⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-24 更新
Assembler: Scalable 3D Part Assembly via Anchor Point Diffusion
Authors:Wang Zhao, Yan-Pei Cao, Jiale Xu, Yuejiang Dong, Ying Shan
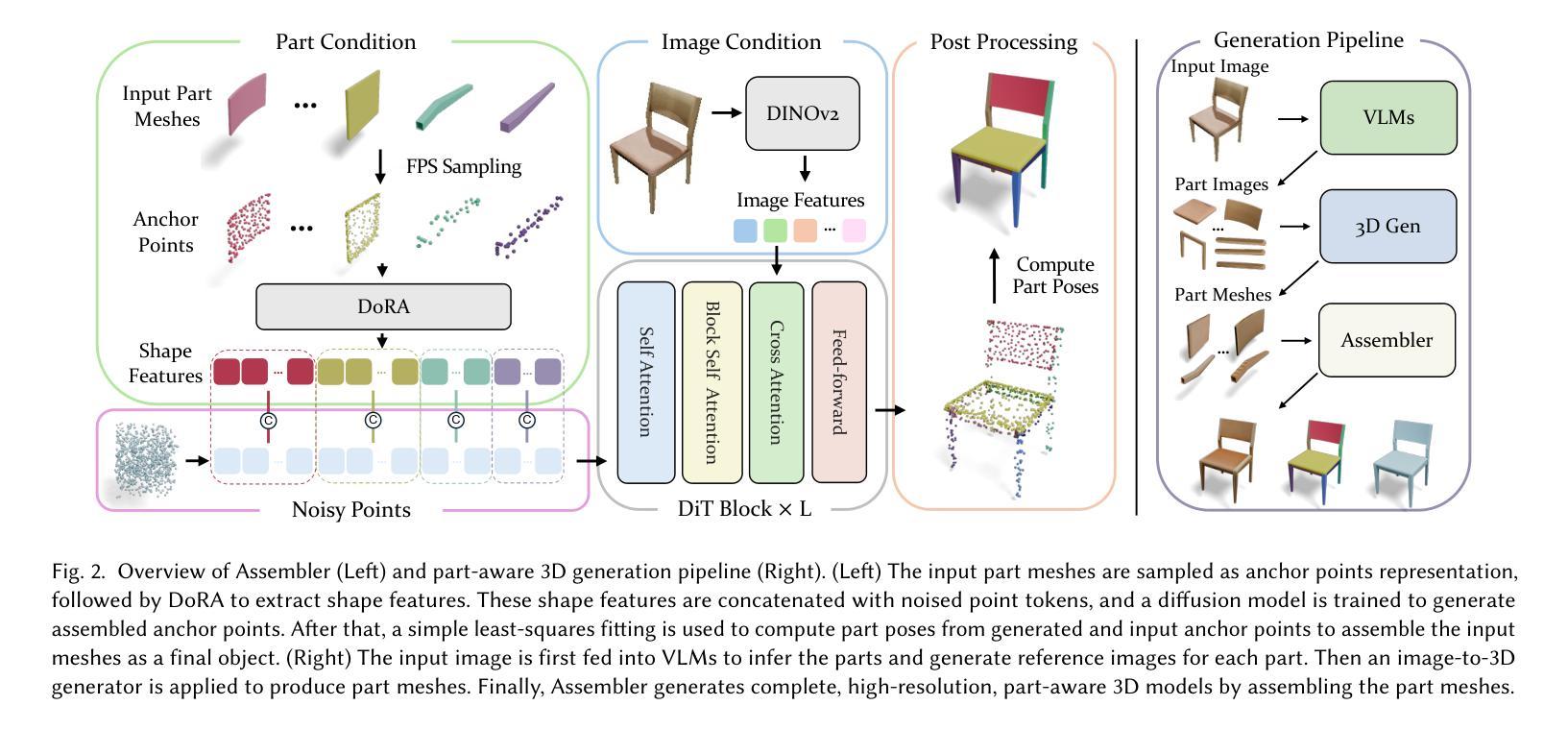
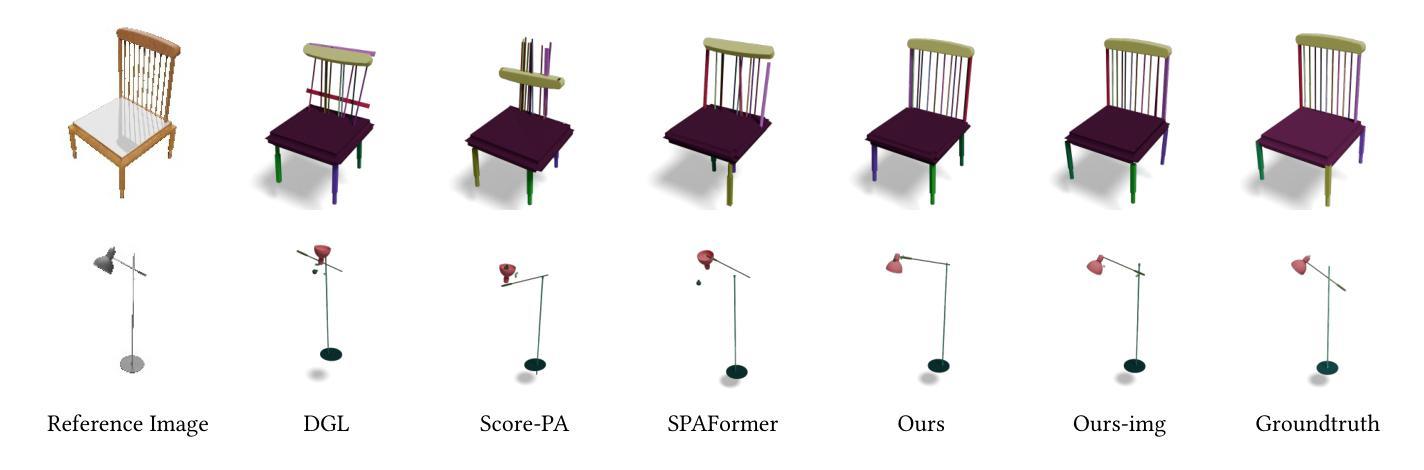
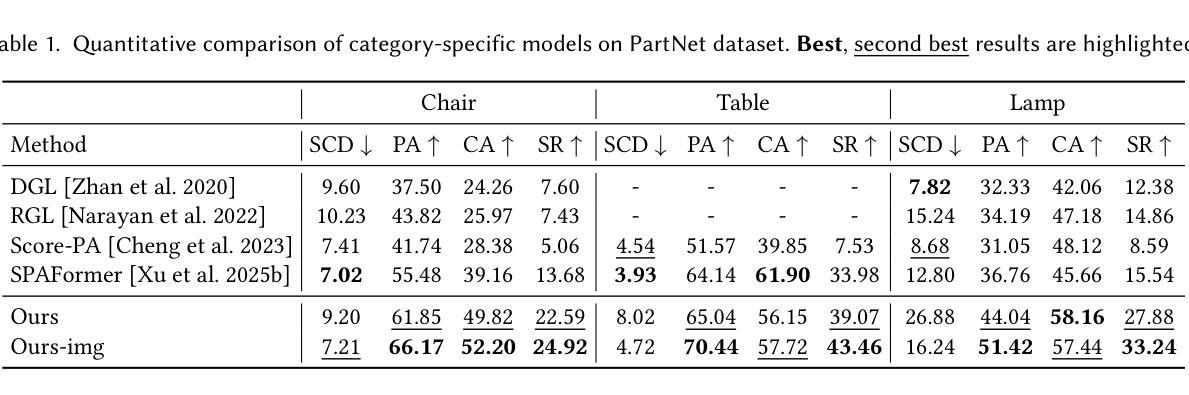
We present Assembler, a scalable and generalizable framework for 3D part assembly that reconstructs complete objects from input part meshes and a reference image. Unlike prior approaches that mostly rely on deterministic part pose prediction and category-specific training, Assembler is designed to handle diverse, in-the-wild objects with varying part counts, geometries, and structures. It addresses the core challenges of scaling to general 3D part assembly through innovations in task formulation, representation, and data. First, Assembler casts part assembly as a generative problem and employs diffusion models to sample plausible configurations, effectively capturing ambiguities arising from symmetry, repeated parts, and multiple valid assemblies. Second, we introduce a novel shape-centric representation based on sparse anchor point clouds, enabling scalable generation in Euclidean space rather than SE(3) pose prediction. Third, we construct a large-scale dataset of over 320K diverse part-object assemblies using a synthesis and filtering pipeline built on existing 3D shape repositories. Assembler achieves state-of-the-art performance on PartNet and is the first to demonstrate high-quality assembly for complex, real-world objects. Based on Assembler, we further introduce an interesting part-aware 3D modeling system that generates high-resolution, editable objects from images, demonstrating potential for interactive and compositional design. Project page: https://assembler3d.github.io
我们推出了Assembler,这是一个用于3D零件装配的可扩展和通用性框架,它可以从输入零件网格和参考图像重建完整的物体。不同于大多数依赖于确定性零件姿态预测和特定类别训练的方法,Assembler被设计来处理各种真实世界的物体,具有不同的零件数量、几何形状和结构。它通过任务制定、表征和数据方面的创新来解决扩展到通用3D零件装配的核心挑战。首先,Assembler将零件装配作为生成性问题,并采用扩散模型对可能的配置进行采样,从而有效地解决由对称性、重复零件和多个有效装配所引起的歧义。其次,我们引入了一种基于稀疏锚点云的新型形状中心表征,能够在欧几里得空间中进行可扩展生成,而不是进行SE(3)姿态预测。第三,我们使用建立在现有3D形状存储库上的合成和过滤管道,构建了一个包含超过32万个多样化零件物体装配的大型数据集。Assembler在PartNet上达到了最新性能水平,并且是第一个展示针对复杂现实世界物体高质量装配的系统。基于Assembler,我们还进一步推出了一款有趣的零件感知3D建模系统,该系统可以从图像生成高分辨率的可编辑物体,展示了其在交互式和组合设计方面的潜力。项目页面:https://assembler3d.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report. Project page: https://assembler3d.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了名为Assembler的框架,它可以从输入的部分网格和参考图像重建完整的物体,实现3D部件组装。不同于大多数依赖于确定性部件姿态预测和特定类别训练的方法,Assembler设计用于处理各种野生对象,具有不同的部件数量、几何形状和结构。它通过任务制定、表示和数据创新解决核心挑战,将部件组装转化为生成问题,并采用扩散模型对可能的配置进行采样,有效捕捉由对称性、重复部件和多个有效组装引起的歧义。此外,引入基于稀疏锚点的形状中心表示法,实现欧几里得空间中的可扩展生成,而不是SE(3)姿态预测。使用基于现有3D形状仓库的合成和过滤管道构建的大型部件对象组装数据集,包含超过32万个多样化样本。Assembler在PartNet上达到最新性能,并首次为复杂现实世界对象实现高质量组装。基于Assembler,进一步引入有趣的部件感知3D建模系统,从图像生成高分辨率、可编辑的对象,展示交互式和组合设计的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Assembler是一个用于3D部件组装的可伸缩和通用框架,能够从输入部分网格和参考图像重建完整物体。
- 与传统方法不同,Assembler能够处理具有不同部件数量、几何形状和结构的各种对象。
- Assembler通过将部件组装转化为生成问题,并采用扩散模型采样来解决核心挑战。
- Assembler引入基于稀疏锚点的形状中心表示法,实现欧几里得空间中的可扩展生成。
- 该框架使用合成和过滤管道构建的大型数据集,包含超过32万个多样化的部件对象组装样本。
- Assembler在PartNet上表现出最新性能,并为复杂现实世界对象提供高质量组装能力。
点此查看论文截图

Reward-Agnostic Prompt Optimization for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Semin Kim, Yeonwoo Cha, Jaehoon Yoo, Seunghoon Hong
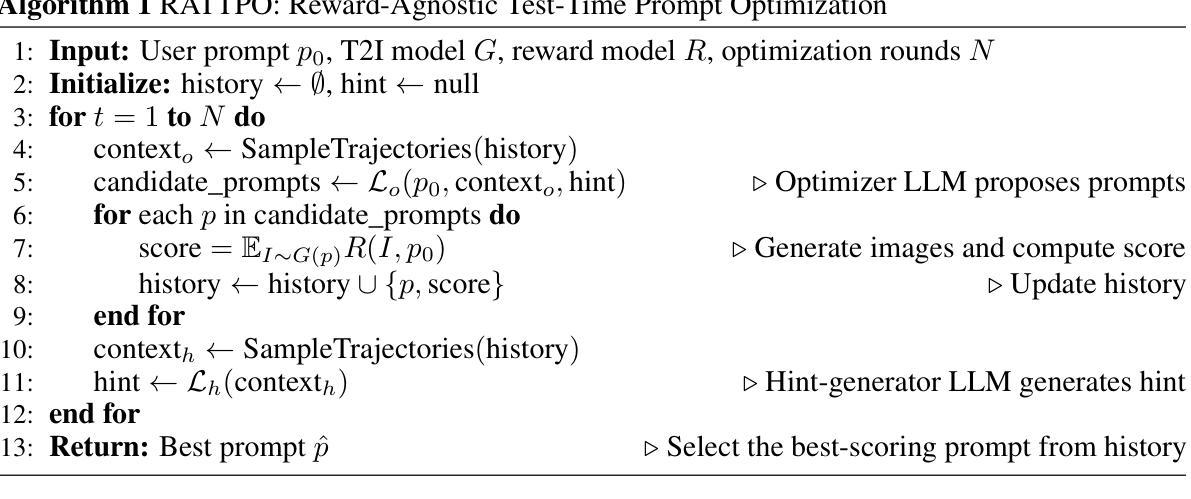
We investigate a general approach for improving user prompts in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models by finding prompts that maximize a reward function specified at test-time. Although diverse reward models are used for evaluating image generation, existing automated prompt engineering methods typically target specific reward configurations. Consequently, these specialized designs exhibit suboptimal performance when applied to new prompt engineering scenarios involving different reward models. To address this limitation, we introduce RATTPO (Reward-Agnostic Test-Time Prompt Optimization), a flexible test-time optimization method applicable across various reward scenarios without modification. RATTPO iteratively searches for optimized prompts by querying large language models (LLMs) \textit{without} requiring reward-specific task descriptions. Instead, it uses the optimization trajectory and a novel reward-aware feedback signal (termed a “hint”) as context. Empirical results demonstrate the versatility of RATTPO, effectively enhancing user prompts across diverse reward setups that assess various generation aspects, such as aesthetics, general human preference, or spatial relationships between objects. RATTPO surpasses other test-time search baselines in search efficiency, using up to 3.5 times less inference budget, and, given sufficient inference budget, achieves performance comparable to learning-based baselines that require reward-specific fine-tuning. The code is available at https://github.com/seminkim/RATTPO.
我们研究了一种通过寻找在测试时最大化指定奖励函数的提示来改善文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型中的用户提示的通用方法。尽管用于评估图像生成的不同奖励模型被广泛应用,但现有的自动化提示工程方法通常针对特定的奖励配置。因此,当应用于涉及不同奖励模型的新提示工程场景时,这些专业设计表现出次优性能。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了与奖励无关的测试时间提示优化(RATTPO),这是一种灵活的在测试时间进行优化方法,可在各种奖励场景中适用而无需修改。RATTPO通过查询大型语言模型(LLM)来迭代搜索优化的提示,而无需特定的奖励任务描述。相反,它使用优化轨迹和一种新颖的奖励感知反馈信号(称为“线索”)作为上下文。经验结果表明RATTPO的通用性,它能够有效地增强用户提示,涵盖评估各种生成方面的不同奖励设置,如美学、一般人类偏好或对象之间的空间关系。RATTPO在搜索效率上超越了其他测试时间搜索基准测试,使用高达3.5倍的推理预算更少,并且在给定足够的推理预算的情况下,它的性能与需要针对奖励进行特定微调的学习基准相当。代码可在https://github.com/seminkim/RATTPO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, Under review
Summary:
本文探讨了如何通过寻找最大化测试时指定的奖励函数的提示来改进文本到图像扩散模型中的用户提示。为解决现有自动化提示工程方法对新奖励模型的不适应问题,提出一种通用方法RATTPO(奖励无关的测试时间提示优化)。RATTPO可以在不同奖励场景下灵活应用,无需进行修改。它可以通过查询大型语言模型进行优化的提示搜索,使用优化轨迹和一种新颖的奖励感知反馈信号(称为“线索”)作为上下文。实验结果表明,RATTPO在各种奖励设置下可有效提高用户提示效果,并超越了其他测试时间搜索基线,提高了搜索效率,减少了高达3.5倍的推理预算。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways:
- 本文介绍了一种改进文本到图像扩散模型中用户提示的通用方法RATTPO。
- RATTPO解决了现有自动化提示工程方法对新奖励模型的不适应问题。
- RATTPO可在不同奖励场景下灵活应用,无需修改。
- RATTPO通过查询大型语言模型进行优化的提示搜索。
- RATTPO使用优化轨迹和奖励感知反馈信号(称为“线索”)作为上下文。
- 实验结果表明,RATTPO在各种奖励设置下可有效提高用户提示效果。
点此查看论文截图


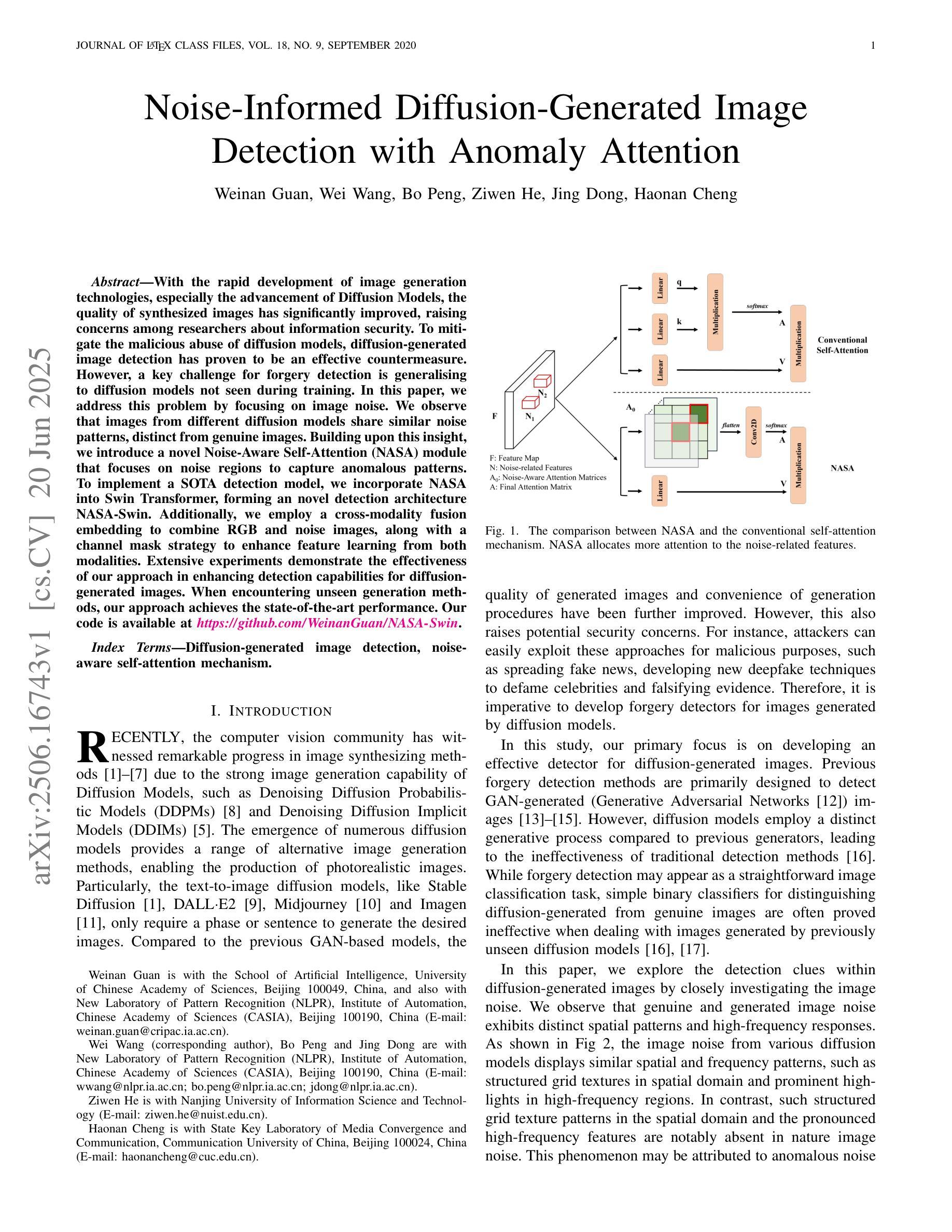
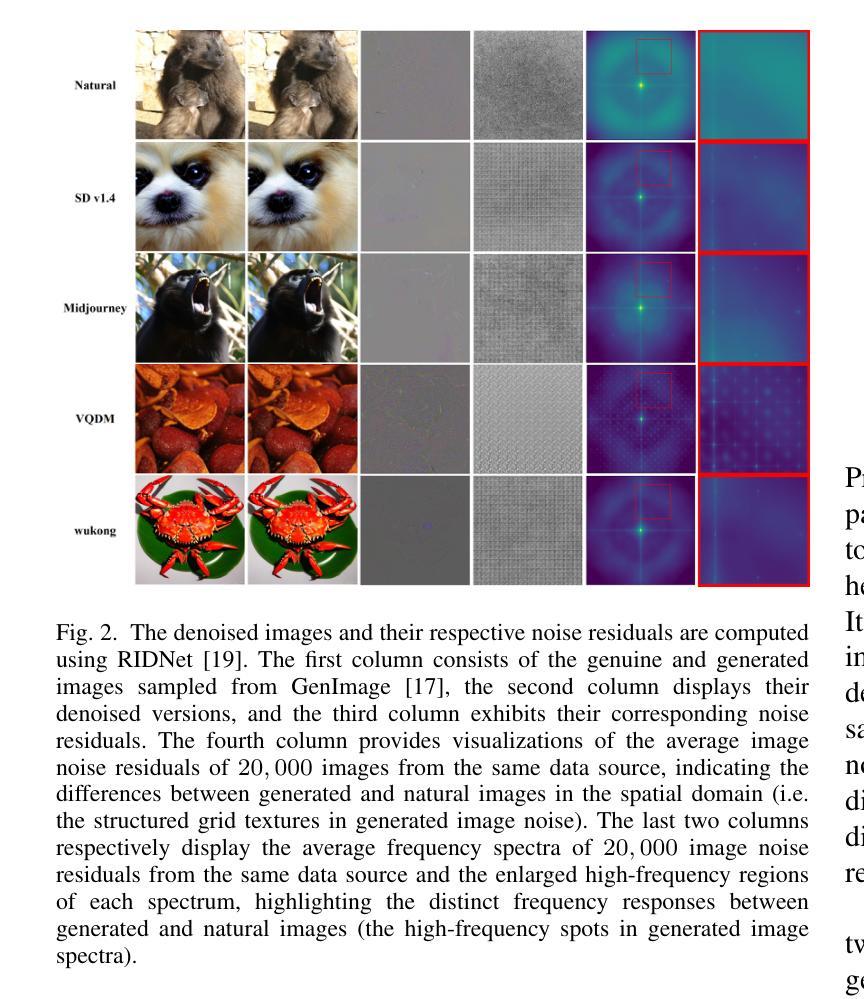
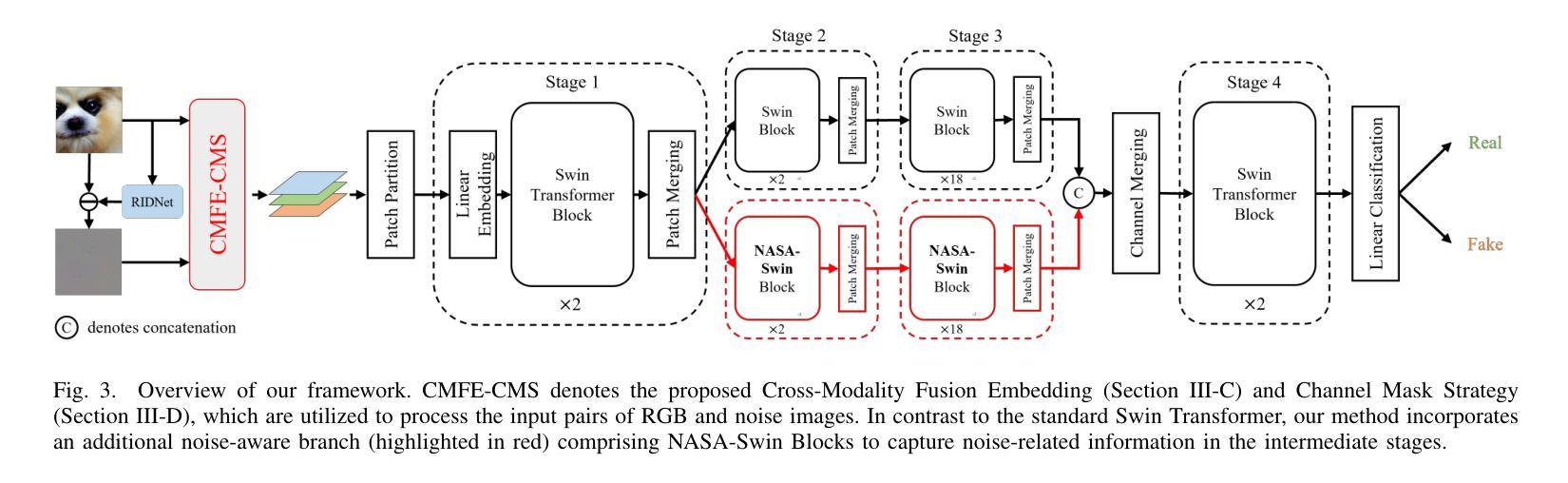
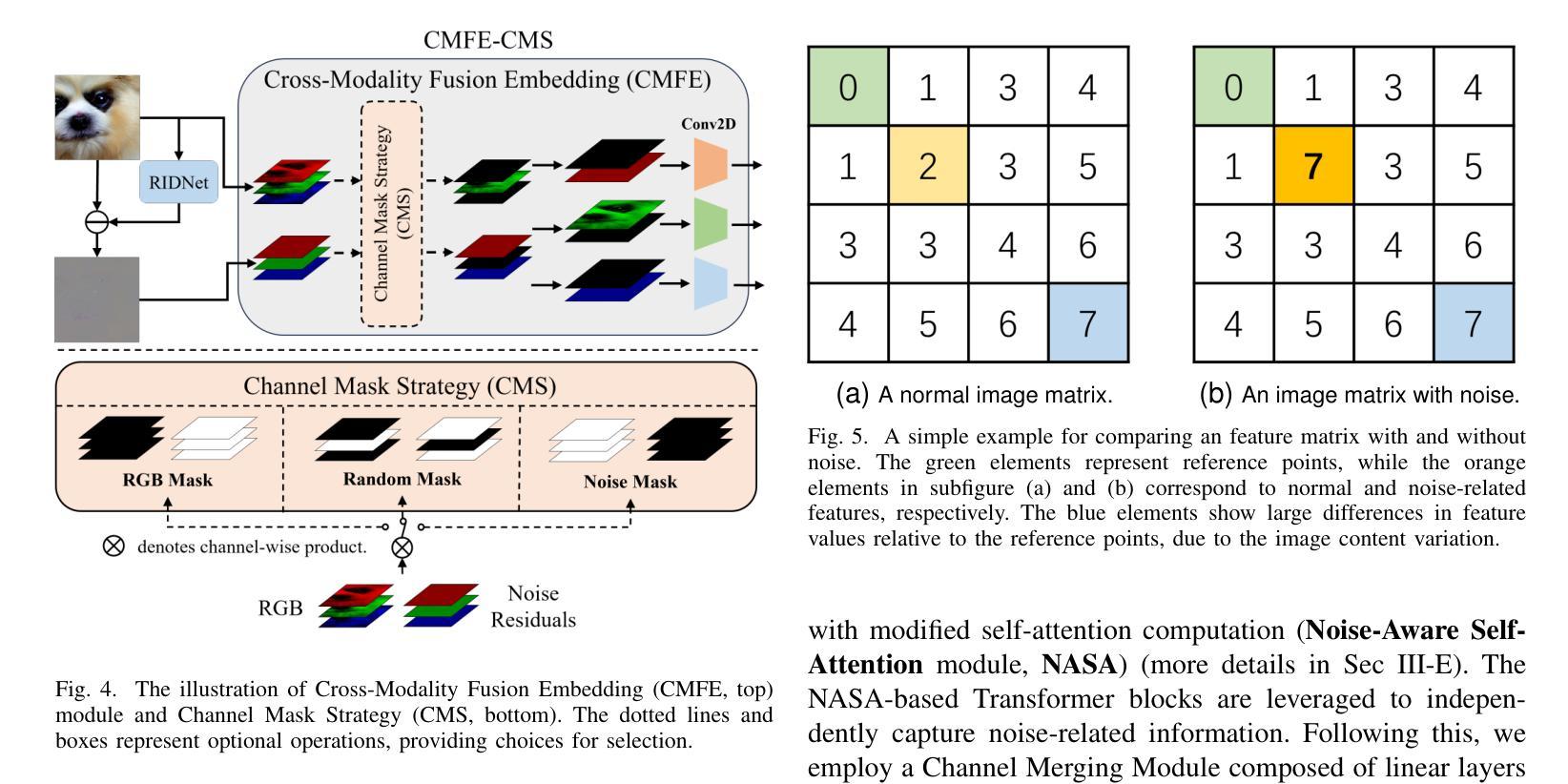
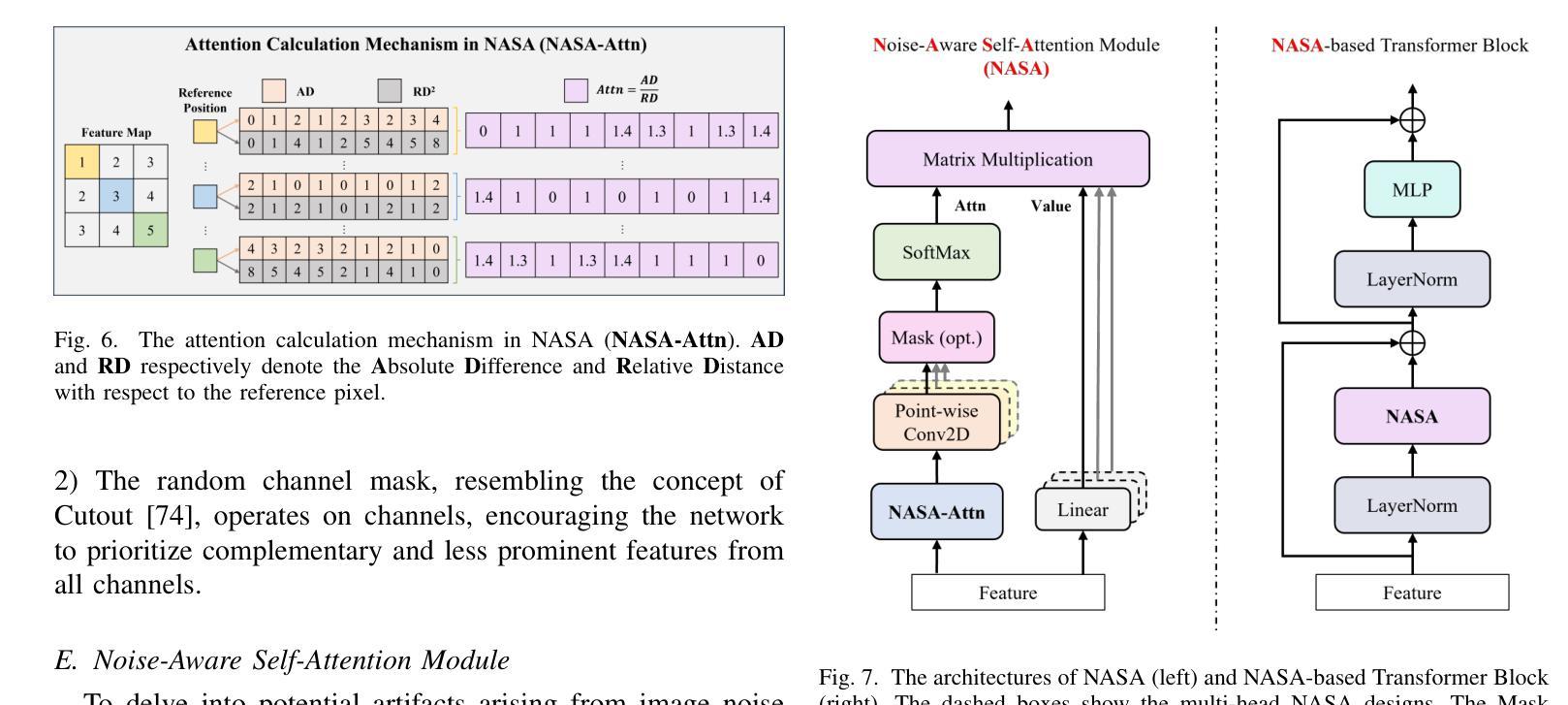
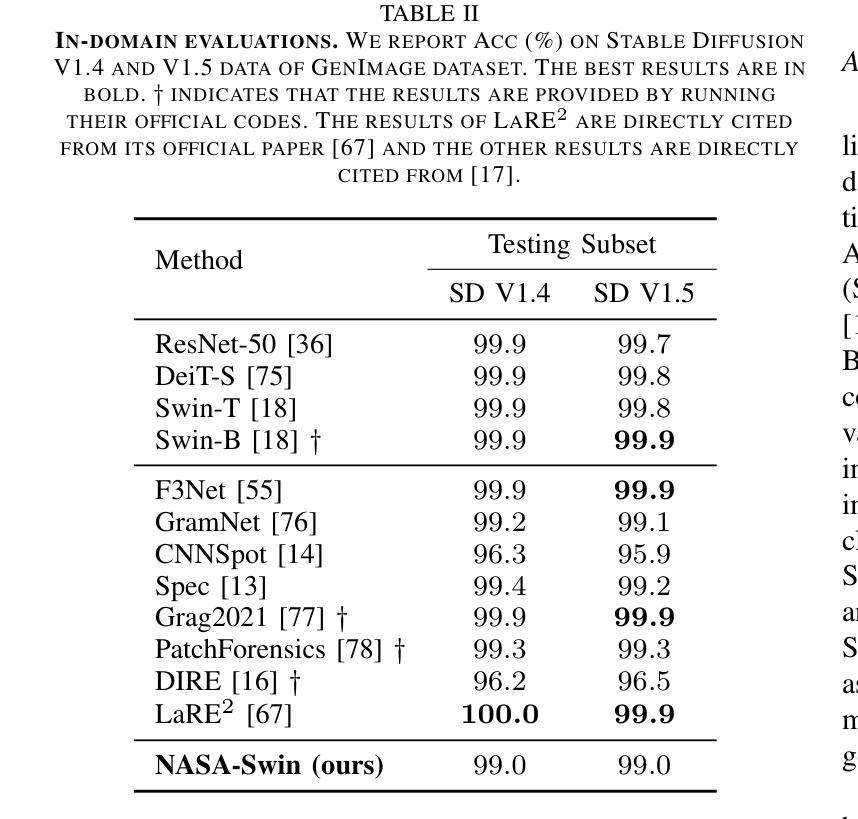
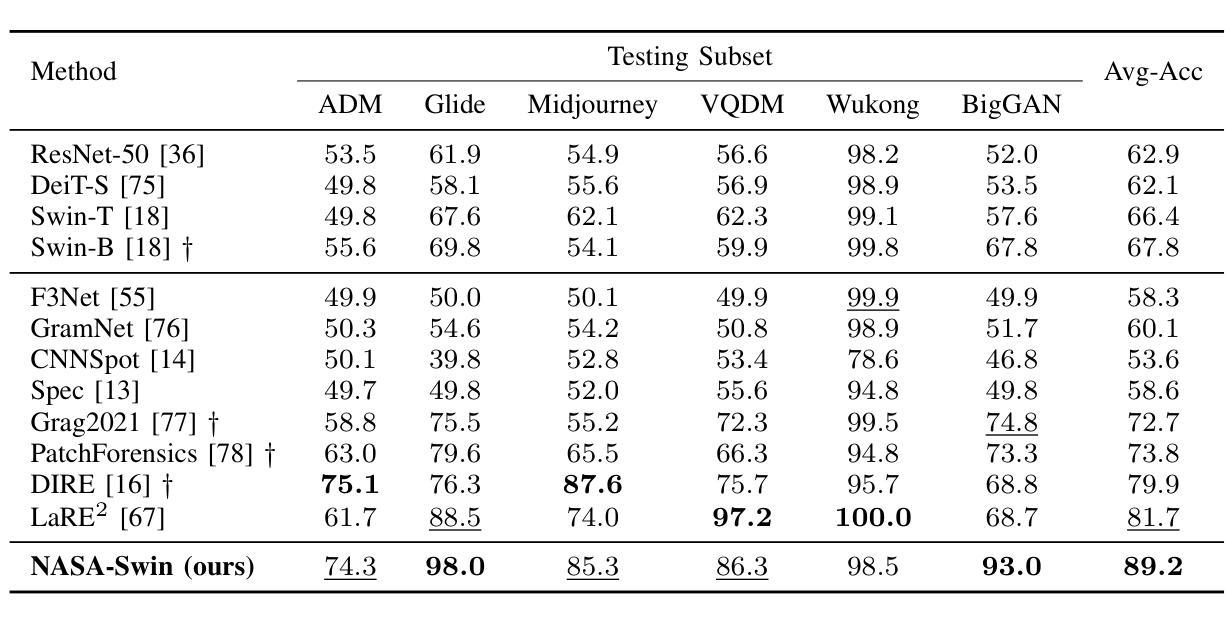
Noise-Informed Diffusion-Generated Image Detection with Anomaly Attention
Authors:Weinan Guan, Wei Wang, Bo Peng, Ziwen He, Jing Dong, Haonan Cheng
With the rapid development of image generation technologies, especially the advancement of Diffusion Models, the quality of synthesized images has significantly improved, raising concerns among researchers about information security. To mitigate the malicious abuse of diffusion models, diffusion-generated image detection has proven to be an effective countermeasure.However, a key challenge for forgery detection is generalising to diffusion models not seen during training. In this paper, we address this problem by focusing on image noise. We observe that images from different diffusion models share similar noise patterns, distinct from genuine images. Building upon this insight, we introduce a novel Noise-Aware Self-Attention (NASA) module that focuses on noise regions to capture anomalous patterns. To implement a SOTA detection model, we incorporate NASA into Swin Transformer, forming an novel detection architecture NASA-Swin. Additionally, we employ a cross-modality fusion embedding to combine RGB and noise images, along with a channel mask strategy to enhance feature learning from both modalities. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing detection capabilities for diffusion-generated images. When encountering unseen generation methods, our approach achieves the state-of-the-art performance.Our code is available at https://github.com/WeinanGuan/NASA-Swin.
随着图像生成技术的快速发展,尤其是扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的进步,合成图像的质量得到了显著提高,这引起了研究者对信息安全的关注。为了减少扩散模型的恶意滥用,扩散生成图像检测已被证明是一种有效的对策。然而,检测伪造图像的一个关键挑战是如何对训练时未见到的扩散模型进行通用化。在本文中,我们通过关注图像噪声来解决这个问题。我们发现,来自不同扩散模型的图像具有相似的噪声模式,这与真实图像截然不同。基于这一观察,我们引入了一种新型噪声感知自注意力(NASA)模块,该模块专注于噪声区域以捕获异常模式。为了实现先进的检测模型,我们将NASA融入Swin Transformer,形成了新型的检测架构NASA-Swin。此外,我们采用跨模态融合嵌入方法,结合RGB图像和噪声图像,以及通道掩码策略,以增强两种模态的特征学习。大量实验表明,我们的方法在增强扩散生成图像的检测能力方面非常有效。当遇到未见过的生成方法时,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/WeinanGuan/NASA-Swin获取。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TIFS 2025. Our code is availabel at https://github.com/WeinanGuan/NASA-Swin
Summary
扩散模型生成的图像检测已成为应对恶意滥用扩散模型的有效对策。本文关注图像噪声,发现不同扩散模型生成的图像具有相似的噪声模式,与真实图像不同。基于此,我们引入了新型的噪声感知自注意力(NASA)模块,该模块专注于噪声区域以捕获异常模式。通过结合NASA和Swin Transformer,我们构建了先进的检测架构NASA-Swin。实验证明,该方法在提高检测扩散生成图像的能力方面非常有效,并在遇到未见过的生成方法时达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型生成的图像质量提高引发了信息安全的关注。
- 扩散模型生成的图像具有特定的噪声模式,与真实图像不同。
- 噪声感知自注意力(NASA)模块被引入,专注于噪声区域以检测异常模式。
- 结合NASA和Swin Transformer构建了先进的检测架构NASA-Swin。
- 采用跨模态融合嵌入技术,结合RGB和噪声图像。
- 通道掩码策略被用来增强两种模态的特征学习。
点此查看论文截图
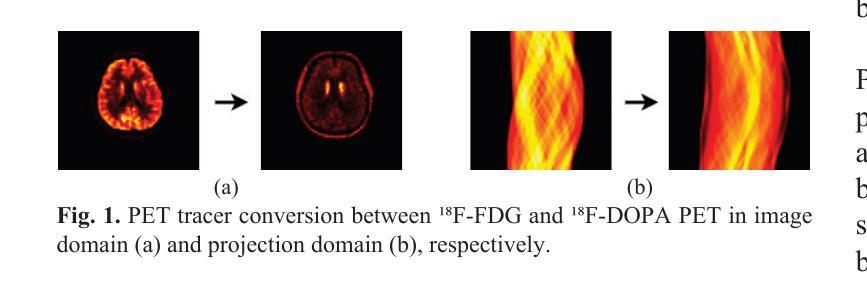
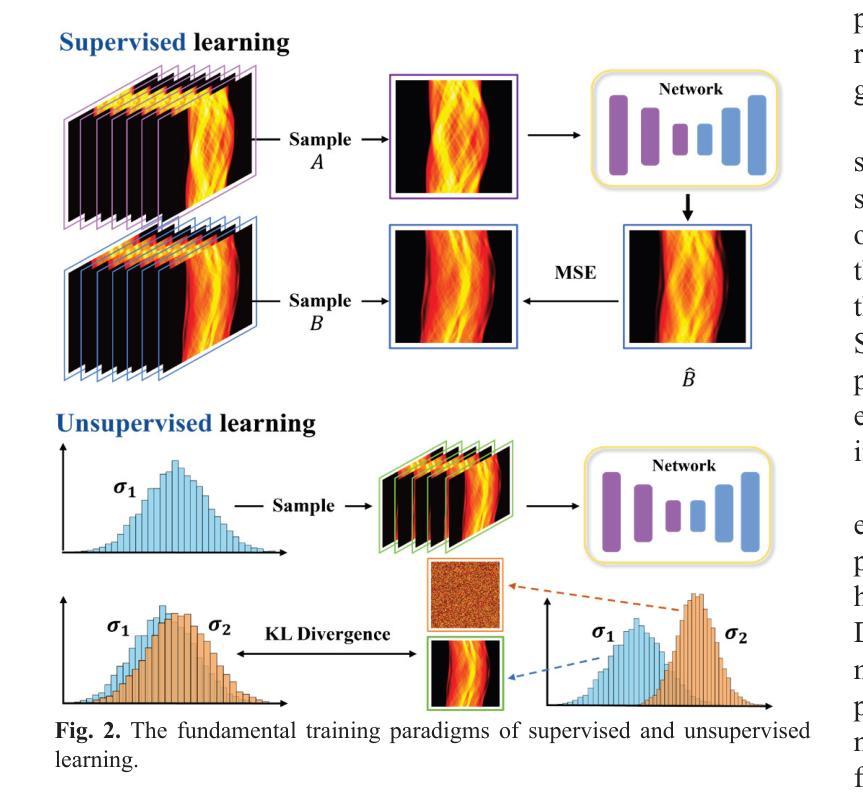
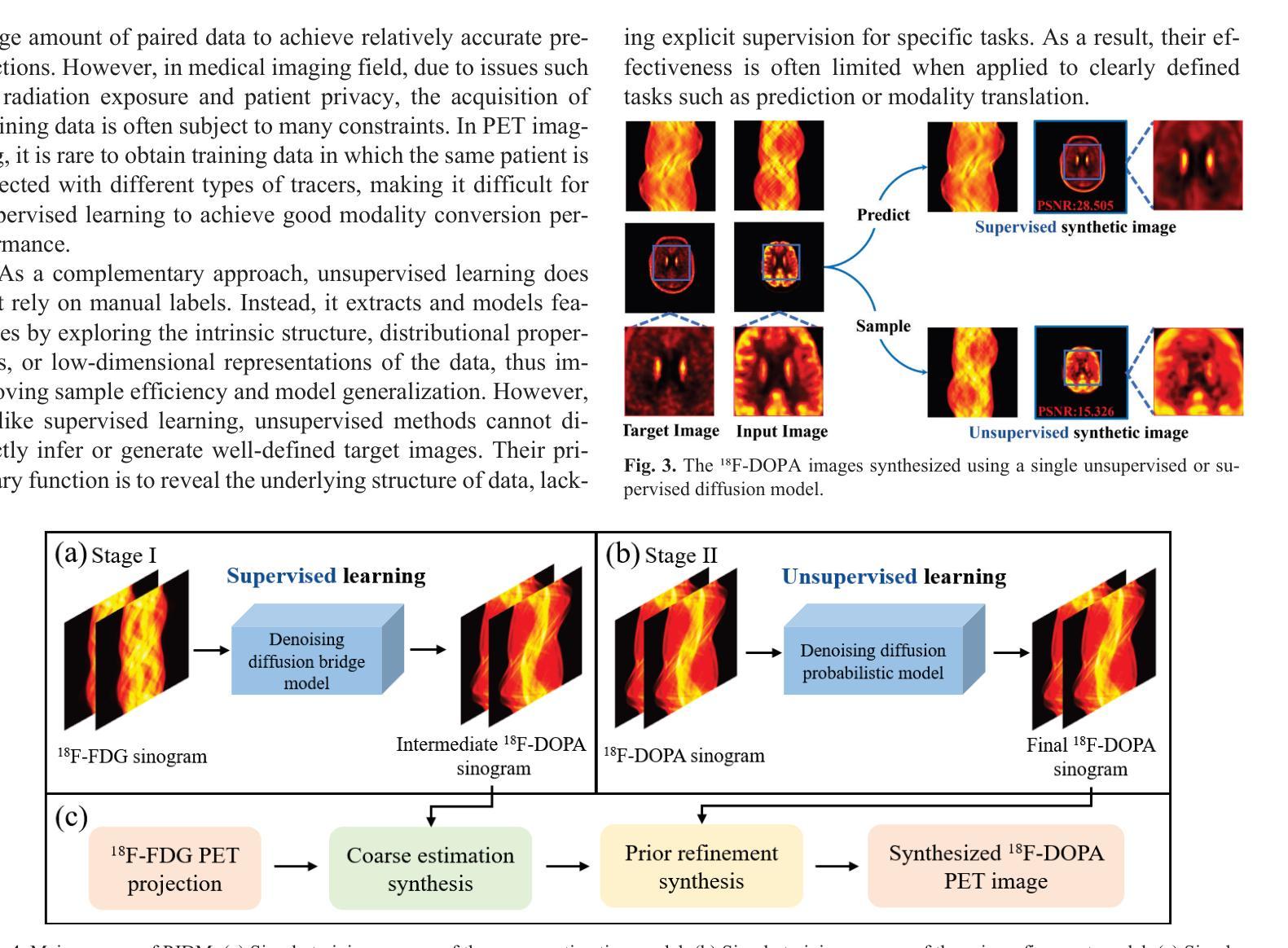
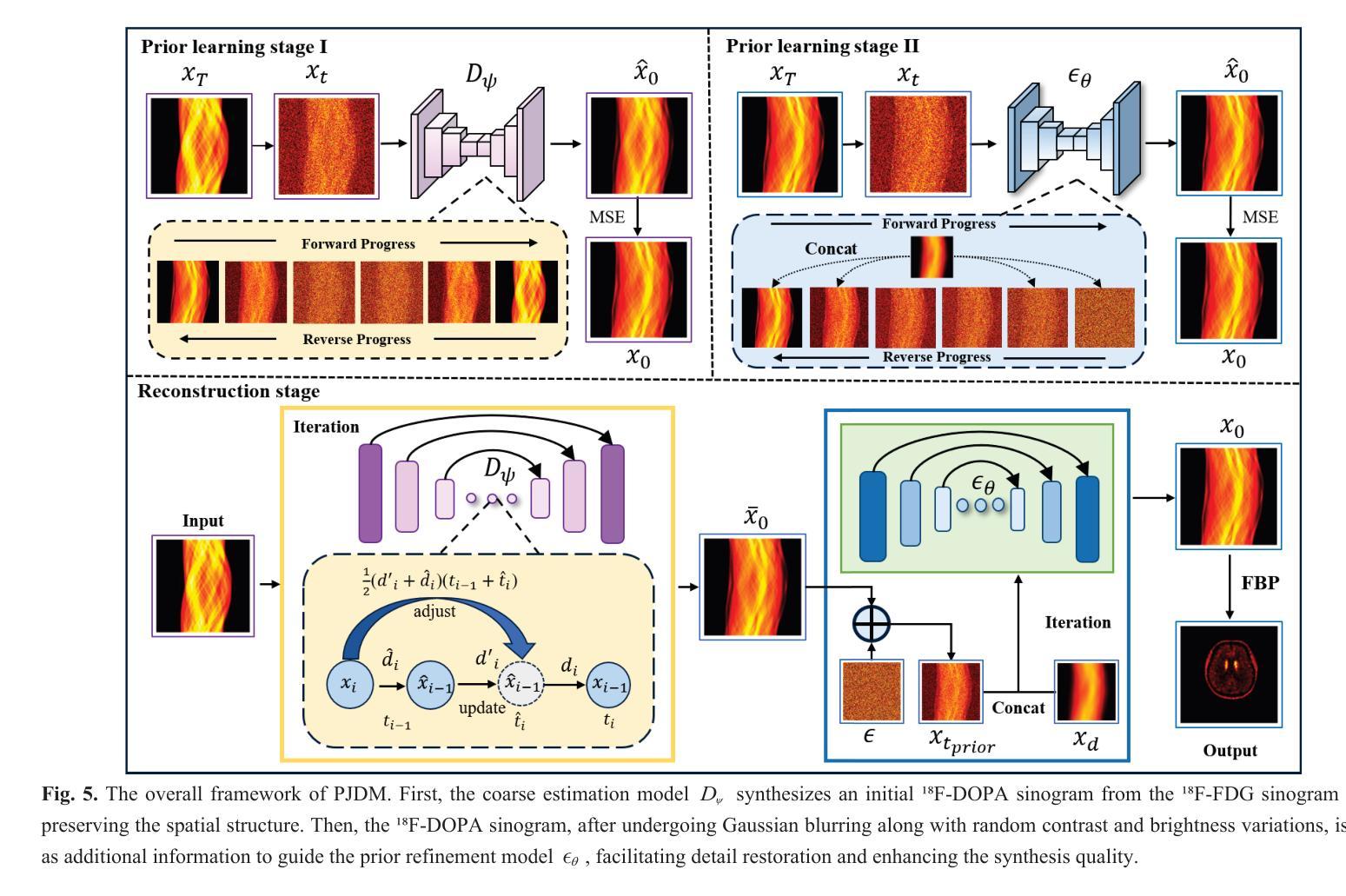
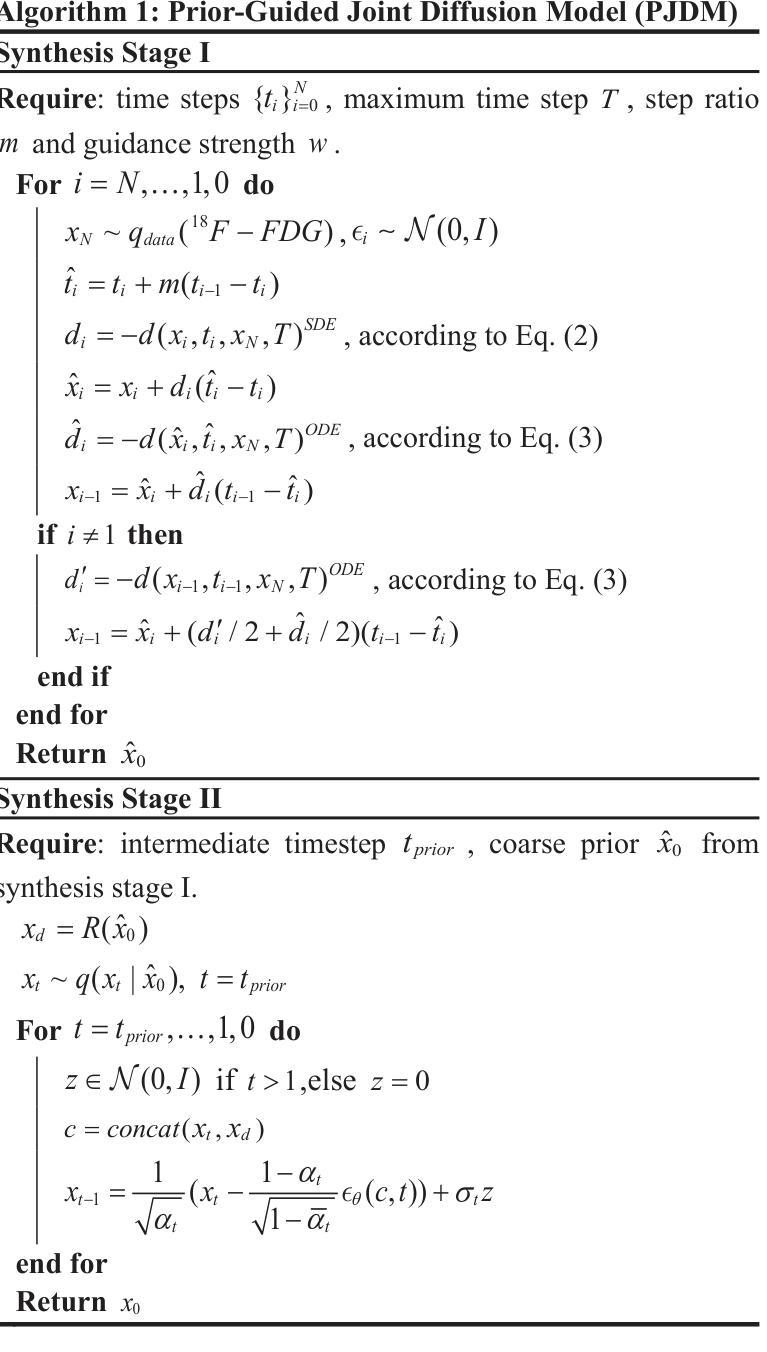
A Prior-Guided Joint Diffusion Model in Projection Domain for PET Tracer Conversion
Authors:Fang Chen, Weifeng Zhang, Xingyu Ai, BingXuan Li, An Li, Qiegen Liu
Positron emission tomography (PET) is widely used to assess metabolic activity, but its application is limited by the availability of radiotracers. 18F-labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) is the most commonly used tracer but shows limited effectiveness for certain tumors. In contrast, 6-18F-fluoro-3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (18F-DOPA) offers higher specificity for neuroendocrine tumors and neurological disorders. However, its complex synthesis and limitations in transportation and clinical use hinder widespread adoption. During PET imaging, the sinogram represents a form of raw data acquired by the scanner. Therefore, modeling in projection domain enables more direct utilization of the original information, potentially reducing the accumulation of errors introduced during the image reconstruction process. Inspired by these factors, this study proposes a prior-guided joint diffusion model (PJDM) for transforming 18F-FDG PET images into 18F-DOPA PET images in projection domain. Specifically, a coarse estimation model and a prior refinement model are trained independently. During inference, an initial synthetic 18F-DOPA PET sinogram is generated using a higher-order hybrid sampler. This sinogram is then degraded and serves as an additional condition to guide the iterative refinement process using learned prior. Experimental results demonstrated that PJDM effectively improved both sinogram quality and synthetic outcomes. The code is available at: https://github.com/yqx7150/PJDM.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)广泛应用于评估代谢活性,但其应用受到放射性示踪剂可用性的限制。¹⁸F标记的氟脱氧葡萄糖(¹⁸F-FDG)是最常用的示踪剂,但对某些肿瘤的有效性有限。相比之下,6-¹⁸F-氟-3,4-二羟基-L-苯丙氨酸(¹⁸F-DOPA)对神经内分泌肿瘤和神经障碍具有更高的特异性。然而,其复杂的合成以及运输和临床使用的限制阻碍了其广泛采用。在PET成像中,辛格图(sinogram)代表由扫描仪获得的一种原始数据形式。因此,投影域建模能够更直接地利用原始信息,可能减少图像重建过程中引入的误差积累。受这些因素启发,本研究提出了一种先验引导联合扩散模型(PJDM),用于在投影域中将¹⁸F-FDG PET图像转换为¹⁸F-DOPA PET图像。具体而言,训练了一个粗略估计模型和先验优化模型。在推理过程中,使用高阶混合采样器生成初始合成¹⁸F-DOPA PET辛格图,然后对其进行退化处理,作为迭代优化过程的附加条件,以引导学习先验。实验结果表明,PJDM有效提高了辛格图的质量和合成效果。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/yqx7150/PJDM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于先验引导的联合扩散模型(PJDM),用于在投影域将18F-FDG PET图像转换为18F-DOPA PET图像。该模型通过训练粗略估算模型和先验优化模型,生成初始的18F-DOPA PET正弦图,并对其进行退化处理,作为引导迭代优化过程的条件。实验结果表明,PJDM能有效提高正弦图质量和合成效果。
Key Takeaways
- PET在代谢活性评估中广泛应用,但受限于放射示踪剂的可获得性。
- 18F-FDG是最常用的示踪剂,但对某些肿瘤的效用有限。
- 18F-DOPA为神经内分泌肿瘤和神经疾病提供了更高的特异性,但其合成复杂且临床应用受限。
- 研究提出了基于先验引导的联合扩散模型(PJDM)进行图像转换。
- 该模型通过训练粗略估算模型和先验优化模型来生成初始的18F-DOPA PET正弦图。
- 初始合成的正弦图经过退化处理,用作迭代优化过程的引导条件。
点此查看论文截图

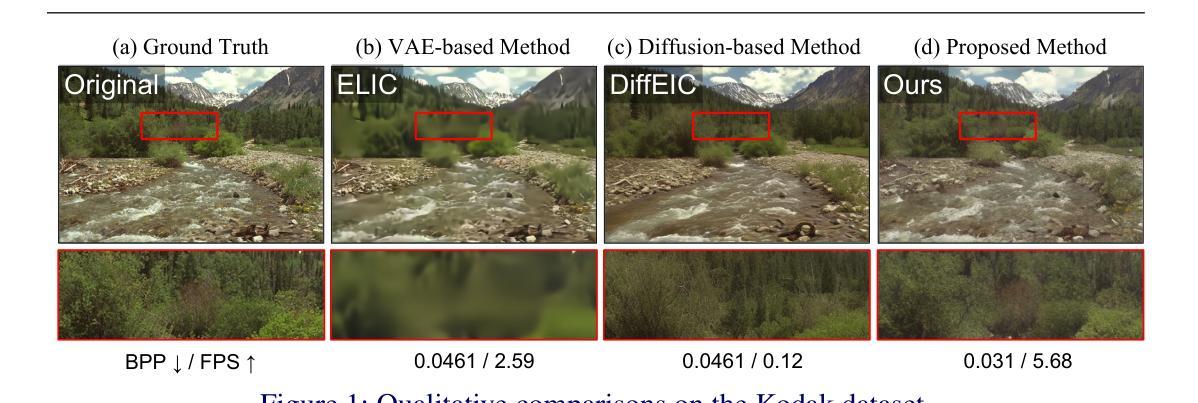
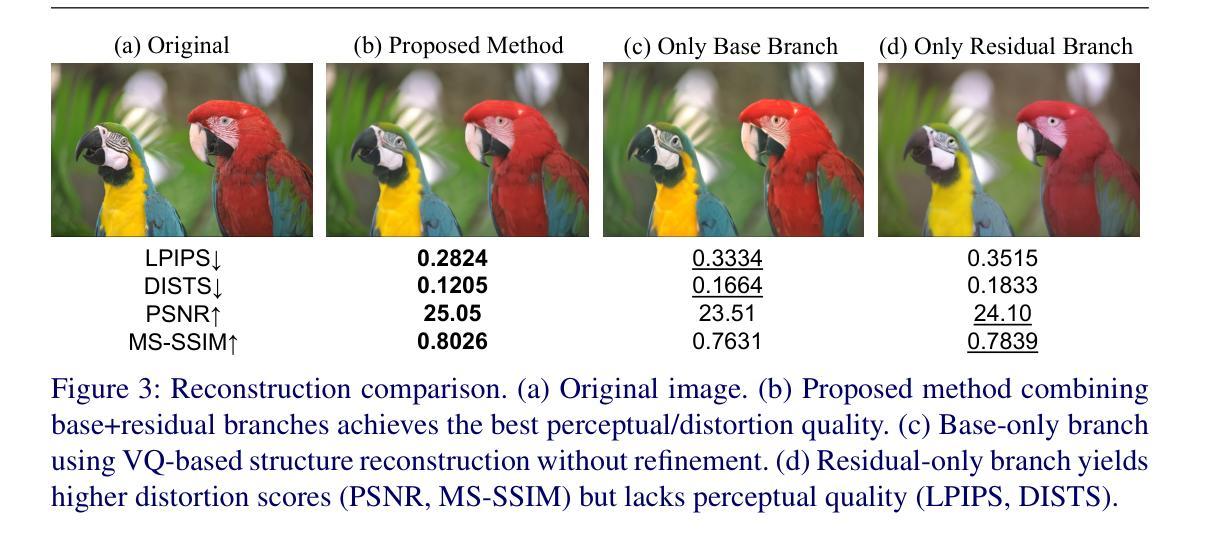
DiffO: Single-step Diffusion for Image Compression at Ultra-Low Bitrates
Authors:Chanung Park, Joo Chan Lee, Jong Hwan Ko
Although image compression is fundamental to visual data processing and has inspired numerous standard and learned codecs, these methods still suffer severe quality degradation at extremely low bits per pixel. While recent diffusion based models provided enhanced generative performance at low bitrates, they still yields limited perceptual quality and prohibitive decoding latency due to multiple denoising steps. In this paper, we propose the first single step diffusion model for image compression (DiffO) that delivers high perceptual quality and fast decoding at ultra low bitrates. DiffO achieves these goals by coupling two key innovations: (i) VQ Residual training, which factorizes a structural base code and a learned residual in latent space, capturing both global geometry and high frequency details; and (ii) rate adaptive noise modulation, which tunes denoising strength on the fly to match the desired bitrate. Extensive experiments show that DiffO surpasses state of the art compression performance while improving decoding speed by about 50x compared to prior diffusion-based methods, greatly improving the practicality of generative codecs. The code will be available at https://github.com/Freemasti/DiffO.
尽管图像压缩是视觉数据处理的基础,并激发了许多标准和学习的编码技术,但这些方法在极低比特率下仍面临严重的质量下降问题。虽然最近的扩散模型在低比特率下提供了增强的生成性能,但它们仍然因多步去噪而具有有限的感知质量和较高的解码延迟。在本文中,我们提出了第一个用于图像压缩的单步扩散模型(DiffO),该模型在超低比特率下提供高质量的感知和快速解码。DiffO通过两个关键创新实现了这些目标:(i)VQ残差训练,它在潜在空间中分解了一个结构基础码和一个学习到的残差,同时捕捉全局几何信息和高频细节;(ii)速率自适应噪声调制,它即时调整去噪强度以匹配所需的比特率。大量实验表明,DiffO的压缩性能超过了现有技术,与先前的扩散方法相比,解码速度提高了约50倍,大大提高了生成编码技术的实用性。代码将在https://github.com/Freemasti/DiffO上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的单步图像压缩方法(DiffO),可在超低比特率下实现高感知质量和快速解码。DiffO通过两个关键创新实现目标:一是VQ残差训练,它分解了一个结构基础码和潜在空间中的学习残差,捕捉全局几何结构和高频细节;二是速率自适应噪声调制,它可实时调整去噪强度,以适应所需的比特率。实验表明,DiffO在压缩性能上超越了现有技术,并将解码速度提高了约50倍,大大提高了生成编码器的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于扩散模型的单步图像压缩方法(DiffO)。
- DiffO能在超低比特率下工作,实现高感知质量和快速解码。
- VQ残差训练用于分解结构基础码和学习残差,捕捉全局几何和高频细节。
- 速率自适应噪声调制可实时调整去噪强度,适应所需比特率。
- DiffO在压缩性能上超越了现有技术。
- 与先前的扩散方法相比,DiffO将解码速度提高了约50倍。
点此查看论文截图

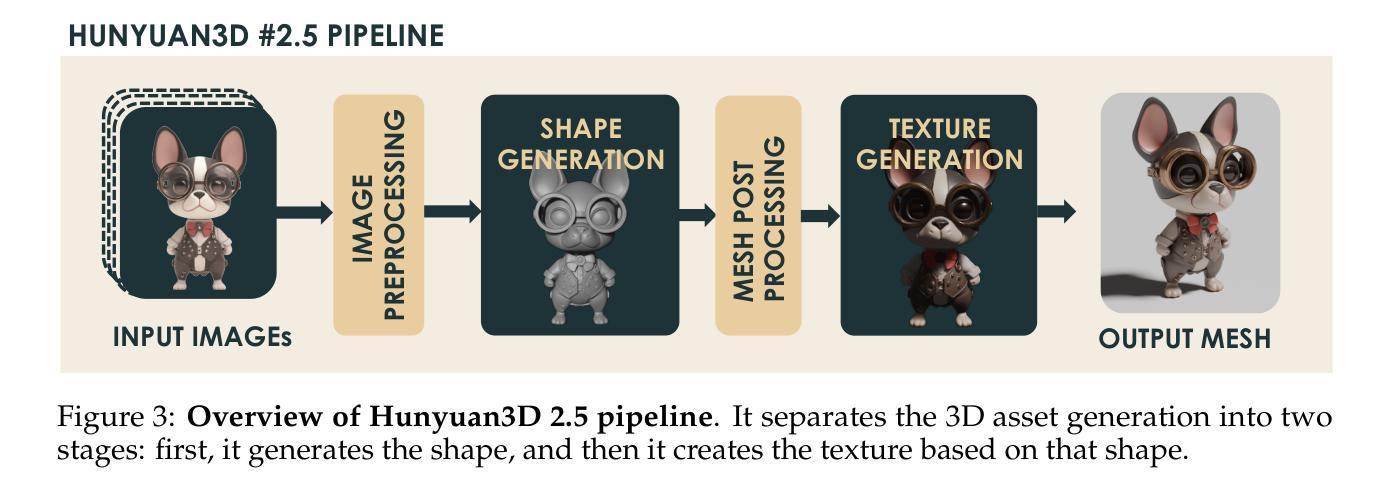
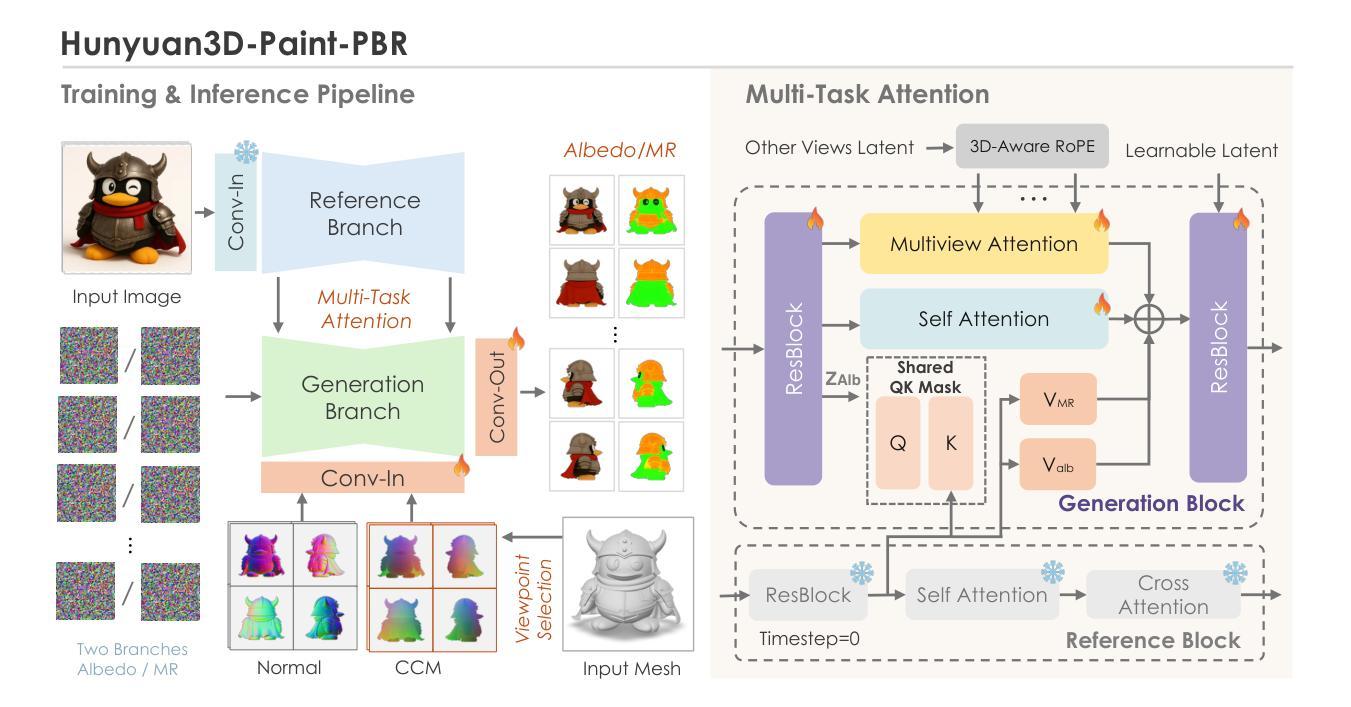
Hunyuan3D 2.5: Towards High-Fidelity 3D Assets Generation with Ultimate Details
Authors:Zeqiang Lai, Yunfei Zhao, Haolin Liu, Zibo Zhao, Qingxiang Lin, Huiwen Shi, Xianghui Yang, Mingxin Yang, Shuhui Yang, Yifei Feng, Sheng Zhang, Xin Huang, Di Luo, Fan Yang, Fang Yang, Lifu Wang, Sicong Liu, Yixuan Tang, Yulin Cai, Zebin He, Tian Liu, Yuhong Liu, Jie Jiang, Linus, Jingwei Huang, Chunchao Guo
In this report, we present Hunyuan3D 2.5, a robust suite of 3D diffusion models aimed at generating high-fidelity and detailed textured 3D assets. Hunyuan3D 2.5 follows two-stages pipeline of its previous version Hunyuan3D 2.0, while demonstrating substantial advancements in both shape and texture generation. In terms of shape generation, we introduce a new shape foundation model – LATTICE, which is trained with scaled high-quality datasets, model-size, and compute. Our largest model reaches 10B parameters and generates sharp and detailed 3D shape with precise image-3D following while keeping mesh surface clean and smooth, significantly closing the gap between generated and handcrafted 3D shapes. In terms of texture generation, it is upgraded with phyiscal-based rendering (PBR) via a novel multi-view architecture extended from Hunyuan3D 2.0 Paint model. Our extensive evaluation shows that Hunyuan3D 2.5 significantly outperforms previous methods in both shape and end-to-end texture generation.
在这份报告中,我们介绍了亨源3D 2.5版本,这是一套稳健的3D扩散模型套件,旨在生成高保真和具有纹理细节的3D资产。亨源3D 2.5遵循其前版亨源3D 2.0的两阶段流程,同时在形状和纹理生成方面实现了重大进展。在形状生成方面,我们引入了一种新的形状基础模型——点阵模型(LATTICE),它采用规模化高质量数据集、模型大小和计算能力进行训练。我们的大型模型达到10亿个参数,可以生成清晰且详细的3D形状,精确跟随图像-3D,同时保持网格表面清洁光滑,显著缩小了生成的和手工制作的3D形状之间的差距。在纹理生成方面,它通过从亨源3D 2.0的画笔模型扩展出来的新型多视图架构升级为基于物理的渲染(PBR)。我们的全面评估显示,亨源3D 2.5在形状和端到端纹理生成方面都显著优于之前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
胡园三维技术团队推出的新版软件Hunyuan3D 2.5采用了升级版的深度学习模型体系。与旧版本相比,不仅继续优化了整体的两阶段处理流程,还进行了更深度的系统提升与更新,使三维形状生成与纹理渲染都实现了更高的精度与清晰度。胡园3D 2.5的全新模型生成的三维形状具有更清晰和更精细的细节,更准确的图像到三维的映射效果,同时保持网格表面清洁光滑。此外,其物理渲染技术也通过全新的多视角架构得到了提升,显著提升了纹理渲染的质量。整体而言,胡园三维技术团队的新版软件显著超越了现有技术的表现。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图



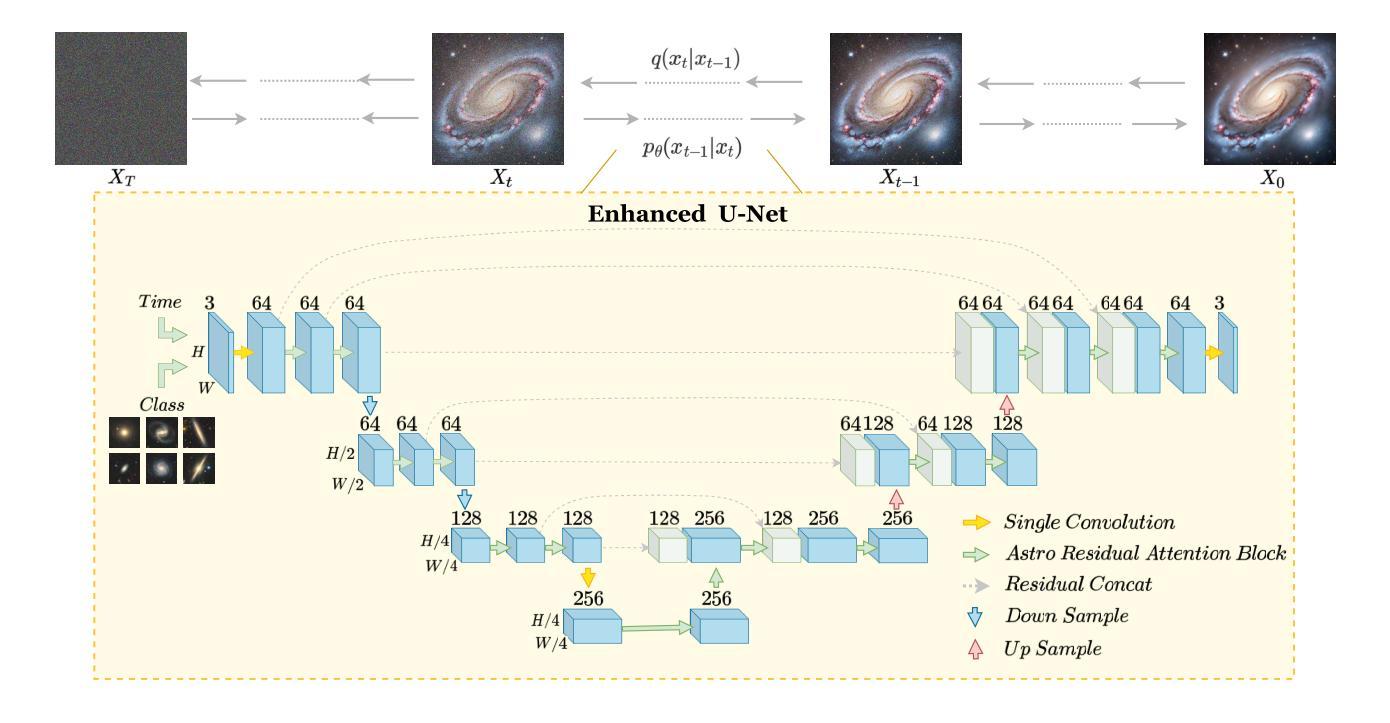
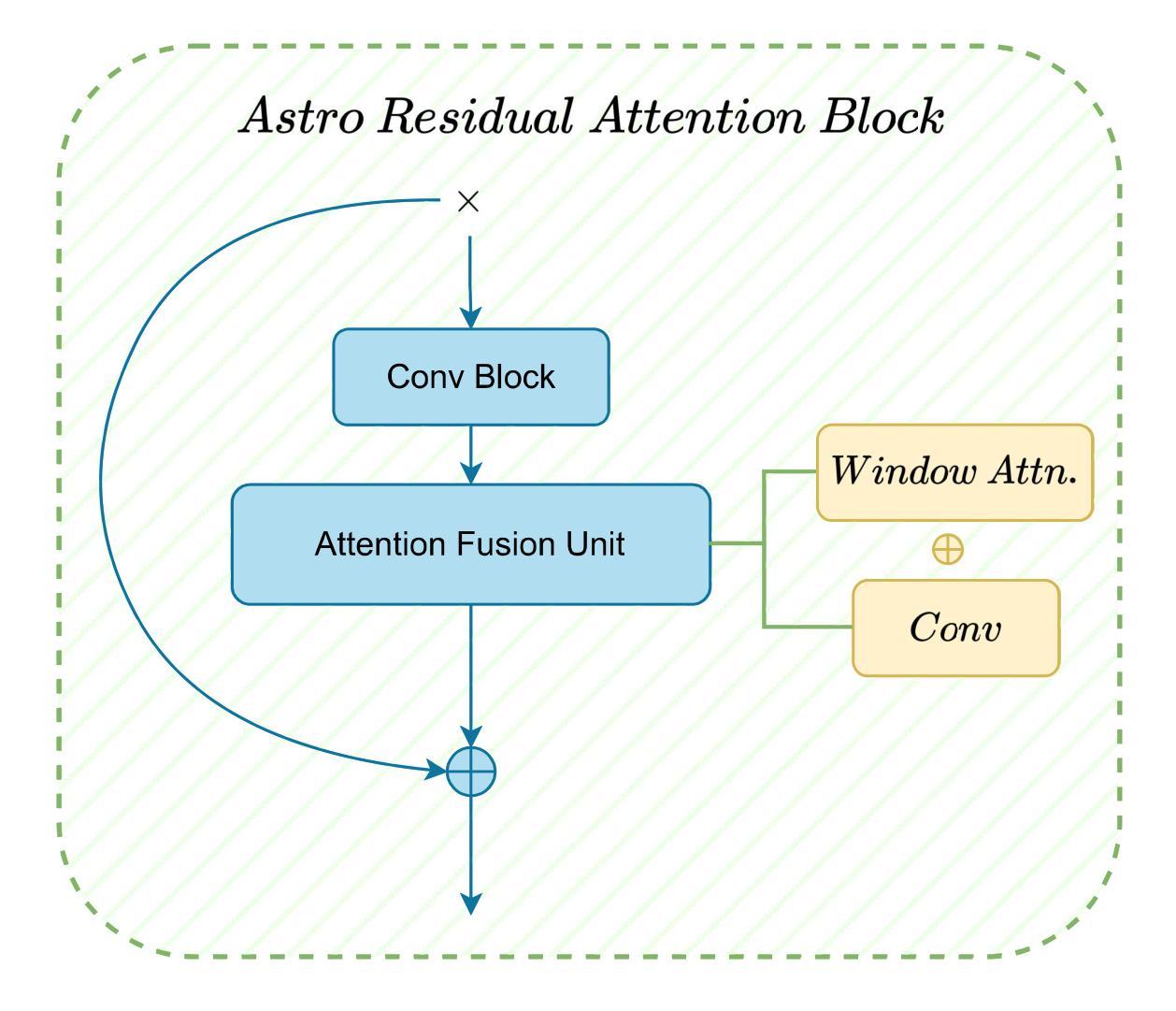
Category-based Galaxy Image Generation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Xingzhong Fan, Hongming Tang, Yue Zeng, M. B. N. Kouwenhoven, Guangquan Zeng
Conventional galaxy generation methods rely on semi-analytical models and hydrodynamic simulations, which are highly dependent on physical assumptions and parameter tuning. In contrast, data-driven generative models do not have explicit physical parameters pre-determined, and instead learn them efficiently from observational data, making them alternative solutions to galaxy generation. Among these, diffusion models outperform Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in quality and diversity. Leveraging physical prior knowledge to these models can further enhance their capabilities. In this work, we present GalCatDiff, the first framework in astronomy to leverage both galaxy image features and astrophysical properties in the network design of diffusion models. GalCatDiff incorporates an enhanced U-Net and a novel block entitled Astro-RAB (Residual Attention Block), which dynamically combines attention mechanisms with convolution operations to ensure global consistency and local feature fidelity. Moreover, GalCatDiff uses category embeddings for class-specific galaxy generation, avoiding the high computational costs of training separate models for each category. Our experimental results demonstrate that GalCatDiff significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of the consistency of sample color and size distributions, and the generated galaxies are both visually realistic and physically consistent. This framework will enhance the reliability of galaxy simulations and can potentially serve as a data augmentor to support future galaxy classification algorithm development.
传统星系生成方法依赖于半解析模型和水动力学模拟,这些方法高度依赖于物理假设和参数调整。相比之下,数据驱动的生成模型没有预先确定的明确物理参数,而是从观测数据中有效地学习这些参数,使其成为星系生成的替代解决方案。在这些模型中,扩散模型在质量和多样性方面优于变分自动编码器(VAEs)和生成对抗网络(GANs)。利用物理先验知识可以进一步提高这些模型的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了GalCatDiff,这是天文学中第一个利用星系图像特征和天文物理属性来设计扩散模型的网络框架。GalCatDiff集成了增强型U-Net和一个名为Astro-RAB(残差注意力块)的新颖模块,它动态地将注意力机制与卷积操作相结合,以确保全局一致性和局部特征保真度。此外,GalCatDiff使用类别嵌入进行特定类别的星系生成,避免了为每个类别训练单独模型的高计算成本。我们的实验结果表明,在样本颜色和大小分布的一致性方面,GalCatDiff显著优于现有方法,并且生成的星系在视觉上很真实且物理上一致。该框架将提高星系模拟的可靠性,并可能作为数据增强器支持未来星系分类算法的开发。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 6 figures. Submitted to AAS Astronomical Journal (AJ) and is under revision. See another indenpdent work for furthur reference – Can AI Dream of Unseen Galaxies? Conditional Diffusion Model for Galaxy Morphology Augmentation (Ma, Sun et al.). Comments are welcome
Summary
基于数据驱动的生成模型已成为一种新兴的替代方法用于星系生成,特别是其中的扩散模型相较于其他生成模型有更好的性能和多样性。本文将物理先验知识应用于扩散模型的设计,构建了一个名为GalCatDiff的新框架,结合了星系图像特征和天体物理属性。该框架使用增强型U-Net和创新的Astro-RAB模块进行动态特征处理,并且通过使用类别嵌入实现类别特定星系生成。实验结果显示,GalCatDiff显著提高了样本颜色与大小分布的一致性,生成的星系既具有视觉真实性又符合物理一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据驱动生成模型已成为星系生成的新兴替代方法。
- 扩散模型在性能和多样性上优于其他生成模型。
- GalCatDiff结合了星系图像特征和天体物理属性进行扩散模型设计。
- GalCatDiff使用增强型U-Net和创新模块Astro-RAB进行特征处理。
- GalCatDiff通过类别嵌入实现特定类别的星系生成,降低计算成本。
- 实验结果显示GalCatDiff提高了样本颜色与大小分布的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

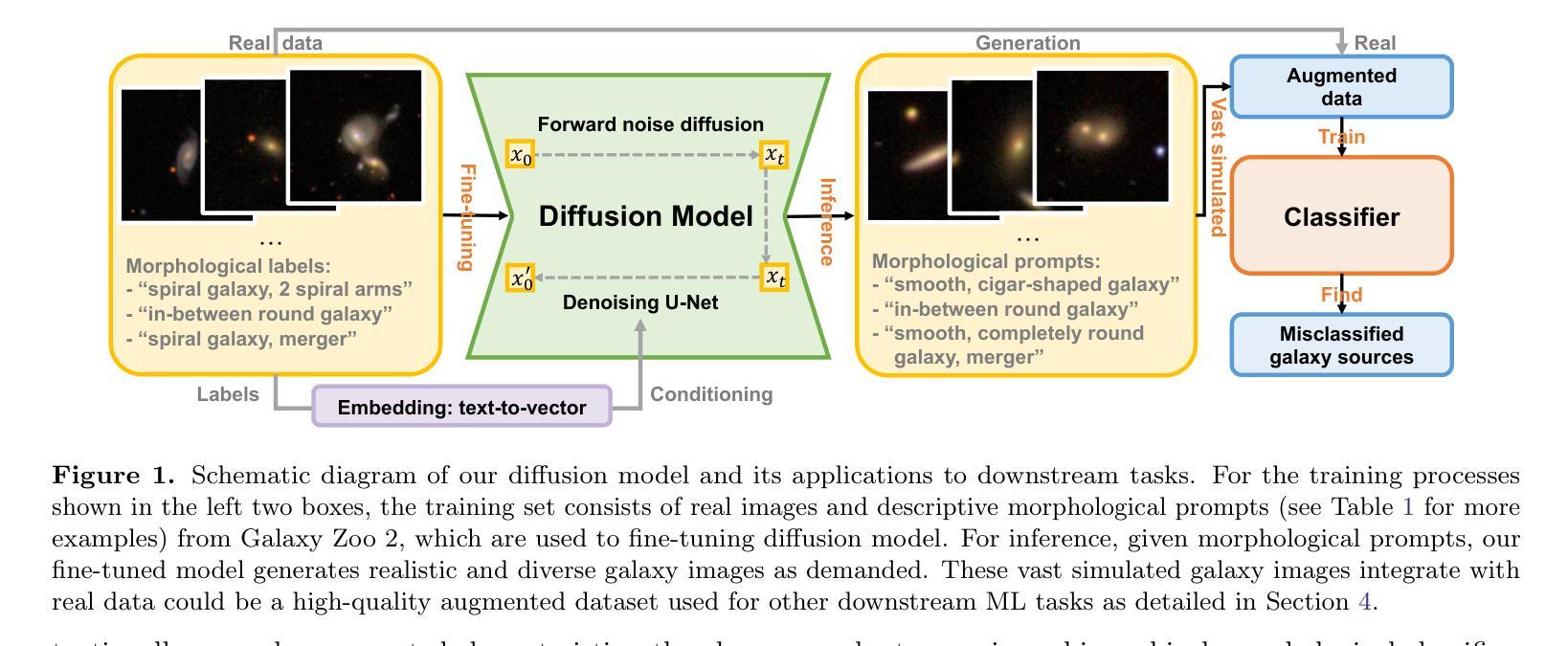
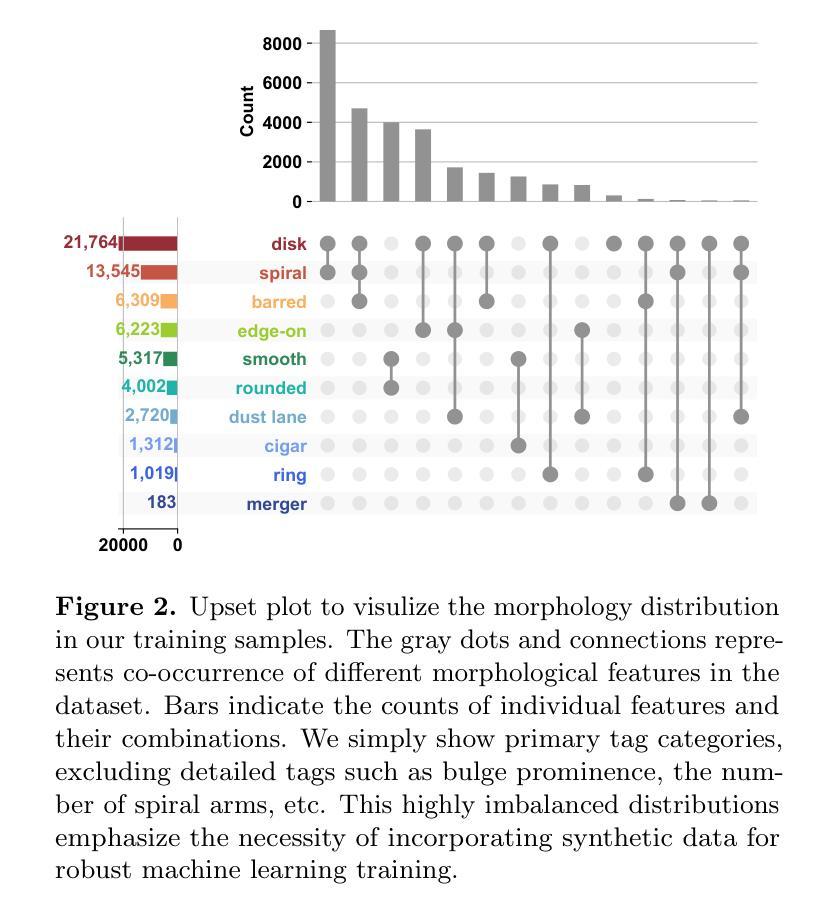
Can AI Dream of Unseen Galaxies? Conditional Diffusion Model for Galaxy Morphology Augmentation
Authors:Chenrui Ma, Zechang Sun, Tao Jing, Zheng Cai, Yuan-Sen Ting, Song Huang, Mingyu Li
Observational astronomy relies on visual feature identification to detect critical astrophysical phenomena. While machine learning (ML) increasingly automates this process, models often struggle with generalization in large-scale surveys due to the limited representativeness of labeled datasets – whether from simulations or human annotation – a challenge pronounced for rare yet scientifically valuable objects. To address this, we propose a conditional diffusion model to synthesize realistic galaxy images for augmenting ML training data. Leveraging the Galaxy Zoo 2 dataset which contains visual feature – galaxy image pairs from volunteer annotation, we demonstrate that our model generates diverse, high-fidelity galaxy images closely adhere to the specified morphological feature conditions. Moreover, this model enables generative extrapolation to project well-annotated data into unseen domains and advancing rare object detection. Integrating synthesized images into ML pipelines improves performance in standard morphology classification, boosting completeness and purity by up to 30% across key metrics. For rare object detection, using early-type galaxies with prominent dust lane features ( $\sim$0.1% in GZ2 dataset) as a test case, our approach doubled the number of detected instances from 352 to 872, compared to previous studies based on visual inspection. This study highlights the power of generative models to bridge gaps between scarce labeled data and the vast, uncharted parameter space of observational astronomy and sheds insight for future astrophysical foundation model developments. Our project homepage is available at https://galaxysd-webpage.streamlit.app/.
观测天文学依赖于视觉特征识别来检测关键的天体物理现象。虽然机器学习(ML)越来越自动化这一过程,但由于模拟或人工标注的数据集代表性有限,模型在大规模调查中的泛化能力常常面临挑战——这对于稀少但具有科学价值的物体来说是一个更大的挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种条件扩散模型,用于合成逼真的星系图像,以扩充机器学习的训练数据。我们利用Galaxy Zoo 2数据集,该数据集包含来自志愿者标注的视觉特征——星系图像对,演示了我们的模型能够生成多样、高保真度的星系图像,紧密符合指定的形态特征条件。此外,该模型能够进行生成外推,将标注良好的数据投影到未见过的领域,并推动稀有物体的检测。将合成图像集成到机器学习管道中,提高了标准形态分类的性能,在关键指标上,完性和纯度提高了高达30%。在检测稀有物体方面,以具有明显尘埃通道特征的早期星系(在GZ2数据集中约为0.1%)为试验案例,我们的方法将检测到的实例数量从352个增加到872个,与之前的基于人工检查的研究相比翻了一番。该研究突显了生成模型在稀缺标注数据和观测天文学广阔的、未探索的参数空间之间的桥梁作用,并为未来的天体物理基础模型开发提供了见解。我们的项目主页可在https://galaxysd-webpage.streamlit.app/上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We have submitted to AAS journals. See another independent work for further reference – Category-based Galaxy Image Generation via Diffusion Models (Fan, Tang et al.). Comments are welcome
Summary
本研究利用条件扩散模型合成逼真的星系图像,以扩充机器学习训练数据。研究使用Galaxy Zoo 2数据集,展示了模型能够根据指定的形态特征条件生成多样、高保真度的星系图像。此外,该模型能够进行生成外推,将已标注的数据投影到未知领域,并推动稀有目标检测的发展。集成合成图像到机器学习管道中,提高了标准形态分类的性能,并在关键指标上提高了完整性和纯度达30%。对于罕见目标检测,以具有突出尘埃通道特征的早期类型星系为例(在GZ2数据集中约占0.1%),该研究将检测到的实例数量从之前的视觉检查中的352个增加到872个。这凸显了生成模型在缩小稀缺标记数据与广阔的未被探索的参数空间之间的差距中的潜力,并为未来的天体物理基础模型发展提供了启示。项目主页位于:[链接地址]。此摘要全文不超过百字限制。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出一种基于条件扩散模型的星系图像合成方法,用于扩充机器学习训练数据。
- 模型能够根据指定的形态特征条件生成多样、高保真度的星系图像。
- 模型能够生成外推,将标注数据投影到未知领域。
- 集成合成图像提高了机器学习在标准形态分类上的性能,并提升了检测结果的完整性和纯度。
- 在罕见目标检测方面,模型显著增加了检测到具有特定特征的星系数量。
- 研究强调了生成模型在连接稀缺数据和未被探索的参数空间中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

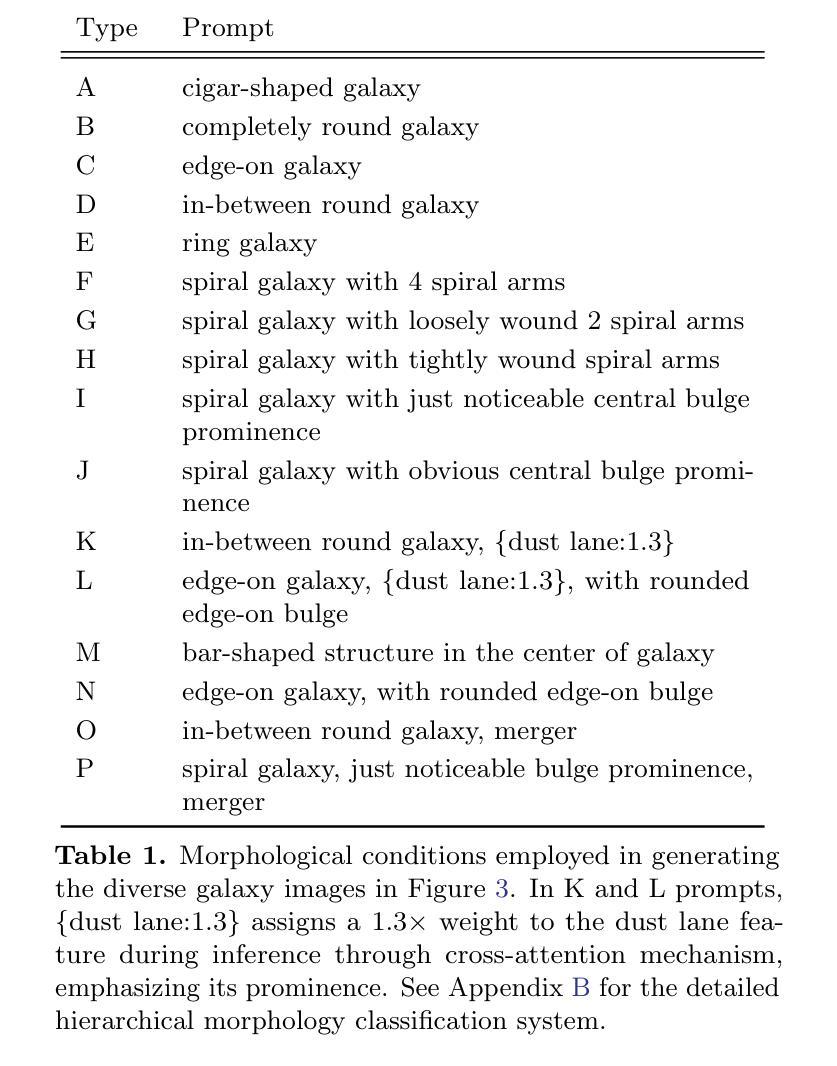
LoRA-Edit: Controllable First-Frame-Guided Video Editing via Mask-Aware LoRA Fine-Tuning
Authors:Chenjian Gao, Lihe Ding, Xin Cai, Zhanpeng Huang, Zibin Wang, Tianfan Xue
Video editing using diffusion models has achieved remarkable results in generating high-quality edits for videos. However, current methods often rely on large-scale pretraining, limiting flexibility for specific edits. First-frame-guided editing provides control over the first frame, but lacks flexibility over subsequent frames. To address this, we propose a mask-based LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) tuning method that adapts pretrained Image-to-Video (I2V) models for flexible video editing. Our approach preserves background regions while enabling controllable edits propagation. This solution offers efficient and adaptable video editing without altering the model architecture. To better steer this process, we incorporate additional references, such as alternate viewpoints or representative scene states, which serve as visual anchors for how content should unfold. We address the control challenge using a mask-driven LoRA tuning strategy that adapts a pre-trained image-to-video model to the editing context. The model must learn from two distinct sources: the input video provides spatial structure and motion cues, while reference images offer appearance guidance. A spatial mask enables region-specific learning by dynamically modulating what the model attends to, ensuring that each area draws from the appropriate source. Experimental results show our method achieves superior video editing performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project Page: https://cjeen.github.io/LoraEditPaper
使用扩散模型进行视频编辑已经在为高质量视频生成编辑方面取得了显著成果。然而,当前的方法通常依赖于大规模预训练,这限制了特定编辑的灵活性。虽然首帧引导编辑可以控制首帧,但对后续帧的控制不足。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于掩膜的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,该方法可适应预训练的图到视频(I2V)模型,用于灵活的视频编辑。我们的方法能够保留背景区域,同时实现可控的编辑传播。这一解决方案提供了高效且可适应的视频编辑,而不会改变模型架构。为了更好地引导这一过程,我们引入了额外的参考,如不同的观点或代表性的场景状态,它们作为内容如何展开的可视锚点。我们采用掩膜驱动的LoRA调优策略来解决控制挑战,该策略使预训练的图到视频模型适应编辑上下文。模型必须从两个独特的信息源中学习:输入视频提供空间结构和运动线索,而参考图像提供外观指导。空间掩膜通过动态调制模型所关注的点,实现特定区域的学习,确保每个区域都从适当的源中汲取信息。实验结果表明,我们的方法与最先进的方法相比,在视频编辑性能方面表现更优越。项目页面:https://cjeen.github.io/LoraEditPaper
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
本文介绍了使用扩散模型进行视频编辑的最新研究成果。针对现有方法预训练规模大、特定编辑灵活性不足的问题,提出了基于掩膜的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,该方法可适应预训练图像到视频(I2V)模型,实现灵活视频编辑。该方法可在保留背景区域的同时,实现可控的编辑传播,提供高效、可适应的视频编辑,而无需改变模型架构。为更好地引导这一过程,引入了额外的参考图像,作为内容展开的视觉锚点。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在视频编辑中表现卓越,能生成高质量的视频编辑。
- 当前方法依赖大规模预训练,限制特定编辑的灵活性。
- 提出基于掩膜的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,适应预训练图像到视频(I2V)模型,实现灵活视频编辑。
- 方法可保留背景区域,实现可控的编辑传播。
- 提供高效、可适应的视频编辑,无需改变模型架构。
- 引入额外参考图像作为视觉锚点,更好地引导编辑过程。
- 采用掩膜驱动的LoRA调优策略,从输入视频和参考图像中学习,实现区域特定的学习,确保从适当来源获取信息。
点此查看论文截图


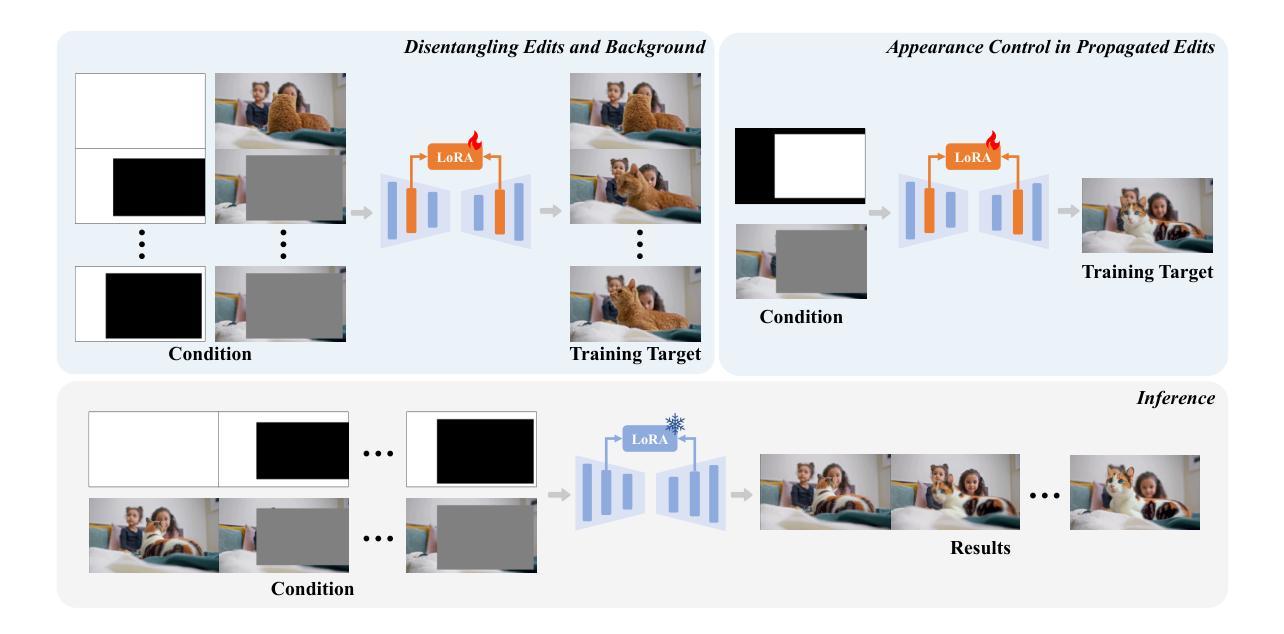
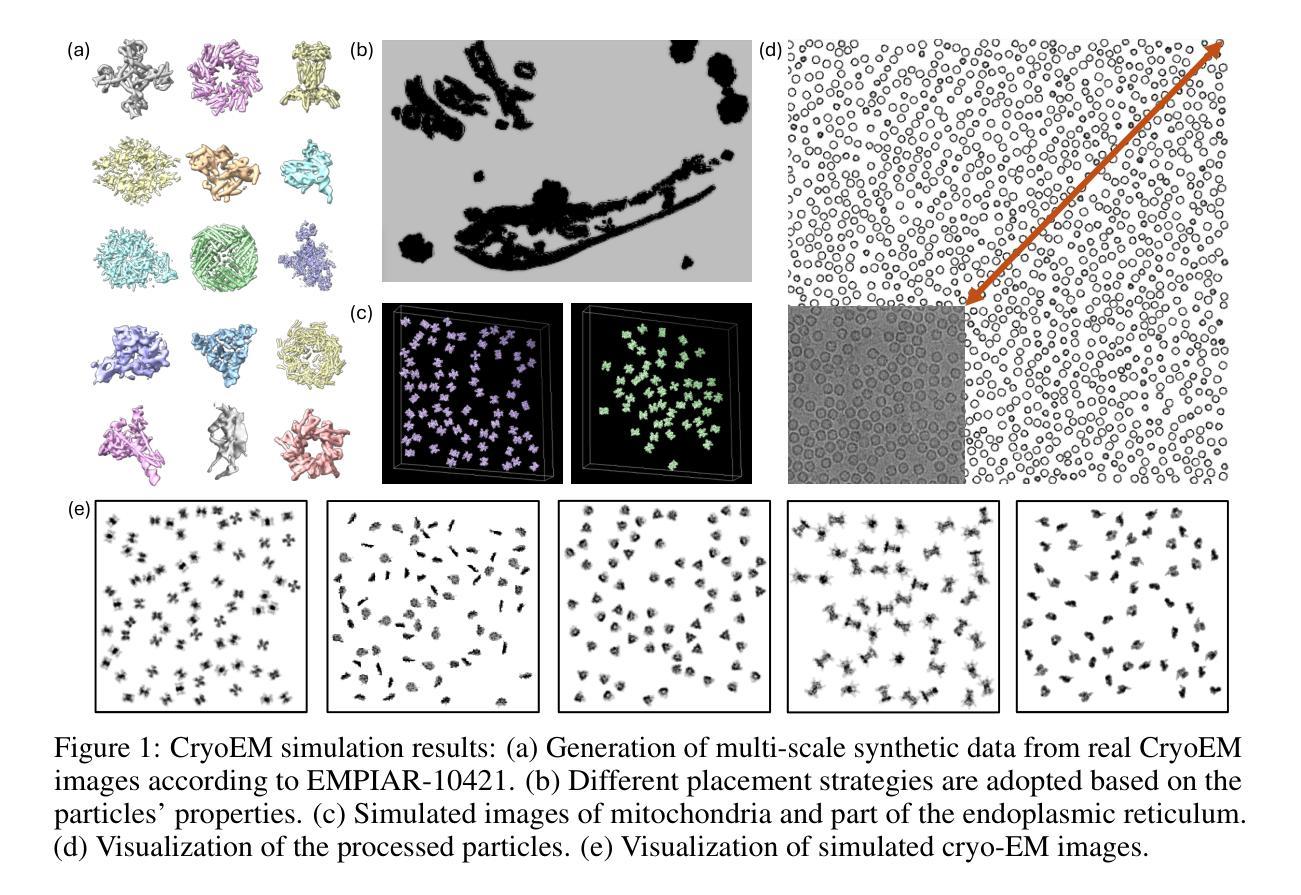
CryoCCD: Conditional Cycle-consistent Diffusion with Biophysical Modeling for Cryo-EM Synthesis
Authors:Runmin Jiang, Genpei Zhang, Yuntian Yang, Siqi Wu, Yuheng Zhang, Wanyue Feng, Yizhou Zhao, Xi Xiao, Xiao Wang, Tianyang Wang, Xingjian Li, Min Xu
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) offers near-atomic resolution imaging of macromolecules, but developing robust models for downstream analysis is hindered by the scarcity of high-quality annotated data. While synthetic data generation has emerged as a potential solution, existing methods often fail to capture both the structural diversity of biological specimens and the complex, spatially varying noise inherent in cryo-EM imaging. To overcome these limitations, we propose CryoCCD, a synthesis framework that integrates biophysical modeling with generative techniques. Specifically, CryoCCD produces multi-scale cryo-EM micrographs that reflect realistic biophysical variability through compositional heterogeneity, cellular context, and physics-informed imaging. To generate realistic noise, we employ a conditional diffusion model, enhanced by cycle consistency to preserve structural fidelity and mask-aware contrastive learning to capture spatially adaptive noise patterns. Extensive experiments show that CryoCCD generates structurally accurate micrographs and enhances performance in downstream tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines in both particle picking and reconstruction.
冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)能够为宏观分子提供接近原子分辨率的成像,但是高质量标注数据的稀缺阻碍了下游分析稳健模型的发展。虽然合成数据生成已经出现为潜在的解决方案,但现有方法往往无法捕捉到生物样本的结构多样性和冷冻电子显微镜成像中固有的复杂、空间变化的噪声。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了CryoCCD,一个将生物物理建模与生成技术相结合的合成框架。具体来说,CryoCCD产生多尺度的冷冻电子显微镜微图,通过组成异质性、细胞上下文和物理信息成像反映现实生物物理的变异性。为了生成真实的噪声,我们采用条件扩散模型,通过循环一致性增强来保持结构保真度,并通过掩膜感知对比学习来捕捉空间自适应噪声模式。大量实验表明,CryoCCD生成的微图结构准确,提高了下游任务的性能,在粒子挑选和重建方面都超越了最先进的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一个名为CryoCCD的合成数据生成框架,用于解决低温电子显微镜(cryo-EM)下游分析缺乏高质量标注数据的难题。通过整合生物物理建模与生成技术,CryoCCD能够生成反映真实生物物理变异性的多尺度低温电子显微镜图像,包括组成异质性、细胞上下文以及物理成像信息。采用条件扩散模型生成真实噪声,通过循环一致性增强结构保真度,并通过掩膜感知对比学习捕捉空间自适应噪声模式。实验证明,CryoCCD生成的图像结构准确,并在下游任务中表现优异,在粒子挑选和重建方面超越现有基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 低温电子显微镜(cryo-EM)成像中缺乏高质量标注数据,阻碍了下游分析的模型开发。
- 合成数据生成是解决此问题的一种潜在解决方案。
- 现有方法往往无法捕捉生物标本的结构多样性和低温电子显微镜成像中的复杂空间变化噪声。
- CryoCCD框架整合生物物理建模与生成技术来解决这些问题。
- 条件扩散模型用于生成真实噪声,保持结构保真度并通过掩膜感知对比学习捕捉空间自适应噪声模式。
- 实验证明CryoCCD生成的图像结构准确并在下游任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

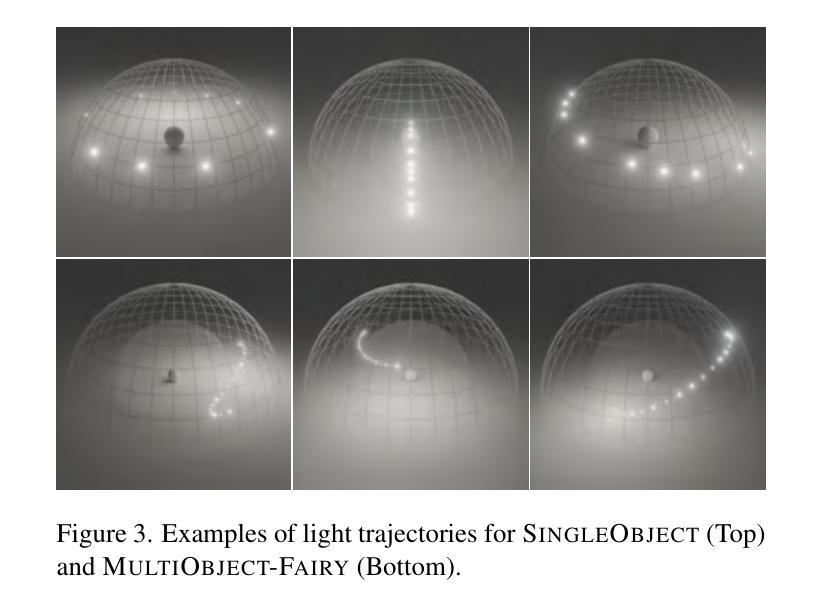
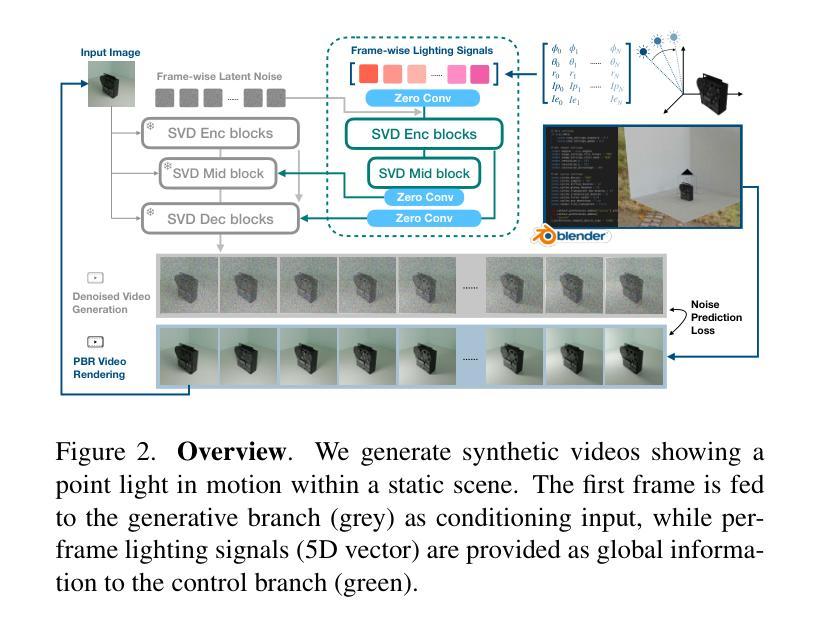
GenLit: Reformulating Single-Image Relighting as Video Generation
Authors:Shrisha Bharadwaj, Haiwen Feng, Giorgio Becherini, Victoria Fernandez Abrevaya, Michael J. Black
Manipulating the illumination of a 3D scene within a single image represents a fundamental challenge in computer vision and graphics. This problem has traditionally been addressed using inverse rendering techniques, which involve explicit 3D asset reconstruction and costly ray-tracing simulations. Meanwhile, recent advancements in visual foundation models suggest that a new paradigm could soon be possible – one that replaces explicit physical models with networks that are trained on large amounts of image and video data. In this paper, we exploit the physical world understanding of a video diffusion model, particularly Stable Video Diffusion, to relight a single image. We introduce GenLit, a framework that distills the ability of a graphics engine to perform light manipulation into a video-generation model, enabling users to directly insert and manipulate a point light in the 3D world within a given image, and generate results directly as a video sequence. We find that a model fine-tuned on only a small synthetic dataset generalizes to real-world scenes, enabling single-image relighting with plausible and convincing shadows. Our results highlight the ability of video foundation models to capture rich information about lighting, material, and, shape and our findings indicate that such models, with minimal training, can be used to perform relighting without explicit asset reconstruction or complex ray tracing. Project page: https://genlit.is.tue.mpg.de/.
在单幅图像内操纵3D场景的照明是计算机视觉和图形学中的一项基本挑战。传统上,这个问题是通过逆向渲染技术来解决的,这涉及到明确的3D资产重建和昂贵的光线追踪模拟。同时,视觉基础模型的最新进展表明,一种新的范式即将到来——用大量图像和视频数据训练的网络取代明确的物理模型。在本文中,我们利用视频扩散模型(特别是稳定的视频扩散)对物理世界的理解来对单幅图像进行重新照明。我们引入了GenLit框架,它将图形引擎进行光线操纵的能力提炼成视频生成模型,使用户能够在给定的图像中直接在3D世界中插入并操纵点光源,并直接生成视频序列的结果。我们发现仅在小型合成数据集上微调过的模型可以推广到真实场景,能够实现具有合理性和说服力的阴影的单图像重新照明。我们的结果突出了视频基础模型在捕捉关于照明、材质和形状的丰富信息方面的能力,我们的研究结果表明,通过最小的训练,这种模型可用于执行重新照明,无需明确的资产重建或复杂的光线追踪。项目页面:https://genlit.is.tue.mpg.de/(链接无法直接打开)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用视频扩散模型进行单图像照明操控的新方法。通过引入GenLit框架,结合图形引擎的能力,将光照操控能力融入视频生成模型,实现在给定图像中直接插入和操控点光源,并生成视频序列结果。研究发现在小型合成数据集上微调后的模型能够泛化到真实场景,实现具有可信阴影的单图像重照明。
Key Takeaways
- 利用视觉基础模型的新范式,通过大型图像和视频数据训练网络,替换传统显式物理模型解决照明操控问题。
- 提出了GenLit框架,能够提炼图形引擎的光照操控能力,并将其融入视频生成模型。
- 可在给定图像中直接插入和操控点光源,生成视频序列结果。
- 模型在小型合成数据集上微调后,能够泛化到真实场景。
- 实现单图像重照明,具有可信的阴影效果。
- 扩散模型在捕捉关于照明、材质、形状等丰富信息方面表现出能力。
点此查看论文截图