⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-23 更新
VideoHallu: Evaluating and Mitigating Multi-modal Hallucinations on Synthetic Video Understanding
Authors:Zongxia Li, Xiyang Wu, Guangyao Shi, Yubin Qin, Hongyang Du, Tianyi Zhou, Dinesh Manocha, Jordan Lee Boyd-Graber
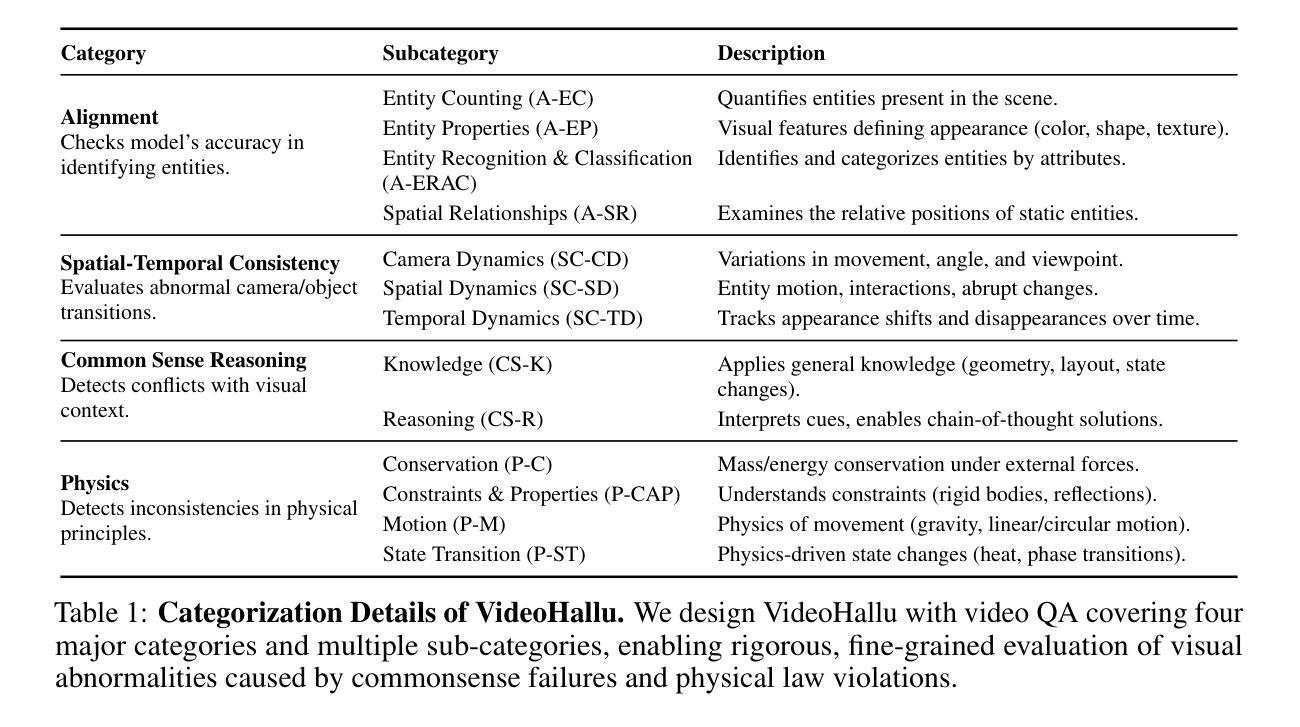
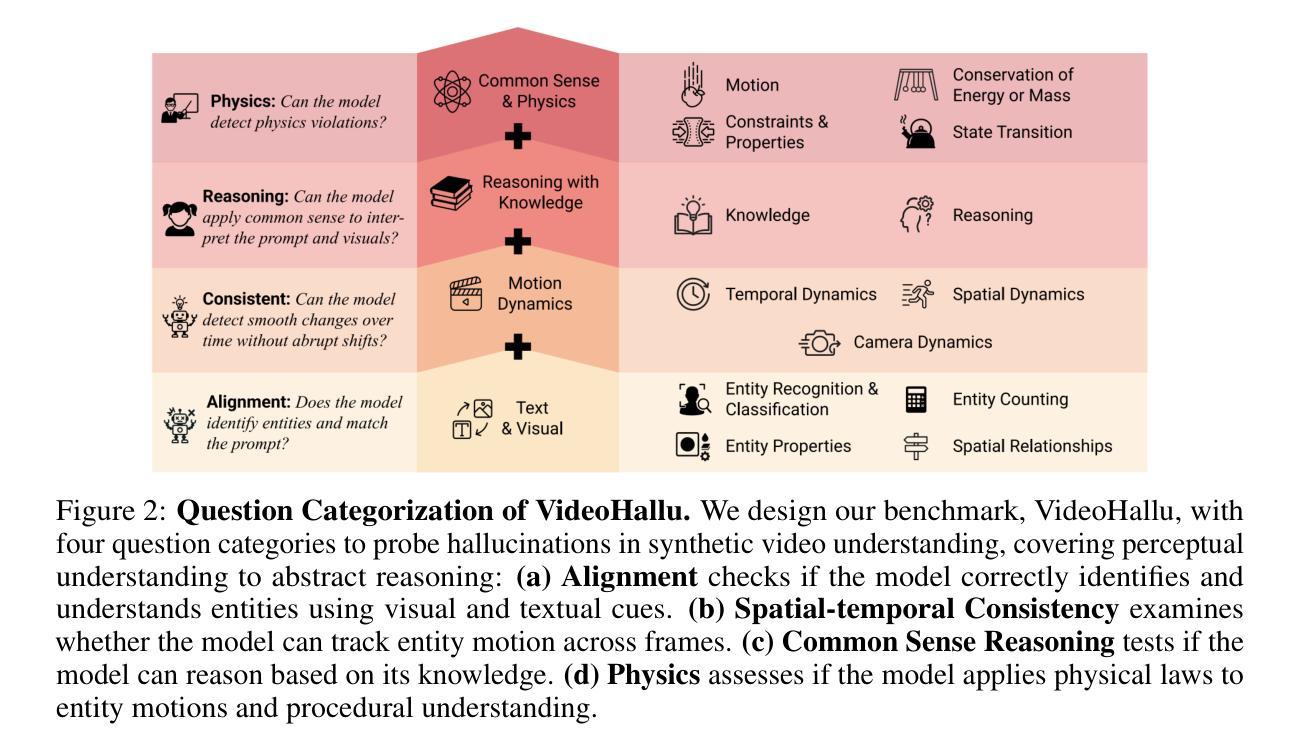
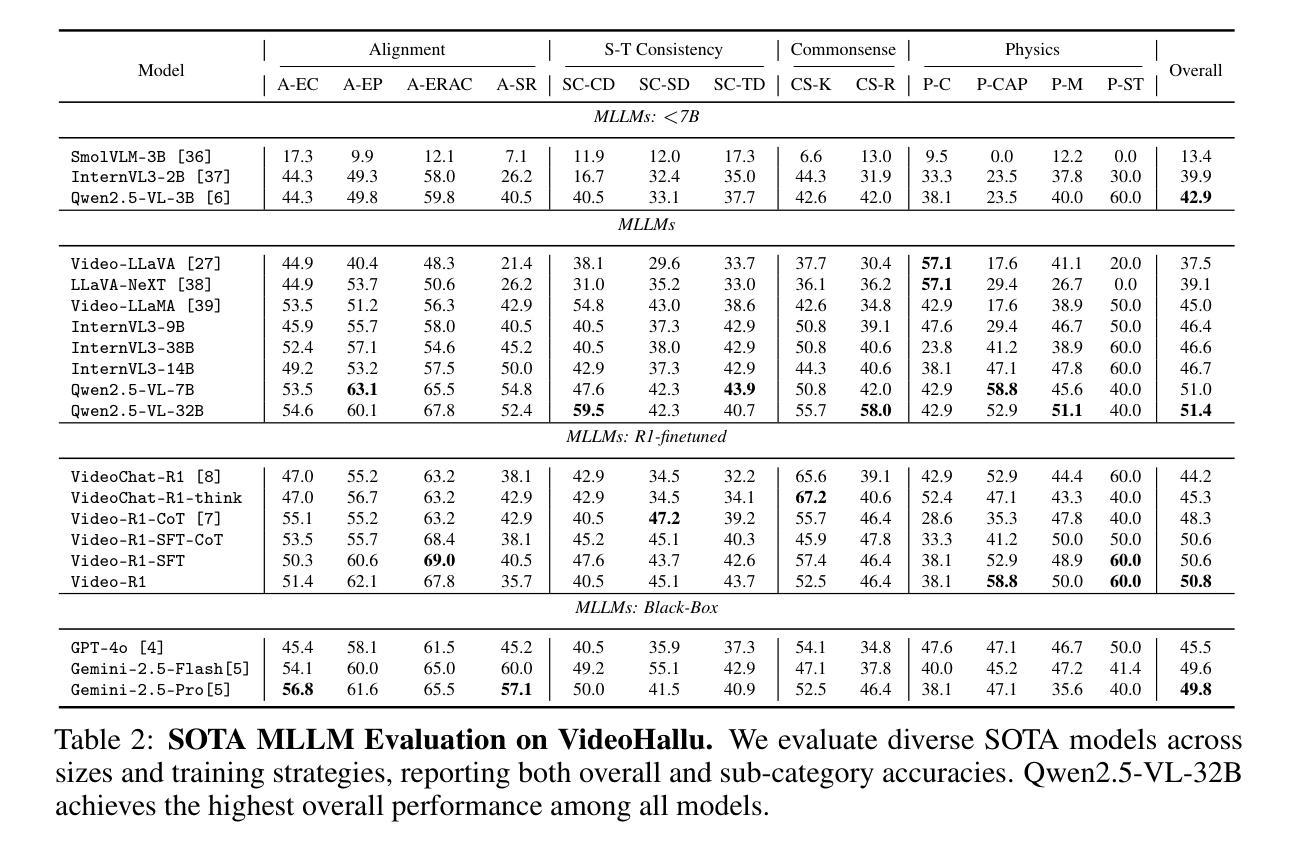
Synthetic video generation has gained significant attention for its realism and broad applications, but remains prone to violations of common sense and physical laws. This highlights the need for reliable abnormality detectors that understand such principles and are robust to hallucinations. To address this, we introduce VideoHallu, a benchmark of over 3,000 video QA pairs built from synthetic videos generated by models like Veo2, Sora, and Kling, paired with expert-crafted counterintuitive QA to evaluate the critical thinking abilities of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on abnormalities that are perceptually obvious to humans but often hallucinated due to language priors. VideoHallu evaluates MLLMs’ abnormality detection abilities with examples across alignment, consistency, commonsense, and physics. We benchmark SOTA MLLMs, including GPT-4o, Gemini-2.5-Pro, Qwen2.5-VL, Video-R1, and VideoChat-R1. We observe that these models perform well on many real-world benchmarks like MVBench and MovieChat, but still struggle with basic physics-based and commonsense reasoning in synthetic videos. We further show that post-training with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), using curriculum learning on datasets combining video QA with counterintuitive commonsense and physics reasoning over real and synthetic videos, improves MLLMs’ abnormality detection and critical thinking, demonstrating the value of targeted training for improving their understanding of commonsense and physical laws. Our code is available at https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu.git.
视频生成技术因其真实感和广泛应用而备受关注,但仍然存在违反常识和物理定律的问题。这凸显了需要可靠的异常检测器的必要性,这些检测器需要理解这些原则,并对幻觉具有鲁棒性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了VideoHallu基准测试,它包含超过3000个视频问答对,这些视频是由Veo2、Sora和Kling等模型生成的合成视频,与专家设计的反直觉问答相结合,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在异常检测方面的批判性思维能力,这些异常对人类来说感知明显,但由于语言先验而常常出现幻觉。VideoHallu通过一致性、连贯性、常识和物理等多个方面的例子来评估MLLMs的异常检测能力。我们对包括GPT-4o、Gemini-2.5-Pro、Qwen2.5-VL、Video-R1和VideoChat-R1在内的最新MLLMs进行了基准测试。我们发现这些模型在MVBench和MovieChat等现实世界基准测试中的表现很好,但在合成视频中的基本物理和常识推理方面仍然存在困难。我们进一步表明,使用组合视频问答与反直觉常识和物理推理的数据集进行课程学习的后训练,通过群体相对策略优化(GRPO),可以改善MLLMs的异常检测和批判性思维,这证明了有针对性的训练对于提高它们对常识和物理定律的理解的价值。我们的代码可在https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu.git上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
合成视频生成因其真实感和广泛应用而受到关注,但仍存在违反常识和物理定律的问题。因此,需要可靠的异常检测器来理解这些原理,并对幻觉具有鲁棒性。为解决这一问题,我们引入了VideoHallu基准测试,包含超过3000个视频QA对,由模型生成的合成视频与专家设计的反直觉QA组成,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在异常检测方面的能力。这些异常对人类来说是显而易见的,但由于语言先验知识往往会被幻觉所影响。VideoHallu评估了MLLMs在一致性、常识和物理方面的异常检测能力。我们对包括GPT-4o、Gemini-2.5-Pro等在内的顶尖MLLMs进行了基准测试,这些模型在MVBench和MovieChat等现实世界的基准测试中表现良好,但在合成视频的基于物理常识的推理方面仍面临挑战。此外,通过在数据集上结合视频QA与反直觉常识和物理推理的分组相对策略优化(GRPO)进行课程学习,可以改善MLLMs的异常检测和批判性思维。我们的代码可在https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu.git上找到。
关键见解
- 合成视频生成存在违反常识和物理定律的问题,需要可靠的异常检测器。
- VideoHallu基准测试旨在评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在异常检测方面的能力,特别是处理幻觉的能力。
- MLLMs在现实世界基准测试中表现良好,但在合成视频的基于物理常识的推理方面面临挑战。
- 通过课程学习结合视频QA与反直觉常识和物理推理的分组相对策略优化(GRPO),可以改善MLLMs的异常检测和批判性思维。
- VideoHallu为评估语言模型在处理合成视频时的性能提供了一个重要的工具,强调了常识和物理理解的重要性。
- 目前的语言模型在某些情况下可能难以识别明显的异常现象,这突显了需要进一步研究和改进的必要性。
点此查看论文截图



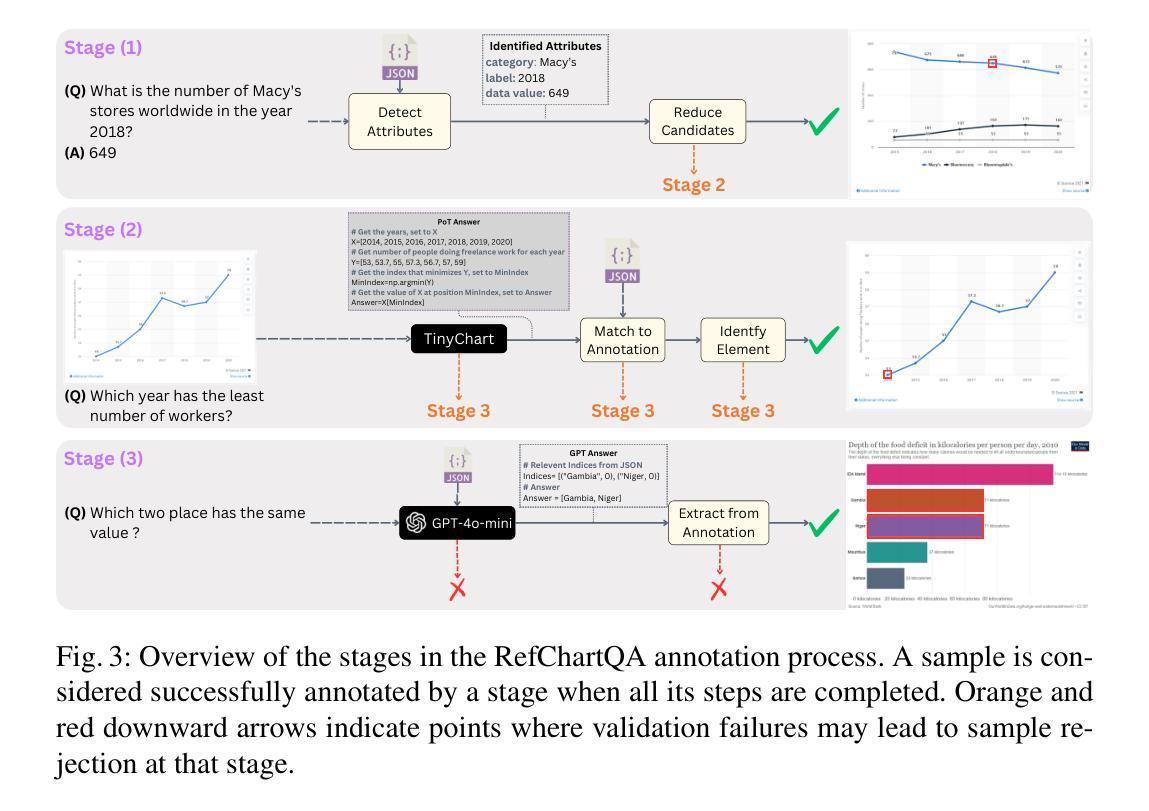
RefChartQA: Grounding Visual Answer on Chart Images through Instruction Tuning
Authors:Alexander Vogel, Omar Moured, Yufan Chen, Jiaming Zhang, Rainer Stiefelhagen
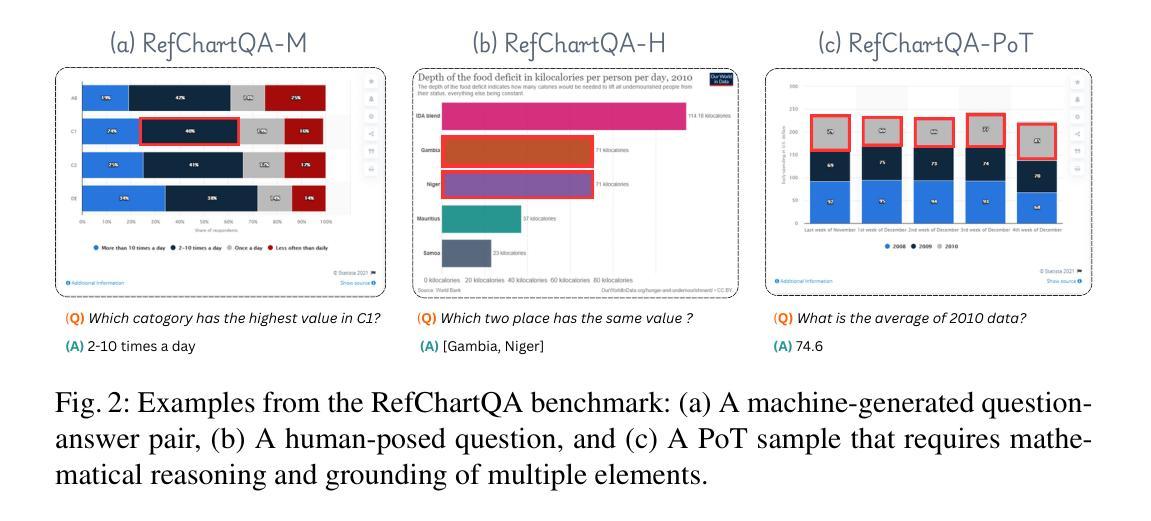
Recently, Vision Language Models (VLMs) have increasingly emphasized document visual grounding to achieve better human-computer interaction, accessibility, and detailed understanding. However, its application to visualizations such as charts remains under-explored due to the inherent complexity of interleaved visual-numerical relationships in chart images. Existing chart understanding methods primarily focus on answering questions without explicitly identifying the visual elements that support their predictions. To bridge this gap, we introduce RefChartQA, a novel benchmark that integrates Chart Question Answering (ChartQA) with visual grounding, enabling models to refer elements at multiple granularities within chart images. Furthermore, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation by instruction-tuning 5 state-of-the-art VLMs across different categories. Our experiments demonstrate that incorporating spatial awareness via grounding improves response accuracy by over 15%, reducing hallucinations, and improving model reliability. Additionally, we identify key factors influencing text-spatial alignment, such as architectural improvements in TinyChart, which leverages a token-merging module for enhanced feature fusion. Our dataset is open-sourced for community development and further advancements. All models and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA.
最近,视觉语言模型(VLMs)越来越强调文档的视觉定位,以实现更好的人机交互、可访问性和深入理解。然而,由于其对于图表图像中交织的视觉数字关系的内在复杂性,其在图表等可视化应用方面的应用仍然未被充分探索。现有的图表理解方法主要关注回答问题,而没有明确识别支持其预测的视觉元素。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了RefChartQA,这是一个将图表问答(ChartQA)与视觉定位相结合的新型基准测试,使模型能够在图表图像内的多个粒度级别上参考元素。此外,我们通过指令调整不同类别的5个最新VLMs进行了全面评估。我们的实验表明,通过定位融入空间意识可以提高回答准确率超过15%,减少幻觉,提高模型可靠性。另外,我们还确定了影响文本空间对齐的关键因素,如TinyChart的架构改进,它利用令牌合并模块增强特征融合。我们的数据集已开源供社区发展和进一步进步。所有模型和代码将在https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICDAR 2025. All models and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLMs)近年来越来越强调文档的视觉定位,以实现更好的人机交互、可访问性和深入理解。然而,其在图表等可视化方面的应用仍被忽视,这主要是由于图表图像中视觉与数字关系的交织复杂性。为解决这一差距,我们推出了RefChartQA基准测试,它将图表问答(ChartQA)与视觉定位相结合,使模型能够在图表图像内的多个粒度级别上引用元素。通过五个最先进的大型语言模型的分类指令调优进行了全面的评估。实验表明,通过融入定位技术的空间意识能提高响应准确率超过15%,减少了幻觉并提高了模型的可靠性。我们还公开了数据集并提供了相关模型和代码,以供社区发展和进一步进步。公开数据集网址:https://github.com/moured/RefChartQA。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs正逐渐重视文档视觉定位,以提升人机交互和深入理解。
- 图表等可视化在VLMs中的应用尚未得到充分探索。
- RefChartQA基准测试结合了ChartQA与视觉定位,使模型能在图表图像的多个粒度上引用元素。
- 通过融入定位技术的空间意识能提高模型的响应准确率、减少幻觉并增强可靠性。
- RefChartQA数据集已开源,供社区发展和进一步的研究与进步。
- 五个顶尖的大型语言模型通过分类指令调优进行了全面评估。
点此查看论文截图

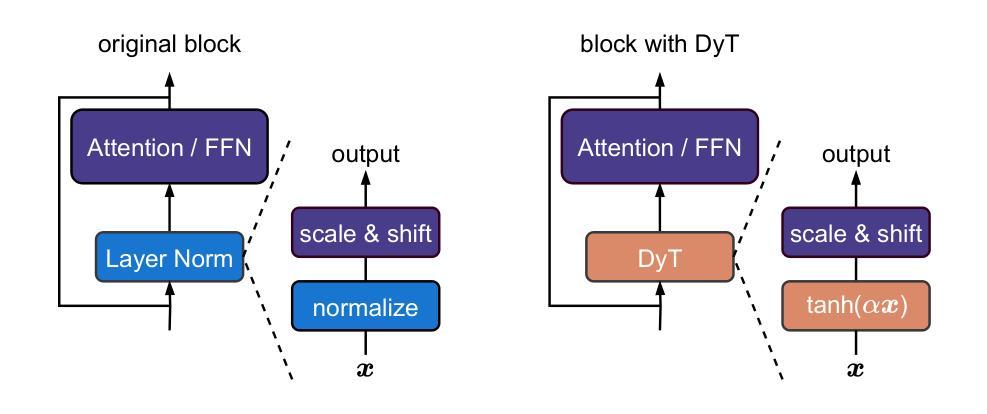
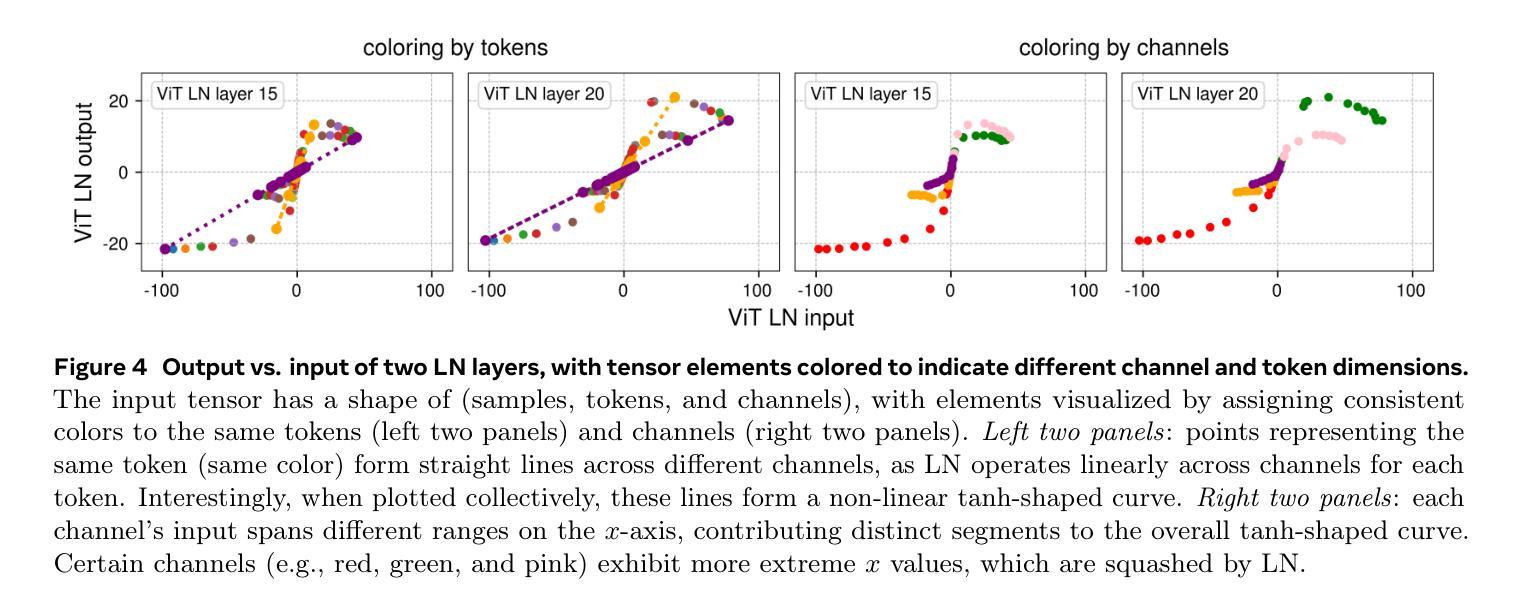
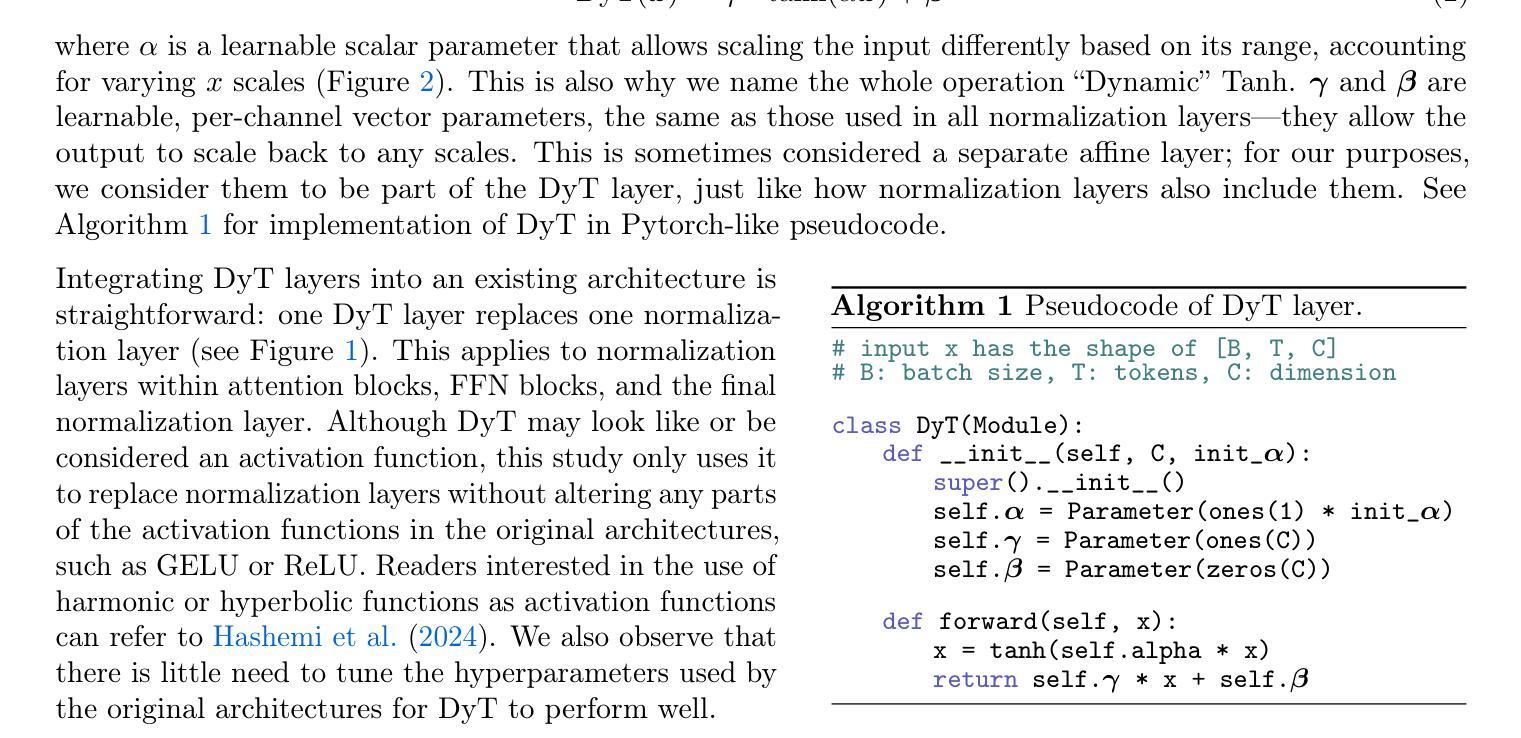
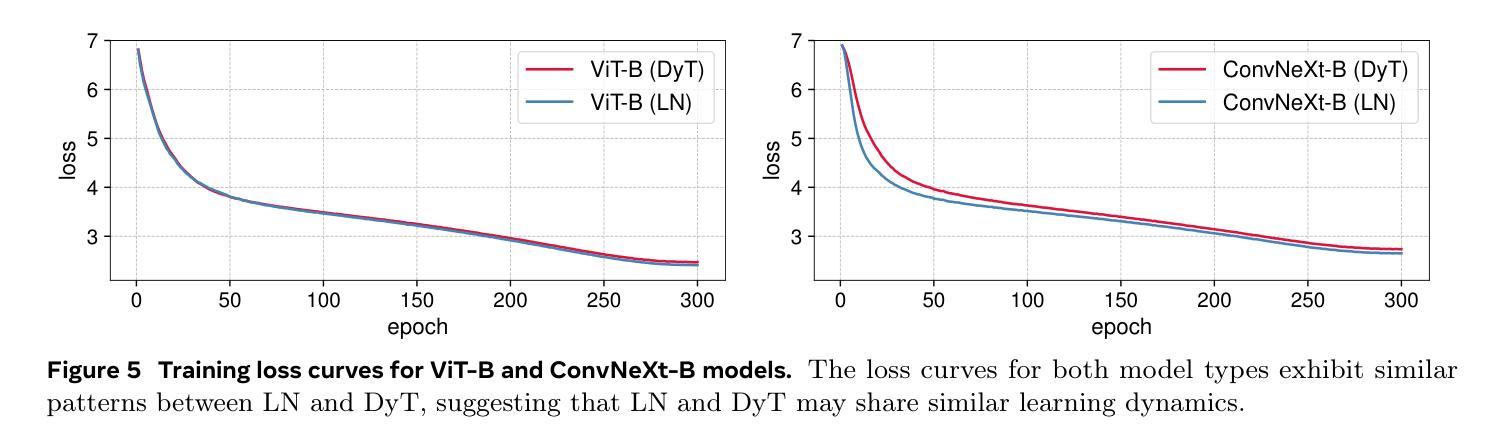
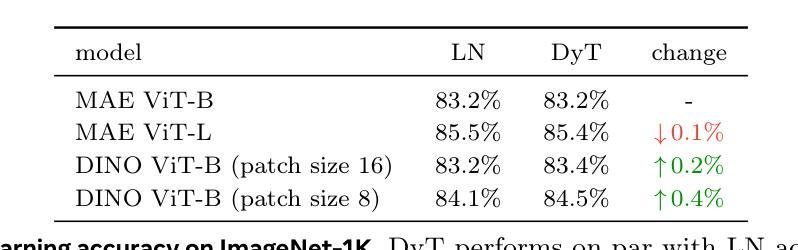
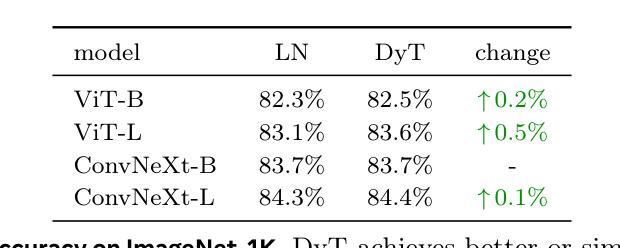
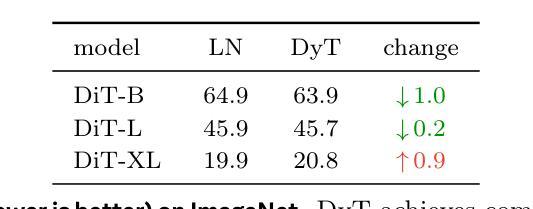
Transformers without Normalization
Authors:Jiachen Zhu, Xinlei Chen, Kaiming He, Yann LeCun, Zhuang Liu
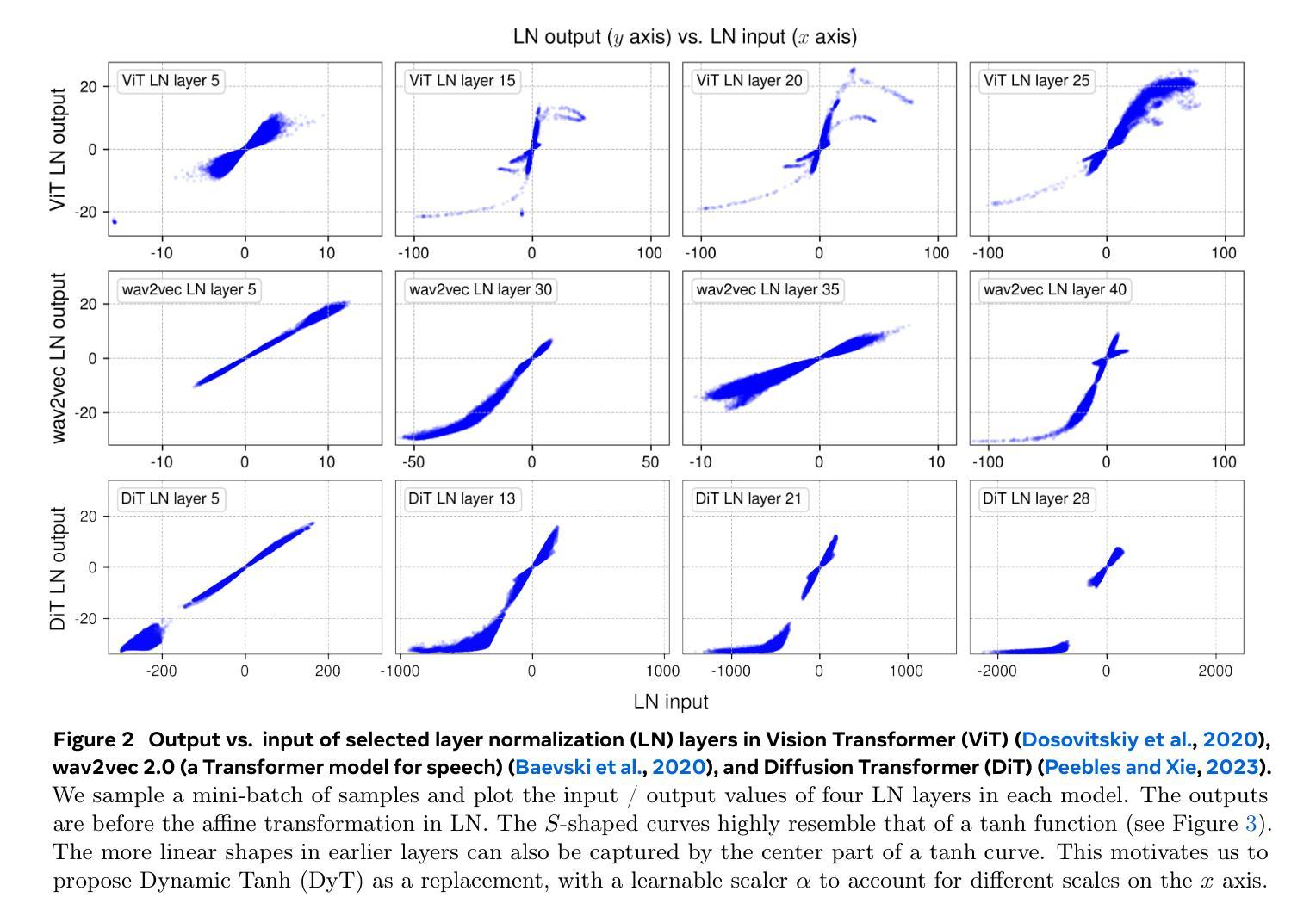
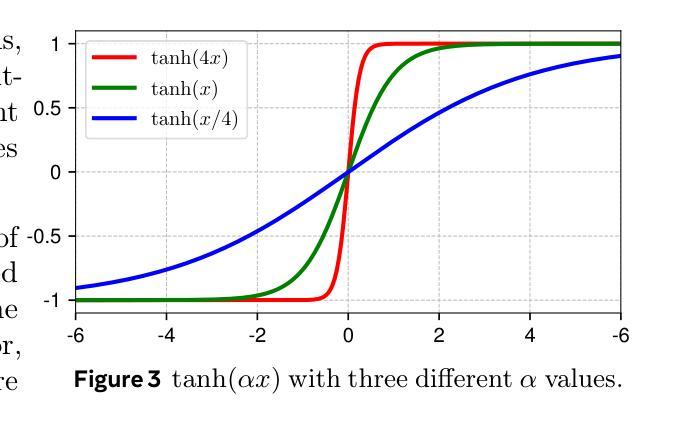
Normalization layers are ubiquitous in modern neural networks and have long been considered essential. This work demonstrates that Transformers without normalization can achieve the same or better performance using a remarkably simple technique. We introduce Dynamic Tanh (DyT), an element-wise operation $DyT($x$) = \tanh(\alpha $x$)$, as a drop-in replacement for normalization layers in Transformers. DyT is inspired by the observation that layer normalization in Transformers often produces tanh-like, $S$-shaped input-output mappings. By incorporating DyT, Transformers without normalization can match or exceed the performance of their normalized counterparts, mostly without hyperparameter tuning. We validate the effectiveness of Transformers with DyT across diverse settings, ranging from recognition to generation, supervised to self-supervised learning, and computer vision to language models. These findings challenge the conventional understanding that normalization layers are indispensable in modern neural networks, and offer new insights into their role in deep networks.
标准化层在现代神经网络中无处不在,并且长期以来一直被认为是必不可少的。这项工作证明了不使用标准化的Transformer可以使用一种非常简单的技术达到相同或更好的性能。我们引入了Dynamic Tanh(DyT),这是一种逐元素操作$DyT(x) = \tanh(\alpha x)$,作为Transformer中标准化层的即插即用替代品。DyT的灵感来自于观察Transformer中的层标准化通常会产生类似于双曲正切的S形输入输出映射。通过融入DyT,不使用标准化的Transformer可以在大多数情况下匹配或超过其标准化对应模型的性能,而无需调整超参数。我们在多种设置中对带有DyT的Transformer的有效性进行了验证,包括识别与生成、监督学习与自我监督学习、计算机视觉和语言模型等。这些发现挑战了常规观念,即标准化层是现代神经网络不可或缺的组成部分,并为深度学习网络中的标准化层作用提供了新的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025; Project page: https://jiachenzhu.github.io/DyT/
Summary
现代神经网络中普遍存在的归一化层被认为是必要的,但这项工作展示了不使用归一化的Transformer可以通过一种极其简单的方法实现相同或更好的性能。引入了一种动态双曲正切(DyT)作为Transformer中归一化层的替代方案。DyT受到Transformer中层归一化通常产生双曲正切型输入输出映射的启发。通过采用DyT,不使用归一化的Transformer可以匹配或超过使用归一化的同类模型的性能,并且大部分情况下无需调整超参数。我们在多种设置下验证了使用DyT的Transformer的有效性,包括识别、生成、监督到自我监督学习,以及计算机视觉和语言模型。这些发现挑战了常规认知中归一化层在现代神经网络中的不可或缺性,并为深入了解其在深度网络中的作用提供了新的见解。
Key Takeaways
- Transformers不使用归一化层也能实现良好性能。
- 引入了一种名为动态双曲正切(DyT)的元素级操作作为Transformer中归一化层的替代方案。
- DyT受启发于Transformer中层归一化产生的双曲正切型输入输出映射。
- 使用DyT的Transformer在多种任务上表现出与或超过使用归一化的模型的性能。
- 在大多数情况下,使用DyT的Transformer无需调整超参数。
- 研究结果挑战了常规认知中归一化层在现代神经网络中的不可或缺性。
点此查看论文截图

EgoBlind: Towards Egocentric Visual Assistance for the Blind
Authors:Junbin Xiao, Nanxin Huang, Hao Qiu, Zhulin Tao, Xun Yang, Richang Hong, Meng Wang, Angela Yao
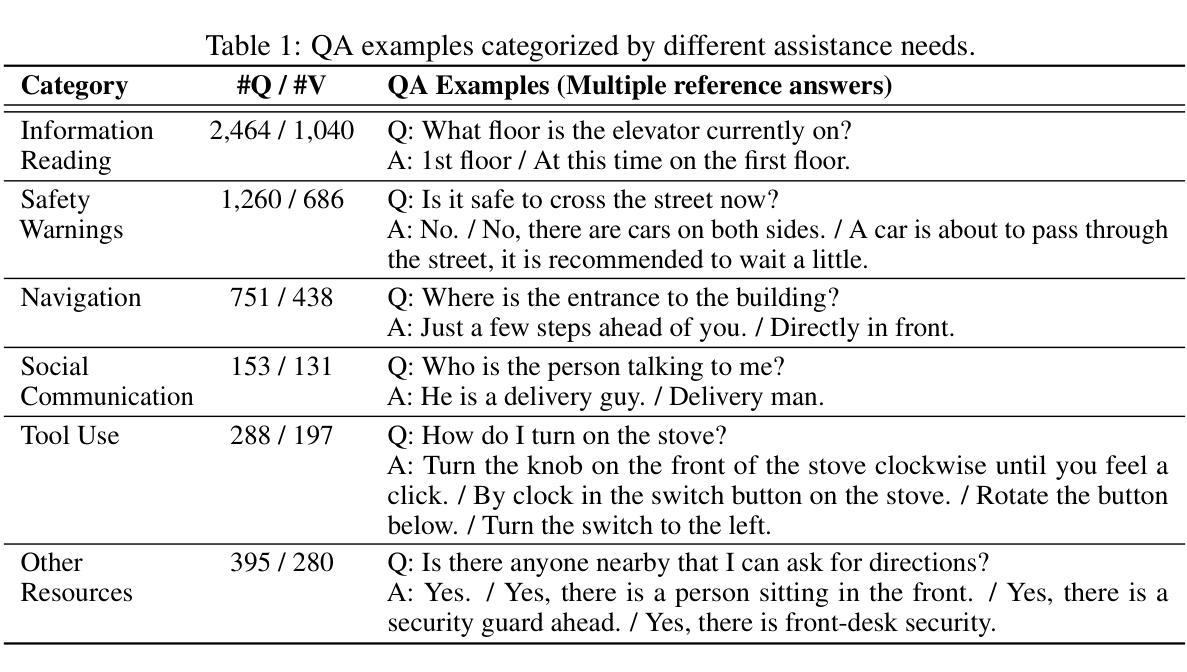
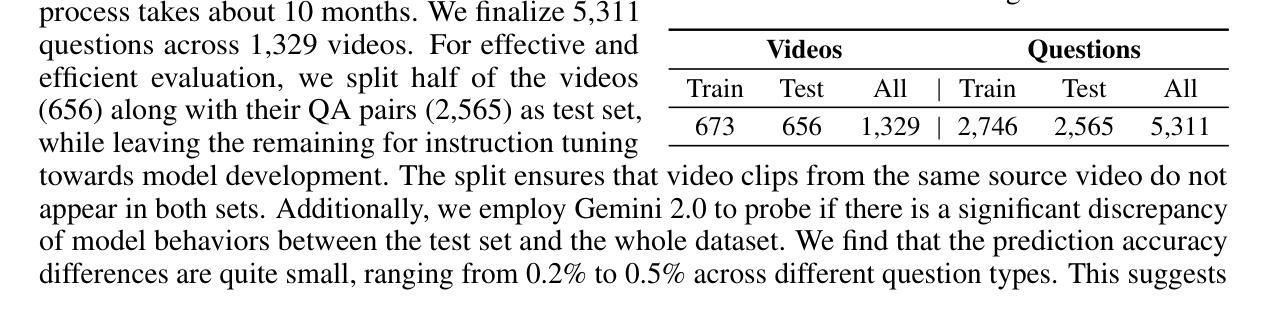
We present EgoBlind, the first egocentric VideoQA dataset collected from blind individuals to evaluate the assistive capabilities of contemporary multimodal large language models (MLLMs). EgoBlind comprises 1,392 videos that record the daily lives of real blind users from a first-person perspective. It also features 5,311 questions directly posed or generated and verified by blind individuals to reflect their in-situation needs for visual assistance under various scenarios. We provide each question with an average of 3 reference answers to alleviate subjective evaluation. Using EgoBlind, we comprehensively evaluate 16 advanced MLLMs and find that all models struggle, with the best performers achieving accuracy near 60%, far behind human performance of 87.4%. To guide future advancements, we identify and summarize major limitations of existing MLLMs in egocentric visual assistance for the blind and explore heuristic solutions for improvement. With these efforts, we hope EgoBlind can serve as a valuable foundation for developing more effective AI assistants to enhance the independence of the blind individuals’ lives. Data and evaluation code are available at https://github.com/doc-doc/EgoBlind.
我们推出了EgoBlind,这是从盲人群体收集的第一个以自我为中心的视频问答(VideoQA)数据集,旨在评估当前多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的辅助能力。EgoBlind包含1392个视频,这些视频以第一人称视角记录了真实盲人的日常生活。此外,该数据集还包含了由盲人直接提出或由系统生成并经过盲人验证的5311个问题,反映了各种场景下盲人在视觉辅助方面的实际需求。针对每个问题,我们提供了平均三个参考答案,以缓解主观评价的问题。使用EgoBlind数据集,我们对16个先进的大型语言模型进行了全面评估,发现所有模型都存在困难,表现最好的模型准确率接近60%,而人类的准确率高达87.4%。为了指导未来的进步,我们总结了现有大型语言模型在面向盲人的自我中心视觉辅助方面的主要局限性,并探索了改进启发式解决方案。我们希望EgoBlind能成为开发更有效的AI助手的有价值的基础,以提高盲人生活的独立性。数据和评估代码可在https://github.com/doc-doc/EgoBlind获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We extend and resplit the dataset
Summary:
我们推出了EgoBlind数据集,这是首个面向盲人的第一人称视频问答数据集,用于评估当前多模态大型语言模型的辅助能力。EgoBlind包含来自真实盲人日常生活的1,392个第一人称视角的视频,以及由盲人直接提出或生成并验证的5,311个问题,反映了不同场景下他们对视觉辅助的需求。我们为每个问题提供了平均三个参考答案来缓解主观评价。使用EgoBlind数据集,我们对十六个先进的大型语言模型进行了全面评估,发现所有模型都存在困难,最佳模型准确率接近百分之六十,远低于人类的百分之八十七点四。我们希望EgoBlind可以为开发更有效的AI助手提供有价值的基础,以提高盲人的独立性。数据和评估代码可在公开链接找到。
Key Takeaways:
- EgoBlind是首个针对盲人的第一人称视频问答数据集。
- 数据集包含来自真实盲人日常生活的视频和提出的问题,用于评估多模态大型语言模型的辅助能力。
- 多模态大型语言模型在处理这些问题时面临困难,最佳模型的准确率远低于人类水平。
- 数据集旨在为开发更有效的AI助手提供基础,以增强盲人的独立性。
- 数据集包含了丰富的视觉辅助场景中的问题,为模型评估提供了多样化的场景和数据支持。
- 当前多模态大型语言模型在视觉辅助方面存在局限性,需要进一步的改进和创新。
点此查看论文截图



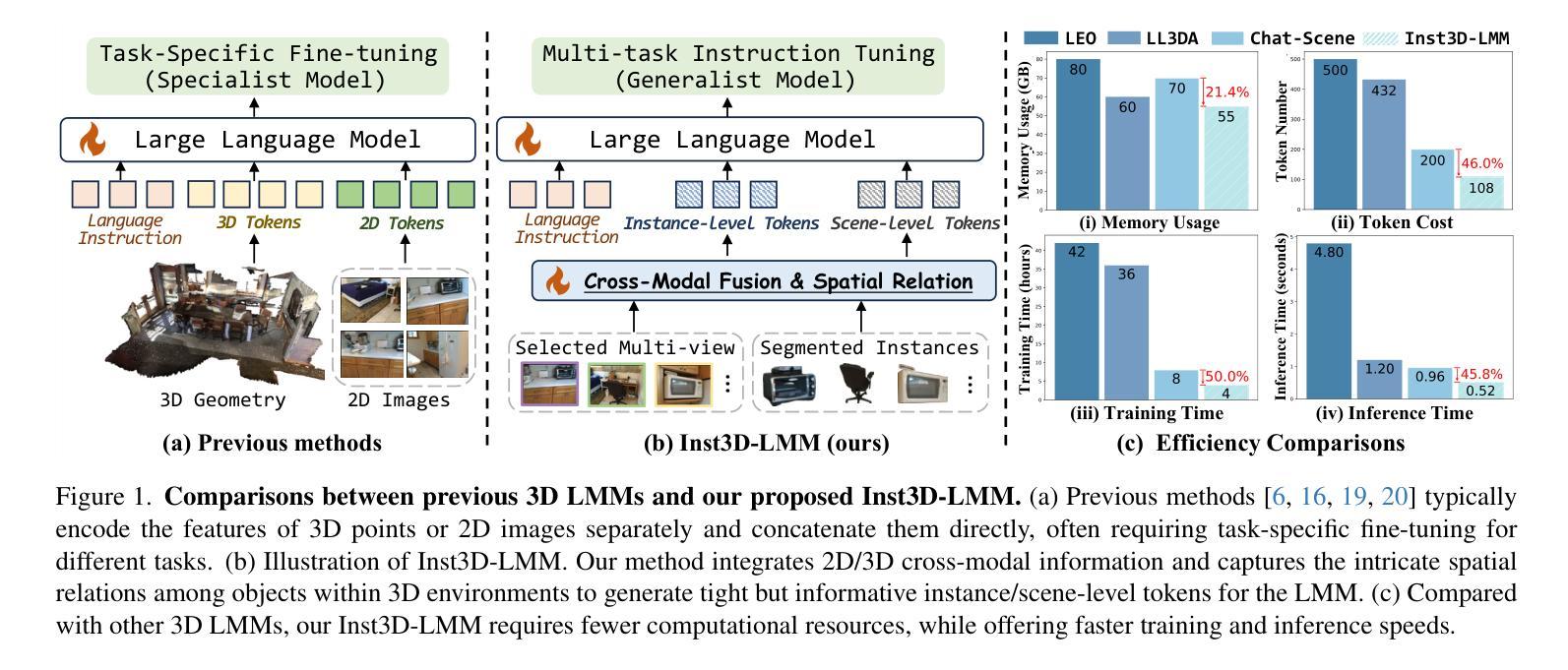
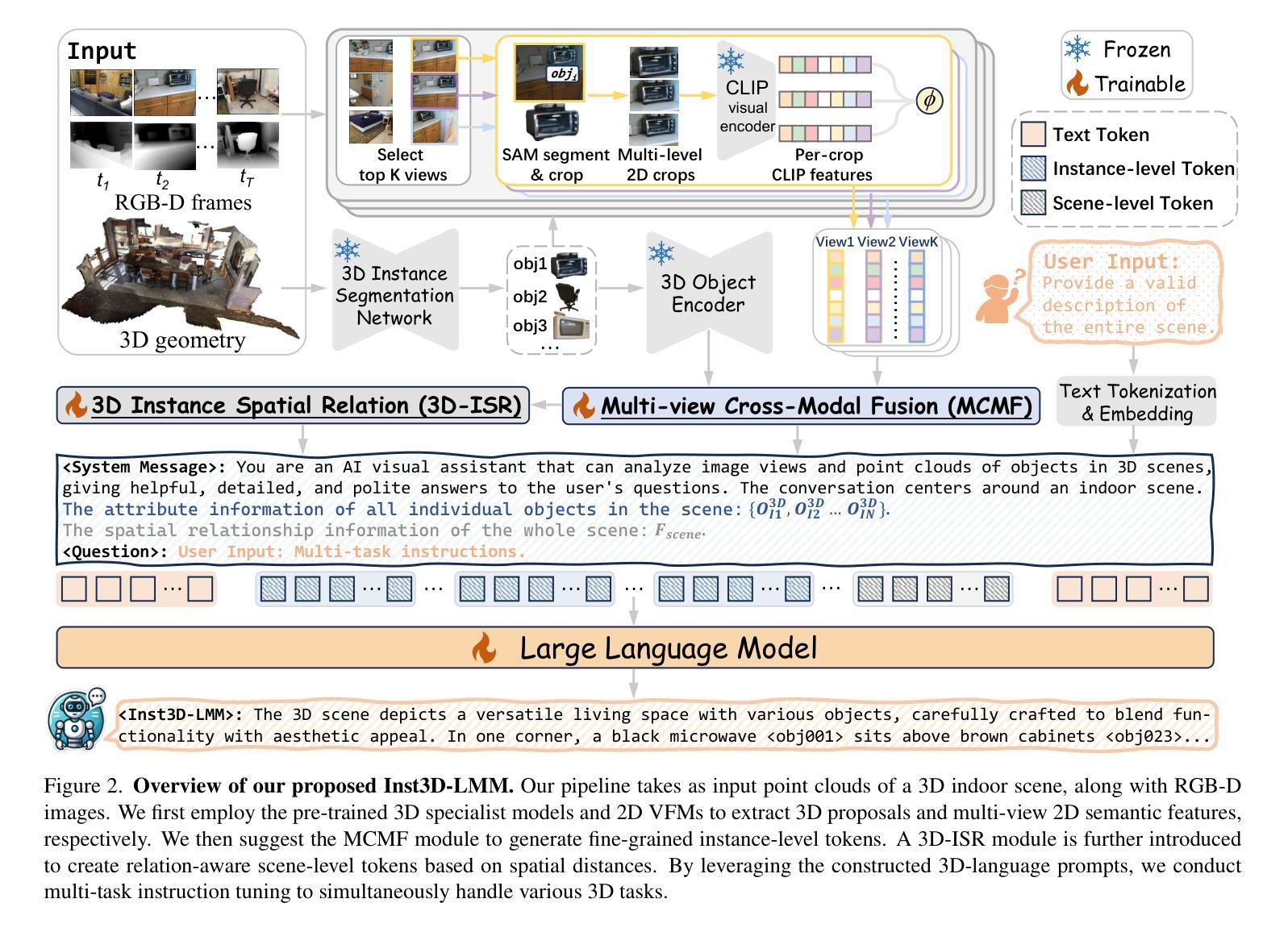
Inst3D-LMM: Instance-Aware 3D Scene Understanding with Multi-modal Instruction Tuning
Authors:Hanxun Yu, Wentong Li, Song Wang, Junbo Chen, Jianke Zhu
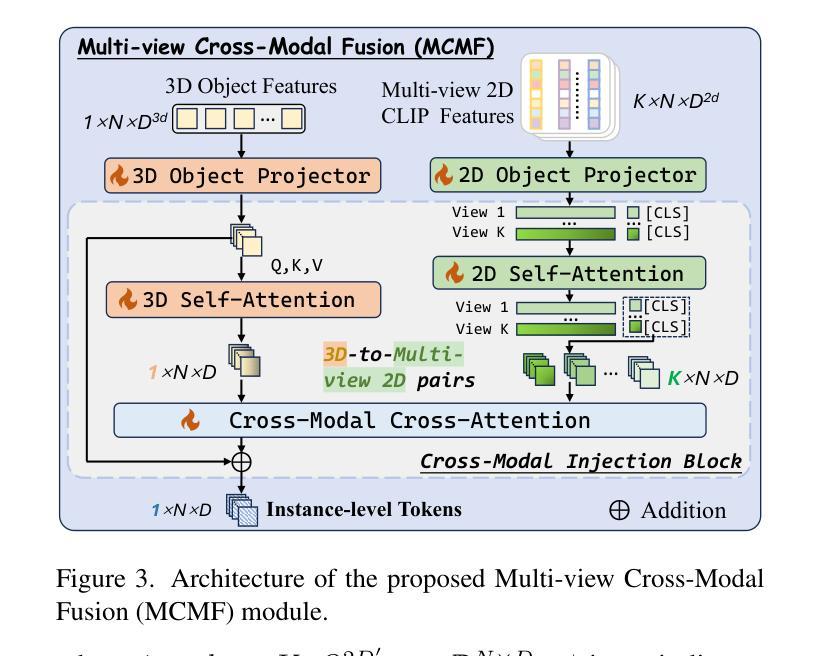
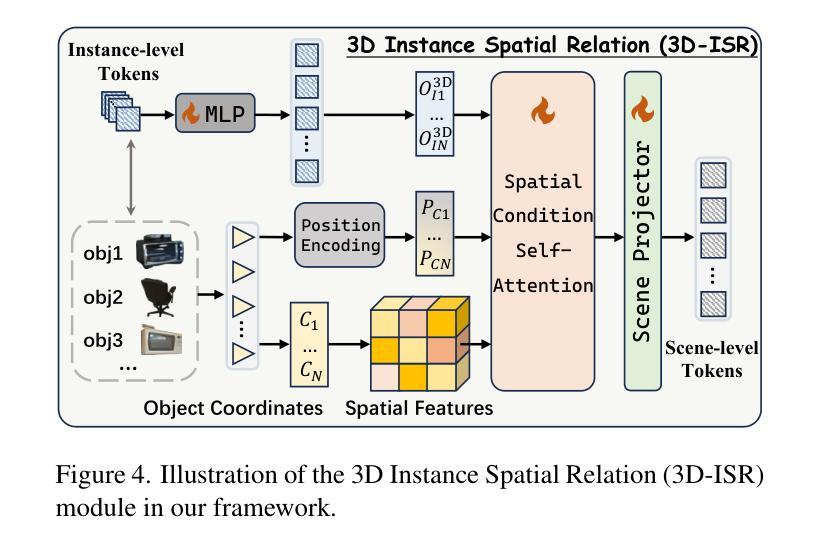
Despite encouraging progress in 3D scene understanding, it remains challenging to develop an effective Large Multi-modal Model (LMM) that is capable of understanding and reasoning in complex 3D environments. Most previous methods typically encode 3D point and 2D image features separately, neglecting interactions between 2D semantics and 3D object properties, as well as the spatial relationships within the 3D environment. This limitation not only hinders comprehensive representations of 3D scene, but also compromises training and inference efficiency. To address these challenges, we propose a unified Instance-aware 3D Large Multi-modal Model (Inst3D-LMM) to deal with multiple 3D scene understanding tasks simultaneously. To obtain the fine-grained instance-level visual tokens, we first introduce a novel Multi-view Cross-Modal Fusion (MCMF) module to inject the multi-view 2D semantics into their corresponding 3D geometric features. For scene-level relation-aware tokens, we further present a 3D Instance Spatial Relation (3D-ISR) module to capture the intricate pairwise spatial relationships among objects. Additionally, we perform end-to-end multi-task instruction tuning simultaneously without the subsequent task-specific fine-tuning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods across 3D scene understanding, reasoning and grounding tasks. Source code is available at https://github.com/hanxunyu/Inst3D-LMM
尽管在3D场景理解方面取得了令人鼓舞的进展,但开发能够在复杂3D环境中进行理解和推理的有效大型多模态模型(LMM)仍然是一个挑战。大多数之前的方法通常分别编码3D点和2D图像特征,忽略了2D语义和3D对象属性之间的交互,以及3D环境内的空间关系。这种局限性不仅阻碍了3D场景的综合表示,还影响了训练和推理的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025, Code Link: https://github.com/hanxunyu/Inst3D-LMM
摘要
尽管在三维场景理解方面取得了令人鼓舞的进展,但开发能够在复杂三维环境中进行理解和推理的有效大型多模式模型(LMM)仍然具有挑战性。针对这一挑战,我们提出了一种统一的实例感知三维大型多模式模型(Inst3D-LMM),以同时处理多个三维场景理解任务。通过引入多视图跨模态融合(MCMF)模块,我们将多视图二维语义注入到其对应的三维几何特征中,以获得细粒度的实例级视觉标记。为了进一步捕获物体之间复杂的一对一空间关系,我们提出了三维实例空间关系(3D-ISR)模块。此外,我们进行了端到端多任务指令调整,同时进行了多项实验,证明了我们的方法在三维场景理解、推理和定位任务上的表现优于现有技术。
关键见解
- 开发一种有效的大型多模式模型(LMM)以理解复杂的三维环境仍然具有挑战性。
- 大多数以前的方法分别编码三维点和二维图像特征,忽略了二维语义和三维对象属性之间的交互以及三维环境内的空间关系。
- 为了解决这些挑战,提出了一种统一的实例感知三维大型多模式模型(Inst3D-LMM)。
- 通过多视图跨模态融合(MCMF)模块注入多视图二维语义到三维几何特征中。
- 提出了三维实例空间关系(3D-ISR)模块来捕获物体之间复杂的一对一空间关系。
- 同时进行端到端多任务指令调整,无需后续的任务特定微调。
点此查看论文截图

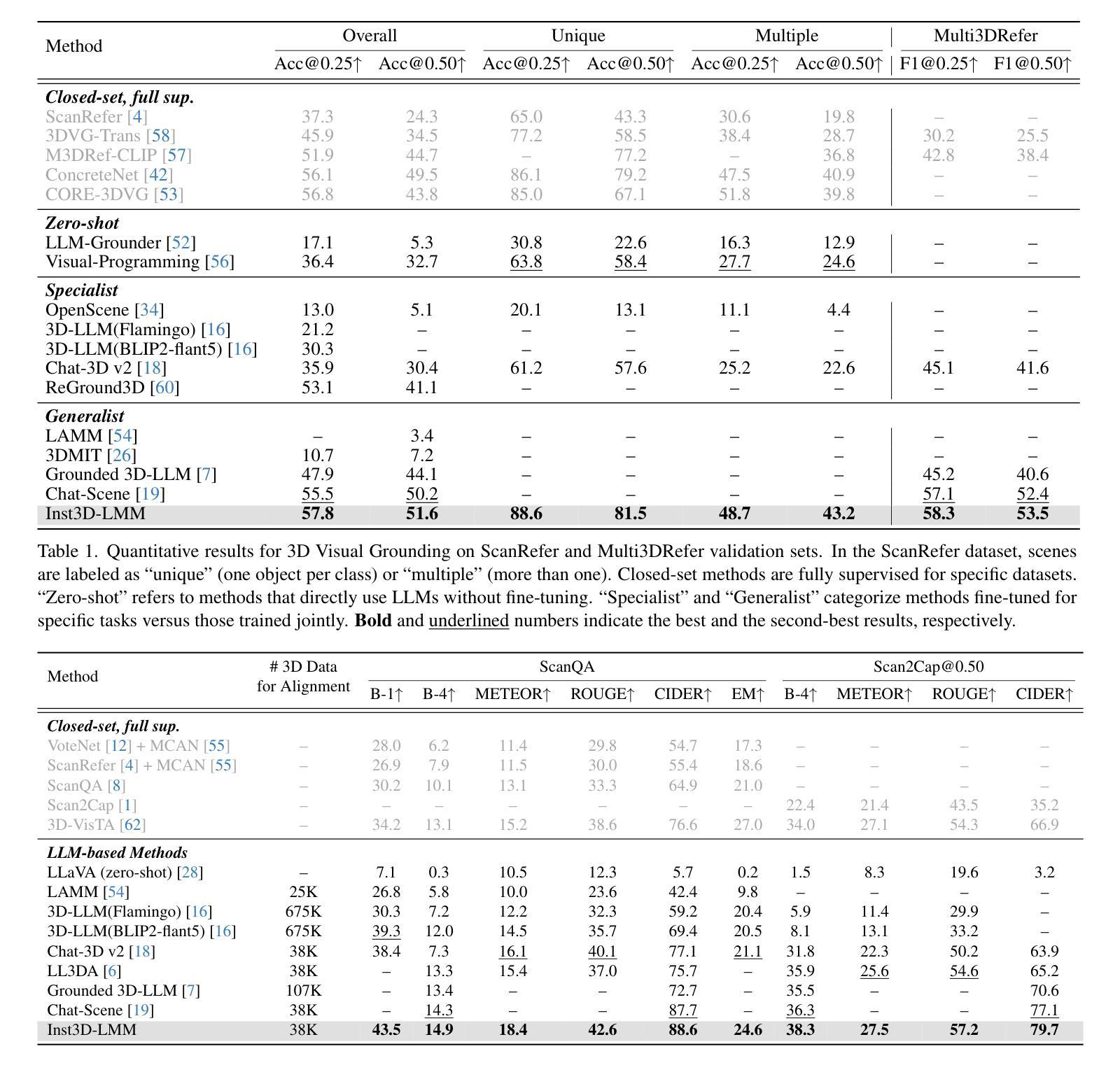
The Sharpness Disparity Principle in Transformers for Accelerating Language Model Pre-Training
Authors:Jinbo Wang, Mingze Wang, Zhanpeng Zhou, Junchi Yan, Weinan E, Lei Wu
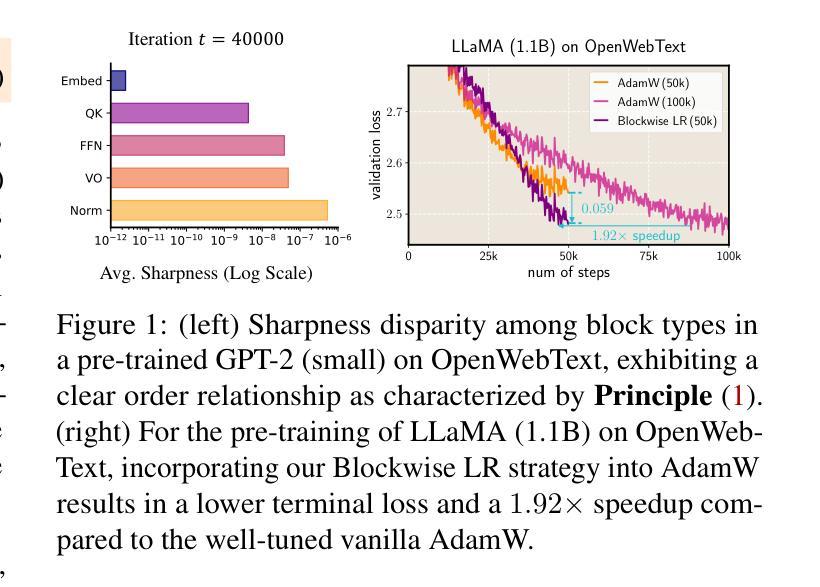
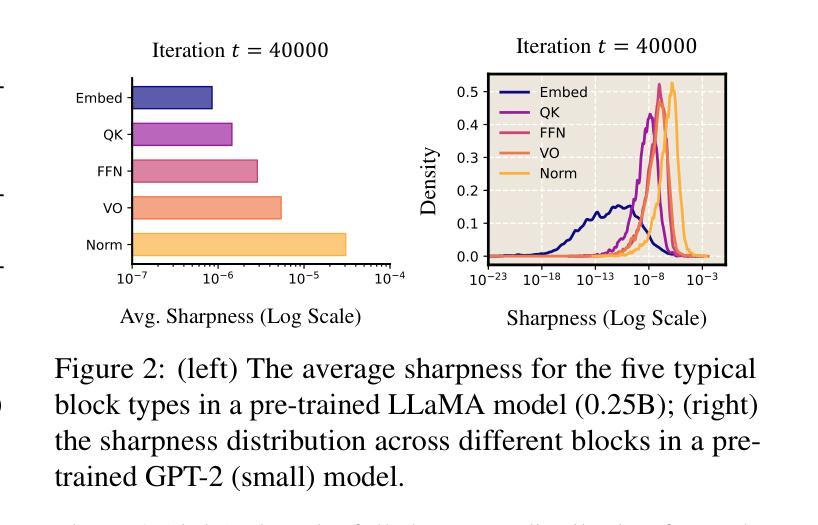
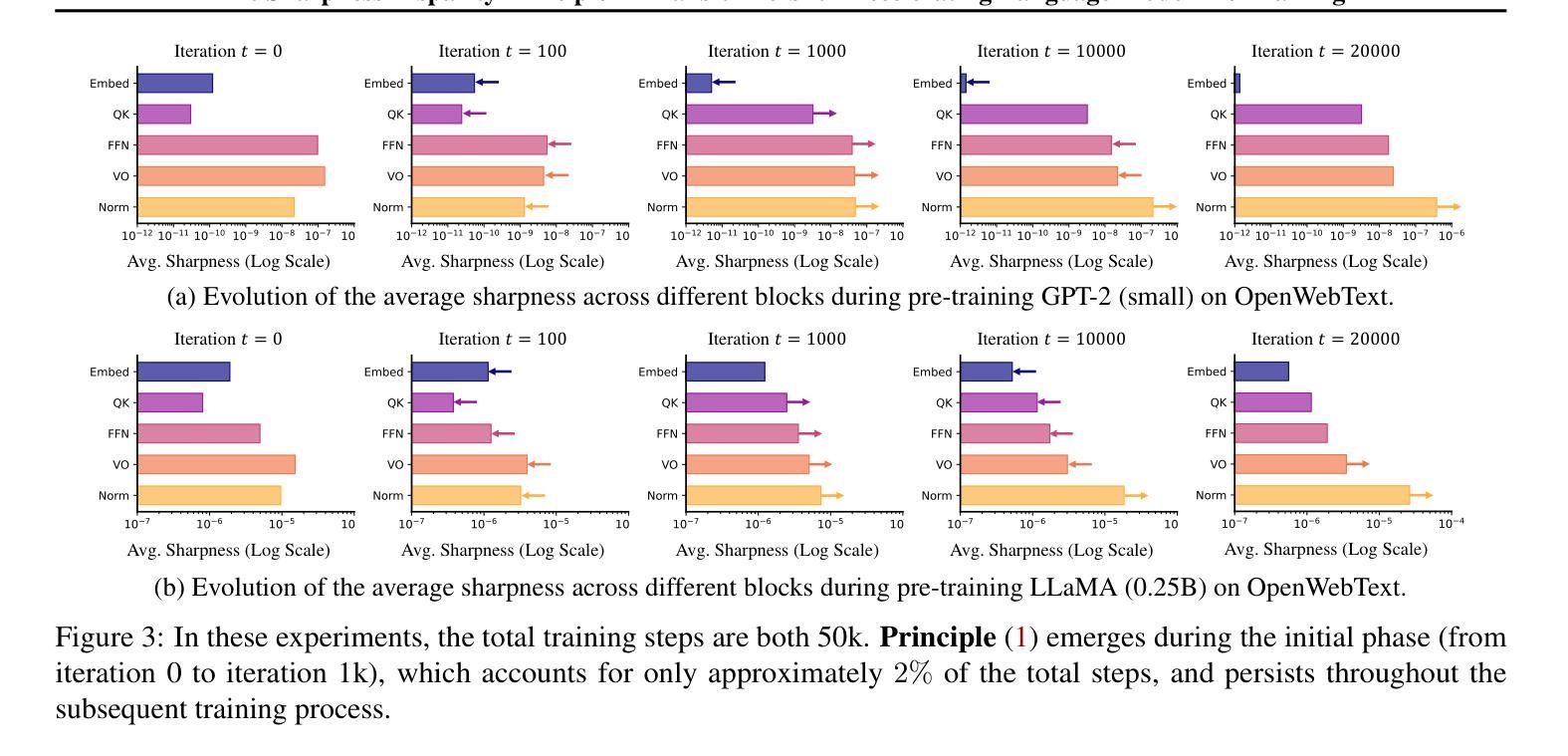
Transformers consist of diverse building blocks, such as embedding layers, normalization layers, self-attention mechanisms, and point-wise feedforward networks. Thus, understanding the differences and interactions among these blocks is important. In this paper, we uncover a clear Sharpness Disparity across these blocks, which emerges early in training and intriguingly persists throughout the training process. Motivated by this finding, we propose Blockwise Learning Rate (LR), a strategy that tailors the LR to each block’s sharpness, accelerating large language model (LLM) pre-training. By integrating Blockwise LR into AdamW, we consistently achieve lower terminal loss and nearly $2\times$ speedup compared to vanilla AdamW. We demonstrate this acceleration across GPT-2 and LLaMA, with model sizes ranging from 0.12B to 2B and datasets of OpenWebText, MiniPile, and C4. Finally, we incorporate Blockwise LR into Adam-mini (Zhang et al., 2024), a recently proposed memory-efficient variant of Adam, achieving a combined $2\times$ speedup and $2\times$ memory saving. These results underscore the potential of exploiting the sharpness disparity to improve LLM training.
Transformer由多种构建块组成,如嵌入层、归一化层、自注意力机制和逐点前馈网络。因此,了解这些模块之间的差异和交互非常重要。在本文中,我们发现了这些模块之间存在明显的尖锐度差异(Sharpness Disparity),这种差异在训练早期就会出现,并且令人困惑的是,它会一直存在于整个训练过程中。受这一发现的启发,我们提出了分块学习率(LR)策略,即根据每个模块的尖锐度量身定制学习率,以加速大型语言模型(LLM)的预训练。通过将分块LR集成到AdamW中,我们始终实现了更低的终端损失和与标准AdamW相比近2倍的速度提升。我们在GPT-2和LLaMA上展示了这种加速效果,模型大小范围从0.12B到2B,数据集包括OpenWebText、MiniPile和C4。最后,我们将分块LR集成到Adam-mini(Zhang等人,2024年)——一种新提出的内存高效的Adam变体,实现了2倍的速度提升和2倍的内存节省。这些结果突显了利用尖锐度差异改进LLM训练的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer模型各组件(如嵌入层、归一化层、自注意力机制和点式前馈网络)之间的尖锐度差异,并提出了一种针对每个组件的尖锐度的块级学习率(LR)策略,以加速大型语言模型(LLM)的预训练。通过集成Blockwise LR到AdamW优化器,实验结果显示,与原始的AdamW相比,新策略能够达到更低的终端损失并加速近2倍。此外,该策略在GPT-2和LLaMA模型上表现出一致的加速效果,并在模型规模和数据集上展现出良好的泛化能力。最后,研究还将Blockwise LR集成到Adam-mini优化器中,实现了速度和内存的双倍提升。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer模型包含多种构建块,理解这些块之间的差异和交互非常重要。
- 研究发现Transformer模型各组件之间存在尖锐度差异,这种差异在训练早期就会出现,并会贯穿整个训练过程。
- 提出了一种块级学习率(LR)策略,该策略根据每个组件的尖锐度来定制学习率,以加速大型语言模型(LLM)的预训练。
- 集成Blockwise LR到AdamW优化器,实现了比原始AdamW更低的终端损失和近2倍的加速。
- Blockwise LR策略在GPT-2和LLaMA模型上表现出良好的加速效果,且具有良好的泛化能力。
- Blockwise LR策略在模型规模和数据集上的表现具有一致性。
点此查看论文截图

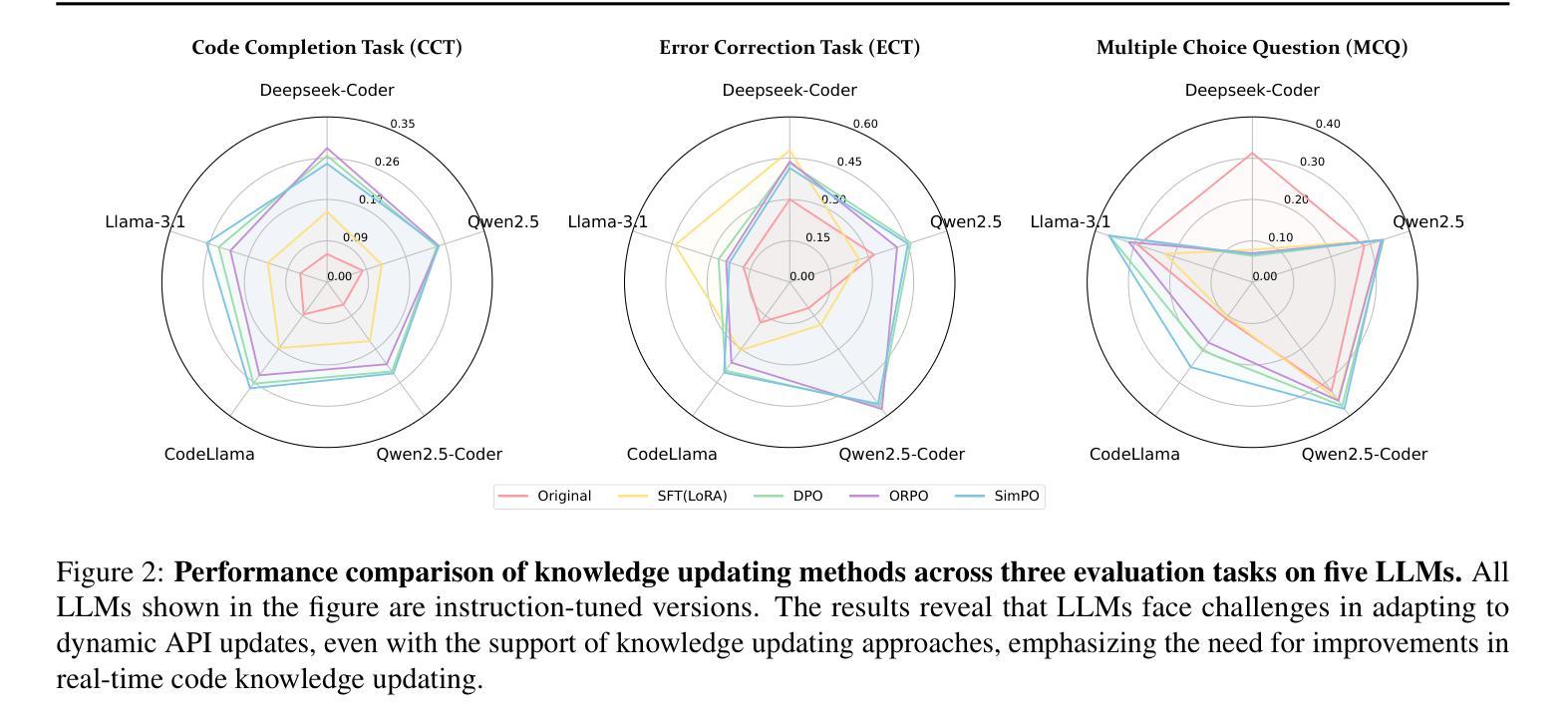
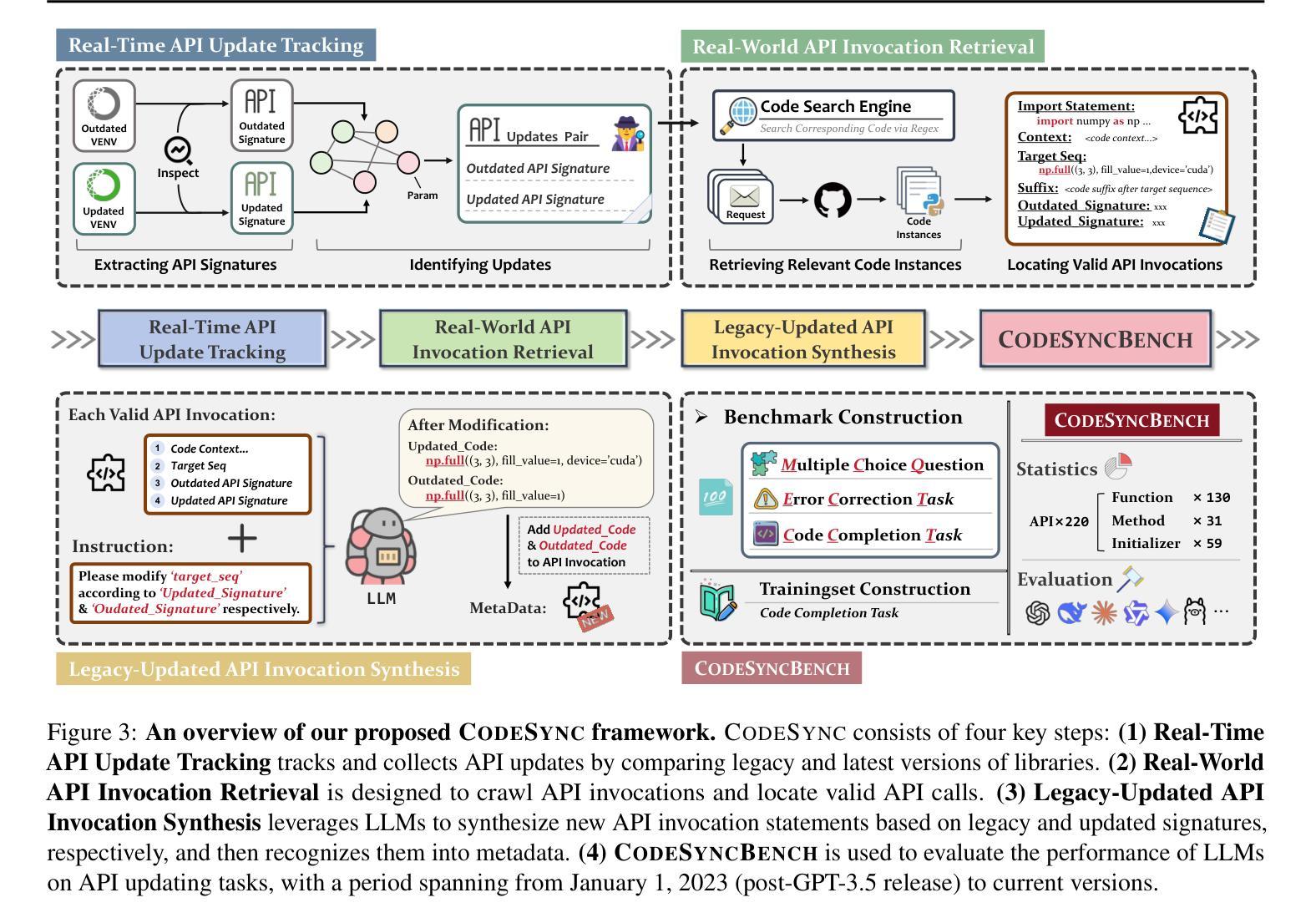
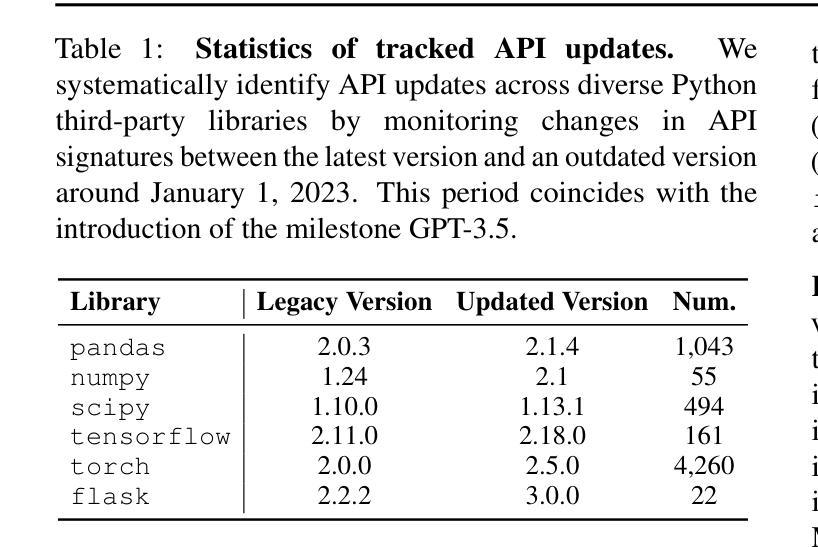
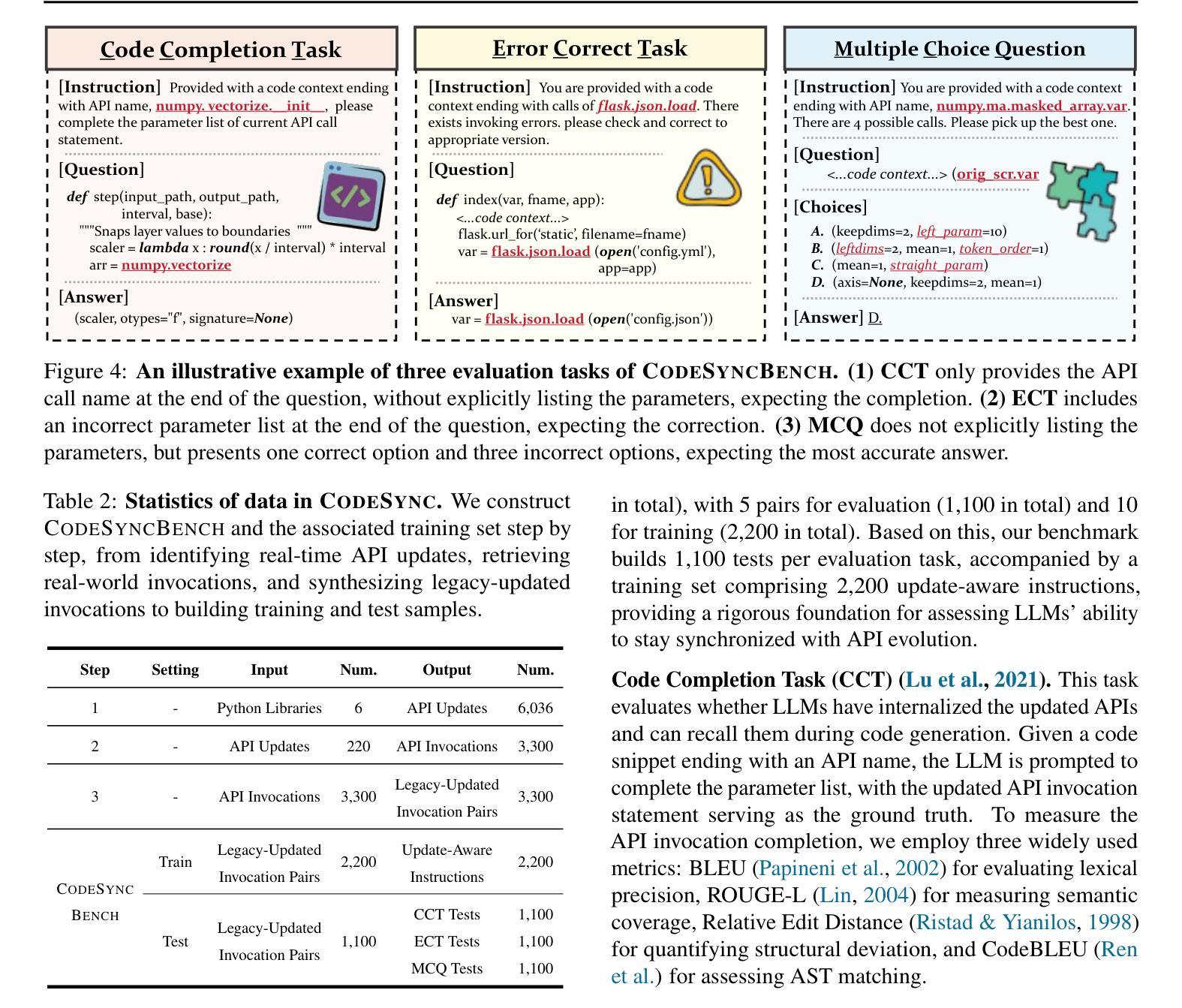
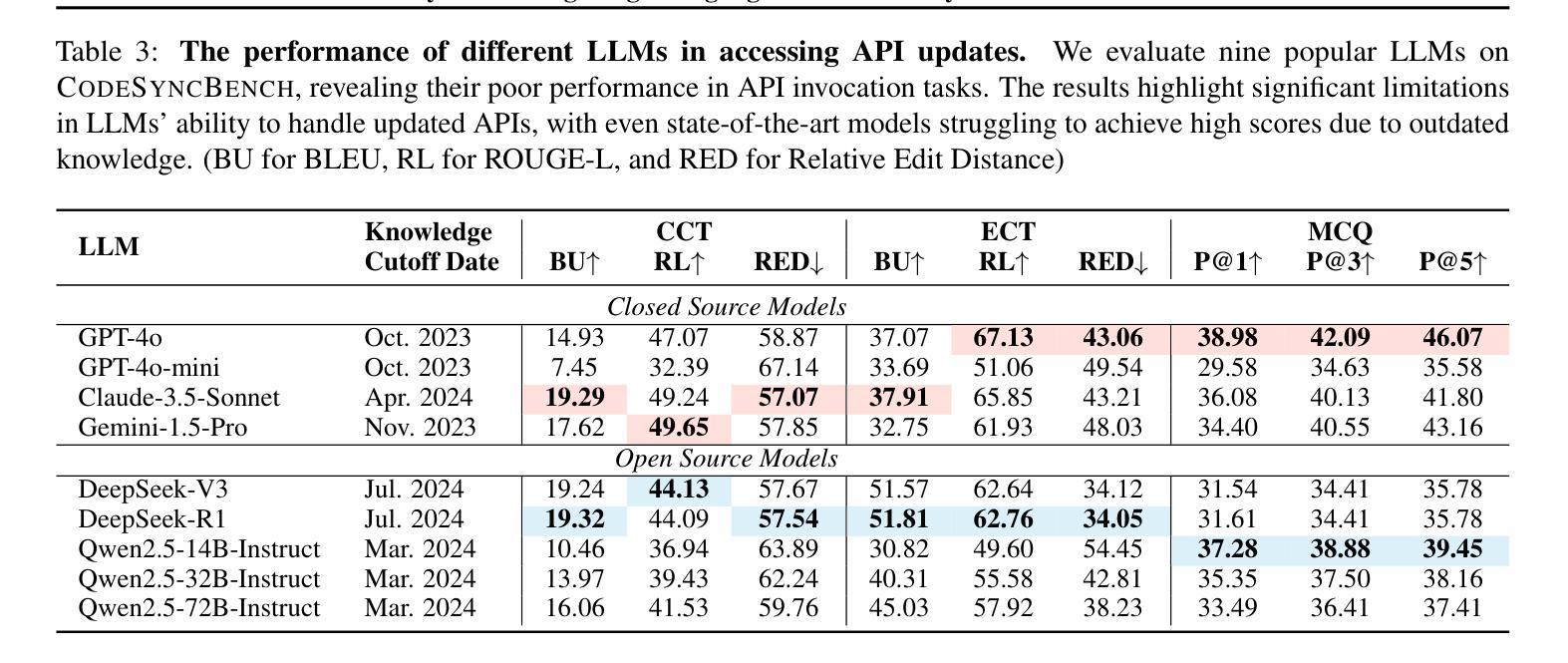
CODESYNC: Synchronizing Large Language Models with Dynamic Code Evolution at Scale
Authors:Chenlong Wang, Zhaoyang Chu, Zhengxiang Cheng, Xuyi Yang, Kaiyue Qiu, Yao Wan, Zhou Zhao, Xuanhua Shi, Dongping Chen
Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited exceptional performance in software engineering yet face challenges in adapting to continually evolving code knowledge, particularly regarding the frequent updates of third-party library APIs. This limitation, stemming from static pre-training datasets, often results in non-executable code or implementations with suboptimal safety and efficiency. To this end, this paper introduces CODESYNC, a data engine for identifying outdated code patterns and collecting real-time code knowledge updates from Python third-party libraries. Building upon CODESYNC, we develop CODESYNCBENCH, a comprehensive benchmark for assessing LLMs’ ability to stay synchronized with code evolution, which covers real-world updates for 220 APIs from six Python libraries. Our benchmark offers 3,300 test cases across three evaluation tasks and an update-aware instruction tuning dataset consisting of 2,200 training samples. Extensive experiments on 14 state-of-the-art LLMs reveal that they struggle with dynamic code evolution, even with the support of advanced knowledge updating methods (e.g., DPO, ORPO, and SimPO). We believe that our benchmark can offer a strong foundation for the development of more effective methods for real-time code knowledge updating in the future. The experimental code and dataset are publicly available at: https://github.com/Lucky-voyage/Code-Sync.
大型语言模型(LLM)在软件工程领域表现出卓越的性能,但在适应不断演变的代码知识方面仍面临挑战,特别是关于第三方库API的频繁更新。这一局限性源于静态的预训练数据集,往往导致生成的代码不可执行,或在安全性和效率方面存在次优的实现。针对这一问题,本文介绍了CODESYNC,一个用于识别过时代码模式并从Python第三方库中实时收集代码知识更新的数据引擎。基于CODESYNC,我们开发了CODESYNCBENCH,这是一个全面评估LLM与代码演化同步能力的基准测试,涵盖了来自六个Python库的220个API的实时更新。我们的基准测试包括三项评估任务的3300个测试用例和一个包含2200个训练样本的更新感知指令调优数据集。对14种最新LLM的广泛实验表明,它们在动态代码演化方面面临困难,即使在先进的知识更新方法(如DPO、ORPO和SimPO)的支持下也是如此。我们相信,我们的基准测试可以为未来开发更有效的实时代码知识更新方法提供坚实的基础。实验代码和数据集可公开访问:https://github.com/Lucky-voyage/Code-Sync。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在软件工程领域表现出卓越性能,但在适应不断演变的代码知识方面面临挑战,尤其是第三方库API的频繁更新。本文提出CODESYNC数据引擎和CODESYNCBENCH基准测试,旨在解决此问题并评估LLM同步适应代码进化的能力。实验结果显示,即使是支持先进知识更新方法的大型语言模型,在动态代码进化方面也面临困难。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在软件工程中表现出卓越性能,但在适应不断变化的代码知识方面存在挑战。
- 第三方库API的频繁更新给大型语言模型带来适应难题。
- CODESYNC数据引擎用于识别过时的代码模式和从Python第三方库收集实时代码知识更新。
- CODESYNCBENCH基准测试用于评估大型语言模型同步适应代码进化的能力。
- 该基准测试涵盖了来自六个Python库的220个API的真实世界更新,提供3300个测试用例和更新感知指令调整数据集。
- 广泛实验表明,即使是支持先进知识更新方法的大型语言模型,在动态代码进化方面仍面临困难。
点此查看论文截图

Truth Knows No Language: Evaluating Truthfulness Beyond English
Authors:Blanca Calvo Figueras, Eneko Sagarzazu, Julen Etxaniz, Jeremy Barnes, Pablo Gamallo, Iria De Dios Flores, Rodrigo Agerri
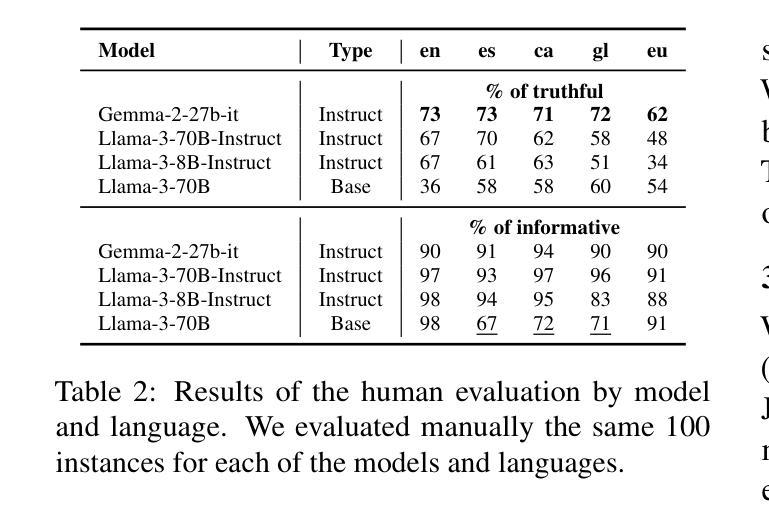
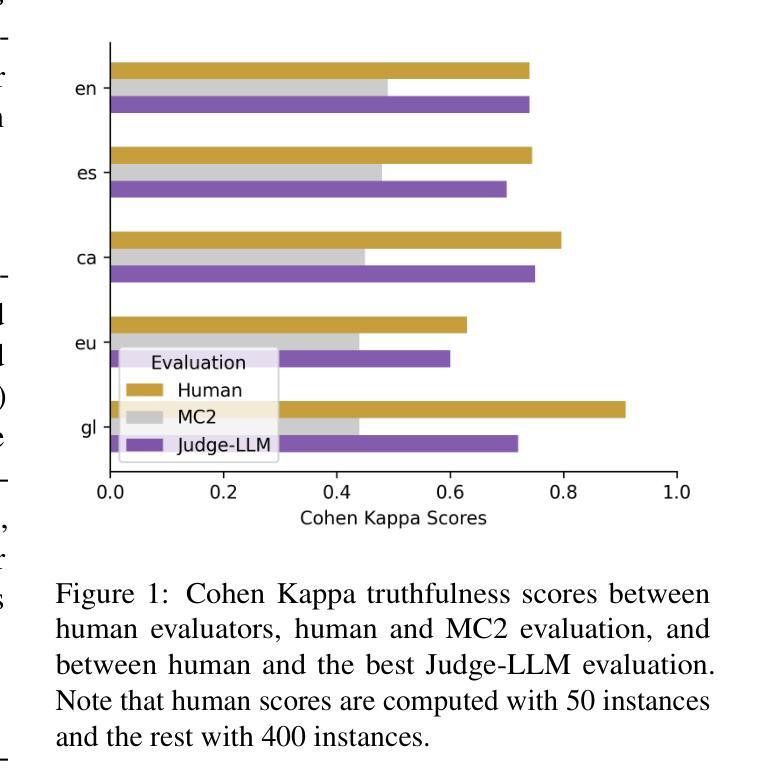
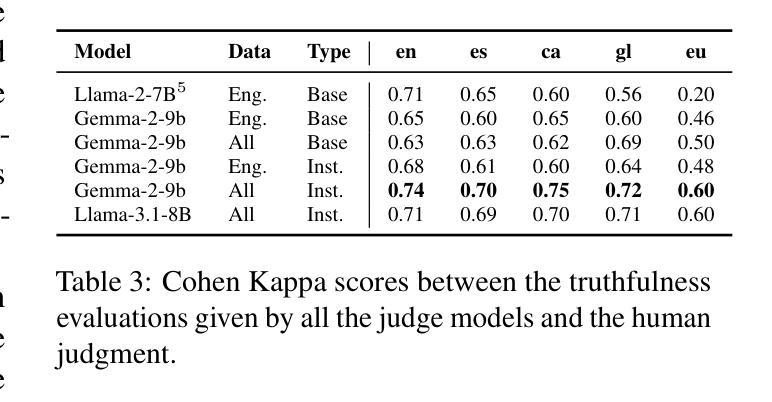
We introduce a professionally translated extension of the TruthfulQA benchmark designed to evaluate truthfulness in Basque, Catalan, Galician, and Spanish. Truthfulness evaluations of large language models (LLMs) have primarily been conducted in English. However, the ability of LLMs to maintain truthfulness across languages remains under-explored. Our study evaluates 12 state-of-the-art open LLMs, comparing base and instruction-tuned models using human evaluation, multiple-choice metrics, and LLM-as-a-Judge scoring. Our findings reveal that, while LLMs perform best in English and worst in Basque (the lowest-resourced language), overall truthfulness discrepancies across languages are smaller than anticipated. Furthermore, we show that LLM-as-a-Judge correlates more closely with human judgments than multiple-choice metrics, and that informativeness plays a critical role in truthfulness assessment. Our results also indicate that machine translation provides a viable approach for extending truthfulness benchmarks to additional languages, offering a scalable alternative to professional translation. Finally, we observe that universal knowledge questions are better handled across languages than context- and time-dependent ones, highlighting the need for truthfulness evaluations that account for cultural and temporal variability. Dataset and code are publicly available under open licenses.
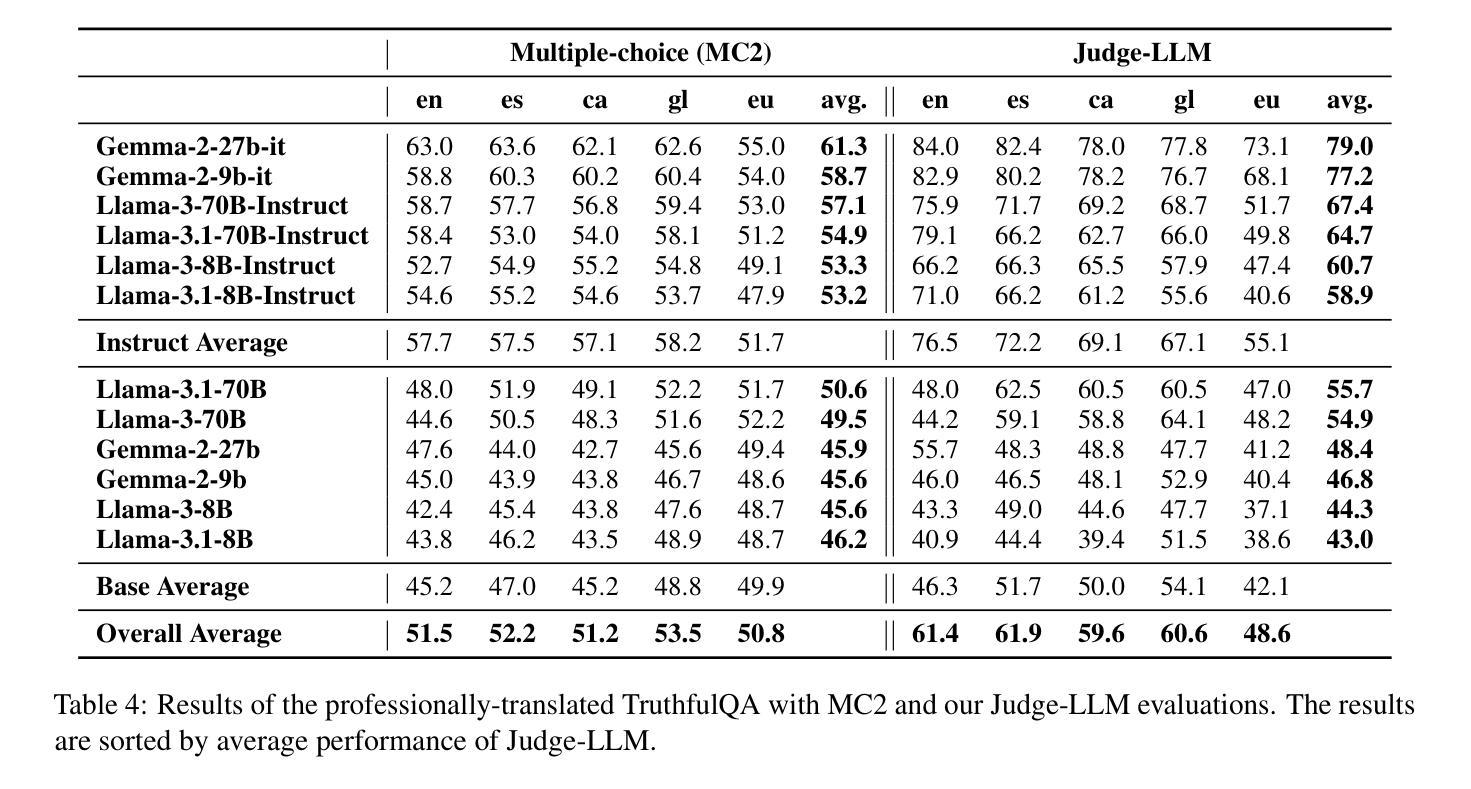
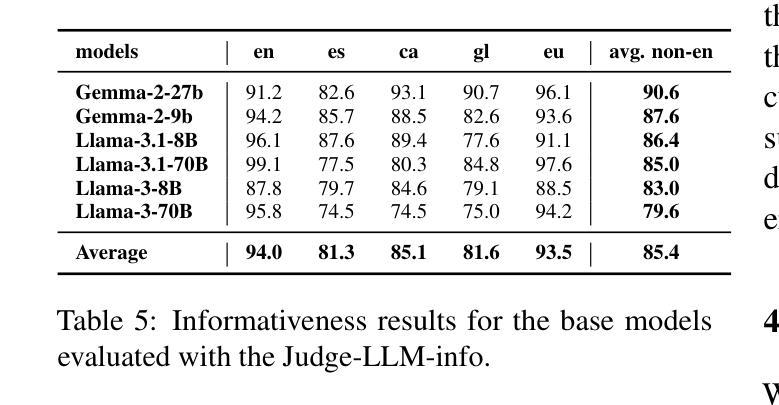
我们介绍了一个专业翻译的TruthfulQA基准测试扩展版,该版本旨在评估巴斯克语、加泰罗尼亚语、加利西亚语和西班牙语中的真实性评估。迄今为止,大型语言模型(LLM)的真实性评估主要都在英语中进行。然而,LLM在不同语言中保持真实性的能力仍待探索。我们的研究评估了12种最先进的开源LLM,通过人工评估、多项选择指标和LLM-as-a-Judge评分对比基础模型和指令优化模型。我们发现,虽然LLM在英语中的表现最好,在巴斯克语(资源最少的语言)中的表现最差,但总体来说,不同语言之间的真实性差异比预期的要小。此外,我们还发现LLM-as-a-Judge与人类判断的相关性比多项选择指标更为密切,而信息性在真实性评估中起着关键作用。我们的结果还表明,机器翻译是扩展真实性基准测试到更多语言的一种可行方法,为专业翻译提供了一种可扩展的替代方案。最后,我们观察到,与上下文和时间相关的通用知识问题在不同语言中的处理情况要好于其他类型的问题,这强调了在进行真实性评估时需要考虑到文化和时间变化的因素。数据集和代码均公开开放许可。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures, 8 tables
摘要
该文介绍了一个专业翻译的TruthfulQA基准测试扩展版本,旨在评估巴斯克语、加泰罗尼亚语、加利西亚语和西班牙语的真实性评估。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在英文中的真实性评估已相当普遍,但LLM在不同语言的真实性保持能力尚待研究。该研究评估了12个最先进的开源LLM,对比基础模型和指令调整模型,采用人工评估、多项选择指标和LLM-as-a-Judge评分法。研究结果显示,LLM在英语中表现最佳,在巴斯克语(资源最少)中表现最差,但整体真实性跨语言差异小于预期。此外,LLM-as-a-Judge与人类判断的相关性高于多项选择指标,而信息性在真实性评估中起着关键作用。研究结果还表明,机器翻译可作为扩展真实性基准测试至其他语言的可行方法,提供一种可扩展的替代专业翻译的途径。最后观察到,通用知识问题在跨语言处理上优于上下文和时间依赖性问题,强调在进行真实性评估时需要考虑到文化和时间变化。数据集和代码均公开开放许可。
关键见解
- 研究人员对巴斯克语、加泰罗尼亚语、加利西亚语和西班牙语进行了真实性评估的LLM扩展研究。
- LLM在英语中表现最佳,在巴斯克语中最差,但跨语言的真实性差异总体较小。
- LLM-as-a-Judge评分法与人类判断的相关性更高。
- 信息性在真实性评估中起关键作用。
- 机器翻译是扩展真实性基准测试至其他语言的可行方法。
- 通用知识问题的跨语言处理能力优于上下文和时间依赖性问题。
点此查看论文截图


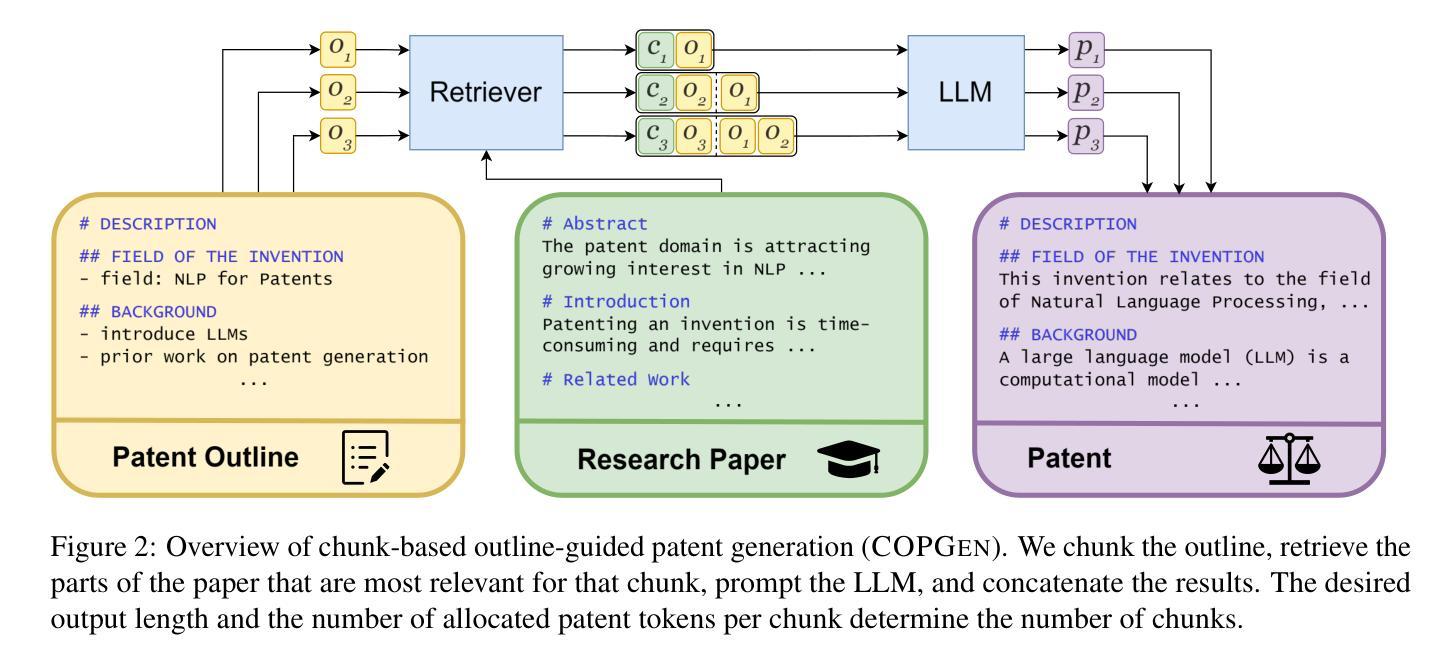
Pap2Pat: Benchmarking Outline-Guided Long-Text Patent Generation with Patent-Paper Pairs
Authors:Valentin Knappich, Simon Razniewski, Anna Hätty, Annemarie Friedrich
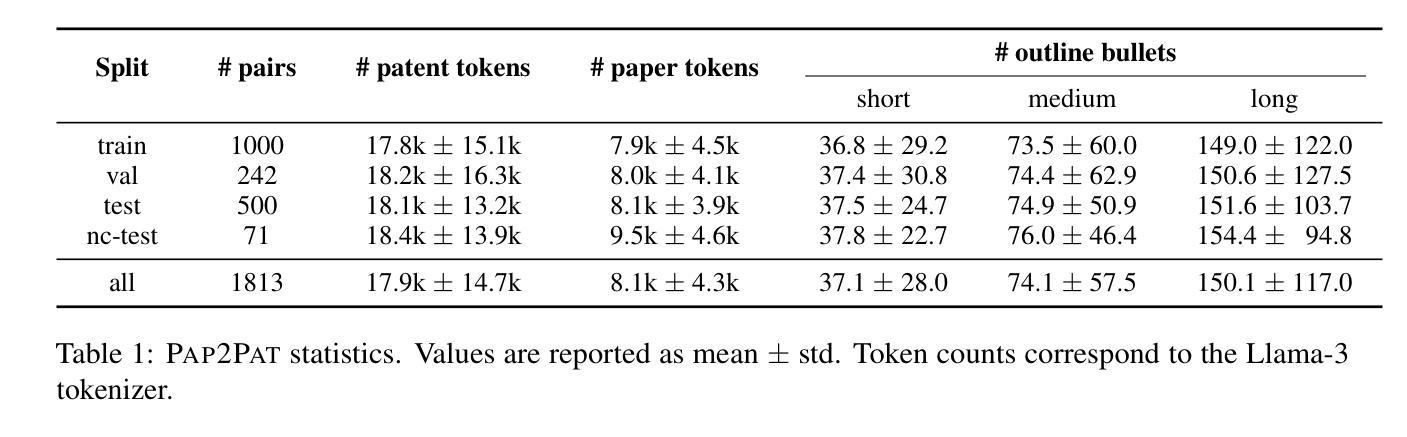
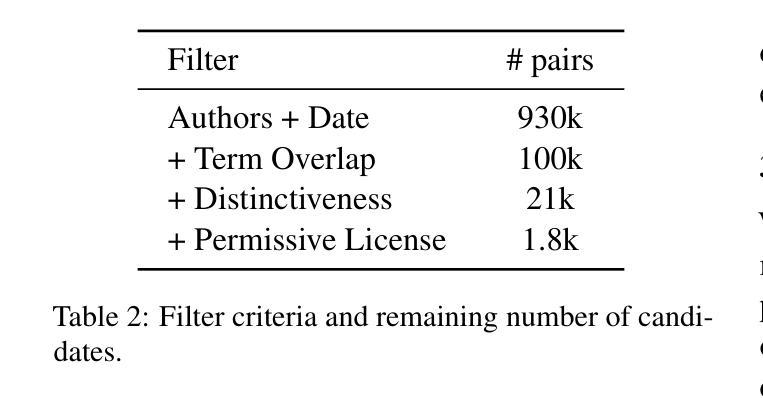
Dealing with long and highly complex technical text is a challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs), which still have to unfold their potential in supporting expensive and timeintensive processes like patent drafting. Within patents, the description constitutes more than 90% of the document on average. Yet, its automatic generation remains understudied. When drafting patent applications, patent attorneys typically receive invention reports (IRs), which are usually confidential, hindering research on LLM-supported patent drafting. Often, prepublication research papers serve as IRs. We leverage this duality to build PAP2PAT, an open and realistic benchmark for patent drafting consisting of 1.8k patent-paper pairs describing the same inventions. To address the complex longdocument patent generation task, we propose chunk-based outline-guided generation using the research paper as invention specification. Our extensive evaluation using PAP2PAT and a human case study show that LLMs can effectively leverage information from the paper, but still struggle to provide the necessary level of detail. Fine-tuning leads to more patent-style language, but also to more hallucination. We release our data and code https://github.com/boschresearch/Pap2Pat.
处理长而复杂的技术文本对大型语言模型(LLM)来说是一个挑战,这些模型在支持如专利撰写等昂贵且耗时的流程时,仍需发挥其潜力。在专利文档中,描述部分平均占整个文档的90%以上。然而,其自动生成仍然研究不足。在撰写专利申请时,专利代理人通常会收到发明报告(IRs),这些报告通常是机密的,阻碍了关于LLM支持的专利撰写的研究。通常,预发布的科研论文会作为IRs。我们利用这种双重性质来构建PAP2PAT,这是一个开放且现实的专利撰写基准,包含1.8k个描述相同发明的专利-论文对。为了解决复杂的长文档专利生成任务,我们提出了基于分块的提纲指导生成方法,以论文作为发明说明书。我们使用PAP2PAT进行广泛评估,并进行人类案例研究,结果显示LLM可以有效地利用论文中的信息,但在提供必要细节方面仍面临困难。微调可以产生更多符合专利风格的语言,但也会产生更多的虚构内容。我们公开了我们的数据和代码:https://github.com/boschresearch/Pap2Pat。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Findings
摘要
LLM在处理长期且高度复杂的技术文本方面存在挑战,尤其是在支持如专利起草等昂贵且耗时的流程时。尽管专利中的描述部分平均占文档超过90%,但其自动生成仍受到的研究较少。专利律师在起草专利申请时会收到通常保密的发明报告(IR)。为此,研究开发了PAP2PAT数据集,它包含了关于相同发明的近一、八万个专利文献配对的数据集。提出了基于分块的概要引导生成方法,利用研究论文作为发明说明书来解决复杂的长期专利生成任务。通过广泛的基于PAP2PAT的数据集评估和案例研究证明,LLM可以有效地利用论文中的信息,但在提供必要的细节方面仍有困难。微调可以增加专利风格的语言,但也可能导致虚构情况的出现。该研究的相关数据和代码已公开发布于开源网站boschresearch/Pap2Pat。
关键见解
- LLM在处理长期复杂技术文本方面存在挑战,特别是在支持专利起草等流程时。
- 专利中的描述部分平均占文档超过90%,但其自动生成的研究仍然有限。
- 研究人员利用发明报告(IR)构建了开放且现实的专利起草基准数据集PAP2PAT。
- 基于分块的概要引导生成方法被提出以解决复杂的长期专利生成任务,利用研究论文作为发明说明书。
点此查看论文截图

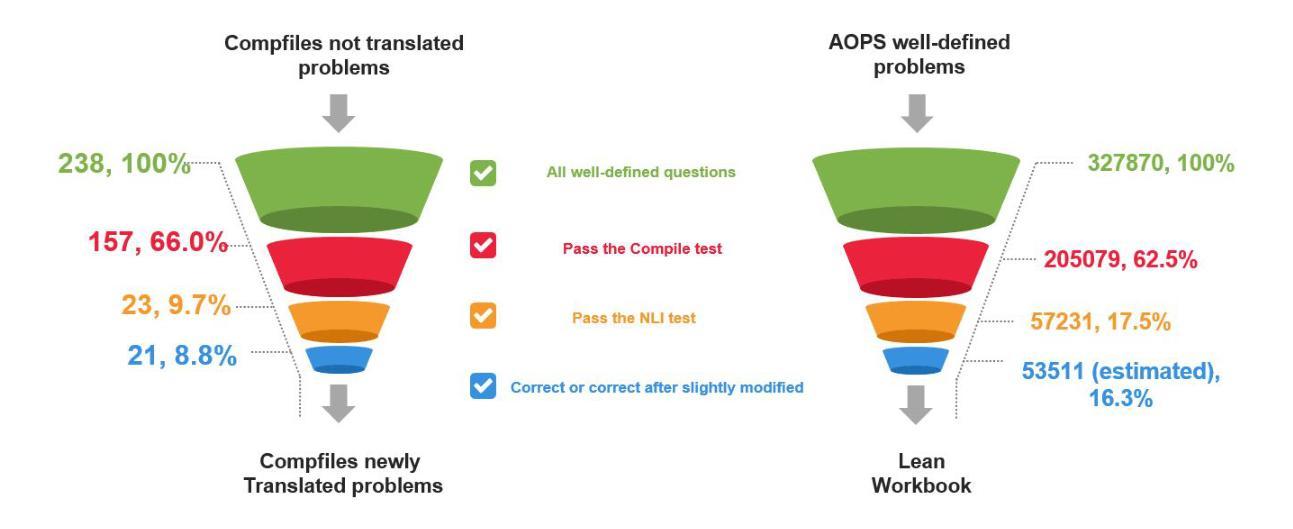
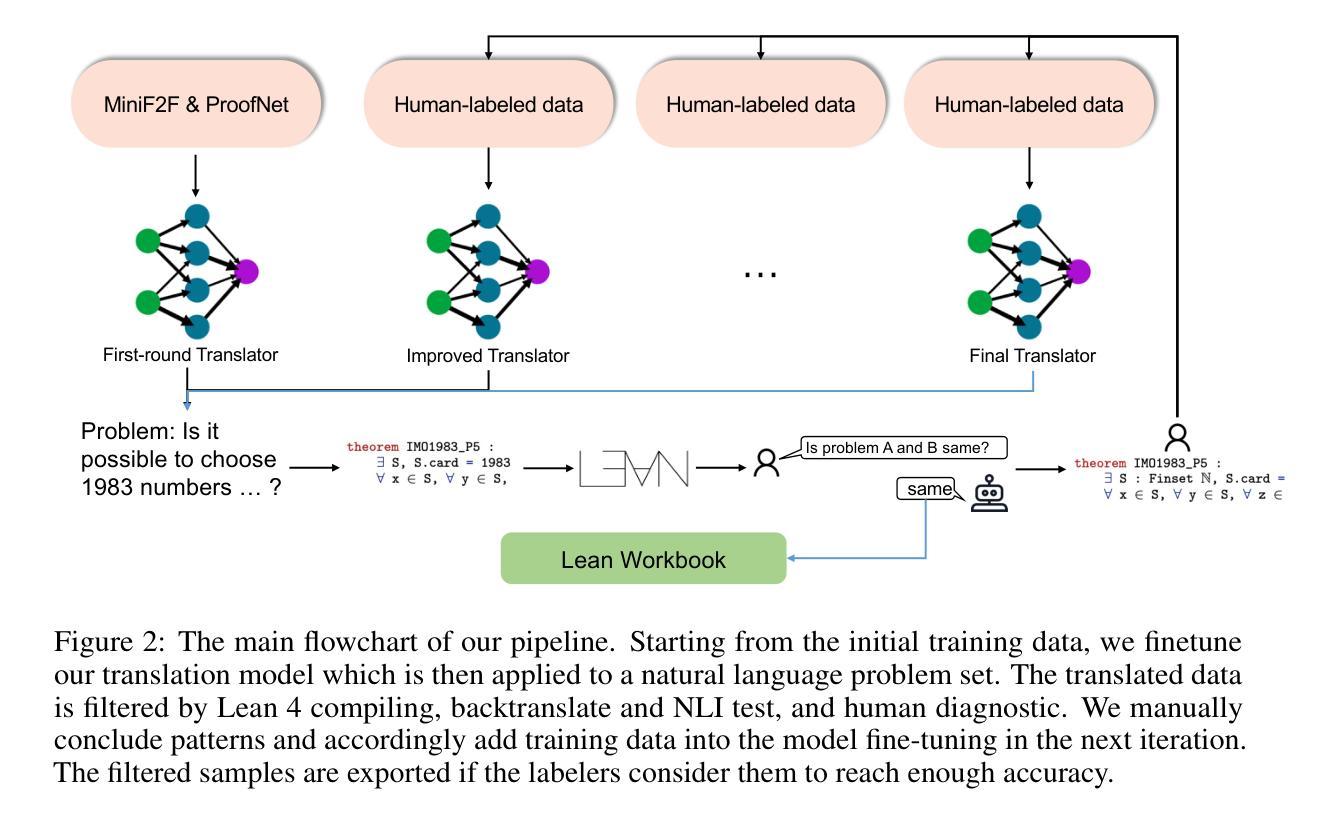
Lean Workbook: A large-scale Lean problem set formalized from natural language math problems
Authors:Huaiyuan Ying, Zijian Wu, Yihan Geng, Zheng Yuan, Dahua Lin, Kai Chen
Large language models have demonstrated impressive capabilities across various natural language processing tasks, especially in solving mathematical problems. However, large language models are not good at math theorem proving using formal languages like Lean. A significant challenge in this area is the scarcity of training data available in these formal languages. To address this issue, we propose a novel pipeline that iteratively generates and filters synthetic data to translate natural language mathematical problems into Lean 4 statements, and vice versa. Our results indicate that the synthetic data pipeline can provide useful training data and improve the performance of LLMs in translating and understanding complex mathematical problems and proofs. Our final dataset contains about 57K formal-informal question pairs along with searched proof from the math contest forum and 21 new IMO questions. We open-source our code at https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-Math and our data at https://huggingface.co/datasets/InternLM/Lean-Workbook.
大型语言模型在各种自然语言处理任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,尤其是在解决数学问题方面。然而,大型语言模型不擅长使用诸如Lean之类的正式语言进行数学定理证明。该领域的一个主要挑战是这些正式语言中可用训练数据的稀缺。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型管道,该管道可迭代生成并过滤合成数据,以将自然语言数学问题转换为Lean 4语句,反之亦然。我们的结果表明,合成数据管道可提供有用的训练数据,提高大型语言模型在翻译和理解复杂数学问题和证明方面的性能。我们的最终数据集包含大约57K个正式与非正式问题对,以及从数学竞赛论坛中搜索到的证明和21个新的国际数学奥林匹克竞赛问题。我们的代码已公开在https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-Math,数据已公开在https://huggingface.co/datasets/InternLM/Lean-Workbook。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在自然语言处理任务中展现出强大的能力,尤其在解决数学问题方面。然而,在利用形式语言(如Lean)进行数学定理证明方面,大型语言模型的表现并不理想。训练数据在正式语言中的匮乏是这一领域的一个重大挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型管道,该管道可迭代生成并过滤合成数据,将自然语言数学问题翻译为Lean 4语句,反之亦然。研究结果证明,该合成数据管道可提供有用的训练数据,提高大型语言模型在处理和理解复杂数学问题和证明方面的性能。我们的最终数据集包含约57K的正式与非正式问题对,以及从数学竞赛论坛检索到的证明和21个新的国际数学奥林匹克竞赛问题。我们已在https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-Math开源了代码,并在https://huggingface.co/datasets/InternLM/Lean-Workbook分享了数据。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在自然语言处理任务中表现优异,尤其是解决数学问题方面。
- 在利用形式语言(如Lean)进行数学定理证明时,大型语言模型面临挑战。
- 训练数据在形式语言中的缺乏是这一挑战的主要原因。
- 提出了一种新型管道,通过迭代生成并过滤合成数据,促进自然语言与形式语言之间的翻译。
- 合成数据管道有助于提高大型语言模型处理和理解复杂数学问题和证明的能力。
- 最终数据集包含正式与非正式问题对、从数学竞赛论坛检索到的证明以及新的国际数学奥林匹克竞赛问题。
点此查看论文截图