⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-22 更新
OpenPath: Open-Set Active Learning for Pathology Image Classification via Pre-trained Vision-Language Models
Authors:Lanfeng Zhong, Xin Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
Pathology image classification plays a crucial role in accurate medical diagnosis and treatment planning. Training high-performance models for this task typically requires large-scale annotated datasets, which are both expensive and time-consuming to acquire. Active Learning (AL) offers a solution by iteratively selecting the most informative samples for annotation, thereby reducing the labeling effort. However, most AL methods are designed under the assumption of a closed-set scenario, where all the unannotated images belong to target classes. In real-world clinical environments, the unlabeled pool often contains a substantial amount of Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) data, leading to low efficiency of annotation in traditional AL methods. Furthermore, most existing AL methods start with random selection in the first query round, leading to a significant waste of labeling costs in open-set scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose OpenPath, a novel open-set active learning approach for pathological image classification leveraging a pre-trained Vision-Language Model (VLM). In the first query, we propose task-specific prompts that combine target and relevant non-target class prompts to effectively select In-Distribution (ID) and informative samples from the unlabeled pool. In subsequent queries, Diverse Informative ID Sampling (DIS) that includes Prototype-based ID candidate Selection (PIS) and Entropy-Guided Stochastic Sampling (EGSS) is proposed to ensure both purity and informativeness in a query, avoiding the selection of OOD samples. Experiments on two public pathology image datasets show that OpenPath significantly enhances the model’s performance due to its high purity of selected samples, and outperforms several state-of-the-art open-set AL methods. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath}{https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath}..
病理学图像分类在准确的医学诊断和治疗计划中发挥至关重要的作用。为此任务训练高性能模型通常需要大规模标注数据集,这些数据的获取既昂贵又耗时。主动学习(AL)通过迭代选择最具信息量的样本进行标注,从而减少了标注工作量,为此提供了解决方案。然而,大多数AL方法的设计是基于封闭集场景的假设,即所有未标注的图像都属于目标类别。在现实世界中的临床环境中,未标注池中经常包含大量超出分布(OOD)的数据,导致传统AL方法的标注效率降低。此外,大多数现有的AL方法在第一次查询时采用随机选择的方式,这在开放集场景中造成了显著的标注成本浪费。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了OpenPath,这是一种利用预训练好的视觉语言模型(VLM)进行病理学图像分类的新型开放集主动学习方法。在第一次查询中,我们提出了任务特定的提示,这些提示结合了目标和相关的非目标类别提示,以有效地从未标注的池中选取In-Distribution(ID)和具有信息量的样本。在随后的查询中,我们提出了包含基于原型ID候选选择的多样化信息ID采样和熵引导随机采样的方法(DIS),以确保查询的纯净度和信息量,避免选择OOD样本。在两个公共病理学图像数据集上的实验表明,由于所选样本的高纯净度,OpenPath显著提高了模型的性能,并优于几种先进的开放集AL方法。代码可在https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 early accept
Summary
病理图像分类在准确的医学诊断和治疗计划中扮演着至关重要的角色。为了解决大规模标注数据集的高成本和耗时的需求,研究提出了一种基于预训练视觉语言模型的新型开放集活性学习(OpenPath)方法,以提高病理图像分类的效率。它通过结合目标类和相关非目标类的任务特定提示来选取具有代表性样本。该方法性能显著,在公开病理学图像数据集上的表现优于其他先进的开放集活性学习方法。相关代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 病理图像分类在医学诊断中的重要性。
- 传统活性学习方法面临获取大规模标注数据集的高成本和耗时问题。
- 提出一种基于预训练视觉语言模型的开放集活性学习方法(OpenPath)。
- 在首次查询时采用任务特定提示来选择样本。
- 后续查询采用多样信息内部采样(DIS),确保所选样本的纯度和信息量,避免选择出界样本。
- 在公开病理学图像数据集上的实验表明,OpenPath显著提高了模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

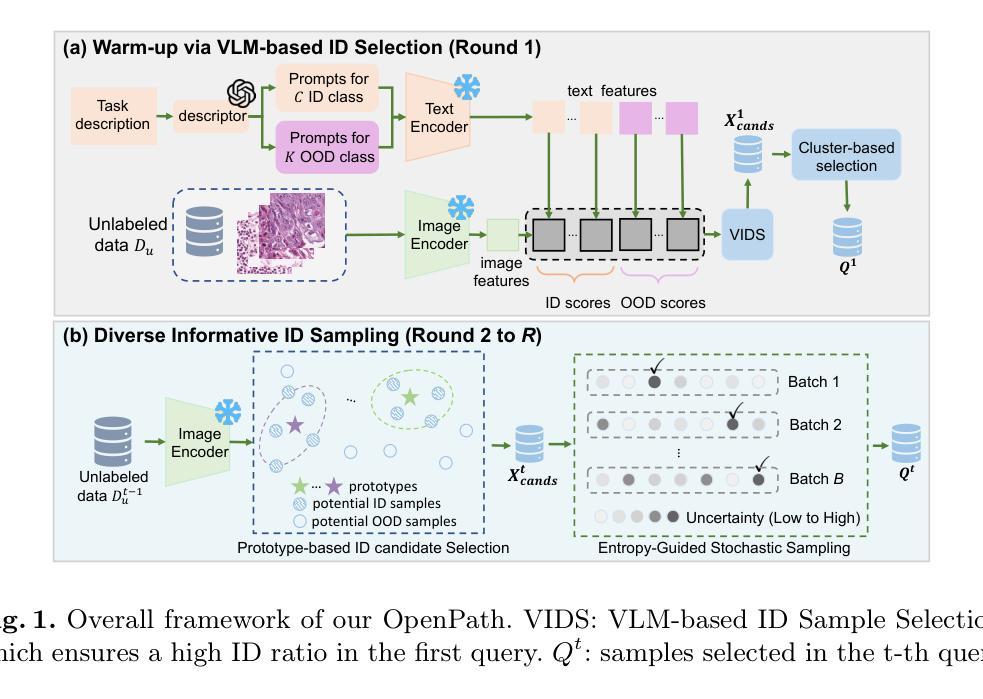
Vision Transformers for End-to-End Quark-Gluon Jet Classification from Calorimeter Images
Authors:Md Abrar Jahin, Shahriar Soudeep, Arian Rahman Aditta, M. F. Mridha, Nafiz Fahad, Md. Jakir Hossen
Distinguishing between quark- and gluon-initiated jets is a critical and challenging task in high-energy physics, pivotal for improving new physics searches and precision measurements at the Large Hadron Collider. While deep learning, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), has advanced jet tagging using image-based representations, the potential of Vision Transformer (ViT) architectures, renowned for modeling global contextual information, remains largely underexplored for direct calorimeter image analysis, especially under realistic detector and pileup conditions. This paper presents a systematic evaluation of ViTs and ViT-CNN hybrid models for quark-gluon jet classification using simulated 2012 CMS Open Data. We construct multi-channel jet-view images from detector-level energy deposits (ECAL, HCAL) and reconstructed tracks, enabling an end-to-end learning approach. Our comprehensive benchmarking demonstrates that ViT-based models, notably ViT+MaxViT and ViT+ConvNeXt hybrids, consistently outperform established CNN baselines in F1-score, ROC-AUC, and accuracy, highlighting the advantage of capturing long-range spatial correlations within jet substructure. This work establishes the first systematic framework and robust performance baselines for applying ViT architectures to calorimeter image-based jet classification using public collider data, alongside a structured dataset suitable for further deep learning research in this domain.
在高能物理学中,区分夸克和胶子引发的喷流是一项关键且具有挑战性的任务,对于提高大型强子对撞机的新物理搜索和精密测量至关重要。深度学习,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNN),已经通过基于图像的表现形式推动了射流标记的发展。然而,对于直接量热仪图像分析,尤其是现实探测器条件和堆积情况下的分析,视觉转换器(Vision Transformer,ViT)架构的潜力尚未得到充分探索,后者以其对全局上下文信息的建模而闻名。本文系统地评估了ViT和ViT-CNN混合模型在模拟的夸克-胶子射流分类中使用2012年CMS公开数据的性能。我们从探测器级别的能量沉积(ECAL、HCAL)和重建轨迹构建了多通道射流视图图像,实现了端到端的学习方法。我们的综合基准测试表明,基于ViT的模型,特别是ViT+MaxViT和ViT+ConvNeXt混合模型,在F1得分、ROC-AUC和准确性方面始终优于已建立的CNN基准测试,这突显了捕获射流子结构中长程空间关联的优势。这项工作建立了使用公共对撞机数据进行基于量热仪图像的射流分类应用ViT架构的第一个系统框架和稳健的性能基准,以及适合在此领域进行深度学习研究的结构化数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in Third International Workshop on Generalizing from Limited Resources in the Open World Workshop at International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) 2025
Summary
该论文探讨了利用Vision Transformer(ViT)架构对高能物理中的夸克和胶子激发的喷射进行分类的问题。该研究使用模拟的CMS Open Data构建多通道喷射图像,并采用ViT和ViT-CNN混合模型进行喷射分类。研究结果表明,基于ViT的模型,特别是ViT+MaxViT和ViT+ConvNeXt混合模型,在F1得分、ROC-AUC和准确度方面均优于传统的CNN基准模型,这得益于其捕捉喷射子结构中长程空间关联的优势。该研究为在公共碰撞数据上应用ViT架构进行基于量能器图像的喷射分类建立了系统的框架和稳健的性能基准。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer(ViT)架构在高能物理中的夸克和胶子引发的喷射分类任务中具有潜力。
- 论文采用多通道喷射图像,包含探测器级能量沉积和重建轨迹信息。
- ViT和ViT-CNN混合模型在喷射分类问题上表现出优异的性能。
- 基于ViT的模型能够捕捉喷射子结构中的长程空间关联。
- 该研究为使用公共碰撞数据应用ViT架构进行基于量能器图像的喷射分类提供了系统的框架和性能基准。
- 研究结果展示了ViT架构在改善新物理搜索和大型强子对撞机的精密测量方面的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

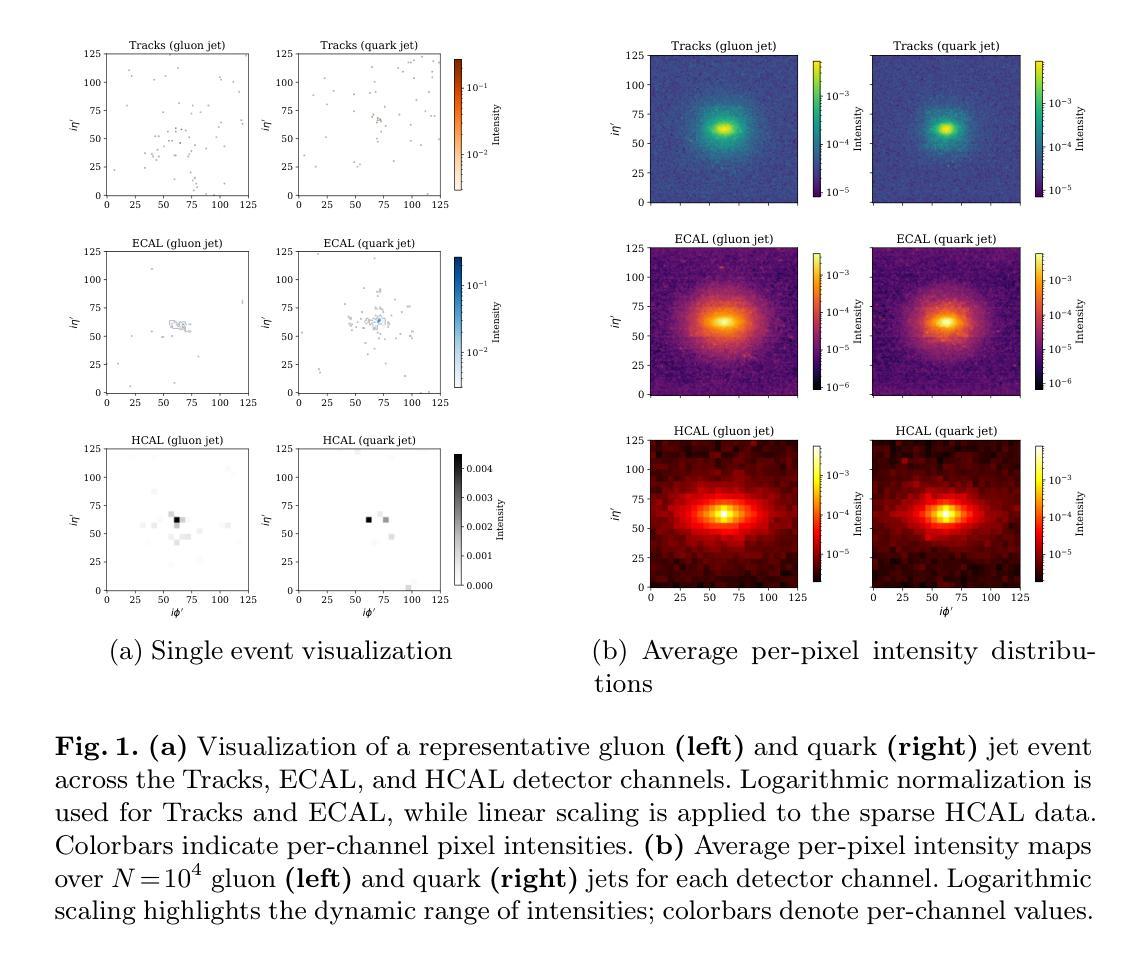
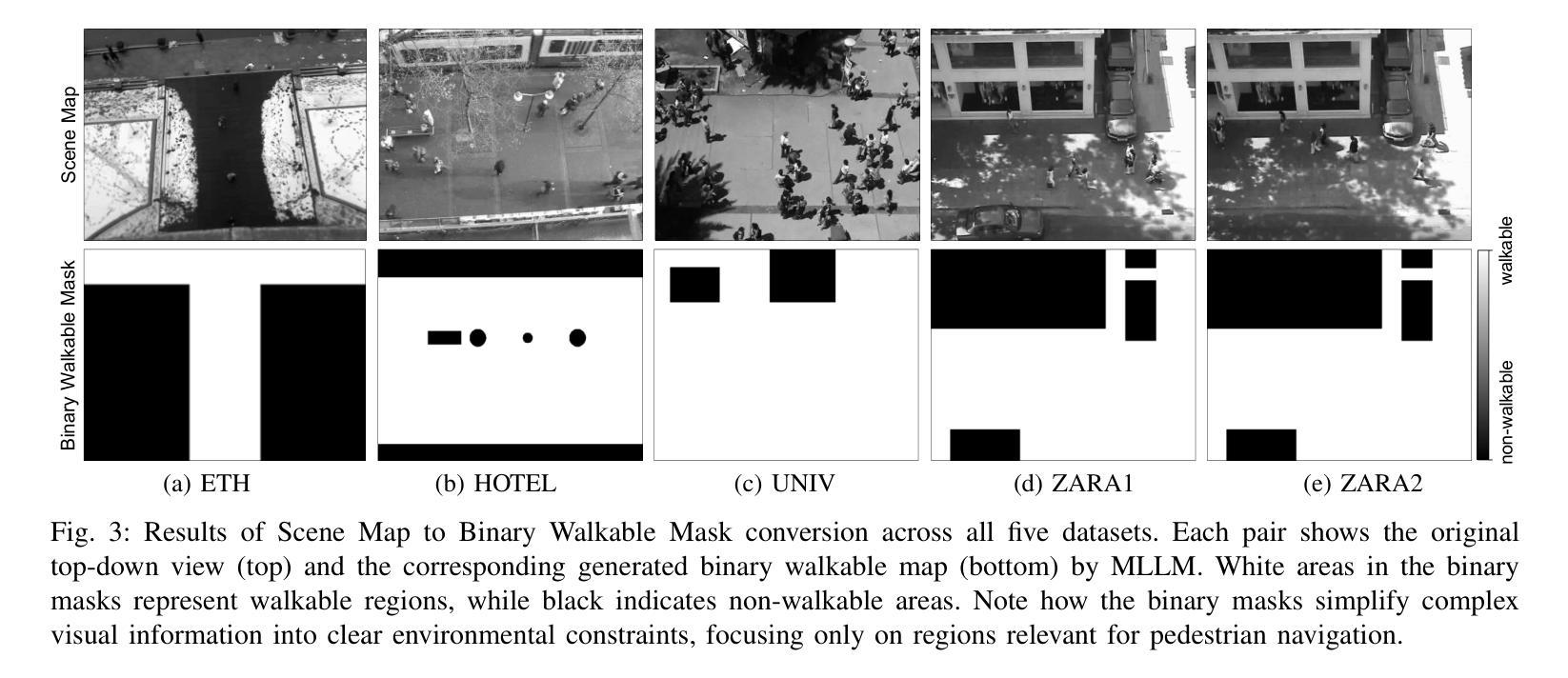
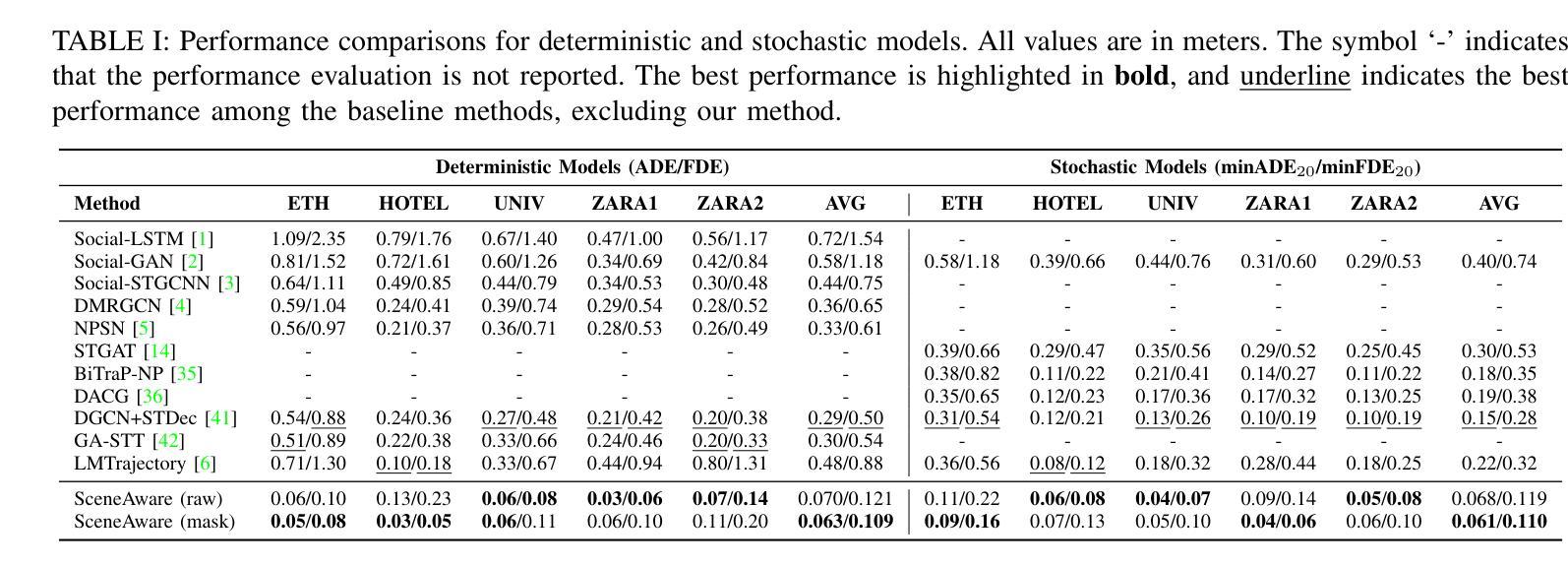
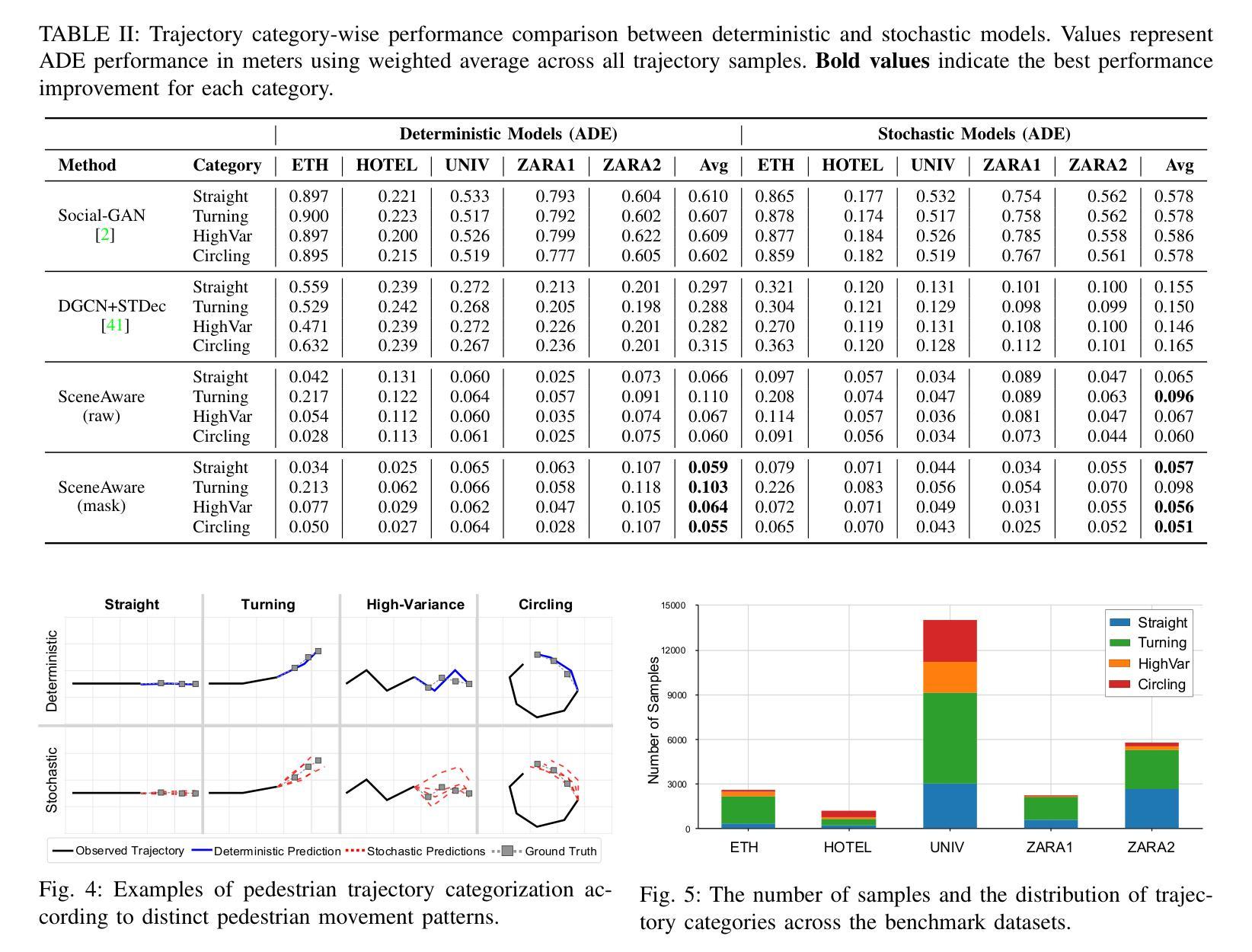
SceneAware: Scene-Constrained Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction with LLM-Guided Walkability
Authors:Juho Bai, Inwook Shim
Accurate prediction of pedestrian trajectories is essential for applications in robotics and surveillance systems. While existing approaches primarily focus on social interactions between pedestrians, they often overlook the rich environmental context that significantly shapes human movement patterns. In this paper, we propose SceneAware, a novel framework that explicitly incorporates scene understanding to enhance trajectory prediction accuracy. Our method leverages a Vision Transformer(ViT) scene encoder to process environmental context from static scene images, while Multi-modal Large Language Models(MLLMs) generate binary walkability masks that distinguish between accessible and restricted areas during training. We combine a Transformer-based trajectory encoder with the ViT-based scene encoder, capturing both temporal dynamics and spatial constraints. The framework integrates collision penalty mechanisms that discourage predicted trajectories from violating physical boundaries, ensuring physically plausible predictions. SceneAware is implemented in both deterministic and stochastic variants. Comprehensive experiments on the ETH/UCY benchmark datasets show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with more than 50% improvement over previous models. Our analysis based on different trajectory categories shows that the model performs consistently well across various types of pedestrian movement. This highlights the importance of using explicit scene information and shows that our scene-aware approach is both effective and reliable in generating accurate and physically plausible predictions. Code is available at: https://github.com/juho127/SceneAware.
行人轨迹的精确预测对于机器人和监控系统应用至关重要。尽管现有方法主要关注行人之间的社会交互,但它们往往忽视了丰富的环境背景,环境背景对人类运动模式有重大影响。在本文中,我们提出了SceneAware,这是一个显式融入场景理解以增强轨迹预测精度的新型框架。我们的方法利用Vision Transformer(ViT)场景编码器处理来自静态场景图像的环境上下文,而多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)生成二进制可步行性掩码,在训练过程中区分可通行和限制区域。我们将基于Transformer的轨迹编码器和基于ViT的场景编码器相结合,捕捉时间动态和空间约束。该框架集成了碰撞惩罚机制,阻止预测轨迹违反物理边界,确保预测结果符合物理规律。SceneAware有确定性和随机性两种实现方式。在ETH/UCY基准数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的方法优于最新技术,较之前模型有50%以上的改进。我们基于不同轨迹类别的分析表明,该模型在各种类型的行人运动中表现一致。这强调了使用明确场景信息的重要性,并表明我们的场景感知方法在生成准确且符合物理规律的预测方面既有效又可靠。代码可访问于:https://github.com/juho127/SceneAware。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
行人轨迹预测对于机器人和监控系统应用至关重要。当前方法主要关注行人间的社交互动,却忽略了环境对运动模式的重要影响。本文提出SceneAware框架,通过引入场景理解技术提高轨迹预测准确性。利用Vision Transformer处理静态场景图像的环境上下文信息,并结合多模态大型语言模型生成可步行性掩膜。结合Transformer的轨迹编码器和ViT的场景编码器,捕捉时空约束和动态信息。框架包含碰撞惩罚机制,确保预测轨迹符合物理边界。SceneAware框架在ETH/UCY基准数据集上的表现优于现有方法,模型在各种类型的行人运动上表现稳定。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways:
- 行人轨迹预测在机器人和监控系统中有重要应用。
- 当前方法主要关注社交互动,但环境对行人运动模式影响巨大。
- SceneAware框架引入场景理解技术,提高轨迹预测准确性。
- 利用Vision Transformer处理静态场景图像,捕捉环境上下文信息。
- 结合多模态大型语言模型生成可步行性掩膜,用于训练模型。
- 结合Transformer和ViT技术,捕捉时空约束和动态信息。
点此查看论文截图

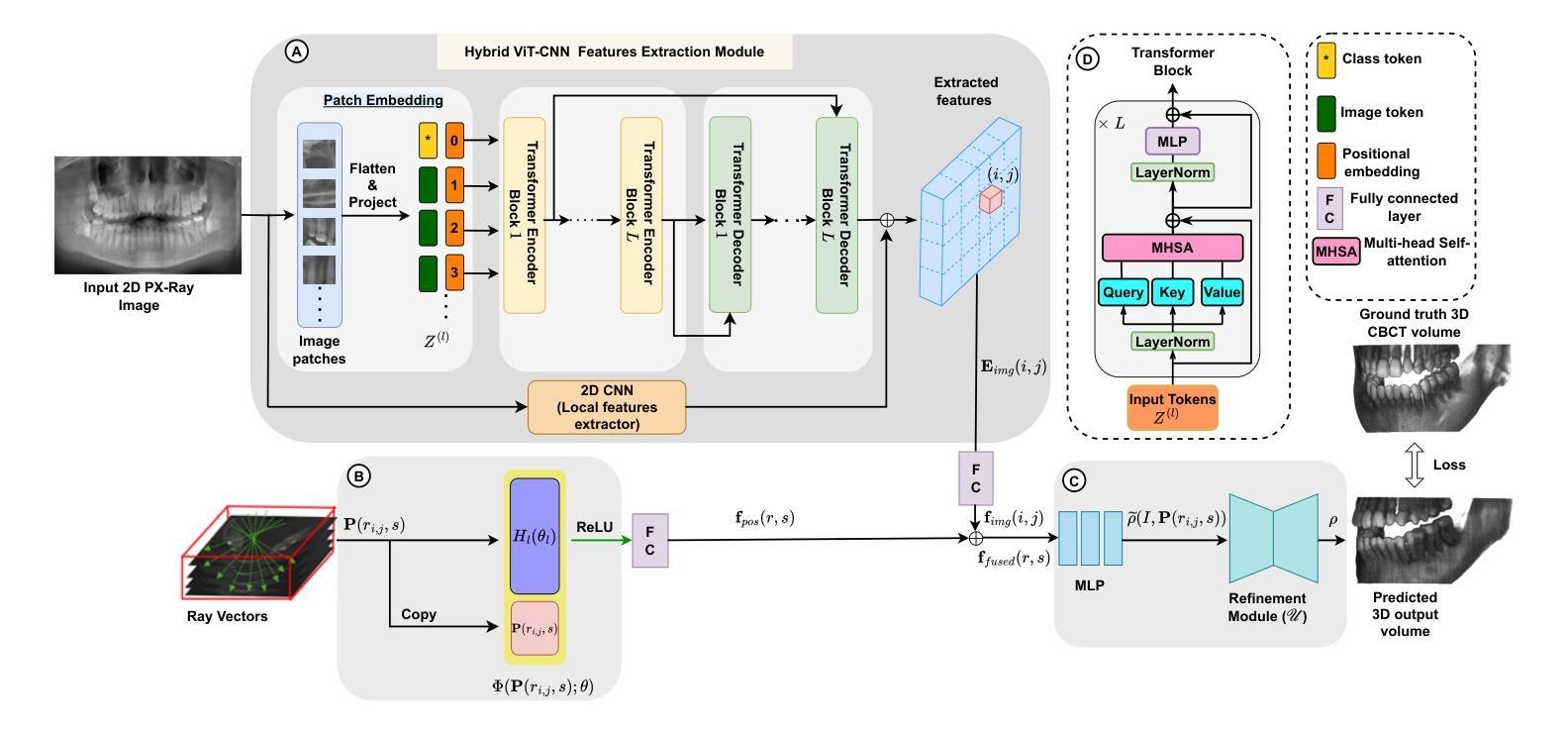
ViT-NeBLa: A Hybrid Vision Transformer and Neural Beer-Lambert Framework for Single-View 3D Reconstruction of Oral Anatomy from Panoramic Radiographs
Authors:Bikram Keshari Parida, Anusree P. Sunilkumar, Abhijit Sen, Wonsang You
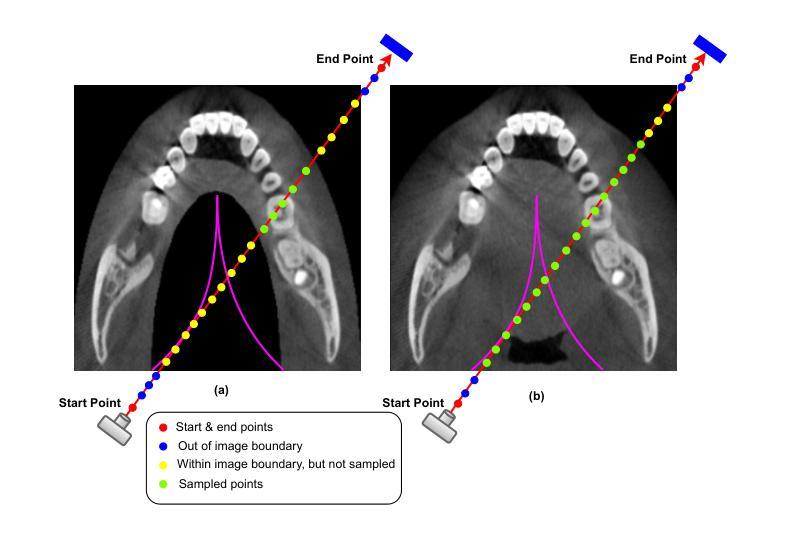
Dental diagnosis relies on two primary imaging modalities: panoramic radiographs (PX) providing 2D oral cavity representations, and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) offering detailed 3D anatomical information. While PX images are cost-effective and accessible, their lack of depth information limits diagnostic accuracy. CBCT addresses this but presents drawbacks including higher costs, increased radiation exposure, and limited accessibility. Existing reconstruction models further complicate the process by requiring CBCT flattening or prior dental arch information, often unavailable clinically. We introduce ViT-NeBLa, a vision transformer-based Neural Beer-Lambert model enabling accurate 3D reconstruction directly from single PX. Our key innovations include: (1) enhancing the NeBLa framework with Vision Transformers for improved reconstruction capabilities without requiring CBCT flattening or prior dental arch information, (2) implementing a novel horseshoe-shaped point sampling strategy with non-intersecting rays that eliminates intermediate density aggregation required by existing models due to intersecting rays, reducing sampling point computations by $52 %$, (3) replacing CNN-based U-Net with a hybrid ViT-CNN architecture for superior global and local feature extraction, and (4) implementing learnable hash positional encoding for better higher-dimensional representation of 3D sample points compared to existing Fourier-based dense positional encoding. Experiments demonstrate that ViT-NeBLa significantly outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively, offering a cost-effective, radiation-efficient alternative for enhanced dental diagnostics.
牙科诊断依赖于两种主要的成像模式:全景X射线(PX)提供二维口腔腔室的表示,而锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)提供详细的3D解剖信息。虽然PX图像成本低且易于获取,但它们缺乏深度信息,限制了诊断的准确性。CBCT解决了这个问题,但也存在一些缺点,包括成本较高、辐射暴露增加以及获取难度较高。现有的重建模型需要进一步复杂化流程,需要CBCT展平或先前的牙齿排列信息,这在临床上往往无法获得。我们引入了ViT-NeBLa,这是一种基于视觉变压器的神经网络Beer-Lambert模型,能够直接从单个PX进行准确的3D重建。我们的关键创新包括:(1)使用视觉变压器增强NeBLa框架,提高了重建能力,无需CBCT展平或先前的牙齿排列信息;(2)实施了一种新颖的马蹄形点采样策略,采用非交叉射线,消除了现有模型因交叉射线所需的中介密度聚集,减少了采样点计算量的52%;(3)用混合ViT-CNN架构替换基于CNN的U-Net,以进行更出色的全局和局部特征提取;(4)实施可学习的哈希位置编码,与现有的基于傅立叶的密集位置编码相比,用于更好地表示3D样本点的高维信息。实验表明,ViT-NeBLa在定量和定性上均显著优于先前最先进的方法,为增强牙科诊断提供了成本低、辐射效率高的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 figures, 19 pages
Summary
本文介绍了基于视觉转换器的神经网络Beer-Lambert模型ViT-NeBLa,可直接从全景X射线图像进行准确的3D重建。模型创新包括增强NeBLa框架与视觉转换器的结合,实现无需CBCT展平或预先牙科弓形信息的重建能力;实施新型马蹄形点采样策略,消除现有模型因射线相交所需的中间密度聚集,减少采样点计算;使用混合ViT-CNN架构替代CNN-based U-Net,实现更优越的全局和局部特征提取;以及实施可学习的哈希位置编码,以更好地表示3D样本点的高维信息。实验表明,ViT-NeBLa在定量和定性方面都显著优于现有方法,提供了一个成本效益高、辐射效率高的增强牙科诊断的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- ViT-NeBLa是一个基于视觉转换器的神经网络模型,用于从全景X射线图像进行3D重建。
- 该模型增强了NeBLa框架,利用视觉转换器提高重建精度,无需CBCT展平或预先的牙科弓形信息。
- 实施新型点采样策略,消除中间密度聚集,减少采样点计算。
- 使用混合ViT-CNN架构提取全局和局部特征,优于传统的CNN-based U-Net。
- 引入了可学习的哈希位置编码,能更有效地表示3D样本点的高维信息。
- 实验显示ViT-NeBLa在牙科诊断的3D重建任务中表现优异,相比现有方法更准确。
点此查看论文截图

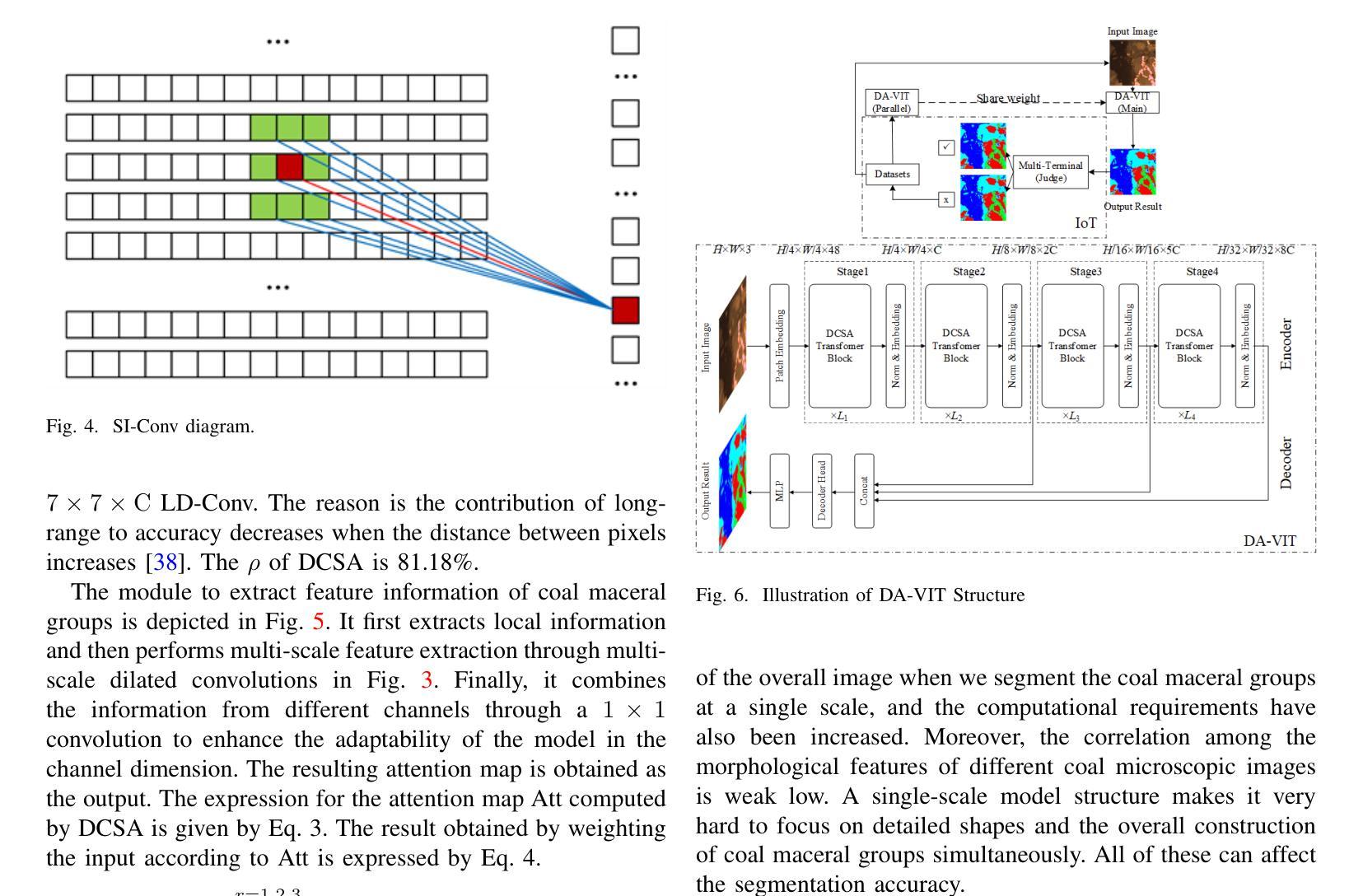
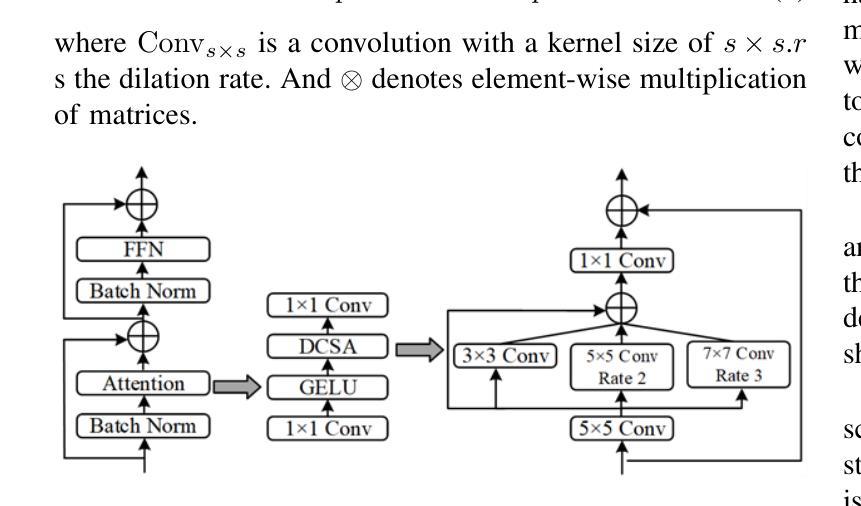
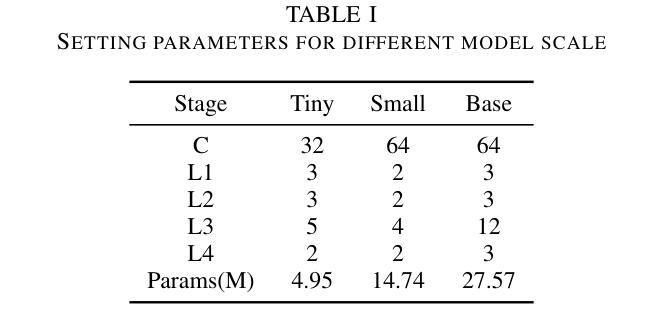
Combining Self-attention and Dilation Convolutional for Semantic Segmentation of Coal Maceral Groups
Authors:Zhenghao Xi, Zhengnan Lv, Yang Zheng, Xiang Liu, Zhuang Yu, Junran Chen, Jing Hu, Yaqi Liu
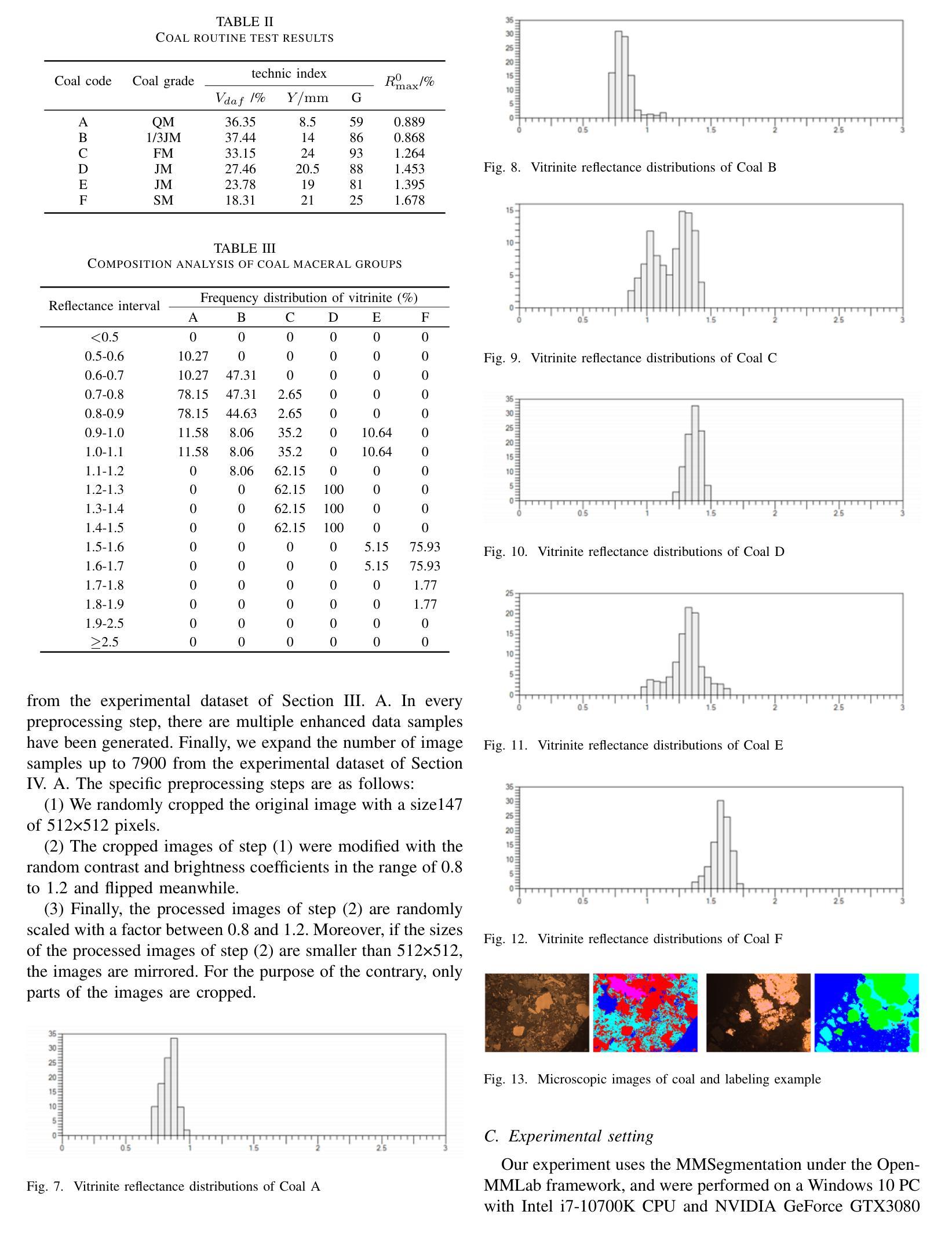
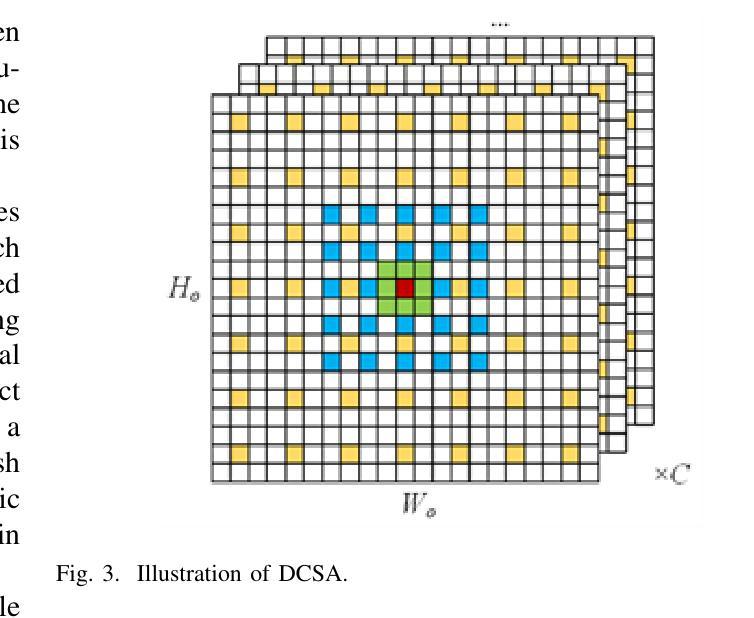
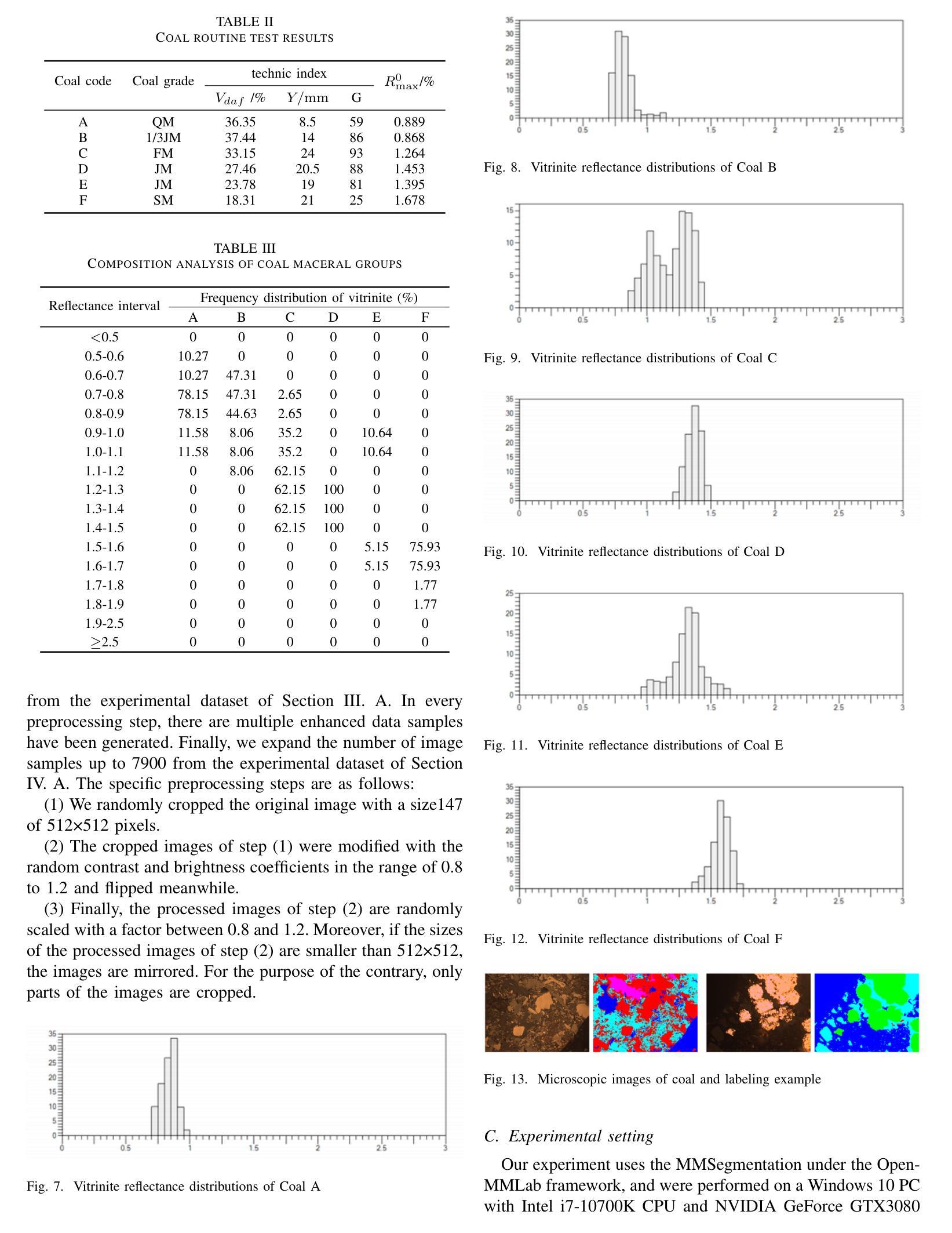
The segmentation of coal maceral groups can be described as a semantic segmentation process of coal maceral group images, which is of great significance for studying the chemical properties of coal. Generally, existing semantic segmentation models of coal maceral groups use the method of stacking parameters to achieve higher accuracy. It leads to increased computational requirements and impacts model training efficiency. At the same time, due to the professionalism and diversity of coal maceral group images sampling, obtaining the number of samples for model training requires a long time and professional personnel operation. To address these issues, We have innovatively developed an IoT-based DA-VIT parallel network model. By utilizing this model, we can continuously broaden the dataset through IoT and achieving sustained improvement in the accuracy of coal maceral groups segmentation. Besides, we decouple the parallel network from the backbone network to ensure the normal using of the backbone network during model data updates. Secondly, DCSA mechanism of DA-VIT is introduced to enhance the local feature information of coal microscopic images. This DCSA can decompose the large kernels of convolutional attention into multiple scales and reduce 81.18% of parameters.Finally, we performed the contrast experiment and ablation experiment between DA-VIT and state-of-the-art methods at lots of evaluation metrics. Experimental results show that DA-VIT-Base achieves 92.14% pixel accuracy and 63.18% mIoU. Params and FLOPs of DA-VIT-Tiny are 4.95M and 8.99G, respectively. All of the evaluation metrics of the proposed DA-VIT are better than other state-of-the-art methods.
煤的显微组分分割可以描述为煤显微组分图像的语义分割过程,这对研究煤的化学性质具有重要意义。目前,现有的煤显微组分语义分割模型通常采用堆叠参数的方法来提高精度,这导致了计算需求的增加和模型训练效率的影响。同时,由于煤显微组分图像采样的专业性和多样性,获取用于模型训练的样本数量需要很长时间和专业人员的操作。为了解决这些问题,我们创新地开发了一个基于物联网的DA-VIT并行网络模型。通过利用该模型,我们可以通过物联网持续扩大数据集,实现煤显微组分分割精度的持续改进。此外,我们将并行网络与骨干网络解耦,以确保在模型数据更新期间骨干网络的正常使用。其次,引入了DA-VIT的DCSA机制,以增强煤微观图像的局部特征信息。DCSA可以将卷积注意力的大内核分解成多个尺度,并减少81.18%的参数。最后,我们在许多评估指标之间对DA-VIT和最新方法进行了对比实验和消融实验。实验结果表明,DA-VIT-Base的像素精度达到92.14%,mIoU达到63.18%。DA-VIT-Tiny的参数和FLOPs分别为4.95M和8.99G。所提出DA-VIT的所有评估指标均优于其他最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对煤炭显微图像进行语义分割的煤岩组分分割具有研究煤化学性质的重要意义。现有方法常采用堆叠参数提高精度,但计算量大且影响模型训练效率。为解决样本采集的专业性和多样性问题,研究团队创新性地构建了基于物联网的DA-VIT并行网络模型,以扩大数据集并持续提高分割精度。此外,该模型通过解耦并行网络确保在数据更新时主干网络的正常使用,引入DA-VIT的DCSA机制提升煤显微图像局部特征信息。实验结果显示,DA-VIT-Base的像素精度达到92.14%,mIoU为63.18%,表现优于其他前沿方法。
Key Takeaways
- 煤炭显微图像的语义分割是研究煤化学性质的重要手段。
- 现有语义分割模型通过堆叠参数提高精度,但计算量大且影响效率。
- 研究团队提出了基于物联网的DA-VIT并行网络模型以解决上述问题。
- 该模型能持续扩大数据集并提高煤炭组分分割的准确性。
- DA-VIT的DCSA机制增强了煤显微图像的局部特征信息。
- DA-VIT-Base的像素精度达到92.14%,mIoU为63.18%。
- DA-VIT模型的表现优于其他前沿方法。
点此查看论文截图

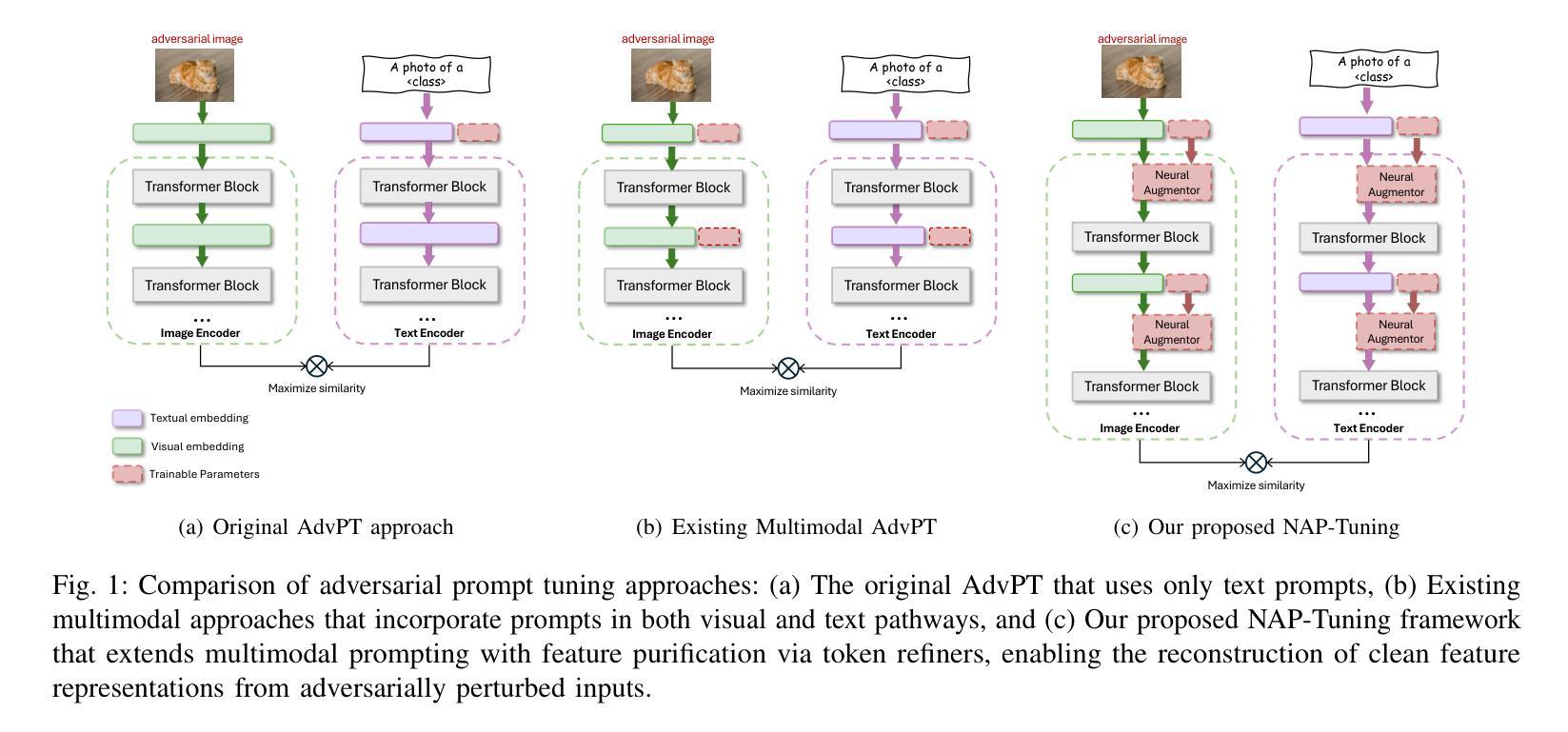
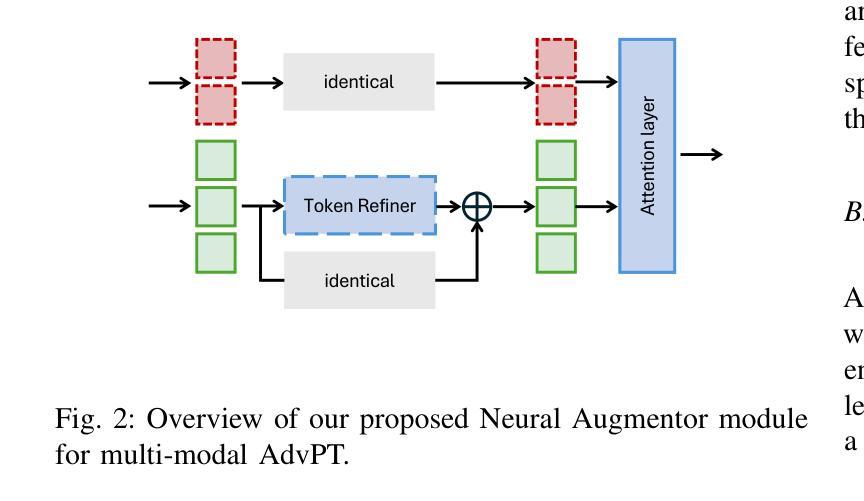
NAP-Tuning: Neural Augmented Prompt Tuning for Adversarially Robust Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jiaming Zhang, Xin Wang, Xingjun Ma, Lingyu Qiu, Yu-Gang Jiang, Jitao Sang
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) such as CLIP have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding relationships between visual and textual data through joint embedding spaces. Despite their effectiveness, these models remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks, particularly in the image modality, posing significant security concerns. Building upon our previous work on Adversarial Prompt Tuning (AdvPT), which introduced learnable text prompts to enhance adversarial robustness in VLMs without extensive parameter training, we present a significant extension by introducing the Neural Augmentor framework for Multi-modal Adversarial Prompt Tuning (NAP-Tuning).Our key innovations include: (1) extending AdvPT from text-only to multi-modal prompting across both text and visual modalities, (2) expanding from single-layer to multi-layer prompt architectures, and (3) proposing a novel architecture-level redesign through our Neural Augmentor approach, which implements feature purification to directly address the distortions introduced by adversarial attacks in feature space. Our NAP-Tuning approach incorporates token refiners that learn to reconstruct purified features through residual connections, allowing for modality-specific and layer-specific feature correction.Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that NAP-Tuning significantly outperforms existing methods across various datasets and attack types. Notably, our approach shows significant improvements over the strongest baselines under the challenging AutoAttack benchmark, outperforming them by 33.5% on ViT-B16 and 33.0% on ViT-B32 architectures while maintaining competitive clean accuracy.
视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,通过联合嵌入空间展示了对视觉和文本数据之间关系的理解方面的卓越能力。尽管它们很有效,但这些模型仍然容易受到对抗性攻击的影响,特别是在图像模态方面,这引发了重大的安全担忧。基于我们之前关于对抗性提示调整(AdvPT)的工作,引入了可学习的文本提示,可以在不进行广泛参数训练的情况下提高VLMs的对抗性稳健性。在此基础上,我们通过一个重要的扩展,引入神经增强器框架进行多模态对抗性提示调整(NAP-Tuning)。我们的主要创新包括:(1)将AdvPT从纯文本扩展到文本和视觉模态的多模态提示,(2)从单层扩展到多层提示架构,(3)通过我们的神经增强器方法提出一种新的架构级重新设计,实现特征净化,直接解决特征空间中对抗攻击引入的失真。我们的NAP-Tuning方法结合了标记精炼器,学习通过残差连接重建净化后的特征,实现模态特定和层特定的特征校正。综合实验表明,NAP-Tuning在各种数据集和攻击类型上显著优于现有方法。值得注意的是,我们的方法在具有挑战性的AutoAttack基准测试上表现出显著的改进,在ViT-B16和ViT-B32架构上分别超越最强基线33.5%和33.0%,同时保持竞争力的清洁精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于CLIP等跨模态模型的联合嵌入空间,理解视觉与文本数据间关系的能力已得到广泛认可。然而,这些模型面临对抗性攻击的威胁,存在显著的安全隐患。为增强模型在视觉和语言模态上的鲁棒性,我们在先前的AdvPT(对抗性提示调优)工作基础上推出显著扩展版本,引入神经扩充器框架实现多模态对抗性提示调优(NAP-Tuning)。NAP-Tuning引入三大创新点:支持文本和视觉模态的多模态提示,由单层扩展至多层的提示架构,并提出全新的架构级重新设计。我们采用特征提纯的方法直接应对对抗性攻击引起的特征空间扭曲问题。NAP-Tuning还包括token精炼器,它通过残差连接学习重建提纯的特征,允许针对特定模态和特定层级的特征修正。实验表明,NAP-Tuning在多个数据集和攻击类型上均显著优于现有方法,特别是在AutoAttack基准测试中表现突出。在ViT-B16和ViT-B32架构上分别超越最强基线模型达33.5%和33.0%,同时保持相当的清洁准确度。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs如CLIP虽能有效理解视觉与文本数据间的关系,但面临对抗性攻击的安全隐患。
- NAP-Tuning在AdvPT基础上进行了显著扩展,支持多模态提示和多层提示架构。
- NAP-Tuning引入神经扩充器框架进行架构级设计,通过特征提纯应对对抗性攻击。
- NAP-Tuning包含token精炼器,可学习重建提纯的特征并实现模态和层级特定的特征修正。
- 实验显示NAP-Tuning在多种数据集和攻击类型上表现优越,特别是在AutoAttack基准测试中显著超越现有方法。
- 在ViT-B16和ViT-B32架构上,NAP-Tuning的鲁棒性改进超过最强基线模型达33%以上。
点此查看论文截图

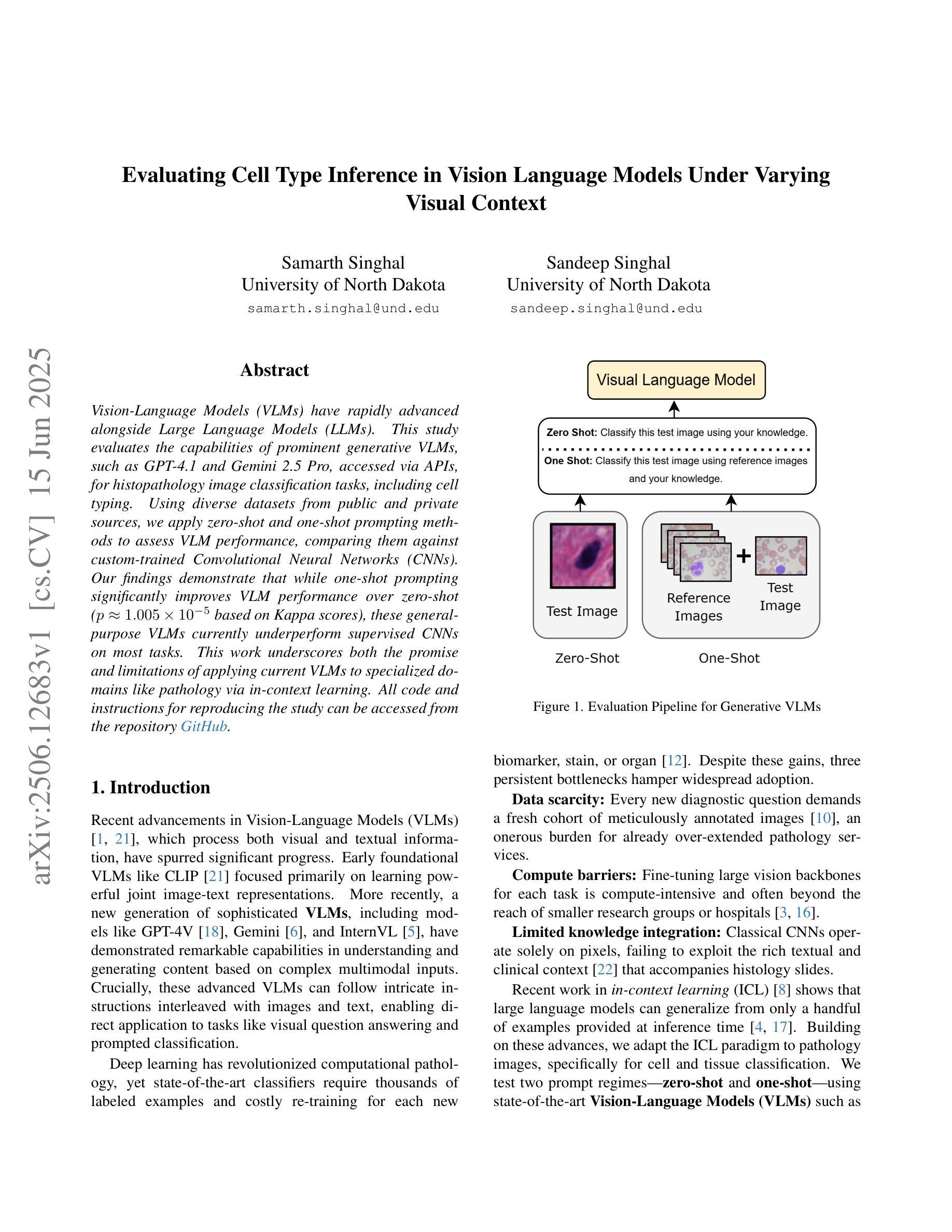
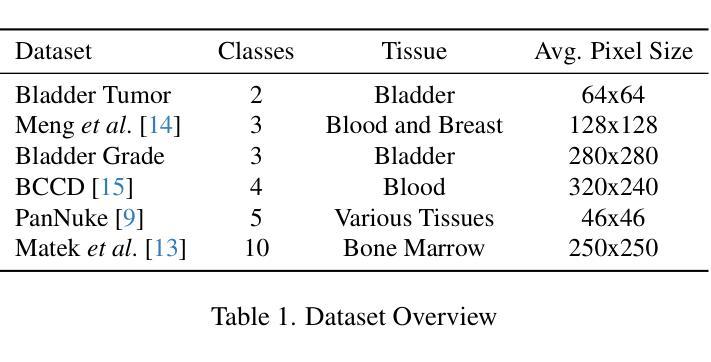
Evaluating Cell Type Inference in Vision Language Models Under Varying Visual Context
Authors:Samarth Singhal, Sandeep Singhal
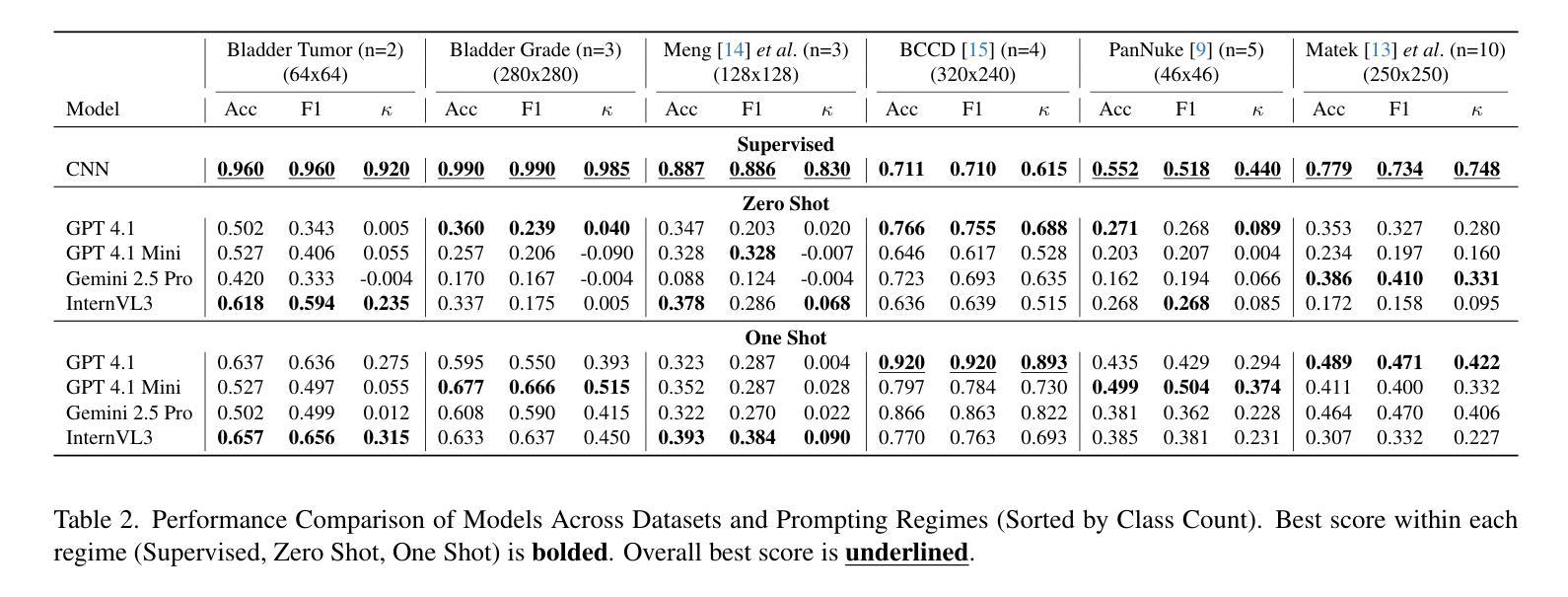
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have rapidly advanced alongside Large Language Models (LLMs). This study evaluates the capabilities of prominent generative VLMs, such as GPT-4.1 and Gemini 2.5 Pro, accessed via APIs, for histopathology image classification tasks, including cell typing. Using diverse datasets from public and private sources, we apply zero-shot and one-shot prompting methods to assess VLM performance, comparing them against custom-trained Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Our findings demonstrate that while one-shot prompting significantly improves VLM performance over zero-shot ($p \approx 1.005 \times 10^{-5}$ based on Kappa scores), these general-purpose VLMs currently underperform supervised CNNs on most tasks. This work underscores both the promise and limitations of applying current VLMs to specialized domains like pathology via in-context learning. All code and instructions for reproducing the study can be accessed from the repository https://www.github.com/a12dongithub/VLMCCE.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展而进步。本研究评估了通过API访问的前瞻性生成式VLMs,如GPT-4.1和Gemini 2.5 Pro,在病理学图像分类任务(包括细胞类型分类)方面的能力。我们使用来自公共和私有源的多样数据集,通过零样本和单次样本提示方法评估VLM的性能,并将其与定制训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)进行比较。我们的研究结果表明,虽然单次样本提示方法相对于零样本提示显著提高了VLM的性能(基于kappa分数的差异值为$p \approx 1.005 \times 10^{-5}$),但这些通用VLMs目前在大多数任务上的表现仍劣于有监督学习的CNN。本研究突出了在当前VLM应用于病理学等特殊领域时的潜力与局限性,可以通过上下文学习实现。所有关于复现该研究的代码和说明可从https://www.github.com/a12dongithub/VLMCCE访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了基于视觉语言模型(VLMs)如GPT-4.1和Gemini 2.5 Pro在病理学图像分类任务(包括细胞类型鉴定)中的性能表现。通过采用来自公共和私有源的多样化数据集,本文利用零次学习和一次学习提示法评估了VLM的性能表现,并将其与经过定制的卷积神经网络(CNN)进行了比较。研究发现,虽然一次学习提示可以显著提高VLM的性能表现,但在大多数任务上,这些通用VLM的表现仍然不及经过监督学习的CNN。本文强调了将当前VLM应用于病理学等特殊领域时面临的挑战和局限性。所有代码和实验重现指南可在https://www.github.com/a12dongithub/VLMCCE中找到。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在病理学图像分类任务中的性能表现被评估。
- 研究对象包括GPT-4.1和Gemini 2.5 Pro等主流生成式VLMs。
- 使用零次和一次学习提示方法来评估VLM的性能。
- VLMs在大多数任务上的表现不及经过训练的CNN。
- 一次学习提示可以显著提高VLM的性能。
- 本文强调了将VLM应用于特殊领域(如病理学)时的挑战和局限性。
点此查看论文截图
Hierarchical Deep Feature Fusion and Ensemble Learning for Enhanced Brain Tumor MRI Classification
Authors:Zahid Ullah, Jihie Kim
Accurate brain tumor classification is crucial in medical imaging to ensure reliable diagnosis and effective treatment planning. This study introduces a novel double ensembling framework that synergistically combines pre-trained deep learning (DL) models for feature extraction with optimized machine learning (ML) classifiers for robust classification. The framework incorporates comprehensive preprocessing and data augmentation of brain magnetic resonance images (MRI), followed by deep feature extraction using transfer learning with pre-trained Vision Transformer (ViT) networks. The novelty lies in the dual-level ensembling strategy: feature-level ensembling, which integrates deep features from the top-performing ViT models, and classifier-level ensembling, which aggregates predictions from hyperparameter-optimized ML classifiers. Experiments on two public Kaggle MRI brain tumor datasets demonstrate that this approach significantly surpasses state-of-the-art methods, underscoring the importance of feature and classifier fusion. The proposed methodology also highlights the critical roles of hyperparameter optimization (HPO) and advanced preprocessing techniques in improving diagnostic accuracy and reliability, advancing the integration of DL and ML for clinically relevant medical image analysis.
精确的大脑肿瘤分类在医学成像中至关重要,能确保可靠的诊断和有效的治疗方案制定。本研究引入了一种新型双重集成框架,该框架协同结合了用于特征提取的预训练深度学习(DL)模型与经过优化的机器学习(ML)分类器,以实现稳健的分类。该框架包含对大脑磁共振图像(MRI)的综合预处理和数据增强,随后利用借助预训练好的视觉转换器(ViT)网络的迁移学习进行深度特征提取。其新颖之处在于双重集成策略:特征级集成,它整合了表现最佳的ViT模型的深度特征;分类器级集成,它聚合了经过超参数优化的ML分类器的预测结果。在两个公共的Kaggle MRI大脑肿瘤数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著超越了最先进的方法,突显了特征和分类器融合的重要性。所提出的方法还强调了超参数优化(HPO)和先进的预处理技术在提高诊断和分类的准确性和可靠性方面的关键作用,推动了深度学习(DL)和机器学习(ML)在临床相关的医学图像分析中的融合。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究提出一种新型双重集成框架,该框架结合预训练的深度学习模型进行特征提取,并使用优化后的机器学习分类器进行稳健分类。通过综合运用磁共振图像预处理和数据增强技术,采用基于预训练Vision Transformer网络的迁移学习进行深度特征提取。其新颖之处在于双重集成策略:特征级集成整合了表现最佳的Vision Transformer模型的深度特征,分类器级集成则聚合了经过超参数优化的机器学习分类器的预测结果。在公共Kaggle MRI脑肿瘤数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著超越了最先进的方法,强调了特征和分类器融合的重要性。此外,该研究还强调了超参数优化和先进预处理技术在提高诊断准确性和可靠性方面的关键作用,推动了深度学习在临床医学图像分析中的应用。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究提出了一个新型双重集成框架,结合了深度学习模型的特征提取和机器学习分类器的优化分类。
- 该框架运用了磁共振图像的预处理和数据增强技术。
- 采用了基于预训练Vision Transformer网络的迁移学习进行深度特征提取。
- 特征级集成和分类器级集成是该框架的双重集成策略的关键。
- 在公共Kaggle MRI脑肿瘤数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著提高了诊断准确性和可靠性。
- 超参数优化在提升模型性能中起到了重要作用。
点此查看论文截图

Interpretable Classification of Levantine Ceramic Thin Sections via Neural Networks
Authors:Sara Capriotti, Alessio Devoto, Simone Scardapane, Silvano Mignardi, Laura Medeghini
Classification of ceramic thin sections is fundamental for understanding ancient pottery production techniques, provenance, and trade networks. Although effective, traditional petrographic analysis is time-consuming. This study explores the application of deep learning models, specifically Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs), as complementary tools to support the classification of Levantine ceramics based on their petrographic fabrics. A dataset of 1,424 thin section images from 178 ceramic samples belonging to several archaeological sites across the Levantine area, mostly from the Bronze Age, with few samples dating to the Iron Age, was used to train and evaluate these models. The results demonstrate that transfer learning significantly improves classification performance, with a ResNet18 model achieving 92.11% accuracy and a ViT reaching 88.34%. Explainability techniques, including Guided Grad-CAM and attention maps, were applied to interpret and visualize the models’ decisions, revealing that both CNNs and ViTs successfully focus on key mineralogical features for the classification of the samples into their respective petrographic fabrics. These findings highlight the potential of explainable AI in archaeometric studies, providing a reproducible and efficient methodology for ceramic analysis while maintaining transparency in model decision-making.
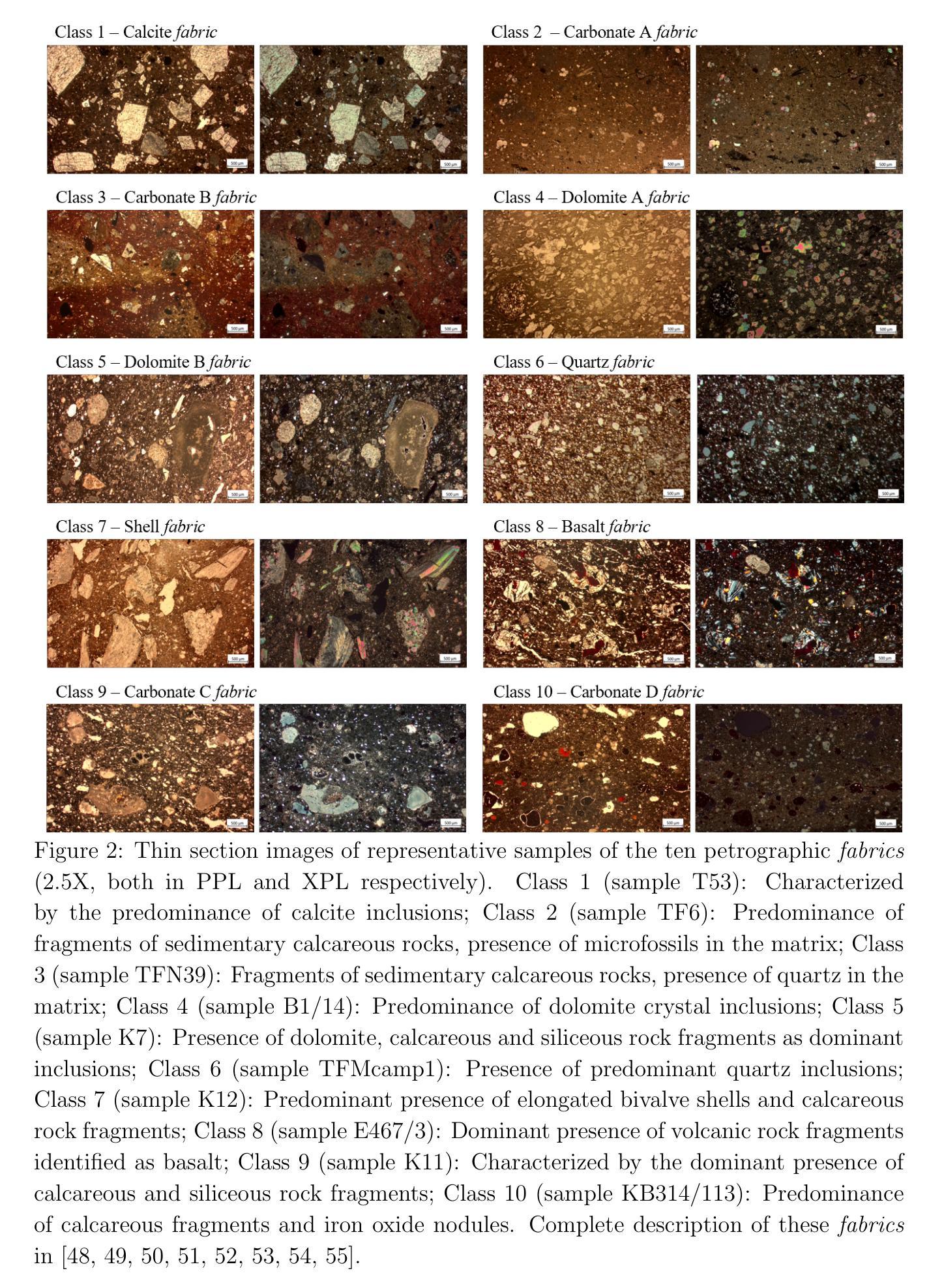
陶瓷薄片分类对于了解古代陶器生产技术、来源和贸易网络具有重要意义。虽然传统岩石学分析有效,但耗时较长。本研究探讨了深度学习模型的应用,特别是卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT),作为支持基于岩石学织构的黎凡特陶瓷分类的补充工具。本研究使用来自黎凡特地区多个考古遗址的178个陶瓷样品的薄片图像数据集进行模型训练和评估,这些样品主要来自青铜时代,少数样品来自铁器时代。结果表明,迁移学习显著提高了分类性能,其中ResNet18模型准确率达到了92.11%,而ViT达到了88.34%。通过梯度引导CAM和注意力图等解释性技术来解读和可视化模型的决策过程,显示出CNN和ViT都能成功关注到矿物学特征,将样本分类到各自的岩石学织构中。这些发现突显了可解释的AI在考古计量研究中的潜力,提供了一种可重复和高效的陶瓷分析方法,同时保持模型决策的透明度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Machine Learning: Science and Technology
Summary
本文研究应用深度学习和视觉转换器技术辅助分类Levantine陶器薄切片。利用来自多个考古遗址的陶器样本图像数据训练模型,发现迁移学习可显著提高分类性能。研究结果显示,ResNet18模型准确率为92.11%,而Vision Transformer准确率为88.34%。解释技术揭示了模型决策的关键矿物学特征,显示出人工智能在考古度量学研究中应用的潜力。该研究为陶瓷分析提供了可重复、高效的检测方式并保持决策透明性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究使用深度学习和视觉转换器技术辅助分类Levantine陶瓷薄切片,探索了新兴技术在考古研究中的应用潜力。
- 采用包含多个遗址的陶瓷样本数据集训练模型,提升了模型的准确性和性能评估的有效性。
- 通过迁移学习提高了分类性能,ResNet18模型和Vision Transformer分别实现了较高的准确率。
- 解释技术揭示了模型在分类过程中关注的关键矿物学特征,增强了模型的可解释性。
- 模型的应用提供了可重复和高效的陶瓷分析方法,促进了陶瓷分析的自动化进程。
- 该研究在保持决策透明性的同时实现了自动化决策的应用,对于陶瓷分类的精准度和客观性有所保障。
点此查看论文截图


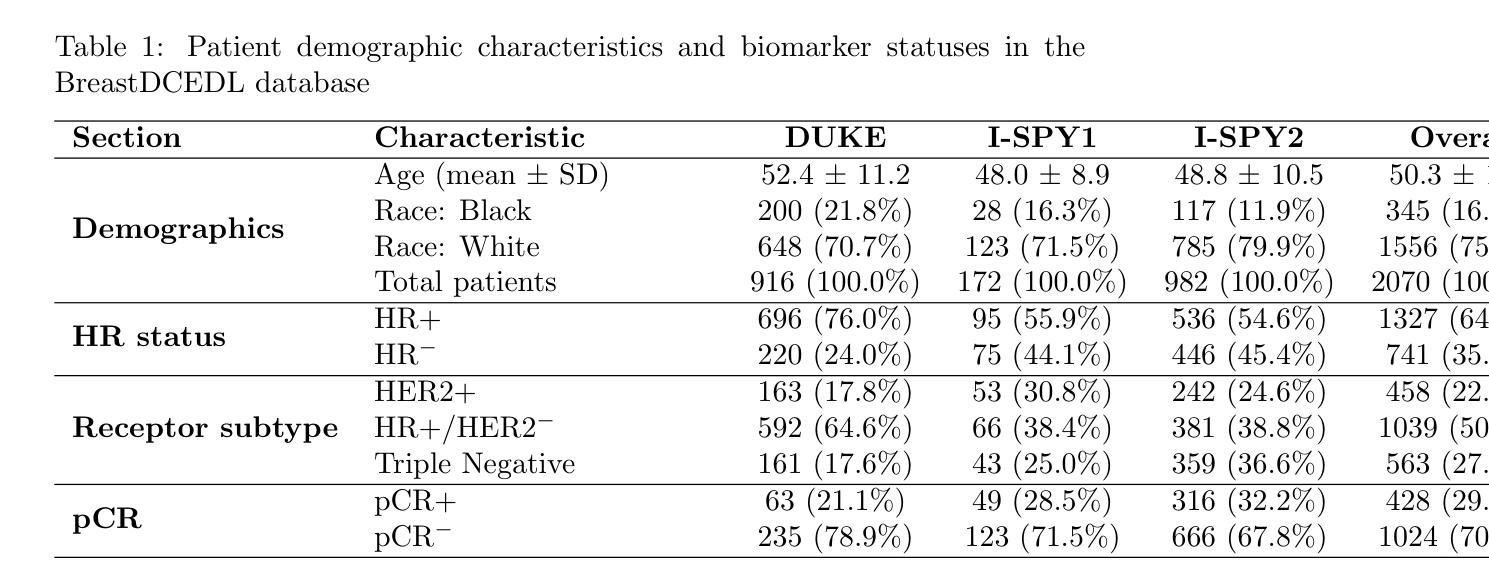
BreastDCEDL: Curating a Comprehensive DCE-MRI Dataset and developing a Transformer Implementation for Breast Cancer Treatment Response Prediction
Authors:Naomi Fridman, Bubby Solway, Tomer Fridman, Itamar Barnea, Anat Goldshtein
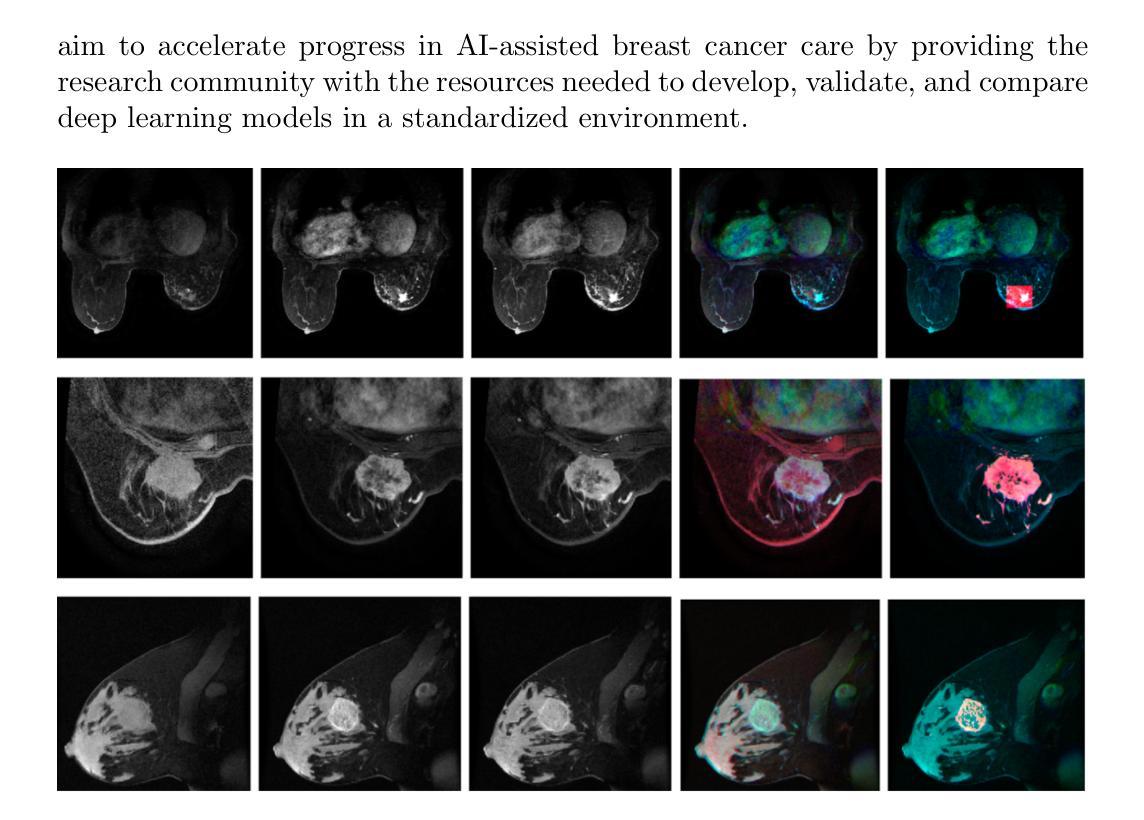
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, making early detection and accurate treatment response monitoring critical priorities. We present BreastDCEDL, a curated, deep learning-ready dataset comprising pre-treatment 3D Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) scans from 2,070 breast cancer patients drawn from the I-SPY1, I-SPY2, and Duke cohorts, all sourced from The Cancer Imaging Archive. The raw DICOM imaging data were rigorously converted into standardized 3D NIfTI volumes with preserved signal integrity, accompanied by unified tumor annotations and harmonized clinical metadata including pathologic complete response (pCR), hormone receptor (HR), and HER2 status. Although DCE-MRI provides essential diagnostic information and deep learning offers tremendous potential for analyzing such complex data, progress has been limited by lack of accessible, public, multicenter datasets. BreastDCEDL addresses this gap by enabling development of advanced models, including state-of-the-art transformer architectures that require substantial training data. To demonstrate its capacity for robust modeling, we developed the first transformer-based model for breast DCE-MRI, leveraging Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture trained on RGB-fused images from three contrast phases (pre-contrast, early post-contrast, and late post-contrast). Our ViT model achieved state-of-the-art pCR prediction performance in HR+/HER2- patients (AUC 0.94, accuracy 0.93). BreastDCEDL includes predefined benchmark splits, offering a framework for reproducible research and enabling clinically meaningful modeling in breast cancer imaging.
乳腺癌仍然是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,因此早期检测和精确的治疗反应监测成为至关重要的优先事项。我们推出了BreastDCEDL,这是一个精选的、准备好用于深度学习数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke队列的2070名乳腺癌患者的治疗前3D动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)扫描,所有数据源均来自癌症成像档案。原始的DICOM成像数据被严格转换为标准化的3DNIfTI体积,保留了信号完整性,并配有统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据,包括病理完全反应(pCR)、激素受体(HR)和HER2状态。尽管DCE-MRI提供了重要的诊断信息,深度学习在分析此类复杂数据方面提供了巨大的潜力,但由于缺乏可访问的、公开的、多中心数据集,进展一直受到限制。BreastDCEDL通过支持开发先进模型来解决这一差距,包括需要大量训练数据的最新变压器架构。为了展示其稳健建模的能力,我们开发了基于变压器的首个乳腺癌DCE-MRI模型,该模型利用在三个对比阶段(预对比、早期对比后和晚期对比后)的RGB融合图像上训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)架构。我们的ViT模型在HR+/HER2-患者中实现了最先进的pCR预测性能(AUC 0.94,准确率0.93)。BreastDCEDL包括预定义的基准分割,为可重复研究提供了框架,并在乳腺癌成像中实现了临床意义的建模。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
乳腺癌仍是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,早期检测和准确的治疗反应监测是关键。我们推出BreastDCEDL数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke等来源的癌症成像档案的2070例乳腺癌患者的预治疗三维动态增强MRI扫描数据。该数据集还包括统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据。利用这一数据集,我们开发了基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的模型,对三种对比阶段的RGB融合图像进行训练,实现了在HR+/HER2-患者中pCR预测的卓越性能。BreastDCEDL包括预设的基准分割,为可重复的研究提供了一个框架,并能在乳腺癌成像中进行临床意义的建模。
Key Takeaways
- BreastDCEDL是一个专为深度学习设计的数据集,包含来自多个来源的乳腺癌患者的预治疗三维动态增强MRI扫描数据。
- 数据集包括标准化的三维NIfTI体积数据、统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据。
- 缺乏公共多中心数据集限制了深度学习在DCE-MRI数据分析方面的进展,而BreastDCEDL填补了这一空白。
- 利用Vision Transformer(ViT)架构开发了一种新型模型,用于处理乳腺癌DCE-MRI数据,实现了在特定患者群体中pCR预测的高性能表现。
- BreastDCEDL设定的基准分割有助于进行可重复的研究。
- 该数据集支持高级模型的开发,并有助于实现乳腺癌成像的临床意义建模。
点此查看论文截图

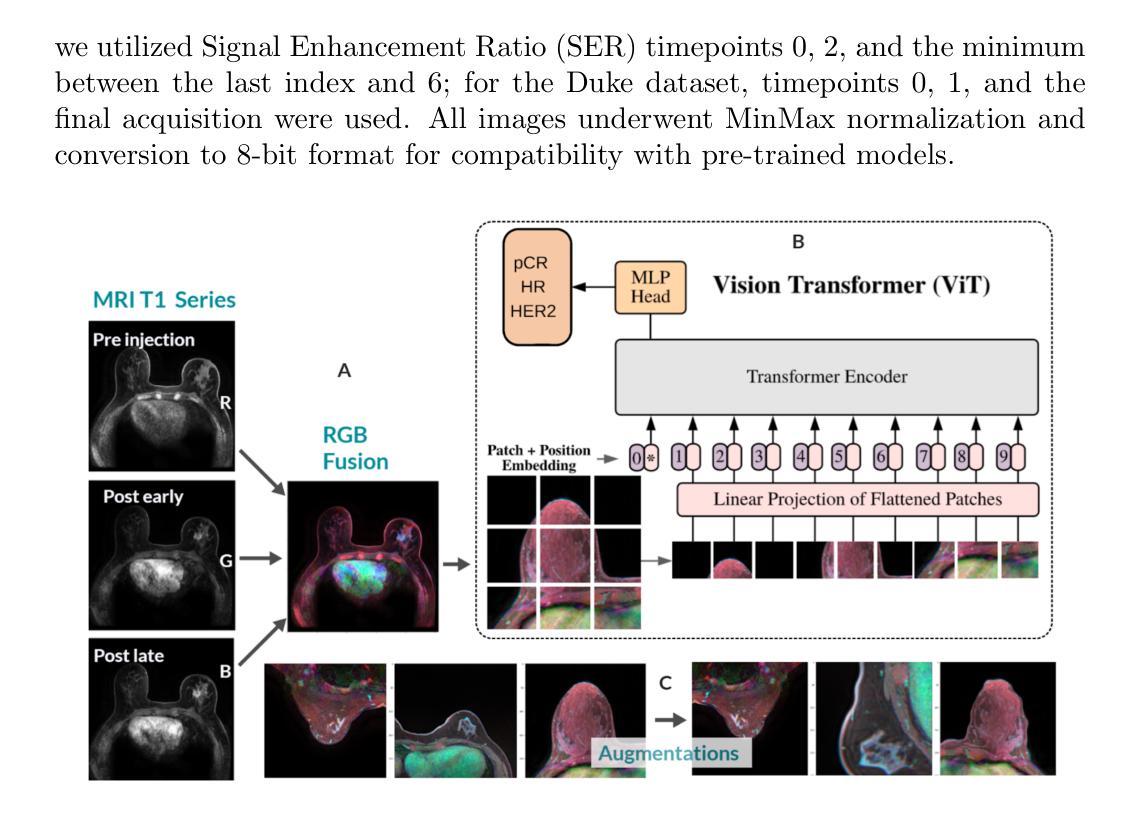
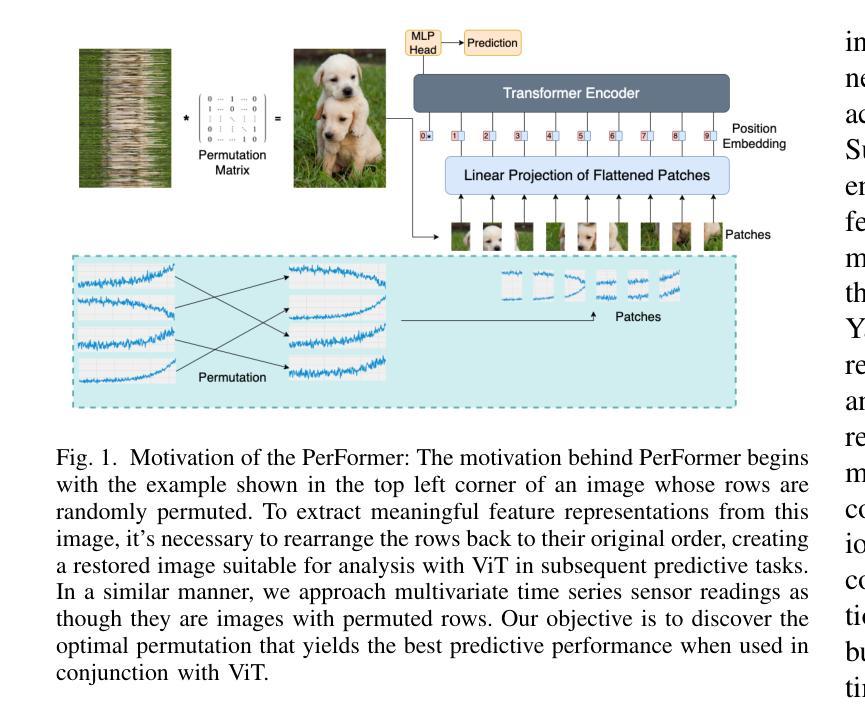
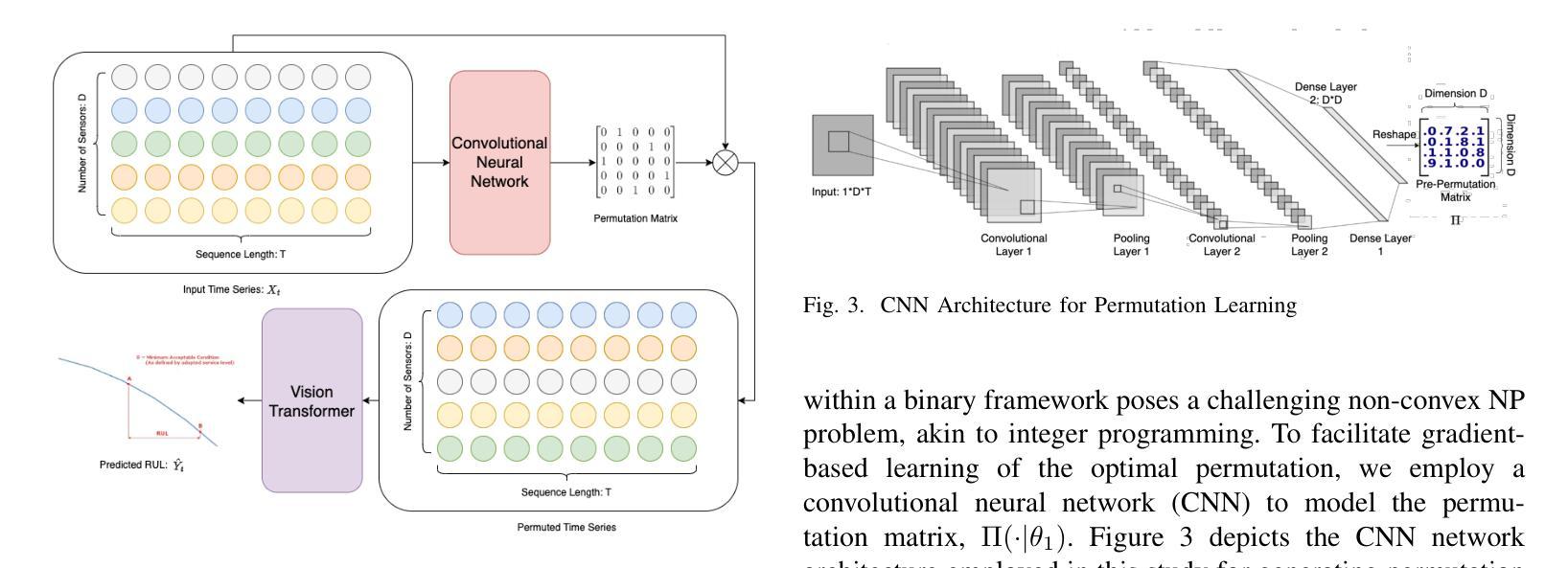
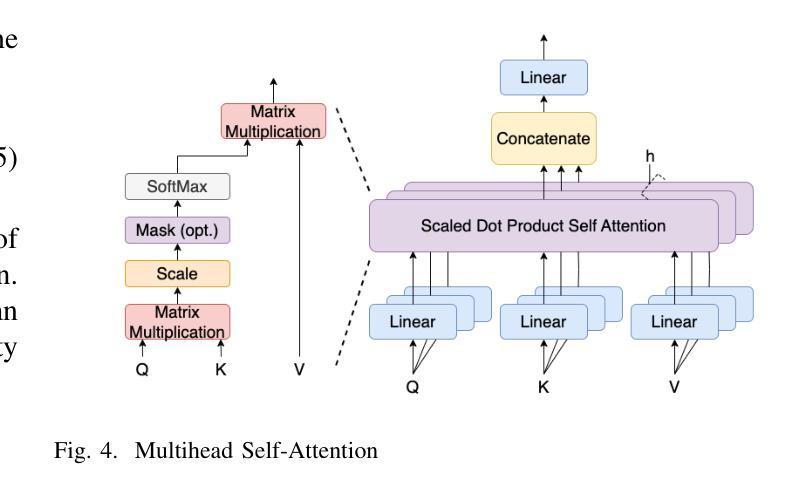
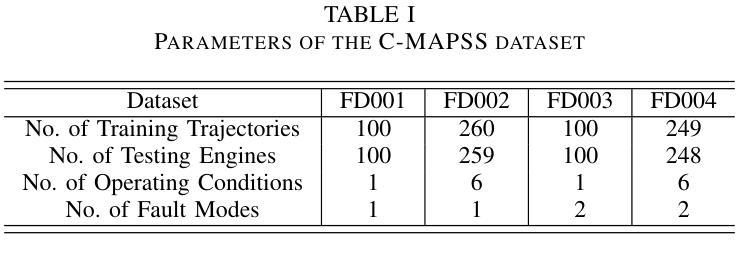
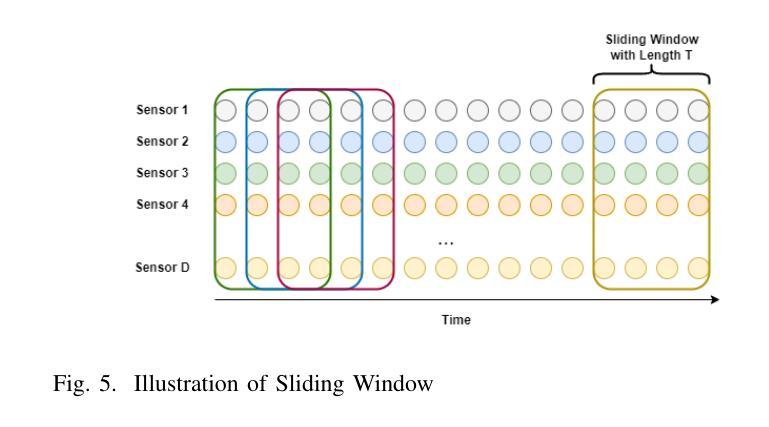
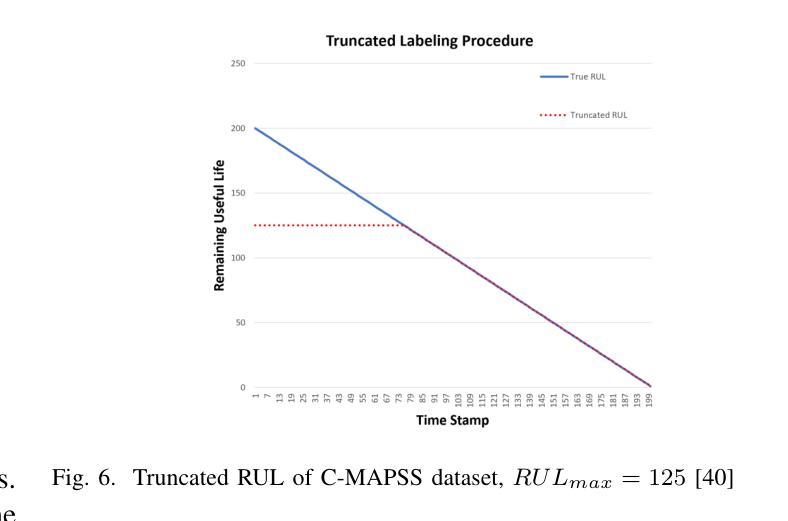
PerFormer: A Permutation Based Vision Transformer for Remaining Useful Life Prediction
Authors:Zhengyang Fan, Wanru Li, Kuo-chu Chang, Ting Yuan
Accurately estimating the remaining useful life (RUL) for degradation systems is crucial in modern prognostic and health management (PHM). Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), initially developed for tasks like image and video recognition, have proven highly effectively in RUL prediction, demonstrating remarkable performance. However, with the emergence of the Vision Transformer (ViT), a Transformer model tailored for computer vision tasks such as image classification, and its demonstrated superiority over CNNs, there is a natural inclination to explore its potential in enhancing RUL prediction accuracy. Nonetheless, applying ViT directly to multivariate sensor data for RUL prediction poses challenges, primarily due to the ambiguous nature of spatial information in time series data. To address this issue, we introduce the PerFormer, a permutation-based vision transformer approach designed to permute multivariate time series data, mimicking spatial characteristics akin to image data, thereby making it suitable for ViT. To generate the desired permutation matrix, we introduce a novel permutation loss function aimed at guiding the convergence of any matrix towards a permutation matrix. Our experiments on NASA’s C-MAPSS dataset demonstrate the PerFormer’s superior performance in RUL prediction compared to state-of-the-art methods employing CNNs, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and various Transformer models. This underscores its effectiveness and potential in PHM applications.
对退化系统的剩余使用寿命(RUL)进行准确估计是现代预测与健康管理(PHM)中的关键。卷积神经网络(CNN)最初是为图像和视频识别等任务而开发的,其在RUL预测中表现出了高度的有效性,并表现出了卓越的性能。然而,随着专为计算机视觉任务如图像分类而定制的视觉变压器(ViT)的出现,以及其相对于CNN的优越性,人们自然倾向于探索其在提高RUL预测精度方面的潜力。然而,直接将ViT应用于多元传感器数据的RUL预测面临挑战,主要是由于时间序列数据中空间信息的模糊性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了PerFormer,这是一种基于排列的视觉变压器方法,旨在排列多元时间序列数据,模仿类似于图像数据的空间特征,从而使其适合ViT。为了生成所需的排列矩阵,我们引入了一种新的排列损失函数,旨在引导任何矩阵向排列矩阵收敛。我们在NASA的C-MAPSS数据集上的实验表明,PerFormer在RUL预测方面的性能优于采用CNN、循环神经网络(RNN)和各种Transformer模型的最先进方法。这突显了其在PHM应用中的有效性和潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF One of the coauthors does not want to post current version of paper, and insists to withdraw the submission
Summary
本文探讨了剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测在现代预测与健康管理(PHM)中的重要性。卷积神经网络(CNN)在RUL预测方面表现出显著性能,但随着专为计算机视觉任务设计的Vision Transformer(ViT)的出现,其优越性引起了人们的关注。本文介绍了PerFormer,一种基于排列的愿景转换器方法,能够将多元时间序列数据排列成类似图像数据的形式,从而适用于ViT。通过引入新的排列损失函数,生成所需的排列矩阵,实现RUL预测性能的提升。在NASA的C-MAPSS数据集上的实验表明,PerFormer相较于采用CNN和RNN等先进方法具有更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测在现代预测与健康管理(PHM)中具有重要作用。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在RUL预测方面已表现出显著性能。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)的出现引起了在RUL预测中的关注,因其对计算机视觉任务的优越性。
- PerFormer是一种基于排列的愿景转换器方法,能将多元时间序列数据排列成类似图像数据的形式。
- 通过引入新的排列损失函数,生成排列矩阵,有助于提高RUL预测性能。
- 在NASA的C-MAPSS数据集上的实验表明,PerFormer在RUL预测方面相较于其他先进方法具有优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Intermediate Features of Vision Transformer for Face Anti-Spoofing
Authors:Mika Feng, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki, Tetsushi Ohki, Masakatsu Nishigaki
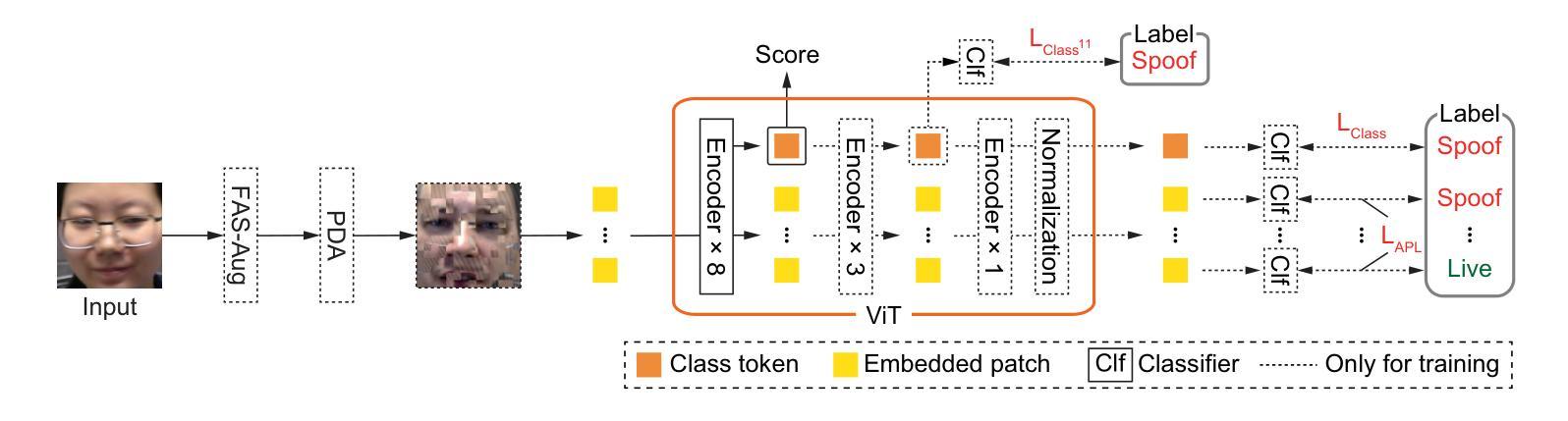
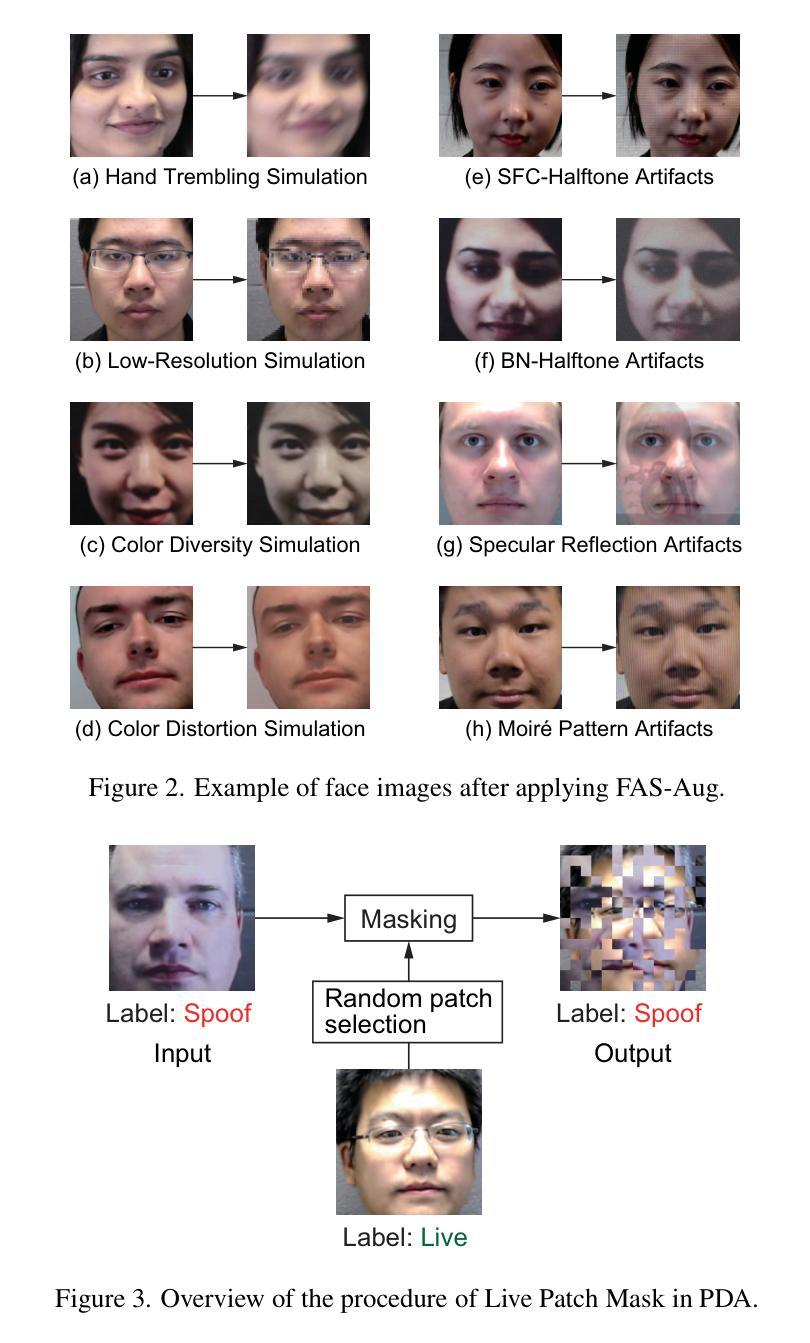
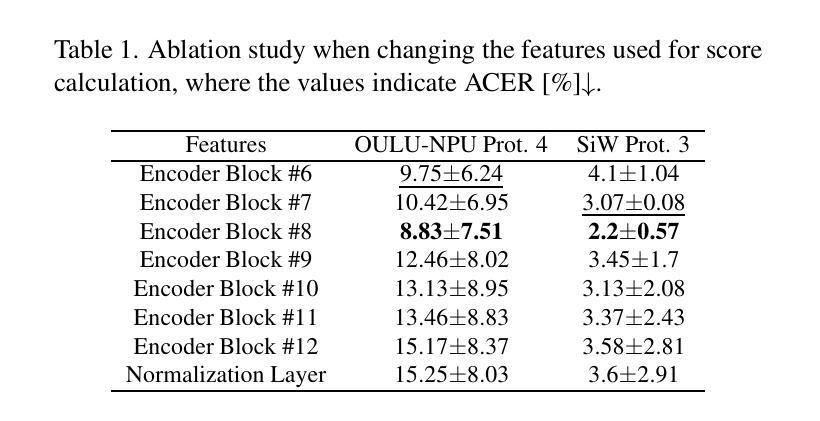
Face recognition systems are designed to be robust against changes in head pose, illumination, and blurring during image capture. If a malicious person presents a face photo of the registered user, they may bypass the authentication process illegally. Such spoofing attacks need to be detected before face recognition. In this paper, we propose a spoofing attack detection method based on Vision Transformer (ViT) to detect minute differences between live and spoofed face images. The proposed method utilizes the intermediate features of ViT, which have a good balance between local and global features that are important for spoofing attack detection, for calculating loss in training and score in inference. The proposed method also introduces two data augmentation methods: face anti-spoofing data augmentation and patch-wise data augmentation, to improve the accuracy of spoofing attack detection. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method through experiments using the OULU-NPU and SiW datasets. The project page is available at: https://gsisaoki.github.io/FAS-ViT-CVPRW/ .
人脸识别系统设计时考虑了头部姿态、光照和图像捕捉过程中的模糊变化。如果恶意人士出示注册用户的面部照片,他们可能会非法绕过身份验证过程。需要在人脸识别之前检测此类欺骗攻击。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的欺骗攻击检测方法,用于检测实时和伪造面部图像之间的微小差异。该方法利用ViT的中间特征,这些特征在局部和全局特征之间有很好的平衡,对于欺骗攻击检测很重要,用于计算训练和推理过程中的损失和得分。该方法还引入两种数据增强方法:面部防欺骗数据增强和补丁级数据增强,以提高欺骗攻击检测的准确性。我们通过使用OULU-NPU和SiW数据集的实验证明了该方法的有效性。项目页面可通过以下网址访问:https://gsisaoki.github.io/FAS-ViT-CVPRW/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
Summary
基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的防伪攻击检测法能有效识别真实与假冒人脸图像间的细微差异,通过利用ViT的中间特征进行训练与推理,实现防伪攻击检测。此法引入两种数据增强方法以提高检测准确性。实验在OULU-NPU和SiW数据集上验证了方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法基于Vision Transformer(ViT)设计,用于检测真实和假冒人脸图像之间的差异。
- 使用ViT的中间特征进行训练与推理,这些特征在本地和全局特征之间取得了良好的平衡,对防伪攻击检测至关重要。
- 引入两种数据增强方法:面部防伪数据增强和补丁级数据增强,以提高防伪攻击检测的准确性。
- 该方法在OULU-NPU和SiW数据集上进行了实验验证,证明了其有效性。
- 该方法旨在防止恶意人士通过伪造用户照片绕过面部识别认证过程。
- 该项目页面提供了更多详细信息:项目链接。
- 该研究展示了Vision Transformer在防伪攻击检测领域的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图