⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
Pre-Trained LLM is a Semantic-Aware and Generalizable Segmentation Booster
Authors:Fenghe Tang, Wenxin Ma, Zhiyang He, Xiaodong Tao, Zihang Jiang, S. Kevin Zhou
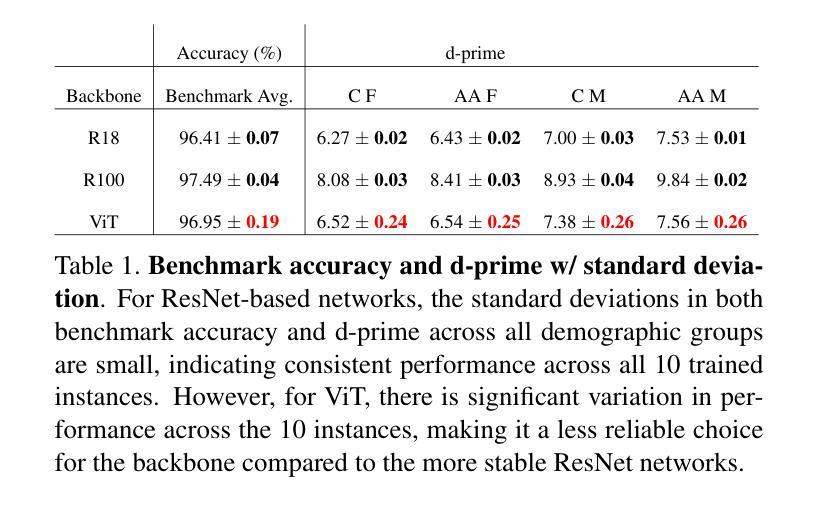
With the advancement of Large Language Model (LLM) for natural language processing, this paper presents an intriguing finding: a frozen pre-trained LLM layer can process visual tokens for medical image segmentation tasks. Specifically, we propose a simple hybrid structure that integrates a pre-trained, frozen LLM layer within the CNN encoder-decoder segmentation framework (LLM4Seg). Surprisingly, this design improves segmentation performance with a minimal increase in trainable parameters across various modalities, including ultrasound, dermoscopy, polypscopy, and CT scans. Our in-depth analysis reveals the potential of transferring LLM’s semantic awareness to enhance segmentation tasks, offering both improved global understanding and better local modeling capabilities. The improvement proves robust across different LLMs, validated using LLaMA and DeepSeek.
随着自然语言处理中大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,本文发现了一个有趣的现象:冻结的预训练LLM层可以处理医学图像分割任务的视觉标记。具体来说,我们提出了一种简单的混合结构,该结构在CNN编码器-解码器分割框架中集成了预训练的冻结LLM层(LLM4Seg)。令人惊讶的是,这种设计在各种模态(包括超声、皮肤镜检查、内窥镜检查和CT扫描)的分割性能上都有所提高,同时可训练参数也略有增加。我们的深入分析揭示了将LLM的语义意识转移到增强分割任务的潜力,既提高了全局理解力又提高了局部建模能力。这一改进在不同LLM中的稳健性得到了证明,通过使用LLaMA和DeepSeek进行了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025. Code: https://github.com/FengheTan9/LLM4Seg
Summary
本文探讨了将预冻结的大型语言模型层应用于医疗图像分割任务的视觉令牌处理。提出了一种将预训练冻结的大型语言模型层与CNN编码器-解码器分割框架相结合的简单混合结构(LLM4Seg)。这种设计在超声、皮肤镜、内窥镜检查和CT扫描等多种模态上提高了分割性能,并且只需增加少量可训练参数。深入分析表明,迁移大型语言模型的语义意识有助于增强分割任务,既提高了全局理解又提高了局部建模能力。不同的大型语言模型的改进均表现稳健,使用LLaMA和DeepSeek进行了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 预冻结的大型语言模型层可用于处理医疗图像分割任务的视觉令牌。
- 提出了一种结合预训练冻结的大型语言模型层与CNN编码器-解码器分割框架的混合结构(LLM4Seg)。
- 该设计在多种模态图像分割任务上提高了性能,包括超声、皮肤镜、内窥镜检查和CT扫描。
- 迁移大型语言模型的语义意识有助于提高分割任务的性能。
- 这种改进方法在不同的大型语言模型中表现稳健,包括LLaMA和DeepSeek。
- 该方法在提高全局理解的同时,也增强了局部建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

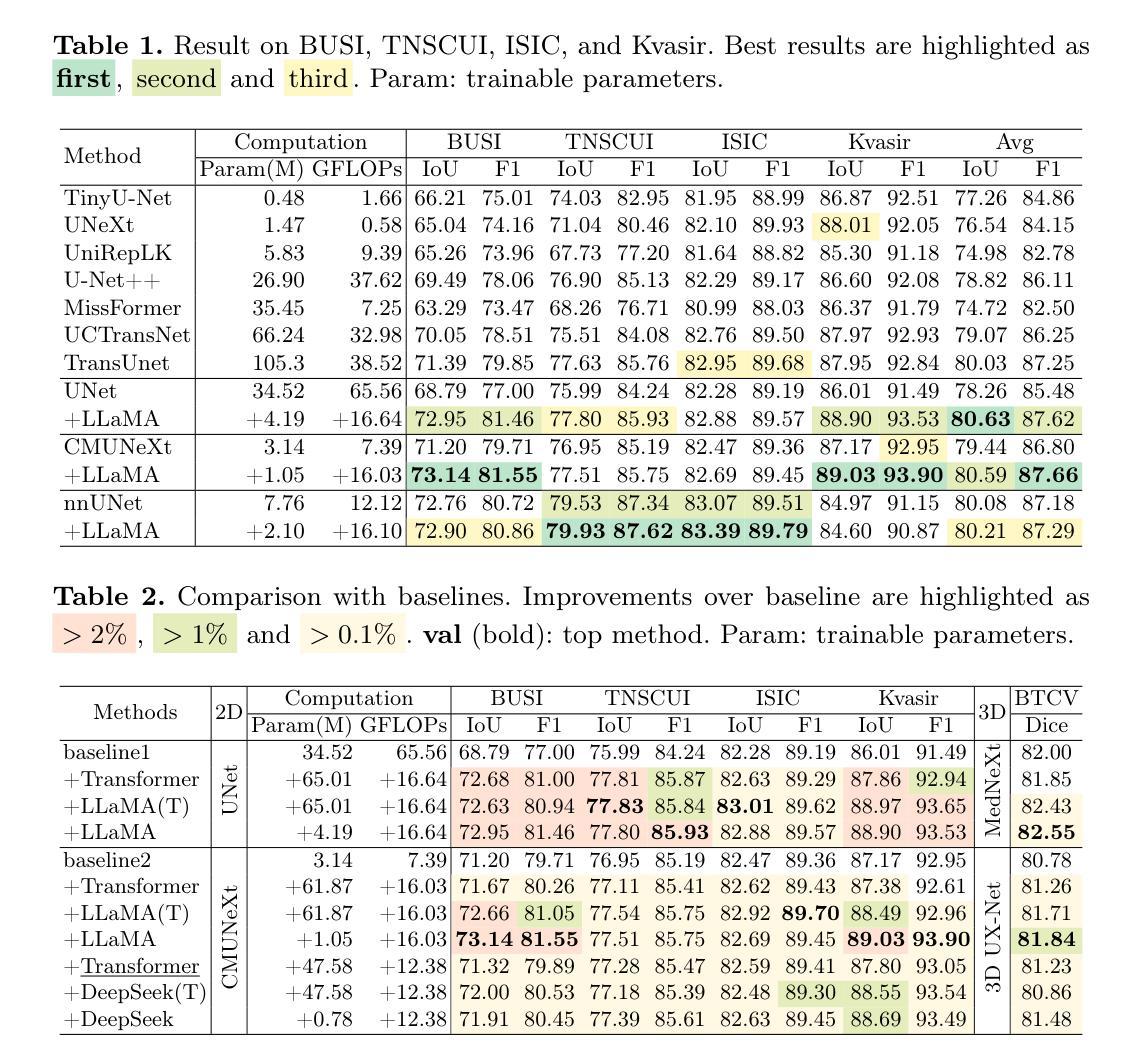
Cross-modal State Space Modeling for Real-time RGB-thermal Wild Scene Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Xiaodong Guo, Zi’ang Lin, Luwen Hu, Zhihong Deng, Tong Liu, Wujie Zhou
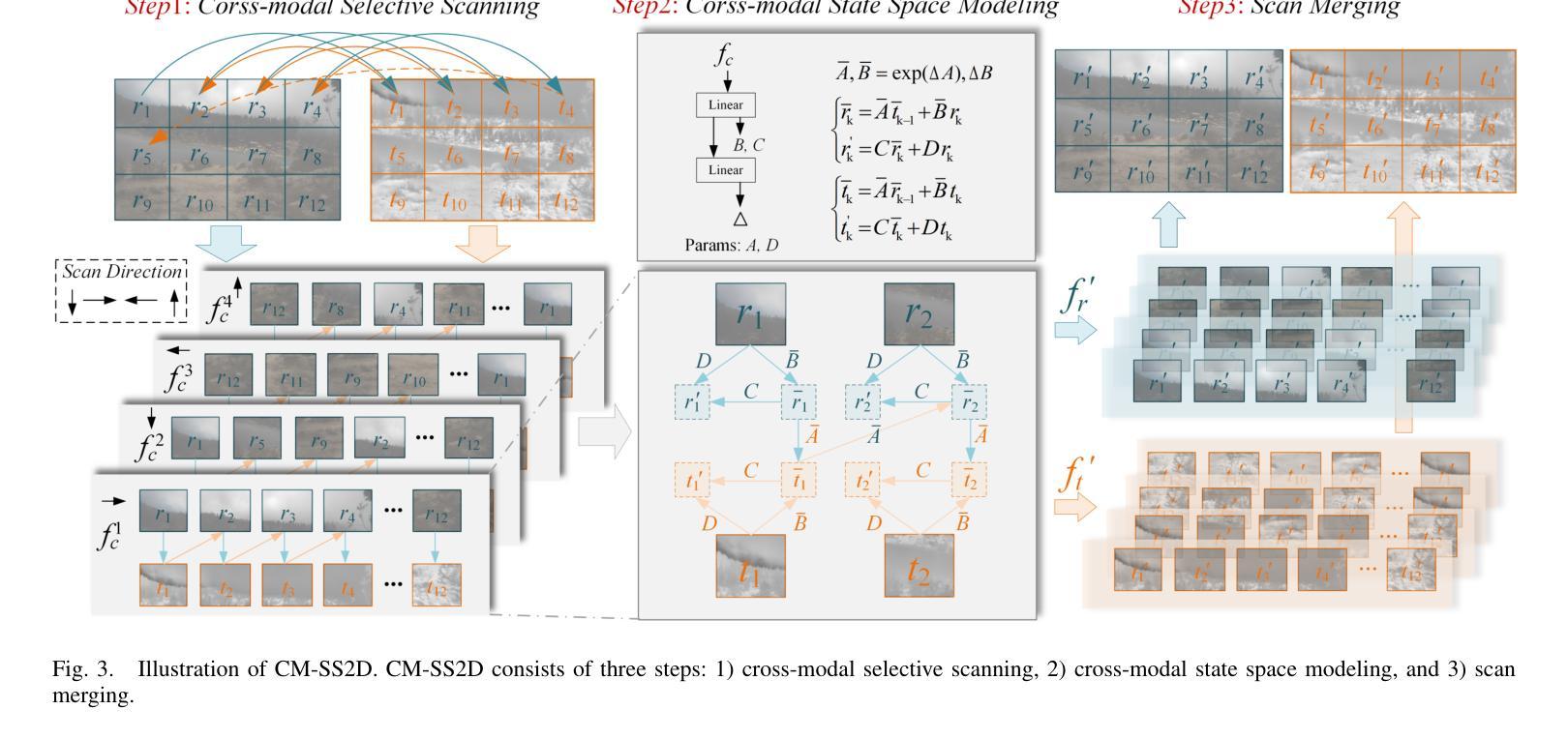
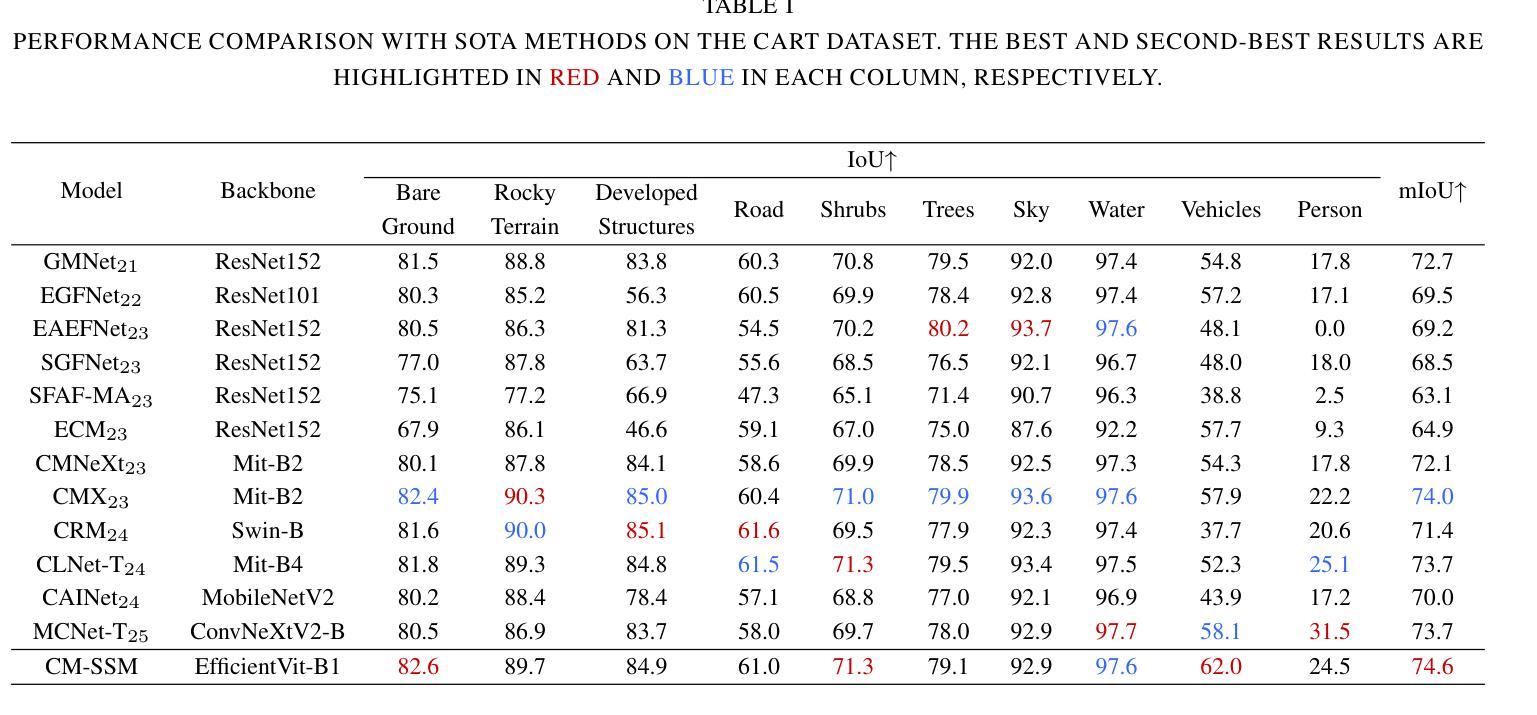
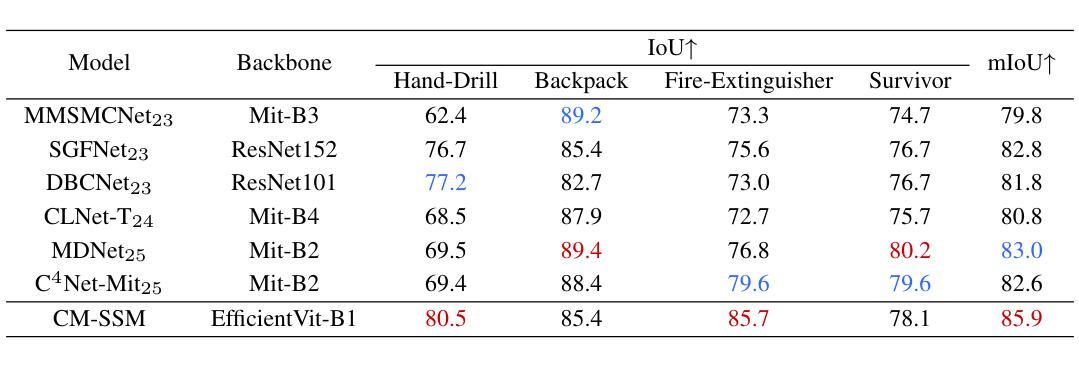
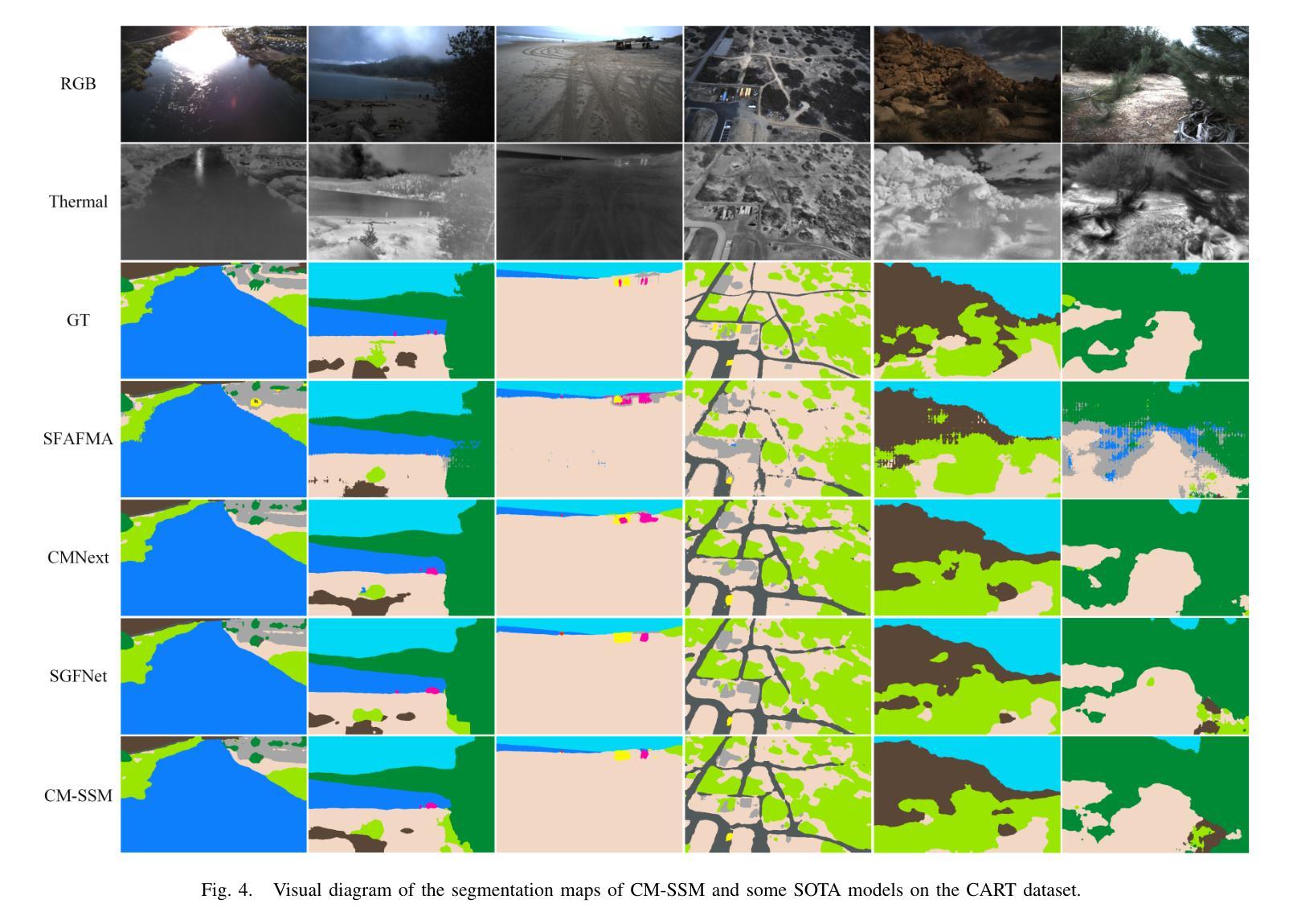
The integration of RGB and thermal data can significantly improve semantic segmentation performance in wild environments for field robots. Nevertheless, multi-source data processing (e.g. Transformer-based approaches) imposes significant computational overhead, presenting challenges for resource-constrained systems. To resolve this critical limitation, we introduced CM-SSM, an efficient RGB-thermal semantic segmentation architecture leveraging a cross-modal state space modeling (SSM) approach. Our framework comprises two key components. First, we introduced a cross-modal 2D-selective-scan (CM-SS2D) module to establish SSM between RGB and thermal modalities, which constructs cross-modal visual sequences and derives hidden state representations of one modality from the other. Second, we developed a cross-modal state space association (CM-SSA) module that effectively integrates global associations from CM-SS2D with local spatial features extracted through convolutional operations. In contrast with Transformer-based approaches, CM-SSM achieves linear computational complexity with respect to image resolution. Experimental results show that CM-SSM achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CART dataset with fewer parameters and lower computational cost. Further experiments on the PST900 dataset demonstrate its generalizability. Codes are available at https://github.com/xiaodonguo/CMSSM.
将RGB和红外数据的融合可以显著提高野外环境中田野机器人的语义分割性能。然而,多源数据处理(例如基于Transformer的方法)带来了很大的计算开销,对资源受限的系统提出了挑战。为了解决这一关键限制,我们引入了CM-SSM,这是一种高效的RGB-红外语义分割架构,它利用跨模态状态空间建模(SSM)方法。我们的框架包含两个关键组成部分。首先,我们引入了跨模态2D选择性扫描(CM-SS2D)模块,以建立RGB和红外模态之间的SSM,构建跨模态视觉序列,并从另一种模态中推导出隐藏状态表示。其次,我们开发了一个跨模态状态空间关联(CM-SSA)模块,该模块有效地将CM-SS2D的全局关联与通过卷积操作提取的局部空间特征结合起来。与基于Transformer的方法相比,CM-SSM在计算复杂度方面实现了与图像分辨率呈线性的计算复杂度。实验结果表明,CM-SSM在CART数据集上达到了最先进的性能,同时参数更少、计算成本更低。在PST900数据集上的进一步实验证明了其泛化能力。代码可在[https://github.com/xiaodonguo/CMSSM获取。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RGB与热数据融合能显著提高野外环境中场机器人的语义分割性能。为解决多源数据处理(如基于Transformer的方法)带来的计算负担,提出CM-SSM架构,采用跨模态状态空间建模(SSM)方法。该架构包含两个关键组件:一是建立RGB和热模态之间SSM的跨模态2D选择性扫描(CM-SS2D)模块;二是整合全局关联的跨模态状态空间关联(CM-SSA)模块。与基于Transformer的方法相比,CM-SSM实现线性计算复杂度,参数更少、计算成本更低,在CART数据集上达到领先水平,并在PST900数据集上展现泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- RGB与热数据融合能提升语义分割性能。
- 多源数据处理带来计算负担,挑战资源受限系统。
- 引入CM-SSM架构,采用跨模态状态空间建模(SSM)方法解决此问题。
- CM-SSM包含跨模态2D选择性扫描(CM-SS2D)和跨模态状态空间关联(CM-SSA)两个关键组件。
- CM-SSM实现线性计算复杂度,参数少、计算成本低。
- CM-SSM在CART数据集上表现优秀,达到领先水平。
- CM-SSM在PST900数据集上展现泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

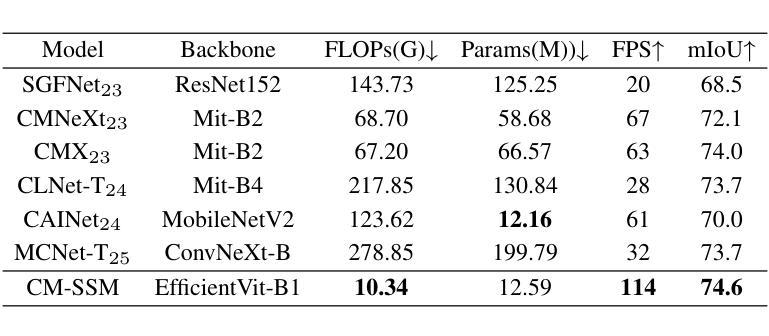
DART: An Automated End-to-End Object Detection Pipeline with Data Diversification, Open-Vocabulary Bounding Box Annotation, Pseudo-Label Review, and Model Training
Authors:Chen Xin, Andreas Hartel, Enkelejda Kasneci
Accurate real-time object detection is vital across numerous industrial applications, from safety monitoring to quality control. Traditional approaches, however, are hindered by arduous manual annotation and data collection, struggling to adapt to ever-changing environments and novel target objects. To address these limitations, this paper presents DART, an innovative automated end-to-end pipeline that revolutionizes object detection workflows from data collection to model evaluation. It eliminates the need for laborious human labeling and extensive data collection while achieving outstanding accuracy across diverse scenarios. DART encompasses four key stages: (1) Data Diversification using subject-driven image generation (DreamBooth with SDXL), (2) Annotation via open-vocabulary object detection (Grounding DINO) to generate bounding box and class labels, (3) Review of generated images and pseudo-labels by large multimodal models (InternVL-1.5 and GPT-4o) to guarantee credibility, and (4) Training of real-time object detectors (YOLOv8 and YOLOv10) using the verified data. We apply DART to a self-collected dataset of construction machines named Liebherr Product, which contains over 15K high-quality images across 23 categories. The current instantiation of DART significantly increases average precision (AP) from 0.064 to 0.832. Its modular design ensures easy exchangeability and extensibility, allowing for future algorithm upgrades, seamless integration of new object categories, and adaptability to customized environments without manual labeling and additional data collection. The code and dataset are released at https://github.com/chen-xin-94/DART.
准确实时的目标检测在众多的工业应用中至关重要,从安全监控到质量控制。然而,传统的方法受到繁琐的手动标注和数据收集的制约,难以适应不断变化的环境和新型目标对象。为了解决这些局限性,本文提出了DART,一种创新的全自动端到端管道,它革新了从数据采集到模型评估的目标检测工作流程。DART不需要繁琐的人工标注和大量的数据收集,同时在各种场景中实现了出色的准确性。DART包含四个阶段:(1)使用主题驱动图像生成(DreamBooth与SDXL)进行数据多样化,(2)通过开放词汇目标检测(Grounding DINO)进行标注,以生成边界框和类别标签,(3)通过大型多模态模型(InternVL-1.5和GPT-4o)审查生成的图像和伪标签,以保证可信度,(4)使用经过验证的数据训练实时目标检测器(YOLOv8和YOLOv10)。我们将DART应用于名为Liebherr Product的自制建筑机械数据集,其中包含超过15K张高质量图像,涵盖23个类别。当前版本的DART将平均精度(AP)从0.064显著提高到了0.832。其模块化设计确保了易于更换和扩展性,允许未来算法升级、无缝集成新的对象类别,以及适应定制环境而无需手动标注和额外的数据收集。代码和数据集已在https://github.com/chen-xin-94/DART上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Corrected minor typos; no changes to results or conclusions
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为DART的创新型自动化端到端管道,用于解决传统目标检测方法的局限性。DART通过数据多样化、开放词汇表目标检测、多模态模型审核和实时对象检测器训练四个阶段,实现了无需人工标注和大量数据收集的高精度目标检测。应用于自我收集的Liebherr产品数据集,平均精度从0.064提高到0.832。DART模块化设计,易于交换和扩展,适用于各种环境。代码和数据集已发布在[网站链接]。
Key Takeaways
- DART是一种自动化端到端管道,用于目标检测工作流程,从数据收集到模型评估。
- DART通过四个阶段实现高精度目标检测:数据多样化、开放词汇表目标检测、多模态模型审核和实时对象检测器训练。
- DART应用于自我收集的Liebherr产品数据集,平均精度显著提高。
- DART采用模块化设计,易于交换和扩展,可适应不同环境和未来算法升级。
- DART不需要人工标注和大量数据收集,降低了目标检测的复杂性和成本。
点此查看论文截图

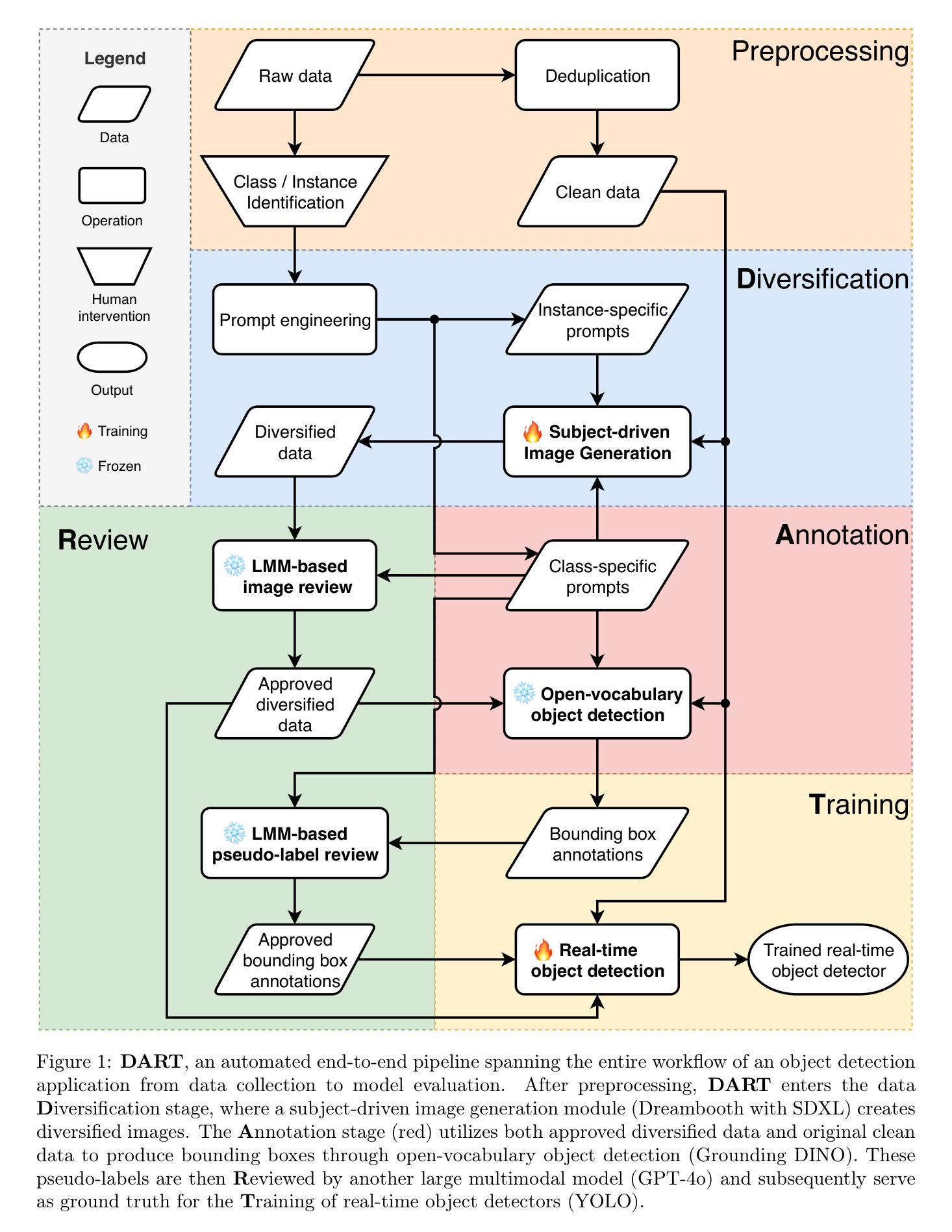
Towards Reflected Object Detection: A Benchmark
Authors:Yiquan Wu, Zhongtian Wang, You Wu, Ling Huang, Hui Zhou, Shuiwang Li
Object detection has greatly improved over the past decade thanks to advances in deep learning and large-scale datasets. However, detecting objects reflected in surfaces remains an underexplored area. Reflective surfaces are ubiquitous in daily life, appearing in homes, offices, public spaces, and natural environments. Accurate detection and interpretation of reflected objects are essential for various applications. This paper addresses this gap by introducing a extensive benchmark specifically designed for Reflected Object Detection. Our Reflected Object Detection Dataset (RODD) features a diverse collection of images showcasing reflected objects in various contexts, providing standard annotations for both real and reflected objects. This distinguishes it from traditional object detection benchmarks. RODD encompasses 10 categories and includes 21,059 images of real and reflected objects across different backgrounds, complete with standard bounding box annotations and the classification of objects as real or reflected. Additionally, we present baseline results by adapting five state-of-the-art object detection models to address this challenging task. Experimental results underscore the limitations of existing methods when applied to reflected object detection, highlighting the need for specialized approaches. By releasing RODD, we aim to support and advance future research on detecting reflected objects. Dataset and code are available at: https://github.com/jirouvan/ROD.
过去十年,由于深度学习和大规模数据集的进步,目标检测得到了极大的提升。然而,在表面反射物体的检测仍然是一个被忽视的领域。反射表面在日常生活中无处不在,出现在家庭、办公室、公共空间和自然环境中。准确检测和解释反射物体对于各种应用至关重要。本文通过引入专门为反射物体检测设计的广泛基准测试来填补这一空白。我们的反射物体检测数据集(RODD)拥有多样化的图像集合,展示了各种背景下的反射物体,并为真实和反射物体提供了标准注释,这使其有别于传统的目标检测基准测试。RODD包含10个类别,跨越不同背景的21059张真实和反射物体图像,带有标准边界框注释以及对象作为真实或反射的分类。此外,我们通过适应五种最先进的物体检测模型来解决这一具有挑战性的任务,并给出了基线结果。实验结果突显了现有方法在处理反射物体检测时的局限性,强调了需要专门的方法。通过发布RODD,我们旨在支持和推动未来关于反射物体的检测研究。数据集和代码可在以下网址获得:https://github.com/jirouvan/ROD 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了对象检测领域的一个新挑战——反射对象检测,并为此创建了一个专门的数据集RODD。该数据集包含多种背景下的反射对象图像,对真实和反射对象进行标准注释。此外,文章还尝试了五种最先进的对象检测模型来解决这一具有挑战性的任务,并指出了现有方法的局限性,强调了需要专门的方法来处理反射对象检测问题。
Key Takeaways:
- 反射对象检测是一个尚未被充分探索的领域,对于各种应用来说,准确检测和解释反射对象是至关重要的。
- 本文介绍了一个新的基准测试数据集——反射对象检测数据集(RODD),其中包含真实和反射对象的图像,并对它们进行了标准注释。
- RODD数据集包含10个类别和21,059张图像,并提供了关于对象是真实还是反射的分类信息。
- 通过适应五种最先进的对象检测模型来解决反射对象检测的挑战,实验结果表明现有方法的局限性。
- 需要专门的方法和策略来处理反射对象检测问题。
- 数据集和代码已公开发布在GitHub上,以支持未来的反射对象检测研究。
点此查看论文截图


PotatoGANs: Utilizing Generative Adversarial Networks, Instance Segmentation, and Explainable AI for Enhanced Potato Disease Identification and Classification
Authors:Fatema Tuj Johora Faria, Mukaffi Bin Moin, Mohammad Shafiul Alam, Ahmed Al Wase, Md. Rabius Sani, Khan Md Hasib
Numerous applications have resulted from the automation of agricultural disease segmentation using deep learning techniques. However, when applied to new conditions, these applications frequently face the difficulty of overfitting, resulting in lower segmentation performance. In the context of potato farming, where diseases have a large influence on yields, it is critical for the agricultural economy to quickly and properly identify these diseases. Traditional data augmentation approaches, such as rotation, flip, and translation, have limitations and frequently fail to provide strong generalization results. To address these issues, our research employs a novel approach termed as PotatoGANs. In this novel data augmentation approach, two types of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are utilized to generate synthetic potato disease images from healthy potato images. This approach not only expands the dataset but also adds variety, which helps to enhance model generalization. Using the Inception score as a measure, our experiments show the better quality and realisticness of the images created by PotatoGANs, emphasizing their capacity to resemble real disease images closely. The CycleGAN model outperforms the Pix2Pix GAN model in terms of image quality, as evidenced by its higher IS scores CycleGAN achieves higher Inception scores (IS) of 1.2001 and 1.0900 for black scurf and common scab, respectively. This synthetic data can significantly improve the training of large neural networks. It also reduces data collection costs while enhancing data diversity and generalization capabilities. Our work improves interpretability by combining three gradient-based Explainable AI algorithms (GradCAM, GradCAM++, and ScoreCAM) with three distinct CNN architectures (DenseNet169, Resnet152 V2, InceptionResNet V2) for potato disease classification.
基于深度学习的自动化农业疾病分割技术已广泛应用于许多领域。然而,当应用于新的条件时,这些应用经常面临过度拟合的困难,导致分割性能下降。在土豆种植业中,疾病对产量有很大影响,因此快速正确地识别这些疾病对农业经济至关重要。传统的数据增强方法,如旋转、翻转和翻译,都有局限性,往往不能提供强大的泛化结果。为了解决这些问题,我们的研究采用了一种新颖的方法,称为PotatoGANs。在这种新型数据增强方法中,利用两种生成对抗网络(GANs)从健康的土豆图像生成合成土豆疾病图像。这种方法不仅扩大了数据集,还增加了多样性,有助于增强模型的泛化能力。我们的实验使用Inception分数作为衡量标准,显示了PotatoGANs创建的图像具有更好的质量和逼真度,强调它们与真实疾病图像高度相似的能力。在图像质量方面,CycleGAN模型优于Pix2Pix GAN模型,其较高的IS分数证明了这一点。CycleGAN针对黑痂病和普通痂癬的Inception分数分别为1.2001和1.0900。这种合成数据可以显著改善大型神经网络的训练。它还可以降低数据收集成本,同时提高数据多样性和泛化能力。我们的工作通过结合三种基于梯度的可解释人工智能算法(GradCAM、GradCAM++和ScoreCAM)与三种不同的CNN架构(DenseNet169、Resnet152 V2、InceptionResNet V2)来改善土豆疾病分类的解读性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的农业疾病分割自动化应用在新型条件下遇到过度拟合问题,影响分割性能。研究采用名为PotatoGANs的新型数据增强方法,利用两种生成对抗网络(GANs)从健康土豆图像生成合成疾病图像,提升模型泛化能力,降低数据采集成本并增强数据多样性和泛化能力。同时,结合三种梯度基的可解释人工智能算法和三种CNN架构进行土豆疾病分类,提高解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化农业疾病分割应用面临新型条件下的过度拟合问题。
- PotatoGANs方法利用GANs生成合成土豆疾病图像,解决数据泛化问题。
- 合成数据可提高大神经网络的训练效果,降低数据采集成本。
- 结合可解释人工智能算法和CNN架构提高土豆疾病分类的准确性和解释性。
- CycleGAN模型在图像质量上优于Pix2Pix GAN模型。
点此查看论文截图