⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-24 更新
Co-Seg++: Mutual Prompt-Guided Collaborative Learning for Versatile Medical Segmentation
Authors:Qing Xu, Yuxiang Luo, Wenting Duan, Zhen Chen
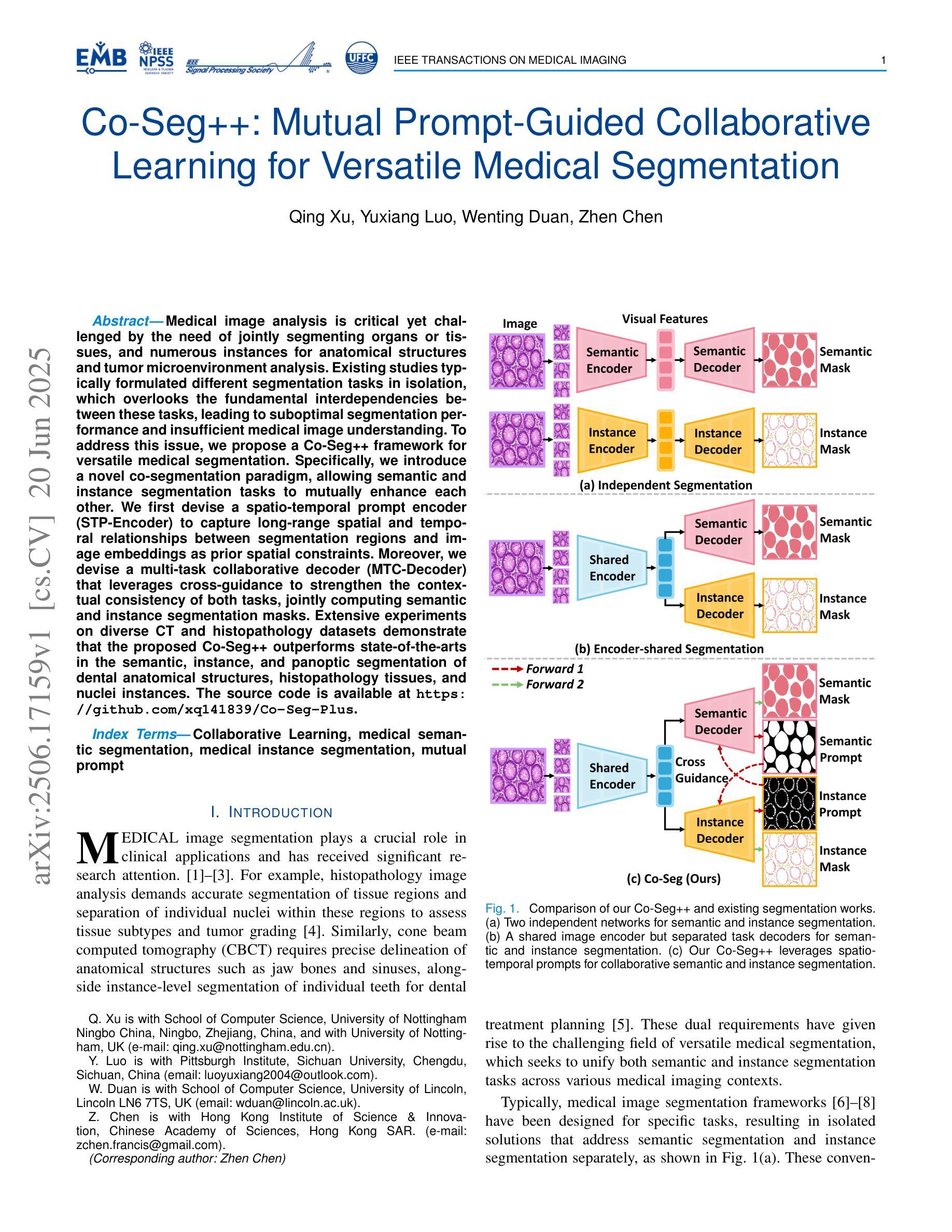
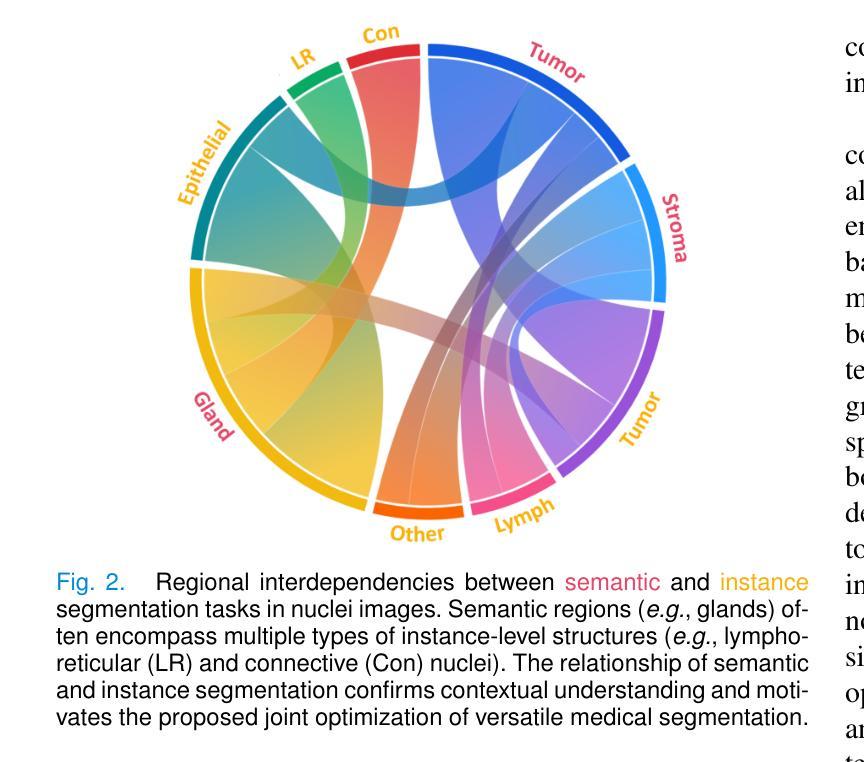
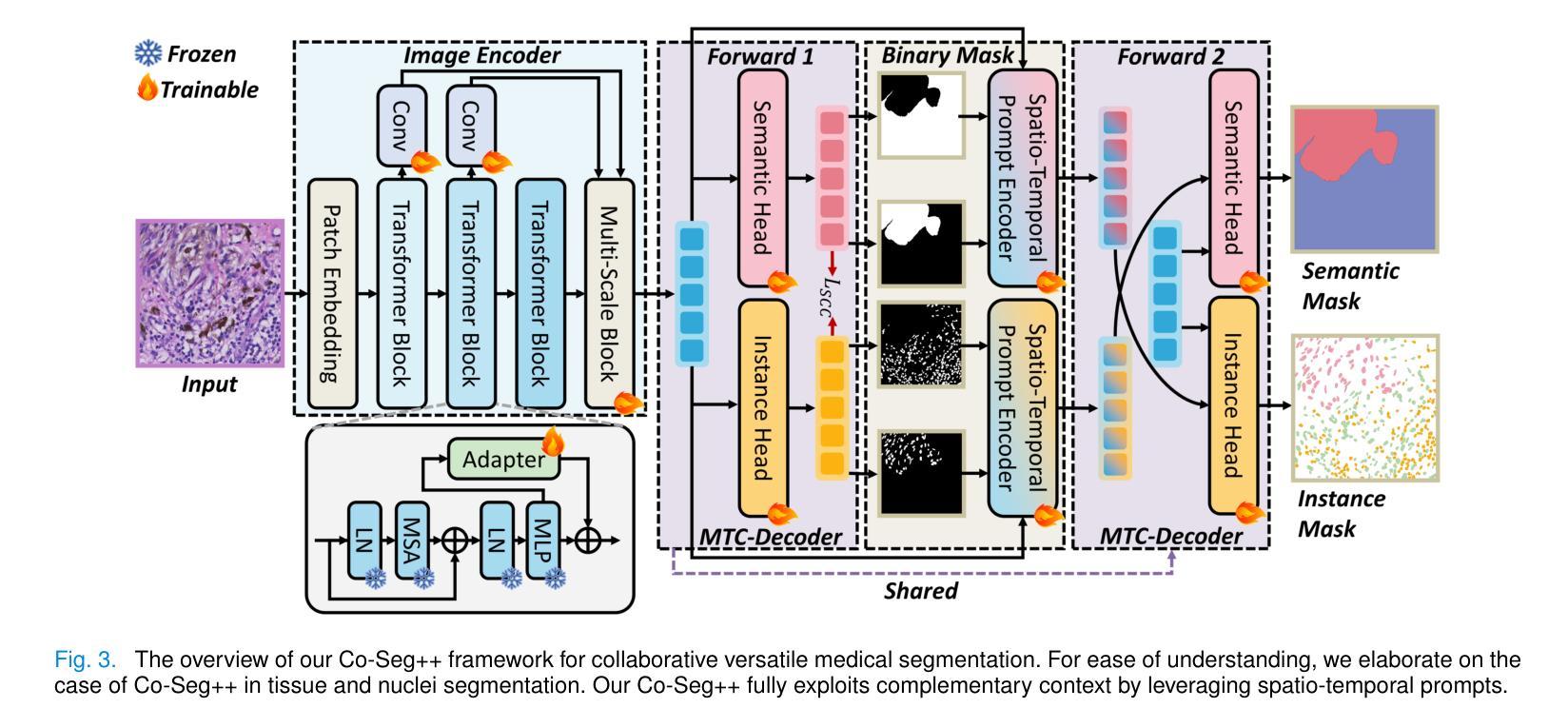
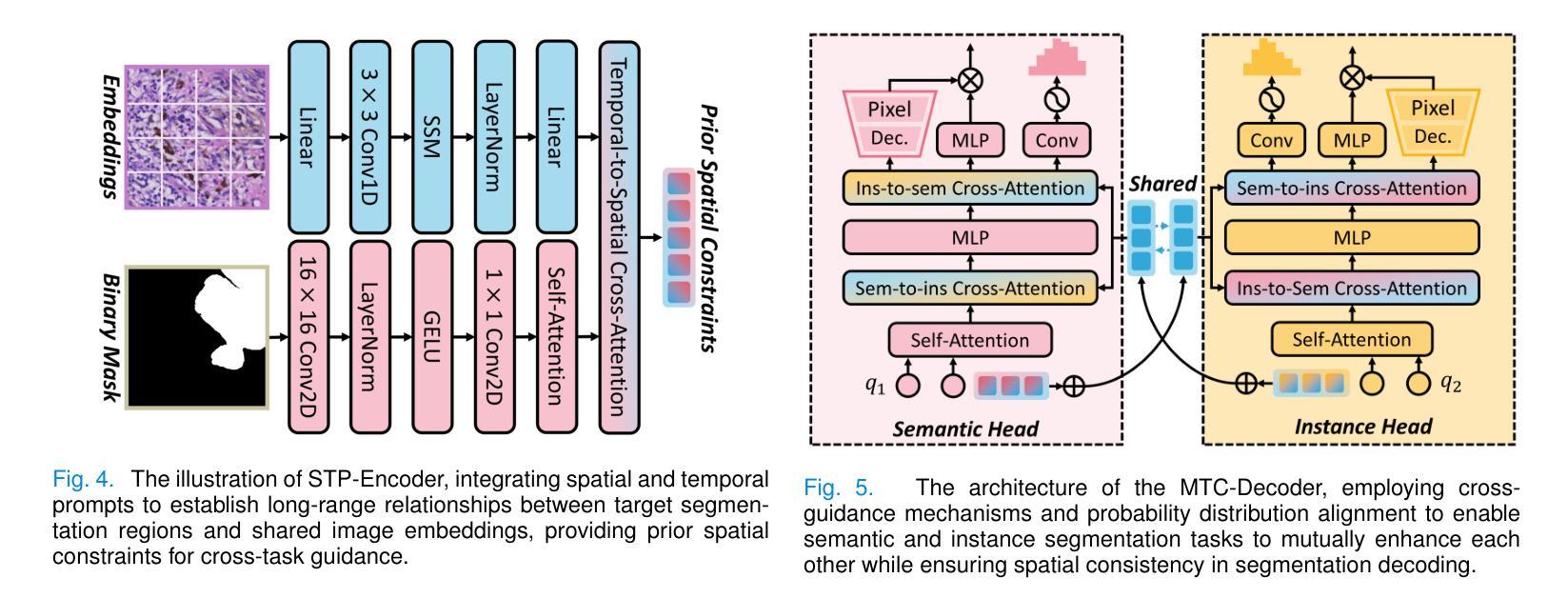
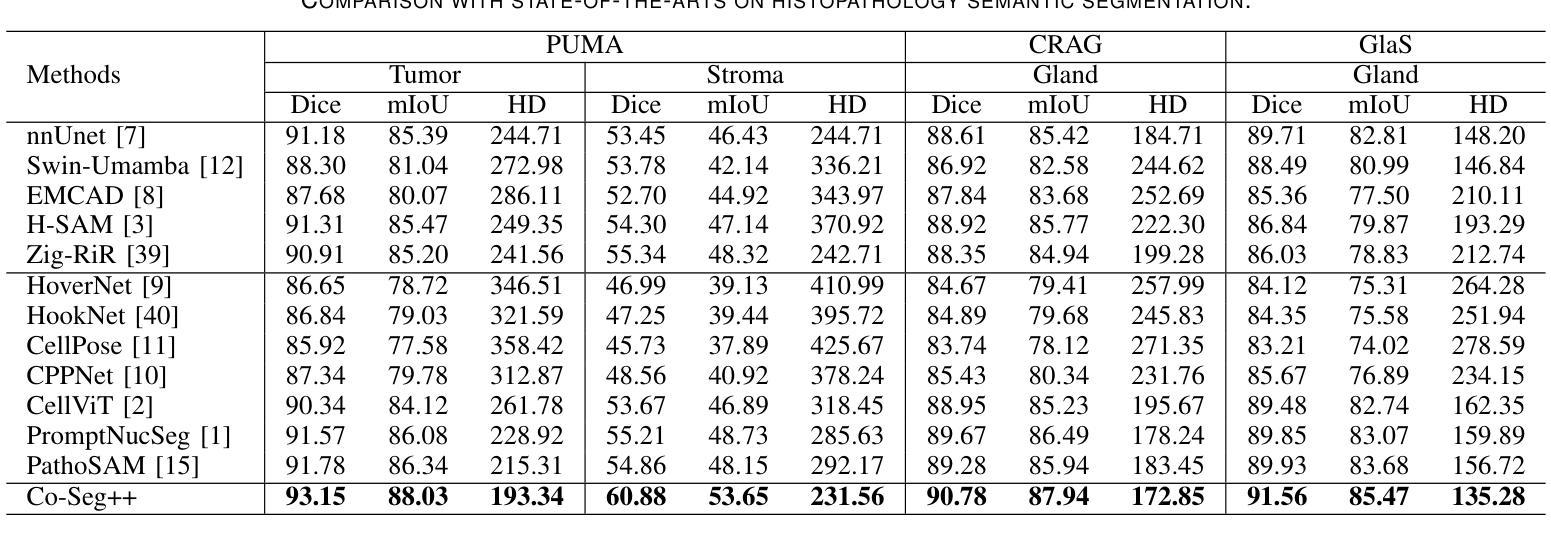
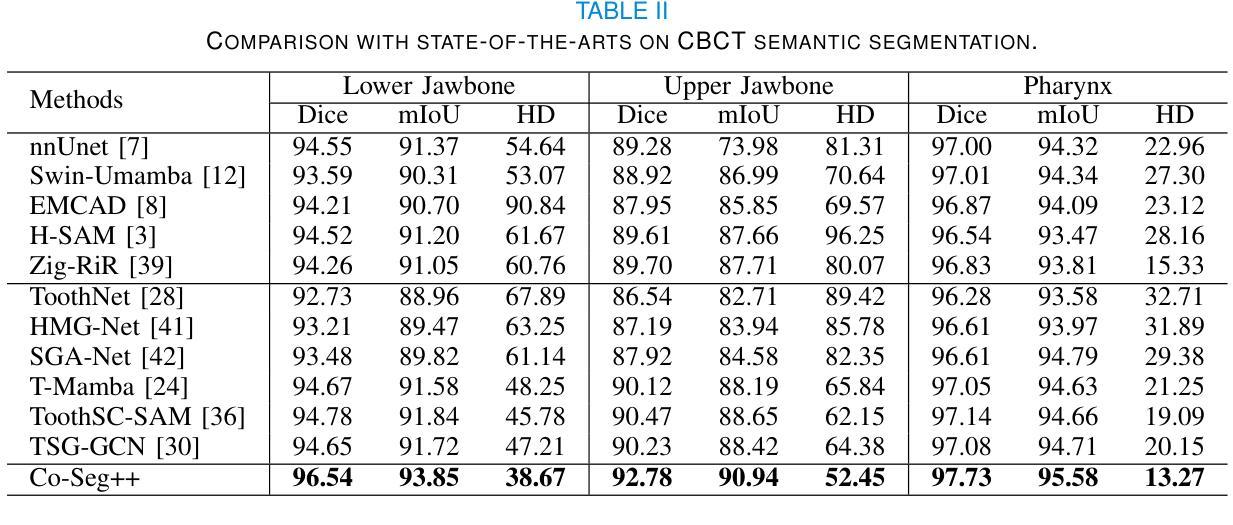
Medical image analysis is critical yet challenged by the need of jointly segmenting organs or tissues, and numerous instances for anatomical structures and tumor microenvironment analysis. Existing studies typically formulated different segmentation tasks in isolation, which overlooks the fundamental interdependencies between these tasks, leading to suboptimal segmentation performance and insufficient medical image understanding. To address this issue, we propose a Co-Seg++ framework for versatile medical segmentation. Specifically, we introduce a novel co-segmentation paradigm, allowing semantic and instance segmentation tasks to mutually enhance each other. We first devise a spatio-temporal prompt encoder (STP-Encoder) to capture long-range spatial and temporal relationships between segmentation regions and image embeddings as prior spatial constraints. Moreover, we devise a multi-task collaborative decoder (MTC-Decoder) that leverages cross-guidance to strengthen the contextual consistency of both tasks, jointly computing semantic and instance segmentation masks. Extensive experiments on diverse CT and histopathology datasets demonstrate that the proposed Co-Seg++ outperforms state-of-the-arts in the semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation of dental anatomical structures, histopathology tissues, and nuclei instances. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/Co-Seg-Plus.
医学图像分析非常重要,但面临着需要联合分割器官或组织以及多个解剖结构和肿瘤微环境分析的实例的挑战。现有研究通常孤立地制定不同的分割任务,这忽略了这些任务之间的基本相互依赖性,导致分割性能不佳和医学图像理解不足。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个用于通用医学分割的Co-Seg++框架。具体来说,我们引入了一种新的协同分割范式,允许语义分割和实例分割任务相互增强。我们首先设计了一种时空提示编码器(STP-Encoder),以捕获分割区域和图像嵌入之间的远程空间和时间关系,作为先验空间约束。此外,我们还设计了一种多任务协作解码器(MTC-Decoder),它利用交叉指导来加强两个任务上下文的一致性,联合计算语义和实例分割掩膜。在多种CT和病理数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的Co-Seg++在牙科解剖结构、病理组织和细胞核实例的语义、实例和全景分割方面优于最新技术。源代码可在https://github.com/xq141839/Co-Seg-Plus上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
医学图像分析面临器官或组织联合分割以及解剖结构、肿瘤微环境分析的多个实例需求。现有研究通常孤立地制定不同的分割任务,忽略了这些任务之间的根本相互依赖性,导致分割性能不佳和医学图像理解不足。为解决这一问题,我们提出Co-Seg++框架进行通用医学分割,引入一种新的协同分割范式,使语义和实例分割任务能够相互促进。采用时空提示编码器(STP-Encoder)捕捉分割区域和图像嵌入之间的远程空间和时间关系,作为先验空间约束。同时,我们设计了多任务协作解码器(MTC-Decoder),利用跨指导增强两个任务上下文一致性,联合计算语义和实例分割掩膜。在多种CT和病理数据集上的实验表明,Co-Seg++在牙齿解剖结构、病理组织以及细胞核实例的语义、实例和全景分割方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析需要同时处理器官或组织的联合分割以及多个实例分割任务。
- 现有研究孤立处理不同分割任务,导致性能不足和医学图像理解受限。
- 提出Co-Seg++框架,通过引入协同分割范式解决这一问题。
- STP-Encoder用于捕捉分割区域与图像嵌入之间的远程空间和时间关系。
- MTC-Decoder利用跨指导增强语义和实例分割任务的上下文一致性。
- Co-Seg++在多种医学图像数据集上表现优越,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
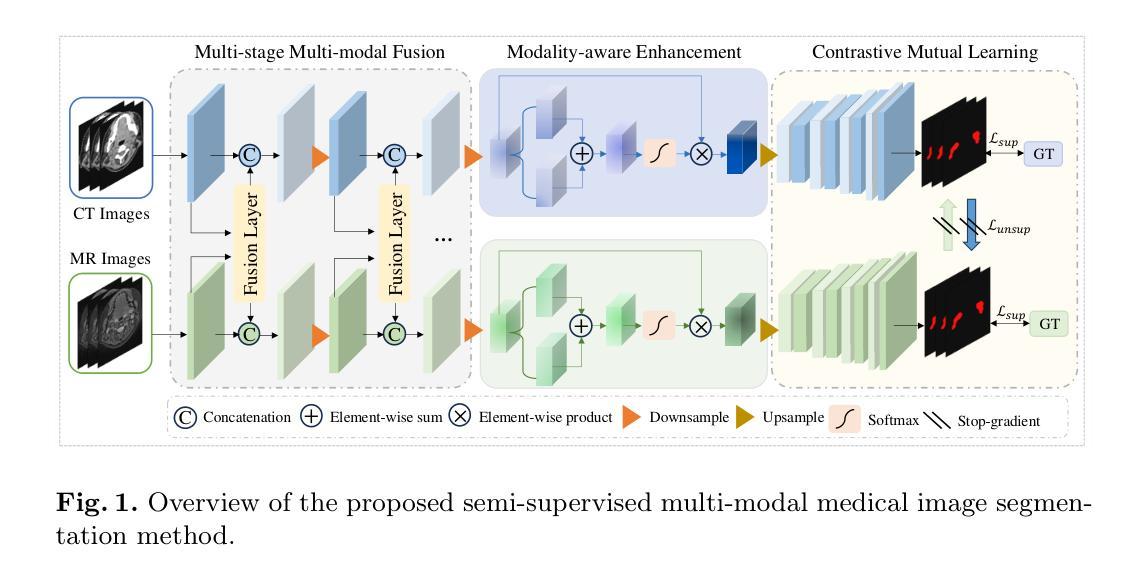
Semi-Supervised Multi-Modal Medical Image Segmentation for Complex Situations
Authors:Dongdong Meng, Sheng Li, Hao Wu, Guoping Wang, Xueqing Yan
Semi-supervised learning addresses the issue of limited annotations in medical images effectively, but its performance is often inadequate for complex backgrounds and challenging tasks. Multi-modal fusion methods can significantly improve the accuracy of medical image segmentation by providing complementary information. However, they face challenges in achieving significant improvements under semi-supervised conditions due to the challenge of effectively leveraging unlabeled data. There is a significant need to create an effective and reliable multi-modal learning strategy for leveraging unlabeled data in semi-supervised segmentation. To address these issues, we propose a novel semi-supervised multi-modal medical image segmentation approach, which leverages complementary multi-modal information to enhance performance with limited labeled data. Our approach employs a multi-stage multi-modal fusion and enhancement strategy to fully utilize complementary multi-modal information, while reducing feature discrepancies and enhancing feature sharing and alignment. Furthermore, we effectively introduce contrastive mutual learning to constrain prediction consistency across modalities, thereby facilitating the robustness of segmentation results in semi-supervised tasks. Experimental results on two multi-modal datasets demonstrate the superior performance and robustness of the proposed framework, establishing its valuable potential for solving medical image segmentation tasks in complex scenarios.
半监督学习有效地解决了医学图像标注数据有限的问题,但在复杂背景和困难任务下,其性能往往不足。多模态融合方法可以通过提供互补信息来显著提高医学图像分割的准确性。然而,由于有效利用无标签数据的挑战,它们在半监督条件下实现显著改进面临困难。因此,迫切需要一个有效可靠的多模态学习策略,以在半监督分割中利用无标签数据。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型半监督多模态医学图像分割方法,该方法利用互补的多模态信息,在有限的标记数据下提高性能。我们的方法采用多阶段多模态融合和增强策略,以充分利用互补的多模态信息,同时减少特征差异,增强特征共享和对齐。此外,我们有效地引入了对比互助学习,以约束跨模态的预测一致性,从而促进半监督任务中分割结果的稳健性。在两个多模态数据集上的实验结果证明了所提框架的优越性能和稳健性,为复杂场景下的医学图像分割任务提供了有价值的潜力解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学图像半监督学习中存在标注数据有限的问题,背景和任务复杂时性能可能不足。多模态融合方法通过提供互补信息提高了医学图像分割的准确性。但在半监督条件下利用未标注数据仍存在挑战。本文提出一种半监督多模态医学图像分割方法,通过融合多模态信息提高性能,采用多阶段多模态融合策略,减少特征差异,增强特征共享和对齐。同时引入对比互学习,约束模态间预测一致性,提高半监督任务分割结果的鲁棒性。实验结果表明,该方法在复杂场景下表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习在医学图像中解决了标注数据有限的问题,但在复杂背景和任务下性能可能不足。
- 多模态融合方法能提供互补信息,提高医学图像分割的准确性。
- 半监督条件下利用未标注数据存在挑战。
- 提出一种半监督多模态医学图像分割方法,融合多模态信息提高性能。
- 采用多阶段多模态融合策略,减少特征差异,增强特征共享和对齐。
- 引入对比互学习,约束模态间预测一致性。
点此查看论文截图

Frequently Used References For Atomic Data In X-ray Spectroscopy
Authors:N. Hell, G. V. Brown, M. E. Eckart, A. J. Fairchild, C. A. Kilbourne, M. A. Leutenegger, F. S. Porter, M. C. Witthoeft
Accurate atomic physics reference data are a crucial requirement for analysis and interpretation of observed spectra, even more so for observations with high spectral resolution. This document provides a curated list of atomic physics references frequently used for plasma diagnostics in X-ray spectroscopy, outside of comprehensive plasma models that typically come with their own underlying atomic databases. The list includes references to physical constants, laboratory benchmarks, transition energies, position and line shapes of neutral fluorescence lines, radiative branching ratios, and commonly used notation for prominent transitions. Quick-look tables for transition energies in H-, He-, and Li-like ions and line positions and shapes for fluorescence lines in neutrals. The main focus is on K-shell transitions. For the H- and He-like tables, we cite state-of-the art calculations that we consider currently the best available reference energies, which are considered high accuracy and thus typically used for energy scale calibration in laboratory measurements. Omissions in these tables are due to the lack of availability in the chosen references, and are not a statement about the relevance of these lines. Due to their complex and highly source-dependent line shape, the atomic data for neutrals is of lower accuracy than that for the highly charged ions, and the best reference data for these line shapes typically consist of empirical models derived from very high-resolution laboratory measurements. The table for neutrals provided here is consistent with the reference used for the energy gain scale calibration of XRISM/Resolve. This document is meant to serve as a resource to help find relevant references and conveniently formatted overview tables. When making use of the information found in these papers, credit should be given to their original authors by citing the appropriate references.
准确的原子物理学参考数据对于分析和解释观察到的光谱至关重要,对于高光谱分辨率的观察更是如此。本文提供了一份经过精心挑选的原子物理学参考文献列表,这些文献通常用于X射线光谱中的等离子体诊断,并且不包括通常带有自己基础原子数据库的全面等离子体模型。列表包括对物理常数、实验室基准、跃迁能、中性荧光线的位置和线形、辐射分支比以及突出跃迁的常用符号的引用。针对H-、He-和Li-类离子的跃迁能以及中性荧光线的线位置和线形的快速查看表,主要关注K层跃迁。对于H-和He-类表格,我们引用了当前认为的最佳可用参考能量值,这些值具有高精度,通常用于实验室测量的能量标度校准。这些表格中的遗漏是由于所选参考文献中缺少相关信息,并不代表这些线的不重要性。由于中性原子数据的线型复杂且高度依赖于源,其精度低于高度带电离子的精度,而线型最佳的参考数据通常由来自超高分辨率实验室测量的经验模型构成。此处提供的中性表格与XRISM/Resolve的能量增益标度校准所参考的文献一致。本文旨在作为帮助查找相关参考文献和方便格式化的概述表格的资源。在使用这些论文中找到的信息时,应通过引用适当的参考文献向原始作者致谢。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 5 tables
Summary
此文本提供了一系列针对X射线光谱中离子和中性原子物理参数的参考数据列表,包括物理常数、实验室基准值、过渡能量等。数据主要关注K层跃迁,旨在为高能谱分析提供准确参考数据。
Key Takeaways
- 文本提供了一系列针对X射线光谱的离子和中性原子的原子物理参考数据。
- 这些数据对于高光谱分辨率的观察至关重要,并包括物理常数、实验室基准值、过渡能量等内容。
- 列表专注于K层跃迁。
- 数据来源于最新的高精度计算,被认为是目前最佳可用的参考能量。
- 中性原子的数据准确性较低,主要因为它们的线形状复杂且高度依赖于源。
- 提供的数据表与XRISM/Resolve的能量增益尺度校准参考一致。
点此查看论文截图

Client Selection Strategies for Federated Semantic Communications in Heterogeneous IoT Networks
Authors:Samer Lahoud, Kinda Khawam
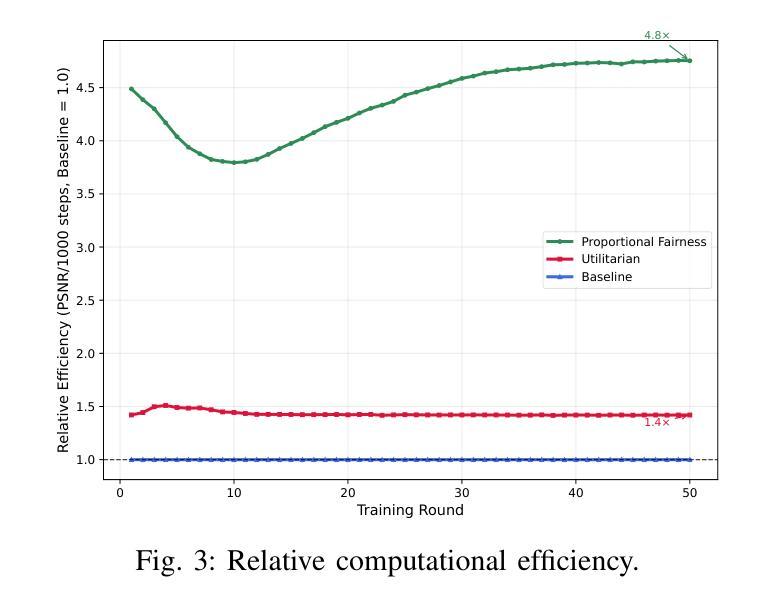
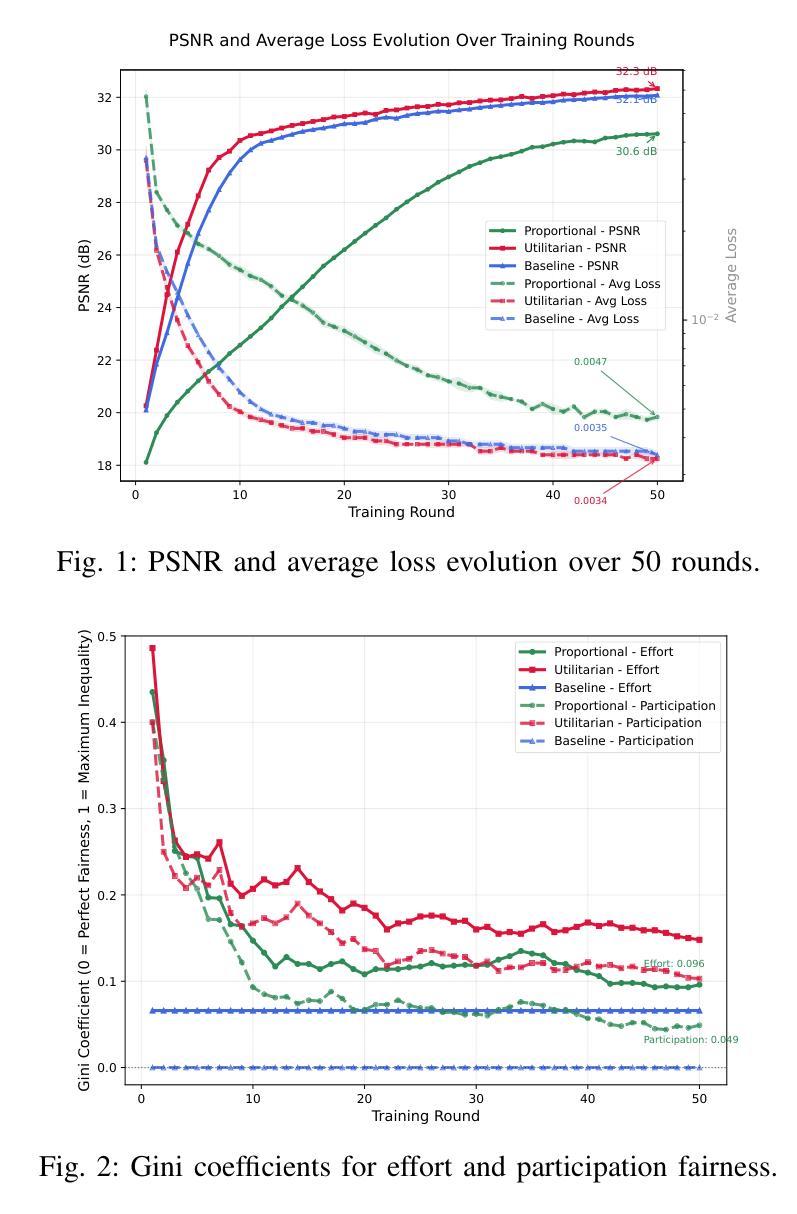
The exponential growth of IoT devices presents critical challenges in bandwidth-constrained wireless networks, particularly regarding efficient data transmission and privacy preservation. This paper presents a novel federated semantic communication (SC) framework that enables collaborative training of bandwidth-efficient models for image reconstruction across heterogeneous IoT devices. By leveraging SC principles to transmit only semantic features, our approach dramatically reduces communication overhead while preserving reconstruction quality. We address the fundamental challenge of client selection in federated learning environments where devices exhibit significant disparities in dataset sizes and data distributions. Our framework implements three distinct client selection strategies that explore different trade-offs between system performance and fairness in resource allocation. The system employs an end-to-end SC architecture with semantic bottlenecks, coupled with a loss-based aggregation mechanism that naturally adapts to client heterogeneity. Experimental evaluation on image data demonstrates that while Utilitarian selection achieves the highest reconstruction quality, Proportional Fairness maintains competitive performance while significantly reducing participation inequality and improving computational efficiency. These results establish that federated SC can successfully balance reconstruction quality, resource efficiency, and fairness in heterogeneous IoT deployments, paving the way for sustainable and privacy-preserving edge intelligence applications.
物联网设备的指数级增长给带宽受限的无线网络带来了重大挑战,特别是在高效数据传输和隐私保护方面。本文针对这一背景,提出了一种新型的联邦语义通信(SC)框架,该框架能够在异构物联网设备之间实现带宽高效模型的协同训练,用于图像重建。通过利用SC原理仅传输语义特征,我们的方法可以在保持重建质量的同时,大幅降低通信开销。我们解决了联邦学习环境中客户选择的根本挑战,在此环境中,设备在数据集大小和数据分布方面存在显著差异。我们的框架实现了三种不同的客户选择策略,在系统性能和资源分配的公平性之间进行不同的权衡。该系统采用了一种端到端的SC架构,带有语义瓶颈,并结合了一种基于损失的聚合机制,该机制能够自然地适应客户端的异构性。在图像数据上的实验评估表明,尽管效用选择达到了最高的重建质量,但比例公平策略在保持竞争力的情况下显著减少了参与不平等并提高了计算效率。这些结果证明了联邦语义通信能够在异构物联网部署中成功平衡重建质量、资源效率和公平性,为可持续和隐私保护的边缘智能应用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
物联网设备的指数级增长给带宽受限的无线网络带来了重大挑战,特别是在数据高效传输和隐私保护方面。本文提出了一种新型的联邦语义通信(SC)框架,该框架能够在异构物联网设备上实现带宽高效模型的协同训练,用于图像重建。通过利用SC原理只传输语义特征,该方法在保持重建质量的同时,大幅降低了通信开销。本文还解决了联邦学习环境中客户选择的根本挑战,该环境中的设备在数据集大小和数据分布上存在显著差异。该框架实现了三种不同的客户选择策略,在系统性能和资源分配的公平性之间进行不同的权衡。系统采用端到端的SC架构,配合基于损失的聚合机制,自然适应客户异质性。在图像数据上的实验评估表明,效用选择策略实现了最高的重建质量,而比例公平性则在保持竞争性能的同时,显著减少了参与不平等并提高了计算效率。这些结果表明,联邦SC能够成功平衡异构物联网部署中的重建质量、资源效率和公平性,为可持续和隐私保护的边缘智能应用铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 物联网设备的增长给带宽受限的无线网络带来了挑战,需要解决高效数据传输和隐私保护的问题。
- 提出了一种新型的联邦语义通信(SC)框架,该框架能够在异构物联网设备上实现带宽高效的模型协同训练,用于图像重建。
- 利用SC原理只传输语义特征,降低通信开销的同时保持重建质量。
- 解决了联邦学习环境中客户选择的挑战,该环境中的设备在数据集大小和分布上存在显著差异。
- 实施了三种客户选择策略,在系统性能和资源分配的公平性之间进行权衡。
- 系统采用端到端的SC架构和基于损失的聚合机制,以适应客户异质性。
点此查看论文截图

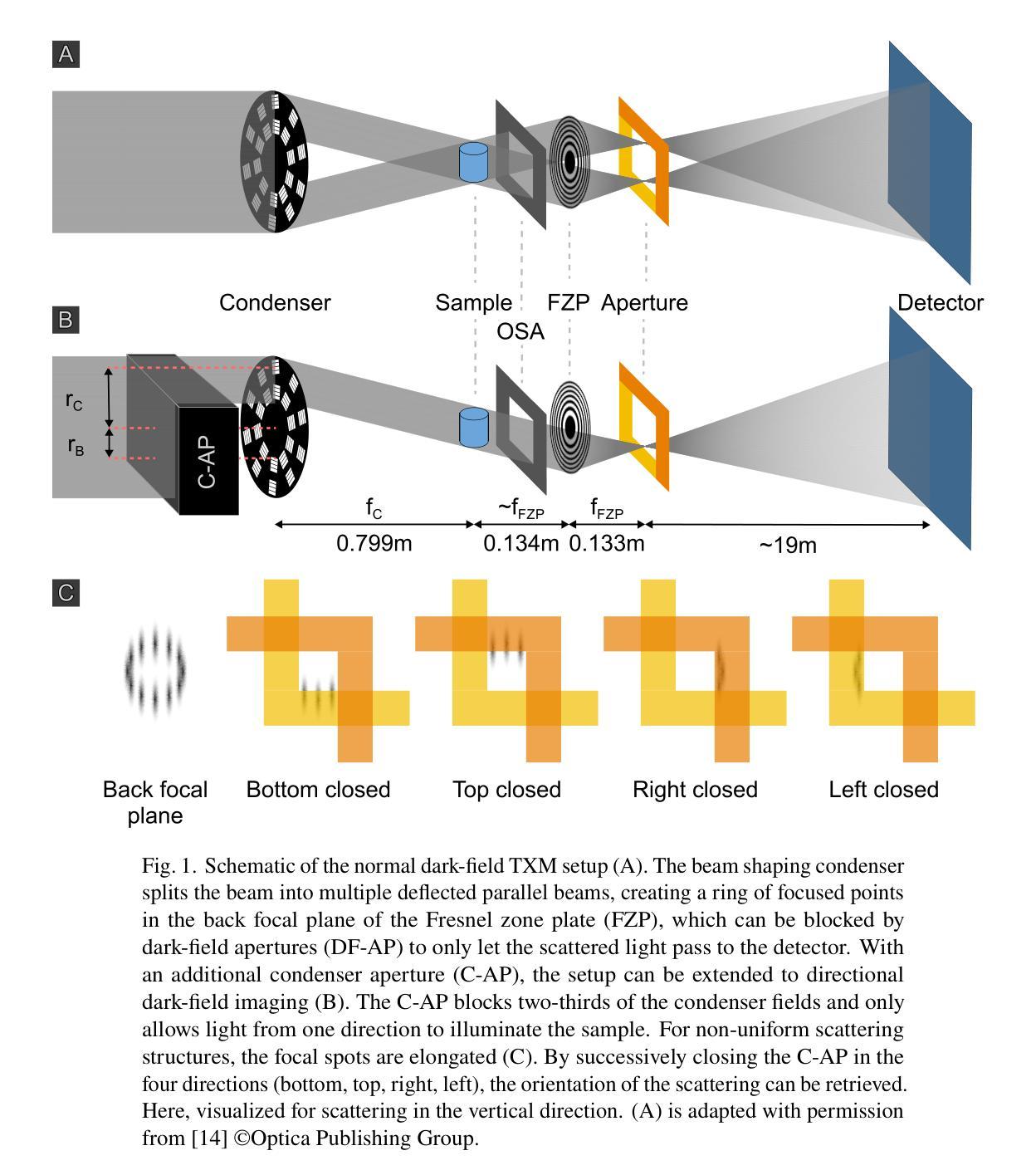
Directional Dark Field for Nanoscale Full-Field Transmission X-Ray Microscopy
Authors:Sami Wirtensohn, Silja Flenner, Dominik John, Peng Qi, Christian David, Julia Herzen, Kritika Singh, Gudrun Lotze, Imke Greving
Dark-field X-ray imaging offers unique insights into material structures by visualizing X-ray scattering rather than attenuation, revealing features invisible to conventional imaging techniques. While established approaches like grating-based and speckle-based imaging have demonstrated the utility of dark-field contrast in medical diagnostics and materials science, these methods have been primarily limited to laboratory and micro-CT systems. Building on the recent demonstration of dark-field imaging at the nanoscale using transmission X-ray microscopy, we extend this technique to retrieve directional small-angle scattering information. By analyzing both a test object and human primary tooth enamel, we show that our transmission X-ray microscopy setup can successfully retrieve directional scattering information with minimal modifications of existing systems. This advancement expands the capabilities of nanoscale dark-field imaging, offering new opportunities for investigating structural properties in a wide range of scientific fields.
暗场X射线成像通过可视化X射线的散射而非衰减,为材料结构提供了独特的洞察视角,揭示出传统成像技术无法观察到的特征。虽然基于光栅和基于斑点成像等现有方法已经证明了暗场对比在医学诊断和材料科学中的实用性,但这些方法主要局限于实验室和显微CT系统。基于最近在透射X射线显微镜下纳米尺度暗场成像的展示,我们将该技术扩展到获取定向小角度散射信息。通过对测试对象和人体乳牙釉质的分析,我们证明我们的透射X射线显微镜装置能够成功获取定向散射信息,且只需对现有的系统进行最小的改造。这一进展扩大了纳米尺度暗场成像的功能,为探索一系列科学领域的结构特性提供了新的机会。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
暗场X射线成像通过可视化X射线散射而非衰减,为材料结构提供了独特见解,暗场成像技术已在医学诊断和材料科学中展现出实用价值,但主要局限于实验室和显微CT系统。近期,基于透射X射线显微镜的纳米尺度暗场成像技术展示,可获取方向性小角度散射信息。通过对测试对象和人类乳牙釉质的实验分析,证明改造现有系统后能够成功获取方向性散射信息,这一进展扩大了纳米尺度暗场成像的能力,为探究广泛科学领域的结构特性提供了新的机遇。
Key Takeaways
- 暗场X射线成像技术可视化X射线散射,为材料结构提供独特见解。
- 传统成像技术无法观察到的特性可通过暗场成像揭示。
- 暗场成像技术在医学诊断和材料科学中具备实用价值。
- 该技术主要局限于实验室和显微CT系统。
- 通过透射X射线显微镜实现的纳米尺度暗场成像技术能够获取方向性小角度散射信息。
- 通过测试对象和人类乳牙釉质的实验分析证明了技术的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

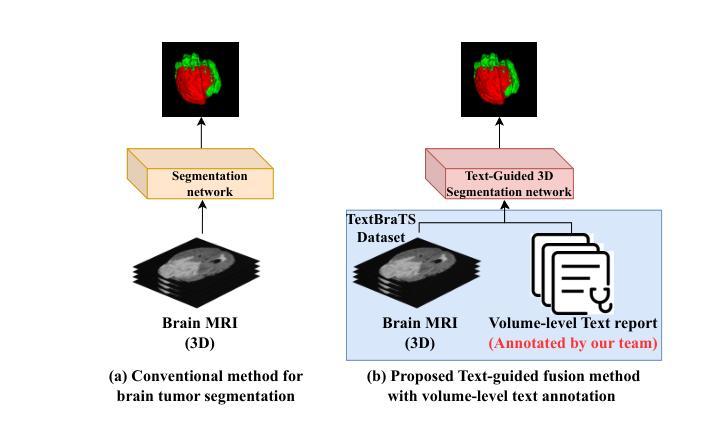
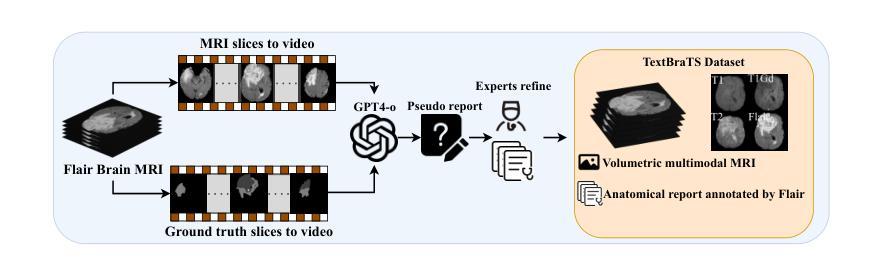
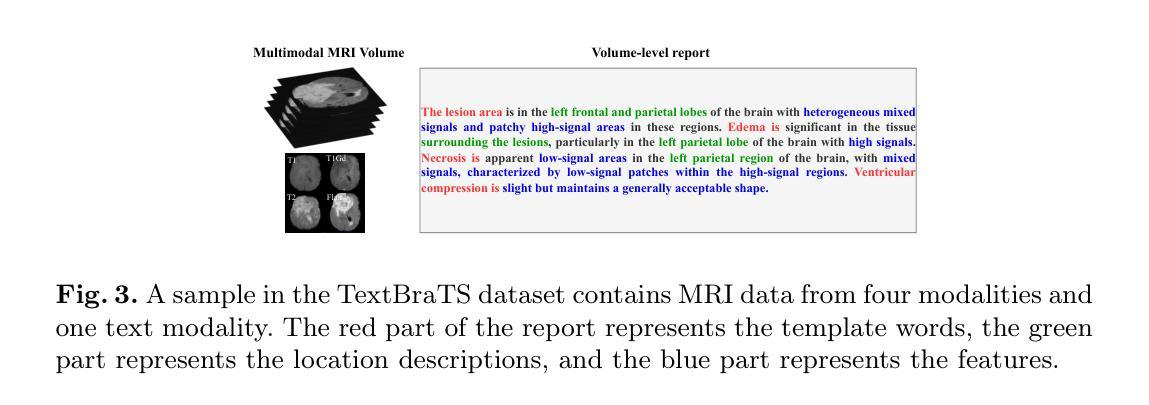
TextBraTS: Text-Guided Volumetric Brain Tumor Segmentation with Innovative Dataset Development and Fusion Module Exploration
Authors:Xiaoyu Shi, Rahul Kumar Jain, Yinhao Li, Ruibo Hou, Jingliang Cheng, Jie Bai, Guohua Zhao, Lanfen Lin, Rui Xu, Yen-wei Chen
Deep learning has demonstrated remarkable success in medical image segmentation and computer-aided diagnosis. In particular, numerous advanced methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance in brain tumor segmentation from MRI scans. While recent studies in other medical imaging domains have revealed that integrating textual reports with visual data can enhance segmentation accuracy, the field of brain tumor analysis lacks a comprehensive dataset that combines radiological images with corresponding textual annotations. This limitation has hindered the exploration of multimodal approaches that leverage both imaging and textual data. To bridge this critical gap, we introduce the TextBraTS dataset, the first publicly available volume-level multimodal dataset that contains paired MRI volumes and rich textual annotations, derived from the widely adopted BraTS2020 benchmark. Building upon this novel dataset, we propose a novel baseline framework and sequential cross-attention method for text-guided volumetric medical image segmentation. Through extensive experiments with various text-image fusion strategies and templated text formulations, our approach demonstrates significant improvements in brain tumor segmentation accuracy, offering valuable insights into effective multimodal integration techniques. Our dataset, implementation code, and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/Jupitern52/TextBraTS.
深度学习在医学图像分割和计算机辅助诊断方面取得了显著的成功。特别是,许多先进的方法在MRI扫描的脑肿瘤分割方面达到了最先进的技术性能。虽然最近在其他医学成像领域的研究表明,将文本报告与视觉数据相结合可以提高分割精度,但脑肿瘤分析领域缺乏一个综合数据集,该数据集结合了放射图像和相应的文本注释。这一局限性阻碍了利用成像和文本数据的多模式方法的探索。为了弥补这一关键差距,我们推出了TextBraTS数据集,这是第一个公开可用的体积级多模式数据集,包含配对的MRI体积和丰富的文本注释,这些注释来源于广泛采用的BraTS2020基准测试。基于这个新颖的数据集,我们提出了一个基线框架和顺序交叉注意方法,用于文本引导的体积医学图像分割。通过采用各种文本图像融合策略和模板文本公式的大量实验,我们的方法在脑肿瘤分割精度方面取得了显著的改进,为有效的多模式集成技术提供了有价值的见解。我们的数据集、实现代码和预训练模型可在[https://github.com/Jupitern52/TextBraTS公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像深度学习在医学图像分割和计算机辅助诊断方面取得了显著成果。针对脑部肿瘤分割的MRI扫描,先进的方法已达到最新性能水平。尽管其他医学影像领域的研究表明,将文本报告与视觉数据相结合可以提高分割精度,但脑肿瘤分析领域缺乏一个结合放射图像和相应文本注释的综合数据集。为弥补这一关键差距,我们推出了TextBraTS数据集,这是第一个公开可用的体积级多模式数据集,包含配对的MRI体积和丰富的文本注释,来源于广泛采用的BraTS2020基准测试。基于此新型数据集,我们提出了一种基线框架和顺序交叉注意方法,用于文本引导的体积医学图像分割。通过采用各种文本图像融合策略和模板文本制定,我们的方法在脑肿瘤分割精度方面取得了显著提高,为有效的多模式集成技术提供了有价值的见解。我们的数据集、实施代码和预先训练的模型可在公开渠道访问:https://github.com/Jupitern52/TextBraTS。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割和计算机辅助诊断中表现卓越,特别是在脑部肿瘤MRI扫描分割方面达到最新水平。
- 尽管结合文本报告和视觉数据在其他医学影像领域已提高分割精度,但脑肿瘤分析领域缺乏综合数据集。
- TextBraTS数据集是首个公开可用的体积级多模式数据集,包含MRI体积和丰富的文本注释。
- 提出了一种新的基线框架和顺序交叉注意方法,利用TextBraTS数据集进行文本引导的医学图像体积分割。
- 通过不同的文本-图像融合策略和模板文本制定进行广泛实验,显著提高脑肿瘤分割精度。
点此查看论文截图

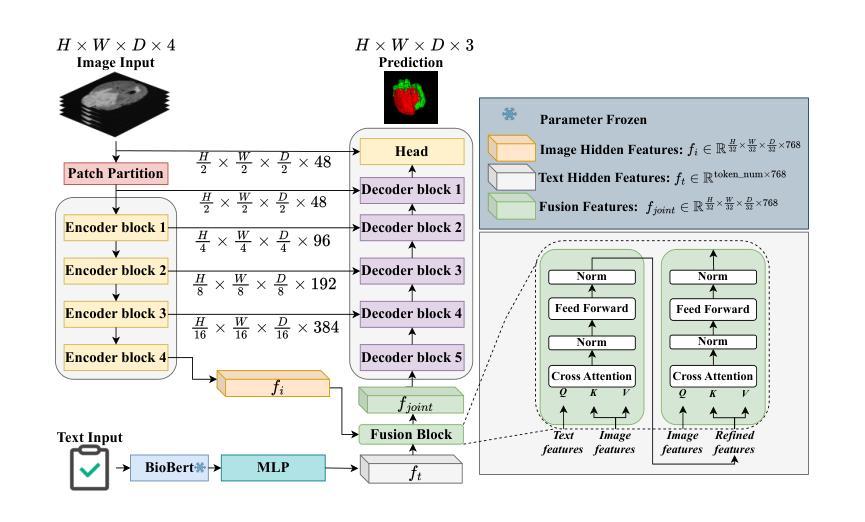
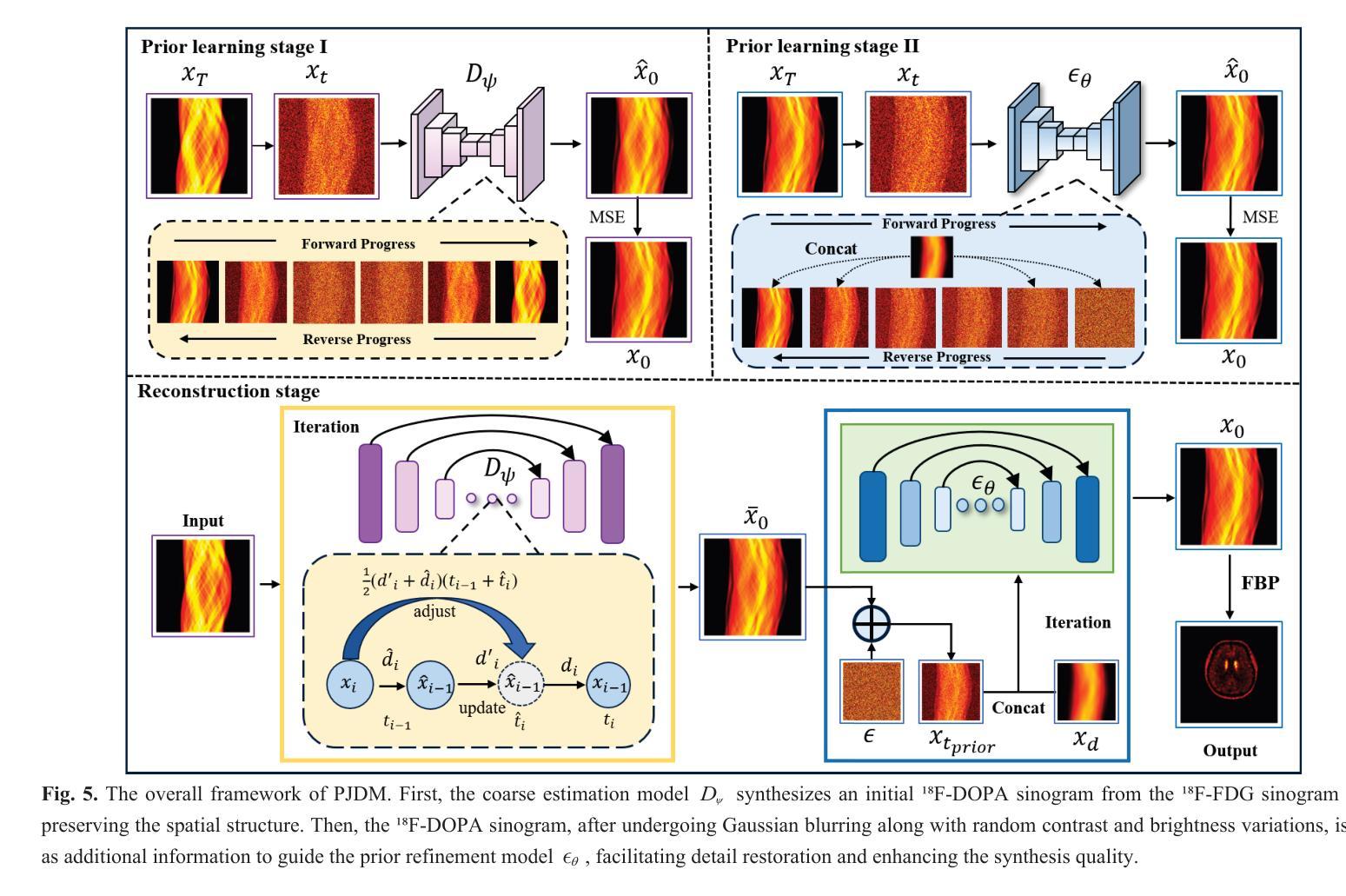
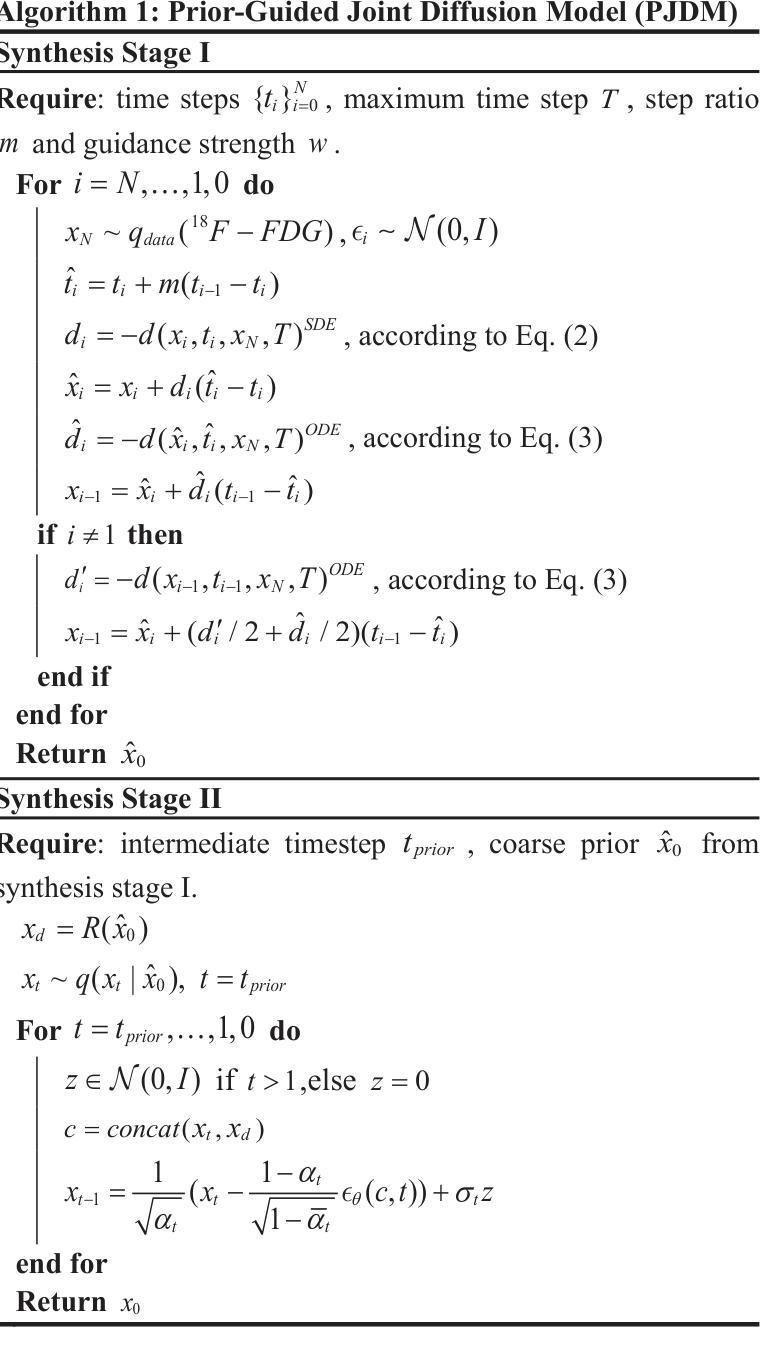
A Prior-Guided Joint Diffusion Model in Projection Domain for PET Tracer Conversion
Authors:Fang Chen, Weifeng Zhang, Xingyu Ai, BingXuan Li, An Li, Qiegen Liu
Positron emission tomography (PET) is widely used to assess metabolic activity, but its application is limited by the availability of radiotracers. 18F-labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) is the most commonly used tracer but shows limited effectiveness for certain tumors. In contrast, 6-18F-fluoro-3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (18F-DOPA) offers higher specificity for neuroendocrine tumors and neurological disorders. However, its complex synthesis and limitations in transportation and clinical use hinder widespread adoption. During PET imaging, the sinogram represents a form of raw data acquired by the scanner. Therefore, modeling in projection domain enables more direct utilization of the original information, potentially reducing the accumulation of errors introduced during the image reconstruction process. Inspired by these factors, this study proposes a prior-guided joint diffusion model (PJDM) for transforming 18F-FDG PET images into 18F-DOPA PET images in projection domain. Specifically, a coarse estimation model and a prior refinement model are trained independently. During inference, an initial synthetic 18F-DOPA PET sinogram is generated using a higher-order hybrid sampler. This sinogram is then degraded and serves as an additional condition to guide the iterative refinement process using learned prior. Experimental results demonstrated that PJDM effectively improved both sinogram quality and synthetic outcomes. The code is available at: https://github.com/yqx7150/PJDM.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)广泛用于评估代谢活动,但其应用受限于放射性示踪剂的可用性。18F标记的氟脱氧葡萄糖(18F-FDG)是最常用的示踪剂,但对于某些肿瘤,其效果有限。相比之下,6-18F-氟-3,4-二羟基-L-苯丙氨酸(18F-DOPA)对神经内分泌肿瘤和神经疾病具有更高的特异性。然而,其复杂的合成以及运输和临床使用的限制阻碍了其广泛应用。在PET成像中,辛图(Sinogram)是由扫描仪获取的一种原始数据形式。因此,在投影域中进行建模能够更直接地利用原始信息,可能减少在图像重建过程中引入的误差积累。受这些因素启发,本研究提出了一种先验引导联合扩散模型(PJDM),用于在投影域中将18F-FDG PET图像转换为18F-DOPA PET图像。具体而言,分别训练了粗略估计模型和先验细化模型。在推理过程中,使用高阶混合采样器生成初始合成18F-DOPA PET辛图。然后,将此辛图退化并作为附加条件,引导使用学习先验的迭代细化过程。实验结果表明,PJDM有效提高辛图质量和合成结果。相关代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/yqx7150/PJDM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于先验引导联合扩散模型(PJDM)将PET中的¹⁸F-FDG图像转化为¹⁸F-DOPA图像的技术。该技术在投影域进行建模,通过训练粗估计模型和先验优化模型,在推理阶段生成初始的¹⁸F-DOPA PET正弦图,并对其进行退化处理以指导迭代优化过程。实验结果表明,PJDM可有效提高正弦图质量和合成效果。
Key Takeaways
- PET常用于评估代谢活动,但受限于放射示踪剂的可获得性。
- ¹⁸F-FDG是最常用的示踪剂,但对某些肿瘤的效用有限。
- ¹⁸F-DOPA对神经内分泌肿瘤和神经障碍具有更高的特异性,但其合成复杂且运输和使用受限。
- 研究提出了一种基于先验引导的联合扩散模型(PJDM)来转换PET图像的技术。
- 该技术在投影域建模,直接利用原始信息,减少图像重建过程中的误差积累。
- 使用粗估计模型和先验优化模型进行训练,生成初始的¹⁸F-DOPA PET正弦图并通过迭代优化过程提高其质量。
点此查看论文截图

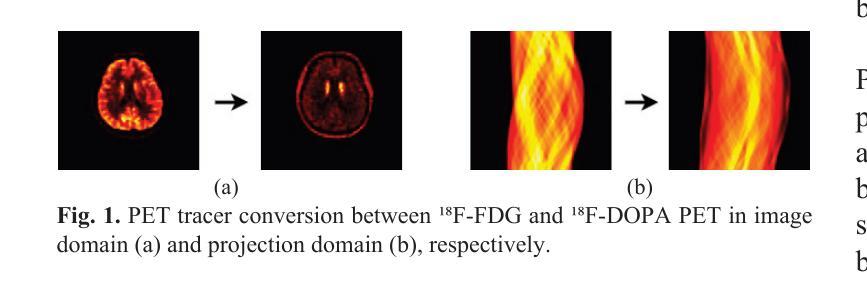
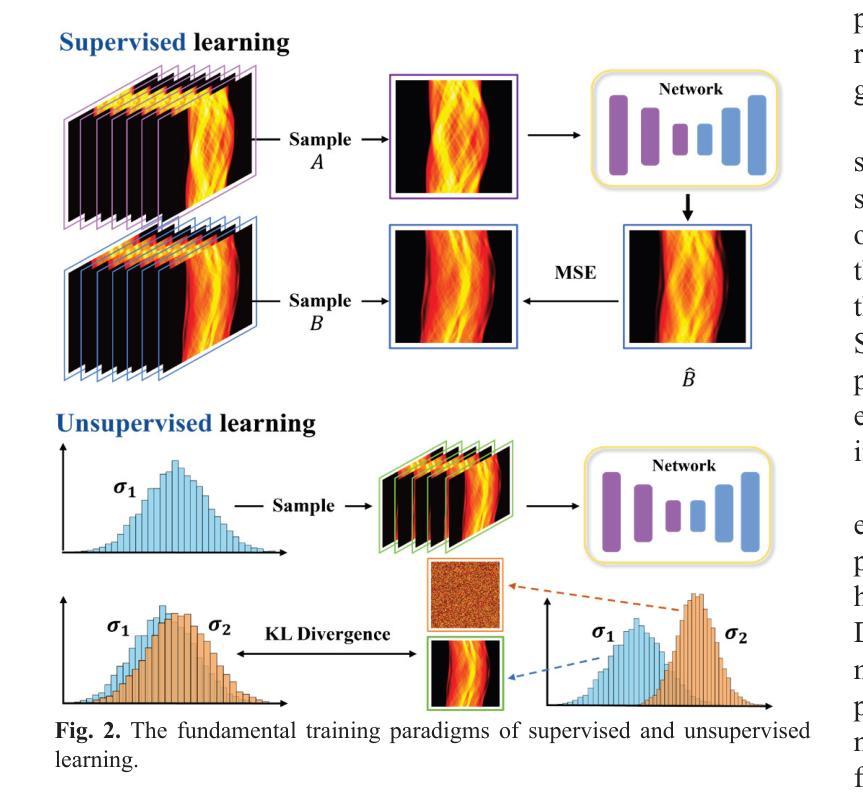
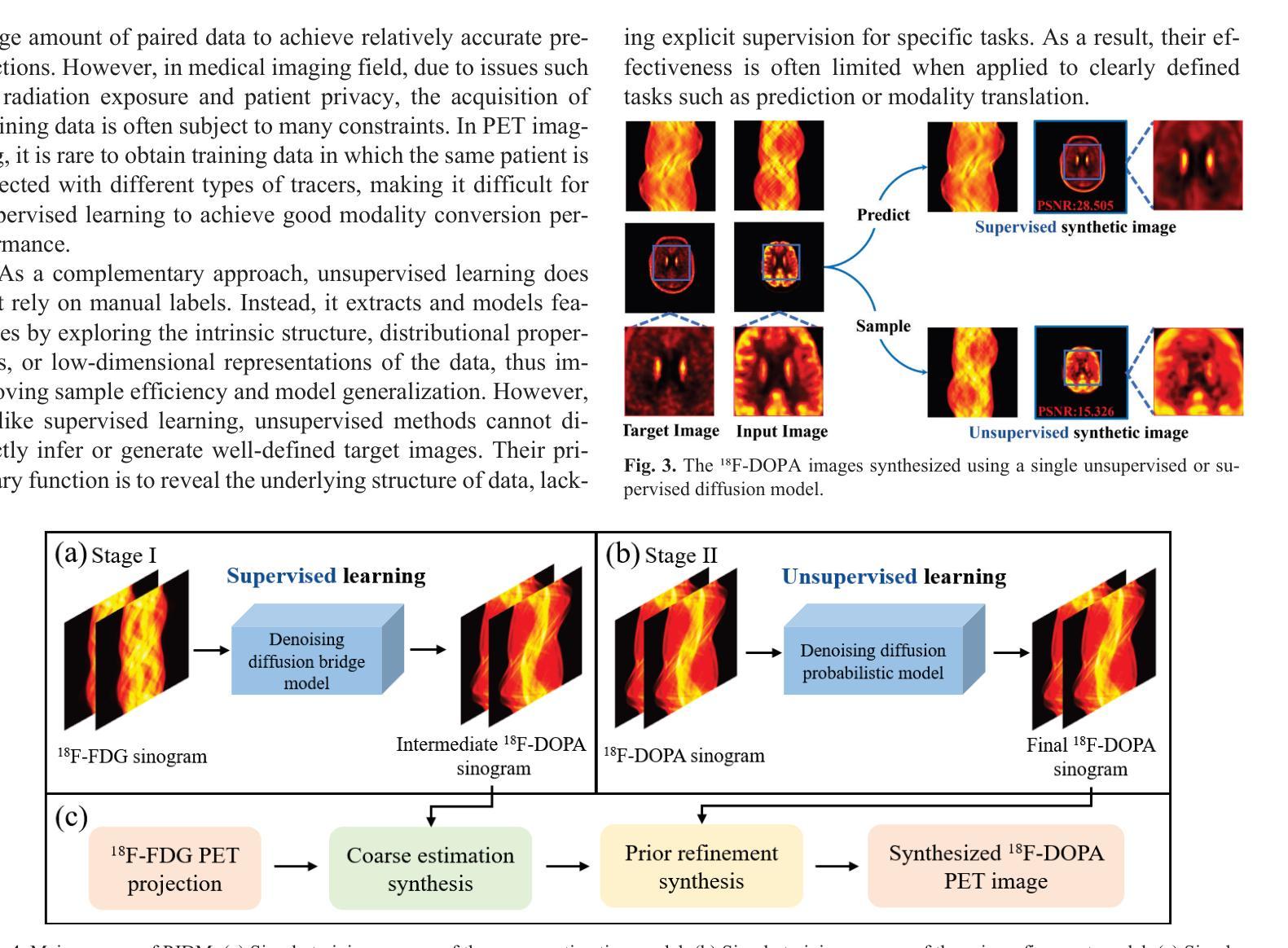
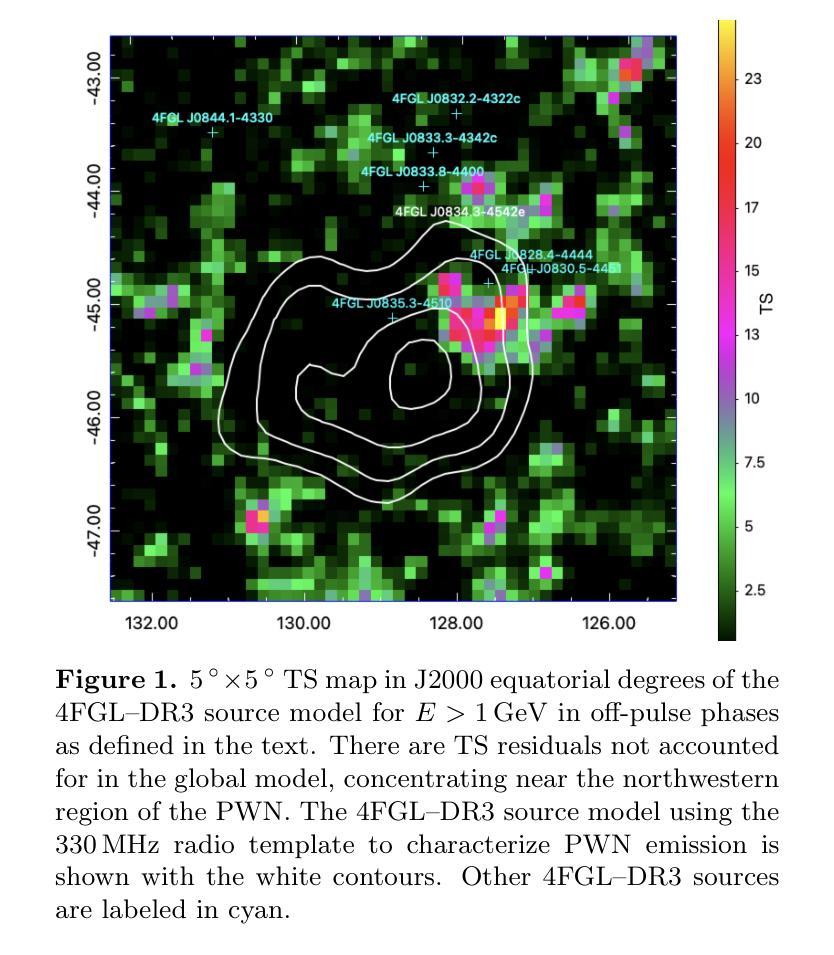
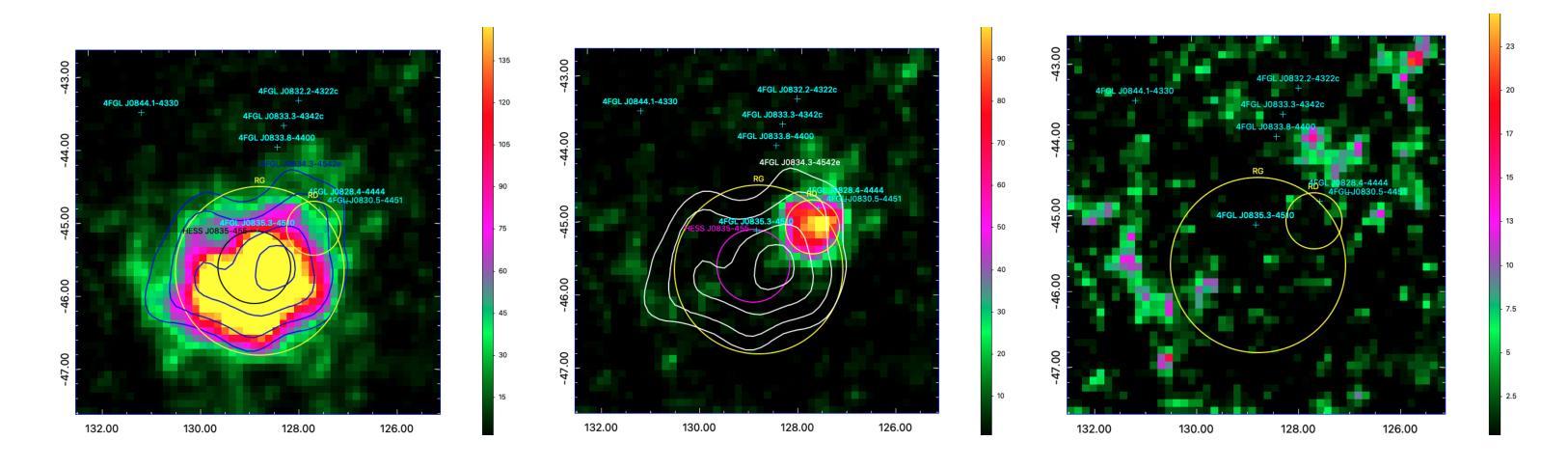
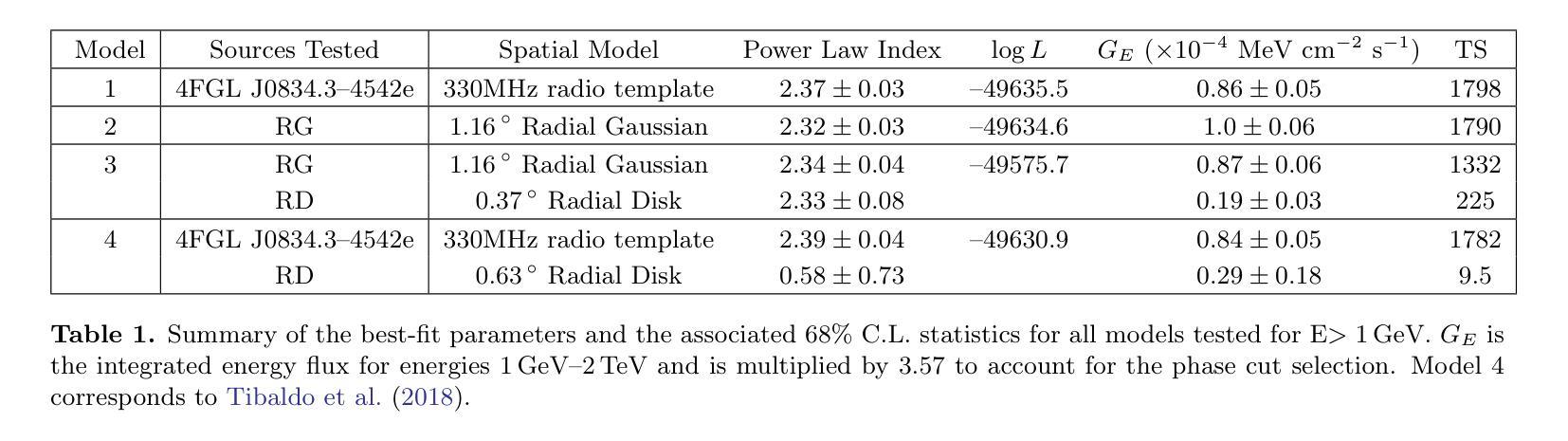
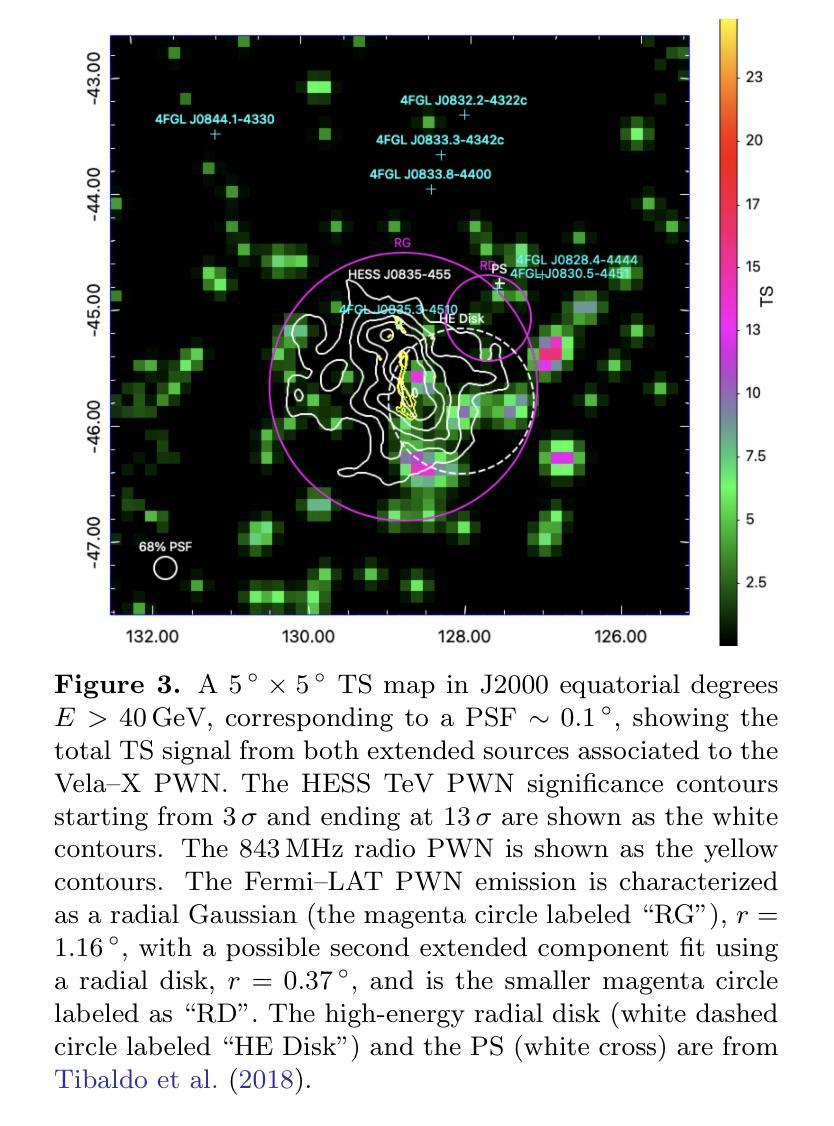
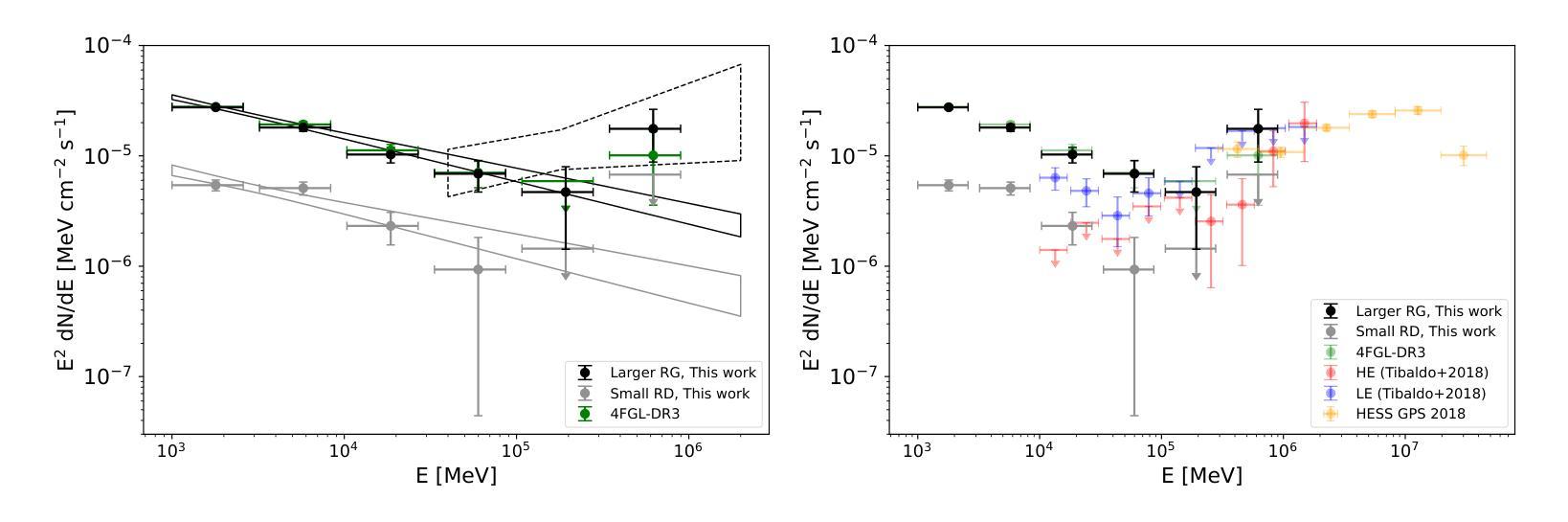
The Vela pulsar and its pulsar wind nebula Vela-X using 13 years of Fermi-LAT Observations
Authors:Alexander Lange, J. Eagle, O. Kargaltsev, Lucien Kuiper, Jeremy Hare
We present results of more than 13 years of Fermi-LAT data analysis for the Vela pulsar from 60 MeV to 100 GeV and its pulsar wind nebula (PWN), Vela-X, for E > 1 GeV in the off-pulse phases. We find the Vela-X PWN can be best characterized using two extended components: a large radial Gaussian accompanied by an off-set, compact radial disk, both with a similar spectral index, \Gamma \sim 2.3. The common spectral properties support a common PWN origin, but a supernova remnant component is plausible for the compact radial disk. With an updated Vela-X model, the phase resolved spectral properties of the Vela pulsar are explored through a phase-resolved analysis. The phase-resolved spectral properties of the pulsar are presented, such as the SED peak energy E$_p$, the width of the SED at its peak, d$_p$, and the asymptotic (low-energy) spectral index, $\Gamma_0$, are presented. The best-fit spectral models for each LAT pulse peak (Peak 1 and Peak 2) are extrapolated to UV energies and compared to archival, phase-resolved spectra at UV, X-ray, soft \gamma-ray and TeV energies. We also discuss the physical implications of our modeling and the data comparisons.
我们对Vela脉冲星和其脉冲风星云(PWN)Vela-X进行了超过13年的费米-LAT数据分析,能量范围从60MeV到100GeV,并针对非脉冲阶段的E > 1 GeV进行了讨论。我们发现Vela-X的PWN最好用两个扩展成分来描述:一个大的径向高斯分布,伴随着一个偏移的紧凑径向盘,它们的谱指数相似,Gamma约为2.3。相同的谱特性支持它们来源于同一个PWN,但对于紧凑径向盘来说,超新星遗迹成分也是可能的。通过更新的Vela-X模型,我们对Vela脉冲星的相位解析谱特性进行了探究。展示了脉冲星的相位解析谱特性,如SED峰值能量Ep、SED峰值的宽度dp、渐近(低能)谱指数Γ0等。将每个LAT脉冲峰值(Peak 1和Peak 2)的最佳拟合谱模型外推到紫外能量,并与档案中的紫外、X射线、软γ射线和TeV能量的相位解析光谱进行了比较。我们还讨论了我们的建模和数据比较的物理意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal. 24 pages, 15 figures
Summary
本文报道了对超过13年的费米LAT数据分析结果,研究了Vela脉冲星和其脉冲风星云Vela-X在60MeV至100GeV的能量范围内的表现。发现Vela-X的最佳特征是由两个扩展成分组成:一个大的径向高斯分布和一个偏移的紧凑径向圆盘,两者具有相似的光谱指数Γ≈2.3。更新的Vela-X模型被用于探索Vela脉冲星的相位解析光谱特性。本文还探讨了模型的物理含义和数据比较。
Key Takeaways
- 报道了对Vela脉冲星超过13年的费米LAT数据分析结果。
- 研究了Vela脉冲星和其脉冲风星云Vela-X在特定能量范围内的表现。
- Vela-X可以被最好地描述为两个扩展成分:一个大的径向高斯分布和一个偏移的紧凑径向圆盘。
- 这两个成分具有相似的光谱指数Γ≈2.3,支持它们来自同一PWN的起源。
- 提出了一个可能是由超新星残骸成分构成的紧凑径向圆盘。
- 通过更新的Vela-X模型,探索了Vela脉冲星的相位解析光谱特性。
点此查看论文截图

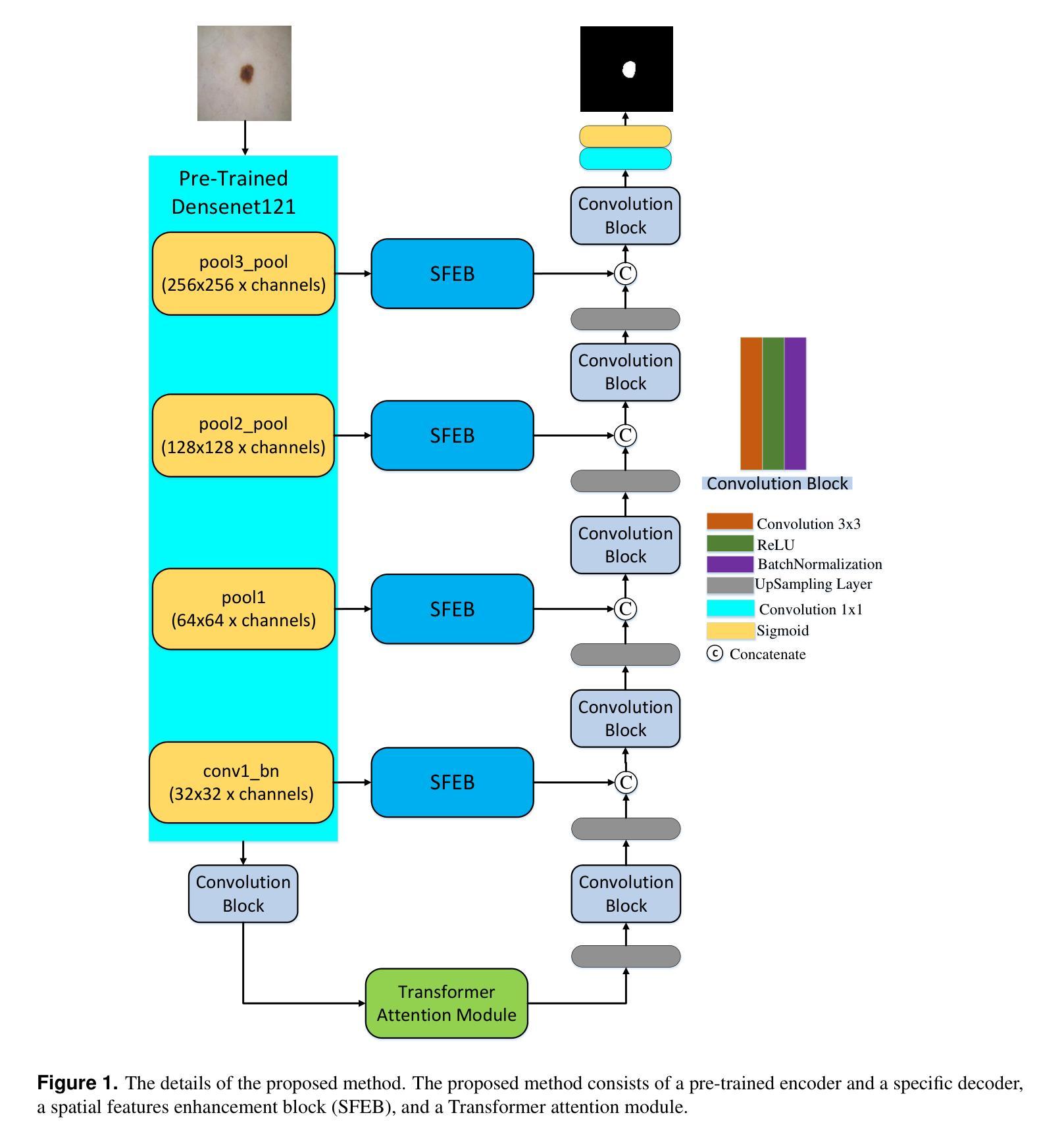
Hybrid Attention Network for Accurate Breast Tumor Segmentation in Ultrasound Images
Authors:Muhammad Azeem Aslam, Asim Naveed, Nisar Ahmed
Breast ultrasound imaging is a valuable tool for early breast cancer detection, but automated tumor segmentation is challenging due to inherent noise, variations in scale of lesions, and fuzzy boundaries. To address these challenges, we propose a novel hybrid attention-based network for lesion segmentation. Our proposed architecture integrates a pre-trained DenseNet121 in the encoder part for robust feature extraction with a multi-branch attention-enhanced decoder tailored for breast ultrasound images. The bottleneck incorporates Global Spatial Attention (GSA), Position Encoding (PE), and Scaled Dot-Product Attention (SDPA) to learn global context, spatial relationships, and relative positional features. The Spatial Feature Enhancement Block (SFEB) is embedded at skip connections to refine and enhance spatial features, enabling the network to focus more effectively on tumor regions. A hybrid loss function combining Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) and Jaccard Index loss optimizes both pixel-level accuracy and region-level overlap metrics, enhancing robustness to class imbalance and irregular tumor shapes. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches, highlighting its potential to assist radiologists in early and accurate breast cancer diagnosis.
乳腺超声成像在早期乳腺癌检测中是一种有价值的工具,但由于其固有的噪声、病灶尺度的变化和模糊的边界,自动化肿瘤分割仍然面临挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型混合注意力网络用于病灶分割。我们的提议架构将预训练的DenseNet121集成到编码器部分进行稳健的特征提取,并结合一个针对乳腺超声图像的多分支注意力增强解码器。瓶颈层结合了全局空间注意力(GSA)、位置编码(PE)和缩放点积注意力(SDPA)来学习全局上下文、空间关系和相对位置特征。空间特征增强块(SFEB)嵌入到跳跃连接中以细化和增强空间特征,使网络更有效地关注肿瘤区域。结合二元交叉熵(BCE)和Jaccard指数损失的混合损失函数优化了像素级精度和区域级重叠指标,提高了对类别不平衡和不规则肿瘤形状的鲁棒性。在公共数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,突显其在帮助放射科医生进行早期和准确的乳腺癌诊断方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对乳腺超声影像中肿瘤分割的挑战,提出一种新型混合注意力网络。该网络结合预训练的DenseNet121进行特征提取,并利用多分支注意力增强解码器处理乳腺超声图像。通过全局空间注意力、位置编码和缩放点积注意力学习全局上下文、空间关系和相对位置特征。实验证明,该方法在公共数据集上的表现优于现有方法,有助于提高乳腺癌的早期诊断准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺超声成像对早期乳腺癌检测具有价值。
- 自动化肿瘤分割在乳腺超声图像中面临挑战,如噪声、病变规模变化和模糊边界。
- 提出一种新型混合注意力网络,结合预训练的DenseNet121进行特征提取。
- 网络利用多分支注意力增强解码器处理乳腺超声图像。
- 通过全局空间注意力、位置编码和缩放点积注意力提高网络性能。
- 网络的实验表现优于现有方法,在公共数据集上取得良好效果。
点此查看论文截图

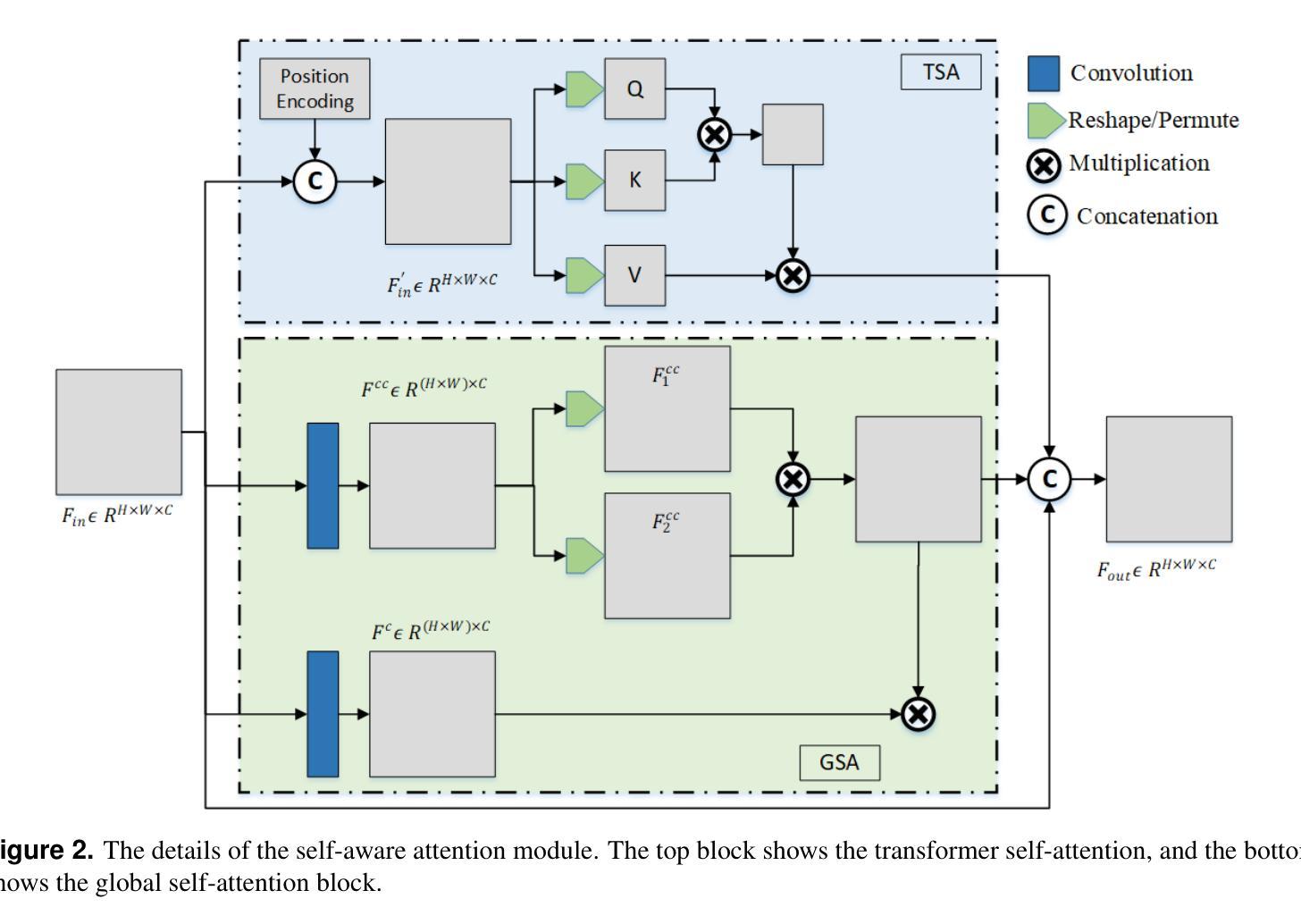
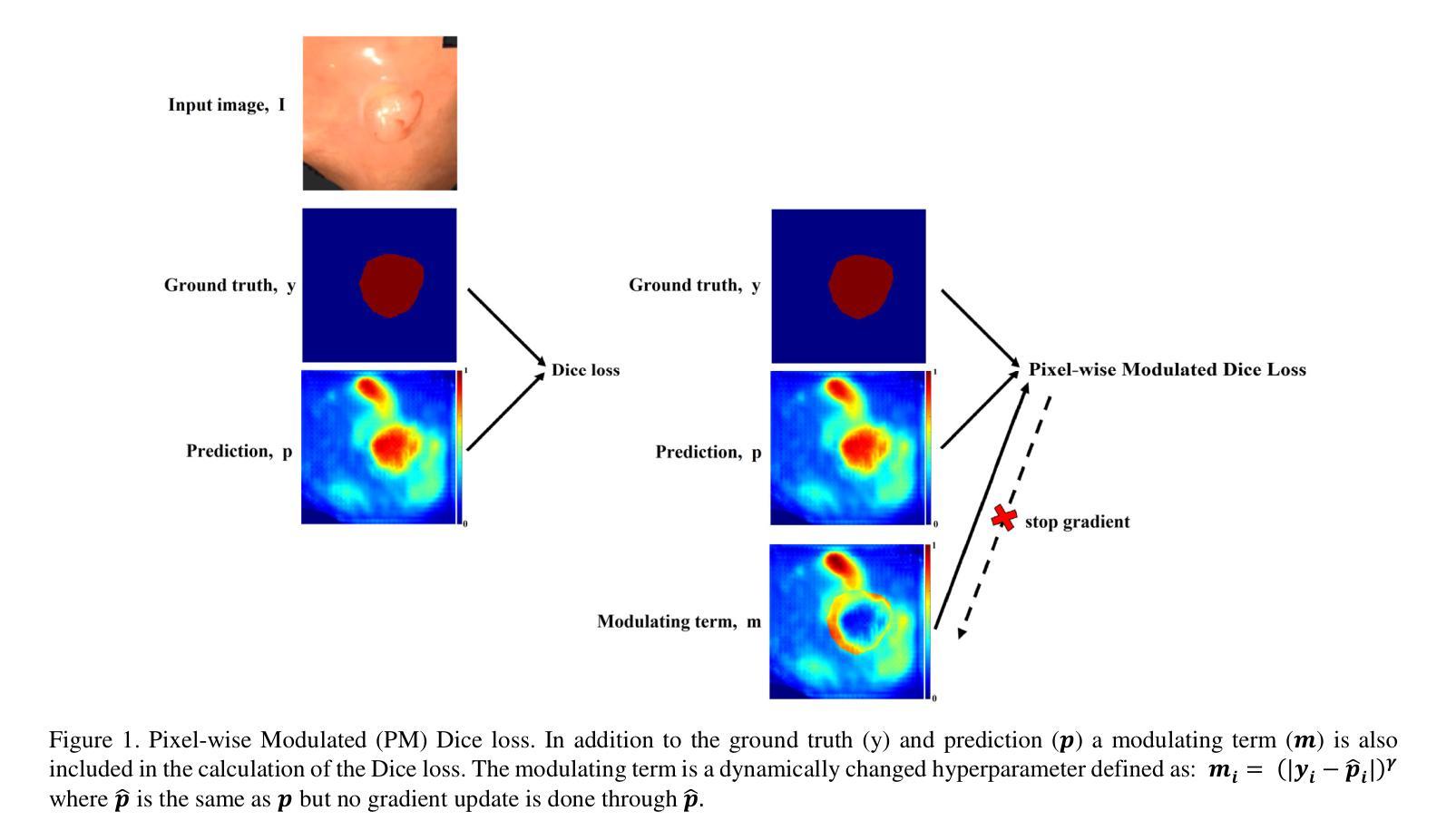
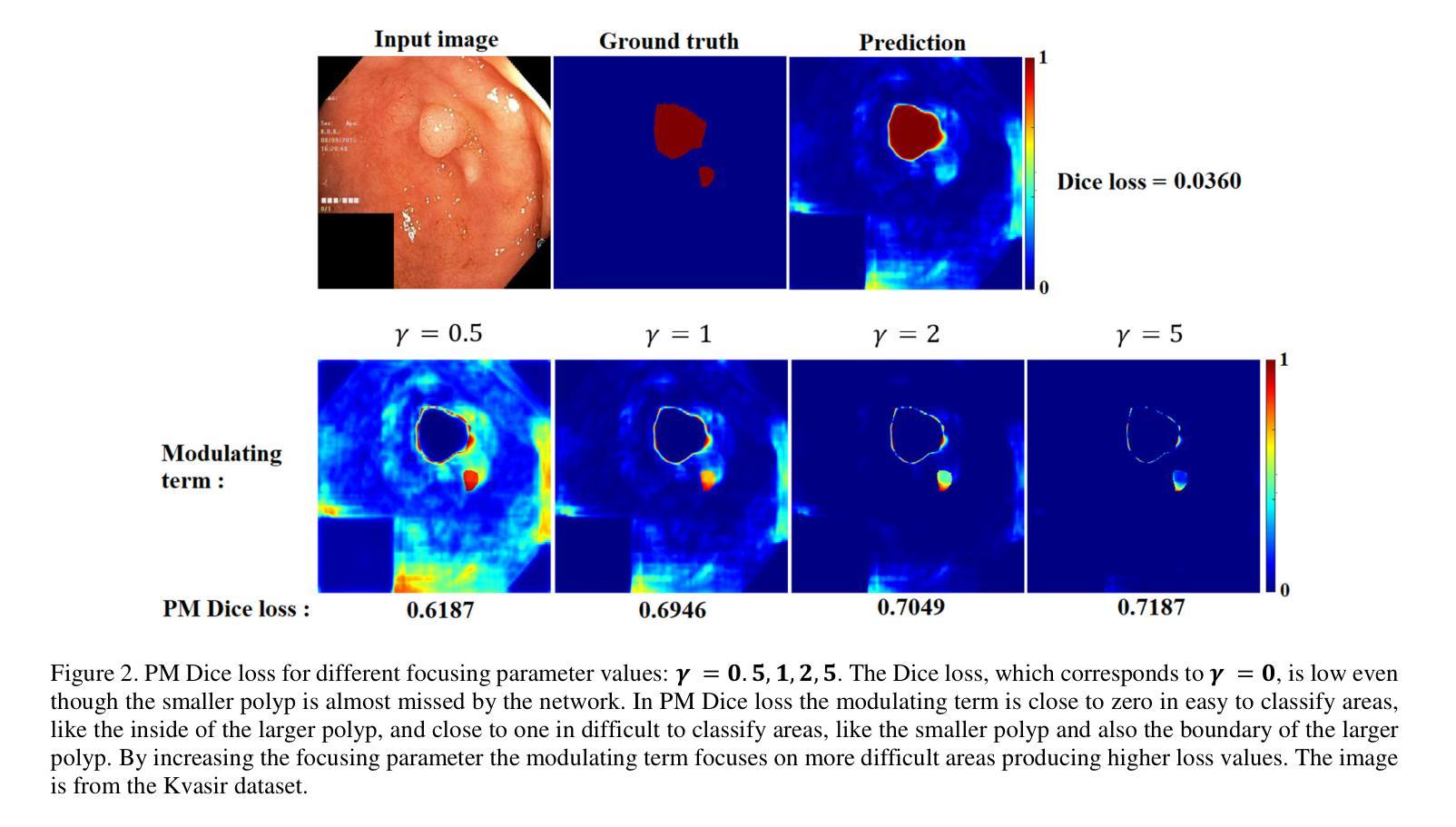
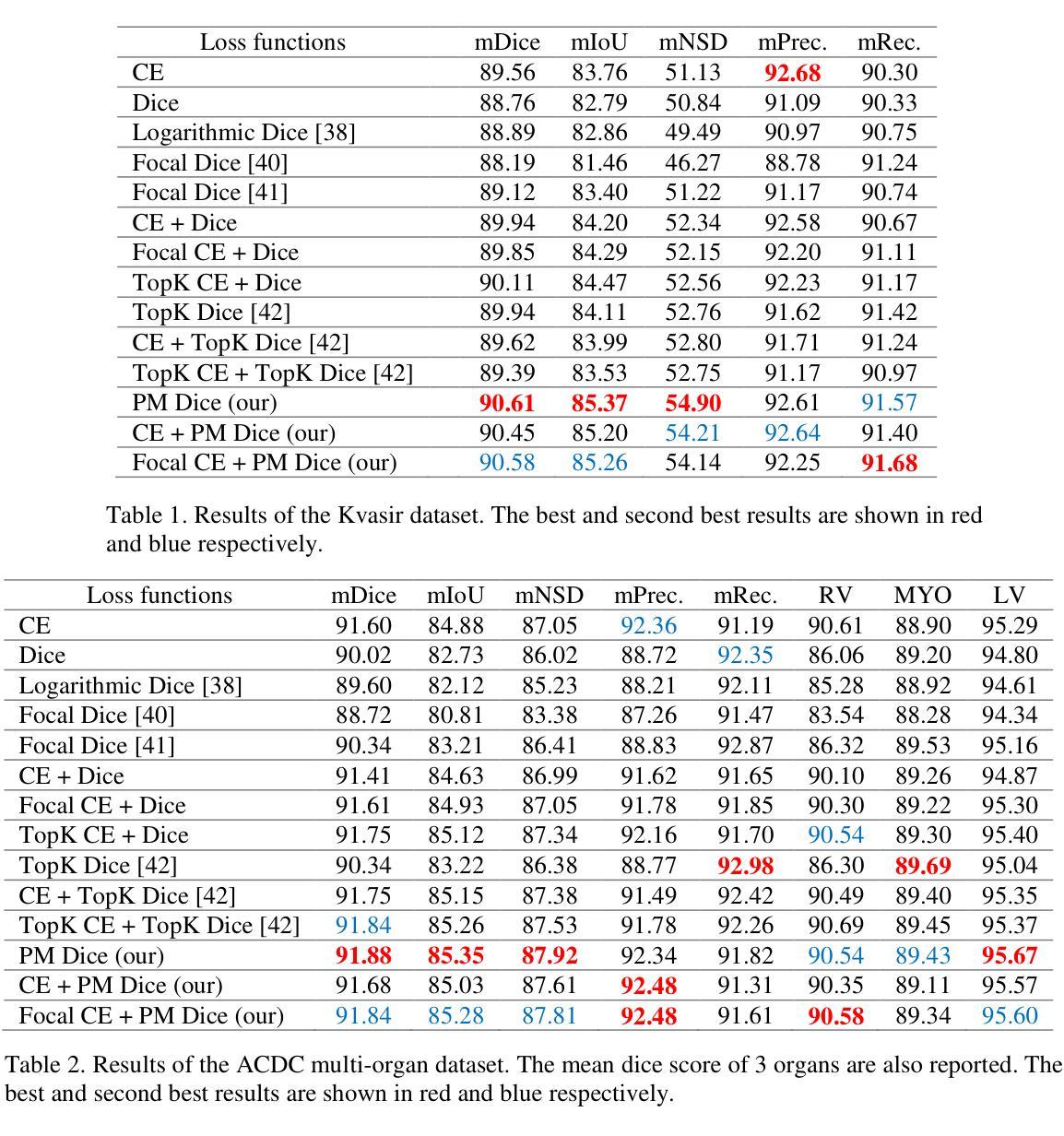
Pixel-wise Modulated Dice Loss for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Seyed Mohsen Hosseini
Class imbalance and the difficulty imbalance are the two types of data imbalance that affect the performance of neural networks in medical segmentation tasks. In class imbalance the loss is dominated by the majority classes and in difficulty imbalance the loss is dominated by easy to classify pixels. This leads to an ineffective training. Dice loss, which is based on a geometrical metric, is very effective in addressing the class imbalance compared to the cross entropy (CE) loss, which is adopted directly from classification tasks. To address the difficulty imbalance, the common approach is employing a re-weighted CE loss or a modified Dice loss to focus the training on difficult to classify areas. The existing modification methods are computationally costly and with limited success. In this study we propose a simple modification to the Dice loss with minimal computational cost. With a pixel level modulating term, we take advantage of the effectiveness of Dice loss in handling the class imbalance to also handle the difficulty imbalance. Results on three commonly used medical segmentation tasks show that the proposed Pixel-wise Modulated Dice loss (PM Dice loss) outperforms other methods, which are designed to tackle the difficulty imbalance problem.
在医学分割任务中,类别不平衡和难度不平衡是影响神经网络性能的两种数据不平衡问题。在类别不平衡中,损失主要由多数类别主导;而在难度不平衡中,损失主要由容易分类的像素主导。这导致了训练效果不佳。Dice损失基于几何度量,在解决类别不平衡问题时相较于直接从分类任务中采纳的交叉熵(CE)损失非常有效。为了解决难度不平衡问题,常见的做法是采用加权CE损失或修改后的Dice损失,以将训练重点放在难以分类的区域。现有的修改方法计算成本较高且成功有限。本研究中,我们提出了对Dice损失的简单修改,且计算成本较低。通过像素级调制项,我们利用Dice损失在处理类别不平衡问题时的有效性,同时也处理难度不平衡问题。在三个常用的医学分割任务上的结果表明,所提出的像素级调制Dice损失(PM Dice损失)优于其他旨在解决难度不平衡问题的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学分割任务中神经网络性能受影响的类别不平衡和难度不平衡问题,本研究提出了一种简单的Dice损失修改方法,以较低的计算成本同时解决两类数据不平衡问题。通过像素级调制项,利用Dice损失在处理类别不平衡方面的有效性,也解决了难度不平衡问题。在三种常用的医学分割任务上,所提的像素级调制Dice损失(PM Dice损失)表现优于其他解决难度不平衡问题的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学分割任务中,神经网络性能受两类数据不平衡影响:类别不平衡和难度不平衡。
- 类别不平衡中,损失主要由多数类别主导;难度不平衡中,损失主要由易分类像素主导。
- Dice损失在处理类别不平衡问题上比交叉熵损失更有效。
- 现有解决难度不平衡问题的方法计算成本高且效果有限。
- 本研究提出一种简单的Dice损失修改方法,以低计算成本同时处理两类数据不平衡问题。
- 通过像素级调制项,利用Dice损失在处理类别不平衡方面的优势,也解决了难度不平衡问题。
点此查看论文截图

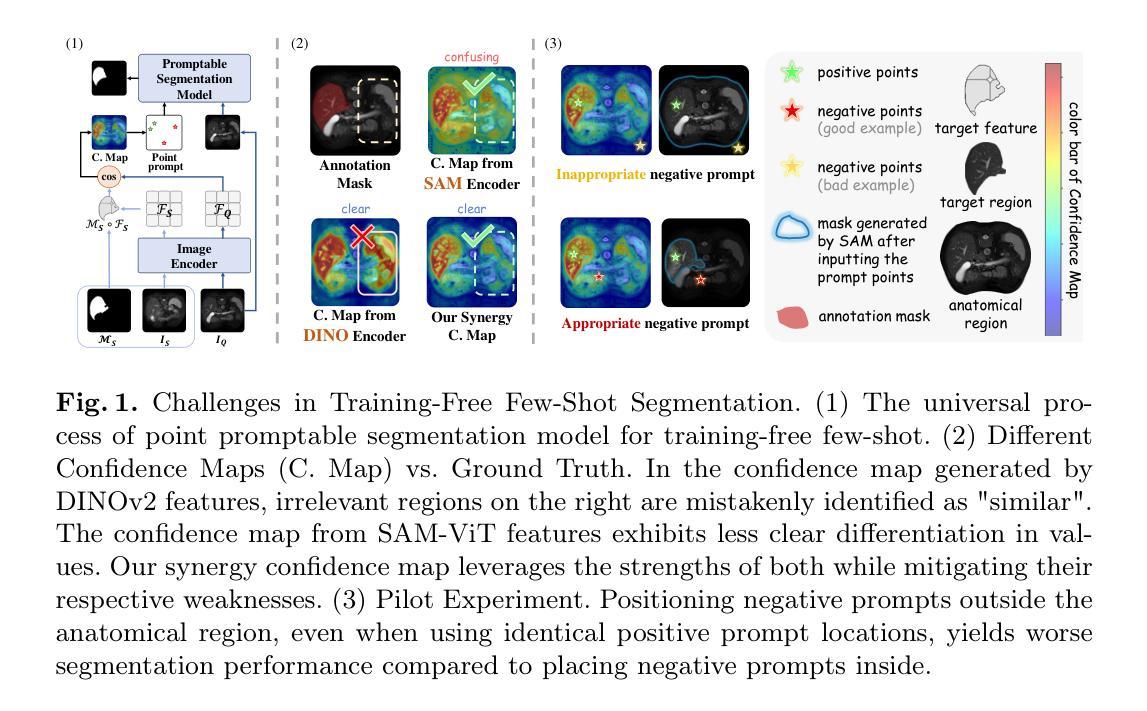
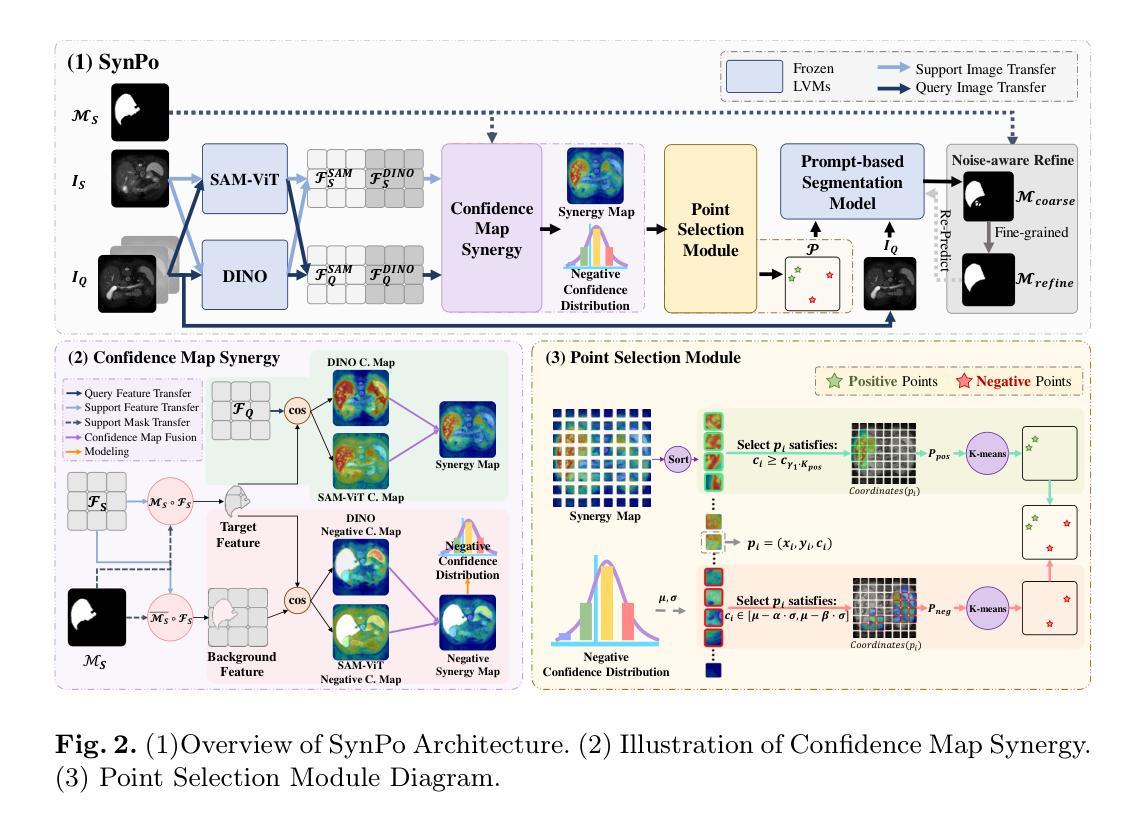
SynPo: Boosting Training-Free Few-Shot Medical Segmentation via High-Quality Negative Prompts
Authors:Yufei Liu, Haoke Xiao, Jiaxing Chai, Yongcun Zhang, Rong Wang, Zijie Meng, Zhiming Luo
The advent of Large Vision Models (LVMs) offers new opportunities for few-shot medical image segmentation. However, existing training-free methods based on LVMs fail to effectively utilize negative prompts, leading to poor performance on low-contrast medical images. To address this issue, we propose SynPo, a training-free few-shot method based on LVMs (e.g., SAM), with the core insight: improving the quality of negative prompts. To select point prompts in a more reliable confidence map, we design a novel Confidence Map Synergy Module by combining the strengths of DINOv2 and SAM. Based on the confidence map, we select the top-k pixels as the positive points set and choose the negative points set using a Gaussian distribution, followed by independent K-means clustering for both sets. Then, these selected points are leveraged as high-quality prompts for SAM to get the segmentation results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SynPo achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art training-based few-shot methods.
大规模视觉模型(LVMs)的出现为少数医学图像分割提供了新的机会。然而,基于LVMs的无训练方法无法有效利用负提示,导致在低对比度医学图像上的性能不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SynPo,这是一种基于LVMs(例如SAM)的无训练少数方法,其核心是改善负提示的质量。为了在更可靠的置信图中选择点提示,我们结合了DINOv2和SAM的优点,设计了一种新型的置信图协同模块。基于置信图,我们选择前k个像素作为正点集,使用高斯分布选择负点集,然后对这两个集合进行独立的K-means聚类。然后,这些选定的点被用作高质量提示,供SAM获取分割结果。大量实验表明,SynPo的性能与基于训练的少数方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Early Accept. Project Page: https://liu-yufei.github.io/synpo-project-page/
Summary
大型视觉模型(LVMs)为少数医疗图像分割提供了新的机会,但现有基于LVMs的无训练方法无法有效利用负提示,导致在低对比度医疗图像上的表现不佳。为解决这一问题,我们提出了基于LVMs的无训练少数方法SynPo,其核心是提高负提示的质量。通过结合DINOv2和SAM的优点,我们设计了一种新型的置信图协同模块,以更可靠的置信图选择点提示。基于置信图,我们选择前k个像素作为正点集,使用高斯分布选择负点集,然后对这两组进行独立的K-means聚类。然后,这些选定的点被用作高质量提示,供SAM进行分割。实验表明,SynPo的性能与基于训练的少数方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型(LVMs)在医疗图像分割中具有潜力。
- 现有基于LVMs的无训练方法在低对比度医疗图像上的表现不佳。
- SynPo方法旨在解决这一问题,通过提高负提示的质量来优化性能。
- SynPo设计了一种新型的置信图协同模块,结合DINOv2和SAM的优点。
- 基于置信图,选择正点集和负点集,然后进行独立的K-means聚类。
- 选定的点被用作高质量提示,供SAM进行分割。
点此查看论文截图

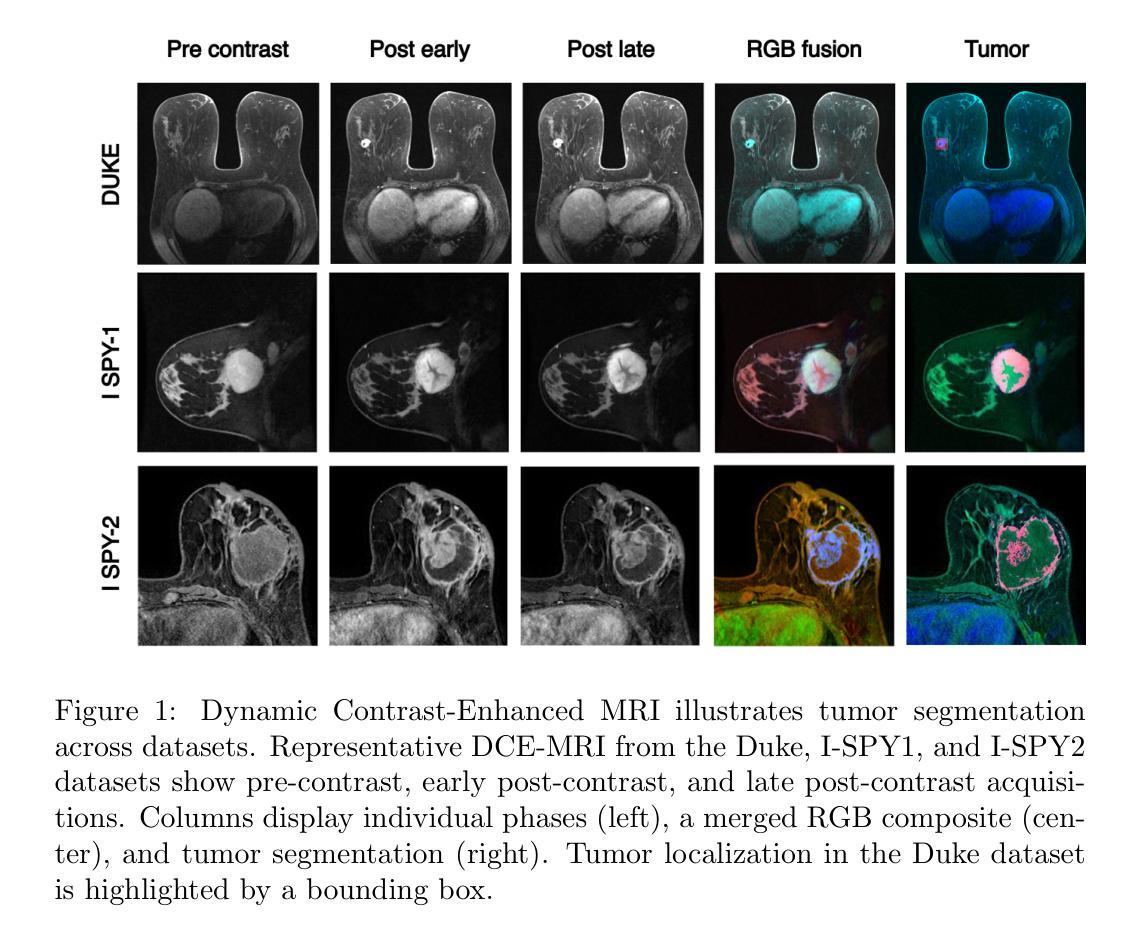
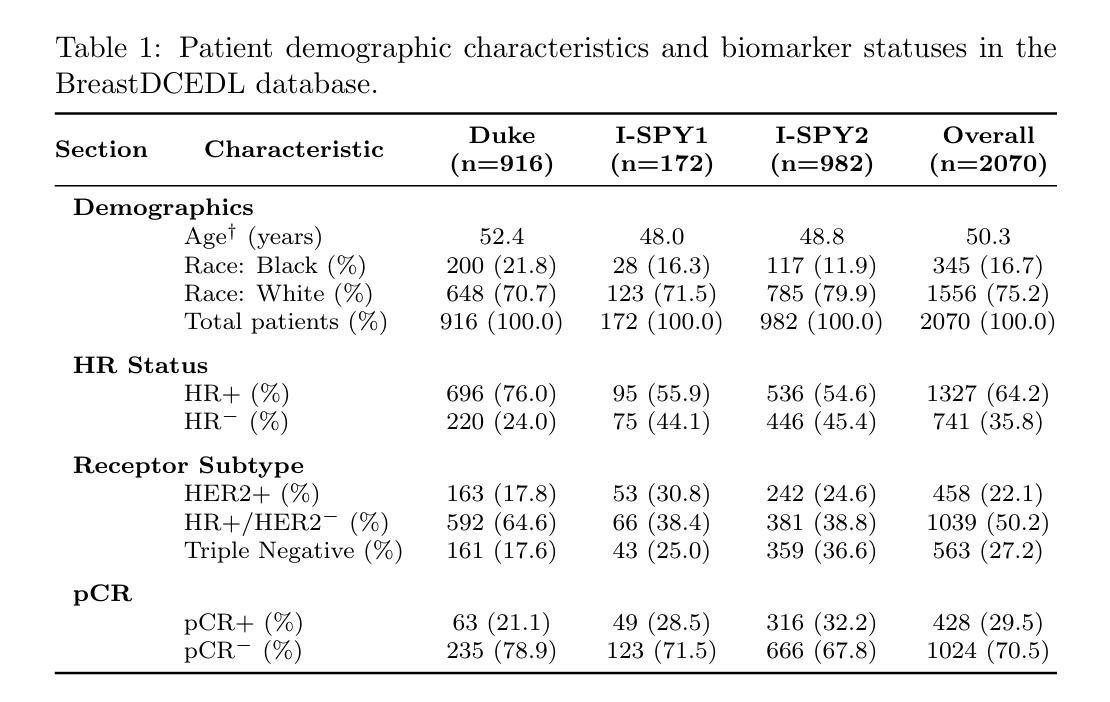
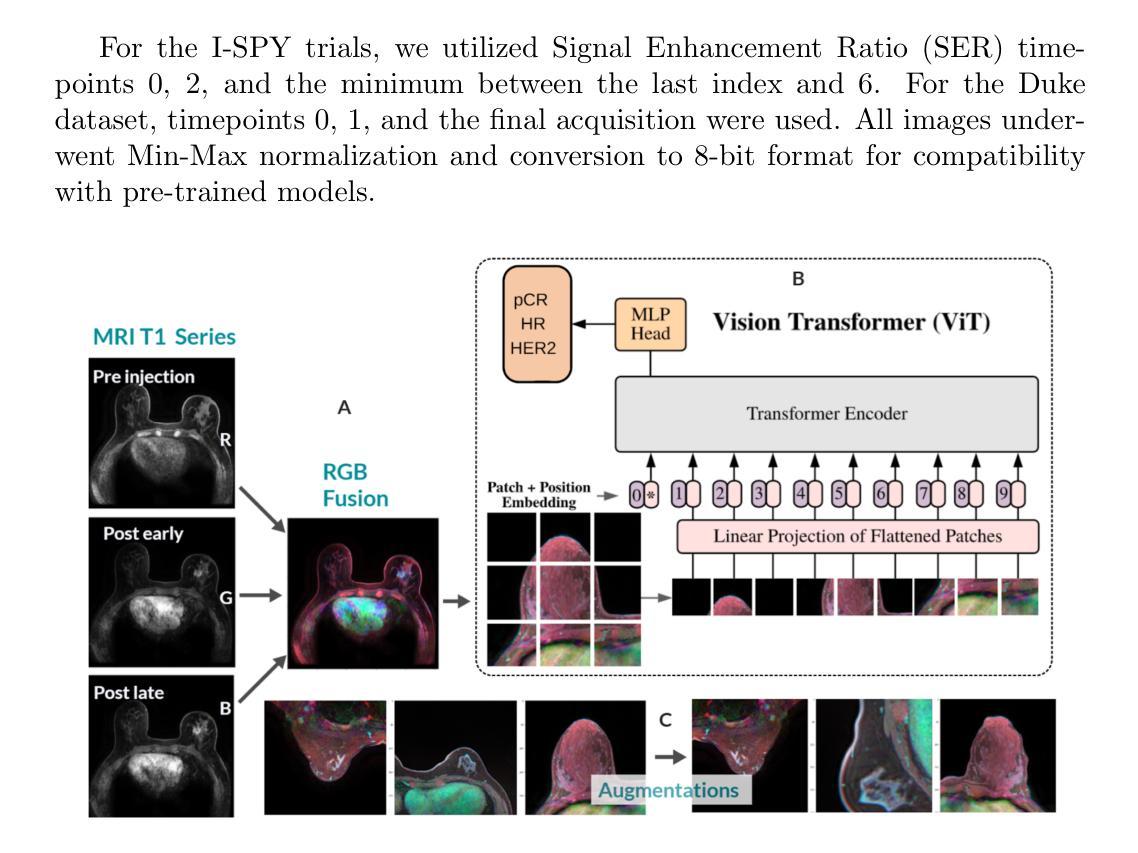
BreastDCEDL: Curating a Comprehensive DCE-MRI Dataset and developing a Transformer Implementation for Breast Cancer Treatment Response Prediction
Authors:Naomi Fridman, Bubby Solway, Tomer Fridman, Itamar Barnea, Anat Goldstein
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, making early detection and accurate treatment response monitoring critical priorities. We present BreastDCEDL, a curated, deep learning-ready dataset comprising pre-treatment 3D Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) scans from 2,070 breast cancer patients drawn from the I-SPY1, I-SPY2, and Duke cohorts, all sourced from The Cancer Imaging Archive. The raw DICOM imaging data were rigorously converted into standardized 3D NIfTI volumes with preserved signal integrity, accompanied by unified tumor annotations and harmonized clinical metadata including pathologic complete response (pCR), hormone receptor (HR), and HER2 status. Although DCE-MRI provides essential diagnostic information and deep learning offers tremendous potential for analyzing such complex data, progress has been limited by lack of accessible, public, multicenter datasets. BreastDCEDL addresses this gap by enabling development of advanced models, including state-of-the-art transformer architectures that require substantial training data. To demonstrate its capacity for robust modeling, we developed the first transformer-based model for breast DCE-MRI, leveraging Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture trained on RGB-fused images from three contrast phases (pre-contrast, early post-contrast, and late post-contrast). Our ViT model achieved state-of-the-art pCR prediction performance in HR+/HER2- patients (AUC 0.94, accuracy 0.93). BreastDCEDL includes predefined benchmark splits, offering a framework for reproducible research and enabling clinically meaningful modeling in breast cancer imaging.
乳腺癌仍然是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,因此早期检测和准确的治疗反应监测成为至关重要的优先事项。我们推出了BreastDCEDL,这是一个精心策划、准备好用于深度学习数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke队列的2070名乳腺癌患者的治疗前3D动态增强MRI(DCE-MRI)扫描。所有数据均来自癌症成像存档。原始的DICOM成像数据被严格转换为标准化的3DNIfTI体积,同时保留了信号完整性,并配有统一的肿瘤注释和协调一致的临床元数据,包括病理完全反应(pCR)、激素受体(HR)和HER2状态。尽管DCE-MRI提供了重要的诊断信息,深度学习在分析此类复杂数据方面拥有巨大潜力,但由于缺乏可访问的公共多中心数据集,进展一直受到限制。BreastDCEDL通过支持开发先进模型来解决这一差距,包括需要大训练数据的最新变压器架构。为了展示其稳健建模的能力,我们开发了基于变压器的首个乳腺癌DCE-MRI模型,利用在三个对比阶段(预对比、早期后对比和晚期后对比)的RGB融合图像上训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)架构。我们的ViT模型在HR+/HER2-患者中实现了最先进的pCR预测性能(AUC 0.94,准确率0.93)。BreastDCEDL包括预定义的基准分割,为可重复的研究提供了一个框架,并在乳腺癌成像中实现了临床意义建模。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
乳腺癌是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,早期发现和准确监测治疗反应是关键。本研究推出BreastDCEDL数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke等队列的2,070例乳腺癌患者的预治疗3D动态增强MRI扫描数据,数据来自癌症成像档案。数据集包括标准化的3DNIfTI体积图像、统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据。本研究开发了基于Vision Transformer的模型,预测HR+/HER2-患者的pCR,性能达到最新水平。BreastDCEDL包括预设的基准分割,为可重复研究和乳腺癌成像的临床意义建模提供了框架。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌仍是全球癌症死亡的主要原因,早期发现和准确监测治疗反应至关重要。
- 研究推出BreastDCEDL数据集,包含来自多个队列的乳腺癌患者的预治疗3D DCE-MRI扫描数据。
- 数据集包括标准化的图像数据、统一的肿瘤注释和临床元数据。
- 深度学习和DCE-MRI在乳腺癌诊断和治疗中潜力巨大,但缺乏公共多中心数据集限制了进展。
- BreastDCEDL填补了这一空白,支持开发先进模型,包括基于Transformer的架构。
- 研究人员开发了基于Vision Transformer的模型,用于预测HR+/HER2-患者的pCR,性能达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

Statistical microlocal analysis in two-dimensional X-ray CT
Authors:Anuj Abhishek, Alexander Katsevich, James W. Webber
In many imaging applications it is important to assess how well the edges of the original object, $f$, are resolved in an image, $f^\text{rec}$, reconstructed from the measured data, $g$. In this paper we consider the case of image reconstruction in 2D X-ray Computed Tomography (CT). Let $f$ be a function describing the object being scanned, and $g=Rf + \eta$ be the Radon transform data in $\mathbb{R}^2$ corrupted by noise, $\eta$, and sampled with step size $\sim\epsilon$. Conventional microlocal analysis provides conditions for edge detectability based on the scanner geometry in the case of continuous, noiseless data (when $\eta = 0$), but does not account for noise and finite sampling step size. We develop a novel technique called Statistical Microlocal Analysis (SMA), which uses a statistical hypothesis testing framework to determine if an image edge (singularity) of $f$ is detectable from $f^\text{rec}$, and we quantify edge detectability using the statistical power of the test. Our approach is based on the theory we developed in previous work, which provides a characterization of $f^\text{rec}$ in local $O(\epsilon)$-size neighborhoods when $\eta \neq 0$. We derive a statistical test for the presence and direction of an edge microlocally given the magnitude of $\eta$ and data sampling step size. Using the properties of the null distribution of the test, we quantify the uncertainty of the edge magnitude and direction. We validate our theory using simulations, which show strong agreement between our predictions and experimental observations. Our work is not only of practical value, but of theoretical value as well. SMA is a natural extension of classical microlocal analysis theory which accounts for practical measurement imperfections, such as noise and finite step size, at the highest possible resolution compatible with the data.
在许多成像应用中,评估原始对象$f$的边缘在由测量数据$g$重建的图像$f^\text{rec}$中解析得有多好是非常重要的。本文考虑二维X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)中的图像重建情况。设$f$为描述被扫描对象的函数,$g=Rf+\eta$为受到噪声$\eta$影响的Radon变换数据在$\mathbb{R}^2$中的表示,并且以步长$\sim\epsilon$进行采样。传统的微局部分析为连续、无噪声数据(当$\eta = 0$时)的扫描仪几何提供了边缘可检测性的条件,但不考虑噪声和有限的采样步长。我们开发了一种称为统计微局部分析(SMA)的新技术,它使用统计假设检验框架来确定从$f^\text{rec}$是否可检测图像边缘(奇异性),并且我们使用检验的统计效力来量化边缘的可检测性。我们的方法基于我们之前的工作所发展的理论,该理论在$\eta \neq 0$的情况下,对$f^\text{rec}$在局部$O(\epsilon)$大小邻域内的特性进行了描述。我们针对边缘的存在性和方向性微局部地推导了一个统计检验,给定$\eta$的幅度和数据采样步长。利用检验的空分布属性,我们对边缘幅度和方向的不确定性进行了量化。我们通过模拟验证了我们的理论,模拟结果显示我们的预测与实验观察结果之间具有很强的一致性。我们的工作不仅具有实用价值,而且具有理论价值。SMA是经典微局部分析理论的自然扩展,它考虑了实际测量中的不完美之处,例如噪声和有限的步长,并在与数据兼容的最高可能分辨率下进行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 13 figures
Summary
该论文关注二维X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)中的图像重建问题。针对传统微局部分析在噪声和有限采样步长方面的不足,提出了一种名为统计微局部分析(SMA)的新技术。该技术使用统计假设检验框架来确定从重建图像$f^{rec}$中是否可检测到对象函数$f$的图像边缘(奇点),并利用检验的统计效力量化边缘检测能力。此外,该研究还利用先前的理论工作,对$\eta \neq 0$时$f^{rec}$在局部$O(\epsilon)$大小邻域内的特性进行了表征。通过模拟验证,该研究的结果与实验观察结果高度一致。统计微局部分析不仅是实践中的有价值工具,也是对传统微局部分析理论的有益补充,能够解决实际测量中的不完美问题,如噪声和有限的步长,并兼容数据实现最高分辨率。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文研究了二维X射线CT中的图像重建问题,关注边缘分辨率的评估。
- 提出了统计微局部分析(SMA)技术,利用统计假设检验框架评估图像边缘的检测性。
- 量化边缘检测能力,通过统计效力评估检验。
- 考虑噪声和有限采样步长等实际测量不完美因素。
- 基于先前的理论工作,对$f^{rec}$在局部邻域的特性进行了表征。
- 通过模拟验证了理论预测与实验观察的高度一致性。
点此查看论文截图

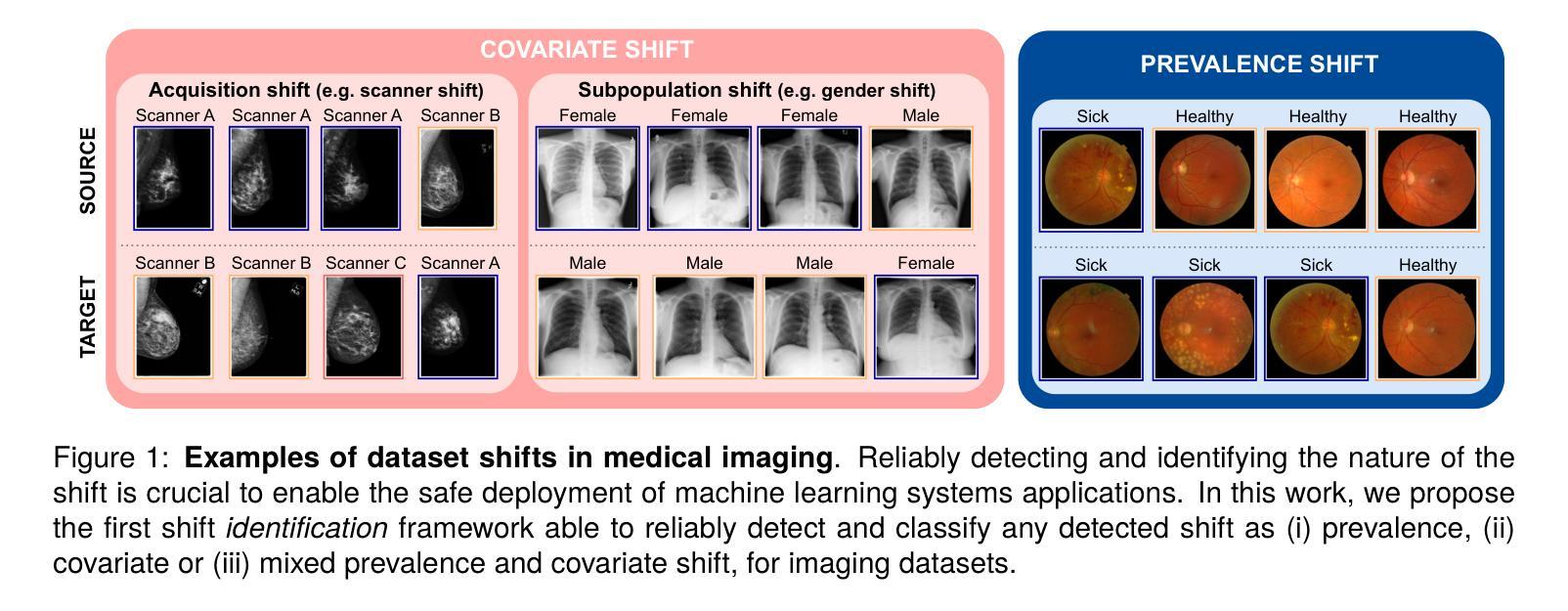
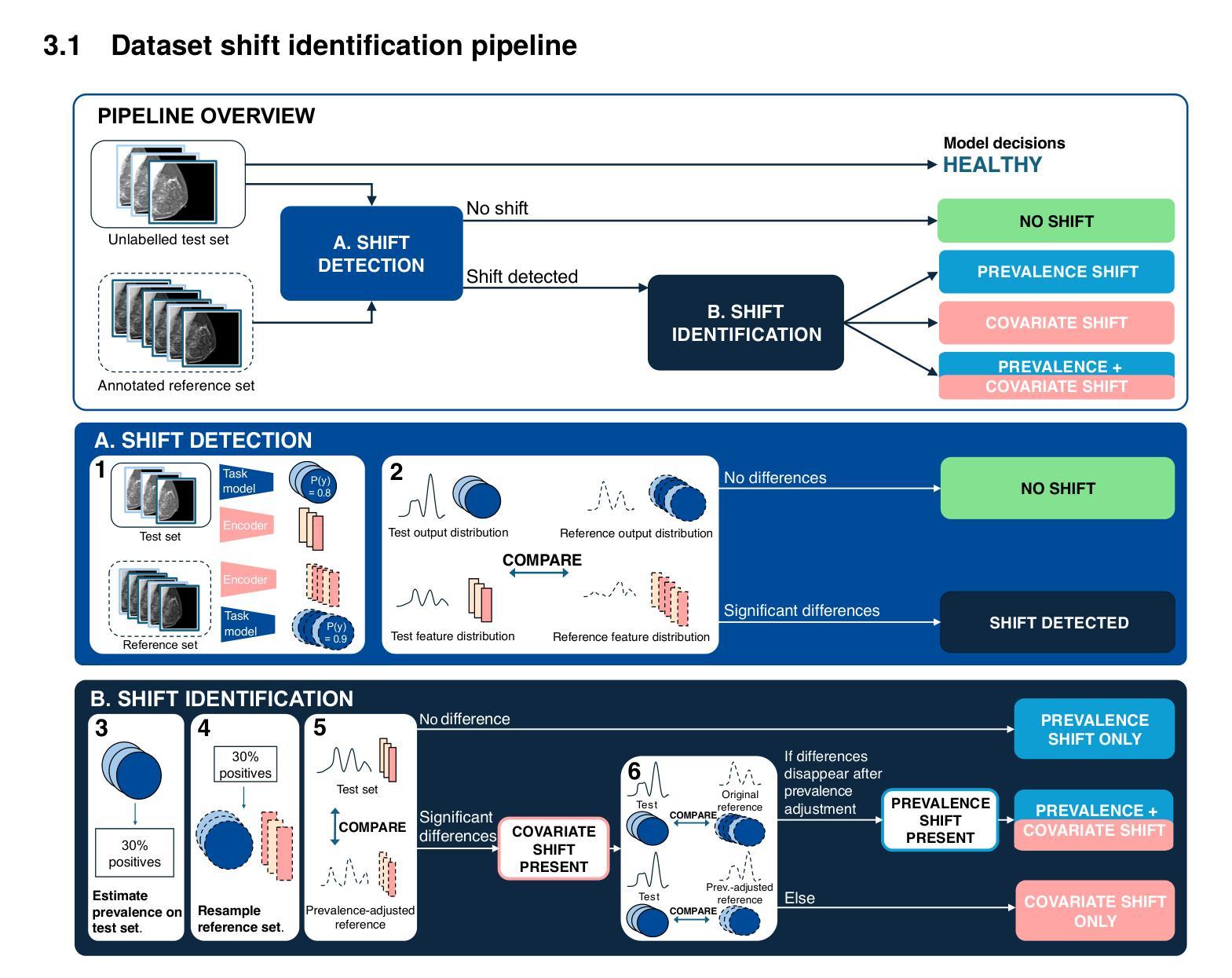
Automatic dataset shift identification to support safe deployment of medical imaging AI
Authors:Mélanie Roschewitz, Raghav Mehta, Charles Jones, Ben Glocker
Shifts in data distribution can substantially harm the performance of clinical AI models and lead to misdiagnosis. Hence, various methods have been developed to detect the presence of such shifts at deployment time. However, the root causes of dataset shifts are diverse, and the choice of shift mitigation strategies is highly dependent on the precise type of shift encountered at test time. As such, detecting test-time dataset shift is not sufficient: precisely identifying which type of shift has occurred is critical. In this work, we propose the first unsupervised dataset shift identification framework for imaging datasets, effectively distinguishing between prevalence shift (caused by a change in the label distribution), covariate shift (caused by a change in input characteristics) and mixed shifts (simultaneous prevalence and covariate shifts). We discuss the importance of self-supervised encoders for detecting subtle covariate shifts and propose a novel shift detector leveraging both self-supervised encoders and task model outputs for improved shift detection. We show the effectiveness of the proposed shift identification framework across three different imaging modalities (chest radiography, digital mammography, and retinal fundus images) on five types of real-world dataset shifts using five large publicly available datasets.
数据分布的变迁可能会显著影响临床人工智能模型的性能,并导致误诊。因此,已经开发了各种方法来检测部署时的这种变迁是否存在。然而,数据集变迁的根源是多样的,所选的变迁缓解策略高度依赖于测试时遇到的精确变迁类型。因此,仅在测试时检测数据集变迁是不够的:精确识别哪种类型的变迁已经发生至关重要。在这项工作中,我们为成像数据集提出了第一个无监督数据集变迁识别框架,能够有效区分由标签分布变化引起的普及变迁、由输入特征变化引起的协变量变迁以及同时发生的普及和协变量混合变迁。我们讨论了自监督编码器在检测细微协变量变迁中的重要性,并提出了一种新型变迁检测器,该检测器利用自监督编码器和任务模型输出进行改进,以提高变迁检测的准确性。我们展示了所提出的数据集变迁识别框架在三种不同成像模式(胸部放射摄影、数字乳腺摄影和视网膜眼底图像)上的有效性,使用了五种大型公开数据集和五种现实世界的数据集变迁类型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025. This version is an extended version with additional experimental results. Code available at https://github.com/biomedia-mira/shift_identification
Summary
临床AI模型在数据分布发生变化时性能会大幅下降,可能导致误诊。为检测部署时的数据分布变化,已开发多种方法。然而,数据集变化的根本原因多样,选择何种变化缓解策略高度依赖于测试时遇到的具体变化类型。因此,仅在测试时检测数据集变化是不够的,精确识别出哪种变化至关重要。本研究提出首个针对成像数据集的无监督数据集变化识别框架,有效区分由标签分布变化引起的普遍变化、由输入特征变化引起的协变量变化和混合变化(同时发生普遍变化和协变量变化)。本文讨论自监督编码器在检测细微协变量变化中的重要性,并提出一种新型变化检测器,该检测器利用自监督编码器和任务模型输出以提高变化检测效果。实验证明,该变化识别框架在三种不同的成像模式(胸部放射、数字乳腺摄影和眼底图像)上对五种现实世界数据集的五种类型变化均有效。
Key Takeaways
- 数据分布的变化可能对临床AI模型的性能产生重大影响,导致误诊断。
- 测试时的数据集变化检测是不够的,需要精确识别变化的类型。
- 普遍变化、协变量变化和混合变化是数据集变化的三种主要类型。
- 自监督编码器在检测细微协变量变化中起到重要作用。
- 提出的无监督数据集变化识别框架能有效区分这三种变化类型。
- 该框架利用自监督编码器和任务模型输出,提高了变化检测的效果。
点此查看论文截图

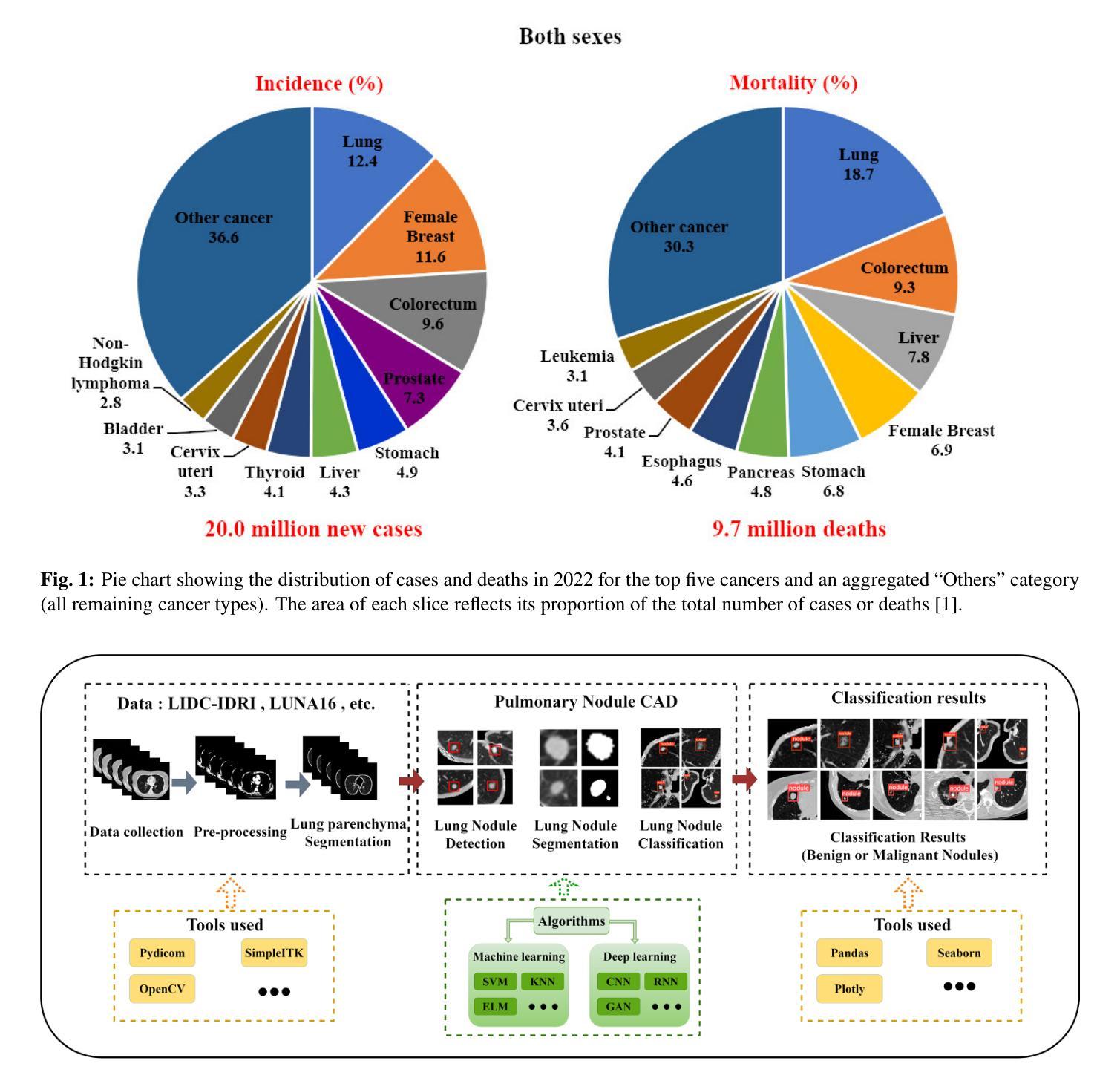
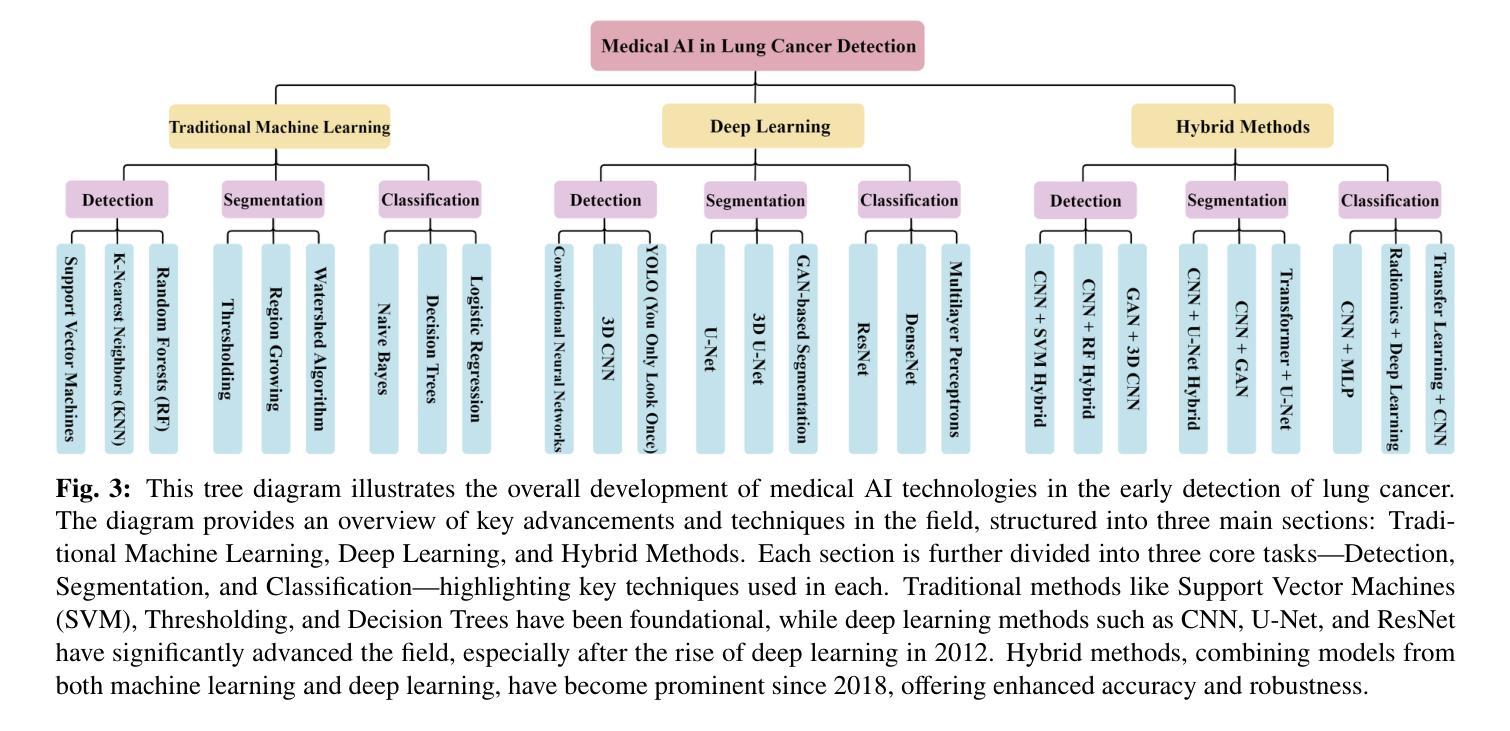
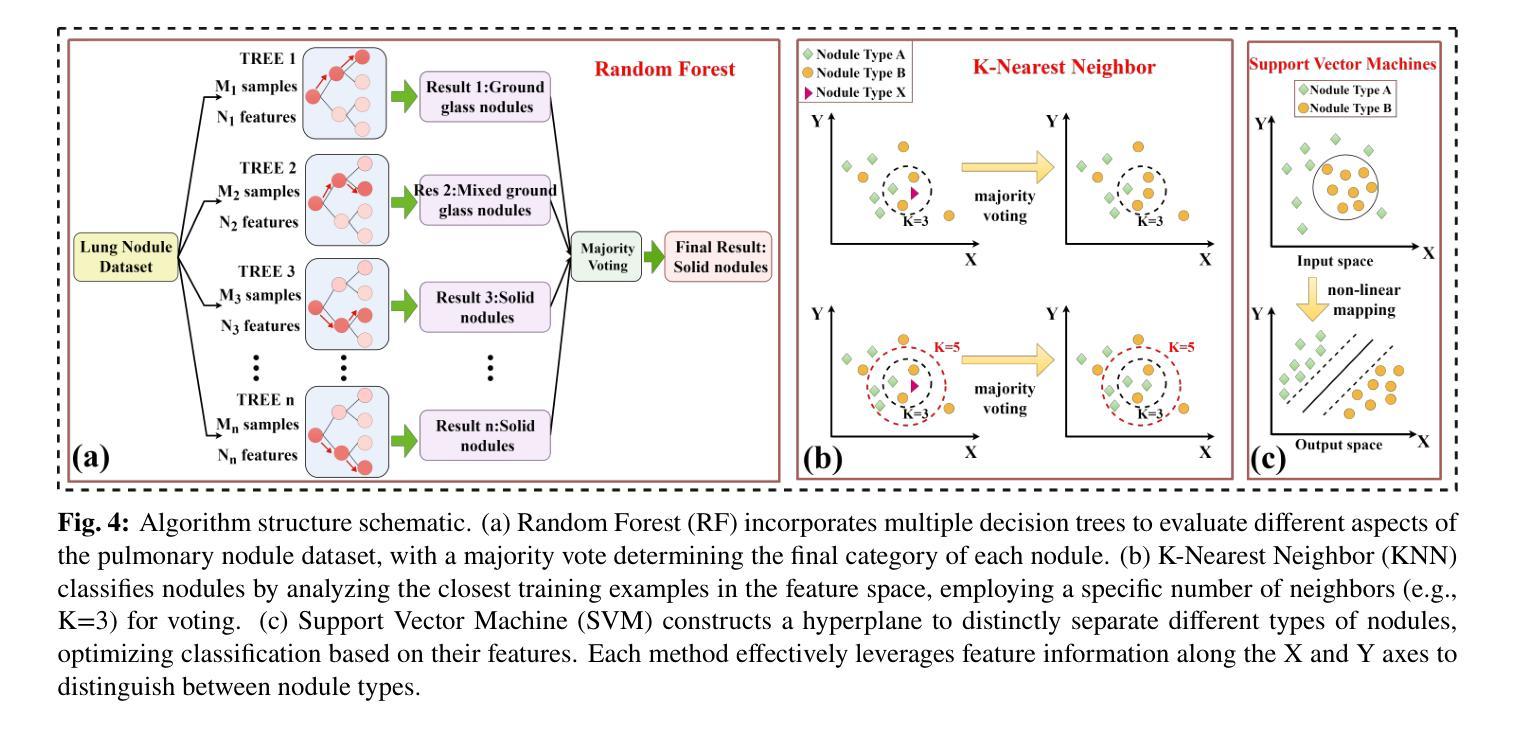
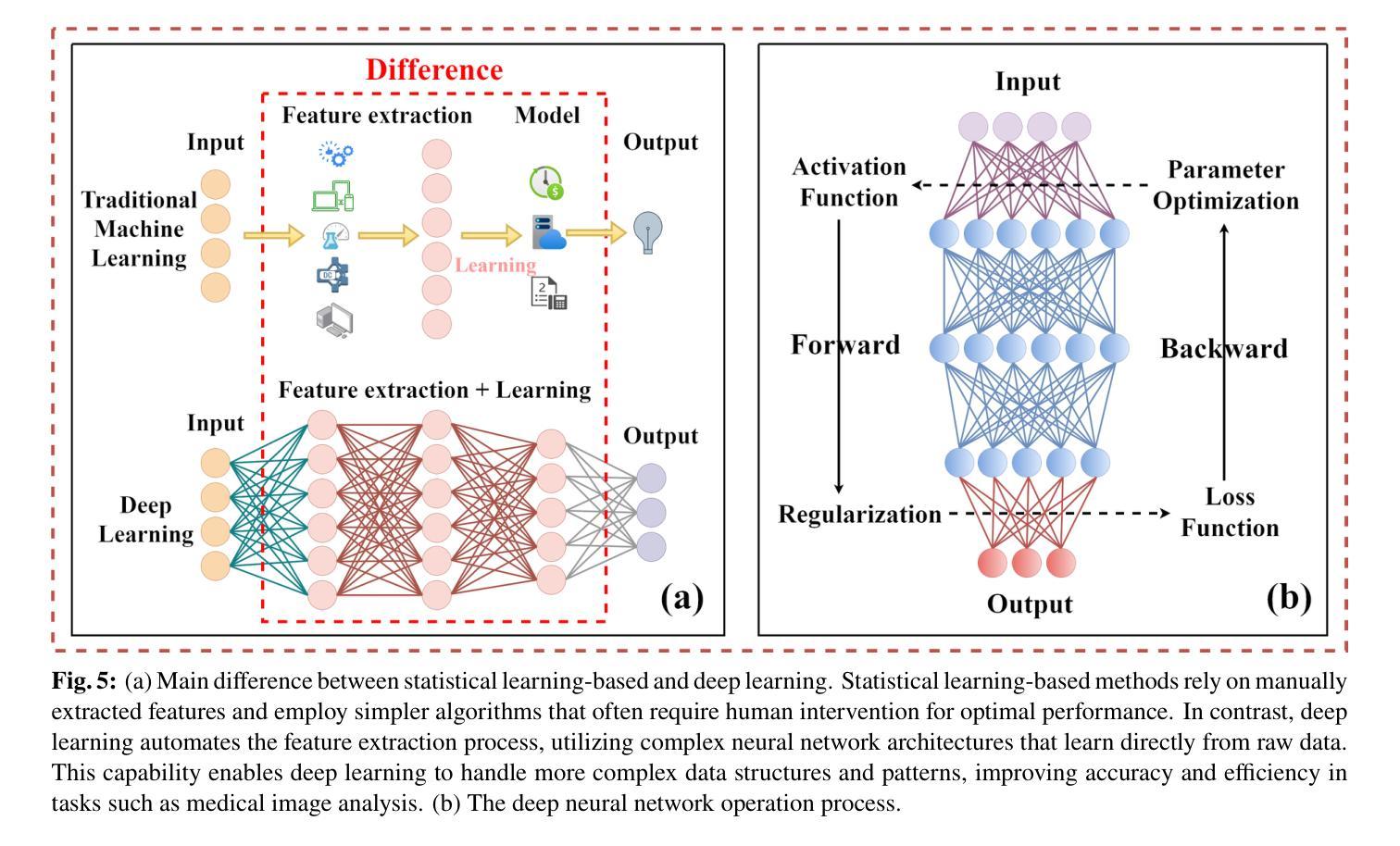
Medical Artificial Intelligence for Early Detection of Lung Cancer: A Survey
Authors:Guohui Cai, Ying Cai, Zeyu Zhang, Yuanzhouhan Cao, Lin Wu, Daji Ergu, Zhinbin Liao, Yang Zhao
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, making early diagnosis critical for improving therapeutic outcomes and patient prognosis. Computer-aided diagnosis systems, which analyze computed tomography images, have proven effective in detecting and classifying pulmonary nodules, significantly enhancing the detection rate of early-stage lung cancer. Although traditional machine learning algorithms have been valuable, they exhibit limitations in handling complex sample data. The recent emergence of deep learning has revolutionized medical image analysis, driving substantial advancements in this field. This review focuses on recent progress in deep learning for pulmonary nodule detection, segmentation, and classification. Traditional machine learning methods, such as support vector machines and k-nearest neighbors, have shown limitations, paving the way for advanced approaches like Convolutional Neural Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, and Generative Adversarial Networks. The integration of ensemble models and novel techniques is also discussed, emphasizing the latest developments in lung cancer diagnosis. Deep learning algorithms, combined with various analytical techniques, have markedly improved the accuracy and efficiency of pulmonary nodule analysis, surpassing traditional methods, particularly in nodule classification. Although challenges remain, continuous technological advancements are expected to further strengthen the role of deep learning in medical diagnostics, especially for early lung cancer detection and diagnosis. A comprehensive list of lung cancer detection models reviewed in this work is available at https://github.com/CaiGuoHui123/Awesome-Lung-Cancer-Detection.
肺癌仍然是全球发病率和死亡率的主要原因之一,因此早期诊断对于提高治疗效果和患者预后至关重要。计算机辅助诊断系统通过分析计算机断层扫描图像,在检测和分类肺结节方面表现出色,显著提高早期肺癌的检测率。虽然传统机器学习算法很有价值,但在处理复杂样本数据方面存在局限性。最近深度学习的出现彻底改变了医学图像分析,为这个领域带来了巨大的进步。这篇综述重点关注了深度学习在肺结节检测、分割和分类方面的最新进展。传统机器学习方法,如支持向量机和k近邻算法,已显示出其局限性,为卷积神经网络、循环神经网络和生成对抗网络等先进方法铺平了道路。还讨论了集成模型和新技术的一体化,强调了肺癌诊断领域的最新发展。深度学习算法结合各种分析技术,显著提高了肺结节分析的准确性和效率,超越了传统方法,特别是在结节分类方面。虽然仍存在挑战,但随着技术的不断进步,预计深度学习在医学诊断中的作用将得到进一步加强,特别是在早期肺癌检测和诊断方面。本工作所综述的肺癌检测模型的详细列表可在https://github.com/CaiGuoHui123/Awesome-Lung-Cancer-Detection上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Summary
本文介绍了肺癌仍是全球主要的疾病致死原因,计算机辅助诊断系统通过分析计算机断层扫描图像在检测早期肺癌方面表现出显著效果。传统机器学习算法在处理复杂样本数据时存在局限性,而深度学习在医学图像分析中的出现推动了该领域的重大进展。本文重点介绍了深度学习在肺结节检测、分割和分类方面的最新进展,以及集成模型和新技术在肺癌诊断中的应用。尽管仍有挑战,但技术的不断进步有望进一步加强深度学习在医学诊断中的作用,特别是在早期肺癌检测与诊断方面。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌仍是全球主要的健康威胁,早期诊断对改善治疗效果和患者预后至关重要。
- 计算机辅助诊断系统通过解析计算机断层扫描图像,在检测肺结节方面表现出显著效果,进而有助于早期肺癌的识别。
- 传统机器学习算法在处理复杂医学图像样本时存在局限性。
- 深度学习在医学图像分析领域带来革命性变化,推动肺结节检测、分割和分类的显著进展。
- 卷积神经网络、递归神经网络和生成对抗网络等先进深度学习技术应用于医学图像分析,提升诊断准确性。
- 集成模型和新技术在肺癌诊断中的最新发展受到关注。
点此查看论文截图

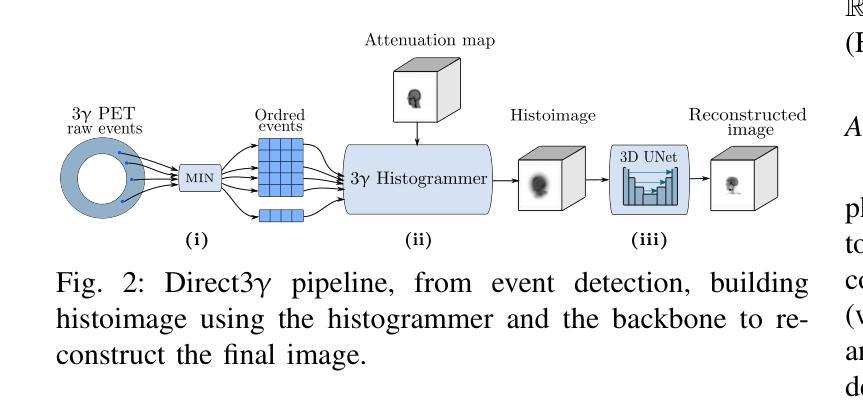
Direct3γ: A Pipeline for Direct Three-gamma PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:Youness Mellak, Alexandre Bousse, Thibaut Merlin, Debora Giovagnoli, Dimitris Visvikis
This paper presents a novel image reconstruction pipeline for three-gamma (3-{\gamma}) positron emission tomography (PET) aimed at improving spatial resolution and reducing noise in nuclear medicine; the proposed Direct3{\gamma} pipeline addresses the inherent challenges in 3-{\gamma} PET systems, such as detector imperfections and uncertainty in photon interaction points, with a key feature being its ability to determine the order of interactions through a model trained on Monte Carlo (MC) simulations using the Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission (GATE) toolkit, thus providing the necessary information to construct Compton cones which intersect with the line of response (LOR) to estimate the emission point; the pipeline processes 3-{\gamma} PET raw data, reconstructs histoimages by propagating energy and spatial uncertainties along the LOR, and applies a 3-D convolutional neural network (CNN) to refine these intermediate images into high-quality reconstructions, further enhancing image quality through supervised learning and adversarial losses that preserve fine structural details; experimental results show that Direct3{\gamma} consistently outperforms conventional 200-ps time-of-flight (TOF) PET in terms of structural similarity index measure (SSIM) and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
本文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)的新型图像重建流程,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。所提出的Direct3γ流程解决了3-γ PET系统固有的挑战,如探测器的不完美性和光子交互点的不确定性。其主要功能是通过使用Geant4发射断层扫描应用程序(GATE)工具包进行蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟训练的模型来确定交互的顺序,从而提供构建交于响应线(LOR)的康普顿锥所必需的信息来估计发射点。该流程处理3-γ PET原始数据,通过沿LOR传播能量和空间不确定性来重建直方图像,并应用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)来将这些中间图像细化为高质量重建,通过保留精细结构细节的监督和对抗损失,进一步提高图像质量。实验结果表明,Direct3γ在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面始终优于传统的200皮秒飞行时间(TOF)PET。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 11 figures, 2 tables
摘要
本文介绍了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)的新型图像重建流程,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。提出的Direct3γ流程解决了3-γ PET系统固有的挑战,如探测器缺陷和光子交互点的不确定性。其关键功能是通过使用Geant4发射断层扫描应用程序(GATE)工具包进行蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟训练模型来确定交互的顺序,从而提供构建与线性响应(LOR)相交的康普顿锥的必要信息,以估计发射点。该流程处理3-γ PET原始数据,通过沿LOR传播能量和空间不确定性来重建直方图像,并应用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)对这些中间图像进行精细化处理,生成高质量的重构图像。通过保留精细结构细节的监督学习和对抗性损失,进一步提高图像质量。实验结果表明,Direct3γ在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面始终优于传统的200皮秒时间飞行(TOF)PET。
关键见解
- Direct3γ是一种针对三伽马(3-γ)PET的新型图像重建流程,旨在改善核医学中的空间分辨率和噪声问题。
- 该流程解决了3-γ PET系统的固有挑战,如探测器缺陷和光子交互点的不确定性。
- Direct3γ通过训练模型确定光子交互的顺序,该模型使用GATE工具包进行蒙特卡洛模拟。
- 流程包括处理3-γ PET原始数据,重建直方图像,并通过CNN精细化处理生成高质量重构图像。
- Direct3γ通过结合监督学习和对抗性损失,提高了图像质量并保留了精细结构细节。
- 实验结果表明,Direct3γ在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面优于传统的时间飞行PET技术。
- 该流程有望为核医学中的图像重建提供更高的空间分辨率和更低的噪声水平。
点此查看论文截图

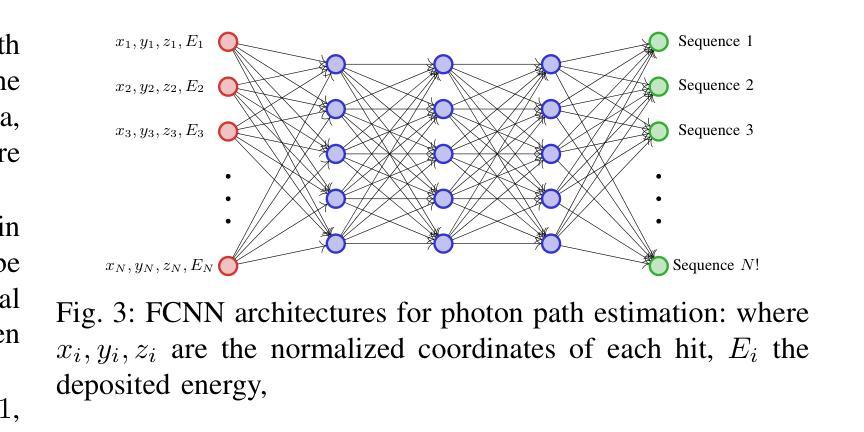
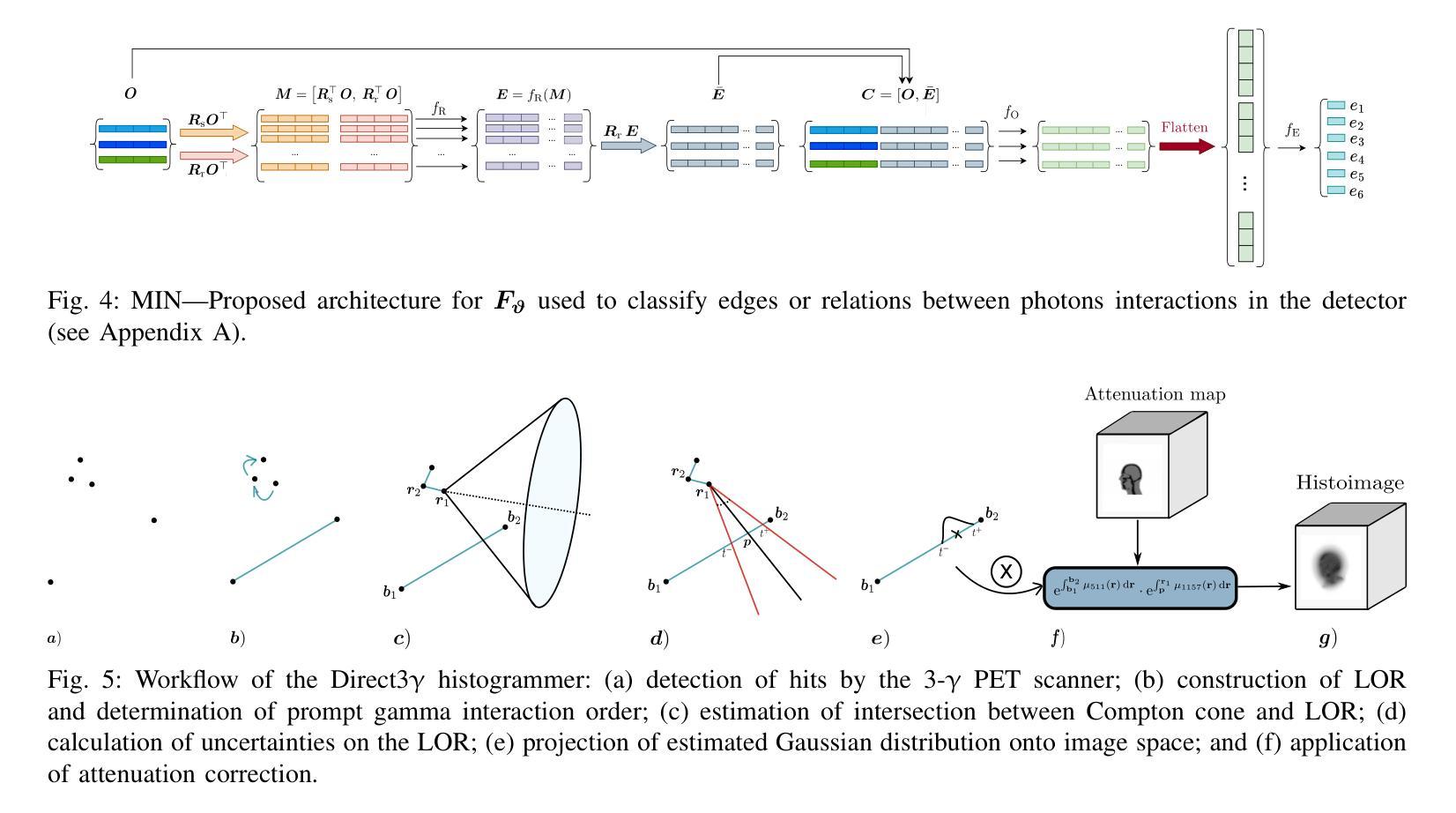
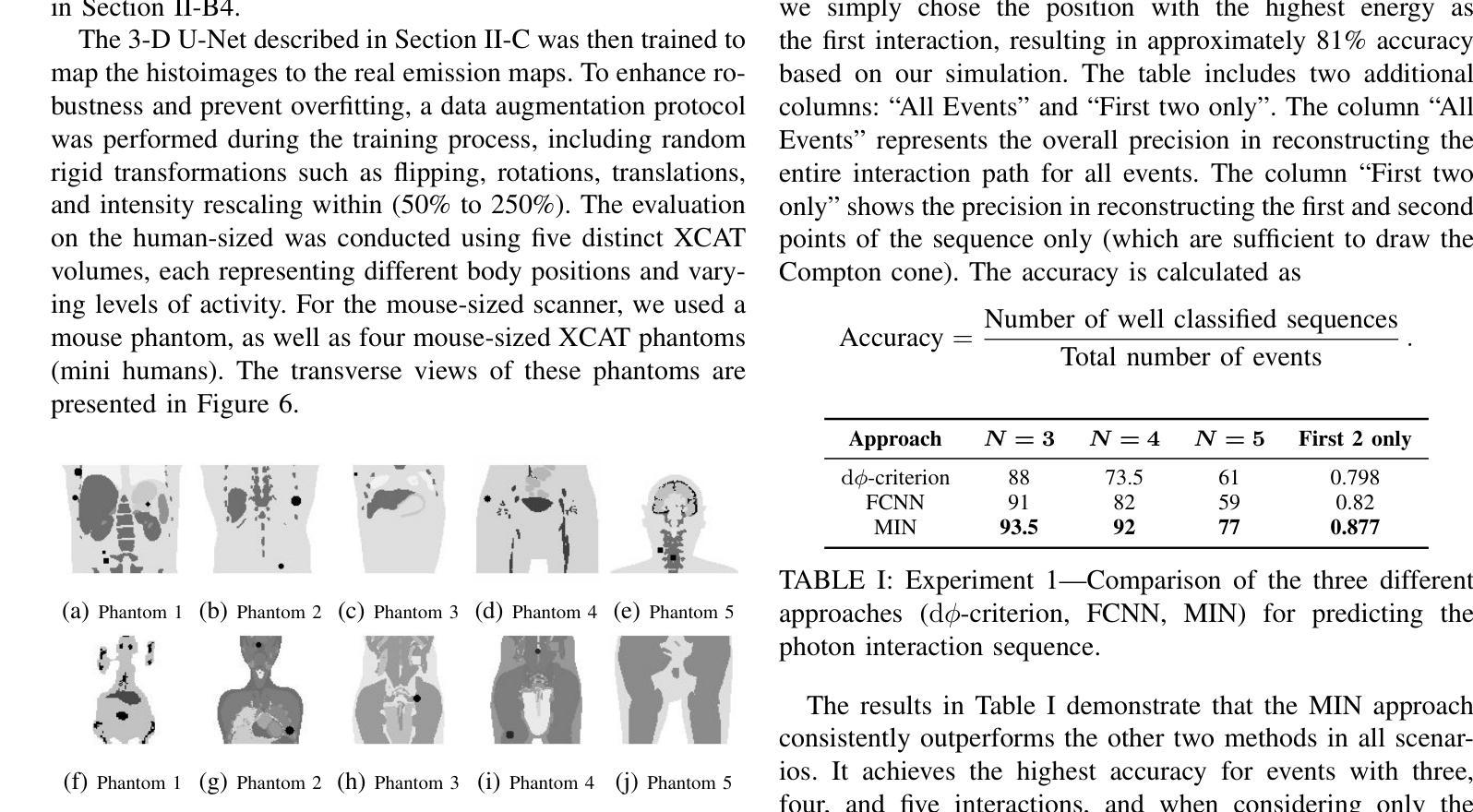
Enhancing Weakly Supervised 3D Medical Image Segmentation through Probabilistic-aware Learning
Authors:Runmin Jiang, Zhaoxin Fan, Junhao Wu, Lenghan Zhu, Xin Huang, Tianyang Wang, Heng Huang, Min Xu
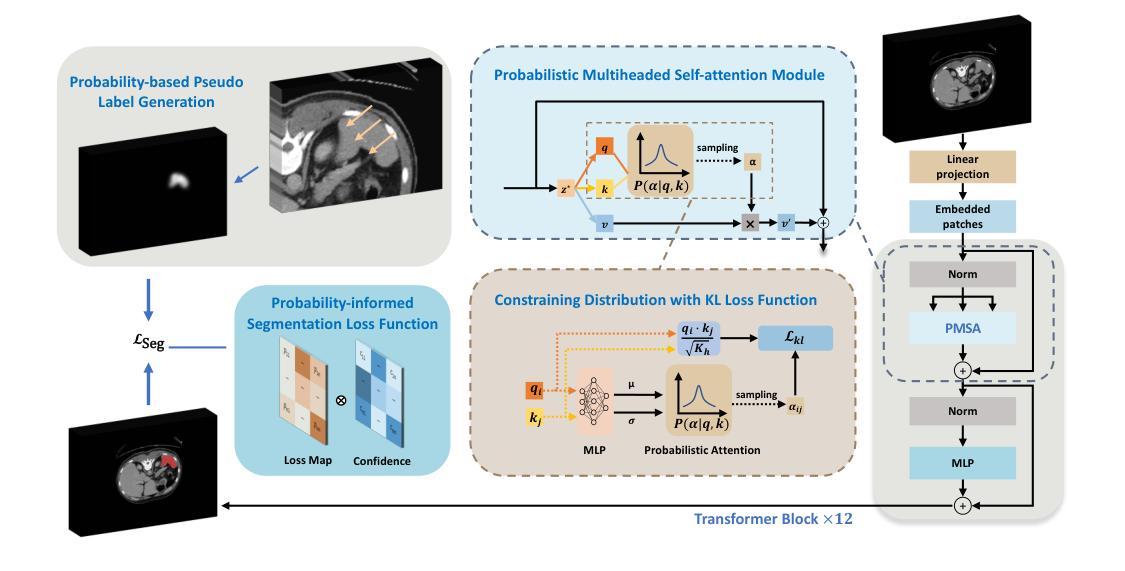
3D medical image segmentation is a challenging task with crucial implications for disease diagnosis and treatment planning. Recent advances in deep learning have significantly enhanced fully supervised medical image segmentation. However, this approach heavily relies on labor-intensive and time-consuming fully annotated ground-truth labels, particularly for 3D volumes. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel probabilistic-aware weakly supervised learning pipeline, specifically designed for 3D medical imaging. Our pipeline integrates three innovative components: a Probability-based Pseudo Label Generation technique for synthesizing dense segmentation masks from sparse annotations, a Probabilistic Multi-head Self-Attention network for robust feature extraction within our Probabilistic Transformer Network, and a Probability-informed Segmentation Loss Function to enhance training with annotation confidence. Demonstrating significant advances, our approach not only rivals the performance of fully supervised methods but also surpasses existing weakly supervised methods in CT and MRI datasets, achieving up to 18.1% improvement in Dice scores for certain organs. The code is available at https://github.com/runminjiang/PW4MedSeg.
三维医学图像分割是一项具有挑战性的任务,对于疾病诊断和治疗计划具有重要意义。深度学习的最新进展极大地促进了完全监督的医学图像分割。然而,这种方法严重依赖于劳动密集型和耗时的大量真实标签,特别是对于三维体积数据。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种新型的概率感知弱监督学习流程,专门用于三维医学影像。我们的流程集成了三个创新组件:一种基于概率的伪标签生成技术,用于从稀疏注释中合成密集分割掩膜;一个概率多头自注意力网络,用于在我们的概率变换网络中实现稳健的特征提取;以及一种基于概率的分割损失函数,利用注释置信度增强训练。通过展示显著进展,我们的方法不仅与全监督方法性能相当,而且在CT和MRI数据集上的表现超过了现有的弱监督方法,在某些器官的狄克得分上提高了高达18.1%。代码可在https://github.com/runminjiang/PW4MedSeg获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对3D医学图像分割的新型概率感知弱监督学习管道,包括概率伪标签生成技术、概率多头自注意力网络和概率感知分割损失函数。该方法不仅与全监督方法性能相当,而且在CT和MRI数据集上超越了现有弱监督方法,某些器官的Dice得分提高了18.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 3D医学图像分割是疾病诊断和治疗计划中的关键任务。
- 深度学习在全监督医学图像分割中取得了显著进展,但依赖大量手动标注数据。
- 本文提出了一种新型概率感知弱监督学习管道,用于3D医学图像分割。
- 管道包含概率伪标签生成技术、概率多头自注意力网络和概率感知分割损失函数。
- 所提方法性能与全监督方法相当,并在CT和MRI数据集上超越了现有弱监督方法。
- 方法的代码已公开,可在特定GitHub仓库中找到。
点此查看论文截图