⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
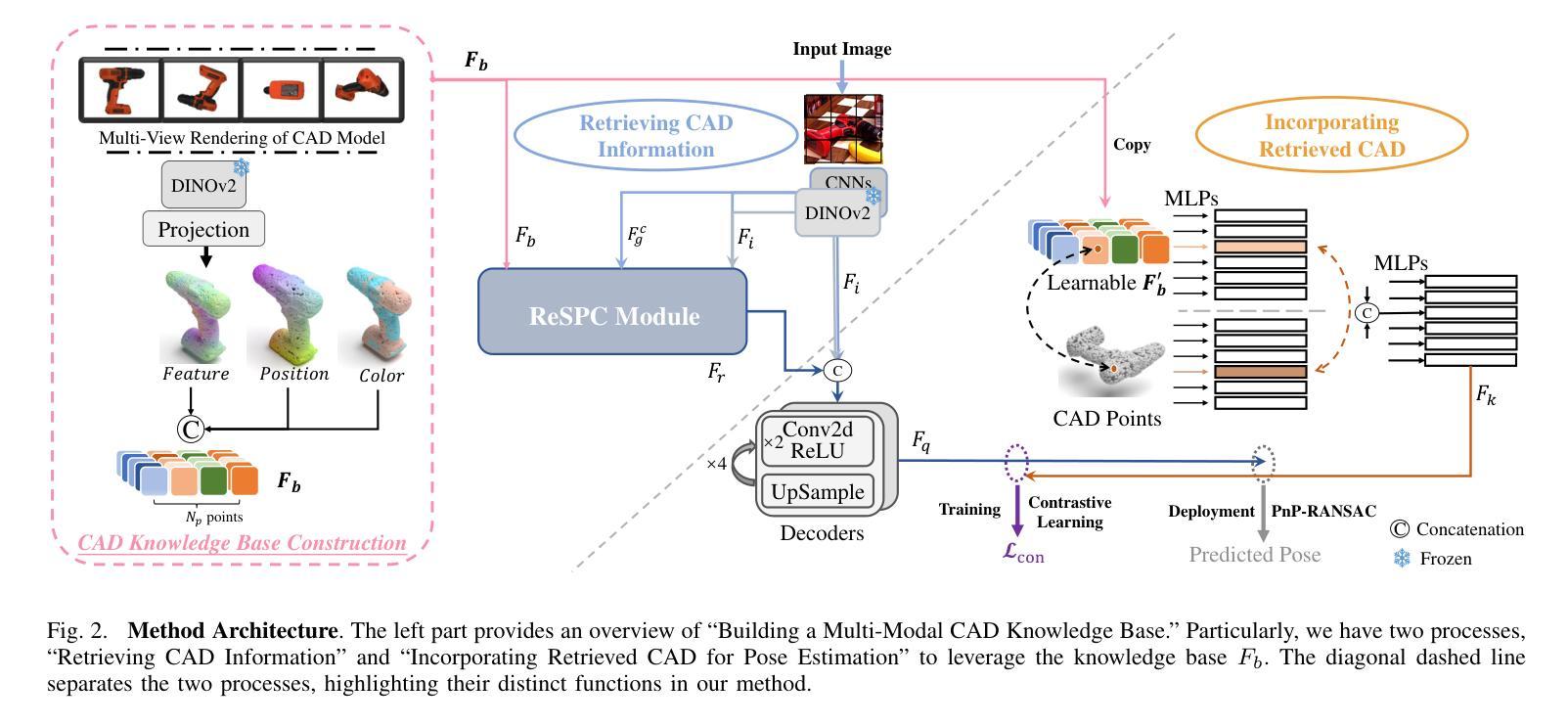
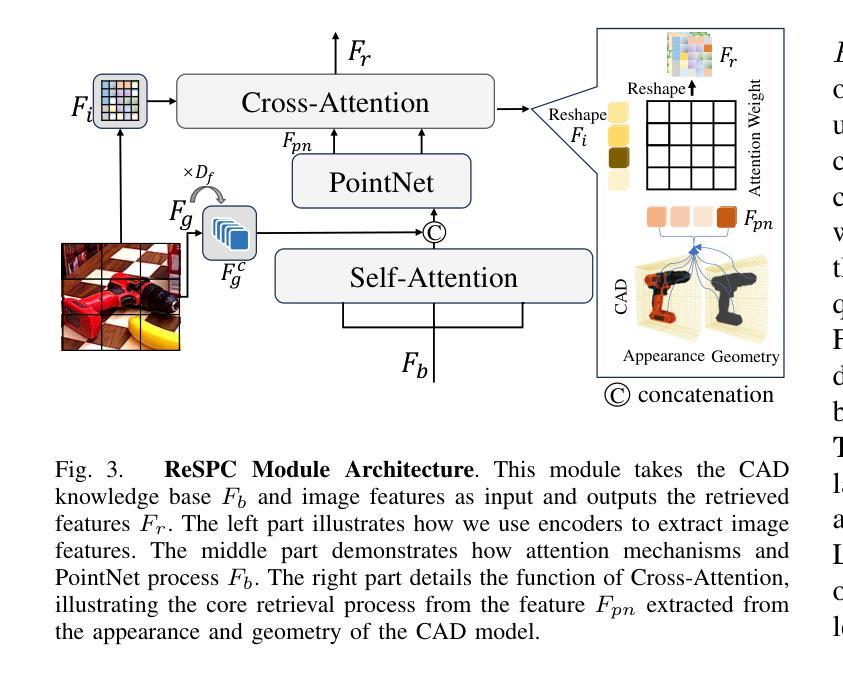
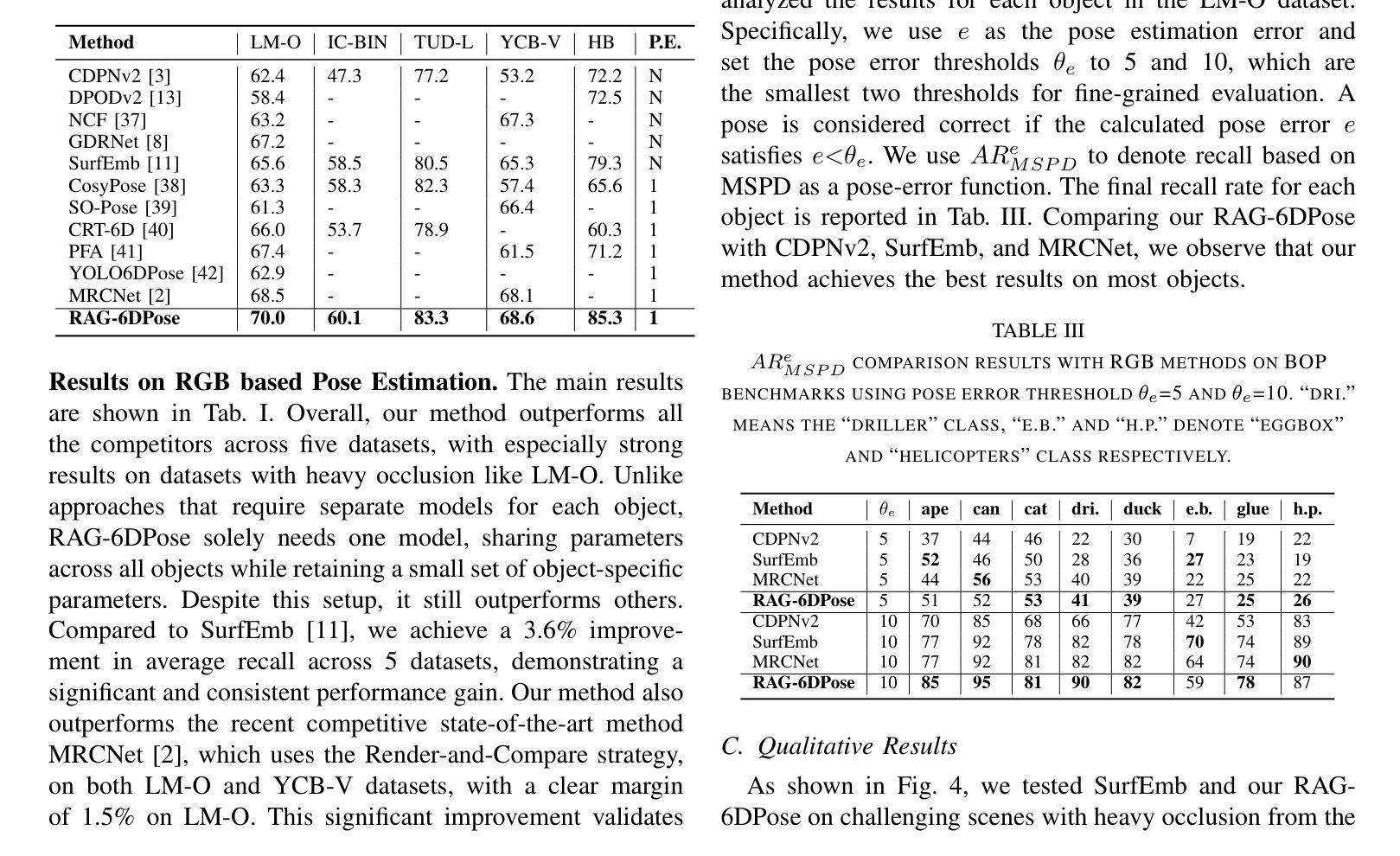
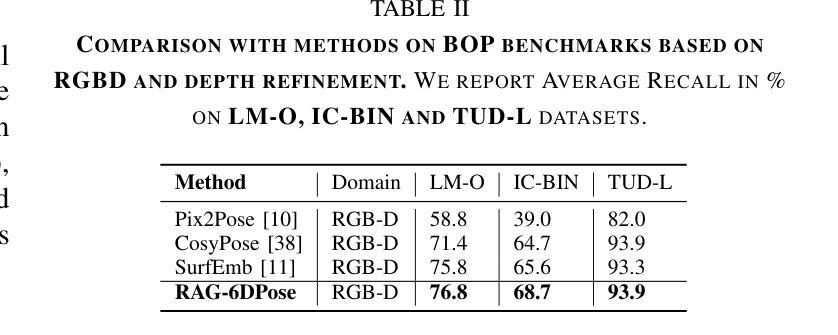
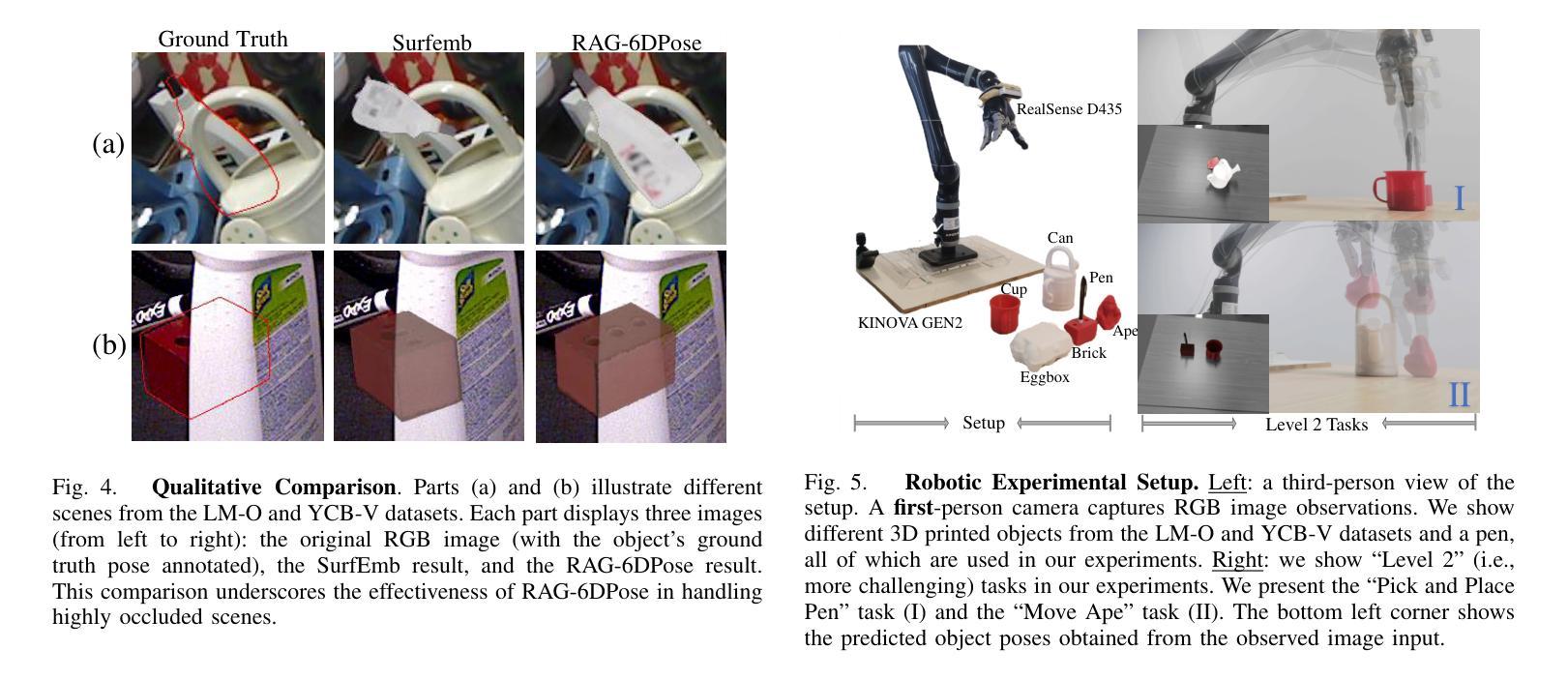
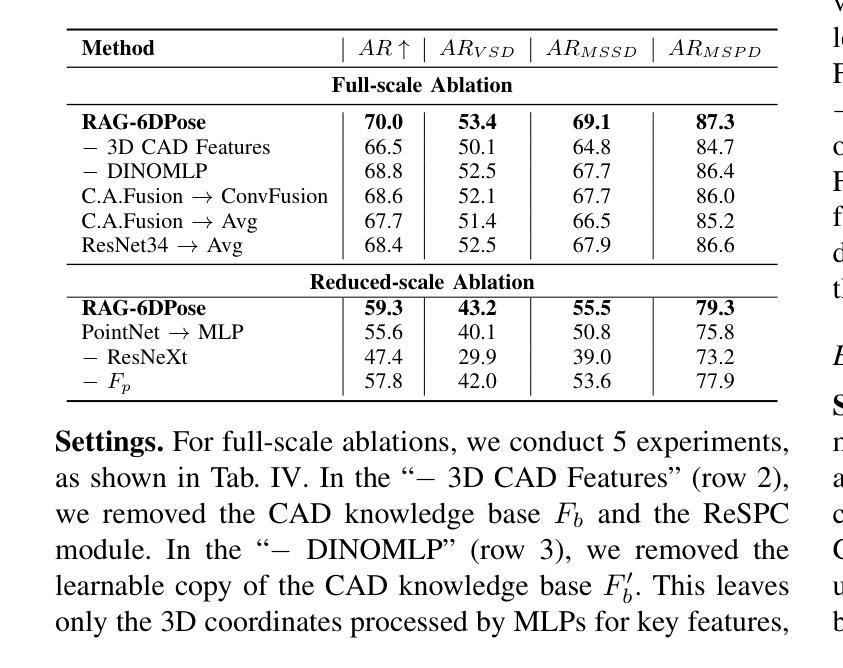
RAG-6DPose: Retrieval-Augmented 6D Pose Estimation via Leveraging CAD as Knowledge Base
Authors:Kuanning Wang, Yuqian Fu, Tianyu Wang, Yanwei Fu, Longfei Liang, Yu-Gang Jiang, Xiangyang Xue
Accurate 6D pose estimation is key for robotic manipulation, enabling precise object localization for tasks like grasping. We present RAG-6DPose, a retrieval-augmented approach that leverages 3D CAD models as a knowledge base by integrating both visual and geometric cues. Our RAG-6DPose roughly contains three stages: 1) Building a Multi-Modal CAD Knowledge Base by extracting 2D visual features from multi-view CAD rendered images and also attaching 3D points; 2) Retrieving relevant CAD features from the knowledge base based on the current query image via our ReSPC module; and 3) Incorporating retrieved CAD information to refine pose predictions via retrieval-augmented decoding. Experimental results on standard benchmarks and real-world robotic tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our approach, particularly in handling occlusions and novel viewpoints. Supplementary material is available on our project website: https://sressers.github.io/RAG-6DPose .
精确的6D姿态估计是机器人操作的关键,它为抓取等任务提供了精确的对象定位能力。我们提出了RAG-6DPose,这是一种增强检索的方法,它利用3D CAD模型作为知识库,通过融合视觉和几何线索。我们的RAG-6DPose大致包含三个阶段:1)通过建立多模态CAD知识库,从多视图CAD渲染图像中提取2D视觉特征,并附加3D点;2)通过我们的ReSPC模块,根据当前查询图像从知识库中检索相关的CAD特征;3)通过增强检索解码融合检索到的CAD信息来优化姿态预测。在标准基准测试和真实世界机器人任务上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性和稳健性,特别是在处理遮挡和新颖观点时。补充材料可在我们的项目网站上找到:https://sressers.github.io/RAG-6DPose。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IROS 2025
Summary
医学图像领域的研究人员提出了一种名为RAG-6DPose的新方法,用于增强机器人操作的精确性。该方法结合了视觉和几何线索,利用三维CAD模型作为知识库进行辅助检索,包括建立多模态CAD知识库、基于查询图像进行CAD特征检索以及利用检索到的CAD信息优化姿态预测三个阶段。该方法在标准基准和实际机器人任务上的实验结果表明,该方法在处理遮挡和新颖视角时具有有效性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- RAG-6DPose是一种用于机器人操作的姿态估计方法,重点在于精确的6D姿态估计。
- 该方法结合视觉和几何线索,利用三维CAD模型作为知识库。
- RAG-6DPose包括三个阶段:建立多模态CAD知识库、基于查询图像进行CAD特征检索以及利用检索到的CAD信息优化姿态预测。
- 通过实验验证,RAG-6DPose在标准基准测试和实际机器人任务中表现出有效性和稳健性。
- 该方法特别擅长处理遮挡和新颖视角的情况。
- RAG-6DPose方法的详细信息和补充材料可在项目网站上找到。
点此查看论文截图

Temporal Neural Cellular Automata: Application to modeling of contrast enhancement in breast MRI
Authors:Daniel M. Lang, Richard Osuala, Veronika Spieker, Karim Lekadir, Rickmer Braren, Julia A. Schnabel
Synthetic contrast enhancement offers fast image acquisition and eliminates the need for intravenous injection of contrast agent. This is particularly beneficial for breast imaging, where long acquisition times and high cost are significantly limiting the applicability of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a widespread screening modality. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of synthetic contrast generation. However, current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods lack sufficient measures for consistent temporal evolution. Neural cellular automata (NCA) offer a robust and lightweight architecture to model evolving patterns between neighboring cells or pixels. In this work we introduce TeNCA (Temporal Neural Cellular Automata), which extends and further refines NCAs to effectively model temporally sparse, non-uniformly sampled imaging data. To achieve this, we advance the training strategy by enabling adaptive loss computation and define the iterative nature of the method to resemble a physical progression in time. This conditions the model to learn a physiologically plausible evolution of contrast enhancement. We rigorously train and test TeNCA on a diverse breast MRI dataset and demonstrate its effectiveness, surpassing the performance of existing methods in generation of images that align with ground truth post-contrast sequences.
合成对比度增强技术可以快速获取图像,并消除了对静脉注入造影剂的需求。这对于乳腺成像特别有益,因为长时间的成像和高成本极大地限制了磁共振成像(MRI)作为广泛筛查方式的适用性。最近的研究已经证明了合成对比度生成的可行性。然而,当前最先进的方法缺乏一致的临时演变的足够措施。神经元细胞自动机(NCA)提供了一个稳健且轻量级的架构,用于模拟相邻细胞或像素之间的演变模式。在这项工作中,我们引入了TeNCA(时间神经元细胞自动机),它扩展并进一步完善了NCA,以有效地模拟时间上稀疏、非均匀采样的成像数据。为了实现这一点,我们通过启用自适应损失计算来改进训练策略,并定义方法的迭代性质以模仿时间的物理进展。这使模型学会对比增强在生理上的可能演变。我们在多样化的乳腺MRI数据集上对TeNCA进行了严格的训练和测试,并证明了其有效性,在生成与真实对比序列相符的图像方面超过了现有方法的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
合成对比增强技术能迅速获取图像,无需注射对比剂。对于乳腺成像而言,这一技术尤其有益,解决了磁共振成像(MRI)获取时间长、成本高昂的问题,限制了其作为广泛筛查手段的应用。本研究引入时序神经网络细胞自动机(TeNCA),结合神经网络细胞自动机(NCA)的优势,有效模拟时序稀疏、非均匀采样的成像数据。通过改进训练策略、定义迭代方法的物理时序性,使模型学习对比增强的生理演变过程。在多样的乳腺MRI数据集上,TeNCA表现卓越,超越现有方法的图像生成效果,与真实对比序列相符。
Key Takeaways
- 合成对比增强技术能迅速获取图像,无需注射对比剂,对乳腺成像有重要意义。
- 现有方法在处理时序稀疏、非均匀采样的成像数据时存在不足。
- 时序神经网络细胞自动机(TeNCA)结合神经网络细胞自动机(NCA)的优势,有效模拟这类数据。
- TeNCA通过改进训练策略,实现自适应损失计算,并定义方法的迭代性质以模拟物理时序过程。
- TeNCA模型能够学习对比增强的生理演变过程。
- 在乳腺MRI数据集上,TeNCA表现优越,超越现有方法的图像生成效果。
- TeNCA生成的图像与真实对比序列相符。
点此查看论文截图

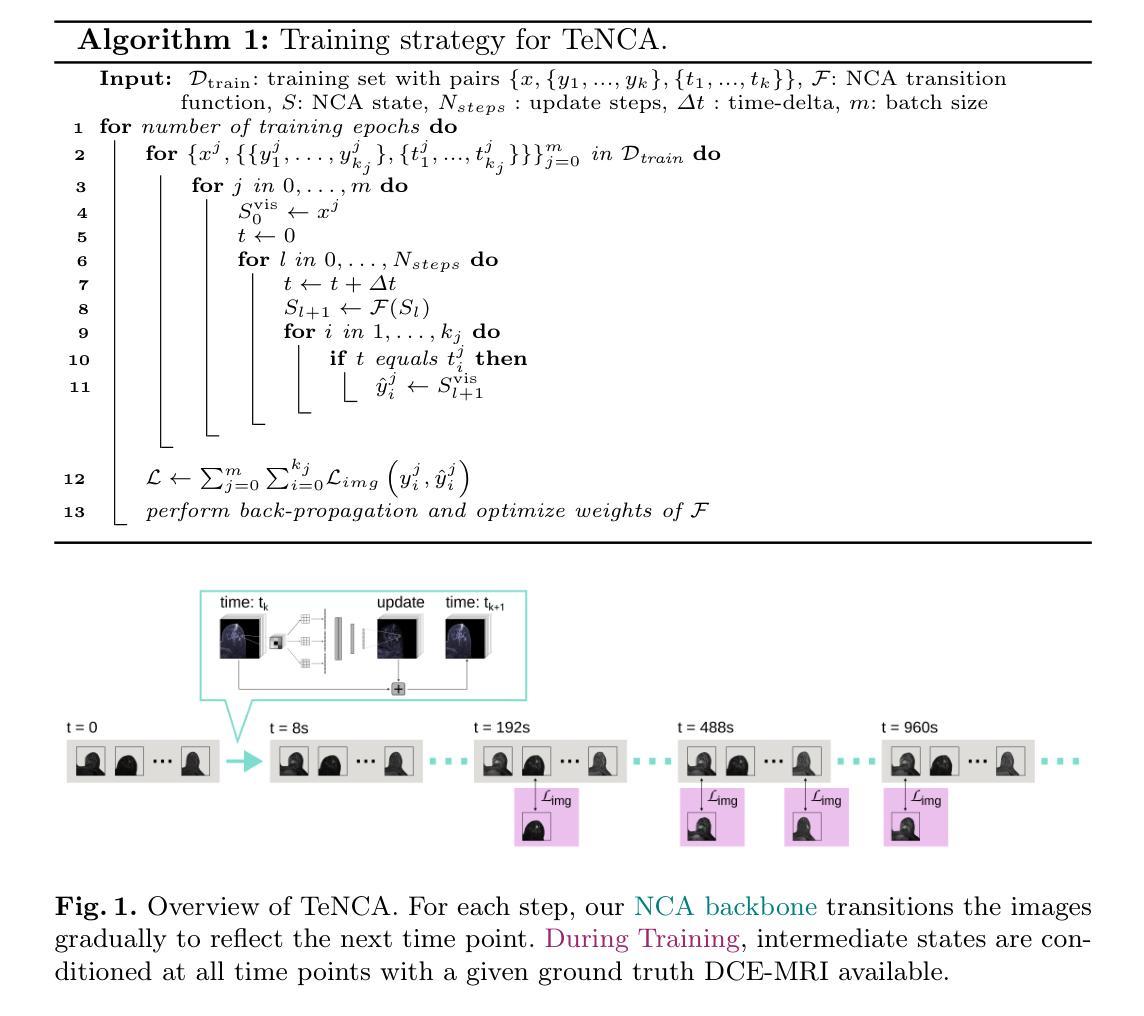
MARL-MambaContour: Unleashing Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Active Contour Optimization in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ruicheng Zhang, Yu Sun, Zeyu Zhang, Jinai Li, Xiaofan Liu, Au Hoi Fan, Haowei Guo, Puxin Yan
We introduce MARL-MambaContour, the first contour-based medical image segmentation framework based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). Our approach reframes segmentation as a multi-agent cooperation task focused on generate topologically consistent object-level contours, addressing the limitations of traditional pixel-based methods which could lack topological constraints and holistic structural awareness of anatomical regions. Each contour point is modeled as an autonomous agent that iteratively adjusts its position to align precisely with the target boundary, enabling adaptation to blurred edges and intricate morphologies common in medical images. This iterative adjustment process is optimized by a contour-specific Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm, further enhanced with the Entropy Regularization Adjustment Mechanism (ERAM) which dynamically balance agent exploration with contour smoothness. Furthermore, the framework incorporates a Mamba-based policy network featuring a novel Bidirectional Cross-attention Hidden-state Fusion Mechanism (BCHFM). This mechanism mitigates potential memory confusion limitations associated with long-range modeling in state space models, thereby facilitating more accurate inter-agent information exchange and informed decision-making. Extensive experiments on five diverse medical imaging datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of MARL-MambaContour, highlighting its potential as an accurate and robust clinical application.
我们引入了基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的首个轮廓基础医学图像分割框架——MARL-MambaContour。我们的方法将分割重新构建为一个多智能体合作任务,侧重于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓,解决了传统像素级方法可能缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知解剖区域的局限性。每个轮廓点都被建模为一个自主智能体,可以迭代调整其位置以精确与目标边界对齐,从而适应医学图像中常见的模糊边缘和复杂形态。这种迭代调整过程通过轮廓特定的柔性演员评论家(SAC)算法进行优化,通过熵正则化调整机制(ERAM)进一步增强,动态平衡智能体的探索与轮廓平滑度。此外,该框架采用基于Mamba的策略网络,并引入了一种新型双向交叉注意隐藏状态融合机制(BCHFM)。该机制缓解了状态空间模型中长程建模可能带来的潜在记忆混淆限制,从而促进了更准确的跨智能体信息交换和决策。在五个不同的医学成像数据集上的广泛实验证明了MARL-MambaContour的卓越性能,凸显了其在临床应用中作为准确且稳健工具的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MARL-MambaContour是首个基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的轮廓基础医学图像分割框架。它将分割重新构建为一个多智能体合作任务,侧重于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓,解决了传统像素级方法缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知区域的问题。
Key Takeaways
- MARL-MambaContour是首个基于Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL)的轮廓基础医学图像分割框架。
- 该方法将医学图像分割重新构建为多智能体合作任务,侧重于生成拓扑一致的物体轮廓。
- 传统像素级方法的局限性在于缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知区域的能力。
- 每个轮廓点被建模为一个自主智能体,可迭代调整其位置以精确对准目标边界。
- 采用了轮廓特定的Soft Actor-Critic (SAC)算法,并结合了��nropy Regularization Adjustment Mechanism (ERAM)来平衡智能体的探索与轮廓平滑。
- 框架中融入了Mamba策略网络,并引入了Bidirectional Cross-attention Hidden-state Fusion Mechanism (BCHFM)机制来解决长期建模中的潜在记忆混淆问题。
点此查看论文截图

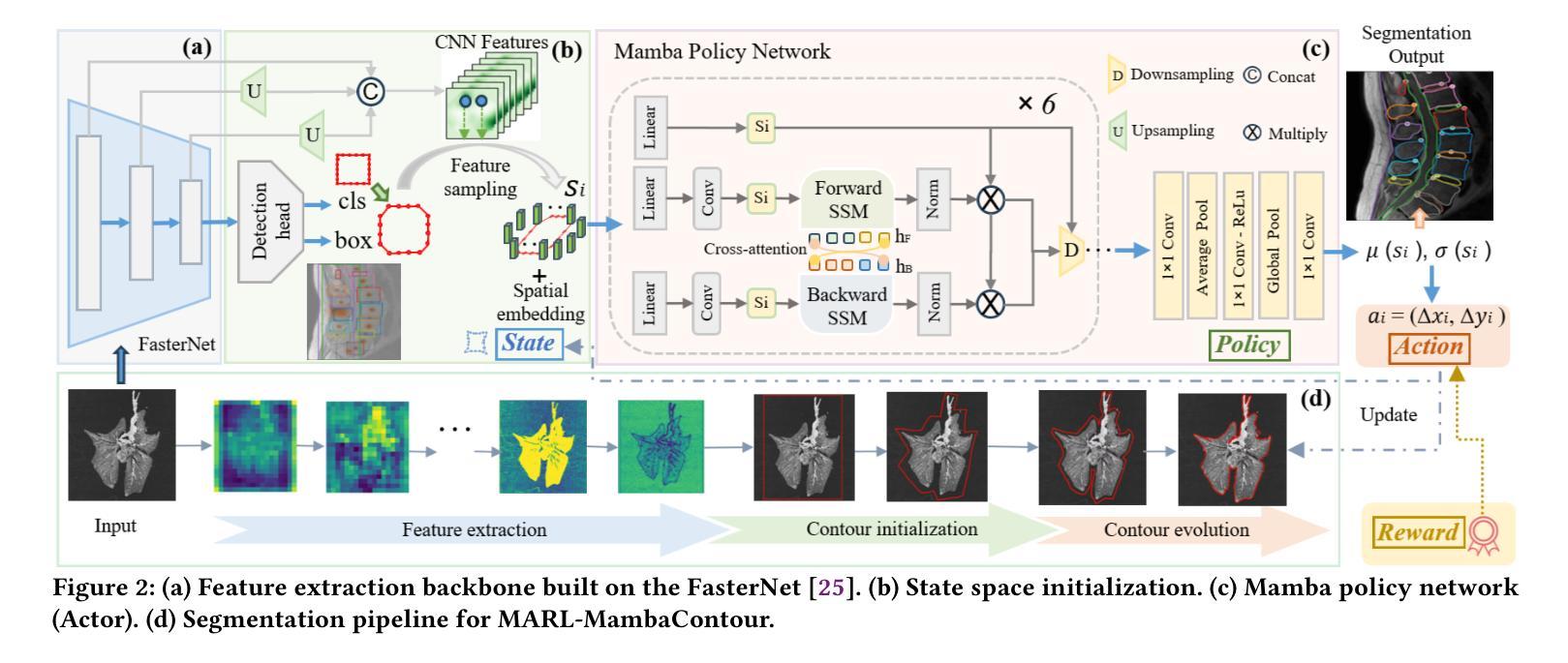
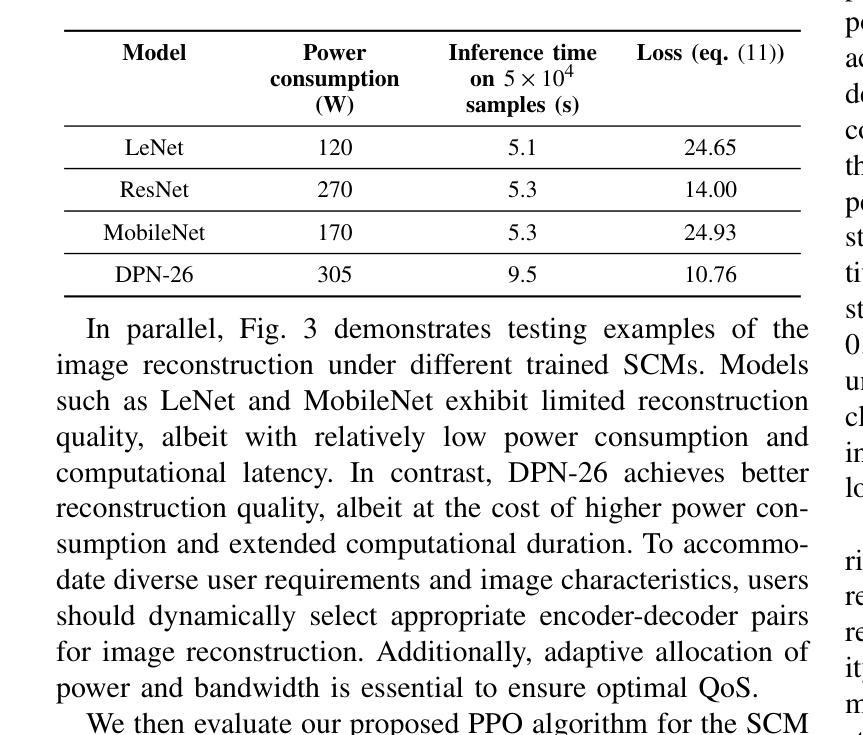
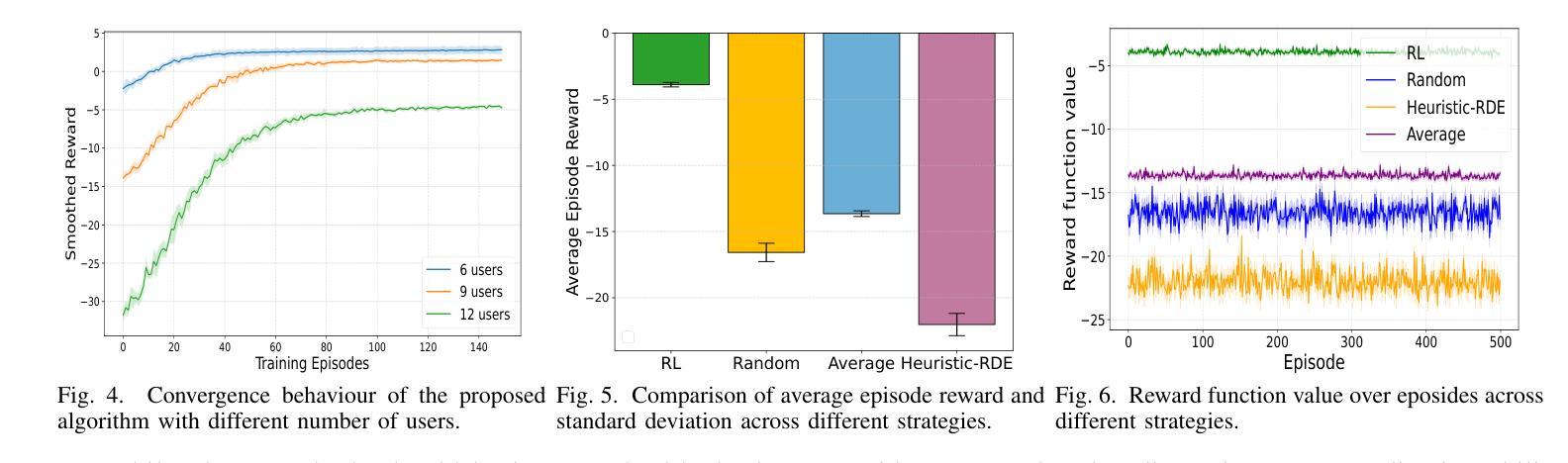
RL-Driven Semantic Compression Model Selection and Resource Allocation in Semantic Communication Systems
Authors:Xinyi Lin, Peizheng Li, Adnan Aijaz
Semantic communication (SemCom) is an emerging paradigm that leverages semantic-level understanding to improve communication efficiency, particularly in resource-constrained scenarios. However, existing SemCom systems often overlook diverse computational and communication capabilities and requirements among different users. Motivated by the need to adaptively balance semantic accuracy, latency, and energy consumption, this paper presents a reinforcement learning (RL)-driven framework for semantic compression model (SCM) selection and resource allocation in multi-user SemCom systems. To address the challenges of balancing image reconstruction quality and communication performance, a system-level optimization metric called Rate-Distortion Efficiency (RDE) has been defined. The framework considers multiple SCMs with varying complexity and resource requirements. A proximal policy optimization (PPO)-based RL approach is developed to dynamically select SCMs and allocate bandwidth and power under non-convex constraints. Simulations demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms several baseline strategies. This paper also discusses the generalization ability, computational complexity, scalability, and practical implications of the framework for real-world SemCom systems.
语义通信(SemCom)是一种新兴范式,利用语义级理解来提高通信效率,特别是在资源受限的场景中。然而,现有的SemCom系统往往忽视了不同用户之间计算和通信能力的多样性和要求。为了自适应地平衡语义准确性、延迟和能耗的需求,本文提出了一种基于强化学习(RL)的语义压缩模型(SCM)选择及多用户SemCom系统中资源分配的框架。为了解决图像重建质量与通信性能之间的平衡挑战,定义了一种系统级优化指标——速率失真效率(RDE)。该框架考虑了具有不同复杂度和资源要求的多个SCM。开发了一种基于近端策略优化(PPO)的RL方法,以在非线性约束下动态选择SCM并分配带宽和功率。模拟结果表明,所提出的方法优于几种基线策略。本文还讨论了该框架在现实世界SemCom系统中的泛化能力、计算复杂性、可扩展性和实际影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by PIMRC 2025
Summary
语义通信(SemCom)利用语义级理解提高通信效率,尤其在资源受限场景中。当前SemCom系统忽视了不同用户的计算和通信能力差异。为平衡语义准确性、延迟和能耗,本文提出一种基于强化学习(RL)的语义压缩模型(SCM)选择及资源分配框架。为解决图像重建质量与通信性能平衡问题,定义了系统级优化指标——速率失真效率(RDE)。框架考虑多种不同复杂度和资源需求的SCM。采用基于近端策略优化(PPO)的RL方法,在非线性约束下动态选择SCM并分配带宽和功率。模拟结果表明,该方法优于多种基线策略,并讨论了框架的通用性、计算复杂性、可扩展性和对实际SemCom系统的实践意义。
Key Takeaways
- SemCom利用语义级理解提高通信效率,特别是在资源受限环境中。
- 当前SemCom系统忽略了不同用户之间的计算和通信能力差异。
- 为平衡语义准确性、延迟和能耗,提出了一个基于强化学习的框架。
- 定义了系统级优化指标——速率失真效率(RDE)以平衡图像重建质量和通信性能。
- 框架考虑了多种不同复杂度和资源需求的语义压缩模型(SCM)。
- 采用基于近端策略优化(PPO)的RL方法,动态选择SCM并分配资源。
点此查看论文截图

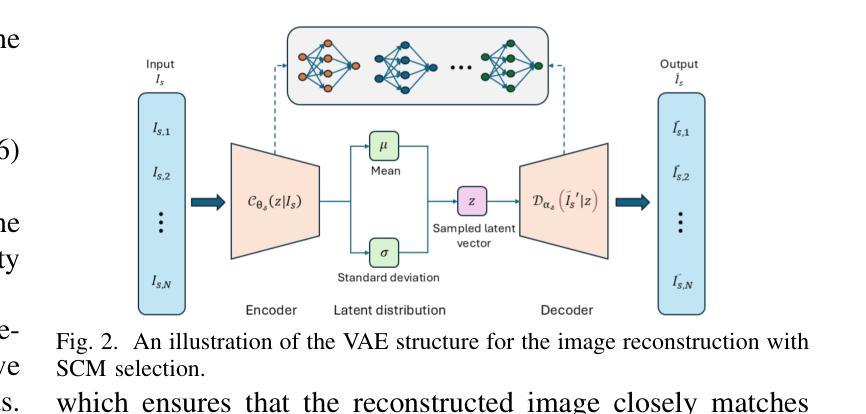

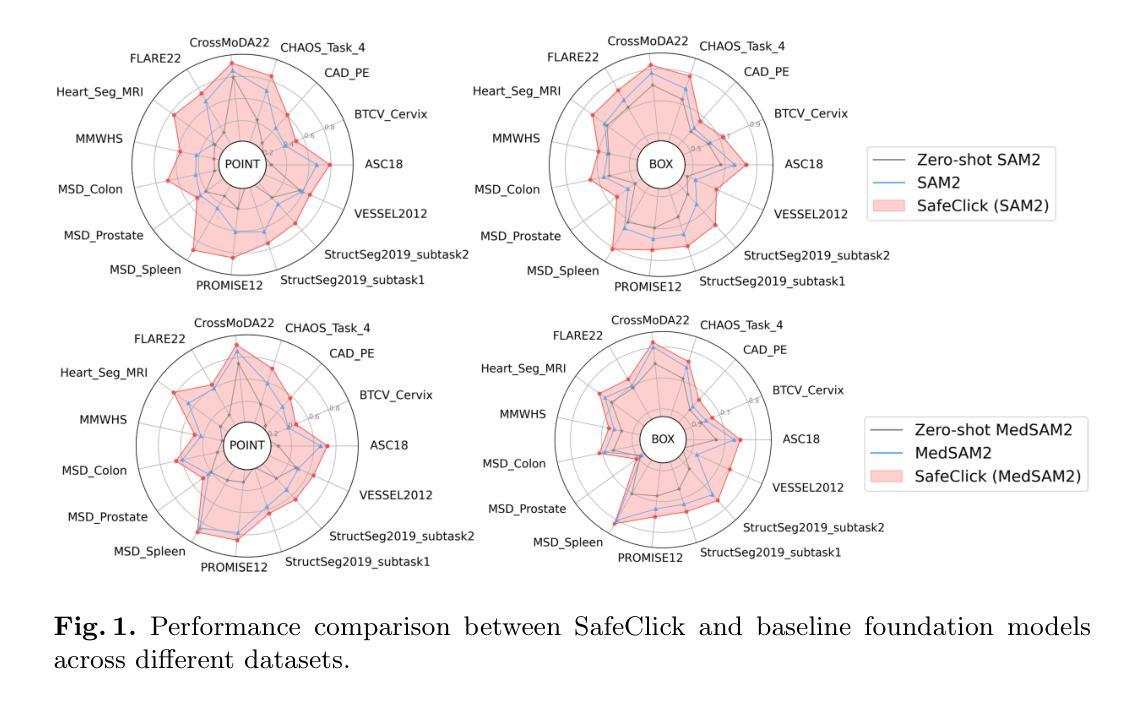
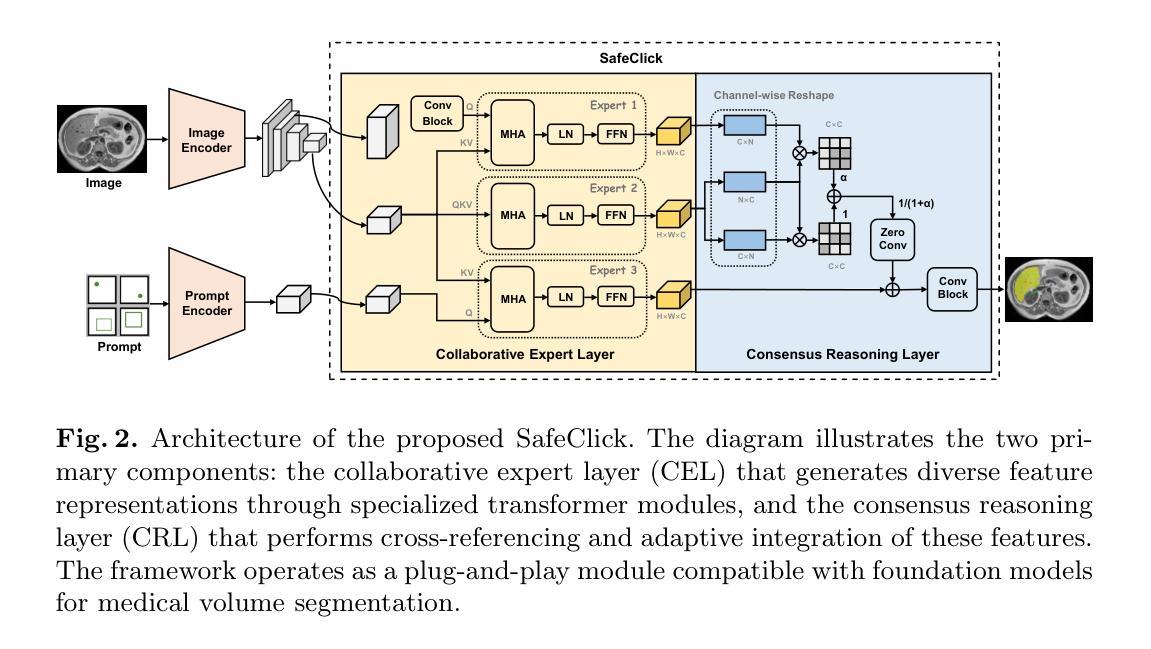
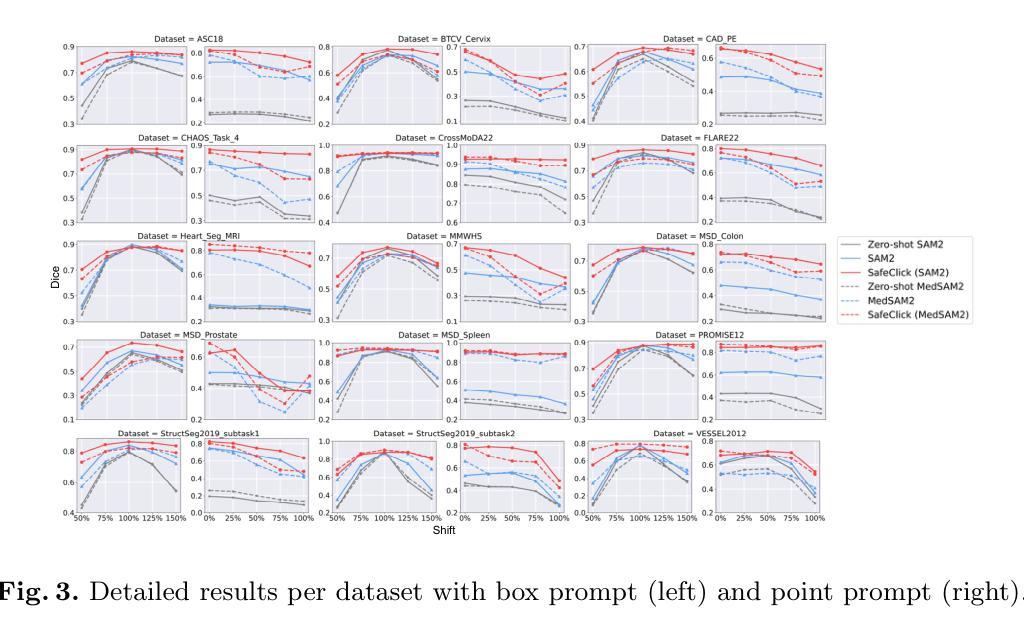
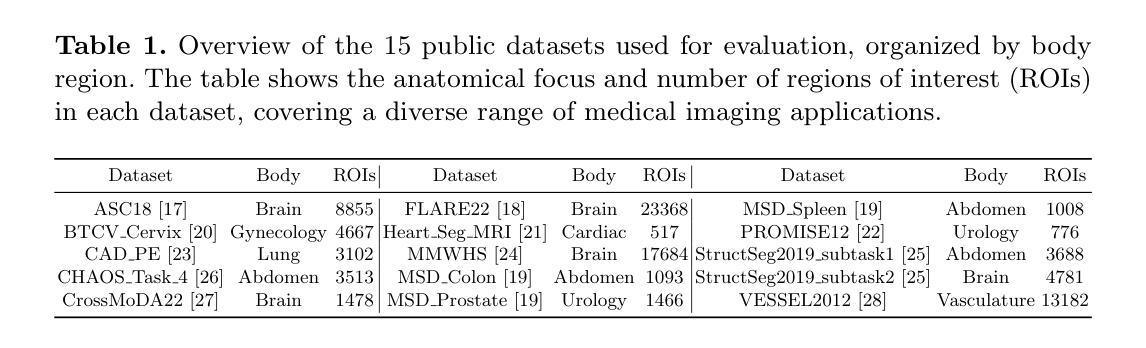
SafeClick: Error-Tolerant Interactive Segmentation of Any Medical Volumes via Hierarchical Expert Consensus
Authors:Yifan Gao, Jiaxi Sheng, Wenbin Wu, Haoyue Li, Yaoxian Dong, Chaoyang Ge, Feng Yuan, Xin Gao
Foundation models for volumetric medical image segmentation have emerged as powerful tools in clinical workflows, enabling radiologists to delineate regions of interest through intuitive clicks. While these models demonstrate promising capabilities in segmenting previously unseen anatomical structures, their performance is strongly influenced by prompt quality. In clinical settings, radiologists often provide suboptimal prompts, which affects segmentation reliability and accuracy. To address this limitation, we present SafeClick, an error-tolerant interactive segmentation approach for medical volumes based on hierarchical expert consensus. SafeClick operates as a plug-and-play module compatible with foundation models including SAM 2 and MedSAM 2. The framework consists of two key components: a collaborative expert layer (CEL) that generates diverse feature representations through specialized transformer modules, and a consensus reasoning layer (CRL) that performs cross-referencing and adaptive integration of these features. This architecture transforms the segmentation process from a prompt-dependent operation to a robust framework capable of producing accurate results despite imperfect user inputs. Extensive experiments across 15 public datasets demonstrate that our plug-and-play approach consistently improves the performance of base foundation models, with particularly significant gains when working with imperfect prompts. The source code is available at https://github.com/yifangao112/SafeClick.
医学图像分割中的基础模型已经作为强大的工具应用于临床工作流程中,使放射科医生能够通过直观点击来划分感兴趣区域。虽然这些模型在分割以前未见过的解剖结构上显示出有前景的能力,但它们的性能受到提示质量的影响。在临床环境中,放射科医生经常提供次优提示,这会影响分割的可靠性和准确性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SafeClick,这是一种基于分层专家共识的容错交互式分割方法,用于医学图像卷积。SafeClick可以作为与基础模型(包括SAM 2和MedSAM 2)兼容的即插即用模块运行。该框架由两个关键组件组成:一个协作专家层(CEL),它通过专用变压器模块生成多样化的特征表示;一个共识推理层(CRL),它执行这些特征的交叉引用和自适应集成。这种架构将分割过程从依赖于提示的操作转变为一个稳健的框架,即使在不完美的用户输入情况下,也能产生准确的结果。在15个公共数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的即插即用方法不断改进基础模型的性能,特别是在处理不完美的提示时获得了特别显著的收益。源代码可在https://github.com/yifangao1d处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
摘要
基于分层专家共识的SafeClick错误容忍交互分割方法,提升了医学体积图像分割的可靠性及准确性。SafeClick作为模块即插即用,可与SAM 2和MedSAM 2等基准模型兼容。其包括协作专家层(CEL)与共识推理层(CRL)。CEL通过特殊transformer模块生成多样化特征表示,CRL则进行特征交叉引用和自适应集成。SafeClick将依赖提示的分割过程转变为稳健框架,可产出准确结果,即使面对不完美的用户输入。在15个公开数据集上的广泛实验显示,该即插即用方法持续提升了基础模型的性能,在不完美提示下表现尤为突出。源码已上传至链接。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割模型已成为临床流程中的强大工具,使放射科医生能够通过直观点击划分感兴趣区域。
- 尽管这些模型在分割未见解剖结构方面显示出巨大潜力,但其性能强烈受到提示质量的影响。
- 在临床环境中,放射科医生提供的提示通常不理想,影响分割的可靠性和准确性。
- SafeClick方法通过分层专家共识解决了这一问题,包括协作专家层和共识推理层。
- SafeClick作为模块即插即用,与现有基准模型兼容,可生成多样化特征表示并进行交叉引用和自适应集成。
- SafeClick将依赖提示的分割过程转变为稳健框架,即使面对不完美的用户输入也能产生准确结果。
点此查看论文截图

Taming Vision-Language Models for Medical Image Analysis: A Comprehensive Review
Authors:Haoneng Lin, Cheng Xu, Jing Qin
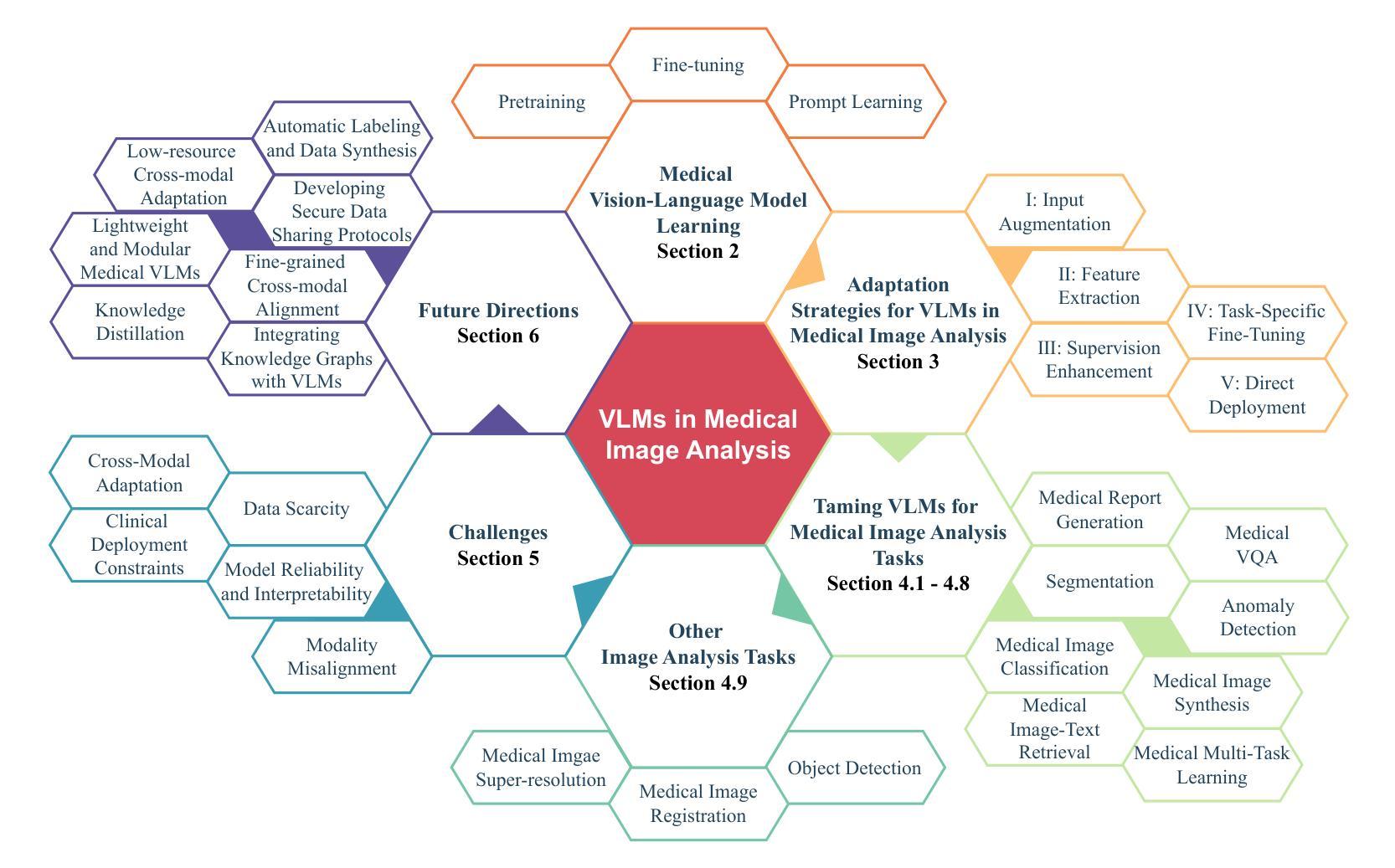
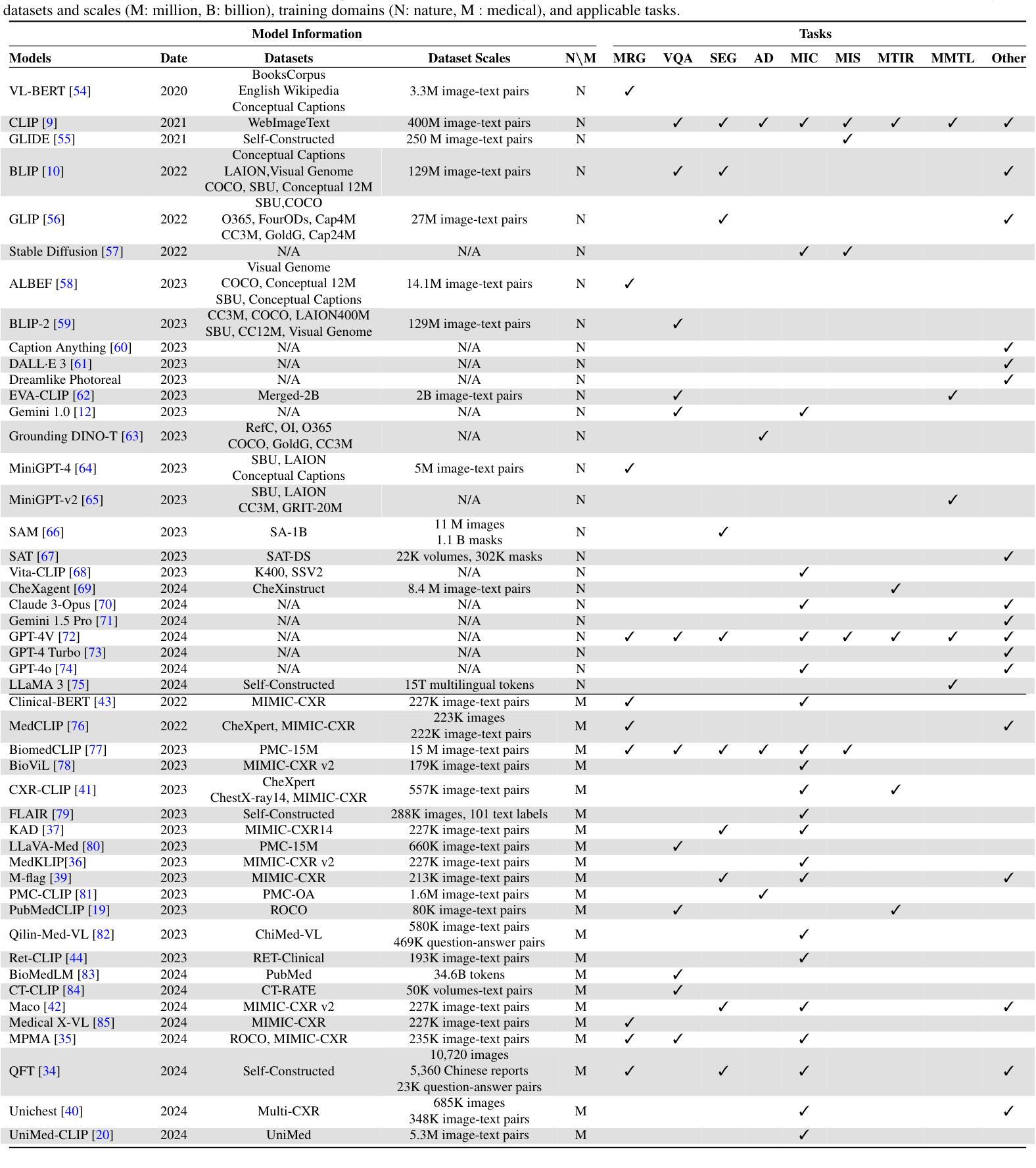
Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit unprecedented capabilities in cross-modal semantic understanding between visual and textual modalities. Given the intrinsic need for multi-modal integration in clinical applications, VLMs have emerged as a promising solution for a wide range of medical image analysis tasks. However, adapting general-purpose VLMs to medical domain poses numerous challenges, such as large domain gaps, complicated pathological variations, and diversity and uniqueness of different tasks. The central purpose of this review is to systematically summarize recent advances in adapting VLMs for medical image analysis, analyzing current challenges, and recommending promising yet urgent directions for further investigations. We begin by introducing core learning strategies for medical VLMs, including pretraining, fine-tuning, and prompt learning. We then categorize five major VLM adaptation strategies for medical image analysis. These strategies are further analyzed across eleven medical imaging tasks to illustrate their current practical implementations. Furthermore, we analyze key challenges that impede the effective adaptation of VLMs to clinical applications and discuss potential directions for future research. We also provide an open-access repository of related literature to facilitate further research, available at https://github.com/haonenglin/Awesome-VLM-for-MIA. It is anticipated that this article can help researchers who are interested in harnessing VLMs in medical image analysis tasks have a better understanding on their capabilities and limitations, as well as current technical barriers, to promote their innovative, robust, and safe application in clinical practice.
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视觉和文本模态之间的跨模态语义理解方面展现出了前所未有的能力。考虑到临床应用中对多模态集成的内在需求,VLMs已经作为一种有前景的解决方案广泛应用于医学影像分析任务。然而,将通用VLMs适应于医学领域面临着诸多挑战,如领域差距大、病理变化复杂以及不同任务的多样性和独特性。本文的中心目的是系统地总结近期将VLMs应用于医学影像分析的进展,分析当前面临的挑战,并为进一步的调查推荐有前景且紧迫的方向。我们首先介绍医学VLMs的核心学习策略,包括预训练、微调、提示学习。然后我们将五大VLM适应策略分类为医学影像分析,并进一步在十一个医学影像任务中分析了这些策略的实际应用情况。此外,我们还分析了阻碍VLMs有效适应临床应用的关键挑战,并讨论了未来研究的方向。我们还提供了一个开放访问的相关文献仓库,以促进进一步的研究,可通过https://github.com/haonenglin/Awesome-VLM-for-MIA访问。预计本文能帮助对在医学影像分析任务中使用VLMs感兴趣的研究人员更好地了解它们的能力、局限性以及当前的技术障碍,以促进其在临床实践中的创新、稳健和安全应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 34 pages
Summary
本文综述了现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学图像分析领域的最新进展,介绍了五大医学图像分析领域的VLM适应策略,分析了当前面临的挑战,并探讨了未来研究的潜在方向。本文旨在帮助研究人员更好地了解VLMs在医学图像分析任务中的能力和局限性,以及当前的技术障碍,以促进其在临床实践中的创新、稳健和安全应用。
Key Takeaways
- 现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在跨模态语义理解方面具有前所未有的能力,为医学图像分析任务提供了有前景的解决方案。
- VLMs在医学领域面临诸多挑战,如领域差距大、病理变化复杂以及任务的多样性和独特性。
- 核心学习策略包括预训练、微调、提示学习等。
- VLM适应策略主要分为五大类,并在十一个医学成像任务中进行了实践应用。
- 当前挑战包括如何有效适应医学应用,未来的研究方向包括改进模型性能、增强可解释性和鲁棒性等。
- 文献库可通过链接访问,便于进一步研究。
点此查看论文截图

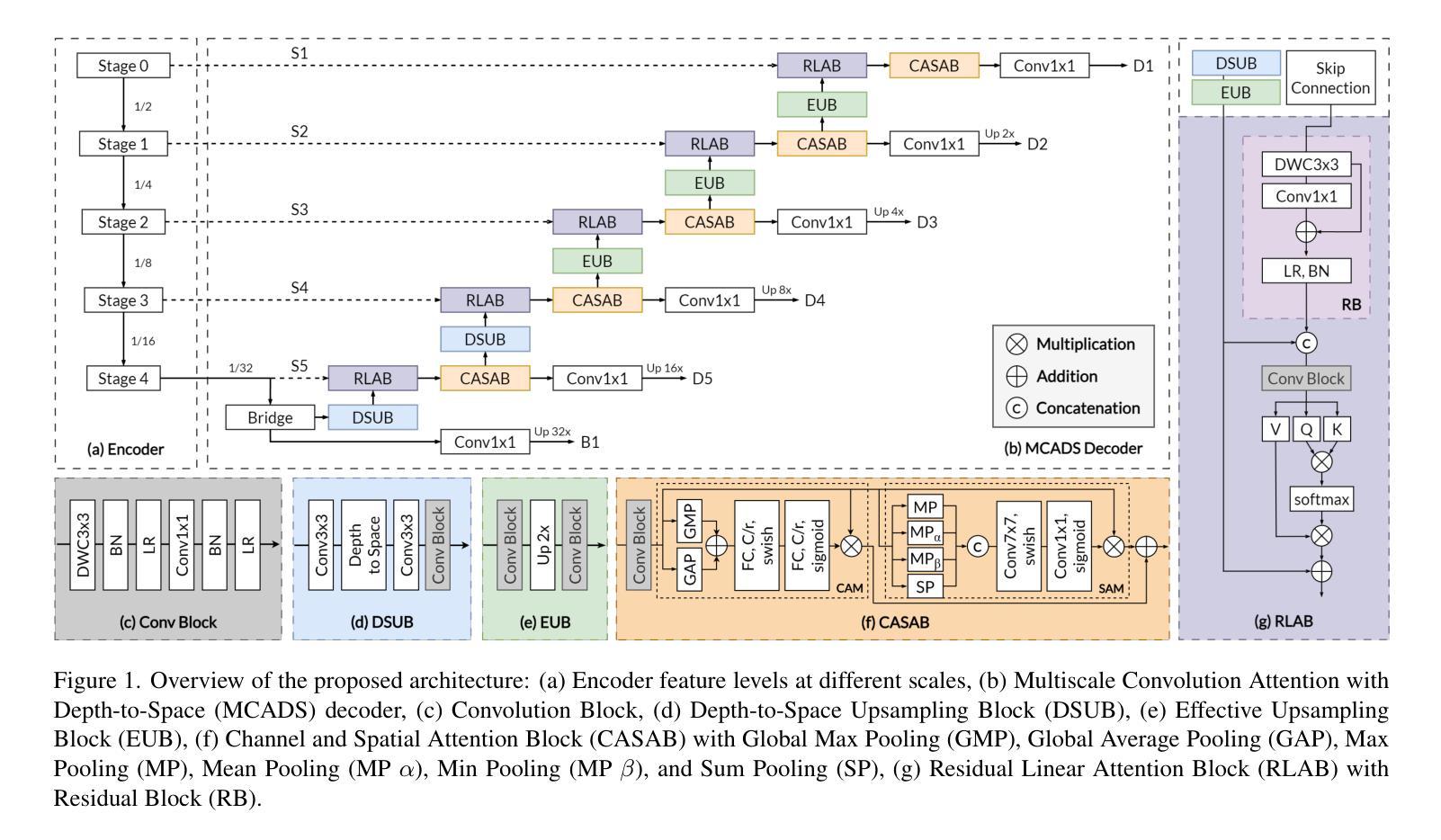
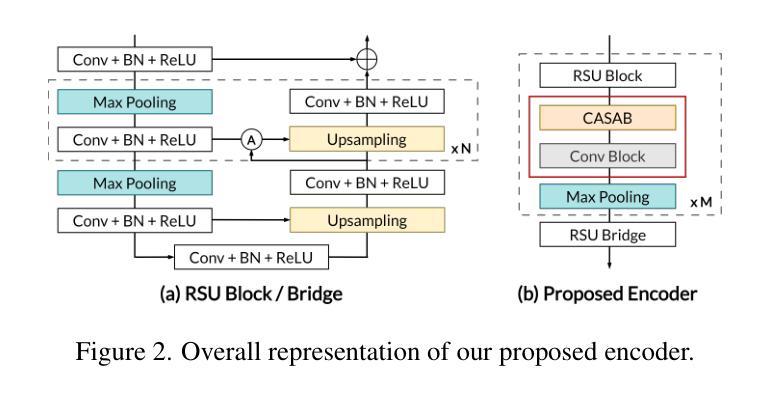
Rethinking Decoder Design: Improving Biomarker Segmentation Using Depth-to-Space Restoration and Residual Linear Attention
Authors:Saad Wazir, Daeyoung Kim
Segmenting biomarkers in medical images is crucial for various biotech applications. Despite advances, Transformer and CNN based methods often struggle with variations in staining and morphology, limiting feature extraction. In medical image segmentation, where datasets often have limited sample availability, recent state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods achieve higher accuracy by leveraging pre-trained encoders, whereas end-to-end methods tend to underperform. This is due to challenges in effectively transferring rich multiscale features from encoders to decoders, as well as limitations in decoder efficiency. To address these issues, we propose an architecture that captures multi-scale local and global contextual information and a novel decoder design, which effectively integrates features from the encoder, emphasizes important channels and regions, and reconstructs spatial dimensions to enhance segmentation accuracy. Our method, compatible with various encoders, outperforms SOTA methods, as demonstrated by experiments on four datasets and ablation studies. Specifically, our method achieves absolute performance gains of 2.76% on MoNuSeg, 3.12% on DSB, 2.87% on Electron Microscopy, and 4.03% on TNBC datasets compared to existing SOTA methods. Code: https://github.com/saadwazir/MCADS-Decoder
在医学图像中分割生物标志物对于各种生物技术应用至关重要。尽管有所进展,基于Transformer和CNN的方法仍然经常面临染色和形态变化带来的挑战,限制了特征提取。在医学图像分割中,由于数据集通常样本有限,最近的最先进方法通过利用预训练编码器实现更高的准确性,而端到端的方法往往表现不佳。这是由于从编码器到解码器有效传输丰富的多尺度特征的挑战以及解码器效率的局限性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种架构,该架构能够捕获多尺度局部和全局上下文信息,以及一种新型解码器设计,该解码器能够有效地整合来自编码器的特征,强调重要的通道和区域,并重建空间维度以提高分割准确性。我们的方法与各种编码器兼容,通过四个数据集和消融研究进行的实验证明,我们的方法超越了最先进的方法。具体来说,我们的方法在MoNuSeg数据集上实现了对现有先进方法2.76%的绝对性能提升,在DSB数据集上实现了3.12%的提升,在电子显微镜数据集上实现了2.87%的提升,并在TNBC数据集上实现了4.03%的提升。代码地址:https://github.com/saadwazir/MCADS-Decoder
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), 2025, pp. 30861-30871
Summary
医学图像中的生物标志物分割对于多种生物技术应用至关重要。现有方法面临染色和形态变化挑战,以及数据集样本有限的问题。为提升分割精度,我们提出了一种新型架构和解码器设计,能捕捉多尺度局部和全局上下文信息,并有效整合编码器特征。该方法兼容多种编码器,在四个数据集上的表现均超越现有最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中的生物标志物分割对生物技术应用非常重要。
- 当前方法面临染色和形态变化挑战以及数据集样本有限的问题。
- 提出了一种新型架构和解码器设计以解决上述问题。
- 该方法能捕捉多尺度局部和全局上下文信息。
- 有效整合编码器特征,提升分割精度。
- 方法兼容多种编码器,表现优于现有最先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

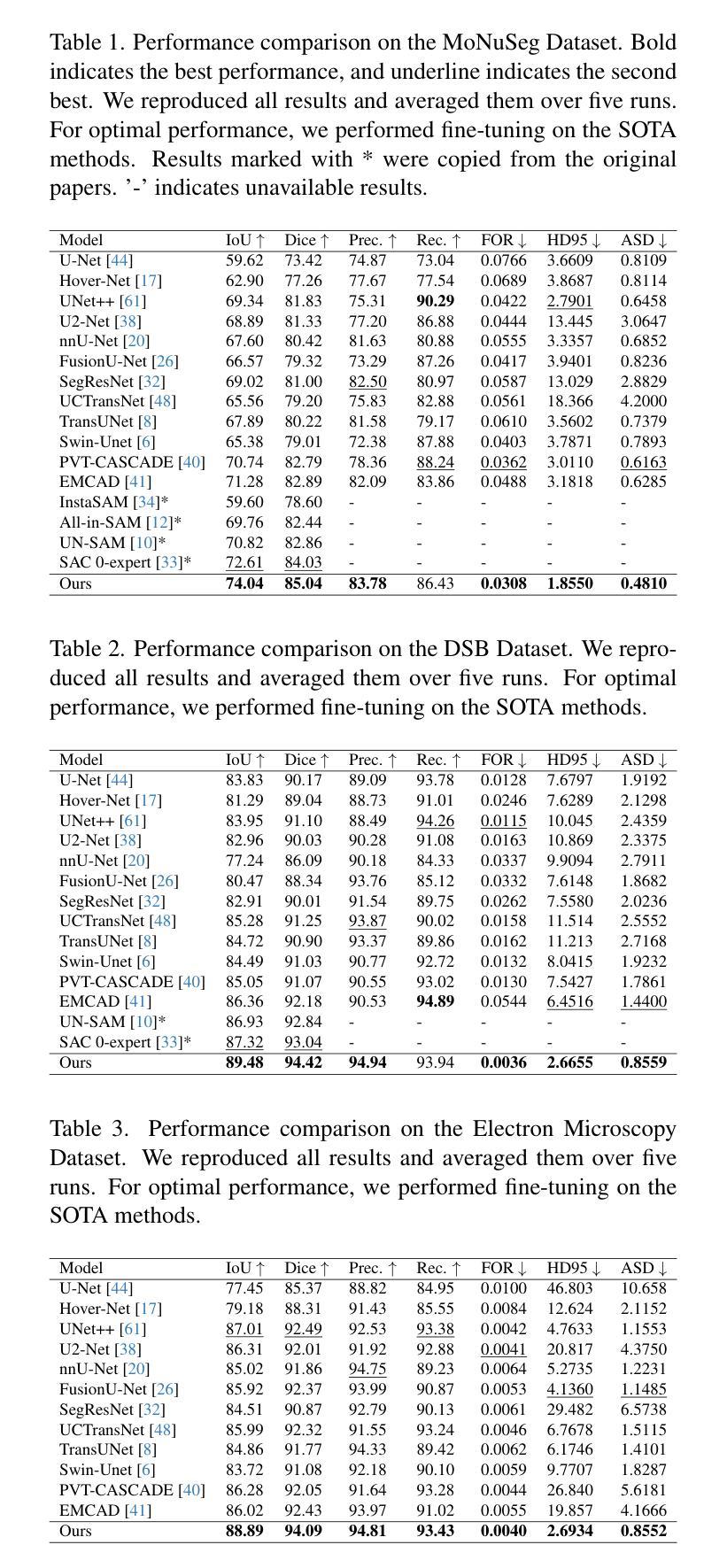
BrainSymphony: A Transformer-Driven Fusion of fMRI Time Series and Structural Connectivity
Authors:Moein Khajehnejad, Forough Habibollahi, Adeel Razi
Existing foundation models for neuroimaging are often prohibitively large and data-intensive. We introduce BrainSymphony, a lightweight, parameter-efficient foundation model that achieves state-of-the-art performance while being pre-trained on significantly smaller public datasets. BrainSymphony’s strong multimodal architecture processes functional MRI data through parallel spatial and temporal transformer streams, which are then efficiently distilled into a unified representation by a Perceiver module. Concurrently, it models structural connectivity from diffusion MRI using a novel signed graph transformer to encode the brain’s anatomical structure. These powerful, modality-specific representations are then integrated via an adaptive fusion gate. Despite its compact design, our model consistently outperforms larger models on a diverse range of downstream benchmarks, including classification, prediction, and unsupervised network identification tasks. Furthermore, our model revealed novel insights into brain dynamics using attention maps on a unique external psilocybin neuroimaging dataset (pre- and post-administration). BrainSymphony establishes that architecturally-aware, multimodal models can surpass their larger counterparts, paving the way for more accessible and powerful research in computational neuroscience.
现有的神经成像基础模型通常规模庞大且数据密集。我们推出了BrainSymphony,这是一个轻量级、参数高效的基础模型,它在较小的公共数据集上进行预训练即可实现最先进的性能。BrainSymphony强大的多模态架构通过并行空间和时间转换器流处理功能磁共振成像数据,然后通过感知器模块有效地蒸馏成统一表示。同时,它使用新型符号图变换器对扩散磁共振成像进行结构连接建模,以编码大脑的结构。这些强大且针对特定模态的表示然后通过自适应融合门进行集成。尽管设计紧凑,我们的模型在多种下游基准测试上始终表现出色,包括分类、预测和无监督网络识别任务。此外,我们的模型利用独特的外源性迷幻菇神经成像数据集(给药前后的数据)的注意力图揭示了大脑动态的全新见解。BrainSymphony证明,结构感知的多模态模型可以超越其大型同类模型,为计算神经科学的研究开辟更加便捷和强大的道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 8 figures
Summary
BrainSymphony是一个轻量级、参数高效的神经影像基础模型,可在较小的公共数据集上进行预训练,实现最先进的性能。它通过并行空间和时间转换器流处理功能磁共振成像数据,并由感知器模块有效地蒸馏成统一表示。同时,它通过签名的图变换器对扩散磁共振成像的结构连通性进行建模,以编码大脑的解剖结构。这些强大而特定的表示形式通过自适应融合门进行集成。尽管设计紧凑,该模型在包括分类、预测和无监督网络识别任务在内的各种下游基准测试中始终表现出超越大型模型的性能。此外,该模型利用独特的外部裸盖酰二胺酸神经成像数据集上的注意力地图揭示了大脑动态的全新见解,为计算神经科学的研究开辟了更加便捷和强大的道路。
Key Takeaways
- BrainSymphony是一个轻量级、参数高效的基础模型,适用于神经影像研究。
- 它通过并行空间和时间转换器处理功能磁共振成像数据,实现高效的数据表示。
- 模型采用感知器模块将不同表示形式统一起来。
- 通过签名的图变换器对扩散磁共振成像的结构连通性进行建模。
- 该模型通过自适应融合门集成多种表示形式。
- 在多种下游任务中表现优秀,包括分类、预测和无监督网络识别等。
点此查看论文截图

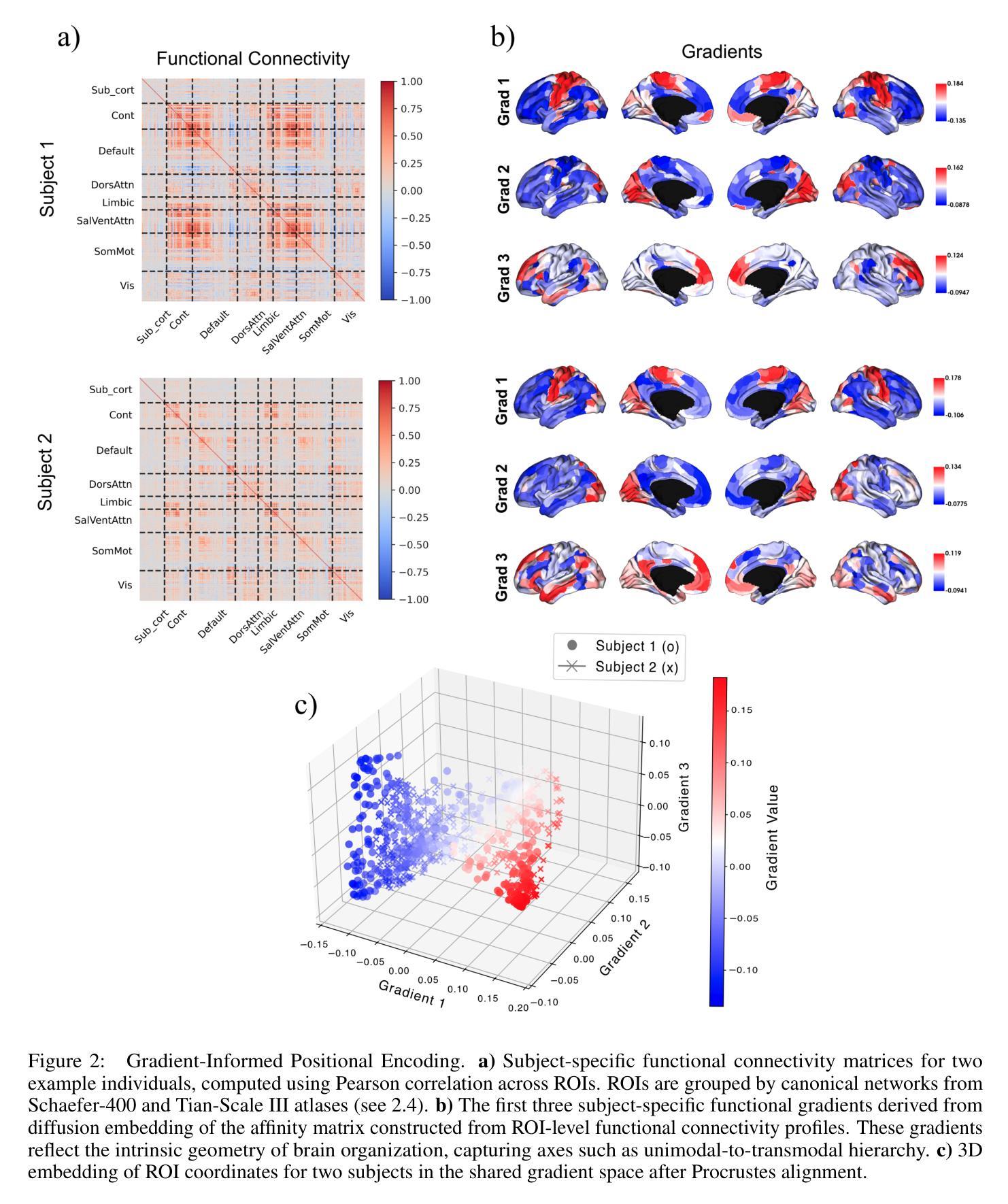
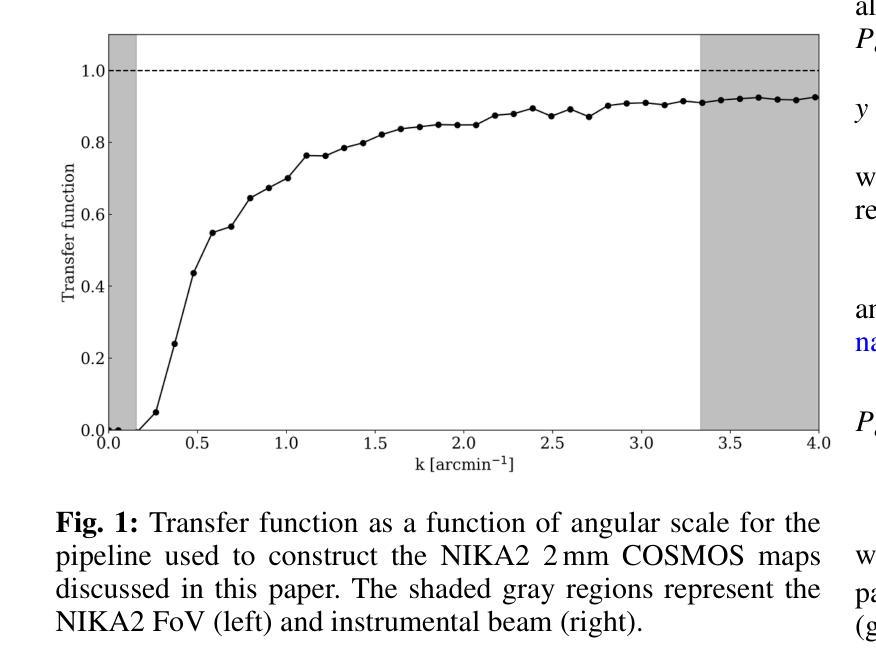
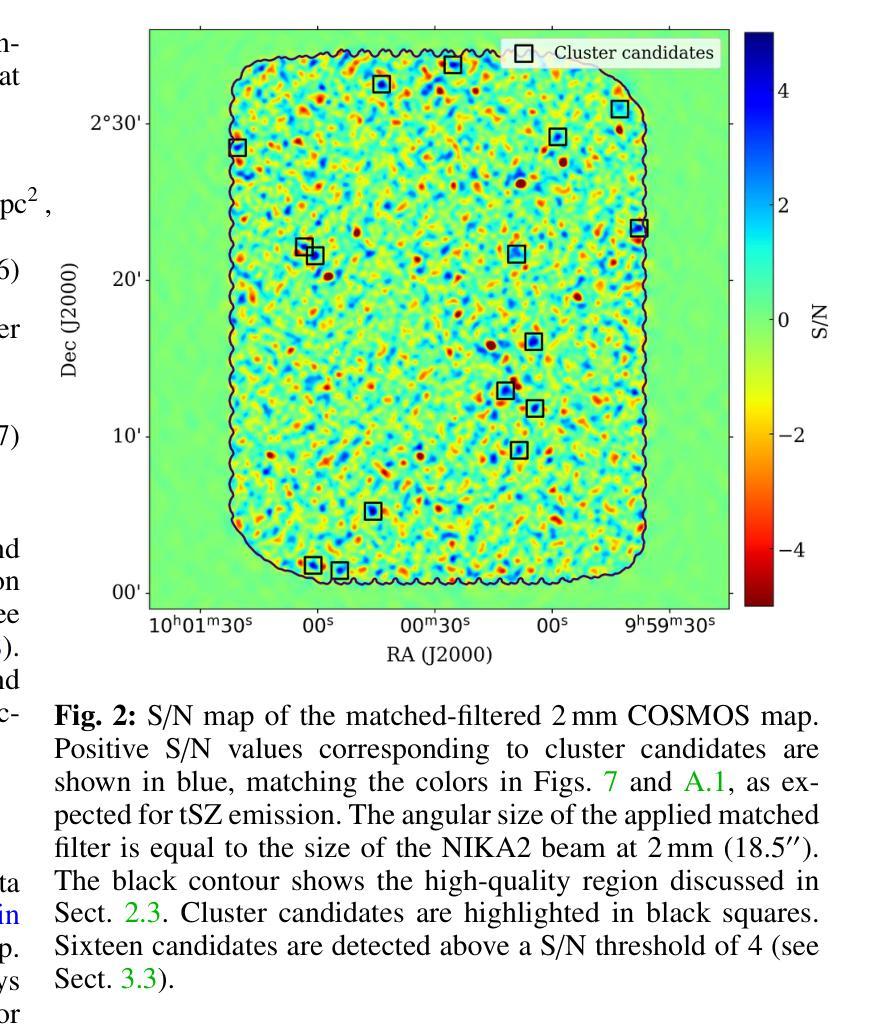
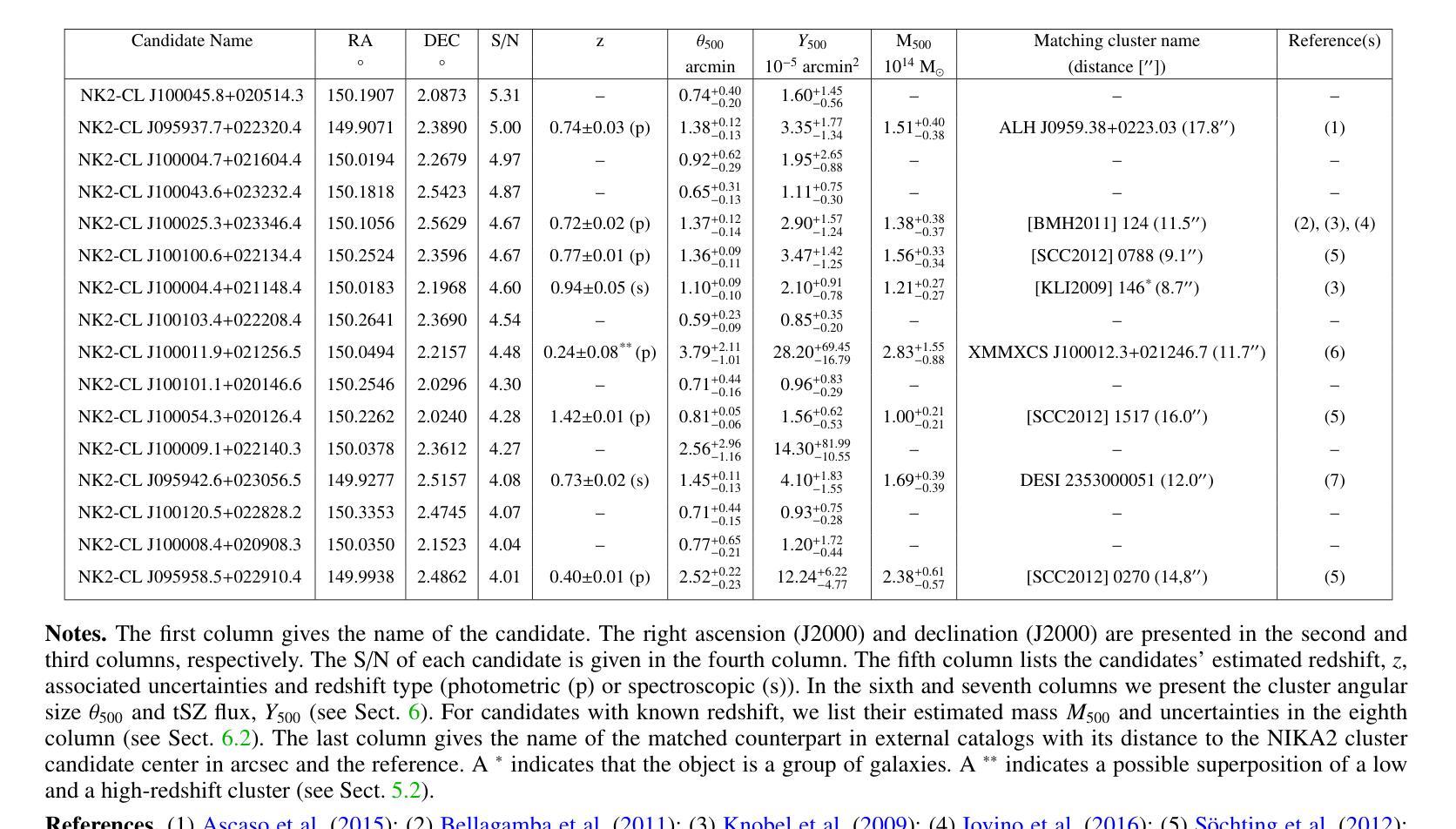
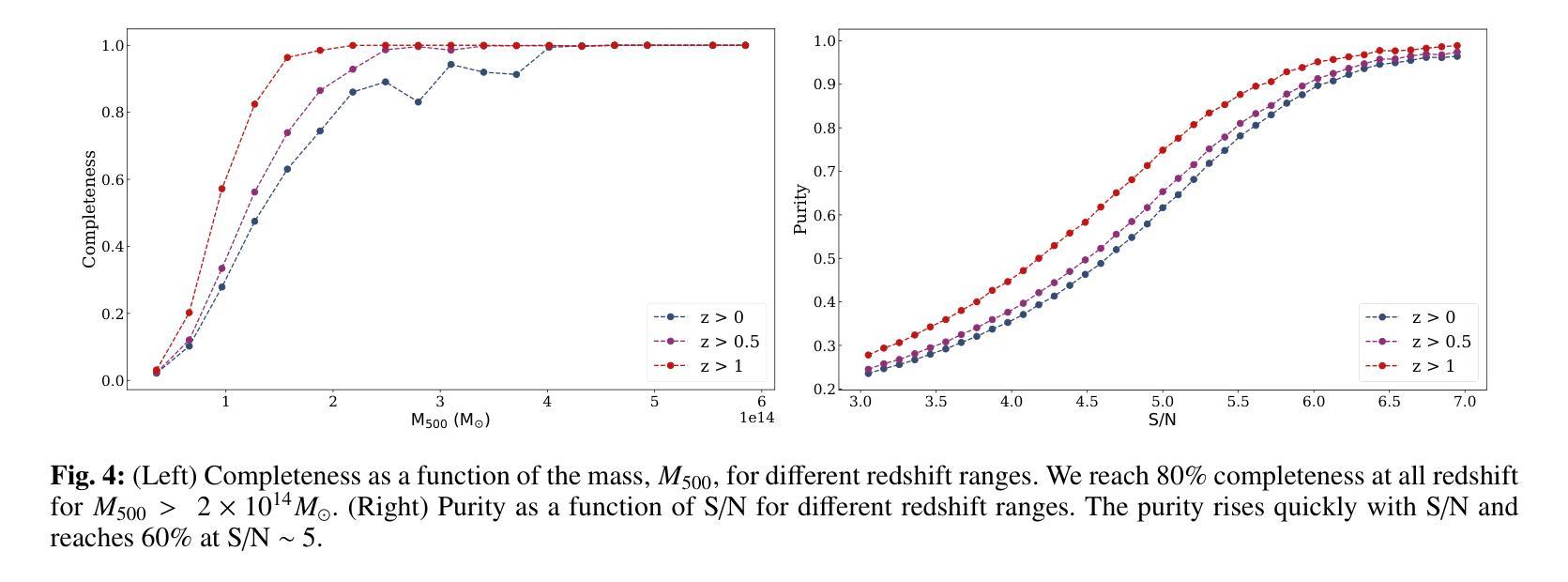
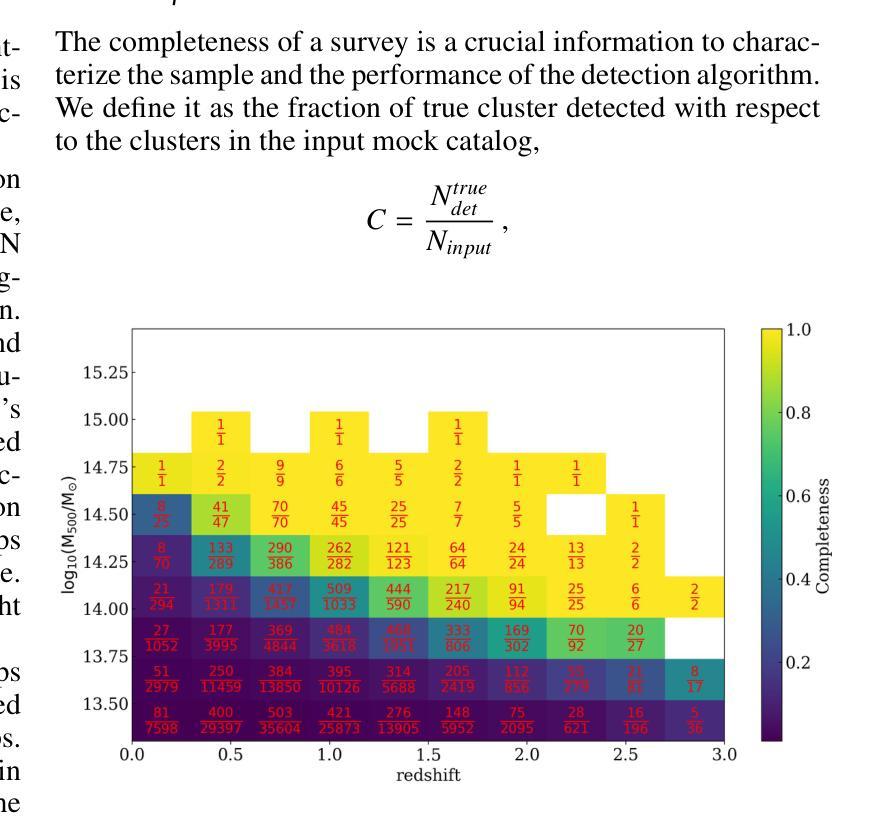
NIKA2 Cosmological Legacy Survey: Blind detection of galaxy clusters in the COSMOS field via the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect
Authors:D. Chérouvrier, J. F. Macias-Perez, F. X. Désert, R. Adam, P. Ade, H. Ajeddig, S. Amarantidis, P. André, H. Aussel, R. Barrena, A. Beelen, A. Benoit, S. Berta, M. Béthermin, A. Bongiovanni, J. Bounmy, O. Bourrion, L. -J. Bing, M. Calvo, A. Catalano, M. De Petris, S. Doyle, E. F. C. Driessen, G. Ejlali, A. Ferragamo, M. Fernandez-Torreiro, A. Gomez, J. Goupy, C. Hanser, S. Katsioli, F. Kéruzoré, C. Kramer, B. Ladjelate, G. Lagache, S. Leclercq, J. -F. Lestrade, S. C. Madden, A. Maury, F. Mayet, J. -B. Melin, A. Monfardini, A. Moyer-Anin, M. Mu noz-Echeverria, I. Myserlis, R. Neri, A. Paliwal, L. Perotto, G. Pisano, E. Pointecouteau, N. Ponthieu, G. W. Pratt, V. Reveret, A. J. Rigby, A. Ritacco, H. Roussel, F. Ruppin, M. Sanchez-Portal, S. Savorgnano, K. Schuster, A. Sievers, C. Tucker, R. Zylka
(Abridged) Clusters of galaxies, formed in the latest stages of structure formation, are unique cosmological probes. With the advent of large CMB surveys like those from the Planck satellite, the ACT and SPT telescopes, we now have access to a large number of galaxy clusters detected at millimeter wavelengths via the thermal Sunyaev-Zel’dovich (tSZ) effect. Nevertheless, it is interesting to complement them with high-angular-resolution (tens of arcseconds) observations to target the lowest-mass and highest-redshift clusters. This is the case of observations with the NIKA2 camera, which is installed on the IRAM 30–m telescope in Pico Veleta, Spain. We used the existing 150 GHz (2 mm) data from the NIKA2 Cosmological Legacy Survey (N2CLS) Large Program to blindly search for galaxy clusters in the well-known COSMOS field, across a 877 arcmin$^2$ region centered on (R.A., Dec.)$_{J2000}$ = (10h00m28.81s, +02d17m30.44s). We first developed a dedicated data reduction pipeline to construct NIKA2 maps at 2 mm. We then used a matched-filter algorithm to extract cluster candidates assuming a universal pressure profile to model the expected cluster tSZ signal. We computed the purity and completeness of the sample by applying the previous algorithm to simulated maps of the sky signal in the COSMOS field. We find a total of 16 cluster candidates at S/N > 4, from which eight have either an optical or X-ray cluster (or group of galaxies) counterpart. This is the first blind detection of clusters of galaxies at mm wavelengths at 18” angular resolution. From this analysis, we confirm that NIKA2 and the IRAM 30–m telescope should be sensitive to low-mass clusters at intermediate and high redshift, complementing current and planned large tSZ-based cluster surveys.
星系团是在结构形成后期形成的独特宇宙学探针。随着像普朗克卫星、ACT和SPT望远镜等大型宇宙微波背景辐射调查的出现,我们现在可以通过热Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(tSZ)效应在毫米波范围内检测到大量星系团。然而,为了瞄准质量最低、红移最高的星系团,对其进行高分辨率(几十角秒)的观测是有意义的。这是使用安装在西班牙皮科韦莱塔IRAM 30米望远镜上的NIKA2相机进行的观测的情况。我们在著名的宇宙学大尺度结构观测场(COSMOS场)内,以(赤经,赤纬)J2000=(10时0分28.81秒,+ 2度17分30.44秒)为中心,对面积约为877平方角分的区域进行了NIKA2宇宙学遗产调查(N2CLS)大型项目的现有150 GHz(2毫米)数据,以盲搜方式寻找星系团。我们首先开发了一个专门的数据缩减管道来构建NIKA2的2毫米地图。然后,我们使用匹配滤波器算法,假设普遍的压力分布模型预期的星系团的tSZ信号,来提取集群候选者。我们通过将上述算法应用于模拟的天图信号地图来计算机样本的纯度和完整性。我们发现共有信噪比大于4的16个集群候选者,其中8个有光学或X射线集群(或星系团)对应体。这是在毫米波波长下首次以18角秒分辨率进行盲探探测到的星系团。从这项分析中,我们证实NIKA2和IRAM 30米望远镜对中间和红移的低质量集群敏感,可补充当前和计划中的大型基于tSZ的集群普查。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
使用毫米波观测技术,通过NIKA2相机在IRAM 30米望远镜对宇宙星系团进行盲探测。研究团队对宇宙中的著名区域COSMOS进行了观察,并发现了低质量、高红移的星系团候选者。这是首次在毫米波波长下以高角度分辨率进行星系团盲探测。研究证实,NIKA2与IRAM 30米望远镜能够补充当前及计划的大规模热Sunyaev-Zel’dovich效应为基础的星系团调查,对中间和红移的低质量星系团敏感。
Key Takeaways
- 星系团是宇宙结构形成的晚期阶段的独特宇宙探针。
- 大型CMB调查如Planck卫星、ACT和SPT望远镜提供了大量通过热Sunyaev-Zel’dovich效应在毫米波波长下检测的星系团数据。
- 使用IRAM 30米望远镜上的NIKA2相机进行高角度分辨率(几十角秒)观测可以针对低质量和高红移的星系团。
- 在著名的COSMOS区域进行盲探测发现了低质量、高红移的星系团候选者。
- 这是首次在毫米波波长下进行的高分辨率星系团盲探测。
- NIKA2和IRAM 30米望远镜能够补充当前和计划的大规模热Sunyaev-Zel’dovich效应为基础的星系团调查。
点此查看论文截图

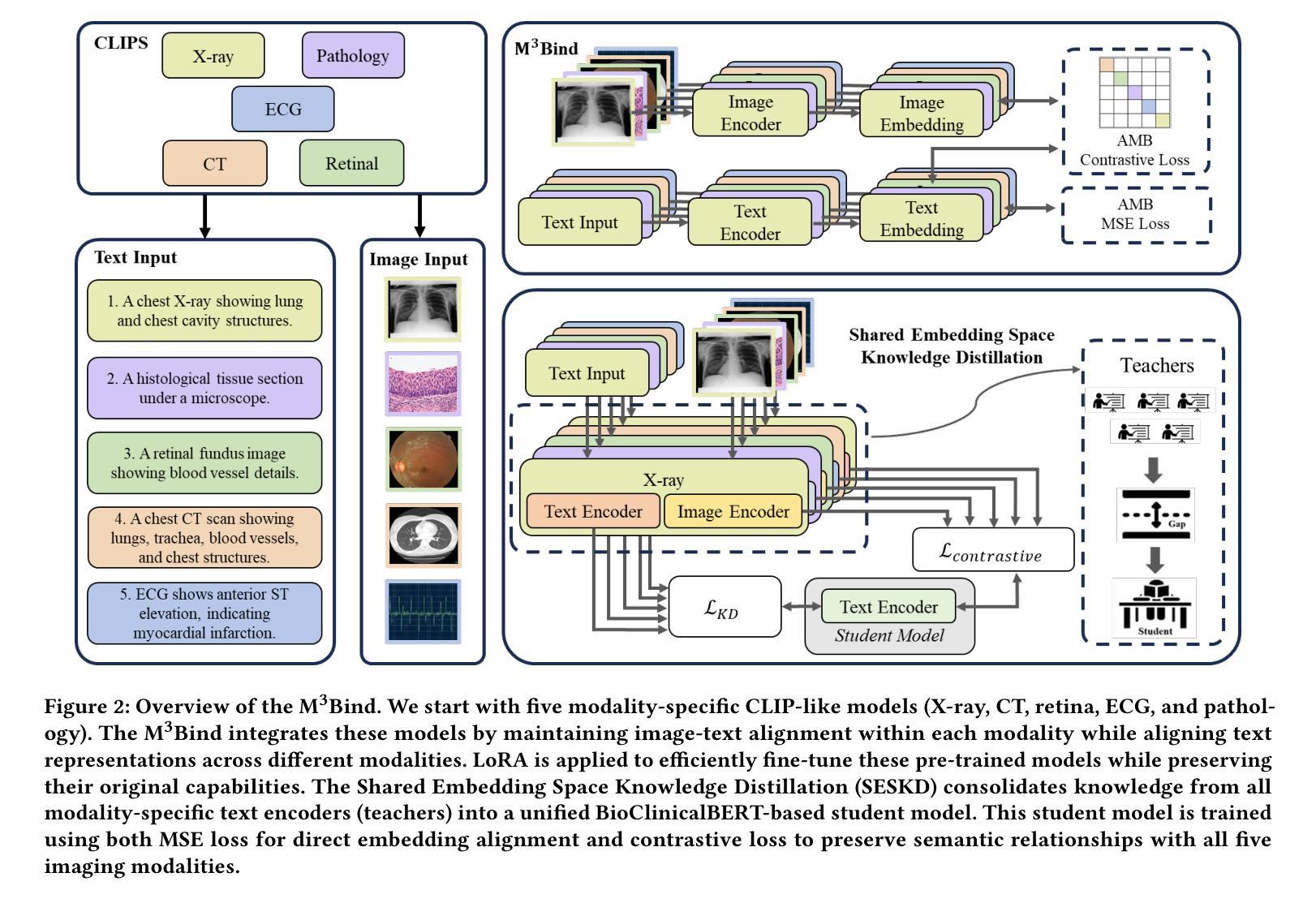
Multimodal Medical Image Binding via Shared Text Embeddings
Authors:Yunhao Liu, Suyang Xi, Shiqi Liu, Hong Ding, Chicheng Jin, Chenxi Yang, Junjun He, Yiqing Shen
Medical image analysis increasingly relies on the integration of multiple imaging modalities to capture complementary anatomical and functional information, enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Achieving aligned feature representations across these diverse modalities is therefore important for effective multimodal analysis. While contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) and its variant have enabled image-text alignments, they require explicitly paired data between arbitrary two modalities, which is difficult to acquire in medical contexts. To address the gap, we present Multimodal Medical Image Binding with Text (M\textsuperscript{3}Bind), a novel pre-training framework that enables seamless alignment of multiple medical imaging modalities through a shared text representation space without requiring explicit paired data between any two medical image modalities. Specifically, based on the insight that different images can naturally bind with text, M\textsuperscript{3}Bind first fine-tunes pre-trained CLIP-like image-text models to align their modality-specific text embedding space while preserving their original image-text alignments. Subsequently, we distill these modality-specific text encoders into a unified model, creating a shared text embedding space. Experiments on X-ray, CT, retina, ECG, and pathological images on multiple downstream tasks demonstrate that M\textsuperscript{3}Bind achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot, few-shot classification and cross-modal retrieval tasks compared to its CLIP-like counterparts. These results validate M\textsuperscript{3}Bind’s effectiveness in achieving cross-image-modal alignment for medical analysis.
医学图像分析越来越依赖于多种成像方式的融合,以捕捉互补的解剖和功能性信息,从而实现更准确的诊断和制定治疗方案。因此,在这些不同的方式中实现对齐的特征表示对于有效的多模式分析至关重要。尽管对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)及其变体实现了图像文本的对齐,但它们需要在任意两种模式之间明确配对的数据,这在医学背景下很难获取。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了基于文本的多模式医学图像绑定(M\textsuperscript{3}Bind),这是一种新的预训练框架,它可以通过共享文本表示空间实现多种医学成像方式的无缝对齐,而无需在任意两种医学图像方式之间明确配对数据。具体来说,基于不同图像可以自然绑定到文本上的见解,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind首先微调预训练的CLIP类图像文本模型,以对齐其特定于方式的文本嵌入空间,同时保留其原始的图像文本对齐。随后,我们将这些特定于方式的文本编码器蒸馏到统一模型中,创建一个共享的文本嵌入空间。在X光、CT、视网膜、心电图和病理图像等多种下游任务上的实验表明,与CLIP类模型相比,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模式检索任务上实现了最先进的性能。这些结果验证了M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在实现医学分析中的跨图像模式对齐方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures
Summary
医学图像分析越来越依赖于多种成像模式的整合,以捕捉互补的解剖和功能性信息,从而实现更准确的诊断和制定治疗方案。因此,实现这些不同模式之间的对齐特征表示对于有效的多模式分析至关重要。我们提出了多模式医学图像绑定文本(M\textsuperscript{3}Bind)预训练框架,通过共享文本表示空间,无需任意两种医学图像模式之间的明确配对数据,即可实现无缝对齐多个医学成像模式。实验表明,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上实现了最先进的性能,验证了其在医学分析中的跨图像模态对齐的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析依赖于多模态成像技术的结合,以获取更全面的诊断信息。
- 实现不同医学成像模态之间的对齐特征表示对于多模态分析至关重要。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind是一种新的预训练框架,能在无需明确配对数据的情况下,实现多种医学成像模态与文本的无缝对齐。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind基于不同图像自然绑定文本的理念。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind首先微调预训练的CLIP类图像-文本模型,以对齐模态特定的文本嵌入空间,同时保留其原始的图像-文本对齐。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在多种下游任务上的实验结果表明,其在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

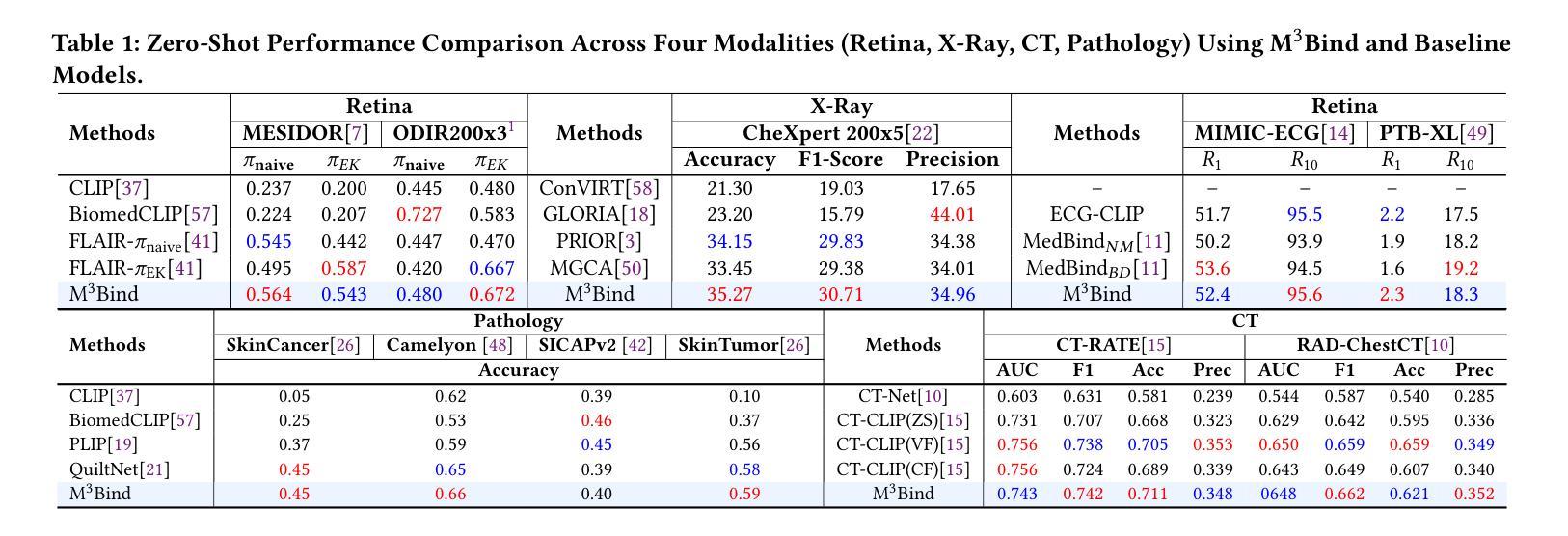
Training-free Test-time Improvement for Explainable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Hangzhou He, Jiachen Tang, Lei Zhu, Kaiwen Li, Yanye Lu
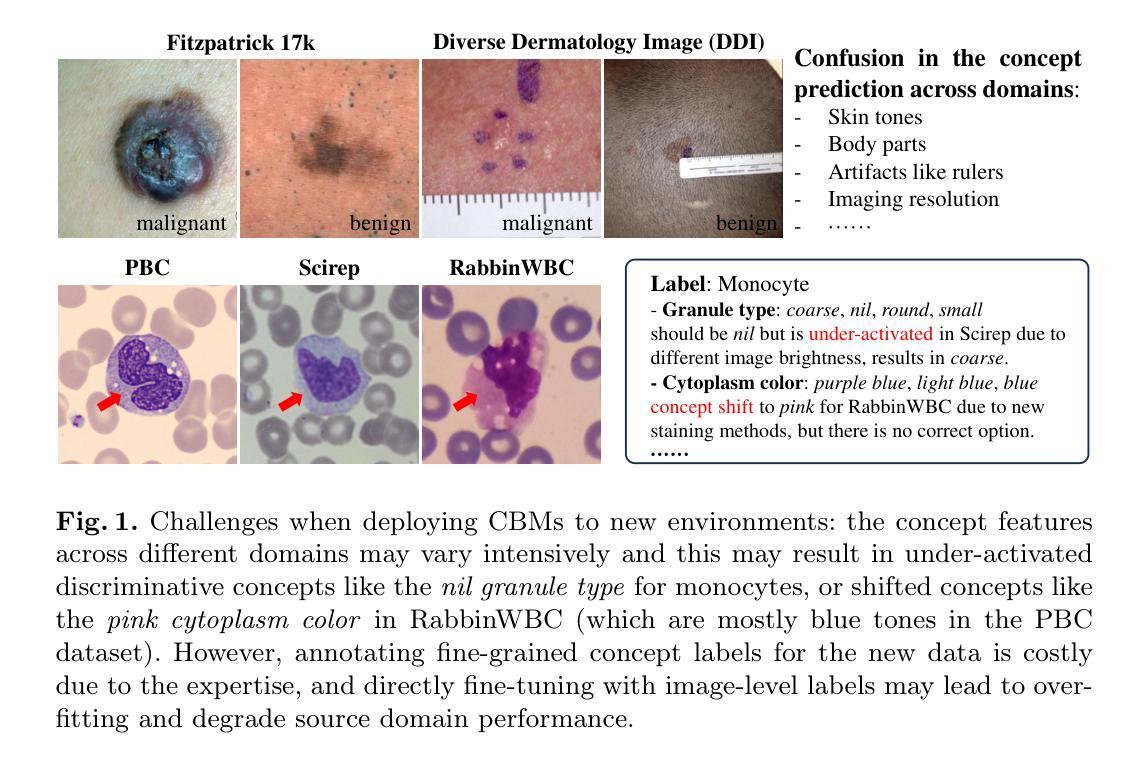
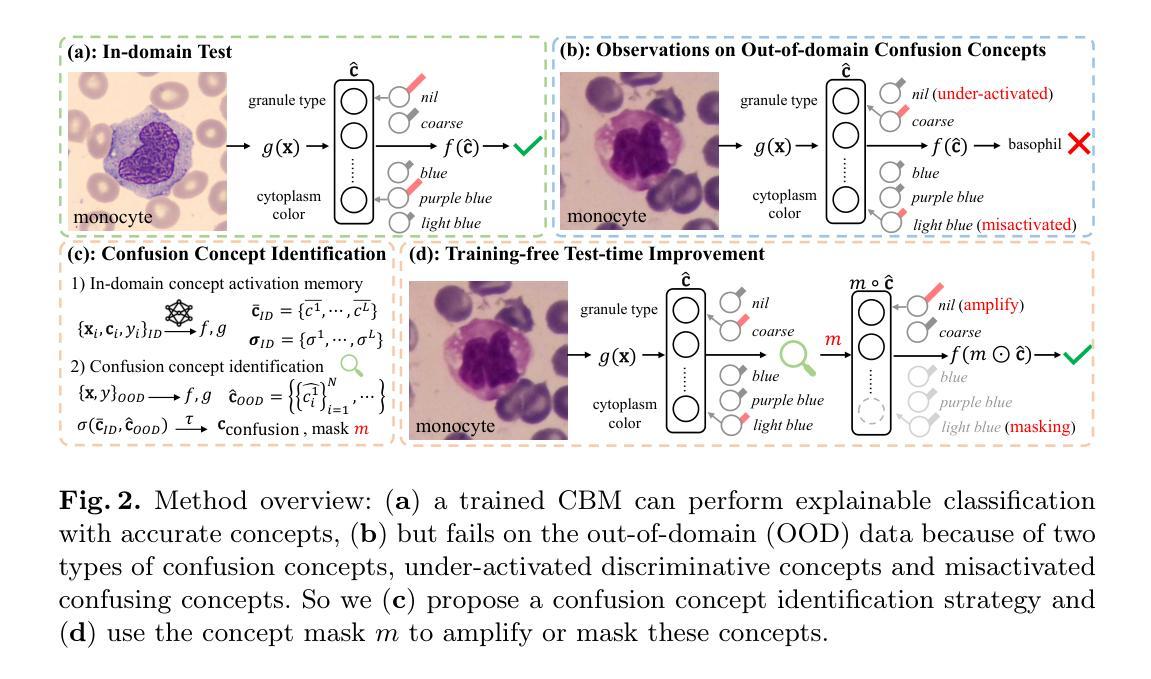
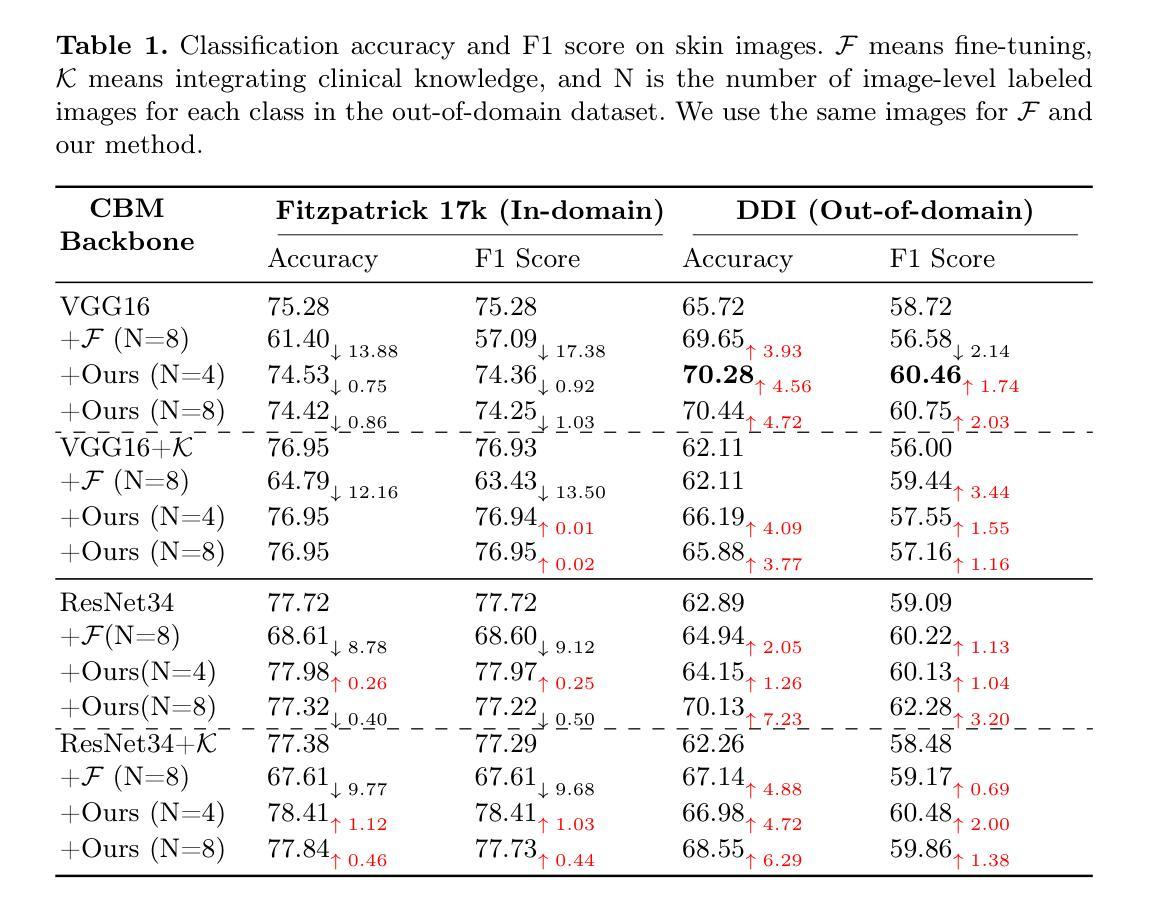
Deep learning-based medical image classification techniques are rapidly advancing in medical image analysis, making it crucial to develop accurate and trustworthy models that can be efficiently deployed across diverse clinical scenarios. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs), which first predict a set of explainable concepts from images and then perform classification based on these concepts, are increasingly being adopted for explainable medical image classification. However, the inherent explainability of CBMs introduces new challenges when deploying trained models to new environments. Variations in imaging protocols and staining methods may induce concept-level shifts, such as alterations in color distribution and scale. Furthermore, since CBM training requires explicit concept annotations, fine-tuning models solely with image-level labels could compromise concept prediction accuracy and faithfulness - a critical limitation given the high cost of acquiring expert-annotated concept labels in medical domains. To address these challenges, we propose a training-free confusion concept identification strategy. By leveraging minimal new data (e.g., 4 images per class) with only image-level labels, our approach enhances out-of-domain performance without sacrificing source domain accuracy through two key operations: masking misactivated confounding concepts and amplifying under-activated discriminative concepts. The efficacy of our method is validated on both skin and white blood cell images. Our code is available at: https://github.com/riverback/TF-TTI-XMed.
基于深度学习的医学图像分类技术在医学图像分析领域正快速发展,因此需要开发能够高效部署在不同临床场景中的准确且可靠的模型。概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)首先通过图像预测一组可解释的概念,然后基于这些概念进行分类,越来越被广泛地应用于可解释的医学图像分类。然而,CBMs的内在可解释性在向新环境部署训练好的模型时带来了新的挑战。成像协议和染色方法的差异可能导致概念层面的变化,如颜色分布和尺度的变化。此外,由于CBM训练需要明确的概念注释,仅使用图像级别的标签对模型进行微调可能会损害概念预测准确性和忠实度——考虑到在医学领域获取专家注释的概念标签成本高昂,这是一个关键的局限性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种无需训练的混淆概念识别策略。通过利用少量新数据(例如,每类4张图像)和仅带有图像级别标签的数据,我们的方法通过两个关键操作——掩盖错误激活的混淆概念和放大未激活的判别概念——提高了域外性能,同时不牺牲源域准确性。我们的方法在皮肤和白细胞图像上的有效性已经得到验证。我们的代码可用在:https://github.com/riverback/TF-TTI-XMed。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is the initial version of our work accepted by MICCAI 2025. We’ll include a link to the version on SpringerLink after this becomes available
Summary
本文介绍了基于深度学习的医学图像分类技术的快速发展及其在医学图像分析中的应用。文章重点介绍了概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)在可解释的医学图像分类中的使用及其面临的挑战。文章提出一种无训练混淆概念识别策略,通过利用少量新数据(如每类4张图像)和仅图像级别的标签,增强模型在新环境下的性能,同时不牺牲源域准确性。该方法通过掩盖误激活的混淆概念和放大未激活的判别概念来实现有效性,并在皮肤和白细胞图像上得到验证。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法在医学图像分类中的快速发展,需要开发准确、可靠的模型以适应不同的临床场景。
- 概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)是一种用于解释医学图像分类的新兴技术,它通过预测图像中的一系列可解释概念来进行分类。
- CBMs在部署到新的环境时面临挑战,如成像协议和染色方法的差异可能导致概念层面的变化。
- CBM训练需要明确的概念注释,仅使用图像级别的标签对模型进行微调可能会降低概念预测的准确性,这是一个关键的局限性。
- 针对以上挑战,提出了一种无训练混淆概念识别策略。
- 该策略利用少量新数据和仅图像级别的标签来增强模型在新环境下的性能。
点此查看论文截图

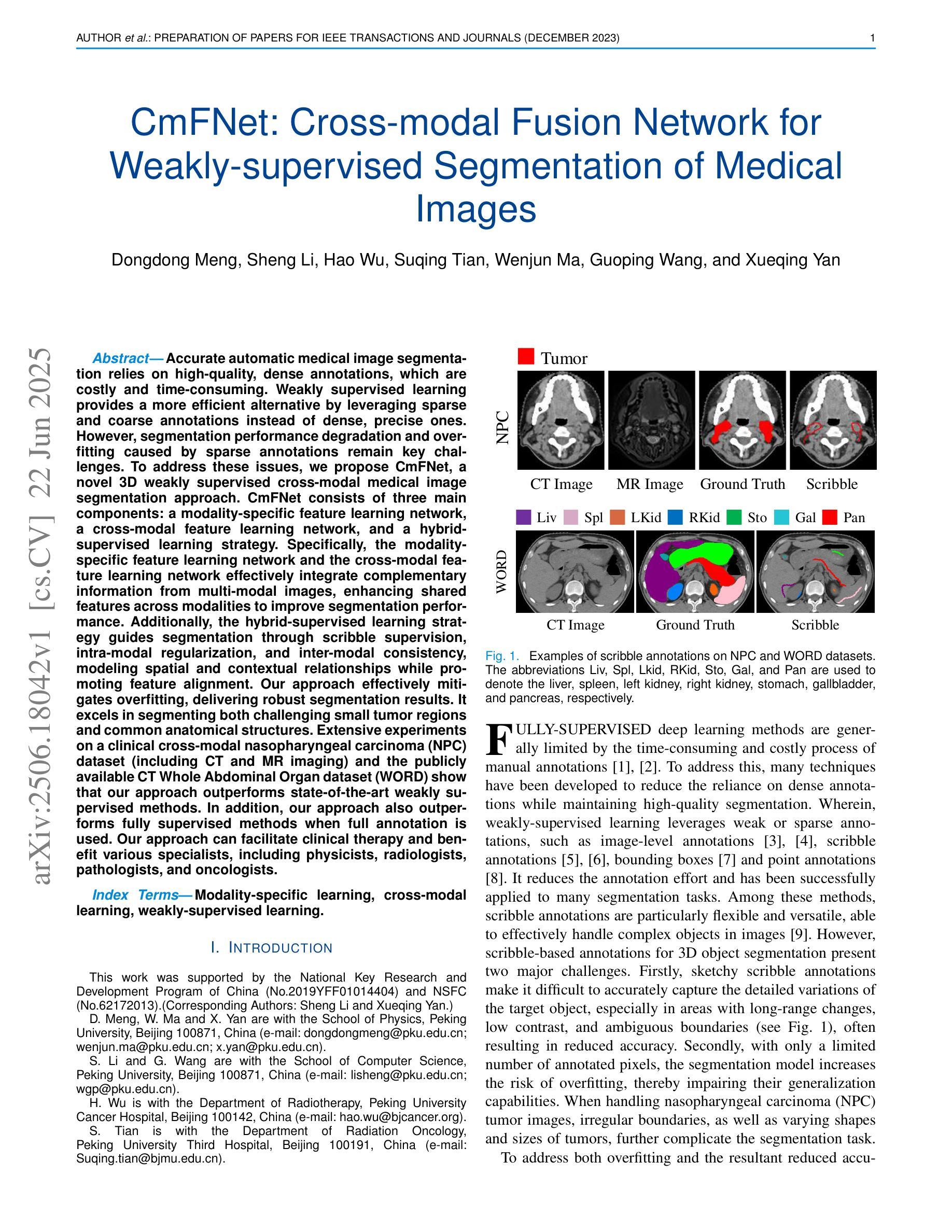
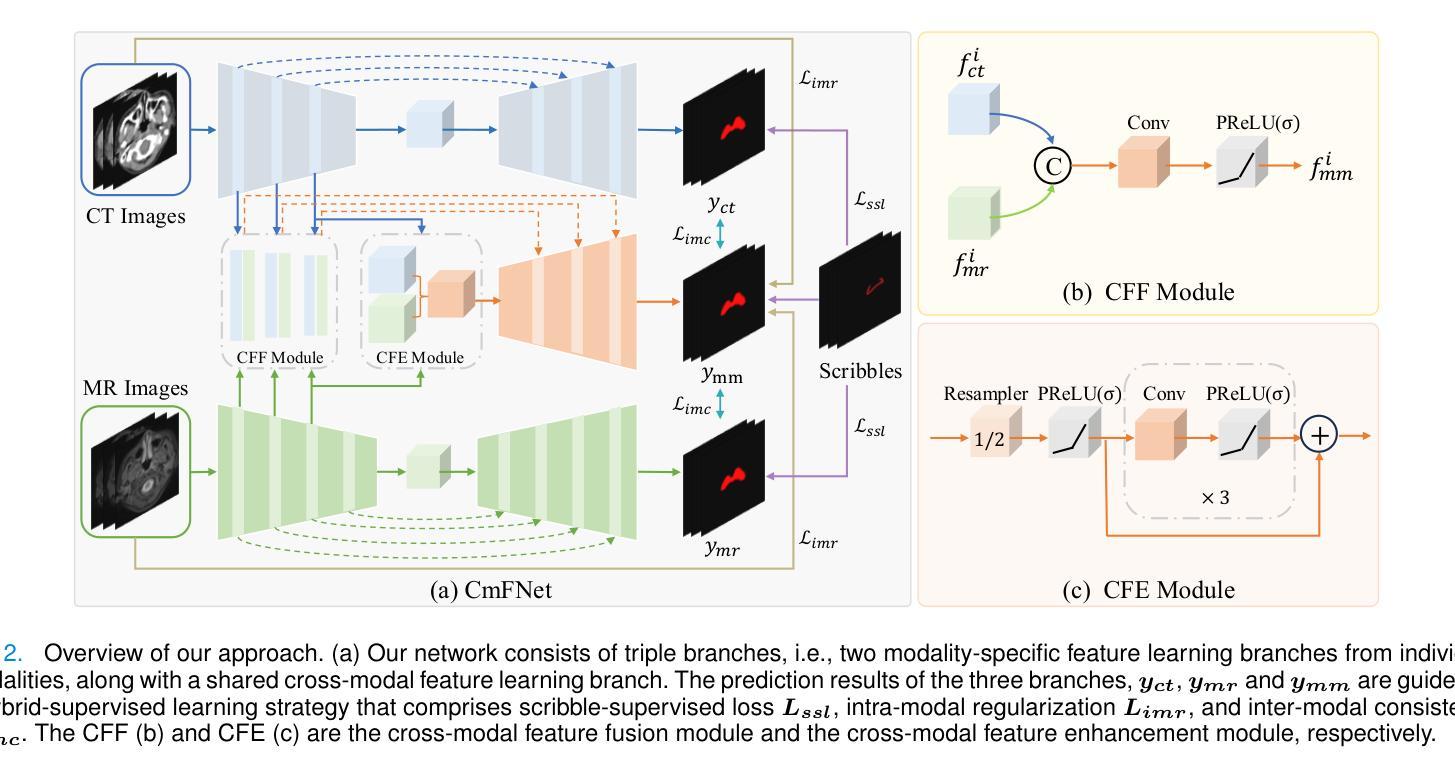
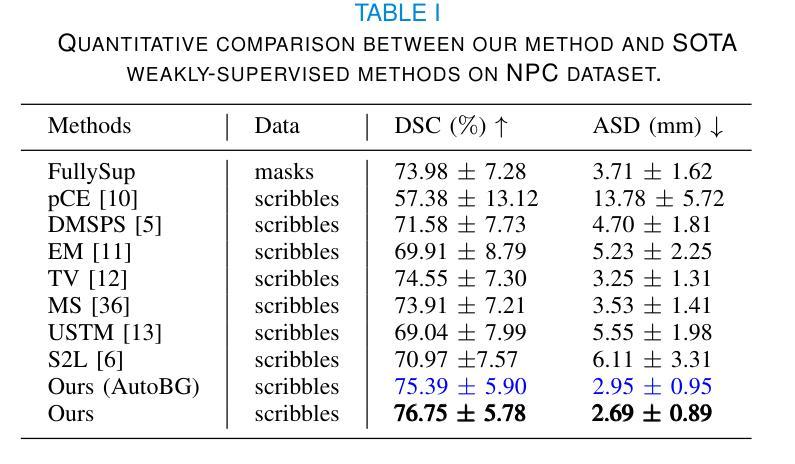
CmFNet: Cross-modal Fusion Network for Weakly-supervised Segmentation of Medical Images
Authors:Dongdong Meng, Sheng Li, Hao Wu, Suqing Tian, Wenjun Ma, Guoping Wang, Xueqing Yan
Accurate automatic medical image segmentation relies on high-quality, dense annotations, which are costly and time-consuming. Weakly supervised learning provides a more efficient alternative by leveraging sparse and coarse annotations instead of dense, precise ones. However, segmentation performance degradation and overfitting caused by sparse annotations remain key challenges. To address these issues, we propose CmFNet, a novel 3D weakly supervised cross-modal medical image segmentation approach. CmFNet consists of three main components: a modality-specific feature learning network, a cross-modal feature learning network, and a hybrid-supervised learning strategy. Specifically, the modality-specific feature learning network and the cross-modal feature learning network effectively integrate complementary information from multi-modal images, enhancing shared features across modalities to improve segmentation performance. Additionally, the hybrid-supervised learning strategy guides segmentation through scribble supervision, intra-modal regularization, and inter-modal consistency, modeling spatial and contextual relationships while promoting feature alignment. Our approach effectively mitigates overfitting, delivering robust segmentation results. It excels in segmenting both challenging small tumor regions and common anatomical structures. Extensive experiments on a clinical cross-modal nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) dataset (including CT and MR imaging) and the publicly available CT Whole Abdominal Organ dataset (WORD) show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art weakly supervised methods. In addition, our approach also outperforms fully supervised methods when full annotation is used. Our approach can facilitate clinical therapy and benefit various specialists, including physicists, radiologists, pathologists, and oncologists.
准确的自动医学图像分割依赖于高质量、密集的注释,而这些注释是昂贵且耗时的。弱监督学习通过利用稀疏和粗略的注释而不是密集、精确的注释,提供了一种更高效的替代方案。然而,由稀疏注释引起的分割性能下降和过拟合仍是关键挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了CmFNet,这是一种新的3D弱监督跨模态医学图像分割方法。CmFNet由三个主要组件构成:特定模态特征学习网络、跨模态特征学习网络和混合监督学习策略。具体而言,特定模态特征学习网络和跨模态特征学习网络有效地融合了多模态图像的互补信息,增强了跨模态的共享特征,提高了分割性能。此外,混合监督学习策略通过涂鸦监督、内部模态正则化和跨模态一致性来指导分割,建立空间关系和上下文关系,同时促进特征对齐。我们的方法有效地减轻了过拟合问题,提供了稳健的分割结果。它在分割具有挑战性的小肿瘤区域和常见的解剖结构方面表现出色。在临床跨模态鼻咽癌(NPC)数据集(包括CT和MR成像)和公共可用的CT全腹部器官数据集(WORD)上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于最新的弱监督方法。当使用完整注释时,我们的方法也优于全监督方法。我们的方法可以辅助临床治疗,并惠及包括物理学家、放射科医生、病理医生和肿瘤学家在内的各种专家。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为CmFNet的新型三维弱监督跨模态医学图像分割方法,该方法能有效解决医学图像分割中的挑战问题。通过结合特定模态特征学习网络、跨模态特征学习网络和混合监督学习策略,CmFNet能有效利用稀疏、粗略的标注数据提高分割性能,并成功减轻过拟合问题。该方法在肿瘤区域和常见解剖结构的分割上都表现出卓越性能,显著提升了临床诊疗的效率。实验结果表明,该方法的性能超过了当前主流的弱监督方法和某些全监督方法。它有助于物理学家、放射科医生、病理学家和肿瘤学家等不同专业领域的医生进行诊断和治疗。
Key Takeaways
- 提出新型医学图像分割方法CmFNet,利用弱监督学习减少成本和时间。
- 方法包含特定模态特征学习网络、跨模态特征学习网络和混合监督学习策略三个主要组件。
- 通过集成多模态图像信息提高分割性能,并有效减轻过拟合问题。
- 在肿瘤区域和解剖结构分割上表现优越,实验结果超过其他弱监督方法和部分全监督方法。
点此查看论文截图
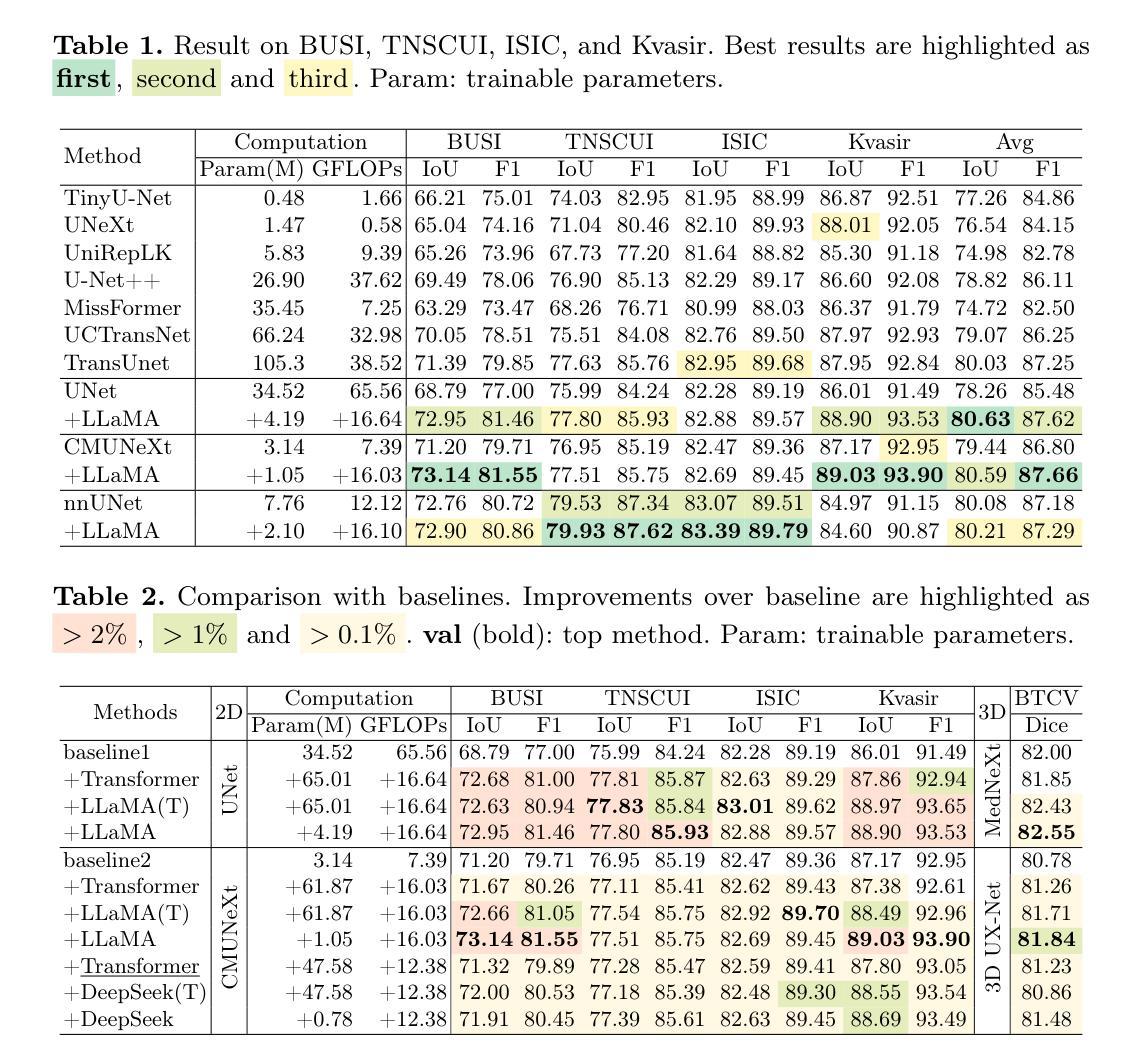
Pre-Trained LLM is a Semantic-Aware and Generalizable Segmentation Booster
Authors:Fenghe Tang, Wenxin Ma, Zhiyang He, Xiaodong Tao, Zihang Jiang, S. Kevin Zhou
With the advancement of Large Language Model (LLM) for natural language processing, this paper presents an intriguing finding: a frozen pre-trained LLM layer can process visual tokens for medical image segmentation tasks. Specifically, we propose a simple hybrid structure that integrates a pre-trained, frozen LLM layer within the CNN encoder-decoder segmentation framework (LLM4Seg). Surprisingly, this design improves segmentation performance with a minimal increase in trainable parameters across various modalities, including ultrasound, dermoscopy, polypscopy, and CT scans. Our in-depth analysis reveals the potential of transferring LLM’s semantic awareness to enhance segmentation tasks, offering both improved global understanding and better local modeling capabilities. The improvement proves robust across different LLMs, validated using LLaMA and DeepSeek.
随着自然语言处理中大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,本文呈现了一项有趣的发现:冻结的预训练LLM层可以处理医学图像分割任务的视觉标记。具体来说,我们提出了一种简单的混合结构,该结构在CNN编码器-解码器分割框架中集成了预训练的冻结LLM层(LLM4Seg)。令人惊讶的是,这种设计在各种模态(包括超声、皮肤镜检查、结肠镜检查和CT扫描)的分割性能上都有所提高,同时可训练参数只增加了很小的一部分。我们的深入分析揭示了将LLM的语义感知能力转移到增强分割任务中的潜力,提供了更好的全局理解和局部建模能力。改进在不同的大型语言模型中表现稳健,通过使用LLaMA和DeepSeek进行了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025. Code: https://github.com/FengheTan9/LLM4Seg
Summary
本研究结合自然语言处理中的大型语言模型(LLM),提出一种用于医学图像分割任务的新方法。研究结果表明,预训练LLM层的冻结结构可用于处理医学图像中的视觉符号,结合卷积神经网络编码器解码器分割框架(LLM4Seg),能够提高不同模态(如超声、皮肤镜、结肠镜检查和CT扫描)图像的分割性能,且具有最少的参数增量。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练的LLM层可应用于医学图像分割任务,提高性能。
- 提出的混合结构LLM4Seg结合了预训练的冻结LLM层,增强了分割任务的性能。
- 在不同模态的医学图像上均实现了性能提升,包括超声、皮肤镜、结肠镜检查和CT扫描。
- LLM的语义意识能够增强分割任务的性能,提高了全局理解和局部建模能力。
- 性能提升在不同的LLMs中均得到了验证,包括LLaMA和DeepSeek。
- 这种新方法具有最小的参数增量。
点此查看论文截图

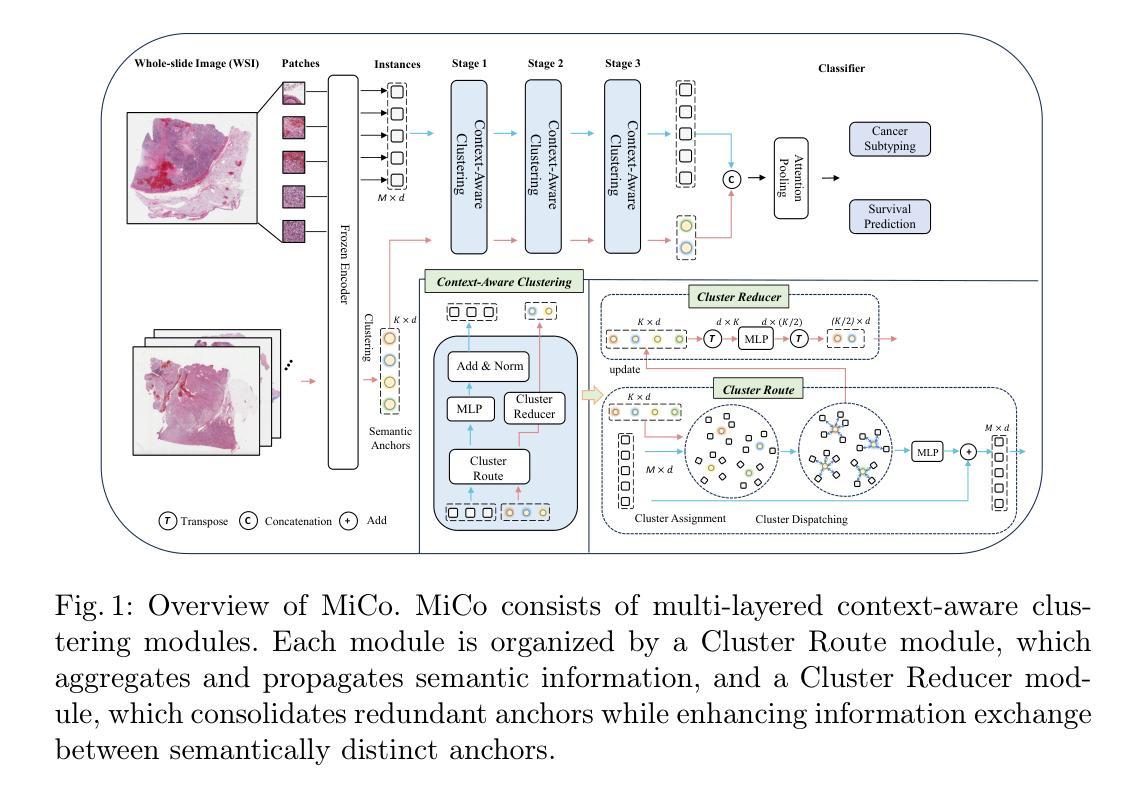
MiCo: Multiple Instance Learning with Context-Aware Clustering for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Junjian Li, Hulin Kuang, Jin Liu, Hailin Yue, Mengshen He, Jianxin Wang
Multiple instance learning (MIL) has shown significant promise in histopathology whole slide image (WSI) analysis for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. However, the inherent spatial heterogeneity of WSIs presents critical challenges, as morphologically similar tissue types are often dispersed across distant anatomical regions. Conventional MIL methods struggle to model these scattered tissue distributions and capture cross-regional spatial interactions effectively. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Multiple instance learning framework with Context-Aware Clustering (MiCo), designed to enhance cross-regional intra-tissue correlations and strengthen inter-tissue semantic associations in WSIs. MiCo begins by clustering instances to distill discriminative morphological patterns, with cluster centroids serving as semantic anchors. To enhance cross-regional intra-tissue correlations, MiCo employs a Cluster Route module, which dynamically links instances of the same tissue type across distant regions via feature similarity. These semantic anchors act as contextual hubs, propagating semantic relationships to refine instance-level representations. To eliminate semantic fragmentation and strengthen inter-tissue semantic associations, MiCo integrates a Cluster Reducer module, which consolidates redundant anchors while enhancing information exchange between distinct semantic groups. Extensive experiments on two challenging tasks across nine large-scale public cancer datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of MiCo, showcasing its superiority over state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/junjianli106/MiCo.
多实例学习(MIL)在病理学全切片图像(WSI)分析中,对于癌症诊断和预后方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,WSI固有的空间异质性带来了重大挑战,因为形态上相似的组织类型通常分布在遥远的解剖区域。传统的MIL方法难以对这些分散的组织分布进行建模,并有效地捕获跨区域的空间交互。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种带有上下文感知聚类的多实例学习框架(MiCo),旨在增强跨区域的组织内相关性和加强WSI中的组织间语义关联。MiCo首先通过聚类实例来提炼判别性形态模式,以聚类中心作为语义锚点。为了增强跨区域的组织内相关性,MiCo采用了一种集群路由模块,该模块通过特征相似性动态链接相同组织类型的实例,跨越遥远区域。这些语义锚点作为上下文中心,传播语义关系以优化实例级表示。为了消除语义碎片并加强组织间的语义关联,MiCo集成了一个集群缩减模块,该模块整合了冗余的锚点,同时增强了不同语义组之间的信息交换。在两个具有挑战性的任务上的九个大型公开癌症数据集上的广泛实验证明了MiCo的有效性,展示了其在最新技术上的优越性。代码可在https://github.com/junjianli106/MiCo上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个名为MiCo的新型多实例学习框架,用于增强全滑片图像(WSI)分析中跨区域的组织内关联性和组织间的语义关联。通过聚类实例和采用Cluster Route模块,MiCo能够动态链接同一组织类型的实例,增强跨区域的组织内关联性。同时,MiCo的Cluster Reducer模块能够整合冗余锚点,强化不同组织间的语义关联。在九个大型公共癌症数据集上的实验证明,MiCo的有效性优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- MiCo是一个基于多实例学习框架的新型方法,用于解决全滑片图像分析中的空间异质性挑战。
- MiCo通过聚类实例来提取判别性形态模式,并使用簇中心作为语义锚点。
- Cluster Route模块能够动态链接同一组织类型的实例,增强跨区域的组织内关联性。
- Cluster Reducer模块整合冗余锚点,强化组织间的语义关联。
- MiCo在九个大型公共癌症数据集上的实验表现优异,证明了其有效性。
- MiCo适用于癌症诊断和治疗预后中的全滑片图像分析。
点此查看论文截图

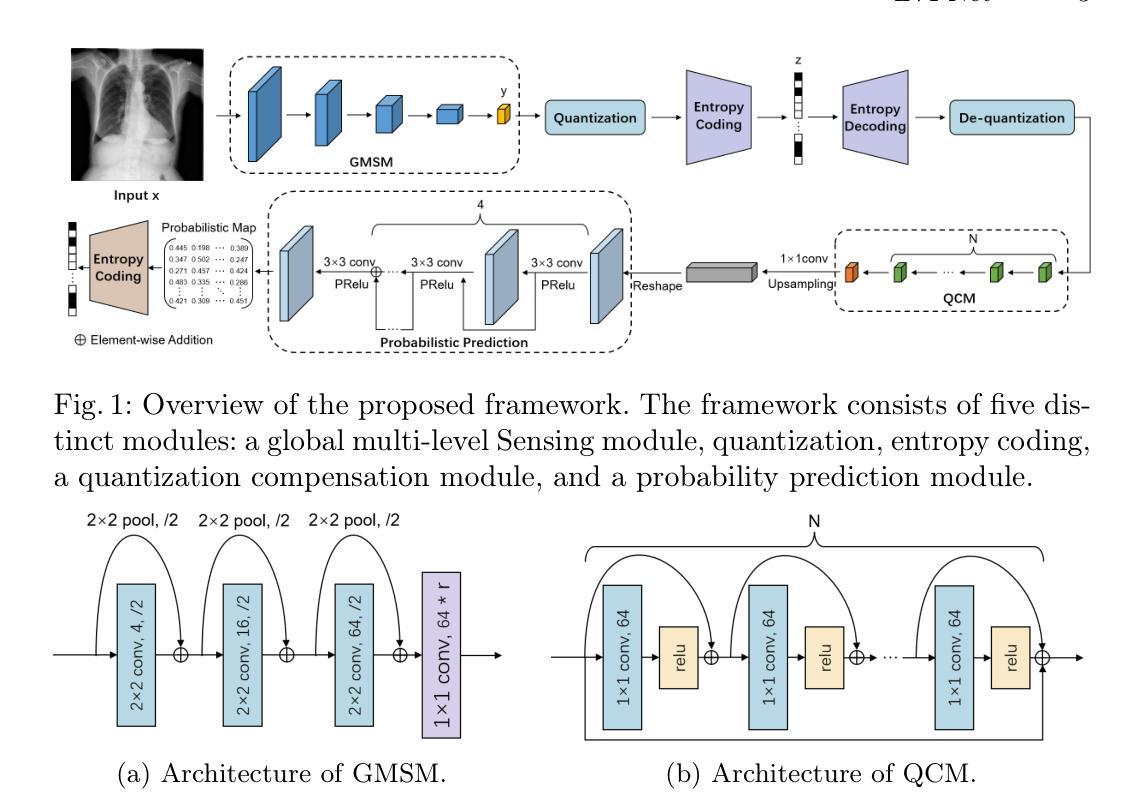
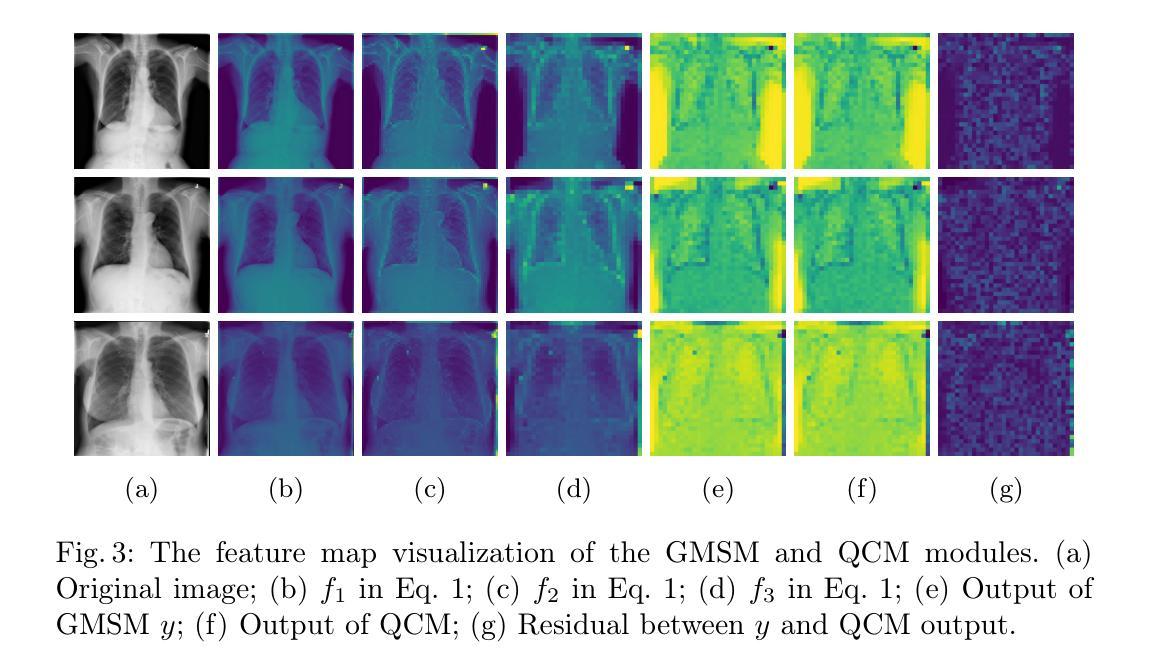
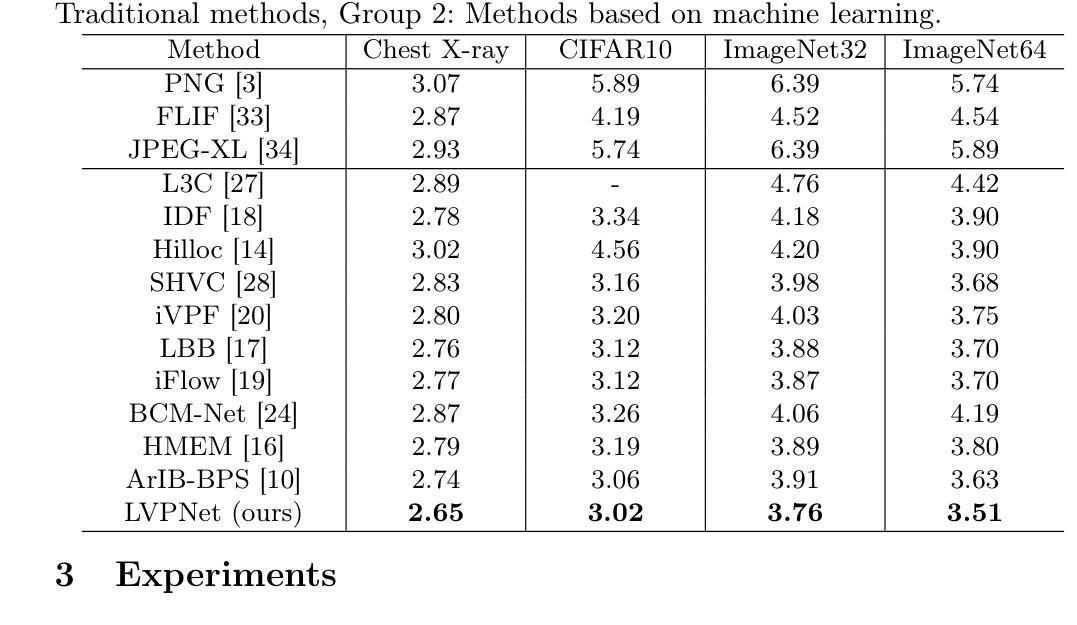
LVPNet: A Latent-variable-based Prediction-driven End-to-end Framework for Lossless Compression of Medical Images
Authors:Chenyue Song, Chen Hui, Qing Lin, Wei Zhang, Siqiao Li, Shengping Zhang, Haiqi Zhu, Zhixuan Li, Shaohui Liu, Feng Jiang, Xiang Li
Autoregressive Initial Bits is a framework that integrates sub-image autoregression and latent variable modeling, demonstrating its advantages in lossless medical image compression. However, in existing methods, the image segmentation process leads to an even distribution of latent variable information across each sub-image, which in turn causes posterior collapse and inefficient utilization of latent variables. To deal with these issues, we propose a prediction-based end-to-end lossless medical image compression method named LVPNet, leveraging global latent variables to predict pixel values and encoding predicted probabilities for lossless compression. Specifically, we introduce the Global Multi-scale Sensing Module (GMSM), which extracts compact and informative latent representations from the entire image, effectively capturing spatial dependencies within the latent space. Furthermore, to mitigate the information loss introduced during quantization, we propose the Quantization Compensation Module (QCM), which learns the distribution of quantization errors and refines the quantized features to compensate for quantization loss. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves superior compression efficiency compared to state-of-the-art lossless image compression approaches, while maintaining competitive inference speed. The code is at https://github.com/Anonymity00000/Anonymity-repository/.
“Autoregressive Initial Bits”是一个融合了子图像自回归和潜在变量建模的框架,在无损医学图像压缩中展示了其优势。然而,在现有方法中,图像分割过程导致潜在变量信息均匀分布在每个子图像中,这进而导致后崩溃和潜在变量的低效利用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于预测的端到端无损医学图像压缩方法,名为LVPNet。该方法利用全局潜在变量来预测像素值,并对预测概率进行编码以实现无损压缩。具体来说,我们引入了全局多尺度感知模块(GMSM),该模块从整个图像中提取紧凑且信息丰富的潜在表示,有效地捕获潜在空间中的空间依赖性。此外,为了减轻量化过程中引入的信息损失,我们提出了量化补偿模块(QCM),该模块学习量化误差的分布,并细化量化特征以补偿量化损失。在具有挑战性的基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法相较于最新的无损图像压缩方法,实现了更高的压缩效率,同时保持了竞争性的推理速度。代码位于https://github.com/Anonymity00000/Anonymity-repository/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学图像无损压缩新技术——LVPNet。该方法利用全局潜变量预测像素值,并编码预测概率以实现无损压缩。通过引入全局多尺度感知模块(GMSM)和量化补偿模块(QCM),提高压缩效率和量化损失补偿。
Key Takeaways
- LVPNet是一个基于预测的无损医学图像压缩方法,利用全局潜变量预测像素值。
- 引入Global Multi-scale Sensing Module (GMSM),从整个图像中提取紧凑且信息丰富的潜在表示。
- 提出Quantization Compensation Module (QCM),学习量化误差的分布,并优化量化特征以补偿量化损失。
- LVPNet在具有挑战性的基准测试上实现了高效的压缩性能,优于现有的无损图像压缩方法。
- 保持了较高的推理速度,具有竞争性。
- 方法的代码已公开,可供进一步研究和使用。
点此查看论文截图

Mobile Image Analysis Application for Mantoux Skin Test
Authors:Liong Gele, Tan Chye Cheah
This paper presents a newly developed mobile application designed to diagnose Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) using the Mantoux Skin Test (TST). Traditional TST methods often suffer from low follow-up return rates, patient discomfort, and subjective manual interpretation, particularly with the ball-point pen method, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. Moreover, previous developed mobile applications that used 3D reconstruction, this app utilizes scaling stickers as reference objects for induration measurement. This mobile application integrates advanced image processing technologies, including ARCore, and machine learning algorithms such as DeepLabv3 for robust image segmentation and precise measurement of skin indurations indicative of LTBI. The system employs an edge detection algorithm to enhance accuracy. The application was evaluated against standard clinical practices, demonstrating significant improvements in accuracy and reliability. This innovation is crucial for effective tuberculosis management, especially in resource-limited regions. By automating and standardizing TST evaluations, the application enhances the accessibility and efficiency of TB di-agnostics. Future work will focus on refining machine learning models, optimizing measurement algorithms, expanding functionalities to include comprehensive patient data management, and enhancing ARCore’s performance across various lighting conditions and operational settings.
本文介绍了一款新开发的移动应用程序,该程序采用Mantoux皮肤试验(TST)设计来诊断潜伏性结核感染(LTBI)。传统的TST方法常常受到后续回访率低、患者不适以及手动解读主观性(特别是用圆珠笔方法)的影响,导致误诊和延迟治疗。此外,与之前使用3D重建技术的移动应用不同,本应用使用刻度贴纸作为测量硬结时的参考对象。该移动应用程序集成了先进图像处理技术,包括ARCore,以及机器学习算法,如DeepLabv3,用于稳健的图像分割和精确测量皮肤硬结,这是LTBI的重要指标。系统采用边缘检测算法来提高准确性。该应用程序与标准临床实践进行了评估,在准确性和可靠性方面显示出显着改善。这一创新对于有效管理结核病,特别是在资源有限的地区,至关重要。通过自动化和标准化TST评估,该应用程序提高了结核诊断的可访问性和效率。未来的工作将侧重于改进机器学习模型、优化测量算法、扩展功能以包括全面的患者数据管理,以及提高ARCore在不同照明条件和操作环境下的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文介绍了一款新开发的移动应用程序,用于通过Mantoux皮肤试验(TST)诊断隐性结核感染(LTBI)。该程序解决了传统TST方法面临的回访率低、患者不适和手动解读主观等问题,特别是使用圆珠笔方法导致的误诊和延迟治疗。该程序采用先进的图像处理技术,包括ARCore和机器学习算法,如DeepLabv3,进行皮肤硬结测量,以准确诊断LTBI。系统采用边缘检测算法提高准确性。该应用程序已按照标准临床实践进行评估,证明其在准确性和可靠性方面有明显改进。这一创新对于有效管理结核病,尤其是在资源有限的地区,具有重要意义。通过自动化和标准化TST评估,该应用程序提高了结核诊断的可达性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 新移动应用程序用于诊断隐性结核感染(LTBI),基于Mantoux皮肤试验(TST)。
- 传统TST方法存在回访率低、患者不适和主观解读等问题。
- 该应用程序采用先进的图像处理技术和机器学习算法进行皮肤硬结测量。
- 应用了DeepLabv3算法和ARCore技术,提高了诊断准确性和可靠性。
- 系统采用边缘检测算法增强测量精度。
- 应用程序已在标准临床环境中评估,证明其效果。
点此查看论文截图

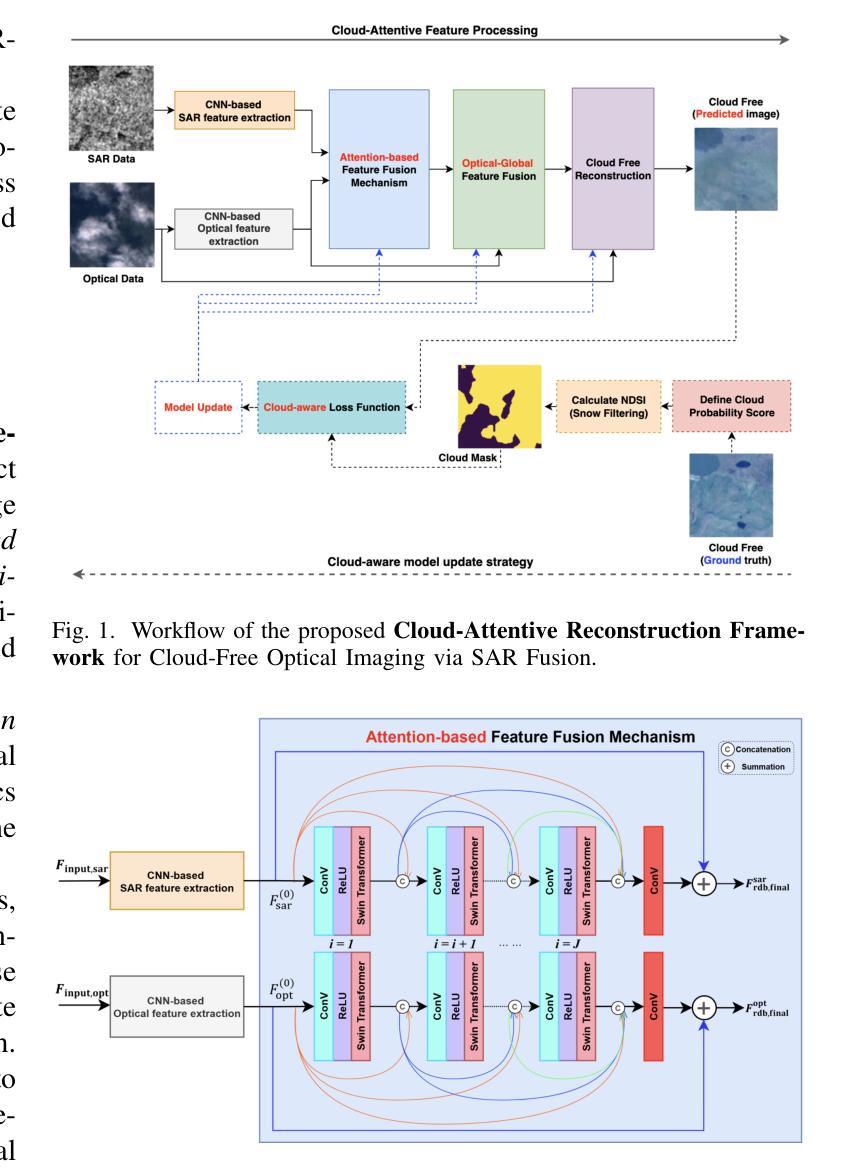
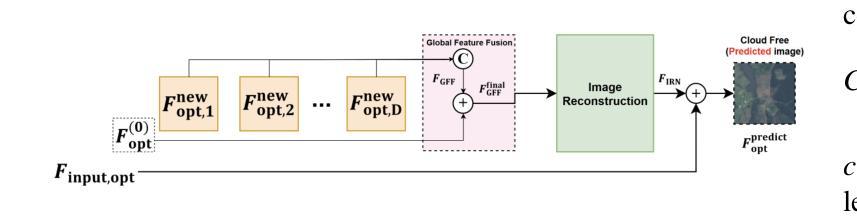
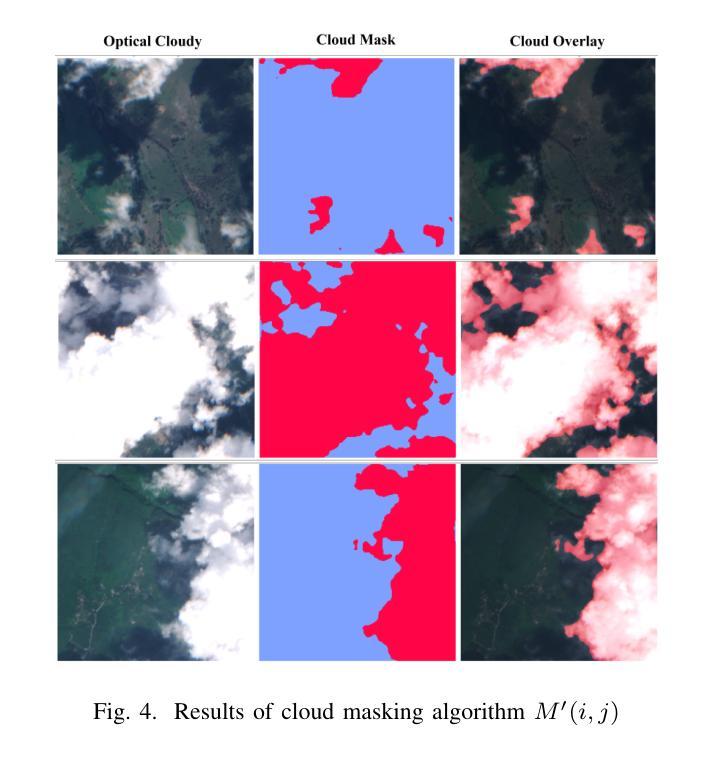
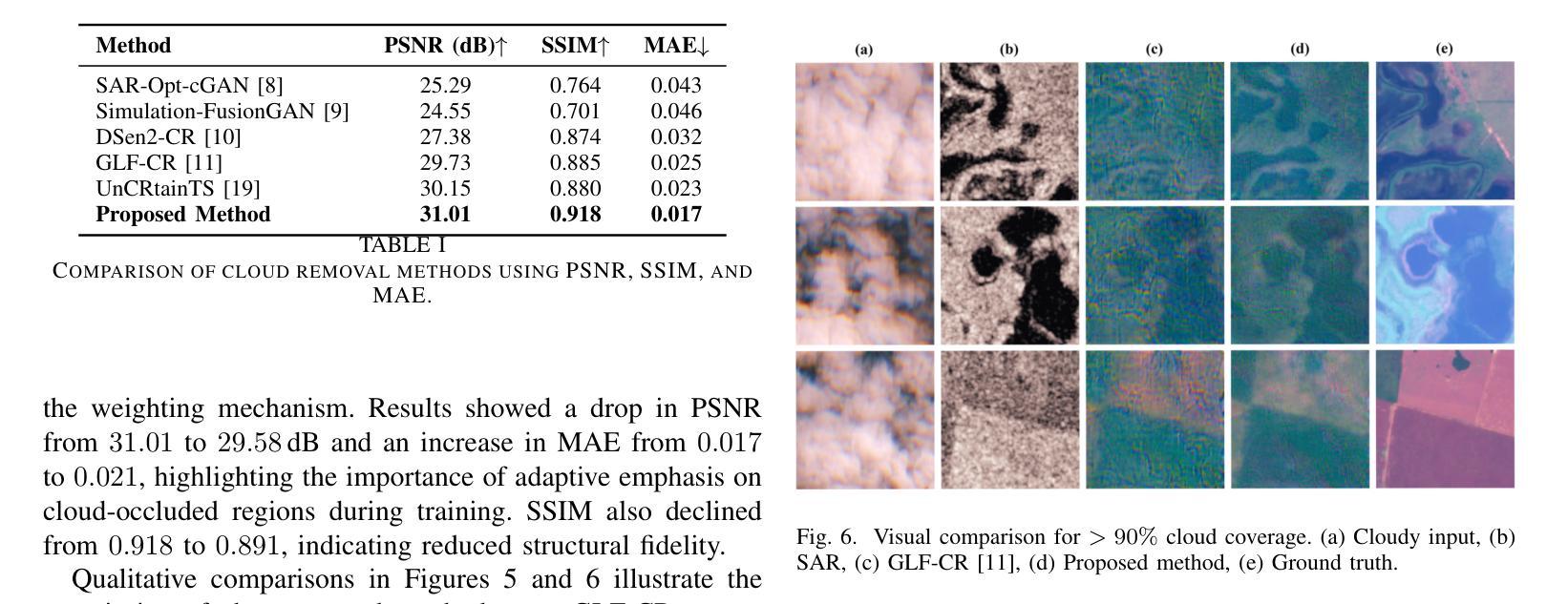
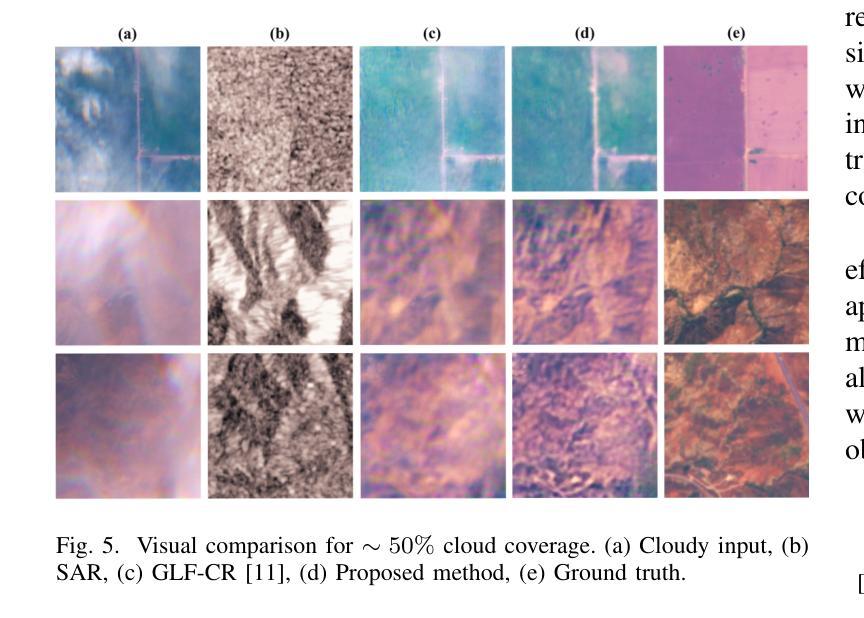
Cloud-Aware SAR Fusion for Enhanced Optical Sensing in Space Missions
Authors:Trong-An Bui, Thanh-Thoai Le
Cloud contamination significantly impairs the usability of optical satellite imagery, affecting critical applications such as environmental monitoring, disaster response, and land-use analysis. This research presents a Cloud-Attentive Reconstruction Framework that integrates SAR-optical feature fusion with deep learning-based image reconstruction to generate cloud-free optical imagery. The proposed framework employs an attention-driven feature fusion mechanism to align complementary structural information from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) with spectral characteristics from optical data. Furthermore, a cloud-aware model update strategy introduces adaptive loss weighting to prioritize cloud-occluded regions, enhancing reconstruction accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches, achieving a PSNR of 31.01 dB, SSIM of 0.918, and MAE of 0.017. These outcomes highlight the framework’s effectiveness in producing high-fidelity, spatially and spectrally consistent cloud-free optical images.
云污染严重损害了光学卫星图像的使用性能,对诸如环境监测、灾害响应和土地利用分析等关键应用产生了影响。本研究提出了一种云意识重建框架,该框架融合了SAR-光学特征融合和基于深度学习的图像重建技术,以生成无云光学图像。所提出的框架采用注意力驱动的特征融合机制,将合成孔径雷达(SAR)的互补结构信息与光学数据的光谱特征进行对齐。此外,云感知模型更新策略引入了自适应损失权重,以优先处理云遮挡区域,提高重建精度。实验结果表明,该方法优于现有方法,达到峰值信噪比(PSNR)31.01分贝,结构相似性(SSIM)0.918,平均绝对误差(MAE)0.017。这些结果突出了该框架在生成高保真、空间和光谱一致的无云光学图像方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出一种云感知重建框架,结合SAR-光学特征融合和深度学习图像重建技术,生成无云光学影像。该框架采用注意力驱动的特征融合机制,将SAR的互补结构信息与光学数据的光谱特征相结合。此外,云感知模型更新策略通过自适应损失加权来优先处理云遮挡区域,提高重建精度。
Key Takeaways
- 云污染严重影响光学卫星图像的使用,影响环境监控、灾害响应和土地利用分析等关键应用。
- 提出的Cloud-Attentive重建框架通过结合SAR-光学特征融合和深度学习图像重建技术,有效生成无云光学影像。
- 注意力驱动的特征融合机制用于结合SAR的互补结构信息和光学数据的光谱特征。
- 云感知模型更新策略通过自适应损失加权优化模型,优先处理云遮挡区域,提高重建准确性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法优于现有方法,达到PSNR 31.01 dB,SSIM 0.918,MAE 0.017。
- 这些结果证明了框架在生成高保真、空间和光谱一致的无云光学图像方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

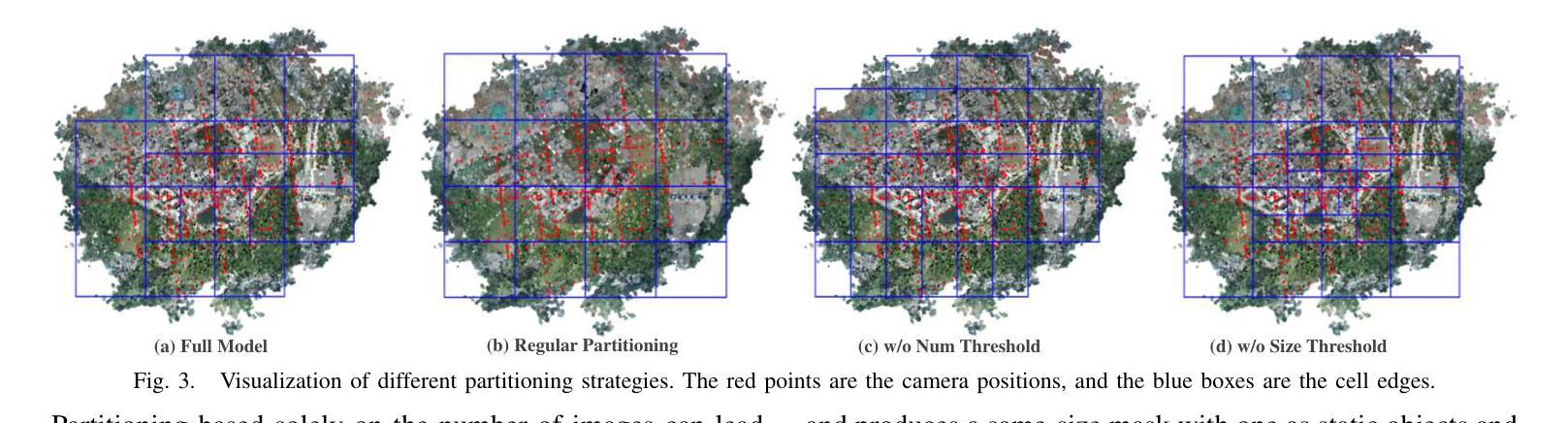
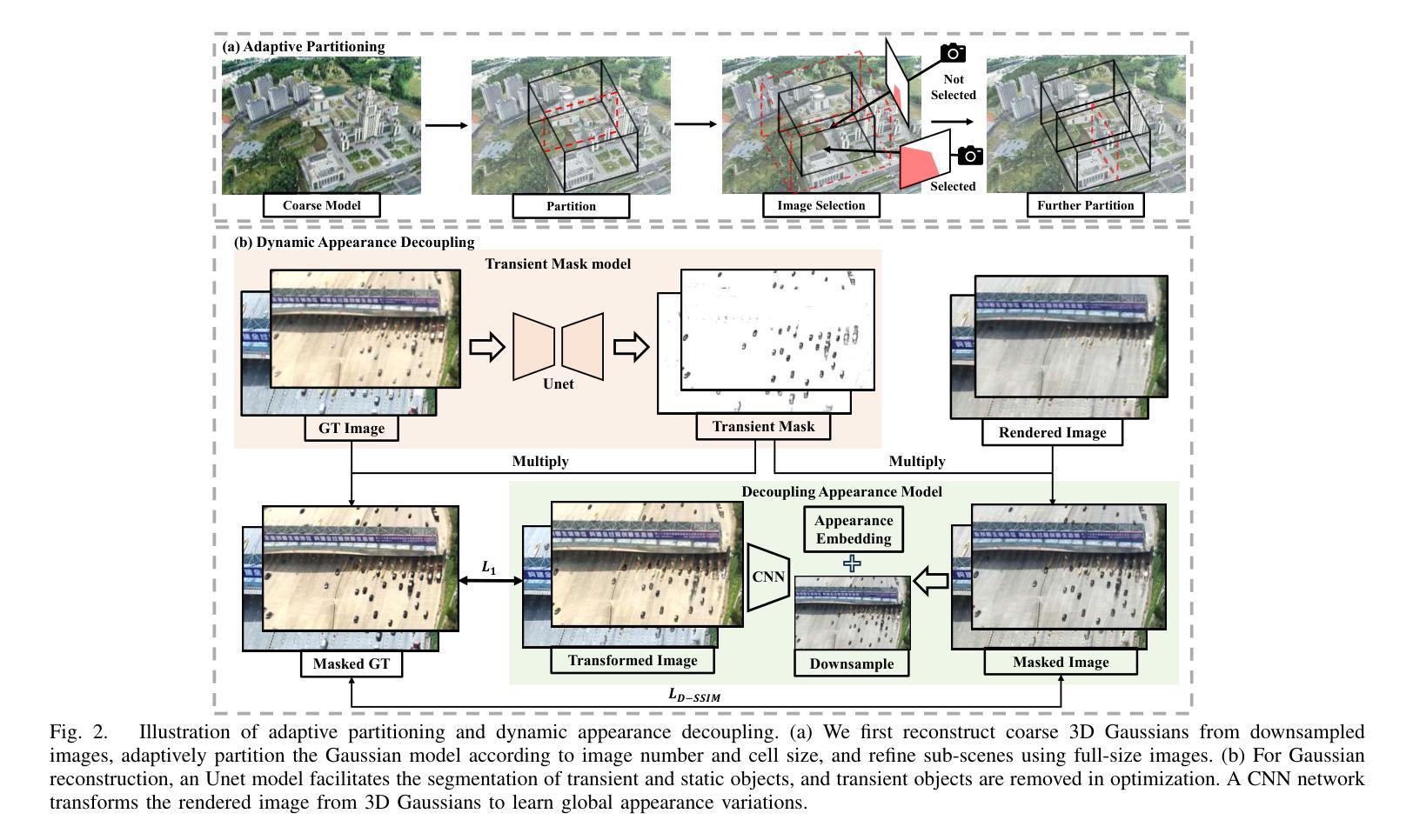
3D Gaussian Splatting for Fine-Detailed Surface Reconstruction in Large-Scale Scene
Authors:Shihan Chen, Zhaojin Li, Zeyu Chen, Qingsong Yan, Gaoyang Shen, Ran Duan
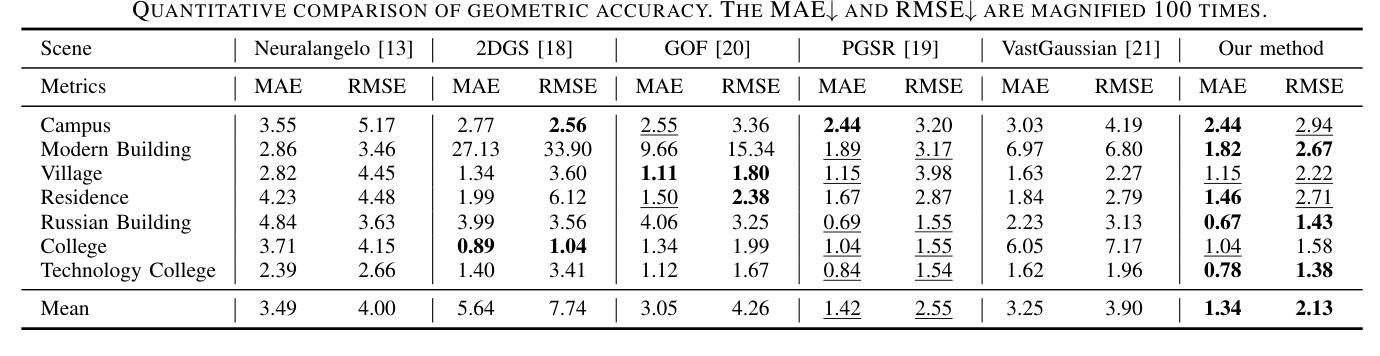
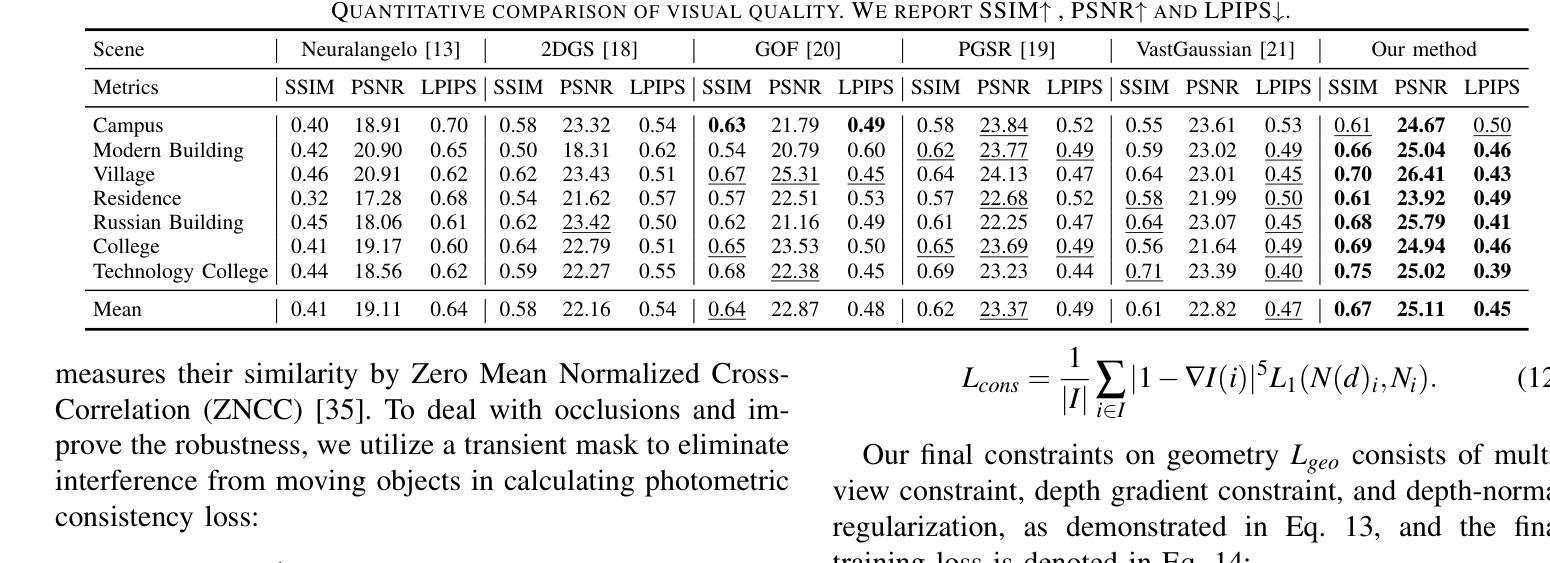
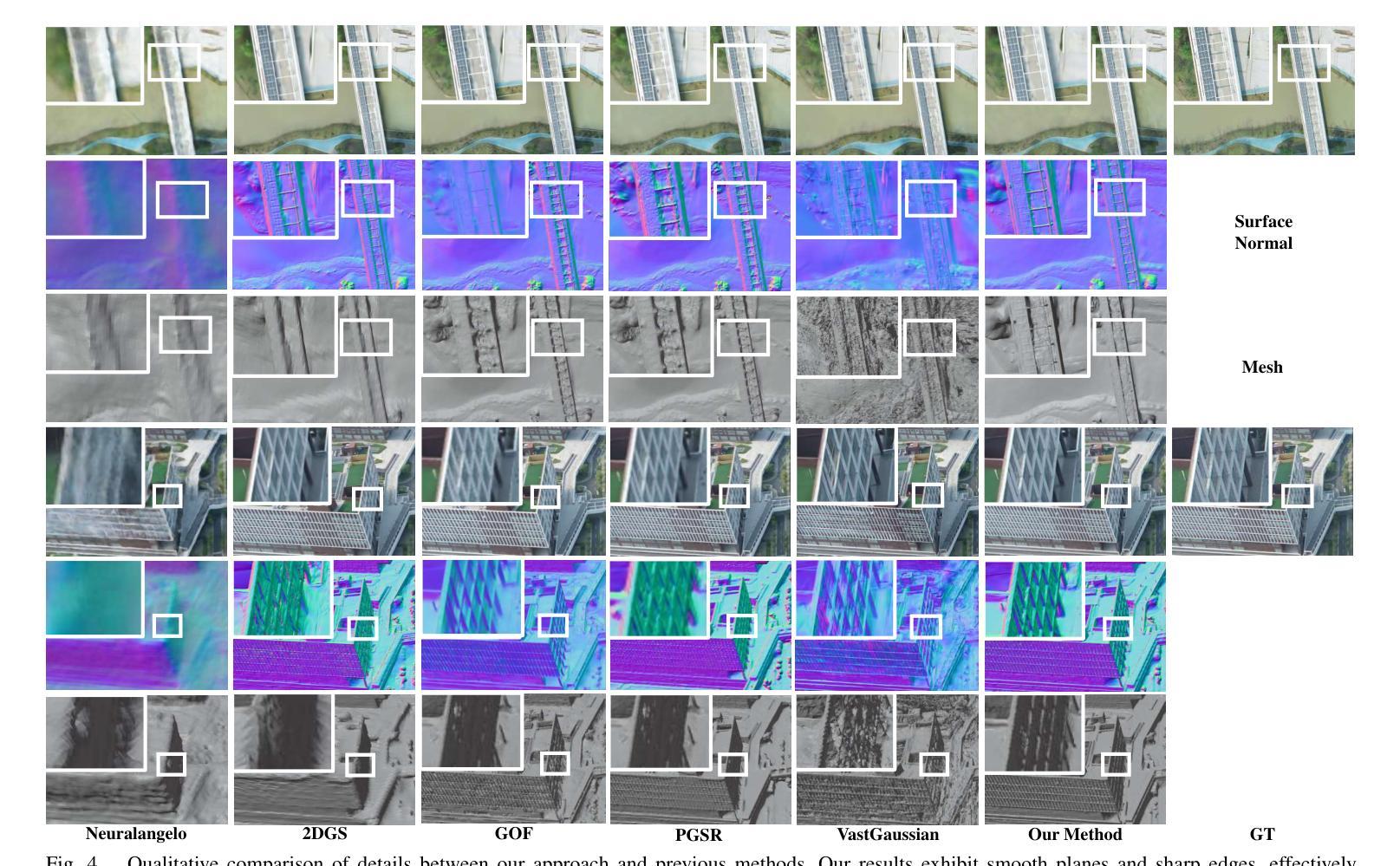
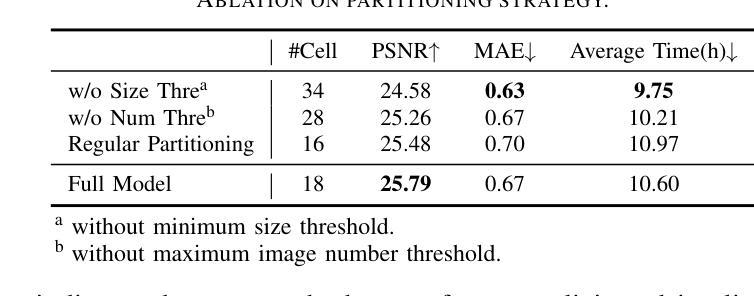
Recent developments in 3D Gaussian Splatting have made significant advances in surface reconstruction. However, scaling these methods to large-scale scenes remains challenging due to high computational demands and the complex dynamic appearances typical of outdoor environments. These challenges hinder the application in aerial surveying and autonomous driving. This paper proposes a novel solution to reconstruct large-scale surfaces with fine details, supervised by full-sized images. Firstly, we introduce a coarse-to-fine strategy to reconstruct a coarse model efficiently, followed by adaptive scene partitioning and sub-scene refining from image segments. Additionally, we integrate a decoupling appearance model to capture global appearance variations and a transient mask model to mitigate interference from moving objects. Finally, we expand the multi-view constraint and introduce a single-view regularization for texture-less areas. Our experiments were conducted on the publicly available dataset GauU-Scene V2, which was captured using unmanned aerial vehicles. To the best of our knowledge, our method outperforms existing NeRF-based and Gaussian-based methods, achieving high-fidelity visual results and accurate surface from full-size image optimization. Open-source code will be available on GitHub.
近期三维高斯扩展(3D Gaussian Splatting)在表面重建方面取得了显著进展。然而,由于户外环境的高计算需求和复杂动态外观,将这些方法扩展到大规模场景仍然具有挑战性。这些挑战阻碍了其在航空勘察和自动驾驶中的应用。本文提出了一种由全尺寸图像监督的重建大规模表面细节的新解决方案。首先,我们采用从粗到细的策略高效重建粗略模型,随后进行自适应场景分割和图像段的子场景细化。此外,我们集成了一个解耦的外观模型来捕捉全局外观变化和一个瞬态掩膜模型来缓解移动物体的干扰。最后,我们扩展了多视角约束并为无纹理区域引入了单视角正则化。我们在公开可用的GauU-Scene V2数据集上进行了实验,该数据集是通过无人机捕获的。据我们所知,我们的方法优于现有的基于NeRF和基于高斯的方法,实现了高保真视觉结果和通过全尺寸图像优化得到的精确表面。开源代码将在GitHub上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IROS 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于全尺寸图像监督的大规模场景表面重建新方法,采用从粗到细的重建策略,通过自适应场景分割和子场景细化技术,结合解耦外观模型和瞬态掩模模型,实现高保真视觉效果和精确的表面重建。该方法在公开数据集GauU-Scene V2上进行了实验验证,表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于全尺寸图像监督的大规模场景表面重建方法。
- 采用从粗到细的重建策略,先构建粗略模型,再进行细化。
- 通过自适应场景分割和子场景细化技术,提高重建精度。
- 结合解耦外观模型和瞬态掩模模型,捕捉全局外观变化和减轻移动物体的干扰。
- 拓展了多视角约束,引入了单视角正则化,用于处理纹理缺失区域。
- 在公开数据集GauU-Scene V2上进行了实验验证,该方法优于现有的NeRF和Gaussian方法。
点此查看论文截图


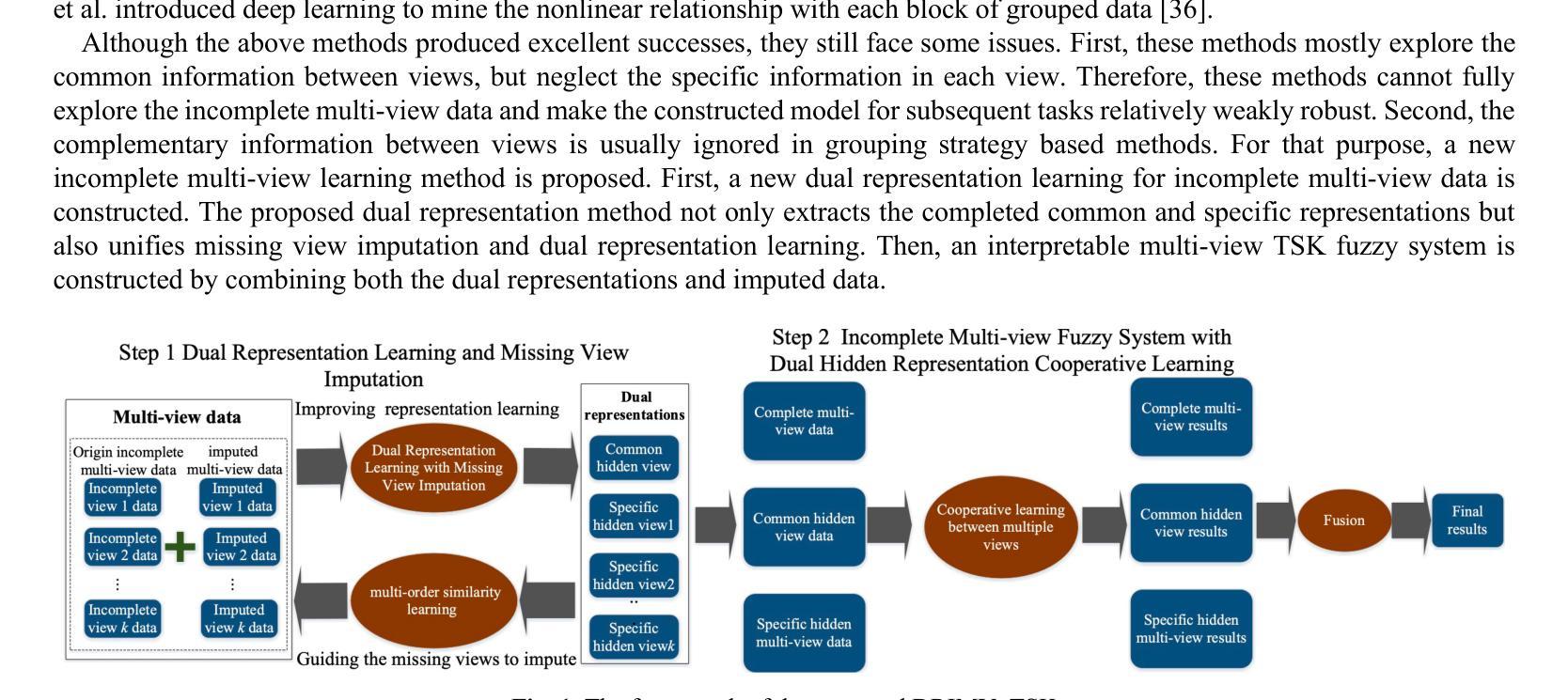
DRIMV_TSK: An Interpretable Surgical Evaluation Model for Incomplete Multi-View Rectal Cancer Data
Authors:Wei Zhang, Zi Wang, Hanwen Zhou, Zhaohong Deng, Weiping Ding, Yuxi Ge, Te Zhang, Yuanpeng Zhang, Kup-Sze Choi, Shitong Wang, Shudong Hu
A reliable evaluation of surgical difficulty can improve the success of the treatment for rectal cancer and the current evaluation method is based on clinical data. However, more data about rectal cancer can be collected with the development of technology. Meanwhile, with the development of artificial intelligence, its application in rectal cancer treatment is becoming possible. In this paper, a multi-view rectal cancer dataset is first constructed to give a more comprehensive view of patients, including the high-resolution MRI image view, pressed-fat MRI image view, and clinical data view. Then, an interpretable incomplete multi-view surgical evaluation model is proposed, considering that it is hard to obtain extensive and complete patient data in real application scenarios. Specifically, a dual representation incomplete multi-view learning model is first proposed to extract the common information between views and specific information in each view. In this model, the missing view imputation is integrated into representation learning, and second-order similarity constraint is also introduced to improve the cooperative learning between these two parts. Then, based on the imputed multi-view data and the learned dual representation, a multi-view surgical evaluation model with the TSK fuzzy system is proposed. In the proposed model, a cooperative learning mechanism is constructed to explore the consistent information between views, and Shannon entropy is also introduced to adapt the view weight. On the MVRC dataset, we compared it with several advanced algorithms and DRIMV_TSK obtained the best results.
对手术难度的可靠评估可以提高直肠癌治疗成功率,目前的评估方法主要基于临床数据。然而,随着科技的发展,可以收集到更多关于直肠癌的数据。同时,随着人工智能的发展,其在直肠癌治疗中的应用也成为可能。本文首先构建了一个多视角直肠癌数据集,为患者提供更全面的视角,包括高分辨率MRI图像视角、受压脂肪MRI图像视角和临床数据视角。然后,提出了一种可解释的、不完全的多视角手术评估模型,考虑到在实际应用场景中很难获得全面完整的病人数据。具体来说,首先提出了一种双重表示的不完全多视角学习模型,以提取各视角间的共同信息和每个视角的特定信息。在该模型中,将缺失视角的填补整合到表示学习中,并引入了二阶相似性约束,以提高这两部分的协同学习。然后,基于补齐的多视角数据和学到的双重表示,结合TSK模糊系统,提出了一种多视角手术评估模型。在该模型中,构建了一种协同学习机制来探索各视角间的共同信息,并引入了香农熵来适应视角权重。在MVRC数据集上,与几种先进算法相比,DRIMV_TSK取得了最佳结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要构建了一个多视角的直肠癌数据集,并基于该数据集提出了一种可解释的不完全多视角手术评估模型。通过整合缺失视角的插补和表示学习,该模型能够提取不同视角间的共同信息和特定信息。引入二阶相似度约束以改善这两部分之间的协同学习。并结合插补的多视角数据和学习的双重表示,提出了一种基于TSK模糊系统的多视角手术评估模型。该模型通过合作机制探索视角间的一致性信息,并引入香农熵来适应视角权重。在MVRC数据集上的实验结果表明,DRIMV_TSK获得了最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 文本提出了构建多视角的直肠癌数据集的重要性,旨在提供更全面的患者信息,包括高分辨率MRI图像、受压脂肪MRI图像和临床数据。
- 针对实际应用场景中患者数据不全面和缺失的问题,文本提出了一种可解释的不完全多视角手术评估模型。
- 该模型结合了缺失视角插补和表示学习,以提取不同视角间的共同信息和特定信息。
- 为了提高模型性能,引入了二阶相似度约束,改善了不同部分之间的协同学习。
- 结合插补的多视角数据和学习的双重表示,文本还提出了一种基于TSK模糊系统的多视角手术评估模型。
- 该模型通过合作机制探索视角间的一致性信息,增强了模型的决策能力。
点此查看论文截图

Exploring Strategies for Personalized Radiation Therapy Part II Predicting Tumor Drift Patterns with Diffusion Models
Authors:Hao Peng, Steve Jiang, Robert Timmerman
Radiation therapy outcomes are decided by two key parameters, dose and timing, whose best values vary substantially across patients. This variability is especially critical in the treatment of brain cancer, where fractionated or staged stereotactic radiosurgery improves safety compared to single fraction approaches, but complicates the ability to predict treatment response. To address this challenge, we employ Personalized Ultra-fractionated Stereotactic Adaptive Radiotherapy (PULSAR), a strategy that dynamically adjusts treatment based on how each tumor evolves over time. However, the success of PULSAR and other adaptive approaches depends on predictive tools that can guide early treatment decisions and avoid both overtreatment and undertreatment. However, current radiomics and dosiomics models offer limited insight into the evolving spatial and temporal patterns of tumor response. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel framework using Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM), which learns data-driven mappings from pre to post treatment imaging. In this study, we developed single step and iterative denoising strategies and compared their performance. The results show that diffusion models can effectively simulate patient specific tumor evolution and localize regions associated with treatment response. The proposed strategy provides a promising foundation for modeling heterogeneous treatment response and enabling early, adaptive interventions, paving the way toward more personalized and biologically informed radiotherapy.
放疗效果由剂量和时间这两个关键参数决定,而最佳值在不同患者之间有很大的差异。这种差异在脑癌的治疗中尤其关键,分段或分期立体定向放射手术与单次手术相比提高了安全性,但增加了预测治疗反应的能力的难度。为了应对这一挑战,我们采用了个性化超分段立体定向自适应放疗(PULSAR)策略,该策略根据每个肿瘤的随时间演变情况动态调整治疗。然而,PULSAR和其他自适应方法的成功取决于能够指导早期治疗决策并避免过度治疗和不足治疗的预测工具。然而,当前的放射学组和剂量学模型对于肿瘤反应的空间和时间模式的演变提供了有限的见解。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了一种使用去噪扩散隐式模型(DDIM)的新框架,该模型可以从治疗前到治疗后的成像中学习数据驱动映射。在这项研究中,我们开发了单步和迭代去噪策略并比较了它们的性能。结果表明,扩散模型可以有效地模拟患者特定的肿瘤演变,并定位与治疗反应相关的区域。所提出的策略为模拟异质治疗反应和早期自适应干预提供了有前途的基础,为更个性化和生物学信息驱动的放射治疗铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了放射治疗结果由剂量和时间两个关键参数决定,不同患者最佳值差异较大。在治疗脑癌时,分次或分期立体定向放射手术相较于单次放射治疗更为安全,但预测治疗反应的能力却复杂化。为应对这一挑战,本文采用个性化超分次立体定向自适应放射治疗(PULSAR)策略,根据肿瘤随时间的变化动态调整治疗。但PULSAR等自适应策略的成功取决于能够指导早期治疗决策并避免过度或不足治疗的预测工具。当前放射学和剂量学模型对肿瘤反应的空间和时间模式演变了解有限。本文提出一种新型框架,采用去噪扩散隐模型(DDIM),从治疗前到治疗后的成像学习数据驱动映射。本研究开发了单步和迭代去噪策略,并比较了它们的性能。结果表明,扩散模型可有效模拟患者特定的肿瘤演变,并定位与治疗反应相关的区域。所提策略为模拟异质性治疗反应和早期自适应干预提供了有前途的基础,为更个性化和生物学信息驱动的放射治疗铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 放射治疗结果受剂量和时间的双重影响,不同患者的最佳值差异显著。
- 在脑癌治疗中,分次或分期立体定向放射手术能提高安全性,但预测治疗反应的难度增加。
- PULSAR策略能根据肿瘤变化动态调整治疗,但成功依赖于预测工具。
- 当前放射学和剂量学模型对肿瘤反应的空间和时间模式演变了解有限。
- 新型去噪扩散隐模型(DDIM)框架被提出,以从治疗前到治疗后的成像中学习数据驱动映射。
- 扩散模型能有效模拟患者特定肿瘤演变,并定位与治疗反应相关区域。
点此查看论文截图