⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-24 更新
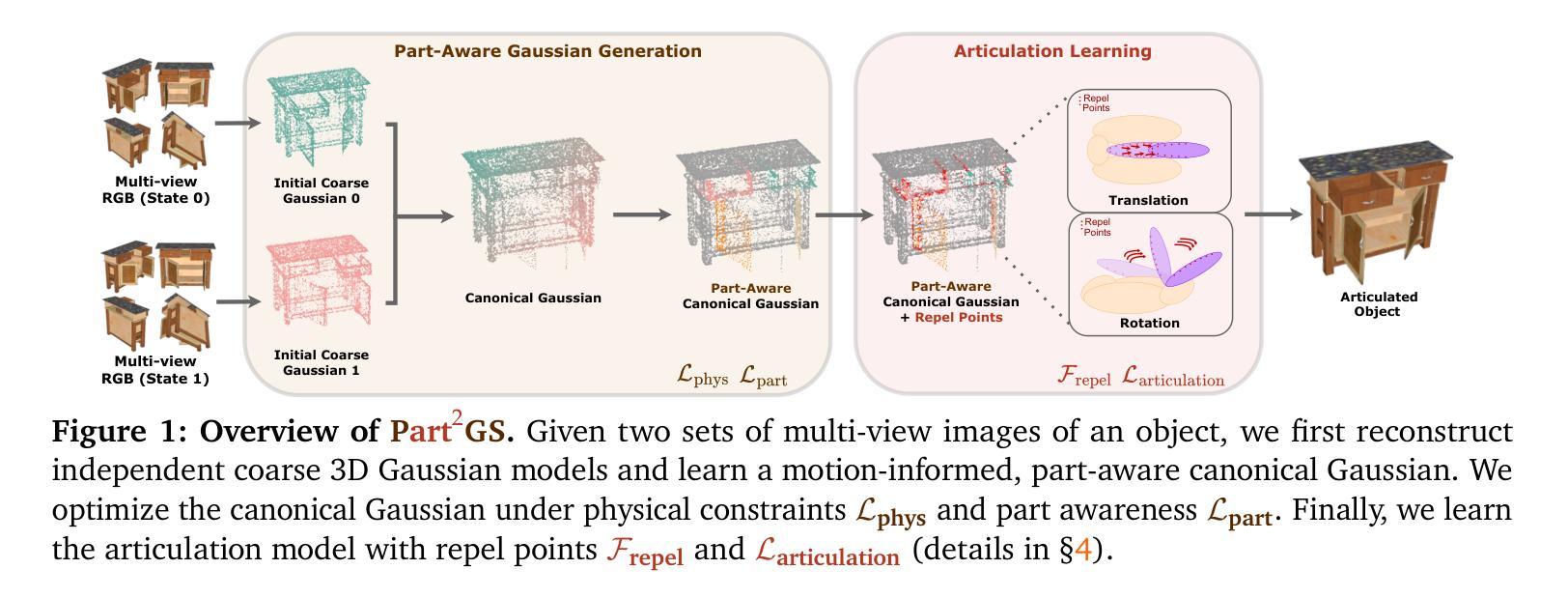
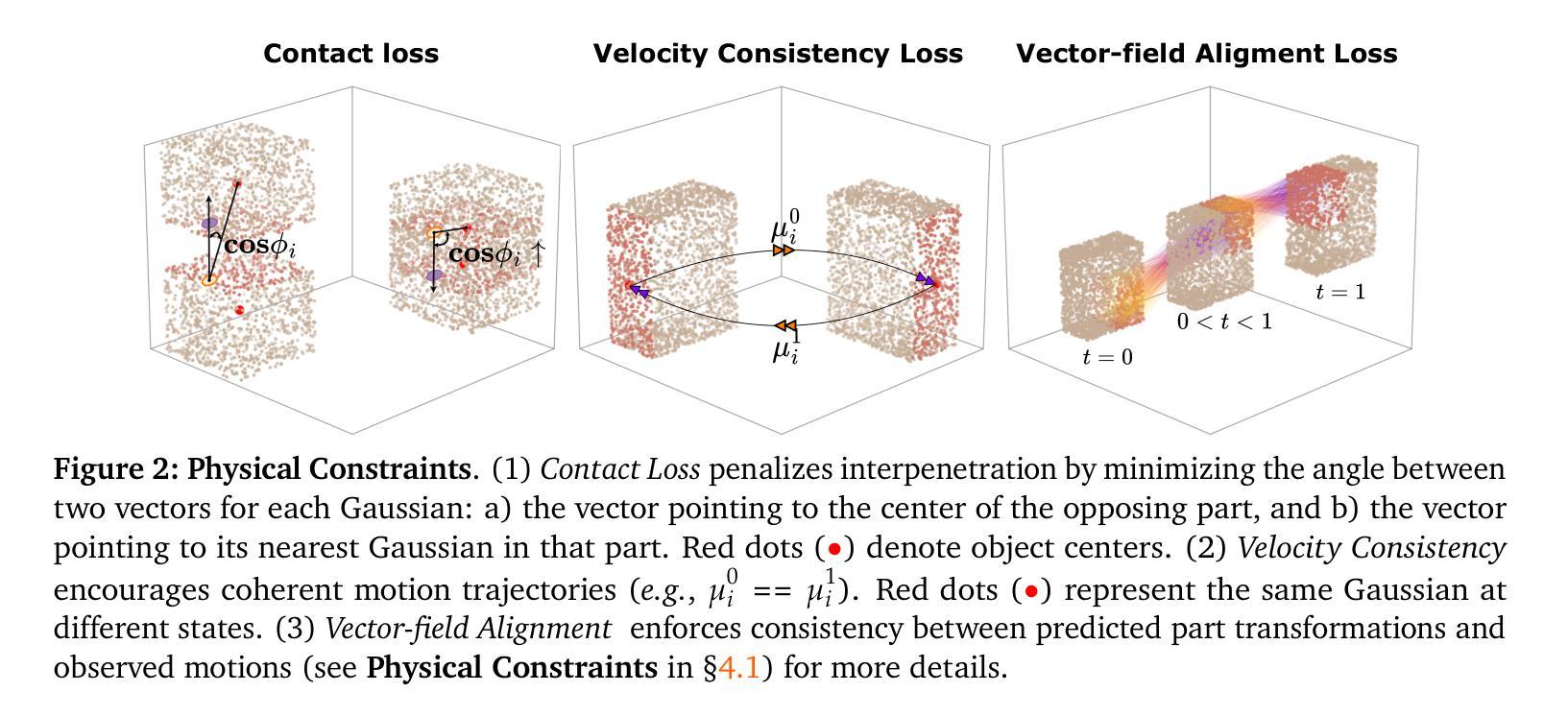
Part$^{2}$GS: Part-aware Modeling of Articulated Objects using 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Tianjiao Yu, Vedant Shah, Muntasir Wahed, Ying Shen, Kiet A. Nguyen, Ismini Lourentzou
Articulated objects are common in the real world, yet modeling their structure and motion remains a challenging task for 3D reconstruction methods. In this work, we introduce Part$^{2}$GS, a novel framework for modeling articulated digital twins of multi-part objects with high-fidelity geometry and physically consistent articulation. Part$^{2}$GS leverages a part-aware 3D Gaussian representation that encodes articulated components with learnable attributes, enabling structured, disentangled transformations that preserve high-fidelity geometry. To ensure physically consistent motion, we propose a motion-aware canonical representation guided by physics-based constraints, including contact enforcement, velocity consistency, and vector-field alignment. Furthermore, we introduce a field of repel points to prevent part collisions and maintain stable articulation paths, significantly improving motion coherence over baselines. Extensive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets show that Part$^{2}$GS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods by up to 10$\times$ in Chamfer Distance for movable parts.
现实世界中的可组装物体十分常见,然而为其构建模型和模拟运动对于三维重建方法来说仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在这项工作中,我们引入了Part$^{2}$GS,这是一个用于模拟多部件物体的可组装数字孪生的新型框架,该框架拥有高保真几何结构和物理一致的可组装性。Part$^{2}$GS采用了一种可识别部件的三维高斯表示法,这种表示法能够编码可组装组件的可学习属性,从而实现结构化、解耦的转换并保持高保真几何结构。为了确保物理一致的运动,我们提出了一种以物理约束为指导的运动规范表示法,包括接触强制实施、速度一致性和矢量场对齐。此外,我们还引入了一个排斥点场来防止部件碰撞并保持稳定的组装路径,这大大提高了运动的连贯性,超越了基准线。在合成和真实世界数据集上的广泛评估表明,Part$^{2}$GS在可移动部件的Chamfer距离上始终优于最新方法,最高可达10倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了一种名为Part$^{2}$GS的新型框架,用于模拟多部件物体的动态数字孪生。该框架采用部分感知的3D高斯表示,结合可学习的属性,实现了结构化的解耦变换,同时保持高保真几何。为确保物理一致性运动,该文提出了基于物理约束的运动感知规范表示,包括接触强制、速度一致性和矢量场对齐。此外,引入排斥点场以防止部件碰撞并保持稳定的关节路径,显著提高了运动连贯性。在合成和真实世界数据集上的广泛评估表明,Part$^{2}$GS在可动部件的Chamfer距离上始终优于现有技术,提高了高达10倍。
Key Takeaways
- Part$^{2}$GS是一种用于模拟多部件物体动态数字孪生的新型框架。
- 该框架采用部分感知的3D高斯表示,实现结构化的解耦变换和高保真几何。
- 通过引入运动感知规范表示,确保物理一致性运动,包括接触强制、速度一致性和矢量场对齐。
- 排斥点场的引入有效防止了部件碰撞,并保持了稳定的关节路径。
- Part$^{2}$GS在合成和真实世界数据集上的评估表现出卓越性能。
- 与现有技术相比,Part$^{2}$GS在可动部件的Chamfer距离指标上提高了高达10倍。
点此查看论文截图

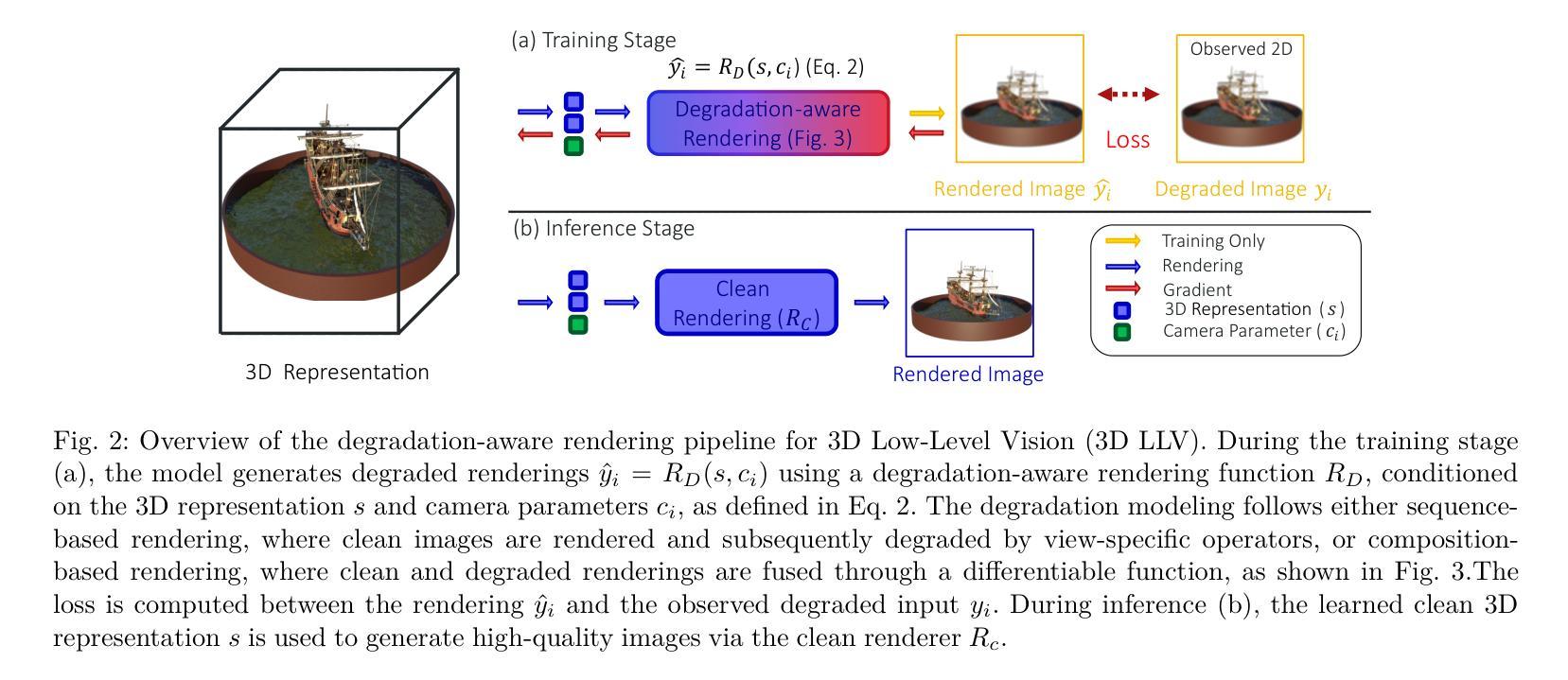
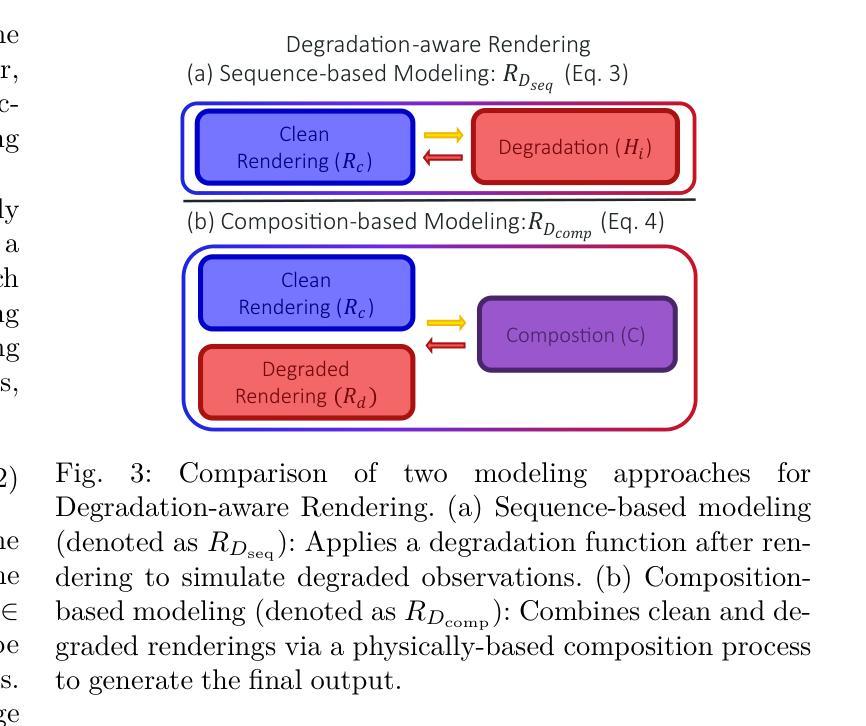
R3eVision: A Survey on Robust Rendering, Restoration, and Enhancement for 3D Low-Level Vision
Authors:Weeyoung Kwon, Jeahun Sung, Minkyu Jeon, Chanho Eom, Jihyong Oh
Neural rendering methods such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have achieved significant progress in photorealistic 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, most existing models assume clean and high-resolution (HR) multi-view inputs, which limits their robustness under real-world degradations such as noise, blur, low-resolution (LR), and weather-induced artifacts. To address these limitations, the emerging field of 3D Low-Level Vision (3D LLV) extends classical 2D Low-Level Vision tasks including super-resolution (SR), deblurring, weather degradation removal, restoration, and enhancement into the 3D spatial domain. This survey, referred to as R\textsuperscript{3}eVision, provides a comprehensive overview of robust rendering, restoration, and enhancement for 3D LLV by formalizing the degradation-aware rendering problem and identifying key challenges related to spatio-temporal consistency and ill-posed optimization. Recent methods that integrate LLV into neural rendering frameworks are categorized to illustrate how they enable high-fidelity 3D reconstruction under adverse conditions. Application domains such as autonomous driving, AR/VR, and robotics are also discussed, where reliable 3D perception from degraded inputs is critical. By reviewing representative methods, datasets, and evaluation protocols, this work positions 3D LLV as a fundamental direction for robust 3D content generation and scene-level reconstruction in real-world environments.
神经渲染方法,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),在真实感3D场景重建和新型视图合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,大多数现有模型假设干净且高分辨率(HR)的多视角输入,这限制了它们在现实世界退化(如噪声、模糊、低分辨率(LR)和天气引起的伪影)下的稳健性。为了解决这些局限性,新兴的3D低级视觉(3D LLV)领域将经典的2D低级视觉任务,包括超分辨率(SR)、去模糊、去除天气退化、恢复和增强任务扩展到3D空间域。这篇综述被称为R\textsuperscript{3}eVision,全面概述了3D LLV的鲁棒渲染、恢复和增强,通过形式化退化感知渲染问题并确定与时空一致性和不适定优化相关的关键挑战。将LLV整合到神经渲染框架中的最近方法被分类阐述,以说明它们在不利条件下实现高保真3D重建的能力。还讨论了自动驾驶、AR/VR和机器人等领域,在这些领域中,从退化输入中可靠地获取3D感知至关重要。通过回顾代表性方法、数据集和评估协议,这项工作将3D LLV定位为真实世界环境中鲁棒3D内容生成和场景级别重建的基本方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Please visit our project page at https://github.com/CMLab-Korea/Awesome-3D-Low-Level-Vision
Summary
神经网络渲染方法,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯涂抹(3DGS),在逼真的三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,大多数现有模型假设输入是清晰且高分辨率的,这限制了它们在现实世界中的稳健性,如噪声、模糊、低分辨率和天气引起的伪影。为了克服这些局限性,新兴的三维低级视觉(3D LLV)领域将传统的二维低级视觉任务扩展到三维空间域,包括超分辨率(SR)、去模糊、去除天气退化、修复和增强等。这篇综述被称为R\textsuperscript{3}eVision,提供了对三维LLV的稳健渲染、修复和增强的全面概述,通过形式化退化感知渲染问题并确定与时空一致性和病态优化相关的关键挑战。近期将LLV集成到神经渲染框架的方法被归类起来,以展示它们在恶劣条件下实现高保真三维重建的能力。还讨论了自主驾驶、增强现实/虚拟现实和机器人等领域,在这些领域中,从退化输入中可靠的三维感知至关重要。通过回顾具有代表性的方法、数据集和评估协议,这项工作将三维LLV定位为真实环境中稳健的三维内容生成和场景级重建的基本方向。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络渲染方法如NeRF和3DGS在三维场景重建和视角合成上取得进展。
- 现有模型大多假设清晰、高分辨率的多视角输入,限制了其在现实世界的稳健性。
- 3D LLV领域扩展了传统的二维低级视觉任务到三维空间域,包括SR、去模糊、去除天气退化等。
- R\textsuperscript{3}eVision综述提供了对三维LLV的稳健渲染、修复和增强的全面概述。
- 退化感知渲染问题被形式化,并确定了与时空一致性和病态优化相关的挑战。
- 集成了LLV的近期神经渲染方法展示了在恶劣条件下的高保真三维重建能力。
点此查看论文截图

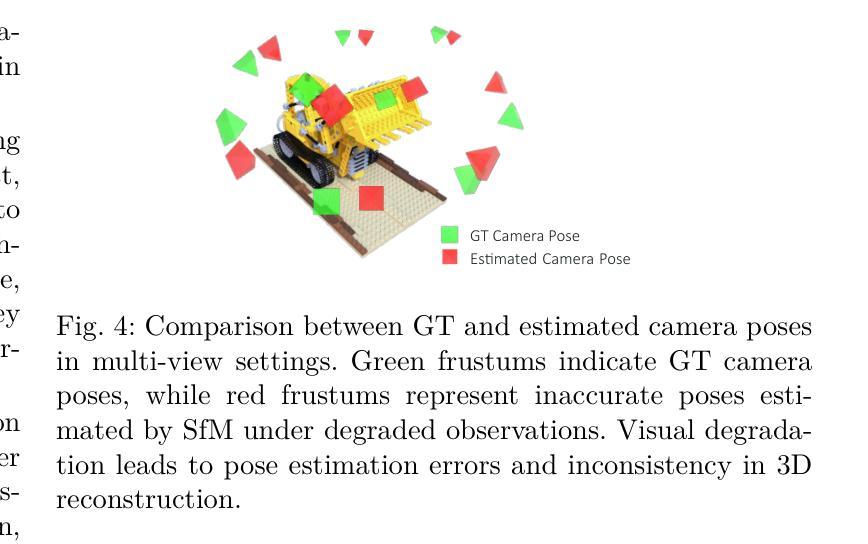
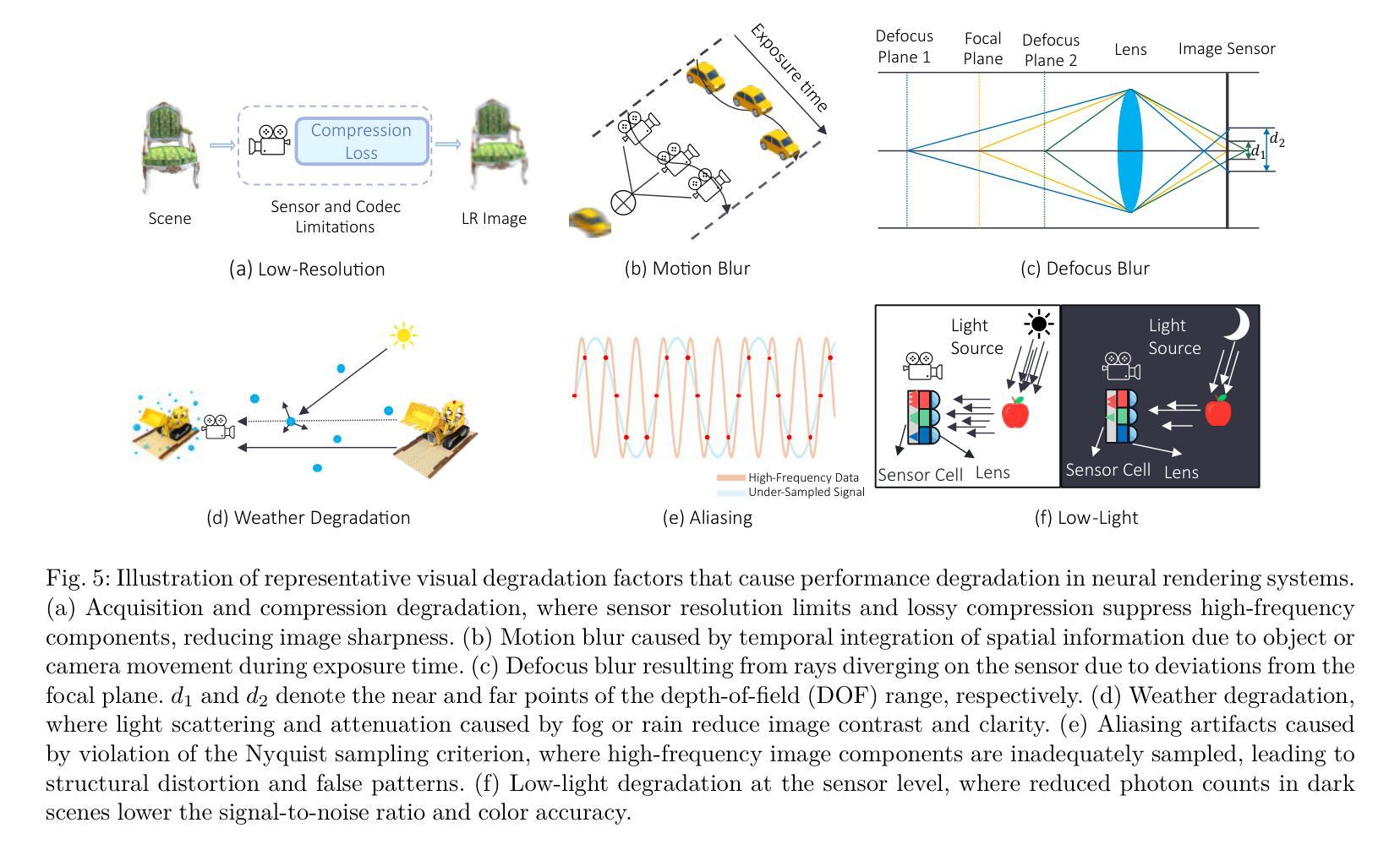
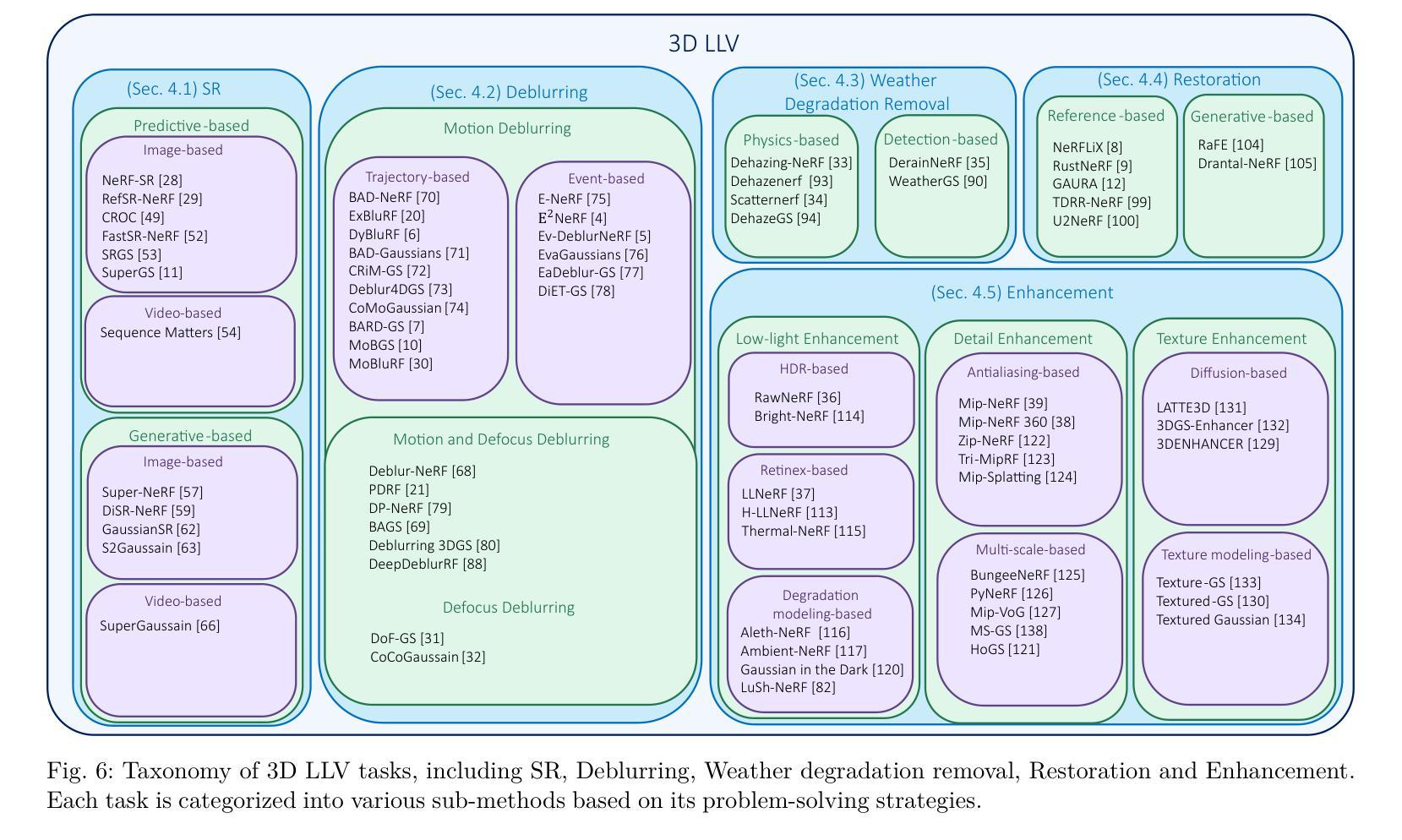
Perceptual-GS: Scene-adaptive Perceptual Densification for Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Hongbi Zhou, Zhangkai Ni
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful technique for novel view synthesis. However, existing methods struggle to adaptively optimize the distribution of Gaussian primitives based on scene characteristics, making it challenging to balance reconstruction quality and efficiency. Inspired by human perception, we propose scene-adaptive perceptual densification for Gaussian Splatting (Perceptual-GS), a novel framework that integrates perceptual sensitivity into the 3DGS training process to address this challenge. We first introduce a perception-aware representation that models human visual sensitivity while constraining the number of Gaussian primitives. Building on this foundation, we develop a perceptual sensitivity-adaptive distribution to allocate finer Gaussian granularity to visually critical regions, enhancing reconstruction quality and robustness. Extensive evaluations on multiple datasets, including BungeeNeRF for large-scale scenes, demonstrate that Perceptual-GS achieves state-of-the-art performance in reconstruction quality, efficiency, and robustness. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/eezkni/Perceptual-GS
三维高斯溅出技术(3DGS)已成为新颖视图合成的一种强大技术。然而,现有方法难以根据场景特性自适应优化高斯基元的分布,因此在平衡重建质量和效率方面面临挑战。受人类感知的启发,我们提出了基于场景感知的高斯溅出增密(Perceptual-GS)新框架,将感知敏感度集成到3DGS训练过程中,以应对这一挑战。我们首先引入了一种感知感知表示法,对人类的视觉敏感度进行建模,同时约束高斯基元的数量。在此基础上,我们开发了一种感知敏感度自适应分布,将更精细的高斯粒度分配给视觉关键区域,提高了重建质量和稳健性。在包括BungeeNeRF的大规模场景在内的多个数据集上的广泛评估表明,Perceptual-GS在重建质量、效率和稳健性方面均达到了最先进的性能。代码可在公开网站上获取:https://github.com/eezkni/Perceptual-GS
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
摘要
三维高斯涂抹技术(3DGS)已成为新型视角合成的一种强大技术。然而,现有方法难以根据场景特性自适应优化高斯原始数据的分布,从而难以在重建质量和效率之间取得平衡。受人类感知启发,我们提出了场景自适应感知密集化的高斯涂抹(Perceptual-GS)新框架,将感知灵敏度集成到3DGS训练过程中以解决此挑战。我们首先引入了一种感知意识表示法,对人类的视觉灵敏度进行建模,同时限制高斯原始数据的数量。在此基础上,我们开发了一种感知灵敏度自适应分布,将更精细的高斯粒度分配给视觉关键区域,以提高重建质量和稳健性。在包括用于大规模场景的BungeeNeRF等多个数据集上的广泛评估表明,Perceptual-GS在重建质量、效率和稳健性方面均达到了最新水平。代码公开于:https://github.com/eezkni/Perceptual-GS 。
关键见解
- 现有三维高斯涂抹技术面临难以平衡重建质量和效率的难题。
- 提出了一种新的框架——场景自适应感知密集化的高斯涂抹(Perceptual-GS)。
- Perceptual-GS集成了感知灵敏度,以优化训练过程。
- 引入感知意识表示法,模拟人类视觉灵敏度并限制高斯原始数据数量。
- 开发感知灵敏度自适应分布,将高斯粒度更精细地分配给视觉关键区域。
- 在多个数据集上的评估表明,Perceptual-GS在重建质量、效率和稳健性方面达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

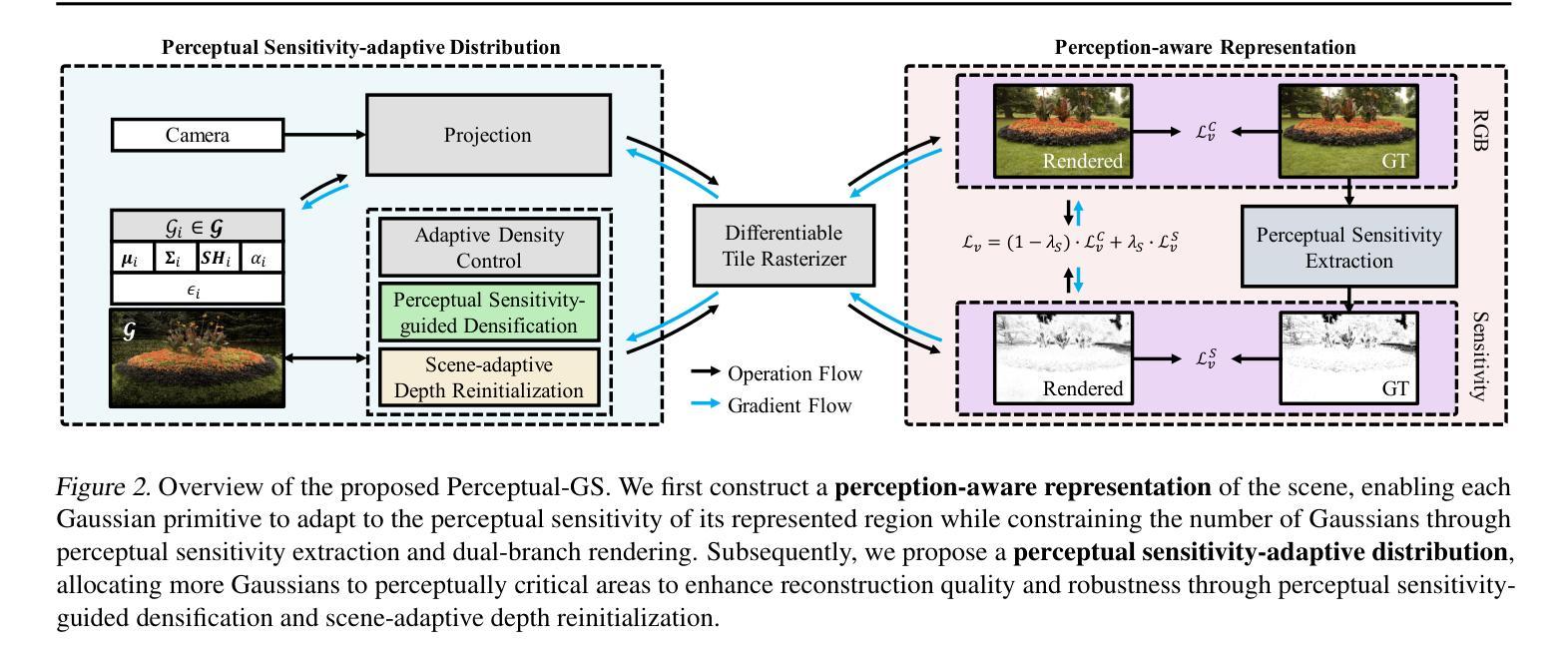
Real-time Free-view Human Rendering from Sparse-view RGB Videos using Double Unprojected Textures
Authors:Guoxing Sun, Rishabh Dabral, Heming Zhu, Pascal Fua, Christian Theobalt, Marc Habermann
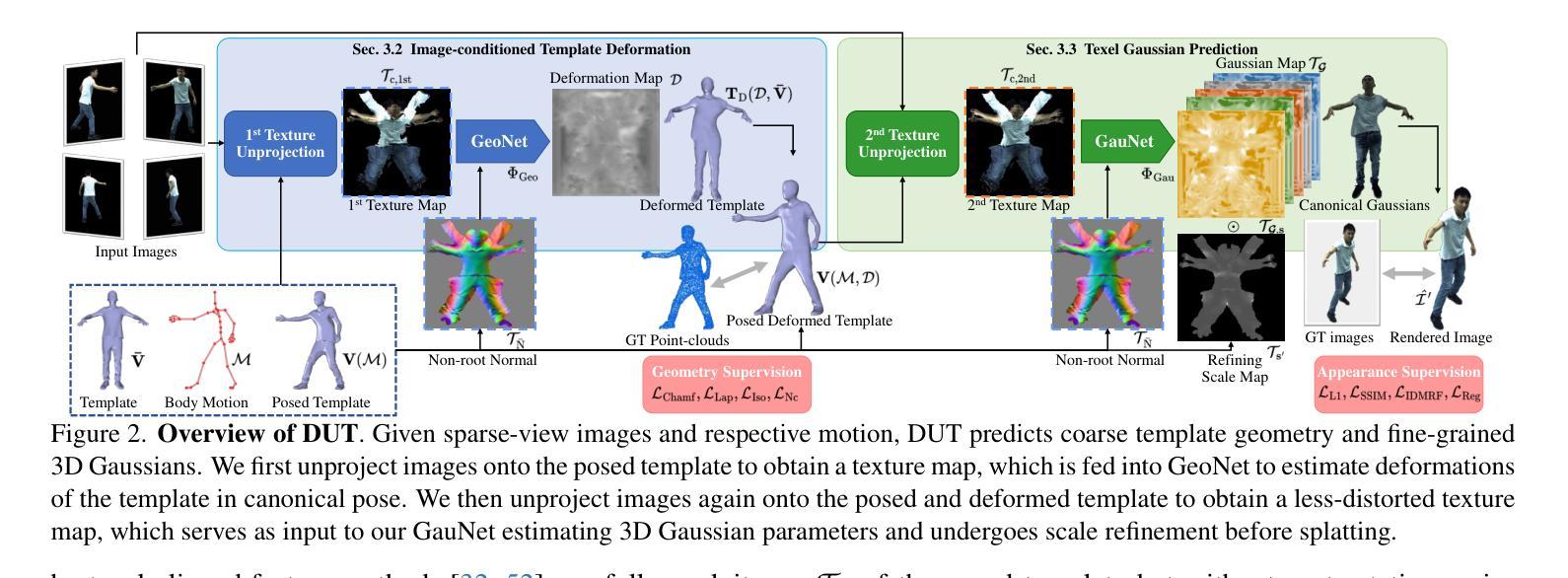
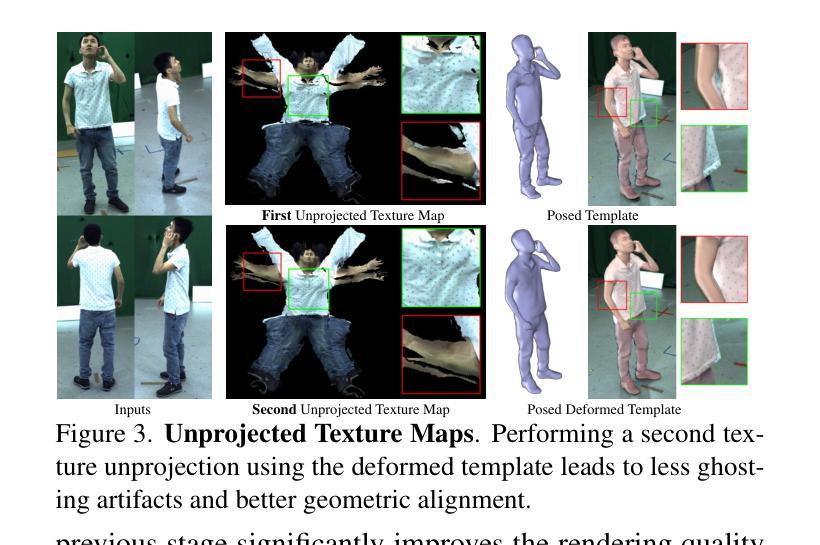
Real-time free-view human rendering from sparse-view RGB inputs is a challenging task due to the sensor scarcity and the tight time budget. To ensure efficiency, recent methods leverage 2D CNNs operating in texture space to learn rendering primitives. However, they either jointly learn geometry and appearance, or completely ignore sparse image information for geometry estimation, significantly harming visual quality and robustness to unseen body poses. To address these issues, we present Double Unprojected Textures, which at the core disentangles coarse geometric deformation estimation from appearance synthesis, enabling robust and photorealistic 4K rendering in real-time. Specifically, we first introduce a novel image-conditioned template deformation network, which estimates the coarse deformation of the human template from a first unprojected texture. This updated geometry is then used to apply a second and more accurate texture unprojection. The resulting texture map has fewer artifacts and better alignment with input views, which benefits our learning of finer-level geometry and appearance represented by Gaussian splats. We validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method in quantitative and qualitative experiments, which significantly surpasses other state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
从稀疏视角的RGB输入进行实时自由视角的人体渲染是一项具有挑战性的任务,这主要是因为传感器稀缺且时间紧迫。为了保证效率,最近的方法利用在纹理空间操作的2D卷积神经网络来学习渲染原始数据。然而,它们要么联合学习几何和外观,要么完全忽略稀疏图像的几何估计信息,这严重损害了视觉质量和对未见姿态的鲁棒性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了“双重未投影纹理”(Double Unprojected Textures),其核心在于将粗糙的几何变形估计与外观合成分开,从而实现实时稳健且逼真的4K渲染。具体来说,我们首先引入了一种新型图像条件模板变形网络,该网络从第一个未投影纹理估计人体模板的粗糙变形。然后,使用这个更新的几何信息来进行第二次更准确的纹理反投影。得到的纹理映射具有较少的伪影,并与输入视图更好地对齐,这有利于我们学习由高斯点表示的更精细级别的几何和外观。我们在定量和定性实验中都验证了所提出方法的有效性和效率,显著超越了其他最先进的方法。项目页面:https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025, Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
Summary
本文解决实时稀疏视角RGB输入下的人体渲染难题,通过双重纹理反投影技术实现粗糙几何变形估计与外观合成的分离,从而实现实时、逼真的4K渲染。首先提出图像条件模板变形网络,从第一次反投影纹理估计人体粗糙变形。更新后的几何信息用于进行第二次更准确纹理反投影,生成纹理图减少了伪影并与输入视角更好地对齐,这有利于我们学习更精细级别的几何结构和外观表示。所提出的方法在定量和定性实验中验证了其有效性和效率,并超越了其他最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文解决实时稀疏视角RGB输入的人体渲染难题。
- 提出双重纹理反投影技术,实现粗糙几何变形估计与外观合成的分离。
- 引入图像条件模板变形网络,从第一次反投影纹理估计人体粗糙变形。
- 更新后的几何信息用于第二次更准确纹理反投影。
- 生成纹理图减少伪影并与输入视角对齐,有助于学习更精细的几何结构和外观。
- 方法在定量和定性实验中表现优越,显著超越其他最新方法。
点此查看论文截图