⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
Exploiting Music Source Separation for Automatic Lyrics Transcription with Whisper
Authors:Jaza Syed, Ivan Meresman Higgs, Ondřej Cífka, Mark Sandler
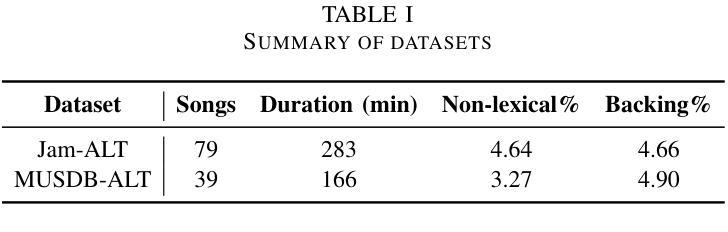
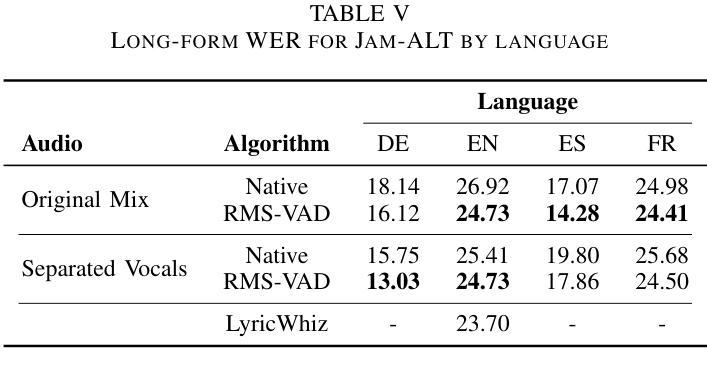
Automatic lyrics transcription (ALT) remains a challenging task in the field of music information retrieval, despite great advances in automatic speech recognition (ASR) brought about by transformer-based architectures in recent years. One of the major challenges in ALT is the high amplitude of interfering audio signals relative to conventional ASR due to musical accompaniment. Recent advances in music source separation have enabled automatic extraction of high-quality separated vocals, which could potentially improve ALT performance. However, the effect of source separation has not been systematically investigated in order to establish best practices for its use. This work examines the impact of source separation on ALT using Whisper, a state-of-the-art open source ASR model. We evaluate Whisper’s performance on original audio, separated vocals, and vocal stems across short-form and long-form transcription tasks. For short-form, we suggest a concatenation method that results in a consistent reduction in Word Error Rate (WER). For long-form, we propose an algorithm using source separation as a vocal activity detector to derive segment boundaries, which results in a consistent reduction in WER relative to Whisper’s native long-form algorithm. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results for an open source system on the Jam-ALT long-form ALT benchmark, without any training or fine-tuning. We also publish MUSDB-ALT, the first dataset of long-form lyric transcripts following the Jam-ALT guidelines for which vocal stems are publicly available.
自动歌词转录(ALT)仍是音乐信息检索领域中的一个具有挑战性的任务。尽管近年来基于转换器的架构在自动语音识别(ASR)方面取得了巨大进展,但ALT仍然面临许多困难。ALT的主要挑战之一是音乐伴奏产生的干扰音频信号幅度较高,这使得相对于传统ASR来说更具挑战性。音乐源分离方面的最新进展使得能够自动提取高质量的分开的声音,这可能会提高ALT的性能。然而,为了建立最佳实践,源分离的影响尚未进行系统性的研究。这项工作使用Whisper(一种先进的开源ASR模型)来检查源分离对ALT的影响。我们评估了Whisper在原始音频、分离后的声音、以及语音茎上的性能,涵盖了短期和长期转录任务。对于短期任务,我们提出了一种拼接方法,该方法导致单词错误率(WER)持续下降。对于长期任务,我们提出了一种使用源分离作为语音活动检测器来推导段边界的算法,相对于Whisper的本地长期算法,该算法在WER方面实现了持续的降低。我们的方法在遵循Jam-ALT指导方针的长期ALT基准测试上达到了开放源代码系统的最新成果水平,无需进行任何训练或微调。我们还发布了第一个遵循Jam-ALT指导方针的长期歌词转录数据集MUSDB-ALT,该数据集提供的歌词录音均为公开可用的语音茎。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 2025 ICME Workshop AI for Music
摘要
尽管近年来基于转换器的架构在自动语音识别(ASR)方面取得了巨大进步,但自动歌词转录(ALT)仍是音乐信息检索领域的一项具有挑战性的任务。ALT的主要挑战之一是音乐伴奏产生的干扰音频信号幅度较高,与常规ASR相比,这对ALT提出了更高的要求。音乐源分离的近期进展使得能够自动提取高质量的分离人声,这可能会提高ALT的性能。然而,源分离的影响尚未进行系统性的研究,以建立其最佳实践。本研究使用Whisper这一先进的开源ASR模型,探讨了源分离对ALT的影响。我们评估了Whisper在原始音频、分离的人声和语音片段上的性能,涵盖了短形式和长形式的转录任务。对于短形式,我们提出了一种拼接方法,导致词错误率(WER)持续降低。对于长形式,我们提出了一种使用源分离作为语音活动检测器来推导段落边界的算法,与Whisper的内置长形式算法相比,该算法导致WER持续降低。我们的方法在遵循Jam-ALT长形式ALT基准的MUSDB-ALT数据集上实现了开源系统的最新结果,无需进行任何训练或微调。
关键见解
- 自动歌词转录(ALT)是音乐信息检索领域的一项具有挑战性的任务,主要挑战之一是音乐伴奏产生的高幅度干扰音频信号。
- 近期音乐源分离的进展为ALT的改进提供了可能,能够自动提取高质量的分离人声。
- 本研究使用Whisper这一先进的开源ASR模型,探讨了源分离对ALT的影响。
- 对于短形式的转录任务,提出了一种拼接方法,能够降低词错误率(WER)。
- 对于长形式的转录任务,使用源分离作为语音活动检测器来推导段落边界的算法能够有效降低WER。
- 提出的方法在遵循Jam-ALT长形式ALT基准的MUSDB-ALT数据集上实现了最新结果,且无需任何训练或微调。
- 研究还发布了遵循Jam-ALT指南的长形式歌词转录数据集MUSDB-ALT,其中人声素材可公开获取。
点此查看论文截图

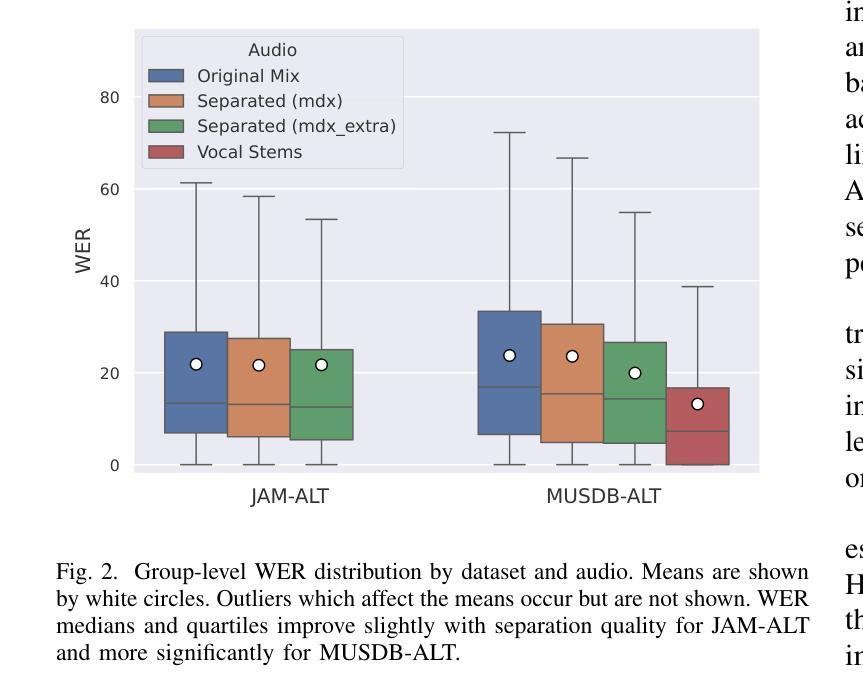
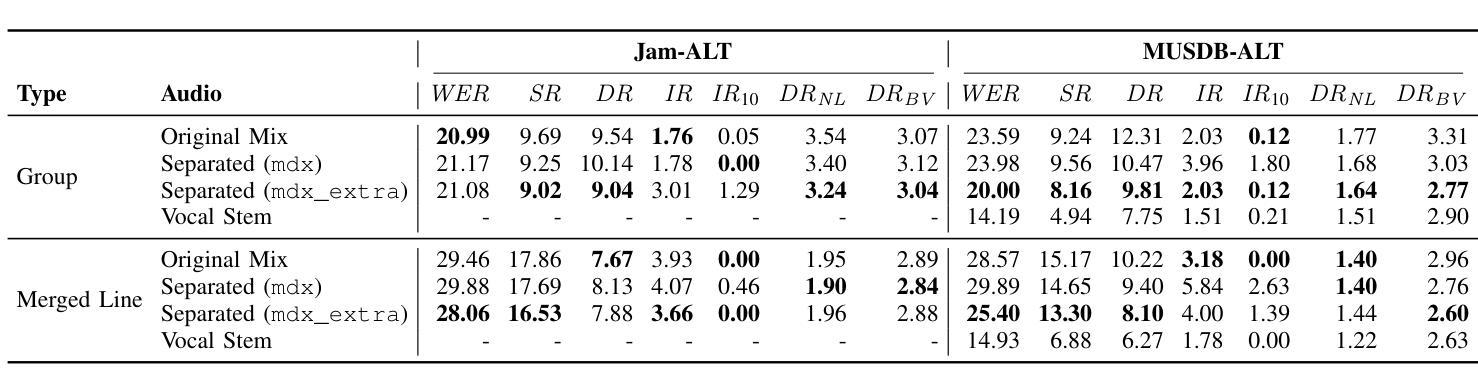
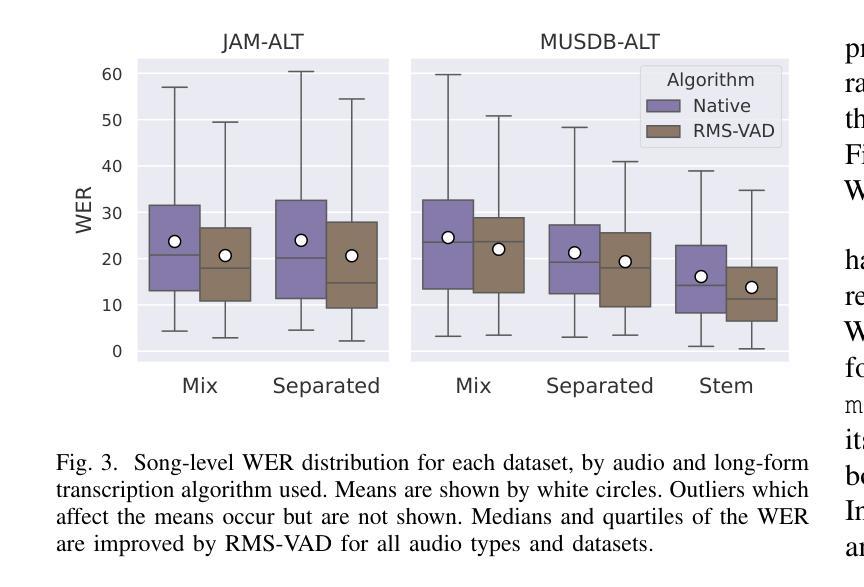
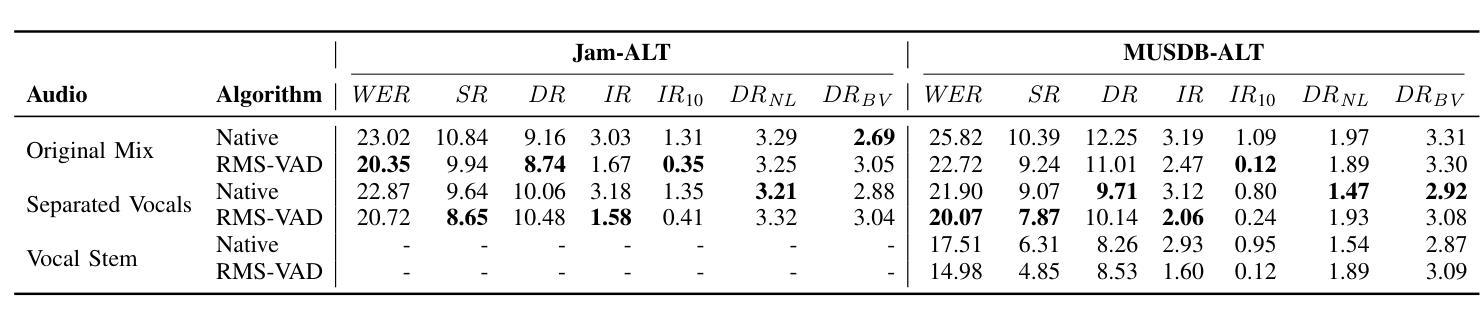
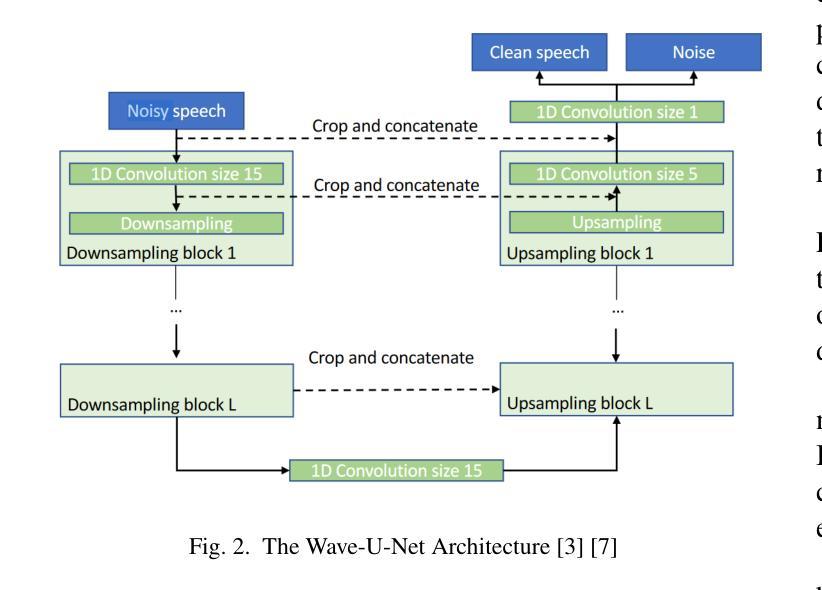
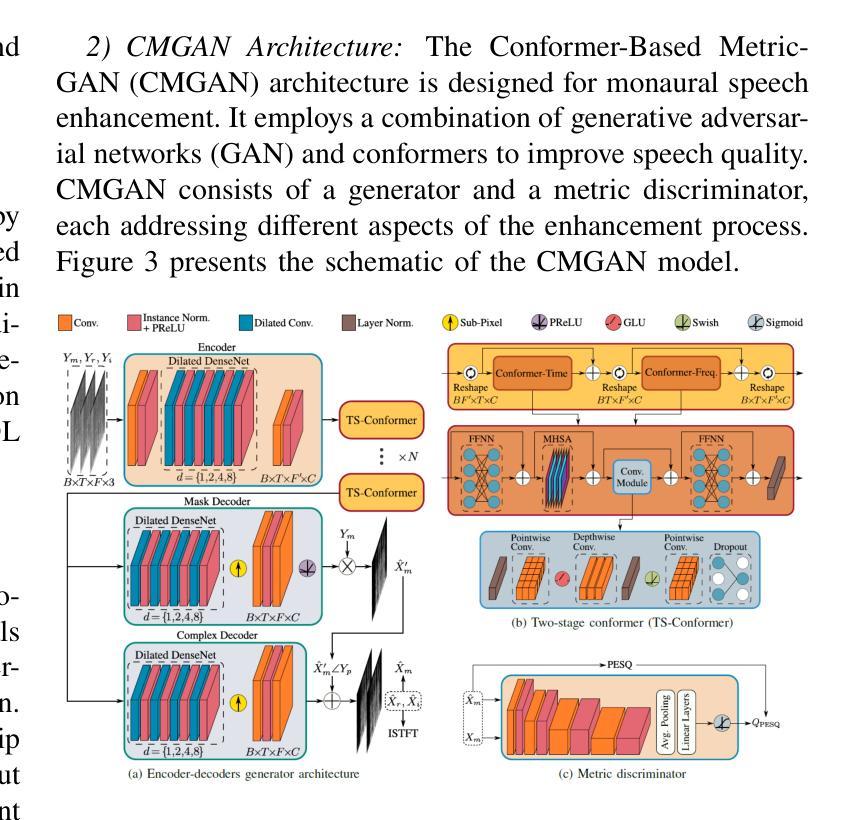
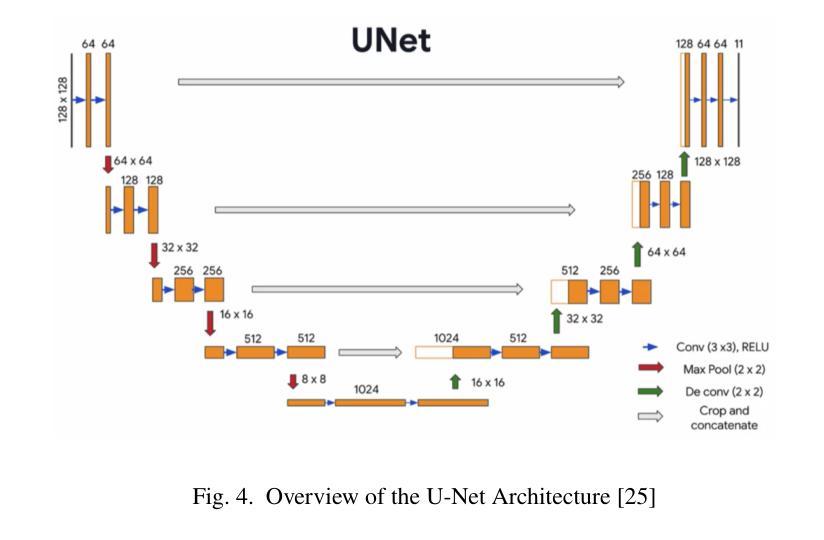
A Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Speech Enhancement in Real-World Noisy Environments
Authors:Md Jahangir Alam Khondkar, Ajan Ahmed, Masudul Haider Imtiaz, Stephanie Schuckers
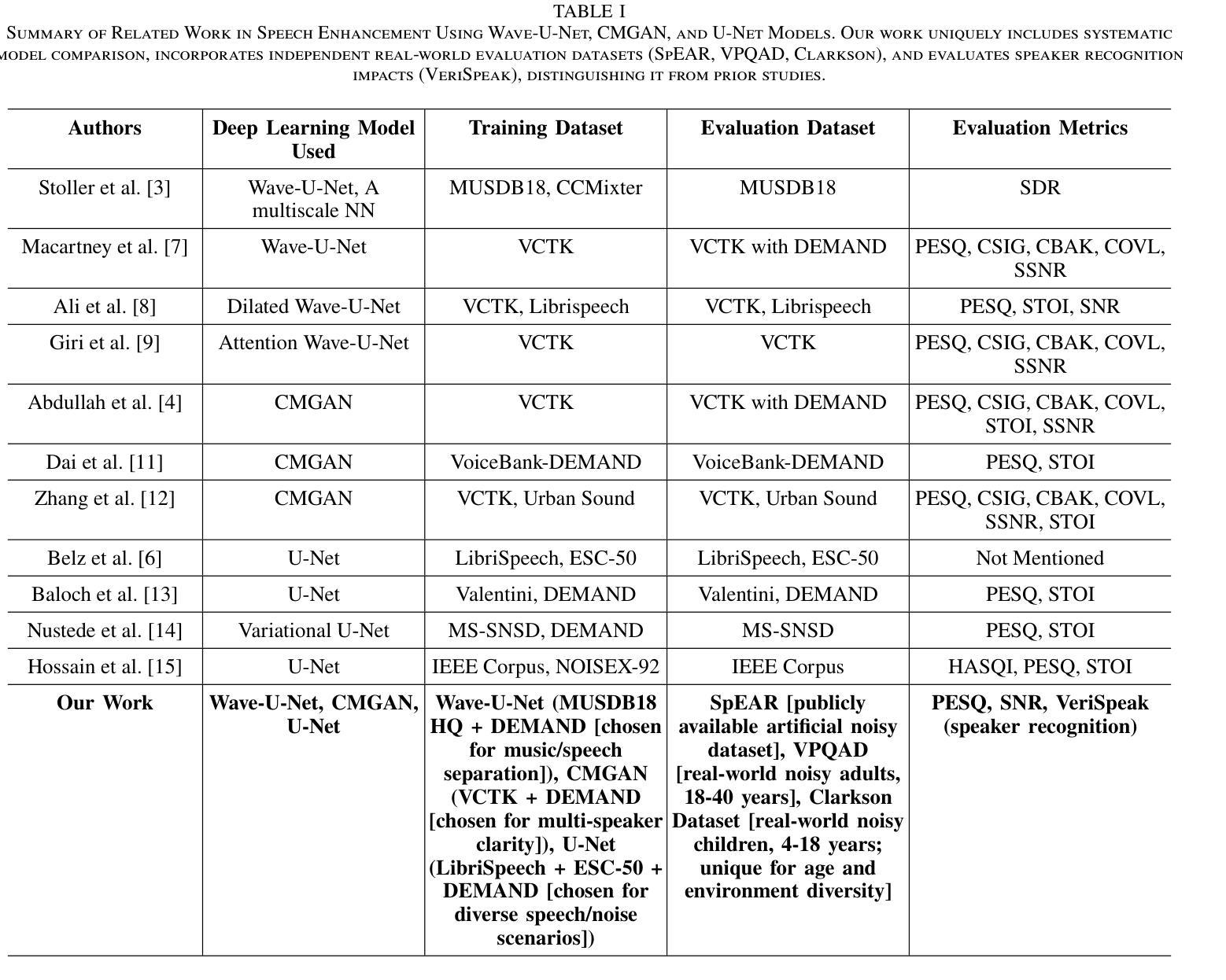
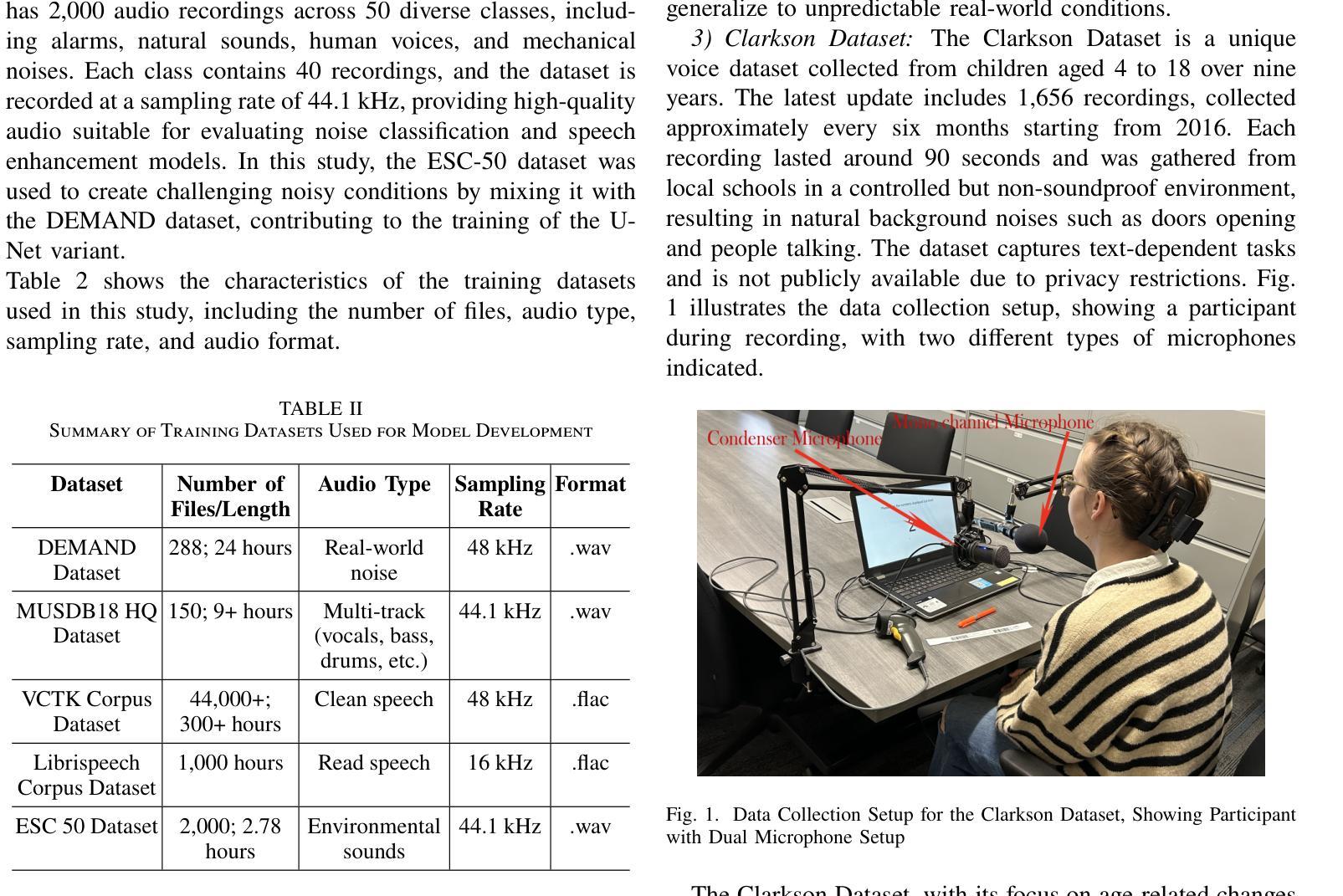
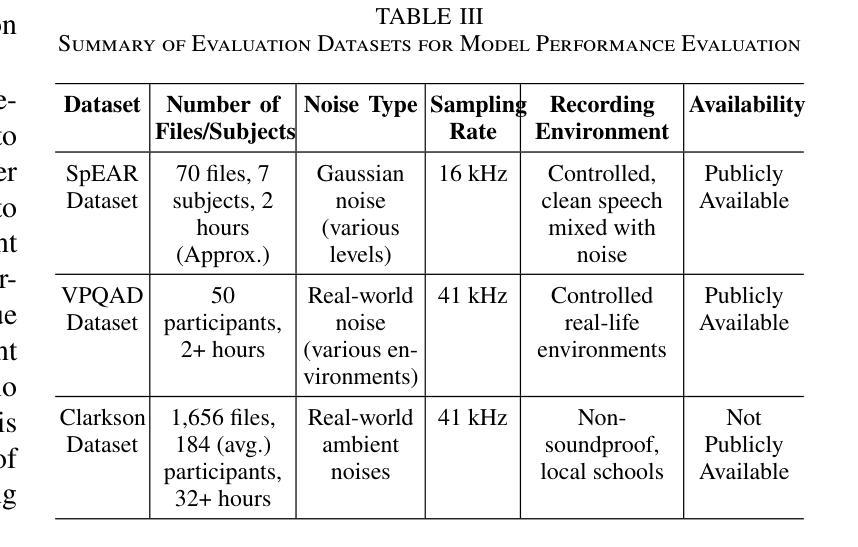
Speech enhancement, particularly denoising, is vital in improving the intelligibility and quality of speech signals for real-world applications, especially in noisy environments. While prior research has introduced various deep learning models for this purpose, many struggle to balance noise suppression, perceptual quality, and speaker-specific feature preservation, leaving a critical research gap in their comparative performance evaluation. This study benchmarks three state-of-the-art models Wave-U-Net, CMGAN, and U-Net, on diverse datasets such as SpEAR, VPQAD, and Clarkson datasets. These models were chosen due to their relevance in the literature and code accessibility. The evaluation reveals that U-Net achieves high noise suppression with SNR improvements of +71.96% on SpEAR, +64.83% on VPQAD, and +364.2% on the Clarkson dataset. CMGAN outperforms in perceptual quality, attaining the highest PESQ scores of 4.04 on SpEAR and 1.46 on VPQAD, making it well-suited for applications prioritizing natural and intelligible speech. Wave-U-Net balances these attributes with improvements in speaker-specific feature retention, evidenced by VeriSpeak score gains of +10.84% on SpEAR and +27.38% on VPQAD. This research indicates how advanced methods can optimize trade-offs between noise suppression, perceptual quality, and speaker recognition. The findings may contribute to advancing voice biometrics, forensic audio analysis, telecommunication, and speaker verification in challenging acoustic conditions.
语音增强,尤其是去噪,在改善真实世界应用中语音信号的清晰度和质量方面至关重要,特别是在嘈杂的环境中。虽然之前的研究已经引入了各种深度学习模型来实现这一目标,但许多模型在平衡噪声抑制、感知质量和说话人特定特征保留方面存在困难,使得它们在性能比较评估方面存在关键的研究空白。本研究对Wave-U-Net、CMGAN和U-Net三种前沿模型进行了评估,使用的数据集包括SpEAR、VPQAD和Clarkson数据集等多样化数据集。这些模型之所以被选中,是因为它们在文献中的相关性和代码的可访问性。评估结果表明,U-Net在SpEAR数据集上实现了+71.96%、在VPQAD数据集上实现了+64.83%、在Clarkson数据集上实现了+364.2%的信噪比提高,取得了很高的噪声抑制效果。CMGAN在感知质量方面表现突出,在SpEAR和VPQAD上分别获得了4.04和1.46的PESQ高分,使其成为优先考虑自然和可理解语音的应用的理想选择。Wave-U-Net在说话人特定特征保留方面有所提高,平衡了这些特点,这在SpEAR和VPQAD的VeriSpeak得分增长+10.84%和+27.38%中得到了证明。这项研究表明,先进的方法如何优化噪声抑制、感知质量和说话人识别之间的权衡。这些发现可能有助于推动语音生物识别、音频分析鉴定、电信和具有挑战性的声学条件下的说话人验证的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了三种先进的语音增强模型(Wave-U-Net、CMGAN和U-Net)在噪声环境下的性能表现。U-Net在噪声抑制方面表现优秀,特别是在SpEAR、VPQAD和Clarkson数据集上的信号噪声比(SNR)提升显著。CMGAN在感知质量方面表现最佳,适合需要自然和可理解语音的应用。Wave-U-Net则在平衡噪声抑制、感知质量和说话人特征保留方面表现出优势。研究对于优化这些模型在噪声环境下的性能具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 语音增强在噪声环境中对改善语音信号的清晰度和质量至关重要。
- U-Net在噪声抑制方面表现突出,特别是在多个数据集上的SNR提升显著。
- CMGAN在感知质量方面最佳,适用于需要自然和可理解语音的应用场景。
- Wave-U-Net在平衡噪声抑制、感知质量和说话人特征保留方面具备优势。
- 说话人特征保留对于语音生物识别、语音验证等应用至关重要。
- 研究结果有助于深入了解不同模型在噪声环境下的性能差异。
点此查看论文截图

A Variational Framework for Improving Naturalness in Generative Spoken Language Models
Authors:Li-Wei Chen, Takuya Higuchi, Zakaria Aldeneh, Ahmed Hussen Abdelaziz, Alexander Rudnicky
The success of large language models in text processing has inspired their adaptation to speech modeling. However, since speech is continuous and complex, it is often discretized for autoregressive modeling. Speech tokens derived from self-supervised models (known as semantic tokens) typically focus on the linguistic aspects of speech but neglect prosodic information. As a result, models trained on these tokens can generate speech with reduced naturalness. Existing approaches try to fix this by adding pitch features to the semantic tokens. However, pitch alone cannot fully represent the range of paralinguistic attributes, and selecting the right features requires careful hand-engineering. To overcome this, we propose an end-to-end variational approach that automatically learns to encode these continuous speech attributes to enhance the semantic tokens. Our approach eliminates the need for manual extraction and selection of paralinguistic features. Moreover, it produces preferred speech continuations according to human raters. Code, samples and models are available at https://github.com/b04901014/vae-gslm.
文本处理中大型语言模型的成功激发了其在语音建模中的应用。然而,由于语音是连续且复杂的,通常需要进行离散化以进行自回归建模。从自监督模型派生的语音令牌(称为语义令牌)主要关注语音的语言方面,但忽略了韵律信息。因此,在这些令牌上训练的模型生成的语音会降低自然度。现有方法试图通过向语义令牌添加音调特征来解决这个问题。然而,单独的音调不能完全代表副语言属性的范围,并且选择正确的特征需要仔细的手工设计。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了一种端到端的变分方法,该方法能够自动学习编码这些连续的语音属性以增强语义令牌。我们的方法消除了手动提取和选择副语言特征的需求。此外,它根据人类评估者产生了更受欢迎的语音延续。代码、样本和模型可在https://github.com/b04901014/vae-gslm获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
总结
基于大型语言模型在文本处理方面的成功,人们尝试将其应用于语音建模。然而,由于语音的连续性和复杂性,通常需要进行离散化以进行自回归建模。从自监督模型派生的语音令牌(称为语义令牌)主要关注语音的语言方面,但忽略了韵律信息。因此,在这些令牌上训练的模型生成的语音自然度降低。现有方法试图通过向语义令牌添加音高特征来解决这一问题。然而,音高无法完全代表多种副语言属性,选择合适的特征需要精心手工设计。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了一种端到端的变分方法,该方法可自动学习编码这些连续的语音属性以增强语义令牌。我们的方法消除了手动提取和选择副语言特征的需求。此外,根据人类评分者的评估,它产生了更受欢迎的语音连续内容。相关代码、样本和模型可在 https://github.com/b04901014/vae-gslm 获得。
要点
- 大型语言模型在文本处理中的成功推动了其在语音建模中的应用。
- 语音由于其连续性和复杂性,常常需要离散化以进行自回归建模。
- 现有研究中常用的语音令牌忽略了韵律信息,影响生成的语音的自然度。
- 现有方法试图通过向语义令牌添加音高特征来解决语音自然度问题。但音高不足以代表所有副语言属性且特征选择需要精细的手工设计。
- 提出了一种端到端的变分方法,自动学习编码连续的语音属性以增强语义令牌。这一方法无需手动提取和选择副语言特征。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法生成的语音内容更受欢迎,根据人类评分者的评估。
点此查看论文截图

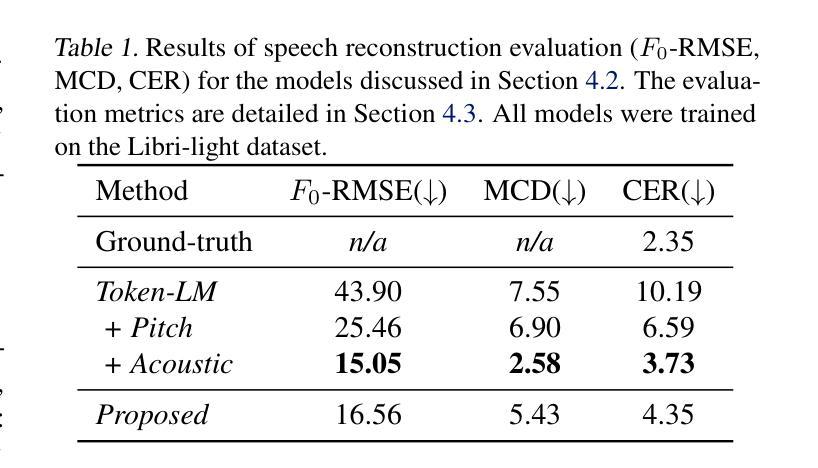
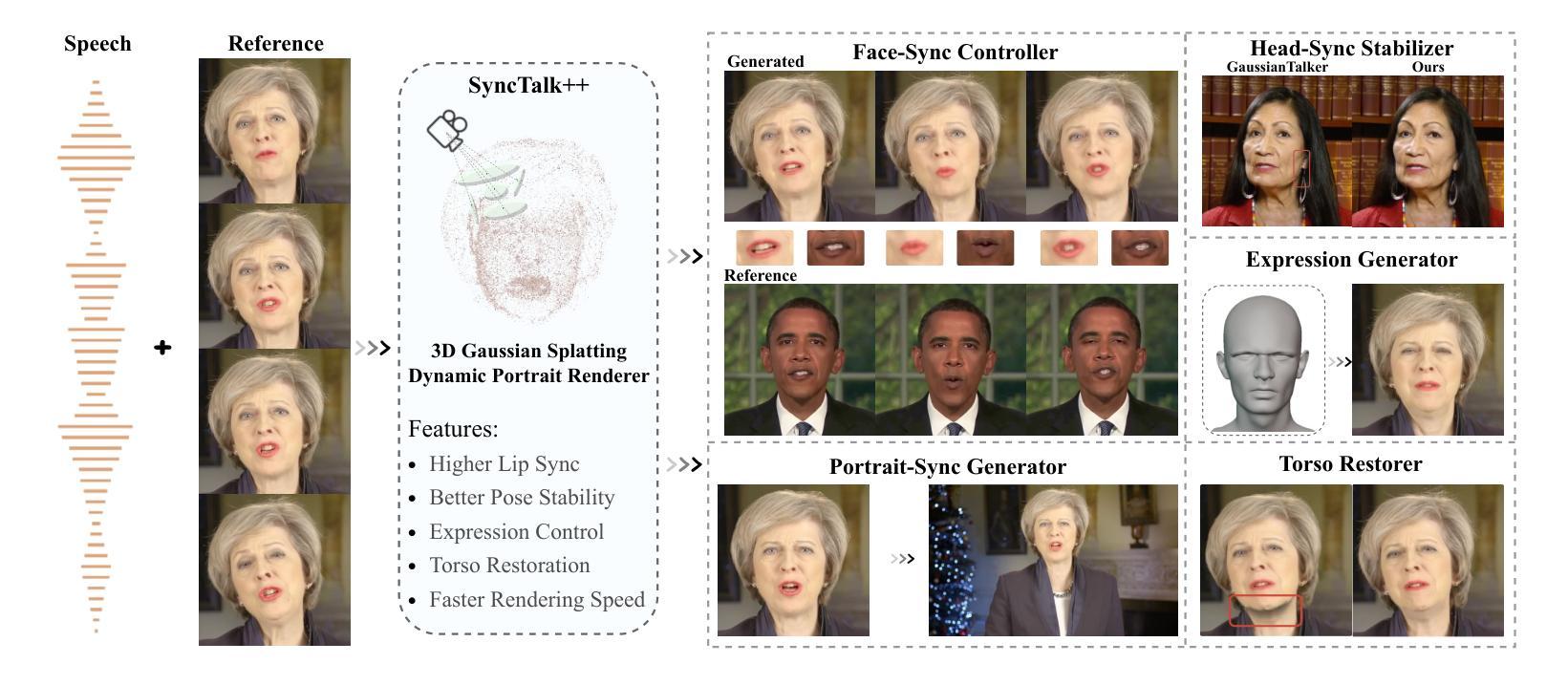
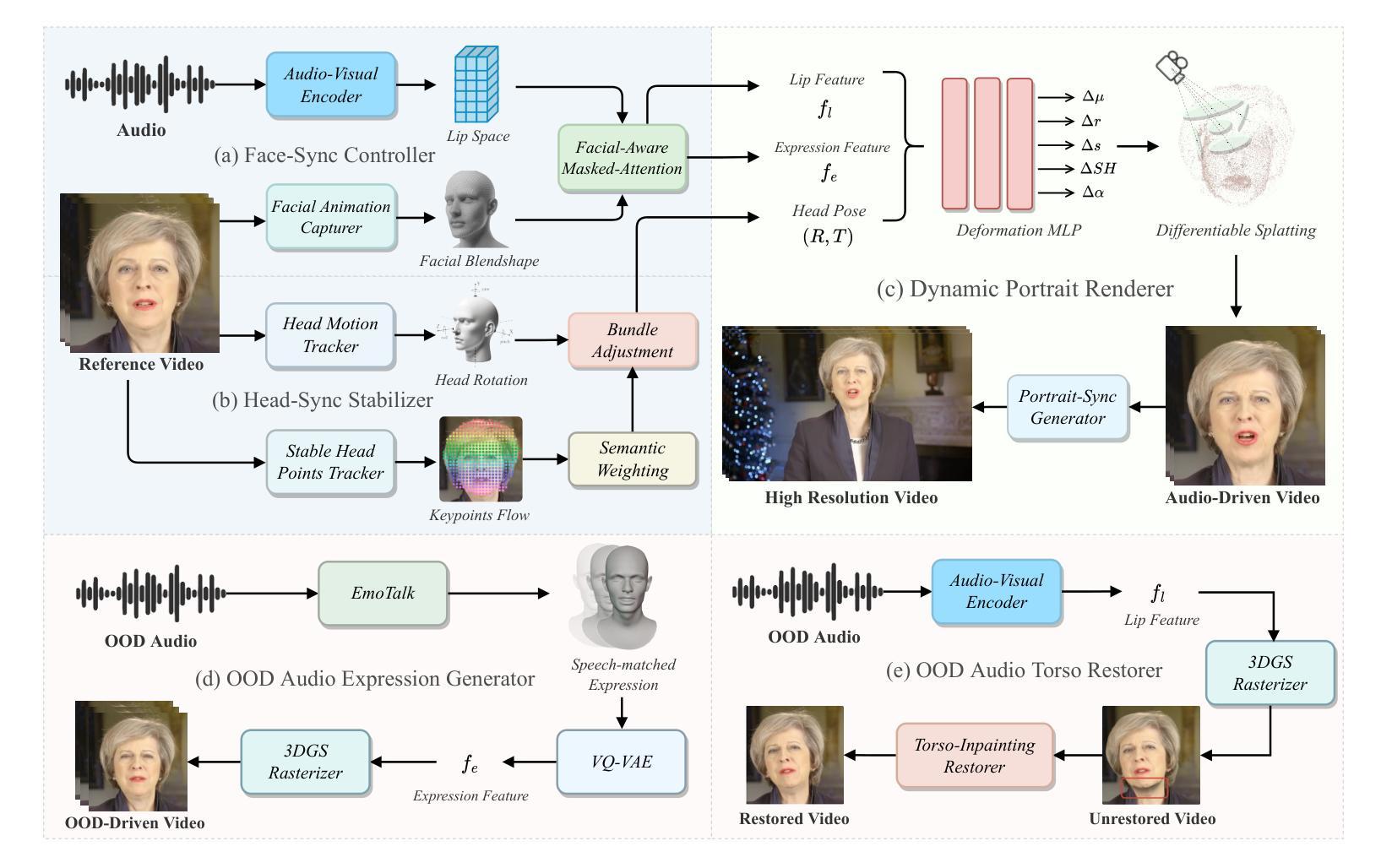
SyncTalk++: High-Fidelity and Efficient Synchronized Talking Heads Synthesis Using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Ziqiao Peng, Wentao Hu, Junyuan Ma, Xiangyu Zhu, Xiaomei Zhang, Hao Zhao, Hui Tian, Jun He, Hongyan Liu, Zhaoxin Fan
Achieving high synchronization in the synthesis of realistic, speech-driven talking head videos presents a significant challenge. A lifelike talking head requires synchronized coordination of subject identity, lip movements, facial expressions, and head poses. The absence of these synchronizations is a fundamental flaw, leading to unrealistic results. To address the critical issue of synchronization, identified as the ‘’devil’’ in creating realistic talking heads, we introduce SyncTalk++, which features a Dynamic Portrait Renderer with Gaussian Splatting to ensure consistent subject identity preservation and a Face-Sync Controller that aligns lip movements with speech while innovatively using a 3D facial blendshape model to reconstruct accurate facial expressions. To ensure natural head movements, we propose a Head-Sync Stabilizer, which optimizes head poses for greater stability. Additionally, SyncTalk++ enhances robustness to out-of-distribution (OOD) audio by incorporating an Expression Generator and a Torso Restorer, which generate speech-matched facial expressions and seamless torso regions. Our approach maintains consistency and continuity in visual details across frames and significantly improves rendering speed and quality, achieving up to 101 frames per second. Extensive experiments and user studies demonstrate that SyncTalk++ outperforms state-of-the-art methods in synchronization and realism. We recommend watching the supplementary video: https://ziqiaopeng.github.io/synctalk++.
在合成逼真的语音驱动式说话人头视频时,实现高同步率是一个巨大的挑战。一个栩栩如生的说话人头部需要同步协调主体身份、嘴唇动作、面部表情和头部姿态。缺乏这些同步是一个基本缺陷,会导致不真实的结果。为了解决同步这一关键问题,我们将其视为创建逼真说话头部的“魔鬼”,并引入了SyncTalk++。它具备动态肖像渲染器和高斯拼贴技术,确保主体身份的一致保留,以及面部同步控制器,该控制器使嘴唇动作与语音对齐,同时创新地使用3D面部混合形状模型来重建准确的面部表情。为了确保自然的头部动作,我们提出了头部同步稳定器,它优化了头部姿态,提高了稳定性。此外,SyncTalk++通过融入表情生成器和躯干恢复器,增强了处理离群值(OOD)音频的稳健性,这两个组件可生成与语音相匹配的表情和无缝的躯干区域。我们的方法保持了跨帧的视觉细节的一致性和连续性,并显著提高了渲染速度和品质,达到了每秒101帧。大量的实验和用户研究表明,SyncTalk++在同步和逼真度方面超过了最新技术方法。我们推荐观看补充视频:https://ziqiaopeng.github.io/synctalk++.html
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了SyncTalk++技术,该技术用于合成高度同步的、以语音驱动的真实谈话视频。它包含动态肖像渲染器、面部同步控制器和头部同步稳定器等多个组件,确保主体身份、嘴唇动作、面部表情和头部姿态的同步协调。此外,SyncTalk++还提高了对离群音频的稳健性,并通过表达生成器和躯干恢复器等技术,生成与语音匹配的面部表情和无缝的躯干区域。SyncTalk++提高了渲染速度和视频质量,在同步和逼真度方面超过了现有技术。建议观看补充视频以获取更多详细信息。
Key Takeaways
- SyncTalk++技术旨在合成高度同步的、以语音驱动的谈话视频,确保主体身份、嘴唇动作和面部表情的同步协调。
- 包含动态肖像渲染器,采用高斯涂抹技术以确保一致的主体身份保留。
- 引入面部同步控制器,将嘴唇动作与语音对齐,并使用3D面部blendshape模型重建准确的面部表情。
- 提出头部同步稳定器,优化头部姿态以实现更大的稳定性。
- SyncTalk++通过表达生成器和躯干恢复器等技术提高了对离群音频的稳健性,并生成与语音匹配的面部表情和无缝的躯干区域。
- SyncTalk++可以维持跨帧的视觉细节的一致性和连续性,并提高渲染速度和视频质量。
点此查看论文截图



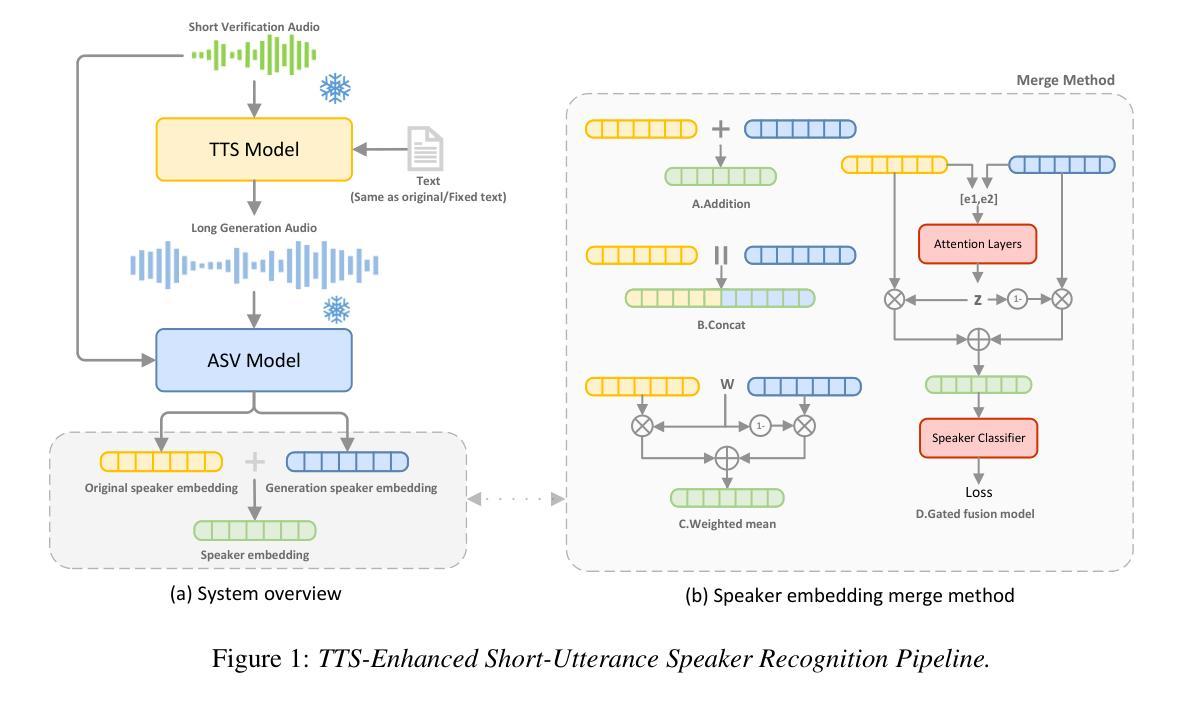
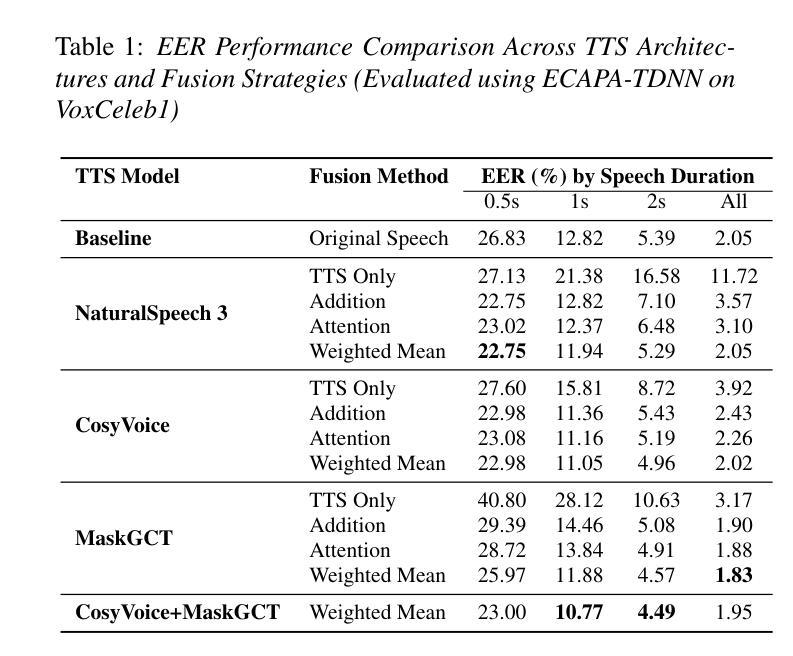
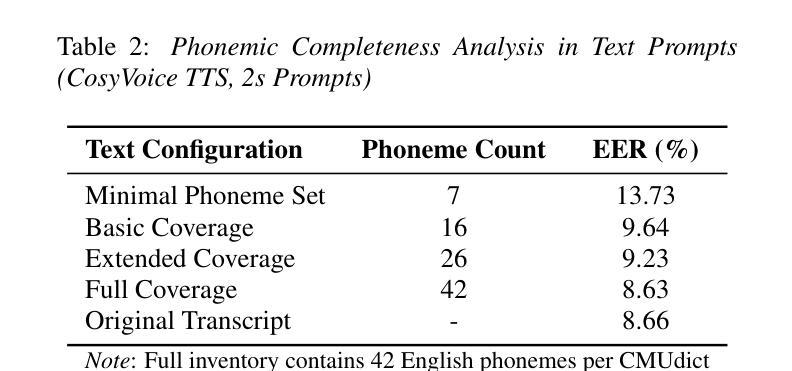
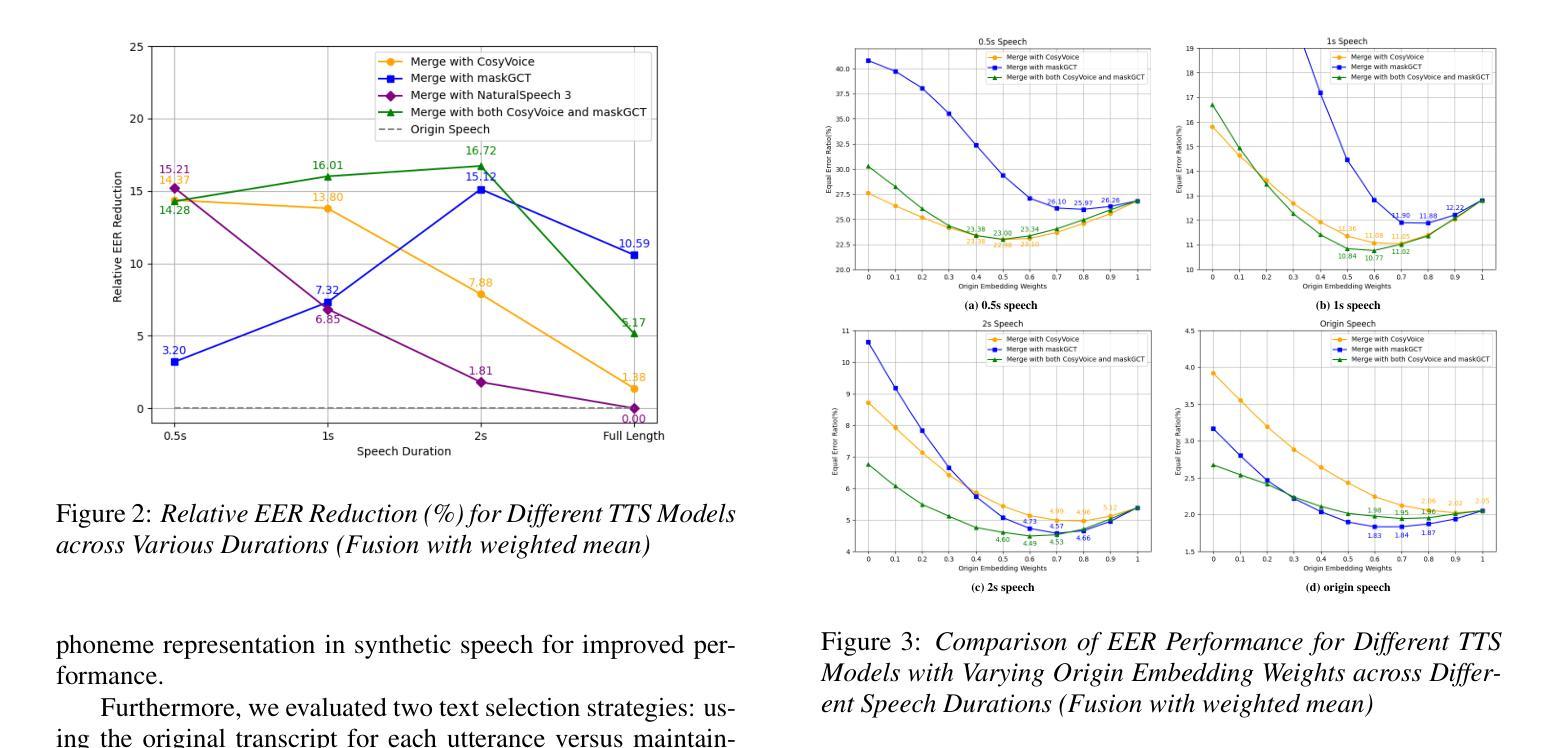
Investigation of Zero-shot Text-to-Speech Models for Enhancing Short-Utterance Speaker Verification
Authors:Yiyang Zhao, Shuai Wang, Guangzhi Sun, Zehua Chen, Chao Zhang, Mingxing Xu, Thomas Fang Zheng
Short-utterance speaker verification presents significant challenges due to the limited information in brief speech segments, which can undermine accuracy and reliability. Recently, zero-shot text-to-speech (ZS-TTS) systems have made considerable progress in preserving speaker identity. In this study, we explore, for the first time, the use of ZS-TTS systems for test-time data augmentation for speaker verification. We evaluate three state-of-the-art pre-trained ZS-TTS systems, NatureSpeech 3, CosyVoice, and MaskGCT, on the VoxCeleb 1 dataset. Our experimental results show that combining real and synthetic speech samples leads to 10%-16% relative equal error rate (EER) reductions across all durations, with particularly notable improvements for short utterances, all without retraining any existing systems. However, our analysis reveals that longer synthetic speech does not yield the same benefits as longer real speech in reducing EERs. These findings highlight the potential and challenges of using ZS-TTS for test-time speaker verification, offering insights for future research.
短时长说话人验证面临着巨大的挑战,由于简短语音片段中的信息有限,这可能会降低准确性和可靠性。最近,零样本文本到语音(ZS-TTS)系统在保持说话人身份方面取得了重大进展。在这项研究中,我们首次探索了ZS-TTS系统在测试时间数据增强在说话人验证中的应用。我们在VoxCeleb 1数据集上评估了三种最先进的预训练ZS-TTS系统,包括NatureSpeech 3、CosyVoice和MaskGCT。我们的实验结果表明,结合真实和合成语音样本在所有时长上导致相对等错误率(EER)降低了10%-16%,对于短时长语音的改进尤为显著,且无需对任何现有系统进行再训练。然而,我们的分析表明,较长的合成语音在降低EER方面并没有带来与较长真实语音相同的益处。这些发现突显了使用ZS-TTS进行测试时间说话人验证的潜力和挑战,为未来的研究提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了零样本文本到语音(ZS-TTS)系统在测试时间数据增强中的首次应用在短讲话验证中的应用。在VoxCeleb 1数据集上评估了三个最新的预训练ZS-TTS系统(NatureSpeech 3、CosyVoice和MaskGCT)。结合真实和合成语音样本后,相对等误率(EER)在所有时长上降低了10%-16%,特别是短语的改进尤为显著,且无需对现有系统进行任何重新训练。然而,分析表明,较长的合成语音在降低EER方面并未产生与较长真实语音相同的好处。该研究突出了使用ZS-TTS在测试时间说话人验证中的潜力和挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 短语说话人验证面临由于信息有限而导致的准确性和可靠性问题。
- 零样本文本到语音(ZS-TTS)系统在保留说话人身份方面取得了显著进步。
- 研究首次探索了将ZS-TTS系统应用于测试时间数据增强在说话人验证中的潜力。
- 在VoxCeleb 1数据集上评估的三个预训练ZS-TTS系统显示,结合真实和合成语音样本可以降低等误率(EER)。
- 合成语音在短讲话验证中的改进尤为显著,且无需对现有系统进行重新训练。
- 较长的合成语音在降低EER方面并未产生与较长真实语音相同的效果。
点此查看论文截图

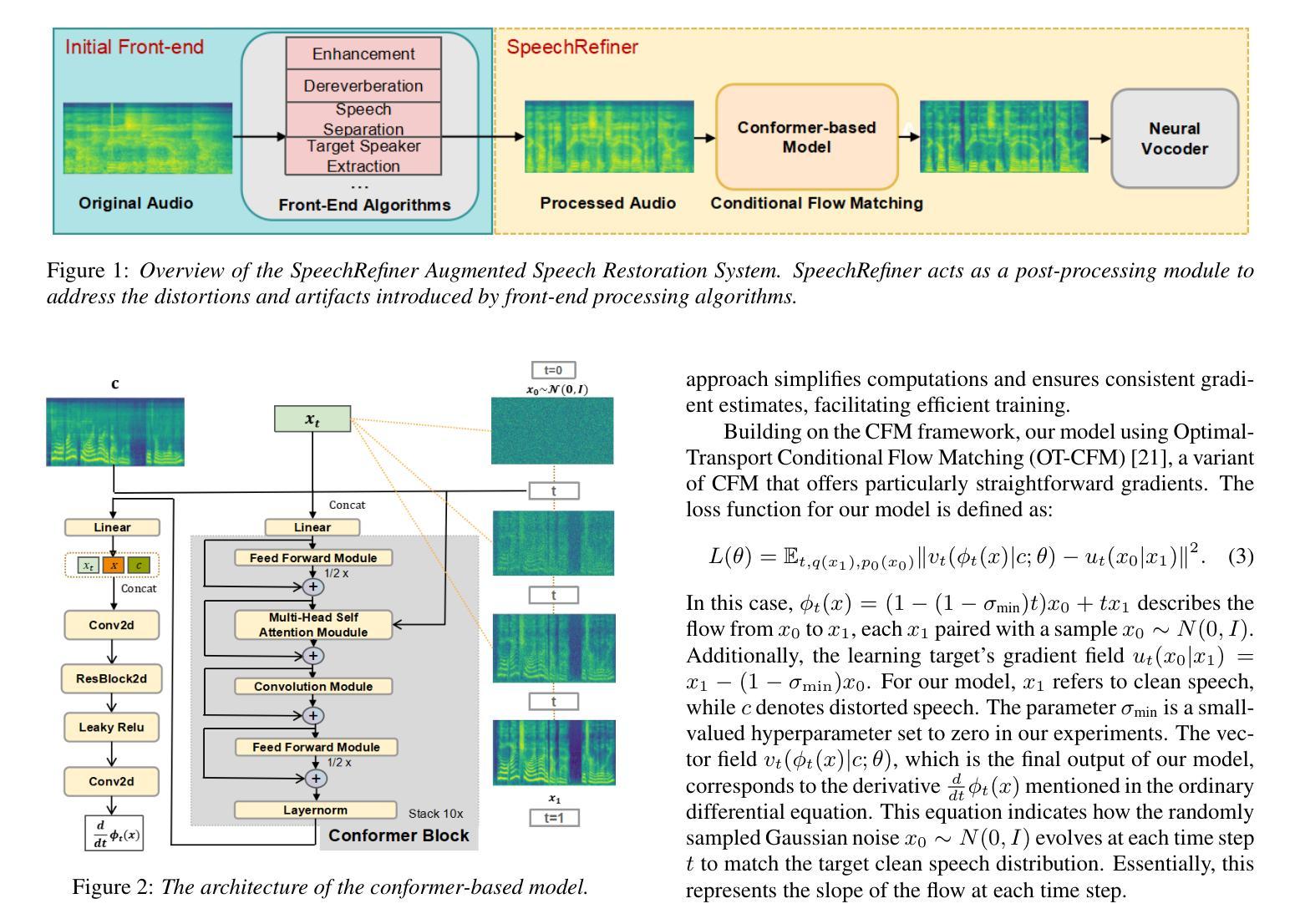
SpeechRefiner: Towards Perceptual Quality Refinement for Front-End Algorithms
Authors:Sirui Li, Shuai Wang, Zhijun Liu, Zhongjie Jiang, Yannan Wang, Haizhou Li
Speech pre-processing techniques such as denoising, de-reverberation, and separation, are commonly employed as front-ends for various downstream speech processing tasks. However, these methods can sometimes be inadequate, resulting in residual noise or the introduction of new artifacts. Such deficiencies are typically not captured by metrics like SI-SNR but are noticeable to human listeners. To address this, we introduce SpeechRefiner, a post-processing tool that utilizes Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) to improve the perceptual quality of speech. In this study, we benchmark SpeechRefiner against recent task-specific refinement methods and evaluate its performance within our internal processing pipeline, which integrates multiple front-end algorithms. Experiments show that SpeechRefiner exhibits strong generalization across diverse impairment sources, significantly enhancing speech perceptual quality. Audio demos can be found at https://speechrefiner.github.io/SpeechRefiner/.
语音预处理技术,如降噪、去混响和分离等,通常被用作各种下游语音处理任务的前端。然而,这些方法有时可能不够充分,导致残留噪声或引入新的失真。这些缺陷通常不会被SI-SNR等指标所捕获,但对于人类听众来说是显而易见的。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SpeechRefiner,这是一种后处理工具,它利用条件流匹配(CFM)来提高语音的感知质量。在这项研究中,我们将SpeechRefiner与最新的特定任务细化方法进行了基准测试,并在我们的集成多个前端算法的内部处理管道中评估了其性能。实验表明,SpeechRefiner在不同来源的缺陷上具有强大的泛化能力,显著提高了语音感知质量。音频演示可在https://speechrefiner.github.io/SpeechRefiner/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary:为提高语音感知质量,推出了一种名为SpeechRefiner的后处理工具,采用条件流匹配(CFM)技术,针对语音预处理技术如降噪、去混响和分离等存在的缺陷进行改善。相较于近期特定的任务优化方法,SpeechRefiner在内部处理管道中表现出强大的泛化能力,能应对多种不同的损伤来源,显著提升语音感知质量。详情可访问链接了解。
Key Takeaways:
- 语音预处理技术如降噪、去混响和分离等是下游语音处理任务的前端,但存在不足,可能产生残余噪声或新引入的伪迹。
- SpeechRefiner是一种后处理工具,采用条件流匹配(CFM)技术改善语音感知质量。
- SpeechRefiner相较于近期特定的任务优化方法表现出强大的泛化能力。
- SpeechRefiner能有效应对多种不同的语音损伤来源。
- SpeechRefiner能显著提升语音感知质量,其效果可通过音频演示进行展示。
- SpeechRefiner工具的内部处理管道集成了多种前端算法。
点此查看论文截图

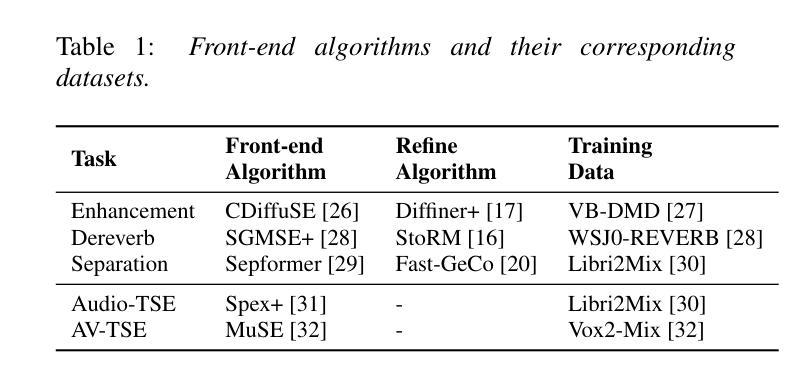
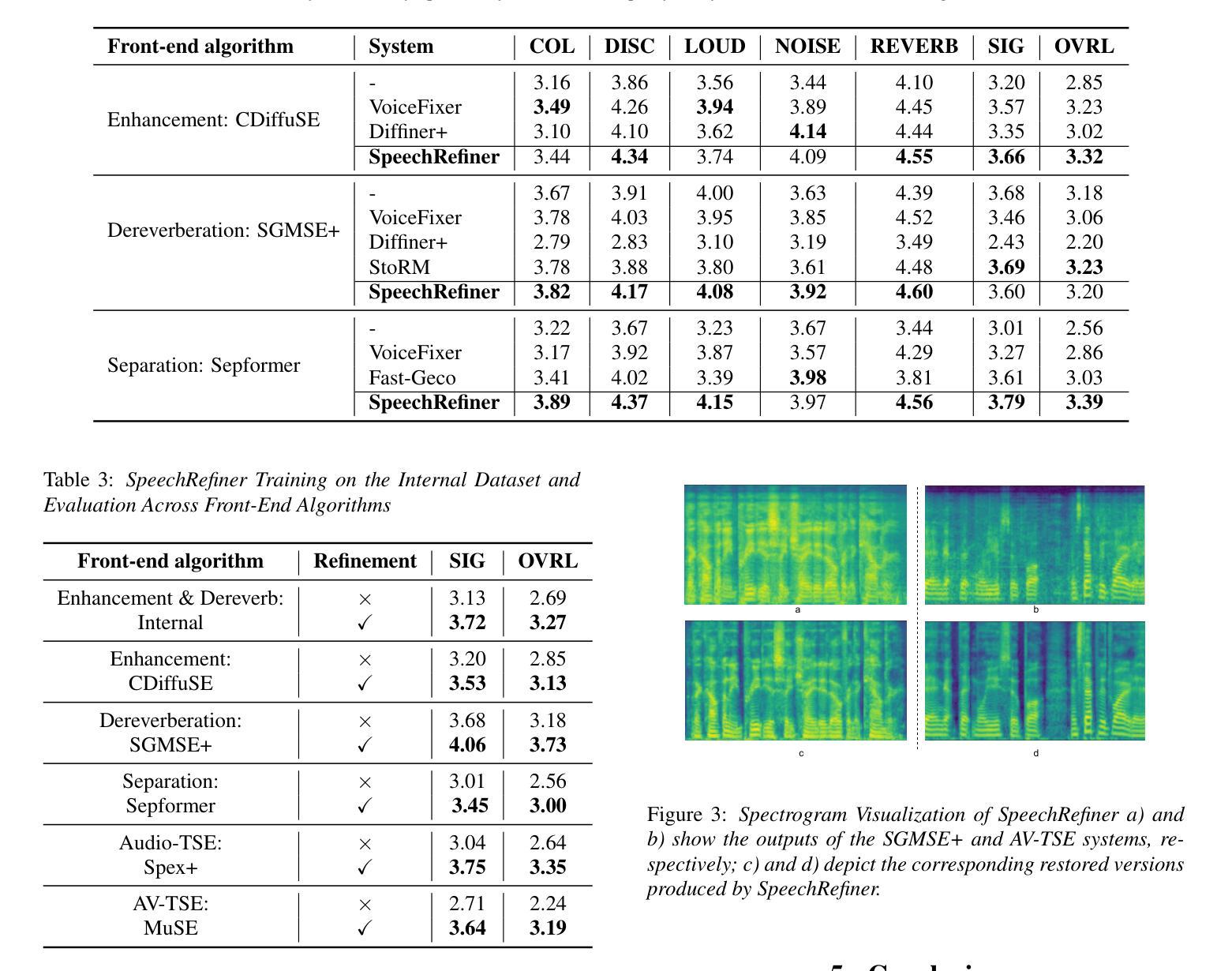
Qwen vs. Gemma Integration with Whisper: A Comparative Study in Multilingual SpeechLLM Systems
Authors:Tuan Nguyen, Long-Vu Hoang, Huy-Dat Tran
This paper presents our system for the MLC-SLM Challenge 2025, focusing on multilingual speech recognition and language modeling with large language models (LLMs). Our approach combines a fine-tuned Whisper-large-v3 encoder with efficient projector architectures and various decoder configurations. We employ a three-stage training methodology that progressively optimizes the encoder, projector, and LLM components. Our system achieves competitive performance with a private test average WER/CER result of 16.63% using the Gemma3-12B and 18.6% using the Qwen2.5-7B as decoder-only language model.
本文介绍了我们为MLC-SLM挑战2025设计的系统,主要侧重于使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行多语种语音识别和语言建模。我们的方法结合了经过微调后的Whisper-large-v3编码器、高效的投影仪架构和各种解码器配置。我们采用三阶段训练方法,逐步优化编码器、投影仪和LLM组件。我们的系统使用仅解码器语言模型Gemma3-12B取得了具有竞争力的性能表现,平均单词错误率(WER)/字符错误率(CER)为16.63%,使用Qwen2.5-7B时的性能为18.6%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report for Interspeech 2025 MLC-SLM Challenge
Summary
本文介绍了针对MLC-SLM挑战2025的系统,重点研究多语种语音识别和语言建模。本系统结合了微调过的Whisper-large-v3编码器、高效投影架构以及多种解码器配置。采用三阶段训练方法,逐步优化编码器、投影器和大模型组件。系统在仅使用解码器语言模型的情况下取得了具有竞争力的性能表现,使用Gemma3-12B模型时的私有测试平均WER/CER结果为16.63%,使用Qwen2.5-7B模型时为18.6%。
Key Takeaways
- 系统针对MLC-SLM挑战,研究多语种语音识别和语言建模。
- 结合微调过的编码器、高效投影架构和多种解码器配置。
- 采用三阶段训练方法优化系统组件。
- 系统使用解码器语言模型取得了具有竞争力的性能表现。
- 使用Gemma3-12B模型时,私有测试平均WER/CER结果为16.63%。
- 使用Qwen2.5-7B模型时,性能表现略有不同。
点此查看论文截图

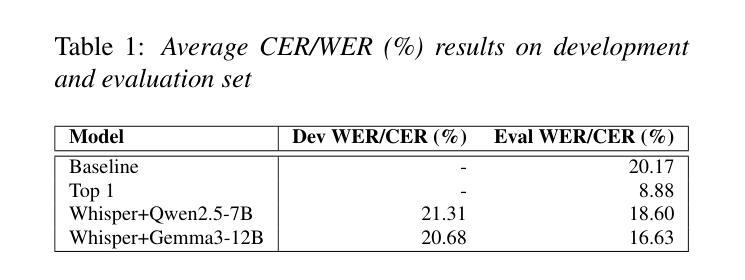
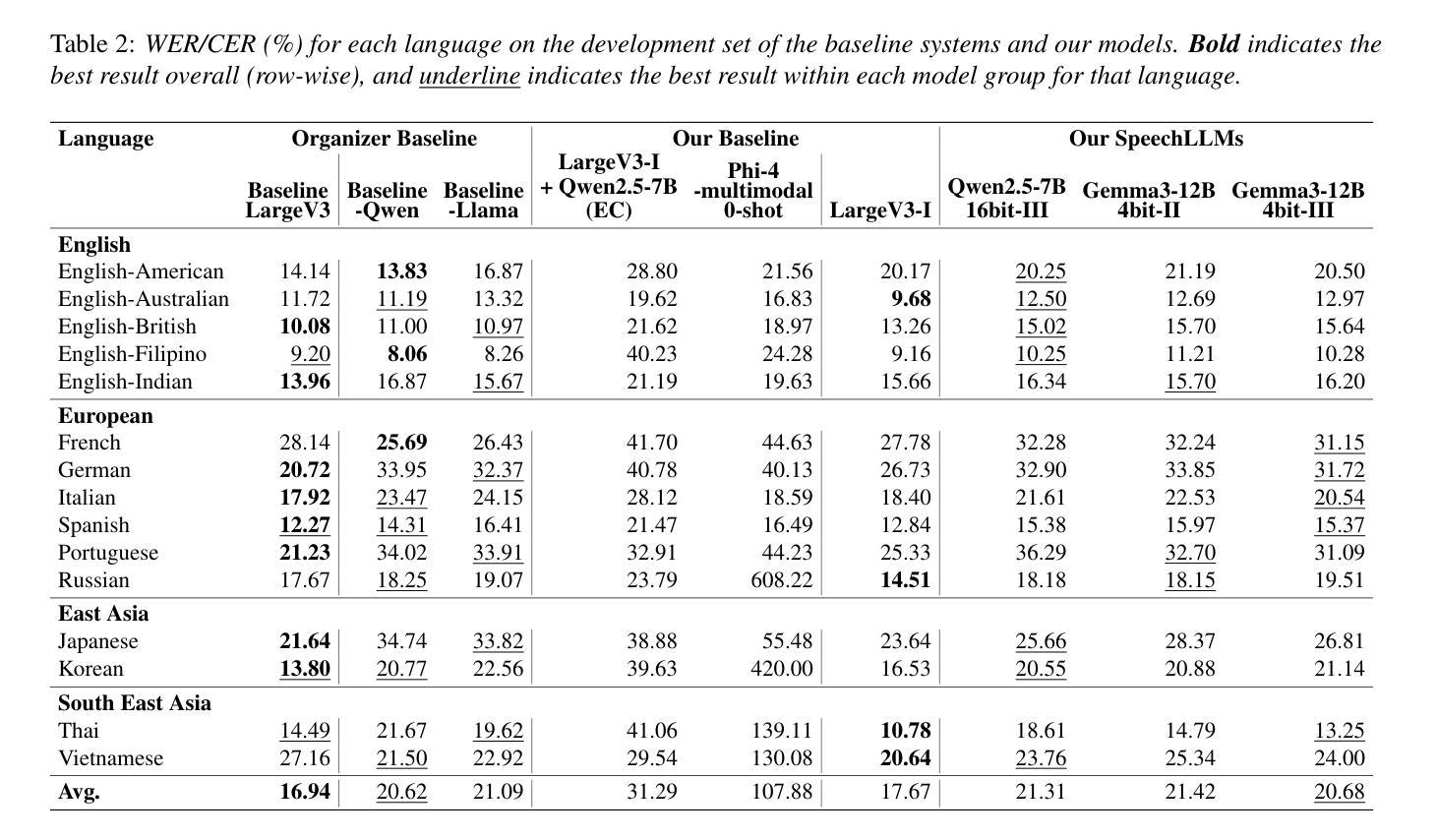
BUT System for the MLC-SLM Challenge
Authors:Alexander Polok, Jiangyu Han, Dominik Klement, Samuele Cornell, Jan Černocký, Lukáš Burget
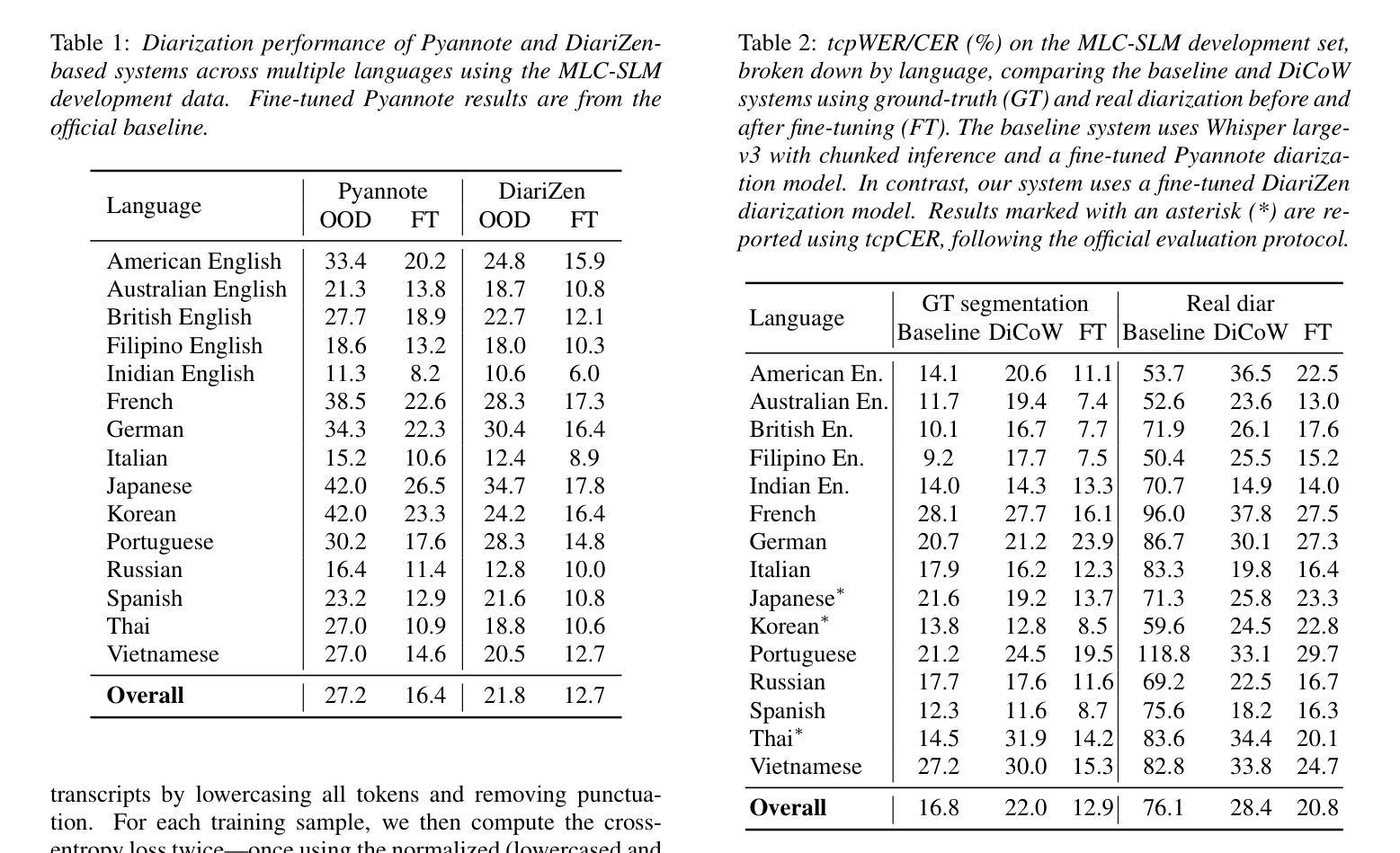
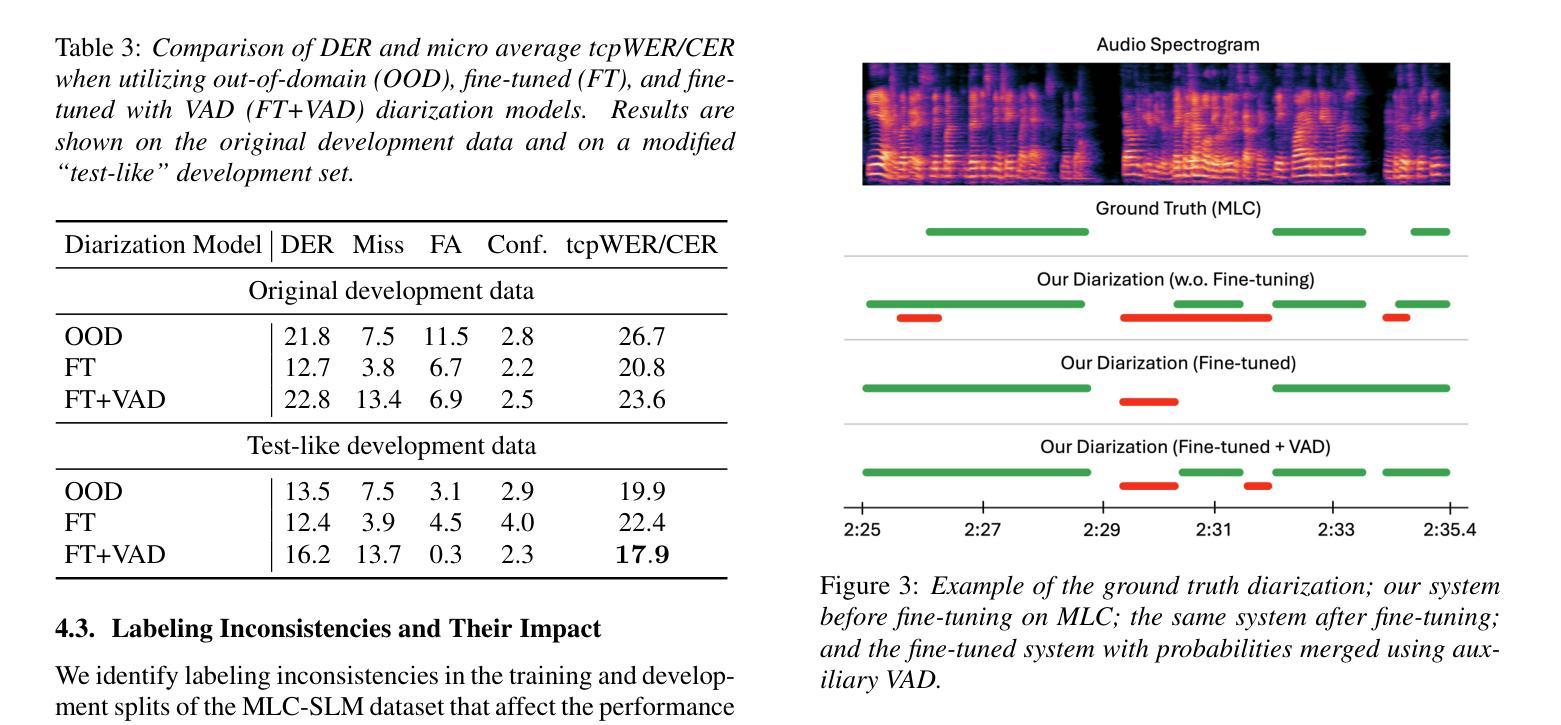
We present a two-speaker automatic speech recognition (ASR) system that combines DiCoW – a diarization-conditioned variant of Whisper – with DiariZen, a diarization pipeline built on top of Pyannote. We first evaluate both systems in out-of-domain (OOD) multilingual scenarios without any fine-tuning. In this scenario, DiariZen consistently outperforms the baseline Pyannote diarization model, demonstrating strong generalization. Despite being fine-tuned on English-only data for target-speaker ASR, DiCoW retains solid multilingual performance, indicating that encoder modifications preserve Whisper’s multilingual capabilities. We then fine-tune both DiCoW and DiariZen on the MLC-SLM challenge data. The fine-tuned DiariZen continues to outperform the fine-tuned Pyannote baseline, while DiCoW sees further gains from domain adaptation. Our final system achieves a micro-average tcpWER/CER of 16.75% and ranks second in Task 2 of the MLC-SLM challenge. Lastly, we identify several labeling inconsistencies in the training data – such as missing speech segments and incorrect silence annotations – which can hinder diarization fine-tuning. We propose simple mitigation strategies to address these issues and improve system robustness.
我们提出了一种结合DiCoW(一种基于Whisper的说话人分割条件变体)和DiariZen(一种基于Pyannote的说话人分割管道)的双人自动语音识别(ASR)系统。我们首先在没有进行任何微调的情况下,在跨领域(OOD)多语言场景中对两个系统进行了评估。在这种情况下,DiariZen始终优于基准Pyannote说话人分割模型,显示出强大的泛化能力。尽管DiCoW是针对目标说话人ASR的英语唯一数据进行微调,但它仍具有强大的多语言能力,表明编码器修改保留了Whisper的多语言能力。然后我们对DiCoW和DiariZen进行了MLC-SLM挑战数据的微调。经过微调后,DiariZen继续超越经过微调Pyannote基准线,而DiCoW从域适应中看到了进一步的收益。我们的最终系统达到了16.75%的微观平均tcpWER/CER,并在MLC-SLM挑战的第二项任务中获得了第二名。最后,我们发现了训练数据中存在若干标签不一致的问题,如缺失语音片段和错误的静音注释等,这些问题可能会阻碍说话人分割的微调。我们提出了一些简单的缓解策略来解决这些问题并提高系统的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合DiCoW和DiariZen的两人自动语音识别(ASR)系统。在跨领域多语言场景下,DiariZen表现出强大的泛化能力,相较于基线Pyannote模型有更好的表现。DiCoW在不需要针对目标说话者ASR进行微调的情况下,仍能保持强大的多语言能力。在MLC-SLM挑战数据上进行微调后,DiariZen继续优于经过调整的Pyannote模型,而DiCoW从领域适应中获得了进一步的提升。最终系统取得了第二名的成绩。同时,文章还指出了训练数据中存在的一些标注不一致问题,并提出了简单的缓解策略来提高系统的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了结合DiCoW和DiariZen的两人自动语音识别(ASR)系统。
- DiariZen在跨领域多语言场景下表现出强大的泛化能力,优于基线Pyannote模型。
- DiCoW具有强大的多语言能力,在不需要针对目标说话者ASR进行微调的情况下仍能良好运行。
- 经过在MLC-SLM挑战数据上的微调,DiariZen继续优于Pyannote模型,而DiCoW获得了进一步的性能提升。
- 最终系统取得了第二名的好成绩。
- 文中指出了训练数据存在的标注不一致问题,如缺失语音段和错误的静音注释。
点此查看论文截图

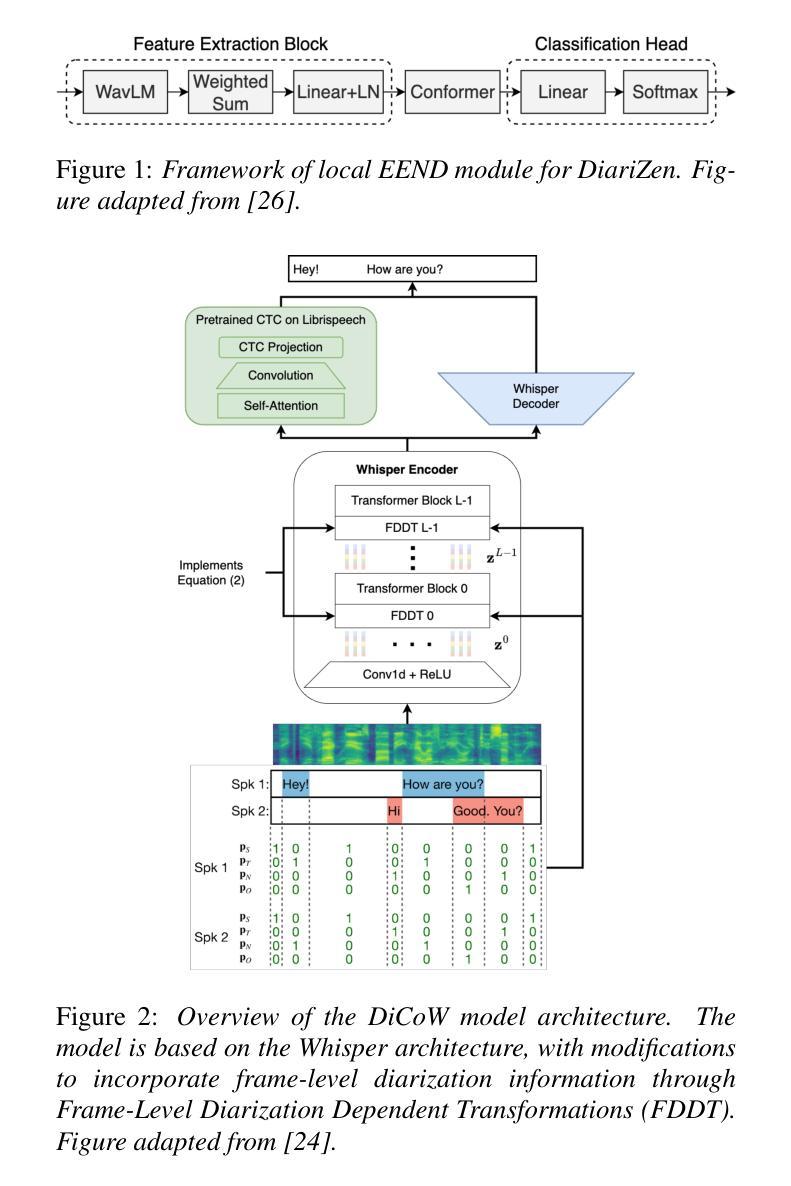
Bi-directional Context-Enhanced Speech Large Language Models for Multilingual Conversational ASR
Authors:Yizhou Peng, Hexin Liu, Eng Siong Chng
This paper introduces the integration of language-specific bi-directional context into a speech large language model (SLLM) to improve multilingual continuous conversational automatic speech recognition (ASR). We propose a character-level contextual masking strategy during training, which randomly removes portions of the context to enhance robustness and better emulate the flawed transcriptions that may occur during inference. For decoding, a two-stage pipeline is utilized: initial isolated segment decoding followed by context-aware re-decoding using neighboring hypotheses. Evaluated on the 1500-hour Multilingual Conversational Speech and Language Model (MLC-SLM) corpus covering eleven languages, our method achieves an 18% relative improvement compared to a strong baseline, outperforming even the model trained on 6000 hours of data for the MLC-SLM competition. These results underscore the significant benefit of incorporating contextual information in multilingual continuous conversational ASR.
本文介绍了将特定语言的双向上下文集成到语音大语言模型(SLLM)中,以提高跨语言连续对话自动语音识别(ASR)的效果。我们提出了一种字符级上下文掩码策略,在训练过程中随机移除部分上下文,以增强模型的稳健性并更好地模拟推理过程中可能出现的错误转录。在解码方面,我们采用了两阶段流程:首先是初步的独立分段解码,然后是使用相邻假设进行上下文感知的重新解码。在涵盖十一种语言的1500小时多语言对话语音和语言模型(MLC-SLM)语料库上进行了评估,我们的方法与强大的基线相比,实现了18%的相对改进,甚至超越了为MLC-SLM竞赛训练的6000小时模型的性能。这些结果强调了在多语言连续对话ASR中加入上下文信息的重大益处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Interspeech 2025 MLC-SLM workshop as a Research Paper
总结
本文介绍了一种将语言特定双向上下文集成到语音大语言模型(SLLM)中的方法,以改进多语种连续对话自动语音识别(ASR)。通过训练过程中的字符级上下文掩码策略,随机移除部分上下文以增强模型的稳健性,并更好地模拟推理过程中可能出现的错误转录。解码采用两阶段流程:先进行初步的独立分段解码,然后使用相邻假设进行上下文感知的再解码。在涵盖11种语言的Multilingual Conversational Speech and Language Model(MLC-SLM)语料库上进行评估,该方法相对于表现良好的基线模型实现了相对改进率18%,甚至在MLC-SLM竞赛中表现优于经过6000小时数据训练的模型。这些结果突显了在多语种连续对话ASR中融入上下文信息的显著优势。
要点
- 引入语言特定双向上下文到语音大语言模型中,旨在改进多语种连续对话自动语音识别(ASR)。
- 训练过程中采用字符级上下文掩码策略,随机移除部分上下文以增强模型的稳健性。
- 通过模拟推理过程中可能出现的错误转录,提高模型的实用性。
- 采用两阶段解码流程:初步独立分段解码后,进行上下文感知的再解码。
- 在MLC-SLM语料库上的实验表明,该方法相对于基线模型有显著的相对改进率。
- 与经过更多数据训练的模型相比,该方法在多语种连续对话ASR任务上表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

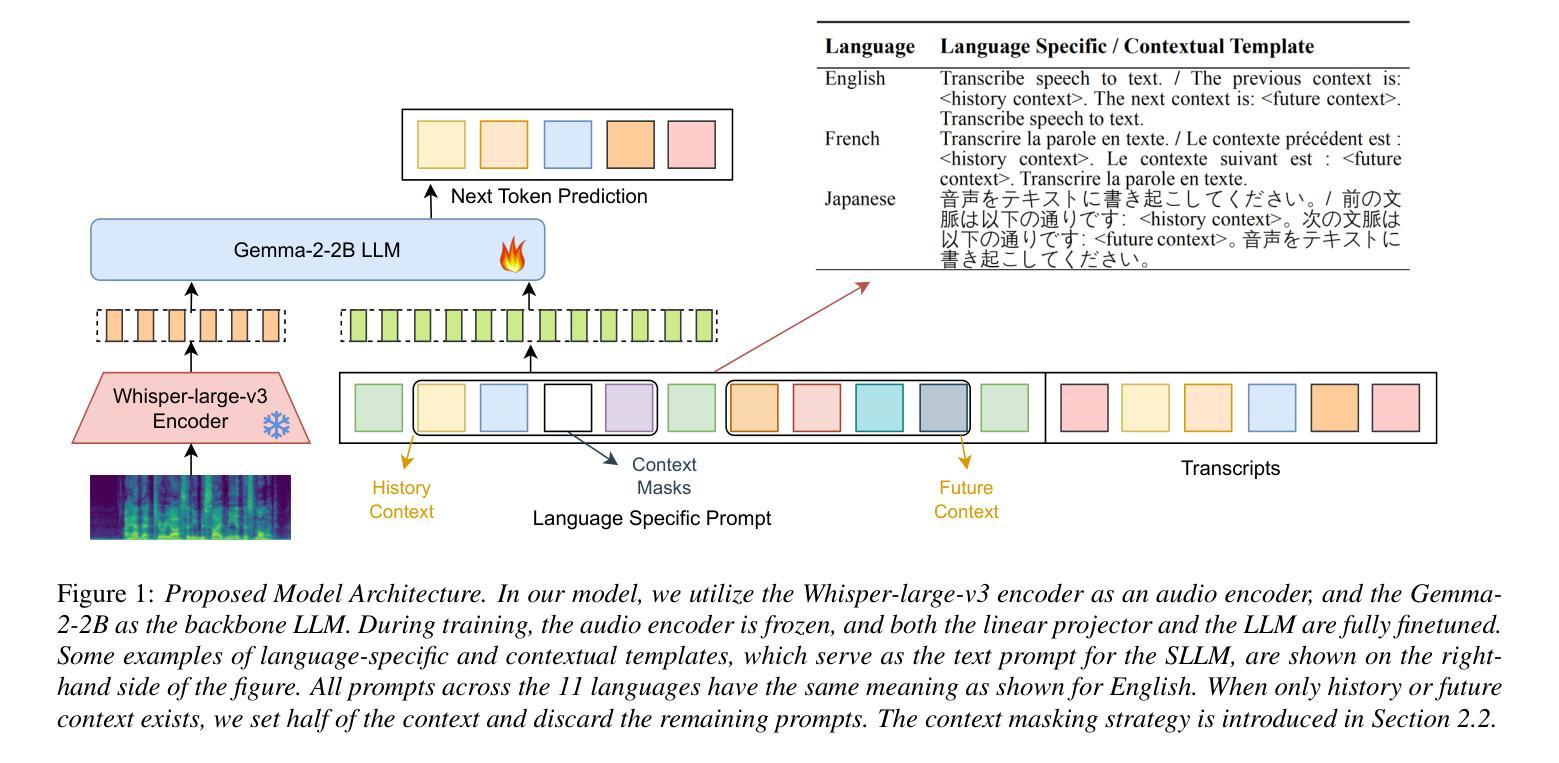

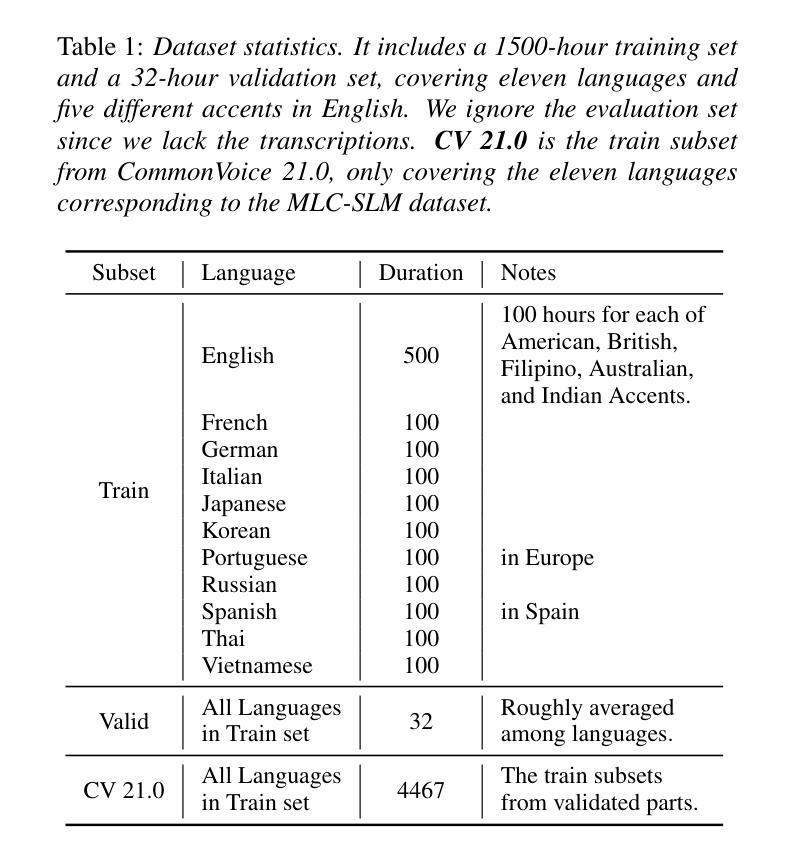
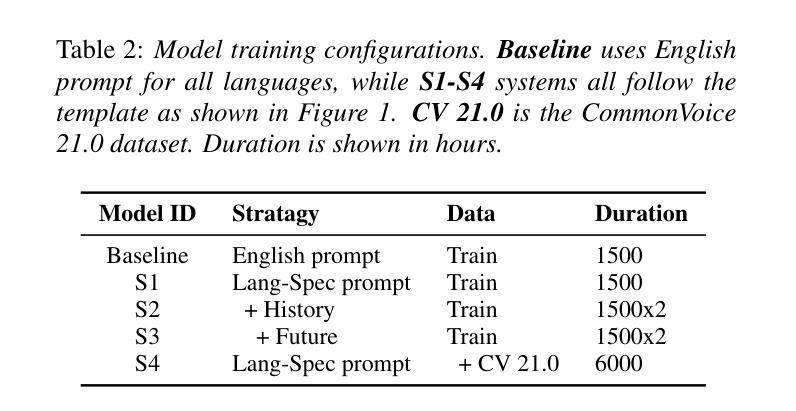
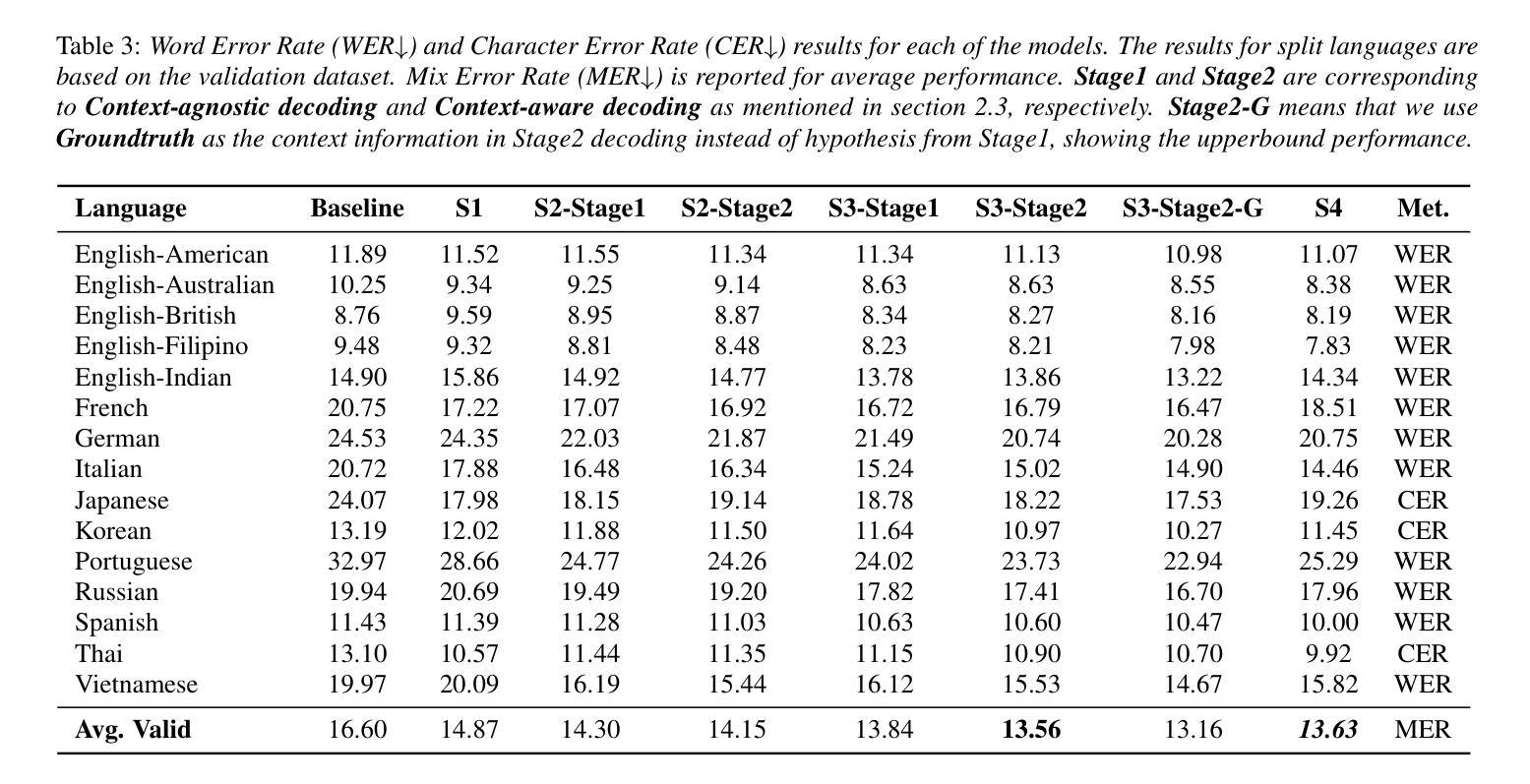
NTU Speechlab LLM-Based Multilingual ASR System for Interspeech MLC-SLM Challenge 2025
Authors:Yizhou Peng, Bin Wang, Yi-Wen Chao, Ziyang Ma, Haoyang Zhang, Hexin Liu, Xie Chen, Eng Siong Chng
This report details the NTU Speechlab system developed for the Interspeech 2025 Multilingual Conversational Speech and Language Model (MLC-SLM) Challenge (Task I), where we achieved 5th place. We present comprehensive analyses of our multilingual automatic speech recognition system, highlighting key advancements in model architecture, data selection, and training strategies. In particular, language-specific prompts and model averaging techniques were instrumental in boosting system performance across diverse languages. Compared to the initial baseline system, our final model reduced the average Mix Error Rate from 20.2% to 10.6%, representing an absolute improvement of 9.6% (a relative improvement of 48%) on the evaluation set. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach and offer practical insights for future Speech Large Language Models.
本报告详细介绍了为Interspeech 2025多语种对话语音和语言模型(MLC-SLM)挑战赛(任务一)开发的NTU Speechlab系统,我们在比赛中取得了第五名。我们对我们的多语种自动语音识别系统进行了全面的分析,重点介绍了模型架构、数据选择和训练策略方面的关键进展。特别是,语言特定的提示和模型平均技术对提高系统在多种语言中的性能起到了关键作用。与初始基线系统相比,我们的最终模型将平均混合错误率从20.2%降低到10.6%,在评估集上实现了绝对改进9.6%(相对改进48%)。我们的结果证明了我们的方法的有效性,并为未来的语音大语言模型提供了实际见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Interspeech 2025 MLC-SLM challenge (5th place). System report
Summary
这是一份关于NTU Speechlab系统为Interspeech 2025多语种对话语音和语言模型(MLC-SLM)挑战任务设计的详细报告。本报告全面分析了我们的多语种自动语音识别系统的主要进步,如模型架构、数据选择及训练策略等。与初始基线系统相比,最终模型在测试集上将平均混合错误率降低了近一半,这体现了该方法的有效性。它为未来大型语言模型的构建提供了实用的见解。该系统成功在比赛中取得了第五名的好成绩。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于文本内容的七个关键见解:
- NTU Speechlab系统针对Interspeech 2025的多语种对话语音和语言模型挑战进行了系统设计。
- 系统分析涵盖了模型架构、数据选择和训练策略等重要方面。
- 语言特定提示和模型平均技术对于提高多语种系统的性能起到了关键作用。
- 与初始基线系统相比,最终模型的平均混合错误率降低了9.6%,相对改善率为48%。
- 该系统在比赛中取得了第五名的好成绩。
- 此方法的有效性为未来的语音大型语言模型构建提供了实践指导。
点此查看论文截图

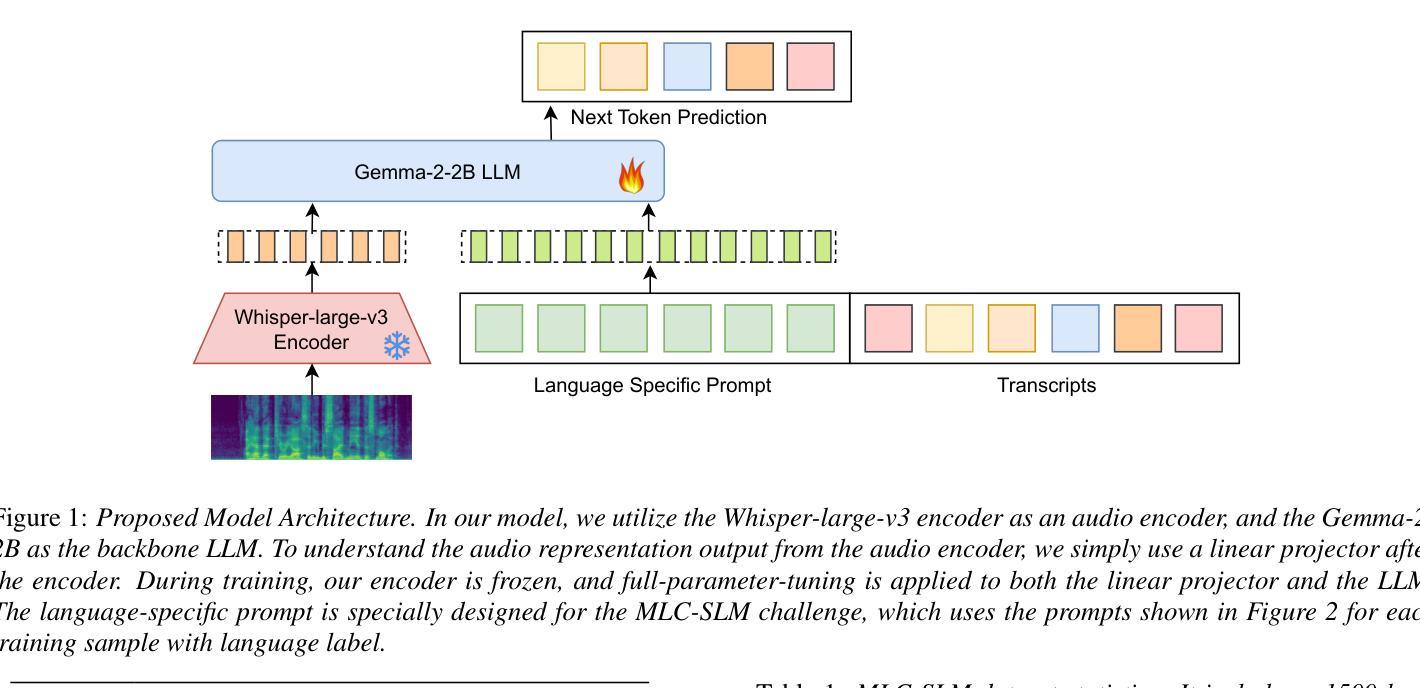

Seewo’s Submission to MLC-SLM: Lessons learned from Speech Reasoning Language Models
Authors:Bo Li, Chengben Xu, Wufeng Zhang
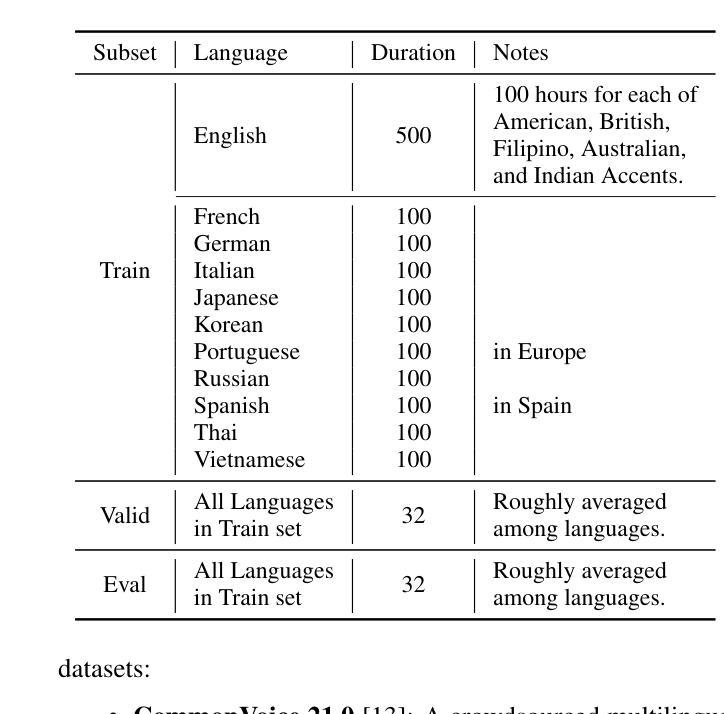
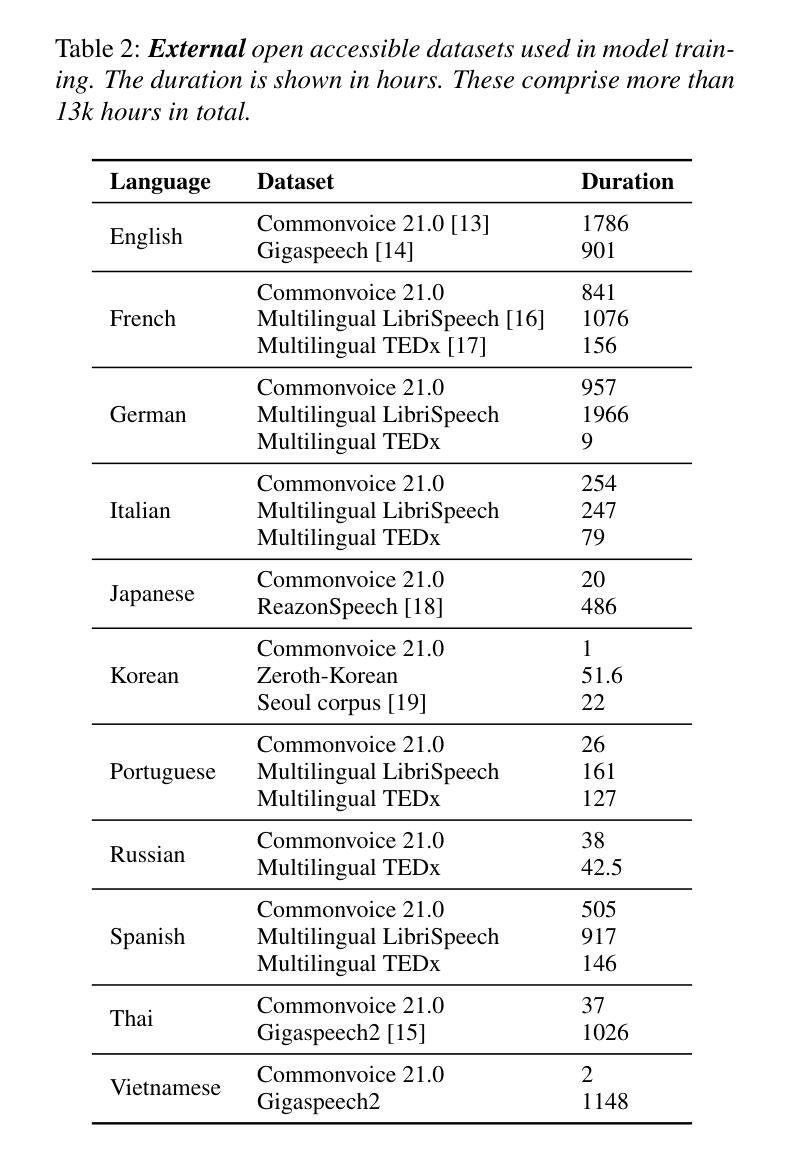
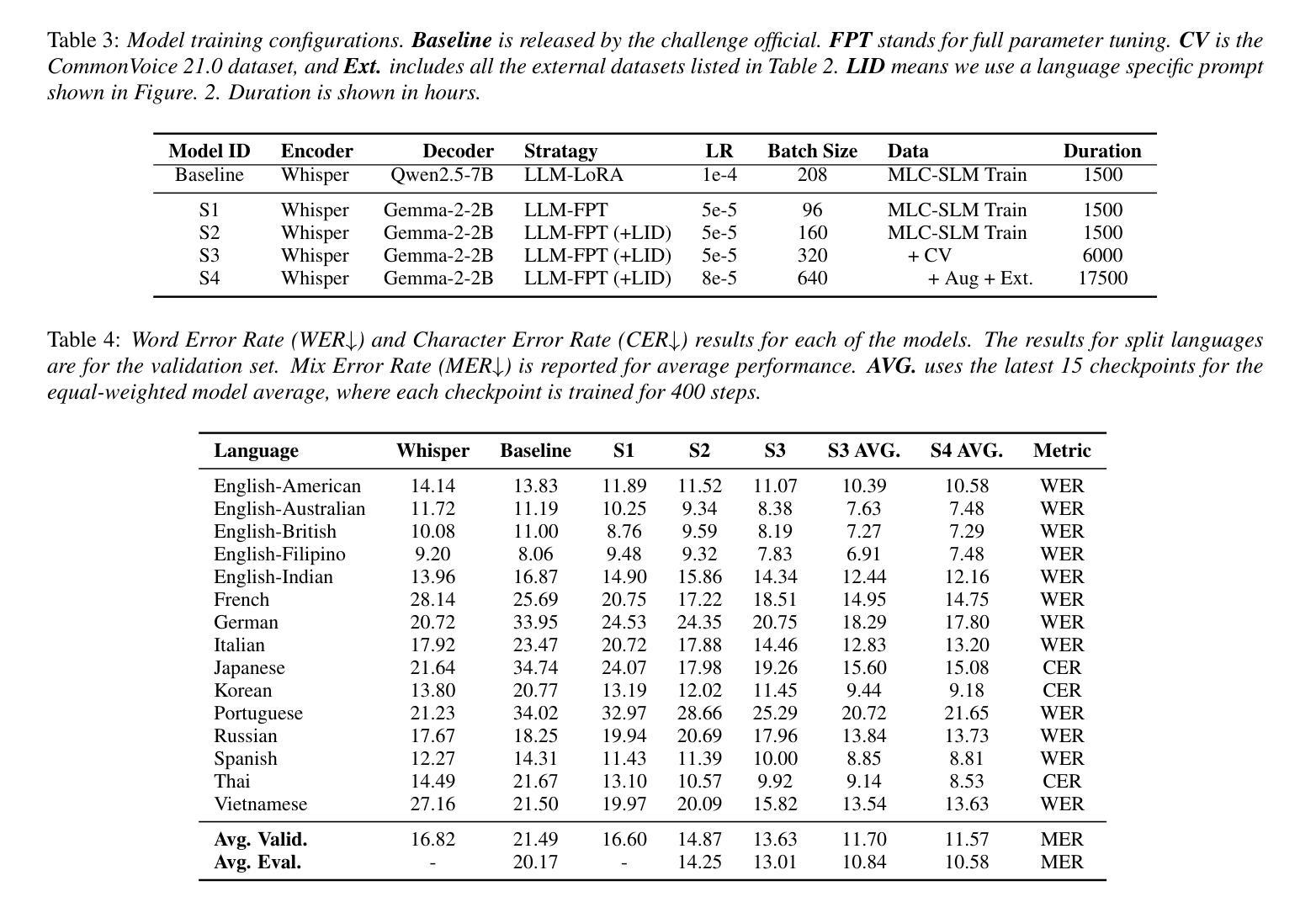
This paper presents Seewo’s systems for both tracks of the Multilingual Conversational Speech Language Model Challenge (MLC-SLM), addressing automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speaker diarization with ASR (SD-ASR). We introduce a multi-stage training pipeline that explicitly enhances reasoning and self-correction in speech language models for ASR. Our approach combines curriculum learning for progressive capability acquisition, Chain-of-Thought data augmentation to foster intermediate reflection, and Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) to further refine self-correction through reward-driven optimization. This approach achieves substantial improvements over the official challenge baselines. On the evaluation set, our best system attains a WER/CER of 11.57% for Track 1 and a tcpWER/tcpCER of 17.67% for Track 2. Comprehensive ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of each component under challenge constraints.
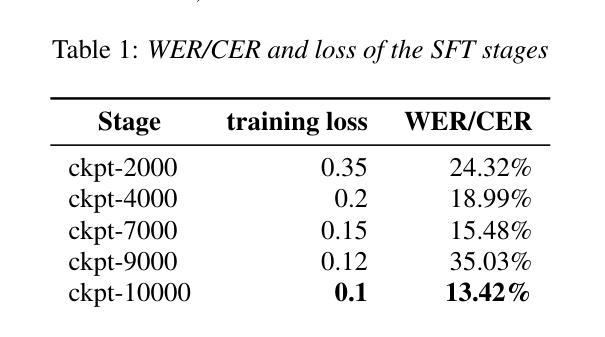
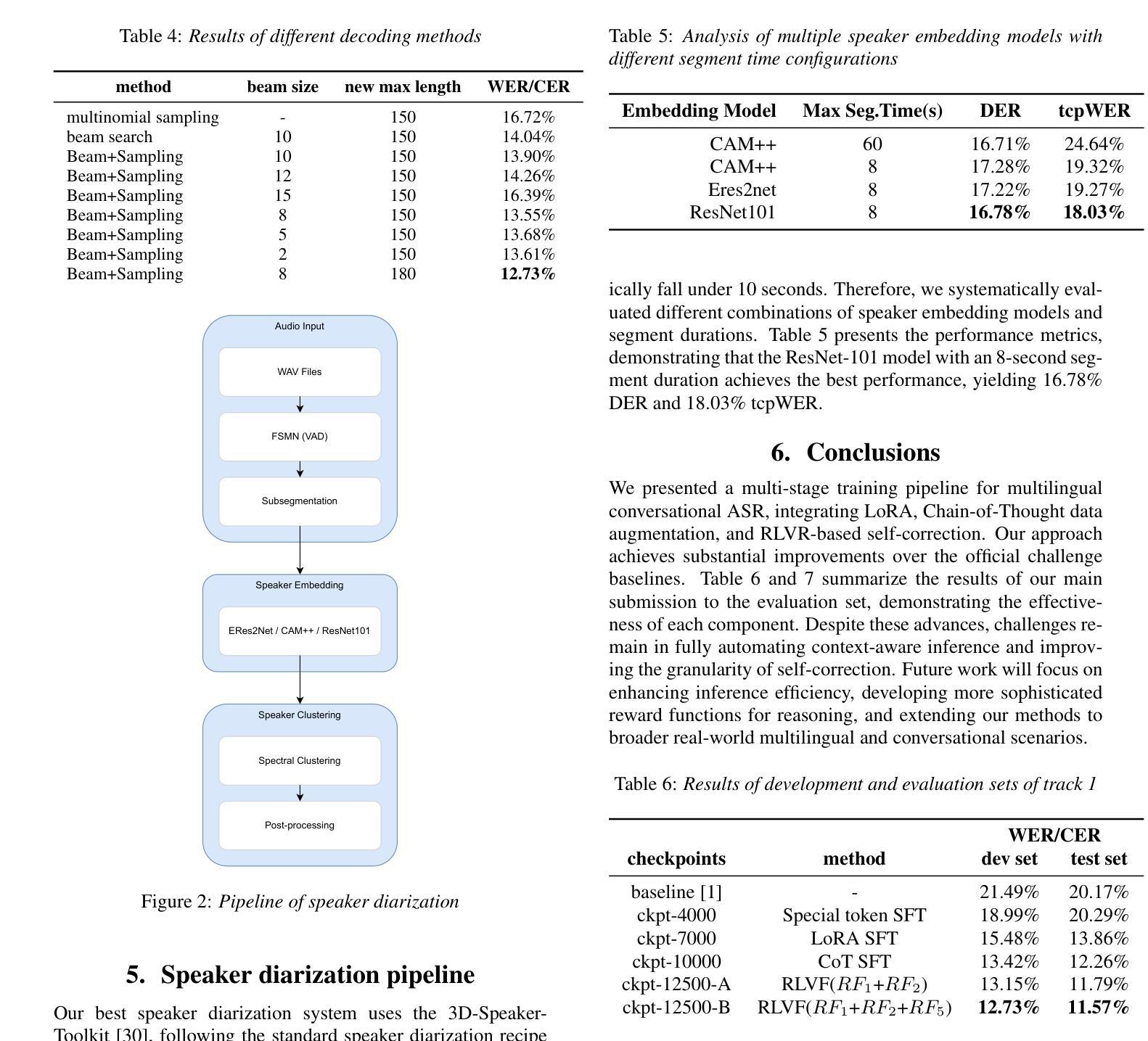
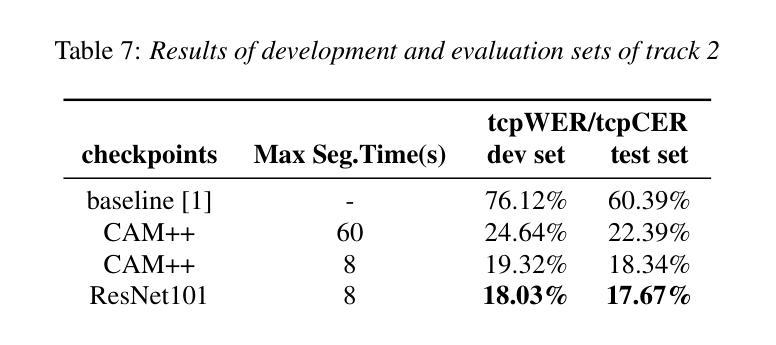
本文介绍了Seewo在多元语言对话语音语言模型挑战(MLC-SLM)的两个赛道中的系统,涵盖了自动语音识别(ASR)和带有ASR的说话人日记化(SD-ASR)。我们引入了一个多阶段训练流程,该流程在语音语言模型中显式增强推理和自我校正功能,以用于ASR。我们的方法结合了课程学习以逐步获取能力、思维链数据增强以促进中间反思,以及可验证奖励强化学习(RLVR),通过奖励驱动优化进一步改进自我校正。该方法在官方挑战基线的基础上取得了重大改进。在评估集上,我们最好的系统在第1赛道上达到了11.57%的WER/CER,在第2赛道上达到了17.67%的tcpWER/tcpCER。全面的消融研究证明了每个组件在挑战约束下的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了Seewo在Multilingual Conversational Speech Language Model Challenge(MLC-SLM)中的两个赛道(自动语音识别(ASR)和带有ASR的说话人分块化(SD-ASR))的系统。文章提出了一种多阶段训练管道,旨在提高语音语言模型中的推理和自纠错能力。结合课程学习实现渐进能力获取,利用Chain-of-Thought数据进行增强以推动中间阶段的反思,并通过强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)进一步通过奖励驱动优化进行自纠错。此方法相较于官方挑战基线有显著改善,最佳系统在评估集上的表现达到Track 1的WER/CER为11.57%,Track 2的tcpWER/tcpCER为17.67%。全面的消融研究证明了在挑战约束下每个组件的有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- Seewo提出的多阶段训练管道用于增强语音语言模型的推理和自纠错能力。
- 通过课程学习实现渐进能力获取。
- 采用Chain-of-Thought数据增强推动中间阶段反思。
- 强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)用于优化自纠错能力。
- 该方法在多语种对话语音语言模型挑战中实现了显著成果,较官方基线有显著改善。
- 最佳系统表现优异,Track 1的WER/CER为11.57%,Track 2的tcpWER/tcpCER为17.67%。
点此查看论文截图


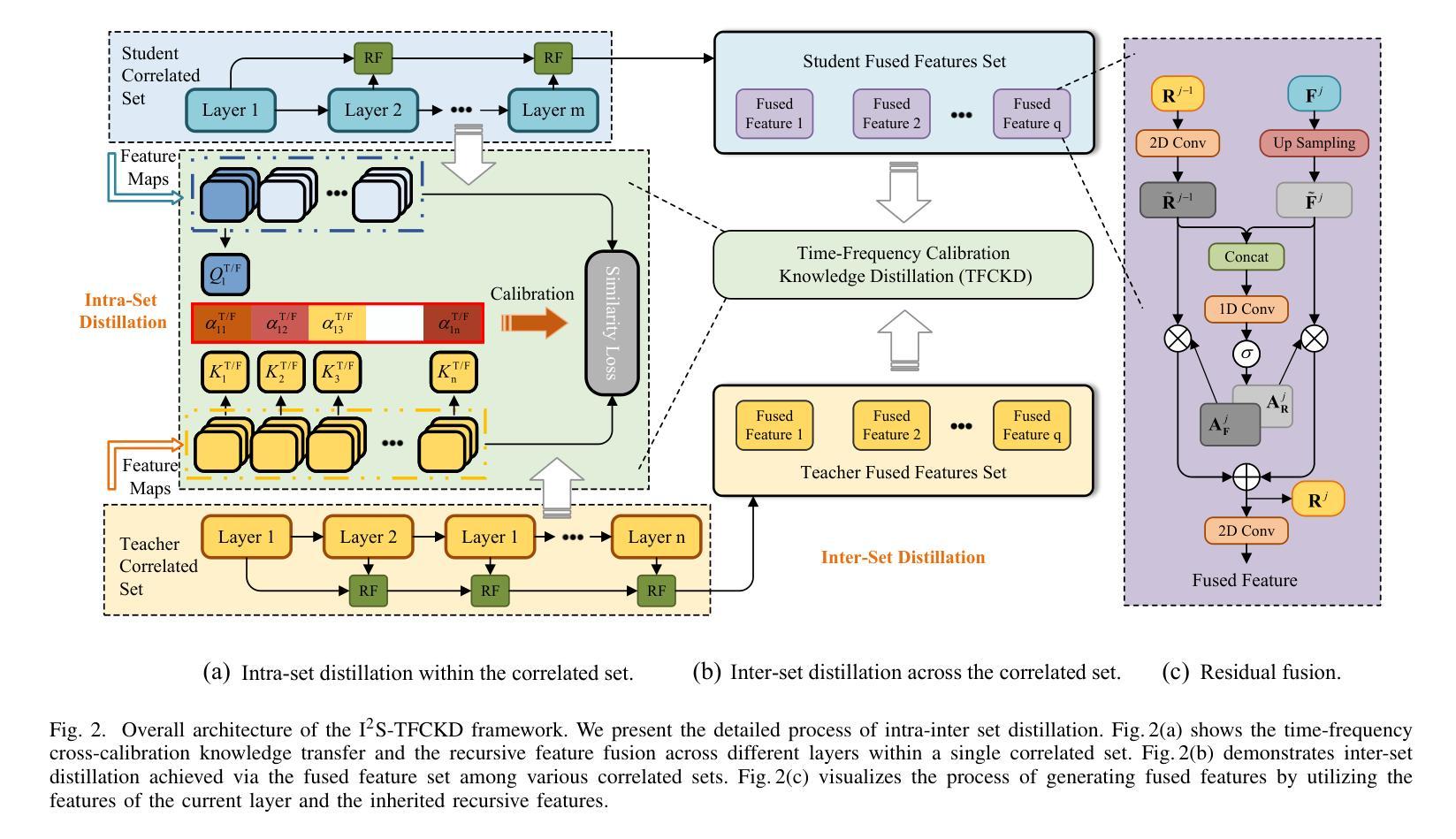
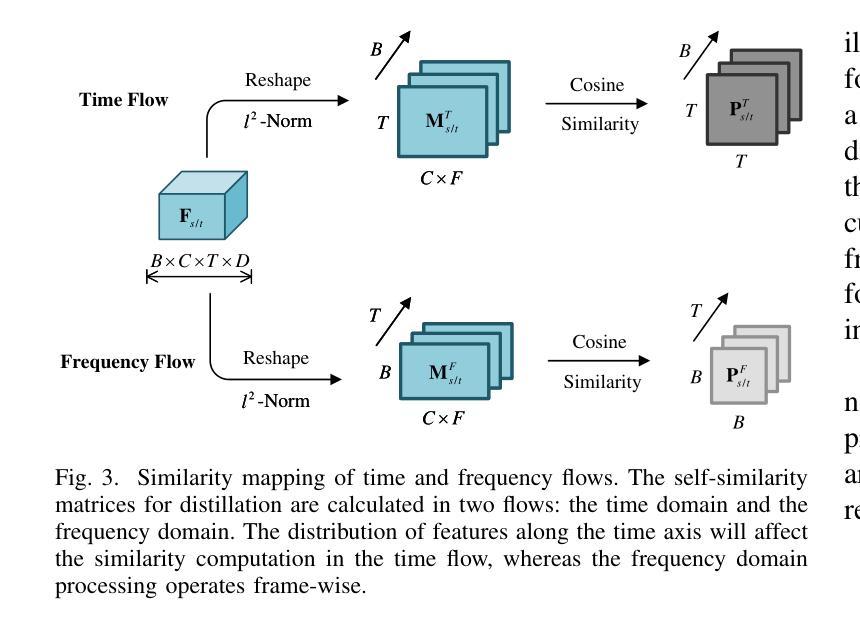
I$^2$S-TFCKD: Intra-Inter Set Knowledge Distillation with Time-Frequency Calibration for Speech Enhancement
Authors:Jiaming Cheng, Ruiyu Liang, Chao Xu, Ye Ni, Wei Zhou, Björn W. Schuller, Xiaoshuai Hao
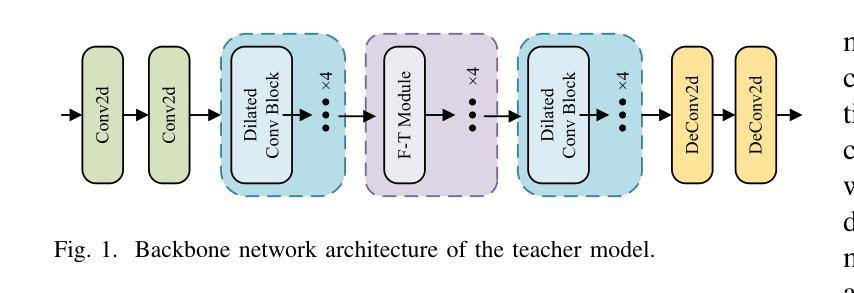
In recent years, complexity compression of neural network (NN)-based speech enhancement (SE) models has gradually attracted the attention of researchers, especially in scenarios with limited hardware resources or strict latency requirements. The main difficulties and challenges lie in achieving a balance between complexity and performance according to the characteristics of the task. In this paper, we propose an intra-inter set knowledge distillation (KD) framework with time-frequency calibration (I$^2$S-TFCKD) for SE. Different from previous distillation strategies for SE, the proposed framework fully utilizes the time-frequency differential information of speech while promoting global knowledge flow. Firstly, we propose a multi-layer interactive distillation based on dual-stream time-frequency cross-calibration, which calculates the teacher-student similarity calibration weights in the time and frequency domains respectively and performs cross-weighting, thus enabling refined allocation of distillation contributions across different layers according to speech characteristics. Secondly, we construct a collaborative distillation paradigm for intra-set and inter-set correlations. Within a correlated set, multi-layer teacher-student features are pairwise matched for calibrated distillation. Subsequently, we generate representative features from each correlated set through residual fusion to form the fused feature set that enables inter-set knowledge interaction. The proposed distillation strategy is applied to the dual-path dilated convolutional recurrent network (DPDCRN) that ranked first in the SE track of the L3DAS23 challenge. Objective evaluations demonstrate that the proposed KD strategy consistently and effectively improves the performance of the low-complexity student model and outperforms other distillation schemes.
近年来,神经网络(NN)基于的语音增强(SE)模型的复杂度压缩逐渐引起了研究人员的关注,特别是在硬件资源有限或延迟要求严格的情况下。主要的困难和挑战在于根据任务特点在复杂度和性能之间取得平衡。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于时间频率校准的组内组间知识蒸馏(I$^2$S-TFCKD)框架,用于语音增强。不同于以前的SE知识蒸馏策略,所提出的框架充分利用了语音的时间频率差异信息,同时促进了全局知识流。首先,我们提出了一种基于双流时间频率交叉校准的多层交互蒸馏方法,该方法分别在时间和频率域计算教师学生相似度校准权重,并执行交叉加权,从而能够根据语音特征在不同的层之间精细分配蒸馏贡献。其次,我们构建了组内和组间相关性的协作蒸馏模式。在相关集合内,多层教师学生特征是成对匹配的,进行校准蒸馏。随后,我们通过残差融合生成每个相关集合的代表特征,形成融合特征集,从而实现组间知识交互。所提出的知识蒸馏策略应用于双路径膨胀卷积循环网络(DPDCRN),在L3DAS23挑战的SE赛道中排名第一。客观评估表明,所提出的知识蒸馏策略持续有效地提高了低复杂度学生模型的性能,并优于其他蒸馏方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
摘要
近年来,基于神经网络(NN)的语音增强(SE)模型的复杂度压缩逐渐引起研究人员的关注,特别是在硬件资源有限或延迟要求严格的情况下。主要难点和挑战在于根据任务特点在复杂度和性能之间取得平衡。本文提出了一种用于SE的基于时间频率校准的内外集合知识蒸馏(KD)框架(I$^2$S-TFCKD)。不同于以前的SE蒸馏策略,该框架充分利用语音的时间频率差异信息,同时促进全局知识流。首先,我们提出了一种基于双流时间频率交叉校准的多层交互蒸馏,分别计算时间和频率域的教师学生相似度校准权重,并执行交叉加权,从而根据语音特点在不同层上精细分配蒸馏贡献。其次,我们构建了用于内部和外部集合关系的协同蒸馏范式。在相关集合内,对多层教师学生特征进行配对校准蒸馏。然后我们通过残差融合生成各相关集合的特征表示,形成融合特征集,实现集合间的知识交互。所提出的蒸馏策略应用于双路径膨胀卷积循环网络(DPDCRN),在L3DAS23挑战的SE赛道中排名第一。客观评估表明,所提出KD策略持续有效地提高了低复杂度学生模型的性能并超越了其他蒸馏方案。
关键见解
- 神经网络的语音增强模型复杂度压缩是近年来的研究热点,特别是在硬件资源受限或延迟要求严格的场景下。
- 论文提出了一种新的知识蒸馏框架I$^2$S-TFCKD,用于SE模型,该框架能充分利用语音的时间频率差异信息。
- 论文采用多层交互蒸馏方法,基于双流时间频率交叉校准,根据语音特点在不同层上分配蒸馏贡献。
- 论文构建了内外集合关系的协同蒸馏范式,实现了集合间的知识交互。
- 提出的蒸馏策略被应用于DPDCRN模型,并在L3DAS23挑战的SE赛道中取得了第一名。
- 客观评估显示,该蒸馏策略提高了低复杂度学生模型的性能并超越了其他蒸馏方案。
点此查看论文截图


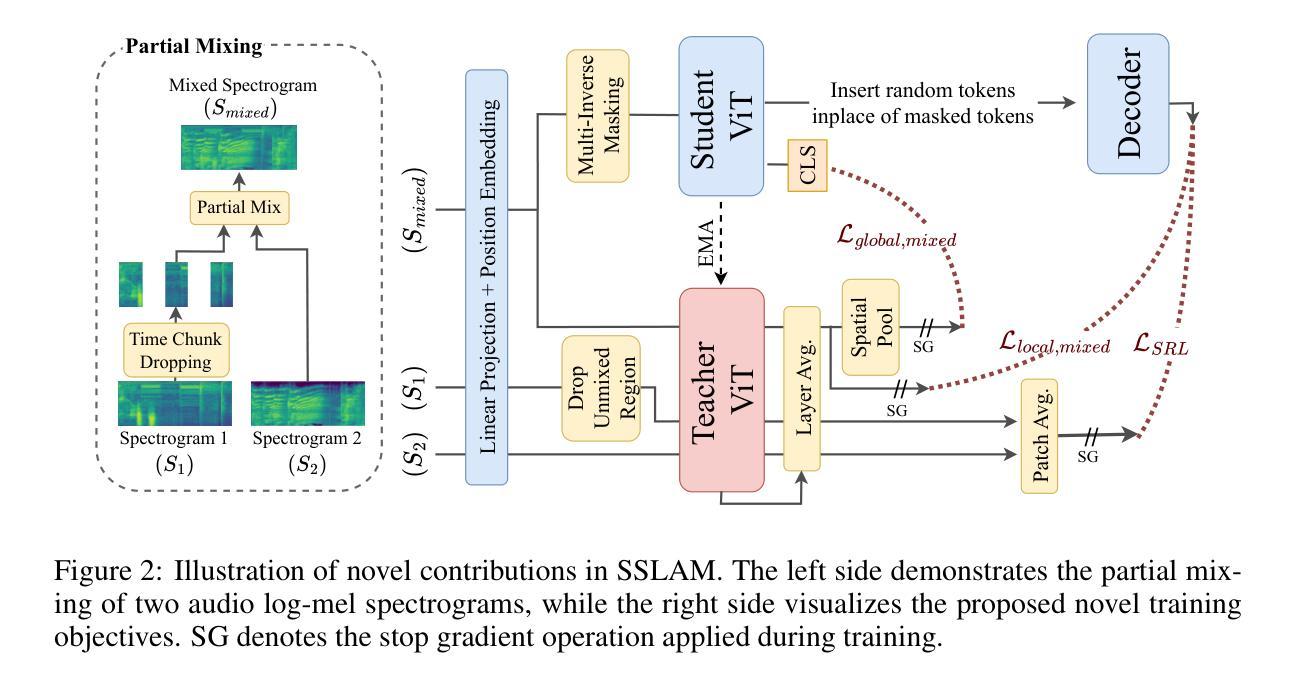
SSLAM: Enhancing Self-Supervised Models with Audio Mixtures for Polyphonic Soundscapes
Authors:Tony Alex, Sara Ahmed, Armin Mustafa, Muhammad Awais, Philip JB Jackson
Self-supervised pre-trained audio networks have seen widespread adoption in real-world systems, particularly in multi-modal large language models. These networks are often employed in a frozen state, under the assumption that the SSL pre-training has sufficiently equipped them to handle real-world audio. However, a critical question remains: how well do these models actually perform in real-world conditions, where audio is typically polyphonic and complex, involving multiple overlapping sound sources? Current audio SSL methods are often benchmarked on datasets predominantly featuring monophonic audio, such as environmental sounds, and speech. As a result, the ability of SSL models to generalize to polyphonic audio, a common characteristic in natural scenarios, remains underexplored. This limitation raises concerns about the practical robustness of SSL models in more realistic audio settings. To address this gap, we introduce Self-Supervised Learning from Audio Mixtures (SSLAM), a novel direction in audio SSL research, designed to improve, designed to improve the model’s ability to learn from polyphonic data while maintaining strong performance on monophonic data. We thoroughly evaluate SSLAM on standard audio SSL benchmark datasets which are predominantly monophonic and conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis against SOTA methods using a range of high-quality, publicly available polyphonic datasets. SSLAM not only improves model performance on polyphonic audio, but also maintains or exceeds performance on standard audio SSL benchmarks. Notably, it achieves up to a 3.9% improvement on the AudioSet-2M (AS-2M), reaching a mean average precision (mAP) of 50.2. For polyphonic datasets, SSLAM sets new SOTA in both linear evaluation and fine-tuning regimes with performance improvements of up to 9.1% (mAP).
自监督预训练音频网络已在真实世界系统中得到广泛应用,特别是在多模态大型语言模型中。这些网络通常处于冻结状态,假设SSL预训练已经使他们足以处理真实世界的音频。但有一个关键问题仍然存在:这些模型在真实世界条件下的表现如何,那里的音频通常是多音的和复杂的,涉及多个重叠的声音源?当前的音频SSL方法通常主要在以单音音频为主的数据集上进行基准测试,如环境声和语音。因此,SSL模型泛化到多音音频的能力,这在自然场景中是一个常见特征,仍然被探索得不够。这一局限性引发了人们对SSL模型在更现实的音频设置中的实际稳健性的担忧。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了自监督学习从混合音频(SSLAM),这是音频SSL研究的一个新方向,旨在提高模型从多音数据学习能力的同时,保持对单音数据的强劲表现。我们对SSLAM在标准的音频SSL基准数据集上进行了全面评估,这些数据集主要是单音的,并使用一系列高质量、公开可用的多音数据集与最新方法进行了综合比较分析。SSLAM不仅提高了模型在多音音频上的性能,而且在标准音频SSL基准测试中保持了性能或有所提高。值得注意的是,它在AudioSet-2M(AS-2M)上实现了高达3.9%的改进,达到平均精度(mAP)为50.2。对于多音数据集,SSLAM在线性评估和微调方案中都达到了新的最佳状态,性能提高了高达9.1%(mAP)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR 2025. Code and pre-trained models are available at \url{https://github.com/ta012/SSLAM}
Summary
本摘要简要介绍了自我监督预训练的音频网络在多模态大型语言模型中的广泛应用,并指出了它们在处理复杂多变现实环境中的音频时存在的局限性。文章强调了在现实条件下,音频通常是多音调和复杂的,涉及多个重叠的声音源。现有的音频SSL方法主要在以单音音频为主的数据集上进行评估,如环境声和语音。因此,SSL模型泛化到多音音频的能力——自然场景中的常见特征,仍待探索。为解决这个问题,研究引入了从音频混合物的自我监督学习(SSLAM),旨在提高模型从多音数据中学习的能力,同时保持对单音数据的强劲表现。通过严格的评估,显示SSLAM不仅提高了模型在多音音频上的性能,而且在标准音频SSL基准数据集上的表现也得以维持或提高。
Key Takeaways
- 自我监督预训练的音频网络在多模态语言模型中受到广泛应用。
- 现有方法在复杂多变的现实音频条件下表现受限。
- 音频通常是多音调和复杂的,涉及多个重叠的声音源。
- SSL模型在泛化到多音音频方面的能力仍待探索。
- SSLAM的引入旨在提高模型从多音数据中学习的能力。
- SSLAM在标准音频SSL基准数据集上的表现优秀,并在多音音频上的性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

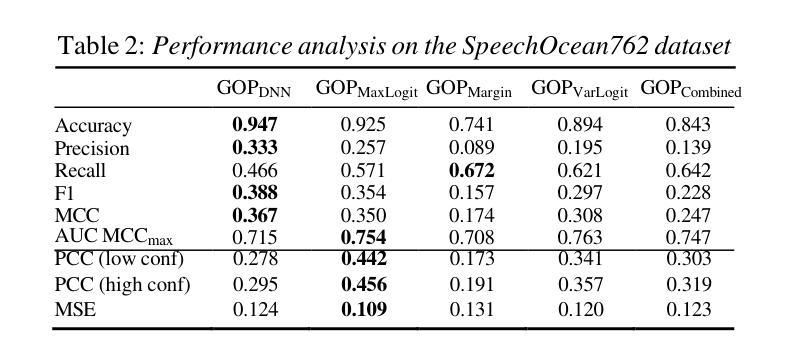
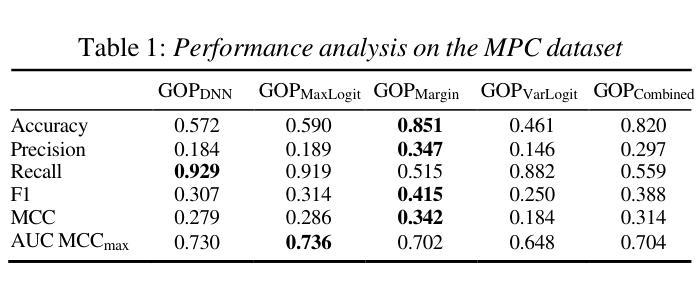
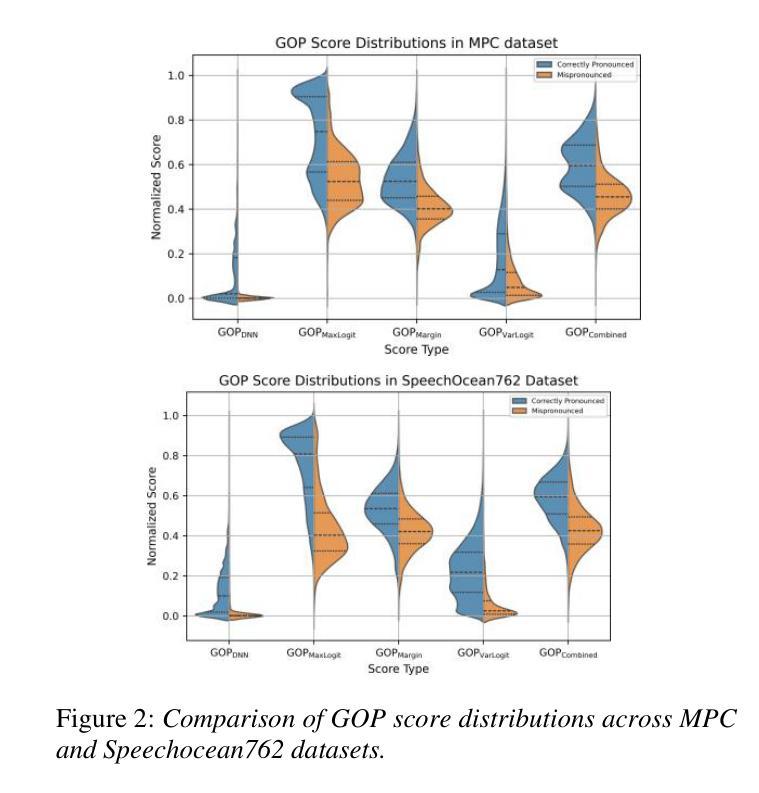
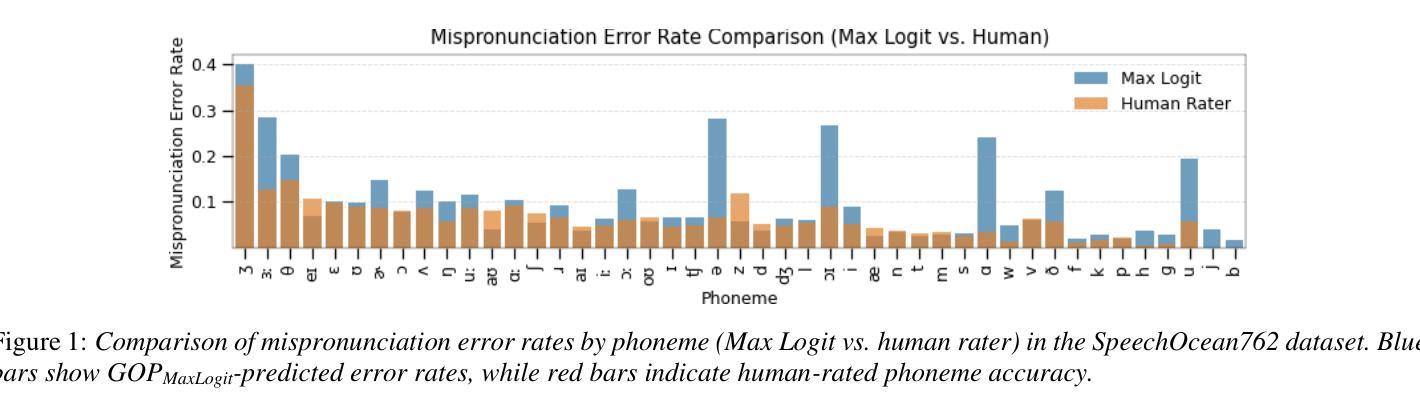
Evaluating Logit-Based GOP Scores for Mispronunciation Detection
Authors:Aditya Kamlesh Parikh, Cristian Tejedor-Garcia, Catia Cucchiarini, Helmer Strik
Pronunciation assessment relies on goodness of pronunciation (GOP) scores, traditionally derived from softmax-based posterior probabilities. However, posterior probabilities may suffer from overconfidence and poor phoneme separation, limiting their effectiveness. This study compares logit-based GOP scores with probability-based GOP scores for mispronunciation detection. We conducted our experiment on two L2 English speech datasets spoken by Dutch and Mandarin speakers, assessing classification performance and correlation with human ratings. Logit-based methods outperform probability-based GOP in classification, but their effectiveness depends on dataset characteristics. The maximum logit GOP shows the strongest alignment with human perception, while a combination of different GOP scores balances probability and logit features. The findings suggest that hybrid GOP methods incorporating uncertainty modeling and phoneme-specific weighting improve pronunciation assessment.
发音评估依赖于发音质量(GOP)分数,这些分数传统上由基于softmax的后验概率得出。然而,后验概率可能会遭受过度自信和不准确的音素分离问题的影响,从而限制了其有效性。本研究对比了基于对数似然率的GOP分数与基于概率的GOP分数在发音错误检测中的应用。我们在由荷兰语和汉语使用者说的两个英语二级语音数据集上进行了实验,评估了分类性能与人类评分的相关性。基于对数似然率的方法在分类方面优于基于概率的GOP方法,但其有效性取决于数据集的特征。最大对数似然率GOP与人类感知最为吻合,而结合不同的GOP分数可以平衡概率和对数似然率特征。研究结果表明,结合不确定性建模和音素特定权重的混合GOP方法可以改善发音评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025. This publication is part of the project Responsible AI for Voice Diagnostics (RAIVD) with file number NGF.1607.22.013 of the research programme NGF AiNed Fellowship Grants which is financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO)
Summary
本文探讨了发音评估中的语音清晰度评分问题。研究发现,基于对数几率(logit)的语音清晰度评分在分类性能上优于基于概率的评分方法,特别是在针对荷兰语和英语二语者的英语语音数据集上。最大对数几率语音清晰度评分与人类感知最为一致,而结合不同语音清晰度评分的混合方法则平衡了概率和对数几率特征。研究结果表明,结合不确定性建模和音素特定权重的混合语音清晰度评分方法能提高发音评估的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 发音评估依赖于语音清晰度(GOP)评分。
- 传统上,GOP评分基于softmax生成的后验概率,但存在过度自信及音素分离不佳的问题。
- 对比了基于对数几率和基于概率的GOP评分方法进行发音误读检测。
- 在针对荷兰语和英语二语者的英语语音数据集上进行了实验。
- 对数几率方法(特别是最大对数几率)在分类性能上优于基于概率的GOP方法,与人类感知一致性更高。
- 混合方法结合了概率和对数几率特征,表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

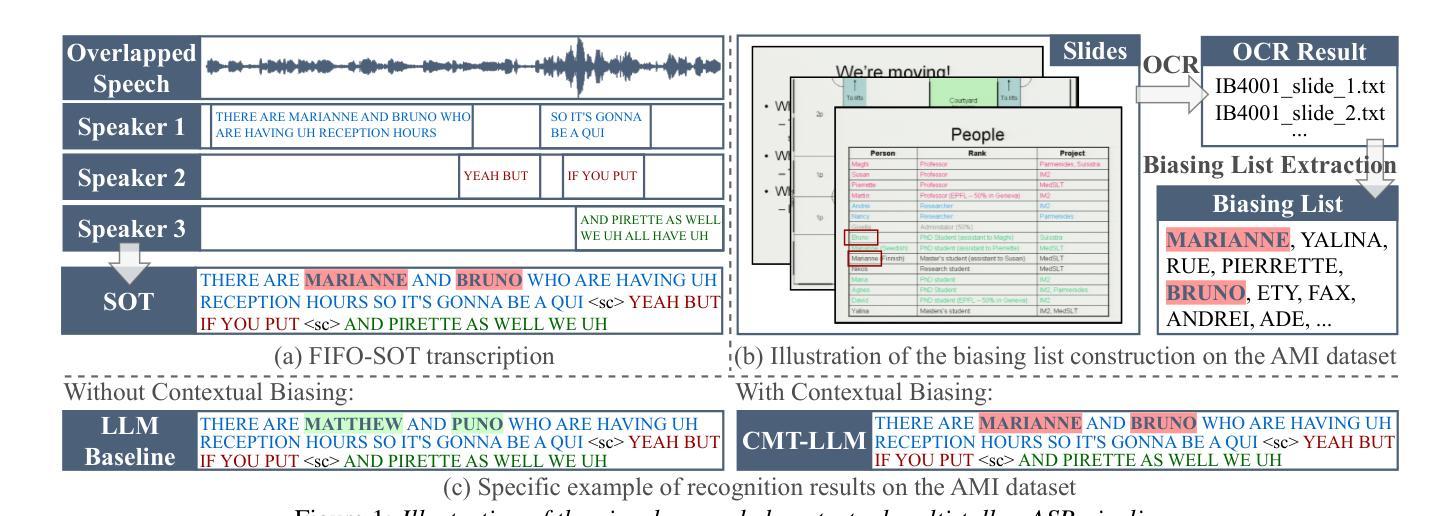
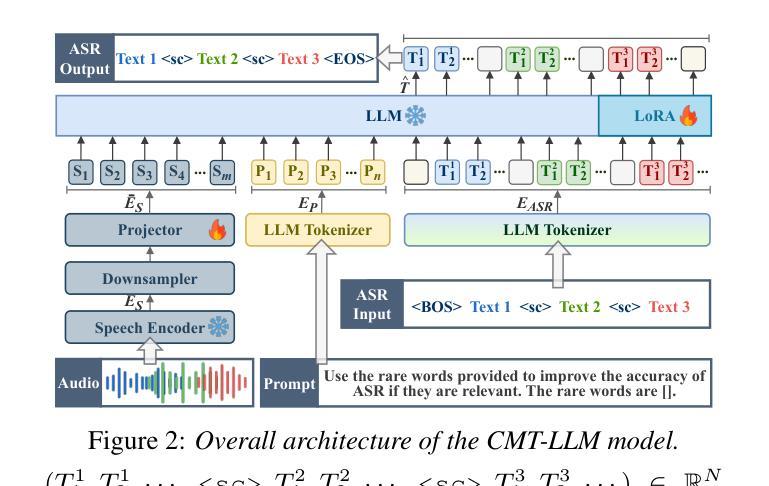
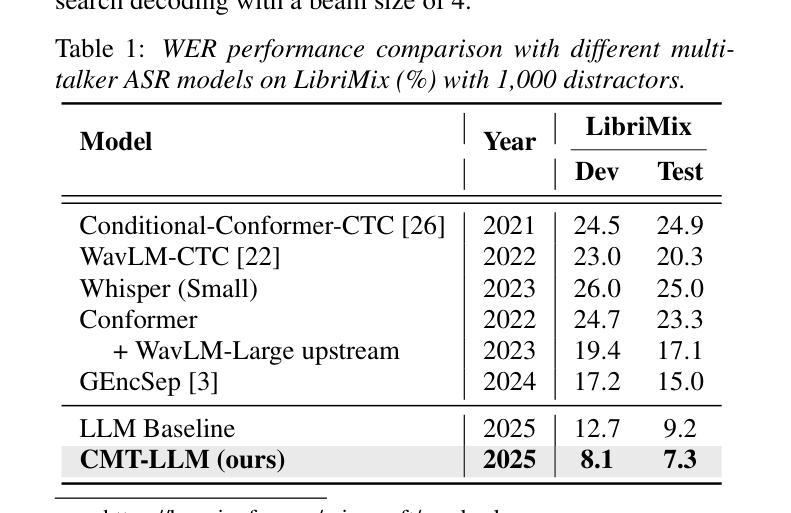
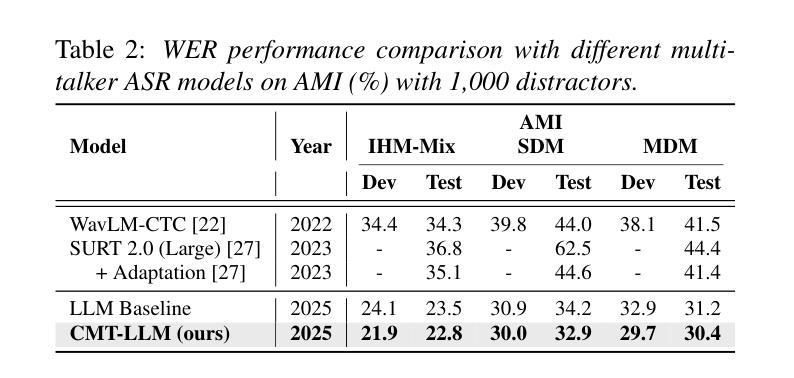
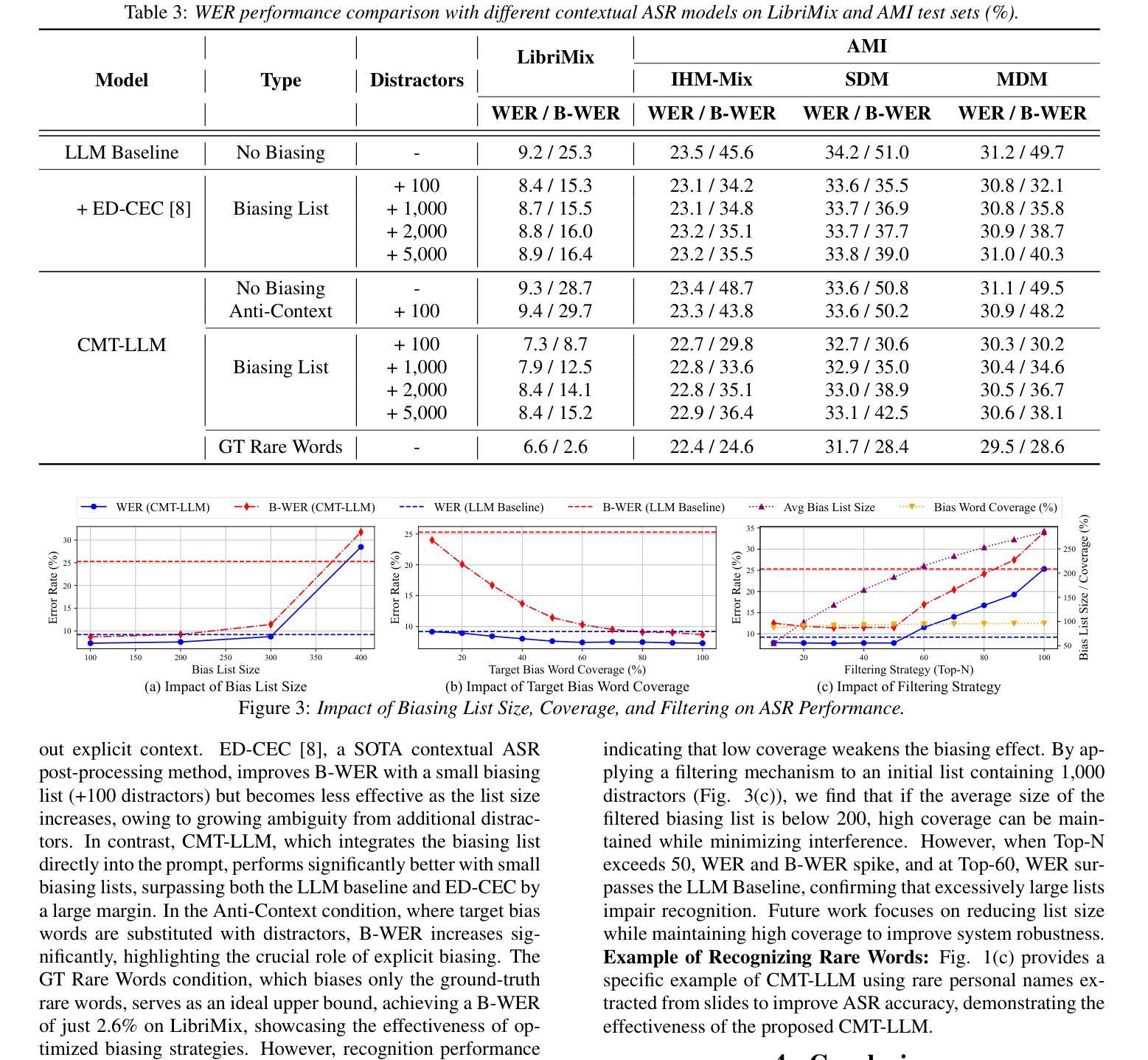
CMT-LLM: Contextual Multi-Talker ASR Utilizing Large Language Models
Authors:Jiajun He, Naoki Sawada, Koichi Miyazaki, Tomoki Toda
In real-world applications, automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems must handle overlapping speech from multiple speakers and recognize rare words like technical terms. Traditional methods address multi-talker ASR and contextual biasing separately, limiting performance in complex scenarios. We propose a unified framework that combines multi-talker overlapping speech recognition and contextual biasing into a single task. Our ASR method integrates pretrained speech encoders and large language models (LLMs), using optimized finetuning strategies. We also introduce a two-stage filtering algorithm to efficiently identify relevant rare words from large biasing lists and incorporate them into the LLM’s prompt input, enhancing rare word recognition. Experiments show that our approach outperforms traditional contextual biasing methods, achieving a WER of 7.9% on LibriMix and 32.9% on AMI SDM when the biasing size is 1,000, demonstrating its effectiveness in complex speech scenarios.
在实际应用中,自动语音识别(ASR)系统必须处理来自多个发言者的重叠语音,并识别诸如技术术语之类的罕见词汇。传统方法分别处理多发言人ASR和上下文偏差,这在复杂场景中限制了性能。我们提出了一个统一框架,将多发言人重叠语音识别和上下文偏差结合成一项任务。我们的ASR方法集成了预训练的语音编码器和大型语言模型(LLM),采用优化的微调策略。我们还引入了一种两阶段过滤算法,有效地从大量偏差列表中识别出相关的罕见词汇,并将其纳入LLM的提示输入,从而提高罕见词汇的识别率。实验表明,我们的方法在LibriMix上取得了7.9%的WER(词错误率),在AMI SDM上取得了32.9%的WER,当偏差大小为1000时,我们的方法表现出在复杂语音场景中的有效性,并优于传统的上下文偏差方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary:本文提出一个统一的框架,结合了多说话人重叠语音识别和上下文偏差纠正,以提高复杂场景中的语音识别性能。通过集成预训练的语音编码器和大型语言模型,并采用优化的微调策略,同时引入两阶段过滤算法以提高对罕见词的识别能力。实验表明,该方法在LibriMix和AMI SDM上分别实现了词错误率为7.9%和32.9%的优异表现。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出一个统一框架,整合多说话人重叠语音识别和上下文偏差纠正。
- 集成预训练的语音编码器和大型语言模型,优化微调策略以提高性能。
- 引入两阶段过滤算法,从大量偏差列表中有效识别相关罕见词汇。
- 方法在LibriMix和AMI SDM复杂语音场景下表现出色。
- 实验结果显示,与传统上下文偏差纠正方法相比,该方法具有优越性。
- 在LibriMix上实现词错误率为7.9%,在AMI SDM上实现词错误率为32.9%。
- 该方法对于提高语音识别系统在复杂环境中的实用性和性能具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

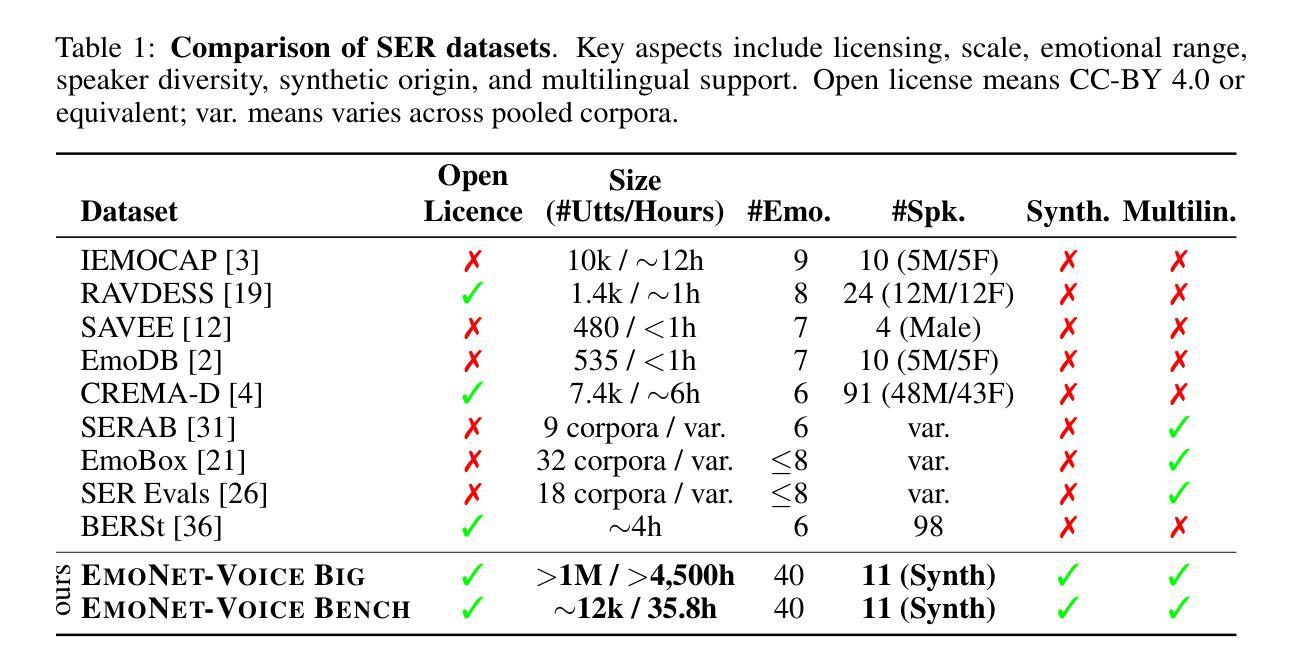
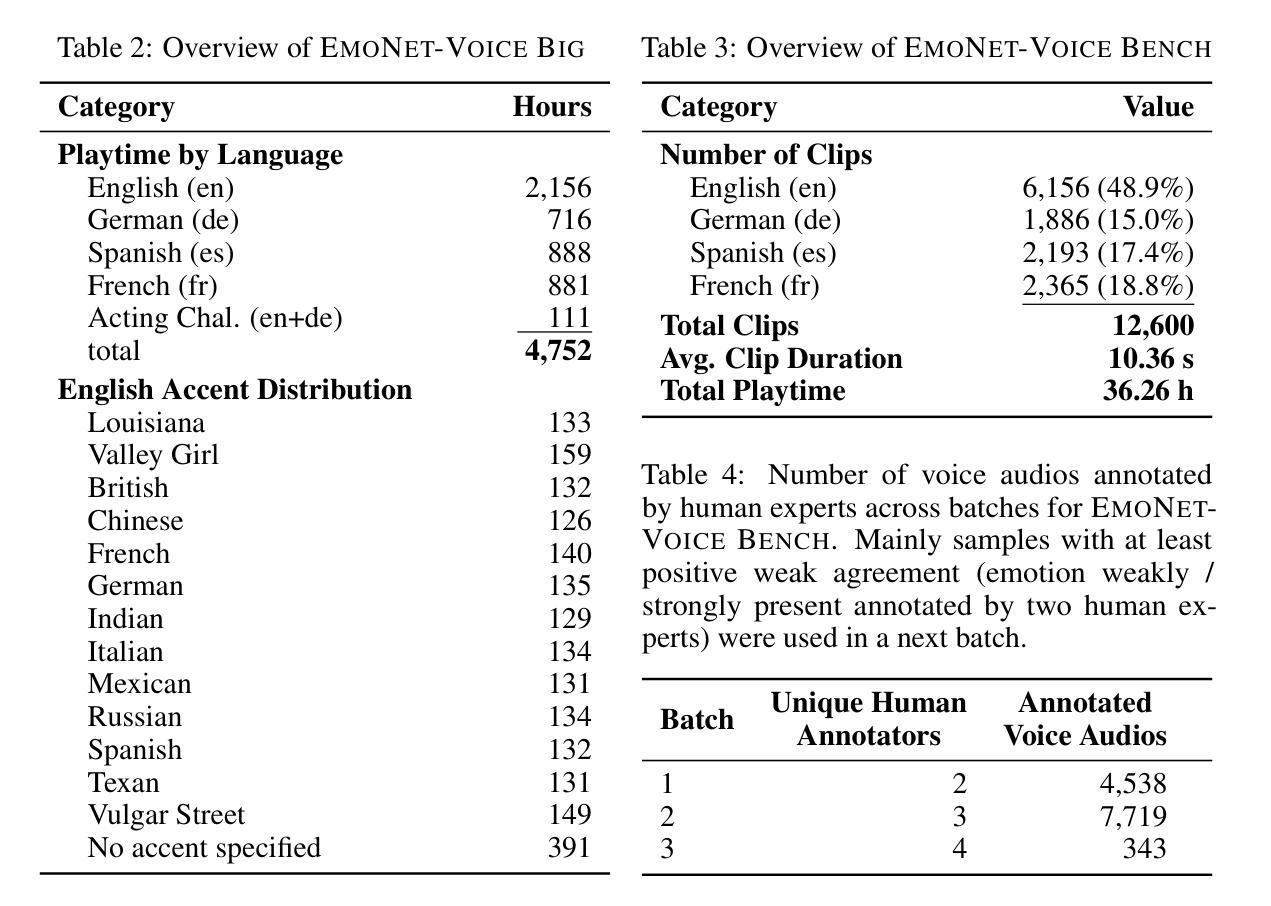
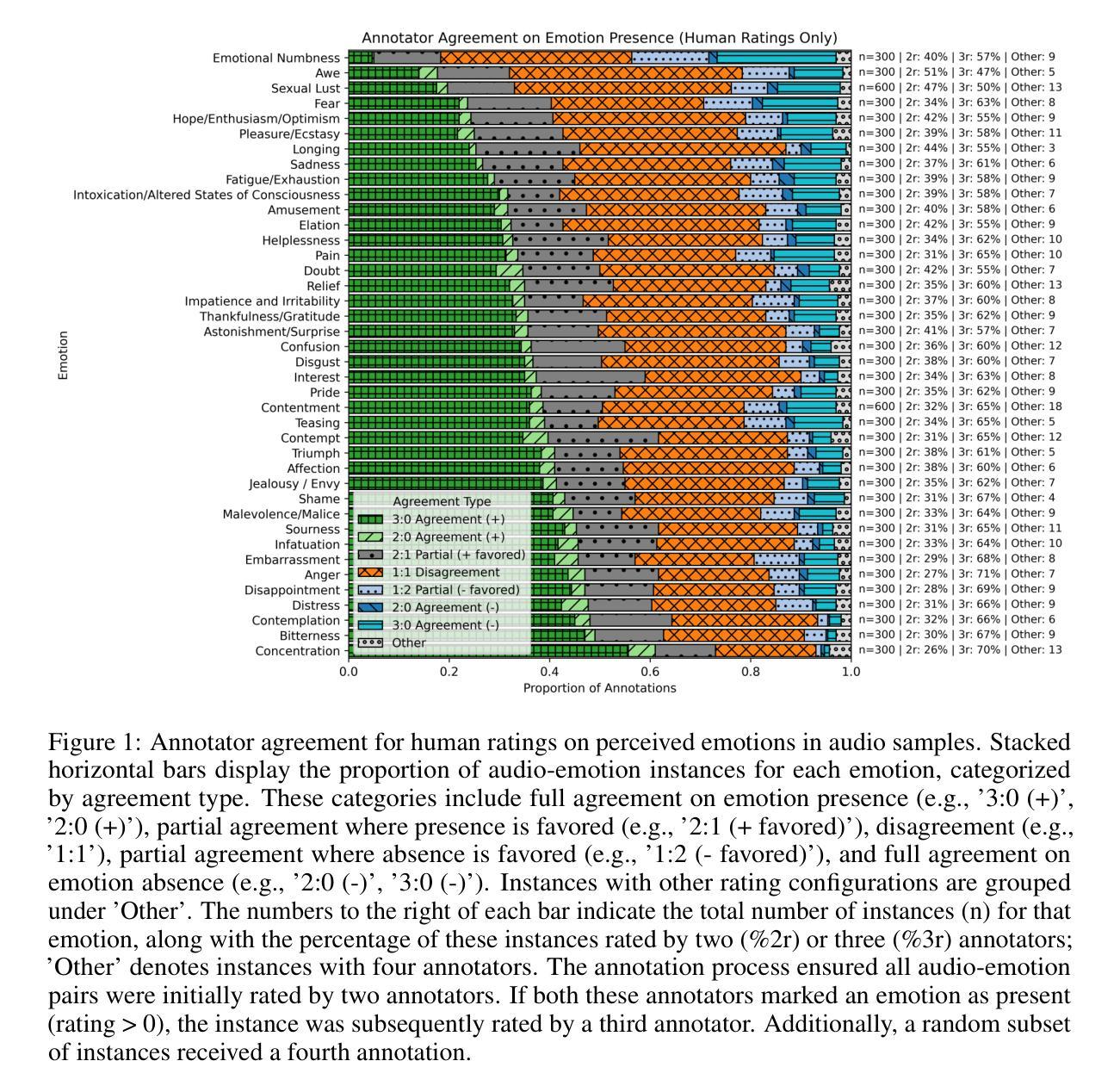
EmoNet-Voice: A Fine-Grained, Expert-Verified Benchmark for Speech Emotion Detection
Authors:Christoph Schuhmann, Robert Kaczmarczyk, Gollam Rabby, Felix Friedrich, Maurice Kraus, Kourosh Nadi, Huu Nguyen, Kristian Kersting, Sören Auer
The advancement of text-to-speech and audio generation models necessitates robust benchmarks for evaluating the emotional understanding capabilities of AI systems. Current speech emotion recognition (SER) datasets often exhibit limitations in emotional granularity, privacy concerns, or reliance on acted portrayals. This paper introduces EmoNet-Voice, a new resource for speech emotion detection, which includes EmoNet-Voice Big, a large-scale pre-training dataset (featuring over 4,500 hours of speech across 11 voices, 40 emotions, and 4 languages), and EmoNet-Voice Bench, a novel benchmark dataset with human expert annotations. EmoNet-Voice is designed to evaluate SER models on a fine-grained spectrum of 40 emotion categories with different levels of intensities. Leveraging state-of-the-art voice generation, we curated synthetic audio snippets simulating actors portraying scenes designed to evoke specific emotions. Crucially, we conducted rigorous validation by psychology experts who assigned perceived intensity labels. This synthetic, privacy-preserving approach allows for the inclusion of sensitive emotional states often absent in existing datasets. Lastly, we introduce Empathic Insight Voice models that set a new standard in speech emotion recognition with high agreement with human experts. Our evaluations across the current model landscape exhibit valuable findings, such as high-arousal emotions like anger being much easier to detect than low-arousal states like concentration.
文本转语音和音频生成模型的进步要求对AI系统的情感理解能力进行稳健的基准测试。当前语音情感识别(SER)数据集在情感粒度、隐私担忧或依赖表演表现等方面存在局限性。本文介绍了EmoNet-Voice,一个用于语音情感检测的新资源,包括EmoNet-Voice Big,一个大规模预训练数据集(跨越11个声音、40种情感和4种语言,包含超过4500小时的语音),以及EmoNet-Voice Bench,一个带有专家注释的新型基准数据集。EmoNet-Voice旨在评估SER模型在40个情感类别的精细粒度光谱上的表现,这些情感类别的强度不同。我们利用最先进的语音生成技术,精心制作了模拟演员表现特定情感场景的合成音频片段。关键的是,我们邀请了心理学专家进行了严格的验证,他们分配了感知强度标签。这种合成的、保护隐私的方法可以包含现有数据集中通常不存在的敏感情感状态。最后,我们引入了Empathic Insight Voice模型,该模型在语音情感识别方面树立了新的标准,与人类专家的共识高度一致。我们在当前模型景观中的评估展现了有价值的发现,例如高唤醒情绪(如愤怒)比低唤醒状态(如专注)更容易检测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个新型的语音情感识别数据集EmoNet-Voice,包括用于预训练的EmoNet-Voice Big和作为基准测试集的EmoNet-Voice Bench。该数据集具有40种情感类别,不同强度水平,并由语音生成模型模拟真实场景生成音频片段。通过心理学专家进行严格的验证,并赋予情感强度标签。此外,还引入了Empathic Insight Voice模型,在语音情感识别方面与人类专家高度一致。研究结果表明,高唤醒情绪如愤怒比低唤醒状态如专注更容易检测。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了新型的语音情感识别数据集EmoNet-Voice,包含大规模预训练数据集EmoNet-Voice Big和基准测试集EmoNet-Voice Bench。
- EmoNet-Voice数据集具有40种情感类别,涵盖不同强度水平,可评估模型的精细情感识别能力。
- 利用先进的语音生成技术,模拟真实场景生成音频片段,以增强数据集的实用性和真实性。
- 通过心理学专家进行严格的验证,并赋予情感强度标签,提高数据集的准确性和可靠性。
- 引入了Empathic Insight Voice模型,在语音情感识别方面与人类专家高度一致。
- 评估结果显示,高唤醒情绪相对容易检测,而低唤醒状态如专注等情感的识别更具挑战性。
点此查看论文截图

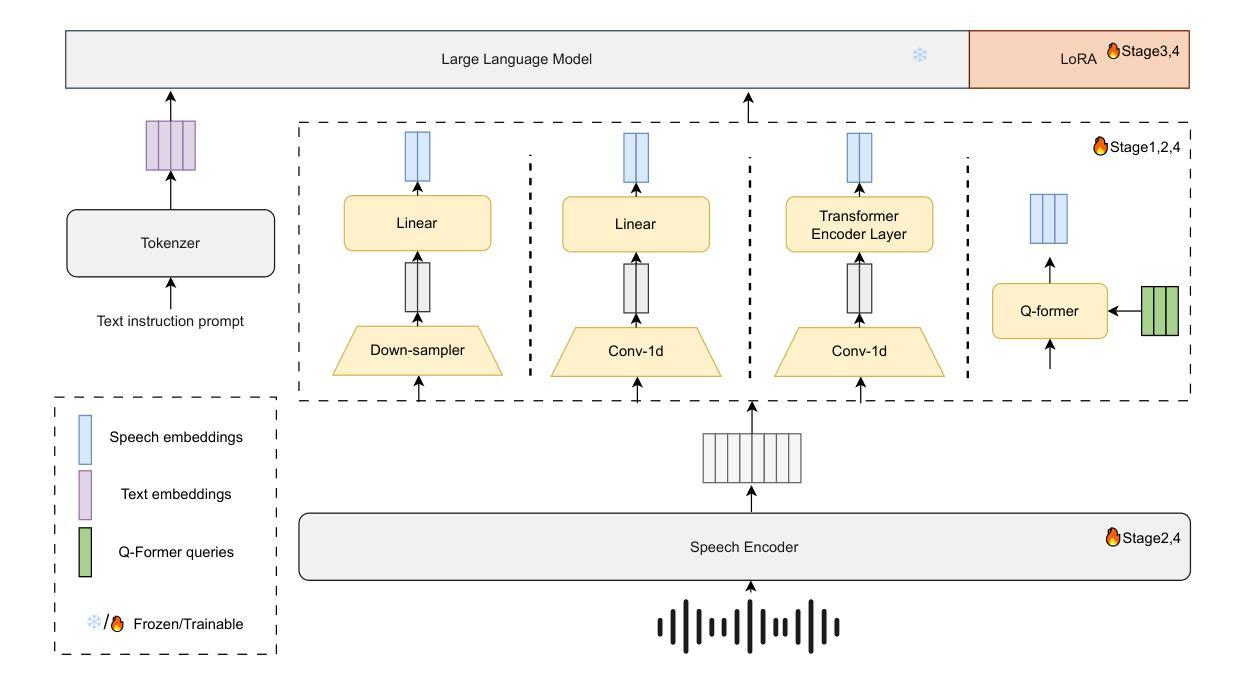
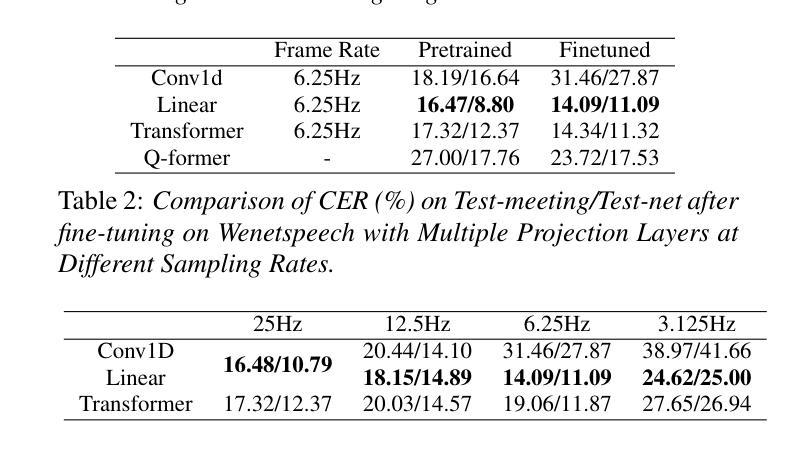
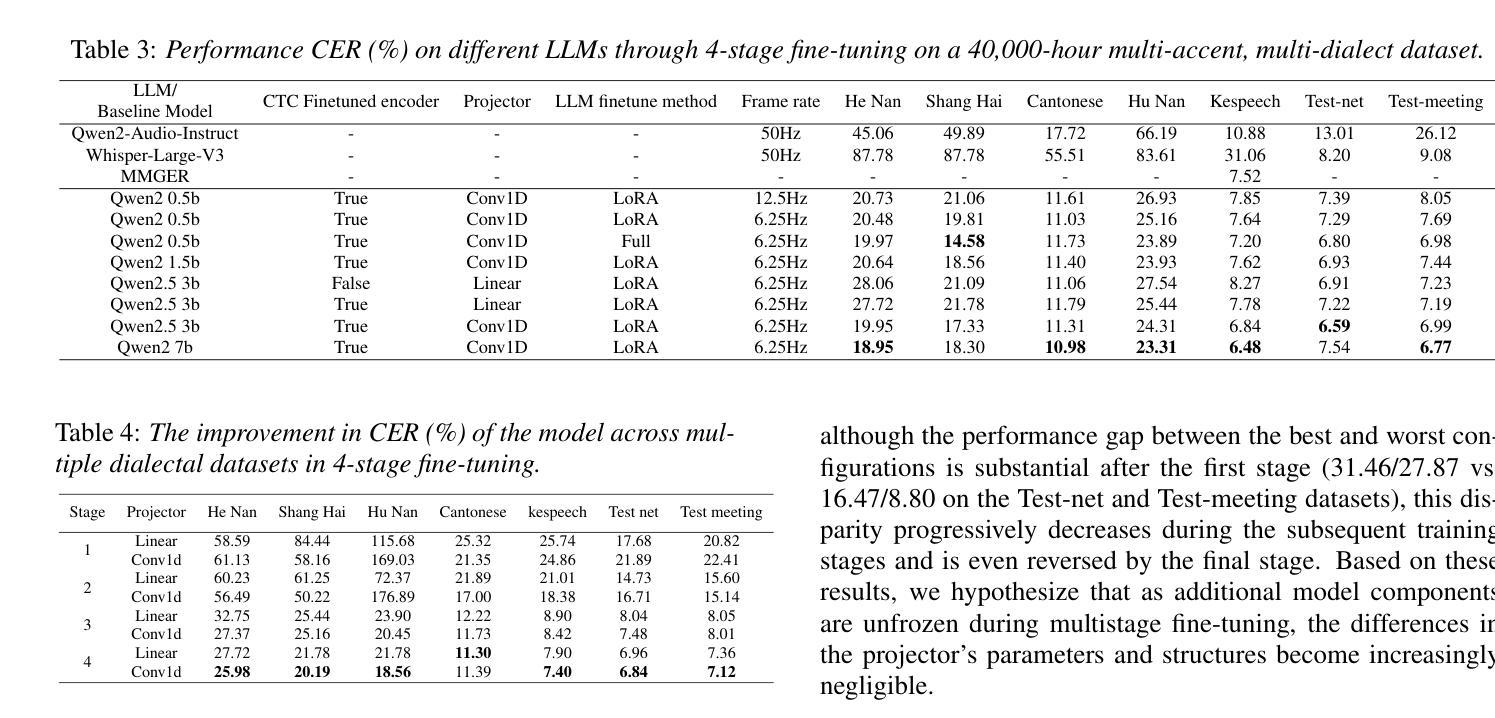
Leveraging LLM and Self-Supervised Training Models for Speech Recognition in Chinese Dialects: A Comparative Analysis
Authors:Tianyi Xu, Hongjie Chen, Wang Qing, Lv Hang, Jian Kang, Li Jie, Zhennan Lin, Yongxiang Li, Xie Lei
Large-scale training corpora have significantly improved the performance of ASR models. Unfortunately, due to the relative scarcity of data, Chinese accents and dialects remain a challenge for most ASR models. Recent advancements in self-supervised learning have shown that self-supervised pre-training, combined with large language models (LLM), can effectively enhance ASR performance in low-resource scenarios. We aim to investigate the effectiveness of this paradigm for Chinese dialects. Specifically, we pre-train a Data2vec2 model on 300,000 hours of unlabeled dialect and accented speech data and do alignment training on a supervised dataset of 40,000 hours. Then, we systematically examine the impact of various projectors and LLMs on Mandarin, dialect, and accented speech recognition performance under this paradigm. Our method achieved SOTA results on multiple dialect datasets, including Kespeech. We will open-source our work to promote reproducible research
大规模训练语料库已经显著提高了语音识别模型性能。然而,由于数据相对稀缺,中文口音和方言仍然是大多数语音识别模型的挑战。最近的自监督学习进展表明,自监督预训练与大型语言模型(LLM)的结合,可以在低资源情况下有效提高语音识别性能。我们的目标是研究这种范式在中文方言中的有效性。具体来说,我们在30万小时的无标签方言和带口音语音数据上预训练了一个Data2vec2模型,并在一个4万小时的监督数据集上进行对齐训练。然后,我们系统地研究了在这种范式下,各种投影仪和LLM对普通话、方言和带口音语音识别性能的影响。我们的方法在多个方言数据集上达到了最佳结果,包括Kespeech。我们将开源我们的工作,以促进可复制的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:大规模训练语料库显著提高了语音识别模型性能。然而,由于数据相对稀缺,中文口音和方言仍是大多数语音识别模型的挑战。最近自监督学习的进展显示,自监督预训练与大型语言模型的结合,可有效提高低资源场景中的语音识别性能。本研究旨在探究这一模式在中文方言中的有效性。具体来说,我们在30万小时的无标签方言和口音语音数据上预训练了Data2vec2模型,并在一个4万小时的监督数据集上进行对齐训练。然后,我们系统地研究了该模式下各种投影器和大型语言模型对普通话、方言和口音语音识别的性能影响。我们的方法在多个方言数据集上达到了最新技术水平,包括Kespeech数据集。我们将开源我们的工作以促进可复现研究。
Key Takeaways:
- 大规模训练语料库增强了语音识别模型的性能。
- 中文口音和方言仍是语音识别模型的一个挑战。
- 自监督预训练与大型语言模型的结合在低资源场景中的语音识别性能提升显著。
- 研究者使用Data2vec2模型在30万小时的无标签方言和口音语音数据上进行预训练。
- 对齐训练在4万小时的监督数据集上进行,以提高模型性能。
- 研究者系统地研究了不同投影器和大型语言模型对语音识别的性能影响。
点此查看论文截图

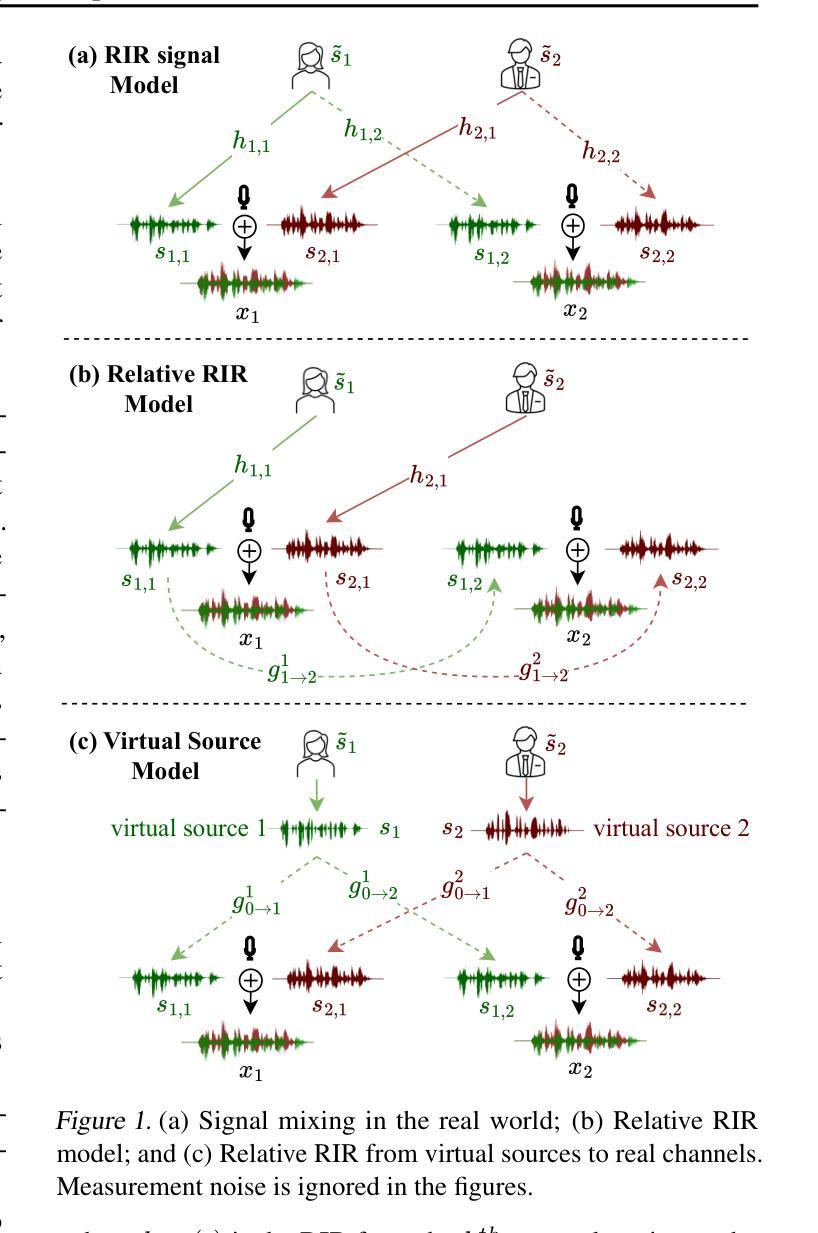
ArrayDPS: Unsupervised Blind Speech Separation with a Diffusion Prior
Authors:Zhongweiyang Xu, Xulin Fan, Zhong-Qiu Wang, Xilin Jiang, Romit Roy Choudhury
Blind Speech Separation (BSS) aims to separate multiple speech sources from audio mixtures recorded by a microphone array. The problem is challenging because it is a blind inverse problem, i.e., the microphone array geometry, the room impulse response (RIR), and the speech sources, are all unknown. We propose ArrayDPS to solve the BSS problem in an unsupervised, array-agnostic, and generative manner. The core idea builds on diffusion posterior sampling (DPS), but unlike DPS where the likelihood is tractable, ArrayDPS must approximate the likelihood by formulating a separate optimization problem. The solution to the optimization approximates room acoustics and the relative transfer functions between microphones. These approximations, along with the diffusion priors, iterate through the ArrayDPS sampling process and ultimately yield separated voice sources. We only need a simple single-speaker speech diffusion model as a prior along with the mixtures recorded at the microphones; no microphone array information is necessary. Evaluation results show that ArrayDPS outperforms all baseline unsupervised methods while being comparable to supervised methods in terms of SDR. Audio demos are provided at: https://arraydps.github.io/ArrayDPSDemo/.
盲语音分离(BSS)旨在从麦克风阵列记录的音频混合物中分离出多个语音源。这个问题具有挑战性,因为它是一个盲反问题,即麦克风阵列的几何形状、房间冲击响应(RIR)和语音源都是未知的。我们提出ArrayDPS以无监督、阵列无关和生成的方式解决BSS问题。其核心思想建立在扩散后采样(DPS)的基础上,但与DPS不同的是,DPS的可能性是明确的,ArrayDPS必须通过制定一个单独的优化问题来近似可能性。优化的解决方案近似于房间声学以及麦克风之间的相对传递函数。这些近似值,结合扩散先验,在ArrayDPS采样过程中进行迭代,并最终产生分离的语音源。我们只需要一个简单的单说话人语音扩散模型作为先验,以及麦克风记录的混合物;不需要麦克风阵列的信息。评估结果表明,ArrayDPS在SDR方面优于所有基线无监督方法,同时与有监督方法相当。音频演示请访问:https://arraydps.github.io/ArrayDPSDemo/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper Accepted at ICML2025 Demo: https://arraydps.github.io/ArrayDPSDemo/ Code: https://github.com/ArrayDPS/ArrayDPS
Summary
盲语音分离(BSS)是从麦克风阵列录制的音频混合中分离多个语音源的问题。提出ArrayDPS以无监督、阵列无关和生成的方式解决BSS问题。其核心思想建立在扩散后采样(DPS)的基础上,但ArrayDPS必须通过单独的优化问题来近似可能性。解决方案近似房间声学及麦克风之间的相对传递函数。这些近似与扩散先验相结合,在ArrayDPS采样过程中进行迭代,最终产生分离的语音源。只需简单的单说话人语音扩散模型先验和麦克风录制的混音,无需知道麦克风阵列信息。
Key Takeaways
- 盲语音分离(BSS)是从音频混合中分离多个未知语音源的问题,具有挑战性。
- ArrayDPS是一种解决BSS问题的新方法,采用无监督、阵列无关和生成的方式。
- ArrayDPS建立在扩散后采样(DPS)的基础上,但必须通过单独的优化问题来近似可能性。
- ArrayDPS的解决方案可以近似房间声学和麦克风之间的相对传递函数。
- 该方法只需单说话人语音扩散模型先验和混音,无需知道麦克风阵列的具体信息。
- 评价结果显示,ArrayDPS在无监督方法中的表现优于所有基线方法,并且在SDR方面与监督方法相当。
点此查看论文截图

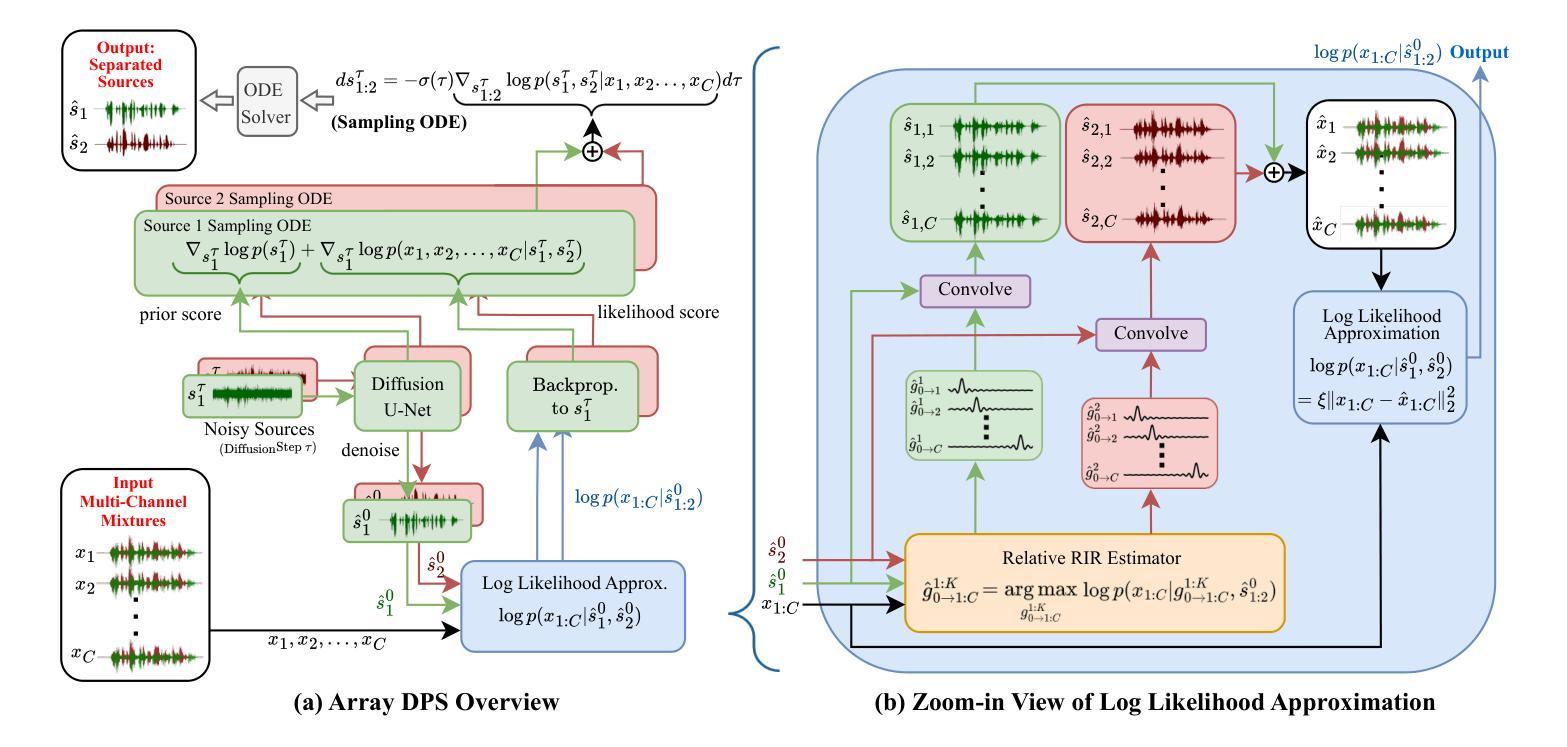

QualiSpeech: A Speech Quality Assessment Dataset with Natural Language Reasoning and Descriptions
Authors:Siyin Wang, Wenyi Yu, Xianzhao Chen, Xiaohai Tian, Jun Zhang, Lu Lu, Yu Tsao, Junichi Yamagishi, Yuxuan Wang, Chao Zhang
This paper explores a novel perspective to speech quality assessment by leveraging natural language descriptions, offering richer, more nuanced insights than traditional numerical scoring methods. Natural language feedback provides instructive recommendations and detailed evaluations, yet existing datasets lack the comprehensive annotations needed for this approach. To bridge this gap, we introduce QualiSpeech, a comprehensive low-level speech quality assessment dataset encompassing 11 key aspects and detailed natural language comments that include reasoning and contextual insights. Additionally, we propose the QualiSpeech Benchmark to evaluate the low-level speech understanding capabilities of auditory large language models (LLMs). Experimental results demonstrate that finetuned auditory LLMs can reliably generate detailed descriptions of noise and distortion, effectively identifying their types and temporal characteristics. The results further highlight the potential for incorporating reasoning to enhance the accuracy and reliability of quality assessments. The dataset will be released at https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech.
本文探索了一种利用自然语言描述来进行语音质量评估的新视角,提供比传统数字评分方法更丰富、更细微的见解。自然语言反馈提供指导性的建议和详细的评价,但现有的数据集缺乏这种方法的全面注释。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了QualiSpeech数据集,这是一个全面的低层次语音质量评估数据集,涵盖了1 1个关键方面和包含推理和上下文洞察的自然语言评论。此外,我们提出了QualiSpeech基准测试,以评估听觉大型语言模型(LLM)的低层次语音理解能力。实验结果表明,微调后的听觉LLM能够可靠地描述噪声和失真的细节,有效地识别它们的类型和时间特征。结果进一步突显了结合推理来提高质量评估准确性和可靠性的潜力。该数据集将在https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 10 figures
Summary:
本文探索了利用自然语言描述进行语音质量评估的新视角,提供比传统数字评分方法更丰富、更细微的见解。为解决现有数据集缺乏全面注释的问题,提出了QualiSpeech数据集和QualiSpeech基准测试。该数据集包含11个关键方面的低级别语音质量评估,以及包含推理和上下文洞察的自然语言评论。实验结果表明,微调后的听觉大型语言模型(LLMs)可以可靠地描述噪声和失真,有效识别它们的类型和时间特征。该数据集将发布在https://huggingface.co/datasets/tsinghua-ee/QualiSpeech。
Key Takeaways:
- 论文提出了一种新的语音质量评估方法,利用自然语言描述提供丰富的见解。
- 自然语言反馈提供了详细评价和指导性建议。
- 存在缺乏全面注释的现有数据集,为此引入了QualiSpeech数据集。
- QualiSpeech数据集包含低级别语音质量评估的多个关键方面和详细的自然语言评论。
- QualiSpeech基准测试用于评估听觉大型语言模型的低级别语音理解能力。
- 实验结果表明,微调后的听觉大型语言模型可以准确描述语音中的噪声和失真类型及其时间特征。
点此查看论文截图

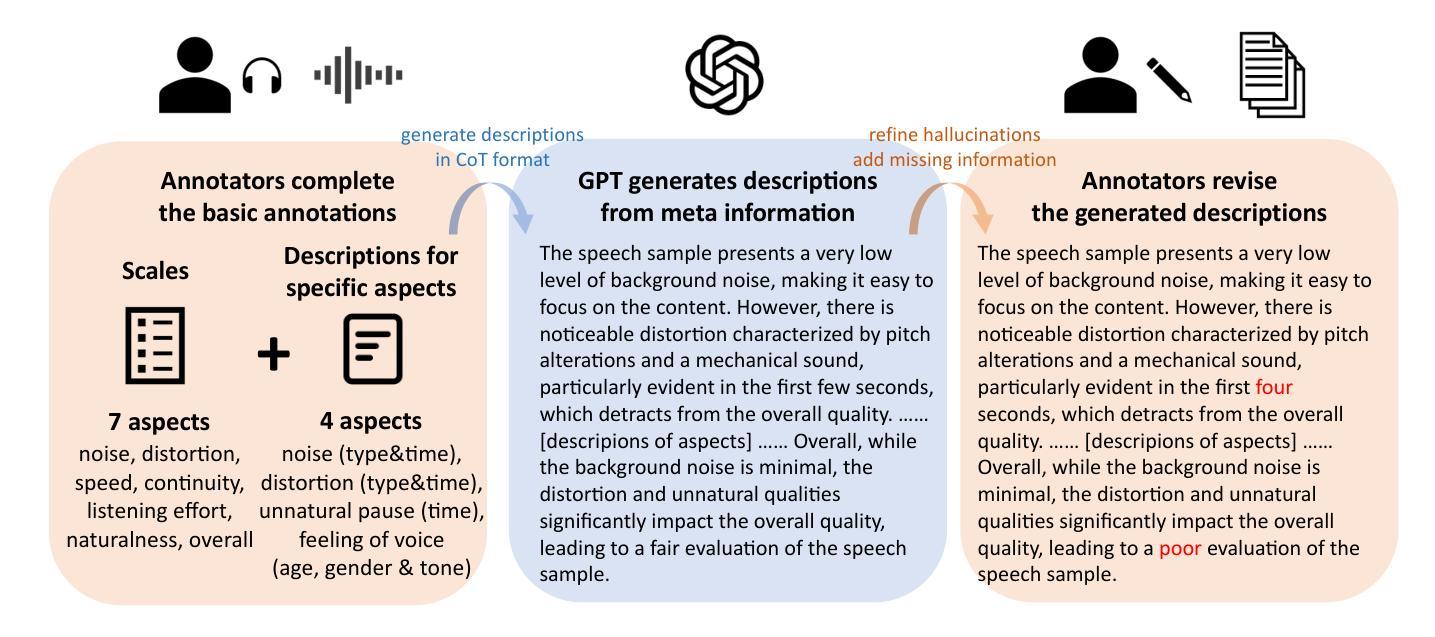

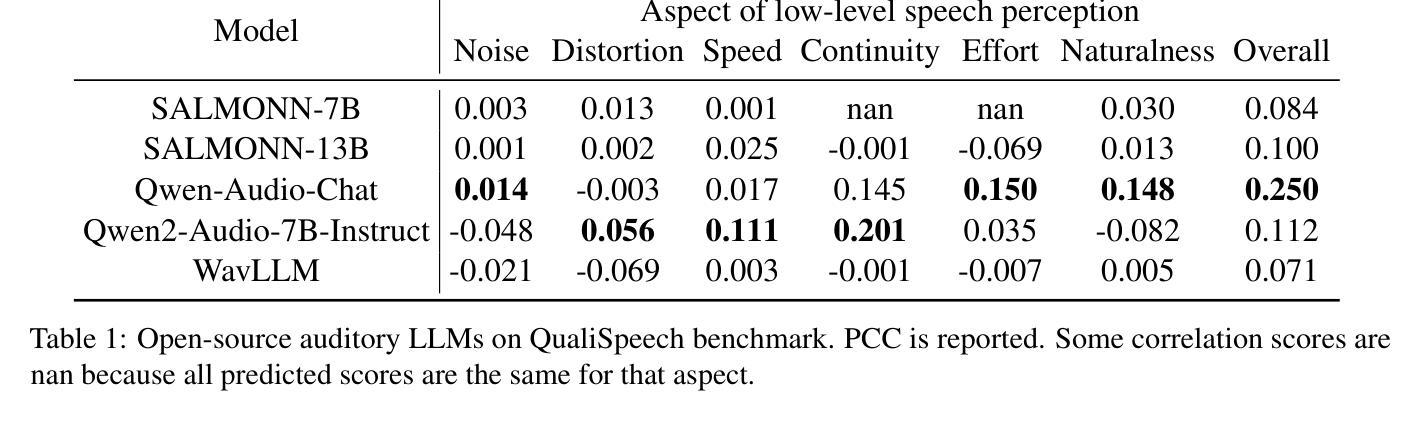
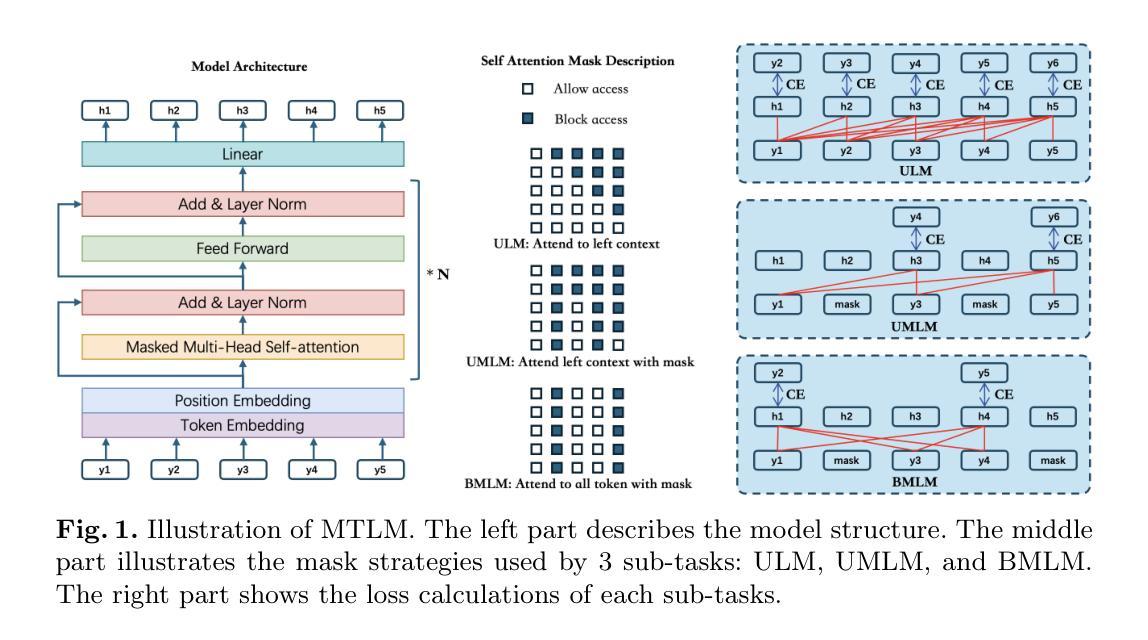
MTLM: Incorporating Bidirectional Text Information to Enhance Language Model Training in Speech Recognition Systems
Authors:Qingliang Meng, Pengju Ren, Tian Li, Changsong Dai, Huizhi Liang
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems normally consist of an acoustic model (AM) and a language model (LM). The acoustic model estimates the probability distribution of text given the input speech, while the language model calibrates this distribution toward a specific knowledge domain to produce the final transcription. Traditional ASR-specific LMs are typically trained in a unidirectional (left-to-right) manner to align with autoregressive decoding. However, this restricts the model from leveraging the right-side context during training, limiting its representational capacity. In this work, we propose MTLM, a novel training paradigm that unifies unidirectional and bidirectional manners through 3 training objectives: ULM, BMLM, and UMLM. This approach enhances the LM’s ability to capture richer linguistic patterns from both left and right contexts while preserving compatibility with standard ASR autoregressive decoding methods. As a result, the MTLM model not only enhances the ASR system’s performance but also support multiple decoding strategies, including shallow fusion, unidirectional/bidirectional n-best rescoring. Experiments on the LibriSpeech dataset show that MTLM consistently outperforms unidirectional training across multiple decoding strategies, highlighting its effectiveness and flexibility in ASR applications.
自动语音识别(ASR)系统通常由声学模型(AM)和语言模型(LM)组成。声学模型估计给定输入语音的文本概率分布,而语言模型则对这个分布进行校准,以面向特定的知识领域,从而产生最终的转录。传统的ASR专用LM通常采用单向(从左到右)的方式进行训练,以符合自回归解码。然而,这限制了模型在训练过程中利用右侧上下文的能力,从而限制了其表征能力。在本文中,我们提出了MTLM,这是一种新的训练范式,通过三个训练目标:ULM、BMLM和UMLM,统一了单向和双向方式。这种方法提高了LM从左右上下文中捕获更丰富语言模式的能力,同时保留了与标准ASR自回归解码方法的兼容性。因此,MTLM模型不仅提高了ASR系统的性能,还支持多种解码策略,包括浅融合、单向/双向n-best重评分。在LibriSpeech数据集上的实验表明,MTLM在多种解码策略上始终优于单向训练,突出了其在ASR应用中的有效性和灵活性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了自动语音识别(ASR)系统中的语言模型(LM)训练新方法——MTLM。该方法结合了单向和双向训练方式,通过ULM、BMLM和UMLM三个训练目标,提高了语言模型捕捉左右语境中更丰富语言模式的能力,同时兼容标准ASR自回归解码方法。实验表明,MTLM模型在多个解码策略下均优于单向训练,有效提高ASR系统性能。
Key Takeaways
- ASR系统通常由声学模型和语言模型组成,前者估计文本的概率分布,后者将此分布校准到特定知识域以产生最终转录。
- 传统ASR特定的语言模型通常以单向(从左到右)方式进行训练,与自回归解码相匹配,这限制了模型在训练过程中对右侧语境的利用。
- MTLM是一种新的训练范式,结合了单向和双向方式,通过ULM、BMLM和UMLM三个训练目标,提高语言模型捕捉左右语境中语言模式的能力。
- MTLM增强了ASR系统的性能,支持多种解码策略,包括浅融合、单向/双向n-best重评分。
- 实验表明,在LibriSpeech数据集上,MTLM在多个解码策略下的表现均优于单向训练。
- MTLM方法既有效又灵活,可应用于不同的ASR场景。
点此查看论文截图