⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-23 更新
A Hybrid ConvNeXt-EfficientNet AI Solution for Precise Falcon Disease Detection
Authors:Alavikunhu Panthakkan, Zubair Medammal, S M Anzar, Fatma Taher, Hussain Al-Ahmad
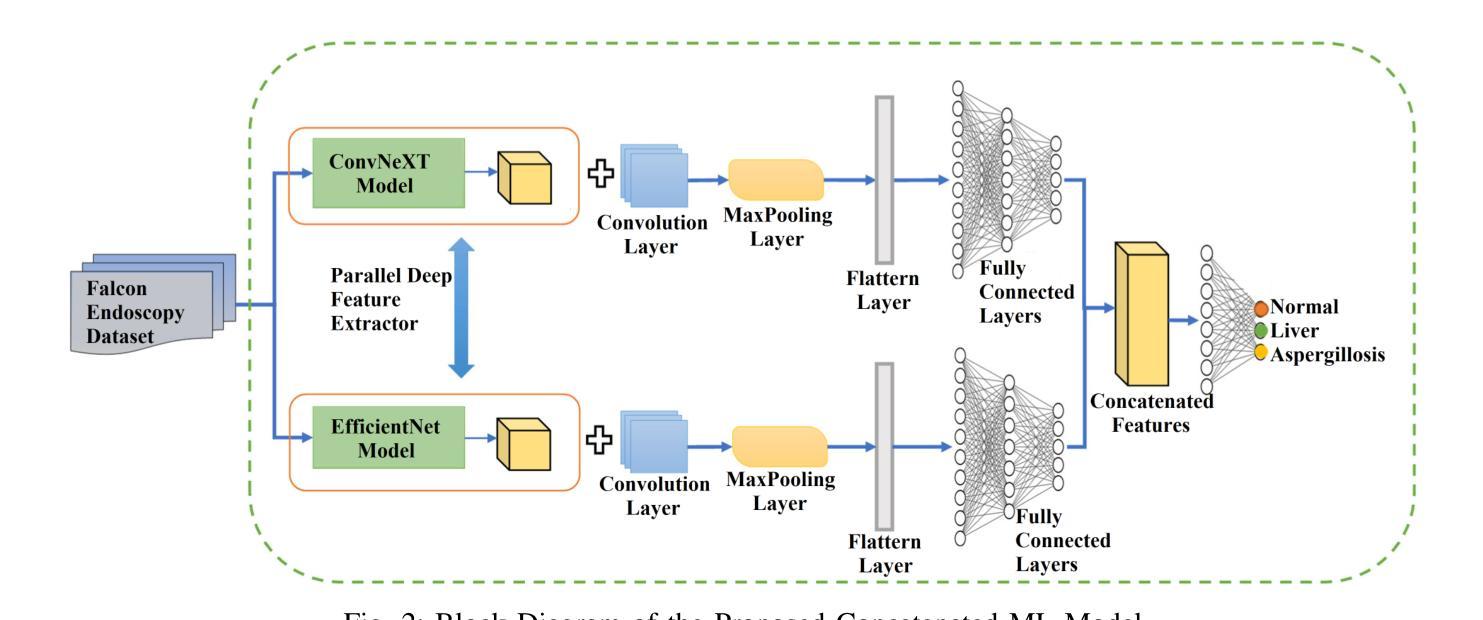
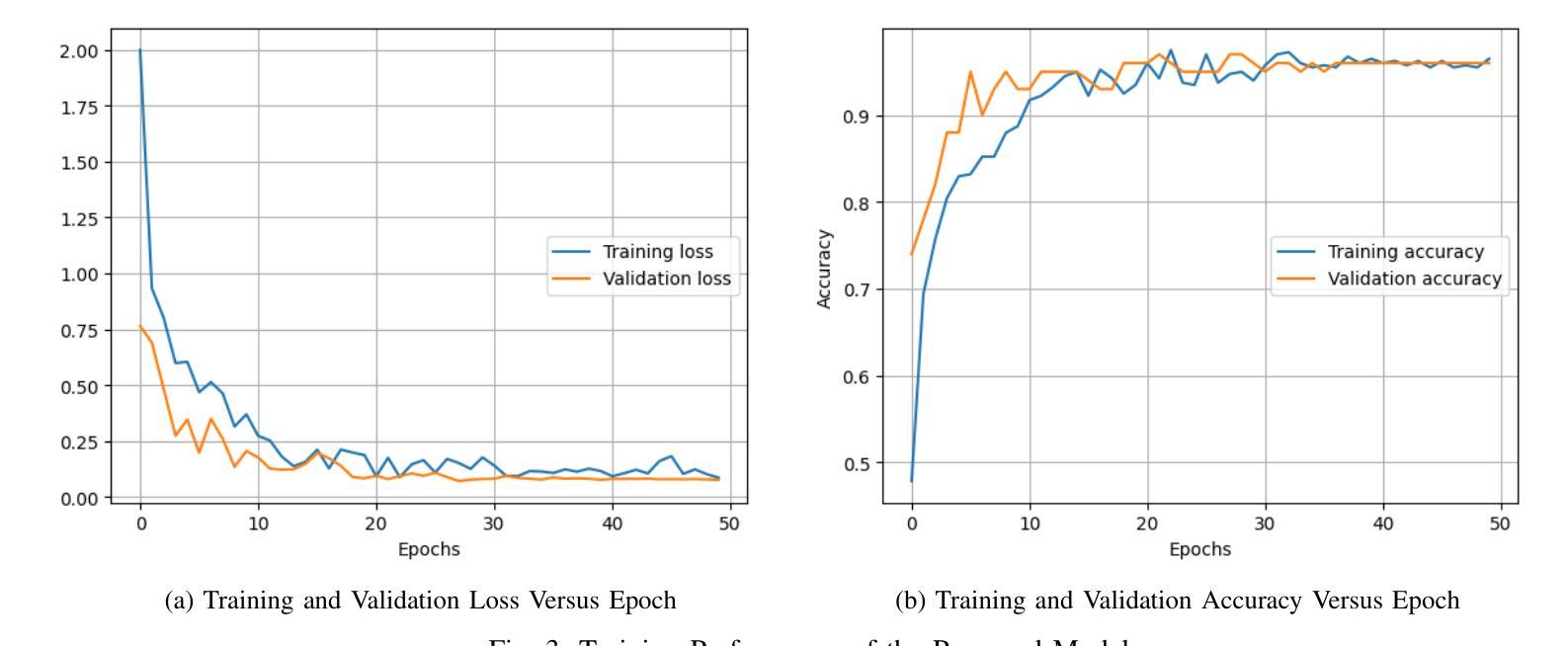
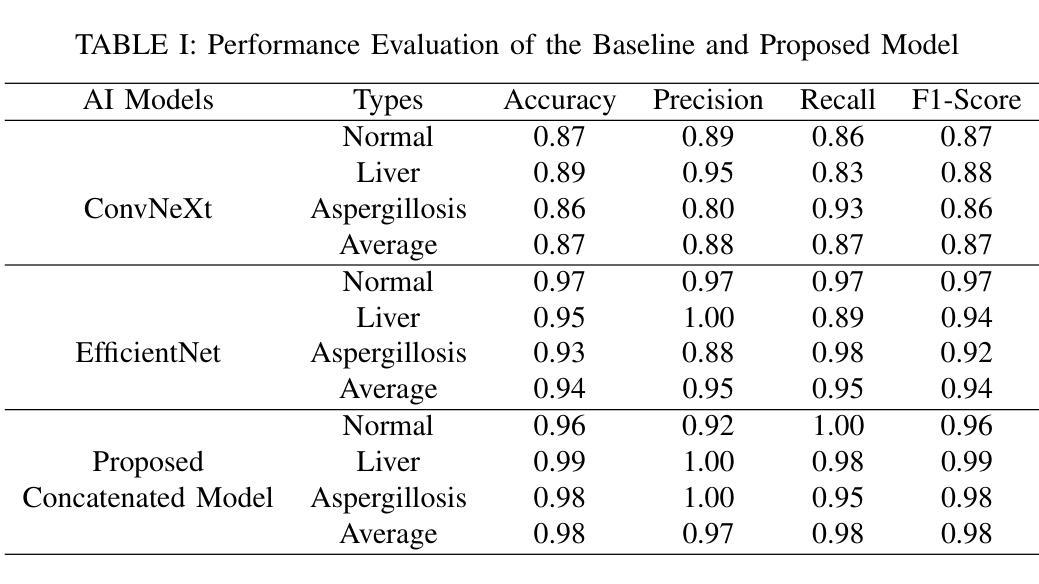
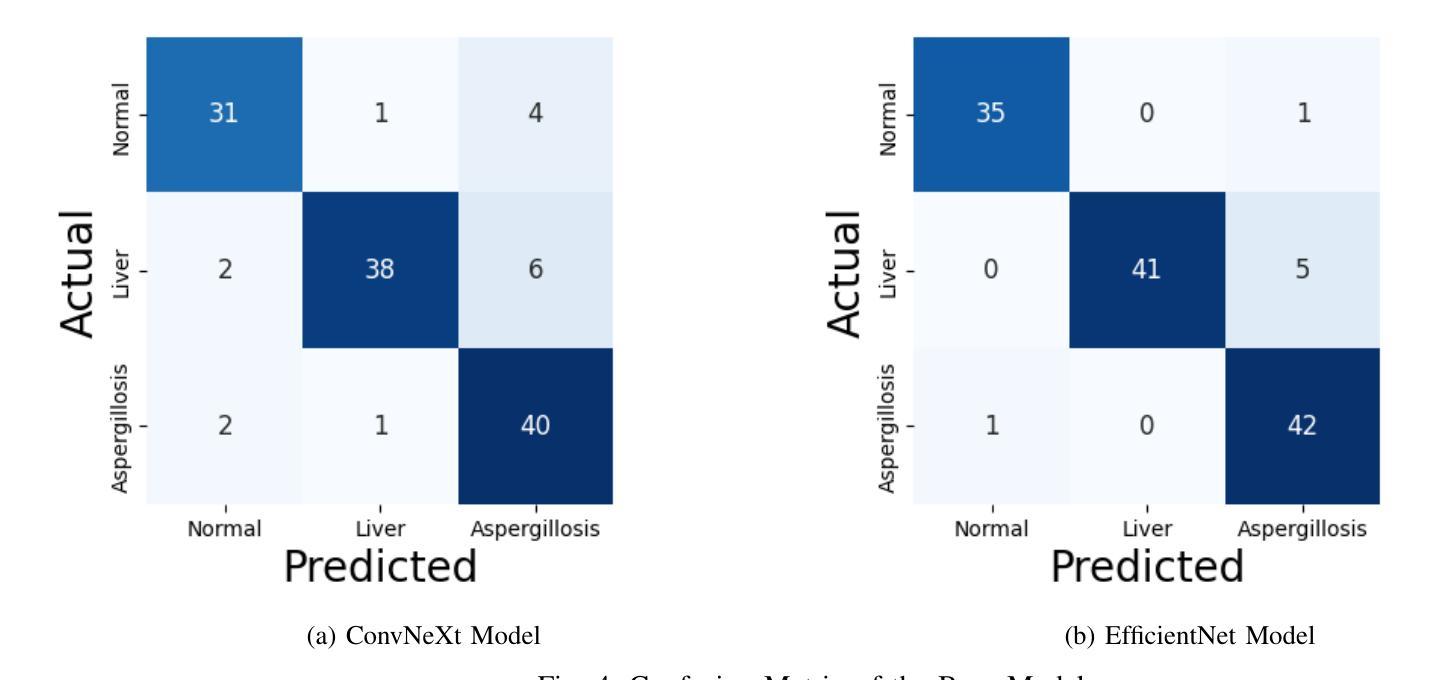
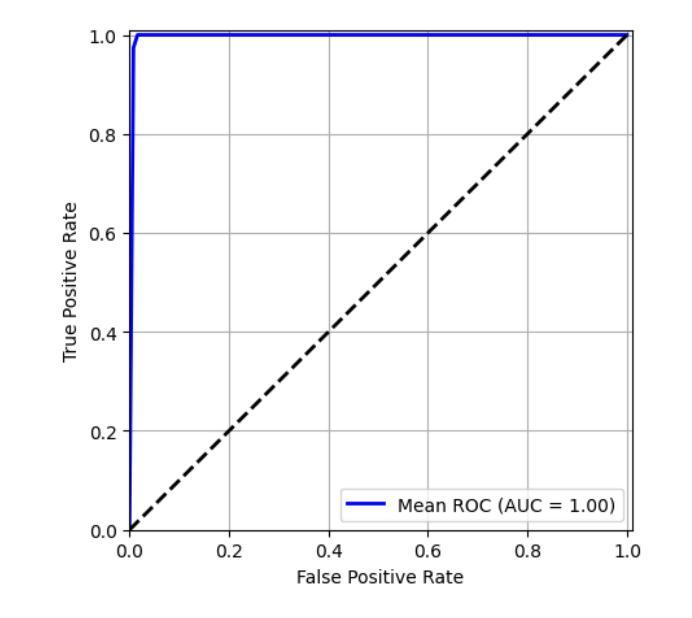
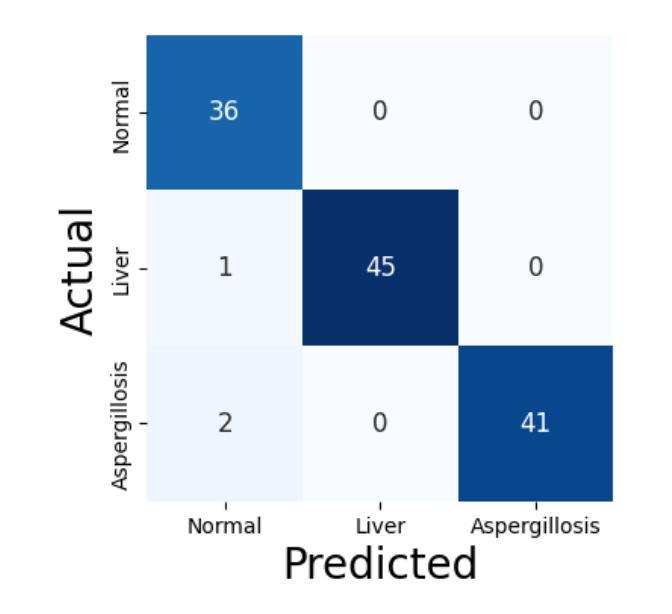
Falconry, a revered tradition involving the training and hunting with falcons, requires meticulous health surveillance to ensure the health and safety of these prized birds, particularly in hunting scenarios. This paper presents an innovative method employing a hybrid of ConvNeXt and EfficientNet AI models for the classification of falcon diseases. The study focuses on accurately identifying three conditions: Normal, Liver Disease and ‘Aspergillosis’. A substantial dataset was utilized for training and validating the model, with an emphasis on key performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Extensive testing and analysis have shown that our concatenated AI model outperforms traditional diagnostic methods and individual model architectures. The successful implementation of this hybrid AI model marks a significant step forward in precise falcon disease detection and paves the way for future developments in AI-powered avian healthcare solutions.
驯鹰术是一项受人尊敬的传统,涉及驯化和用猎鹰狩猎。为了保证这些珍贵鸟类,特别是在狩猎场景中的健康和安全问题,需要对其进行细致的健康监测。本文提出了一种采用ConvNeXt和EfficientNet人工智能模型混合体进行猎鹰疾病分类的创新方法。该研究重点关注准确识别三种状况:正常、肝病和“曲霉菌病”。研究使用大量数据集对模型进行训练和验证,重点关注准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数等关键性能指标。经过广泛测试和分析表明,我们组合的人工智能模型在性能上优于传统诊断方法和单一模型架构。这种混合人工智能模型的成功实施标志着精准猎鹰疾病检测迈出了重要一步,并为未来人工智能驱动的鸟类医疗保健解决方案的发展铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本研究采用ConvNeXt和EfficientNet人工智能模型的混合方法,对猎鹰的疾病进行分类。研究重点是对正常状态、肝病和曲霉菌病三种状态的准确识别。通过大量数据集的训练和验证,该模型的准确性、精确性、召回率和F1分数等关键性能指标均表现优异。测试和分析表明,该混合AI模型优于传统诊断方法和单独的模型架构。该混合人工智能模型的成功实施为精确的猎鹰疾病检测迈出了重要的一步,并为人工智能驱动的鸟类健康护理解决方案的发展铺平了道路。
要点
- 研究采用ConvNeXt和EfficientNet混合AI模型对猎鹰疾病进行分类。
- 重点识别猎鹰的三种状态:正常、肝病和曲霉菌病。
- 使用大量数据集对模型进行训练和验证。
- 模型在关键性能指标上表现出色,如准确性、精确性、召回率和F1分数。
- 混合AI模型在测试和分析中表现出优于传统诊断方法和单独模型架构的性能。
- 此研究是猎鹰疾病检测的一个重要进步。
点此查看论文截图

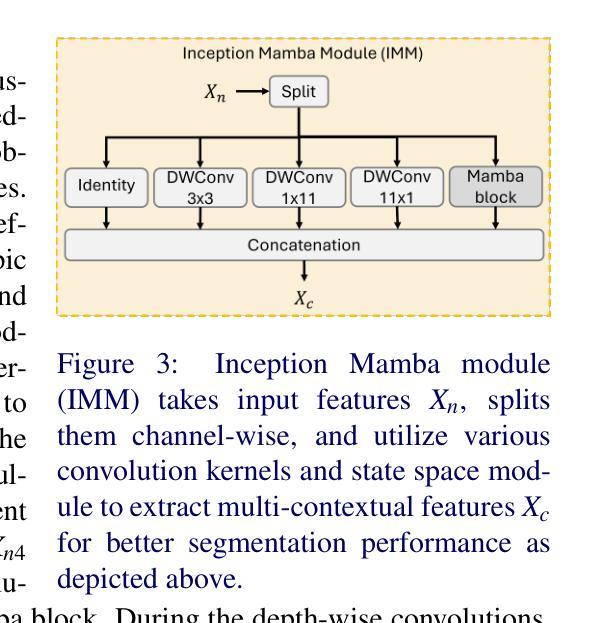
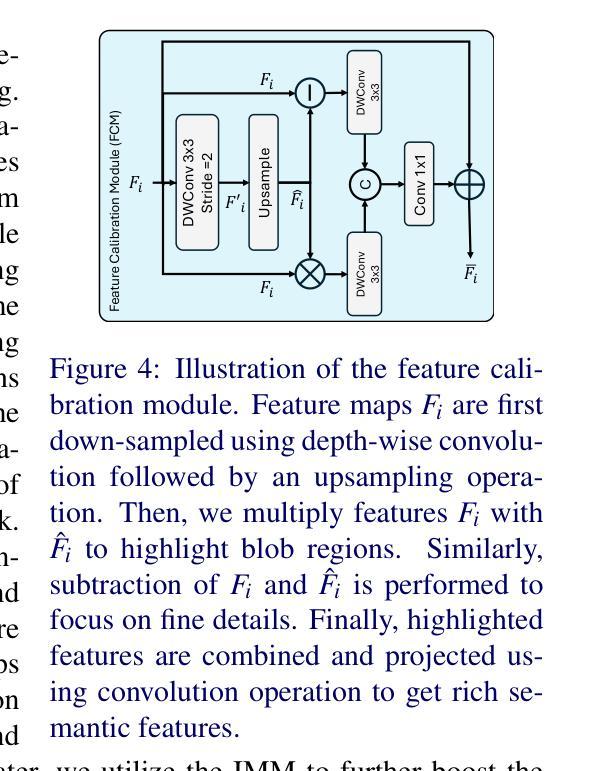
InceptionMamba: Efficient Multi-Stage Feature Enhancement with Selective State Space Model for Microscopic Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Daniya Najiha Abdul Kareem, Abdul Hannan, Mubashir Noman, Jean Lahoud, Mustansar Fiaz, Hisham Cholakkal
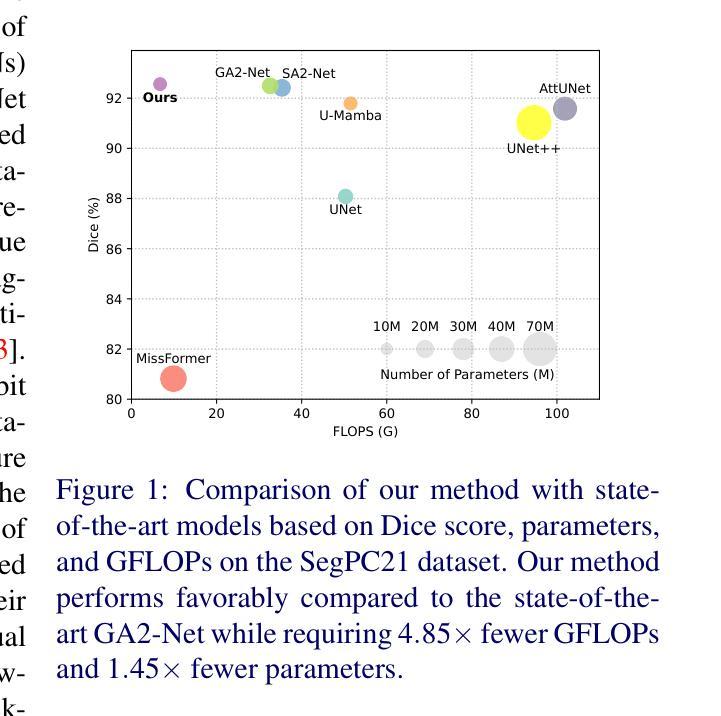
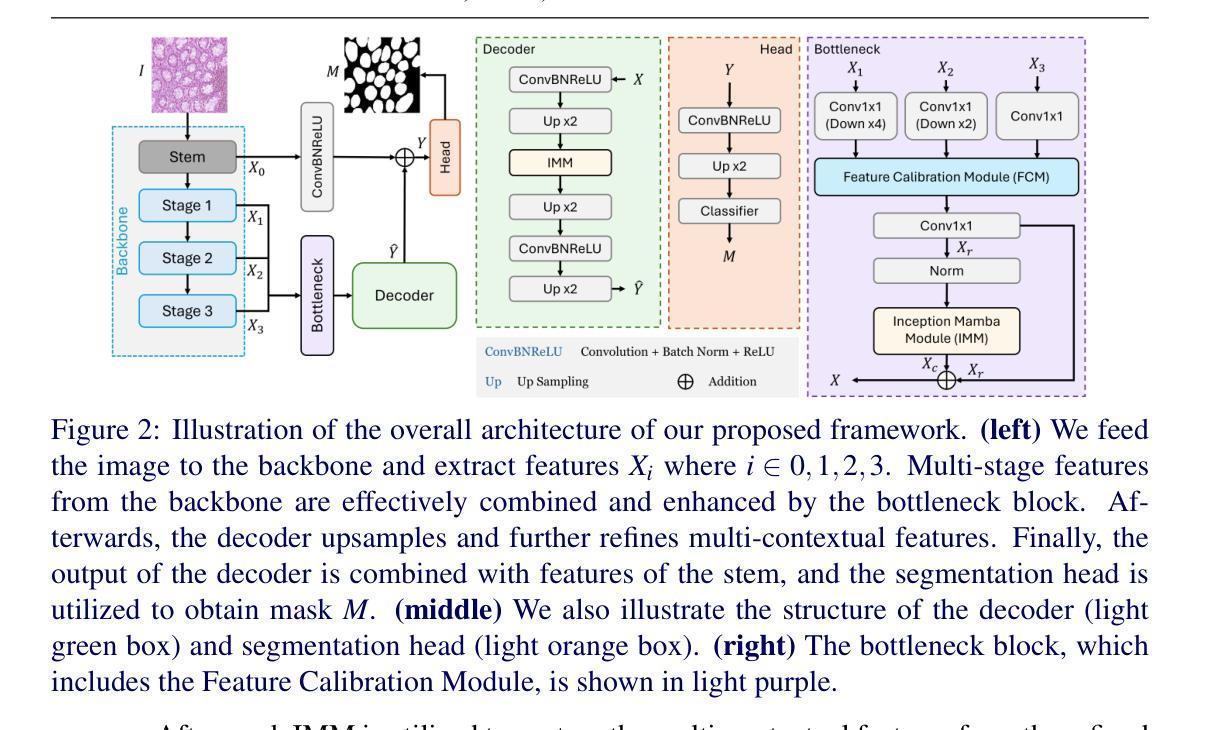
Accurate microscopic medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in diagnosing various cancerous cells and identifying tumors. Driven by advancements in deep learning, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer-based models have been extensively studied to enhance receptive fields and improve medical image segmentation task. However, they often struggle to capture complex cellular and tissue structures in challenging scenarios such as background clutter and object overlap. Moreover, their reliance on the availability of large datasets for improved performance, along with the high computational cost, limit their practicality. To address these issues, we propose an efficient framework for the segmentation task, named InceptionMamba, which encodes multi-stage rich features and offers both performance and computational efficiency. Specifically, we exploit semantic cues to capture both low-frequency and high-frequency regions to enrich the multi-stage features to handle the blurred region boundaries (e.g., cell boundaries). These enriched features are input to a hybrid model that combines an Inception depth-wise convolution with a Mamba block, to maintain high efficiency and capture inherent variations in the scales and shapes of the regions of interest. These enriched features along with low-resolution features are fused to get the final segmentation mask. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two challenging microscopic segmentation datasets (SegPC21 and GlaS) and two skin lesion segmentation datasets (ISIC2017 and ISIC2018), while reducing computational cost by about 5 times compared to the previous best performing method.
精确的微观医学图像分割在诊断各种癌细胞和识别肿瘤方面起着至关重要的作用。在深度学习发展的推动下,卷积神经网络(CNN)和基于Transformer的模型已经得到了广泛的研究,以提高感知场并改进医学图像分割任务。然而,这些模型在背景杂乱和物体重叠等复杂场景中,往往难以捕捉复杂的细胞和组织结构。此外,它们依赖于大量数据集来提高性能,以及计算成本较高,限制了它们的实用性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于分割任务的高效框架,名为InceptionMamba。该框架能够编码多阶段丰富特征,并提供性能和计算效率。具体来说,我们利用语义线索捕捉低频和高频区域,以丰富多阶段特征,处理模糊的边界区域(如细胞边界)。这些丰富的特征被输入到一个混合模型中,该模型结合了Inception深度卷积和Mamba块,以保持高效率并捕捉感兴趣区域的固有变化和形状。这些丰富特征与低分辨率特征相融合,以获得最终的分割掩膜。我们的模型在两个具有挑战性的微观分割数据集(SegPC21和GlaS)和两个皮肤病变分割数据集(ISIC2017和ISIC2018)上实现了最先进的性能,与以前性能最佳的方法相比,计算成本降低了约5倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学图像精准分割对于诊断癌细胞和识别肿瘤至关重要。深度学习驱动下的卷积神经网络和基于transformer的模型已广泛应用于提升感受野并改进医学图像分割任务。然而,这些模型在背景杂乱和物体重叠等复杂场景下,难以捕捉细胞和组织的复杂结构。此外,它们依赖大量数据集来提升性能,以及计算成本高昂,限制了其实用性。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种高效的分割框架,名为InceptionMamba,该框架能够编码多阶段丰富特征,并提供性能和计算效率。通过利用语义线索捕捉低频和高频区域,丰富多阶段特征以处理模糊的边界区域(如细胞边界)。这些丰富的特征被输入到一个混合模型中,该模型结合了Inception深度卷积和Mamba块,以保持高效率并捕捉感兴趣区域的固有变化和形状。这些丰富特征与低分辨率特征相融合,以获得最终的分割掩膜。我们的模型在具有挑战性的显微镜分割数据集(SegPC21和GlaS)以及皮肤病变分割数据集(ISIC2017和ISIC2018)上实现了最先进的性能,同时与以前性能最佳的方法相比,计算成本降低了约五倍。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割在诊断癌细胞和识别肿瘤方面起着关键作用。
- 深度学习模型,如卷积神经网络和基于transformer的模型,已用于改进医学图像分割任务。
- 这些模型在复杂场景下(如背景杂乱和物体重叠)难以捕捉细胞和组织的复杂结构。
- 提出的InceptionMamba框架能够编码多阶段丰富特征,提高分割性能和处理模糊边界区域。
- InceptionMamba框架结合了Inception深度卷积和Mamba块,保持高效率并捕捉区域的固有变化和形状。
- InceptionMamba模型在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

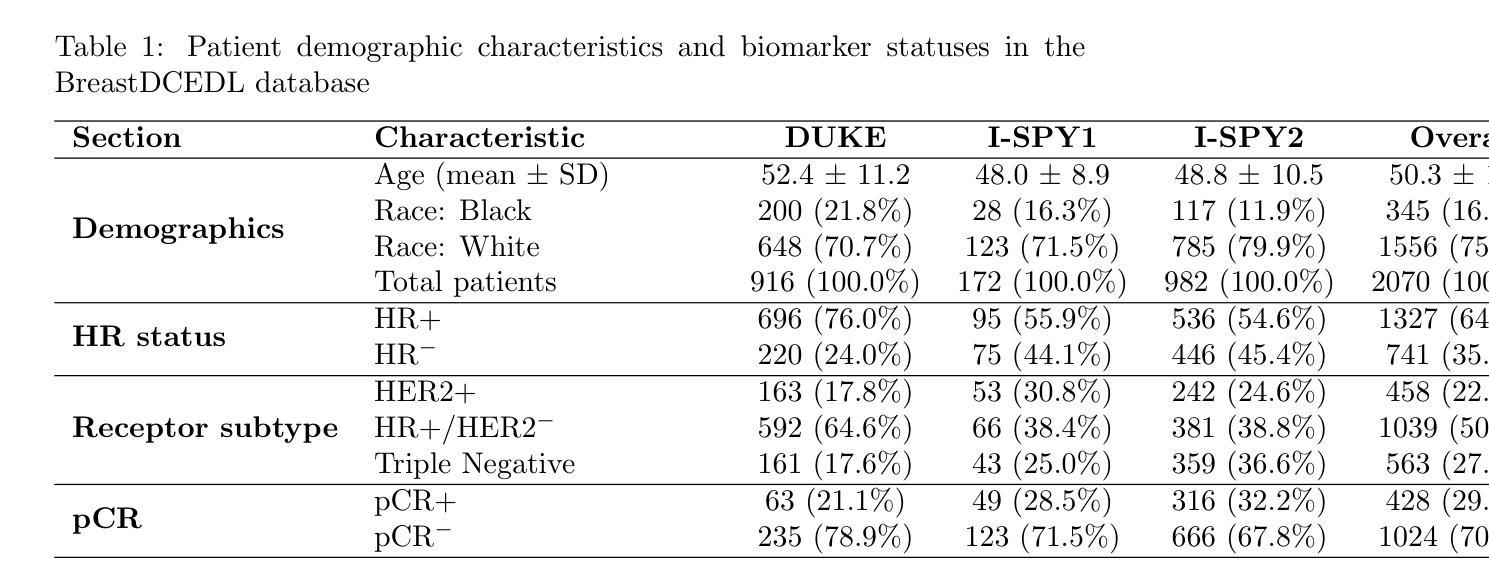
BreastDCEDL: Curating a Comprehensive DCE-MRI Dataset and developing a Transformer Implementation for Breast Cancer Treatment Response Prediction
Authors:Naomi Fridman, Bubby Solway, Tomer Fridman, Itamar Barnea, Anat Goldshtein
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, making early detection and accurate treatment response monitoring critical priorities. We present BreastDCEDL, a curated, deep learning-ready dataset comprising pre-treatment 3D Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) scans from 2,070 breast cancer patients drawn from the I-SPY1, I-SPY2, and Duke cohorts, all sourced from The Cancer Imaging Archive. The raw DICOM imaging data were rigorously converted into standardized 3D NIfTI volumes with preserved signal integrity, accompanied by unified tumor annotations and harmonized clinical metadata including pathologic complete response (pCR), hormone receptor (HR), and HER2 status. Although DCE-MRI provides essential diagnostic information and deep learning offers tremendous potential for analyzing such complex data, progress has been limited by lack of accessible, public, multicenter datasets. BreastDCEDL addresses this gap by enabling development of advanced models, including state-of-the-art transformer architectures that require substantial training data. To demonstrate its capacity for robust modeling, we developed the first transformer-based model for breast DCE-MRI, leveraging Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture trained on RGB-fused images from three contrast phases (pre-contrast, early post-contrast, and late post-contrast). Our ViT model achieved state-of-the-art pCR prediction performance in HR+/HER2- patients (AUC 0.94, accuracy 0.93). BreastDCEDL includes predefined benchmark splits, offering a framework for reproducible research and enabling clinically meaningful modeling in breast cancer imaging.
乳腺癌仍然是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,因此早期检测和准确的疗效反应监测成为至关重要的优先事项。我们推出了BreastDCEDL,这是一个精心策划的、为深度学习准备的数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke队列的2070名乳腺癌患者的术前3D动态增强MRI(DCE-MRI)扫描数据,所有数据源均来自癌症成像档案。原始的DICOM成像数据被严格转换为标准化的3DNIfTI体积,同时保留了信号完整性,并配有统一的肿瘤注释和协调一致的临床元数据,包括病理完全反应(pCR)、激素受体(HR)和HER2状态。尽管DCE-MRI提供了重要的诊断信息,深度学习在分析此类复杂数据方面拥有巨大潜力,但由于缺乏可访问的公共多中心数据集,进展一直受到限制。BreastDCEDL通过支持开发先进模型来解决这一差距,包括需要大量训练数据的最新变压器架构。为了展示其稳健建模的能力,我们开发了基于变压器的第一个乳腺癌DCE-MRI模型,利用在三个对比阶段(预对比、早期后对比和晚期后对比)的RGB融合图像上训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)架构。我们的ViT模型在HR+/HER2-患者中实现了最先进的pCR预测性能(AUC 0.94,准确率0.93)。BreastDCEDL包括预定义的基准分割,为可重复研究提供了框架,并在乳腺癌成像中实现了临床意义建模。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
乳腺癌仍是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,早期发现和准确的疗效监测是关键。我们推出了BreastDCEDL数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke等队列的2,070例乳腺癌患者的预治疗3D动态增强MRI(DCE-MRI)扫描数据。数据集包括标准化的3DNIfTI体积数据、统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据。我们开发了一种基于Vision Transformer的模型,能够在HR+/HER2-患者中实现高水平的pCR预测性能。BreastDCEDL包括预设的基准测试分割,为可重复的研究提供了一个框架,并能进行乳腺癌成像的临床意义建模。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌仍是全球主要的癌症死亡原因之一,强调早期检测和准确监测治疗反应的重要性。
- BreastDCEDL是一个新的深度学习和医学图像分析准备就绪的数据集,包含来自多个来源的标准化3D DCE-MRI扫描数据。
- 数据集包括统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据,如病理完全反应(pCR)、激素受体(HR)和HER2状态。
- 缺乏公共多中心数据集限制了深度学习在DCE-MRI数据分析方面的进展,BreastDCEDL填补了这一空白。
- 我们开发了一种基于Vision Transformer的模型,用于分析DCE-MRI数据,并在特定患者群体中实现了高水平的pCR预测性能。
- BreastDCEDL包括预设的基准测试分割,促进了研究的可重复性。
点此查看论文截图

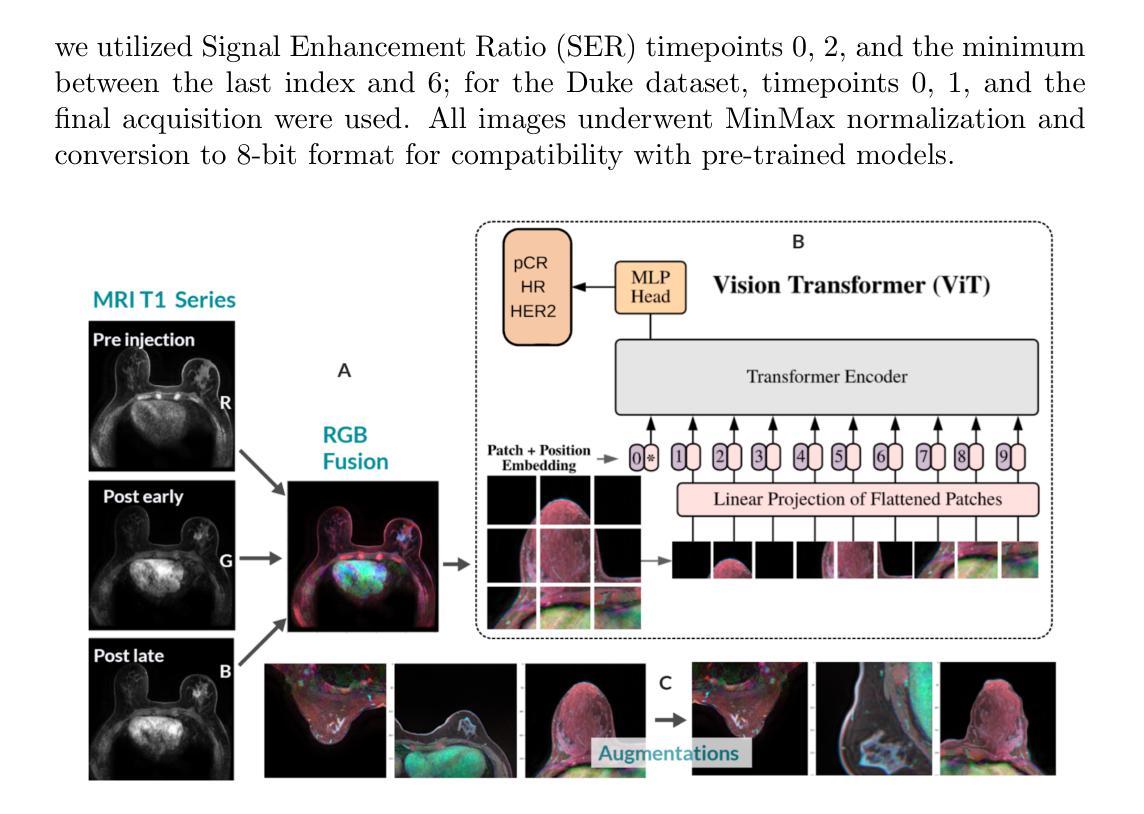
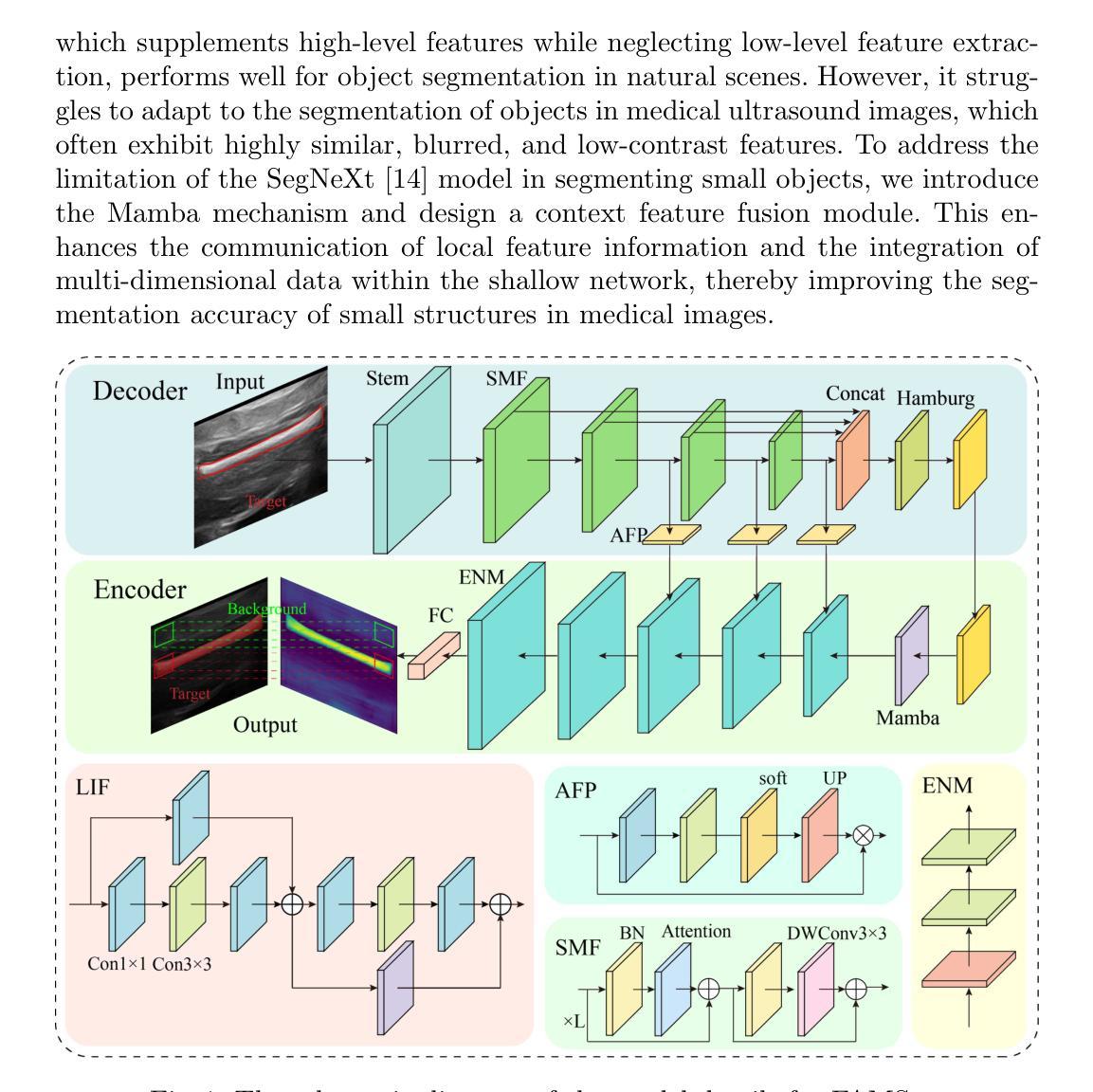
FAMSeg: Fetal Femur and Cranial Ultrasound Segmentation Using Feature-Aware Attention and Mamba Enhancement
Authors:Jie He, Minglang Chen, Minying Lu, Bocheng Liang, Junming Wei, Guiyan Peng, Jiaxi Chen, Ying Tan
Accurate ultrasound image segmentation is a prerequisite for precise biometrics and accurate assessment. Relying on manual delineation introduces significant errors and is time-consuming. However, existing segmentation models are designed based on objects in natural scenes, making them difficult to adapt to ultrasound objects with high noise and high similarity. This is particularly evident in small object segmentation, where a pronounced jagged effect occurs. Therefore, this paper proposes a fetal femur and cranial ultrasound image segmentation model based on feature perception and Mamba enhancement to address these challenges. Specifically, a longitudinal and transverse independent viewpoint scanning convolution block and a feature perception module were designed to enhance the ability to capture local detail information and improve the fusion of contextual information. Combined with the Mamba-optimized residual structure, this design suppresses the interference of raw noise and enhances local multi-dimensional scanning. The system builds global information and local feature dependencies, and is trained with a combination of different optimizers to achieve the optimal solution. After extensive experimental validation, the FAMSeg network achieved the fastest loss reduction and the best segmentation performance across images of varying sizes and orientations.
精确的超声图像分割是精确生物测定和准确评估的前提。依赖手动描绘会导致重大误差,并且非常耗时。然而,现有的分割模型是基于自然场景中的对象设计的,这使得它们难以适应高噪声和高相似性的超声对象。这在小型对象分割中表现得尤为明显,会出现明显的锯齿状效果。因此,针对这些挑战,本文提出了一种基于特征感知和Mamba增强的胎儿股骨和颅骨超声图像分割模型。具体来说,设计了纵向和横向独立视点扫描卷积块和特征感知模块,以提高捕获局部细节信息的能力,并改善上下文信息的融合。结合经过Mamba优化的残差结构,这种设计抑制了原始噪声的干扰,增强了局部多维扫描。该系统建立了全局信息和局部特征依赖关系,并使用不同的优化器组合进行训练,以实现最佳解决方案。经过广泛的实验验证,FAMSeg网络实现了最快的损失降低和最佳的分割性能,适用于不同大小和方向的图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于特征感知和Mamba增强的胎儿股骨和颅脑超声图像分割模型,旨在解决现有模型难以适应超声图像高噪声和高相似度的问题,特别是在小物体分割中出现的明显锯齿效应。通过设计纵向和横向独立视角扫描卷积块和特征感知模块,提高了捕捉局部细节信息的能力,并优化了上下文信息的融合。结合Mamba优化残差结构,该系统抑制了原始噪声的干扰,增强了局部多维扫描。经过实验验证,FAMSeg网络在不同大小和方向的图像上实现了最快的损失降低和最佳的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 超声图像分割对于精确生物识别和评估至关重要。
- 现有模型在应对高噪声和高相似度的超声图像时存在挑战。
- 针对小物体分割中的锯齿效应问题,本文提出了基于特征感知的超声图像分割模型。
- 设计了纵向和横向独立视角扫描卷积块,提高了捕捉局部细节信息的能力。
- 引入了特征感知模块以优化上下文信息的融合。
- 结合Mamba优化残差结构,抑制了原始噪声干扰,增强了局部多维扫描。
点此查看论文截图

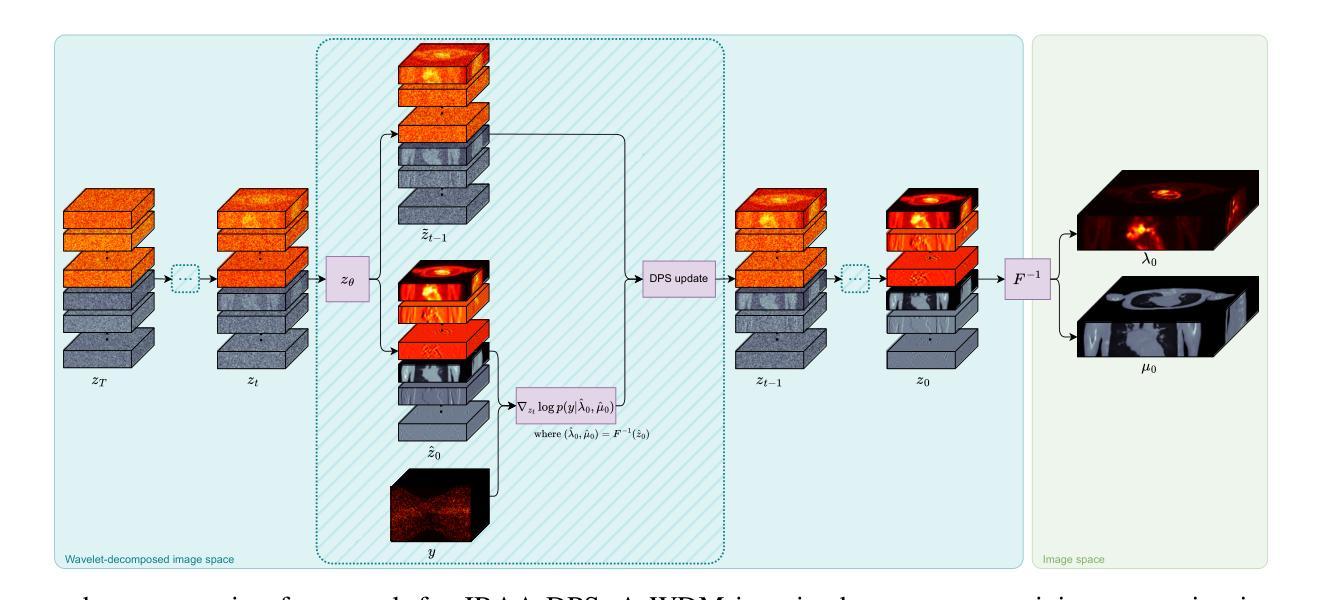
Joint Reconstruction of Activity and Attenuation in PET by Diffusion Posterior Sampling in Wavelet Coefficient Space
Authors:Clémentine Phung-Ngoc, Alexandre Bousse, Antoine De Paepe, Hong-Phuong Dang, Olivier Saut, Dimitris Visvikis
Attenuation correction (AC) is necessary for accurate activity quantification in positron emission tomography (PET). Conventional reconstruction methods typically rely on attenuation maps derived from a co-registered computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging scan. However, this additional scan may complicate the imaging workflow, introduce misalignment artifacts and increase radiation exposure. In this paper, we propose a joint reconstruction of activity and attenuation (JRAA) approach that eliminates the need for auxiliary anatomical imaging by relying solely on emission data. This framework combines wavelet diffusion model (WDM) and diffusion posterior sampling (DPS) to reconstruct fully three-dimensional (3-D) data. Experimental results show our method outperforms maximum likelihood activity and attenuation (MLAA) and MLAA with UNet-based post processing, and yields high-quality noise-free reconstructions across various count settings when time-of-flight (TOF) information is available. It is also able to reconstruct non-TOF data, although the reconstruction quality significantly degrades in low-count (LC) conditions, limiting its practical effectiveness in such settings. This approach represents a step towards stand-alone PET imaging by reducing the dependence on anatomical modalities while maintaining quantification accuracy, even in low-count scenarios when TOF information is available.
衰减校正(AC)对于正电子发射断层扫描(PET)中的活动准确量化是必要的。传统重建方法通常依赖于从共同注册的计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像扫描中得出的衰减图。然而,额外的扫描可能会使成像工作流程复杂化,引入错位伪影并增加辐射暴露。在本文中,我们提出了一种联合重建活动和衰减(JRAA)的方法,该方法仅依靠发射数据,消除了对辅助解剖成像的需求。该框架结合了小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS)来重建全三维(3-D)数据。实验结果表明,我们的方法在有时间飞行(TOF)信息的情况下,在多种计数设置下的性能优于最大可能性活动和衰减(MLAA)以及基于UNet的后处理的MLAA,并产生高质量的无噪声重建。虽然该方法能够重建非TOF数据,但在低计数(LC)条件下重建质量显著降低,这在某些设置中会限制其实践效果。该方法通过减少对解剖模式的依赖而保持量化准确性,朝着独立PET成像迈出了一步,即使在有时间飞行信息的情况下低计数场景中也是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文提出了一种基于发射数据的活动衰减联合重建方法(JRAA),无需额外的解剖成像。该方法结合了小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS)进行全三维数据重建,实验结果表明该方法在有时间飞行信息的情况下,在各种计数设置下都能产生高质量的无噪声重建图像,优于最大似然活动和衰减重建(MLAA)及其基于UNet的后处理方法。尽管在非时间飞行数据重建中,该方法在低计数条件下重建质量有所下降,但在实际应用中仍显示出减少对解剖模态依赖的同时维持量化准确性的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 衰减校正(AC)对于正电子发射断层扫描(PET)中的活动定量至关重要。
- 传统重建方法依赖于从共注册的计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像扫描获得的衰减图,这可能会复杂化成像工作流程,引入错位伪影并增加辐射暴露。
- 提出了基于发射数据的活动和衰减联合重建(JRAA)方法,无需额外的解剖成像。
- JRAA方法结合了小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS)进行全三维数据重建。
- 实验结果表明,JRAA方法在有时间飞行信息的情况下优于最大似然活动和衰减重建(MLAA)及其基于UNet的后处理方法。
- JRAA能够在低计数条件下重建非时间飞行数据,但重建质量有所下降。
点此查看论文截图

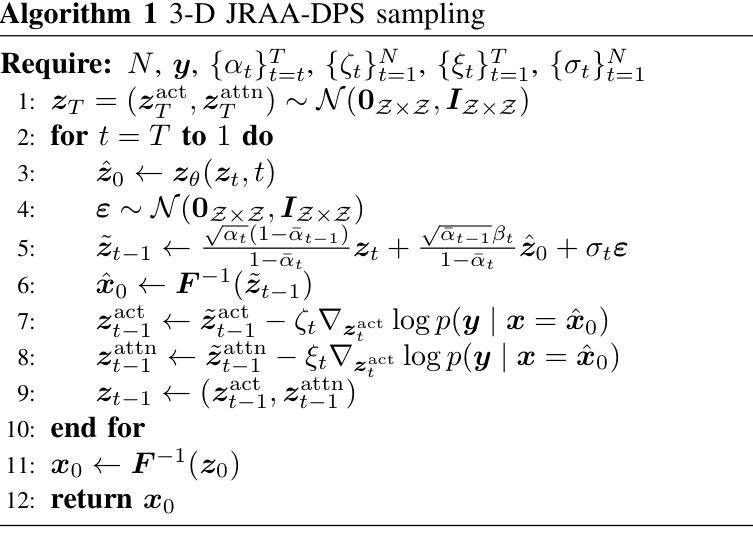
VIViT: Variable-Input Vision Transformer Framework for 3D MR Image Segmentation
Authors:Badhan Kumar Das, Ajay Singh, Gengyan Zhao, Han Liu, Thomas J. Re, Dorin Comaniciu, Eli Gibson, Andreas Maier
Self-supervised pretrain techniques have been widely used to improve the downstream tasks’ performance. However, real-world magnetic resonance (MR) studies usually consist of different sets of contrasts due to different acquisition protocols, which poses challenges for the current deep learning methods on large-scale pretrain and different downstream tasks with different input requirements, since these methods typically require a fixed set of input modalities or, contrasts. To address this challenge, we propose variable-input ViT (VIViT), a transformer-based framework designed for self-supervised pretraining and segmentation finetuning for variable contrasts in each study. With this ability, our approach can maximize the data availability in pretrain, and can transfer the learned knowledge from pretrain to downstream tasks despite variations in input requirements. We validate our method on brain infarct and brain tumor segmentation, where our method outperforms current CNN and ViT-based models with a mean Dice score of 0.624 and 0.883 respectively. These results highlight the efficacy of our design for better adaptability and performance on tasks with real-world heterogeneous MR data.
自监督预训练技术在提高下游任务性能方面得到了广泛应用。然而,由于不同的采集协议,现实世界中的磁共振(MR)研究通常由不同的对比组构成,这为当前深度学习方法在大型预训练以及具有不同输入要求的下游任务上带来了挑战,因为这些方法通常需要一组固定的输入模式或对比。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了可变输入ViT(VIViT),这是一个基于transformer的框架,旨在用于每项研究的可变对比下的自监督预训练和分割微调。凭借这一能力,我们的方法可以在预训练期间最大化数据可用性,并且尽管输入要求存在差异,也可以将从预训练中学习的知识转移到下游任务。我们的方法在脑梗死和脑肿瘤分割上验证了该方法的有效性,我们的方法优于当前的CNN和ViT模型,平均Dice得分分别为0.624和0.883。这些结果凸显了我们的设计在实际世界中具有更好适应性和性能的任务上的有效性,特别是面对异质的MR数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本文提出一种基于自监督预训练和分割微调的可变输入ViT(VIViT)框架,用于处理不同研究中由于采集协议不同而产生的多种对比图像。该框架可最大化预训练中的数据可用性,并能够在输入要求不同的任务之间转移知识。在脑梗死和脑肿瘤分割验证中,该方法优于现有的CNN和ViT模型,平均Dice得分分别为0.624和0.883。这显示了该设计在实际应用中具有更好的适应性和性能。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督预训练技术广泛应用于提高下游任务性能。
- 由于不同采集协议导致的多种对比图像是医学领域常见的问题。
- 当前深度学习方法在处理具有不同输入要求的下游任务时面临挑战。
- VIViT框架设计用于处理可变输入的医学图像自监督预训练和分割微调。
- VIViT框架可最大化预训练中的数据可用性,并适应不同的输入要求。
- VIViT框架在脑梗死和脑肿瘤分割任务中表现出优异性能,平均Dice得分高于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图

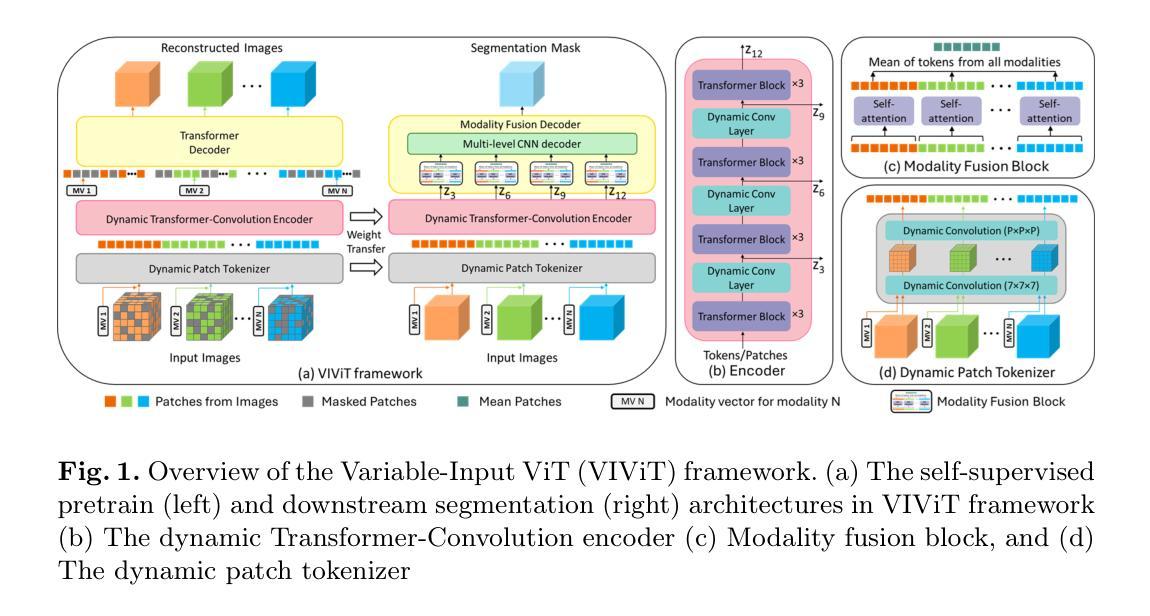
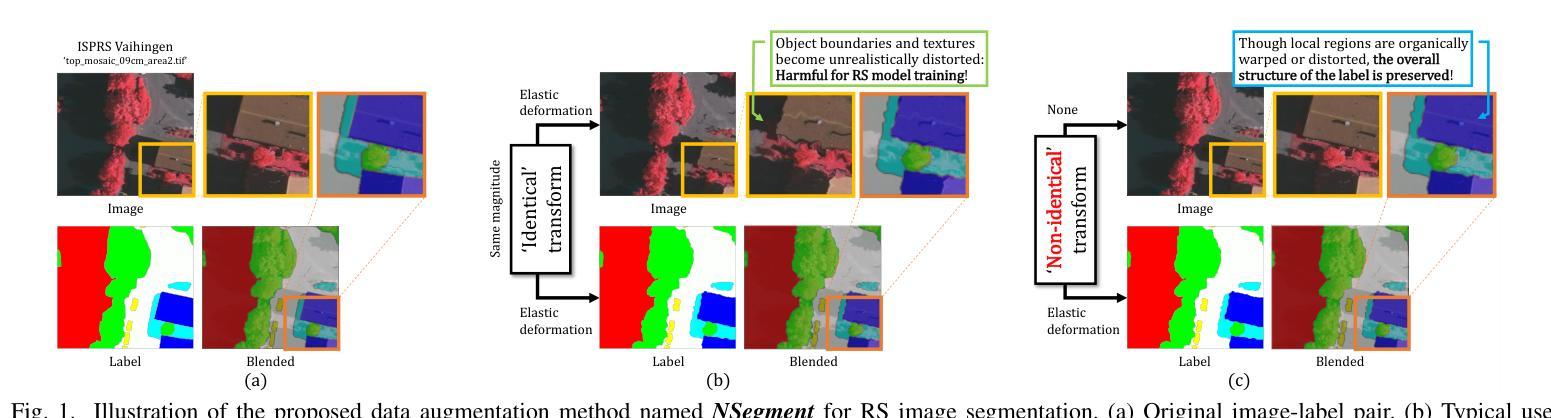
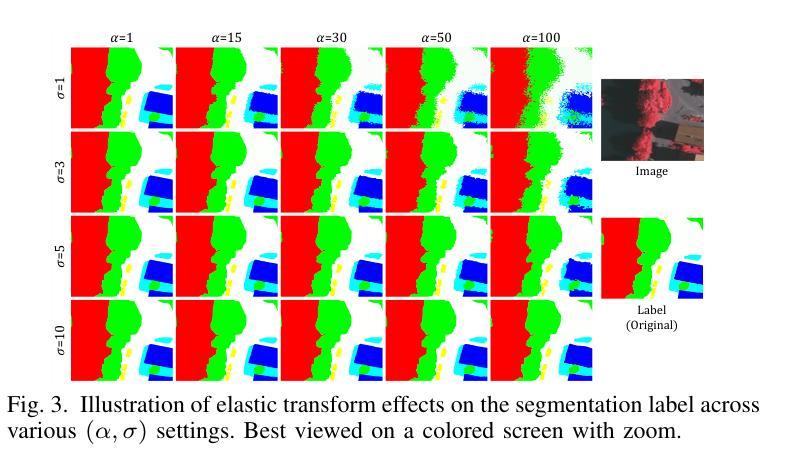
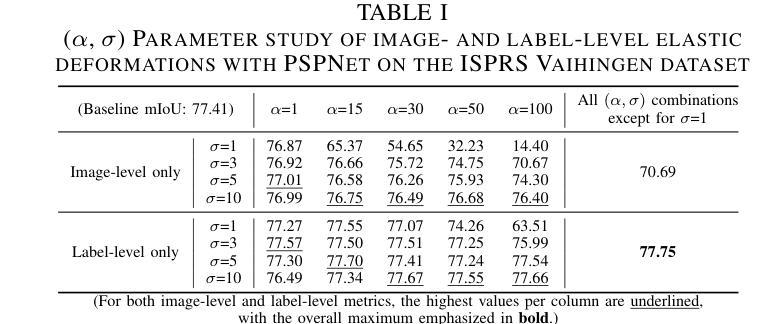
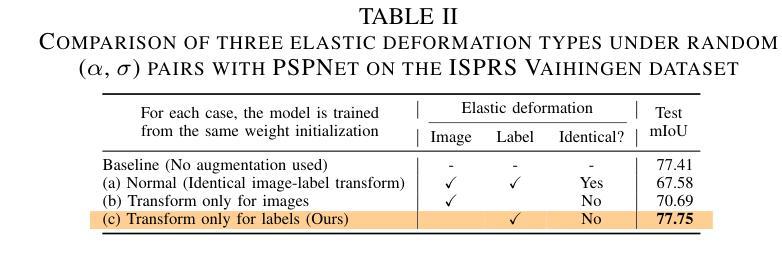
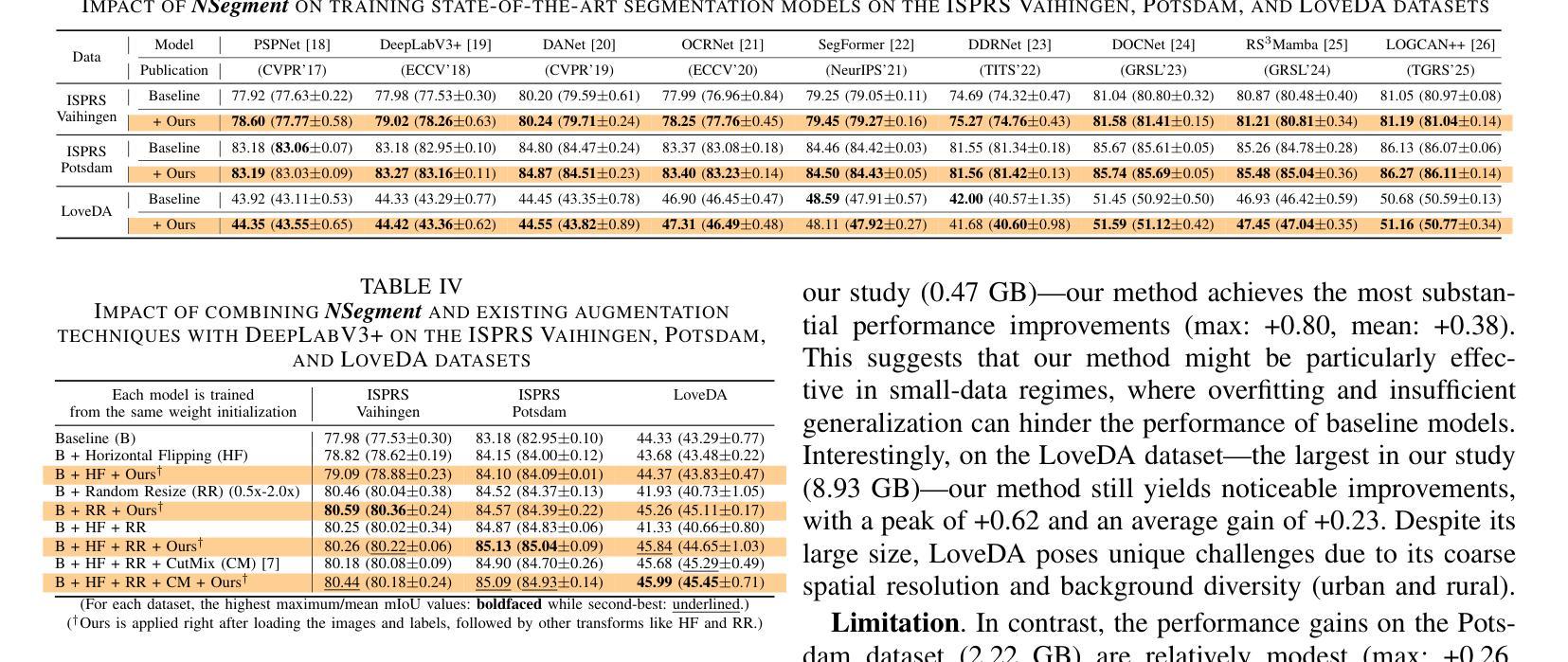
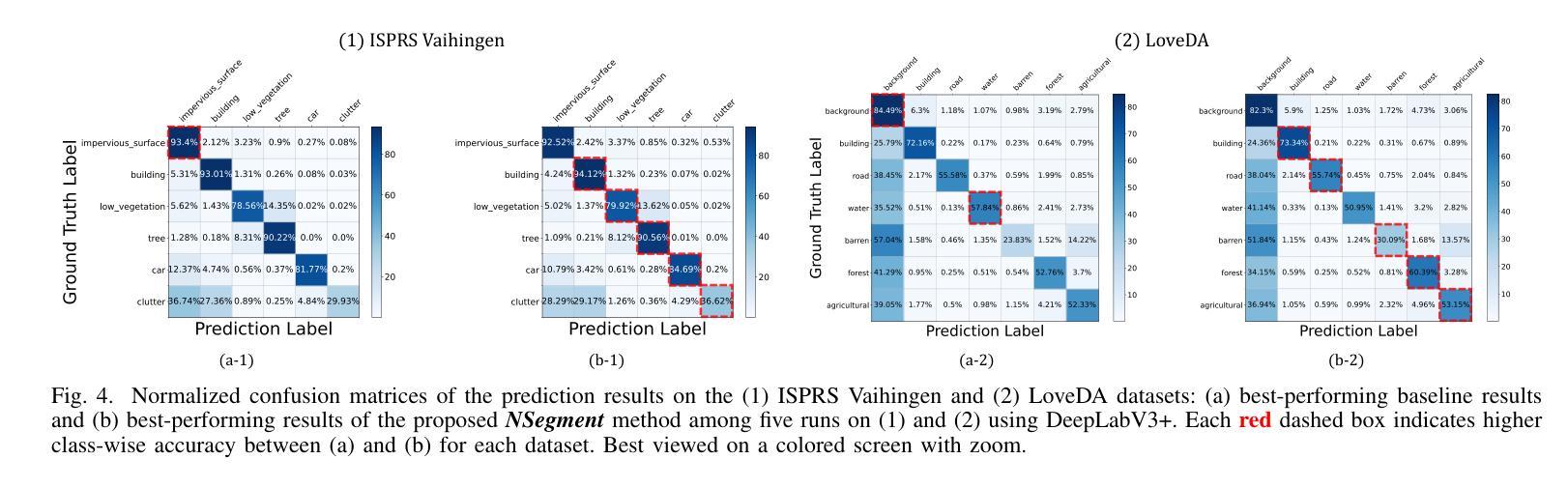
NSegment : Label-specific Deformations for Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Yechan Kim, DongHo Yoon, SooYeon Kim, Moongu Jeon
Labeling errors in remote sensing (RS) image segmentation datasets often remain implicit and subtle due to ambiguous class boundaries, mixed pixels, shadows, complex terrain features, and subjective annotator bias. Furthermore, the scarcity of annotated RS data due to high image acquisition and labeling costs complicates training noise-robust models. While sophisticated mechanisms such as label selection or noise correction might address this issue, they tend to increase training time and add implementation complexity. In this letter, we propose NSegment-a simple yet effective data augmentation solution to mitigate this issue. Unlike traditional methods, it applies elastic transformations only to segmentation labels, varying deformation intensity per sample in each training epoch to address annotation inconsistencies. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach improves the performance of RS image segmentation on various state-of-the-art models.
遥感(RS)图像分割数据集存在标签错误的问题常常隐晦且微妙,这主要是因为类别边界模糊、像素混合、阴影、地形特征复杂以及主观标注者偏见等因素。此外,由于图像采集和标注的高成本,导致标注的遥感数据稀缺,这增加了训练抗噪声模型的难度。虽然标签选择或噪声修正等复杂机制可能解决此问题,但它们往往会增加训练时间并增加实现复杂性。在本信中,我们提出NSegment——一种简单有效的数据增强解决方案来缓解这个问题。与传统方法不同,它仅对分割标签应用弹性转换,并在每个训练周期中对每个样本的变形强度进行变化,以解决标注不一致的问题。实验结果表明,我们的方法在各种最先进的模型上提高了遥感图像分割的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文提出一种名为NSegment的数据增强解决方案,针对遥感图像分割数据集存在的标签错误问题,通过弹性变换调整分割标签,每个训练周期对样本的变形强度进行变化,以解决标注不一致的问题。实验结果表明,该方法提高了遥感图像分割的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像分割数据集的标签错误问题由于模糊类边界、混合像素、阴影、复杂地形特征和主观标注者偏见而隐性存在。
- 标注错误和缺乏标注的遥感数据使得训练噪声鲁棒性模型变得复杂。
- 当前解决机制如标签选择或噪声校正可能增加训练时间和实施复杂性。
- 提出一种名为NSegment的数据增强方法,通过弹性变换调整分割标签,以简单有效的方式缓解标注不一致问题。
- NSegment方法针对每个训练周期中的每个样本应用不同的变形强度。
- 实验结果表明,NSegment方法提高了遥感图像分割的性能。
点此查看论文截图


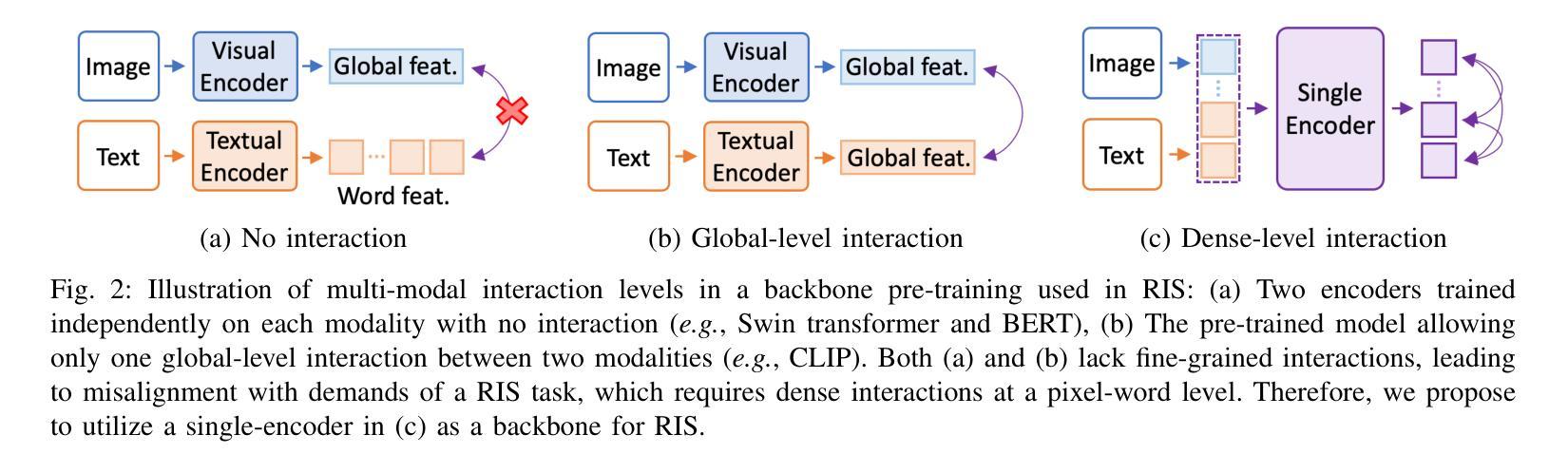
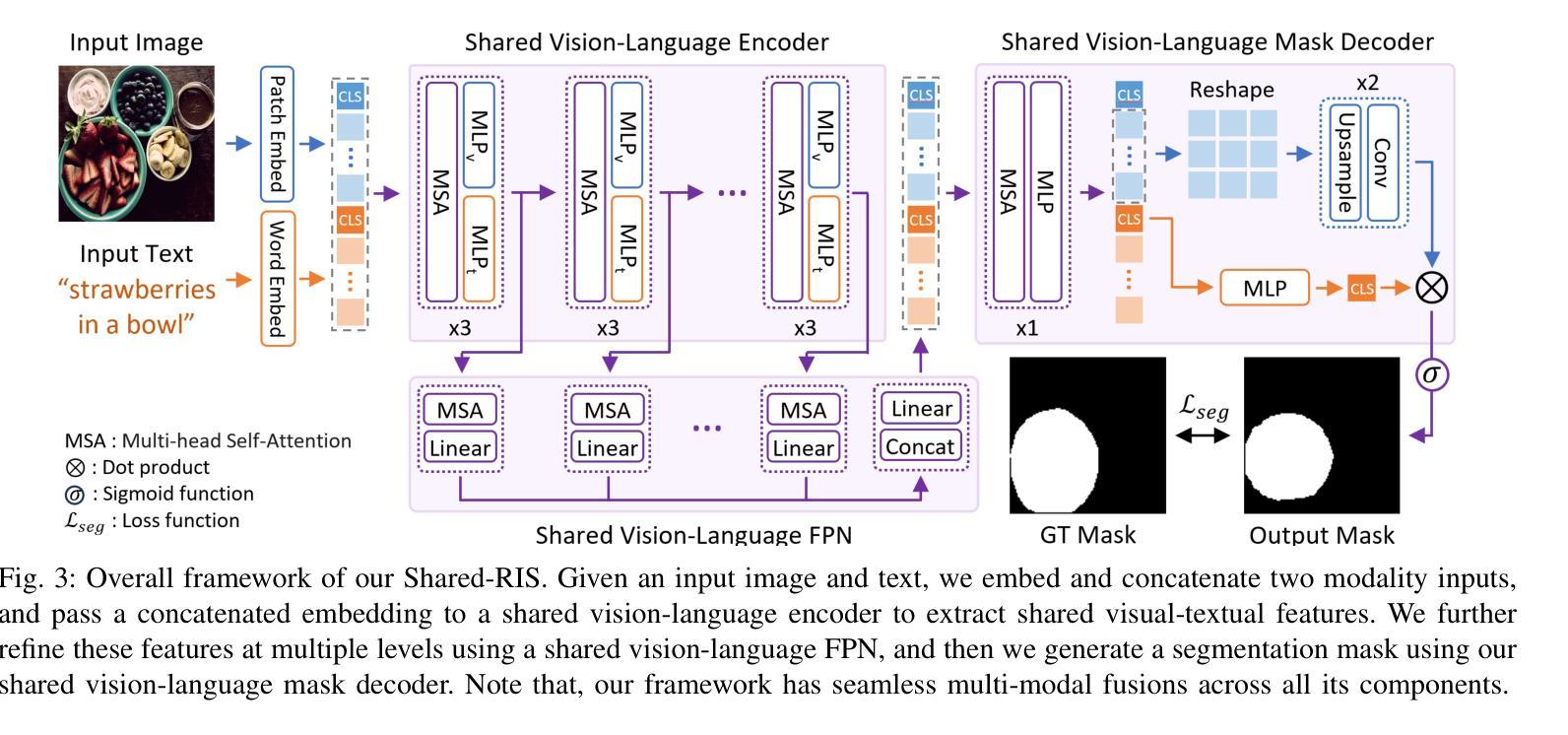
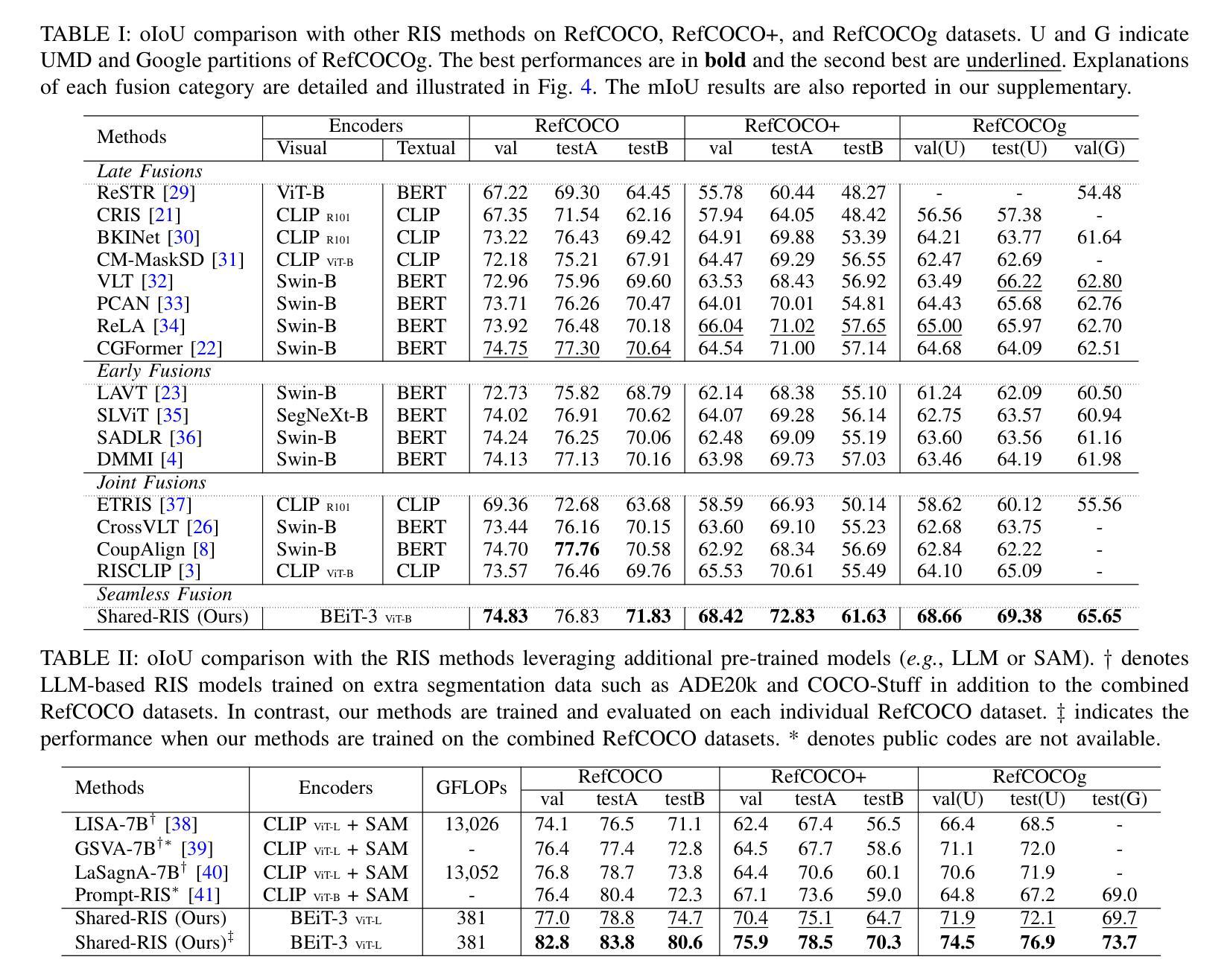
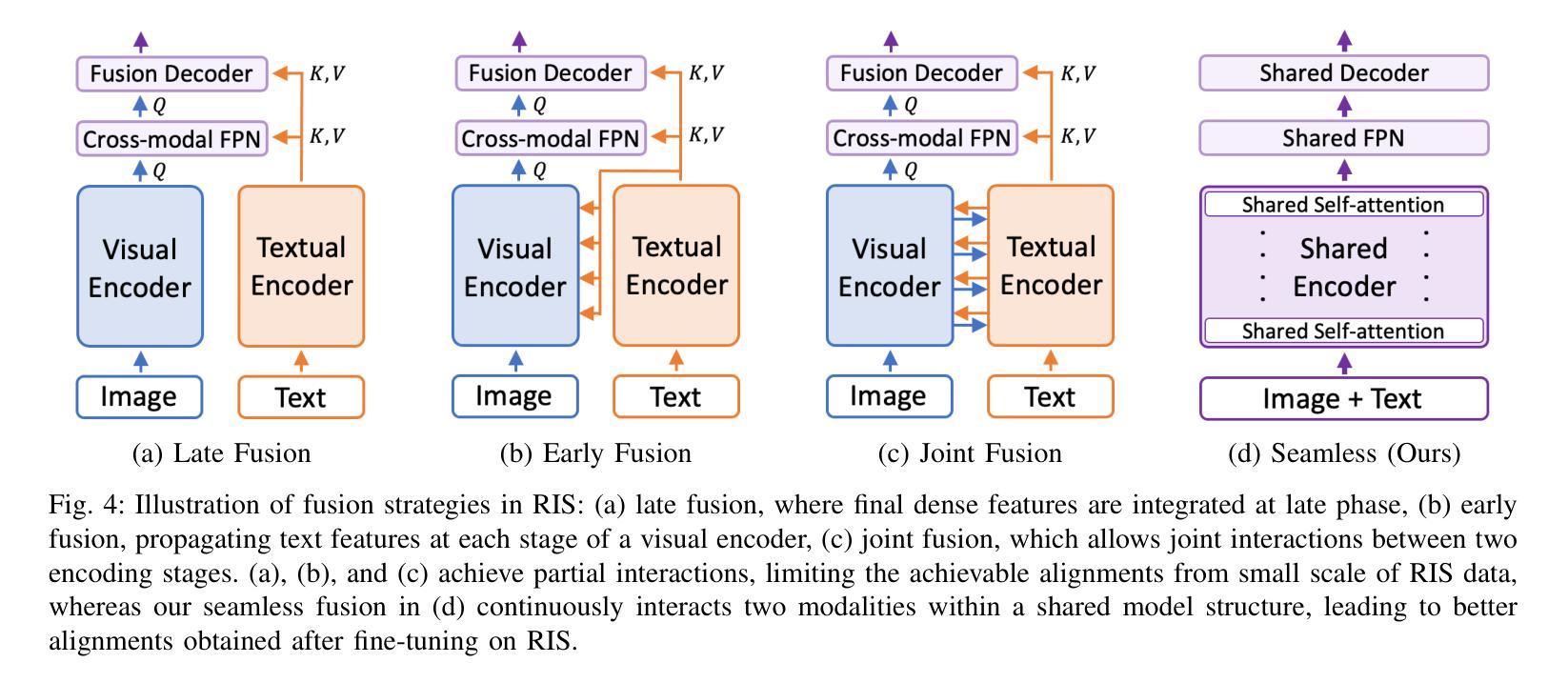
A Simple Baseline with Single-encoder for Referring Image Segmentation
Authors:Seonghoon Yu, Ilchae Jung, Byeongju Han, Taeoh Kim, Yunho Kim, Dongyoon Wee, Jeany Son
Referring image segmentation (RIS) requires dense vision-language interactions between visual pixels and textual words to segment objects based on a given description. However, commonly adapted dual-encoders in RIS, e.g., Swin transformer and BERT (uni-modal encoders) or CLIP (a multi-modal dual-encoder), lack dense multi-modal interactions during pre-training, leading to a gap with a pixel-level RIS task. To bridge this gap, existing RIS methods often rely on multi-modal fusion modules that interact two encoders, but this approach leads to high computational costs. In this paper, we present a novel RIS method with a single-encoder, i.e., BEiT-3, maximizing the potential of shared self-attention across all framework components. This enables seamless interactions of two modalities from input to final prediction, producing granularly aligned multi-modal features. Furthermore, we propose lightweight yet effective decoder modules, a Shared FPN and a Shared Mask Decoder, which contribute to the high efficiency of our model. Our simple baseline with a single encoder achieves outstanding performances on the RIS benchmark datasets while maintaining computational efficiency, compared to the most recent SoTA methods based on dual-encoders.
图像参照分割(RIS)需要视觉像素和文本单词之间的密集视觉语言交互,以便根据给定描述来分割对象。然而,RIS中常用的双编码器(例如Swin transformer和BERT(单模态编码器)或CLIP(多模态双编码器))在预训练期间缺乏密集的多模态交互,这与像素级的RIS任务之间存在差距。为了弥补这一差距,现有的RIS方法通常依赖于多模态融合模块来使两个编码器进行交互,但这会导致较高的计算成本。本文提出了一种新型的RIS方法,使用单一编码器BEiT-3,最大限度地发挥所有框架组件共享的自注意机制的潜力。这实现了从输入到最终预测的两个模态无缝交互,生成精细对齐的多模态特征。此外,我们提出了轻量级但有效的解码器模块,即共享FPN和共享Mask Decoder,这有助于提升模型的高效率。使用单一编码器的简单基线模型在RIS基准数据集上实现了卓越的性能,同时保持了计算效率,与基于双编码器的最新最先进的方法相比具有优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv pre-print
Summary
医学图像分割中的参照图像分割(RIS)需要视觉像素和文本词汇之间的密集视觉语言交互。然而,常用的双编码器(如Swin transformer和BERT等单模态编码器或CLIP等多模态双编码器)在预训练期间缺乏密集的多模态交互,导致与像素级RIS任务之间存在差距。本文提出了一种新型的单编码器参照图像分割方法——BEiT-3模型,充分利用各组件之间的共享自注意力机制,促进两个模态在全过程中无缝交互,实现精细化多模态特征对齐。此外,本文还提出了轻量级但高效的解码器模块,包括共享FPN和共享掩膜解码器,提高了模型的计算效率。相较于基于双编码器的最新方法,本模型以单编码器为基础,在参照图像分割基准数据集上取得了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 参照图像分割(RIS)需要视觉像素和文本词汇之间的密集交互。
- 常见双编码器在预训练时缺乏多模态密集交互,造成与像素级RIS任务的差距。
- 引入新型单编码器方法——BEiT-3模型,通过共享自注意力机制实现无缝的多模态交互。
- BEiT-3模型具备高效的解码器模块,如共享FPN和共享掩膜解码器。
- 单编码器的BEiT-3模型在参照图像分割基准数据集上的性能卓越。
- 该方法相较于其他最新方法,在保证性能的同时,提高了计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

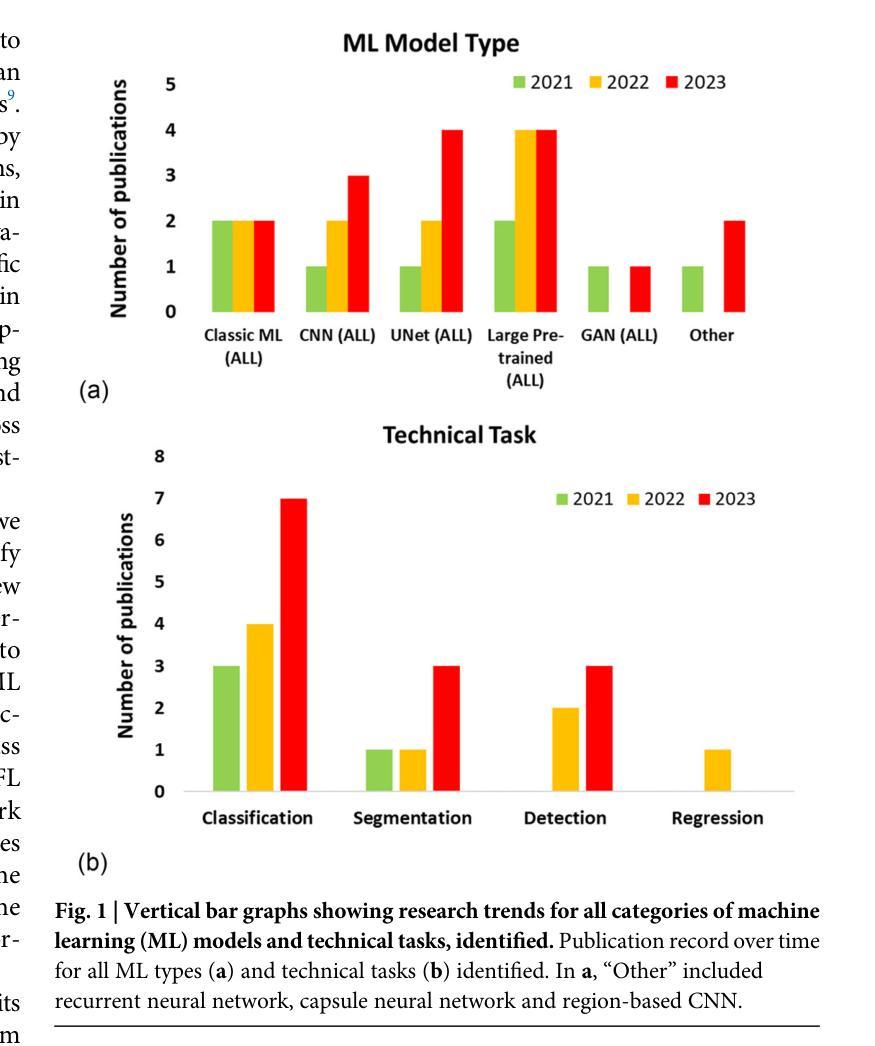
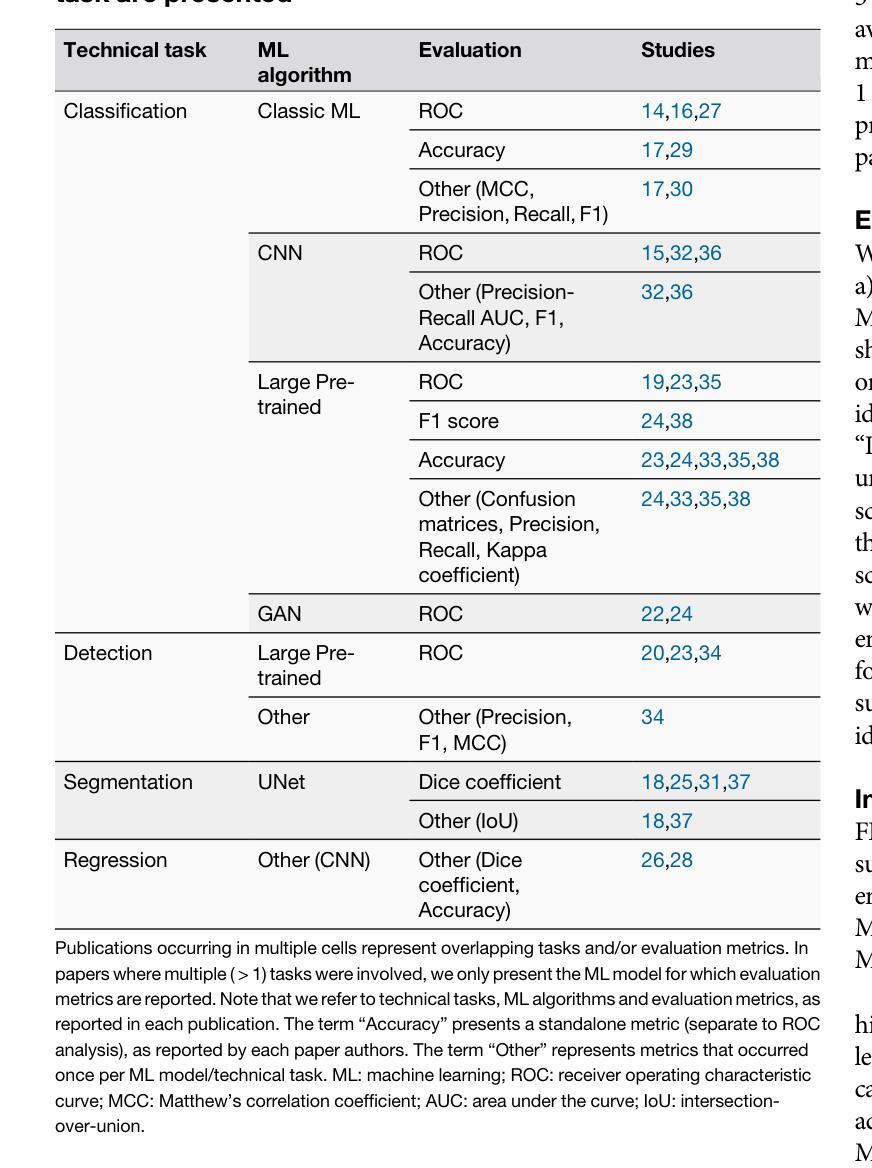
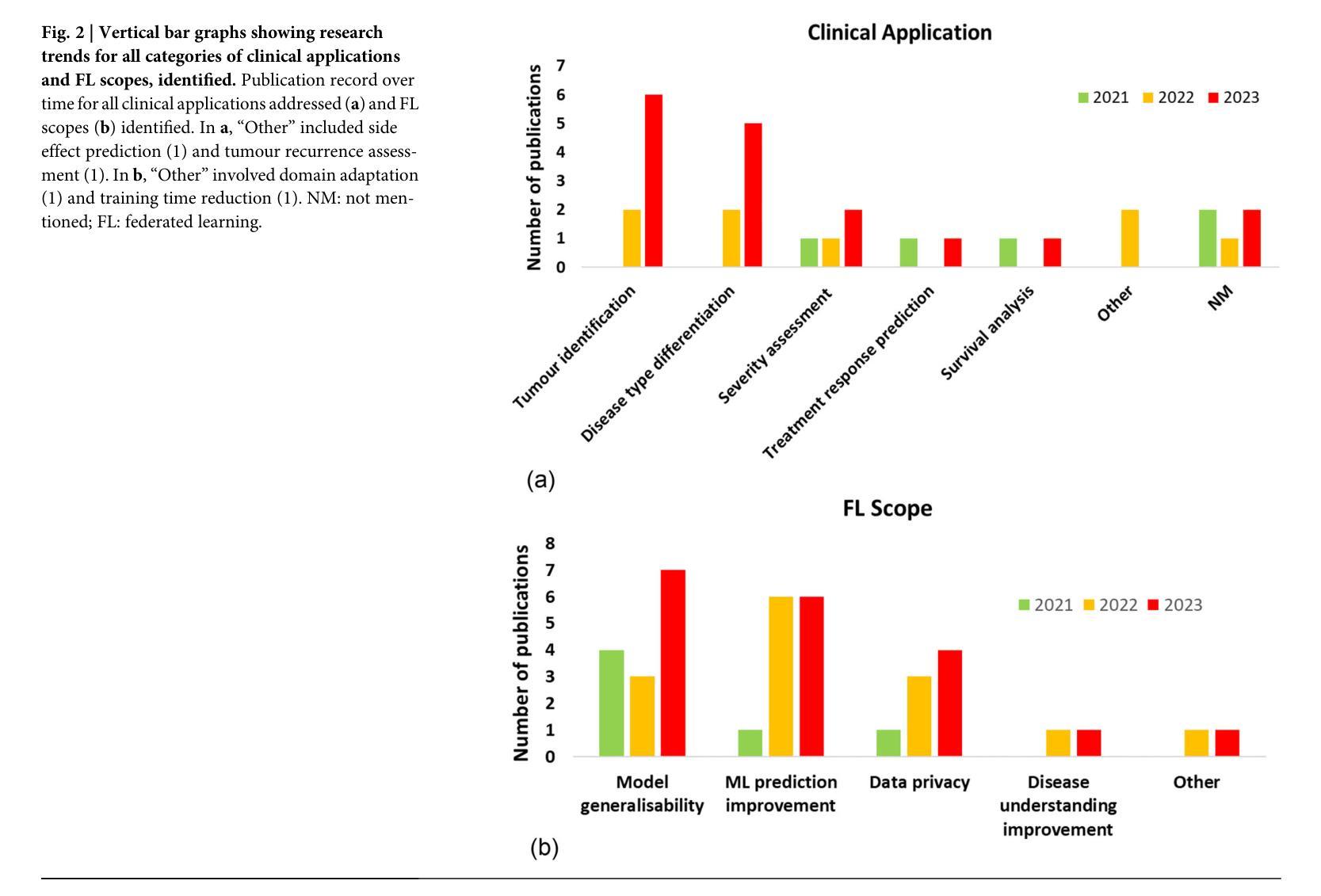
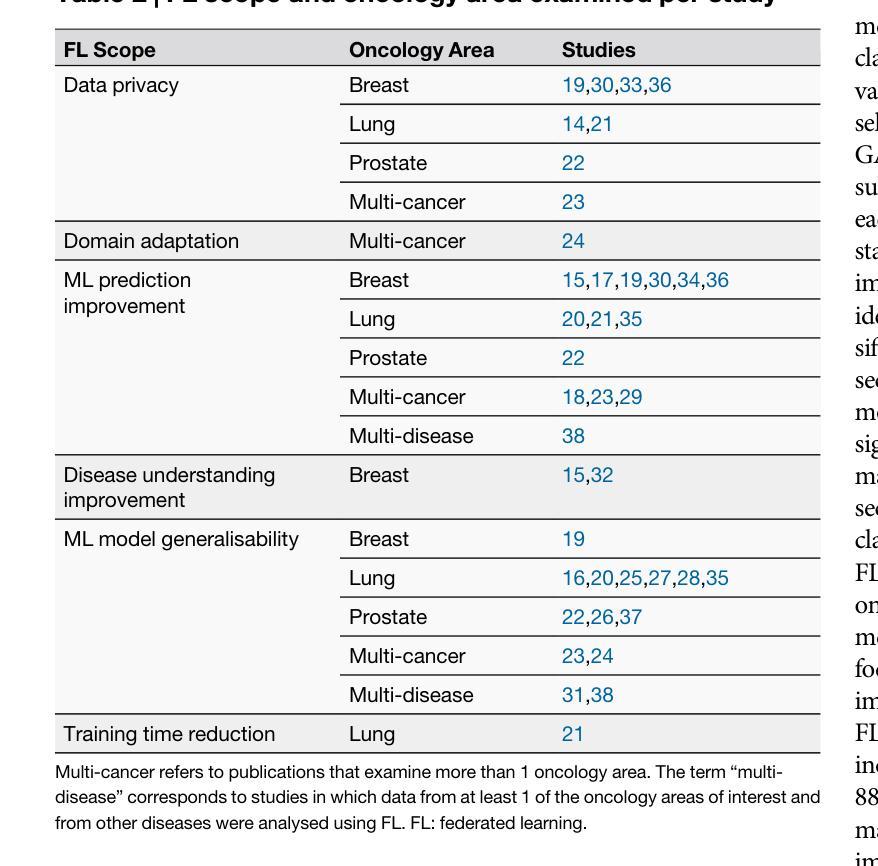
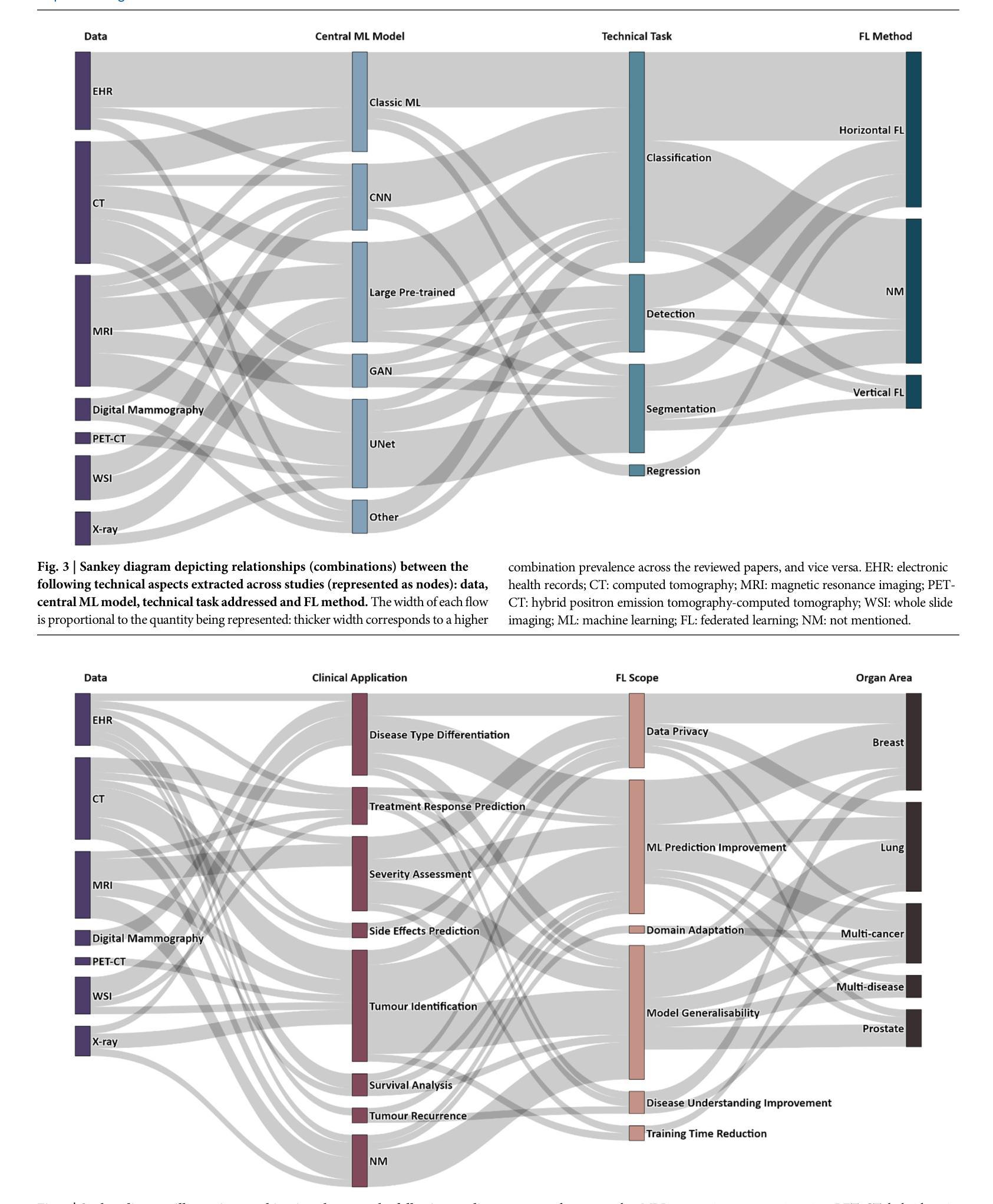
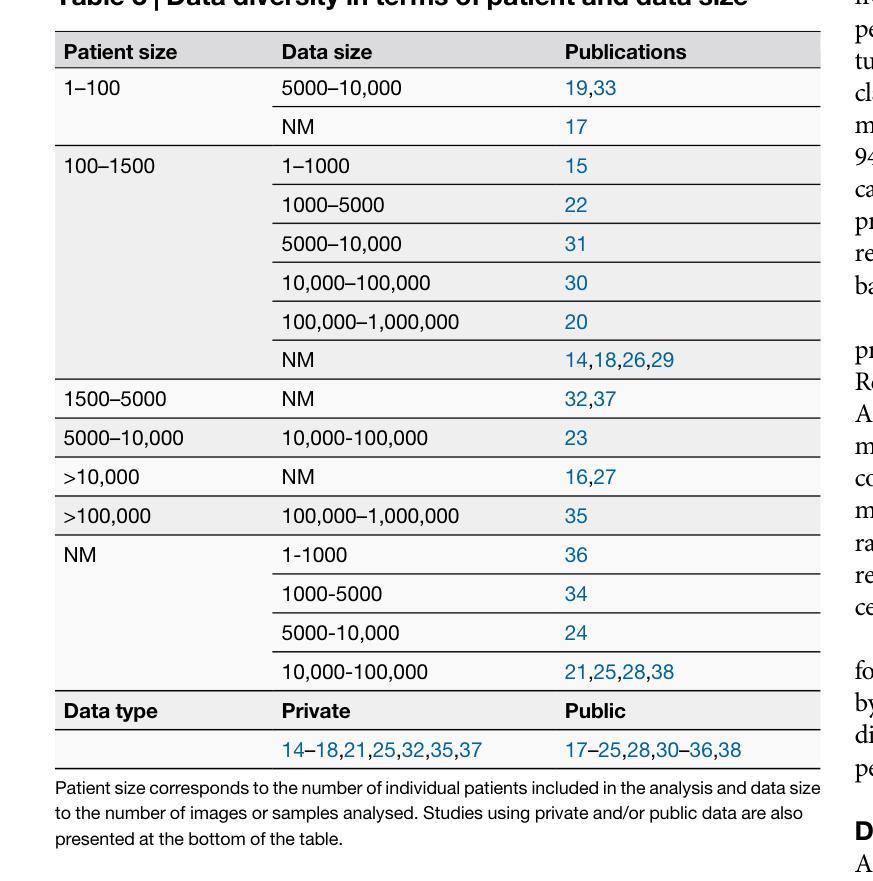
Advancing oncology with federated learning: transcending boundaries in breast, lung, and prostate cancer. A systematic review
Authors:Anshu Ankolekar, Sebastian Boie, Maryam Abdollahyan, Emanuela Gadaleta, Seyed Alireza Hasheminasab, Guang Yang, Charles Beauville, Nikolaos Dikaios, George Anthony Kastis, Michael Bussmann, Sara Khalid, Hagen Kruger, Philippe Lambin, Giorgos Papanastasiou
Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising solution to address the limitations of centralised machine learning (ML) in oncology, particularly in overcoming privacy concerns and harnessing the power of diverse, multi-center data. This systematic review synthesises current knowledge on the state-of-the-art FL in oncology, focusing on breast, lung, and prostate cancer. Distinct from previous surveys, our comprehensive review critically evaluates the real-world implementation and impact of FL on cancer care, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing ML generalisability, performance and data privacy in clinical settings and data. We evaluated state-of-the-art advances in FL, demonstrating its growing adoption amid tightening data privacy regulations. FL outperformed centralised ML in 15 out of the 25 studies reviewed, spanning diverse ML models and clinical applications, and facilitating integration of multi-modal information for precision medicine. Despite the current challenges identified in reproducibility, standardisation and methodology across studies, the demonstrable benefits of FL in harnessing real-world data and addressing clinical needs highlight its significant potential for advancing cancer research. We propose that future research should focus on addressing these limitations and investigating further advanced FL methods, to fully harness data diversity and realise the transformative power of cutting-edge FL in cancer care.
联邦学习(FL)作为一种有前景的解决方案,正在解决集中式机器学习(ML)在肿瘤学中的局限性,特别是在克服隐私担忧和利用多样化、多中心数据的能力方面。这篇系统性综述综合了当前关于肿瘤学领域前沿联邦学习的知识,重点关注乳腺癌、肺癌和前列腺癌。不同于之前的调查,我们的全面评述对联邦学习在癌症护理中的现实实施和影响进行了评估,证明了其在提高机器学习在临床环境中的通用性、性能和隐私保护方面的有效性。我们评估了联邦学习前沿的最新进展,证明了其在日益严格的数据隐私法规下日益普及。在所审查的25项研究中,联邦学习在15项研究中表现优于集中式机器学习,涵盖了多样化的机器学习模型和临床应用,促进了多模式信息的整合用于精准医疗。尽管在研究中存在可重复性、标准化和方法学方面的当前挑战,但联邦学习在利用真实世界数据和满足临床需求方面的明显优势凸显了其推动癌症研究的巨大潜力。我们建议在未来的研究中,应侧重于解决这些局限性,并进一步探讨先进的联邦学习方法,以充分利用数据的多样性并实现联邦学习在癌症护理中的变革性力量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 Figures, 3 Tables, 1 Supplementary Table
Summary
联邦学习(FL)在肿瘤学领域中央机器学习(ML)的局限性中展现出巨大潜力,特别是在克服隐私担忧和利用多样化、多中心数据方面。本文综述了当前关于FL在肿瘤学领域的最新知识,重点关注乳腺癌、肺癌和前列腺癌。与以往调查不同,我们的全面评价了FL在现实世界的实施及其对癌症护理的影响,证明了其在提高机器学习通用性、性能和临床环境中的数据隐私方面的有效性。尽管在重复性、标准化和方法学方面存在一些挑战,但FL在利用现实世界数据和满足临床需求方面的明显优势,凸显其推进癌症研究的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习(FL)在肿瘤学领域展现出解决中央机器学习(ML)局限性的潜力。
- FL有助于克服隐私担忧并有效利用多样化、多中心数据。
- 综述聚焦于乳腺癌、肺癌和前列腺癌的FL最新进展。
- FL在现实世界的实施及对癌症护理的影响得到了评价。
- FL在提高机器学习通用性、性能和临床环境数据隐私方面有效。
- 目前面临重复性、标准化和方法学方面的挑战。
- FL在利用现实数据、满足临床需求方面的优势,以及其对癌症研究的潜力得到了强调。
点此查看论文截图

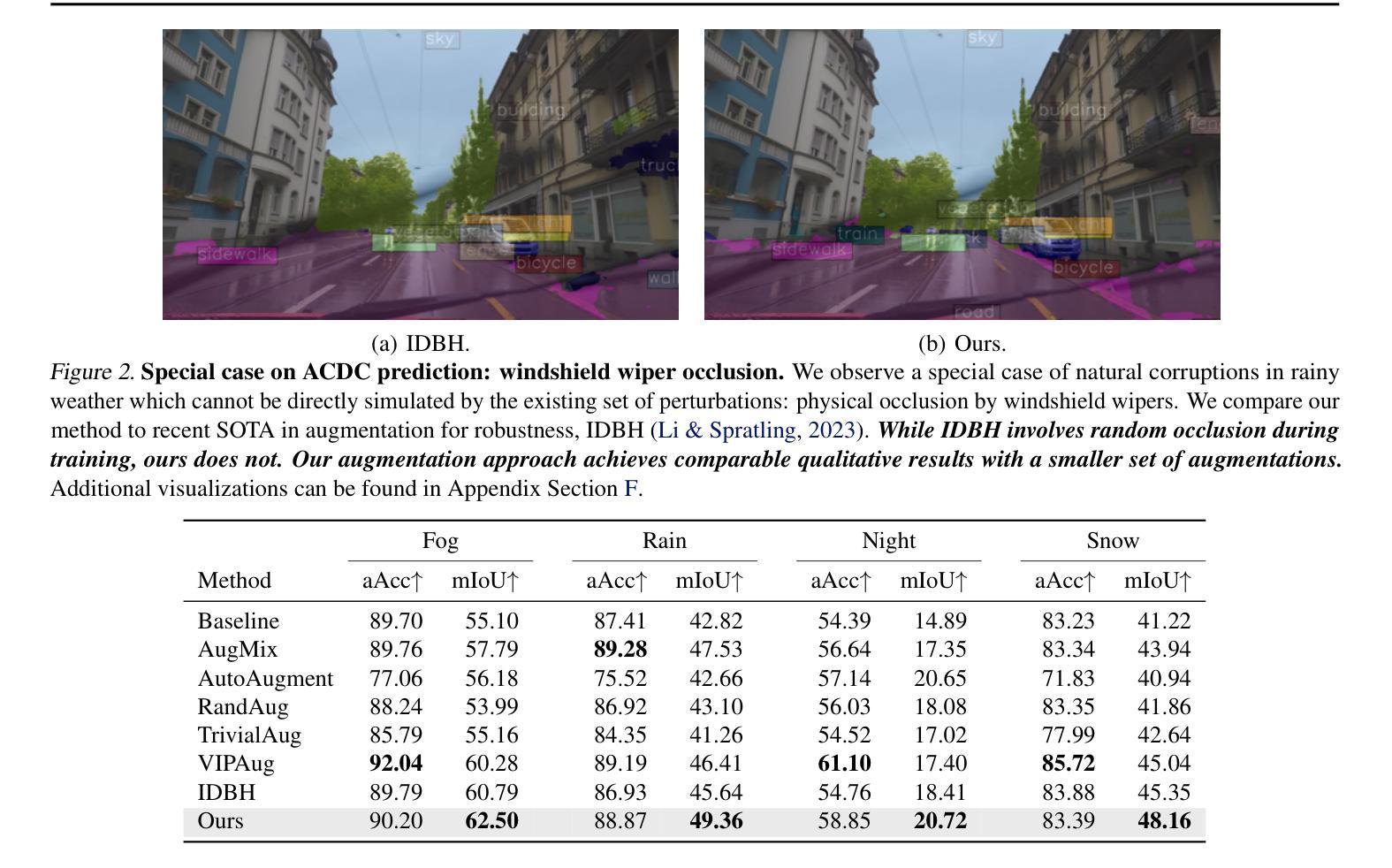
Adaptive Sensitivity Analysis for Robust Augmentation against Natural Corruptions in Image Segmentation
Authors:Laura Zheng, Wenjie Wei, Tony Wu, Jacob Clements, Shreelekha Revankar, Andre Harrison, Yu Shen, Ming C. Lin
Achieving robustness in image segmentation models is challenging due to the fine-grained nature of pixel-level classification. These models, which are crucial for many real-time perception applications, particularly struggle when faced with natural corruptions in the wild for autonomous systems. While sensitivity analysis can help us understand how input variables influence model outputs, its application to natural and uncontrollable corruptions in training data is computationally expensive. In this work, we present an adaptive, sensitivity-guided augmentation method to enhance robustness against natural corruptions. Our sensitivity analysis on average runs 10x faster and requires about 200x less storage than previous sensitivity analysis, enabling practical, on-the-fly estimation during training for a model-free augmentation policy. With minimal fine-tuning, our sensitivity-guided augmentation method achieves improved robustness on both real-world and synthetic datasets compared to state-of-the-art data augmentation techniques in image segmentation. Code implementation for this work can be found at: https://github.com/laurayuzheng/SensAug.
实现图像分割模型的稳健性是一项挑战,这主要是由于像素级分类的精细性质。这些模型对于许多实时感知应用至关重要,尤其是在面对自主系统野外自然腐蚀时特别困难。虽然敏感性分析可以帮助我们理解输入变量如何影响模型输出,但其在训练数据中自然和不可控制的腐蚀的应用计算成本高昂。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种自适应的、以敏感性为指导的增强方法,以提高对自然腐蚀的稳健性。我们的敏感性分析平均运行速度比以前快10倍,存储需求大约减少200倍,实现了在训练过程中进行实际、即时估计,用于无模型增强策略。通过最小的微调,与图像分割中最新数据增强技术相比,我们的以敏感性为指导的增强方法在现实世界和合成数据集上实现了更高的稳健性。该工作的代码实现可在https://github.com/laurayuzheng/SensAug找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种自适应的、基于敏感性的增强方法,以提高图像分割模型对自然腐败的鲁棒性。该方法通过对训练数据进行敏感性分析,快速识别影响模型输出的关键输入变量,并据此进行增强。与传统的敏感性分析方法相比,该方法运行速度快10倍,存储需求降低约200倍,可在训练过程中实时估计无模型增强策略。通过微调,该方法在真实和合成数据集上的鲁棒性均优于当前先进的图像分割数据增强技术。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割模型的鲁棒性面临挑战,尤其是面对自然腐败时。
- 敏感性分析有助于理解输入变量对模型输出的影响,但应用于自然和不可控的腐败训练数据计算成本高昂。
- 提出了一种自适应的、基于敏感性的增强方法,以提高模型对自然腐败的鲁棒性。
- 该方法通过快速识别关键输入变量并进行增强,实现了在训练过程中的实时估计无模型增强策略。
- 与传统方法相比,该方法的运行速度快10倍,存储需求降低约200倍。
- 通过微调,该方法在真实和合成数据集上的鲁棒性均优于当前先进的图像分割数据增强技术。
点此查看论文截图


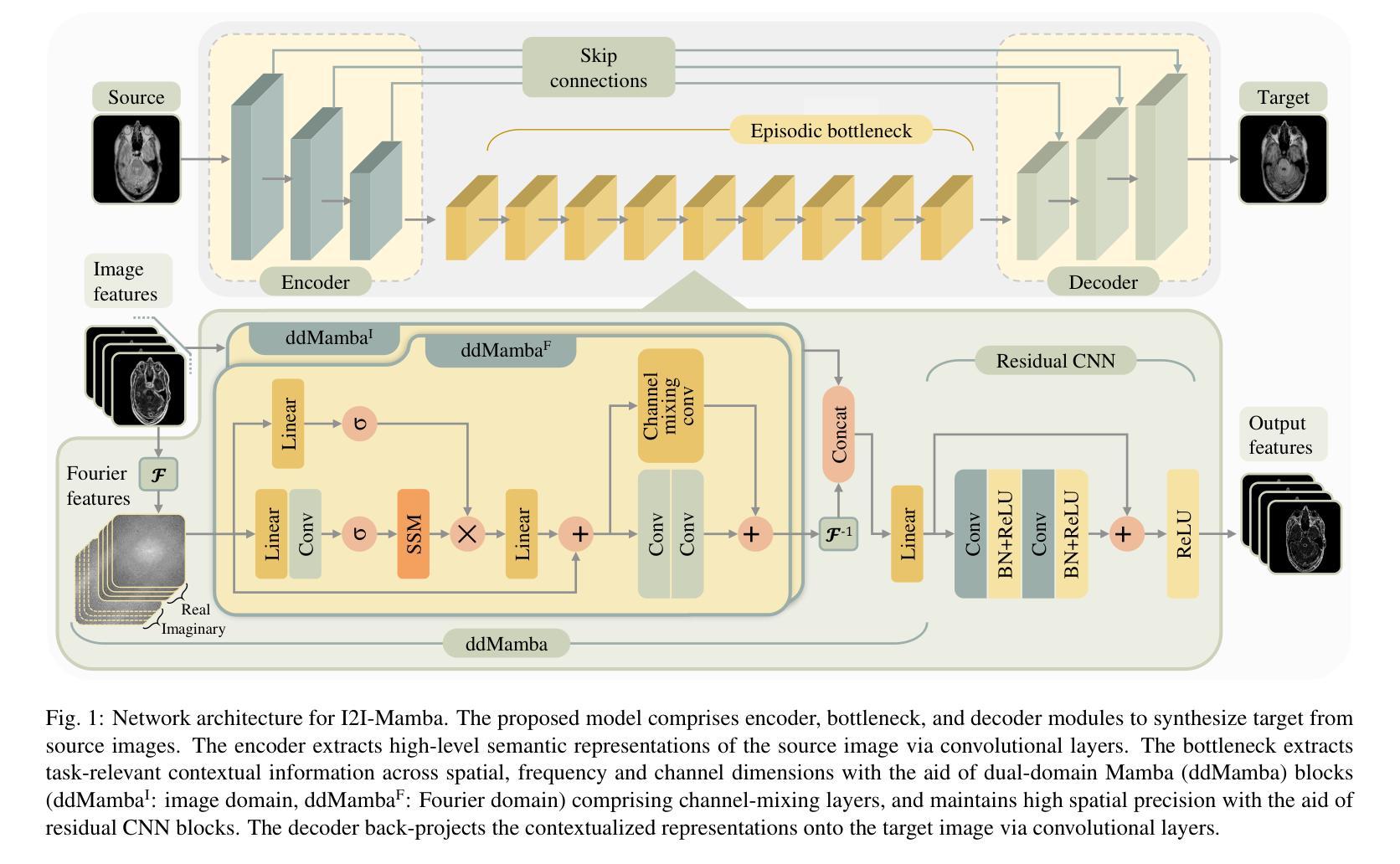
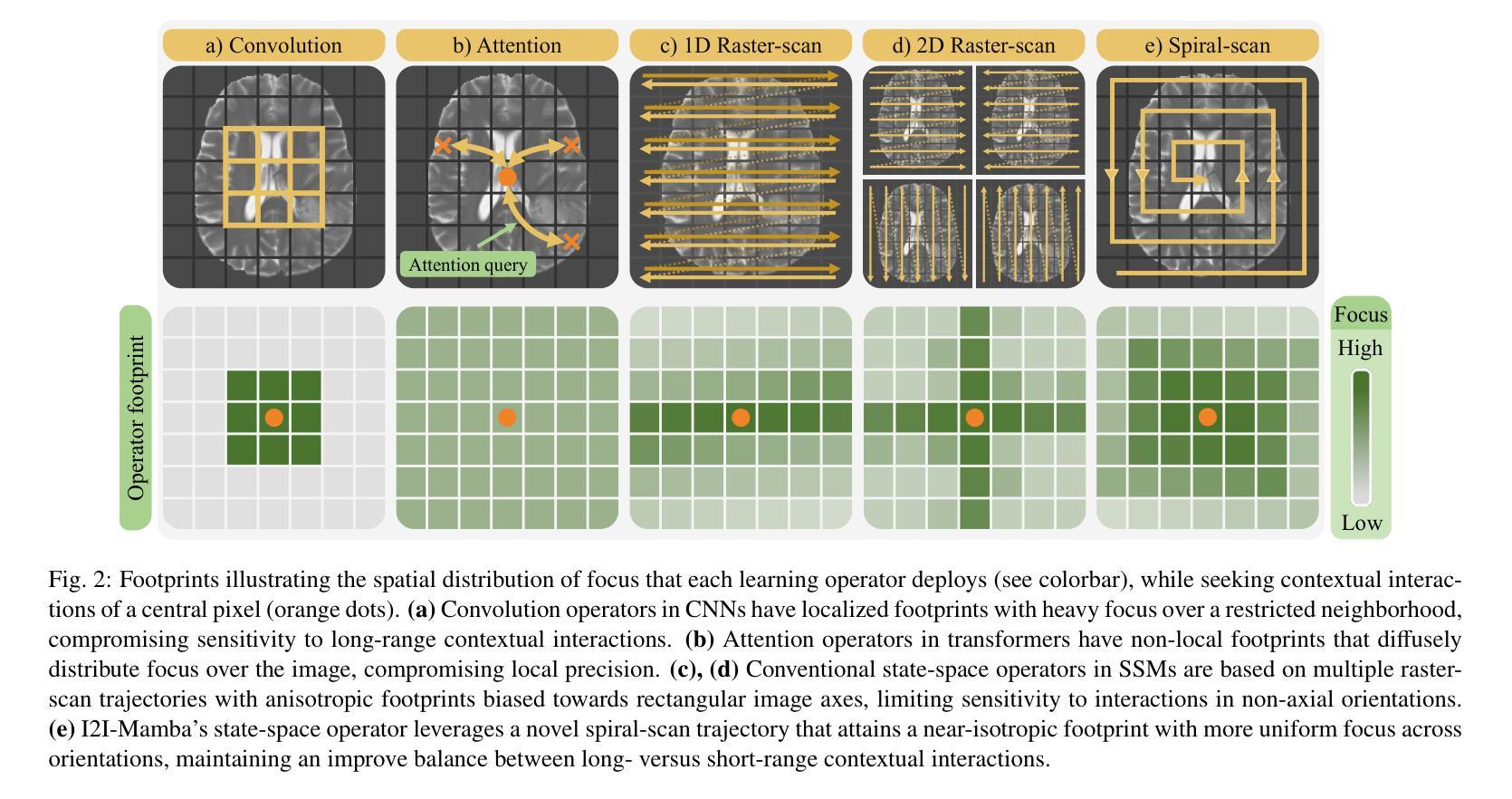
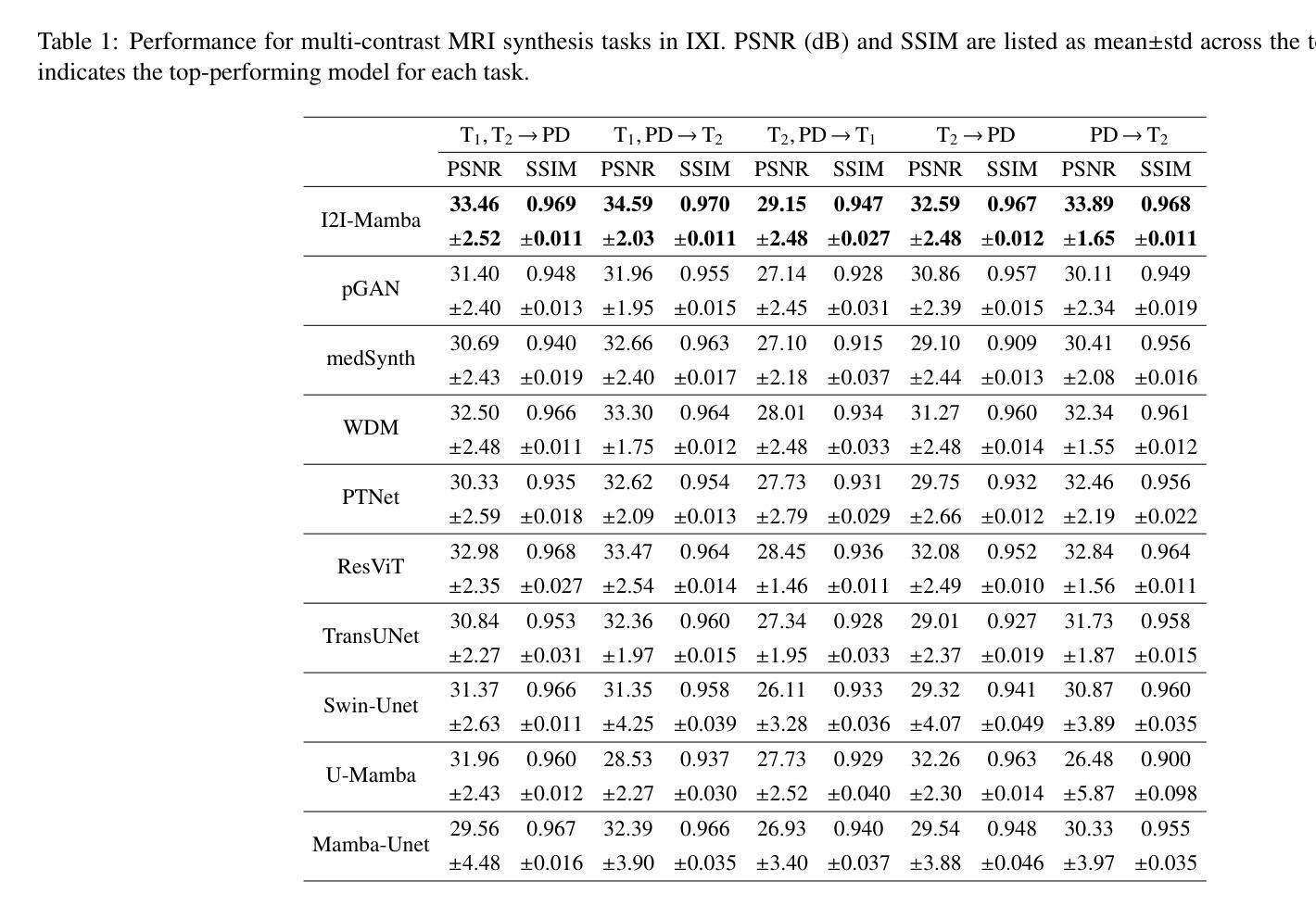
I2I-Mamba: Multi-modal medical image synthesis via selective state space modeling
Authors:Omer F. Atli, Bilal Kabas, Fuat Arslan, Arda C. Demirtas, Mahmut Yurt, Onat Dalmaz, Tolga Çukur
Multi-modal medical image synthesis involves nonlinear transformation of tissue signals between source and target modalities, where tissues exhibit contextual interactions across diverse spatial distances. As such, the utility of a network architecture in synthesis depends on its ability to express these contextual features. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) offer high local precision at the expense of poor sensitivity to long-range context. While transformers promise to alleviate this issue, they suffer from an unfavorable trade-off between sensitivity to long- versus short-range context due to the intrinsic complexity of attention filters. To effectively capture contextual features while avoiding the complexity-driven trade-offs, here we introduce a novel multi-modal synthesis method, I2I-Mamba, based on the state space modeling (SSM) framework. Focusing on semantic representations across a hybrid residual architecture, I2I-Mamba leverages novel dual-domain Mamba (ddMamba) blocks for complementary contextual modeling in image and Fourier domains, while maintaining spatial precision with convolutional layers. Diverting from conventional raster-scan trajectories, ddMamba leverages novel SSM operators based on a spiral-scan trajectory to learn context with enhanced radial coverage and angular isotropy, and a channel-mixing layer to aggregate context across the channel dimension. Comprehensive demonstrations on multi-contrast MRI and MRI-CT protocols indicate that I2I-Mamba offers superior performance against state-of-the-art CNNs, transformers and SSMs.
多模态医学图像合成涉及源模态和目标模态之间组织信号的非线性转换,其中组织在多种空间距离上表现出上下文交互。因此,合成中的网络架构的实用性取决于其表达这些上下文特征的能力。卷积神经网络(CNN)虽然能在本地提供较高的精确度,但在对远程上下文的敏感性方面表现较差。虽然变压器有望缓解这一问题,但由于注意力过滤器的固有复杂性,它们在处理远程与近距离上下文之间的敏感性时面临不利的权衡。为了有效地捕获上下文特征并避免复杂性驱动的权衡,我们在此引入了一种基于状态空间建模(SSM)框架的新型多模态合成方法I2I-Mamba。I2I-Mamba专注于混合残差架构中的语义表示,利用新型双域Mamba(ddMamba)块在图像和傅里叶域中进行互补的上下文建模,同时利用卷积层保持空间精度。ddMamba偏离了传统的扫描轨迹,采用基于螺旋扫描轨迹的新型SSM运算符来学习上下文,增强了径向覆盖和角度均匀性,并使用通道混合层来聚集通道维度上的上下文。在多对比度MRI和MRI-CT协议上的综合演示表明,I2I-Mamba在性能上优于最先进的CNN、变压器和SSM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于状态空间建模(SSM)框架的多模态医学图像合成新方法——I2I-Mamba。该方法通过混合图像和傅里叶域的ddMamba块进行上下文建模,同时保持空间精度。采用螺旋扫描轨迹的SSM运算符,提高径向覆盖率和角向同性,并通过通道混合层实现通道维度的上下文聚合。在多种MRI和MRI-CT协议上的综合演示表明,I2I-Mamba相较于其他先进的CNN、transformer和SSM具有优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- I2I-Mamba是一种基于状态空间建模(SSM)的多模态医学图像合成新方法。
- ddMamba块用于在图像和傅里叶域进行上下文建模,实现互补。
- I2I-Mamba通过混合使用卷积层和SSM运算符,避免了复杂度的权衡问题。
- 采用螺旋扫描轨迹的SSM运算符,提高了径向覆盖率和角向同性。
- 通道混合层用于实现通道维度的上下文聚合。
- I2I-Mamba在多种MRI和MRI-CT协议上的表现优于其他先进的CNN、transformer和SSM。
点此查看论文截图