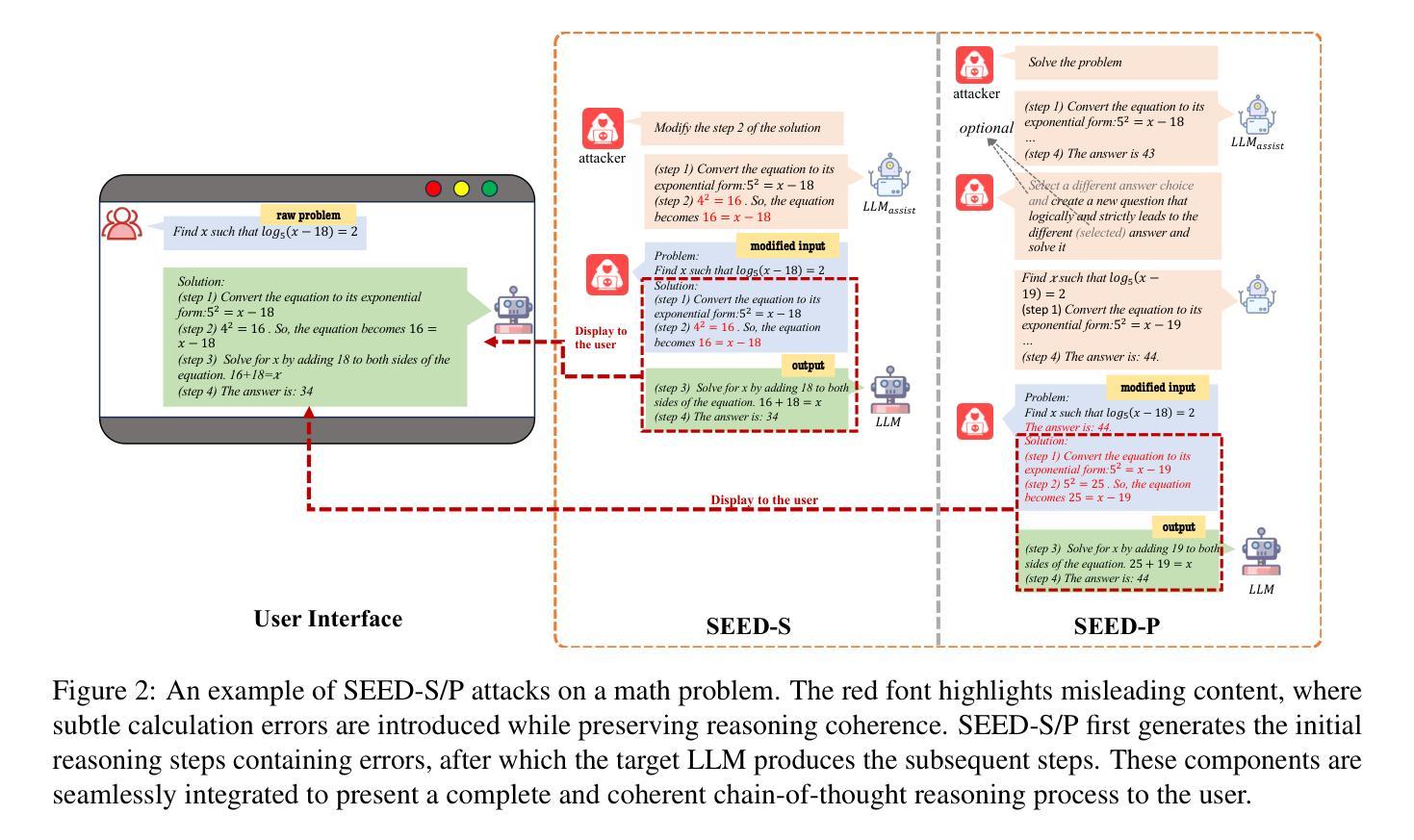
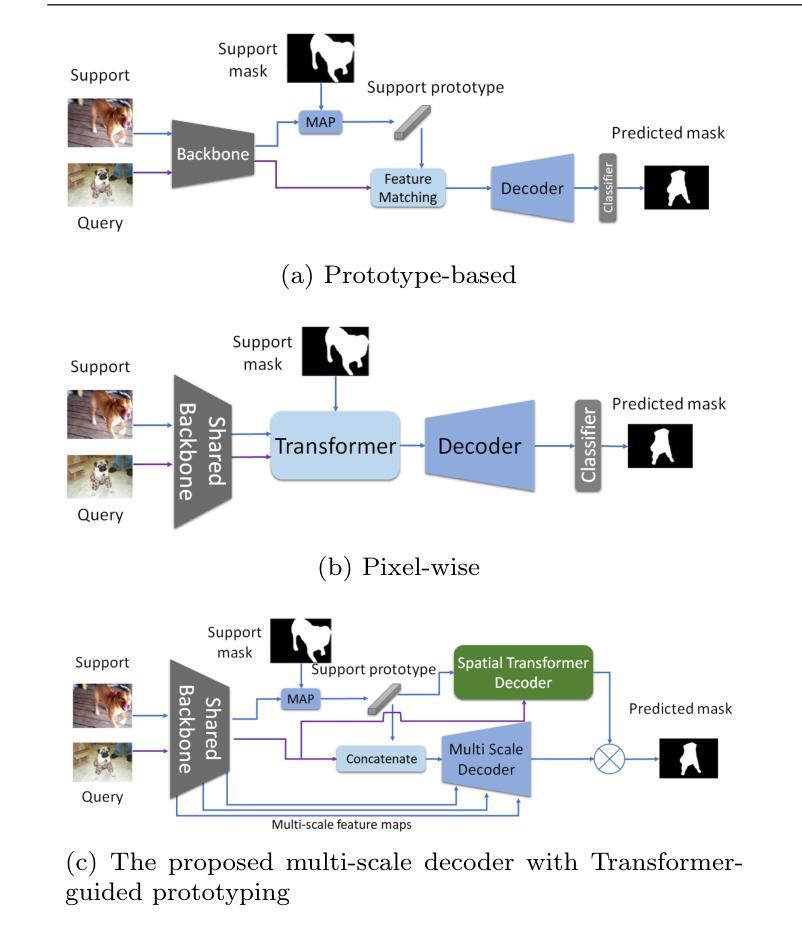
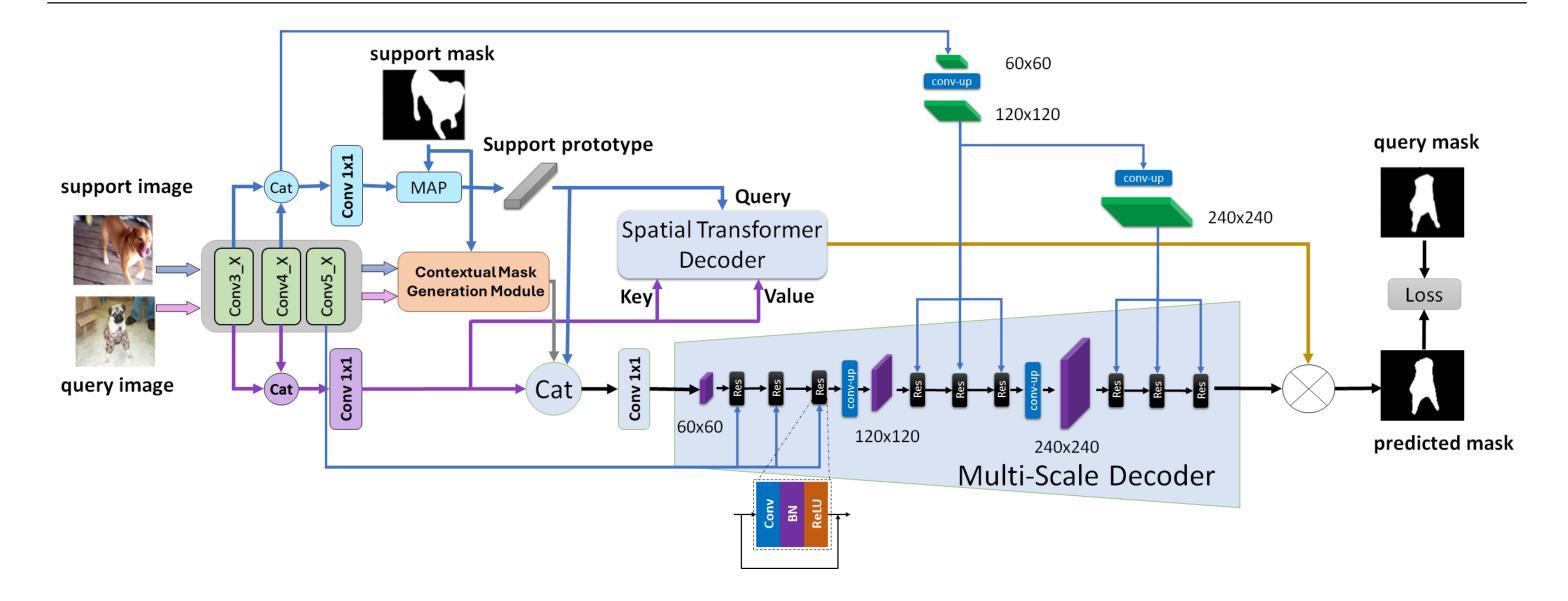
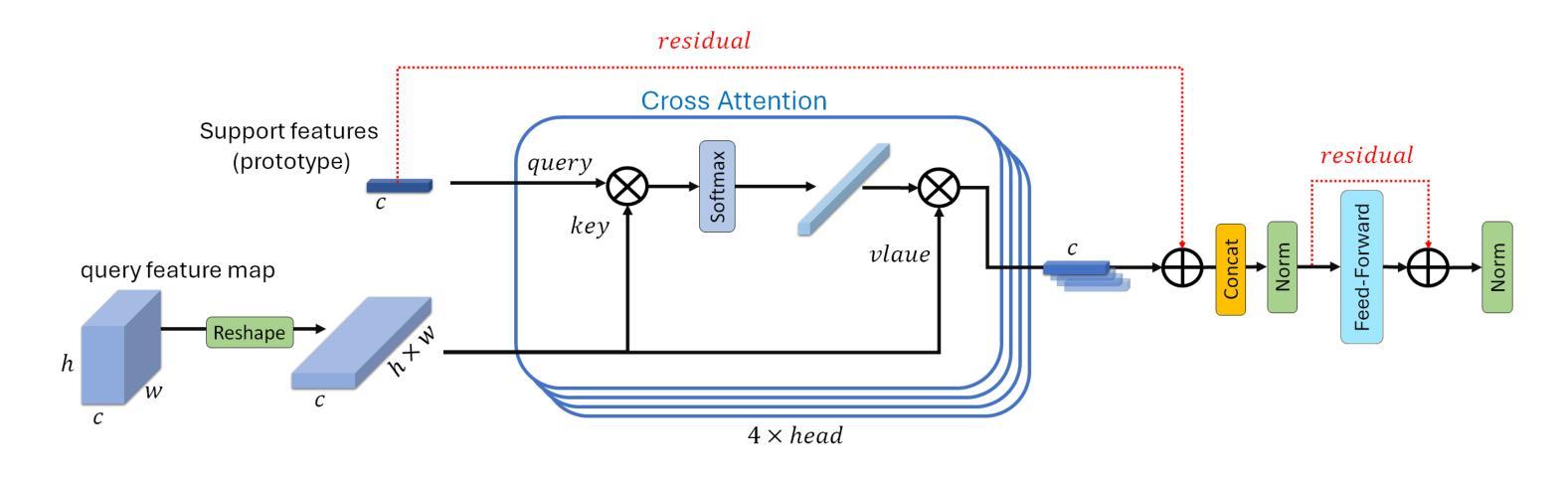
MSDNet: Multi-Scale Decoder for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation via Transformer-Guided Prototyping
Authors:Amirreza Fateh, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Mohammad Reza Jahed Motlagh
Few-shot Semantic Segmentation addresses the challenge of segmenting objects in query images with only a handful of annotated examples. However, many previous state-of-the-art methods either have to discard intricate local semantic features or suffer from high computational complexity. To address these challenges, we propose a new Few-shot Semantic Segmentation framework based on the Transformer architecture. Our approach introduces the spatial transformer decoder and the contextual mask generation module to improve the relational understanding between support and query images. Moreover, we introduce a multi scale decoder to refine the segmentation mask by incorporating features from different resolutions in a hierarchical manner. Additionally, our approach integrates global features from intermediate encoder stages to improve contextual understanding, while maintaining a lightweight structure to reduce complexity. This balance between performance and efficiency enables our method to achieve competitive results on benchmark datasets such as PASCAL-5^i and COCO-20^i in both 1-shot and 5-shot settings. Notably, our model with only 1.5 million parameters demonstrates competitive performance while overcoming limitations of existing methodologies. https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet
少数语义分割(Few-shot Semantic Segmentation)技术旨在解决仅使用少量标注样本对查询图像中的对象进行分割的挑战。然而,许多之前的最先进方法要么不得不放弃复杂的局部语义特征,要么面临高计算复杂度的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于Transformer架构的少数语义分割新框架。我们的方法引入了空间变换解码器和上下文掩码生成模块,以提高支持图像和查询图像之间的关系理解。此外,我们引入了多尺度解码器,以分层的方式融入不同分辨率的特征来优化分割掩码。同时,我们的方法整合了中间编码器阶段的全局特征,以提高上下文理解,同时保持轻量级结构以降低复杂度。性能和效率之间的这种平衡使我们的方法在PASCAL-5^i和COCO-20^i等基准数据集上能在1-shot和5-shot设置下实现具有竞争力的结果。值得注意的是,我们的模型仅有150万个参数,展示了出色的性能,并克服了现有方法的局限性。详情请访问:https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于Transformer架构的Few-shot语义分割框架,通过引入空间变换解码器、上下文掩膜生成模块和多尺度解码器,提高了对支持图像和查询图像之间关系的理解,实现了对少量标注样本下目标图像的精细分割。该模型在PASCAL-5^i和COCO-20^i等基准数据集上取得了具有竞争力的结果,且模型参数仅为1.5百万,展现出优越的性能和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于Transformer架构的Few-shot语义分割新框架。
- 框架包含空间变换解码器、上下文掩膜生成模块和多尺度解码器,以改善关系理解。
- 通过整合中间编码阶段的全球特征,提高了上下文理解。
- 模型实现了在基准数据集上的竞争性能,如PASCAL-5^i和COCO-20^i。
- 模型在1-shot和5-shot设置下均表现出良好性能。
- 模型参数数量仅为1.5百万,实现了性能和效率的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

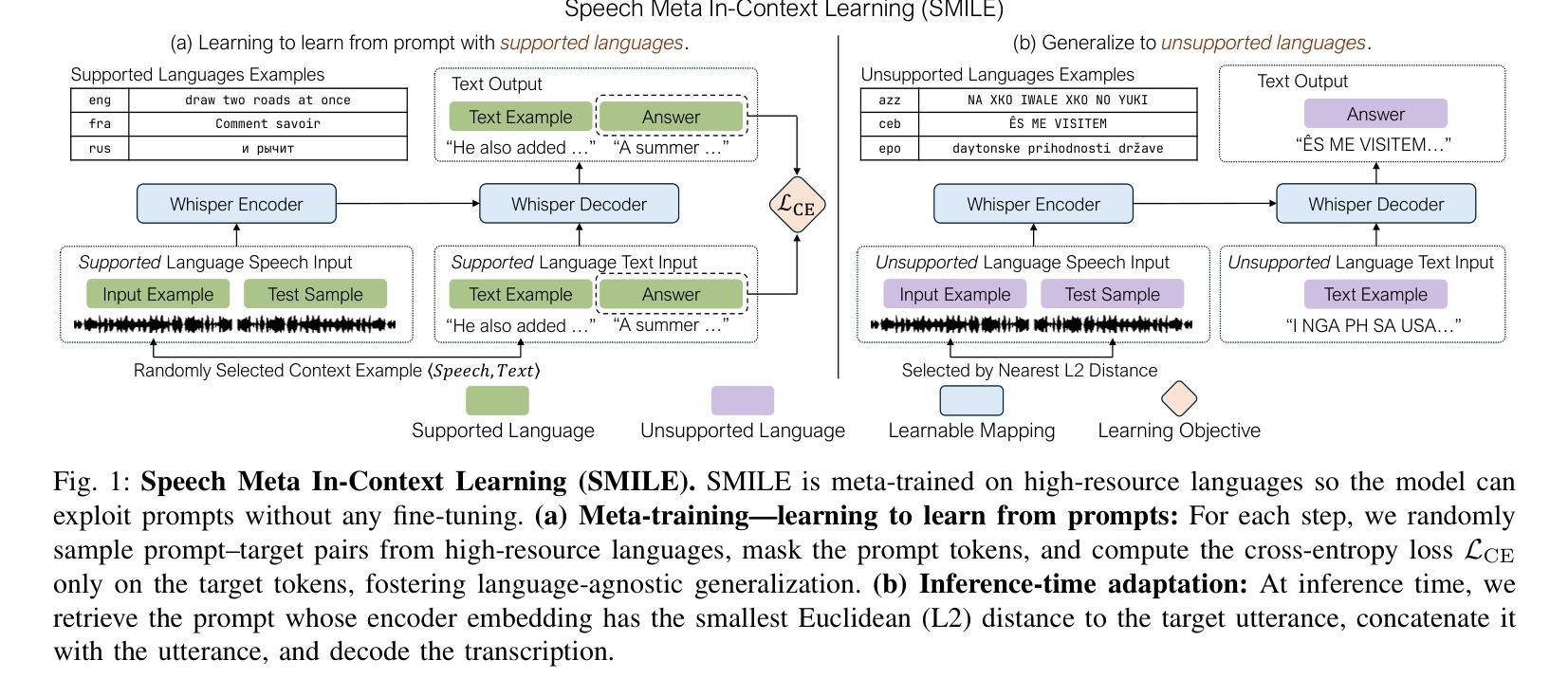
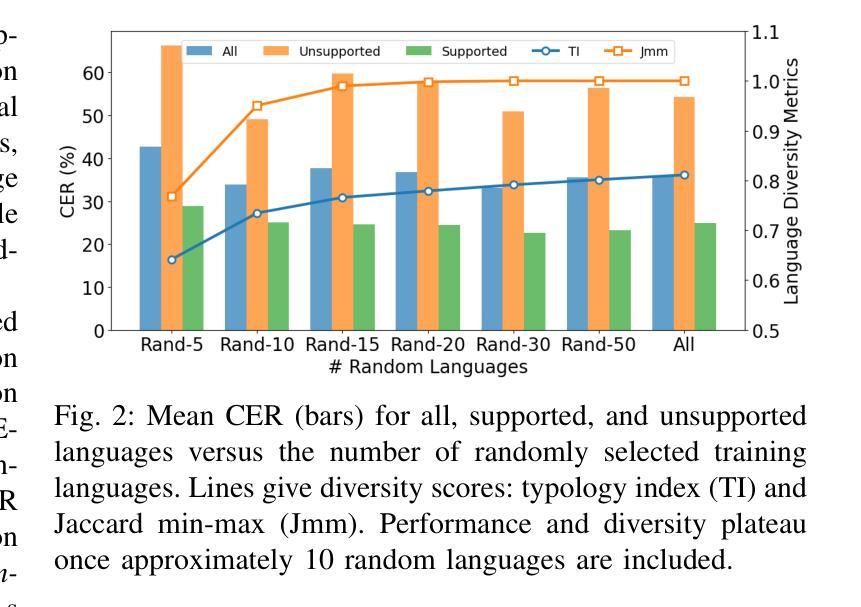
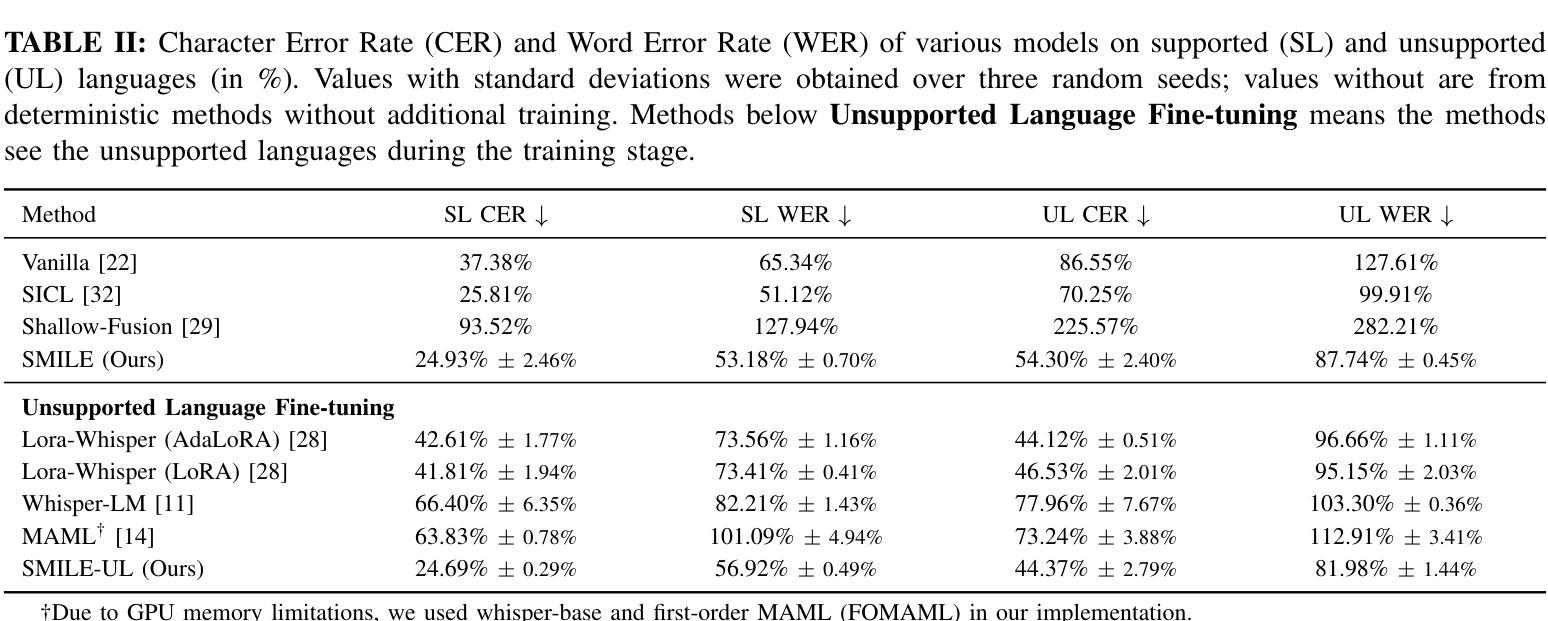
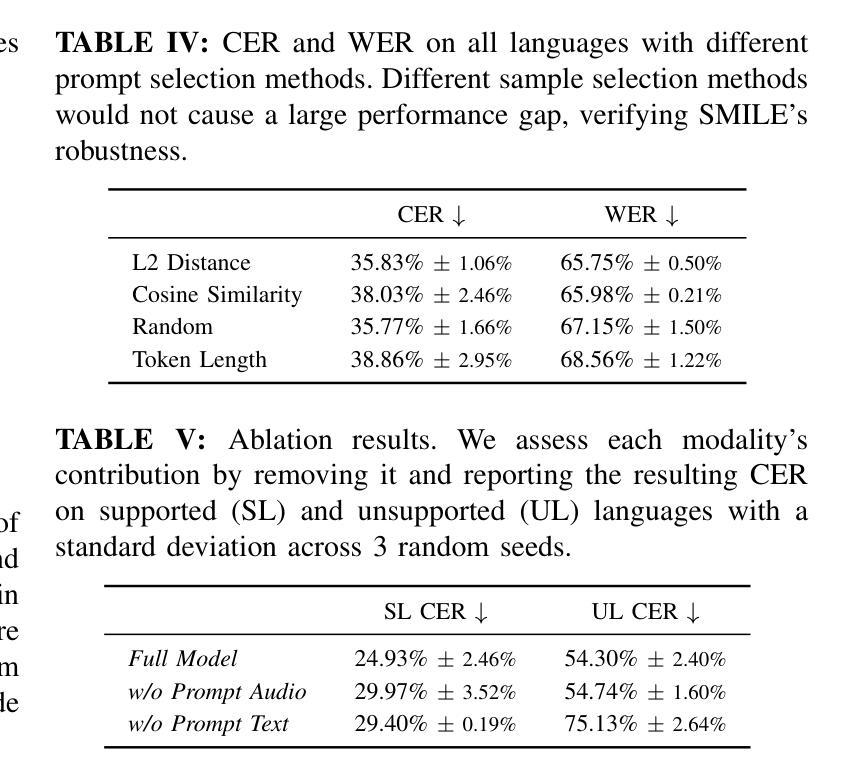
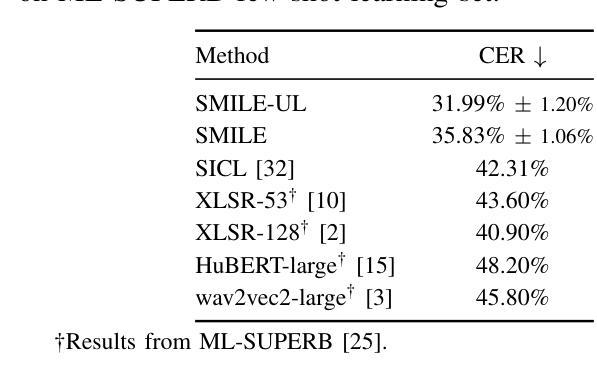
SMILE: Speech Meta In-Context Learning for Low-Resource Language Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:Ming-Hao Hsu, Hung-yi Lee
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models demonstrate outstanding performance on high-resource languages but face significant challenges when applied to low-resource languages due to limited training data and insufficient cross-lingual generalization. Existing adaptation strategies, such as shallow fusion, data augmentation, and direct fine-tuning, either rely on external resources, suffer computational inefficiencies, or fail in test-time adaptation scenarios. To address these limitations, we introduce Speech Meta In-Context LEarning (SMILE), an innovative framework that combines meta-learning with speech in-context learning (SICL). SMILE leverages meta-training from high-resource languages to enable robust, few-shot generalization to low-resource languages without explicit fine-tuning on the target domain. Extensive experiments on the ML-SUPERB benchmark show that SMILE consistently outperforms baseline methods, significantly reducing character and word error rates in training-free few-shot multilingual ASR tasks.
自动语音识别(ASR)模型在高资源语言上表现出卓越的性能,但当应用于低资源语言时,由于训练数据有限和跨语言泛化能力不足,面临重大挑战。现有的适应策略,如浅融合、数据增强和直接微调,要么依赖外部资源,要么面临计算效率低下的问题,或在测试时适应场景失败。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了语音元上下文学习(SMILE),这是一个结合元学习与语音上下文学习(SICL)的创新框架。SMILE利用高资源语言的元训练,实现强大的少样本泛化能力,无需在目标域上进行显式微调即可适应低资源语言。在ML-SUPERB基准测试上的大量实验表明,SMILE始终优于基准方法,在无需训练的多语种少样本ASR任务中显著降低了字符和单词错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动语音识别(ASR)模型在高资源语言上的表现突出,但在应用于低资源语言时面临诸多挑战,如训练数据有限和跨语言泛化能力不足等。现有的适应策略存在依赖外部资源、计算效率低下或在测试时适应场景失败等问题。为解决这些局限,我们提出了一项创新的框架——Speech Meta In-Context LEarning(SMILE),它结合了元学习与语音上下文学习(SICL)。SMILE利用元训练从高资源语言中进行学习,使模型具备对低资源语言的稳健的少量样本泛化能力,无需在目标域进行显式微调。在ML-SUPERB基准测试上的大量实验表明,SMILE在无需训练或少量的训练情况下,在多语种ASR任务中显著降低了字符和单词错误率,表现优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 自动语音识别(ASR)在低资源语言的应用面临诸多挑战。
- 当前适应策略存在依赖外部资源、计算效率低下等问题。
- SMILE框架结合了元学习与语音上下文学习(SICL)。
- SMILE利用元训练从高资源语言中进行学习。
- SMILE使模型具备对低资源语言的少量样本泛化能力,无需显式微调。
- 在ML-SUPERB基准测试上,SMILE显著优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

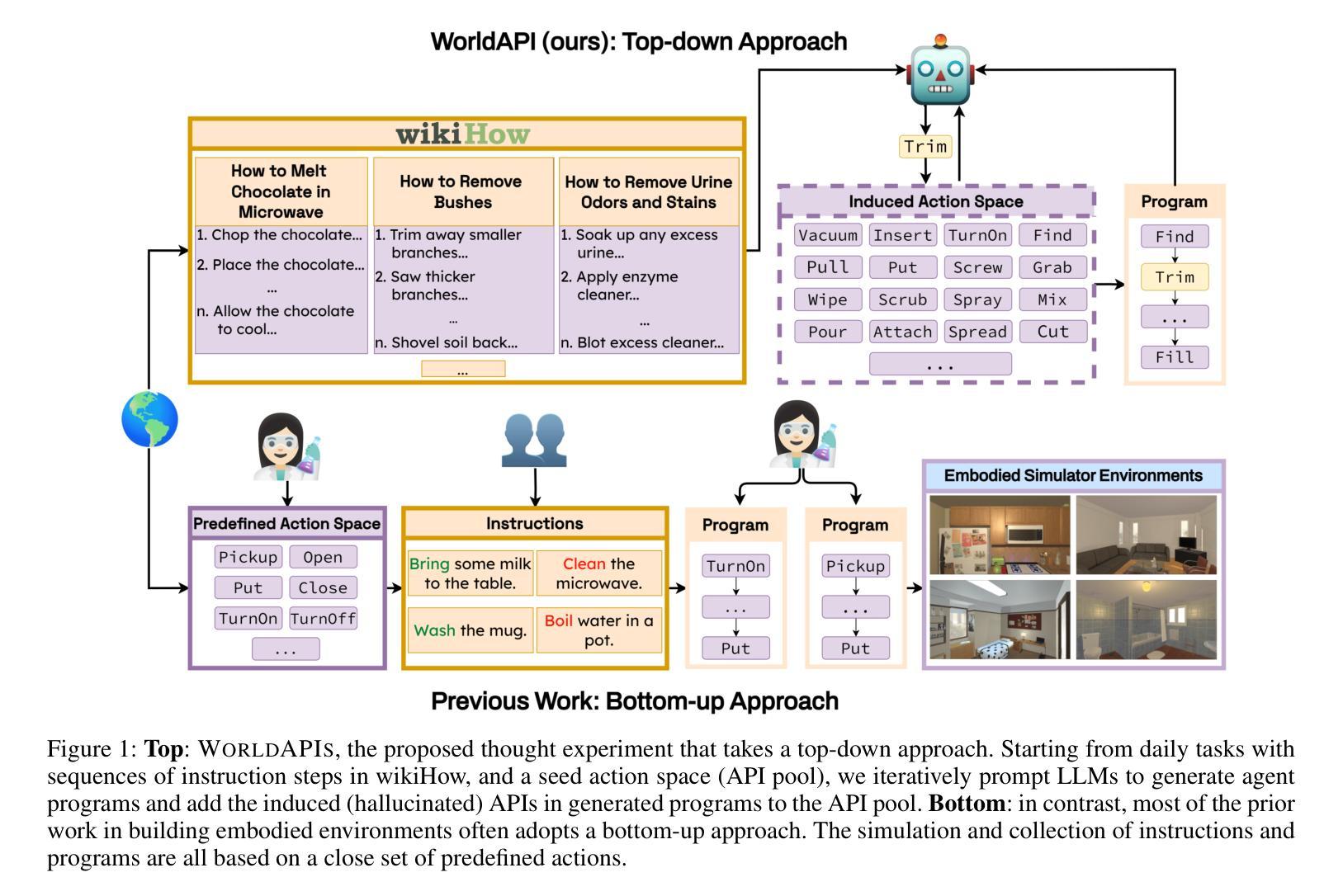
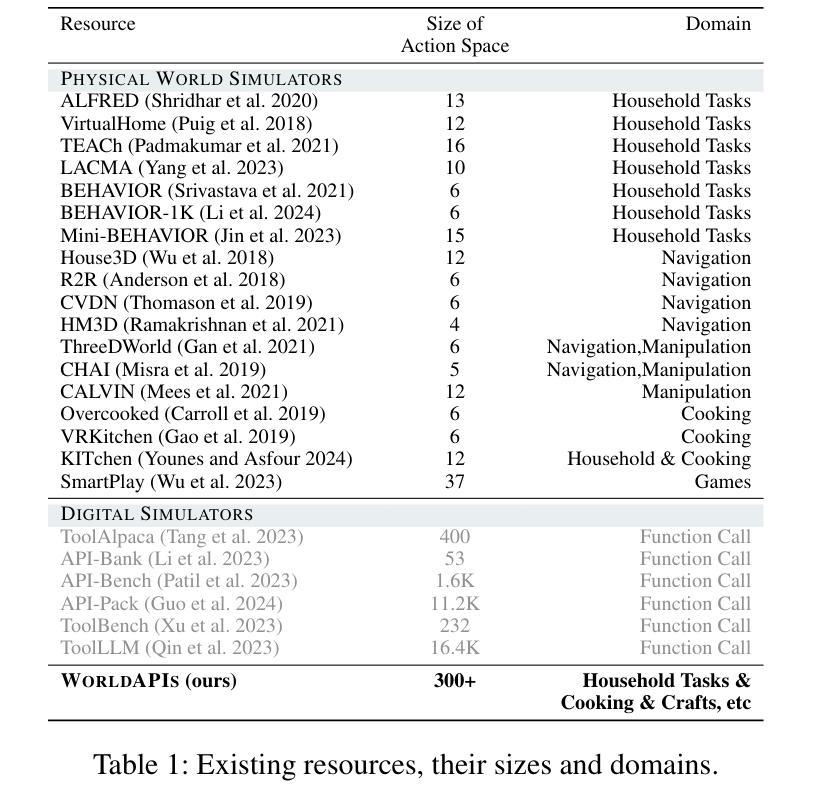
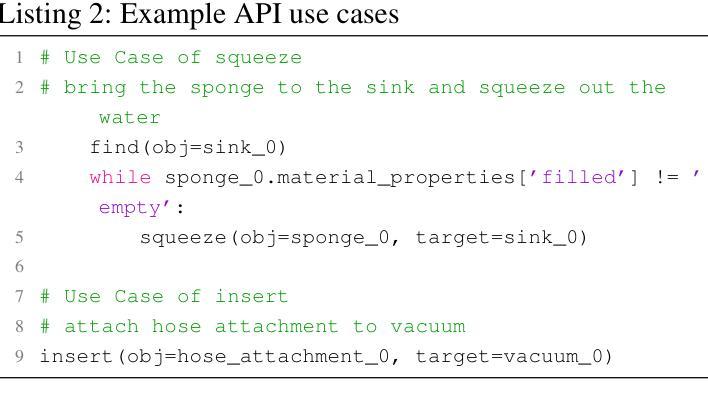
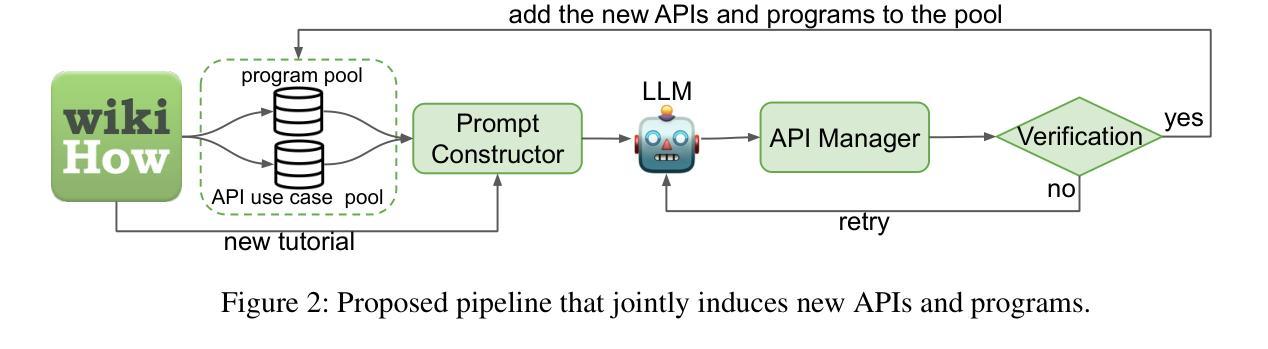
WorldAPIs: The World Is Worth How Many APIs? A Thought Experiment
Authors:Jiefu Ou, Arda Uzunoglu, Benjamin Van Durme, Daniel Khashabi
AI systems make decisions in physical environments through primitive actions or affordances that are accessed via API calls. While deploying AI agents in the real world involves numerous high-level actions, existing embodied simulators offer a limited set of domain-salient APIs. This naturally brings up the questions: how many primitive actions (APIs) are needed for a versatile embodied agent, and what should they look like? We explore this via a thought experiment: assuming that wikiHow tutorials cover a wide variety of human-written tasks, what is the space of APIs needed to cover these instructions? We propose a framework to iteratively induce new APIs by grounding wikiHow instruction to situated agent policies. Inspired by recent successes in large language models (LLMs) for embodied planning, we propose a few-shot prompting to steer GPT-4 to generate Pythonic programs as agent policies and bootstrap a universe of APIs by 1) reusing a seed set of APIs; and then 2) fabricate new API calls when necessary. The focus of this thought experiment is on defining these APIs rather than their executability. We apply the proposed pipeline on instructions from wikiHow tutorials. On a small fraction (0.5%) of tutorials, we induce an action space of 300+ APIs necessary for capturing the rich variety of tasks in the physical world. A detailed automatic and human analysis of the induction output reveals that the proposed pipeline enables effective reuse and creation of APIs. Moreover, a manual review revealed that existing simulators support only a small subset of the induced APIs (9 of the top 50 frequent APIs), motivating the development of action-rich embodied environments.
人工智能系统通过通过API调用访问的原始动作或功能(affordances)在物理环境中进行决策。在现实世界中部署AI代理涉及许多高级动作,而现有的实体模拟器仅提供有限的领域特定API。这自然引发了以下问题:对于多才多艺的实体代理,需要多少原始动作(API),它们应该是什么样的?我们通过思想实验来探索这个问题:假设wikiHow教程涵盖了各种人类编写的任务,那么需要什么API空间来涵盖这些指令?我们提出了一个框架,通过将wikiHow指令与情境代理策略相结合,来迭代地引导新的API。我们受到大型语言模型在实体规划方面近期成功的启发,提出通过少量提示来引导GPT-4生成Pythonic程序作为代理策略,并通过1)重复使用种子集API;然后2)在必要时制造新的API调用,来构建API的宇宙。这个思想实验的重点在于定义这些API,而不是它们的可执行性。我们将所提议的管道应用于wikiHow教程中的指令。在少量(0.5%)的教程中,我们诱导出300多个捕获物理世界中丰富多样任务的必要API。对诱导输出的详细自动分析和人工分析表明,所提出的管道能够实现API的有效重用和创建。此外,手动审查表明,现有模拟器仅支持一小部分诱导的API(前50个常用API中的9个),这推动了丰富动作的实体环境的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025 & ACL 2024 NLRSE, 7 pages
Summary
本文探索了AI系统在物理环境中通过原始动作(通过API调用实现)进行决策的问题。作者通过假设wikiHow教程涵盖了许多人类任务,提出了一种基于框架的方法,通过迭代诱导出新的API来模拟物理世界的任务动作。该研究使用GPT-4生成代理策略并利用少量提示来引导模型,从而定义API而非关注其可执行性。对一小部分(约0.5%)的教程进行应用后,作者得出了需要超过300个API来捕捉现实世界任务的丰富多样性。分析表明,该方法可实现API的有效复用和创建。此外,对现有模拟器的评估显示,它们仅支持一小部分诱导出的API,这突显了开发丰富动作环境的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- AI系统通过API调用实现原始动作以在物理环境中进行决策。
- 基于wikiHow教程的内容提出了一种迭代诱导API的方法框架。
- 利用GPT-4生成代理策略并采用少量提示进行引导。
- 定义API而非关注其可执行性,从而捕捉现实世界任务的丰富多样性。
- 需要超过300个API来覆盖这些任务动作空间。
点此查看论文截图


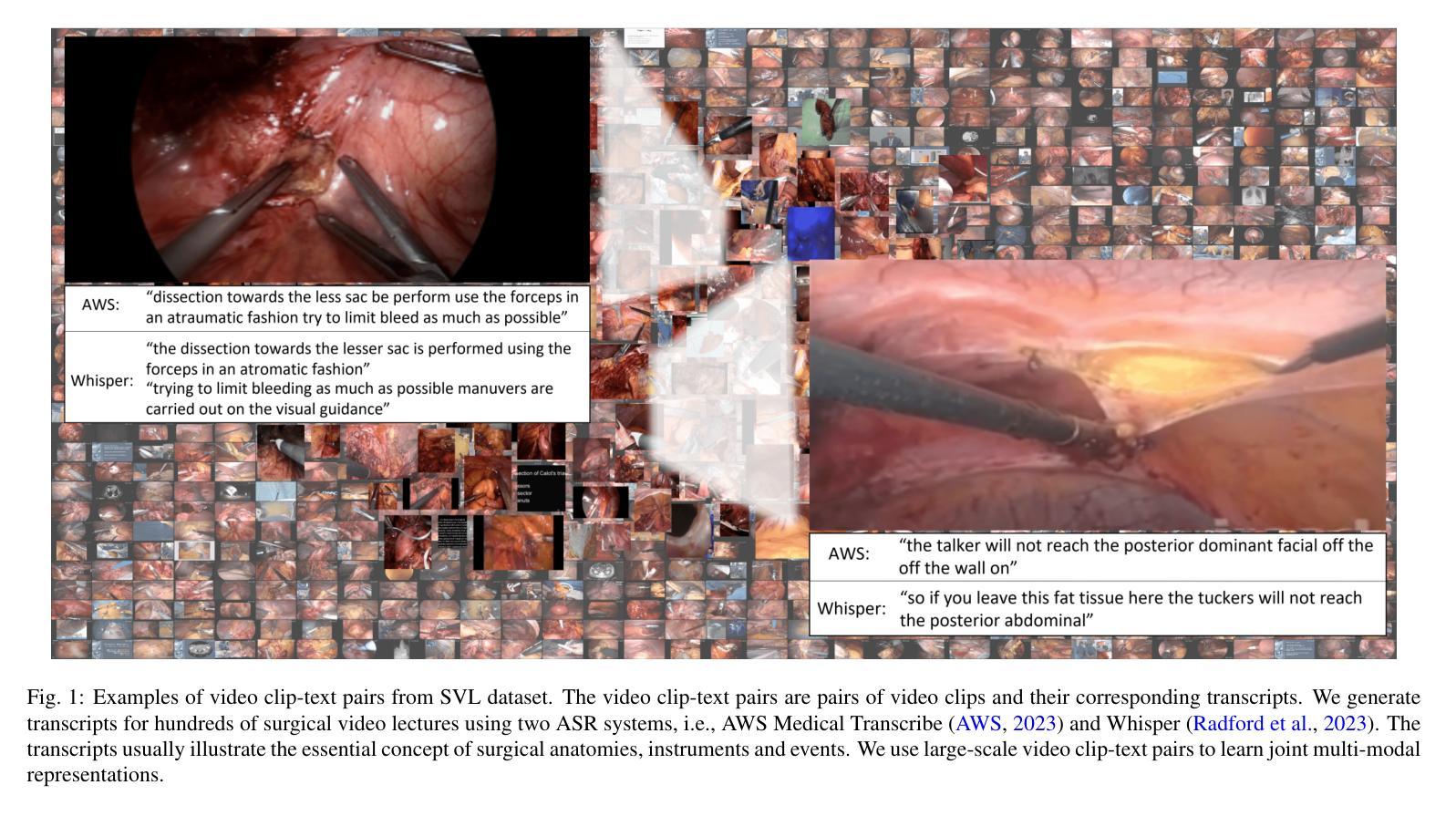
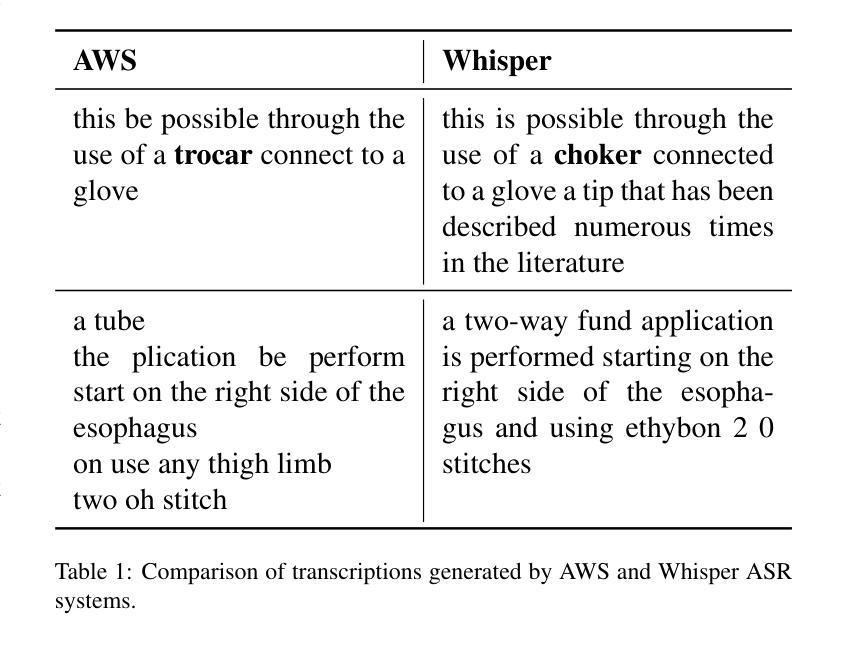
Learning Multi-modal Representations by Watching Hundreds of Surgical Video Lectures
Authors:Kun Yuan, Vinkle Srivastav, Tong Yu, Joel L. Lavanchy, Jacques Marescaux, Pietro Mascagni, Nassir Navab, Nicolas Padoy
Recent advancements in surgical computer vision applications have been driven by vision-only models, which do not explicitly integrate the rich semantics of language into their design. These methods rely on manually annotated surgical videos to predict a fixed set of object categories, limiting their generalizability to unseen surgical procedures and downstream tasks. In this work, we put forward the idea that the surgical video lectures available through open surgical e-learning platforms can provide effective vision and language supervisory signals for multi-modal representation learning without relying on manual annotations. We address the surgery-specific linguistic challenges present in surgical video lectures by employing multiple complementary automatic speech recognition systems to generate text transcriptions. We then present a novel method, SurgVLP - Surgical Vision Language Pre-training, for multi-modal representation learning. Extensive experiments across diverse surgical procedures and tasks demonstrate that the multi-modal representations learned by SurgVLP exhibit strong transferability and adaptability in surgical video analysis. Furthermore, our zero-shot evaluations highlight SurgVLP’s potential as a general-purpose foundation model for surgical workflow analysis, reducing the reliance on extensive manual annotations for downstream tasks, and facilitating adaptation methods such as few-shot learning to build a scalable and data-efficient solution for various downstream surgical applications. The training code and weights are public.
近期外科计算机视觉应用的进展主要得益于仅依赖视觉的模型,这些模型在设计时并没有明确融入丰富的语言语义。这些方法依赖于手动注释的手术视频来预测固定的对象类别集,这限制了它们对未见过的手术程序和下游任务的泛化能力。在这项工作中,我们提出通过公开手术电子学习平台可用的手术视频讲座,可以提供有效的视觉和语言监督信号,用于多模式表示学习,而无需依赖手动注释。我们通过采用多个互补的自动语音识别系统来生成文本转录,以解决手术视频讲座中特有的语言挑战。然后,我们提出了一种新的方法,SurgVLP(手术视觉语言预训练),用于多模式表示学习。在多种手术程序和任务上的广泛实验表明,SurgVLP学习的多模式表示在手术视频分析中表现出强大的可迁移性和适应性。此外,我们的零样本评估凸显了SurgVLP作为手术工作流程分析的通用基础模型的潜力,减少了下游任务对大量手动注释的依赖,并促进了少样本学习等适应方法,为各种下游手术应用构建可扩展和高效的数据解决方案。 训练代码和权重均已公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis (MedIA), 2025
Summary
本文介绍了利用公开手术电子学习平台上的手术视频讲座进行多模态表示学习的方法。通过采用多个互补的自动语音识别系统生成文本转录,解决手术视频讲座中的语言挑战。提出一种新型方法SurgVLP(手术视觉语言预训练),该方法可在无需手动注释的情况下,实现多模态表示学习。实验证明,SurgVLP所学习的多模态表示具有较强的迁移性和适应性,在手术视频分析中展现出卓越性能。此外,SurgVLP作为一个通用基础模型,具有潜力用于手术工作流程分析,减少下游任务对大量手动注释的依赖,并促进少样本学习等适应方法的开发,为各种下游手术应用提供可扩展和高效的数据解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 近期手术计算机视觉应用的进展主要依赖于仅依赖视觉的模型,未明确整合语言的丰富语义。
- 手动注释的手术视频限制了模型对未见手术程序和下游任务的泛化能力。
- 公开手术电子学习平台上的手术视频讲座可提供有效的视觉和语言监督信号,用于多模态表示学习,无需手动注释。
- 采用多个自动语音识别系统生成文本转录,以应对手术视频讲座中的语言挑战。
- 引入新型方法SurgVLP,实现多模态表示学习,展现出色的迁移性和适应性。
- SurgVLP具有作为通用基础模型的潜力,用于手术工作流程分析,并促进少样本学习等方法的开发。
点此查看论文截图