⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-24 更新
Category-based Galaxy Image Generation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Xingzhong Fan, Hongming Tang, Yue Zeng, M. B. N. Kouwenhoven, Guangquan Zeng
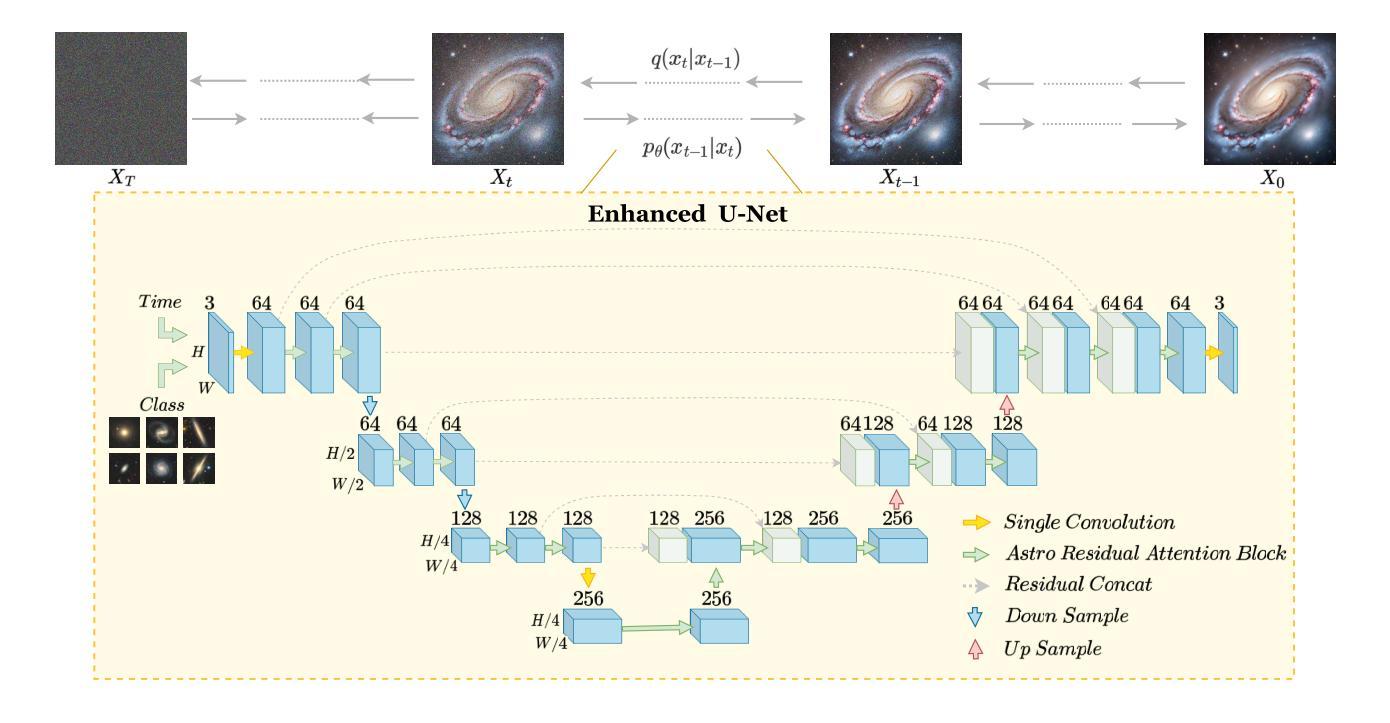
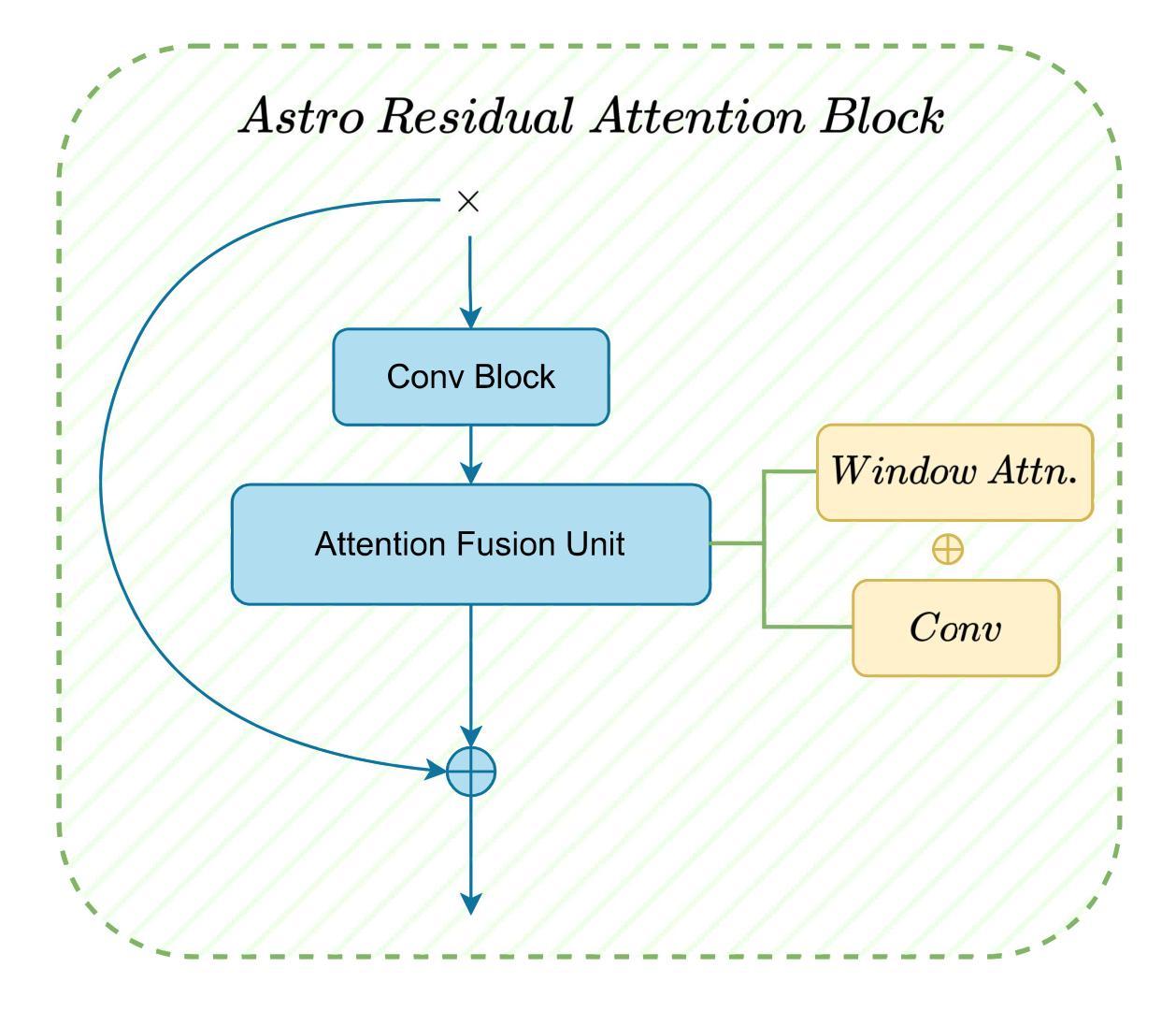
Conventional galaxy generation methods rely on semi-analytical models and hydrodynamic simulations, which are highly dependent on physical assumptions and parameter tuning. In contrast, data-driven generative models do not have explicit physical parameters pre-determined, and instead learn them efficiently from observational data, making them alternative solutions to galaxy generation. Among these, diffusion models outperform Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in quality and diversity. Leveraging physical prior knowledge to these models can further enhance their capabilities. In this work, we present GalCatDiff, the first framework in astronomy to leverage both galaxy image features and astrophysical properties in the network design of diffusion models. GalCatDiff incorporates an enhanced U-Net and a novel block entitled Astro-RAB (Residual Attention Block), which dynamically combines attention mechanisms with convolution operations to ensure global consistency and local feature fidelity. Moreover, GalCatDiff uses category embeddings for class-specific galaxy generation, avoiding the high computational costs of training separate models for each category. Our experimental results demonstrate that GalCatDiff significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of the consistency of sample color and size distributions, and the generated galaxies are both visually realistic and physically consistent. This framework will enhance the reliability of galaxy simulations and can potentially serve as a data augmentor to support future galaxy classification algorithm development.
传统星系生成方法依赖于半解析模型和水动力模拟,这高度依赖于物理假设和参数调整。相比之下,数据驱动的生成模型没有预先确定的明确物理参数,而是从观测数据中有效地学习这些参数,使其成为星系生成的替代解决方案。其中,扩散模型在质量和多样性方面优于变分自动编码器(VAE)和生成对抗网络(GAN)。利用物理先验知识可以进一步增强这些模型的能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了GalCatDiff,这是天文学中第一个利用星系图像特征和天体物理属性来设计扩散模型网络的框架。GalCatDiff融入了一种增强的U-Net和一个名为Astro-RAB(残差注意力块)的新颖块,它将注意力机制与卷积操作动态结合,以确保全局一致性和局部特征保真度。此外,GalCatDiff使用类别嵌入进行特定类别的星系生成,避免了为每个类别训练单独模型的高计算成本。我们的实验结果表明,在样本颜色和大小分布的一致性方面,GalCatDiff显著优于现有方法,生成的星系在视觉上既真实又符合物理规律。该框架将提高星系模拟的可靠性,并可能作为数据增强器,支持未来星系分类算法的开发。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 6 figures. Submitted to AAS Astronomical Journal (AJ) and is under revision. See another indenpdent work for furthur reference – Can AI Dream of Unseen Galaxies? Conditional Diffusion Model for Galaxy Morphology Augmentation (Ma, Sun et al.). Comments are welcome
Summary
本文介绍了传统的星系生成方法依赖于半解析模型和流体动力学模拟,这些方法高度依赖于物理假设和参数调整。与之相比,数据驱动的生成模型能够从观测数据中有效学习,无需预先确定明确的物理参数,因此成为星系生成的替代解决方案。扩散模型在质量和多样性方面超越了变分自编码器(VAEs)和生成对抗网络(GANs)。结合物理先验知识进一步增强了这些模型的能力。本研究提出了GalCatDiff,这是天文学中第一个结合星系图像特征和天体物理属性的扩散模型网络设计框架。GalCatDiff采用增强的U-Net和名为Astro-RAB(残差注意力块)的新颖块,通过动态结合注意力机制和卷积操作,确保全局一致性和局部特征保真度。此外,GalCatDiff使用类别嵌入进行特定类别的星系生成,避免了为每个类别训练单独模型的高计算成本。实验结果表明,GalCatDiff在样本颜色和大小分布的一致性方面显著优于现有方法,生成的星系在视觉上很真实且物理上是一致的。该框架将提高星系模拟的可靠性,并有望作为数据增强器支持未来的星系分类算法开发。
Key Takeaways
- 传统的星系生成方法高度依赖于物理假设和参数调整,而数据驱动的生成模型能从观测数据中学习,更具优势。
- 扩散模型在质量和多样性方面超越了VAEs和GANs。
- GalCatDiff是首个结合星系图像特征和天体物理属性的扩散模型网络设计框架,采用增强的U-Net和新颖块Astro-RAB。
- Astro-RAB能够动态结合注意力机制和卷积操作,确保全局一致性和局部特征保真度。
- GalCatDiff使用类别嵌入进行特定类别的星系生成,降低了计算成本。
- GalCatDiff在样本颜色和大小分布的一致性方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Integrating Generative Adversarial Networks and Convolutional Neural Networks for Enhanced Traffic Accidents Detection and Analysis
Authors:Zhenghao Xi, Xiang Liu, Yaqi Liu, Yitong Cai, Yangyu Zheng
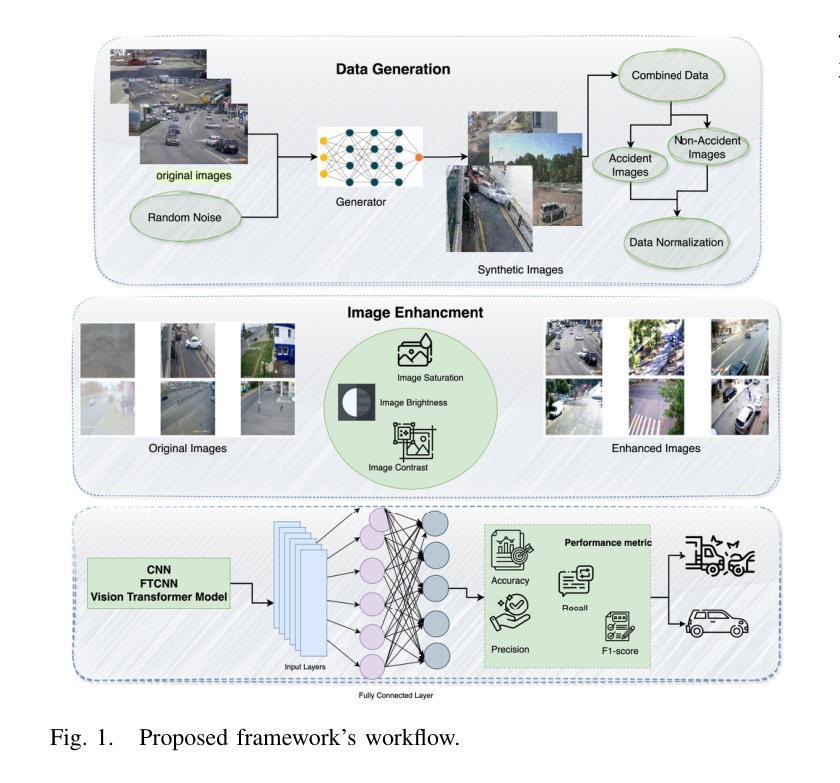
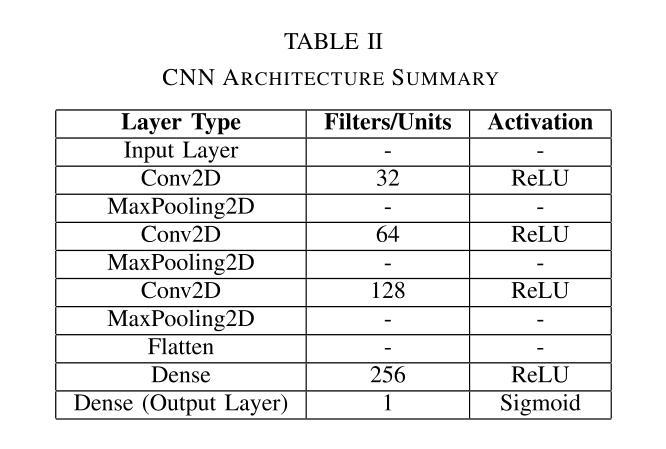
Accident detection using Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) footage is one of the most imperative features for enhancing transport safety and efficient traffic control. To this end, this research addresses the issues of supervised monitoring and data deficiency in accident detection systems by adapting excellent deep learning technologies. The motivation arises from rising statistics in the number of car accidents worldwide; this calls for innovation and the establishment of a smart, efficient and automated way of identifying accidents and calling for help to save lives. Addressing the problem of the scarcity of data, the presented framework joins Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for synthesizing data and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for model training. Video frames for accidents and non-accidents are collected from YouTube videos, and we perform resizing, image enhancement and image normalisation pixel range adjustments. Three models are used: CNN, Fine-tuned Convolutional Neural Network (FTCNN) and Vision Transformer (VIT) worked best for detecting accidents from CCTV, obtaining an accuracy rate of 94% and 95%, while the CNN model obtained 88%. Such results show that the proposed framework suits traffic safety applications due to its high real-time accident detection capabilities and broad-scale applicability. This work lays the foundation for intelligent surveillance systems in the future for real-time traffic monitoring, smart city framework, and integration of intelligent surveillance systems into emergency management systems.
使用闭路电视(CCTV)画面进行事故检测是增强交通安全和有效交通控制的最重要功能之一。为此,本研究通过采用先进的深度学习技术,解决了事故检测系统中监督监测和数据缺乏的问题。其动机源于全球汽车事故数量统计数据的上升;这需要创新并建立一种智能、高效、自动化的方式来识别事故并寻求帮助以挽救生命。为解决数据稀缺问题,所提框架结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)进行数据合成和卷积神经网络(CNN)进行模型训练。我们从YouTube视频中收集了事故和非事故的视频帧,并进行了尺寸调整、图像增强和图像归一化像素范围调整。我们使用了三种模型:CNN、微调卷积神经网络(FTCNN)和视觉转换器(VIT),它们在从CCTV检测事故方面表现最佳,准确率分别为94%和95%,而CNN模型的准确率为88%。这些结果表明,由于具备高度实时的事故检测能力和广泛的适用性,所提框架适用于交通安全应用。这项工作为智能监控系统在未来进行实时交通监控、智能城市框架以及智能监控系统与紧急管理系统集成奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇研究论文利用深度学习和计算机视觉技术,通过闭路电视监控来检测交通事故。该研究利用生成对抗网络(GANs)合成数据,解决数据缺乏的问题,并通过卷积神经网络(CNN)进行模型训练。该研究实现了高效的实时事故检测,准确率达到了94%以上,为智能交通监控、智慧城市框架和紧急管理系统提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究旨在利用深度学习和计算机视觉技术,通过闭路电视监控来检测交通事故,提高交通安全性和交通控制效率。
- 采用生成对抗网络(GANs)合成数据,解决事故检测系统中监督监测和数据缺乏的问题。
- 使用卷积神经网络(CNN)进行模型训练,并使用了三种模型进行检测,包括CNN、微调卷积神经网络(FTCNN)和视觉转换器(VIT)。
- 通过使用YouTube视频收集事故和非事故的视频帧,并进行图像调整、增强和归一化,实现了高效的实时事故检测。
- 该方法具有高实时事故检测能力和广泛的应用性,准确率达到了94%以上。
- 该研究为未来智能交通监控、智慧城市框架和紧急管理系统的智能化监控系统奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图