⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-24 更新
Class Agnostic Instance-level Descriptor for Visual Instance Search
Authors:Qi-Ying Sun, Wan-Lei Zhao, Yi-Bo Miao, Chong-Wah Ngo
Despite the great success of the deep features in content-based image retrieval, the visual instance search remains challenging due to the lack of effective instance level feature representation. Supervised or weakly supervised object detection methods are not among the options due to their poor performance on the unknown object categories. In this paper, based on the feature set output from self-supervised ViT, the instance level region discovery is modeled as detecting the compact feature subsets in a hierarchical fashion. The hierarchical decomposition results in a hierarchy of feature subsets. The non-leaf nodes and leaf nodes on the hierarchy correspond to the various instance regions in an image of different semantic scales. The hierarchical decomposition well addresses the problem of object embedding and occlusions, which are widely observed in the real scenarios. The features derived from the nodes on the hierarchy make up a comprehensive representation for the latent instances in the image. Our instance-level descriptor remains effective on both the known and unknown object categories. Empirical studies on three instance search benchmarks show that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods considerably.
尽管深度特征在基于内容的图像检索中取得了巨大成功,但由于缺乏有效的实例级特征表示,视觉实例搜索仍然具有挑战性。由于其在未知对象类别上的表现不佳,监督或弱监督对象检测方法并不适用。在本文中,基于自监督ViT输出的特征集,将实例级区域发现建模为以分层方式检测紧凑特征子集。分层分解的结果是一系列特征子集。层次结构上的非叶节点和叶节点对应于图像中不同语义尺度的各种实例区域。分层分解很好地解决了对象嵌入和遮挡问题,这些问题在实际场景中广泛存在。从层次结构上的节点派生的特征构成了图像中潜在实例的全面表示。我们的实例级描述符在已知和未知对象类别上均保持有效。在三个实例搜索基准测试上的经验研究表明,它的性能明显优于最新技术的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于自监督ViT的特征集输出,本文将实例级别的区域发现建模为以分层方式检测紧凑特征子集的问题。分层分解产生一系列的特征子集层次结构,其中的非叶子节点和叶子节点对应于图像中不同语义尺度的各种实例区域。分层分解很好地解决了物体嵌入和遮挡问题,这些问题在真实场景中普遍存在。从层次结构上提取的特征为图像中的潜在实例提供了全面的表示。本文的实例级描述符在已知和未知对象类别上均保持有效。在三个实例搜索基准测试上的实证研究表明,该方法显著优于现有技术。
关键见解
- 实例级别的区域发现可以通过检测自监督ViT特征集的紧凑特征子集来解决。
- 分层分解产生一系列特征子集,其中非叶子节点和叶子节点代表图像中不同语义尺度的实例区域。
- 分层分解有效解决了物体嵌入和遮挡问题。
- 从层次结构上提取的特征为图像中的潜在实例提供了全面的表示。
- 实例级描述符对已知和未知对象类别均有效。
- 在三个实例搜索基准测试上,该方法显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

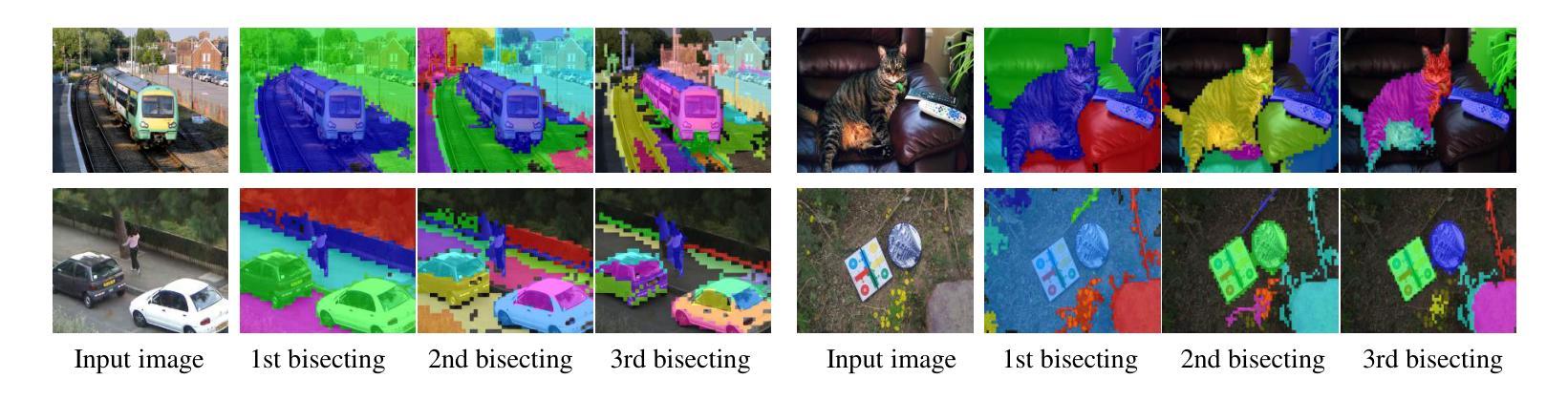

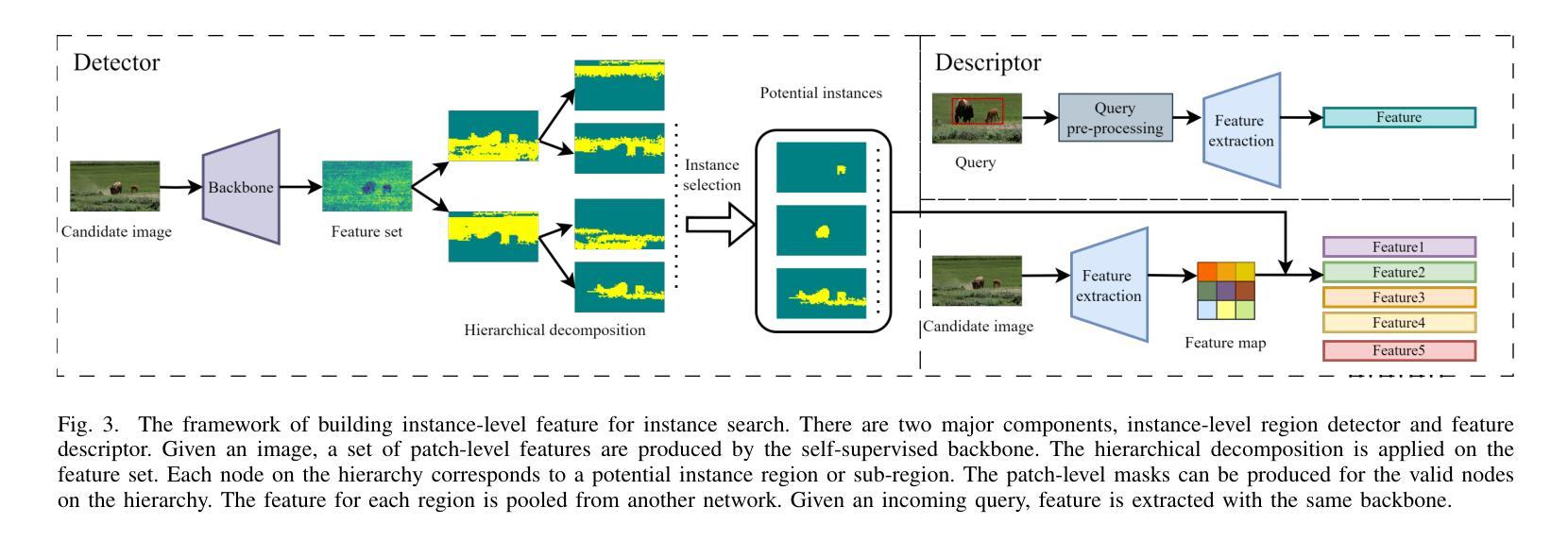
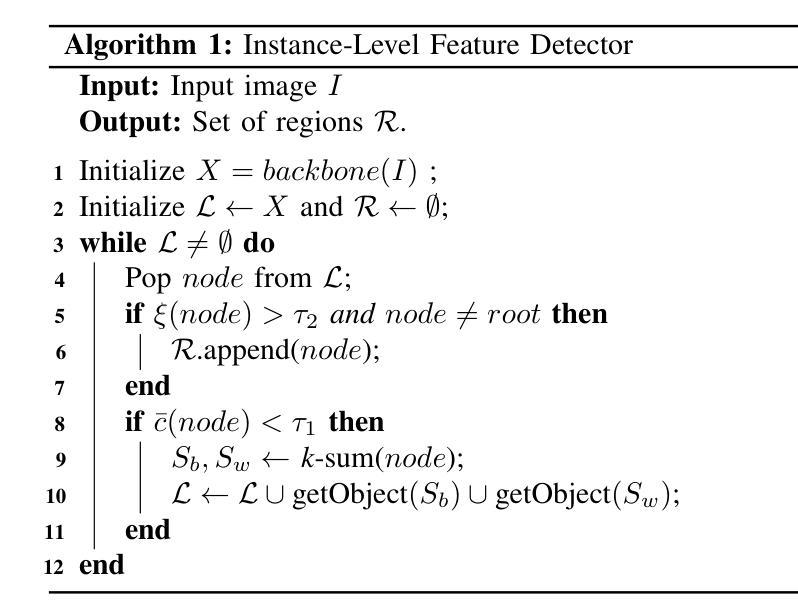
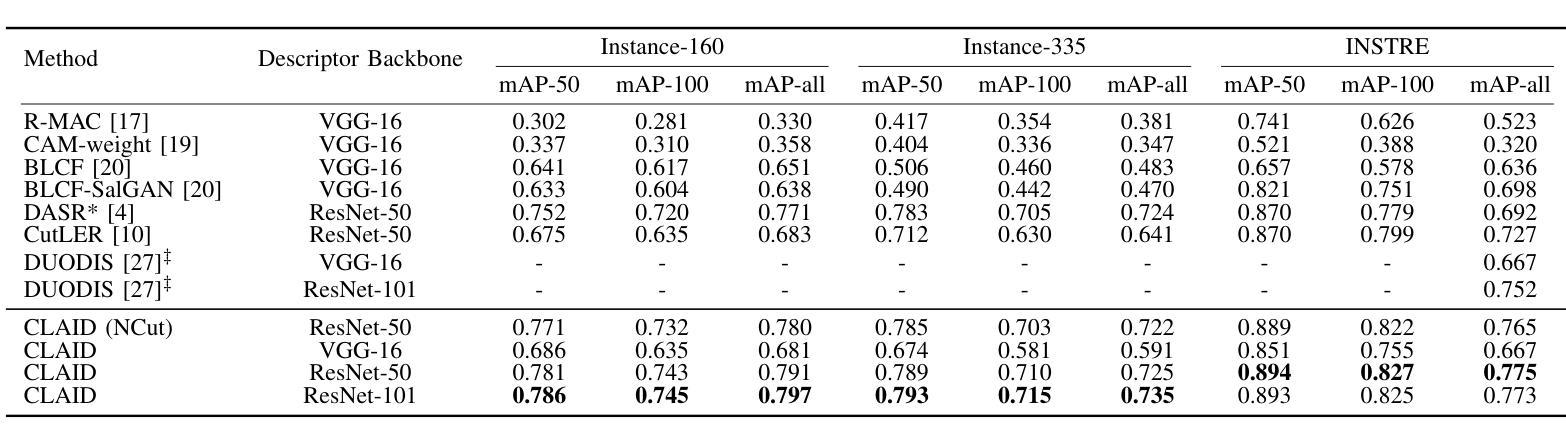
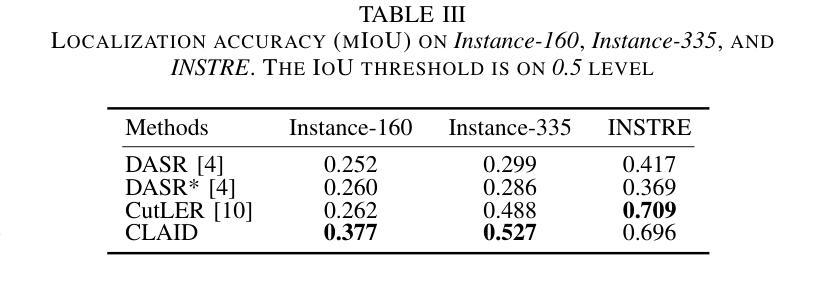
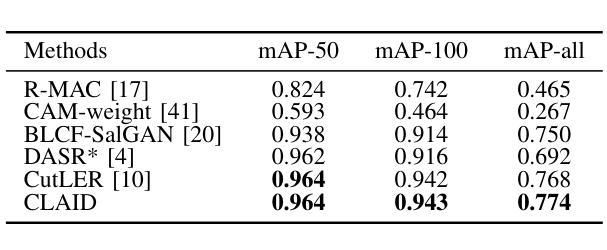
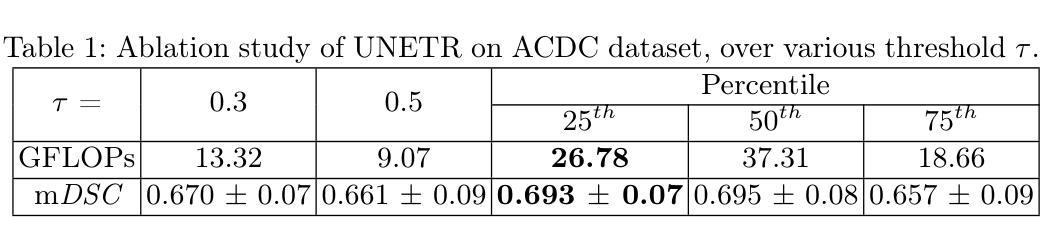
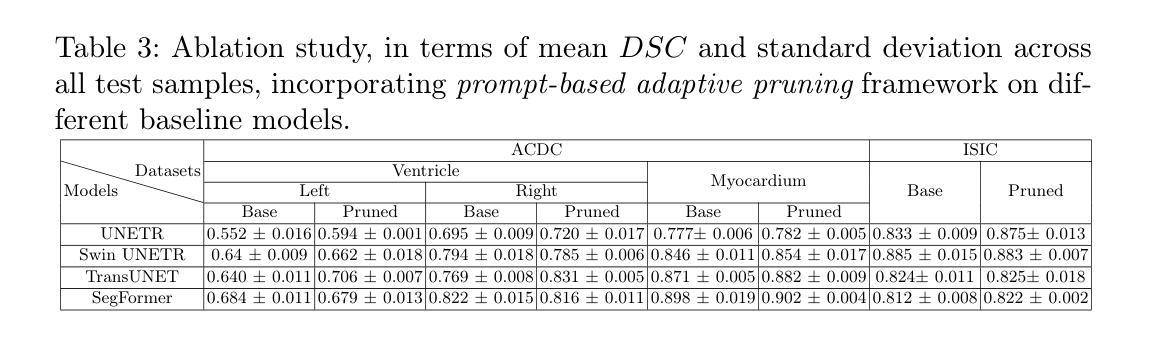
Prompt-based Dynamic Token Pruning to Guide Transformer Attention in Efficient Segmentation
Authors:Pallabi Dutta, Anubhab Maity, Sushmita Mitra
The high computational demands of Vision Transformers (ViTs), in processing a huge number of tokens, often constrain their practical application in analyzing medical images. This research proposes an adaptive prompt-guided pruning method to selectively reduce the processing of irrelevant tokens in the segmentation pipeline. The prompt-based spatial prior helps to rank the tokens according to their relevance. Tokens with low-relevance scores are down-weighted, ensuring that only the relevant ones are propagated for processing across subsequent stages. This data-driven pruning strategy facilitates end-to-end training, maintains gradient flow, and improves segmentation accuracy by focusing computational resources on essential regions. The proposed framework is integrated with several state-of-the-art models to facilitate the elimination of irrelevant tokens; thereby, enhancing computational efficiency while preserving segmentation accuracy. The experimental results show a reduction of $\sim$ 35-55% tokens; thus reducing the computational costs relative to the baselines. Cost-effective medical image processing, using our framework, facilitates real-time diagnosis by expanding its applicability in resource-constrained environments.
视觉Transformer(ViT)的计算需求极高,在处理大量标记时,经常限制其在医学图像分析中的实际应用。本研究提出了一种自适应提示引导修剪方法,有选择地减少分割管道中不相关标记的处理。基于提示的空间先验有助于根据相关性对标记进行排名。低相关性得分的标记被降权,确保只有相关的标记在后续阶段进行处理。这种数据驱动的修剪策略促进了端到端的训练,保持了梯度流,并通过将计算资源集中在关键区域上,提高了分割的准确度。所提出的框架与多种最新模型集成,以消除不相关的标记,从而提高计算效率,同时保持分割精度。实验结果表明减少了约35-55%的标记,与基线相比降低了计算成本。使用我们的框架实现经济高效的医学图像处理,通过扩大其在资源受限环境中的应用,促进实时诊断。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一种自适应提示引导裁剪方法,用于选择性减少处理医学图像分析中Vision Transformer(ViT)的不相关令牌。提示空间先验有助于根据相关性对令牌进行排名。低相关性得分的令牌被降权处理,确保只处理相关的令牌。这种数据驱动的裁剪策略便于端到端的训练,保持梯度流动,并通过集中计算资源于关键区域提高分割精度。该框架与多个最新模型集成,以消除不相关的令牌,从而提高计算效率并保持分割精度。实验结果显示令牌数量减少了约35-55%,相对于基线降低了计算成本。使用此框架的经济型医学图像处理扩大了其在资源受限环境中的适用性,有助于实时诊断。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs)面临高计算需求,处理大量令牌时存在实践应用上的限制。
- 研究提出了一种自适应提示引导裁剪方法,以选择性减少不相关令牌的处理。
- 提示空间先验用于根据令牌的相关性进行排名。
- 低相关性令牌被降权处理,确保仅处理相关令牌。
- 数据驱动的裁剪策略支持端到端训练,维持梯度流动,并提高分割精度。
- 框架与多个最新模型集成,能够有效消除不相关令牌,提高计算效率并保持分割精度。
- 实验结果显示计算成本相对较低,令牌数量减少了约35-55%,适用于资源受限环境,有助于实时诊断。
点此查看论文截图

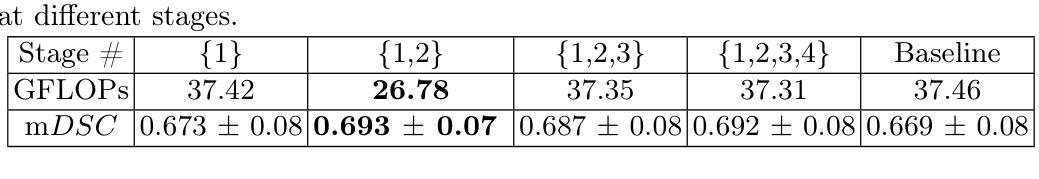
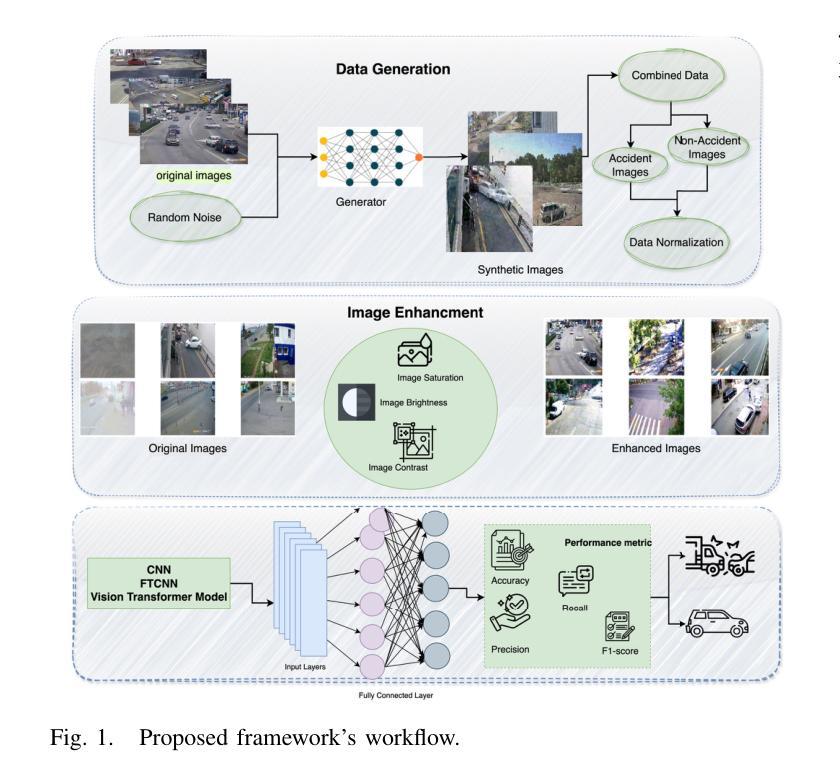
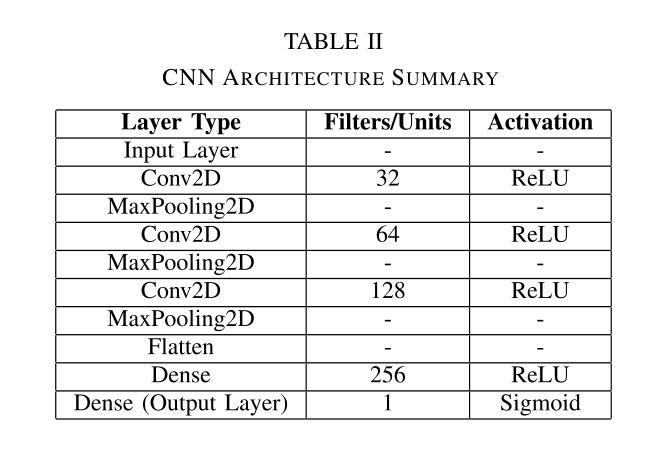
Integrating Generative Adversarial Networks and Convolutional Neural Networks for Enhanced Traffic Accidents Detection and Analysis
Authors:Zhenghao Xi, Xiang Liu, Yaqi Liu, Yitong Cai, Yangyu Zheng
Accident detection using Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) footage is one of the most imperative features for enhancing transport safety and efficient traffic control. To this end, this research addresses the issues of supervised monitoring and data deficiency in accident detection systems by adapting excellent deep learning technologies. The motivation arises from rising statistics in the number of car accidents worldwide; this calls for innovation and the establishment of a smart, efficient and automated way of identifying accidents and calling for help to save lives. Addressing the problem of the scarcity of data, the presented framework joins Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for synthesizing data and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for model training. Video frames for accidents and non-accidents are collected from YouTube videos, and we perform resizing, image enhancement and image normalisation pixel range adjustments. Three models are used: CNN, Fine-tuned Convolutional Neural Network (FTCNN) and Vision Transformer (VIT) worked best for detecting accidents from CCTV, obtaining an accuracy rate of 94% and 95%, while the CNN model obtained 88%. Such results show that the proposed framework suits traffic safety applications due to its high real-time accident detection capabilities and broad-scale applicability. This work lays the foundation for intelligent surveillance systems in the future for real-time traffic monitoring, smart city framework, and integration of intelligent surveillance systems into emergency management systems.
使用闭路电视(CCTV)画面进行事故检测是增强交通安全性和提高交通效率的关键功能之一。为此,本研究通过适应卓越的深度学习技术来解决事故检测系统中的监督监控和数据缺乏问题。这种动机源于全球汽车事故数量统计数据的上升;这需要创新并建立一种智能、高效、自动化的方式来识别事故并寻求帮助以挽救生命。针对数据稀缺的问题,所提出的框架结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)进行数据合成和卷积神经网络(CNN)进行模型训练。我们从YouTube视频中收集了事故和非事故的视频帧,并进行了尺寸调整、图像增强和图像归一化像素范围调整。我们使用了三种模型:卷积神经网络(CNN)、微调卷积神经网络(FTCNN)和视觉转换器(VIT),它们在从CCTV检测事故方面表现最佳,准确率分别为94%和95%,而CNN模型的准确率为88%。这些结果表明,所提出的框架因其高实时事故检测能力和广泛的适用性而适用于交通安全应用。这项工作为未来智能监控系统在实时交通监控、智能城市框架以及智能监控系统与紧急管理系统集成中的应用奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
利用闭路电视(CCTV)视频进行事故检测是提升交通安全和有效交通控制的关键功能之一。本研究通过应用优秀的深度学习技术解决事故检测系统中的监控和监督以及数据缺失问题。本研究的动机源于全球汽车事故数量的上升统计,这要求创新和建立一个智能、高效、自动化的识别事故和呼叫救援系统以挽救生命。为解决数据稀缺问题,研究结合生成对抗网络(GANs)进行数据合成和卷积神经网络(CNN)进行模型训练。从YouTube视频收集事故和非事故的视频帧,并进行尺寸调整、图像增强和图像归一化像素范围调整。其中卷积神经网络(CNN)、微调卷积神经网络(FTCNN)和视觉变压器(VIT)在检测CCTV事故方面表现最佳,准确率分别达到94%和95%,而CNN模型准确率为88%。这些结果表明,所提出的框架适用于交通安全应用,具有实时事故检测能力并在大规模应用上有潜力。此工作为未来智能交通监控系统打下坚实的基础,助力实时监控交通和集成到智能城市框架及紧急管理系统之中。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究解决了提高交通安全及高效交通控制的关键问题之一 —— 利用闭路电视监控系统进行事故检测。
- 本研究使用深度学习技术中的优秀方法,特别结合了生成对抗网络和卷积神经网络处理事故检测系统面临的监督监控和数据缺乏的问题。
点此查看论文截图



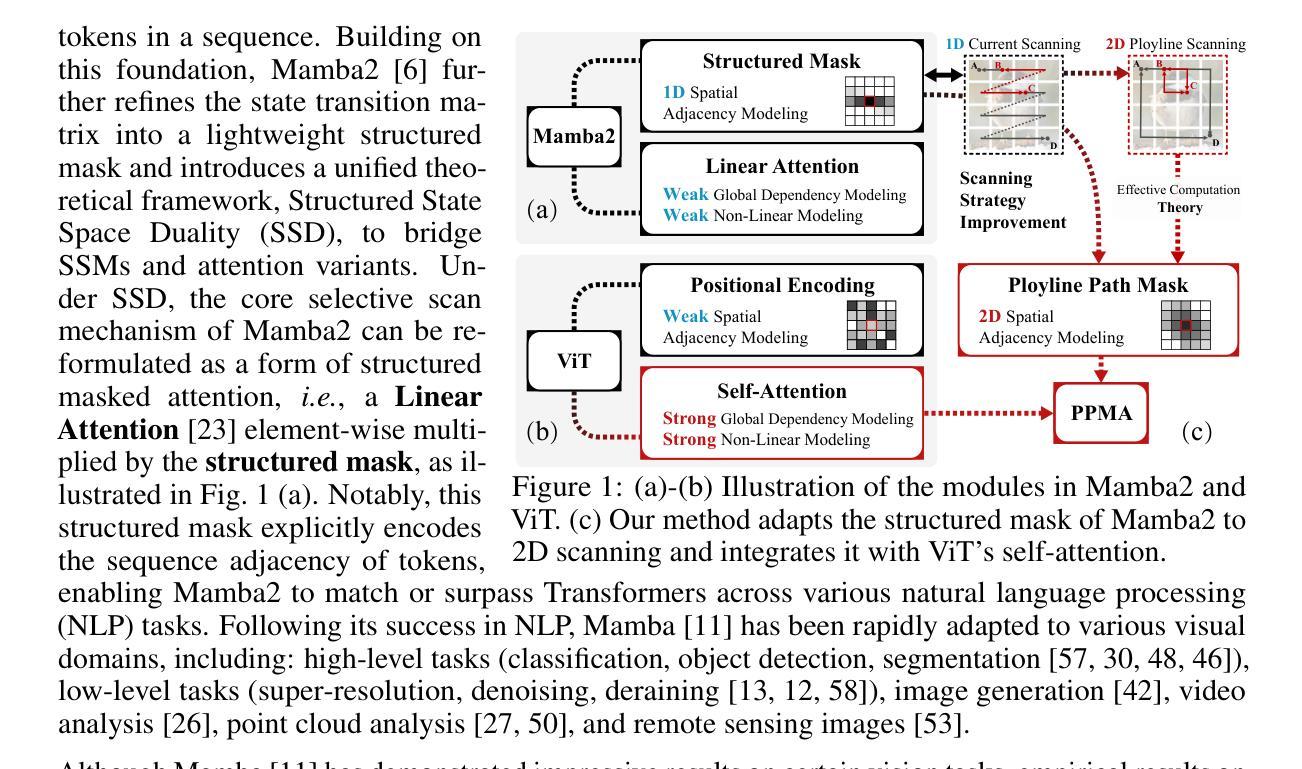
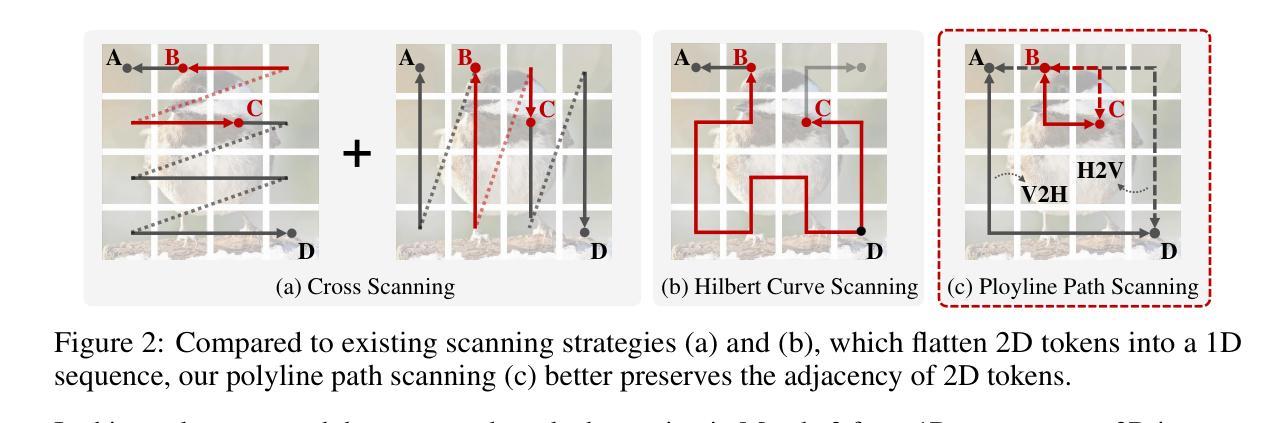
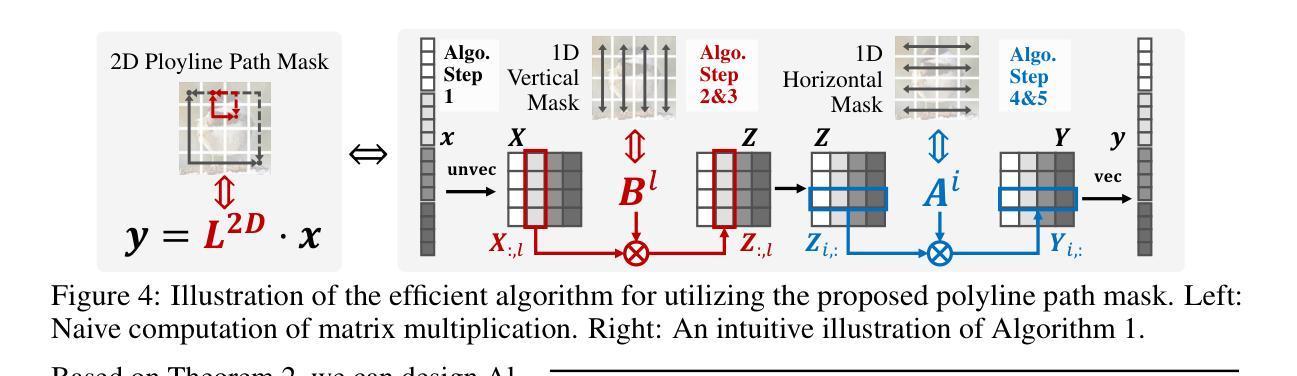
Polyline Path Masked Attention for Vision Transformer
Authors:Zhongchen Zhao, Chaodong Xiao, Hui Lin, Qi Xie, Lei Zhang, Deyu Meng
Global dependency modeling and spatial position modeling are two core issues of the foundational architecture design in current deep learning frameworks. Recently, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved remarkable success in computer vision, leveraging the powerful global dependency modeling capability of the self-attention mechanism. Furthermore, Mamba2 has demonstrated its significant potential in natural language processing tasks by explicitly modeling the spatial adjacency prior through the structured mask. In this paper, we propose Polyline Path Masked Attention (PPMA) that integrates the self-attention mechanism of ViTs with an enhanced structured mask of Mamba2, harnessing the complementary strengths of both architectures. Specifically, we first ameliorate the traditional structured mask of Mamba2 by introducing a 2D polyline path scanning strategy and derive its corresponding structured mask, polyline path mask, which better preserves the adjacency relationships among image tokens. Notably, we conduct a thorough theoretical analysis on the structural characteristics of the proposed polyline path mask and design an efficient algorithm for the computation of the polyline path mask. Next, we embed the polyline path mask into the self-attention mechanism of ViTs, enabling explicit modeling of spatial adjacency prior. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks, including image classification, object detection, and segmentation, demonstrate that our model outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches based on both state-space models and Transformers. For example, our proposed PPMA-T/S/B models achieve 48.7%/51.1%/52.3% mIoU on the ADE20K semantic segmentation task, surpassing RMT-T/S/B by 0.7%/1.3%/0.3%, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/zhongchenzhao/PPMA.
全局依赖建模和空间位置建模是当前深度学习框架基础架构设计中的两个核心问题。最近,Vision Transformers(ViTs)利用自注意力机制的强大全局依赖建模能力,在计算机视觉领域取得了显著的成功。此外,Mamba2通过明确的空间邻接先验建模,在自然语言处理任务中展示了其显著潜力。在本文中,我们提出了Polyline Path Masked Attention(PPMA),它结合了ViTs的自注意力机制和Mamba2的增强结构掩码,充分利用了两种架构的互补优势。
具体来说,我们首先通过引入2D折线路径扫描策略,改进了Mamba2的传统结构掩码,并派生出其相应的结构掩码,即折线路径掩码,能更好地保留图像标记之间的邻接关系。值得注意的是,我们对所提出的折线路径掩码的结构特性进行了全面的理论分析,并设计了计算折线路径掩码的高效算法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出将Vision Transformer与Mamba2的结构化掩码结合的Polyline Path Masked Attention(PPMA)。新方法通过引入2D折线路径扫描策略改进了Mamba2的结构化掩码,得到Polyline Path Mask,更好地保留了图像标记间的邻接关系。在标准图像分类、目标检测和分割任务上进行的实验表明,新方法性能优于当前最前沿模型。
Key Takeaways
- PPMA结合了Vision Transformer的自注意力机制和Mamba2的结构化掩码技术。
- PPMA引入的2D折线路径掩码能够更好地保留图像标记间的邻接关系。
- 对提出的polyline path mask进行了理论分析和高效算法设计。
- PPMA在图像分类、目标检测和语义分割任务上实现了性能超越。
- 在ADE20K语义分割任务上,PPMA-T/S/B模型相较于RMT-T/S/B分别提高了0.7%/1.3%/0.3%的mIoU。
- 该模型强化了空间邻接先验的建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

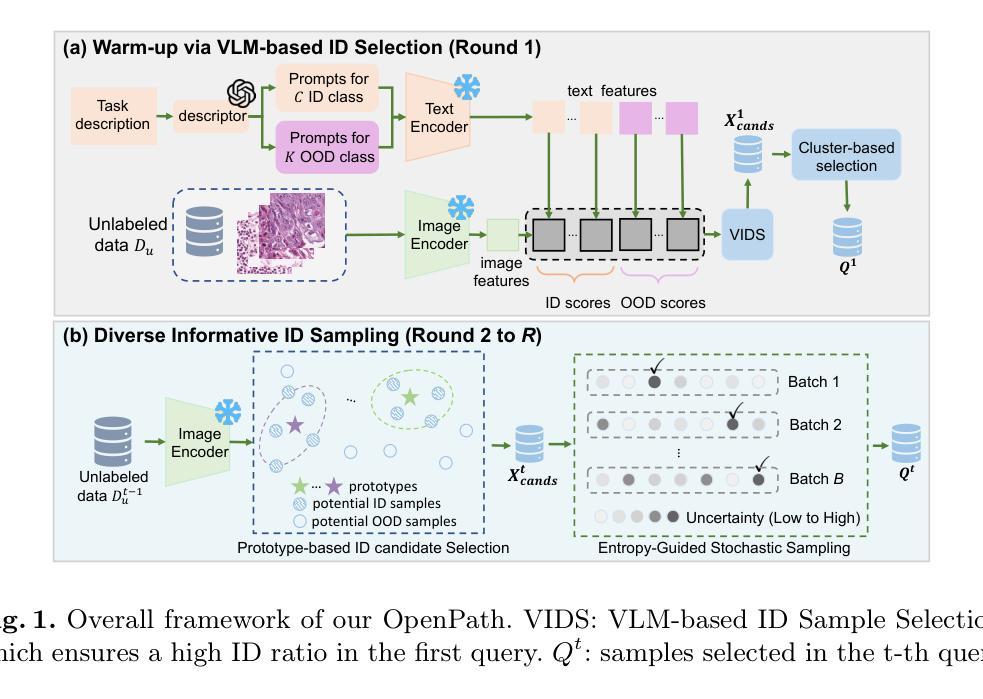
OpenPath: Open-Set Active Learning for Pathology Image Classification via Pre-trained Vision-Language Models
Authors:Lanfeng Zhong, Xin Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
Pathology image classification plays a crucial role in accurate medical diagnosis and treatment planning. Training high-performance models for this task typically requires large-scale annotated datasets, which are both expensive and time-consuming to acquire. Active Learning (AL) offers a solution by iteratively selecting the most informative samples for annotation, thereby reducing the labeling effort. However, most AL methods are designed under the assumption of a closed-set scenario, where all the unannotated images belong to target classes. In real-world clinical environments, the unlabeled pool often contains a substantial amount of Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) data, leading to low efficiency of annotation in traditional AL methods. Furthermore, most existing AL methods start with random selection in the first query round, leading to a significant waste of labeling costs in open-set scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose OpenPath, a novel open-set active learning approach for pathological image classification leveraging a pre-trained Vision-Language Model (VLM). In the first query, we propose task-specific prompts that combine target and relevant non-target class prompts to effectively select In-Distribution (ID) and informative samples from the unlabeled pool. In subsequent queries, Diverse Informative ID Sampling (DIS) that includes Prototype-based ID candidate Selection (PIS) and Entropy-Guided Stochastic Sampling (EGSS) is proposed to ensure both purity and informativeness in a query, avoiding the selection of OOD samples. Experiments on two public pathology image datasets show that OpenPath significantly enhances the model’s performance due to its high purity of selected samples, and outperforms several state-of-the-art open-set AL methods. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath}{https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath}..
病理学图像分类在准确的医学诊断和治疗计划中发挥至关重要的作用。为此任务训练高性能模型通常需要大规模标注数据集,这些数据的获取既昂贵又耗时。主动学习(AL)通过迭代选择最具信息量的样本进行标注,从而减少了标注工作量,为此提供了解决方案。然而,大多数AL方法的设计是基于封闭集场景的假设,即所有未标注的图像都属于目标类别。在现实世界中的临床环境中,未标注池中经常包含大量来自域外的数据(OOD),这导致传统AL方法的标注效率降低。此外,大多数现有的AL方法在第一次查询轮次中随机选择样本,在开放式场景中导致标注成本的大量浪费。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了OpenPath,这是一种利用预训练视觉语言模型(VLM)进行病理学图像分类的新型开放式主动学习。在第一次查询中,我们提出了任务特定的提示,这些提示结合了目标和相关的非目标类别提示,以有效地从未标注池中选择来自域内(ID)和具有信息量的样本。在随后的查询中,我们提出了多样化的信息ID采样(DIS),其中包括基于原型的ID候选样本选择(PIS)和基于熵引导的随机采样(EGSS),以确保查询中的纯净度和信息量,避免选择域外样本。在两个公共病理学图像数据集上的实验表明,由于所选样本的高纯净度,OpenPath显著提高了模型的性能,并优于几种先进的开放式AL方法。代码可通过链接https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 early accept
Summary
本文提出一种开放集下的病理学图像分类主动学习方法,名为OpenPath。该方法利用预训练的视觉语言模型,通过任务特定提示和多样信息采样策略,有效选择样本并避免选择出分布外的样本。实验证明,OpenPath在公开病理学图像数据集上的性能优于其他主流开放集主动学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 病理学图像分类在医疗诊断和治疗计划中至关重要,需要大规模标注数据集来训练高性能模型,但标注成本高昂且耗时。
- 主动学习方法可通过选择信息量最大的样本进行标注,降低标注成本。
- 现有主动学习方法多在封闭集场景下设计,难以处理真实世界中的开放集场景,特别是包含大量非目标分布的数据。
- OpenPath方法利用预训练的视觉语言模型,通过任务特定提示和多样信息采样策略来选择样本,确保选择的样本既有代表性又信息量丰富。
- OpenPath方法在公共病理学图像数据集上的实验表现优异,选样纯度较高。
- OpenPath代码已公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

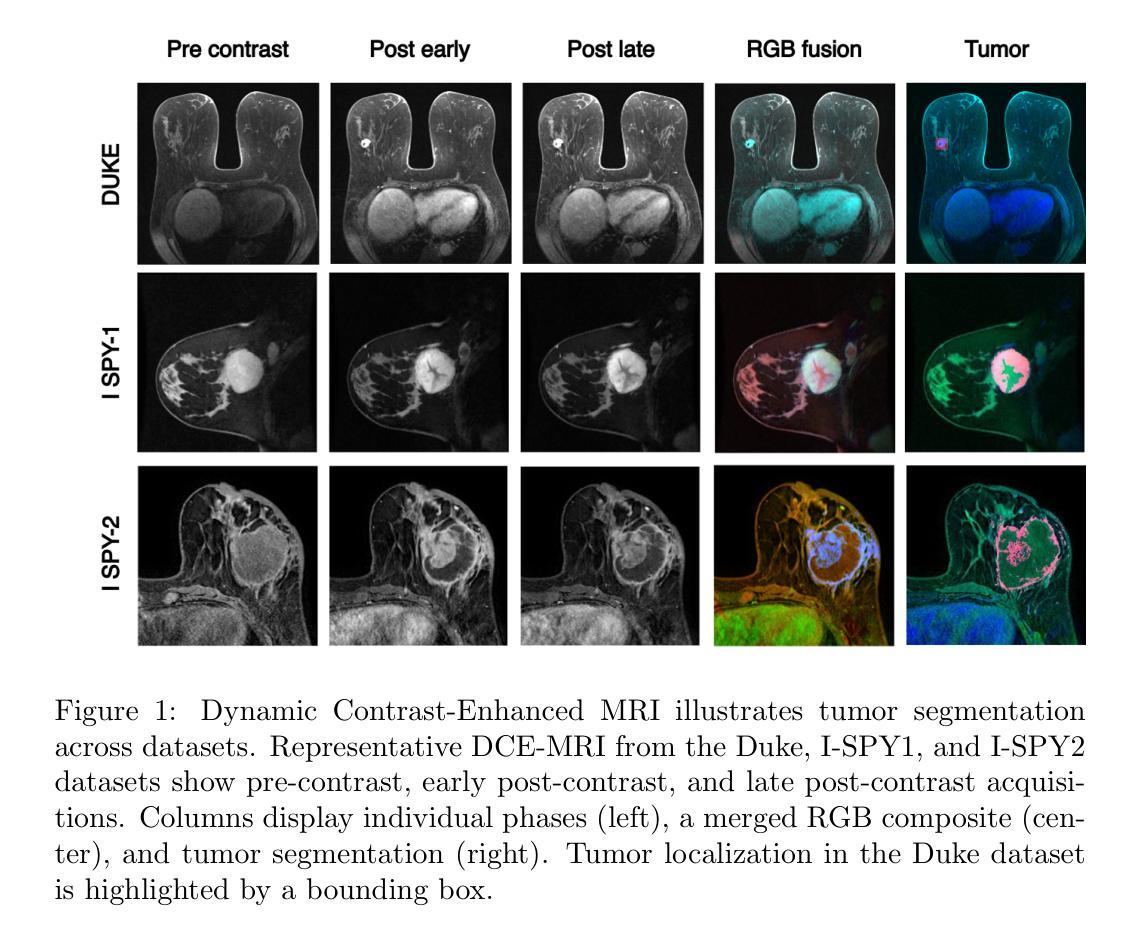
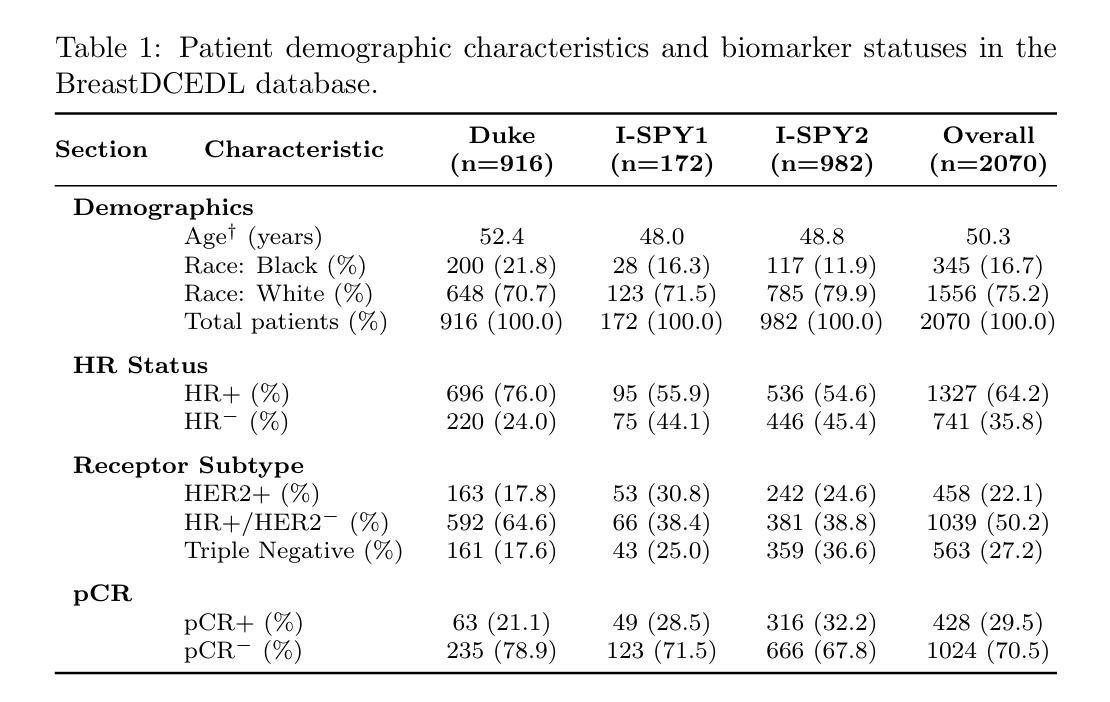
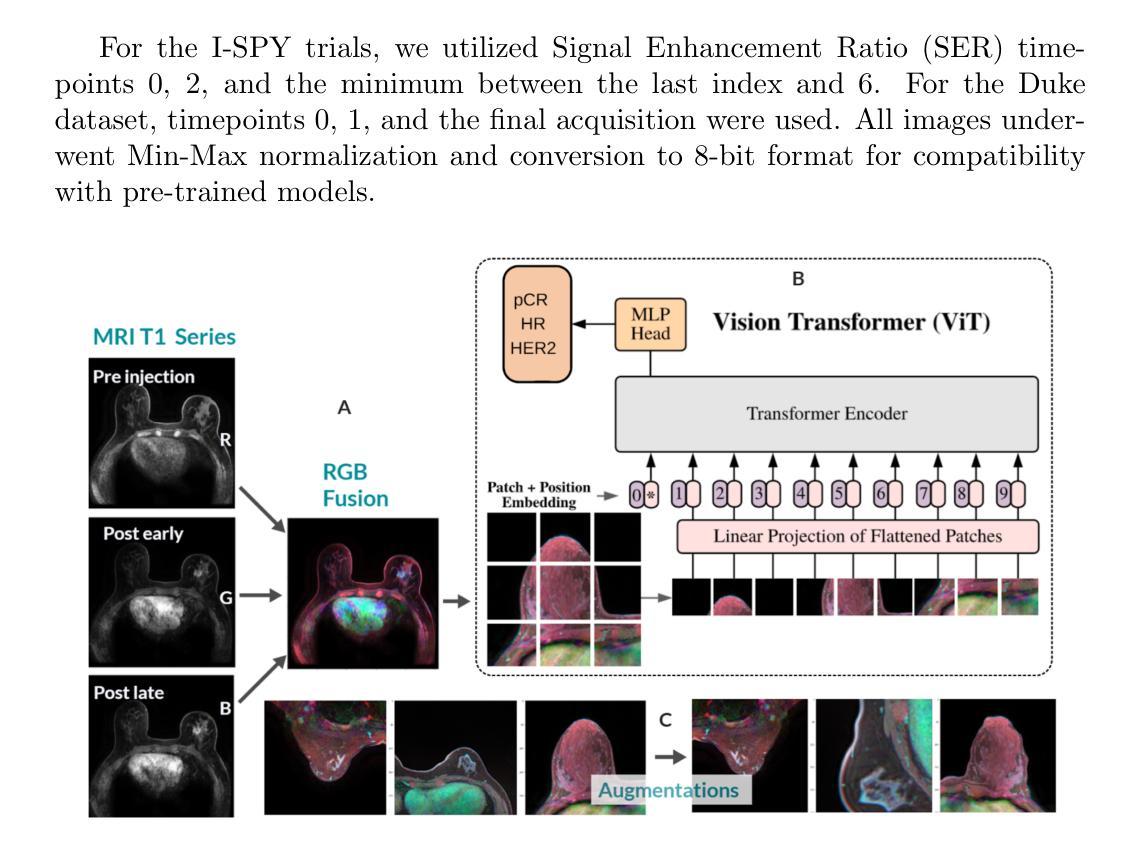
BreastDCEDL: Curating a Comprehensive DCE-MRI Dataset and developing a Transformer Implementation for Breast Cancer Treatment Response Prediction
Authors:Naomi Fridman, Bubby Solway, Tomer Fridman, Itamar Barnea, Anat Goldstein
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, making early detection and accurate treatment response monitoring critical priorities. We present BreastDCEDL, a curated, deep learning-ready dataset comprising pre-treatment 3D Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) scans from 2,070 breast cancer patients drawn from the I-SPY1, I-SPY2, and Duke cohorts, all sourced from The Cancer Imaging Archive. The raw DICOM imaging data were rigorously converted into standardized 3D NIfTI volumes with preserved signal integrity, accompanied by unified tumor annotations and harmonized clinical metadata including pathologic complete response (pCR), hormone receptor (HR), and HER2 status. Although DCE-MRI provides essential diagnostic information and deep learning offers tremendous potential for analyzing such complex data, progress has been limited by lack of accessible, public, multicenter datasets. BreastDCEDL addresses this gap by enabling development of advanced models, including state-of-the-art transformer architectures that require substantial training data. To demonstrate its capacity for robust modeling, we developed the first transformer-based model for breast DCE-MRI, leveraging Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture trained on RGB-fused images from three contrast phases (pre-contrast, early post-contrast, and late post-contrast). Our ViT model achieved state-of-the-art pCR prediction performance in HR+/HER2- patients (AUC 0.94, accuracy 0.93). BreastDCEDL includes predefined benchmark splits, offering a framework for reproducible research and enabling clinically meaningful modeling in breast cancer imaging.
乳腺癌仍然是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,因此早期检测和精确的治疗反应监测成为至关重要的优先事项。我们推出了BreastDCEDL,这是一个精选的、准备好用于深度学习数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke队列的2070例乳腺癌患者的治疗前3D动态增强MRI(DCE-MRI)扫描,所有数据源均来自癌症成像档案。原始的DICOM成像数据被严格转换为标准化的3DNIfTI体积数据,同时保留了信号完整性,并附有统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据,包括病理完全反应(pCR)、激素受体(HR)和HER2状态。尽管DCE-MRI提供了重要的诊断信息,深度学习在分析此类复杂数据方面具有巨大潜力,但由于缺乏可访问的、公开的、多中心数据集,进展一直受到限制。BreastDCEDL通过支持开发先进模型来解决这一差距,包括需要大量训练数据的最新变压器架构。为了展示其稳健建模的能力,我们开发了基于变压器的首个乳腺癌DCE-MRI模型,该模型利用在三个对比阶段(预对比、早期对比后和晚期对比后)的RGB融合图像上训练的Vision Transformer(ViT)架构。我们的ViT模型在HR+/HER2-患者中实现了最先进的pCR预测性能(AUC 0.94,准确率0.93)。BreastDCEDL包括预定义的基准测试分割,为可重复的研究提供了一个框架,并在乳腺癌成像中实现了具有临床意义的建模。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
乳腺癌仍是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,早期检测和精确的治疗反应监测是关键。我们推出BreastDCEDL,这是一个经过深度学习的数据集,包含来自I-SPY1、I-SPY2和Duke等队伍的2,070例乳腺癌患者的预治疗三维动态增强MRI扫描数据。原始DICOM图像数据被严格转换为标准化的三维NIfTI体积,保留了信号完整性,并配有统一的肿瘤注释和协调的临床元数据。虽然DCE-MRI提供了重要的诊断信息,深度学习在分析这些数据方面潜力巨大,但由于缺乏公开的多中心数据集,进展一直受到限制。BreastDCEDL通过支持先进模型的发展解决了这一差距,包括需要大量训练数据的最新变压器架构。为了展示其在稳健建模方面的能力,我们开发了基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的首个乳腺癌DCE-MRI模型,该模型在RGB融合图像上进行训练,来自三个对比阶段(预对比、早期后对比和晚期后对比)。我们的ViT模型在HR+/HER2-患者中实现了最先进的pCR预测性能(AUC 0.94,准确率0.93)。BreastDCEDL包括预设的基准分割,为可重复的研究提供了一个框架,并能实现乳腺癌成像的临床意义建模。
要点
- 乳腺癌仍是全球关注的癌症致死原因,早期检测和精准治疗反应监测至关重要。
- BreastDCEDL是一个经过深度学习的数据集,包含来自多个来源的乳腺癌患者的预治疗三维动态增强MRI扫描数据。
- 数据集解决了缺乏公开多中心数据集的难题,支持先进模型的发展。
- 基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的模型在RGB融合图像上进行训练,并在HR+/HER2-患者中实现优越的pCR预测性能。
- BreastDCEDL包含预设的基准分割,为研究者提供可重复的研究框架。
- 数据集可实现乳腺癌成像的临床意义建模。
点此查看论文截图