⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
Beyond Black Boxes: Enhancing Interpretability of Transformers Trained on Neural Data
Authors:Laurence Freeman, Philip Shamash, Vinam Arora, Caswell Barry, Tiago Branco, Eva Dyer
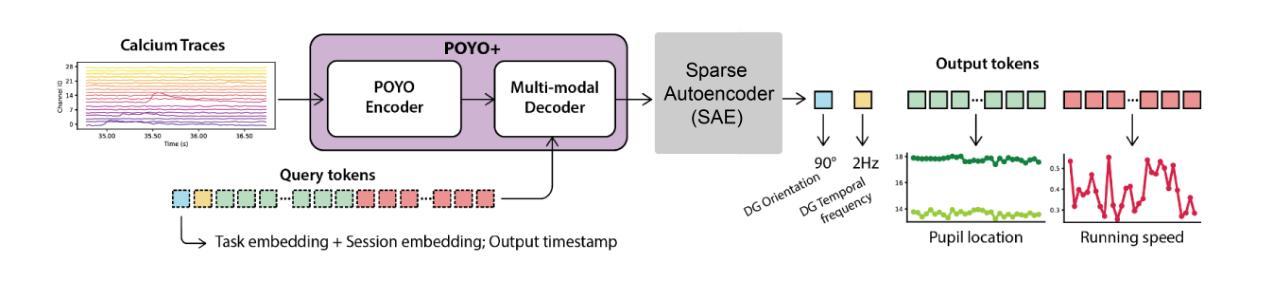
Transformer models have become state-of-the-art in decoding stimuli and behavior from neural activity, significantly advancing neuroscience research. Yet greater transparency in their decision-making processes would substantially enhance their utility in scientific and clinical contexts. Sparse autoencoders offer a promising solution by producing hidden units that respond selectively to specific variables, enhancing interpretability. Here, we introduce SAEs into a neural decoding framework by augmenting a transformer trained to predict visual stimuli from calcium imaging in the mouse visual cortex. The enhancement of the transformer model with an SAE preserved its original performance while yielding hidden units that selectively responded to interpretable features, such as stimulus orientation and genetic background. Furthermore, ablating units associated with a given variable impaired the model’s ability to process that variable, revealing how specific internal representations support downstream computations. Together, these results demonstrate that integrating SAEs with transformers combines the power of modern deep learning with the interpretability essential for scientific understanding and clinical translation.
Transformer模型在解码神经活动中的刺激和行为方面已处于最前沿技术地位,显著推动了神经科学研究的发展。然而,在决策制定过程中需要提高更大的透明度才能使其更好地服务于科学和临床环境。稀疏自编码器通过产生选择性地响应特定变量的隐藏单元,提供了一种前景广阔的解决方案,提高了可解释性。在这里,我们通过在一个神经网络解码框架中引入SAE来增强变压器的性能,该变压器经过训练,能够从老鼠视觉皮层的钙成像中预测视觉刺激。在变压器模型中增强SAE保留了其原始性能,同时产生了选择性地响应可解释特征的隐藏单元,如刺激方向和遗传背景。此外,消除与给定变量相关的单元会损害模型处理该变量的能力,揭示了特定的内部表示如何支持下游计算。总之,这些结果表明,将SAE与变压器相结合,结合了现代深度学习的能力与对科学理解和临床翻译至关重要的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:变压器模型在解码神经活动中的刺激和行为方面已达到最新水平,显著推动了神经科学研究的发展。然而,决策过程的更高透明度将在科学和临床环境中大大提高其实用性。稀疏自动编码器通过产生选择性响应特定变量的隐藏单元,提供了提高解释性的有前途的解决方案。这里,我们将SAEs引入神经解码框架,通过增强训练有素的变压器来预测小鼠视觉皮层中的钙成像的视觉刺激。增强型变压器模型与SAE的结合保持了其原始性能,同时产生了选择性响应于可解释特征的隐藏单元,如刺激取向和遗传背景。此外,消除与给定变量相关的单位会损害模型处理该变量的能力,揭示了特定内部表示如何支持下游计算。总之,这些结果表明,将SAE与变压器相结合,结合了现代深度学习的力量和对科学理解和临床翻译至关重要的解释性。
Key Takeaways:
- 变压器模型已成为解码神经活动中刺激和行为的最新技术,对神经科学研究有重大贡献。
- 稀疏自动编码器(SAE)通过产生选择性响应特定变量的隐藏单元,提高了模型解释性。
- 在神经解码框架中引入SAE增强了变压器模型,同时保持原始性能并产生可解释性的隐藏单元。
- 隐藏单元的选择性响应可以揭示模型对刺激取向和遗传背景等变量的处理。
- 消除与特定变量相关的隐藏单位会损害模型处理该变量的能力。
- 结合SAE与变压器可实现现代深度学习的强大功能,同时提高科学理解和临床应用的解释性。
- 该方法揭示了特定内部表示如何支持模型的下游计算。
点此查看论文截图

Translation-Equivariance of Normalization Layers and Aliasing in Convolutional Neural Networks
Authors:Jérémy Scanvic, Quentin Barthélemy, Julián Tachella
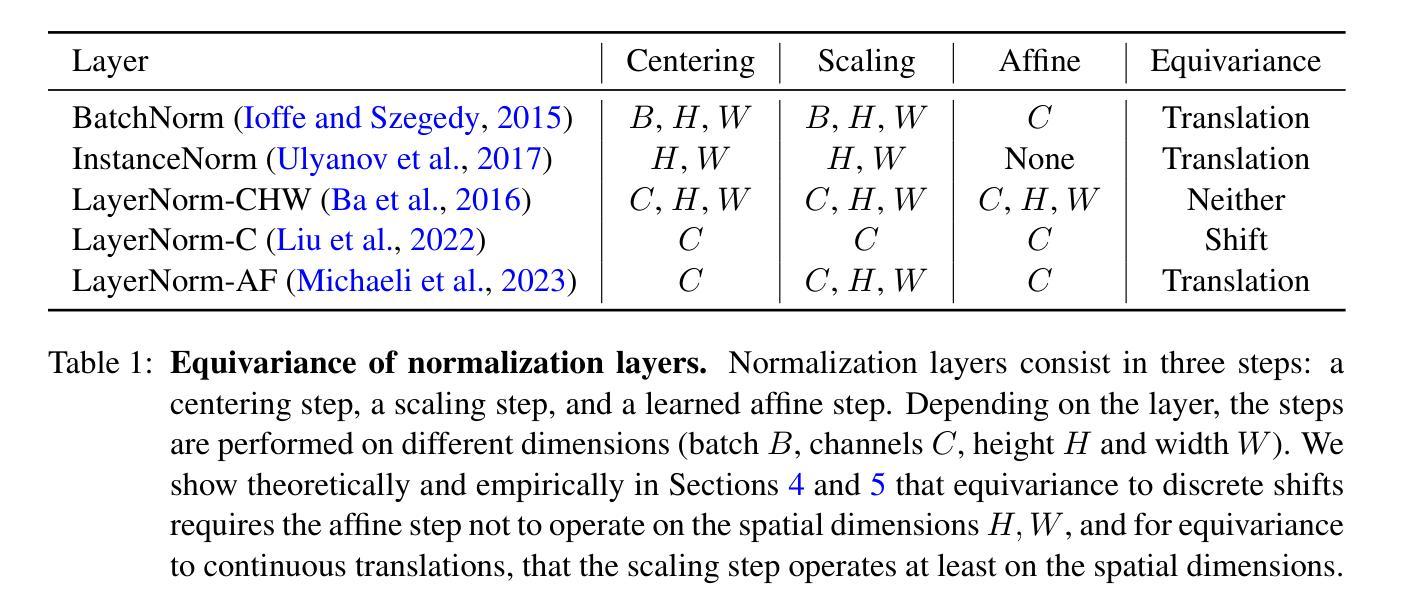
The design of convolutional neural architectures that are exactly equivariant to continuous translations is an active field of research. It promises to benefit scientific computing, notably by making existing imaging systems more physically accurate. Most efforts focus on the design of downsampling/pooling layers, upsampling layers and activation functions, but little attention is dedicated to normalization layers. In this work, we present a novel theoretical framework for understanding the equivariance of normalization layers to discrete shifts and continuous translations. We also determine necessary and sufficient conditions for normalization layers to be equivariant in terms of the dimensions they operate on. Using real feature maps from ResNet-18 and ImageNet, we test those theoretical results empirically and find that they are consistent with our predictions.
关于卷积神经网络架构对连续平移进行精确等价设计是一个活跃的研究领域。它有望为科学计算带来好处,特别是使现有成像系统更加物理准确。大多数努力都集中在设计下采样/池化层、上采样层和激活函数上,而对归一化层却关注较少。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个新型的理论框架,用以理解归一化层对离散平移和连续平移的等价性。我们还确定了归一化层在维度操作上的等价性的必要和充分条件。我们利用ResNet-18和ImageNet的真实特征映射对理论结果进行了实证测试,发现它们与我们的预测一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the Workshop on the Theory of AI for Scientific Computing (COLT 2025)
Summary
本文研究卷积神经网络架构对连续平移的精确等价性设计,有望提高科学计算中成像系统的物理准确性。文章重点关注下采样/池化层、上采样层和激活函数的设计,但对归一化层的研究较少。本文提出一个理解归一化层对离散移位和连续平移等价性的新理论框架,并确定其在操作维度上的必要和充分条件。通过对ResNet-18和ImageNet的实际特征图进行实证研究,发现理论结果与预测一致。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积神经网络架构对连续平移的等价性研究是活跃领域,旨在提高成像系统的物理准确性。
- 归一化层在卷积神经网络中的研究相对较少,但对该层的等价性研究具有重要意义。
- 文章提出了一个关于归一化层等价性的新理论框架,包括其对离散移位和连续平移的反应。
- 确定了归一化层在操作维度上达到等价的必要和充分条件。
- 通过实证研究验证了理论结果,使用ResNet-18和ImageNet的实际特征图测试了预测结果的一致性。
- 这一研究有望促进科学计算领域中对卷积神经网络架构设计的深入理解和创新。
点此查看论文截图

Categorical Schrödinger Bridge Matching
Authors:Grigoriy Ksenofontov, Alexander Korotin
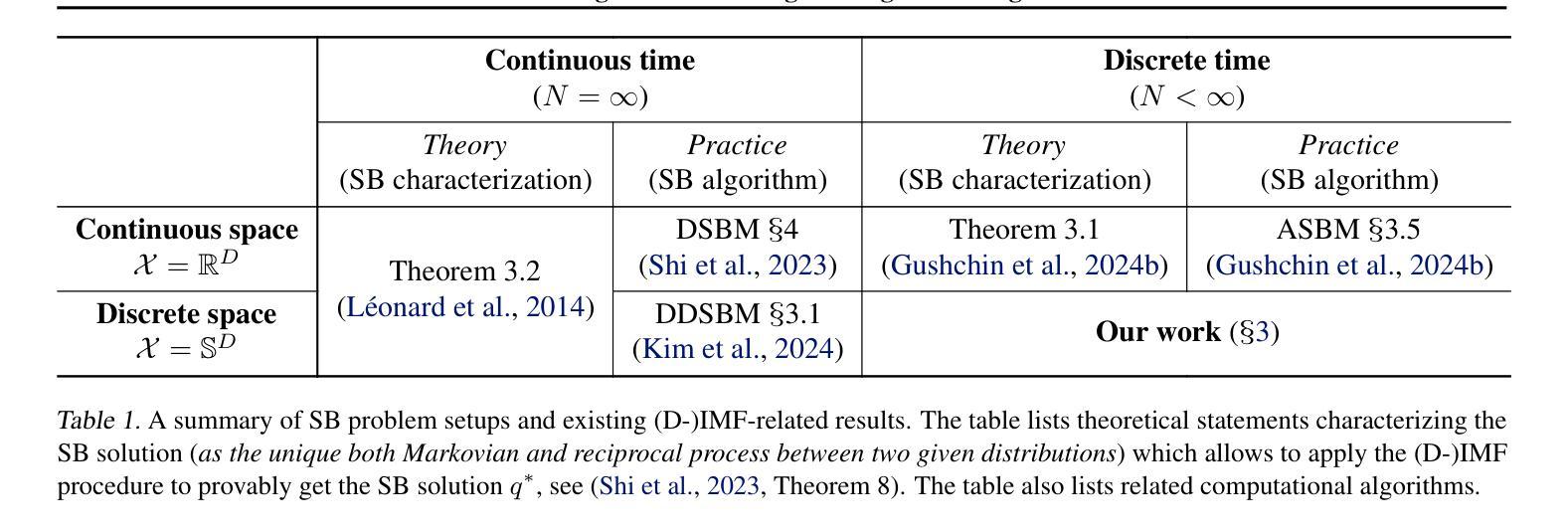
The Schr"odinger Bridge (SB) is a powerful framework for solving generative modeling tasks such as unpaired domain translation. Most SB-related research focuses on continuous data space $\mathbb{R}^{D}$ and leaves open theoretical and algorithmic questions about applying SB methods to discrete data, e.g, on finite spaces $\mathbb{S}^{D}$. Notable examples of such sets $\mathbb{S}$ are codebooks of vector-quantized (VQ) representations of modern autoencoders, tokens in texts, categories of atoms in molecules, etc. In this paper, we provide a theoretical and algorithmic foundation for solving SB in discrete spaces using the recently introduced Iterative Markovian Fitting (IMF) procedure. Specifically, we theoretically justify the convergence of discrete-time IMF (D-IMF) to SB in discrete spaces. This enables us to develop a practical computational algorithm for SB, which we call Categorical Schr"odinger Bridge Matching (CSBM). We show the performance of CSBM via a series of experiments with synthetic data and VQ representations of images. The code of CSBM is available at https://github.com/gregkseno/csbm.
薛定谔桥(SB)是一个强大的框架,用于解决如非配对域翻译等生成建模任务。大多数与SB相关的研究都集中在连续数据空间$\mathbb{R}^{D}$上,而将SB方法应用于离散数据(例如在有限空间$\mathbb{S}^{D}$上)的理论和算法问题留待解决。集合$\mathbb{S}$的著名例子包括现代自动编码器的向量量化(VQ)表示的代码本、文本中的标记、分子的原子类别等。在本文中,我们利用最近引入的迭代马尔可夫拟合(IMF)程序,为解决离散空间中的SB提供了理论和算法基础。特别是我们从理论上证明了离散时间IMF(D-IMF)在离散空间收敛到SB的合理性。这使我们能够为SB开发一种实用的计算算法,我们称之为分类薛定谔桥匹配(CSBM)。我们通过合成数据和VQ图像表示的一系列实验展示了CSBM的性能。CSBM的代码可在https://github.com/gregkseno/csbm找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
量子桥(Schrödinger Bridge,SB)是解决生成建模任务(如非配对域翻译)的强大框架。研究主要集中在连续数据空间上,而将SB方法应用于离散数据(例如有限空间)的理论和算法问题仍然开放。本文利用最近引入的迭代马尔可夫拟合(IMF)程序,为解决离散空间中的SB提供了理论和算法基础。我们证明了离散时间IMF(D-IMF)收敛到SB的理论依据。在此基础上,我们为SB开发了一种实用的计算算法,称为分类量子桥匹配(CSBM)。通过合成数据和向量量化图像表示的系列实验验证了CSBM的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 量子桥(SB)是解决生成建模任务的强大框架,尤其适用于解决非配对域翻译问题。
- 目前的研究主要集中在连续数据空间的SB上,而离散数据空间的SB研究尚待深入。
- 本文首次为离散空间中的SB提供了理论和算法基础。
- 利用迭代马尔可夫拟合(IMF)程序,证明了离散时间IMF(D-IMF)收敛到SB的理论依据。
- 开发了一种名为分类量子桥匹配(CSBM)的实用计算算法,用于解决离散空间中的SB问题。
- CSBM在合成数据和向量量化图像表示的实验中表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图