⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
Temporal Neural Cellular Automata: Application to modeling of contrast enhancement in breast MRI
Authors:Daniel M. Lang, Richard Osuala, Veronika Spieker, Karim Lekadir, Rickmer Braren, Julia A. Schnabel
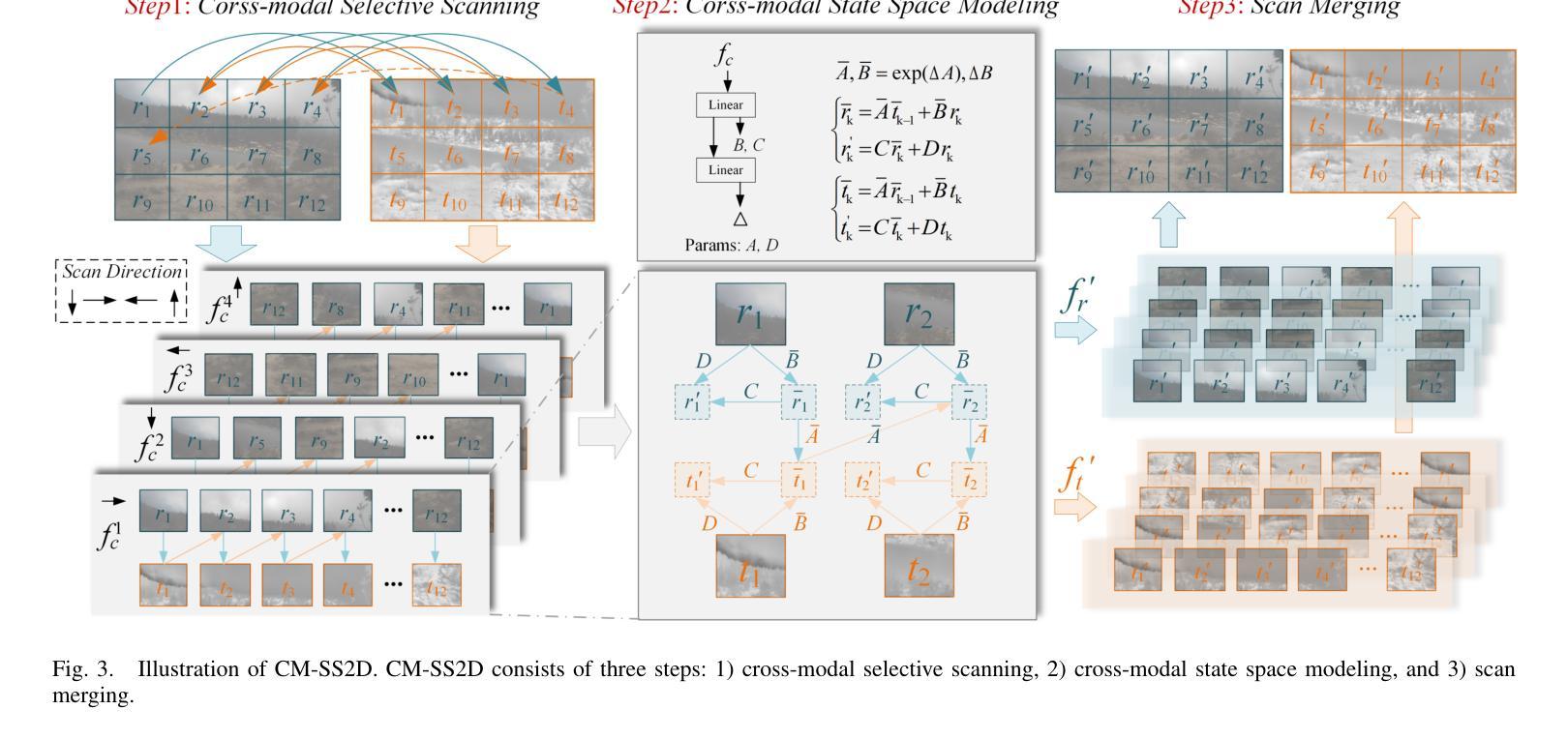
Synthetic contrast enhancement offers fast image acquisition and eliminates the need for intravenous injection of contrast agent. This is particularly beneficial for breast imaging, where long acquisition times and high cost are significantly limiting the applicability of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a widespread screening modality. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of synthetic contrast generation. However, current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods lack sufficient measures for consistent temporal evolution. Neural cellular automata (NCA) offer a robust and lightweight architecture to model evolving patterns between neighboring cells or pixels. In this work we introduce TeNCA (Temporal Neural Cellular Automata), which extends and further refines NCAs to effectively model temporally sparse, non-uniformly sampled imaging data. To achieve this, we advance the training strategy by enabling adaptive loss computation and define the iterative nature of the method to resemble a physical progression in time. This conditions the model to learn a physiologically plausible evolution of contrast enhancement. We rigorously train and test TeNCA on a diverse breast MRI dataset and demonstrate its effectiveness, surpassing the performance of existing methods in generation of images that align with ground truth post-contrast sequences.
合成对比增强法能够实现快速图像采集,并且无需注射对比剂。这在乳腺成像中尤其有益,因为长时间的采集和高成本极大地限制了磁共振成像(MRI)作为一种广泛筛查手段的应用。近期的研究已经证明了合成对比剂生成的可行性。然而,当前最前沿的方法缺乏一致的时序演化衡量标准。神经元细胞自动机(NCA)提供了一种稳健且轻量级的架构,可以模拟相邻细胞或像素之间的演化模式。在这项工作中,我们引入了TeNCA(时序神经元细胞自动机),对NCA进行了扩展和进一步细化,以有效地模拟时序稀疏、非均匀采样的成像数据。为此,我们通过实现自适应损失计算来改进训练策略,并定义了方法的迭代性质,以模拟时间的物理进展。这使得模型能够学习对比增强在生理上的可能演化。我们在多样化的乳腺MRI数据集上对TeNCA进行了严格的训练和测试,并证明了其有效性,在生成与真实对比序列相符的图像方面超越了现有方法的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了合成对比增强技术在快速图像采集中的应用,该技术无需静脉注射对比剂即可实现图像增强。特别是对于乳腺成像,合成对比增强技术解决了长时间采集和高成本的问题,提高了磁共振成像(MRI)作为广泛筛查模式的适用性。研究中引入了一种新的方法——时序神经网络细胞自动机(TeNCA),它能够有效地对时间上稀疏、非均匀采样的成像数据进行建模。通过改进训练策略和实现自适应损失计算,TeNCA能够学习对比增强的生理过程,并在多样化的乳腺MRI数据集上进行严格训练和测试,展现出其有效性,超越了现有方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 合成对比增强技术无需使用对比剂即可快速获取图像。
- 该技术在乳腺成像中特别有益,解决了长时间采集和高成本的问题。
- 当前先进技术缺乏一致的时空演化衡量标准。
- 神经网络细胞自动机(NCA)提供了一个稳健且轻量级的架构来模拟相邻细胞或像素之间的演化模式。
- 引入的时序神经网络细胞自动机(TeNCA)能有效建模时间上稀疏、非均匀采样的成像数据。
- TeNCA通过改进训练策略和自适应损失计算,能够学习对比增强的生理过程。
点此查看论文截图

Resampling Augmentation for Time Series Contrastive Learning: Application to Remote Sensing
Authors:Antoine Saget, Baptiste Lafabregue, Antoine Cornuéjols, Pierre Gançarski
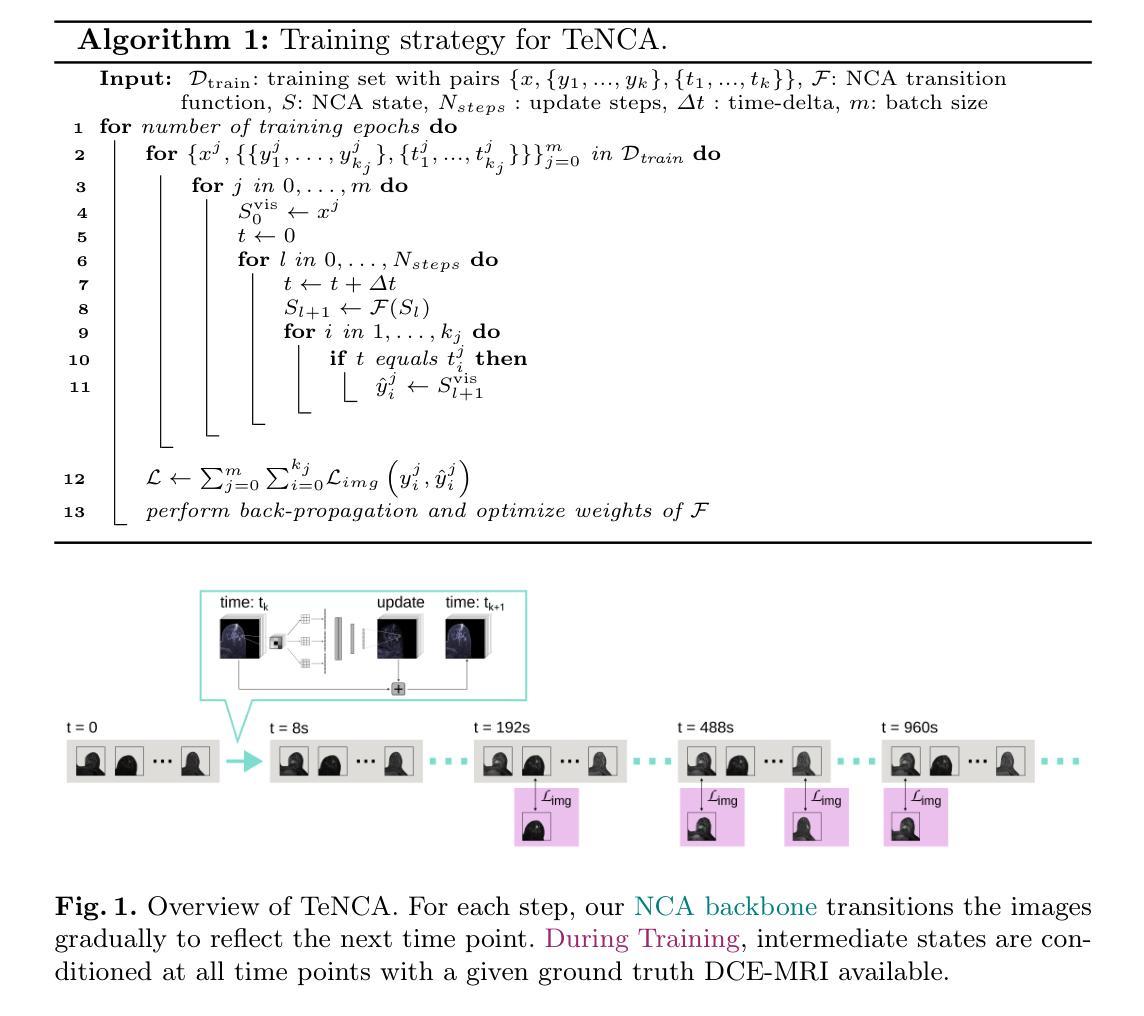
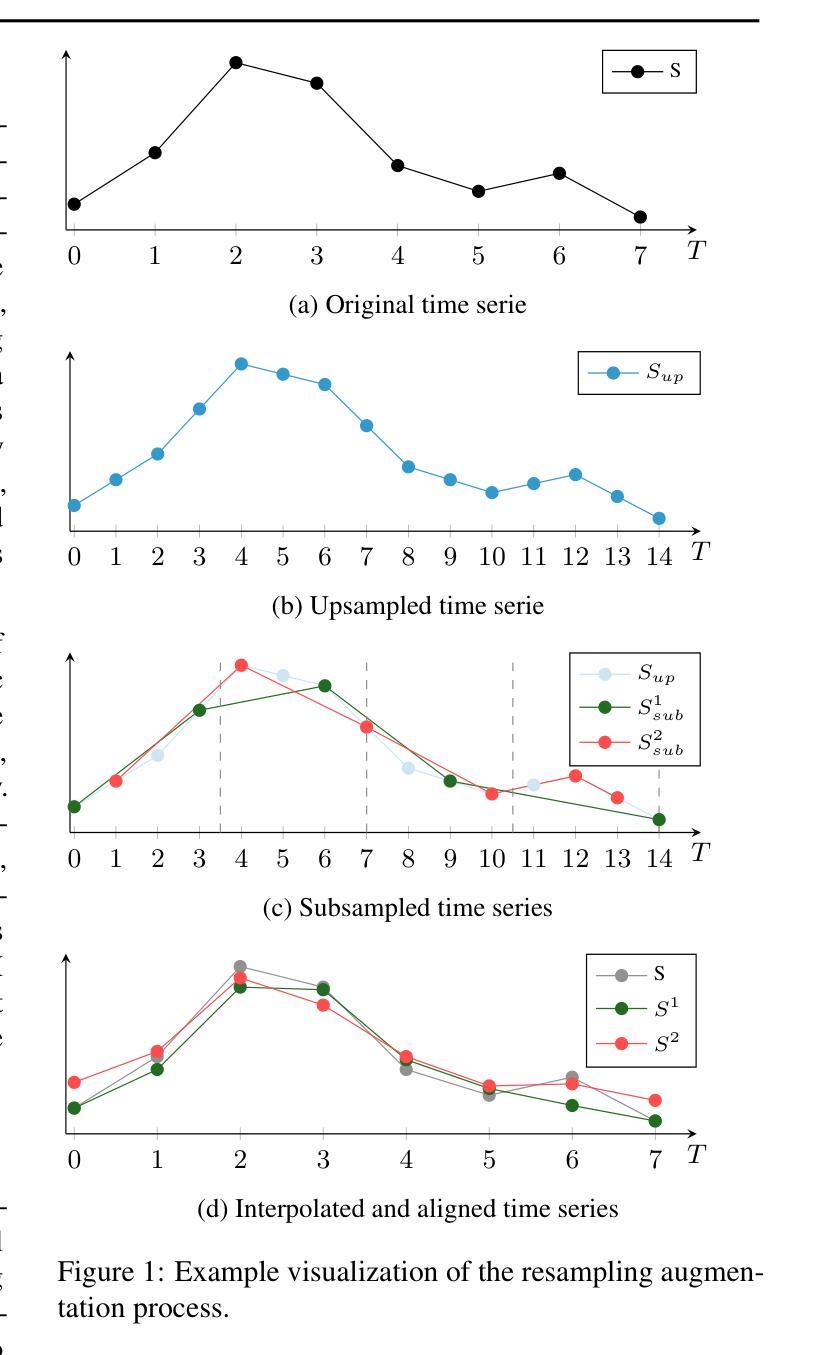
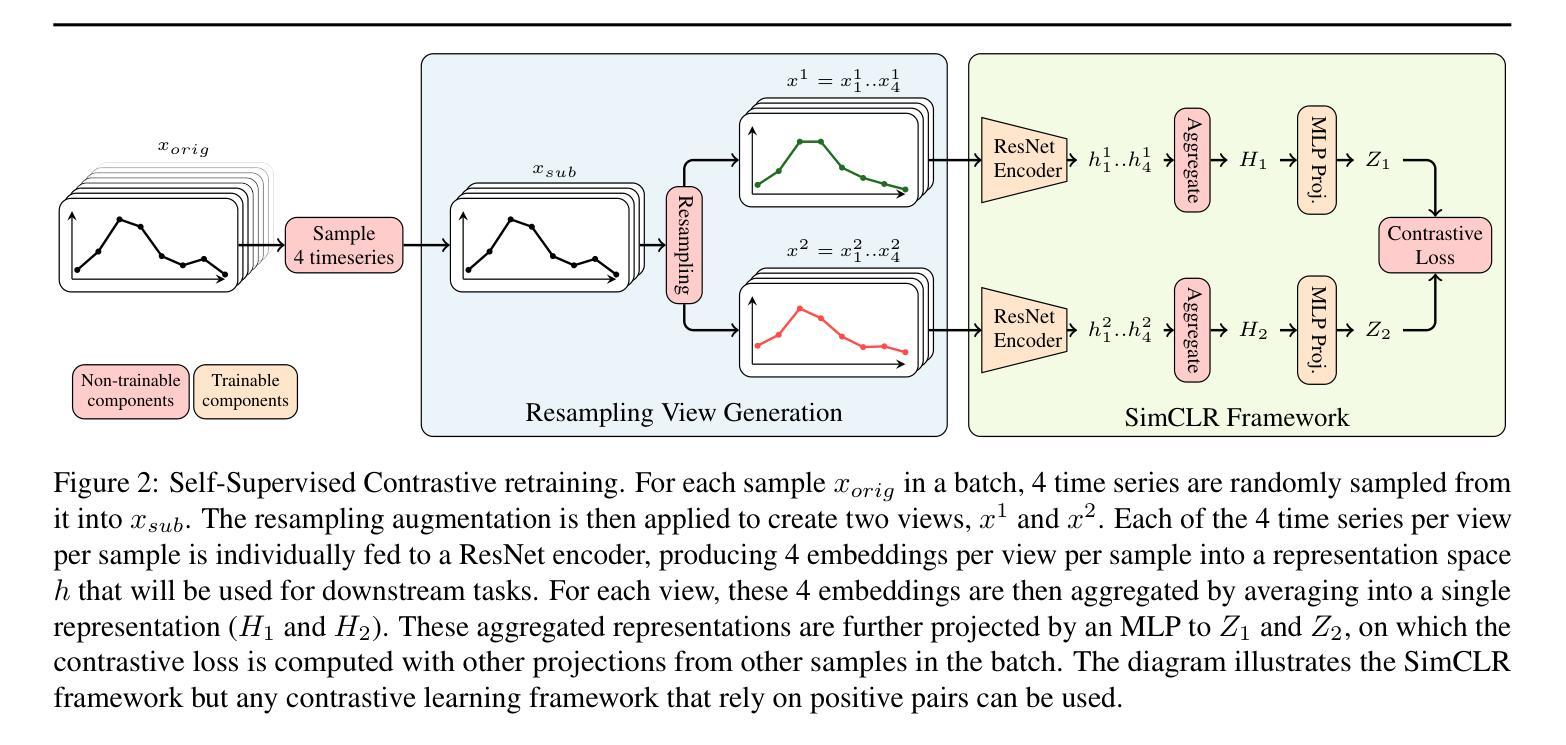
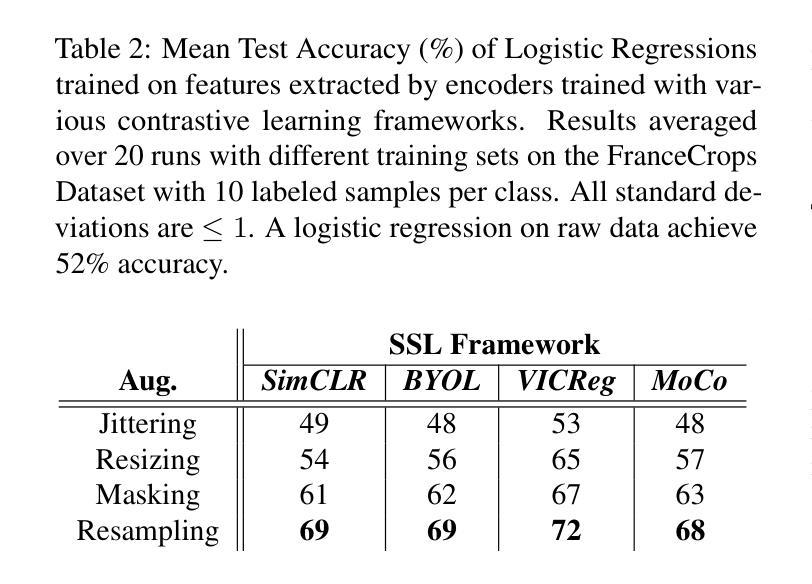
Given the abundance of unlabeled Satellite Image Time Series (SITS) and the scarcity of labeled data, contrastive self-supervised pretraining emerges as a natural tool to leverage this vast quantity of unlabeled data. However, designing effective data augmentations for contrastive learning remains challenging for time series. We introduce a novel resampling-based augmentation strategy that generates positive pairs by upsampling time series and extracting disjoint subsequences while preserving temporal coverage. We validate our approach on multiple agricultural classification benchmarks using Sentinel-2 imagery, showing that it outperforms common alternatives such as jittering, resizing, and masking. Further, we achieve state-of-the-art performance on the S2-Agri100 dataset without employing spatial information or temporal encodings, surpassing more complex masked-based SSL frameworks. Our method offers a simple, yet effective, contrastive learning augmentation for remote sensing time series.
考虑到卫星图像时间序列(SITS)的大量无标签数据以及标签数据的稀缺性,对比自监督预训练成为利用大量无标签数据的自然工具。然而,为对比学习设计有效的数据增强对于时间序列来说仍然具有挑战性。我们引入了一种基于重采样新的数据增强策略,通过上采样时间序列并提取不相邻的子序列来生成正样本对,同时保留时间覆盖。我们在多个农业分类基准测试上,使用Sentinel-2图像验证了我们的方法,表明它优于常见的替代方法,如抖动、改变尺寸和遮罩。此外,在S2-Agri100数据集上,我们在不使用空间信息或时间编码的情况下实现了最先进的性能,超越了更复杂的基于遮罩的SSL框架。我们的方法为遥感时间序列提供了一种简单有效的对比学习增强方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, accepted at 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025) Terrabytes workshop
Summary:针对卫星图像时间序列(SITS)数据量大而标注数据稀缺的问题,对比自监督预训练成为利用大量无标签数据的有效工具。然而,为对比学习设计有效的数据增强仍具有挑战性。研究团队提出了一种基于重采样的新型增强策略,通过上采样时间序列并提取不相交子序列来生成正样本对,同时保持时间覆盖。在多个农业分类基准测试中验证了该方法的有效性,且在不使用空间信息或时间编码的情况下,在S2-Agri100数据集上实现了最先进的性能表现,超越了更复杂的基于掩码的SSL框架。此方法提供了一种简单有效的对比学习增强方法,适用于遥感时间序列。
Key Takeaways:
- 对比自监督预训练能有效利用大量的无标签卫星图像时间序列数据。
- 设计有效的数据增强策略对于对比学习在时间序列中的应用是关键的挑战。
- 研究团队提出了一种基于重采样的新型增强策略,通过上采样时间序列并提取子序列来生成正样本对。
- 该方法在多个农业分类基准测试中表现出良好的性能,且在不使用额外的空间或时间信息的情况下取得了先进的成果。
- 该方法在S2-Agri100数据集上的性能超越了更复杂的基于掩码的SSL框架。
- 此方法提供了一种简单有效的对比学习增强方法,特别适用于遥感时间序列数据。
点此查看论文截图


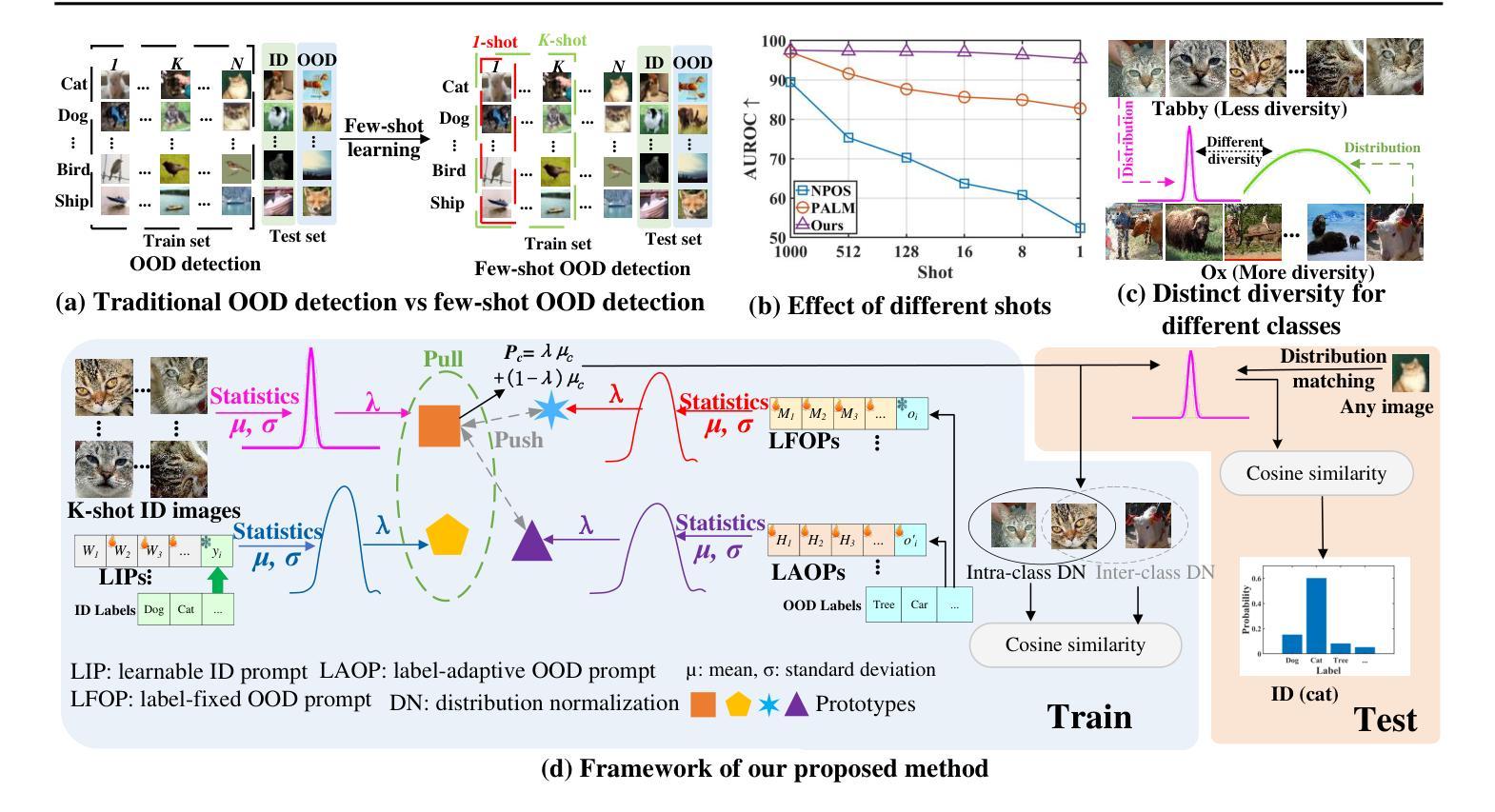
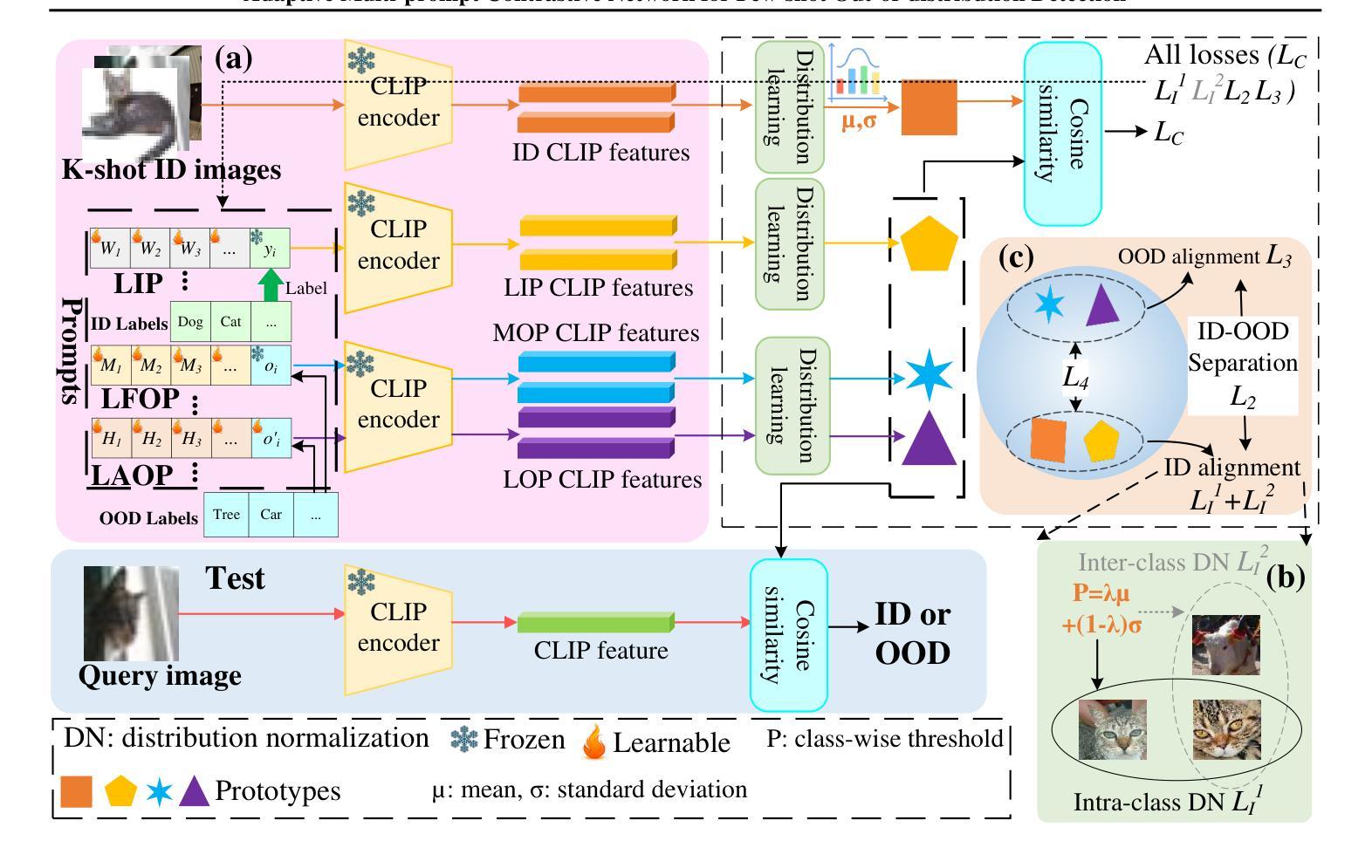
Adaptive Multi-prompt Contrastive Network for Few-shot Out-of-distribution Detection
Authors:Xiang Fang, Arvind Easwaran, Blaise Genest
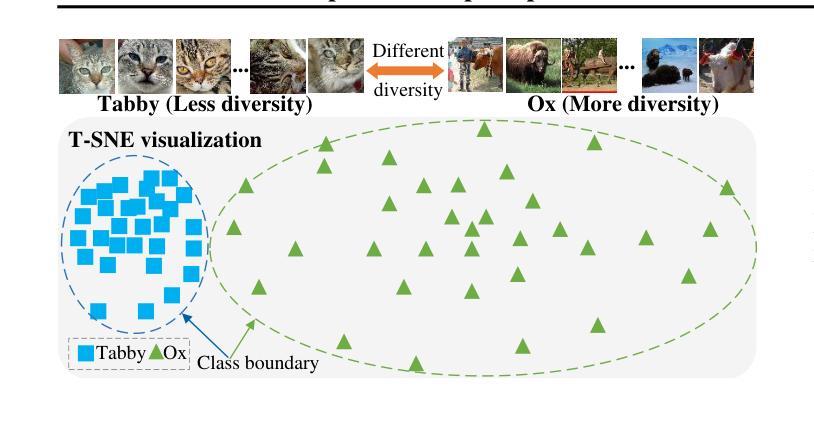
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection attempts to distinguish outlier samples to prevent models trained on the in-distribution (ID) dataset from producing unavailable outputs. Most OOD detection methods require many IID samples for training, which seriously limits their real-world applications. To this end, we target a challenging setting: few-shot OOD detection, where {Only a few {\em labeled ID} samples are available.} Therefore, few-shot OOD detection is much more challenging than the traditional OOD detection setting. Previous few-shot OOD detection works ignore the distinct diversity between different classes. In this paper, we propose a novel network: Adaptive Multi-prompt Contrastive Network (AMCN), which adapts the ID-OOD separation boundary by learning inter- and intra-class distribution. To compensate for the absence of OOD and scarcity of ID {\em image samples}, we leverage CLIP, connecting text with images, engineering learnable ID and OOD {\em textual prompts}. Specifically, we first generate adaptive prompts (learnable ID prompts, label-fixed OOD prompts and label-adaptive OOD prompts). Then, we generate an adaptive class boundary for each class by introducing a class-wise threshold. Finally, we propose a prompt-guided ID-OOD separation module to control the margin between ID and OOD prompts. Experimental results show that AMCN outperforms other state-of-the-art works.
异常检测(Out-of-Distribution, OOD)旨在区分异常样本,防止在分布内(In-Distribution, ID)数据集上训练的模型产生无法使用的输出。大多数OOD检测方法需要大量的IID样本进行训练,这严重限制了它们在现实世界中的应用。为此,我们针对一个具有挑战性的场景:少样本异常检测(few-shot OOD detection),此时只有少量的标记ID样本可用。因此,少样本异常检测比传统的异常检测设置更具挑战性。之前的少样本异常检测工作忽略了不同类别之间的明显差异。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型网络:自适应多提示对比网络(Adaptive Multi-prompt Contrastive Network, AMCN),它通过学习类间和类内分布来适应ID-OOD分割边界。为了弥补异常样本的缺失和ID图像样本的稀缺性,我们利用CLIP技术,将文本与图像相结合,构建可学习的ID和OOD文本提示。具体来说,我们首先生成自适应提示(可学习的ID提示、固定标签的OOD提示和自适应标签的OOD提示)。然后,我们通过引入类别特定的阈值,为每个类别生成自适应的类别边界。最后,我们提出了一个提示引导的ID-OOD分离模块,以控制ID和OOD提示之间的间距。实验结果表明,AMCN优于其他先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型网络结构:自适应多提示对比网络(AMCN),用于处理少样本环境下的异常检测问题。该网络通过生成自适应提示和引入类别级阈值,学习类间和类内分布,以弥补异常样本的缺失和图像样本的稀缺性。实验结果表明,AMCN在少样本异常检测任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 文章解决了真实世界中OOD检测中面临的训练样本有限的问题。提出的自适应多提示对比网络能够在少数标记样本的条件下进行有效学习。
- 利用CLIP技术连接文本和图像,构建可学习的ID和OOD文本提示,以弥补图像样本的稀缺性。
- 提出自适应提示生成,包括可学习的ID提示、固定的OOD提示和标签自适应的OOD提示。
- 通过引入类别级阈值,为每个类别生成自适应的类别边界。
- 提出提示引导的ID-OOD分离模块,控制ID和OOD提示之间的间隔。
点此查看论文截图