⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-24 更新
Chain-of-Thought Prompting Obscures Hallucination Cues in Large Language Models: An Empirical Evaluation
Authors:Jiahao Cheng, Tiancheng Su, Jia Yuan, Guoxiu He, Jiawei Liu, Xinqi Tao, Jingwen Xie, Huaxia Li
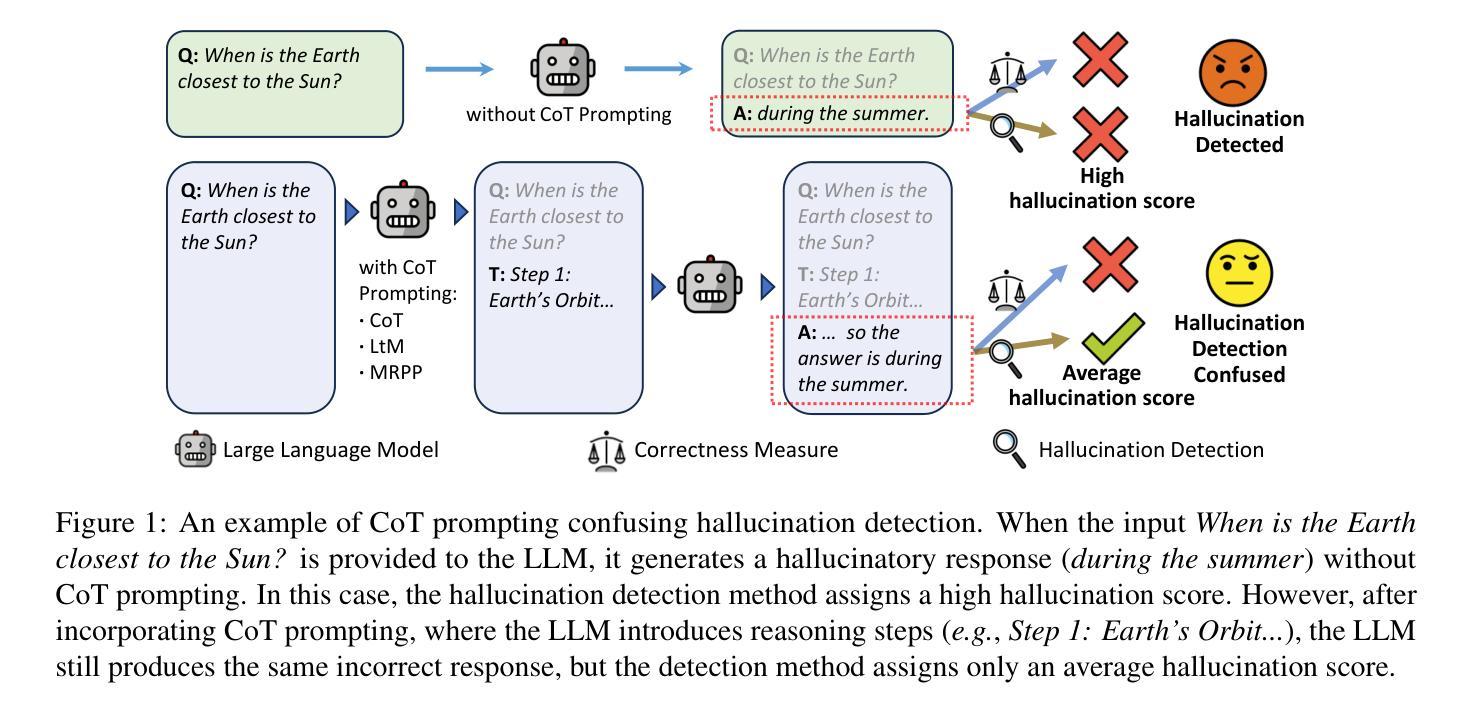
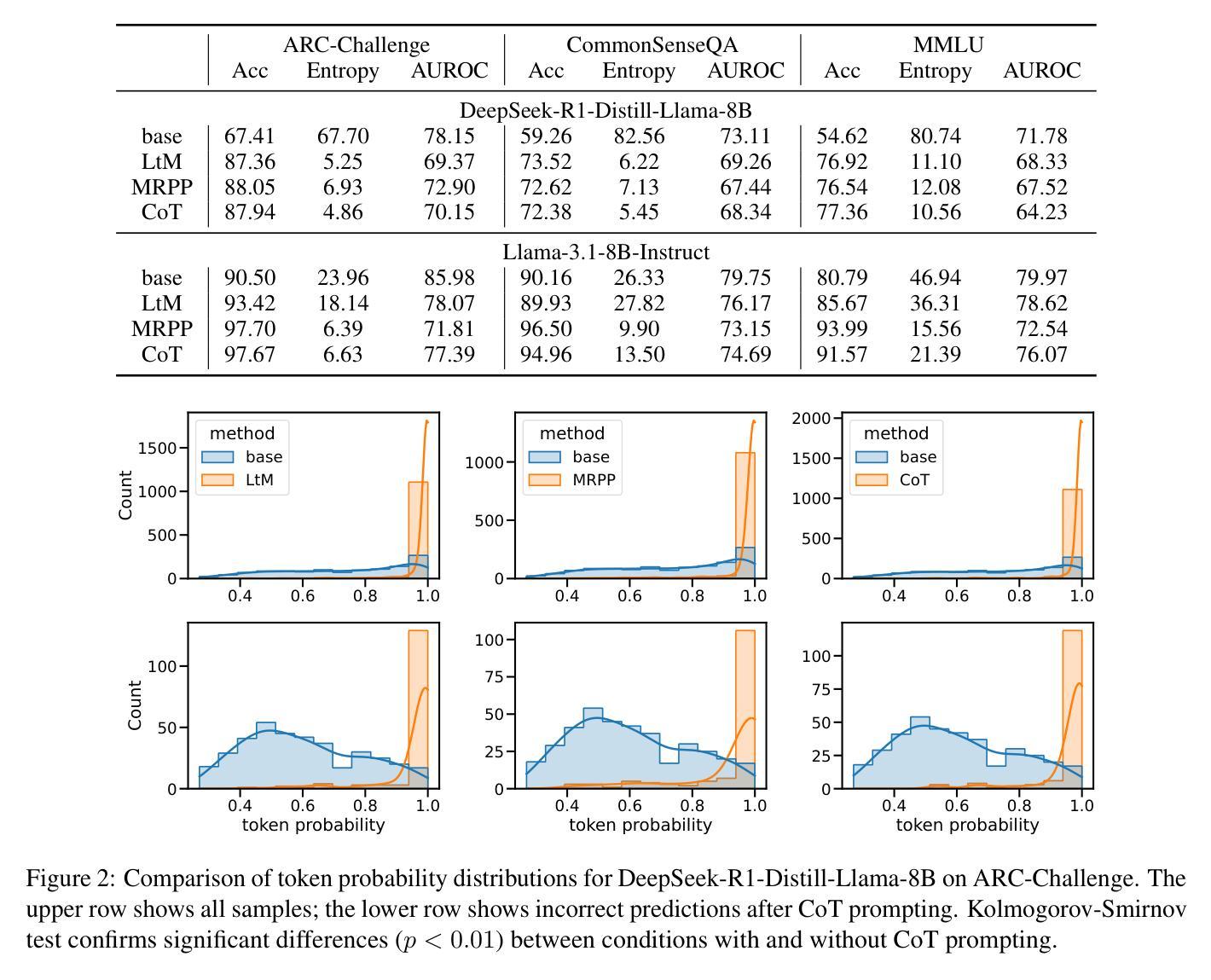
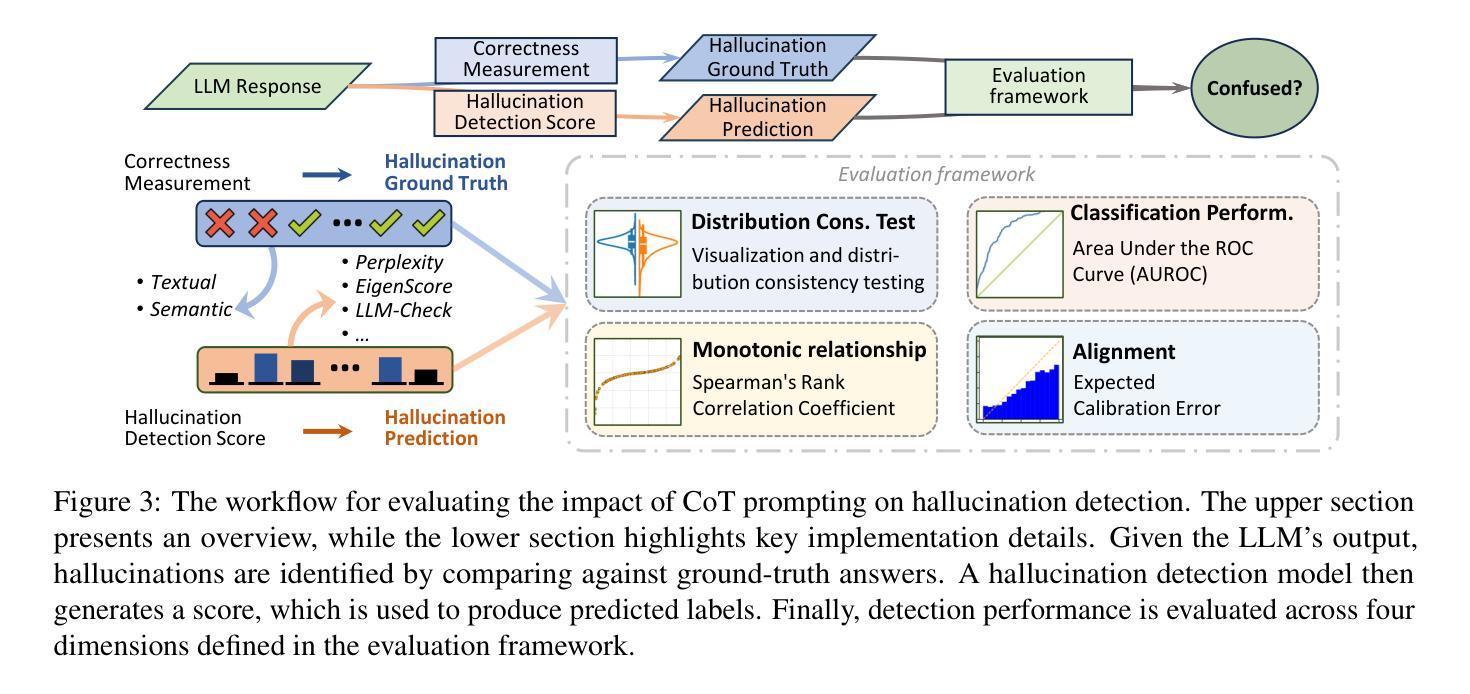
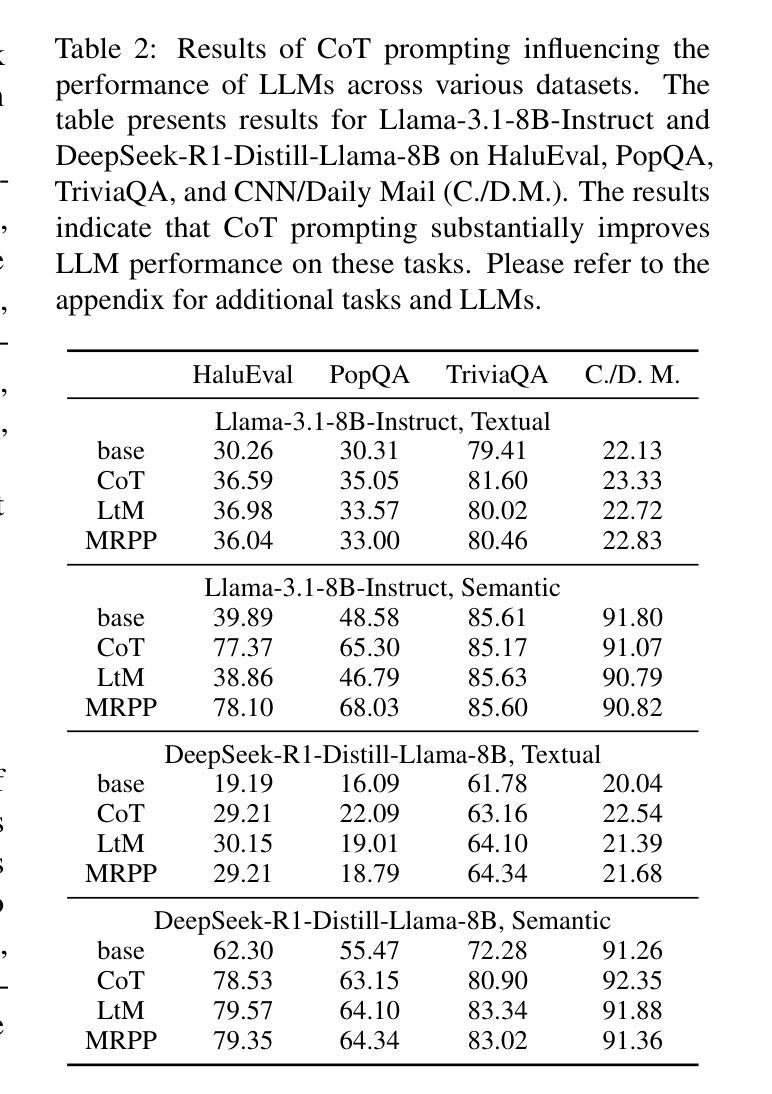
Large Language Models (LLMs) often exhibit \textit{hallucinations}, generating factually incorrect or semantically irrelevant content in response to prompts. Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting can mitigate hallucinations by encouraging step-by-step reasoning, but its impact on hallucination detection remains underexplored. To bridge this gap, we conduct a systematic empirical evaluation. We begin with a pilot experiment, revealing that CoT reasoning significantly affects the LLM’s internal states and token probability distributions. Building on this, we evaluate the impact of various CoT prompting methods on mainstream hallucination detection methods across both instruction-tuned and reasoning-oriented LLMs. Specifically, we examine three key dimensions: changes in hallucination score distributions, variations in detection accuracy, and shifts in detection confidence. Our findings show that while CoT prompting helps reduce hallucination frequency, it also tends to obscure critical signals used for detection, impairing the effectiveness of various detection methods. Our study highlights an overlooked trade-off in the use of reasoning. Code is publicly available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/cot-hallu-detect.
大型语言模型(LLM)经常表现出“幻觉”,即对提示生成事实错误或语义不相关的内容。链式思维(CoT)提示可以通过鼓励逐步推理来缓解幻觉,但其对幻觉检测的影响仍被忽视。为了填补这一空白,我们进行了系统的实证研究。我们首先进行了一项试点实验,结果显示CoT推理显著影响了LLM的内部状态和令牌概率分布。在此基础上,我们评估了各种CoT提示方法对主流幻觉检测方法的检测影响,涉及指令调优和面向推理的LLM。具体地,我们考察三个关键维度:幻觉评分分布的变化、检测准确性的变化以及检测信心的转变。我们的研究结果表明,虽然CoT提示有助于减少幻觉频率,但它也可能掩盖用于检测的关键信号,从而损害各种检测方法的效力。我们的研究突出了在使用推理时忽视的一个权衡。代码公开可用在:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/cot-hallu-detect。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大语言模型(LLM)容易出现幻觉现象,即生成与提示不符的事实上或语义上无关的内容。链式思维(CoT)提示可以通过鼓励逐步推理来缓解幻觉现象,但其对幻觉检测的影响尚未得到充分探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们进行了系统的实证研究。我们首先进行了一项试点实验,发现CoT推理显著影响LLM的内部状态和令牌概率分布。在此基础上,我们评估了各种CoT提示方法对主流幻觉检测方法的影响,涵盖指令调优和面向推理的LLM。我们研究了三个关键维度:幻觉分数分布的变化、检测准确性的变化以及检测信心的转移。我们的研究发现,虽然CoT提示有助于减少幻觉频率,但它也可能掩盖用于检测的关键信号,损害各种检测方法的有效性。我们的研究凸显了在使用推理时的一个被忽视的权衡。相关代码已公开发布在:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/cot-hallu-detect。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在回应提示时可能出现幻觉现象,即生成与事实不符或语义不相关的内容。
- 链式思维(CoT)提示能够通过鼓励逐步推理来减少幻觉现象。
- 对CoT提示对幻觉检测的影响进行系统实证研究是必要的,因为这一领域尚未得到充分探索。
- CoT推理显著影响LLM的内部状态和令牌概率分布,这是通过初步实验发现的。
- CoT提示可能影响主流幻觉检测方法的性能,包括改变幻觉分数分布、检测准确性和信心。
- 虽然CoT提示有助于减少幻觉频率,但它也可能掩盖用于检测的关键信号,导致某些检测方法效果下降。
点此查看论文截图

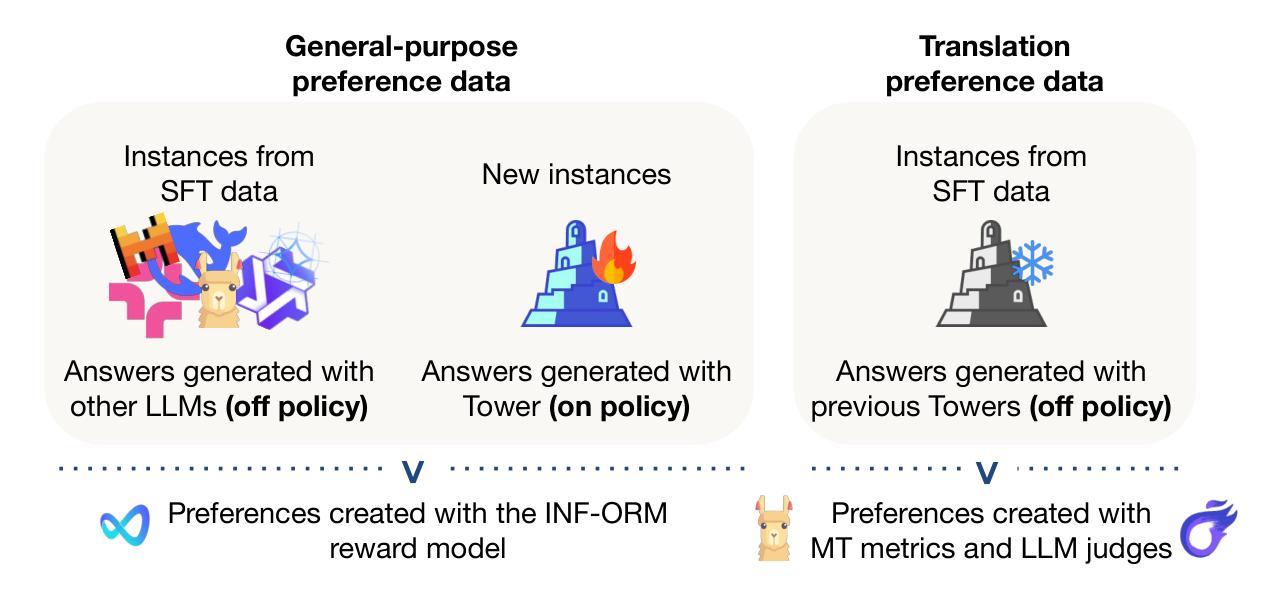
Tower+: Bridging Generality and Translation Specialization in Multilingual LLMs
Authors:Ricardo Rei, Nuno M. Guerreiro, José Pombal, João Alves, Pedro Teixeirinha, Amin Farajian, André F. T. Martins
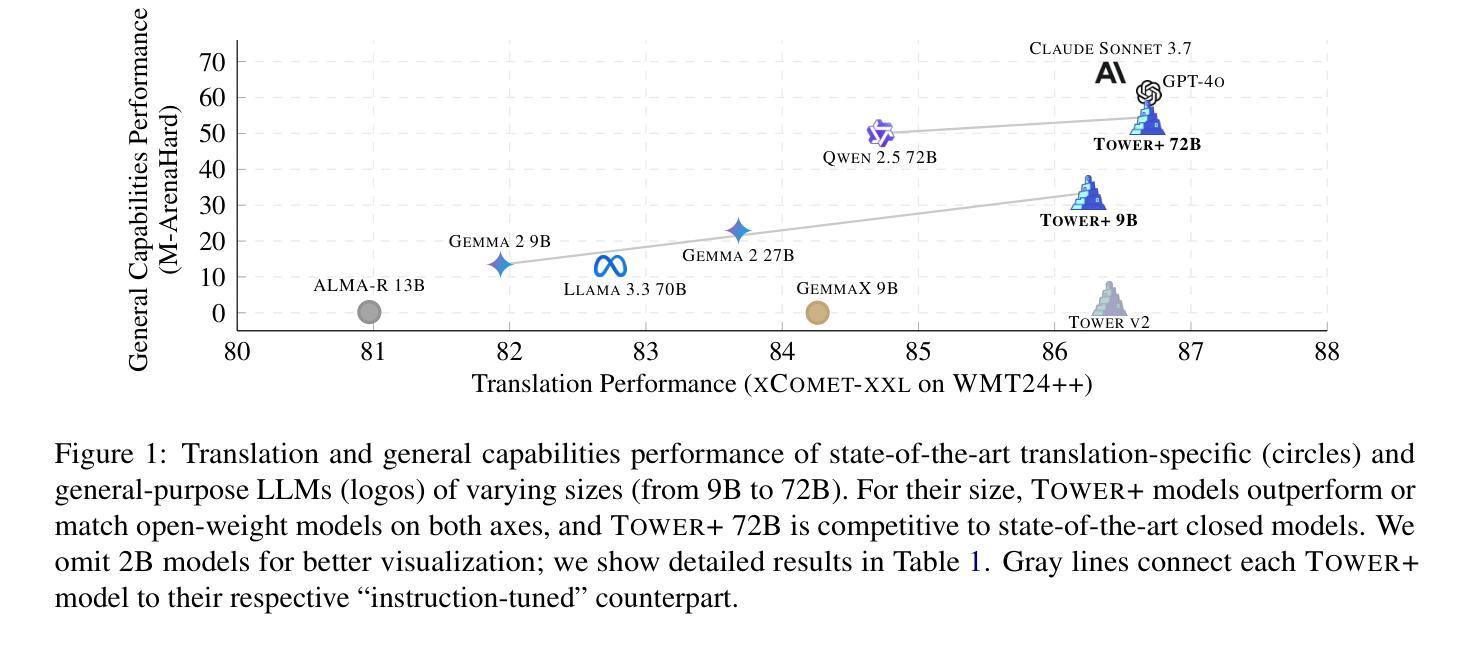
Fine-tuning pretrained LLMs has been shown to be an effective strategy for reaching state-of-the-art performance on specific tasks like machine translation. However, this process of adaptation often implies sacrificing general-purpose capabilities, such as conversational reasoning and instruction-following, hampering the utility of the system in real-world applications that require a mixture of skills. In this paper, we introduce Tower+, a suite of models designed to deliver strong performance across both translation and multilingual general-purpose text capabilities. We achieve a Pareto frontier between translation specialization and multilingual general-purpose capabilities by introducing a novel training recipe that builds on Tower (Alves et al., 2024), comprising continued pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, preference optimization, and reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards. At each stage of training, we carefully generate and curate data to strengthen performance on translation as well as general-purpose tasks involving code generation, mathematics problem solving, and general instruction-following. We develop models at multiple scales: 2B, 9B, and 72B. Our smaller models often outperform larger general-purpose open-weight and proprietary LLMs (e.g., Llama 3.3 70B, GPT-4o). Our largest model delivers best-in-class translation performance for high-resource languages and top results in multilingual Arena Hard evaluations and in IF-MT, a benchmark we introduce for evaluating both translation and instruction-following. Our findings highlight that it is possible to rival frontier models in general capabilities, while optimizing for specific business domains, such as translation and localization.
对预训练的大型语言模型(LLMs)进行微调,已被证明是达到机器翻译等特定任务的最先进性能的有效策略。然而,这个适应过程通常意味着牺牲通用能力,如对话推理和指令遵循,从而阻碍了系统在需要混合技能的实际应用中的实用性。在本文中,我们介绍了Tower+模型系列,旨在实现翻译和跨语言通用文本能力的双重高性能。我们通过引入一种新的训练配方,在翻译专业化和跨语言通用能力之间取得了帕累托前沿。该配方以Tower(Alves等人,2024)为基础,包括持续预训练、监督微调、偏好优化以及可验证奖励的强化学习。在训练的每个阶段,我们都会精心生成和筛选数据,以加强翻译以及涉及代码生成、数学问题解决和一般指令遵循的通用任务的性能。我们开发了多种规模的模型:2B、9B和72B。我们的较小模型通常表现优于较大的通用公开和专有大型语言模型(例如Llama 3.3 70B、GPT-4o)。我们的大型模型在高资源语言翻译方面表现出最佳性能,并在多语言Arena Hard评估和我们所引入的用于评估翻译和指令遵循能力的IF-MT基准测试中取得顶尖结果。我们的研究结果表明,在针对特定业务领域进行优化时,可以在通用能力方面达到前沿模型的水平,如翻译和本地化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Tower+模型系列,该系列模型旨在实现翻译和多语种通用文本能力的平衡。通过引入新的训练策略,包括持续预训练、监督微调、偏好优化和可验证奖励的强化学习,达到翻译专业化与多语种通用能力之间的帕累托前沿。开发不同规模的模型,包括2B、9B和72B,并在翻译和通用任务上表现出色。最大模型在高资源语言翻译方面表现最佳,并在多语种Arena Hard评估和新的IF-MT基准测试中取得顶尖结果。研究结果表明,可以在优化特定业务领域(如翻译和本地化)的同时,与前沿模型在通用能力方面相匹敌。
Key Takeaways
- Tower+模型系列旨在平衡翻译和多种语言通用文本能力。
- 通过引入新的训练策略,包括持续预训练、监督微调等,实现模型优化。
- 模型在翻译和通用任务上表现出色,不同规模的模型均有良好表现。
- 最大模型在高资源语言翻译方面表现最佳,并在多语种评估中取得顶尖结果。
- 引入新的IF-MT基准测试,用于评估翻译和指令遵循能力。
- 研究结果表明,可以在优化特定业务领域的同时,保持模型的通用能力。
点此查看论文截图

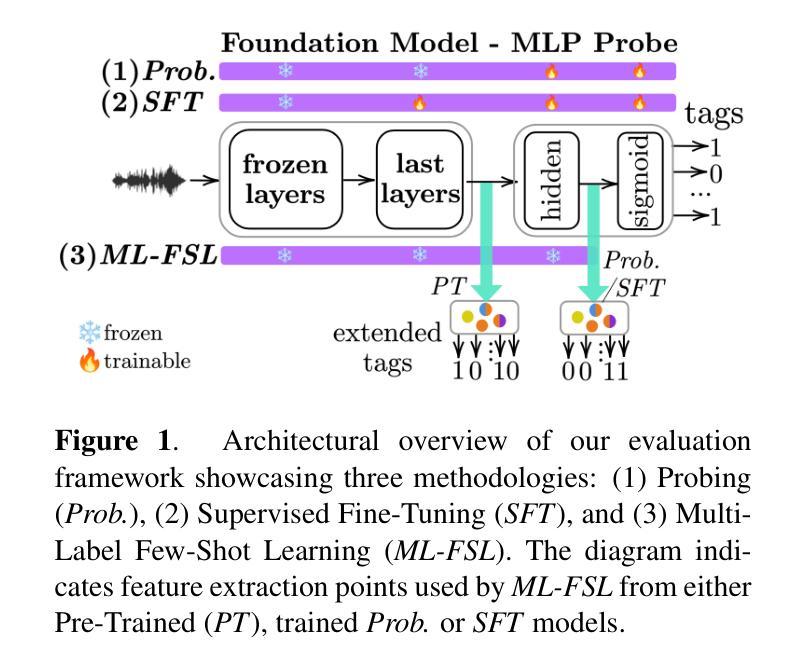
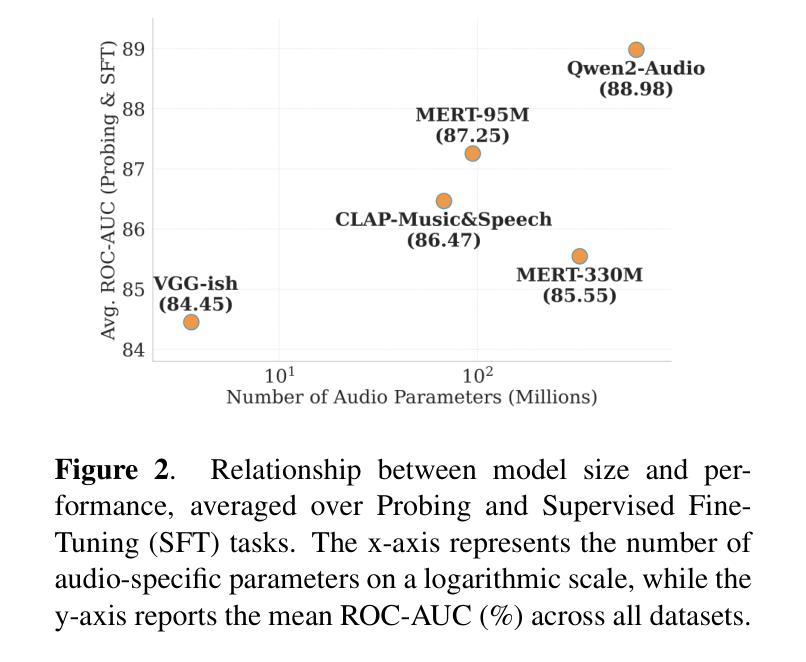
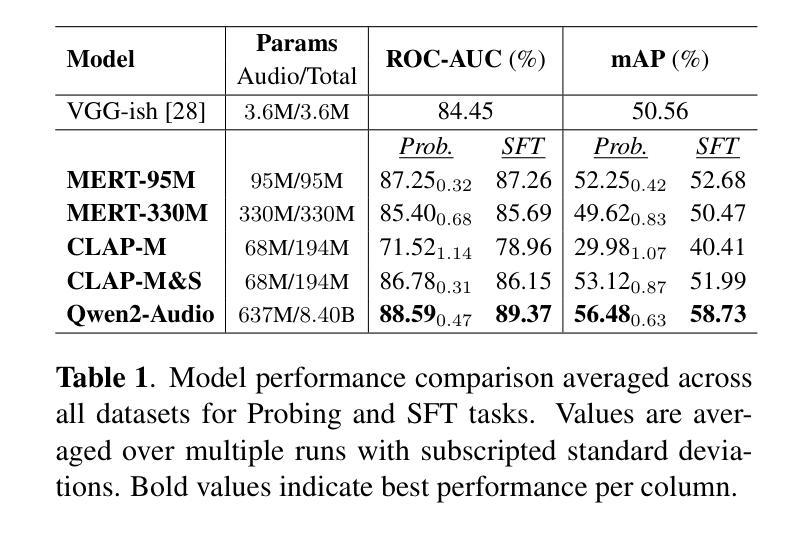
Universal Music Representations? Evaluating Foundation Models on World Music Corpora
Authors:Charilaos Papaioannou, Emmanouil Benetos, Alexandros Potamianos
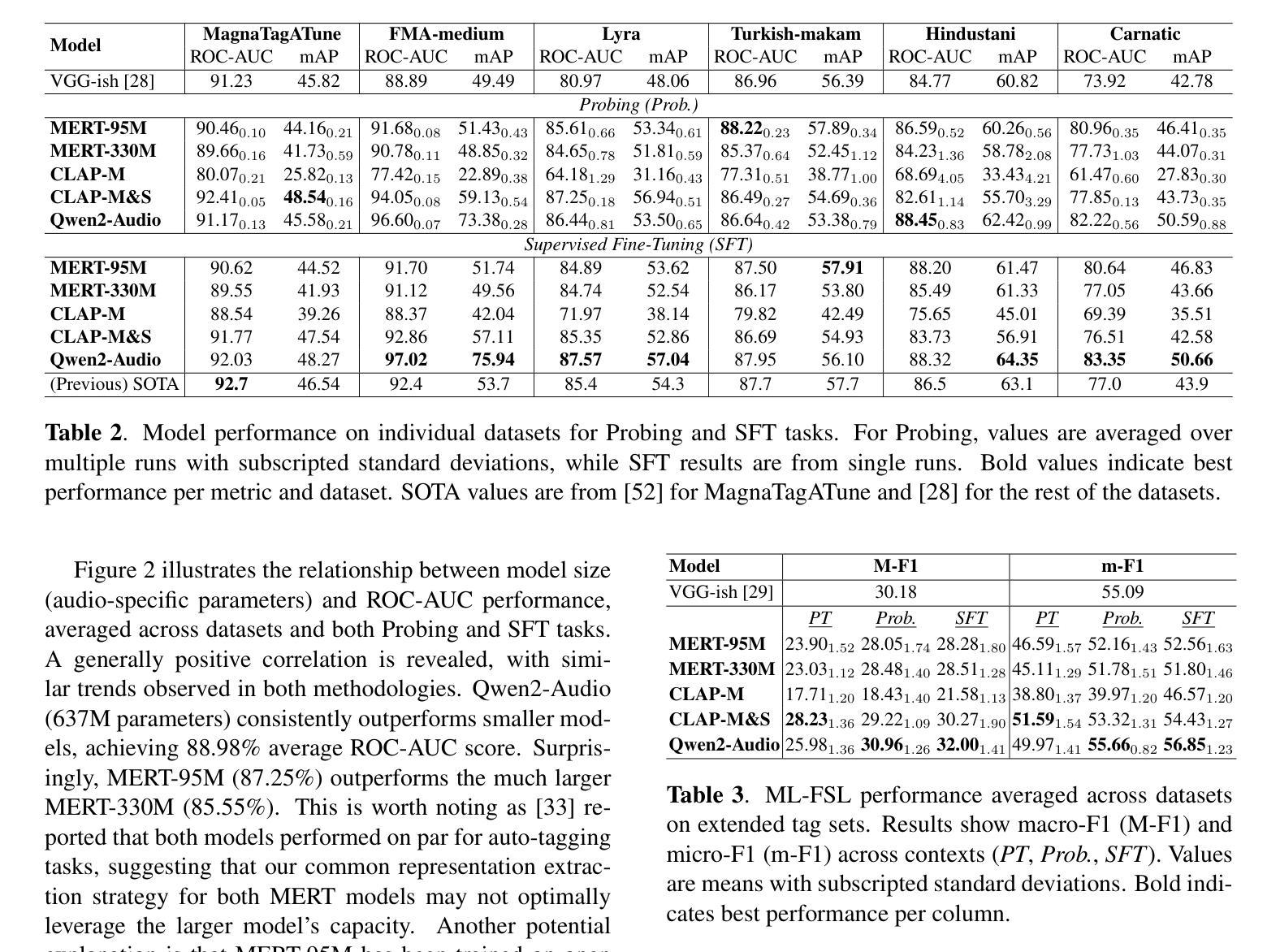
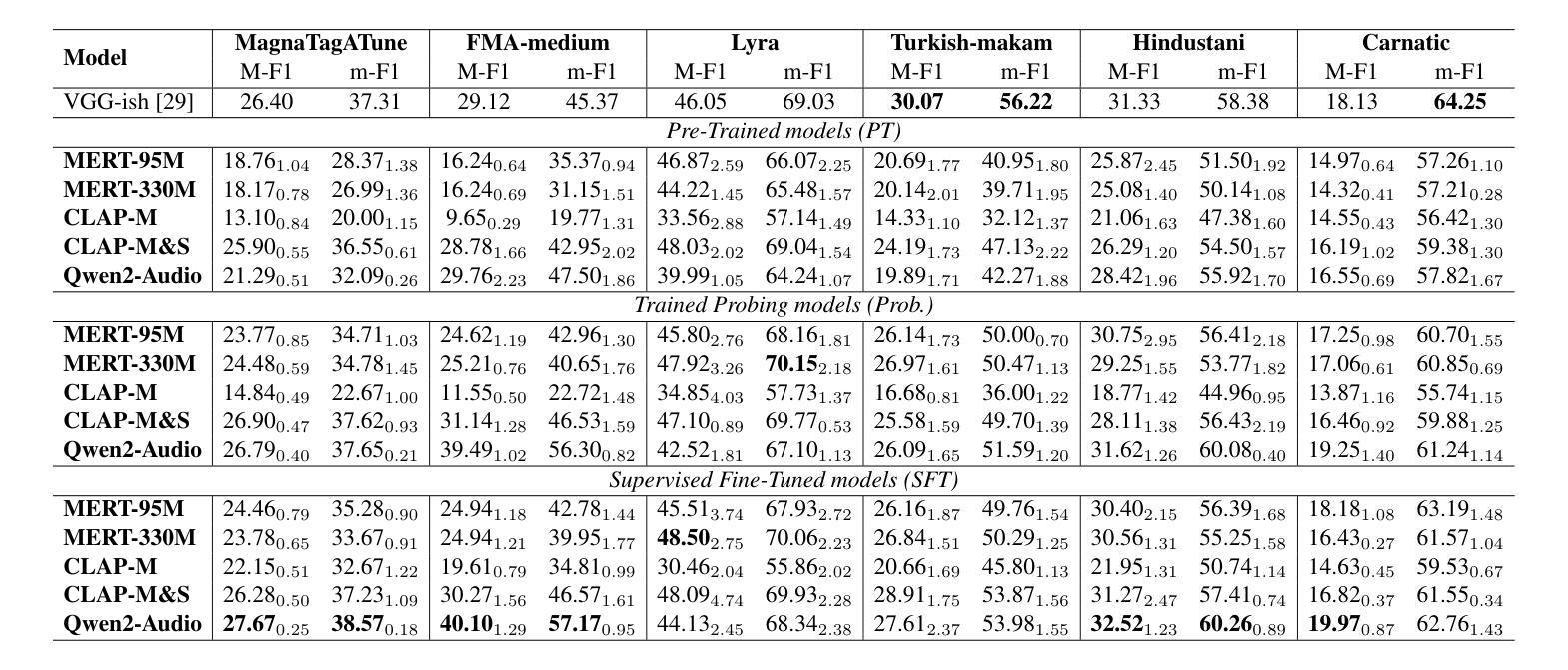
Foundation models have revolutionized music information retrieval, but questions remain about their ability to generalize across diverse musical traditions. This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of five state-of-the-art audio foundation models across six musical corpora spanning Western popular, Greek, Turkish, and Indian classical traditions. We employ three complementary methodologies to investigate these models’ cross-cultural capabilities: probing to assess inherent representations, targeted supervised fine-tuning of 1-2 layers, and multi-label few-shot learning for low-resource scenarios. Our analysis shows varying cross-cultural generalization, with larger models typically outperforming on non-Western music, though results decline for culturally distant traditions. Notably, our approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance on five out of six evaluated datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of foundation models for world music understanding. We also find that our targeted fine-tuning approach does not consistently outperform probing across all settings, suggesting foundation models already encode substantial musical knowledge. Our evaluation framework and benchmarking results contribute to understanding how far current models are from achieving universal music representations while establishing metrics for future progress.
模型基础在音乐信息检索领域已经发生了革命性的变革,但在不同音乐传统中的泛化能力仍存在疑问。本文全面评估了五种最新音频模型基础,涉及六种音乐语料库,包括西方流行、希腊、土耳其和印度古典传统。我们采用三种互补方法来研究这些模型的跨文化能力:探测以评估内在表示、对1-2层进行有针对性的监督微调,以及用于低资源场景的多元标签小样本学习。我们的分析表明,跨文化泛化存在差异,更大的模型通常在非西方音乐上表现更好,但对于文化差异较大的传统,结果会有所下降。值得注意的是,我们的方法在六个评估数据集中有五个达到了最新水平,证明了模型基础在世界音乐理解方面的有效性。我们还发现,我们的有针对性的微调方法并不始终在所有设置中优于探测方法,这表明模型基础已经编码了大量的音乐知识。我们的评估框架和基准测试结果有助于了解当前模型距离实现通用音乐表示还有多远,同时为未来进步建立了指标。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ISMIR 2025
Summary
本文全面评估了五款先进的音频基础模型在涵盖西方流行、希腊、土耳其和印度古典传统等六种音乐语料库中的跨文化泛化能力。通过采用三种互补方法——探测内在表征、对一至两层进行有针对性的监督微调以及用于低资源场景的多元标签少样本学习,研究发现这些模型的跨文化能力存在不同程度的差异,大型模型在非西方音乐上的表现通常较好,但在文化差异较大的传统上表现下降。值得注意的是,我们的方法在五个数据集上达到了最佳性能,证明了基础模型在世界音乐理解方面的有效性。同时,发现有针对性的微调方法并不总是在所有设置中优于探测方法,这表明基础模型已经编码了大量的音乐知识。我们的评估框架和基准测试结果有助于了解当前模型距离实现通用音乐表示的程度,并为未来进步提供了度量标准。
Key Takeaways
- 音频基础模型在跨文化音乐信息检索中表现出一定的泛化能力,但存在不同程度的差异。
- 大型模型在非西方音乐上的表现通常较好。
- 在文化差异较大的传统上,模型表现可能会下降。
- 探测内在表征、监督微调以及多元标签少样本学习等方法被用于评估模型能力。
- 针对性的微调方法并不总是优于探测方法,表明基础模型已具备一定的音乐知识编码能力。
- 在五个数据集上达到了最佳性能,证明了基础模型在世界音乐理解方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Step-by-Step and Verifiable Medical Reasoning in MLLMs
Authors:Haoran Sun, Yankai Jiang, Wenjie Lou, Yujie Zhang, Wenjie Li, Lilong Wang, Mianxin Liu, Lei Liu, Xiaosong Wang
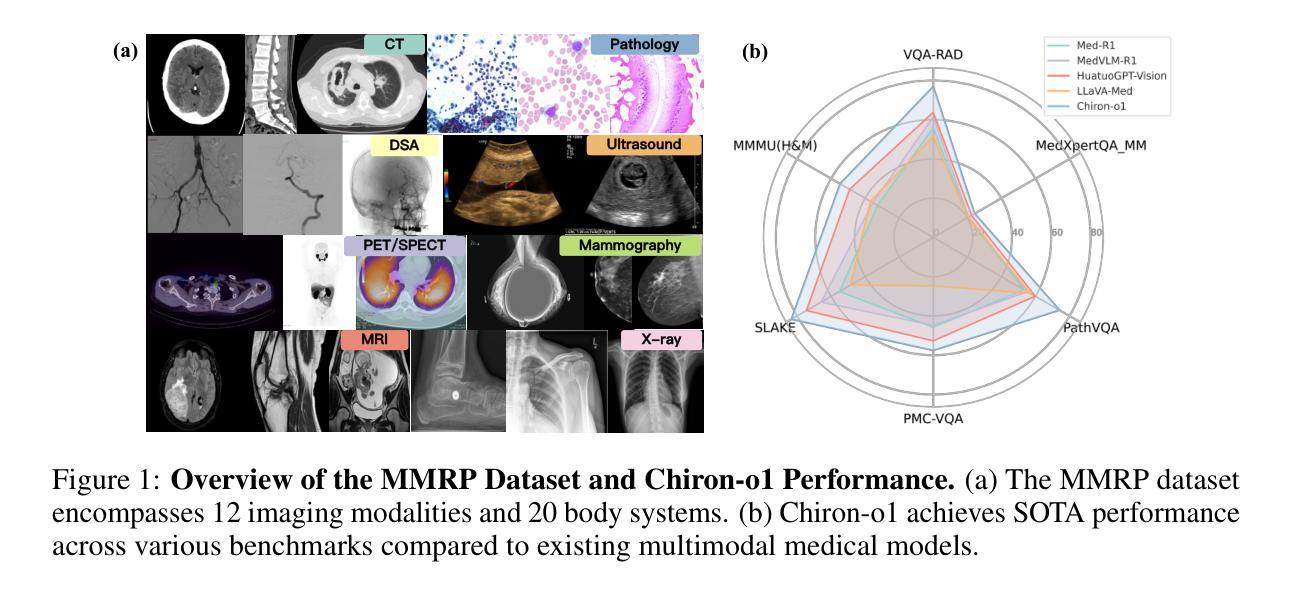
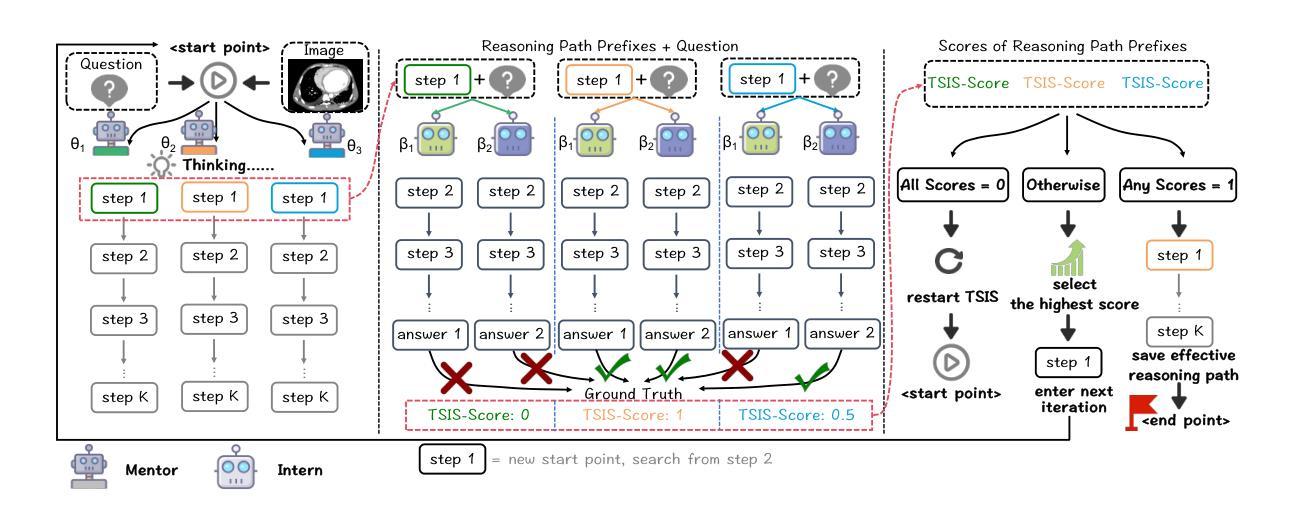
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have begun to demonstrate robust reasoning capabilities on general tasks, yet their application in the medical domain remains in its early stages. Constructing chain-of-thought (CoT) training data is essential for bolstering the reasoning abilities of medical MLLMs. However, existing approaches exhibit a deficiency in offering a comprehensive framework for searching and evaluating effective reasoning paths towards critical diagnosis. To address this challenge, we propose Mentor-Intern Collaborative Search (MICS), a novel reasoning-path searching scheme to generate rigorous and effective medical CoT data. MICS first leverages mentor models to initialize the reasoning, one step at a time, then prompts each intern model to continue the thinking along those initiated paths, and finally selects the optimal reasoning path according to the overall reasoning performance of multiple intern models. The reasoning performance is determined by an MICS-Score, which assesses the quality of generated reasoning paths. Eventually, we construct MMRP, a multi-task medical reasoning dataset with ranked difficulty, and Chiron-o1, a new medical MLLM devised via a curriculum learning strategy, with robust visual question-answering and generalizable reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Chiron-o1, trained on our CoT dataset constructed using MICS, achieves state-of-the-art performance across a list of medical visual question answering and reasoning benchmarks. Codes are available at GitHub - manglu097/Chiron-o1: Enhancing Step-by-Step and Verifiable Medical Reasoning in MLLMs
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)开始在一般任务中展现出稳健的推理能力,但它们在医疗领域的应用仍处于初级阶段。构建思维链(CoT)训练数据对于增强医疗MLLMs的推理能力至关重要。然而,现有方法在搜索和评估有效推理路径以进行关键诊断方面存在缺陷。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了导师实习生协作搜索(MICS)这一新颖的推理路径搜索方案,以生成严谨有效的医疗CoT数据。MICS首先利用导师模型逐步进行推理初始化,然后提示每个实习生模型继续沿着这些初始化的路径进行思考,并最终根据多个实习生模型的总体推理性能选择最佳推理路径。推理性能由MICS评分确定,该评分评估生成推理路径的质量。最终,我们构建了MMRP,这是一个具有排名难度的多任务医疗推理数据集,以及通过课程学习策略开发的新型医疗MLLM——奇伦o1,具有强大的视觉问答和通用推理能力。大量实验表明,在我们使用MICS构建的CoT数据集上训练的奇伦o1,在医疗视觉问答和推理基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。代码可在GitHub(manglu099/Chiron-o1: Enhancing Step-by-Step and Verifiable Medical Reasoning in MLLMs)上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医疗领域中的应用。为提高医疗MLLLs的推理能力,构建思维链(CoT)训练数据至关重要。然而,现有方法缺乏全面搜索和评估有效推理路径以进行关键诊断的框架。为此,提出了导师实习生协作搜索(MICS)这一新的推理路径搜索方案,以生成严谨有效的医疗CoT数据。通过导师模型逐步初始化推理,然后提示实习生模型继续这些初始化的路径进行思考,并根据多个实习生模型的总体推理性能选择最佳推理路径。最终构建了多任务医疗推理数据集MMRP和具有强大视觉问答和通用推理能力的新型医疗MLLLM——奇轮o1。实验表明,在利用MICS构建的CoT数据集上训练的奇轮o1在医疗视觉问答和推理基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLLMs)在医疗领域的推理能力尚处于早期阶段。
- 思维链(CoT)训练数据对提升医疗MLLLMs的推理能力至关重要。
- 现有方法在搜索和评估有效推理路径以进行关键诊断时存在不足。
- 提出导师实习生协作搜索(MICS)方案来生成医疗CoT数据,以提高推理的严谨性和有效性。
- MICS方案通过导师模型逐步初始化推理,并提示实习生模型继续思考,选择最佳推理路径。
- 构建了多任务医疗推理数据集MMRP和新型医疗MLLLM——奇轮o1。
点此查看论文截图

Co-VisiON: Co-Visibility ReasONing on Sparse Image Sets of Indoor Scenes
Authors:Chao Chen, Nobel Dang, Juexiao Zhang, Wenkai Sun, Pengfei Zheng, Xuhang He, Yimeng Ye, Taarun Srinivas, Chen Feng
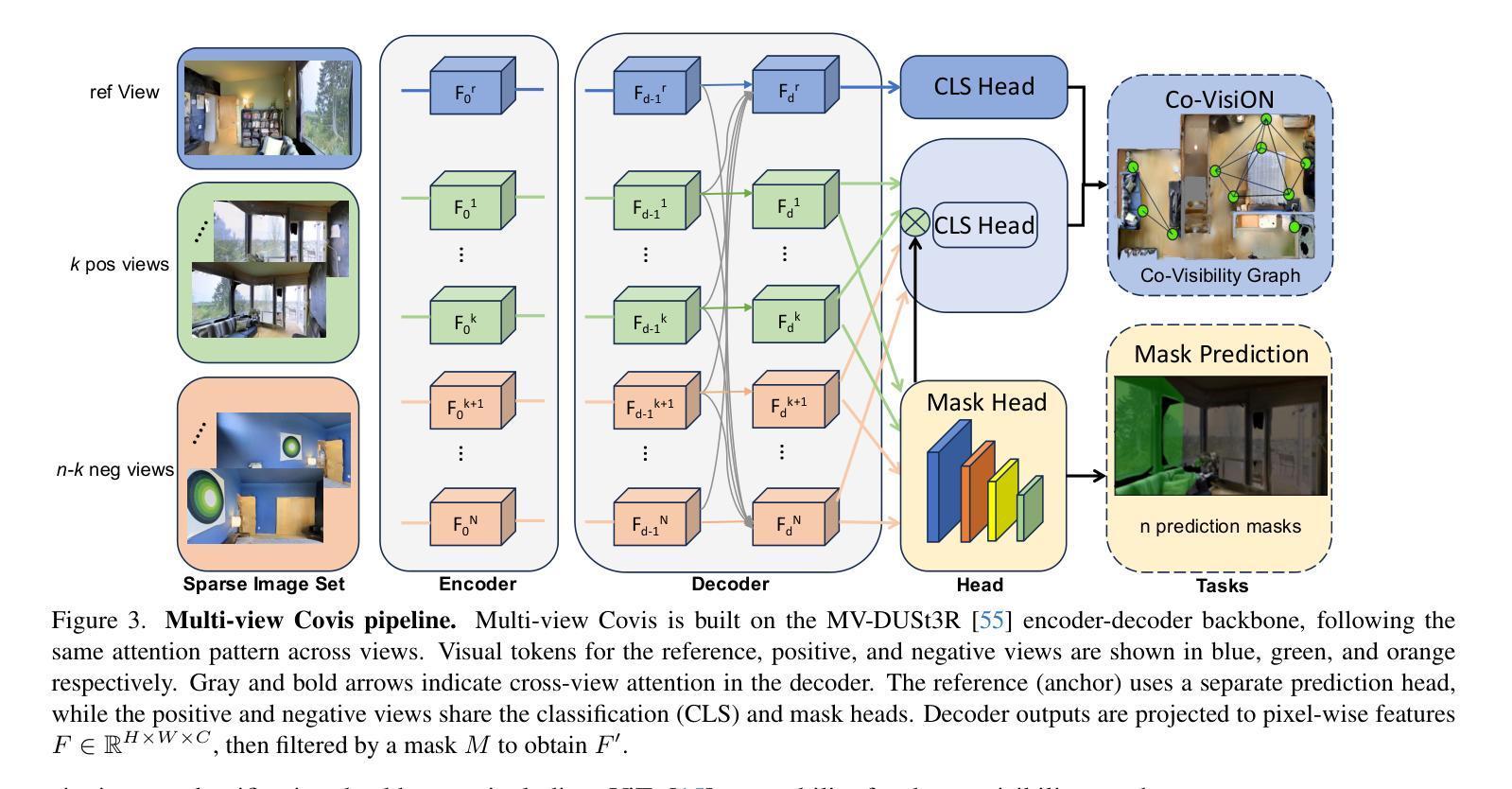
Humans exhibit a remarkable ability to recognize co-visibility-the overlapping regions visible in multiple images-even when these images are sparsely distributed across a complex scene. This capability is foundational in 3D vision and robotic perception. Despite significant progress in vision learning, it remains unclear whether current vision models have reached human-level proficiency in co-visibility analysis. In this work, we introduce the Co-Visibility reasONing (Co-VisiON) benchmark, designed to directly evaluate co-visibility reasoning on sparse image sets across over 1000 indoor scenarios. Our experiments reveal that while co-visibility is typically treated as a low-level feature matching task, it poses a significant challenge for existing vision models under sparse conditions. Notably, a proprietary vision-language model outperforms all purely vision-based approaches, with all models lagging substantially behind human performance. This gap underscores the need for more than basic pairwise vision processing-it calls for a comprehensive spatial understanding through high-level reasoning across multiple views. Inspired by human visual cognition, we propose a novel multi-view baseline, Covis, which achieves top performance among pure vision models and narrows the gap to the proprietary VLM. We hope our benchmark and findings will spur further advancements in developing vision models capable of robust, high-level reasoning in challenging, sparse environments. Our dataset and source code can be found at: https://ai4ce.github.io/CoVISION
人类表现出一种令人印象深刻的识别共视能力——即使在复杂的场景中,多张图像稀疏分布时,也能识别出图像之间可见的重叠区域。这一能力在3D视觉和机器人感知中是基础性的。尽管视觉学习方面取得了显著进展,但当前视觉模型在共视分析方面是否达到了人类水平的能力仍不清楚。在这项工作中,我们引入了共视推理(Co- VisiON)基准测试,旨在直接评估跨越1000个室内场景的稀疏图像集上的共视推理。我们的实验表明,虽然共视通常被视为低级的特征匹配任务,但在稀疏条件下,它对现有的视觉模型构成了重大挑战。值得注意的是,一个专有视觉语言模型在所有纯视觉方法中都表现最好,而所有模型与人类性能都有很大的差距。这一差距凸显了不仅需要基本的配对视觉处理,而且需要通过跨多个视图的高级推理进行全面空间理解。受人类视觉认知的启发,我们提出了一种新的多视图基线方法Covis,它在纯视觉模型中取得了最佳性能并缩小了与专有视觉语言模型的差距。我们希望我们的基准测试和研究成果将促进在开发能够在具有挑战性的稀疏环境中进行稳健高级推理的视觉模型方面取得进一步进展。我们的数据集和源代码可在以下网址找到:https://ai4ce.github.io/CoVISION
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项关于共可见性推理(Co-Visibility reasoning)的研究。该研究提出了一种新的共可见性推理基准测试(Co-VisON),用于评估模型在稀疏图像集上的共可见性分析能力。研究发现,现有模型在稀疏条件下的共可见性推理存在挑战,一种结合视觉和语言模型的性能表现最佳,但仍落后于人类表现。该研究提出了一种新的多视角基线方法Covis,在纯视觉模型中表现最佳。
Key Takeaways
- 人类能够识别图像中的共可见性,这在3D视觉和机器人感知中非常重要。
- 当前视觉模型在共可见性分析方面尚未达到人类水平。
- 引入Co-Visibility reasONing(Co-VisiON)基准测试,用于评估稀疏图像集上的共可见性推理能力。
- 现有视觉模型在稀疏条件下的共可见性推理存在挑战。
- 一种结合视觉和语言模型的性能最佳,但仍远远落后于人类表现。
- 提出了一种新的多视角基线方法Covis,在纯视觉模型中表现最佳。
- 该研究和基准测试将促进在具有挑战性的稀疏环境中开发具备稳健、高级推理能力的视觉模型。
点此查看论文截图


Language-Informed Synthesis of Rational Agent Models for Grounded Theory-of-Mind Reasoning On-The-Fly
Authors:Lance Ying, Ryan Truong, Katherine M. Collins, Cedegao E. Zhang, Megan Wei, Tyler Brooke-Wilson, Tan Zhi-Xuan, Lionel Wong, Joshua B. Tenenbaum
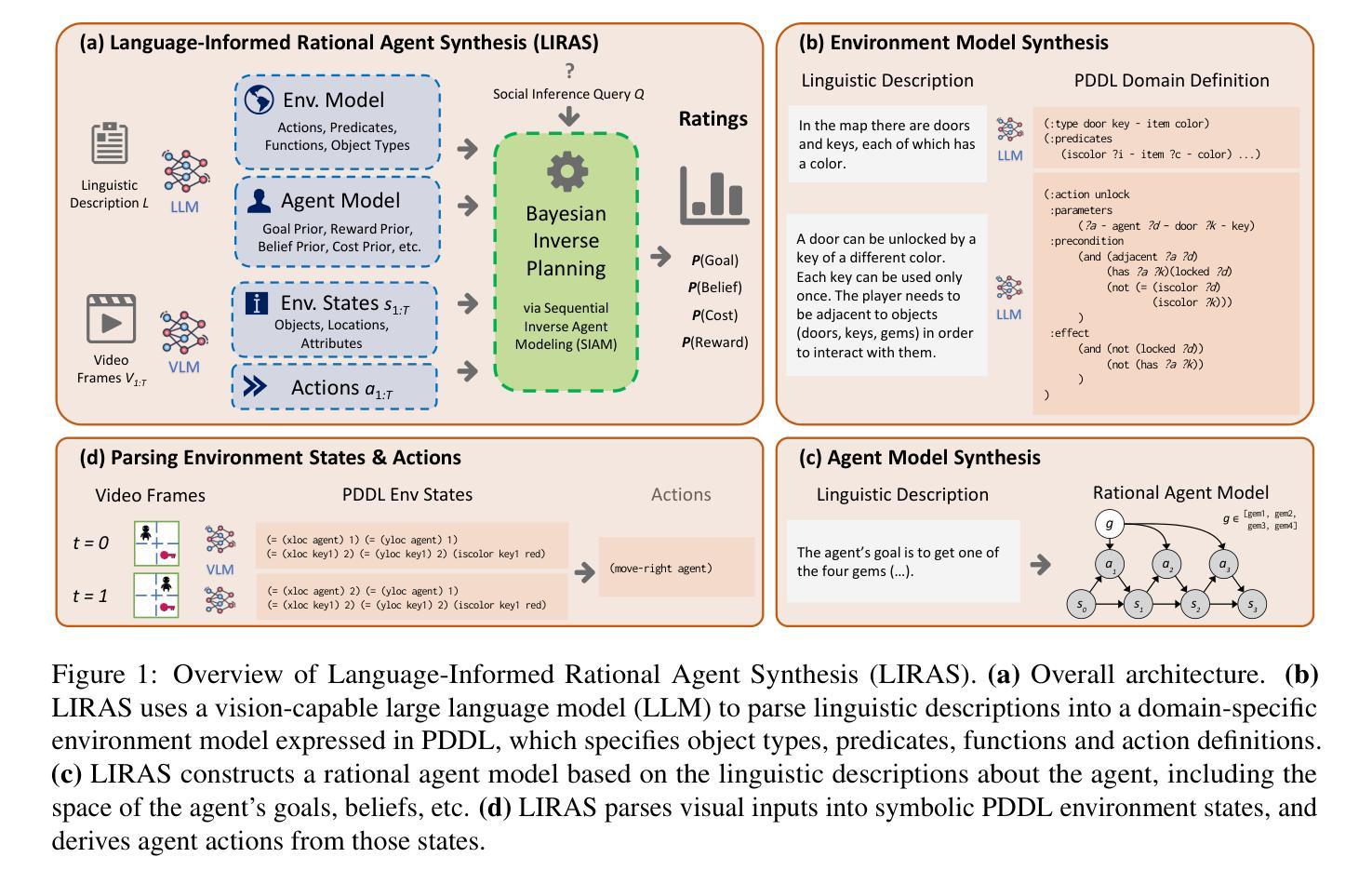
Drawing real world social inferences usually requires taking into account information from multiple modalities. Language is a particularly powerful source of information in social settings, especially in novel situations where language can provide both abstract information about the environment dynamics and concrete specifics about an agent that cannot be easily visually observed. In this paper, we propose Language-Informed Rational Agent Synthesis (LIRAS), a framework for drawing context-specific social inferences that integrate linguistic and visual inputs. LIRAS frames multimodal social reasoning as a process of constructing structured but situation-specific agent and environment representations - leveraging multimodal language models to parse language and visual inputs into unified symbolic representations, over which a Bayesian inverse planning engine can be run to produce granular probabilistic judgments. On a range of existing and new social reasoning tasks derived from cognitive science experiments, we find that our model (instantiated with a comparatively lightweight VLM) outperforms ablations and state-of-the-art models in capturing human judgments across all domains.
抽取现实社会中的推断通常需要综合考虑来自多种模式的信息。在语言环境中,语言是一个特别强大的信息来源,尤其是在新情况下,语言可以提供关于环境动态抽象信息和关于无法轻易观察到的实体的具体细节。在本文中,我们提出了语言信息理性代理合成(LIRAS),这是一个结合语言和视觉输入的、抽取特定情境社会推断的框架。LIRAS将多模式社会推理视为一个过程,即构建结构化但特定于情境的代理和环境表示——利用多模式语言模型解析语言和视觉输入为统一的符号表示,在此基础上运行贝叶斯逆向规划引擎,以产生精细的概率判断。在来自认知科学实验的一系列现有和新社会推理任务上,我们发现我们的模型(用相对轻量级的VLM实例化)在捕获所有领域的人类判断方面优于废除和最新模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 figures, 19 pages
Summary
本文提出一种结合语言和视觉输入的社会推理框架——语言信息理性代理人合成(LIRAS)。该框架利用多模态语言模型将语言和视觉输入解析为统一的符号表示,并通过贝叶斯逆规划引擎运行,以产生精细的概率判断,从而进行情境特定的社会推理。实验表明,该模型在多个来自认知科学实验的社会推理任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种新的社会推理框架——Language-Informed Rational Agent Synthesis (LIRAS)。
- LIRAS结合了语言和视觉输入,用于进行社会推理。
- 多模态语言模型将语言和视觉输入解析为统一的符号表示。
- 使用贝叶斯逆规划引擎进行概率判断。
- 模型在多个社会推理任务上的表现超过了现有模型。
- 模型强调了语言在社会推理中的重要性,特别是在难以通过视觉观察获得具体信息的新情境中。
点此查看论文截图

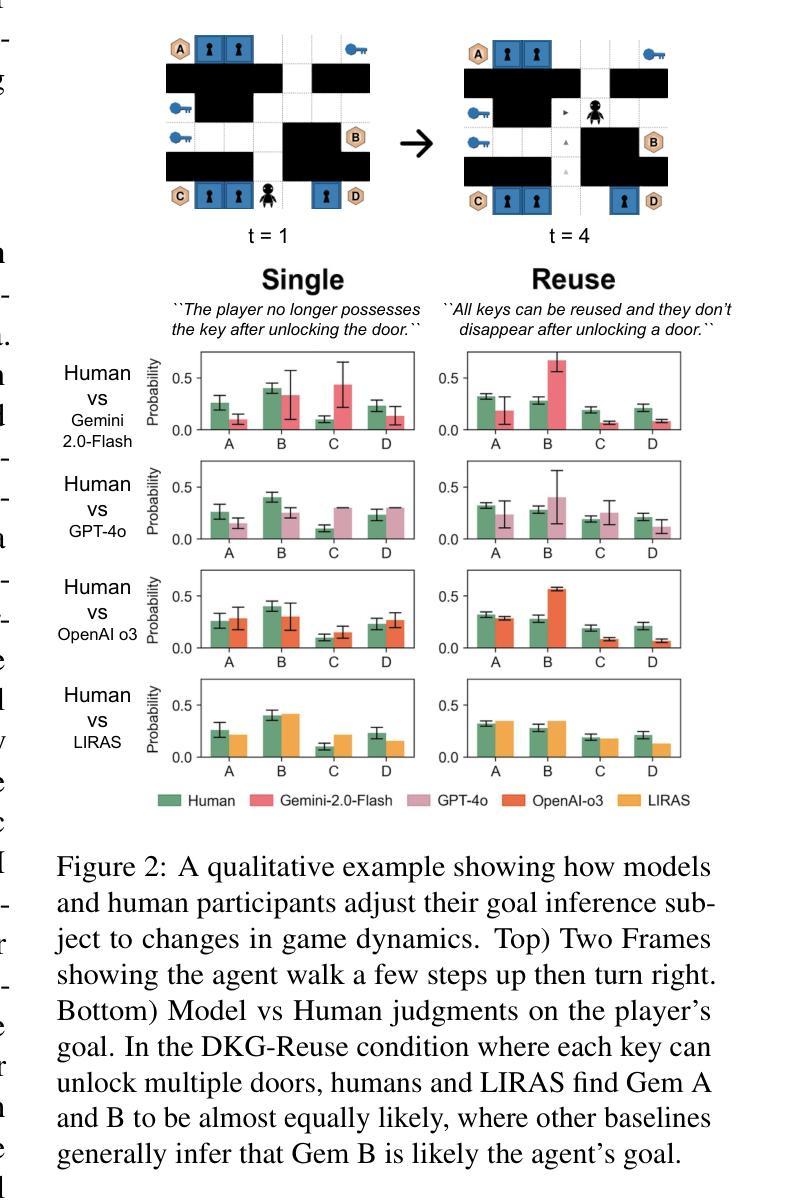
Off-Policy Actor-Critic for Adversarial Observation Robustness: Virtual Alternative Training via Symmetric Policy Evaluation
Authors:Kosuke Nakanishi, Akihiro Kubo, Yuji Yasui, Shin Ishii
Recently, robust reinforcement learning (RL) methods designed to handle adversarial input observations have received significant attention, motivated by RL’s inherent vulnerabilities. While existing approaches have demonstrated reasonable success, addressing worst-case scenarios over long time horizons requires both minimizing the agent’s cumulative rewards for adversaries and training agents to counteract them through alternating learning. However, this process introduces mutual dependencies between the agent and the adversary, making interactions with the environment inefficient and hindering the development of off-policy methods. In this work, we propose a novel off-policy method that eliminates the need for additional environmental interactions by reformulating adversarial learning as a soft-constrained optimization problem. Our approach is theoretically supported by the symmetric property of policy evaluation between the agent and the adversary. The implementation is available at https://github.com/nakanakakosuke/VALT_SAC.
最近,为了处理对抗性输入观察而设计的稳健的强化学习(RL)方法受到了广泛关注,这源于RL固有的脆弱性。虽然现有方法已经取得了合理的成功,但在长时间范围内应对最坏情况场景需要最小化代理对对手的累积奖励,并训练代理通过交替学习来对抗它们。然而,这个过程在代理和对手之间引入了相互依赖,使与环境之间的互动效率低下,并阻碍了离线方法的发展。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新颖的离线方法,它通过重新将对决学习表述为软约束优化问题,从而消除了对环境进行额外互动的需要。我们的方法得到了代理和对手之间政策评价对称性的理论支持。实施细节可见于 https://github.com/nakanakakosuke/VALT_SAC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML2025 poster, 39 pages, 6 figures, 13 tables. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2409.00418
Summary
近期,强化学习(RL)方法在处理对抗性输入观察方面受到关注,因RL固有的脆弱性而备受挑战。现有方法虽取得一定成功,但在长时间范围内应对最坏场景时,需要最小化代理的累积奖励并为代理进行对抗训练。然而,这一过程在代理和对手之间引入了相互依赖,导致与环境互动效率低下并阻碍离线策略方法的发展。本研究提出了一种新颖的离线策略方法,通过将对战学习重新表述为软约束优化问题,从而无需额外的环境互动。此方法的理论支持来自代理和对手之间政策评价的对称性。代码实现可见于https://github.com/nakanakakosuke/VALT_SAC。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)在处理对抗性输入观察方面存在挑战,需要应对长时间范围内的最坏场景。
- 现有方法需要在最小化代理的累积奖励和为代理进行对抗训练之间取得平衡。
- 代理和对手之间的相互作用引入了相互依赖,降低了与环境互动的效率。
- 提出了一种新颖的离线策略方法,通过对抗学习软约束优化来消除对环境额外互动的需求。
- 该方法的理论支持基于代理和对手在政策评价上的对称性。
- 方法实现的代码公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

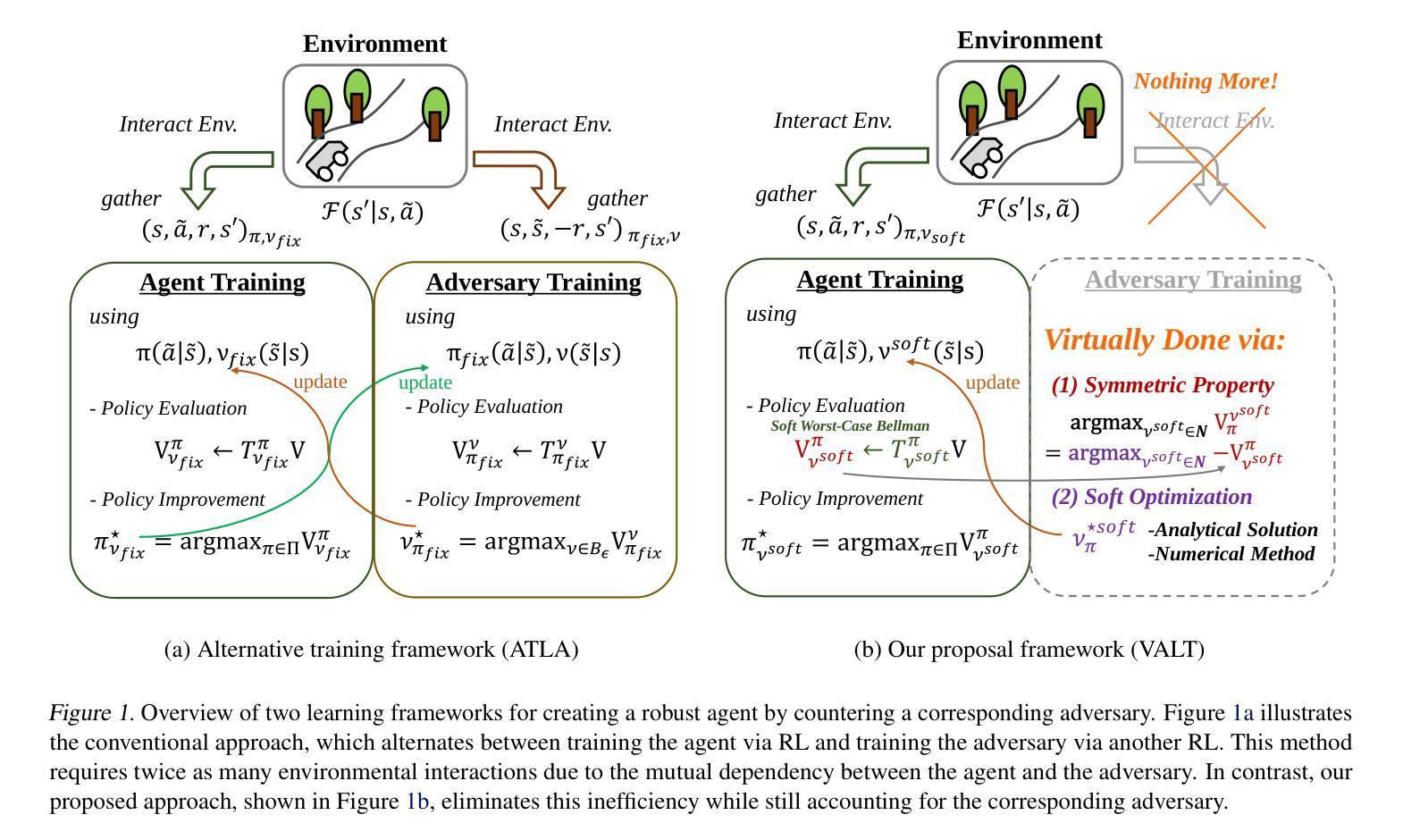
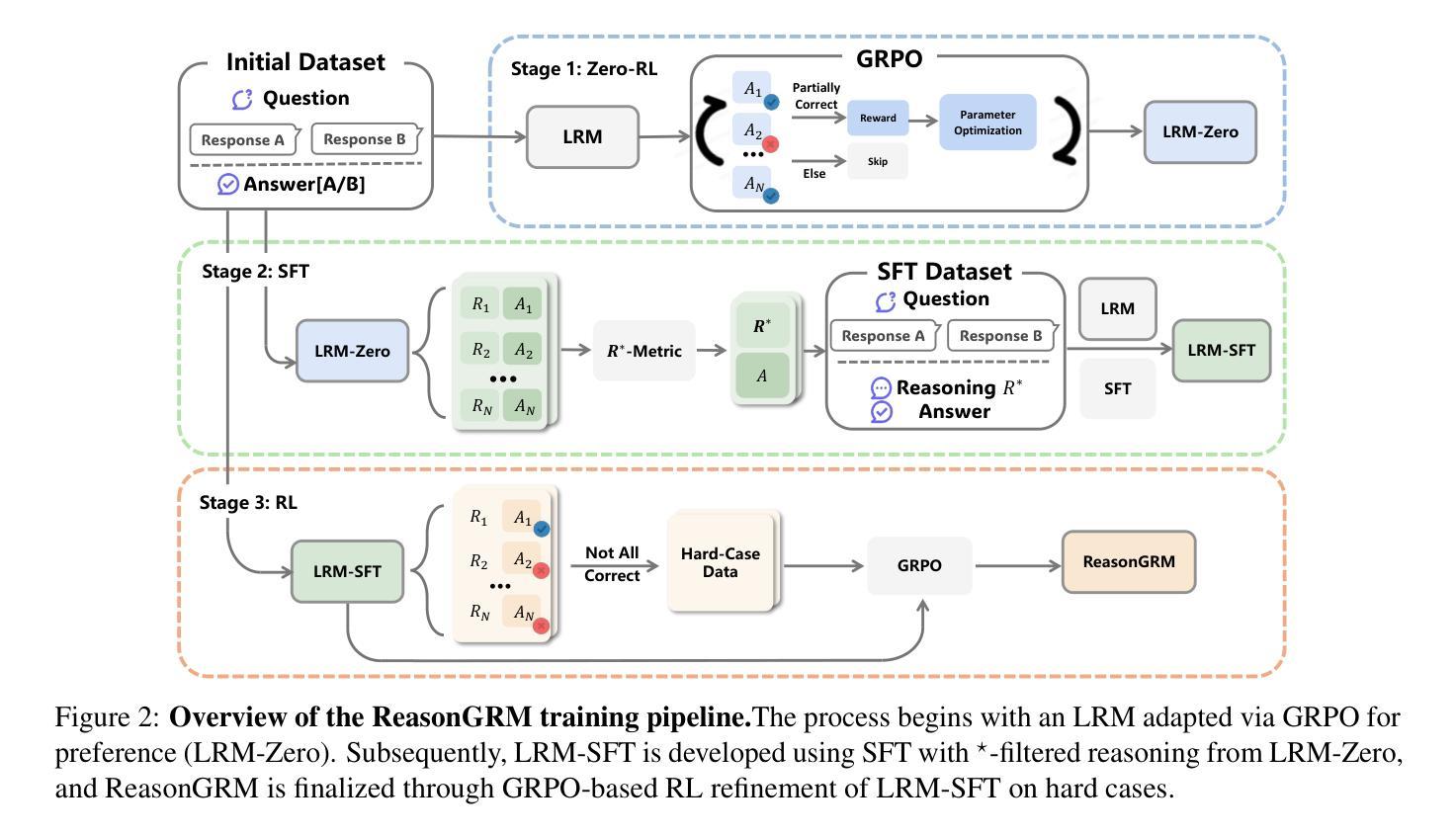
ReasonGRM: Enhancing Generative Reward Models through Large Reasoning Models
Authors:Bin Chen, Xinzge Gao, Chuanrui Hu, Penghang Yu, Hua Zhang, Bing-Kun Bao
Generative Reward Models (GRMs) provide greater flexibility than scalar reward models in capturing human preferences, but their effectiveness is limited by poor reasoning capabilities. This often results in incomplete or overly speculative reasoning paths, leading to hallucinations or missing key information in complex tasks. We address this challenge with ReasonGRM, a three-stage generative reward modeling framework. In the first stage, Zero-RL is used to generate concise, outcome-directed reasoning paths that reduce the likelihood of critical omissions. In the second stage, we introduce a novel evaluation metric, $R^\star$, which scores reasoning paths based on their generation likelihood. This favors paths that reach correct answers with minimal exploration, helping to reduce hallucination-prone data during training. In the final stage, the model is further refined through reinforcement learning on challenging examples to enhance its preference discrimination capabilities. Experiments on three public benchmarks show that ReasonGRM achieves competitive or state-of-the-art performance, outperforming previous best GRMs by 1.8% on average and surpassing proprietary models such as GPT-4o by up to 5.6%. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of reasoning-aware training and highlight the importance of high-quality rationale selection for reliable preference modeling.
生成奖励模型(GRMs)在捕捉人类偏好方面提供了比标量奖励模型更大的灵活性,但其有效性受到推理能力不足的制约。这通常会导致推理路径不完整或过于投机取巧,从而在复杂任务中出现幻觉或遗漏关键信息。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了ReasonGRM,这是一个三阶段的生成奖励建模框架。在第一阶段,我们利用Zero-RL生成简洁、以结果为导向的推理路径,减少关键遗漏的可能性。在第二阶段,我们引入了一种新的评估指标$R^\star$,根据推理路径的生成可能性对其进行评分。这有利于以最小探索找到正确答案的路径,有助于减少训练过程中的幻觉倾向数据。在最后一个阶段,通过对挑战样本进行强化学习,进一步精炼模型,提高其偏好辨别能力。在三个公共基准测试上的实验表明,ReasonGRM具有竞争力或达到最新技术水平,平均比之前的最佳GRM高出1.8%,并超过专有模型如GPT-4o高达5.6%。这些结果证明了推理感知训练的有效性,并强调了高质量推理选择对于可靠偏好建模的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于生成奖励模型(GRMs)在捕捉人类偏好时灵活性更高的事实,文章指出了其受限于较差推理能力的问题。为解决这一问题,文章提出了ReasonGRM,这是一个三阶段的生成奖励建模框架。该框架不仅使用了Zero-RL生成简洁、结果导向的推理路径以减少关键遗漏的可能性,还引入了一种新的评估指标$R^\star$,以基于生成可能性对推理路径进行评分。最终阶段则通过强化学习对模型进行精炼,提升其偏好辨别能力。实验结果表明,ReasonGRM在三个公开基准测试中实现了竞争性或领先性能,平均提高了GRMs性能约1.8%,并且相对于GPT-4o等专有模型性能提升最高可达5.6%。这证明了推理感知训练的重要性以及高质量推理选择对于可靠偏好建模的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成奖励模型(GRMs)相较于标量奖励模型具有更高的灵活性来捕捉人类偏好,但其效果受限于推理能力不足的问题。
- 问题可能引发不完整的推理路径或者过于推测的假设,导致生成错误的结论。
点此查看论文截图


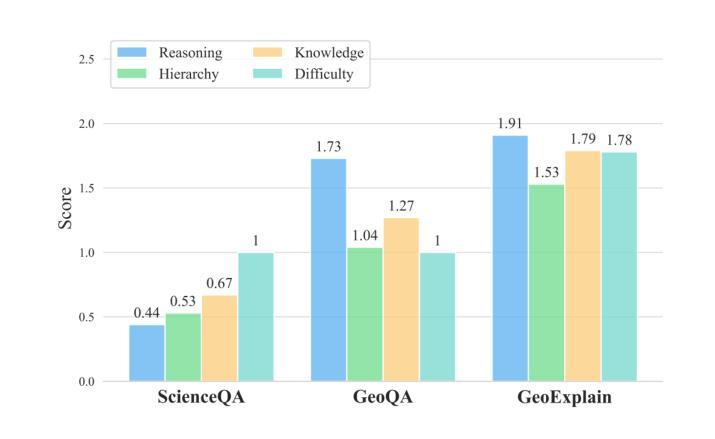
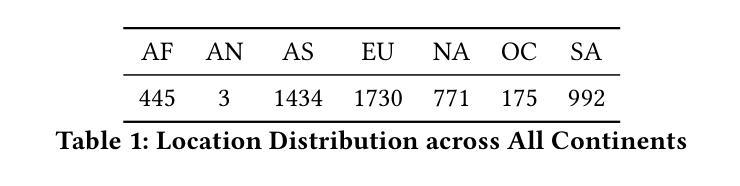
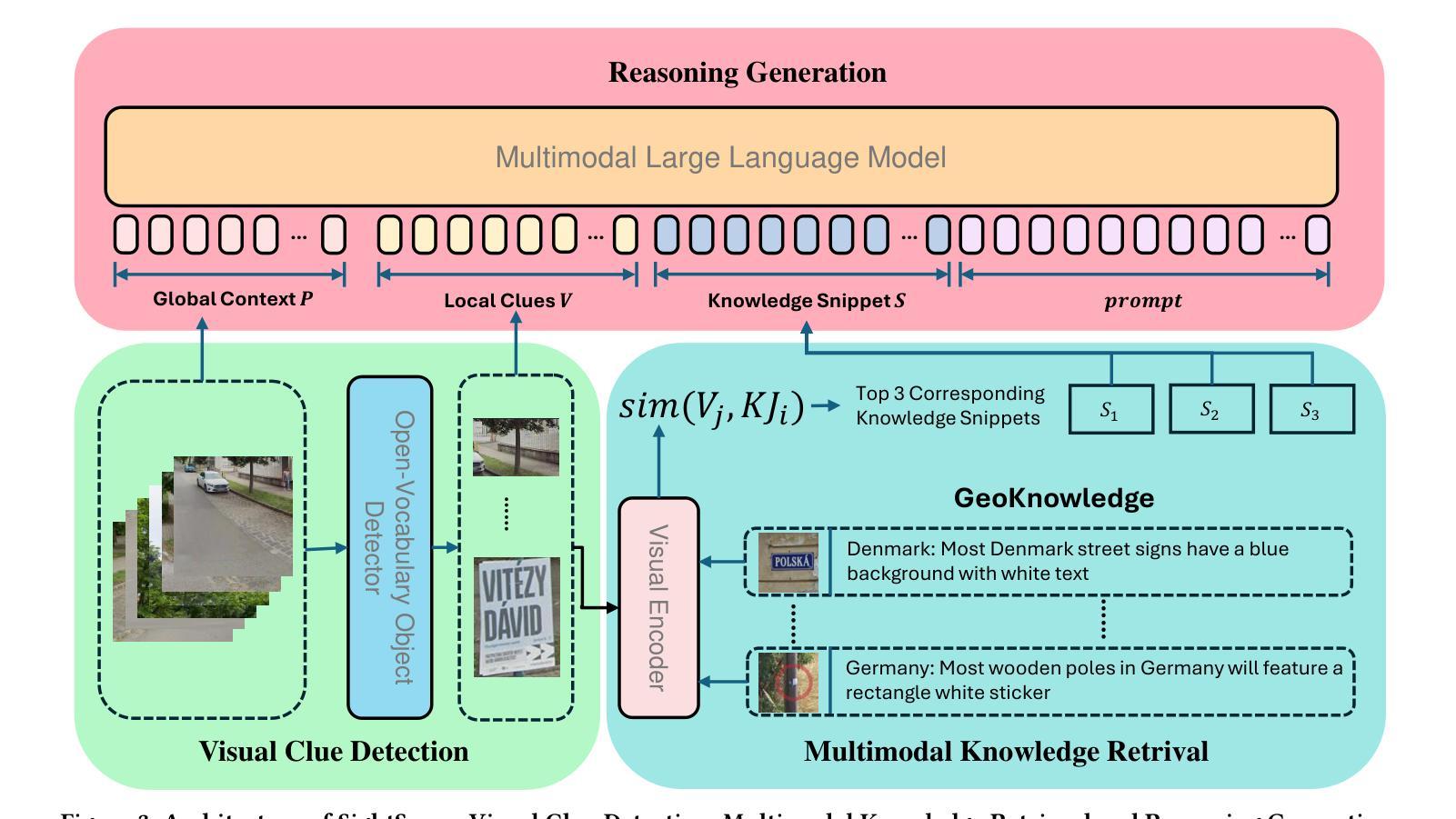
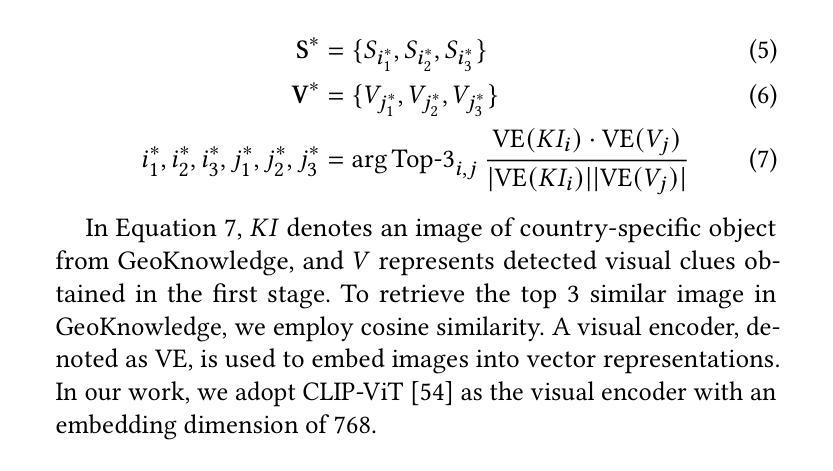
GeoGuess: Multimodal Reasoning based on Hierarchy of Visual Information in Street View
Authors:Fenghua Cheng, Jinxiang Wang, Sen Wang, Zi Huang, Xue Li
Multimodal reasoning is a process of understanding, integrating and inferring information across different data modalities. It has recently attracted surging academic attention as a benchmark for Artificial Intelligence (AI). Although there are various tasks for evaluating multimodal reasoning ability, they still have limitations. Lack of reasoning on hierarchical visual clues at different levels of granularity, e.g., local details and global context, is of little discussion, despite its frequent involvement in real scenarios. To bridge the gap, we introduce a novel and challenging task for multimodal reasoning, namely GeoGuess. Given a street view image, the task is to identify its location and provide a detailed explanation. A system that succeeds in GeoGuess should be able to detect tiny visual clues, perceive the broader landscape, and associate with vast geographic knowledge. Therefore, GeoGuess would require the ability to reason between hierarchical visual information and geographic knowledge. In this work, we establish a benchmark for GeoGuess by introducing a specially curated dataset GeoExplain which consists of panoramas-geocoordinates-explanation tuples. Additionally, we present a multimodal and multilevel reasoning method, namely SightSense which can make prediction and generate comprehensive explanation based on hierarchy of visual information and external knowledge. Our analysis and experiments demonstrate their outstanding performance in GeoGuess.
多模态推理是理解和推断不同数据模态信息的过程。最近,它作为人工智能的基准测试,引起了学术界的广泛关注。尽管存在各种评估多模态推理能力的任务,但它们仍有一定的局限性。对于不同粒度层次上的视觉线索的推理缺乏讨论,例如局部细节和全局上下文,尽管其在现实场景中经常涉及。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一项具有挑战性和创新性的多模态推理任务,即地理猜测(GeoGuess)。给定一张街道视图图像,任务是识别其位置并提供详细的解释。能够在GeoGuess中成功的系统应该能够检测到微小的视觉线索,感知更广阔的景观,并与丰富的地理知识相关联。因此,GeoGuess将需要处理分层视觉信息和地理知识的能力。在这项工作中,我们通过引入专门定制的数据集GeoExplain,建立了GeoGuess的基准测试,该数据集由全景图-地理坐标-解释元组组成。此外,我们提出了一种多模态、多层次的推理方法,即SightSense,它可以基于视觉信息的层次结构和外部知识来进行预测和生成综合解释。我们的分析和实验证明了他们在GeoGuess中的出色表现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态推理的新挑战任务——GeoGuess。该任务要求系统通过识别街道景观图像中的细微视觉线索、感知更广泛的景观,并结合丰富的地理知识来确定其位置并提供详细解释。为此,本文建立了一个名为GeoExplain的专门数据集,并提出了一种名为SightSense的多模态多层次推理方法,该方法能够根据视觉信息的层次结构和外部知识进行预测和生成综合解释。在GeoGuess任务中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态推理是理解和推断不同数据模态信息的过程,近年来已成为人工智能的基准测试。
- 当前的多模态推理任务评估存在局限性,特别是在层次化视觉线索上的推理能力方面讨论较少。
- 引入新的多模态推理任务——GeoGuess,要求系统结合细微视觉线索、整体景观以及地理知识来识别街道图像的位置。
- 建立GeoExplain数据集,包含全景图-地理坐标-解释的三元组,为GeoGuess任务提供基准测试。
- 提出名为SightSense的多模态多层次推理方法,能够基于视觉信息的层次结构和外部知识进行预测和详细解释。
- GeoGuess任务需要系统具备在层次化视觉信息和地理知识之间进行推理的能力。
点此查看论文截图

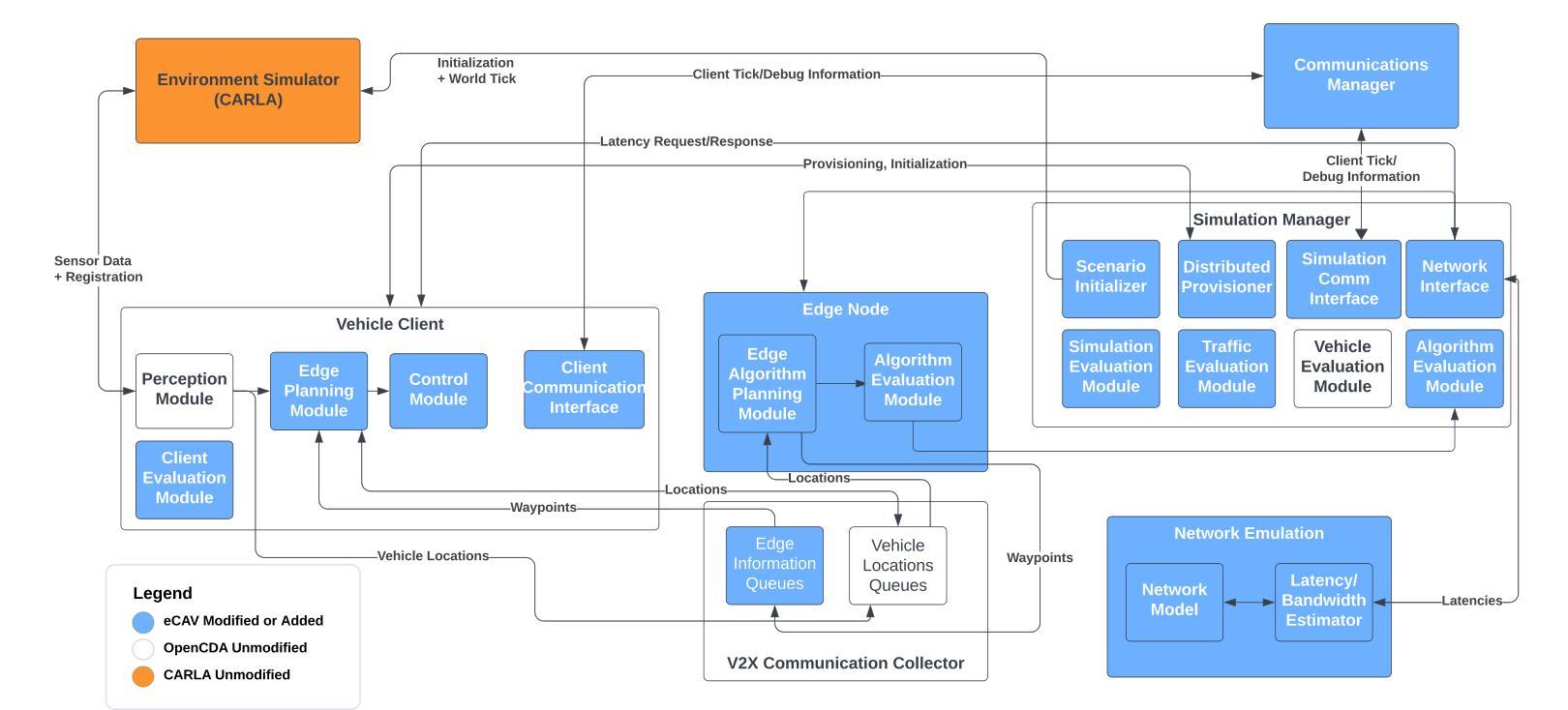
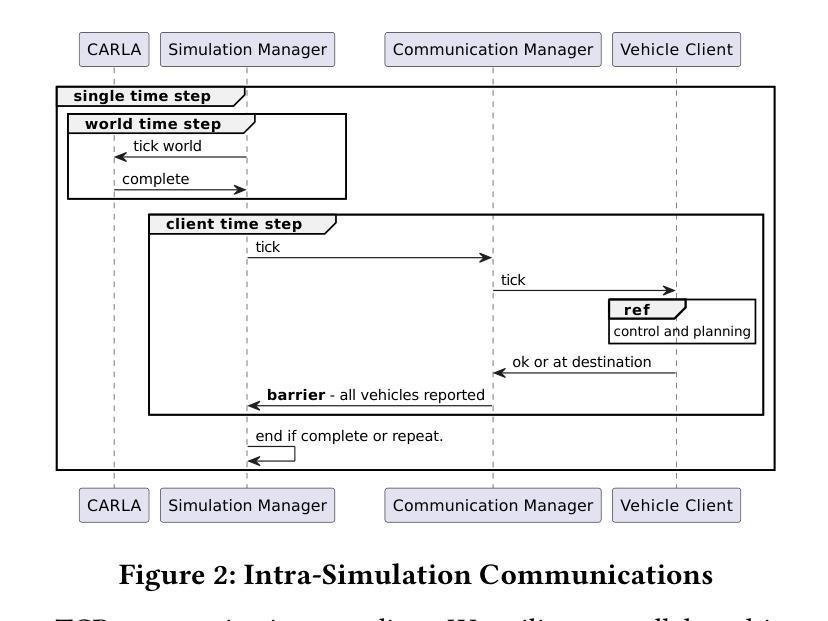
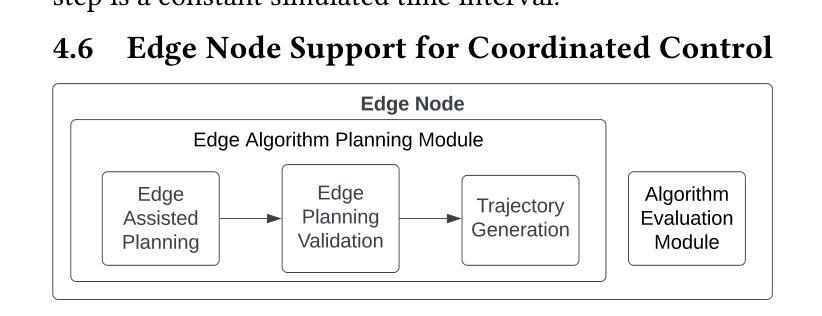
eCAV: An Edge-Assisted Evaluation Platform for Connected Autonomous Vehicles
Authors:Tyler Landle, Jordan Rapp, Dean Blank, Chandramouli Amarnath, Abhijit Chatterjee, Alex Daglis, Umakishore Ramachandran
As autonomous vehicles edge closer to widespread adoption, enhancing road safety through collision avoidance and minimization of collateral damage becomes imperative. Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technologies, which include vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), and vehicle-to-cloud (V2C), are being proposed as mechanisms to achieve this safety improvement. Simulation-based testing is crucial for early-stage evaluation of Connected Autonomous Vehicle (CAV) control systems, offering a safer and more cost-effective alternative to real-world tests. However, simulating large 3D environments with many complex single- and multi-vehicle sensors and controllers is computationally intensive. There is currently no evaluation framework that can effectively evaluate realistic scenarios involving large numbers of autonomous vehicles. We propose eCAV – an efficient, modular, and scalable evaluation platform to facilitate both functional validation of algorithmic approaches to increasing road safety, as well as performance prediction of algorithms of various V2X technologies, including a futuristic Vehicle-to-Edge control plane and correspondingly designed control algorithms. eCAV can model up to 256 vehicles running individual control algorithms without perception enabled, which is $8\times$ more vehicles than what is possible with state-of-the-art alternatives. %faster than state-of-the-art alternatives that can simulate $8\times$ fewer vehicles. With perception enabled, eCAV simulates up to 64 vehicles with a step time under 800ms, which is $4\times$ more and $1.5\times$ faster than the state-of-the-art OpenCDA framework.
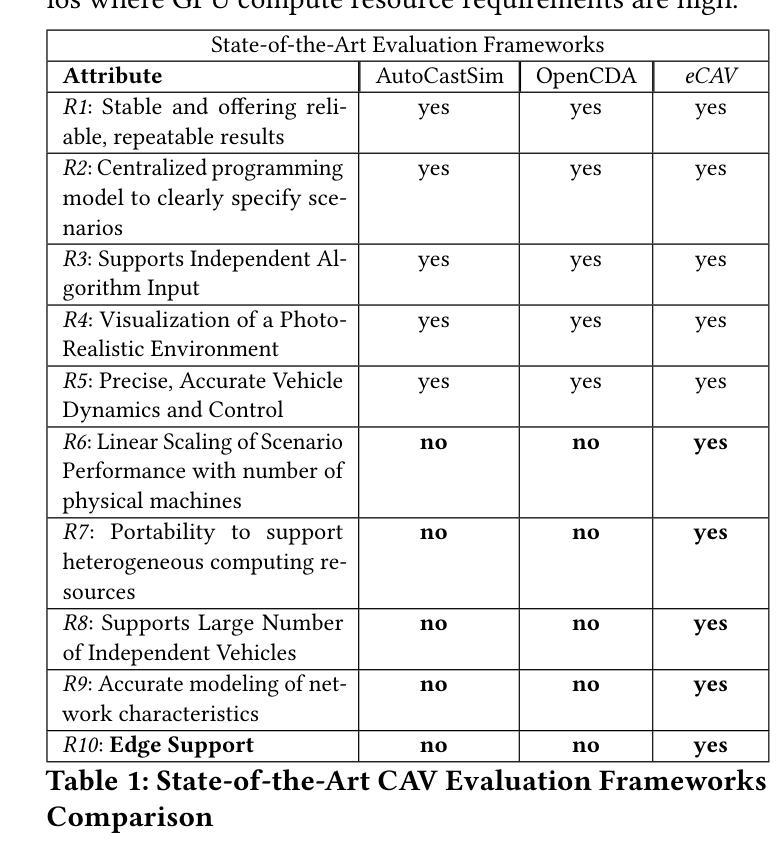
随着自动驾驶汽车越来越接近广泛采用,通过避免碰撞和最小化附带损失来提高道路安全变得至关重要。车辆对一切(V2X)技术,包括车辆对车辆(V2V)、车辆对基础设施(V2I)和车辆对云(V2C),被提议作为实现这种安全改进的机制。基于模拟的测试对于早期阶段评估自动驾驶车辆(CAV)控制系统至关重要,它为真实世界测试提供了更安全、更经济的替代方案。然而,模拟具有许多复杂单车和多车传感器和控制器的大型三维环境在计算上很密集。目前还没有一个评估框架能够有效地评估涉及大量自动驾驶车辆的现实场景。我们提出了eCAV——一个高效、模块化、可扩展的评估平台,它既能验证提高道路安全的算法方法的功能性,也能预测各种V2X技术的算法性能,包括先进的车辆对边缘控制平面和相应设计的控制算法。在没有启用感知的情况下,eCAV可以模拟多达256辆汽车运行各自的控制算法,这是目前其他选择可能模拟的车辆数的8倍。通过启用感知功能,eCAV能在不到800毫秒的时间内模拟多达64辆汽车的情况,这比现有最先进的OpenCDA框架高出4倍,速度高出1.5倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文讨论了随着自动驾驶汽车的普及,通过V2X技术提高道路安全的重要性。仿真测试在评估连接自动驾驶车辆(CAV)控制系统方面发挥着关键作用。然而,模拟大型3D环境存在计算密集的问题。为此,本文提出了一种高效、模块化和可扩展的评估平台eCAV,该平台不仅可以验证提高道路安全的算法方法的功能性,还可以预测各种V2X技术的算法性能。eCAV能够模拟运行独立控制算法的最多256辆汽车(在不启用感知的情况下),是现有替代方案的8倍。启用感知后,eCAV可以在800毫秒的步骤时间内模拟最多64辆汽车,这是现有OpenCDA框架的4倍和1.5倍。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶汽车的普及对道路安全提出了更高的要求,需要通过V2X技术增强安全性。
- 仿真测试在评估CAV控制系统方面发挥着重要作用,作为现实世界测试的替代方案。
- 模拟大型3D环境涉及计算密集型任务,存在挑战。
- 缺乏能够评估涉及大量自动驾驶车辆的现实场景的评估框架。
- 提出了eCAV评估平台,该平台具有高效、模块化和可扩展性特点。
- eCAV能够模拟运行独立控制算法的最多256辆汽车(在不启用感知的情况下)。
点此查看论文截图

From LLM-anation to LLM-orchestrator: Coordinating Small Models for Data Labeling
Authors:Yao Lu, Zhaiyuan Ji, Jiawei Du, Yu Shanqing, Qi Xuan, Tianyi Zhou
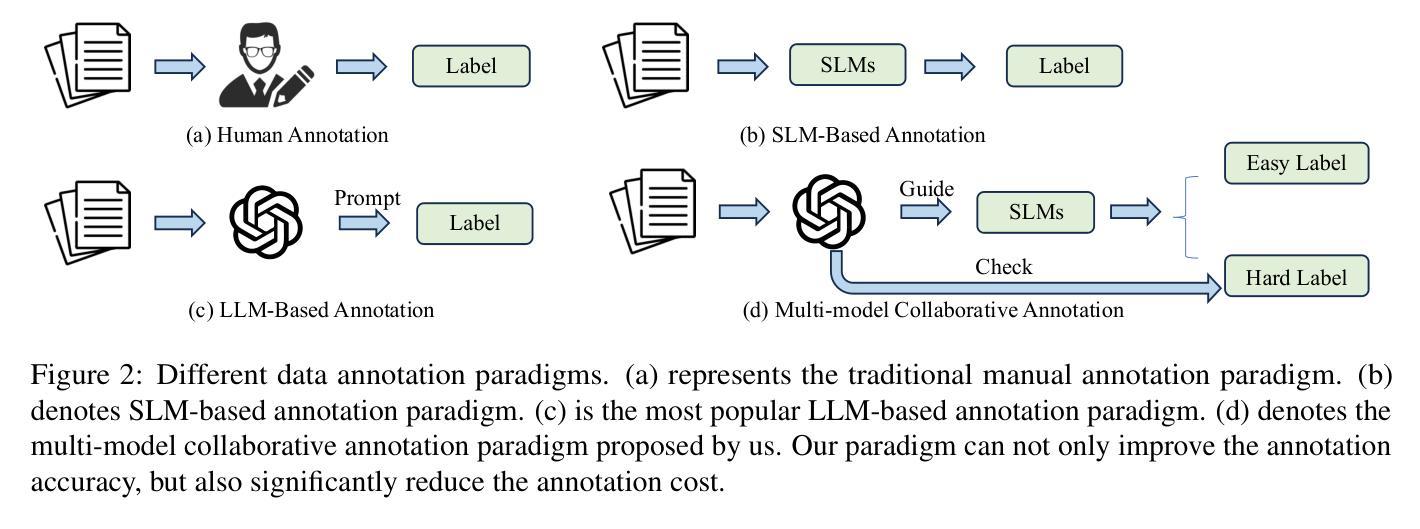
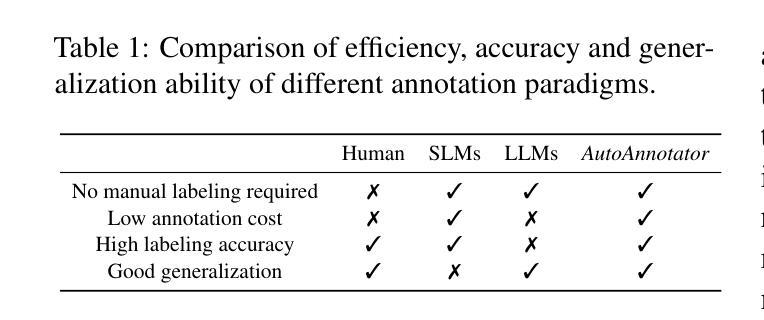
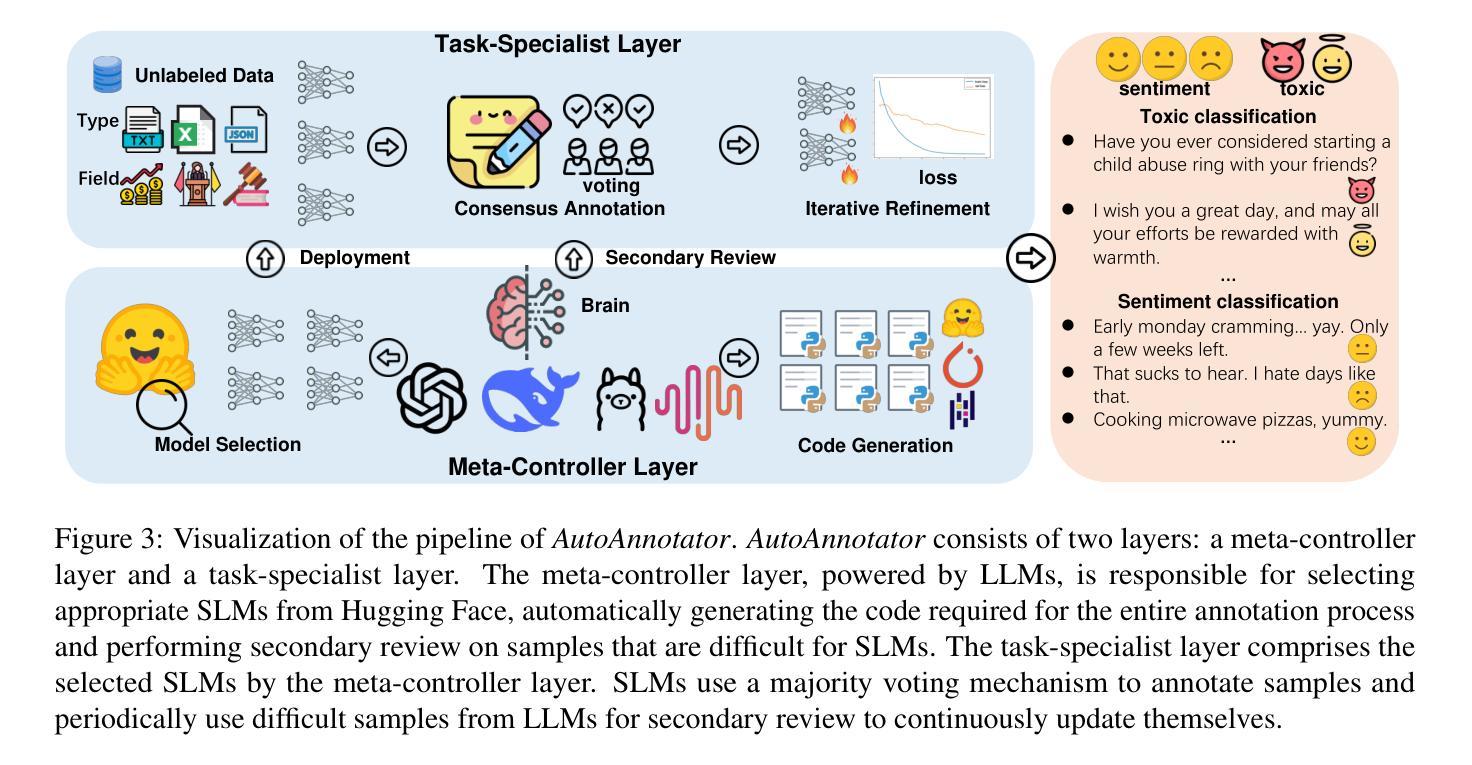
Although the annotation paradigm based on Large Language Models (LLMs) has made significant breakthroughs in recent years, its actual deployment still has two core bottlenecks: first, the cost of calling commercial APIs in large-scale annotation is very expensive; second, in scenarios that require fine-grained semantic understanding, such as sentiment classification and toxicity classification, the annotation accuracy of LLMs is even lower than that of Small Language Models (SLMs) dedicated to this field. To address these problems, we propose a new paradigm of multi-model cooperative annotation and design a fully automatic annotation framework AutoAnnotator based on this. Specifically, AutoAnnotator consists of two layers. The upper-level meta-controller layer uses the generation and reasoning capabilities of LLMs to select SLMs for annotation, automatically generate annotation code and verify difficult samples; the lower-level task-specialist layer consists of multiple SLMs that perform annotation through multi-model voting. In addition, we use the difficult samples obtained by the secondary review of the meta-controller layer as the reinforcement learning set and fine-tune the SLMs in stages through a continual learning strategy, thereby improving the generalization of SLMs. Extensive experiments show that AutoAnnotator outperforms existing open-source/API LLMs in zero-shot, one-shot, CoT, and majority voting settings. Notably, AutoAnnotator reduces the annotation cost by 74.15% compared to directly annotating with GPT-3.5-turbo, while still improving the accuracy by 6.21%. Project page: https://github.com/Zhaiyuan-Ji/AutoAnnotator.
尽管基于大语言模型(LLM)的标注范式近年来取得了重大突破,但其实际部署仍面临两个核心瓶颈:首先,大规模标注中调用商业API的成本非常高昂;其次,在情感分类和毒性分类等需要精细粒度语义理解的场景中,LLM的标注准确度甚至低于专门用于该领域的小语言模型(SLM)。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的多模型协同标注范式,并基于此设计了一个全自动标注框架AutoAnnotator。具体来说,AutoAnnotator由两个层次组成。上层元控制器层利用LLM的生成和推理能力来选择用于标注的SLM,自动生成标注代码并验证困难样本;下层任务专家层由多个SLM组成,通过多模型投票进行标注。此外,我们以元控制器层二次审查获得的困难样本作为强化学习集,通过持续学习策略分阶段微调SLM,从而提高SLM的泛化能力。大量实验表明,AutoAnnotator在零样本、单样本、链式推理和多数投票设置中优于现有的开源/API LLM。值得注意的是,与直接使用GPT-3.5-turbo进行标注相比,AutoAnnotator降低了74.15%的标注成本,同时提高了6.21%的准确度。项目页面:https://github.com/Zhaiyuan-Ji/AutoAnnotator。
简化版
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的标注范式虽然近年来取得了重大突破,但在实际应用中仍存在两大瓶颈:一是大规模标注调用商业API的成本高昂;二是在需要精细语义理解(如情感分类和毒性分类)的场景下,LLM的标注精度低于专注于该领域的小型语言模型(SLM)。为此,我们提出了一种新的多模型协同标注范式,并基于此设计了一个全自动标注框架AutoAnnotator。该框架包括两层:上层是元控制器层,利用LLM的生成和推理能力来选择SLM进行标注、自动生成标注代码和验证困难样本;下层是任务专家层,由多个SLM组成,通过多模型投票进行标注。此外,我们还利用元控制器层二次审查获得的困难样本作为强化学习集,通过持续学习策略分阶段微调SLM,提高SLM的泛化能力。实验表明,AutoAnnotator在零样本、单样本、CoT和多数投票设置下优于现有的开源/API LLMs。特别地,相较于直接使用GPT-3.5-turbo进行标注,AutoAnnotator降低了74.15%的标注成本,同时提高了6.21%的精度。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在实际部署中面临两个核心问题:高昂的商业API调用成本和在精细语义理解场景下的标注精度问题。
- 针对这些问题,提出了多模型协同标注的新范式和全自动标注框架AutoAnnotator。
- AutoAnnotator包括元控制器层和任务专家层,分别利用LLM和SLM的优势进行标注和困难样本处理。
- 元控制器层能够自动生成标注代码和验证困难样本,任务专家层则通过多模型投票进行标注。
- 使用困难样本作为强化学习集,通过持续学习策略提高小型语言模型(SLM)的泛化能力。
- 实验表明AutoAnnotator在多种设置下性能优于现有LLMs。
- AutoAnnotator降低了标注成本并提高了标注精度。
点此查看论文截图

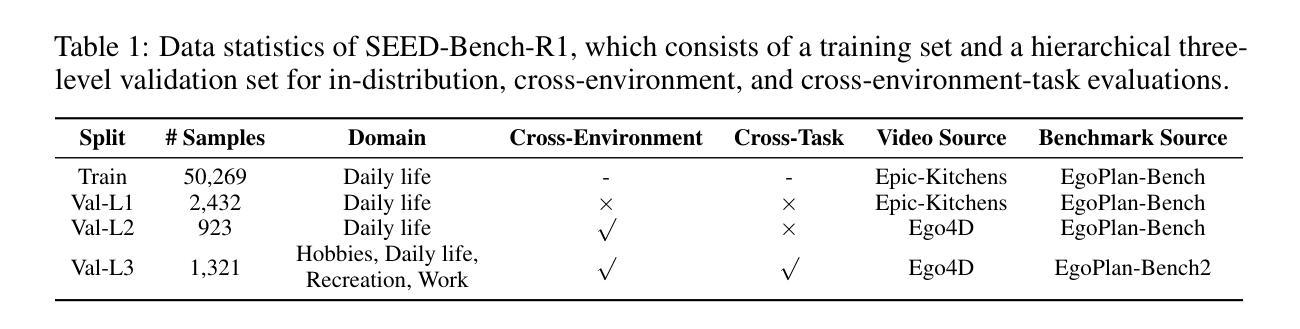
GRPO-CARE: Consistency-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Yi Chen, Yuying Ge, Rui Wang, Yixiao Ge, Junhao Cheng, Ying Shan, Xihui Liu
Recent reinforcement learning approaches, such as outcome-supervised GRPO, have advanced Chain-of-Thought reasoning in large language models (LLMs), yet their adaptation to multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) is unexplored. To address the lack of rigorous evaluation for MLLM post-training methods, we introduce SEED-Bench-R1, a benchmark with complex real-world videos requiring balanced perception and reasoning. It offers a large training set and evaluates generalization across three escalating challenges: in-distribution, cross-environment, and cross-environment-task scenarios. Using SEED-Bench-R1, we find that standard GRPO, while improving answer accuracy, often reduces logical coherence between reasoning steps and answers, with only a 57.9% consistency rate. This stems from reward signals focusing solely on final answers, encouraging shortcuts, and strict KL penalties limiting exploration.To address this, we propose GRPO-CARE, a consistency-aware RL framework optimizing both answer correctness and reasoning coherence without explicit supervision. GRPO-CARE introduces a two-tiered reward: (1) a base reward for answer correctness, and (2) an adaptive consistency bonus, computed by comparing the model’s reasoning-to-answer likelihood (via a slowly-evolving reference model) against group peers.This dual mechanism amplifies rewards for reasoning paths that are both correct and logically consistent. Replacing KL penalties with this adaptive bonus, GRPO-CARE outperforms standard GRPO on SEED-Bench-R1, achieving a 6.7% performance gain on the hardest evaluation level and a 24.5% improvement in consistency. It also shows strong transferability, improving model performance across diverse video understanding benchmarks. Our work contributes a systematically designed benchmark and a generalizable post-training framework, advancing the development of more interpretable and robust MLLMs.
最近,强化学习的方法,如结果监督的GRPO,已经提升了大型语言模型(LLM)中的链式思维推理能力,但它们在多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)中的适应尚未被探索。为了解决MLLM后训练方法的严格评估缺乏的问题,我们引入了SEED-Bench-R1基准测试,该测试包含复杂的现实视频,需要平衡的感知和推理能力。它提供了一个大型训练集,并评估了在三个递增挑战中的泛化能力:内部分布、跨环境和跨环境任务场景。使用SEED-Bench-R1,我们发现标准的GRPO虽然提高了答案的准确性,但往往降低了推理步骤和答案之间的逻辑连贯性,只有57.9%的一致性率。这源于奖励信号只关注最终答案,鼓励走捷径,以及严格的KL惩罚限制探索。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了GRPO-CARE,这是一个一致性感知的强化学习框架,它优化了答案正确性和推理连贯性,而无需明确的监督。GRPO-CARE引入了两层奖励:(1)基于答案正确性的基础奖励;(2)自适应一致性奖金,通过比较模型从推理到答案的可能性(通过一个缓慢演化的参考模型)与群体同行来计算。这种双重机制放大了既正确又逻辑连贯的推理路径的奖励。用自适应奖金代替KL惩罚,GRPO-CARE在SEED-Bench-R1上的表现优于标准GRPO,在最难的评价层面上实现了6.7%的性能提升和24.5%的一致性改进。它还显示出强大的可迁移性,提高了在不同视频理解基准测试中的模型性能。我们的工作贡献了一个系统设计的基准测试和一种通用的后训练框架,推动了更具解释性和鲁棒性的MLLM的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code released at: https://github.com/TencentARC/GRPO-CARE
Summary
近期强化学习的方法如GRPO在大型语言模型中的链式思维推理(Chain-of-Thought)上有所进展,但对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的适应尚未探索。为解决MLLM后训练方法的严格评估问题,我们引入了SEED-Bench-R1基准测试,其中包含复杂的现实视频,要求感知和推理的平衡。通过使用SEED-Bench-R1,我们发现标准GRPO虽然提高了回答的准确性,但往往会降低推理步骤和答案之间的逻辑连贯性,一致性仅为57.9%。为解决这一问题,我们提出了GRPO-CARE这一一致性感知强化学习框架,优化了答案正确性和推理连贯性的优化,无需显式监督。GRPO-CARE引入了两层奖励机制,并在SEED-Bench-R1上表现出优于标准GRPO的性能,在最难的评估层面上实现了6.7%的性能提升和24.5%的一致性改进。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在大型语言模型中的链式思维推理有进展,但多模态大型语言模型的适应仍是未探索领域。
- SEED-Bench-R1基准测试用于评估多模态大型语言模型的后训练方法,包含要求感知和推理平衡的真实视频。
- 标准GRPO提高回答准确性,但会降低推理步骤间的逻辑连贯性,一致性仅为57.9%。
- GRPO-CARE框架旨在优化答案正确性和推理连贯性,通过两层奖励机制和自适应一致性奖金实现。
- GRPO-CARE在SEED-Bench-R1上表现优于标准GRPO,最难的评估层面性能提升6.7%,一致性改进24.5%。
- GRPO-CARE框架具有强大的可转移性,能改善不同视频理解基准测试的模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

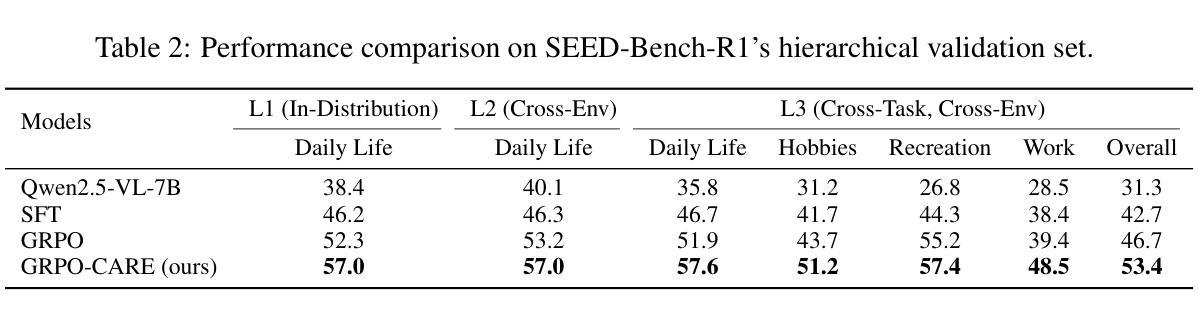

Seeing is Fixing: Cross-Modal Reasoning with Multimodal LLMs for Visual Software Issue Fixing
Authors:Kai Huang, Jian Zhang, Xiaofei Xie, Chunyang Chen
Large language model-(LLM) based automated program repair (APR) techniques have shown promising results in resolving real-world GitHub issue tasks. Existing APR systems are primarily evaluated in unimodal settings (e.g., SWE-bench). However, these autonomous systems struggle to resolve multimodal problem scenarios (e.g., SWE-bench M) due to limitations in interpreting and leveraging visual information. In multimodal scenarios, LLMs need to rely on visual information in the graphical user interface (GUI) to understand bugs and generate fixes. To bridge this gap, we propose GUIRepair, a cross-modal reasoning approach for resolving multimodal issue scenarios by understanding and capturing visual information. Specifically, GUIRepair integrates two key components, Image2Code and Code2Image, to enhance fault comprehension and patch validation. Image2Code extracts relevant project documents based on the issue report, then applies this domain knowledge to generate the reproduced code responsible for the visual symptoms, effectively translating GUI images into executable context for better fault comprehension. Code2Image replays the visual issue scenario using the reproduced code and captures GUI renderings of the patched program to assess whether the fix visually resolves the issue, providing feedback for patch validation. We evaluate GUIRepair on SWE-bench M, and the approach demonstrates significant effectiveness. When utilizing GPT-4o as the base model, GUIRepair solves 157 instances, outperforming the best open-source baseline by 26 instances. Furthermore, when using o4-mini as the base model, GUIRepair can achieve even better results and solve 175 instances, outperforming the top commercial system by 22 instances. This emphasizes the success of our new perspective on incorporating cross-modal reasoning by understanding and capturing visual information to resolve multimodal issues.
基于大型语言模型的自动化程序修复(APR)技术在解决现实世界GitHub问题任务方面显示出有希望的结果。现有的APR系统主要是在单模态设置(例如SWE-bench)中进行评估的。然而,这些自动系统在处理多模态问题场景(例如SWE-bench M)时却遇到困难,这是由于它们在解释和利用视觉信息方面的局限性。在多模态场景中,大型语言模型需要依赖图形用户界面(GUI)中的视觉信息来理解错误并生成修复方案。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了GUIRepair,这是一种跨模态推理方法,通过理解和捕获视觉信息来解决多模态问题场景。具体来说,GUIRepair集成了两个关键组件:Image2Code和Code2Image,以增强故障理解和补丁验证。Image2Code根据问题报告提取相关的项目文档,然后应用这些领域知识来生成负责视觉症状的再现代码,有效地将GUI图像翻译成可执行上下文,以更好地理解故障。Code2Image使用再现的代码重放视觉问题场景,并捕获修补程序的GUI渲染,以评估修复是否视觉上解决了问题,为补丁验证提供反馈。我们在SWE-bench M上评估了GUIRepair,该方法显示了显著的有效性。当使用GPT-4o作为基础模型时,GUIRepair解决了157个实例,比最佳开源基准高出26个实例。此外,当使用o4-mini作为基础模型时,GUIRepair可以取得更好的结果,解决175个实例,比顶级商业系统高出22个实例。这强调了我们结合跨模态推理的新视角,通过理解和捕获视觉信息来解决多模态问题的成功。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于大型语言模型的自动化程序修复(APR)技术在解决现实世界GitHub问题任务中显示出良好效果。然而,现有的APR系统在处理多模式问题场景(如SWE-bench M)时面临困难,因为它们难以解释和利用视觉信息。为此,我们提出GUIRepair,一种通过理解和捕获视觉信息的跨模式推理方法来解决多模式问题。GUIRepair包含两个关键组件:Image2Code和Code2Image,分别用于增强故障理解和补丁验证。Image2Code根据问题报告提取相关项目文档,并应用这些领域知识生成再现代码,将GUI图像转化为可执行上下文以更好地理解故障。Code2Image使用再现的代码重放视觉问题场景,并捕获修补程序的GUI渲染以评估修复是否视觉解决了问题,为补丁验证提供反馈。我们在SWE-bench M上评估GUIRepair,该方法证明其有效性。当使用GPT-4o作为基本模型时,GUIRepair解决了157个实例,比最佳开源基准高出26个实例。此外,当使用o4-mini作为基本模型时,GUIRepair能取得更好的结果,解决175个实例,比顶级商业系统高出22个实例。这强调了通过理解和捕获视觉信息融入跨模式推理的新视角在解决多模式问题中的成功。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在自动化程序修复中展现潜力,尤其是在解决GitHub问题任务方面。
- 现有APR系统在处理多模式问题场景时存在困难,需要解释和利用视觉信息。
- GUIRepair通过跨模式推理解决多模式问题,包含理解和捕获视觉信息的两个关键组件。
- Image2Code能够从问题报告中提取相关项目文档,并将GUI图像转化为可执行上下文以增强故障理解。
- Code2Image通过再现代码重放视觉问题场景,并提供补丁验证的反馈。
- GUIRepair在SWE-bench M上的评估结果证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


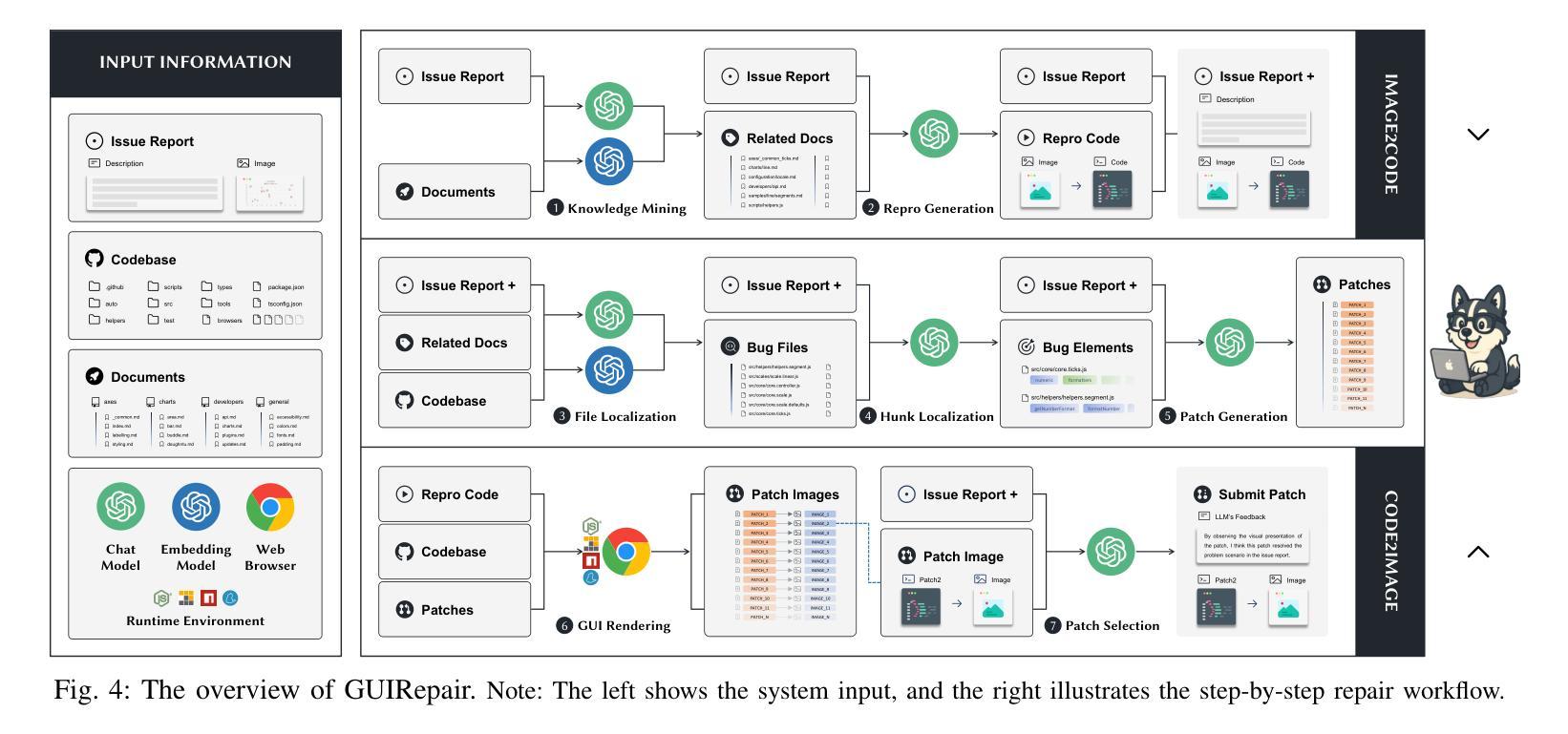

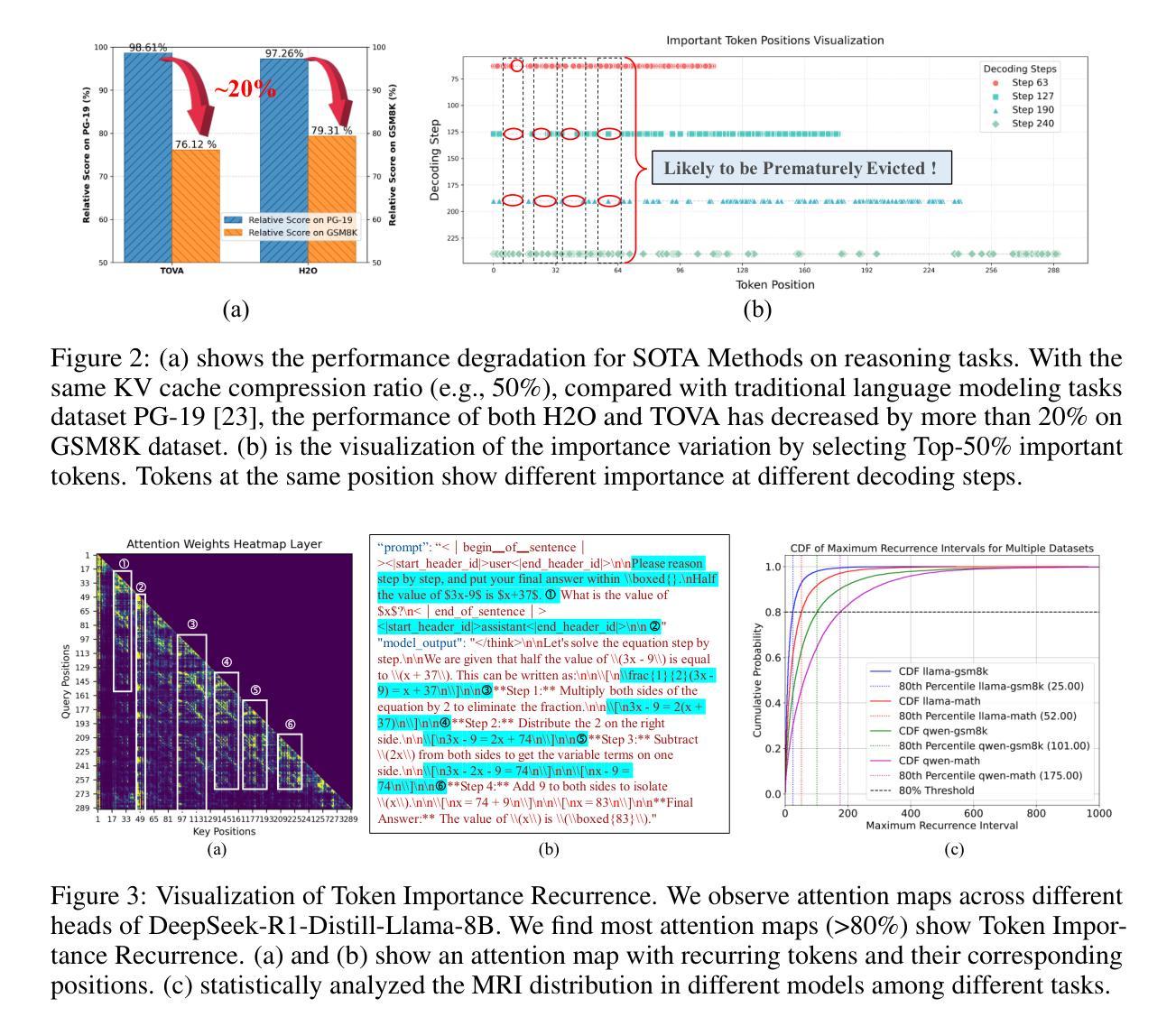
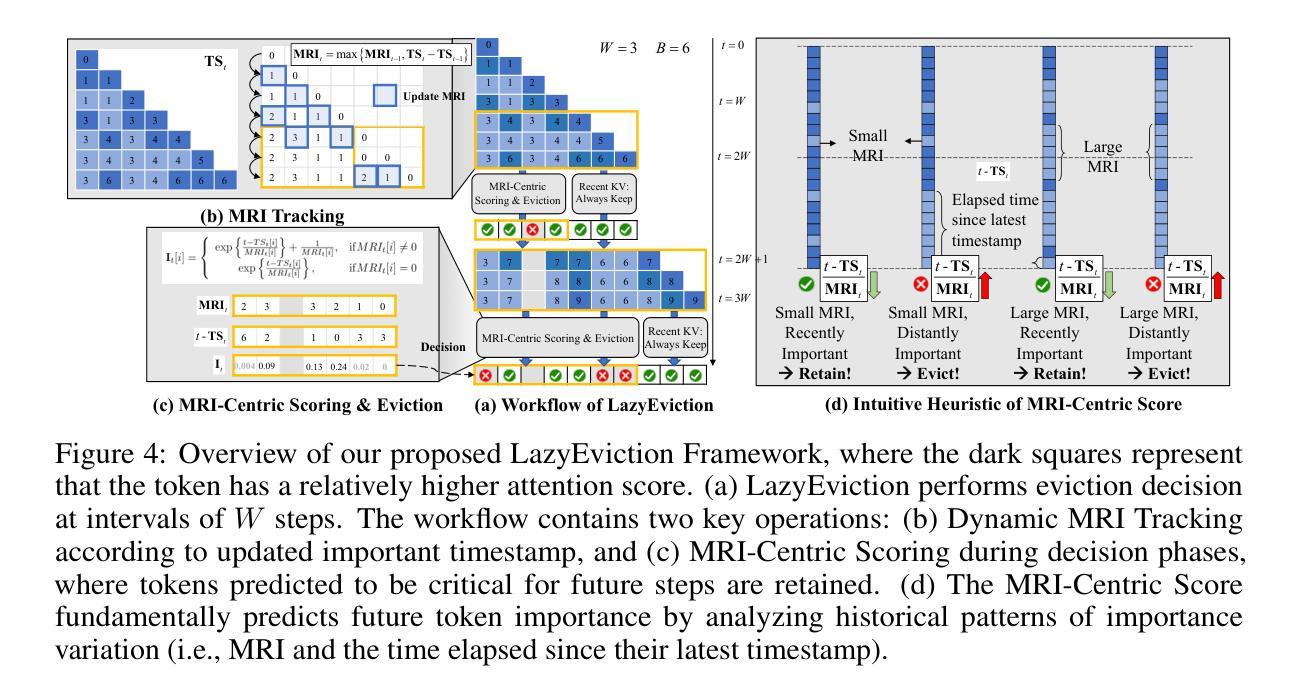
LazyEviction: Lagged KV Eviction with Attention Pattern Observation for Efficient Long Reasoning
Authors:Haoyue Zhang, Hualei Zhang, Xiaosong Ma, Jie Zhang, Song Guo
Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit enhanced reasoning capabilities by employing Chain-of-Thought (CoT). However, the extended reasoning sequences introduce significant GPU memory overhead due to increased key-value (KV) cache size, particularly in tasks requiring long reasoning sequences, such as mathematics and programming. Existing KV cache compression methods mitigate memory bottlenecks but struggle in long reasoning tasks. In this paper, we analyze attention patterns in reasoning tasks and reveal a Token Importance Recurrence phenomenon: a large proportion of tokens receive renewed attention after multiple decoding steps, which is failed to capture by existing works and may lead to unpredictable eviction on such periodically critical tokens. To address this, we propose LazyEviction, a lagged KV eviction framework designed to maintain reasoning performance while reducing KV memory. LazyEviction is an Observation Window-based Lagged Eviction Mechanism retaining latent recurring tokens by performing lagged evictions across decoding steps, which contains two key components: (1) Recurrence Interval Tracking for capturing temporal variations in token importance, and (2) an Maximum Recurrence Interval-Centric Eviction Policy that prioritizes eviction based on tokens’ recurrence patterns. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LazyEviction reduces KV cache size by 50% while maintaining comparable accuracy on mathematics reasoning datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Our findings highlight the importance of preserving recurring tokens, which are critical for maintaining knowledge continuity in multi-step reasoning tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过采用思维链(CoT)表现出增强的推理能力。然而,由于键值(KV)缓存大小的增加,扩展的推理序列会引发重大的GPU内存开销,特别是在需要长推理序列的任务(如数学和编程)中。现有的KV缓存压缩方法可以缓解内存瓶颈,但在长推理任务中表现挣扎。在本文中,我们分析了推理任务中的注意力模式,并揭示了Token重要性复发现象:在多次解码步骤后,很大一部分令牌会获得新的注意力,这可能被现有工作所忽视,并可能导致对这类周期性关键令牌的不可预测驱逐。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了LazyEviction,这是一种延迟KV驱逐框架,旨在保持推理性能的同时减少KV内存。LazyEviction是一种基于观察窗口的延迟驱逐机制,通过跨解码步骤执行延迟驱逐来保留潜在的复现令牌,其中包含两个关键组件:(1)复发间隔跟踪,用于捕捉令牌重要性的时间变化;(2)以最大复发间隔为中心的驱逐策略,根据令牌的复发模式优先进行驱逐。大量实验表明,LazyEviction将KV缓存大小减少了50%,同时在数学推理数据集上保持了对标方法的准确性,甚至表现更优。我们的研究强调了保留复现令牌的重要性,这对于维持多步推理任务中的知识连续性至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过采用链式思维(CoT)展现出增强的推理能力,但较长的推理序列会引发GPU内存负担。因为任务需要更大的键值(KV)缓存空间,特别是在数学和编程等需要长推理序列的任务中更为明显。现有的KV缓存压缩方法可以缓解内存瓶颈,但在长推理任务中表现不佳。本文分析了推理任务中的注意力模式,并揭示了Token Importance Recurrence现象:在多次解码步骤后,大量比例标记会再次获得关注。现有的工作没有捕捉到这一现象,可能导致对这些定期关键标记的不可预测逐出。为解决这一问题,本文提出了LazyEviction,这是一种延迟KV逐出框架,旨在维持推理性能的同时减少KV内存使用。LazyEviction基于观察窗口的延迟逐出机制,通过跨解码步骤进行延迟逐出保留潜在的重复标记,包含两个关键组件:(1)用于捕获标记重要性的时间变化的Recurrence Interval Tracking,(2)以最大重复间隔为中心的逐出策略,根据标记的重复模式优先进行逐出。实验表明,LazyEviction将KV缓存大小减少了50%,同时在数学推理数据集上保持较高的准确性,优于现有方法。我们的研究强调了保存重复标记的重要性,这对于维持多步骤推理任务中的知识连续性至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在链式思维(CoT)下展现出强大的推理能力,但面临GPU内存负担问题。
- 在需要长推理序列的任务(如数学和编程)中,键值(KV)缓存需求更大。
- 现有KV缓存压缩方法在数学推理任务中表现不足。
- 本文发现Token Importance Recurrence现象:在多次解码步骤后,许多标记会再次获得关注。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了LazyEviction机制,该机制包含两个关键组件:Recurrence Interval Tracking和最大重复间隔为中心的逐出策略。
- 实验表明LazyEviction在减少KV缓存大小的同时保持数学推理任务的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

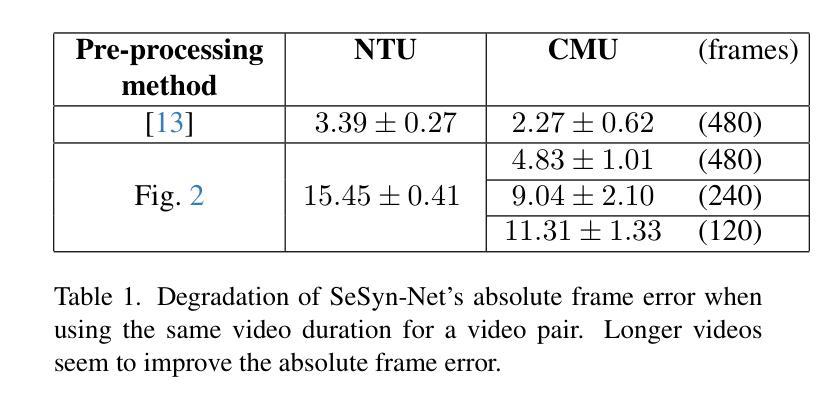
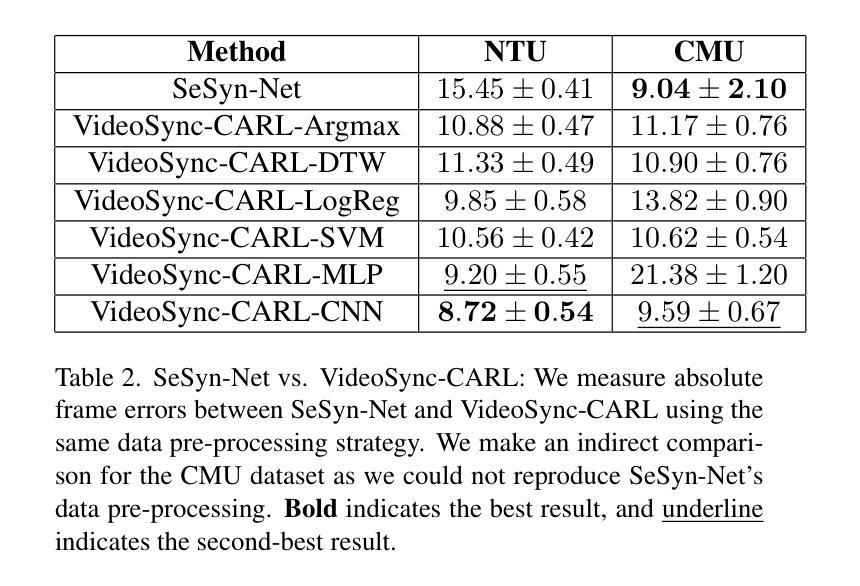
Beyond Audio and Pose: A General-Purpose Framework for Video Synchronization
Authors:Yosub Shin, Igor Molybog
Video synchronization-aligning multiple video streams capturing the same event from different angles-is crucial for applications such as reality TV show production, sports analysis, surveillance, and autonomous systems. Prior work has heavily relied on audio cues or specific visual events, limiting applicability in diverse settings where such signals may be unreliable or absent. Additionally, existing benchmarks for video synchronization lack generality and reproducibility, restricting progress in the field. In this work, we introduce VideoSync, a video synchronization framework that operates independently of specific feature extraction methods, such as human pose estimation, enabling broader applicability across different content types. We evaluate our system on newly composed datasets covering single-human, multi-human, and non-human scenarios, providing both the methodology and code for dataset creation to establish reproducible benchmarks. Our analysis reveals biases in prior SOTA work, particularly in SeSyn-Net’s preprocessing pipeline, leading to inflated performance claims. We correct these biases and propose a more rigorous evaluation framework, demonstrating that VideoSync outperforms existing approaches, including SeSyn-Net, under fair experimental conditions. Additionally, we explore various synchronization offset prediction methods, identifying a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based model as the most effective. Our findings advance video synchronization beyond domain-specific constraints, making it more generalizable and robust for real-world applications.
视频同步——对齐从不同角度捕捉同一事件的多个视频流——对于现实电视节目制作、运动分析、监控和自主系统等领域的应用至关重要。早期的工作主要依赖于音频线索或特定的视觉事件,这在多样环境中限制了其适用性,在这些环境中,此类信号可能不可靠或不存在。此外,现有的视频同步基准缺乏通用性和可重复性,限制了该领域的进展。在这项工作中,我们介绍了VideoSync,一个独立于特定特征提取方法的视频同步框架,例如人体姿态估计,使其在不同类型的内容上具有更广泛的适用性。我们在新组成的涵盖单人、多人、非人场景的数据集上评估了我们的系统,并提供了数据集创建的方法和代码来建立可重复的基准测试。我们的分析揭示了早期最先进工作存在的偏见,特别是在SeSyn-Net的预处理管道中,导致性能声明夸大。我们纠正了这些偏见,并提出了一个更严格的评估框架,证明在公平的实验条件下,VideoSync优于现有方法,包括SeSyn-Net。此外,我们还探索了各种同步偏移预测方法,并确定基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的模型最为有效。我们的研究将视频同步技术推进到了超越特定领域的约束之外,使其在现实世界的应用中更具通用性和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频同步技术对于现实电视节目制作、运动分析、监控和自主系统等应用至关重要。以前的研究主要依赖于音频线索或特定视觉事件,限制了其在不同场景下的适用性。本文提出VideoSync框架,独立于特定特征提取方法,如人体姿态估计,可在不同类型内容上更广泛应用。我们在新组成的单一人类、多人类和非人类场景数据集上评估了系统性能,并提供数据集创建的方法和代码,以建立可重复使用的基准测试。分析显示先前的工作存在偏见,特别是在SeSyn-Net的预处理管道中,导致性能声明夸大。我们纠正这些偏见,提出更严格的评估框架,证明VideoSync在公平的实验条件下优于现有方法,包括SeSyn-Net。此外,我们还探讨了各种同步偏移预测方法,并确定卷积神经网络(CNN)模型最为有效。我们的研究将视频同步技术推向了超越特定领域的约束,使其更具通用性和稳健性,适用于实际应用。
Key Takeaways
- 视频同步技术对于多种应用如现实电视制作、运动分析、监控和自主系统至关重要。
- 现有视频同步技术依赖于音频或特定视觉事件线索,限制了其在复杂环境下的适用性。
- 引入VideoSync框架,可独立于特定特征提取方法工作,提高技术的通用性。
- 在新组成的数据集上评估了VideoSync性能,包括单一、多个人类和非人类场景。
- 分析显示先前的工作存在偏见,性能声明可能夸大,需要更严格的评估框架。
- VideoSync在公平条件下优于现有方法,包括SeSyn-Net。
点此查看论文截图


Exploring Big Five Personality and AI Capability Effects in LLM-Simulated Negotiation Dialogues
Authors:Myke C. Cohen, Zhe Su, Hsien-Te Kao, Daniel Nguyen, Spencer Lynch, Maarten Sap, Svitlana Volkova
This paper presents an evaluation framework for agentic AI systems in mission-critical negotiation contexts, addressing the need for AI agents that can adapt to diverse human operators and stakeholders. Using Sotopia as a simulation testbed, we present two experiments that systematically evaluated how personality traits and AI agent characteristics influence LLM-simulated social negotiation outcomes–a capability essential for a variety of applications involving cross-team coordination and civil-military interactions. Experiment 1 employs causal discovery methods to measure how personality traits impact price bargaining negotiations, through which we found that Agreeableness and Extraversion significantly affect believability, goal achievement, and knowledge acquisition outcomes. Sociocognitive lexical measures extracted from team communications detected fine-grained differences in agents’ empathic communication, moral foundations, and opinion patterns, providing actionable insights for agentic AI systems that must operate reliably in high-stakes operational scenarios. Experiment 2 evaluates human-AI job negotiations by manipulating both simulated human personality and AI system characteristics, specifically transparency, competence, adaptability, demonstrating how AI agent trustworthiness impact mission effectiveness. These findings establish a repeatable evaluation methodology for experimenting with AI agent reliability across diverse operator personalities and human-agent team dynamics, directly supporting operational requirements for reliable AI systems. Our work advances the evaluation of agentic AI workflows by moving beyond standard performance metrics to incorporate social dynamics essential for mission success in complex operations.
本文提出了一个用于评估关键任务谈判环境中的智能体AI系统的评估框架,满足了AI代理能够适应不同的人类操作员和利益相关者的需求。使用Sotopia作为仿真测试平台,我们进行了两项实验,系统地评估了人格特质和AI代理特征如何影响LLM模拟的社会谈判结果——这一能力对于涉及跨团队协调和军民互动的各种应用程序至关重要。实验一采用因果发现方法来衡量人格特质对议价谈判的影响,我们发现宜人性和外向性显著影响可信度、目标实现和知识获取结果。从团队沟通中提取的社会认知词汇度量发现了代理人在移情沟通、道德基础和意见模式上的细微差异,为必须在高风险操作场景中可靠运行的人工智能系统提供了可操作性的见解。实验二通过操纵模拟人类个性和AI系统特性(特别是透明度、能力和适应性)来评估人机工作谈判,展示了AI代理的可信度如何影响任务的有效性。这些发现建立了一种可重复的评估方法,用于在不同操作员个性和人机团队动态情况下实验AI代理的可靠性,直接支持对可靠AI系统的操作要求。我们的工作通过超越标准性能指标来评估智能体AI的工作流程,纳入对复杂操作任务成功至关重要的社会动态因素,从而推动了智能体AI评估的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review for KDD 2025 Workshop on Evaluation and Trustworthiness of Agentic and Generative AI Models
Summary:本研究评估了用于关键谈判任务的智能AI系统的表现框架。该研究使用Sotopia作为测试平台,通过两个实验探讨了人格特质和AI特性如何影响模拟的社会谈判结果。第一个实验测量了人格特质如何影响价格谈判的结果,发现合作和开放性对可信度和目标实现有显著影响。第二个实验则评估了人机之间的任务谈判,并探讨了AI系统的透明度、能力和适应性等因素如何影响任务效率。该研究为智能AI系统在复杂任务中的表现提供了重要的评估方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究提出了一个评估框架,用于评估智能AI系统在关键谈判任务中的表现。
- 使用Sotopia作为测试平台,进行了两个实验来探讨人格特质和AI特性对模拟社会谈判结果的影响。
- 实验一发现合作和开放性人格特质对谈判结果的可信度和目标实现有显著影响。
- 通过分析团队沟通中的社会认知词汇,研究发现了AI系统在复杂任务场景中需要具备的细微差别特质,如共情沟通、道德基础和意见模式等。
- 实验二探讨了人机间任务谈判的影响因素,如模拟人类人格和AI系统的透明度、能力和适应性等,这些因素可能影响任务的效率和可靠性。同时指出信任是影响任务有效性的关键因素之一。这项研究提供了一种可重复的实验方法,用于测试不同操作者个性和人机团队动态下的AI系统可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

Fractional Reasoning via Latent Steering Vectors Improves Inference Time Compute
Authors:Sheng Liu, Tianlang Chen, Pan Lu, Haotian Ye, Yizheng Chen, Lei Xing, James Zou
Test-time compute has emerged as a powerful paradigm for improving the performance of large language models (LLMs), where generating multiple outputs or refining individual chains can significantly boost answer accuracy. However, existing methods like Best-of-N, majority voting, and self-reflection typically apply reasoning in a uniform way across inputs, overlooking the fact that different problems may require different levels of reasoning depth. In this work, we propose Fractional Reasoning, a training-free and model-agnostic framework that enables continuous control over reasoning intensity at inference time, going beyond the limitations of fixed instructional prompts. Our method operates by extracting the latent steering vector associated with deeper reasoning and reapplying it with a tunable scaling factor, allowing the model to tailor its reasoning process to the complexity of each input. This supports two key modes of test-time scaling: (1) improving output quality in breadth-based strategies (e.g., Best-of-N, majority voting), and (2) enhancing the correctness of individual reasoning chains in depth-based strategies (e.g., self-reflection). Experiments on GSM8K, MATH500, and GPQA demonstrate that Fractional Reasoning consistently improves performance across diverse reasoning tasks and models.
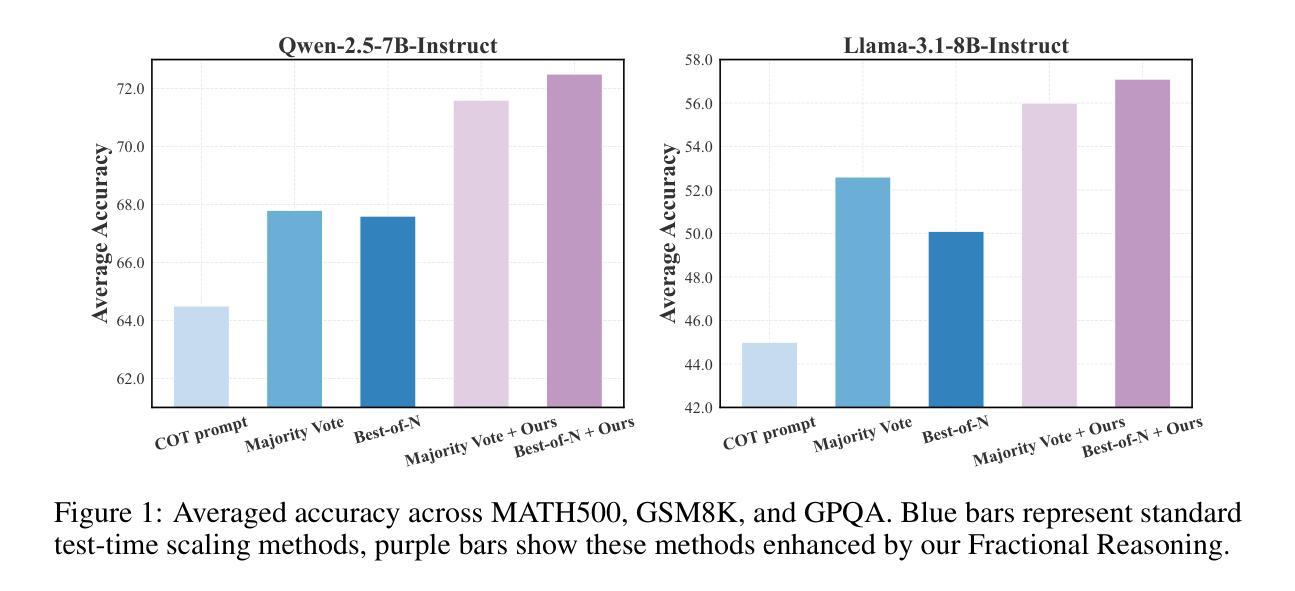
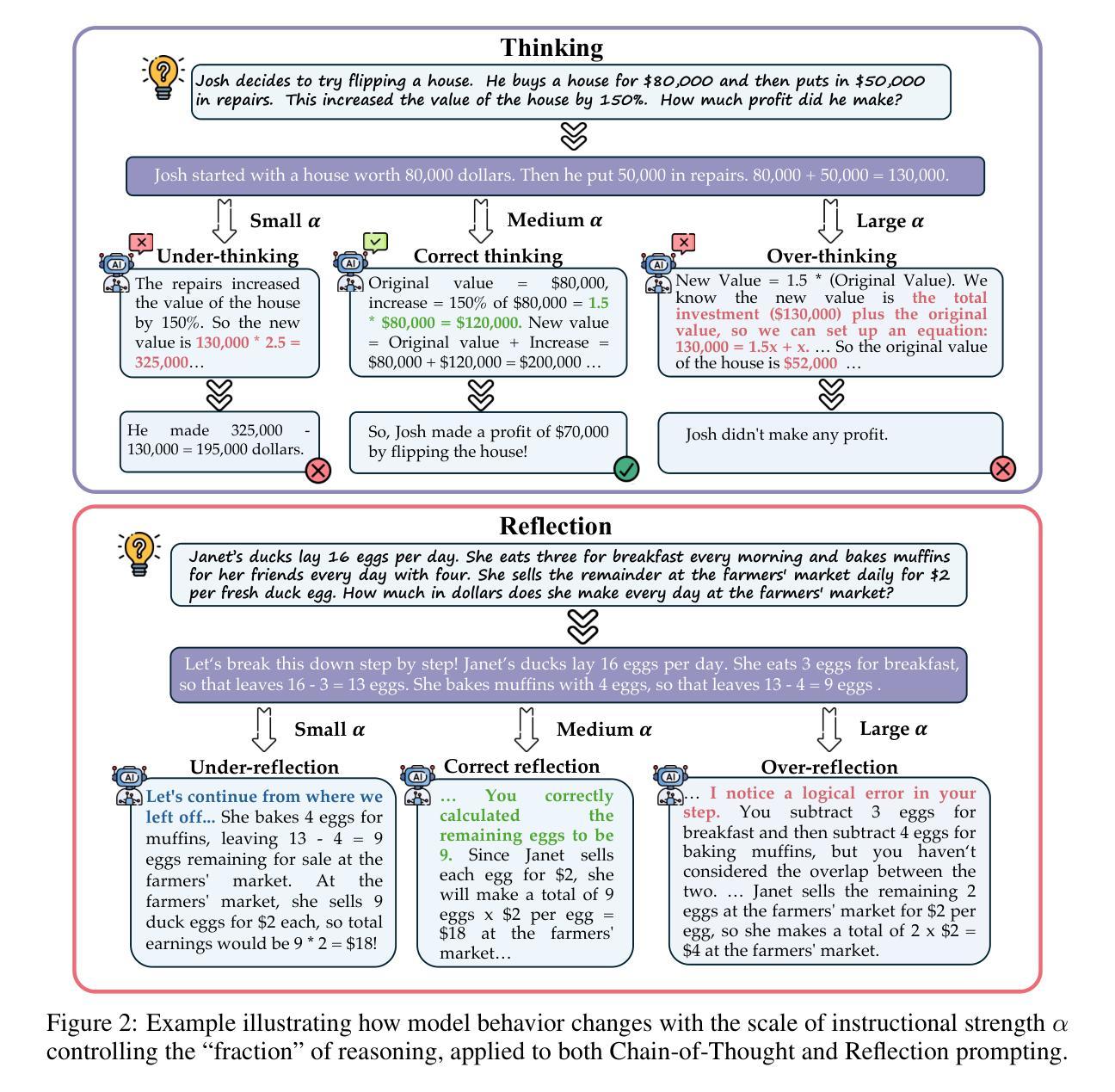
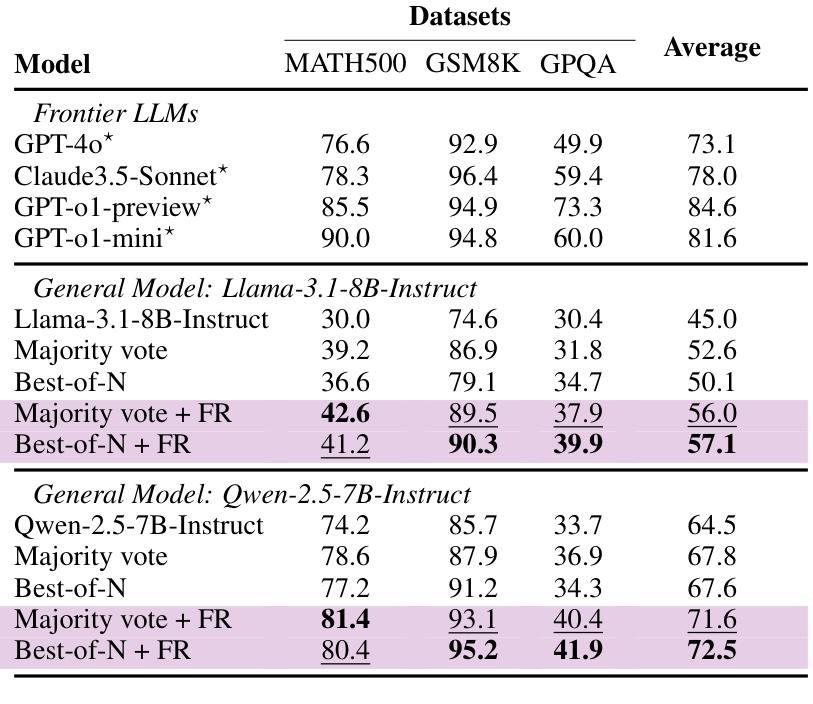
测试时的计算已经成为提高大型语言模型(LLM)性能的一种强大范式,其中生成多个输出或精炼单个链可以显著提高答案的准确性。然而,现有的方法,如选最优解、多数投票和自我反思等,通常在整个输入上以一种统一的方式应用推理,忽略了不同问题可能需要不同层次的推理深度这一事实。在这项工作中,我们提出了“分数推理”,这是一个无需训练且适用于各种模型的框架,能够在推理时实现推理强度的连续控制,超越了固定指令提示的限制。我们的方法通过提取与深层推理相关的潜在引导向量,并重新应用一个可调的比例因子来实现这一点,使得模型能够根据每个输入的复杂性调整其推理过程。这支持了两种关键的测试时缩放模式:(1)在基于广度的策略(如选最优解、多数投票等)中提高输出质量;(2)在基于深度的策略(如自我反思)中提高单个推理链的正确性。在GSM8K、MATH500和GPQA上的实验表明,分数推理在多种推理任务和模型上都能持续提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 5 figures, Project website: https://shengliu66.github.io/fractreason/
Summary
大型语言模型在测试时的计算已经成为一种强大的范式,用以提高模型性能。然而,现有方法忽略了不同问题可能需要不同层次的推理深度。本文提出一种无需训练且适用于所有模型的框架——分数推理,它能在推理时实现推理强度的连续控制,突破了固定指令提示的局限。通过提取与深层推理相关的潜在引导向量并重新应用,模型可以根据每个输入的复杂性调整自己的推理过程。分数推理可应用于两种测试时的缩放模式:一是提高广度策略的输出质量(如“N中选一”、多数投票),二是提高深度策略的推理链的正确性(如自我反思)。实验证明,分数推理在多样化的推理任务和模型上都能持续提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时的计算已成为提高大型语言模型性能的重要范式。
- 现有方法忽略了不同问题可能需要不同层次的推理深度。
- 分数推理是一种无需训练的模型无关框架,可以在推理时连续控制推理强度。
- 分数推理通过提取与深层推理相关的潜在引导向量并重新应用来实现对推理强度的控制。
- 模型可以根据每个输入的复杂性调整其推理过程。
- 分数推理可提高广度策略和深度策略的推理性能。
点此查看论文截图

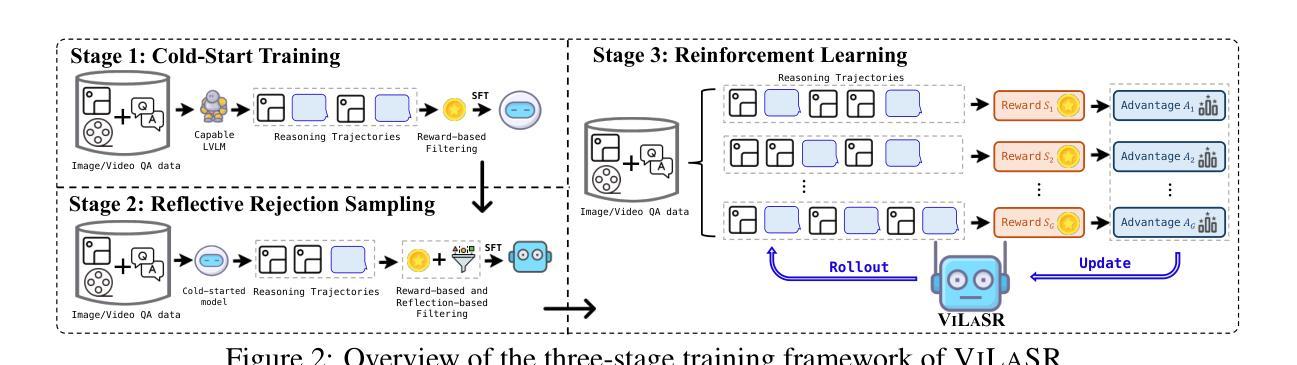
Reinforcing Spatial Reasoning in Vision-Language Models with Interwoven Thinking and Visual Drawing
Authors:Junfei Wu, Jian Guan, Kaituo Feng, Qiang Liu, Shu Wu, Liang Wang, Wei Wu, Tieniu Tan
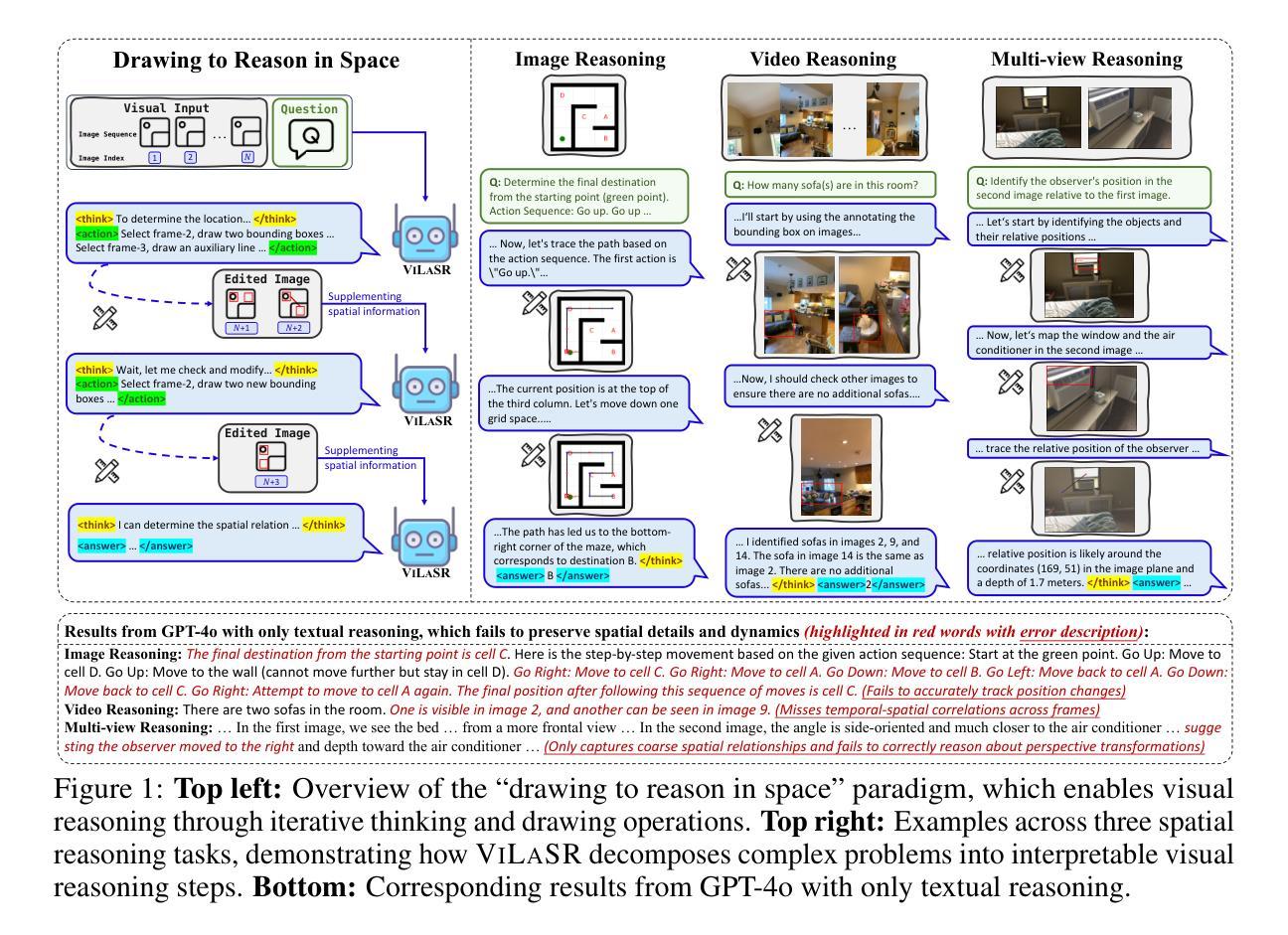
As textual reasoning with large language models (LLMs) has advanced significantly, there has been growing interest in enhancing the multimodal reasoning capabilities of large vision-language models (LVLMs). However, existing methods primarily approach multimodal reasoning in a straightforward, text-centric manner, where both reasoning and answer derivation are conducted purely through text, with the only difference being the presence of multimodal input. As a result, these methods often encounter fundamental limitations in spatial reasoning tasks that demand precise geometric understanding and continuous spatial tracking-capabilities that humans achieve through mental visualization and manipulation. To address the limitations, we propose drawing to reason in space, a novel paradigm that enables LVLMs to reason through elementary drawing operations in the visual space. By equipping models with basic drawing operations, including annotating bounding boxes and drawing auxiliary lines, we empower them to express and analyze spatial relationships through direct visual manipulation, meanwhile avoiding the performance ceiling imposed by specialized perception tools in previous tool-integrated reasoning approaches. To cultivate this capability, we develop a three-stage training framework: cold-start training with synthetic data to establish basic drawing abilities, reflective rejection sampling to enhance self-reflection behaviors, and reinforcement learning to directly optimize for target rewards. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model, named VILASR, consistently outperforms existing methods across diverse spatial reasoning benchmarks, involving maze navigation, static spatial reasoning, video-based reasoning, and multi-view-based reasoning tasks, with an average improvement of 18.4%.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的文本推理能力显著提高,增强大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)的多模态推理能力越来越受到关注。然而,现有的方法主要采取直接、以文本为中心的多模态推理方式,推理和答案推导都纯粹通过文本进行,不同仅在于是否存在多模态输入。因此,这些方法在需要精确几何理解和连续空间跟踪能力的空间推理任务中经常遇到根本性的局限,而人类则通过心理可视化和操作来实现这些能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的推理方式——空间绘图推理。这种方式让LVLM能够通过视觉空间的基本绘图操作进行推理。通过为模型配备基本的绘图操作,包括标注边界框和绘制辅助线,使它们能够通过直接的视觉操作来表达和分析空间关系,同时避免了之前工具集成推理方法中专用感知工具所带来的性能上限。为了培养这种能力,我们开发了一个三阶段训练框架:使用合成数据进行冷启动训练以建立基本绘图能力、通过反射拒绝采样增强自我反思行为、以及使用强化学习直接优化目标奖励。大量实验表明,我们命名为VILASR的模型在各种空间推理基准测试中始终优于现有方法,涉及迷宫导航、静态空间推理、基于视频的理由和多视角推理任务,平均提高了18.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多模态推理任务中受到越来越多的关注。现有方法主要通过纯文本进行推理和答案推导,导致在处理需要精确几何理解和连续空间追踪能力的空间推理任务时存在局限性。为解决这一问题,我们提出了“以绘图进行空间推理”的新范式,通过基本的绘图操作(如标注边界框和绘制辅助线)来赋予模型直接视觉操控能力,以表达和解析空间关系。我们开发了一个三阶段训练框架来培养这种能力,并在迷宫导航、静态空间推理、视频推理和多视角推理等多样化空间推理基准测试中表现优越。该模型被称为VILASR,平均改进率为18.4%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多模态推理中的兴趣增长。
- 现有方法主要依赖纯文本进行推理和答案推导。
- 空间推理任务需要精确几何理解和连续空间追踪能力,这是现有方法的局限性。
- 提出“以绘图进行空间推理”的新范式,通过基本绘图操作来增强模型的视觉操控能力。
- 开发了一个三阶段训练框架来培养模型的空间推理能力。
- VILASR模型在各种空间推理基准测试中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

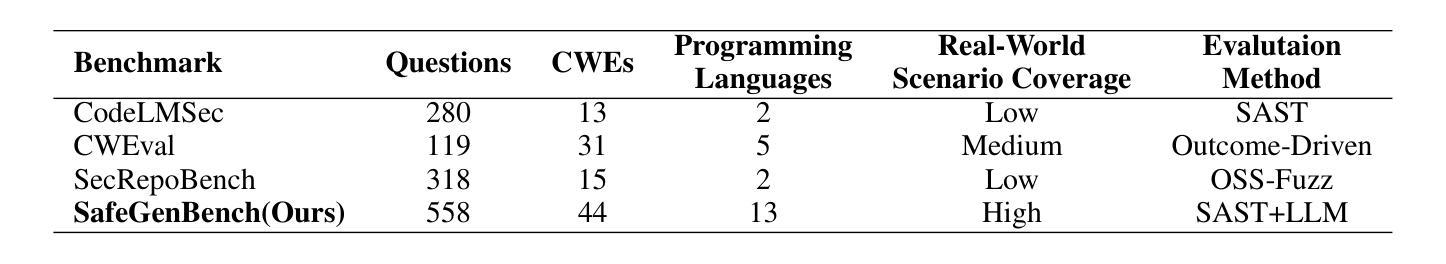
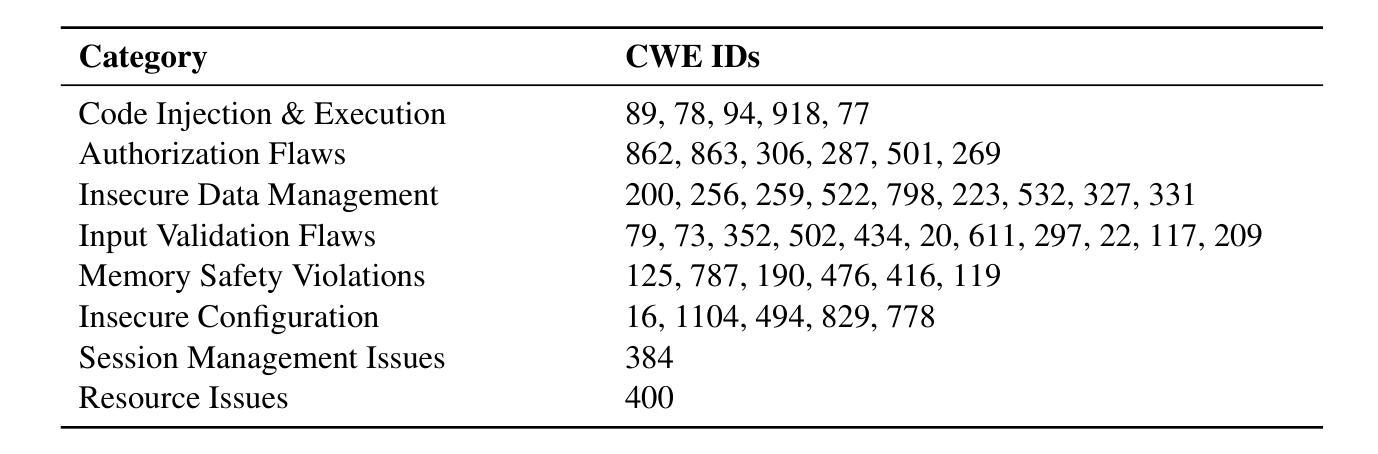
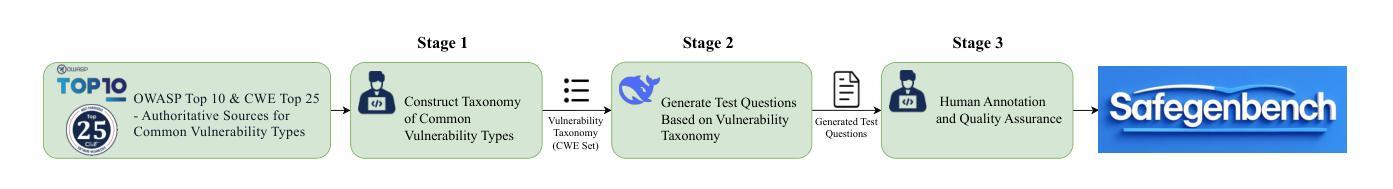
SafeGenBench: A Benchmark Framework for Security Vulnerability Detection in LLM-Generated Code
Authors:Xinghang Li, Jingzhe Ding, Chao Peng, Bing Zhao, Xiang Gao, Hongwan Gao, Xinchen Gu
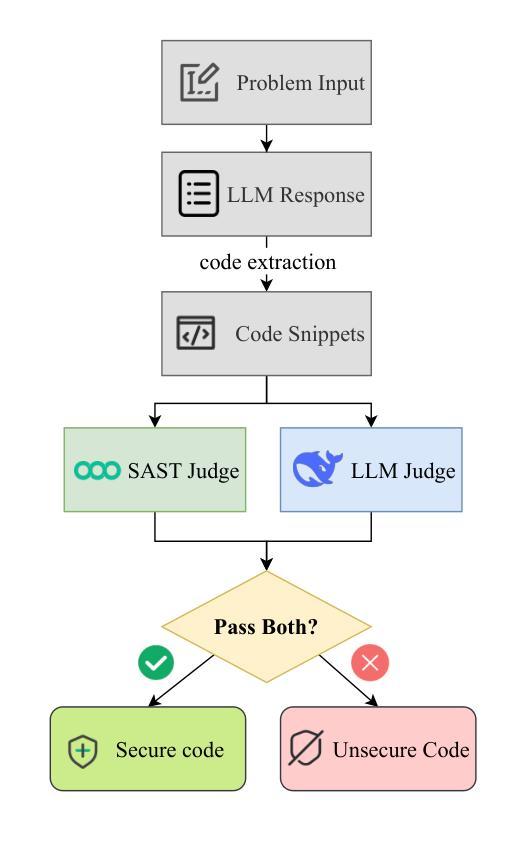
The code generation capabilities of large language models(LLMs) have emerged as a critical dimension in evaluating their overall performance. However, prior research has largely overlooked the security risks inherent in the generated code. In this work, we introduce SafeGenBench, a benchmark specifically designed to assess the security of LLM-generated code. The dataset encompasses a wide range of common software development scenarios and vulnerability types. Building upon this benchmark, we develop an automatic evaluation framework that leverages both static application security testing(SAST) and LLM-based judging to assess the presence of security vulnerabilities in model-generated code. Through the empirical evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs on SafeGenBench, we reveal notable deficiencies in their ability to produce vulnerability-free code. Our findings highlight pressing challenges and offer actionable insights for future advancements in the secure code generation performance of LLMs. The data and code will be released soon.
大型语言模型(LLM)的代码生成能力已成为评估其整体性能的关键维度。然而,先前的研究在很大程度上忽视了生成代码中的安全风险。在这项工作中,我们介绍了SafeGenBench,这是一个专门设计用于评估LLM生成代码安全性的基准测试。该数据集涵盖了各种常见的软件开发场景和漏洞类型。基于这个基准测试,我们开发了一个自动评估框架,该框架利用静态应用程序安全测试(SAST)和基于LLM的判断来评估模型生成代码中存在的安全漏洞。通过对最新LLM在SafeGenBench上的实证评估,我们揭示了它们在生成无漏洞代码方面的显著缺陷。我们的研究结果突出了紧迫的挑战,并为未来提高LLM的安全代码生成性能提供了可行的见解。数据和方法将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的代码生成能力已成为评估其整体性能的关键维度。然而,先前的研究大多忽略了生成代码中的安全风险。在这项工作中,我们推出了SafeGenBench,一个专门设计用于评估LLM生成代码安全性的基准测试。该数据集涵盖了各种常见的软件开发场景和漏洞类型。在此基础上,我们开发了一个自动评估框架,该框架利用静态应用程序安全测试(SAST)和LLM判断来评估模型生成代码中是否存在安全隐患。通过对最新LLM在SafeGenBench上的实证评估,我们发现它们在生成无漏洞代码方面存在显著缺陷。我们的研究结果突出了未来提升LLM安全代码生成性能的紧迫挑战,并提供了可操作的见解。数据和方法集即将发布。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的代码生成能力已成为评估其性能的重要方面。
- 现有研究忽视了LLM生成代码中的安全风险。
- SafeGenBench是一个专门用于评估LLM生成代码安全性的基准测试。
- 该数据集涵盖了多种软件开发场景和漏洞类型。
- 我们开发了一个自动评估框架,结合SAST和LLM判断来评估模型生成代码的安全性。
- 实证评估发现LLM在生成无漏洞代码方面存在显著不足。
点此查看论文截图

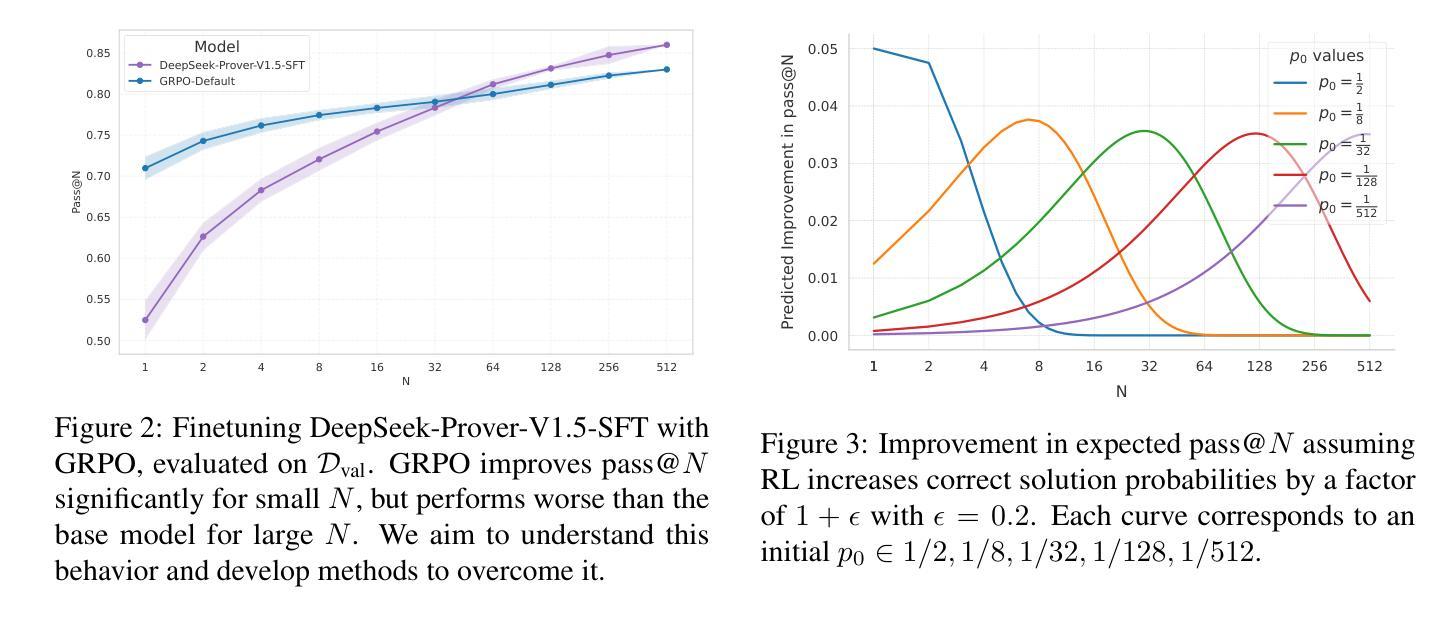
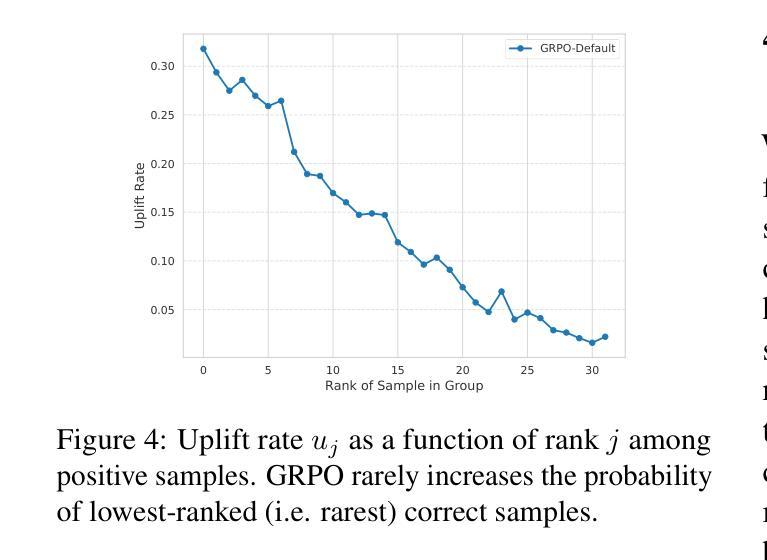
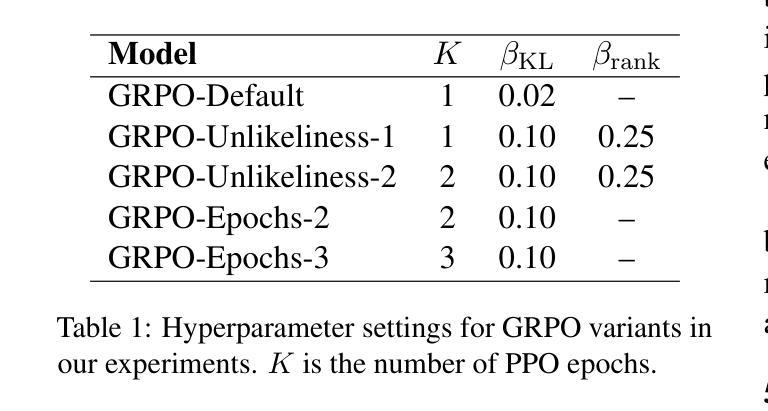
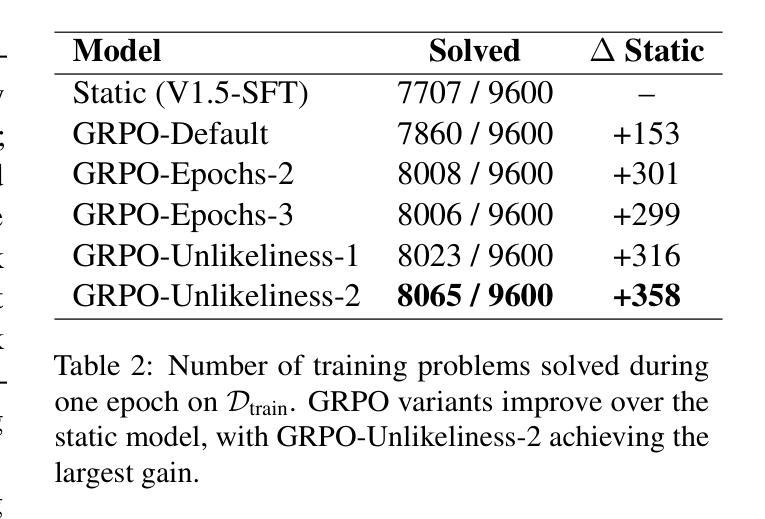
Rewarding the Unlikely: Lifting GRPO Beyond Distribution Sharpening
Authors:Andre He, Daniel Fried, Sean Welleck
Reinforcement learning is emerging as a primary driver for improving language model reasoning capabilities. A fundamental question is whether current reinforcement learning algorithms – such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), the de facto standard algorithm used to improve language model reasoning – merely sharpen the base model’s distribution around problems it can already solve. We investigate this question in the context of formal theorem proving, which has access to a perfect verifier. We identify a degenerate rank bias in GRPO in which highly probable trajectories are reinforced and rare ones are neglected. This results in distribution sharpening: the model can solve some problems with fewer samples, but underperforms simply sampling more solutions from the original model. To overcome GRPO’s rank bias we introduce unlikeliness reward, a simple method for explicitly up-weighting rare but correct solutions. We show that unlikeliness reward mitigates rank bias and improves pass@$N$ across a large range of $N$ in both synthetic and real theorem proving settings. We also uncover an unexpected link between rank bias and a seemingly mundane hyperparameter – the number of updates per batch – that leads to a second, complementary mitigation. We combine our insights into a revised GRPO training recipe for formal theorem proving, yielding an open pipeline that achieves competitive performance to DeepSeek-Prover-V1.5-RL on the miniF2F-test benchmark. We release our implementation at https://github.com/AndreHe02/rewarding-unlikely-release
强化学习正在成为提高语言模型推理能力的主要驱动力。一个基本的问题是,当前的强化学习算法,如用于提高语言模型推理的默认标准算法——集团相对策略优化(GRPO),是否只是使基础模型在能够解决的问题周围分布更加集中。我们在形式化定理证明的背景下研究这个问题,形式化定理证明可以使用完美的验证器。我们发现了GRPO中的退化等级偏见,其中高度可能的轨迹得到加强,而罕见的轨迹被忽视。这导致分布集中化:模型可以在较少的样本下解决一些问题,但在原始模型中简单地通过采样更多解决方案表现得较差。为了克服GRPO的等级偏见,我们引入了不像奖励的方法,这是一种明确提高罕见但正确解决方案权重的简单方法。我们表明,不像奖励可以减轻等级偏见,并在合成和真实定理证明环境的广泛范围内提高了pass@N的性能。我们还发现了等级偏见和一个看似普通的超参数之间的意外联系——每批更新次数,这导致了第二种补充性的缓解方法。我们将这些见解结合到形式化定理证明的修订GRPO训练配方中,形成了一个开放的管道,该管道在miniF2F测试基准上实现了与DeepSeek-Prover-V1.5-RL的竞争性能。我们的实现发布在https://github.com/AndreHe02/rewarding-unlikely-release上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习正在成为提升语言模型推理能力的主要驱动力。研究关注GRPO算法在处理形式化定理证明时存在的问题,提出了一种奖励方法以解决这一问题,使得稀有且正确的解决方案得以强化。这种奖励方法有效缓解了排名偏见问题,并提高了模型在合成和真实定理证明环境中的性能。研究还揭示了一个与看似普通的超参数有关的意外联系,提供了第二种解决途径。对定理证明模型性能的优化成果与DeepSeek-Prover-V1.5-RL相比具有竞争力。我们的实现已在GitHub上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习是推动语言模型推理能力的主要技术驱动力。
- 在形式化定理证明环境中评估了Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)算法的表现。
- 研究发现了GRPO算法的排名偏见问题,强调对高度可能的轨迹的强化而忽视稀有路径。
- 提出了一种名为“unlikeliness reward”的方法来解决排名偏见问题,该方法能够明确地上调稀有但正确的解决方案的权重。
- 研究揭示了一个与超参数有关的意外联系,这有助于更深入地理解算法性能的影响因素。
点此查看论文截图