⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
TTSOps: A Closed-Loop Corpus Optimization Framework for Training Multi-Speaker TTS Models from Dark Data
Authors:Kentaro Seki, Shinnosuke Takamichi, Takaaki Saeki, Hiroshi Saruwatari
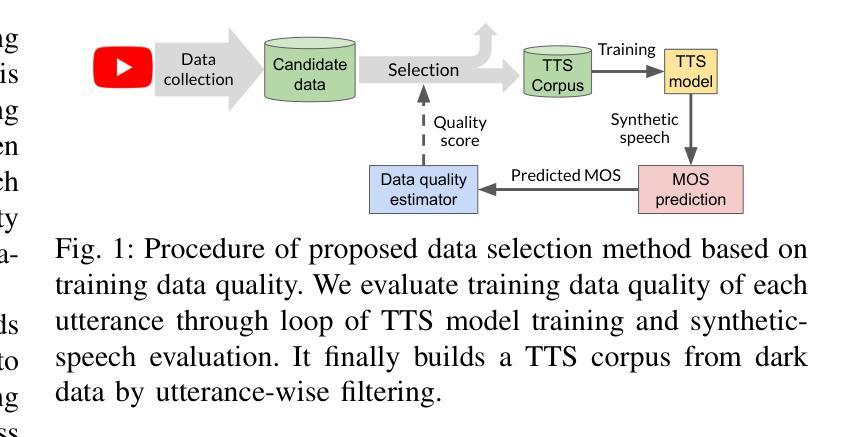
This paper presents TTSOps, a fully automated closed-loop framework for constructing multi-speaker text-to-speech (TTS) systems from noisy, uncurated web-scale speech data, often referred to as ``dark data,’’ such as online videos. Conventional TTS training pipelines require well-curated corpora with high acoustic quality and accurate text-speech alignment, which severely limits scalability, speaker diversity, and real-world applicability. While recent studies have proposed acoustic-quality-based data selection techniques, they often overlook two critical aspects: (1) the inherent robustness of modern TTS models to noise, and (2) the potential contribution of perceptually low-quality yet informative samples. To address these issues, TTSOps introduces a data-centric training pipeline that integrates three core components: (1) automated data collection from dark data sources, (2) utterance-level dynamic selection of data cleansing methods based on training data quality, and (3) evaluation-in-the-loop data selection using automatically predicted mean opinion scores (MOS) to estimate each utterance’s impact on model performance. Furthermore, TTSOps jointly optimizes the corpus and the TTS model in a closed-loop framework by dynamically adapting both data selection and data cleansing processes to the characteristics of the target TTS model. Extensive experiments on Japanese YouTube data demonstrate that TTSOps outperforms conventional acoustic-quality-based baselines in both the naturalness and speaker diversity of synthesized speech.
本文介绍了TTSOps,这是一个全自动的闭环框架,用于从嘈杂的、未整理的网页规模语音数据中构建多说话人文本到语音(TTS)系统,这种数据通常被称为“暗数据”,如在线视频。传统的TTS训练管道需要高质量的声音和准确的文本-语音对齐的精心整理语料库,这严重限制了可扩展性、说话人多样性和现实世界的适用性。虽然最近的研究已经提出了基于声音质量的数据选择技术,但他们往往忽略了两个关键方面:(1)现代TTS模型对噪声的固有鲁棒性;(2)感知质量较低但信息丰富的样本的潜在贡献。为了解决这些问题,TTSOps引入了一个以数据为中心的训练管道,该管道集成了三个核心组件:(1)从暗数据源自动收集数据,(2)基于训练数据质量的语句级动态选择数据清洗方法,(3)使用自动预测的平均意见分数(MOS)进行闭环数据选择,以估计每个语句对模型性能的影响。此外,TTSOps在一个闭环框架中联合优化语料库和TTS模型,通过动态适应数据选择和清洗过程来适应目标TTS模型的特征。在日语YouTube数据上的大量实验表明,TTSOps在自然度和说话人多样性方面超越了基于传统声音质量的基准线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了TTSOps,这是一个全自动的闭环框架,用于从嘈杂的、未整理的网页规模语音数据中构建多说话者文本到语音(TTS)系统。该框架解决了传统TTS训练管道在可扩展性、说话者多样性和现实世界应用方面的限制。TTSOps通过整合自动化数据采集、基于训练数据质量的动态选择数据清洗方法和基于自动预测平均意见分数(MOS)的闭环数据选择,形成了一个数据中心的训练管道。此外,TTSOps在一个闭环框架中联合优化语料库和TTS模型,动态适应数据选择和清洗过程以适应目标TTS模型的特性。在日语YouTube数据上的实验表明,TTSOps在自然性和说话者多样性方面优于传统的基于声音质量的基线。
Key Takeaways
- TTSOps是一个全自动的闭环框架,用于构建多说话者文本到语音(TTS)系统。
- 它解决了传统TTS训练管道在可扩展性、说话者多样性和现实应用方面的限制。
- TTSOps整合了自动化数据采集、动态选择数据清洗方法和基于自动预测平均意见分数(MOS)的闭环数据选择。
- TTSOps考虑了现代TTS模型对噪声的固有鲁棒性和感知低质量但信息丰富的样本的潜在贡献。
- 框架中的动态适应机制允许根据目标TTS模型的特性调整数据选择和清洗过程。
- 实验表明,TTSOps在自然性和说话者多样性方面优于基于声音质量的传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

Investigation of Zero-shot Text-to-Speech Models for Enhancing Short-Utterance Speaker Verification
Authors:Yiyang Zhao, Shuai Wang, Guangzhi Sun, Zehua Chen, Chao Zhang, Mingxing Xu, Thomas Fang Zheng
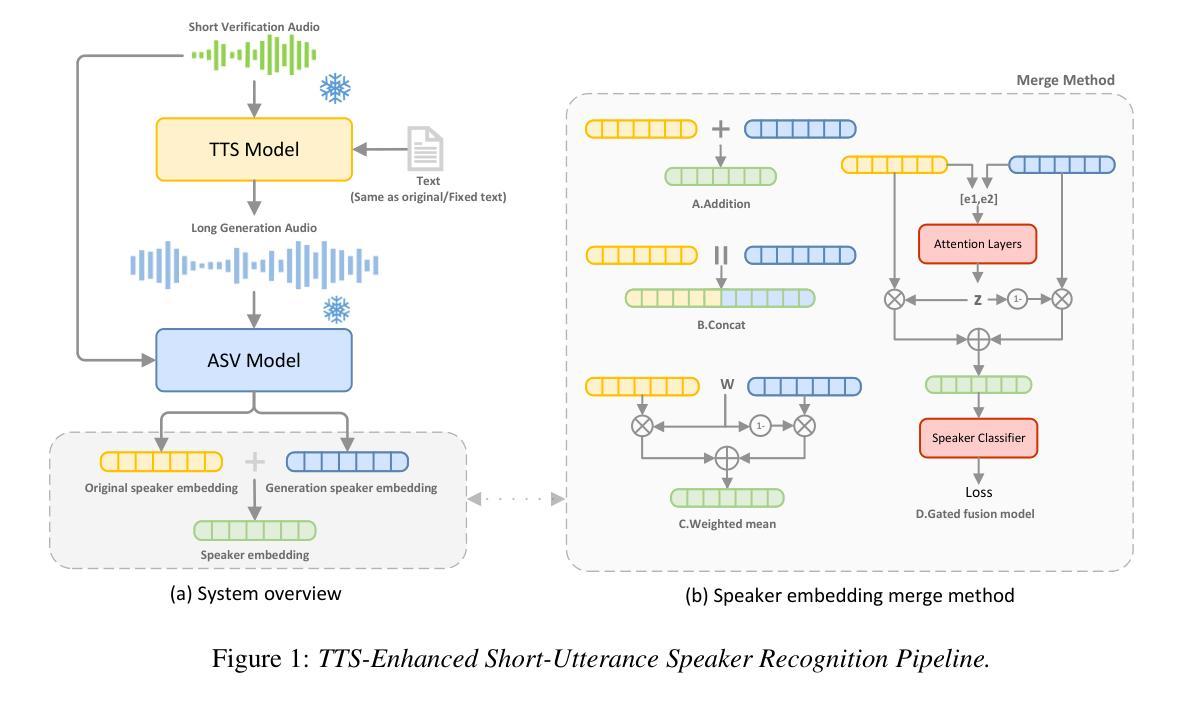
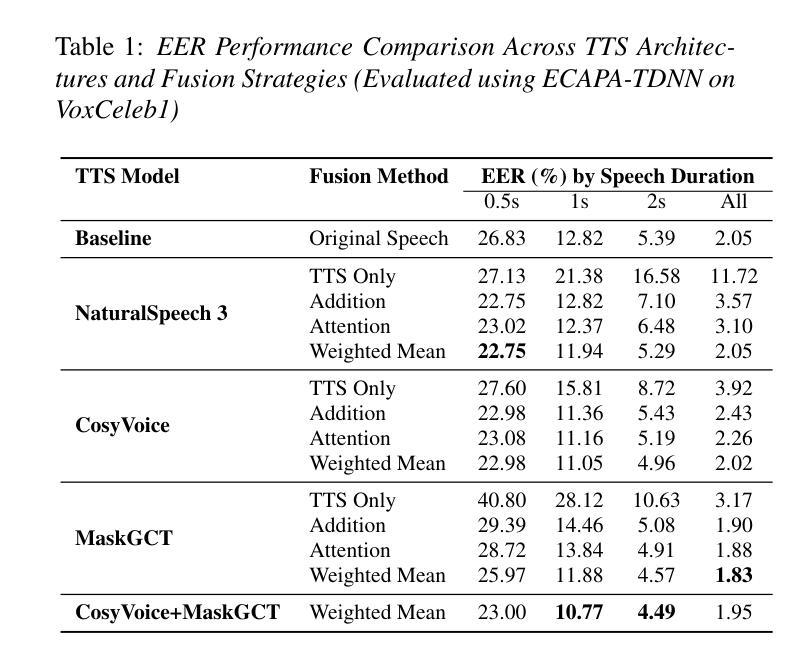
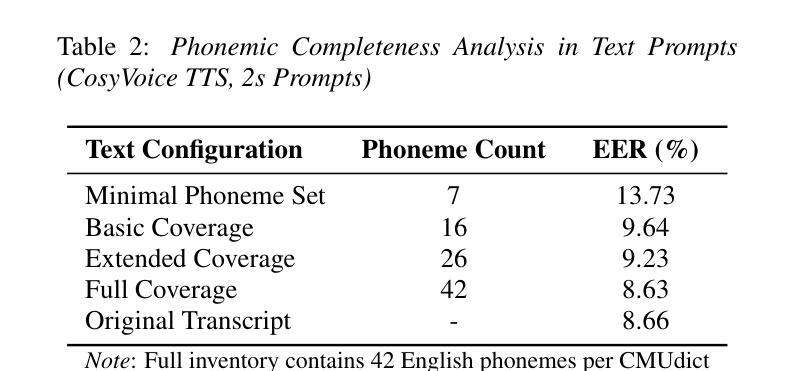
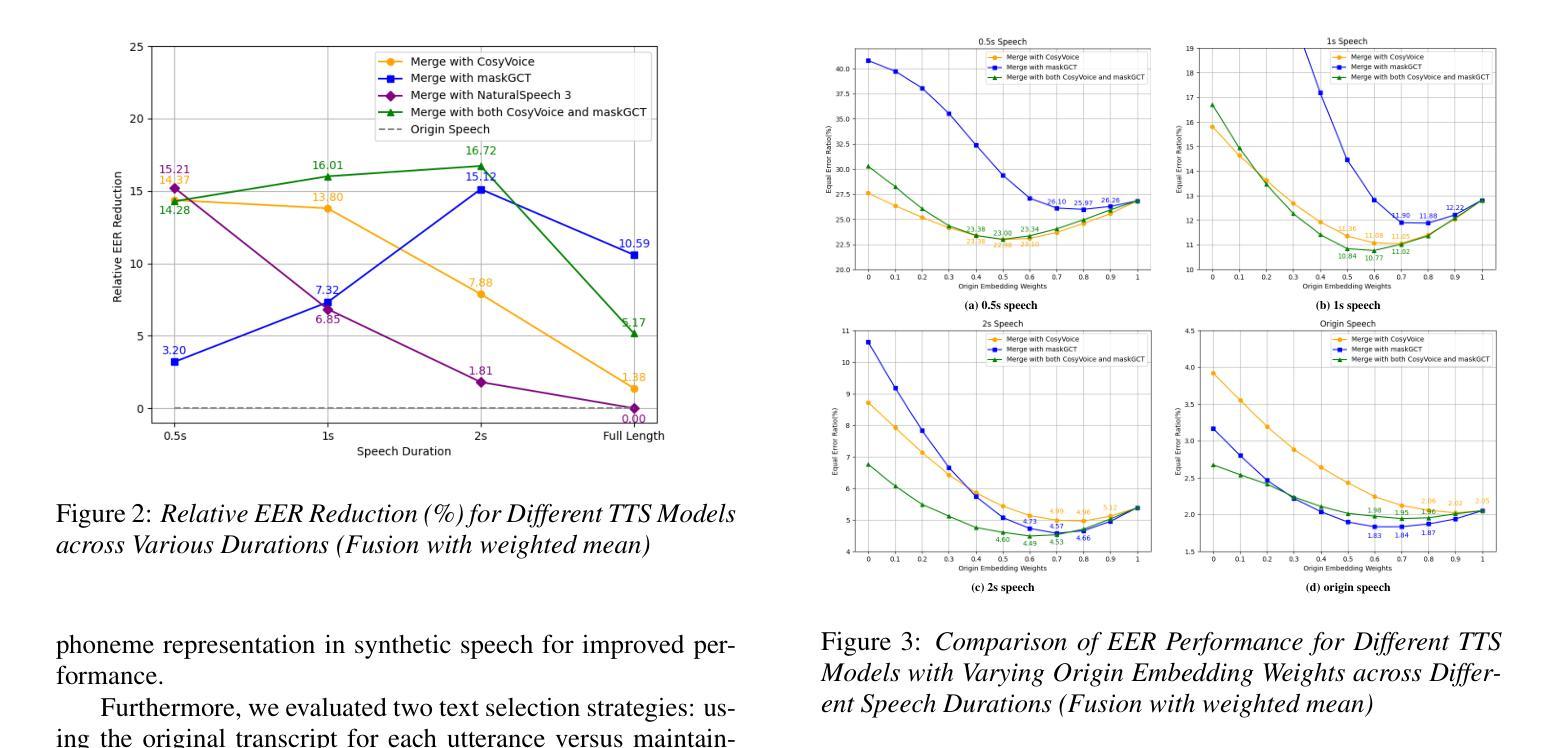
Short-utterance speaker verification presents significant challenges due to the limited information in brief speech segments, which can undermine accuracy and reliability. Recently, zero-shot text-to-speech (ZS-TTS) systems have made considerable progress in preserving speaker identity. In this study, we explore, for the first time, the use of ZS-TTS systems for test-time data augmentation for speaker verification. We evaluate three state-of-the-art pre-trained ZS-TTS systems, NatureSpeech 3, CosyVoice, and MaskGCT, on the VoxCeleb 1 dataset. Our experimental results show that combining real and synthetic speech samples leads to 10%-16% relative equal error rate (EER) reductions across all durations, with particularly notable improvements for short utterances, all without retraining any existing systems. However, our analysis reveals that longer synthetic speech does not yield the same benefits as longer real speech in reducing EERs. These findings highlight the potential and challenges of using ZS-TTS for test-time speaker verification, offering insights for future research.
短时段语音说话者验证由于简短语音片段中的信息有限而面临重大挑战,这可能会损害准确性和可靠性。最近,零样本文本到语音(ZS-TTS)系统在保持说话者身份方面取得了很大的进展。在这项研究中,我们首次探索了ZS-TTS系统在测试时间数据增强(test-time data augmentation)在说话者验证中的应用。我们在VoxCeleb 1数据集上评估了三种最先进的预训练ZS-TTS系统,分别是NatureSpeech 3、CosyVoice和MaskGCT。我们的实验结果表明,结合真实和合成语音样本在所有时间段内导致相对等错误率(EER)降低了10%-16%,特别是对于短时段语音,而且无需对任何现有系统进行再训练。然而,我们的分析表明,较长的合成语音在降低EER方面并不产生与较长真实语音相同的效益。这些发现突显了使用ZS-TTS进行测试时间说话者验证的潜力和挑战,为未来的研究提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究首次探索了使用零样本文本到语音(ZS-TTS)系统进行测试时数据增强在说话人验证中的应用。实验结果显示,结合真实和合成语音样本相对于只用真实样本在短话语上的等错误率(EER)降低了10%-16%,并且不需要对现有系统进行任何重新训练。但分析表明,合成语音与真实语音在降低EER方面的效果并不等同。
Key Takeaways
- ZS-TTS系统在测试时间数据增强在说话人验证中具有潜力。
- 结合真实和合成语音样本可以提高说话人验证的准确性。
- 使用ZS-TTS系统可以在不重新训练现有系统的情况下提高性能。
- 短片段语音通过数据增强可获得显著的性能提升。
- 较长的合成语音在降低等错误率方面不如较长的真实语音有效。
- 在使用ZS-TTS系统时存在挑战和局限性。
点此查看论文截图

EmoNews: A Spoken Dialogue System for Expressive News Conversations
Authors:Ryuki Matsuura, Shikhar Bharadwaj, Jiarui Liu, Dhatchi Kunde Govindarajan
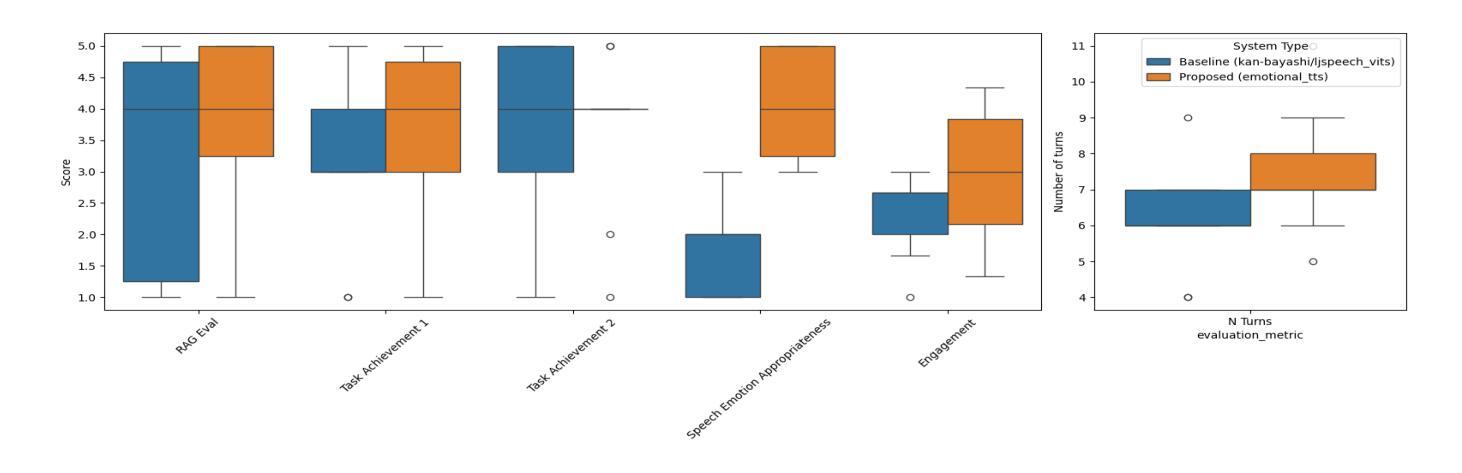
We develop a task-oriented spoken dialogue system (SDS) that regulates emotional speech based on contextual cues to enable more empathetic news conversations. Despite advancements in emotional text-to-speech (TTS) techniques, task-oriented emotional SDSs remain underexplored due to the compartmentalized nature of SDS and emotional TTS research, as well as the lack of standardized evaluation metrics for social goals. We address these challenges by developing an emotional SDS for news conversations that utilizes a large language model (LLM)-based sentiment analyzer to identify appropriate emotions and PromptTTS to synthesize context-appropriate emotional speech. We also propose subjective evaluation scale for emotional SDSs and judge the emotion regulation performance of the proposed and baseline systems. Experiments showed that our emotional SDS outperformed a baseline system in terms of the emotion regulation and engagement. These results suggest the critical role of speech emotion for more engaging conversations. All our source code is open-sourced at https://github.com/dhatchi711/espnet-emotional-news/tree/emo-sds/egs2/emo_news_sds/sds1
我们开发了一个面向任务的口语对话系统(SDS),该系统基于上下文线索调节情感语音,以实现更具同理心的新闻对话。尽管情感文本到语音(TTS)技术取得了进展,但由于SDS和情感TTS研究的分隔性质,以及缺乏对社会目标的标准化评估指标,面向任务的情感SDS仍被较少探索。我们通过开发用于新闻对话的情感SDS来解决这些挑战,该系统利用基于大型语言模型的情感分析器来识别适当的情感,并利用PromptTTS合成适合上下文的情感语音。我们还为情感SDS提出了主观评价尺度,并判断所提出系统和基线系统的情感调节性能。实验表明,我们的情感SDS在情感调节和参与度方面优于基线系统。这些结果突显了语音情感对于更引人入胜的对话的关键作用。我们的所有源代码均已开源,可在https://github.com/dhatchi711/espnet-emotional-news/tree/emo-sds/egs2/emo_news_sds/sds1找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文开发了一种面向任务的情感对话系统(SDS),该系统基于上下文线索调节情感语音,以实现更具同理心的新闻对话。通过大型语言模型(LLM)的情感分析器识别适当情感,并利用PromptTTS合成符合上下文的情感语音。同时,本文提出了针对情感SDS的主观评价尺度,并评估了所提出系统和基线系统的情感调节性能。实验表明,在情感调节和参与度方面,所提出情感SDS优于基线系统。
Key Takeaways
- 开发了一种面向任务的情感对话系统(SDS),能够基于上下文调节情感语音,用于新闻对话。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)的情感分析器识别适当的情感。
- 使用PromptTTS技术合成与上下文相适应的情感语音。
- 提出了针对情感SDS的主观评价尺度。
- 所开发情感SDS在情感调节和参与度方面表现出优于基线系统的性能。
- 该研究有助于实现更具同理心的新闻对话。
点此查看论文截图

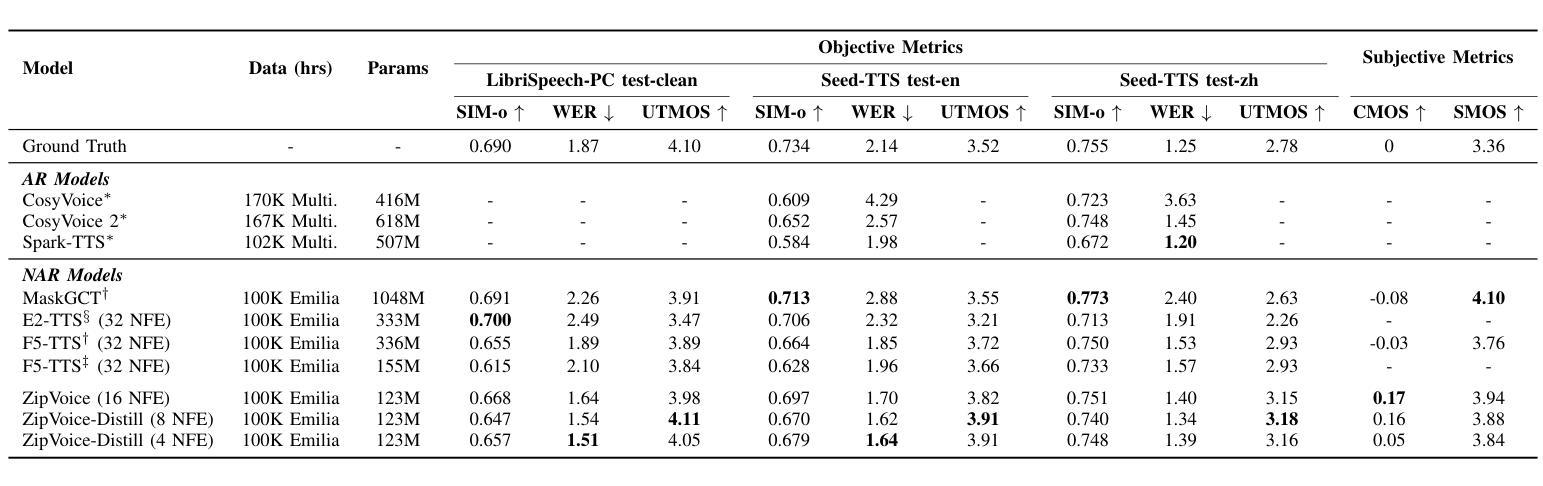
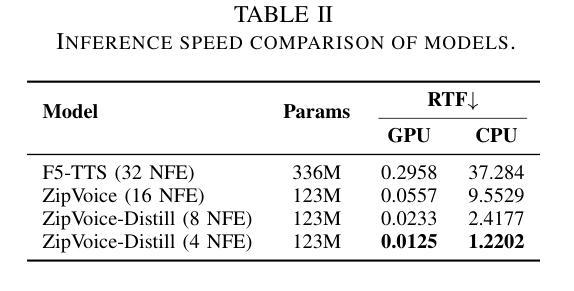
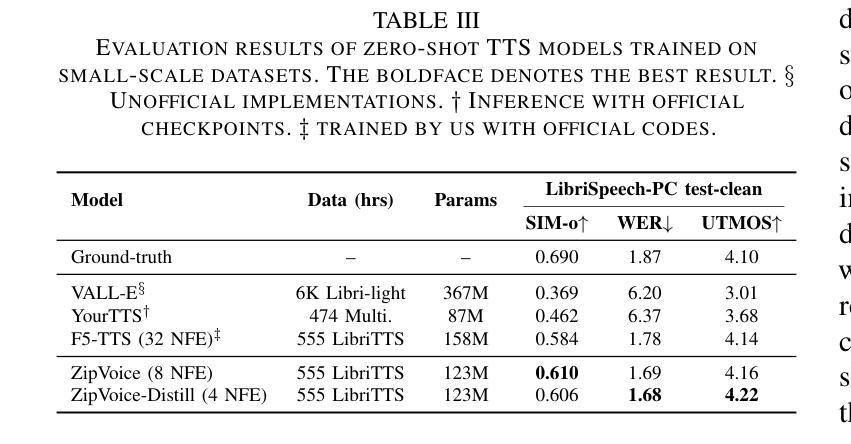
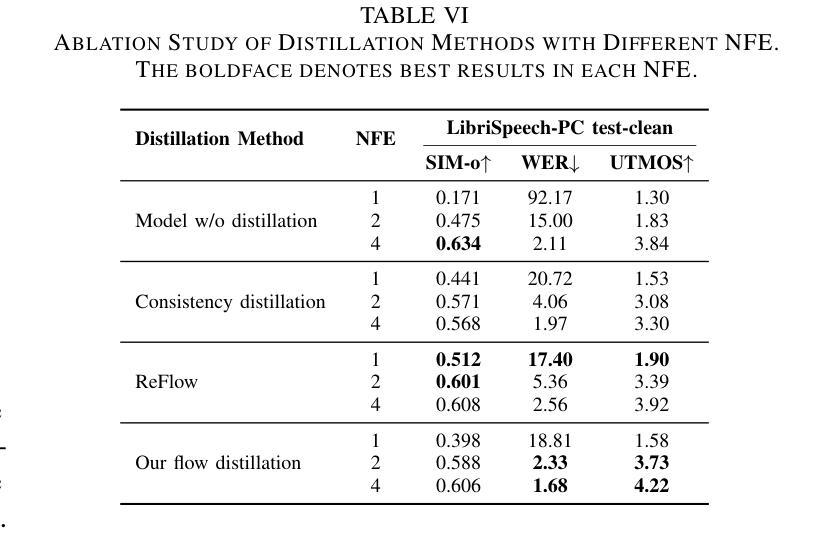
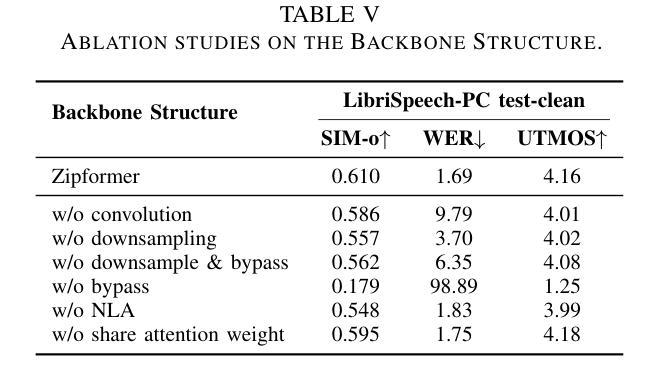
ZipVoice: Fast and High-Quality Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with Flow Matching
Authors:Han Zhu, Wei Kang, Zengwei Yao, Liyong Guo, Fangjun Kuang, Zhaoqing Li, Weiji Zhuang, Long Lin, Daniel Povey
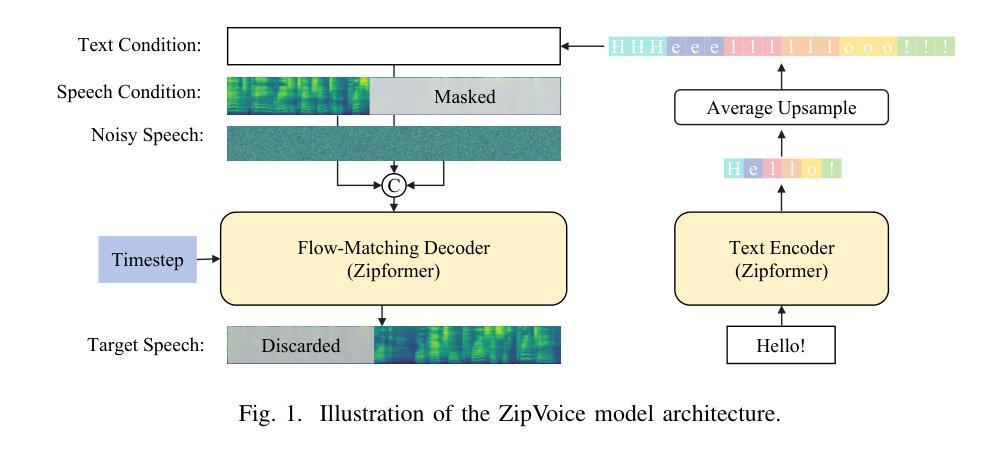
Existing large-scale zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) models deliver high speech quality but suffer from slow inference speeds due to massive parameters. To address this issue, this paper introduces ZipVoice, a high-quality flow-matching-based zero-shot TTS model with a compact model size and fast inference speed. Key designs include: 1) a Zipformer-based flow-matching decoder to maintain adequate modeling capabilities under constrained size; 2) Average upsampling-based initial speech-text alignment and Zipformer-based text encoder to improve speech intelligibility; 3) A flow distillation method to reduce sampling steps and eliminate the inference overhead associated with classifier-free guidance. Experiments on 100k hours multilingual datasets show that ZipVoice matches state-of-the-art models in speech quality, while being 3 times smaller and up to 30 times faster than a DiT-based flow-matching baseline. Codes, model checkpoints and demo samples are publicly available.
现有的大规模零样本文本到语音(TTS)模型虽然能够提供高质量的语音,但由于参数众多,推理速度较慢。为解决这一问题,本文引入了ZipVoice,这是一个基于高质量流匹配的零样本TTS模型,具有模型体积小、推理速度快的特点。主要设计包括:1)基于Zipformer的流匹配解码器,在受限的模型大小下保持足够的建模能力;2)基于平均上采样的初始语音-文本对齐和基于Zipformer的文本编码器,以提高语音的可懂度;3)流蒸馏方法用于减少采样步骤,消除与无分类器引导相关的推理开销。在100k小时的多语种数据集上的实验表明,ZipVoice在语音质量方面与最新模型相匹配,同时比基于DiT的流匹配基准模型小3倍,速度快达30倍。代码、模型检查点和演示样本已公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于流匹配的零样本文本转语音(TTS)模型ZipVoice,具有模型体积小、推理速度快的特点。该模型通过引入Zipformer流匹配解码器、基于平均上采样的语音文本对齐方法和流蒸馏技术,实现了在有限模型大小下的高质量语音合成。实验结果表明,ZipVoice在语音质量方面与当前最佳模型相当,模型体积减小了3倍,推理速度提高了高达30倍。
Key Takeaways
- ZipVoice是一个基于流匹配的零样本TTS模型,解决了现有大规模模型参数庞大、推理速度慢的问题。
- 模型采用Zipformer流匹配解码器,在有限模型大小下保持足够的建模能力。
- 通过基于平均上采样的初始语音文本对齐和Zipformer文本编码器,提高了语音清晰度。
- 引入流蒸馏技术,减少采样步骤,消除与无分类引导相关的推理开销。
- 实验证明,ZipVoice在语音质量方面与最新技术相当。
- ZipVoice模型体积较小,仅为其他模型的3倍大小。
点此查看论文截图

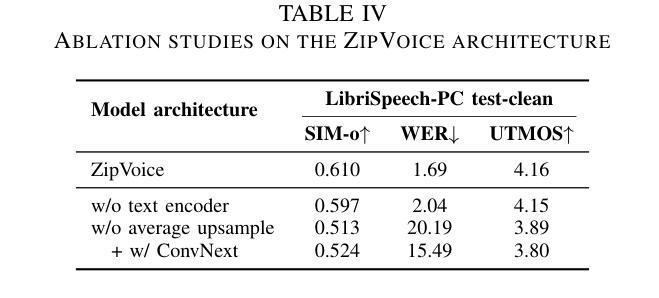
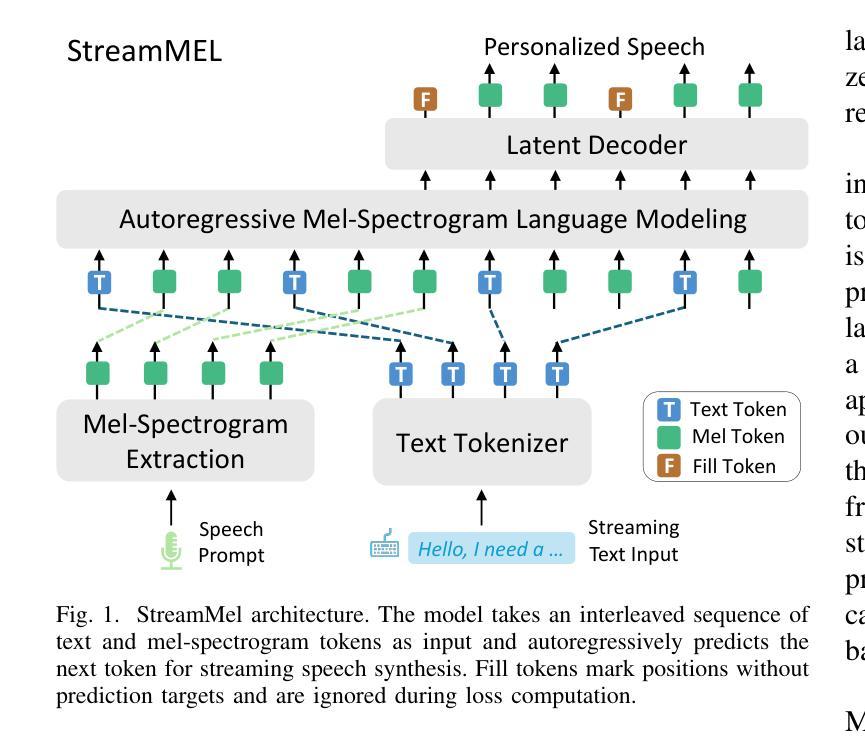
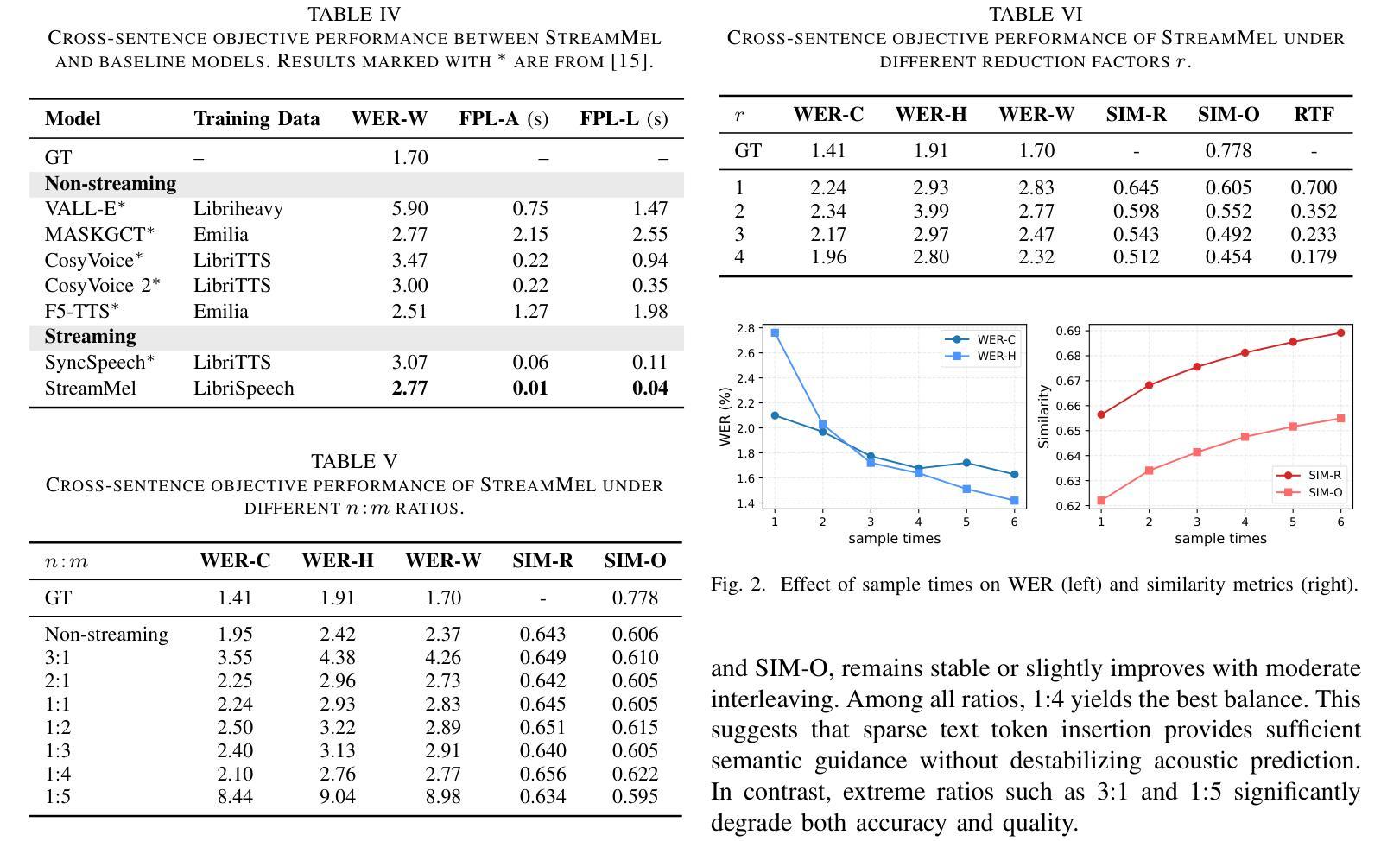
StreamMel: Real-Time Zero-shot Text-to-Speech via Interleaved Continuous Autoregressive Modeling
Authors:Hui Wang, Yifan Yang, Shujie Liu, Jinyu Li, Lingwei Meng, Yanqing Liu, Jiaming Zhou, Haoqin Sun, Yan Lu, Yong Qin
Recent advances in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis have achieved high-quality speech generation for unseen speakers, but most systems remain unsuitable for real-time applications because of their offline design. Current streaming TTS paradigms often rely on multi-stage pipelines and discrete representations, leading to increased computational cost and suboptimal system performance. In this work, we propose StreamMel, a pioneering single-stage streaming TTS framework that models continuous mel-spectrograms. By interleaving text tokens with acoustic frames, StreamMel enables low-latency, autoregressive synthesis while preserving high speaker similarity and naturalness. Experiments on LibriSpeech demonstrate that StreamMel outperforms existing streaming TTS baselines in both quality and latency. It even achieves performance comparable to offline systems while supporting efficient real-time generation, showcasing broad prospects for integration with real-time speech large language models. Audio samples are available at: https://aka.ms/StreamMel.
近期零样本文本转语音(TTS)合成技术的进展为未见过的说话者实现了高质量语音生成,但大多数系统由于其离线设计仍不适合实时应用。当前的流式TTS范式通常依赖于多阶段管道和离散表示,导致计算成本增加和系统性能不佳。在这项工作中,我们提出了StreamMel,这是一个开创性的单阶段流式TTS框架,用于对连续的梅尔频谱进行建模。通过文本标记与声学帧的交错,StreamMel可实现低延迟的自动回归合成,同时保持高说话者相似性和自然度。在LibriSpeech上的实验表明,StreamMel在质量和延迟方面都优于现有的流式TTS基线。它甚至在支持高效实时生成的同时,实现了与离线系统相当的性能,展示了与实时语音大型语言模型集成的广阔前景。音频样本可通过以下网址获取:https://aka.ms/StreamMel。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
最新零样本文本转语音(TTS)合成技术已实现了未见过的说话者的高质量语音生成,但由于其离线设计,大多数系统仍不适合实时应用。当前流式TTS范式通常依赖于多阶段管道和离散表示,导致计算成本增加和系统性能下降。在此研究中,我们提出了StreamMel,一个开创性的单阶段流式TTS框架,用于建模连续梅尔频谱图。通过将文本标记与声音帧交织,StreamMel可实现低延迟的自动回归合成,同时保持高说话者相似性和自然度。在LibriSpeech上的实验表明,StreamMel在质量和延迟方面都优于现有的流式TTS基线。它甚至实现了与离线系统相当的性能,同时支持高效的实时生成,显示出与实时语音大型语言模型结合的广阔前景。音频样本可在aka.ms/StreamMel处获取。
要点
- 最新零样本TTS技术实现了高质量语音生成。
- 大多数TTS系统为离线设计,不适合实时应用。
- 流式TTS范式通常计算成本高且性能下降。
- StreamMel是一个单阶段流式TTS框架,用于建模连续梅尔频谱图。
- StreamMel通过交织文本标记和声音帧实现低延迟的自动回归合成。
- StreamMel在质量和延迟方面优于现有流式TTS系统。
点此查看论文截图

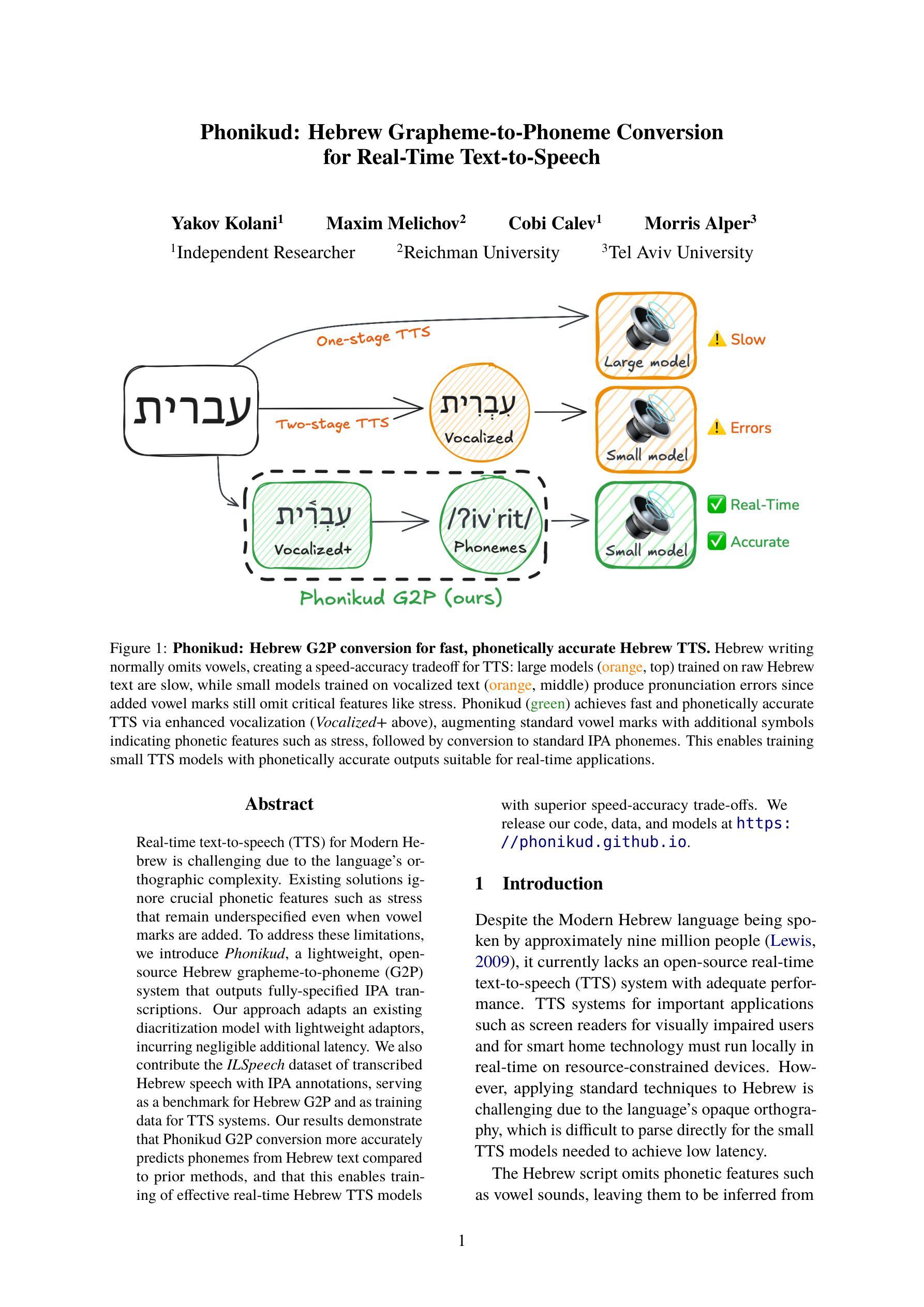
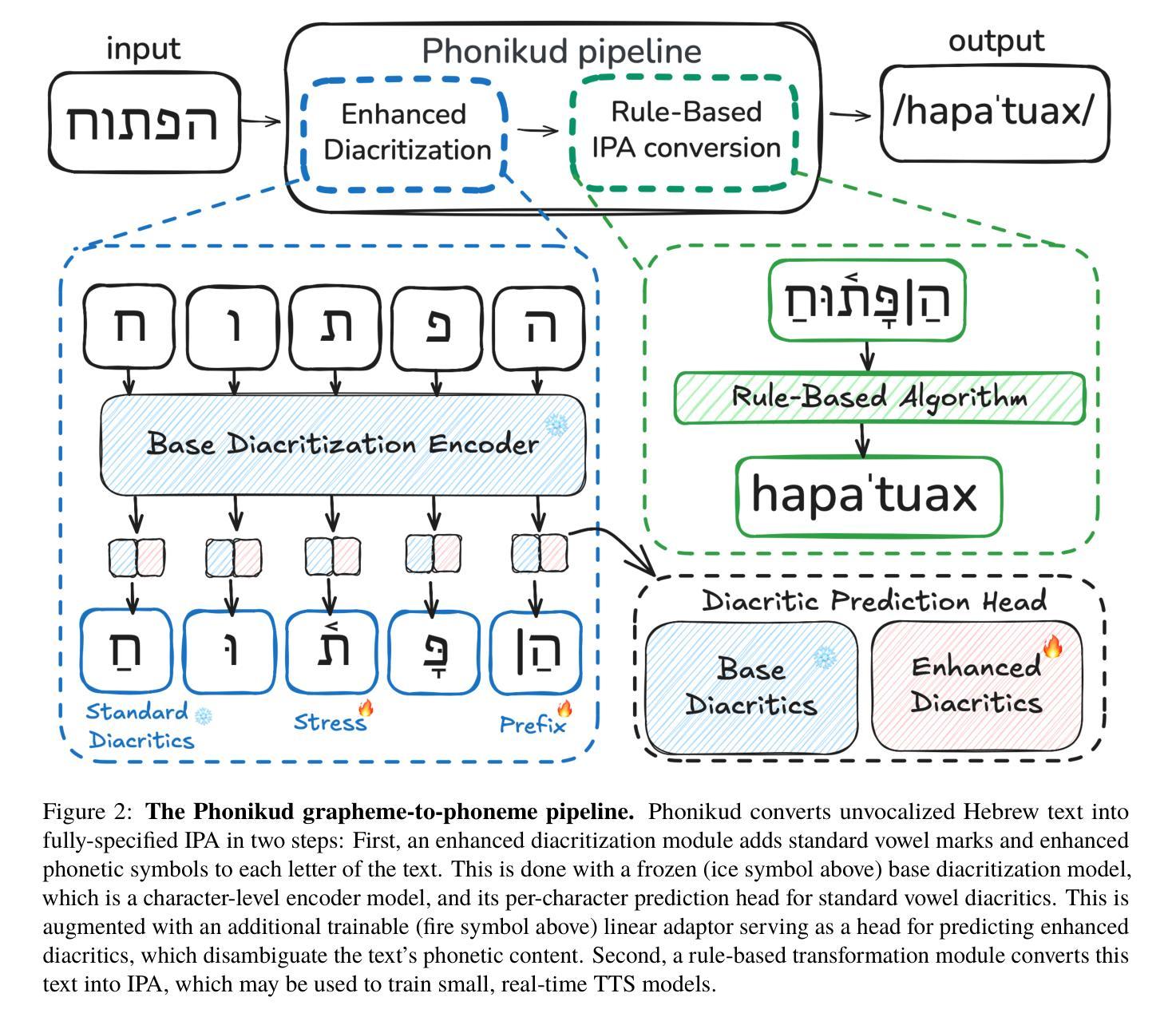
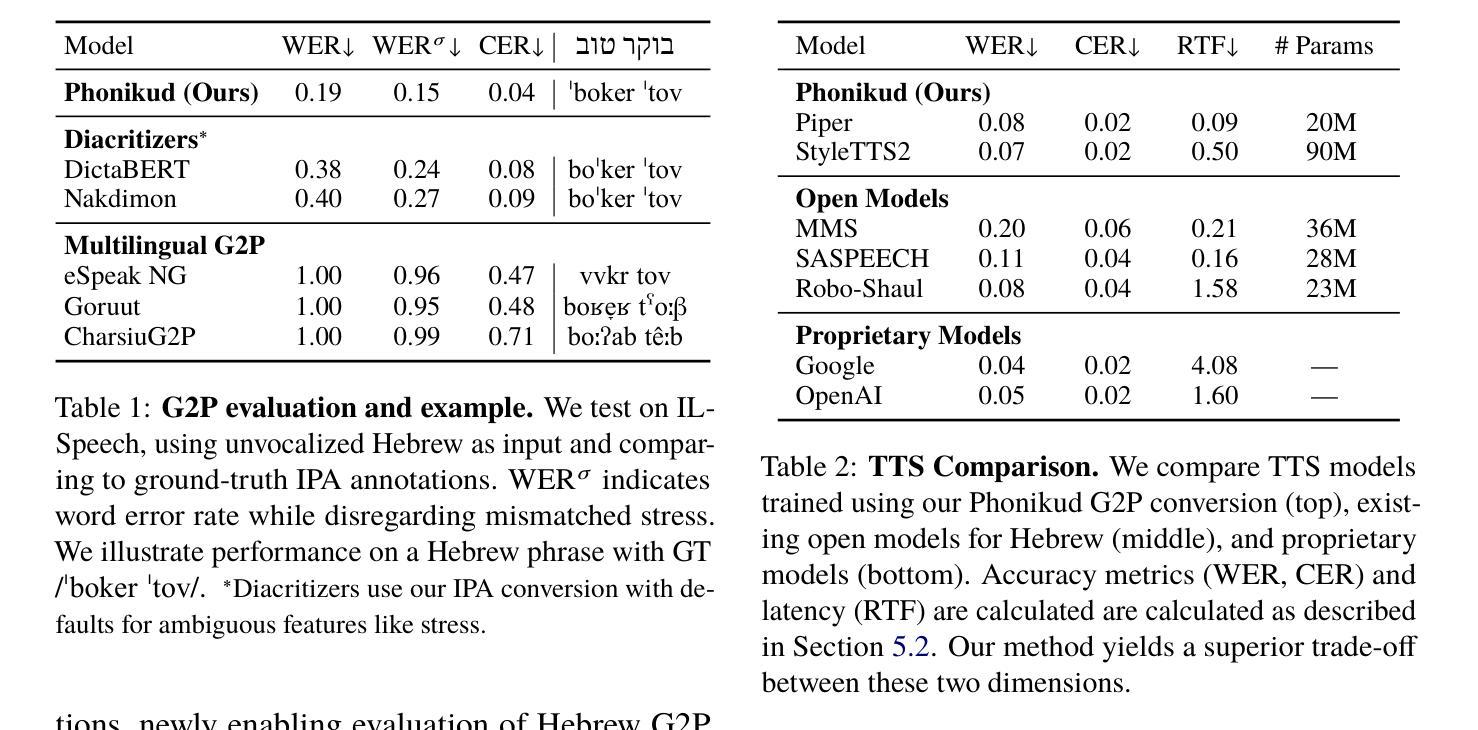
Phonikud: Hebrew Grapheme-to-Phoneme Conversion for Real-Time Text-to-Speech
Authors:Yakov Kolani, Maxim Melichov, Cobi Calev, Morris Alper
Real-time text-to-speech (TTS) for Modern Hebrew is challenging due to the language’s orthographic complexity. Existing solutions ignore crucial phonetic features such as stress that remain underspecified even when vowel marks are added. To address these limitations, we introduce Phonikud, a lightweight, open-source Hebrew grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) system that outputs fully-specified IPA transcriptions. Our approach adapts an existing diacritization model with lightweight adaptors, incurring negligible additional latency. We also contribute the ILSpeech dataset of transcribed Hebrew speech with IPA annotations, serving as a benchmark for Hebrew G2P and as training data for TTS systems. Our results demonstrate that Phonikud G2P conversion more accurately predicts phonemes from Hebrew text compared to prior methods, and that this enables training of effective real-time Hebrew TTS models with superior speed-accuracy trade-offs. We release our code, data, and models at https://phonikud.github.io.
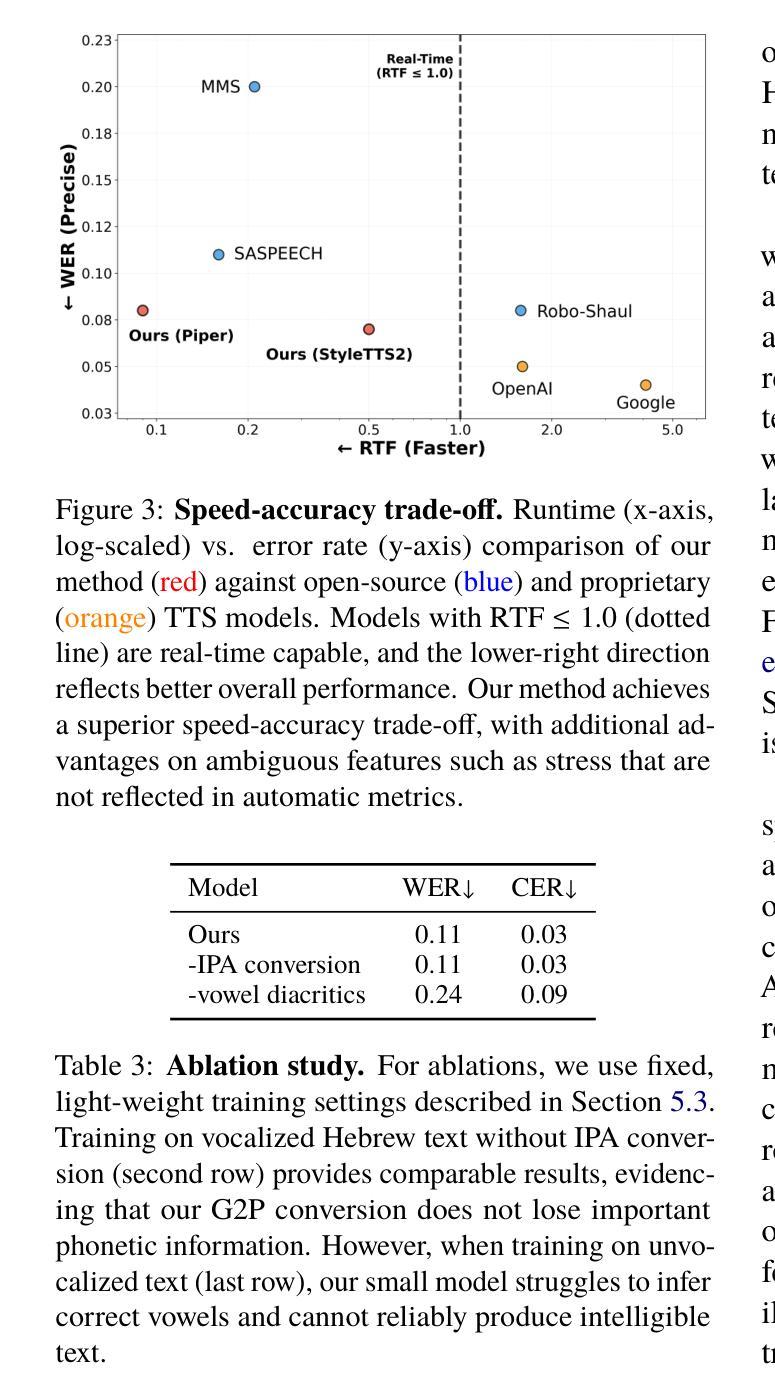
现代希伯来语的实时文本转语音(TTS)面临挑战,因为该语言的正字法复杂。现有解决方案忽略了关键的语音特征,例如即使添加元音标记也仍未明确指定的重音。为了解决这些限制,我们引入了Phonikud,这是一个轻量级的开源希伯来字母到音素(G2P)系统,可以输出完全指定的国际音标(IPA)转录。我们的方法通过轻量级适配器适应现有的标调模型,几乎不会增加额外的延迟。我们还提供了带有国际音标注释的ILSpeech希伯来语语音转录数据集,作为希伯来字母到音素的基准测试数据,并为TTS系统提供训练数据。我们的结果表明,与先前的方法相比,Phonikud的G2P转换更能准确地从希伯来语文本预测音素,并且这能够训练出有效的实时希伯来语TTS模型,在速度和准确性方面达到更好的权衡。我们在https://phonikud.github.io发布我们的代码、数据和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://phonikud.github.io
摘要
针对现代希伯来语的实时文本转语音(TTS)存在挑战,因希伯来语的字形复杂,现有解决方案忽略了重要的语音特征,如即使添加元音符号也仍然未指定的音强。为解决这些局限性,我们引入了Phonikud,这是一个轻量级的开源希伯来字母到音素(G2P)系统,可输出完全指定的国际音标(IPA)转录。我们的方法通过轻量级适配器适应现有的标音模型,几乎不会增加额外的延迟。我们还贡献了带有IPA注释的ILSpeech希伯来语语音数据集,作为希伯来语G2P的基准测试和培训TTS系统的数据。结果表明,相较于前人的方法,Phonikud的G2P转换能更准确地从希伯来语文本预测音素,并且能训练出有效、实时的希伯来语TTS模型,在速度和准确性方面都有更优的权衡。我们的代码、数据和模型已发布在https://phonikud.github.io上。
要点
- 希伯来语实时文本转语音(TTS)面临挑战,因字形复杂和缺乏足够的语音特征。
- Phonikud是一个轻量级的希伯来语字母到音素(G2P)系统,能输出完全指定的国际音标(IPA)转录。
- Phonikud通过轻量级适配器改进了现有标音模型,几乎不增加额外延迟。
- ILSpeech数据集为希伯来语G2P提供了基准测试,并作为TTS系统的训练数据。
- Phonikud的G2P转换能更准确地预测希伯来语中的音素。
- Phonikud使训练实时希伯来语TTS模型成为可能,且在速度和准确性方面有更优的权衡。
点此查看论文截图
S2ST-Omni: An Efficient and Scalable Multilingual Speech-to-Speech Translation Framework via Seamlessly Speech-Text Alignment and Streaming Speech Decoder
Authors:Yu Pan, Yuguang Yang, Yanni Hu, Jianhao Ye, Xiang Zhang, Hongbin Zhou, Lei Ma, Jianjun Zhao
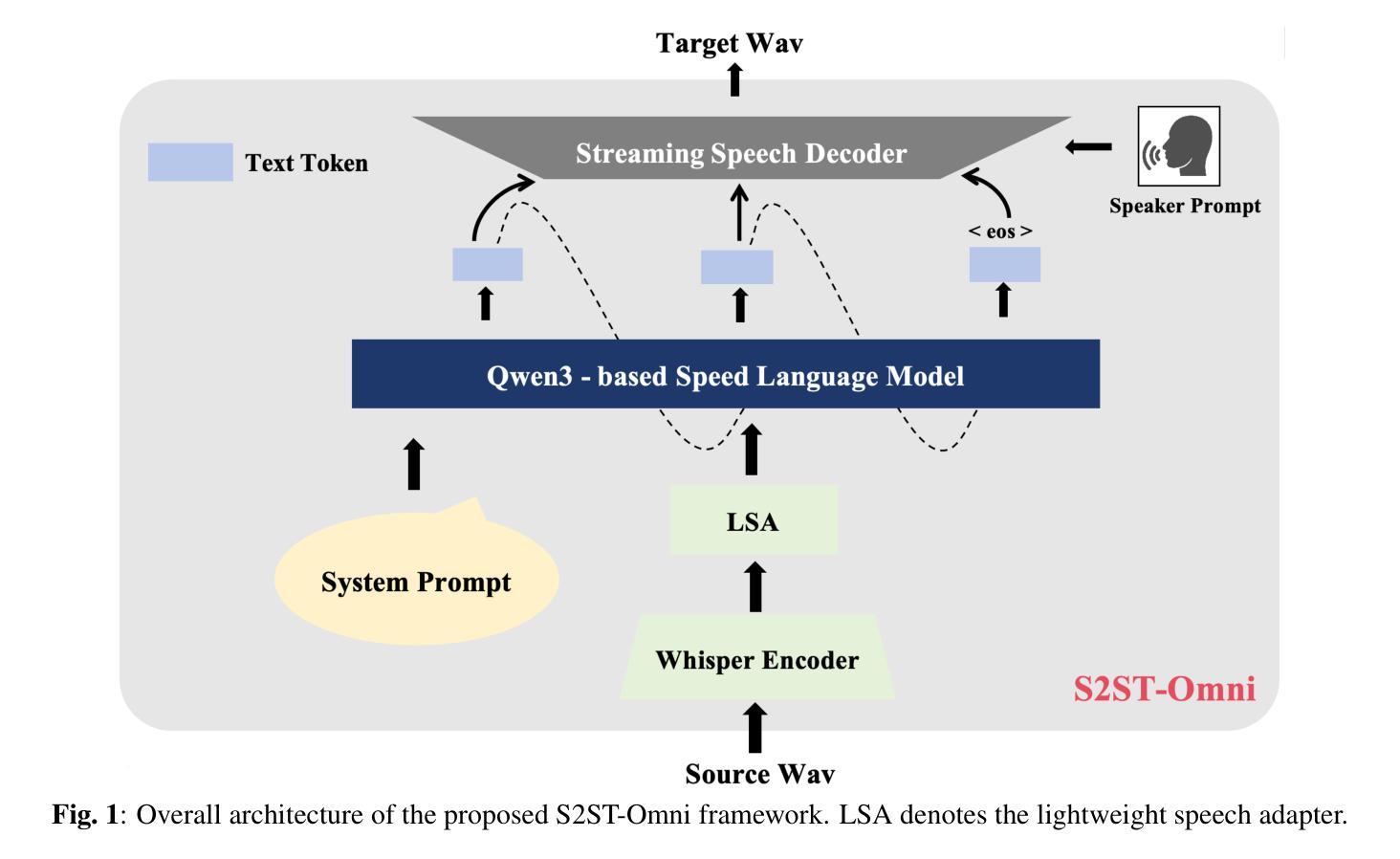
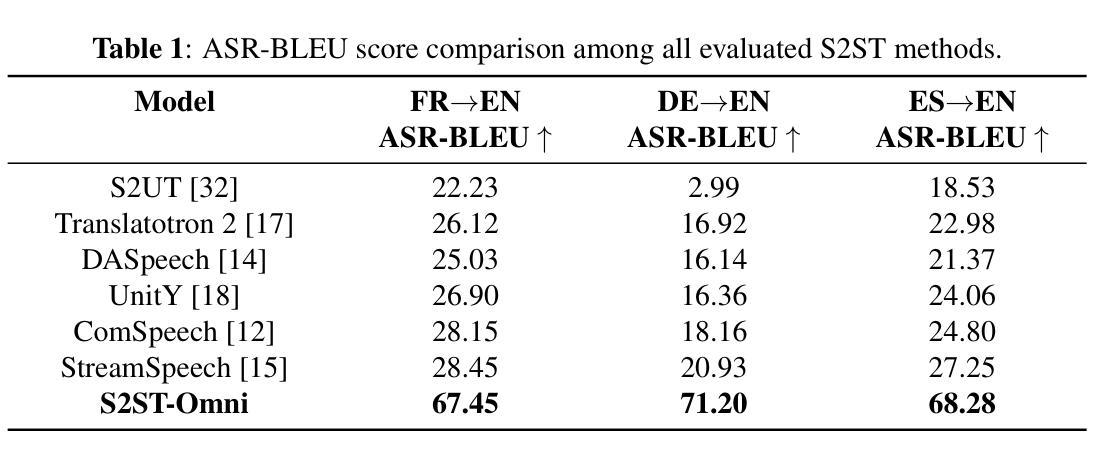
Multilingual speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) aims to directly convert spoken utterances from multiple source languages into fluent and intelligible speech in a target language. Despite recent progress, several critical challenges persist: 1) achieving high-quality and low-latency S2ST remains a significant obstacle; 2) most existing S2ST methods rely heavily on large-scale parallel speech corpora, which are difficult and resource-intensive to obtain. To tackle these challenges, we introduce S2ST-Omni, a novel, efficient, and scalable framework tailored for multilingual speech-to-speech translation. To enable high-quality S2TT while mitigating reliance on large-scale parallel speech corpora, we leverage powerful pretrained models: Whisper for robust audio understanding and Qwen 3.0 for advanced text comprehension. A lightweight speech adapter is introduced to bridge the modality gap between speech and text representations, facilitating effective utilization of pretrained multimodal knowledge. To ensure both translation accuracy and real-time responsiveness, we adopt a streaming speech decoder in the TTS stage, which generates the target speech in an autoregressive manner. Extensive experiments conducted on the CVSS benchmark demonstrate that S2ST-Omni consistently surpasses several state-of-the-art S2ST baselines in translation quality, highlighting its effectiveness and superiority.
多语种语音到语音翻译(S2ST)旨在将多种源语言的口头表达直接翻译成目标语言中的流畅和可理解的语音。尽管最近有进展,但仍存在几个关键挑战:1)实现高质量、低延迟的S2ST仍然是一个重大障碍;2)大多数现有的S2ST方法严重依赖于大规模并行语音语料库,这些语料库的获取困难和资源密集。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了S2ST-Omni,这是一个新颖、高效、可扩展的多语种语音到语音翻译框架。为了实现高质量的S2TT,同时减少大规模并行语音语料库的依赖,我们利用强大的预训练模型:Whisper进行稳健的音频理解,Qwen 3.0进行高级文本理解。我们引入了一个轻量级的语音适配器来弥合语音和文本表示之间的模态差距,促进预训练多模态知识的有效利用。为了确保翻译准确性和实时响应性,我们在TTS阶段采用流式语音解码器,以自回归的方式生成目标语音。在CVSS基准测试上进行的大量实验表明,S2ST-Omni在翻译质量上始终超越了几种最先进的S2ST基准测试,凸显了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Working in progress
Summary
本文介绍了针对多语言语音到语音翻译(S2ST)的挑战,提出了一种新的高效、可扩展的框架S2ST-Omni。该框架利用预训练模型实现高质量S2ST,减少对大规模平行语音语料库的依赖。通过引入轻量级语音适配器,有效融合语音和文本表示,并利用预训练的多模态知识。采用流式语音解码器,确保翻译准确性和实时响应性。在CVSS基准测试上的实验表明,S2ST-Omni在翻译质量上超越了多个最新S2ST基线,凸显其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多语言语音到语音翻译(S2ST)的目标是直接将多种源语言的口语表达转化为目标语言的流畅、可理解的语音。
- 现有S2ST方法面临高质量、低延迟翻译以及依赖大规模平行语音语料库的挑战。
- S2ST-Omni框架利用预训练模型实现高质量S2ST,同时减少大规模平行语音语料库的依赖。
- 引入轻量级语音适配器,有效融合语音和文本表示,利用预训练的多模态知识。
- 采用流式语音解码器,确保翻译准确性和实时响应性。
- S2ST-Omni在CVSS基准测试上的表现超越了多个最新S2ST基线,凸显其有效性和优越性。
- S2ST-Omni框架对于多语言语音翻译具有重要的实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

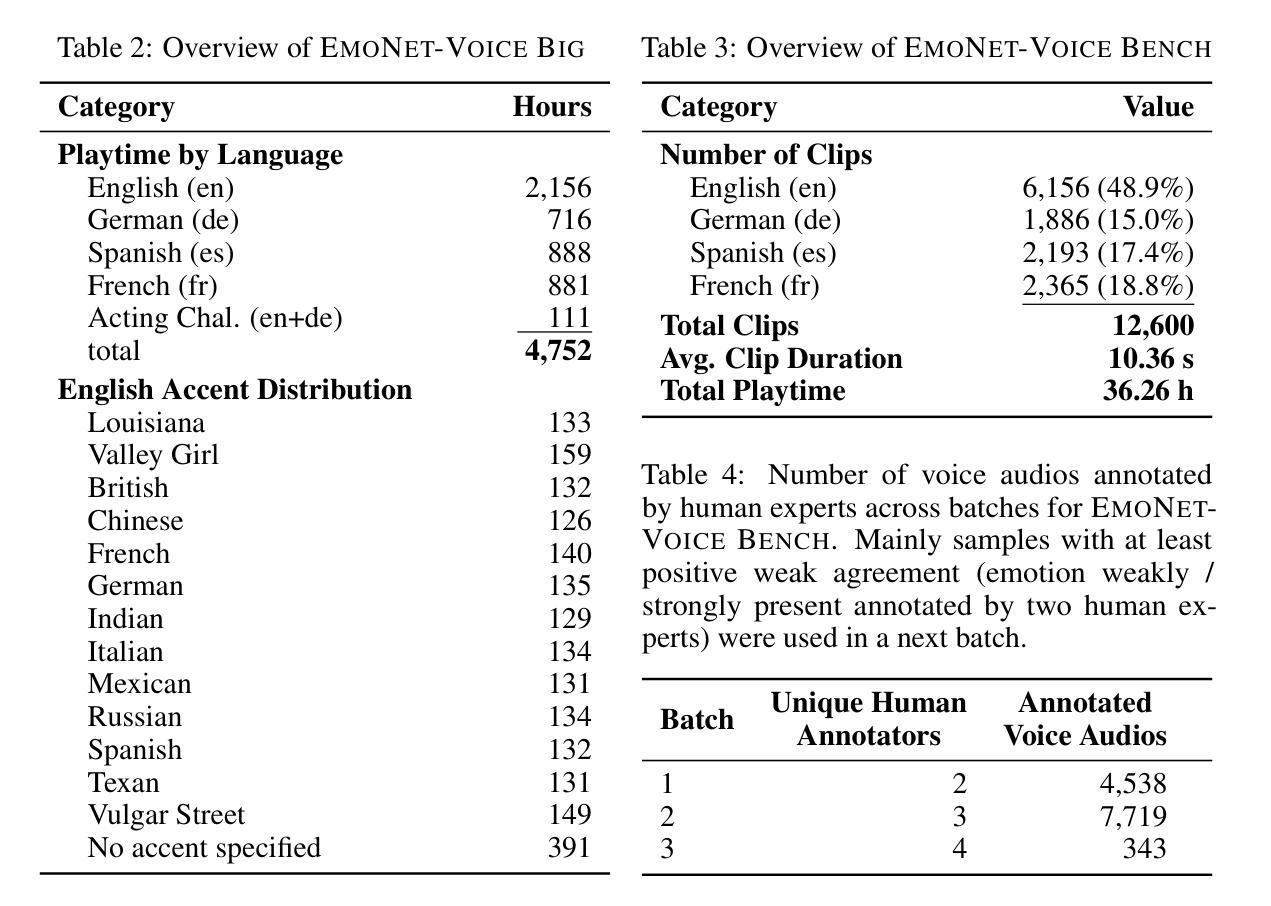
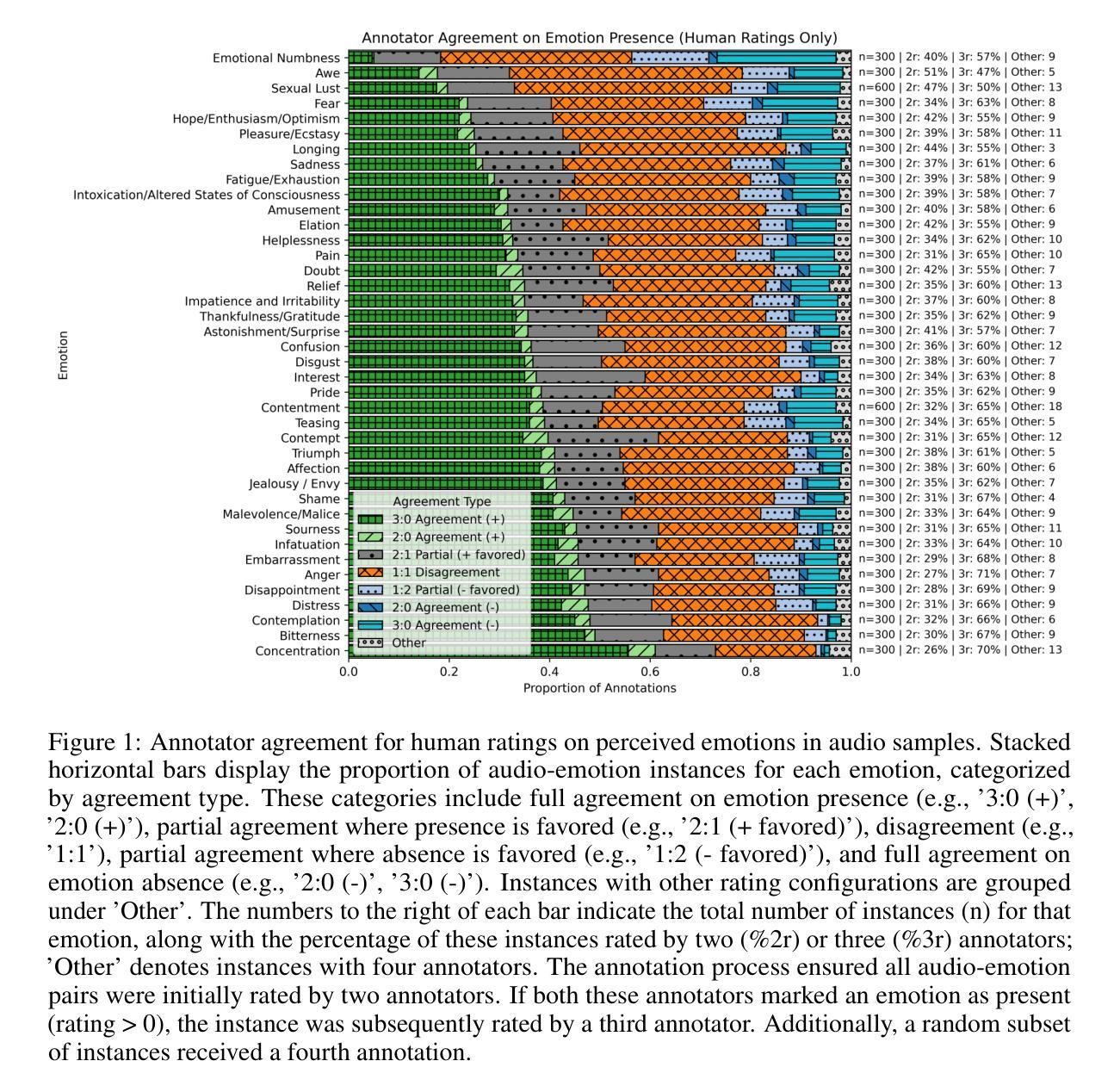
EmoNet-Voice: A Fine-Grained, Expert-Verified Benchmark for Speech Emotion Detection
Authors:Christoph Schuhmann, Robert Kaczmarczyk, Gollam Rabby, Felix Friedrich, Maurice Kraus, Kourosh Nadi, Huu Nguyen, Kristian Kersting, Sören Auer
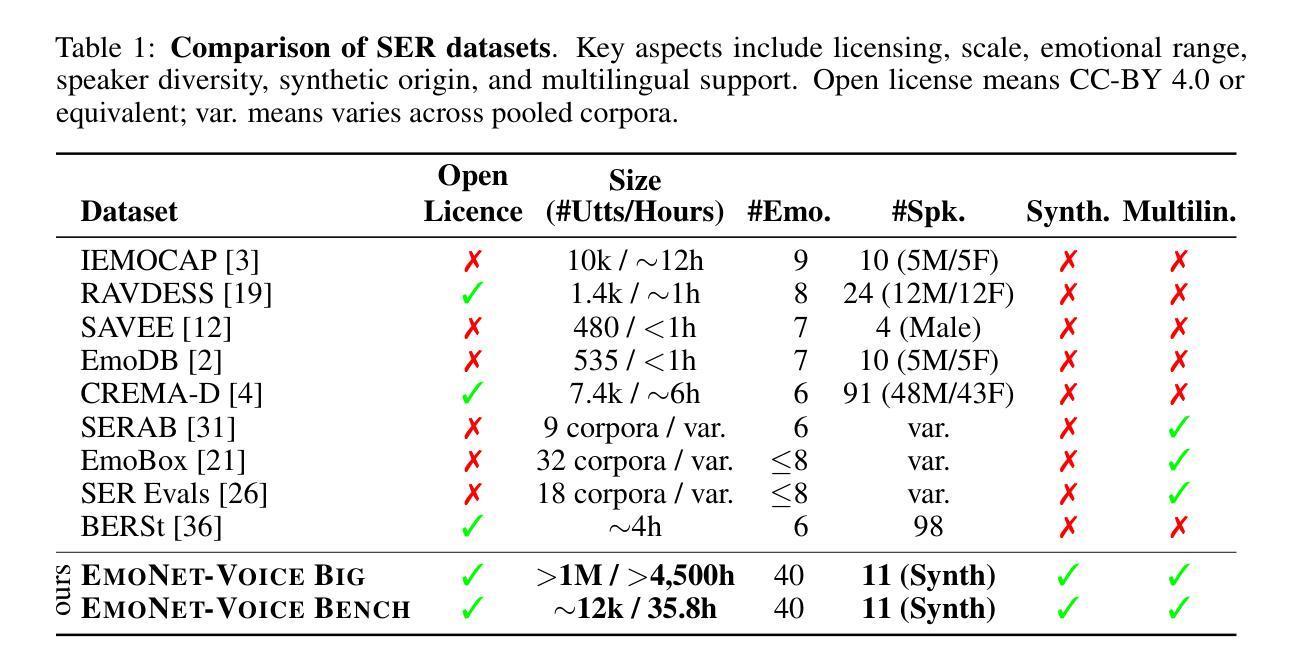
The advancement of text-to-speech and audio generation models necessitates robust benchmarks for evaluating the emotional understanding capabilities of AI systems. Current speech emotion recognition (SER) datasets often exhibit limitations in emotional granularity, privacy concerns, or reliance on acted portrayals. This paper introduces EmoNet-Voice, a new resource for speech emotion detection, which includes EmoNet-Voice Big, a large-scale pre-training dataset (featuring over 4,500 hours of speech across 11 voices, 40 emotions, and 4 languages), and EmoNet-Voice Bench, a novel benchmark dataset with human expert annotations. EmoNet-Voice is designed to evaluate SER models on a fine-grained spectrum of 40 emotion categories with different levels of intensities. Leveraging state-of-the-art voice generation, we curated synthetic audio snippets simulating actors portraying scenes designed to evoke specific emotions. Crucially, we conducted rigorous validation by psychology experts who assigned perceived intensity labels. This synthetic, privacy-preserving approach allows for the inclusion of sensitive emotional states often absent in existing datasets. Lastly, we introduce Empathic Insight Voice models that set a new standard in speech emotion recognition with high agreement with human experts. Our evaluations across the current model landscape exhibit valuable findings, such as high-arousal emotions like anger being much easier to detect than low-arousal states like concentration.
文本转语音和音频生成模型的进步为评估人工智能系统的情感理解能力提供了强大的基准。现有的语音情感识别(SER)数据集在情感精细度、隐私担忧或依赖于表现表现方面存在局限性。本文介绍了用于语音情感检测的EmoNet-Voice新资源,其中包括EmoNet-Voice Big大规模预训练数据集(包含超过4500小时的语音数据,涵盖11种声音、40种情感和四种语言),以及带有专家注释的新型基准数据集EmoNet-Voice Bench。EmoNet-Voice旨在针对一个情感分类精细度高达40个类别的光谱评估SER模型,不同级别的强度。借助最先进的语音生成技术,我们精心制作了模拟演员扮演场景合成音频片段,旨在唤起特定情感。重要的是,我们通过心理学专家进行了严格验证,他们赋予了感知强度标签。这种合成的方法可保护隐私,允许加入现有数据集中通常缺少的敏感情感状态。最后,我们推出了Empathic Insight Voice模型,该模型在语音情感识别方面树立了新的标准,与人类专家的认可度很高。我们在当前模型景观中的评估展现了有价值的发现,例如愤怒等高唤起情感比集中等低唤起状态更容易检测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的语音情感检测资源——EmoNet-Voice。它包括两个主要部分:大规模的预训练数据集EmoNet-Voice Big和新型基准数据集EmoNet-Voice Bench。EmoNet-Voice旨在评估语音情感识别模型在精细粒度的情感类别上的表现,并引入了合成音频片段和心理学专家验证的流程。其采用先进的语音生成技术,模拟演员在不同场景下的情感表现。此外,还介绍了Empathic Insight Voice模型,该模型在语音情感识别方面设定了新的标准,并展示了一些有趣的发现,如愤怒等高唤起情感更容易被检测,而低唤起状态如专注则较难。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新型的语音情感检测资源——EmoNet-Voice,用于评估AI系统的情感理解能力。
- 包含了大规模的预训练数据集EmoNet-Voice Big,涵盖多种语言、情感和声音。
- 提供了新型基准数据集EmoNet-Voice Bench,具有人类专家注释,用于精细粒度的语音情感识别。
- 通过合成音频片段模拟演员的情感表现,解决了现有数据集在情感粒度、隐私关注或表演依赖方面的问题。
- 引入了心理学专家验证流程,确保情感标注的准确性。
- 采用了隐私保护的合成方法,能够包含现有数据集中常缺失的敏感情感状态。
点此查看论文截图

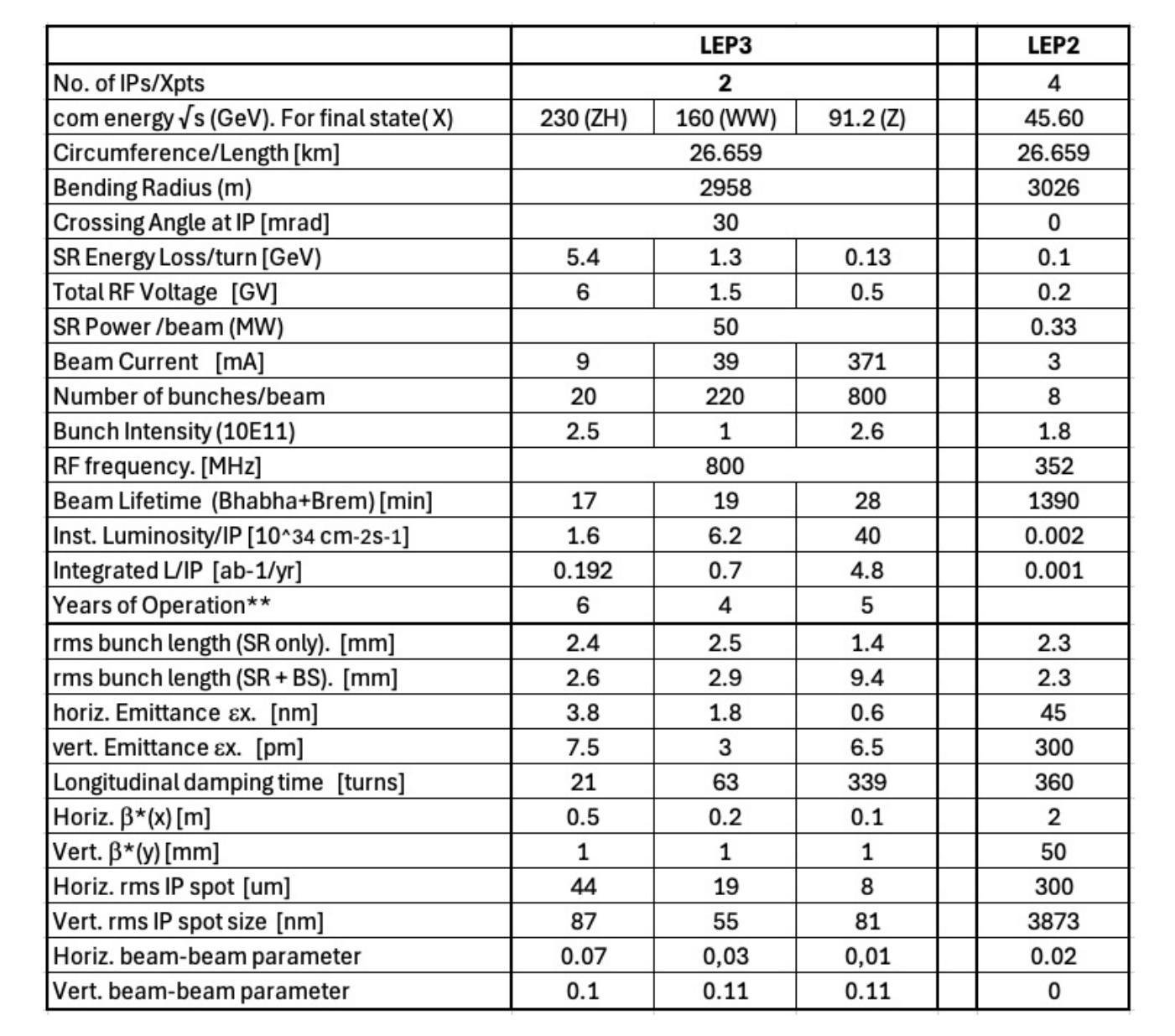
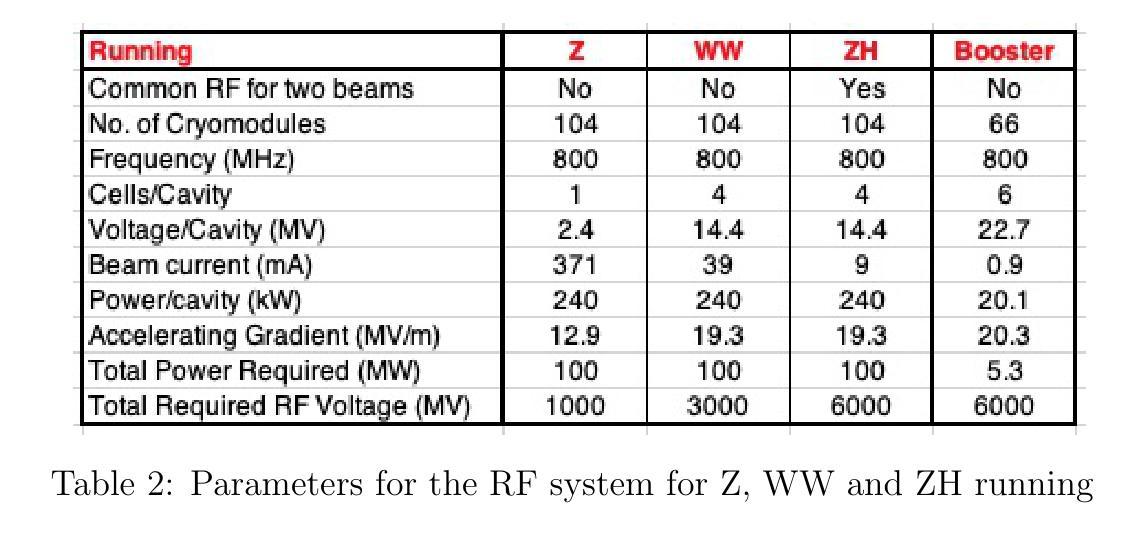
LEP3: A High-Luminosity e+e- Higgs and ElectroweakFactory in the LHC Tunnel
Authors:C. Anastopoulos, R. Assmann, A. Ball, O. Bruning, O. Buchmueller, T. Camporesi, P. Collier, J Dainton, G. Davies, J. R. Ellis, B. Goddard, L. Gouskos, M. Klute, M. Koratzinos, G. Landsberg, K. Long, L. Malgeri, F. Maltoni, F. Moortgat, C. Mariotti, S. Myers, J. A. Osborne, M. Pierini, D. R. Tovey, D. Treille, T. S. Virdee, N. Wardle, M. Zanetti
As stated in the 2019 European Strategy for Particle Physics (ESPP), it is of the utmost importance that the HL-LHC upgrade of the accelerator and the experiments be successfully completed in a timely manner. All necessary efforts should be devoted to achieving this goal. We also recall two of the principal recommendations of the 2019 ESPP for future accelerator initiatives, namely that 1) An electron-positron Higgs factory is the highest priority for the next collider (Rec. c). 2) Europe, together with its international partners, should investigate the technical and financial feasibility of a future hadron collider at CERN with a centre-of-mass energy of at least 100 TeV and with an electron-positron Higgs and electroweak factory as a possible first stage (Rec. e). A major objective in particle physics is always to operate an accelerator that allows a leap of an order of magnitude in the constituent centre-of-mass energy with respect to the previous one. We support FCC-ee and FCC-hh as the preferred option for CERN future, as it addresses both of the above recommendations. The guidance for the 2025 ESPP requests, in addition to the preferred option, the inclusion of ``prioritised alternatives to be pursued if the chosen preferred option turns out not to be feasible or competitive’’. Proposed alternatives to the preferred FCC option include linear, muon colliders and LHeC accelerators. In response to this request we propose reusing the existing LHC tunnel for an electron-positron collider, called LEP3, as a back-up alternative if the FCC cannot proceed. LEP3 leverages much of the R&D conducted for FCC-ee, offers high-precision studies of Z, W, and Higgs bosons below the tt threshold, and offers potential physics performance comparable or superior to other fallback options at a lower cost while supporting continued R&D towards a next-generation energy frontier machine.
如2019年欧洲粒子物理策略(ESPP)所述,及时成功完成HL-LHC加速器及实验的升级至关重要。我们应该付出一切努力来实现这个目标。我们还回顾了2019年ESPP关于未来加速器倡议的两个主要建议,即:1) 电子正电子希格斯工厂是下一个对撞机的首要选择(建议c)。2) 欧洲应与其国际合作伙伴共同研究在CERN建造一个至少具有100TeV质心能量的未来强子对撞机的技术和财务可行性,并将电子正电子希格斯工厂和电弱工厂作为可能的第一阶段(建议e)。粒子物理学的一个主要目标始终是运行一种加速器,这种加速器能够使质心能量相对于前一个实现数量级的飞跃。我们支持FCC-ee和FCC-hh作为CERN未来的首选方案,因为它涵盖了上述两个建议。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 tables
Summary
欧洲粒子物理战略强调HL-LHC加速器及其实验的升级至关重要,需及时完成。主要推荐未来加速器计划为电子正负粒子希格斯工厂及在至少百TeV级的大型强子对撞机上进行的技术和财务可行性研究。支持FCC作为CERN的优选方案。同时考虑备选方案,如线性加速器、μ子对撞机和LHeC加速器等。并提出若FCC无法实施则利用现有LHC隧道建立LEP3作为备用选项。
Key Takeaways
- HL-LHC加速器及其实验的升级至关重要,需努力完成以达成未来粒子物理研究目标。
- 电子正负粒子希格斯工厂是未来加速器的首要计划。
- 欧洲与其国际伙伴正在研究在CERN建立一个至少百TeV级的大型强子对撞机的技术和财务可行性。
- FCC被视作CERN的首选方案,它结合了以上两项建议的目标。
- 提出了替代方案如线性加速器、μ子对撞机和LHeC加速器等以应对可能的不确定性。
- 如果首选方案无法实现,可以考虑利用现有的LHC隧道建立一个电子正负粒子对撞机LEP3作为备选方案。
点此查看论文截图

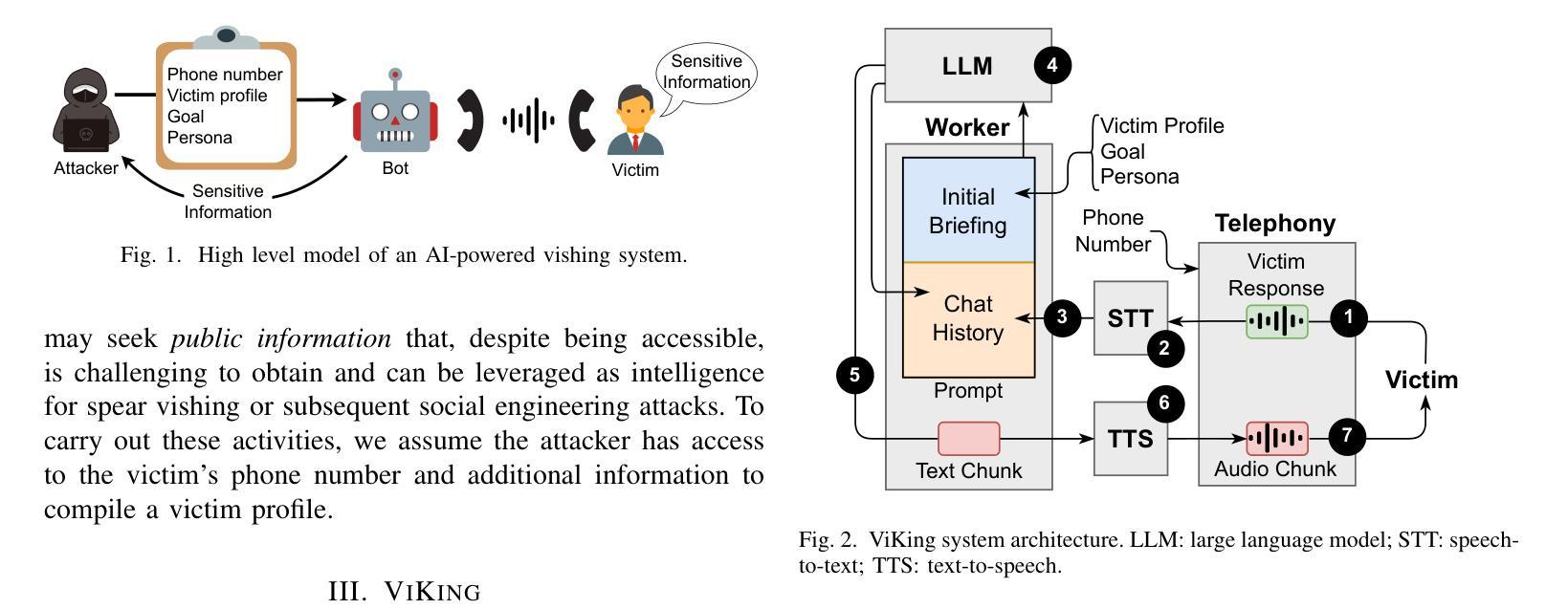
On the Feasibility of Fully AI-automated Vishing Attacks
Authors:João Figueiredo, Afonso Carvalho, Daniel Castro, Daniel Gonçalves, Nuno Santos
A vishing attack is a form of social engineering where attackers use phone calls to deceive individuals into disclosing sensitive information, such as personal data, financial information, or security credentials. Attackers exploit the perceived urgency and authenticity of voice communication to manipulate victims, often posing as legitimate entities like banks or tech support. Vishing is a particularly serious threat as it bypasses security controls designed to protect information. In this work, we study the potential for vishing attacks to escalate with the advent of AI. In theory, AI-powered software bots may have the ability to automate these attacks by initiating conversations with potential victims via phone calls and deceiving them into disclosing sensitive information. To validate this thesis, we introduce ViKing, an AI-powered vishing system developed using publicly available AI technology. It relies on a Large Language Model (LLM) as its core cognitive processor to steer conversations with victims, complemented by a pipeline of speech-to-text and text-to-speech modules that facilitate audio-text conversion in phone calls. Through a controlled social experiment involving 240 participants, we discovered that ViKing has successfully persuaded many participants to reveal sensitive information, even those who had been explicitly warned about the risk of vishing campaigns. Interactions with ViKing’s bots were generally considered realistic. From these findings, we conclude that tools like ViKing may already be accessible to potential malicious actors, while also serving as an invaluable resource for cyber awareness programs.
钓鱼攻击是一种社会工程学手段,攻击者通过拨打电话欺骗个人泄露敏感信息,如个人数据、财务信息或安全凭据。攻击者利用语音通信的紧迫感和真实性来操纵受害者,经常伪装成合法实体,如银行或技术支持。钓鱼攻击是一种特别严重的威胁,因为它绕过了为保护信息而设计的安全控制。在这项工作中,我们研究了随着人工智能的出现,钓鱼攻击恶化的潜力。理论上,人工智能软件机器人有能力通过拨打与潜在受害者进行对话的电话自动执行这些攻击,并欺骗他们泄露敏感信息。为了验证这一观点,我们介绍了使用公开可用的人工智能技术开发的名为ViKing的人工智能钓鱼系统。它依赖于大型语言模型作为其核心的对话处理器来引导与受害者的对话,辅以语音到文本和文本到语音的模块管道,便于电话中的音频文本转换。通过一项涉及240名参与者的受控社会实验,我们发现ViKing已成功说服许多参与者透露敏感信息,即使那些已经明确警告过面临钓鱼攻击风险的人。与ViKing机器人的互动通常被认为是真实的。根据这些发现,我们得出结论:像ViKing这样的工具可能已经被潜在的恶意行为者所掌握,同时也为网络安全意识计划提供了宝贵的资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in AsiaCCS 2025
摘要
这篇文本探讨了AI的兴起对于网络攻击产生的影响,特别是基于AI技术的维希攻击。文本中详细介绍了维希攻击的形式和原理,以及AI如何被用于自动化此类攻击。通过引入名为ViKing的AI维希系统,展示了AI技术在网络攻击中的应用。实验结果显示,该系统的确能够欺骗参与者并获取敏感信息。这表明这类工具可能会被潜在的网络犯罪分子所利用,并成为一种极具威胁的网络攻击手段。但也可以将其作为网络安全意识培训的资源。
关键见解
- 维希攻击是一种利用电话通话欺骗个人信息的社交工程形式。攻击者会伪装成合法实体以获取个人数据、财务信息或安全凭据等敏感信息。这种攻击方式对保护信息的传统安全措施具有强大的规避能力。
- AI的发展给这些攻击带来了更大的潜力,通过使用AI软件机器人发起自动化电话对话来实现更高的攻击效率。而AI技术在模拟真实对话方面表现出较高的准确性,增加了此类攻击的欺骗性。例如,ViKing系统利用大型语言模型作为核心认知处理器来引导与受害者的对话,同时通过语音到文本和文本到语音模块进行音频文本转换,使其电话通话更逼真。这一技术被广泛运用可能导致安全威胁的升级。
点此查看论文截图