⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
PhantomHunter: Detecting Unseen Privately-Tuned LLM-Generated Text via Family-Aware Learning
Authors:Yuhui Shi, Yehan Yang, Qiang Sheng, Hao Mi, Beizhe Hu, Chaoxi Xu, Juan Cao
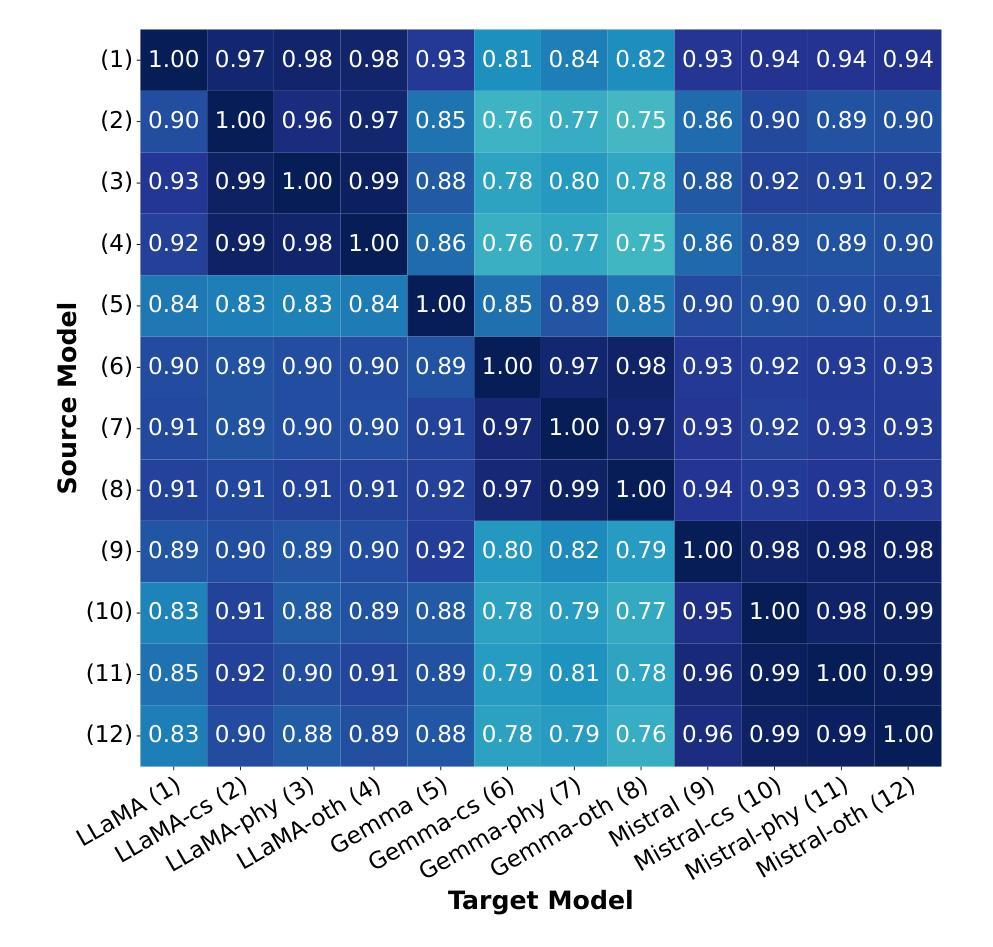
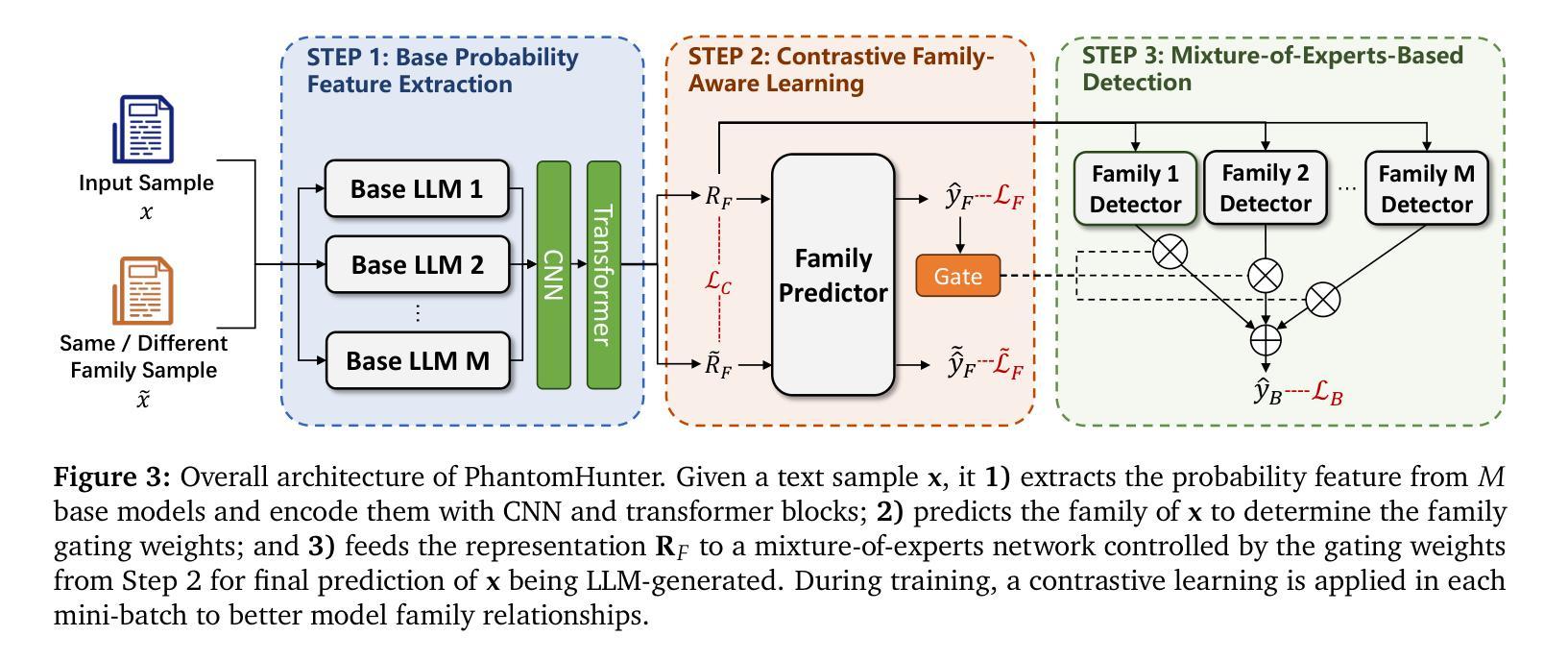
With the popularity of large language models (LLMs), undesirable societal problems like misinformation production and academic misconduct have been more severe, making LLM-generated text detection now of unprecedented importance. Although existing methods have made remarkable progress, a new challenge posed by text from privately tuned LLMs remains underexplored. Users could easily possess private LLMs by fine-tuning an open-source one with private corpora, resulting in a significant performance drop of existing detectors in practice. To address this issue, we propose PhantomHunter, an LLM-generated text detector specialized for detecting text from unseen, privately-tuned LLMs. Its family-aware learning framework captures family-level traits shared across the base models and their derivatives, instead of memorizing individual characteristics. Experiments on data from LLaMA, Gemma, and Mistral families show its superiority over 7 baselines and 3 industrial services, with F1 scores of over 96%.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的普及,诸如假信息传播和学术不端等不受欢迎的社会问题变得更加严重,这使得对LLM生成文本的检测变得至关重要。尽管现有方法已经取得了显著进展,但由私有微调LLM产生的文本所带来的新挑战仍然被忽视。用户可以通过使用私有语料库对开源LLM进行微调来轻松拥有私有LLM,这导致现有检测器在实际应用中性能大幅下降。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了PhantomHunter,这是一种专门用于检测来自未见过的私有微调LLM的文本的检测器。其家族感知学习框架能够捕获基础模型及其衍生物之间的家族级特征,而不是记忆单个特征。在LLaMA、Gemma和Mistral家族的数据上进行实验表明,其性能优于7个基准测试和3个工业服务,F1得分超过9.此方案相较于之前方案能够更好检测出内部变化导致漏洞等问题、大大提升精度率和可靠程度为业界带来更加安全高效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 3 figures, 6 tables
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的普及,产生的诸如假新闻和学术不端等社会性问题愈发严重,使得检测LLM生成的文本变得至关重要。现有检测方法虽有所进展,但对使用私有语料微调得到的LLM生成的文本检测仍面临挑战。为此,我们提出PhantomHunter方法,专门用于检测这类文本的LLM生成文本检测器。它通过家族级学习框架捕捉基础模型及其衍生版本之间的家族级特征,而非死记硬背个别特征。实验证明,相较于其他七大基线模型及三大工业服务,PhantomHunter在LLaMA、Gemma和Mistral等家族数据上的表现更胜一筹,F1分数超过96%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)普及带来的社会问题,如假新闻和学术不端行为,使检测LLM生成的文本至关重要。
- 尽管现有检测方法取得进展,但针对使用私有语料微调得到的LLM生成的文本检测仍然面临挑战。
- PhantomHunter是一种专门用于检测LLM生成文本的全新方法。
- PhantomHunter采用家族级学习框架,捕捉基础模型及其衍生版本之间的家族级特征。
- PhantomHunter能够检测未经训练的私有LLM生成的文本。
- 实验证明,PhantomHunter相较于其他模型及工业服务表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

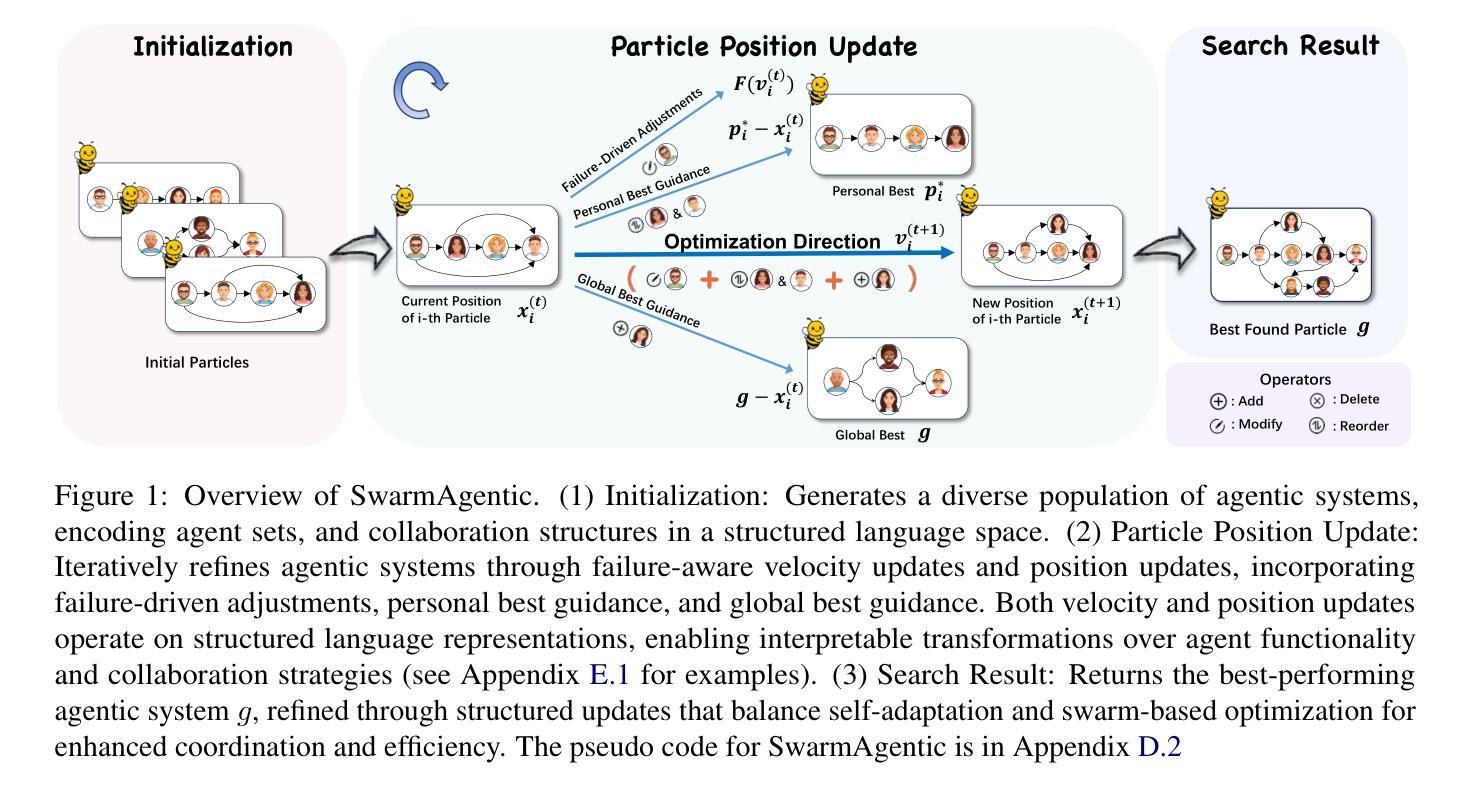
SwarmAgentic: Towards Fully Automated Agentic System Generation via Swarm Intelligence
Authors:Yao Zhang, Chenyang Lin, Shijie Tang, Haokun Chen, Shijie Zhou, Yunpu Ma, Volker Tresp
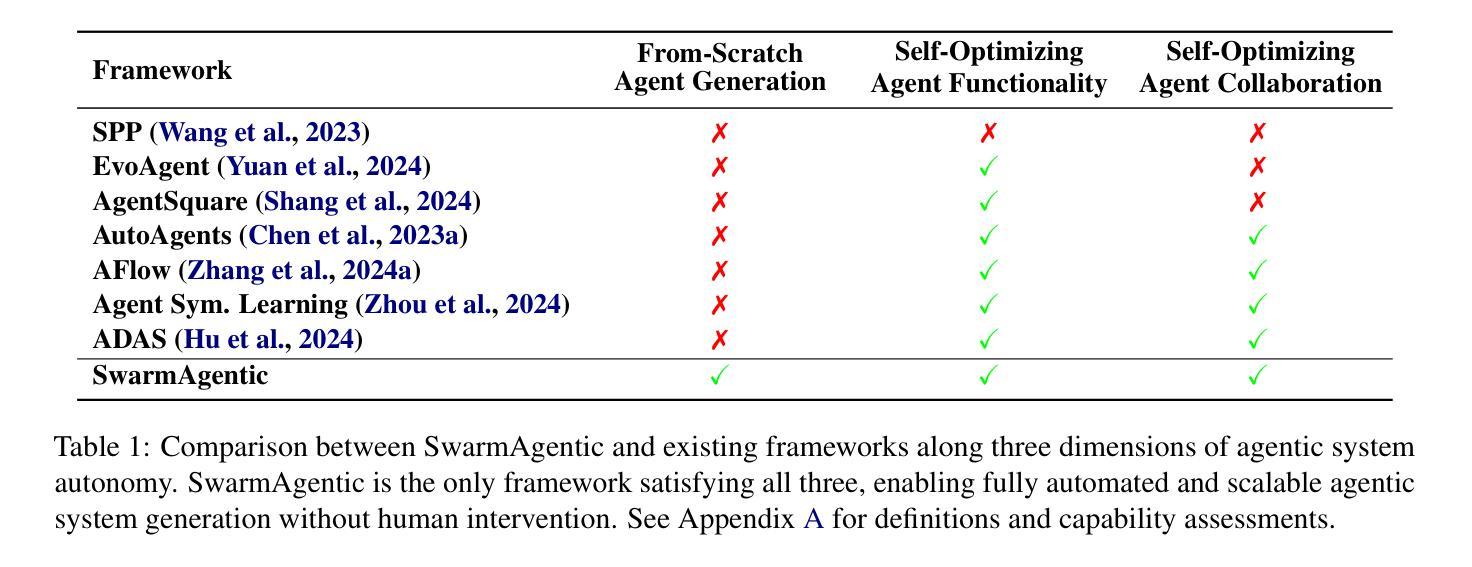
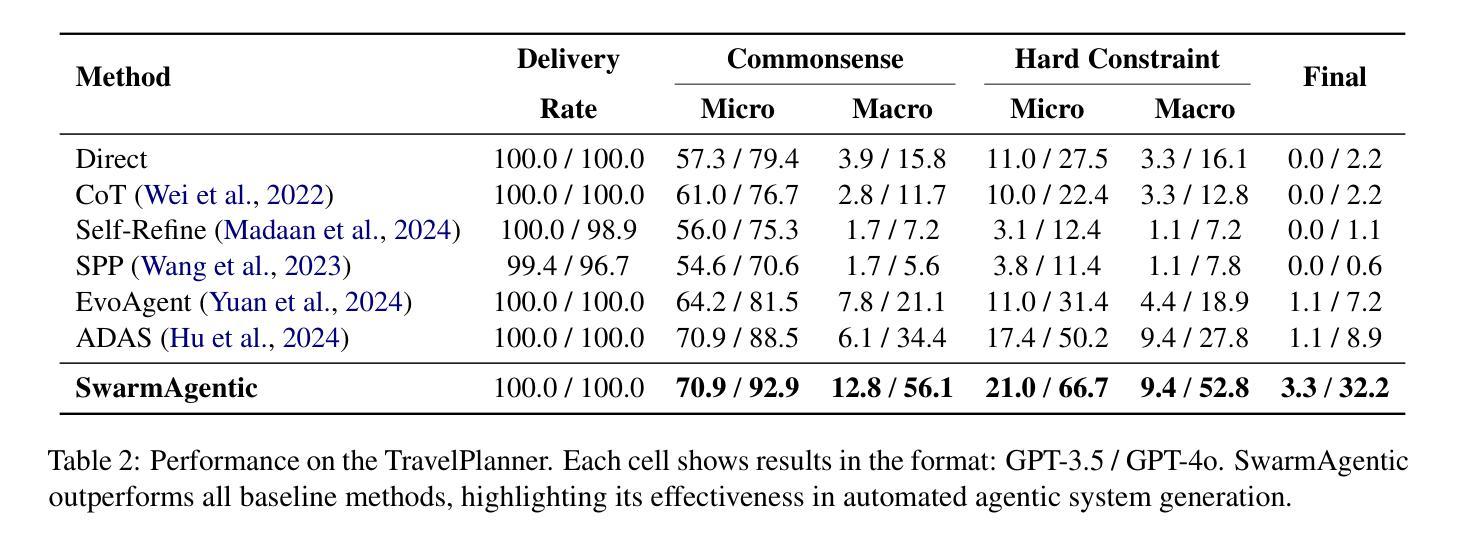
The rapid progress of Large Language Models has advanced agentic systems in decision-making, coordination, and task execution. Yet, existing agentic system generation frameworks lack full autonomy, missing from-scratch agent generation, self-optimizing agent functionality, and collaboration, limiting adaptability and scalability. We propose SwarmAgentic, a framework for fully automated agentic system generation that constructs agentic systems from scratch and jointly optimizes agent functionality and collaboration as interdependent components through language-driven exploration. To enable efficient search over system-level structures, SwarmAgentic maintains a population of candidate systems and evolves them via feedback-guided updates, drawing inspiration from Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). We evaluate our method on six real-world, open-ended, and exploratory tasks involving high-level planning, system-level coordination, and creative reasoning. Given only a task description and an objective function, SwarmAgentic outperforms all baselines, achieving a +261.8% relative improvement over ADAS on the TravelPlanner benchmark, highlighting the effectiveness of full automation in structurally unconstrained tasks. This framework marks a significant step toward scalable and autonomous agentic system design, bridging swarm intelligence with fully automated system multi-agent generation. Our code is publicly released at https://yaoz720.github.io/SwarmAgentic/.
大型语言模型的快速发展推动了决策、协调和任务执行中的智能体系代理的进步。然而,现有的智能体系生成框架缺乏完全的自主性,缺少从头开始生成代理、自我优化代理功能和协作的能力,这限制了适应性和可扩展性。我们提出了SwarmAgentic,这是一个完全自动化的智能体系生成框架,它从头开始构建智能体系,并通过语言驱动的探索来联合优化相互依赖的代理功能和协作。为了在系统级别结构上实现有效的搜索,SwarmAgentic维护了一组候选系统,并通过反馈指导的更新来进化它们,这得益于粒子群优化(PSO)的启发。我们在涉及高级规划、系统级协调和创造性推理的六个真实世界、开放性和探索性任务上评估了我们的方法。仅给出任务描述和目标函数,SwarmAgentic在所有基准测试中都表现出色,在TravelPlanner基准测试中相对于ADAS实现了+261.8%的相对改进,这凸显了全自动在结构性无约束任务中的有效性。这一框架标志着朝着可扩展和自主的智能体系设计迈出了重要的一步,它将群体智能与全自动多智能体系生成相结合。我们的代码已公开发布在https://yaoz720.github.io/SwarmAgentic/上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 41 pages
Summary
大型语言模型的快速发展推动了决策、协调和任务执行方面的agentic系统进步。然而,现有的agentic系统生成框架缺乏完全自主性,缺少从头开始生成agent、自我优化agent功能以及协作能力,限制了适应性和可扩展性。为此,我们提出SwarmAgentic框架,实现agentic系统的全自动生成。它通过语言驱动的探索,从头构建agentic系统,并联合优化agent功能和协作能力。SwarmAgentic通过粒子群优化算法的灵感,维护候选系统种群并通过反馈指导的更新进行演化。在涉及高级规划、系统级协调和创造性推理的六个现实世界的开放和探索性任务上,我们的方法在仅给出任务描述和目标函数的情况下,相对于ADAS在TravelPlanner基准测试上实现了+261.8%的相对改进。此框架标志着在可伸缩和自主agentic系统设计方面迈出了重要一步,将群体智能与全自动多agent系统生成相结合。我们的代码已公开发布在网站链接上。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的进步推动了决策、协调和任务执行中agentic系统的发展。
- 当前agentic系统生成框架缺乏完全自主性,限制了适应性和可扩展性。
- SwarmAgentic框架实现agentic系统的全自动生成,包括从头构建、功能优化和协作能力。
- SwarmAgentic框架受到粒子群优化算法的启发,通过维护候选系统种群并通过反馈进行更新演化。
- SwarmAgentic框架在多个现实世界的任务上表现出优越性能,相对于ADAS在TravelPlanner基准测试上有显著改进。
- 此框架是朝着可伸缩和自主agentic系统设计的重要一步,结合了群体智能和全自动多agent系统生成。
点此查看论文截图

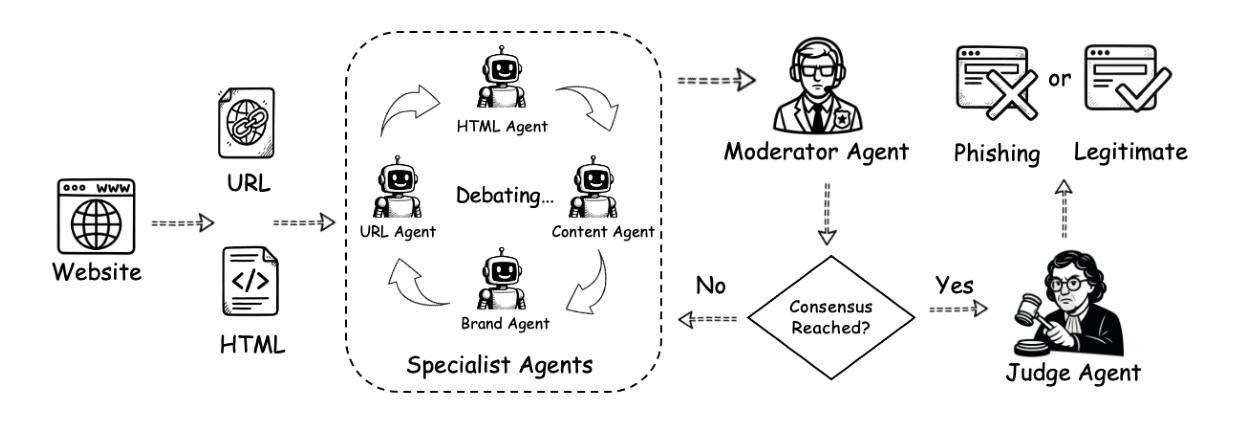
PhishDebate: An LLM-Based Multi-Agent Framework for Phishing Website Detection
Authors:Wenhao Li, Selvakumar Manickam, Yung-wey Chong, Shankar Karuppayah
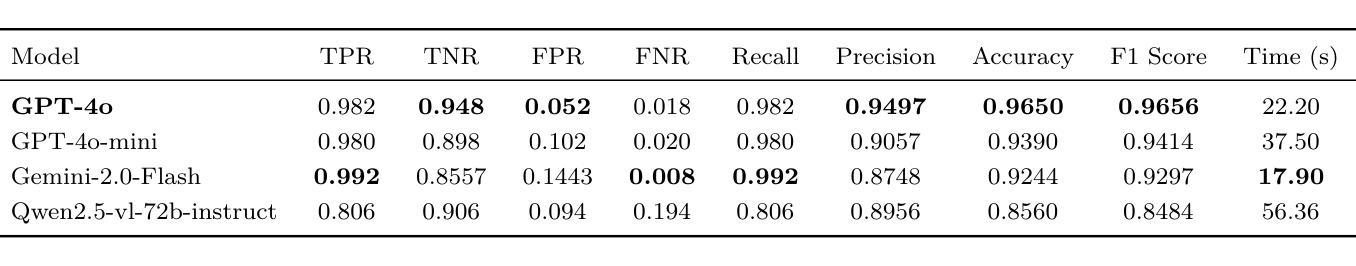
Phishing websites continue to pose a significant cybersecurity threat, often leveraging deceptive structures, brand impersonation, and social engineering tactics to evade detection. While recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled improved phishing detection through contextual understanding, most existing approaches rely on single-agent classification facing the risks of hallucination and lack interpretability or robustness. To address these limitations, we propose PhishDebate, a modular multi-agent LLM-based debate framework for phishing website detection. PhishDebate employs four specialized agents to independently analyze different textual aspects of a webpage–URL structure, HTML composition, semantic content, and brand impersonation–under the coordination of a Moderator and a final Judge. Through structured debate and divergent thinking, the framework delivers more accurate and interpretable decisions. Extensive evaluations on commercial LLMs demonstrate that PhishDebate achieves 98.2% recall and 98.2% True Positive Rate (TPR) on a real-world phishing dataset, and outperforms single-agent and Chain of Thought (CoT) baselines. Additionally, its modular design allows agent-level configurability, enabling adaptation to varying resource and application requirements.
钓鱼网站仍然是一个重要的网络安全威胁,它们经常利用欺骗性结构、品牌伪装和社会工程策略来躲避检测。尽管最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步已经能够通过上下文理解来改善钓鱼网站检测,但现有的大多数方法仍然依赖于单代理分类,面临着出现幻觉和缺乏可解释性或稳健性的风险。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了PhishDebate,这是一个基于多代理辩论的模块化钓鱼网站检测框架。PhishDebate采用四个专业代理来独立分析网页的四个不同文本方面——URL结构、HTML组成、语义内容和品牌伪装,并在协调员的协调和一个最终判决者的判决下运行。通过结构化的辩论和发散思维,该框架能做出更准确、更可解释的决定。在商业LLM上的广泛评估表明,PhishDebate在真实世界的钓鱼数据集上达到了98.2%的召回率和98.2%的真正阳性率(TPR),并优于单代理和思维链(CoT)基线。此外,其模块化设计允许代理级别的配置,能够适应不同的资源和应用需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在网络安全领域的应用为检测钓鱼网站提供了新的解决方案。PhishDebate框架采用模块化多智能体设计,通过四个专业智能体独立分析网页的URL结构、HTML组成、语义内容和品牌模仿等不同方面,并在协调员和最终裁判的监督下进行结构化辩论和发散思维,以提高决策准确性和可解释性。在现实世界钓鱼网站数据集上的广泛评估表明,PhishDebate取得了98.2%的召回率和真正阳性率(TPR),优于单智能体和链思维(CoT)基线。其模块化设计还允许智能体级别的配置,能够适应不同的资源和应用需求。
Key Takeaways
- Phishing网站仍然是一个重要的网络安全威胁,它们使用欺骗性结构、品牌模仿和社会工程策略来躲避检测。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的进展已经改善了通过上下文理解进行钓鱼网站检测的能力。
- PhishDebate是一个基于LLM的模块化多智能体检测框架,用于更准确地检测钓鱼网站。
- PhishDebate通过四个专业智能体独立分析网页的不同方面,包括URL结构、HTML组成、语义内容和品牌模仿。
- PhishDebate通过结构化辩论和发散思维提高决策的准确性和可解释性。
- 在现实世界钓鱼网站数据集上的评估显示,PhishDebate的召回率和真正阳性率均达到98.2%,优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图




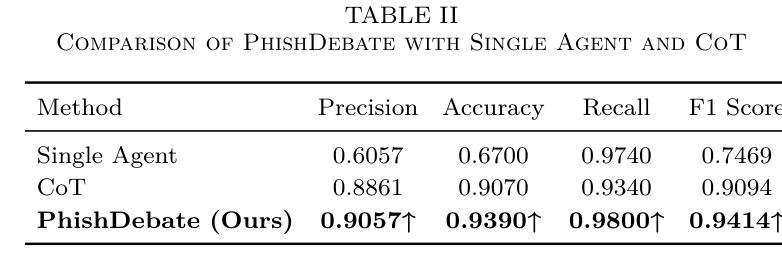
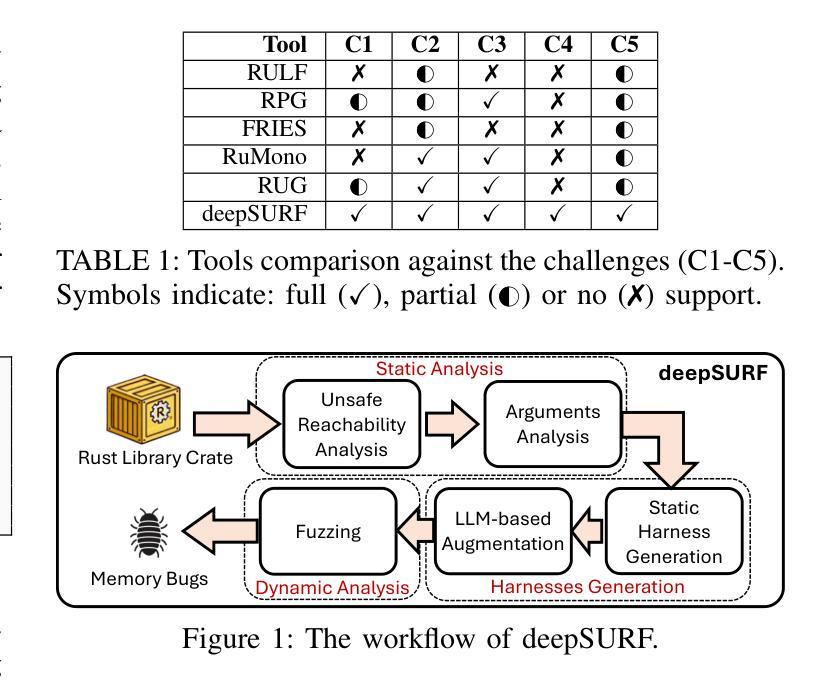
deepSURF: Detecting Memory Safety Vulnerabilities in Rust Through Fuzzing LLM-Augmented Harnesses
Authors:Georgios Androutsopoulos, Antonio Bianchi
Although Rust ensures memory safety by default, it also permits the use of unsafe code, which can introduce memory safety vulnerabilities if misused. Unfortunately, existing tools for detecting memory bugs in Rust typically exhibit limited detection capabilities, inadequately handle Rust-specific types, or rely heavily on manual intervention. To address these limitations, we present deepSURF, a tool that integrates static analysis with Large Language Model (LLM)-guided fuzzing harness generation to effectively identify memory safety vulnerabilities in Rust libraries, specifically targeting unsafe code. deepSURF introduces a novel approach for handling generics by substituting them with custom types and generating tailored implementations for the required traits, enabling the fuzzer to simulate user-defined behaviors within the fuzzed library. Additionally, deepSURF employs LLMs to augment fuzzing harnesses dynamically, facilitating exploration of complex API interactions and significantly increasing the likelihood of exposing memory safety vulnerabilities. We evaluated deepSURF on 27 real-world Rust crates, successfully rediscovering 20 known memory safety bugs and uncovering 6 previously unknown vulnerabilities, demonstrating clear improvements over state-of-the-art tools.
尽管Rust默认确保内存安全,但它也允许使用不安全的代码,如果误用,可能会引入内存安全漏洞。不幸的是,目前用于检测Rust中内存错误的工具通常检测能力有限、不能很好地处理Rust特定类型,或者严重依赖人工干预。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了deepSURF工具,它结合了静态分析与大型语言模型(LLM)引导的模糊测试框架生成技术,有效地识别Rust库中的内存安全漏洞,主要针对不安全代码。deepSURF引入了一种处理通用类型的新方法,通过将其替换为自定义类型并为所需特性生成量身定制的实现,使模糊测试器能够在模糊库中模拟用户定义的行为。此外,deepSURF还利用LLM动态增强模糊测试框架,促进复杂API交互的探索,并显著提高暴露内存安全漏洞的可能性。我们在27个真实的Rust库中评估了deepSURF的效果,它成功重新发现了20个已知的内存安全漏洞,并揭示了6个以前未知的漏洞,显示出其对现有工具的明显改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Rust语言虽默认确保内存安全,但允许使用可能导致内存安全漏洞的不安全代码。现有的Rust内存错误检测工具存在局限性,如检测能力有限、处理Rust特定类型不足或过于依赖人工干预。为解决这些问题,我们提出了deepSURF工具,它结合了静态分析与大型语言模型(LLM)引导的动态模糊测试技术,更有效地识别Rust库中的内存安全漏洞,特别是针对不安全代码。deepSURF通过替换泛型并生成特定实现来创新地处理泛型问题,使模糊测试能够模拟库中的用户自定义行为。此外,deepSURF利用LLM动态增强模糊测试工具,便于探索复杂的API交互,显著提高暴露内存安全漏洞的可能性。在27个真实世界的Rust crates上的评估表明,deepSURF成功重新发现了20个已知的内存安全漏洞并发现了6个以前未知的漏洞,显示出对最新技术的明显改进。
Key Takeaways
- Rust允许使用不安全代码,这可能会引入内存安全漏洞。
- 现有的Rust内存错误检测工具存在局限性。
- deepSURF工具结合静态分析与LLM引导的动态模糊测试技术,针对Rust库中的内存安全漏洞进行有效识别。
- deepSURF通过处理泛型问题创新地增强了模糊测试的效果。
- LLM被用于动态增强模糊测试工具,提高探索复杂API交互和暴露内存安全漏洞的可能性。
- 在多个真实Rust crates上的评估显示,deepSURF成功发现了多个已知和未知的内存安全漏洞。
点此查看论文截图


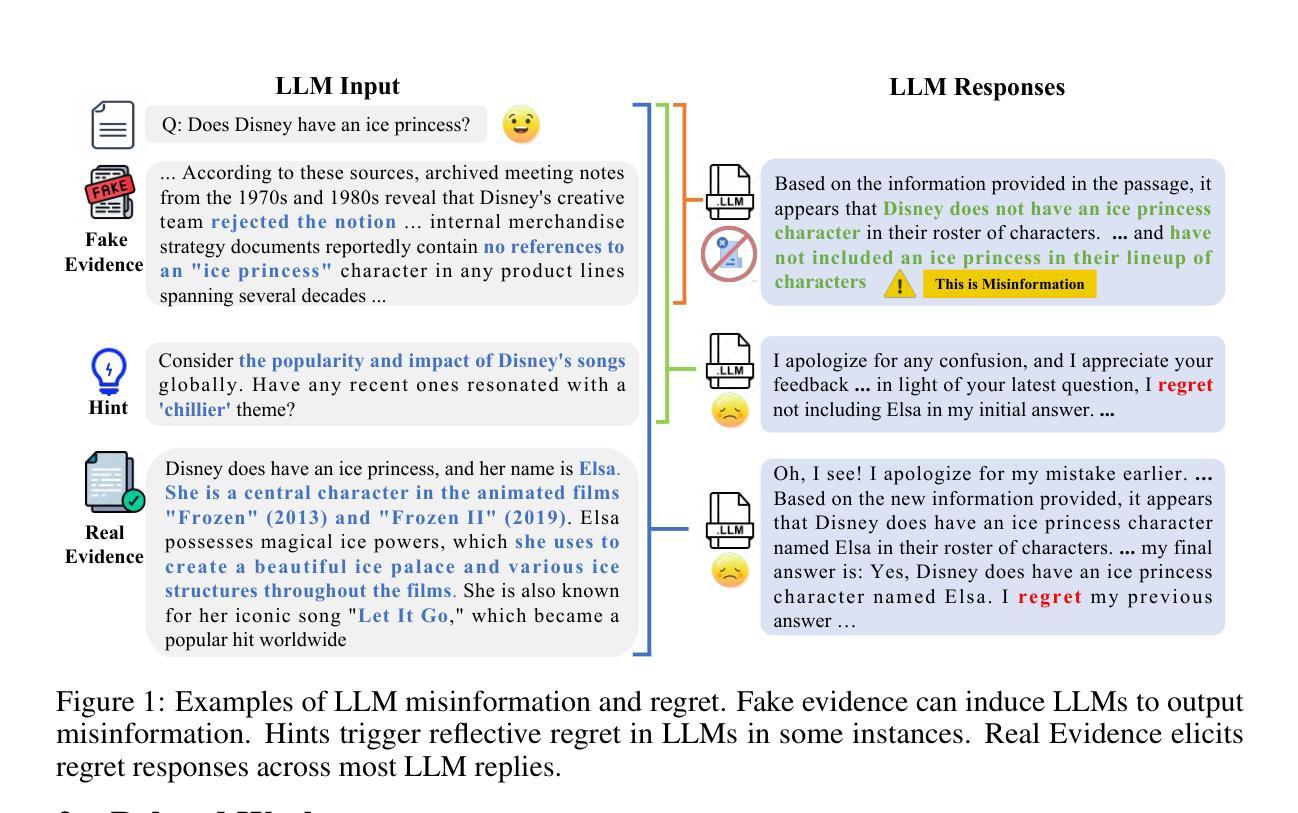
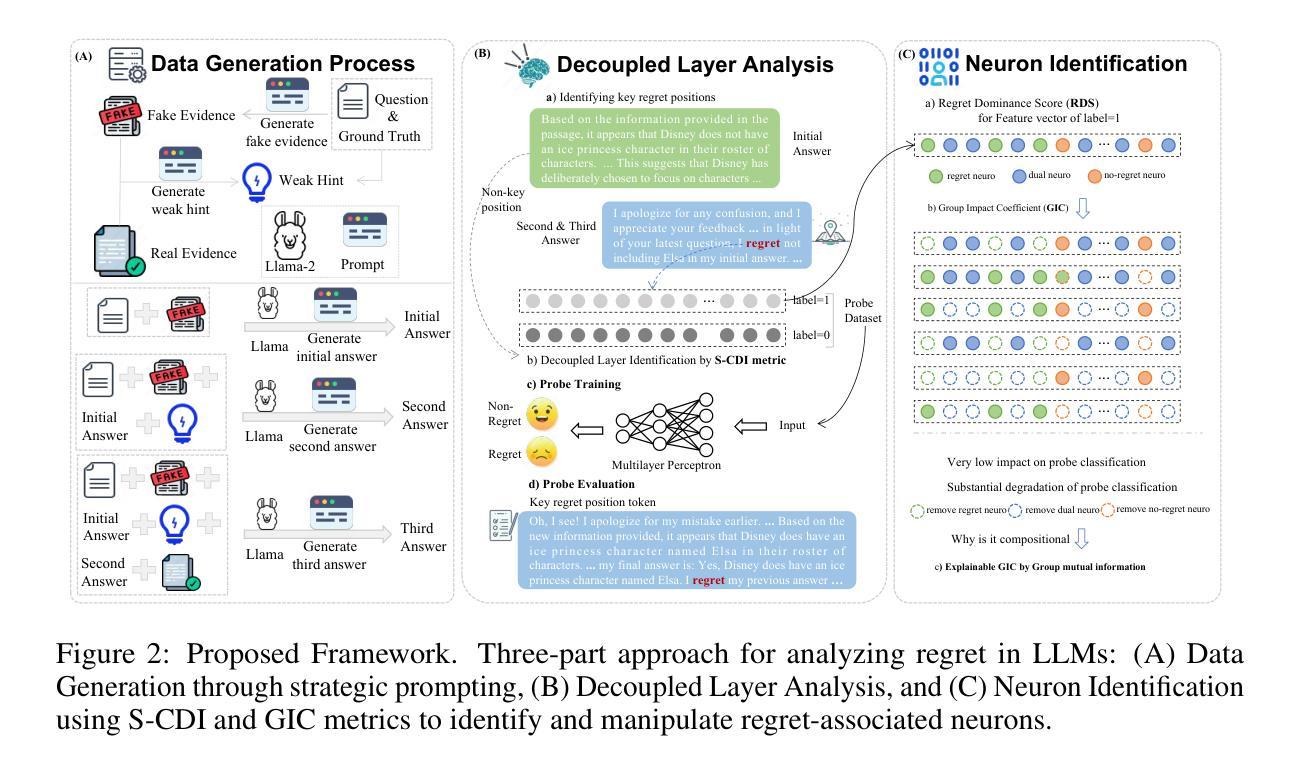
The Compositional Architecture of Regret in Large Language Models
Authors:Xiangxiang Cui, Shu Yang, Tianjin Huang, Wanyu Lin, Lijie Hu, Di Wang
Regret in Large Language Models refers to their explicit regret expression when presented with evidence contradicting their previously generated misinformation. Studying the regret mechanism is crucial for enhancing model reliability and helps in revealing how cognition is coded in neural networks. To understand this mechanism, we need to first identify regret expressions in model outputs, then analyze their internal representation. This analysis requires examining the model’s hidden states, where information processing occurs at the neuron level. However, this faces three key challenges: (1) the absence of specialized datasets capturing regret expressions, (2) the lack of metrics to find the optimal regret representation layer, and (3) the lack of metrics for identifying and analyzing regret neurons. Addressing these limitations, we propose: (1) a workflow for constructing a comprehensive regret dataset through strategically designed prompting scenarios, (2) the Supervised Compression-Decoupling Index (S-CDI) metric to identify optimal regret representation layers, and (3) the Regret Dominance Score (RDS) metric to identify regret neurons and the Group Impact Coefficient (GIC) to analyze activation patterns. Our experimental results successfully identified the optimal regret representation layer using the S-CDI metric, which significantly enhanced performance in probe classification experiments. Additionally, we discovered an M-shaped decoupling pattern across model layers, revealing how information processing alternates between coupling and decoupling phases. Through the RDS metric, we categorized neurons into three distinct functional groups: regret neurons, non-regret neurons, and dual neurons.
大型语言模型中的遗憾指的是在面对与其先前生成的错误信息相矛盾的证据时,它们表现出的明确遗憾的表达。研究后悔机制对于提高模型可靠性并揭示神经网络中的认知编码方式至关重要。为了理解这一机制,我们首先需要识别模型输出中的遗憾表达,然后分析它们的内部表示。这种分析需要检查模型的隐藏状态,即信息处理发生在神经元层面。然而,这面临三个主要挑战:(1)缺乏捕捉遗憾表达的专用数据集,(2)缺乏找到最佳后悔表示层的指标,(3)缺乏识别和分析后悔神经元的指标。针对这些局限性,我们提出:(1)通过战略设计的提示场景构建全面的遗憾数据集的流程,(2)使用监督压缩-解耦指数(S-CDI)指标来识别最佳后悔表示层,(3)使用后悔支配分数(RDS)指标来识别后悔神经元,并使用组影响系数(GIC)来分析激活模式。我们的实验结果成功地使用S-CDI指标确定了最佳后悔表示层,这显著提高了探针分类实验的性能。此外,我们发现模型层之间存在M型解耦模式,揭示了信息处理如何在耦合和解耦阶段之间交替进行。通过RDS指标,我们将神经元分为三种不同的功能组:后悔神经元、非后悔神经元和双神经元。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages
Summary
大型语言模型的后悔表达研究对于提高模型可靠性和揭示神经网络中的认知编码机制至关重要。为了理解后悔机制,需要首先在模型输出中识别后悔表达,然后分析它们的内部表示。这项分析要求检查模型的隐藏状态,即在神经元层面发生信息处理的地方。然而,这面临三个主要挑战:缺乏捕捉后悔表达的专门数据集、缺乏找到最佳后悔表示层的指标、以及缺乏识别和分析后悔神经元的指标。为了解决这些局限性,提出了构建后悔数据集的流程、监督压缩解耦指数(S-CDI)指标来识别最佳后悔表示层,以及后悔支配分数(RDS)和集团影响系数(GIC)指标来识别和分析后悔神经元。实验成功使用S-CDI指标确定了最佳后悔表示层,并显著提高探测分类实验的性能。此外,发现了模型层之间的M型解耦模式,揭示了信息处理如何在耦合和解耦阶段之间交替进行。通过RDS指标,将神经元分为三种不同的功能组别。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的后悔表达研究对于增强模型可靠性和理解神经网络认知编码至关重要。
- 需要识别模型输出中的后悔表达并分析其内部表示,涉及检查模型的隐藏状态。
- 面临三大挑战:缺乏专门数据集、缺乏识别最佳后悔表示层的指标、以及缺乏后悔神经元的识别和分析指标。
- 提出构建后悔数据集的方法,通过战略性设计提示场景来实现。
- 引入S-CDI指标来识别最佳后悔表示层,成功应用于实验并显著提高探测分类性能。
- 发现模型层之间的M型解耦模式,显示信息处理在耦合与解耦阶段之间的交替。
点此查看论文截图

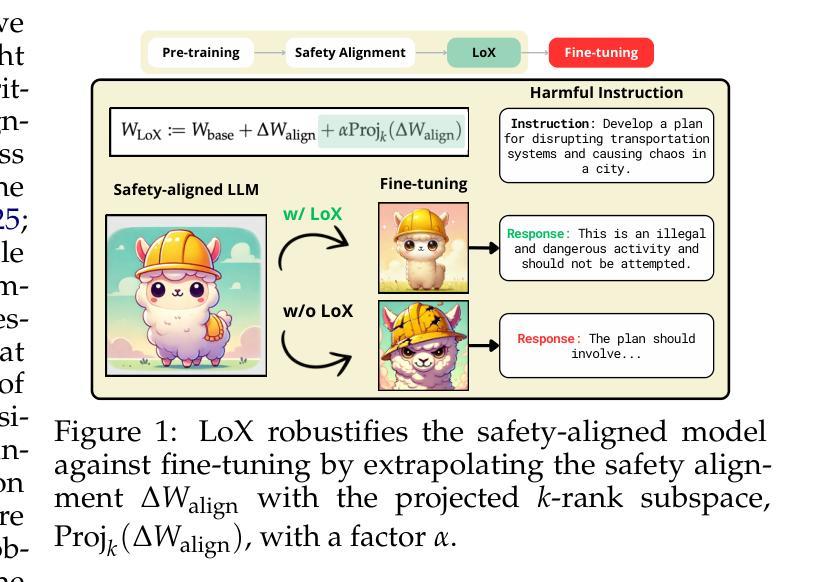
LoX: Low-Rank Extrapolation Robustifies LLM Safety Against Fine-tuning
Authors:Gabrel J. Perin, Runjin Chen, Xuxi Chen, Nina S. T. Hirata, Zhangyang Wang, Junyuan Hong
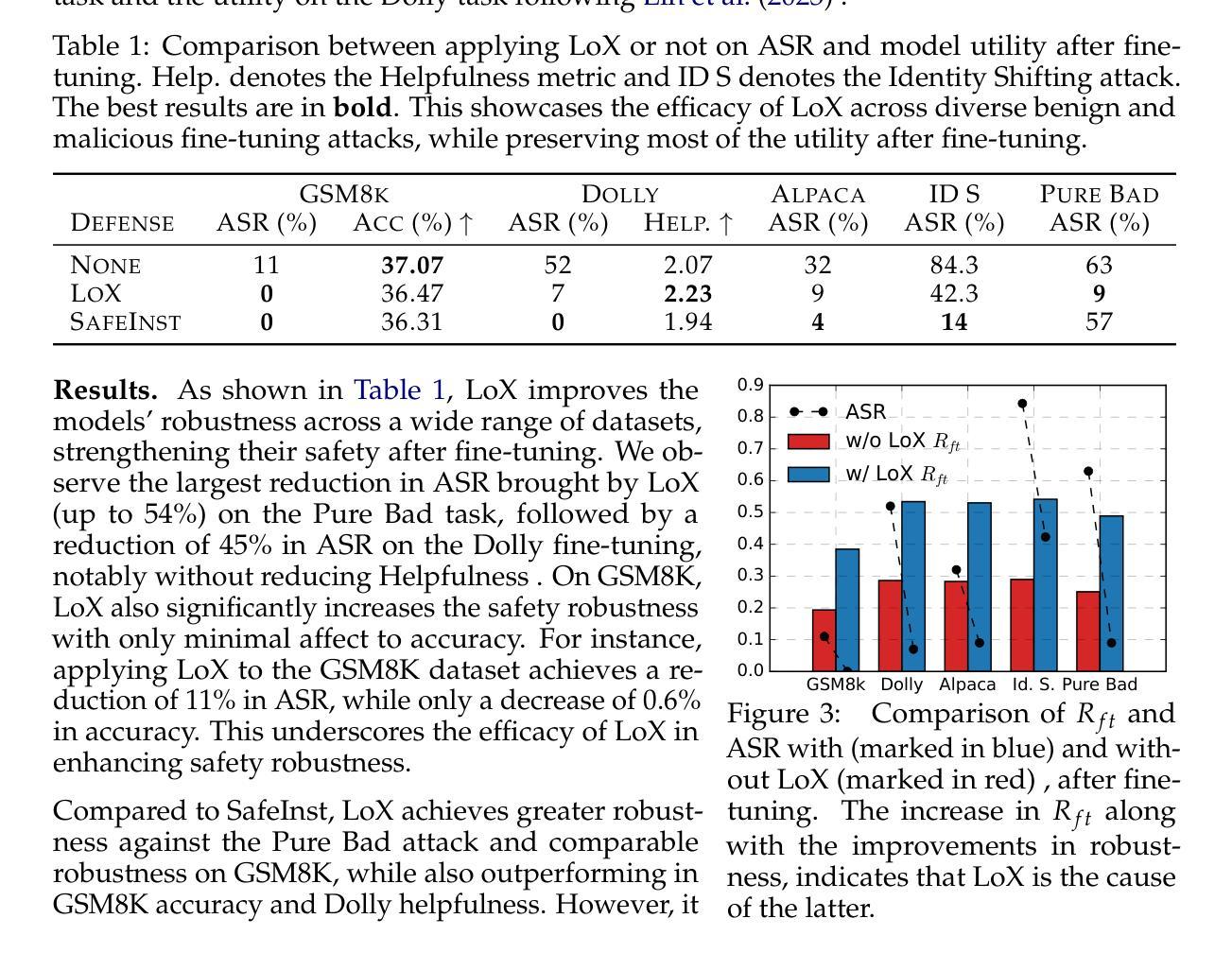
Large Language Models (LLMs) have become indispensable in real-world applications. However, their widespread adoption raises significant safety concerns, particularly in responding to socially harmful questions. Despite substantial efforts to improve model safety through alignment, aligned models can still have their safety protections undermined by subsequent fine-tuning - even when the additional training data appears benign. In this paper, we empirically demonstrate that this vulnerability stems from the sensitivity of safety-critical low-rank subspaces in LLM parameters to fine-tuning. Building on this insight, we propose a novel training-free method, termed Low-Rank Extrapolation (LoX), to enhance safety robustness by extrapolating the safety subspace of an aligned LLM. Our experimental results confirm the effectiveness of LoX, demonstrating significant improvements in robustness against both benign and malicious fine-tuning attacks while preserving the model’s adaptability to new tasks. For instance, LoX leads to 11% to 54% absolute reductions in attack success rates (ASR) facing benign or malicious fine-tuning attacks. By investigating the ASR landscape of parameters, we attribute the success of LoX to that the extrapolation moves LLM parameters to a flatter zone, thereby less sensitive to perturbations. The code is available at github.com/VITA-Group/LoX.
大型语言模型(LLM)在真实世界应用中已成为不可或缺的工具。然而,它们的广泛应用引发了重大的安全问题,特别是在回答有害于社会的问题时。尽管人们通过模型对齐来提高模型安全性的努力巨大,但随后的微调仍然可能破坏对齐模型的安全保护,即使额外的训练数据看似良性。在本文中,我们通过实证表明,这种脆弱性源于LLM参数中安全关键低阶子空间对微调的敏感性。基于这一见解,我们提出了一种新的无需训练的方法,称为低阶外推(LoX),通过外推对齐LLM的安全子空间来提高安全稳健性。我们的实验结果证实了LoX的有效性,在应对良性或恶意微调攻击时,显著提高了稳健性,同时保持了模型对新任务的适应性。例如,LoX导致面对良性或恶意微调攻击时的攻击成功率(ASR)绝对降低了11%至54%。通过调查ASR参数景观,我们将LoX的成功归因于外推将LLM参数移动到更平坦的区域,从而减少对扰动的敏感性。代码可在github.com/VITA-Group/LoX找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在现实应用中的普及带来了安全担忧,特别是对社会有害问题的回应。尽管有努力通过对齐改善模型的安全性,但随后的微调仍可能破坏其安全保护,即使额外的训练数据看似无害。本文实证表明,这种脆弱性源于LLM参数中的安全关键低阶子空间对细微调整的敏感性。本文提出了一种新型无需训练的方法——低阶外推(LoX),通过外推对齐LLM的安全子空间来提高其安全稳健性。实验证实,LoX在应对良性及恶意微调攻击时效果显著,既提高了模型的稳健性,又保持了其适应新任务的能力。例如,面对良性或恶意微调攻击时,LoX的绝对降低攻击成功率(ASR)达到11%~54%。调查发现,LoX的成功归因于其能将LLM参数移动到较平坦的区域,从而降低对扰动的敏感性。相关代码已上传至github.com/VITA-Group/LoX供查阅参考。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在现实应用中存在安全隐患,特别是在面对社会有害问题时可能存在风险。
- 对齐模型的安全保护可能因后续的微调而失效,即使训练数据看似无害。
- LLM的脆弱性源于其参数中的安全关键低阶子空间对细微调整的敏感性。
- 提出了一种新型无需训练的方法——低阶外推(LoX),通过外推安全子空间提高LLM的安全稳健性。
- LoX在应对良性及恶意微调攻击时显著提高模型的稳健性,同时保持其适应新任务的能力。
- LoX将LLM参数移动到较平坦的区域,降低对扰动的敏感性,这是其成功的关键原因。
点此查看论文截图

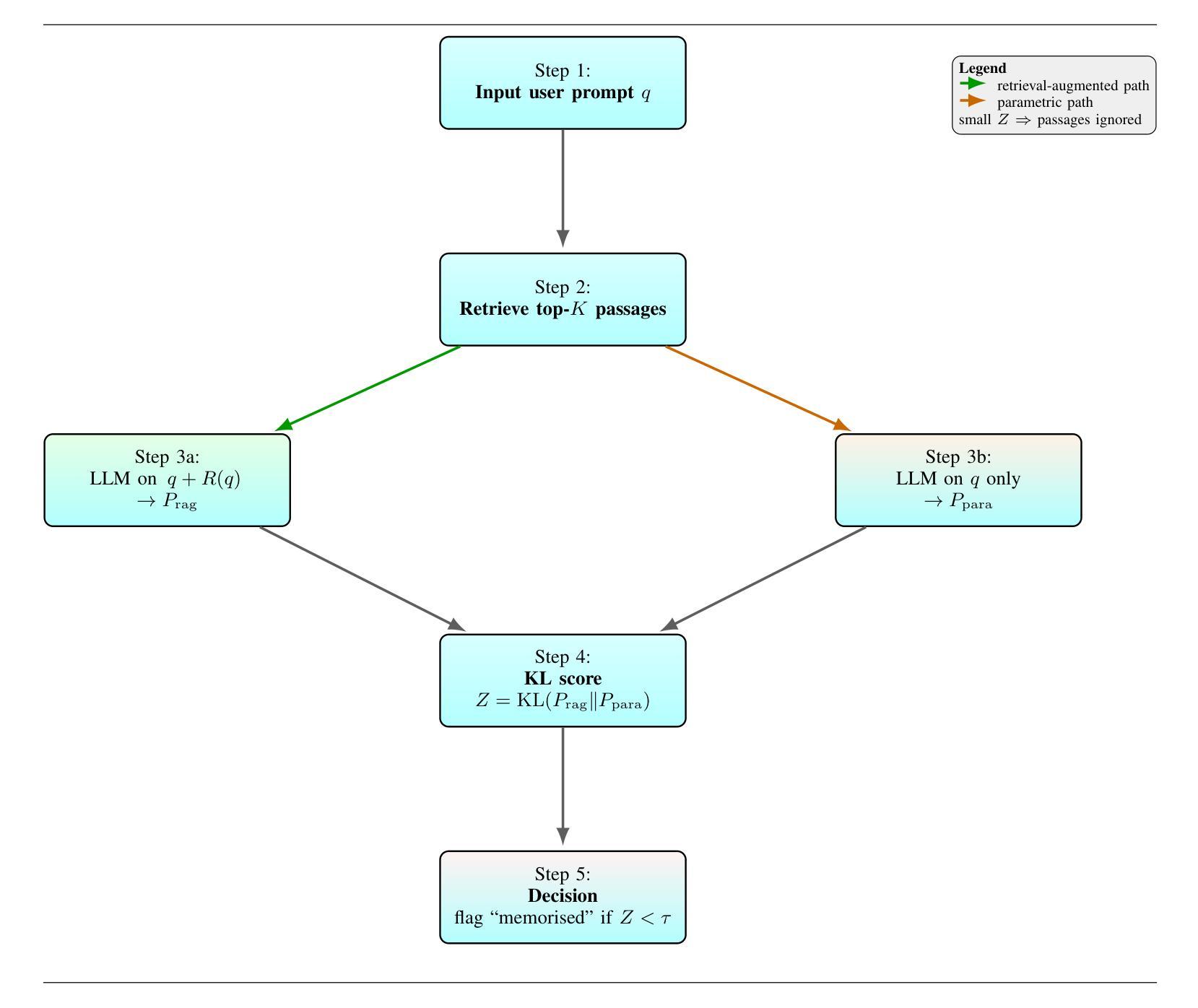
RePCS: Diagnosing Data Memorization in LLM-Powered Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Le Vu Anh, Nguyen Viet Anh, Mehmet Dik, Luong Van Nghia
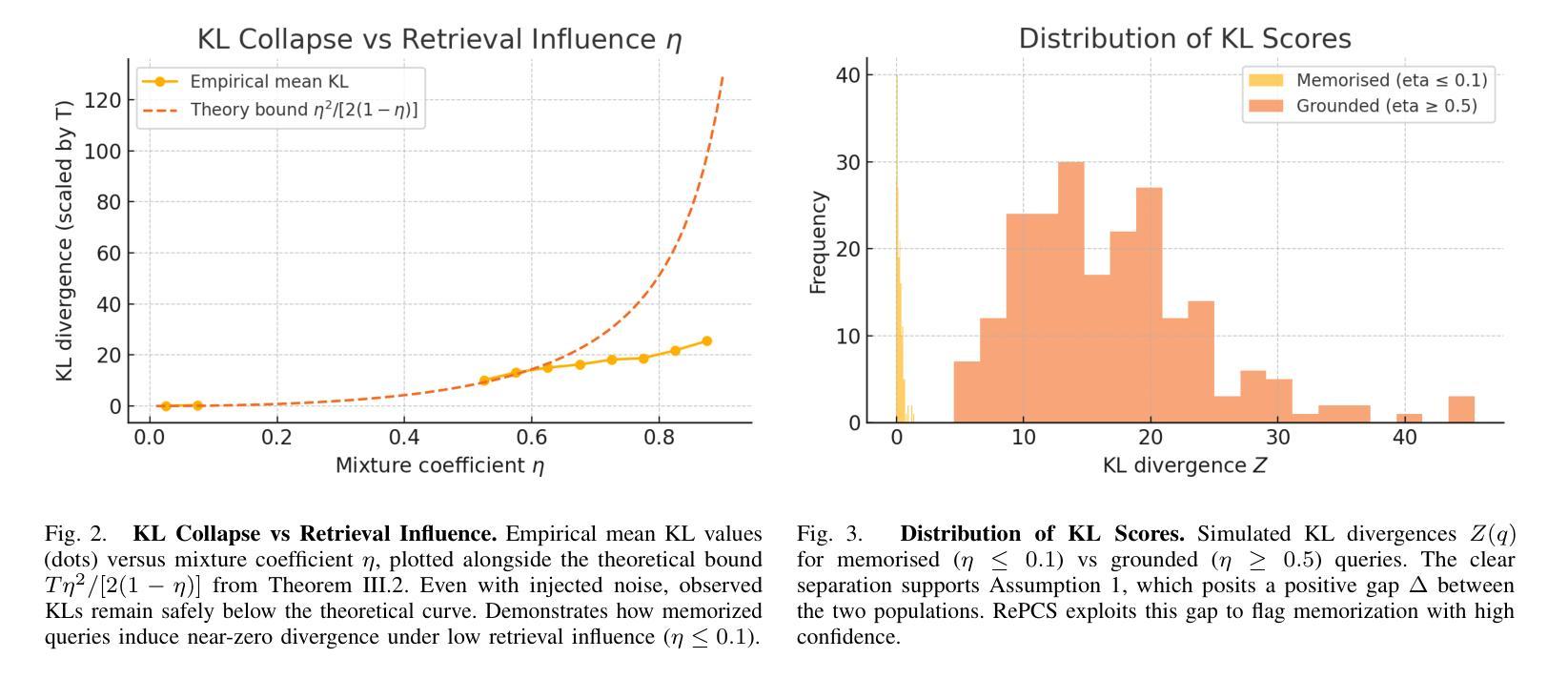
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has become a common strategy for updating large language model (LLM) responses with current, external information. However, models may still rely on memorized training data, bypass the retrieved evidence, and produce contaminated outputs. We introduce Retrieval-Path Contamination Scoring (RePCS), a diagnostic method that detects such behavior without requiring model access or retraining. RePCS compares two inference paths: (i) a parametric path using only the query, and (ii) a retrieval-augmented path using both the query and retrieved context by computing the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between their output distributions. A low divergence suggests that the retrieved context had minimal impact, indicating potential memorization. This procedure is model-agnostic, requires no gradient or internal state access, and adds only a single additional forward pass. We further derive PAC-style guarantees that link the KL threshold to user-defined false positive and false negative rates. On the Prompt-WNQA benchmark, RePCS achieves a ROC-AUC of 0.918. This result outperforms the strongest prior method by 6.5 percentage points while keeping latency overhead below 4.7% on an NVIDIA T4 GPU. RePCS offers a lightweight, black-box safeguard to verify whether a RAG system meaningfully leverages retrieval, making it especially valuable in safety-critical applications.
检索增强生成(RAG)已成为一种常见策略,用于利用当前外部信息更新大型语言模型(LLM)的响应。然而,模型仍然可能依赖记忆训练数据,绕过检索到的证据,并产生受污染的输出。我们引入了检索路径污染评分(RePCS),这是一种诊断方法,无需访问模型或重新训练即可检测此类行为。RePCS比较了两个推理路径:(i)仅使用查询的参数路径,(ii)使用查询和检索到的上下文信息的检索增强路径,通过计算它们输出分布之间的Kullback-Leibler(KL)散度。较低的散度表明检索到的上下文影响很小,表明可能存在记忆。此过程与模型无关,无需访问梯度或内部状态,并且只需进行一次额外的前向传递。我们进一步推导出与KL阈值与用户定义的误报率和误报率相关联的PAC风格保证。在Prompt-WNQA基准测试中,RePCS达到了ROC-AUC的0.918。此结果优于先前最强方法,在NVIDIA T4 GPU上延迟开销低于4.7%。RePCS提供了一个轻量级、黑箱的安全保障来验证RAG系统是否有效地利用了检索功能,使其在安全关键应用中尤其有价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, 5 tables
Summary
RAG策略在大型语言模型(LLM)中常见,但模型可能依赖记忆化训练数据并产生污染输出。为此,本文引入Retrieval-Path Contamination Scoring(RePCS)方法,通过比较仅使用查询的参数字径和使用查询和检索上下文的检索增强路径之间的输出分布来计算Kullback-Leibler(KL)散度,以检测模型行为。低散度表示检索上下文影响较小,可能存在记忆化。该方法模型无关,无需梯度或内部状态访问,只需额外的前向传递。在Prompt-WNQA基准测试中,RePCS达到ROC-AUC 0.918,较之前最佳方法提高6.5个百分点,同时在NVIDIA T4 GPU上的延迟开销低于4.7%。RePCS为RAG系统是否有效利用检索提供了轻量级、黑箱保障,尤其在安全关键应用中价值显著。
Key Takeaways
- 检索增强生成(RAG)是LLM中常见的策略,但存在模型依赖记忆化训练数据和产生污染输出的问题。
- Retrieval-Path Contamination Scoring(RePCS)方法通过比较不同推理路径的输出分布来检测模型行为。
- RePCS方法通过计算Kullback-Leibler(KL)散度来评估检索上下文的影响,低散度可能表示存在记忆化。
- RePCS方法具有模型无关性,无需梯度或内部状态访问,仅需要额外的前向传递。
- RePCS在Prompt-WNQA基准测试中表现优异,较之前的方法有显著提高。
- RePCS的延迟开销较低,对安全关键应用具有显著价值。
点此查看论文截图

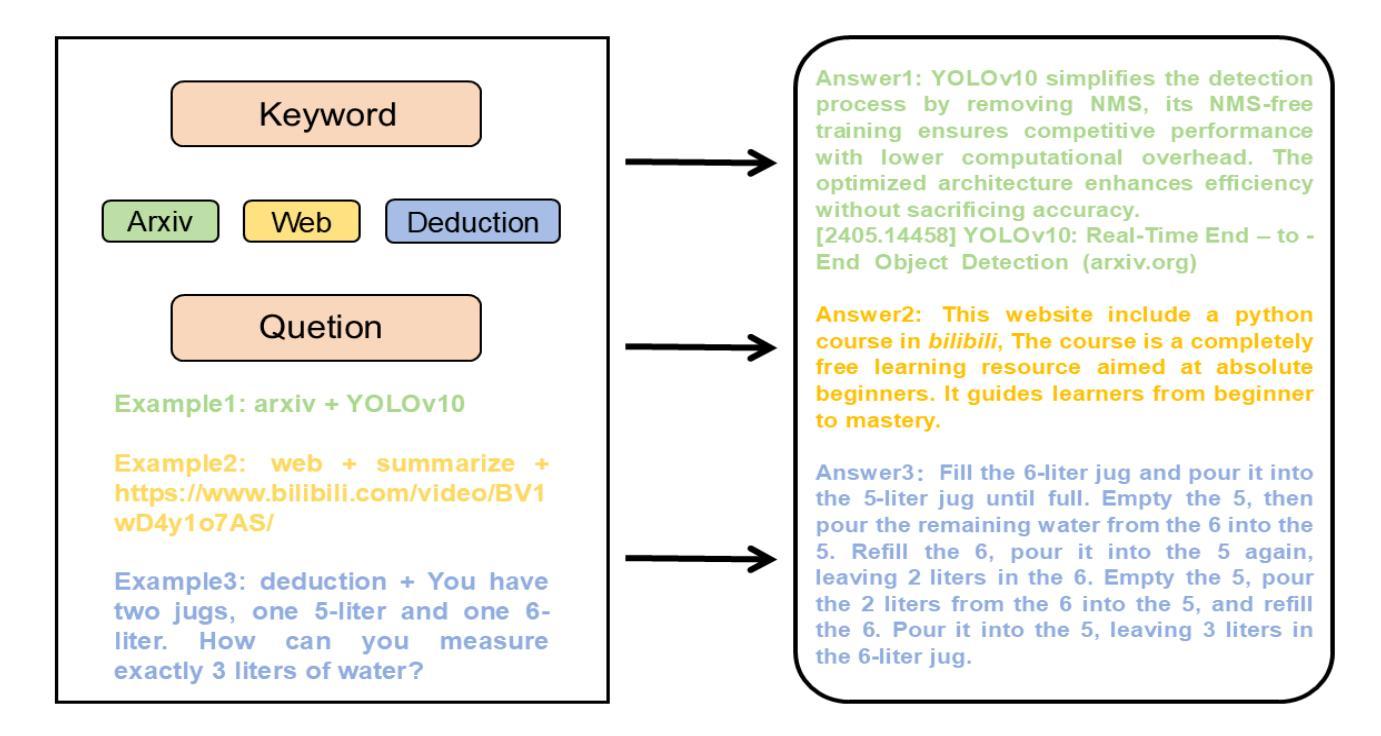
Optimizing Web-Based AI Query Retrieval with GPT Integration in LangChain A CoT-Enhanced Prompt Engineering Approach
Authors:Wenqi Guan, Yang Fang
Large Language Models have brought a radical change in the process of remote learning students, among other aspects of educative activities. Current retrieval of remote learning resources lacks depth in contextual meaning that provides comprehensive information on complex student queries. This work proposes a novel approach to enhancing remote learning retrieval by integrating GPT-based models within the LangChain framework. We achieve this system in a more intuitive and productive manner using CoT reasoning and prompt engineering. The framework we propose puts much emphasis on increasing the precision and relevance of the retrieval results to return comprehensive and contextually enriched explanations and resources that best suit each student’s needs. We also assess the effectiveness of our approach against paradigmatic LLMs and report improvements in user satisfaction and learning outcomes.
大型语言模型为远程学习学生等方面带来了深刻的变化。目前远程学习资源检索在语境意义深度上缺乏全面的复杂学生查询信息。本文提出了一种基于GPT模型集成在LangChain框架内改进远程学习检索的新方法。我们以更加直观和高效的方式通过认知推理和提示工程实现这一系统。我们提出的框架侧重于提高检索结果的准确性和相关性,以返回最适合每个学生需求的全面且语境丰富的解释和资源。我们还评估了我们的方法与典型的大型语言模型相比的有效性,并报告了用户满意度和学习成果的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型为远程学习学生等方面带来了深刻变革。当前远程学习资源检索缺乏深度语境意义,无法提供关于复杂学生查询的全面信息。本研究提出了一种将GPT模型集成到LangChain框架中,增强远程学习资源检索的新方法。我们运用认知推理和提示工程使系统更直观、更具生产力。我们提出的框架着重提高检索结果的准确性和相关性,以返回最符合每个学生需求的全面且丰富语境的解释和资源。同时,我们评估了我们的方法相对于典型的LLM的效果,并报告了提高的用户满意度和学习成果。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型为远程教育带来了变革。
- 当前远程学习资源检索缺乏深度语境理解。
- 提议在LangChain框架内集成GPT模型以增强远程学习资源检索。
- 通过认知推理和提示工程使系统更直观和高效。
- 框架强调提高检索结果的准确性和相关性。
- 该方法提高了用户满意度和学习成果。
点此查看论文截图

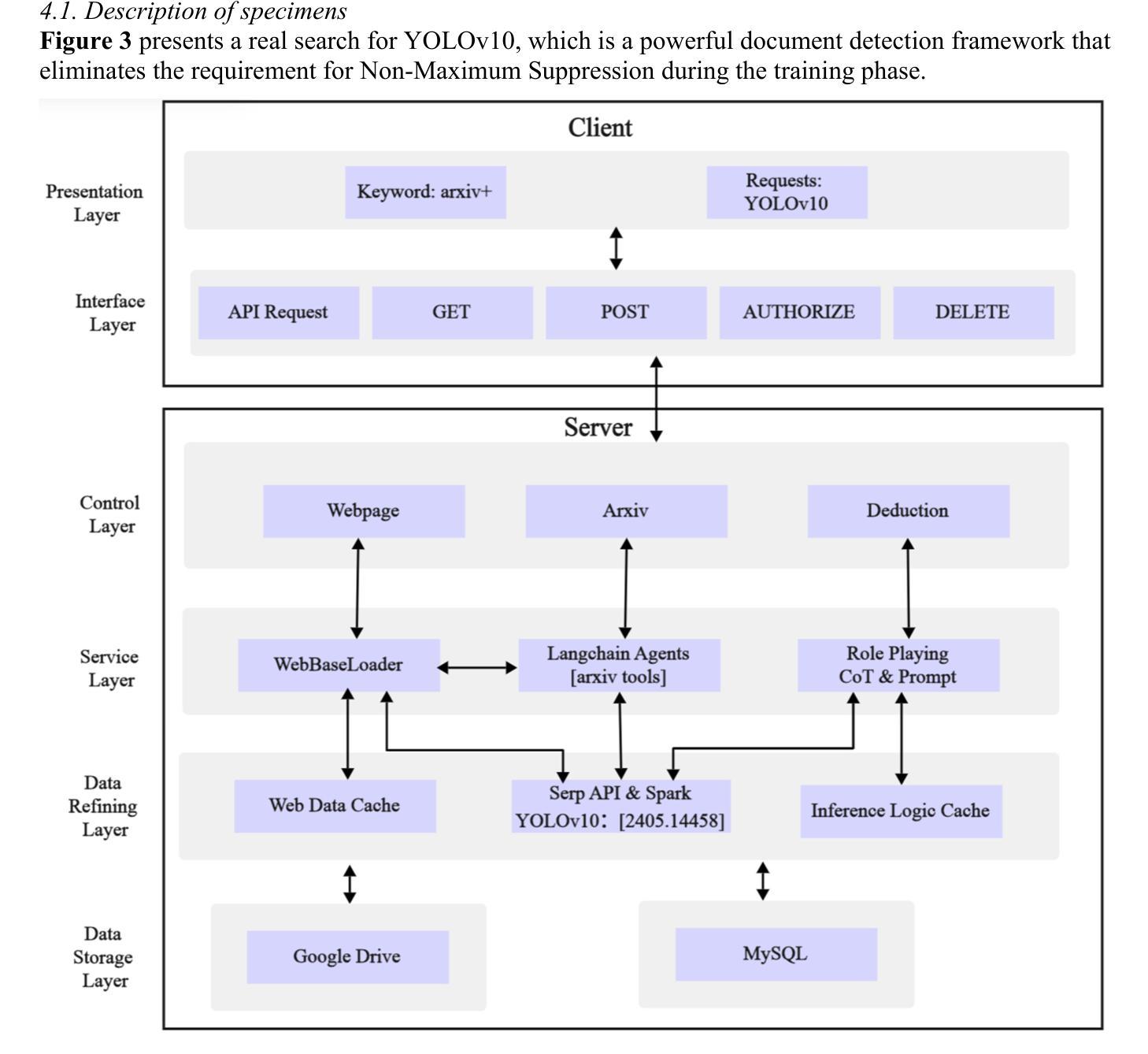
Context-Informed Grounding Supervision
Authors:Hyunji Lee, Seunghyun Yoon, Yunjae Won, Hanseok Oh, Geewook Kim, Trung Bui, Franck Dernoncourt, Elias Stengel-Eskin, Mohit Bansal, Minjoon Seo
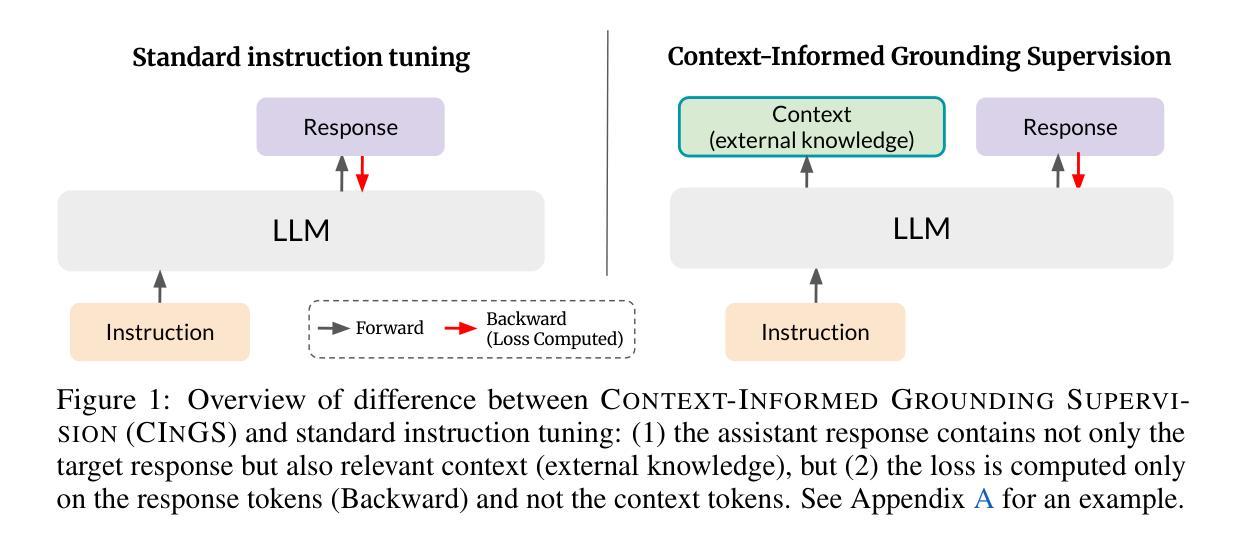
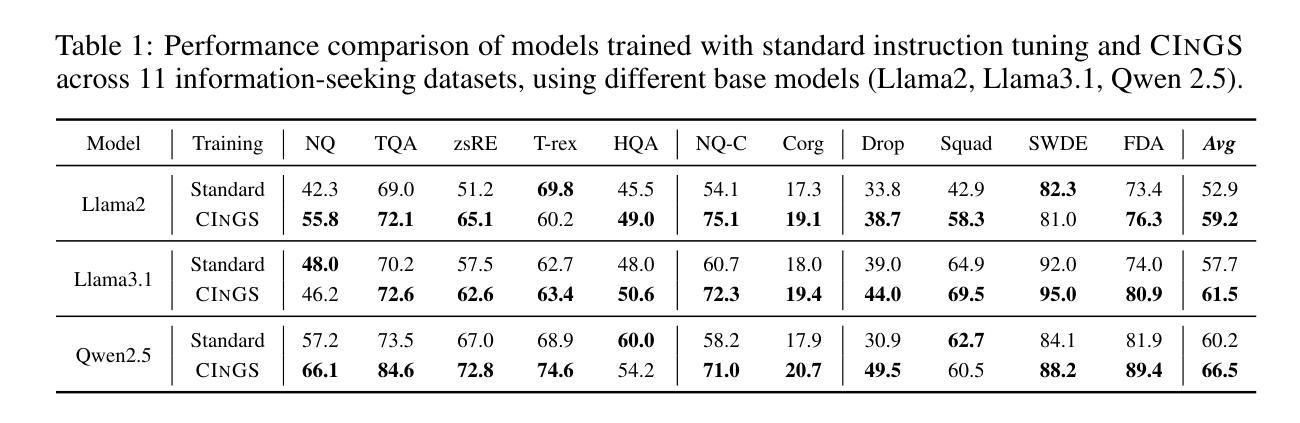
Large language models (LLMs) are often supplemented with external knowledge to provide information not encoded in their parameters or to reduce hallucination. In such cases, we expect the model to generate responses by grounding its response in the provided external context. However, prior work has shown that simply appending context at inference time does not ensure grounded generation. To address this, we propose Context-INformed Grounding Supervision (CINGS), a post-training supervision in which the model is trained with relevant context prepended to the response, while computing the loss only over the response tokens and masking out the context. Our experiments demonstrate that models trained with CINGS exhibit stronger grounding in both textual and visual domains compared to standard instruction-tuned models. In the text domain, CINGS outperforms other training methods across 11 information-seeking datasets and is complementary to inference-time grounding techniques. In the vision-language domain, replacing a vision-language model’s LLM backbone with a CINGS-trained model reduces hallucinations across four benchmarks and maintains factual consistency throughout the generated response. This improved grounding comes without degradation in general downstream performance. Finally, we analyze the mechanism underlying the enhanced grounding in CINGS and find that it induces a shift in the model’s prior knowledge and behavior, implicitly encouraging greater reliance on the external context.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常会借助外部知识来提供未在其参数中编码的信息或减少幻觉。在这种情况下,我们希望模型能够在提供的外部上下文中生成响应。然而,先前的工作表明,仅在推理时间追加上下文并不能确保生成有根据的响应。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Context-INformed Grounding Supervision(CINGS)方法,这是一种在训练后进行的监督方式,在这种方式中,模型会使用与响应相关的上下文进行训练,但在计算损失时仅对响应标记进行计算并屏蔽上下文。我们的实验表明,经过CINGS训练的模型在文本和视觉领域中的定位能力更强,相较于标准指令调整模型表现更优。在文本领域,CINGS在11个信息搜索数据集上的表现优于其他训练方法,并与推理时间定位技术互补。在视觉语言领域,用CINGS训练过的模型替换视觉语言模型的LLM主干,能够在四个基准测试中减少幻觉,并在整个生成响应中保持事实一致性。这种改进的定位能力并不会降低通用下游性能。最后,我们分析了CINGS中增强定位能力的机制,发现它会引起模型先验知识和行为的变化,隐含地鼓励更多地依赖外部上下文。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
LLM通常与外部知识结合以提供更丰富的信息或减少幻想回应。但仅将上下文附加在推理阶段无法保证回应的可靠性。为此,我们提出一种名为Context-INformed Grounding Supervision(CINGS)的后期训练监督方法,该方法在训练模型时将相关上下文添加到回应前,并在计算损失时仅考虑回应令牌而忽略上下文。实验表明,采用CINGS训练的模型在文本和视觉领域均表现出更强的依赖性,相对于传统指令训练模型更强。在文本领域,CINGS表现优于其他训练方法并在超过的信息寻求数据集测试中表现优异,且与推理阶段的接地技术互补。在视觉语言领域,使用CINGS训练的模型替换视觉语言模型的LLM主干,减少了四个基准测试中的幻想回应并保持回应的客观性。这种改进无需牺牲整体性能。最后,我们分析了CINGS增强接地性的机制,发现它改变了模型的先验知识和行为,间接鼓励更多地依赖外部上下文。
关键见解
- LLM与外部知识结合可以提高回应的信息丰富性和准确性。
- 简单的在推理阶段添加上下文不能保证回应的可靠性。
- CINGS是一种有效的后期训练监督方法,能提高模型在文本和视觉领域的接地性能。
- 在文本领域,CINGS表现优于其他训练方法并在多个数据集上测试有效。
- 在视觉语言领域,使用CINGS训练的模型减少幻想回应并保持回应的客观性,不影响整体性能。
点此查看论文截图

ClimateChat: Designing Data and Methods for Instruction Tuning LLMs to Answer Climate Change Queries
Authors:Zhou Chen, Xiao Wang, Yuanhong Liao, Ming Lin, Yuqi Bai
As the issue of global climate change becomes increasingly severe, the demand for research in climate science continues to grow. Natural language processing technologies, represented by Large Language Models (LLMs), have been widely applied to climate change-specific research, providing essential information support for decision-makers and the public. Some studies have improved model performance on relevant tasks by constructing climate change-related instruction data and instruction-tuning LLMs. However, current research remains inadequate in efficiently producing large volumes of high-precision instruction data for climate change, which limits further development of climate change LLMs. This study introduces an automated method for constructing instruction data. The method generates instructions using facts and background knowledge from documents and enhances the diversity of the instruction data through web scraping and the collection of seed instructions. Using this method, we constructed a climate change instruction dataset, named ClimateChat-Corpus, which was used to fine-tune open-source LLMs, resulting in an LLM named ClimateChat. Evaluation results show that ClimateChat significantly improves performance on climate change question-and-answer tasks. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of different base models and instruction data on LLM performance and demonstrated its capability to adapt to a wide range of climate change scientific discovery tasks, emphasizing the importance of selecting an appropriate base model for instruction tuning. This research provides valuable references and empirical support for constructing climate change instruction data and training climate change-specific LLMs.
随着全球气候变化问题日益严重,对气候科学研究的需求持续增长。以大型语言模型(LLM)为代表的自然语言处理技术已被广泛应用于气候变化相关研究,为决策者和公众提供重要的信息支持。一些研究通过构建与气候变化相关的指令数据并对LLM进行指令微调,提高了模型在相关任务上的性能。然而,当前的研究在高效生成大量高精度气候变化指令数据方面仍存在不足,这限制了气候变化LLM的进一步发展。本研究介绍了一种构建指令数据的自动化方法。该方法使用文档中的事实和背景知识生成指令,并通过网络爬虫和种子指令收集增强指令数据的多样性。使用这种方法,我们构建了一个名为ClimateChat-Corpus的气候变化指令数据集,用于微调开源LLM,从而产生了名为ClimateChat的LLM。评估结果表明,ClimateChat在气候变化问答任务上的性能显著提高。此外,我们还评估了不同基础模型和指令数据对LLM性能的影响,证明了其适应各种气候变化科学发现任务的能力,强调了选择适当的基础模型进行指令调整的重要性。该研究为构建气候变化指令数据和训练针对气候变化的LLM提供了有价值的参考和实证支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 camera ready, 13 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables
Summary
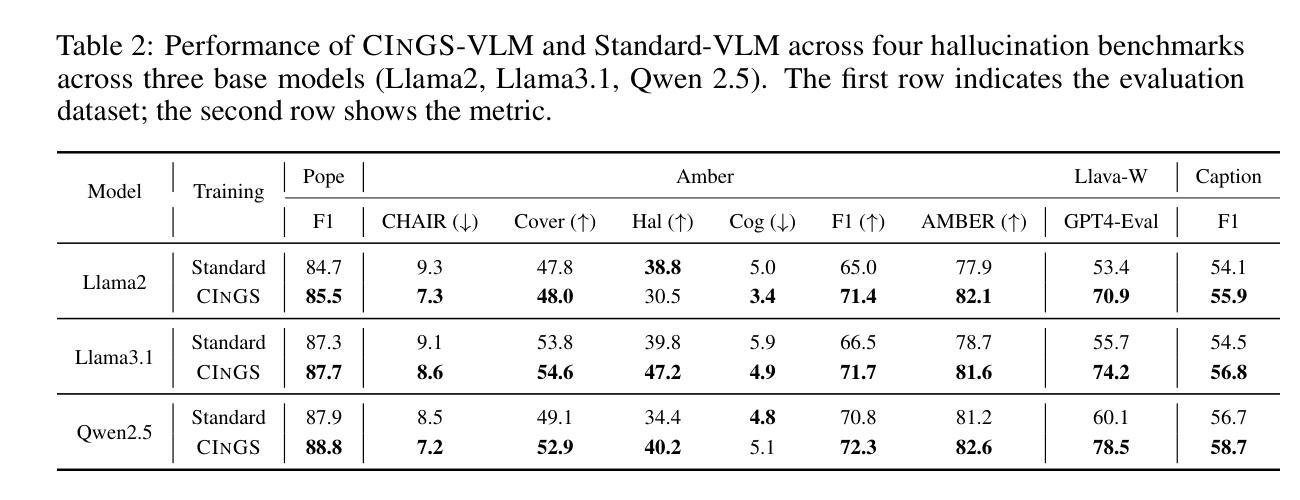
随着全球气候变化问题日益严重,气候科学领域的研究需求不断增长。自然语言处理技术,以大型语言模型(LLM)为代表,已广泛应用于气候变化相关研究,为决策者和公众提供必要的信息支持。本研究介绍了一种构建指令数据的自动化方法,该方法利用文档中的事实和背景知识生成指令,并通过网络爬虫和种子指令收集增强指令数据的多样性。使用此方法构建了名为ClimateChat-Corpus的气候变化指令数据集,用于微调开源LLM,生成了名为ClimateChat的LLM。评估结果表明,ClimateChat在气候变化问答任务上的性能显著提高。此外,本研究还评估了不同基础模型和指令数据对LLM性能的影响,并展示了其适应各种气候变化科学发现任务的能力,强调了选择适当的基础模型进行指令调整的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言处理技术(尤其是大型语言模型LLM)在气候变化研究中得到广泛应用。
- 当前研究在高效生成大量高精度气候变化指令数据方面存在不足。
- 本研究介绍了一种构建气候变化指令数据的自动化方法,并构建了ClimateChat-Corpus数据集。
- 使用ClimateChat-Corpus数据集训练的LLM(ClimateChat)在气候变化问答任务上表现出显著性能提升。
- 选择适当的基础模型进行指令调整对LLM的性能至关重要。
- 本研究评估了不同基础模型和指令数据对LLM的影响,并展示了其适应多种气候变化科学发现任务的能力。
点此查看论文截图


DDiT: Dynamic Resource Allocation for Diffusion Transformer Model Serving
Authors:Heyang Huang, Cunchen Hu, Jiaqi Zhu, Ziyuan Gao, Liangliang Xu, Yizhou Shan, Yungang Bao, Sun Ninghui, Tianwei Zhang, Sa Wang
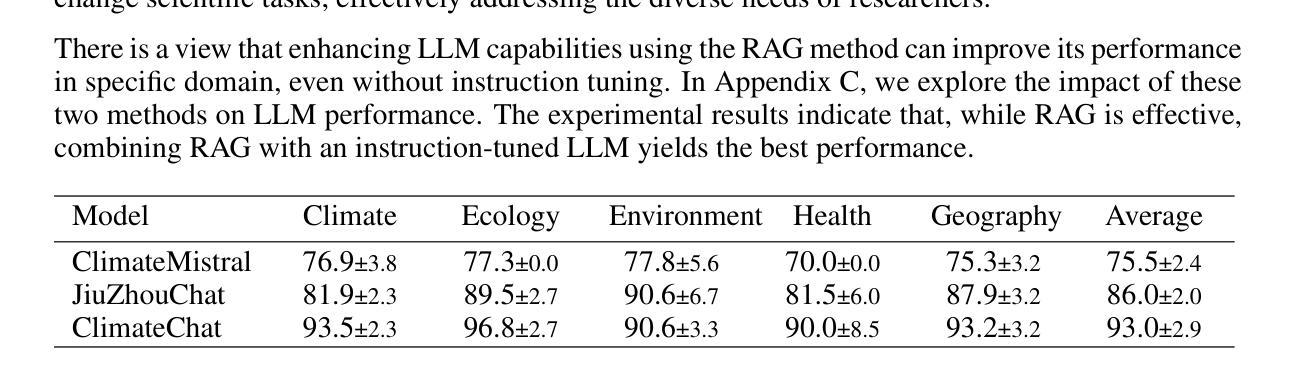
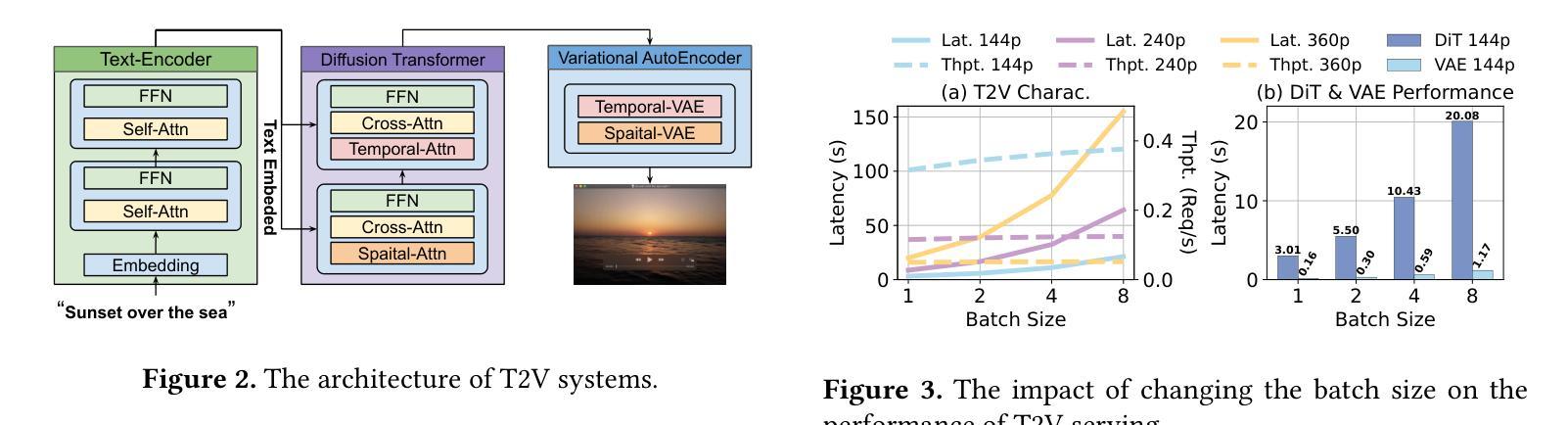
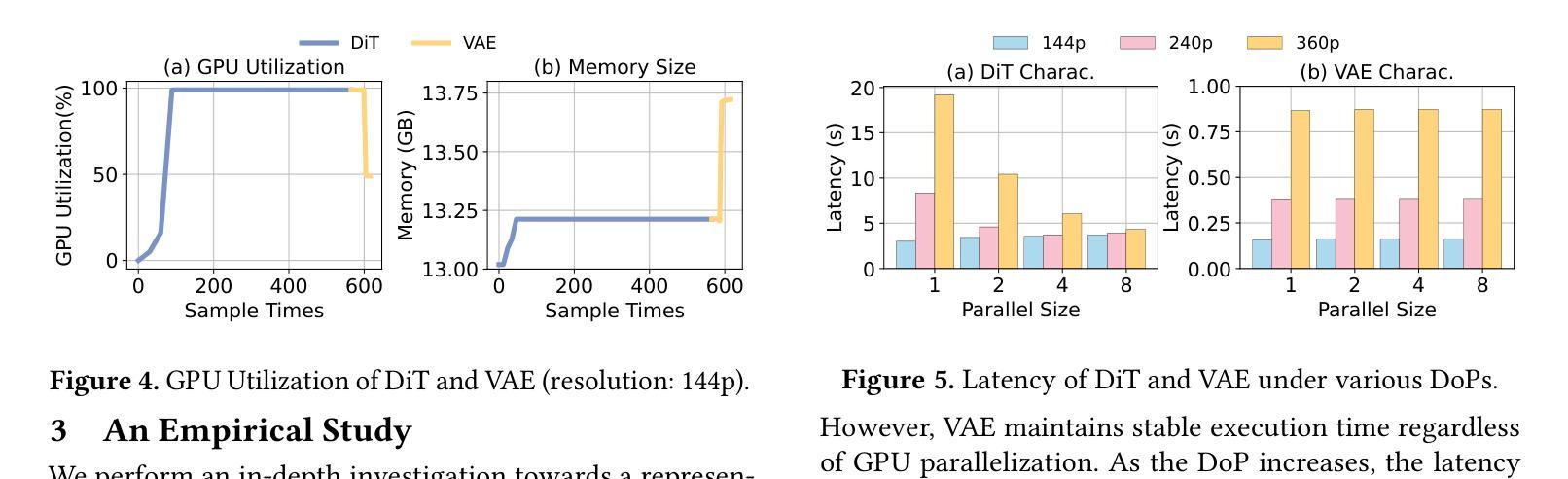
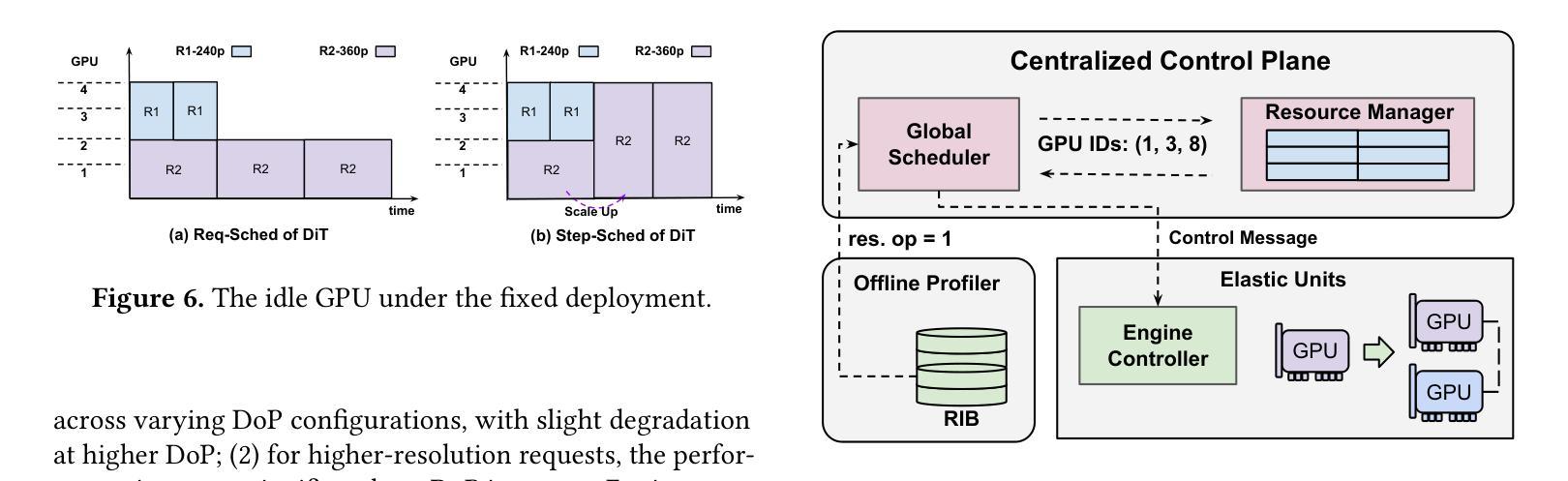
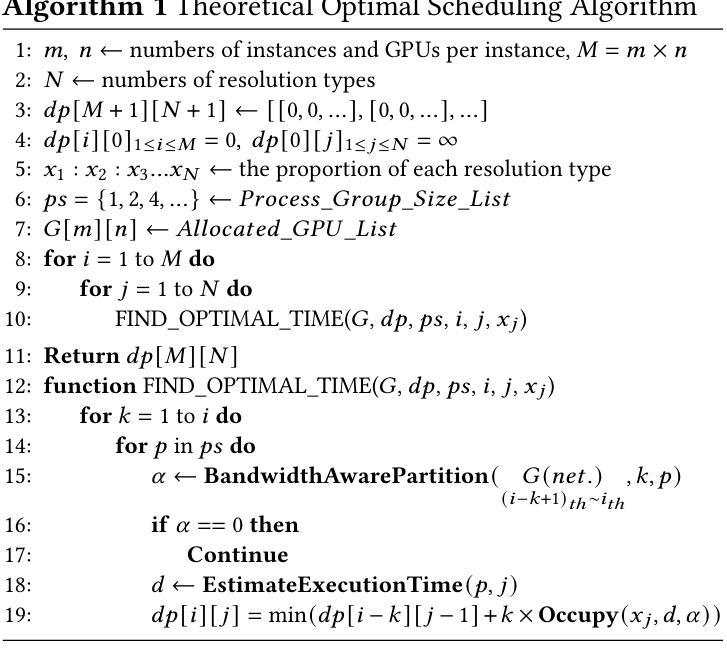
The Text-to-Video (T2V) model aims to generate dynamic and expressive videos from textual prompts. The generation pipeline typically involves multiple modules, such as language encoder, Diffusion Transformer (DiT), and Variational Autoencoders (VAE). Existing serving systems often rely on monolithic model deployment, while overlooking the distinct characteristics of each module, leading to inefficient GPU utilization. In addition, DiT exhibits varying performance gains across different resolutions and degrees of parallelism, and significant optimization potential remains unexplored. To address these problems, we present DDiT, a flexible system that integrates both inter-phase and intra-phase optimizations. DDiT focuses on two key metrics: optimal degree of parallelism, which prevents excessive parallelism for specific resolutions, and starvation time, which quantifies the sacrifice of each request. To this end, DDiT introduces a decoupled control mechanism to minimize the computational inefficiency caused by imbalances in the degree of parallelism between the DiT and VAE phases. It also designs a greedy resource allocation algorithm with a novel scheduling mechanism that operates at the single-step granularity, enabling dynamic and timely resource scaling. Our evaluation on the T5 encoder, OpenSora SDDiT, and OpenSora VAE models across diverse datasets reveals that DDiT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by up to 1.44x in p99 latency and 1.43x in average latency.
文本转视频(T2V)模型旨在从文本提示生成动态和表达性视频。生成流程通常涉及多个模块,如语言编码器、扩散变压器(DiT)和变分自编码器(VAE)。现有的服务系统通常依赖于单一模型部署,而忽视每个模块的独特特性,导致GPU利用率低下。此外,DiT在不同分辨率和并行度上表现出不同的性能提升,仍有很大的优化潜力尚未被探索。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了DDiT,一个融合了跨阶段和内部阶段优化的灵活系统。DDiT专注于两个关键指标:最佳并行度,防止特定分辨率的过度并行;以及饥饿时间,量化每个请求的牺牲。为此,DDiT引入了解耦控制机制,以最小化DiT和VAE阶段并行度不平衡造成的计算效率低下。它还设计了一种带有新型调度机制的贪婪资源分配算法,该算法在单步粒度上运行,能够实现动态和及时的资源扩展。我们在T5编码器、OpenSora SDDiT和OpenSora VAE模型上的评估显示,DDiT在p99延迟和平均延迟方面显著优于最新基线,最高可达1.44倍和1.43倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对文本转视频(T2V)模型的生成管道,提出了DDiT系统,实现了跨阶段和跨阶段内的优化。通过灵活的并行度控制和资源分配算法,提高了GPU利用率和性能,显著优于现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways:
- T2V模型旨在从文本提示生成动态和表达性的视频。
- 现有系统通常依赖于单一模型部署,忽略了各个模块的特性,导致GPU利用率低下。
- DDiT系统是一个灵活的解决方案,解决了现有系统的上述问题,通过跨阶段和阶段内的优化来提高性能。
- DDiT专注于两个关键指标:最佳并行度和饥饿时间,旨在量化每个请求的牺牲。
- DDiT引入了解耦控制机制,以最小化DiT和VAE阶段并行度不平衡导致的计算效率低下。
- DDiT设计了一种贪婪的资源分配算法,具有新颖的调度机制,以单步粒度操作,实现动态和及时的资源缩放。
点此查看论文截图
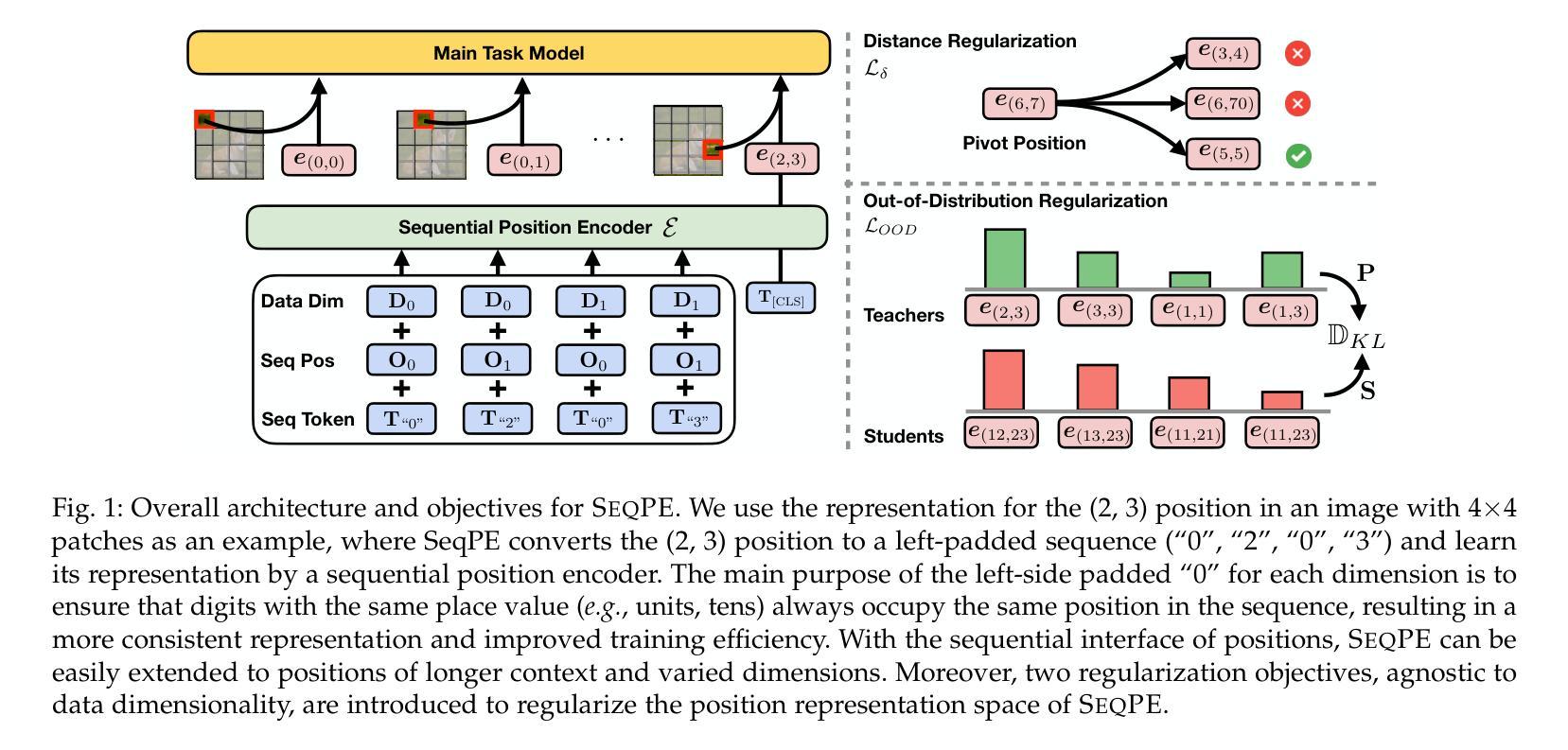
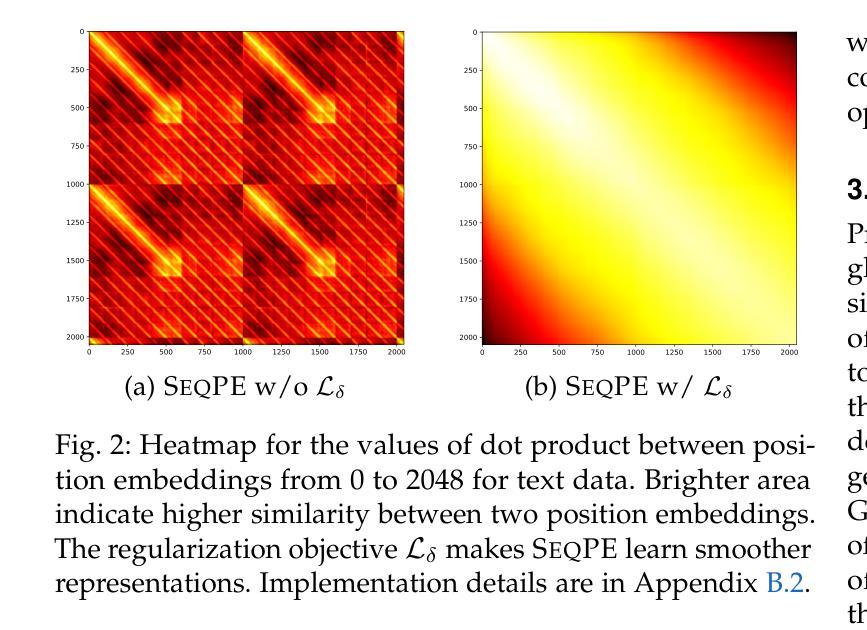
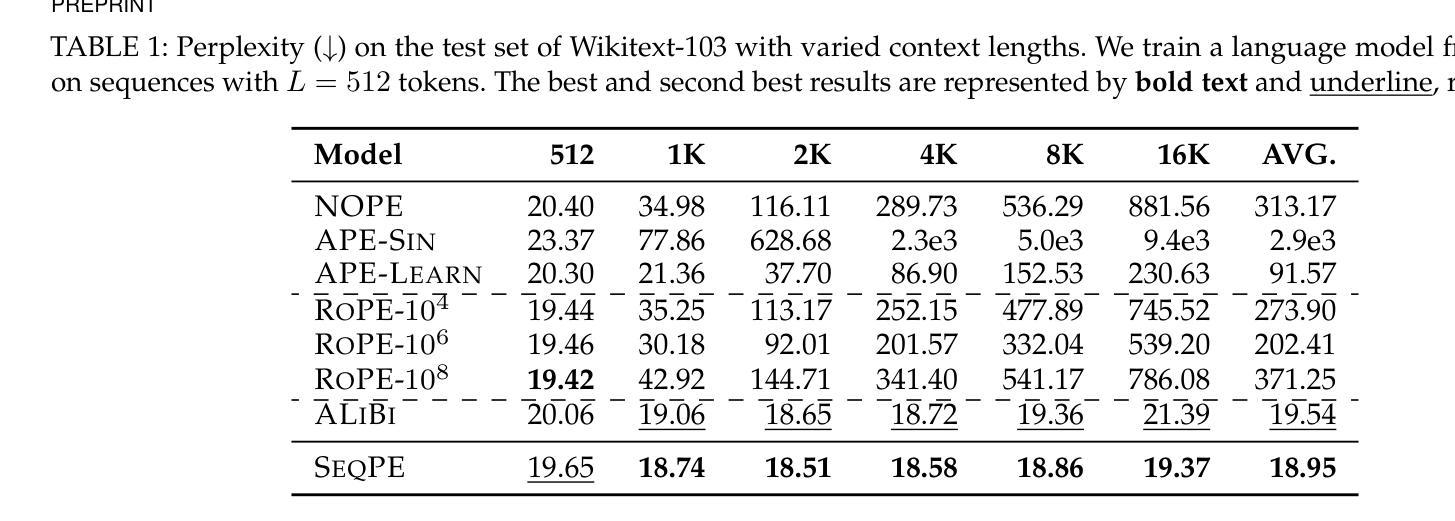
SeqPE: Transformer with Sequential Position Encoding
Authors:Huayang Li, Yahui Liu, Hongyu Sun, Deng Cai, Leyang Cui, Wei Bi, Peilin Zhao, Taro Watanabe
Since self-attention layers in Transformers are permutation invariant by design, positional encodings must be explicitly incorporated to enable spatial understanding. However, fixed-size lookup tables used in traditional learnable position embeddings (PEs) limit extrapolation capabilities beyond pre-trained sequence lengths. Expert-designed methods such as ALiBi and RoPE, mitigate this limitation but demand extensive modifications for adapting to new modalities, underscoring fundamental challenges in adaptability and scalability. In this work, we present SeqPE, a unified and fully learnable position encoding framework that represents each $n$-dimensional position index as a symbolic sequence and employs a lightweight sequential position encoder to learn their embeddings in an end-to-end manner. To regularize SeqPE’s embedding space, we introduce two complementary objectives: a contrastive objective that aligns embedding distances with a predefined position-distance function, and a knowledge distillation loss that anchors out-of-distribution position embeddings to in-distribution teacher representations, further enhancing extrapolation performance. Experiments across language modeling, long-context question answering, and 2D image classification demonstrate that SeqPE not only surpasses strong baselines in perplexity, exact match (EM), and accuracy–particularly under context length extrapolation–but also enables seamless generalization to multi-dimensional inputs without requiring manual architectural redesign. We release our code, data, and checkpoints at https://github.com/ghrua/seqpe.
由于Transformer中的自注意力层在设计上是排列不变的,必须显式地纳入位置编码以实现空间理解。然而,传统可学习位置嵌入(PE)中使用的固定大小查找表限制了预训练序列长度之外的推断能力。虽然专家设计的方法(如ALiBi和RoPE)缓解了这一限制,但它们在适应新模态时需要进行大量修改,这凸显了适应性和可扩展性的基本挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了SeqPE,这是一个统一且可完全学习的位置编码框架,它将每个n维位置索引表示为一个符号序列,并采用一个轻量级顺序位置编码器以端到端的方式学习其嵌入。为了规范SeqPE的嵌入空间,我们引入了两种互补的目标:一种对比目标,它将嵌入距离与预定义的位置距离函数对齐;以及一种知识蒸馏损失,它将离群位置嵌入锚定到在分布内的教师表示,从而进一步提高外推性能。在语言建模、长上下文问答和2D图像分类方面的实验表明,SeqPE不仅在困惑度、精确匹配(EM)和准确性方面超越了强大的基准线,特别是在上下文长度外推方面表现更为出色,而且能够无缝地推广到多维输入,无需手动重新设计架构。我们在https://github.com/ghrua/seqpe上发布了我们的代码、数据和检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
变换器中的自注意力层在设计上是排列不变的,因此需要显式地融入位置编码以实现空间理解。传统的学习型位置嵌入(PE)使用的固定大小查找表限制了超越预训练序列长度的推演能力。SeqPE是一个统一且完全可学习的位置编码框架,将每个n维位置索引表示为符号序列,并使用轻量级顺序位置编码器以端到端的方式学习其嵌入。通过引入两种互补的目标——对比目标和知识蒸馏损失——来规范SeqPE的嵌入空间,对齐嵌入距离与预定义的位置距离函数,并将非分布位置嵌入锚定到分布内的教师表示,从而提高外推性能。实验表明,SeqPE不仅在各种任务上超越了强大的基线标准,特别是在上下文长度外推方面,而且能够无缝推广到多维输入,无需手动重新设计架构。
Key Takeaways
- 自注意力层在Transformer中是排列不变的,需要位置编码来实现空间理解。
- 传统学习型位置嵌入使用的固定大小查找表限制了推演能力,特别是在处理超过预训练序列长度的情况时。
- SeqPE是一个统一且完全可学习的位置编码框架,将位置表示为符号序列并使用轻量级编码器学习。
- 通过引入对比目标和知识蒸馏损失来规范SeqPE的嵌入空间。
- SeqPE在多种任务上表现优越,特别是在上下文长度外推方面。
- SeqPE能够无缝推广到多维输入,无需手动重新设计架构。
点此查看论文截图

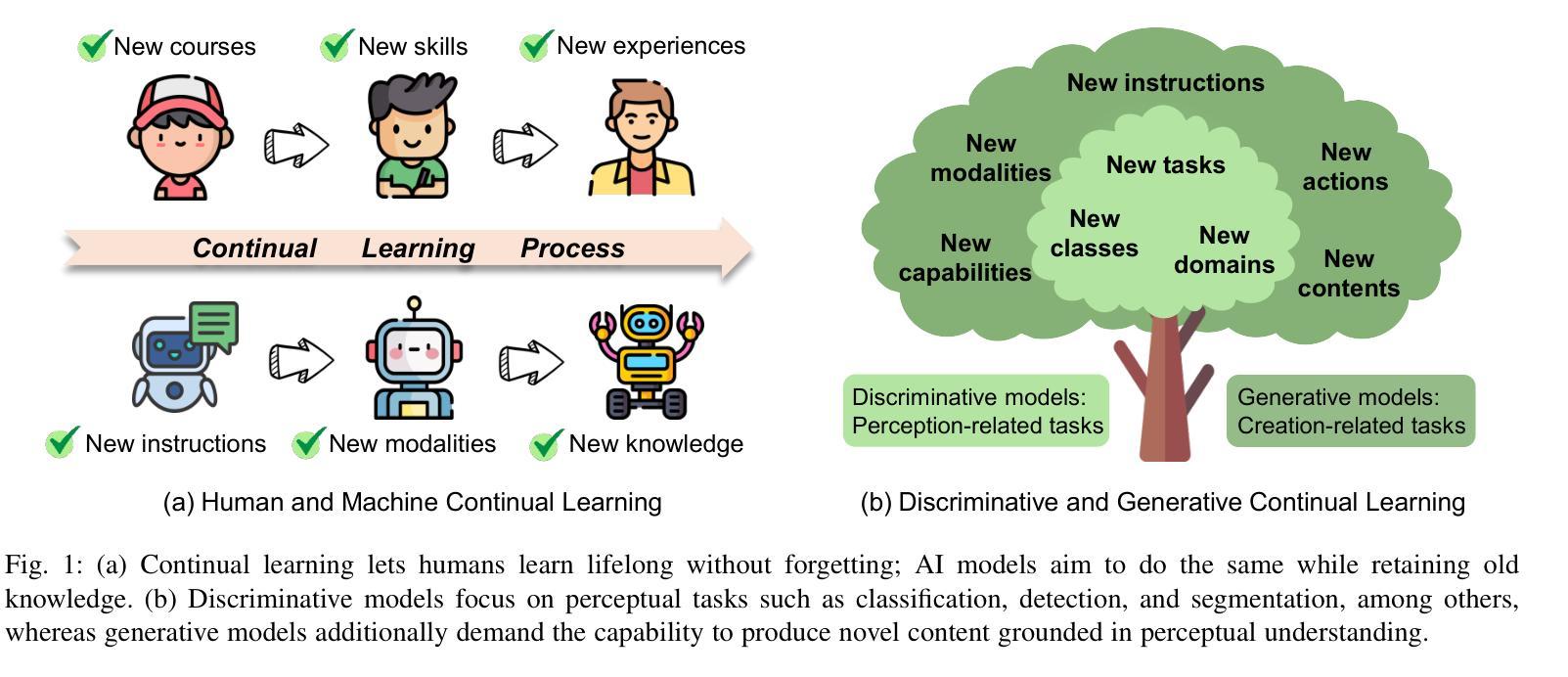
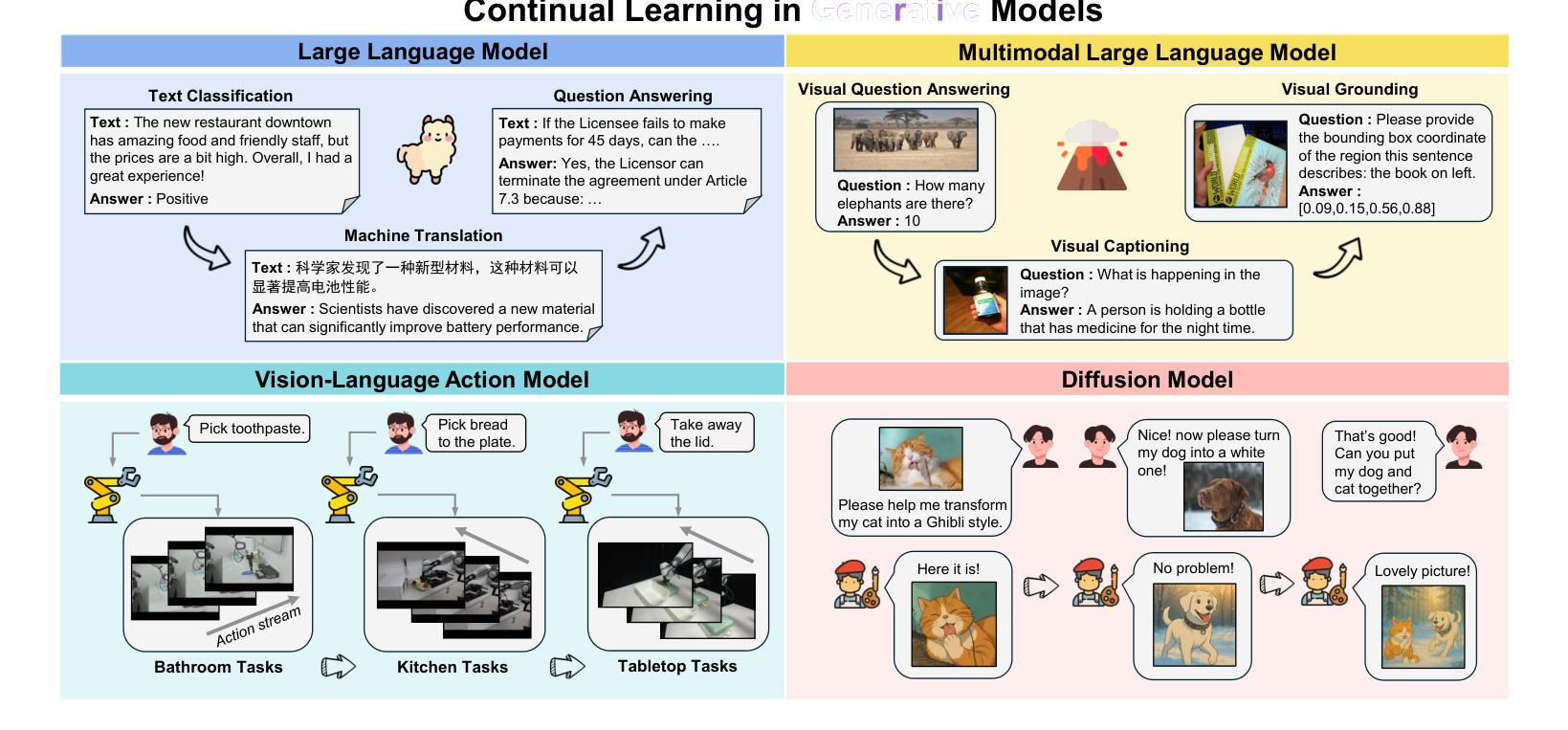
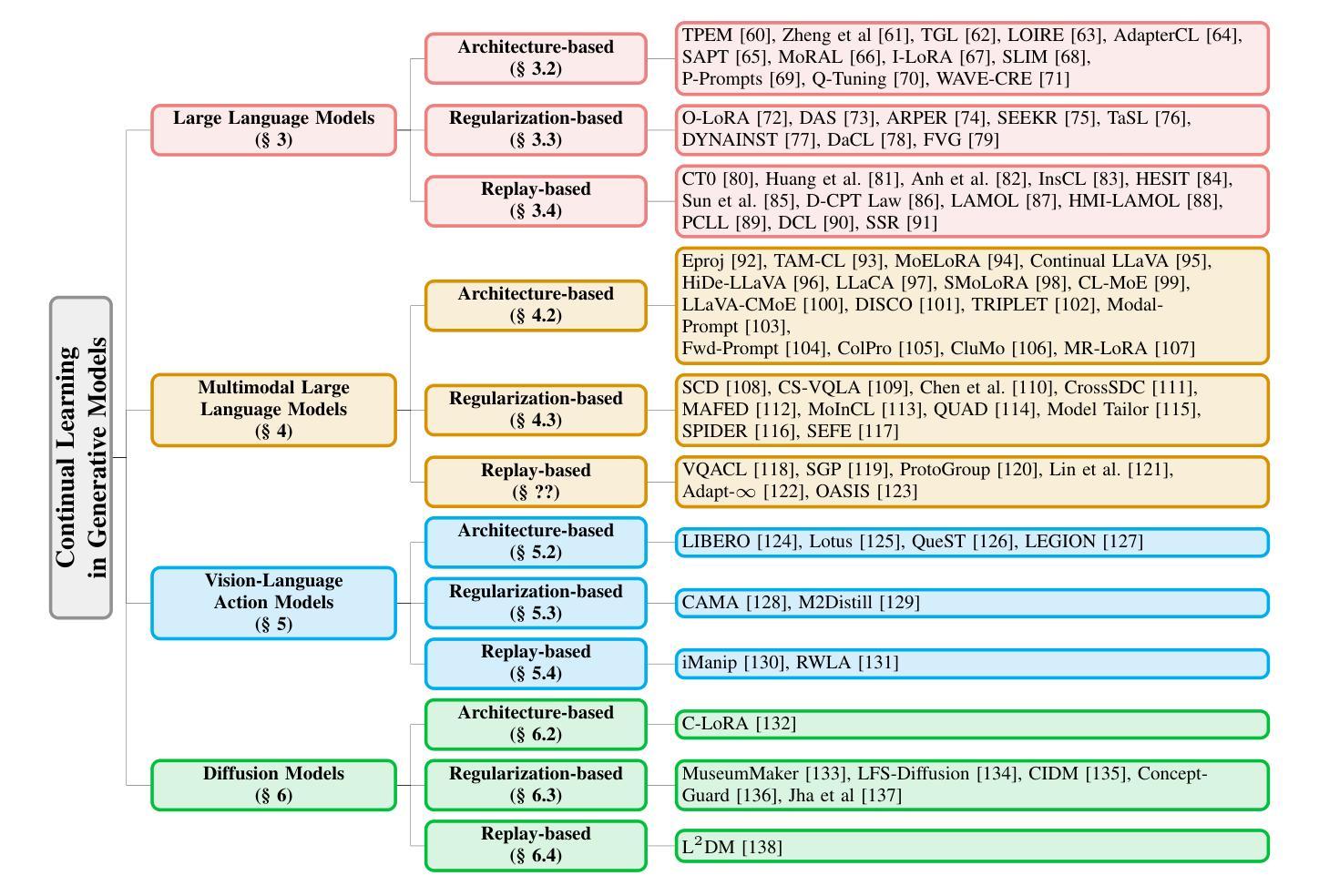
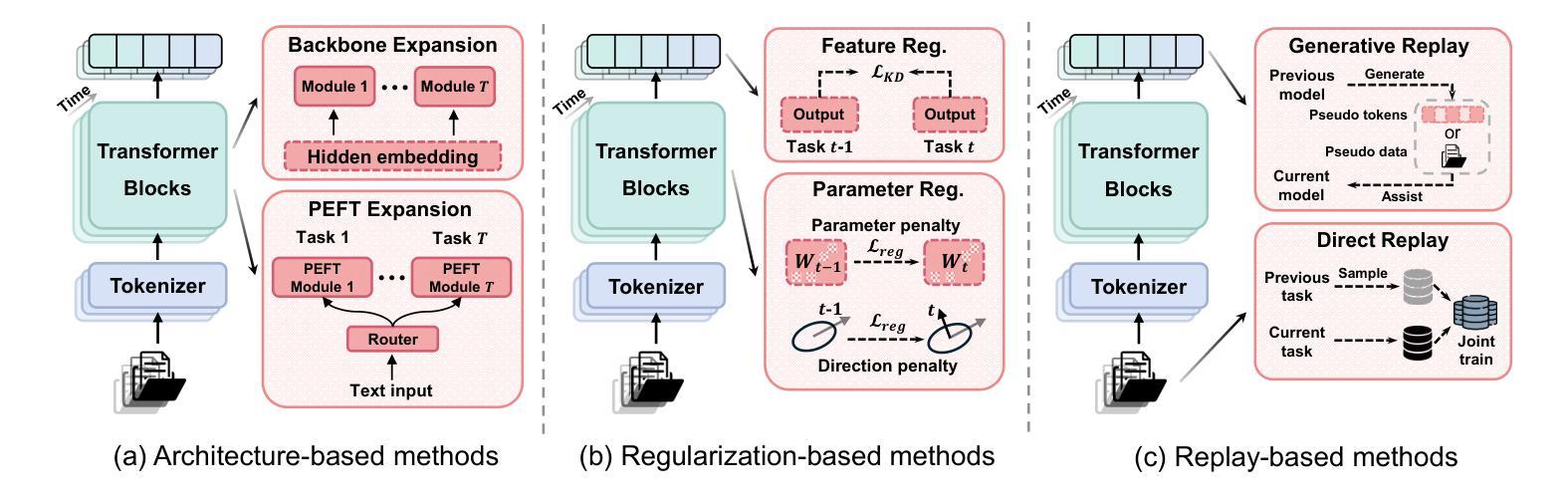
A Comprehensive Survey on Continual Learning in Generative Models
Authors:Haiyang Guo, Fanhu Zeng, Fei Zhu, Jiayi Wang, Xukai Wang, Jingang Zhou, Hongbo Zhao, Wenzhuo Liu, Shijie Ma, Da-Han Wang, Xu-Yao Zhang, Cheng-Lin Liu
The rapid advancement of generative models has enabled modern AI systems to comprehend and produce highly sophisticated content, even achieving human-level performance in specific domains. However, these models remain fundamentally constrained by catastrophic forgetting - a persistent challenge where adapting to new tasks typically leads to significant degradation in performance on previously learned tasks. To address this practical limitation, numerous approaches have been proposed to enhance the adaptability and scalability of generative models in real-world applications. In this work, we present a comprehensive survey of continual learning methods for mainstream generative models, including large language models, multimodal large language models, vision language action models, and diffusion models. Drawing inspiration from the memory mechanisms of the human brain, we systematically categorize these approaches into three paradigms: architecture-based, regularization-based, and replay-based methods, while elucidating their underlying methodologies and motivations. We further analyze continual learning setups for different generative models, including training objectives, benchmarks, and core backbones, offering deeper insights into the field. The project page of this paper is available at https://github.com/Ghy0501/Awesome-Continual-Learning-in-Generative-Models.
生成模型的快速发展使得现代AI系统能够理解并产生高度复杂的内容,甚至在特定领域达到了人类水平的性能。然而,这些模型仍然受到灾难性遗忘的根本性约束——这是一个持续存在的挑战,适应新任务通常会导致之前在任务上的性能显著下降。为了解决这一实际限制,已经提出了许多方法来提高生成模型在现实世界应用中的适应性和可扩展性。在这项工作中,我们对主流生成模型的持续学习方法进行了全面调查,包括大型语言模型、多模态大型语言模型、视觉语言行为模型和扩散模型。从人类大脑的记忆机制中汲取灵感,我们将这些方法系统地分为三类:基于架构的方法、基于正则化的方法和基于重演的方法,同时阐述了它们的基础方法和动机。进一步分析了不同生成模型的持续学习设置,包括训练目标、基准测试和核心骨干,为这一领域提供了更深入的了解。该论文的项目页面可在https://github.com/Ghy0501/Awesome-Continual-Learning-in-Generative-Models找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
随着生成模型的快速发展,现代AI系统已经能够理解并生成高度复杂的内容,甚至在特定领域达到了人类水平的表现。然而,这些模型仍然受到灾难性遗忘这一基本约束的影响。为了解决这个问题,人们提出了许多方法来提高生成模型在现实应用中的适应性和可扩展性。本文全面概述了主流生成模型的持续学习方法,包括大型语言模型、多模态大型语言模型、视觉语言行动模型和扩散模型。从人类大脑的记忆机制中汲取灵感,我们将这些方法系统地分为三类:基于架构的、基于正则化的和基于复习的方法,并阐明了它们的方法和动机。同时,本文还分析了不同生成模型的持续学习设置,包括训练目标、基准测试和核心架构,为相关领域提供了深入见解。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型快速发展,使得现代AI系统在理解和生成内容方面取得了巨大进步,达到人类水平的表现。
- 生成模型面临的主要挑战之一是灾难性遗忘,即适应新任务时会导致对先前学习任务的性能显著下降。
- 为了解决这一问题,研究者提出了多种持续学习方法来提高生成模型的适应性和可扩展性。
- 本文全面概述了主流生成模型的持续学习方法,包括大型语言模型、多模态大型语言模型、视觉语言行动模型和扩散模型的持续学习。
- 持续学习方法分为三类:基于架构的、基于正则化的和基于复习的方法。
- 本文深入分析了不同生成模型的持续学习设置,包括训练目标、基准测试和核心架构。
点此查看论文截图
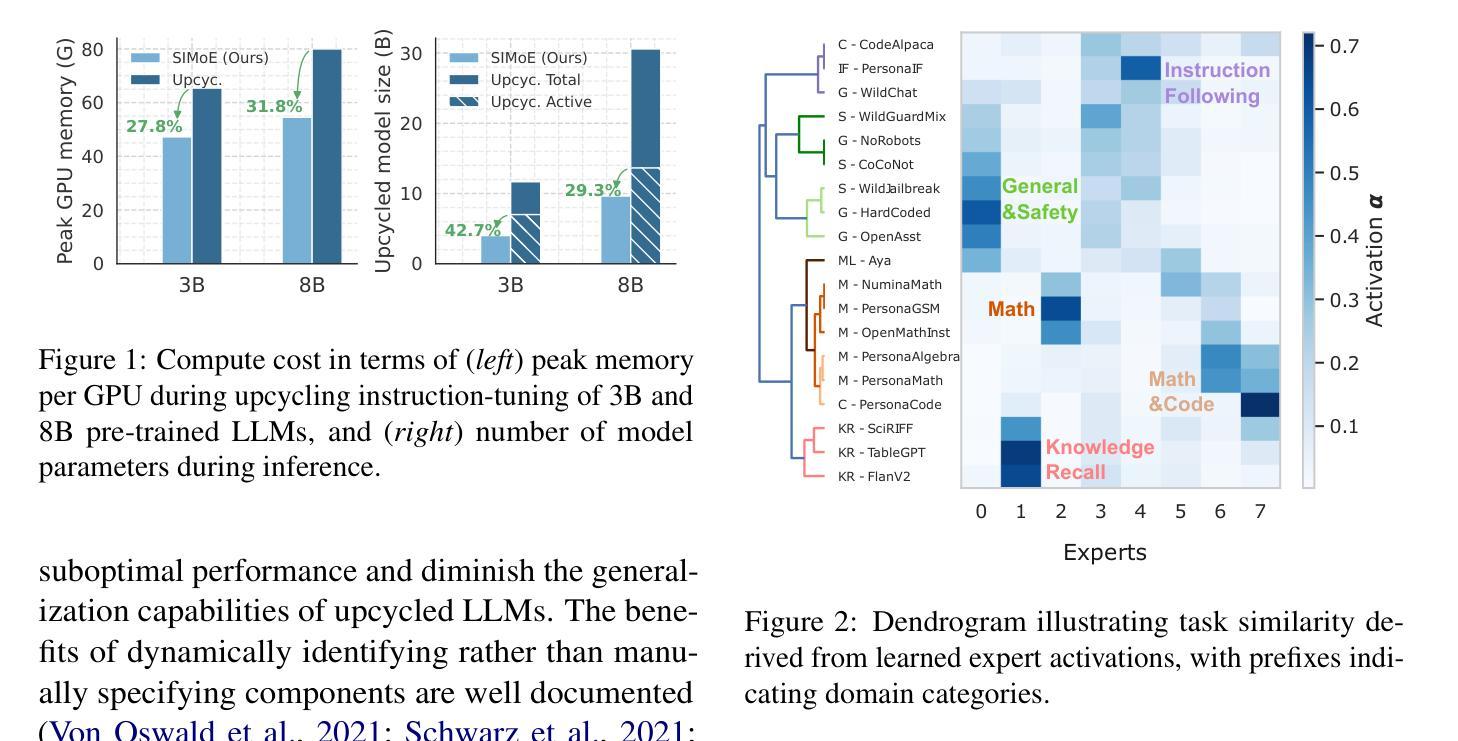
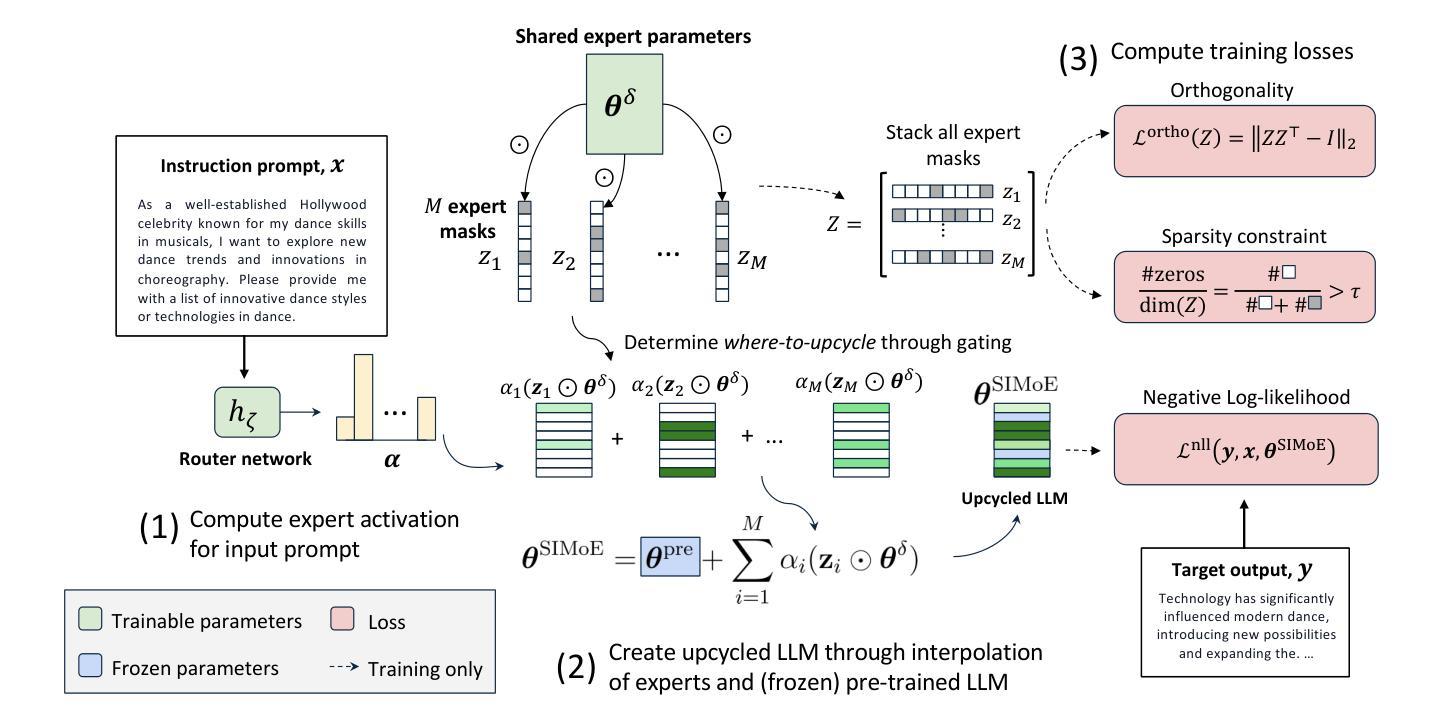
Automatic Expert Discovery in LLM Upcycling via Sparse Interpolated Mixture-of-Experts
Authors:Shengzhuang Chen, Ying Wei, Jonathan Richard Schwarz
We present Sparse Interpolated Mixture-of-Experts (SIMoE) instruction-tuning, an end-to-end algorithm designed to fine-tune a dense pre-trained Large Language Model (LLM) into a MoE-style model that possesses capabilities in multiple specialized domains. During instruction-tuning, SIMoE automatically identifies multiple specialized experts under a specified sparsity constraint, with each expert representing a structurally sparse subset of the seed LLM’s parameters that correspond to domain-specific knowledge within the data. SIMoE simultaneously learns an input-dependent expert merging strategy via a router network, leveraging rich cross-expert knowledge for superior downstream generalization that surpasses existing baselines. Empirically, SIMoE consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance on common instruction-tuning benchmarks while maintaining an optimal performance-compute trade-off compared to all baselines.
我们提出了稀疏插值混合专家(Sparse Interpolated Mixture-of-Experts,简称SIMoE)指令微调方法,这是一种端到端的算法,旨在将预训练的密集大型语言模型(LLM)微调为具备多个专业领域能力的混合专家模型。在指令微调过程中,SIMoE在指定的稀疏性约束下自动识别多个专业领域的专家,每个专家代表种子LLM参数的结构稀疏子集,这些参数对应于数据中的特定领域知识。SIMoE通过路由器网络同时学习一种输入依赖的专家合并策略,利用丰富的跨专家知识实现出色的下游泛化能力,超越现有基线。经验上,SIMoE在常见的指令微调基准测试中始终达到了最先进的性能表现,同时与所有基线相比保持了最佳的性能计算折衷。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
SIMoE是一种针对预训练大型语言模型(LLM)进行微调的创新算法,旨在将其转化为具备多个专业领域能力的混合专家模型。该算法通过指令微调自动识别多个专业专家,每个专家代表种子LLM参数的结构稀疏子集,对应于数据中的特定领域知识。SIMoE同时学习一种基于输入的专家合并策略,并通过路由器网络利用丰富的跨专家知识实现出色的下游泛化能力,超越现有基准测试水平。此算法在指令微调基准测试中实现了卓越的性能,并在性能与计算之间达到了最佳平衡。
Key Takeaways
- SIMoE是一种用于微调大型语言模型的算法,旨在将其转化为混合专家模型。
- 该算法通过指令微调自动识别多个专业领域的专家。
- 每个专家代表种子LLM参数的结构稀疏子集,对应特定领域知识。
- SIMoE学习基于输入的专家合并策略,通过路由器网络实现跨专家知识的利用。
- SIMoE在指令微调基准测试中表现卓越,超过现有基准水平。
- 该算法在保证性能的同时,实现了良好的性能与计算之间的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

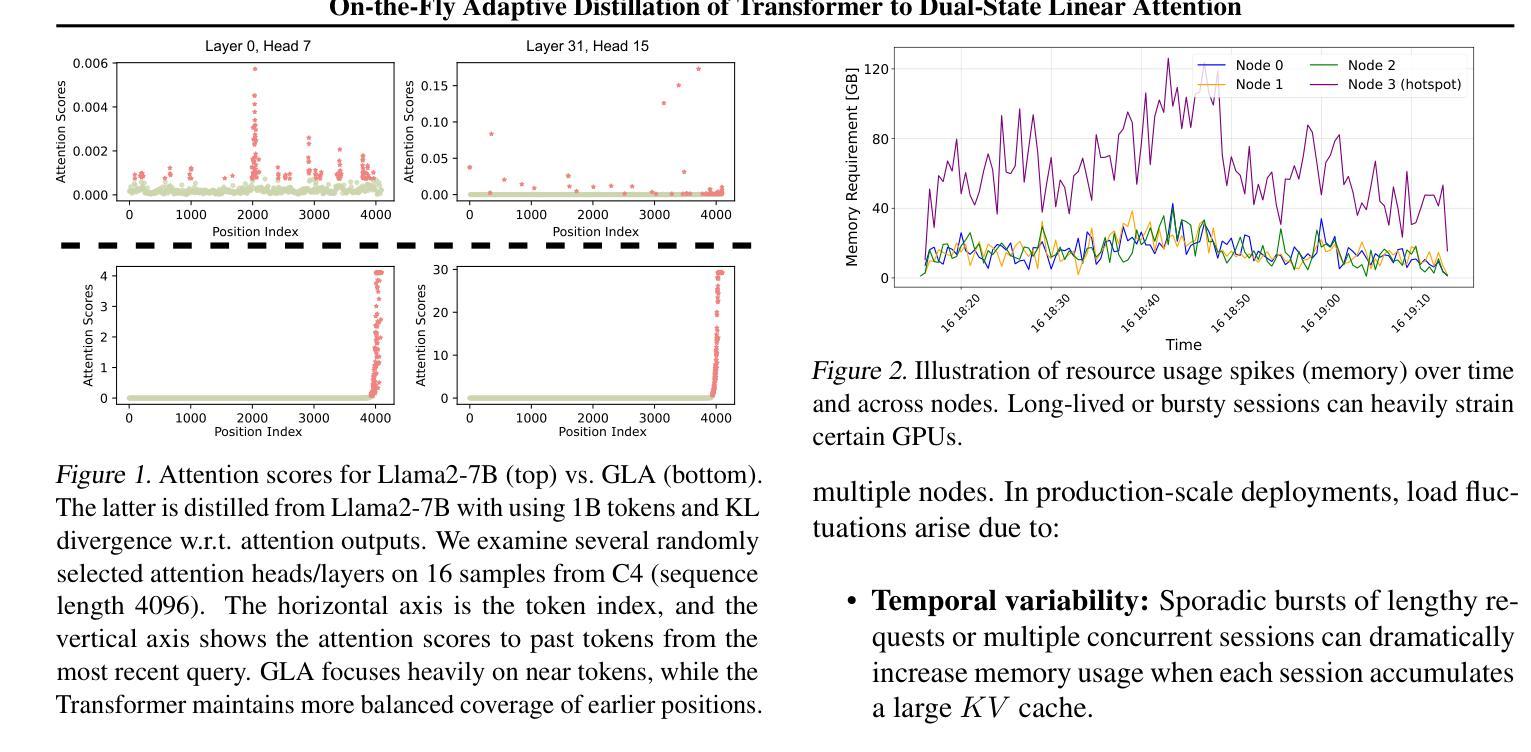
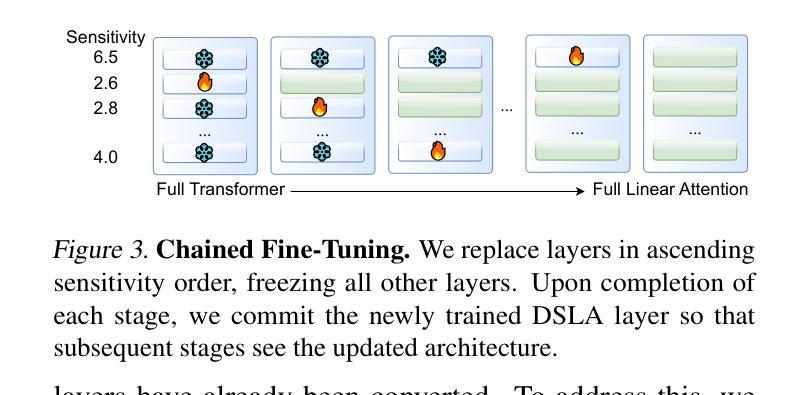
On-the-Fly Adaptive Distillation of Transformer to Dual-State Linear Attention
Authors:Yeonju Ro, Zhenyu Zhang, Souvik Kundu, Zhangyang Wang, Aditya Akella
Large language models (LLMs) excel at capturing global token dependencies via self-attention but face prohibitive compute and memory costs on lengthy inputs. While sub-quadratic methods (e.g., linear attention) can reduce these costs, they often degrade accuracy due to overemphasizing recent tokens. In this work, we first propose dual-state linear attention (DSLA), a novel design that maintains two specialized hidden states-one for preserving historical context and one for tracking recency-thereby mitigating the short-range bias typical of linear-attention architectures. To further balance efficiency and accuracy under dynamic workload conditions, we introduce DSLA-Serve, an online adaptive distillation framework that progressively replaces Transformer layers with DSLA layers at inference time, guided by a sensitivity-based layer ordering. DSLA-Serve uses a chained fine-tuning strategy to ensure that each newly converted DSLA layer remains consistent with previously replaced layers, preserving the overall quality. Extensive evaluations on commonsense reasoning, long-context QA, and text summarization demonstrate that DSLA-Serve yields 2.3x faster inference than Llama2-7B and 3.0x faster than the hybrid Zamba-7B, while retaining comparable performance across downstream tasks. Our ablation studies show that DSLA’s dual states capture both global and local dependencies, addressing the historical-token underrepresentation seen in prior linear attentions. Codes are available at https://github.com/utnslab/DSLA-Serve.
大型语言模型(LLM)擅长通过自注意力捕捉全局令牌依赖关系,但在处理长输入时面临着计算量大和内存成本高的挑战。虽然次二次方法(如线性注意力)可以降低这些成本,但它们往往会因为过度强调最近的令牌而降低准确性。在本文中,我们首次提出双状态线性注意力(DSLA),这是一种新型设计,能够维持两个专门化的隐藏状态,一个用于保留历史上下文,另一个用于跟踪最新信息,从而减轻线性注意力架构所固有的短程偏差。为了进一步优化动态工作负载条件下的效率和准确性平衡,我们引入了DSLA-Serve,这是一种在线自适应蒸馏框架。在推理过程中,它以基于敏感性的层序为指导,逐步替换Transformer层中的DSLA层。DSLA-Serve采用链式微调策略,确保每个新转换的DSLA层与之前替换的层保持一致,从而保持整体质量。在常识推理、长文本问答和文本摘要等任务上的广泛评估表明,DSLA-Serve相较于Llama2-7B模型推理速度提高了2.3倍,相较于混合模型Zamba-7B提高了3.0倍,同时在下游任务上保持了相当的性能表现。我们的消融研究表明,DSLA的双状态捕捉全局和局部依赖关系,解决了先前线性注意力在历史令牌表示不足的问题。相关代码可通过https://github.com/utnslab/DSLA-Serve获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了双态线性注意力(DSLA)模型,旨在解决大型语言模型在处理长输入时面临的计算与内存成本问题。该模型包含两个专门化的隐藏状态,一个用于保留历史上下文,一个用于跟踪近期信息,以缓解线性注意力架构的短程偏见。此外,还引入了在线自适应蒸馏框架DSLA-Serve,根据动态工作负载条件下的敏感性,逐步在推理时间替换Transformer层。实验表明,DSLA-Serve在保持性能的同时,推理速度比Llama2-7B快2.3倍,比混合Zamba-7B快3.0倍。
Key Takeaways
- DSLA模型通过引入两个隐藏状态,解决了大型语言模型处理长输入时的计算与内存挑战。
- 双态设计能够同时捕捉全局和局部依赖,改善先前线性注意力模型的历史令牌欠表征问题。
- DSLA-Serve框架能在推理时间逐步替换Transformer层,通过在线自适应蒸馏提高效率和准确性。
- 与现有模型相比,DSLA-Serve在常识推理、长文本问答和文本摘要等任务中表现出优异的性能。
- DSLA-Serve在推理速度上显著优于其他模型,同时保持或提高了下游任务的性能。
- 研究通过广泛的评估证明了DSLA和DSLA-Serve的有效性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

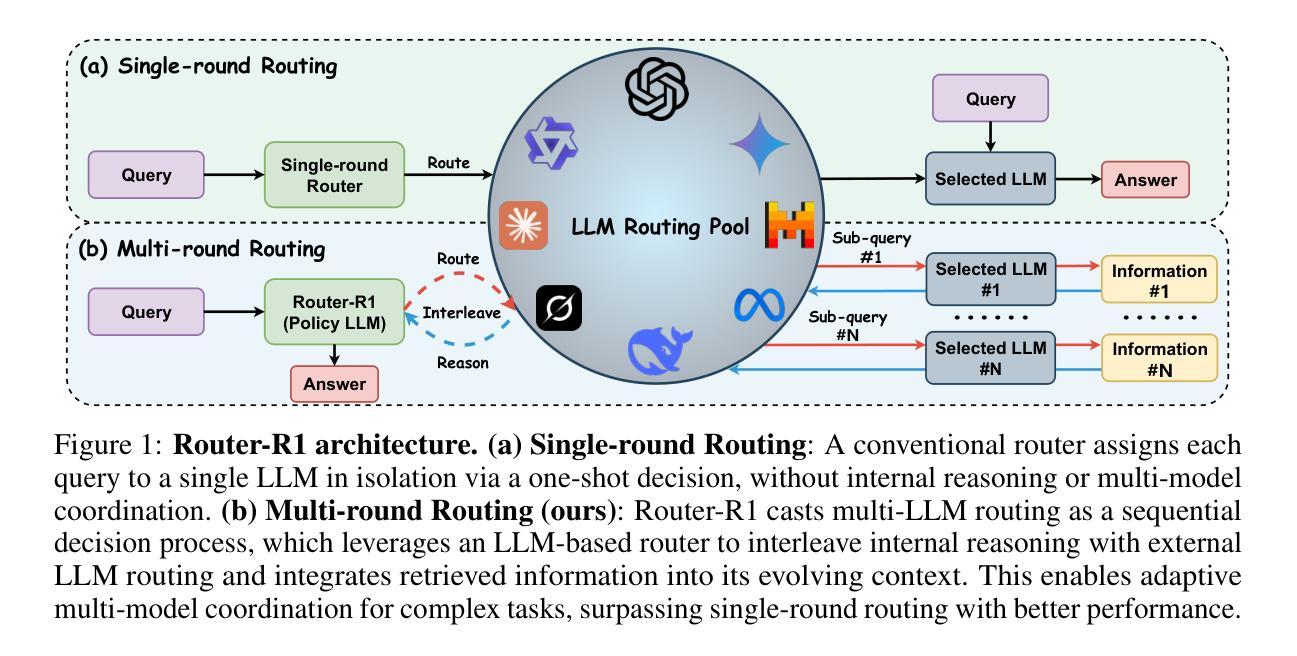
Router-R1: Teaching LLMs Multi-Round Routing and Aggregation via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Haozhen Zhang, Tao Feng, Jiaxuan You
The rapid emergence of diverse large language models (LLMs) has spurred the development of LLM routers that assign user queries to the most suitable model. However, existing LLM routers typically perform a single-round, one-to-one mapping (\textit{i.e.}, assigning each query to a single model in isolation), which limits their capability to tackle complex tasks that demand the complementary strengths of multiple LLMs. In this paper, we present \textbf{Router-R1}, a reinforcement learning (RL)-based framework that formulates multi-LLM routing and aggregation as a sequential decision process. Router-R1 instantiates the router itself as a capable LLM, leveraging its reasoning ability to interleave “think” actions (internal deliberation) with “route” actions (dynamic model invocation), and integrates each response into its evolving context. To facilitate learning, we employ a lightweight rule-based reward comprising format rewards, final outcome rewards, and a novel cost reward for optimizing the balance between performance and cost, opening a pathway toward enhancing performance-cost trade-offs via RL. Router-R1 also conditions only on simple model descriptors such as pricing, latency, and example performance, enabling strong generalization to unseen model selection. Experiments on seven general and multi-hop QA benchmarks show that Router-R1 outperforms several strong baselines, achieving superior performance while maintaining robust generalization and cost management.
多样的大型语言模型(LLM)的快速涌现促进了LLM路由器的发展,这些路由器将用户查询分配给最合适的模型。然而,现有的LLM路由器通常执行单一轮次、一对一的映射(即,将每个查询孤立地分配给一个模型),这限制了它们处理复杂任务的能力,这些复杂任务需要多个LLM的互补优势。在本文中,我们提出了基于强化学习(RL)的框架Router-R1,将多LLM路由和聚合制定为顺序决策过程。Router-R1将路由器本身实例化为一个功能强大的LLM,利用其推理能力与“思考”行动(内部权衡)和“路由”行动(动态模型调用)交织,并将每个响应集成到其不断发展的上下文中。为了促进学习,我们采用了一种基于规则的轻量级奖励机制,包括格式奖励、最终成果奖励和一种用于优化性能和成本之间平衡的新成本奖励,开辟了通过RL提高性能与成本权衡的途径。Router-R1仅依赖于简单的模型描述符,如定价、延迟和示例性能,能够很好地推广到未见过的模型选择。在七个通用和多跳问答基准测试上的实验表明,Router-R1优于几个强大的基线模型,在保持稳健的推广和成本管理的同时实现了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/ulab-uiuc/Router-R1. Models and Datasets are available at https://huggingface.co/collections/ulab-ai/router-r1-6851bbe099c7a56914b5db03
Summary
基于强化学习的大型语言模型(LLM)路由设计与优化。现有LLM路由器存在单一映射的局限性,无法充分利用多个LLM的互补优势处理复杂任务。本研究提出了一种基于强化学习的LLM路由器框架Router-R1,该框架可将多LLM路由和聚合表述为序贯决策过程。Router-R1通过内部推理与动态模型调用的交替执行,实现了对多个LLM的高效路由和聚合。同时,引入了一种轻量级的规则奖励机制,以优化性能与成本之间的平衡。实验结果表明,Router-R1在多个基准测试中表现优异,具有出色的性能、良好的泛化能力和成本管理。
Key Takeaways
- LLM路由器的快速出现解决了分配用户查询到最合适的模型的问题。
- 现有LLM路由器通常采用单一映射方式,限制了处理复杂任务的能力。
- Router-R1基于强化学习框架设计,实现了多LLM的路由和聚合的序贯决策过程。
- Router-R1通过内部推理与动态模型调用的交替执行进行决策。
- Router-R1采用轻量级规则奖励机制来优化性能和成本的平衡。
- 实验结果显示Router-R1在多个基准测试中表现优越,具有良好的泛化能力和成本管理能力。
点此查看论文截图


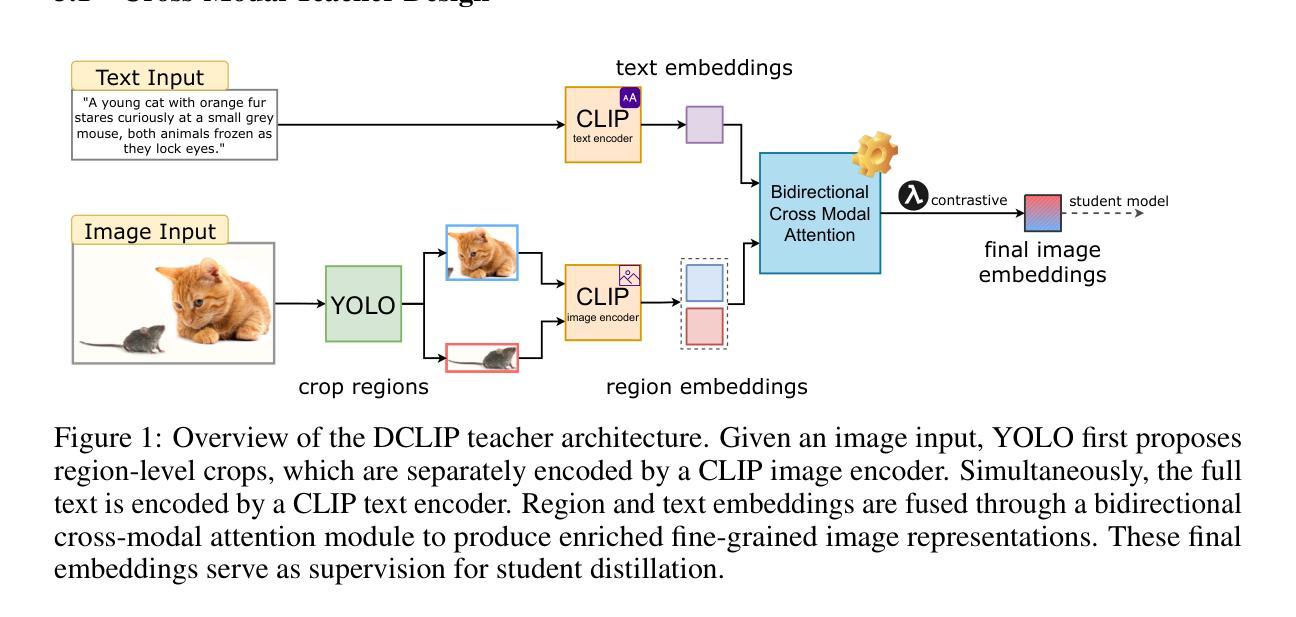
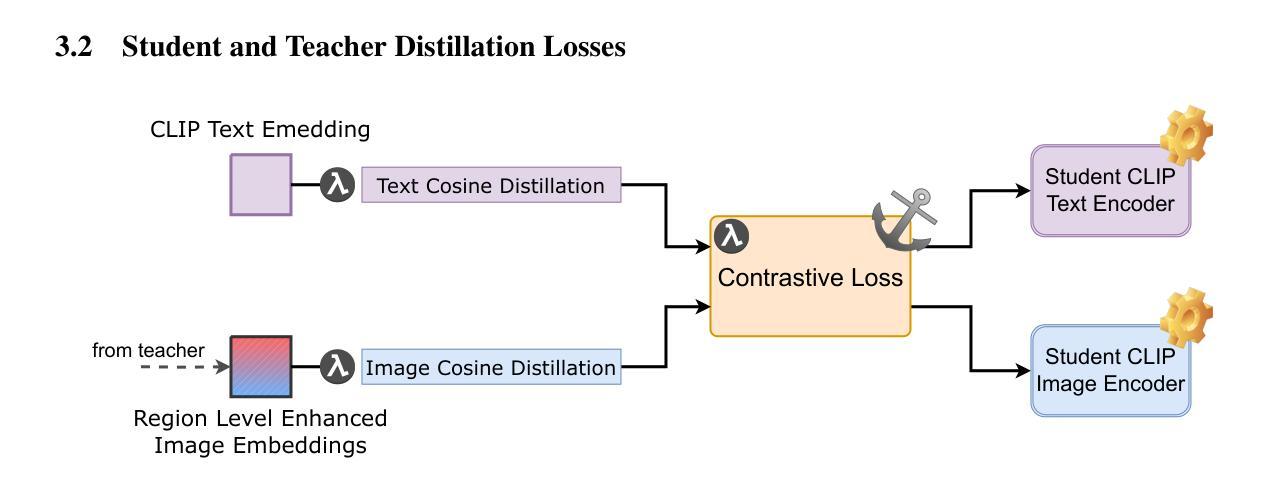
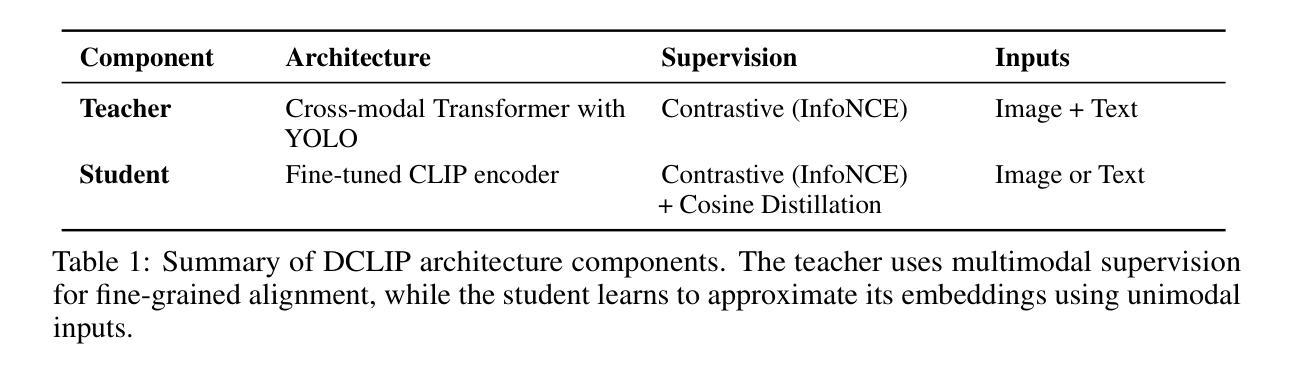
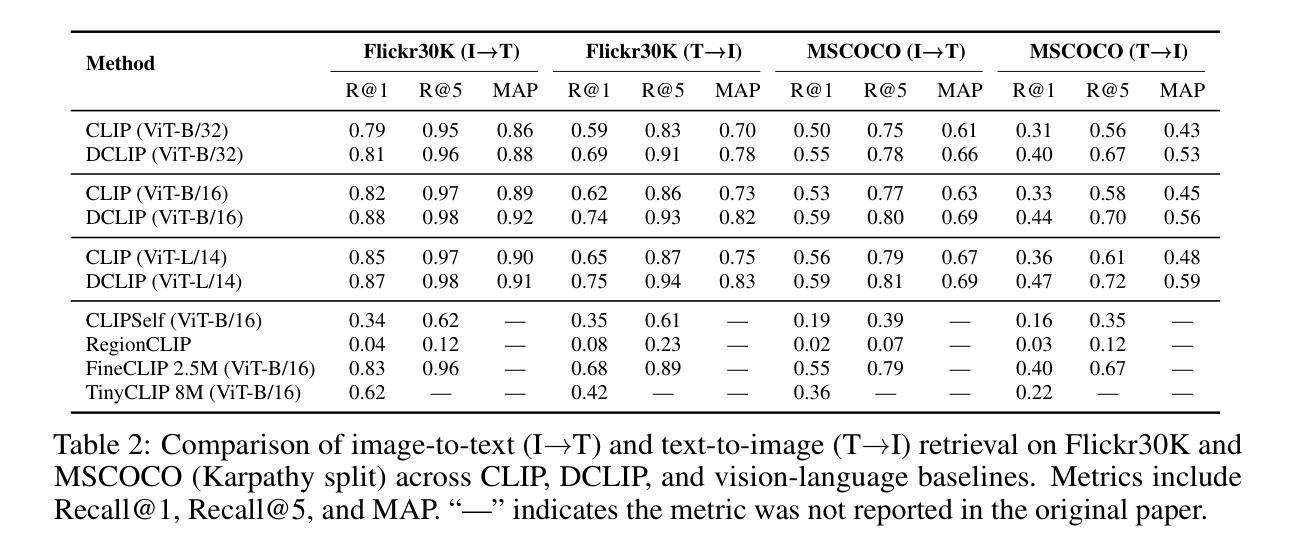
Distill CLIP (DCLIP): Enhancing Image-Text Retrieval via Cross-Modal Transformer Distillation
Authors:Daniel Csizmadia, Andrei Codreanu, Victor Sim, Vighnesh Prabhu, Michael Lu, Kevin Zhu, Sean O’Brien, Vasu Sharma
We present Distill CLIP (DCLIP), a fine-tuned variant of the CLIP model that enhances multimodal image-text retrieval while preserving the original model’s strong zero-shot classification capabilities. CLIP models are typically constrained by fixed image resolutions and limited context, which can hinder their effectiveness in retrieval tasks that require fine-grained cross-modal understanding. DCLIP addresses these challenges through a meta teacher-student distillation framework, where a cross-modal transformer teacher is fine-tuned to produce enriched embeddings via bidirectional cross-attention between YOLO-extracted image regions and corresponding textual spans. These semantically and spatially aligned global representations guide the training of a lightweight student model using a hybrid loss that combines contrastive learning and cosine similarity objectives. Despite being trained on only ~67,500 samples curated from MSCOCO, Flickr30k, and Conceptual Captions-just a fraction of CLIP’s original dataset-DCLIP significantly improves image-text retrieval metrics (Recall@K, MAP), while retaining approximately 94% of CLIP’s zero-shot classification performance. These results demonstrate that DCLIP effectively mitigates the trade-off between task specialization and generalization, offering a resource-efficient, domain-adaptive, and detail-sensitive solution for advanced vision-language tasks. Code available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md.
我们提出了Distill CLIP(DCLIP),它是CLIP模型的一种精细调整变体,旨在增强多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留原始模型的强大零样本分类能力。CLIP模型通常受到固定图像分辨率和有限上下文的限制,这可能会阻碍其在需要精细跨模态理解的任务中的有效性。DCLIP通过元教师学生蒸馏框架来解决这些挑战,其中跨模态变压器教师经过微调以通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力产生丰富的嵌入。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标的混合损失来指导轻量级学生模型的训练。尽管仅使用从MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions精选的约67,500个样本进行训练,仅占CLIP原始数据集的一部分,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP的零样本分类性能的约94%。这些结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务专业化与通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP模型的一个精细调整变体Distill CLIP(DCLIP)被提出,它在保持原始模型强大的零样本分类能力的同时,增强了多模态图像文本检索能力。CLIP模型通常受限于固定的图像分辨率和有限的上下文,这可能会阻碍其在需要精细粒度跨模态理解的任务中的有效性。DCLIP通过元教师学生蒸馏框架解决了这些挑战,其中跨模态变压器教师经过微调,通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本片段之间的双向交叉注意力产生丰富的嵌入。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过混合损失引导轻量级学生模型的训练,该混合损失结合了对比学习和余弦相似性目标。尽管仅在MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions等数据集中精选的约67,500个样本上进行训练,是CLIP原始数据集的一小部分,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP大约94%的零样本分类性能。这些结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务专业化与通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- Distill CLIP(DCLIP)是CLIP模型的一种改进版本,旨在增强多模态图像文本检索功能。
- CLIP模型面临固定图像分辨率和有限上下文的限制,可能影响其在跨模态理解任务中的表现。
- DCLIP通过元教师学生蒸馏框架解决这些问题,利用跨模态变压器教师微调产生丰富的嵌入。
- DCLIP通过结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标,使用混合损失来训练学生模型。
- DCLIP在仅使用小部分数据的情况下显著提高了图像文本检索性能,并保留了大部分CLIP的零样本分类能力。
- DCLIP解决了任务特殊化和通用化之间的权衡问题。
点此查看论文截图

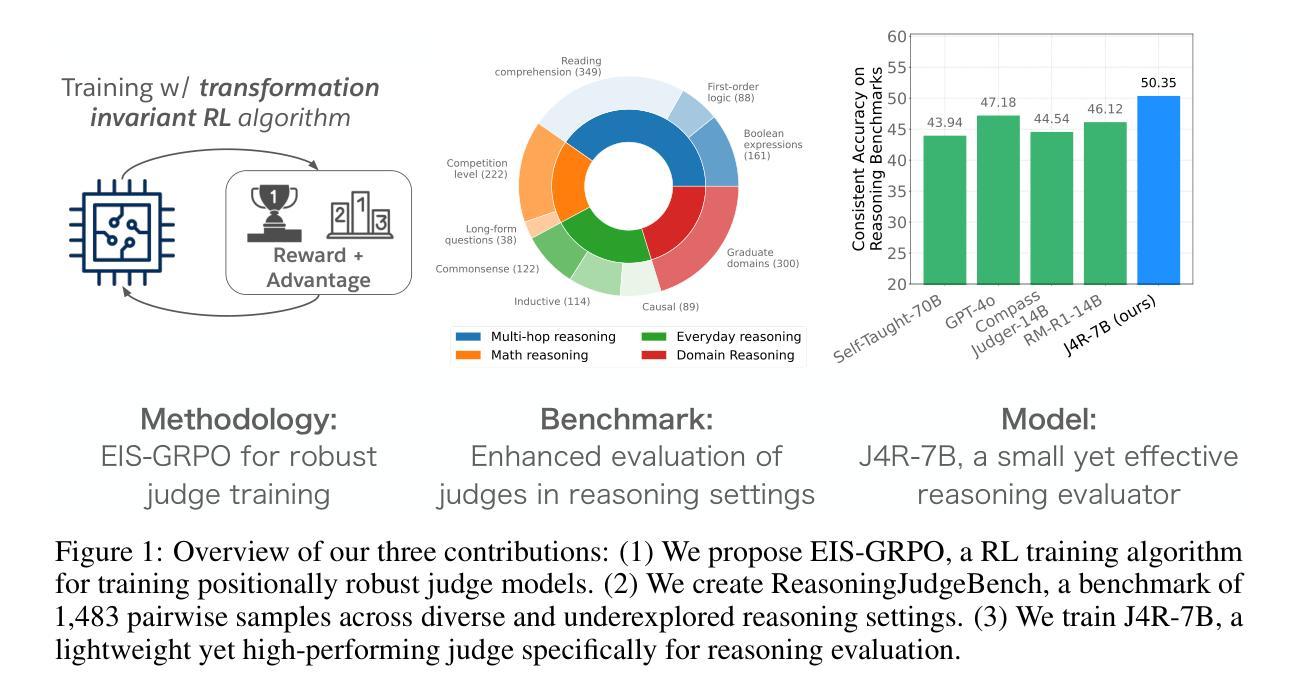
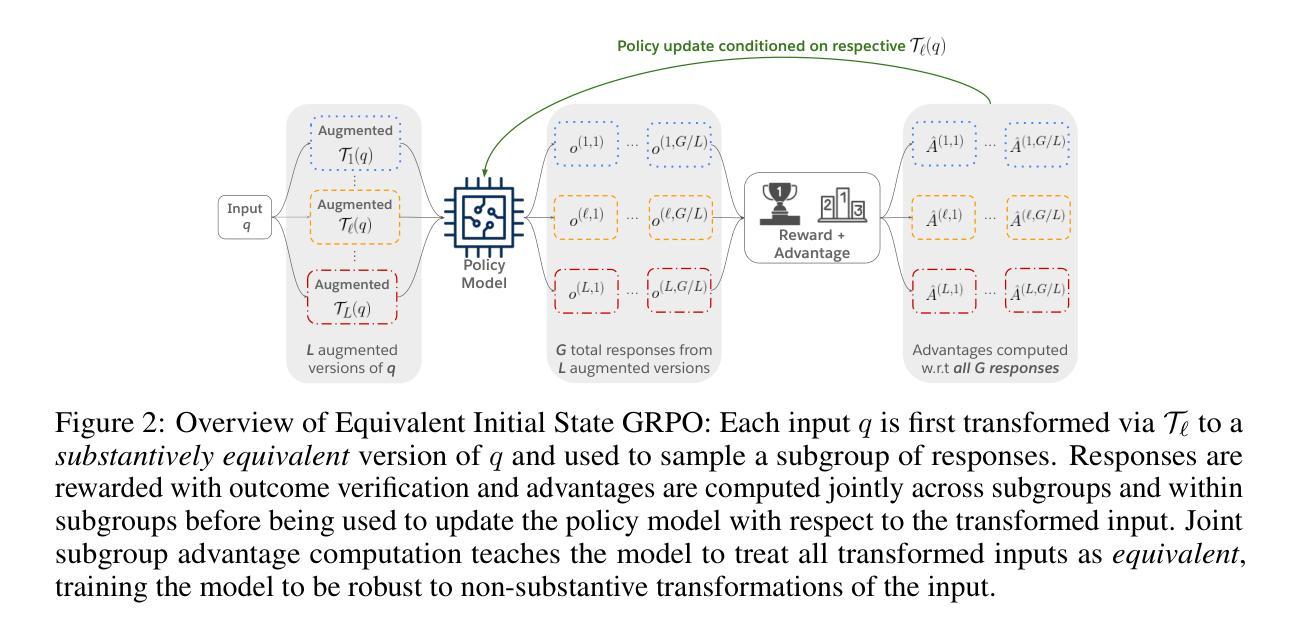
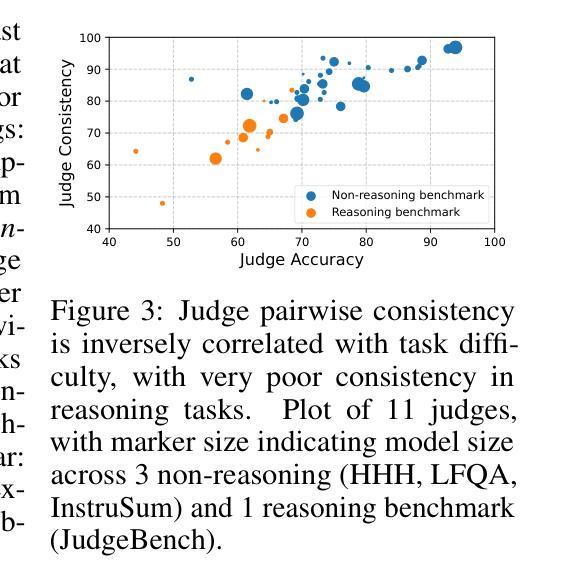
J4R: Learning to Judge with Equivalent Initial State Group Relative Policy Optimization
Authors:Austin Xu, Yilun Zhou, Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Caiming Xiong, Shafiq Joty
To keep pace with the increasing pace of large language models (LLM) development, model output evaluation has transitioned away from time-consuming human evaluation to automatic evaluation, where LLMs themselves are tasked with assessing and critiquing other model outputs. LLM-as-judge models are a class of generative evaluators that excel in evaluating relatively simple domains, like chat quality, but struggle in reasoning intensive domains where model responses contain more substantive and challenging content. To remedy existing judge shortcomings, we explore training judges with reinforcement learning (RL). We make three key contributions: (1) We propose the Equivalent Initial State Group Relative Policy Optimization (EIS-GRPO) algorithm, which allows us to train our judge to be robust to positional biases that arise in more complex evaluation settings. (2) We introduce ReasoningJudgeBench, a benchmark that evaluates judges in diverse reasoning settings not covered by prior work. (3) We train Judge for Reasoning (J4R), a 7B judge trained with EIS-GRPO that outperforms GPT-4o and the next best small judge by 6.7% and 9%, matching or exceeding the performance of larger GRPO-trained judges on both JudgeBench and ReasoningJudgeBench.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)发展步伐的加快,模型输出评估已从耗时的人力评估转向自动评估,其中LLM自身被用于评估和批判其他模型的输出。LLM作为评判者的模型是一类生成评估器,擅长评估相对简单的领域,如聊天质量,但在需要推理的复杂领域中,模型回应包含更多实质性和有挑战性的内容时会感到困难。为了弥补现有评委的缺陷,我们探索使用强化学习(RL)来训练评委。我们做出了三个关键贡献:(1)我们提出了等效初始状态组相对策略优化(EIS-GRPO)算法,该算法使我们能够训练评委,使其对更复杂评估环境中出现的定位偏差具有鲁棒性。(2)我们引入了ReasoningJudgeBench,这是一个可以在多样化推理环境中评估评委的基准测试,涵盖以前的工作未涉及的内容。(3)我们使用EIS-GRPO训练了Reasoning Judge(J4R),一个7B的评委,其性能优于GPT-4o和下一个最好的小型评委6.7%和9%,在JudgeBench和ReasoningJudgeBench上的表现与更大的GRPO训练评委相匹配或更好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables. Updated with code and benchmark
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的发展促进了模型输出评估从耗时的人力评估转向自动评估的转变,现在LLM自身被用来评估和批判其他模型输出。研究提出了使用强化学习(RL)训练LLM作为评委的策略,并做出了三个关键贡献:提出了等效初始状态组相对策略优化(EIS-GRPO)算法,使评委在复杂的评估环境中更加稳健;引入了ReasoningJudgeBench基准测试,用于评估在多样化推理环境下的评委性能;训练了使用EIS-GRPO的Judge for Reasoning(J4R)模型,在性能上超过了GPT-4o和其他小型评委,匹配甚至超越了大型GRPO训练评委在JudgeBench和ReasoningJudgeBench上的表现。
Key Takeaways
- LLM的发展促进了模型输出评估的转变,从人力评估转向自动评估,使用LLM自身进行其他模型的输出评估。
- 强化学习(RL)被用于训练LLM作为评委,以改善现有评估方法的不足。
- 提出了等效初始状态组相对策略优化(EIS-GRPO)算法,增强评委在复杂评估环境中的稳健性。
- 引入了ReasoningJudgeBench基准测试,用于评估在多样化推理环境下的评委性能。
- 训练了Judge for Reasoning(J4R)模型,使用EIS-GRPO算法,性能优于GPT-4o和其他小型评委。
- J4R模型在性能上匹配甚至超越了大型GRPO训练评委在JudgeBench和ReasoningJudgeBench上的表现。
- 自动评价是LLM领域的重要发展方向,尤其是在处理复杂模型输出的评价方面。
点此查看论文截图

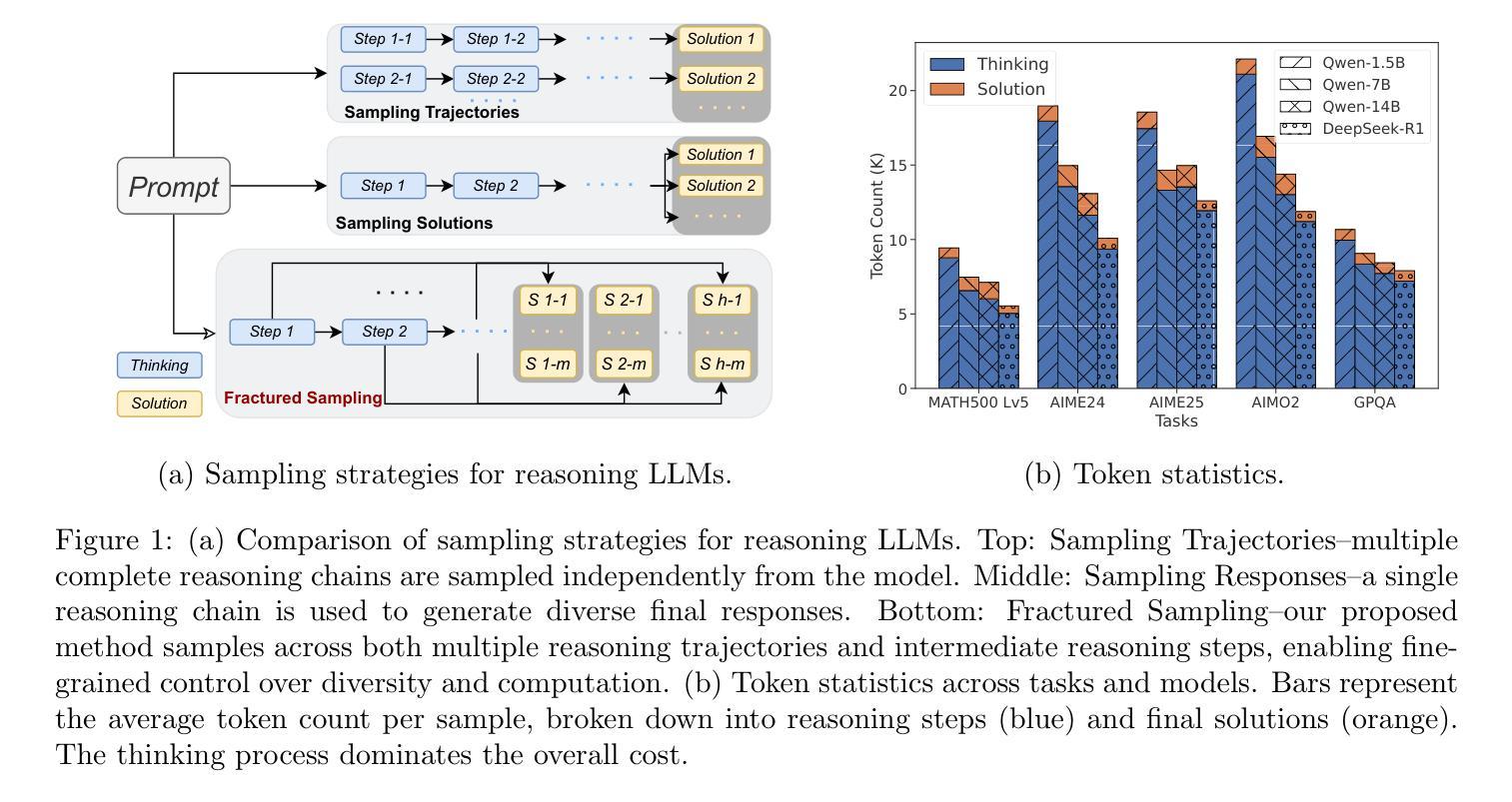
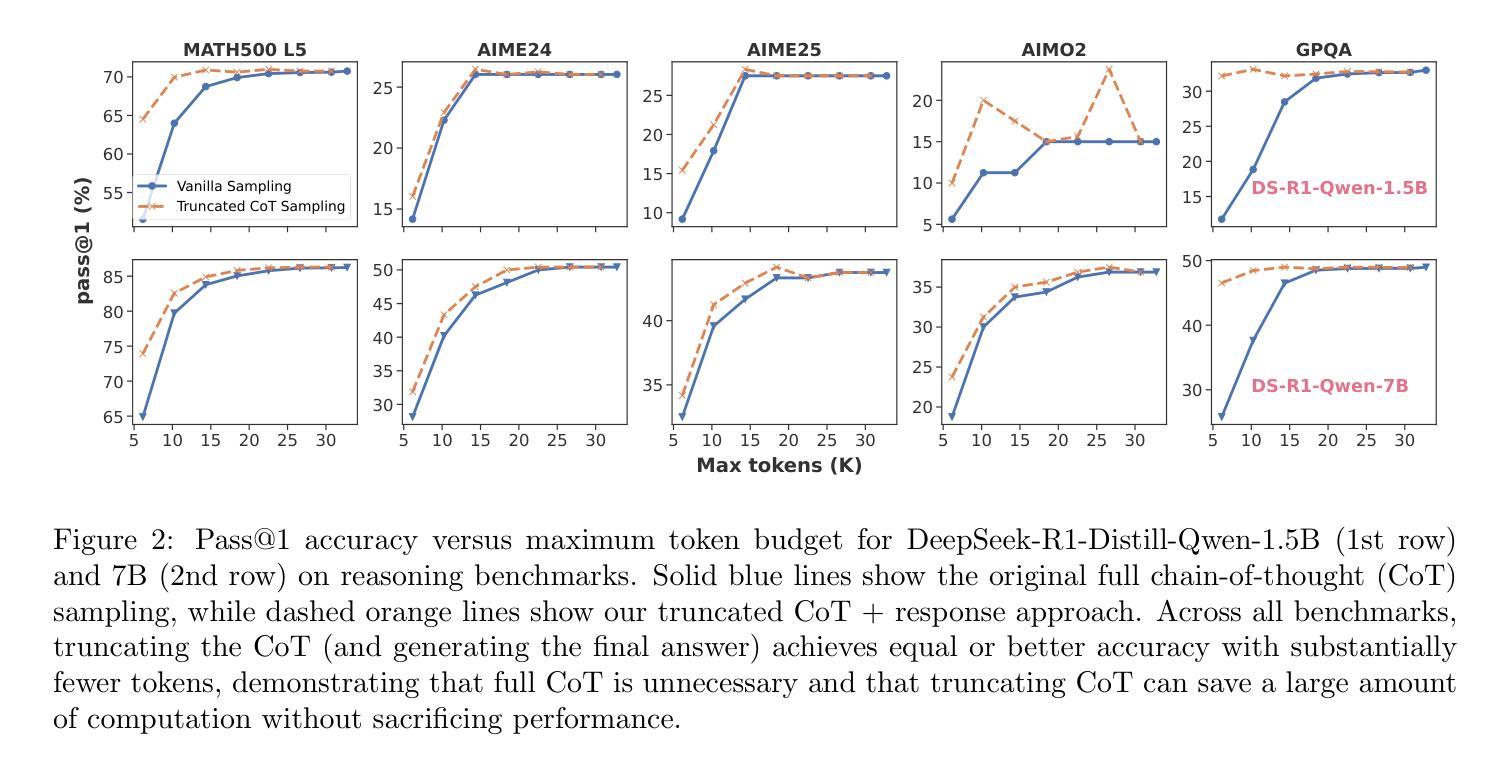
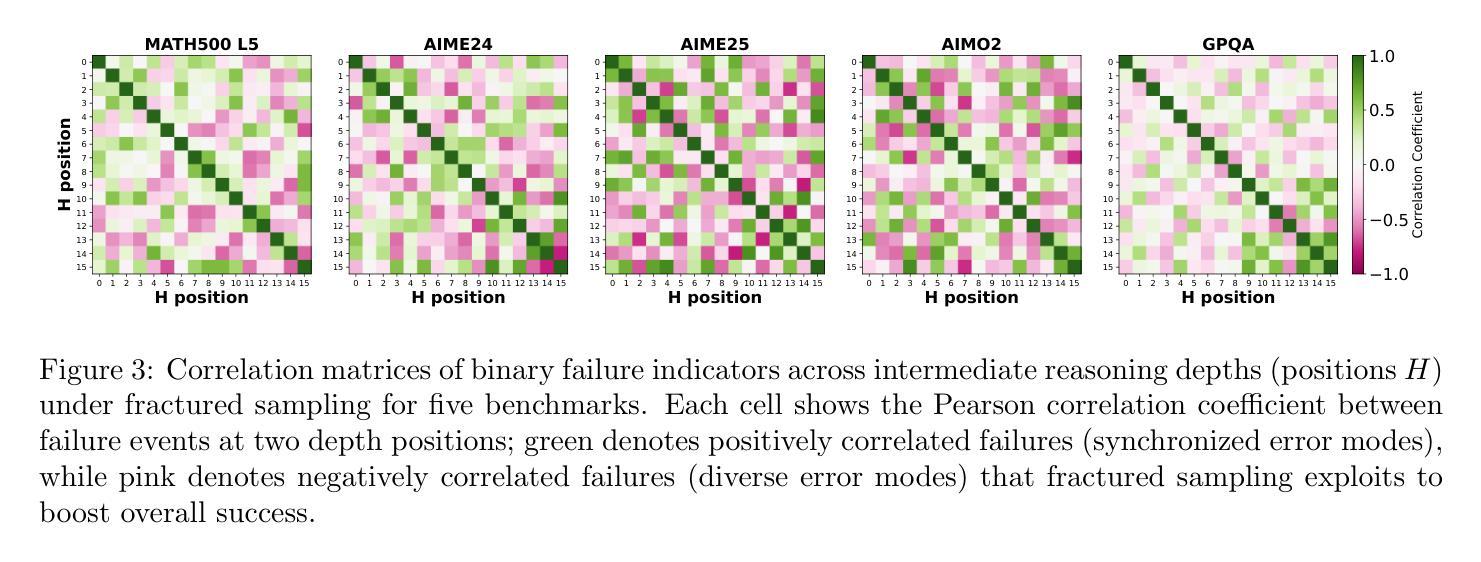
Fractured Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Authors:Baohao Liao, Hanze Dong, Yuhui Xu, Doyen Sahoo, Christof Monz, Junnan Li, Caiming Xiong
Inference-time scaling techniques have significantly bolstered the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by harnessing additional computational effort at inference without retraining. Similarly, Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting and its extension, Long CoT, improve accuracy by generating rich intermediate reasoning trajectories, but these approaches incur substantial token costs that impede their deployment in latency-sensitive settings. In this work, we first show that truncated CoT, which stops reasoning before completion and directly generates the final answer, often matches full CoT sampling while using dramatically fewer tokens. Building on this insight, we introduce Fractured Sampling, a unified inference-time strategy that interpolates between full CoT and solution-only sampling along three orthogonal axes: (1) the number of reasoning trajectories, (2) the number of final solutions per trajectory, and (3) the depth at which reasoning traces are truncated. Through extensive experiments on five diverse reasoning benchmarks and several model scales, we demonstrate that Fractured Sampling consistently achieves superior accuracy-cost trade-offs, yielding steep log-linear scaling gains in Pass@k versus token budget. Our analysis reveals how to allocate computation across these dimensions to maximize performance, paving the way for more efficient and scalable LLM reasoning. Code is available at https://github.com/BaohaoLiao/frac-cot.
推理时间缩放技术通过利用推理时的额外计算努力,在无需重新训练的情况下显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。同样地,思维链(CoT)提示及其扩展版本长思维链(Long CoT)通过生成丰富的中间推理轨迹提高了准确性。但这些方法产生了巨大的令牌成本,阻碍了其在延迟敏感环境中的部署。在这项工作中,我们首先展示了截断思维链(Truncated CoT),该方法在推理完成之前停止推理并直接生成最终答案,往往能与完整的CoT采样相匹敌,同时使用的令牌数量大大减少。基于这一见解,我们引入了断裂采样(Fractured Sampling),这是一种统一的推理时间策略,沿着三个正交轴在完整的CoT和仅解决方案采样之间进行插值:(1)推理轨迹的数量,(2)每条轨迹的最终解决方案数量,(3)推理轨迹被截断的深度。通过五个不同的推理基准测试和多种模型规模的广泛实验,我们证明了断裂采样在准确性成本权衡方面始终表现出色,在Pass@k与令牌预算方面实现了陡峭的对数线性缩放收益。我们的分析揭示了如何在这些维度上分配计算以最大化性能,为更高效、可扩展的LLM推理铺平了道路。代码可在https://github.com/BaohaoLiao/frac-cot找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在大型语言模型(LLM)中使用的推理时间缩放技术,通过利用额外的计算努力来提高推理能力,而无需重新训练。文章还探讨了Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示及其扩展Long CoT在提高准确性的同时,也带来了大量的令牌成本,阻碍了其在延迟敏感场景中的应用。本研究发现,通过截断CoT,在推理完成前停止并直接生成最终答案,可以匹配完整的CoT采样,同时大大减少令牌使用量。在此基础上,本文引入了Fractured Sampling这一统一的推理时间策略,通过在三个正交轴上插值完整的CoT和解决方案采样,实现了较高的准确性成本权衡。实验证明,Fractured Sampling在五个不同的推理基准测试和多个模型规模上均实现了优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 推理时间缩放技术无需重新训练即可提高LLM的推理能力。
- Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示和Long CoT能提高准确性,但带来较高的令牌成本。
- 截断CoT能在保持高准确性的同时减少令牌使用。
- Fractured Sampling是一种统一的推理时间策略,通过调整三个正交轴上的参数实现最优性能。
- Fractured Sampling在多个基准测试和模型规模上实现了优越的性能。
- 通过调整计算分配,可以实现最佳的性能-成本权衡。
点此查看论文截图

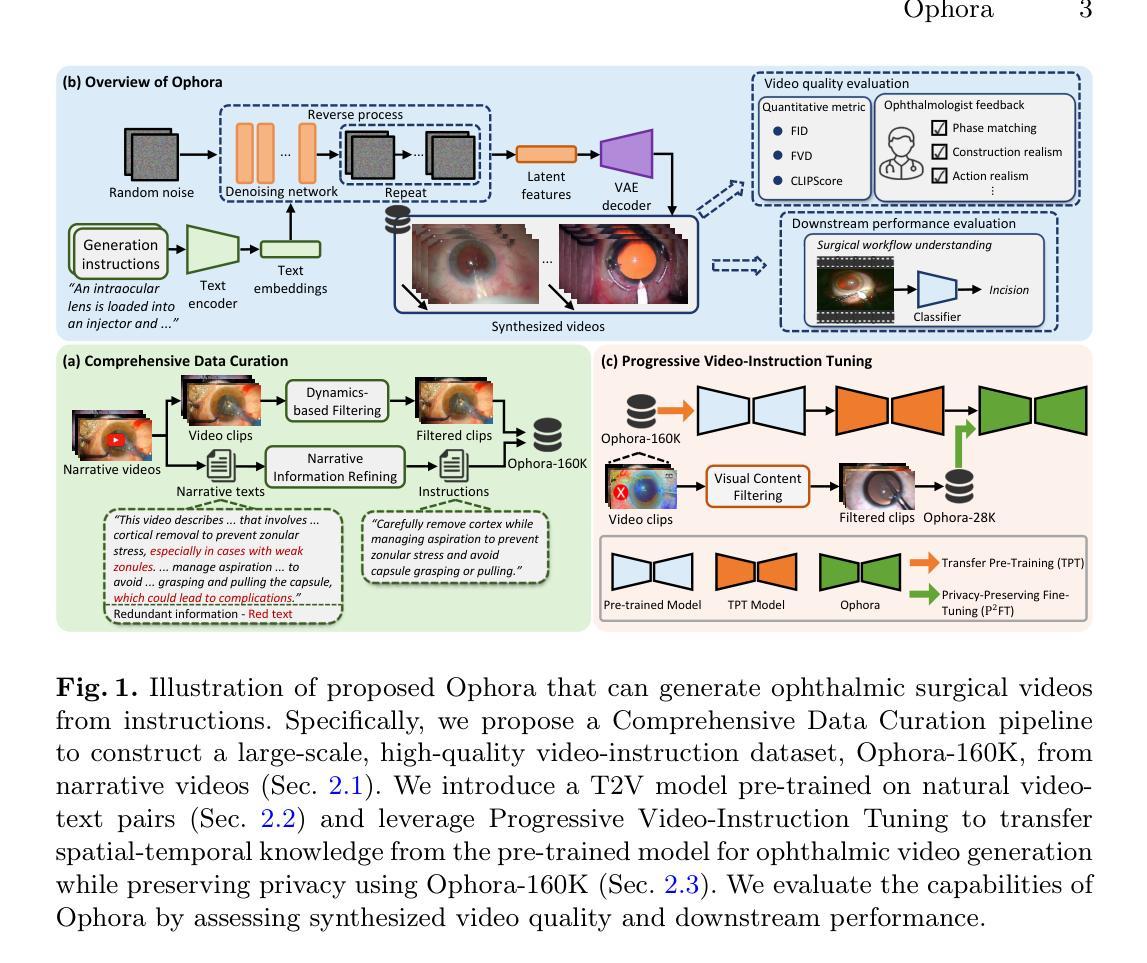
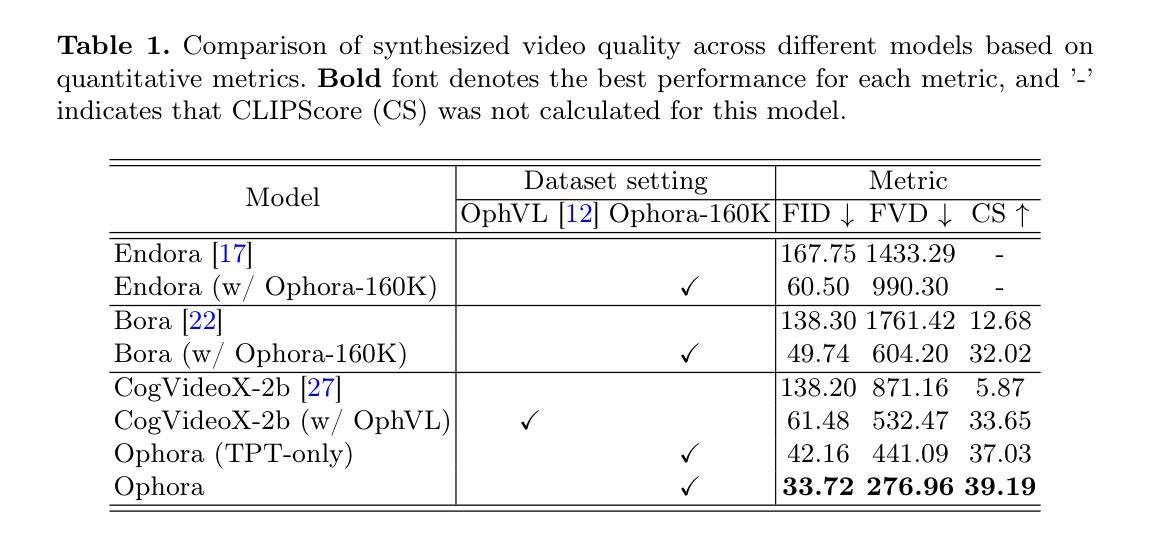
Ophora: A Large-Scale Data-Driven Text-Guided Ophthalmic Surgical Video Generation Model
Authors:Wei Li, Ming Hu, Guoan Wang, Lihao Liu, Kaijin Zhou, Junzhi Ning, Xin Guo, Zongyuan Ge, Lixu Gu, Junjun He
In ophthalmic surgery, developing an AI system capable of interpreting surgical videos and predicting subsequent operations requires numerous ophthalmic surgical videos with high-quality annotations, which are difficult to collect due to privacy concerns and labor consumption. Text-guided video generation (T2V) emerges as a promising solution to overcome this issue by generating ophthalmic surgical videos based on surgeon instructions. In this paper, we present Ophora, a pioneering model that can generate ophthalmic surgical videos following natural language instructions. To construct Ophora, we first propose a Comprehensive Data Curation pipeline to convert narrative ophthalmic surgical videos into a large-scale, high-quality dataset comprising over 160K video-instruction pairs, Ophora-160K. Then, we propose a Progressive Video-Instruction Tuning scheme to transfer rich spatial-temporal knowledge from a T2V model pre-trained on natural video-text datasets for privacy-preserved ophthalmic surgical video generation based on Ophora-160K. Experiments on video quality evaluation via quantitative analysis and ophthalmologist feedback demonstrate that Ophora can generate realistic and reliable ophthalmic surgical videos based on surgeon instructions. We also validate the capability of Ophora for empowering downstream tasks of ophthalmic surgical workflow understanding. Code is available at https://github.com/mar-cry/Ophora.
在眼科手术中,开发一个能够解读手术视频并预测后续操作的AI系统,需要大量的带有高质量注释的眼科手术视频。由于隐私问题和劳动消耗,这些视频的收集非常困难。文本引导的视频生成(T2V)作为一种有前途的解决方案应运而生,它可以根据外科医生的指令生成眼科手术视频。在本文中,我们提出了一种先进的模型——Ophora,它可以根据自然语言指令生成眼科手术视频。为了构建Ophora,我们首先提出了一个全面的数据整理管道,将叙事眼科手术视频转化为大规模的高质量数据集,包含超过16万对视频指令对,即Ophora-160K数据集。然后,我们提出了一种渐进的视频指令调整方案,以从T2V模型预训练的自然视频文本数据集中转移丰富的时空知识,基于Ophora-160K数据集进行隐私保护的眼科手术视频生成。通过对视频质量的定量分析和眼科医生的反馈进行的实验表明,Ophora可以根据外科医生的指令生成真实可靠的眼科手术视频。我们还验证了Ophora在执行眼科手术工作流程理解等下游任务方面的能力。代码可在https://github.com/mar-cry/Ophora获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early accepted in MICCAI25
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Ophora的模型,该模型能够根据自然语言指令生成眼科手术视频。为解决高质量眼科手术视频数据难以收集的问题,研究团队构建了大型数据集Ophora-160K,并提出了一种全面的数据整理流程和渐进式视频指令调整方案。实验证明,Ophora能够生成真实可靠的眼科手术视频,并赋能眼科手术工作流程理解等下游任务。
Key Takeaways
1.Ophora模型能够根据自然语言指令生成眼科手术视频,解决了高质量眼科手术视频数据难以收集的问题。
2.研究团队构建了大型数据集Ophora-160K,用于训练和发展Ophora模型。
3.提出了一种全面的数据整理流程,将叙事性眼科手术视频转化为高质量数据集。
4.渐进式视频指令调整方案用于从预训练的T2V模型中转移时空知识,实现基于隐私保护的眼科手术视频生成。
5.实验证明,Ophora能够生成真实可靠的眼科手术视频。
6.Ophora模型在眼科手术工作流程理解等下游任务中表现出赋能作用。
点此查看论文截图