⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
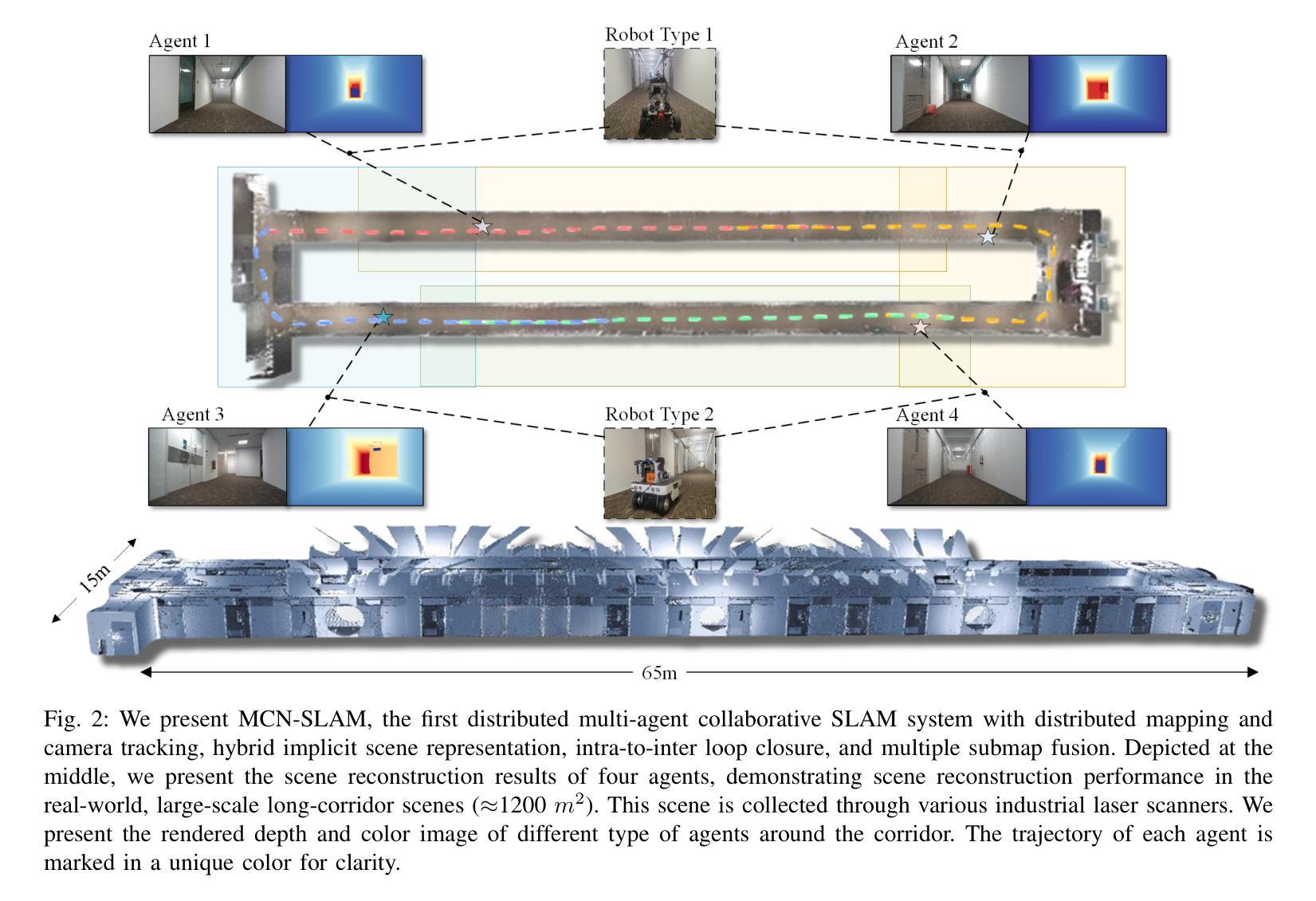
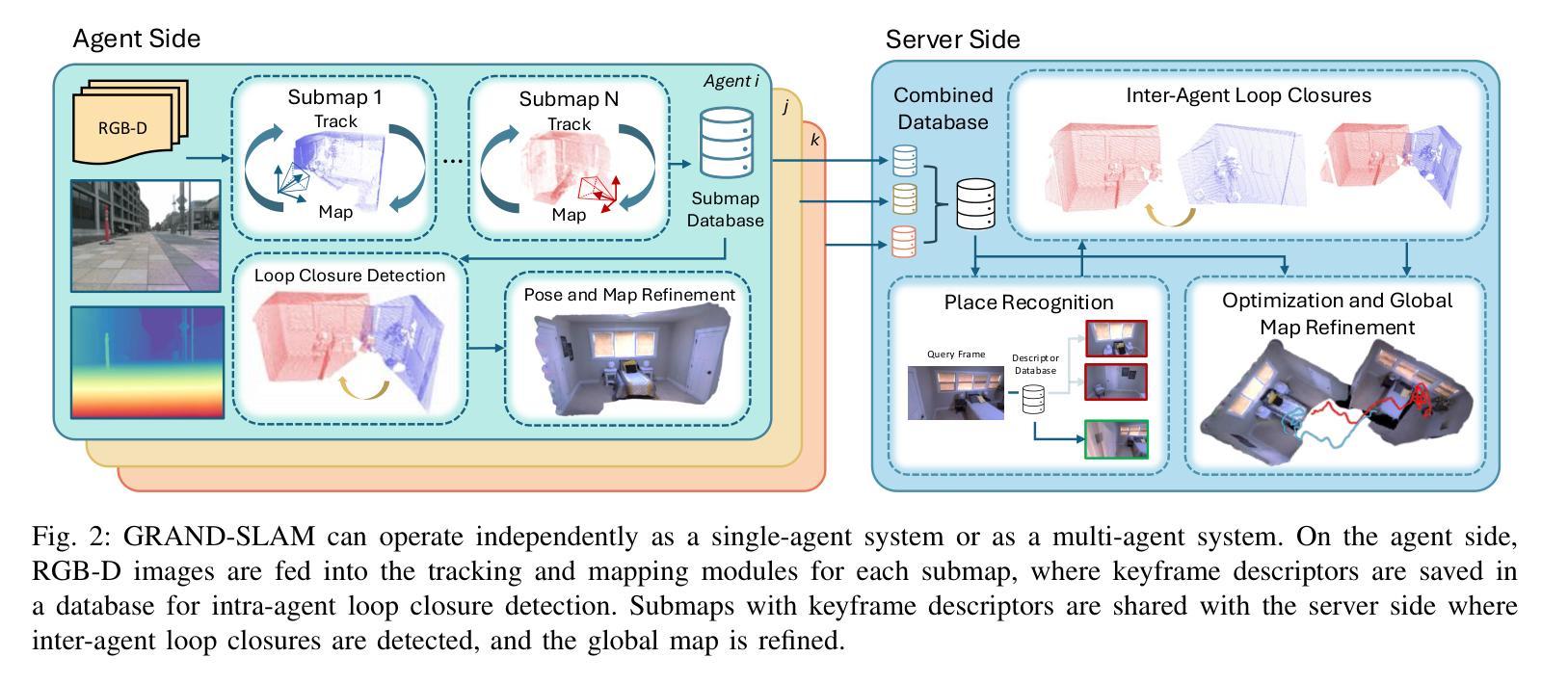
GRAND-SLAM: Local Optimization for Globally Consistent Large-Scale Multi-Agent Gaussian SLAM
Authors:Annika Thomas, Aneesa Sonawalla, Alex Rose, Jonathan P. How
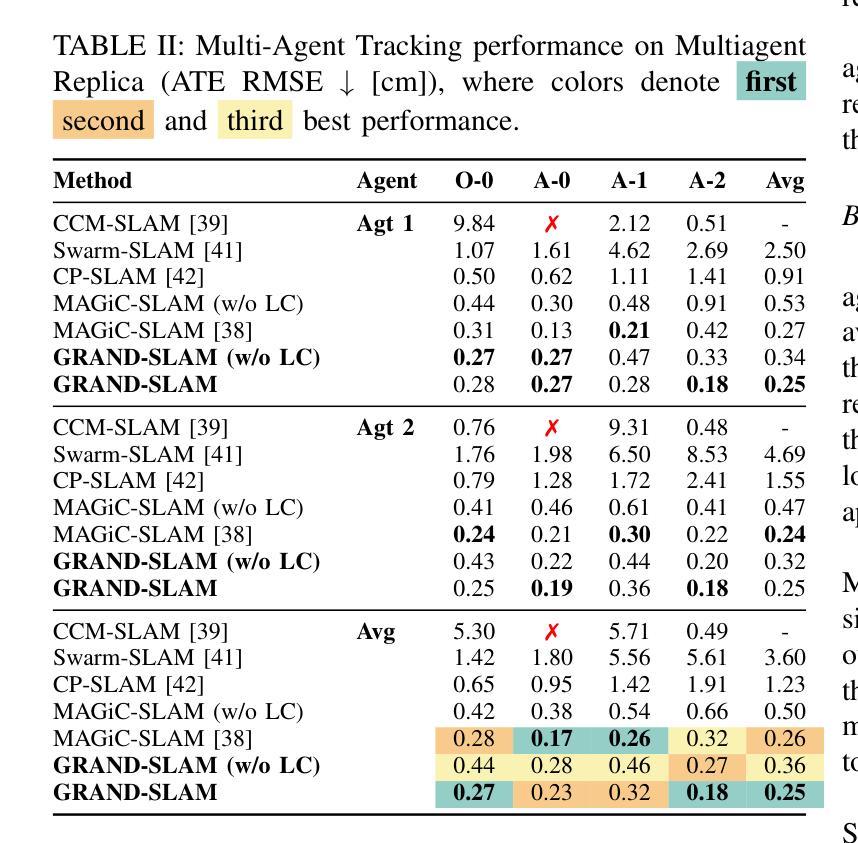
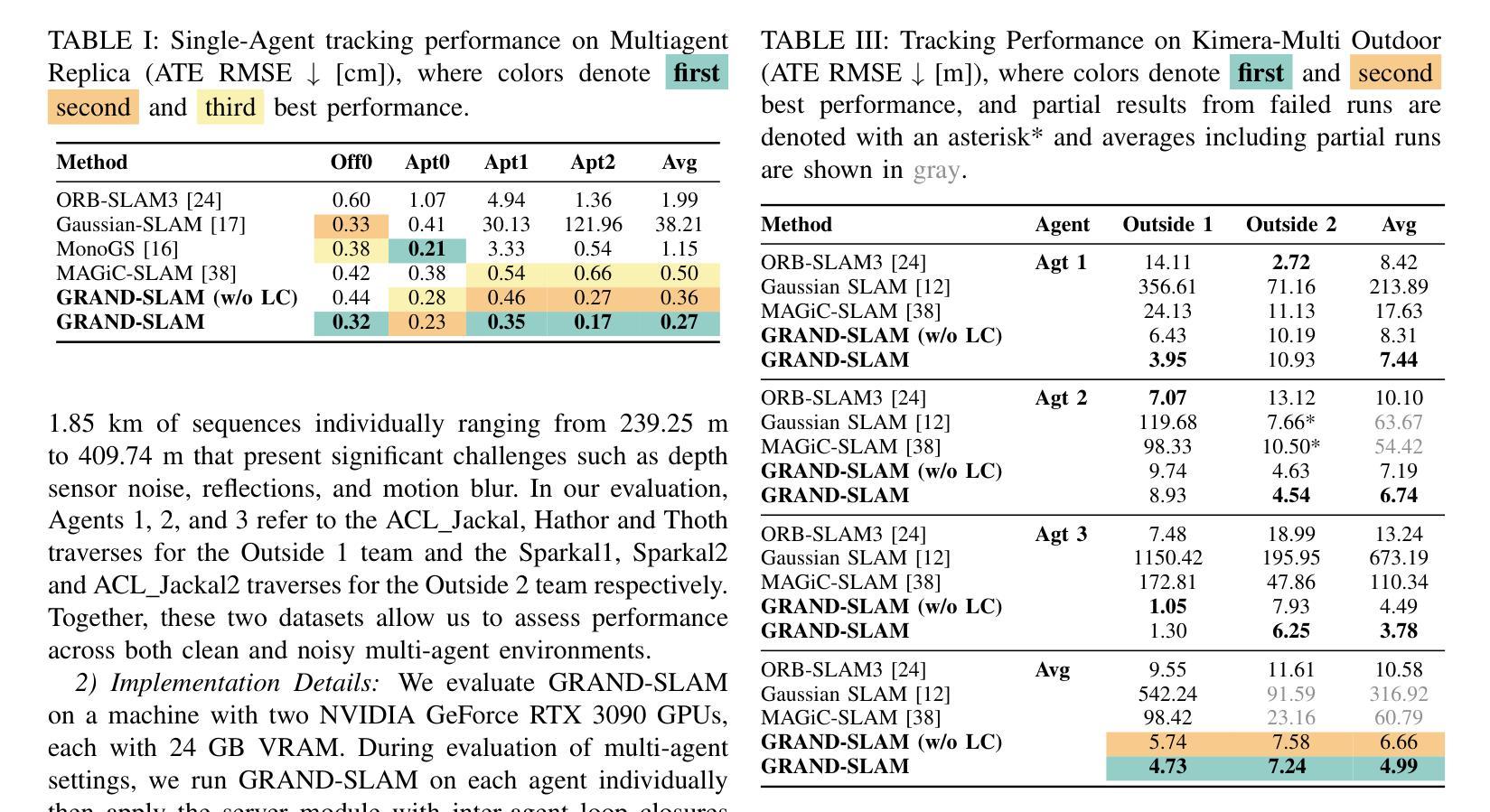
3D Gaussian splatting has emerged as an expressive scene representation for RGB-D visual SLAM, but its application to large-scale, multi-agent outdoor environments remains unexplored. Multi-agent Gaussian SLAM is a promising approach to rapid exploration and reconstruction of environments, offering scalable environment representations, but existing approaches are limited to small-scale, indoor environments. To that end, we propose Gaussian Reconstruction via Multi-Agent Dense SLAM, or GRAND-SLAM, a collaborative Gaussian splatting SLAM method that integrates i) an implicit tracking module based on local optimization over submaps and ii) an approach to inter- and intra-robot loop closure integrated into a pose-graph optimization framework. Experiments show that GRAND-SLAM provides state-of-the-art tracking performance and 28% higher PSNR than existing methods on the Replica indoor dataset, as well as 91% lower multi-agent tracking error and improved rendering over existing multi-agent methods on the large-scale, outdoor Kimera-Multi dataset.
三维高斯插铺技术已发展为RGB-D视觉SLAM的一种表现丰富的场景表示方法,但其在大规模、多智能体室外环境的应用尚未被探索。多智能体高斯SLAM是一种有前景的方法,可以快速探索并重建环境,提供可扩展的环境表示,但现有方法仅限于小规模室内环境。为此,我们提出了基于多智能体密集SLAM的高斯重建(简称GRAND-SLAM),这是一种协作式高斯插铺SLAM方法,它融合了i)基于子图局部优化的隐式跟踪模块和ii)一种集成到姿态图优化框架中的机器人内外回路闭合方法。实验表明,GRAND-SLAM在Replica室内数据集上提供了最先进的跟踪性能,较现有方法提高了28%的峰值信噪比(PSNR),同时在大规模室外Kimera-Multi数据集上,多智能体跟踪误差降低了91%,渲染效果也有所改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将多智能体高斯SLAM技术应用于大规模户外环境的问题。提出了一种基于高斯喷绘的协作SLAM方法——GRAND-SLAM,它在子图局部优化基础上建立了隐式跟踪模块,并将机器人间和机器人内部闭环集成到姿态图优化框架中。实验表明,GRAND-SLAM在Replica室内数据集上提供了先进的跟踪性能和更高的峰值信噪比(PSNR),而在大规模户外Kimera-Multi数据集上,其多智能体跟踪误差降低了91%,渲染效果也有所改善。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯喷绘在RGB-D视觉SLAM中的场景表示得到了发展,但其在多智能体户外大规模环境中的应用尚未得到探索。
- 多智能体高斯SLAM是实现环境快速探索和重建的有前途的方法,提供可伸缩的环境表示。
- GRAND-SLAM是一种协作式高斯喷绘SLAM方法,结合了隐式跟踪模块和姿态图优化框架中的机器人间和机器人内部闭环方法。
- 实验表明GRAND-SLAM在跟踪性能和图像质量方面达到了先进水平。
- GRAND-SLAM在室内数据集上提供了较高的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。
- 在户外大规模数据集上,GRAND-SLAM的多智能体跟踪误差较低。
点此查看论文截图


4Real-Video-V2: Fused View-Time Attention and Feedforward Reconstruction for 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Chaoyang Wang, Ashkan Mirzaei, Vidit Goel, Willi Menapace, Aliaksandr Siarohin, Avalon Vinella, Michael Vasilkovsky, Ivan Skorokhodov, Vladislav Shakhrai, Sergey Korolev, Sergey Tulyakov, Peter Wonka
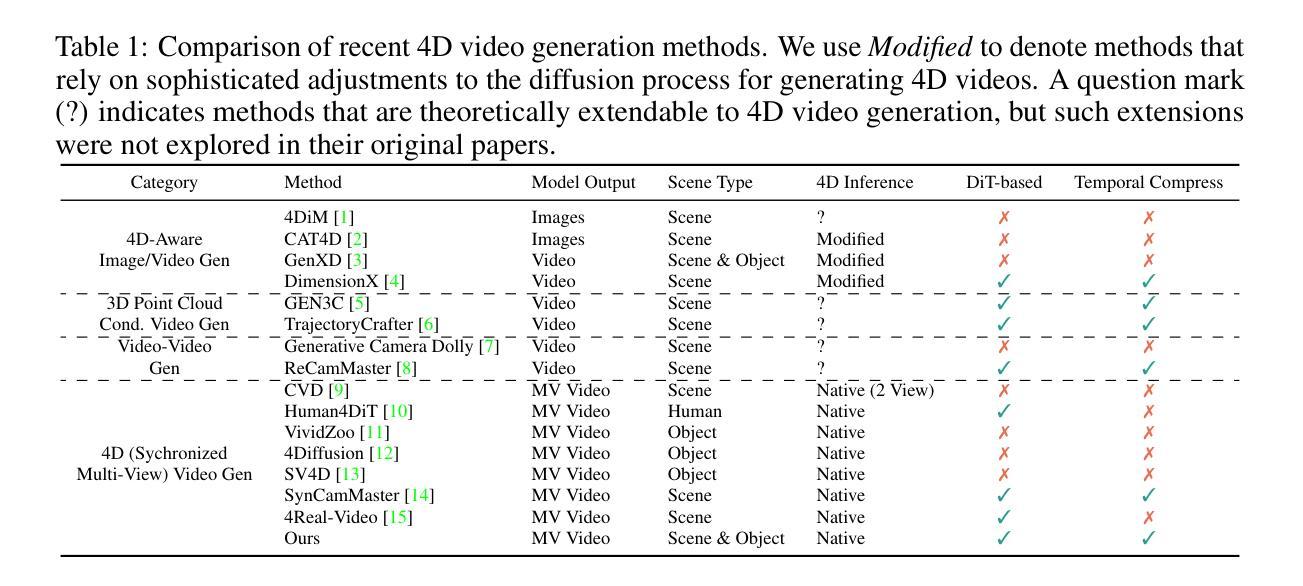
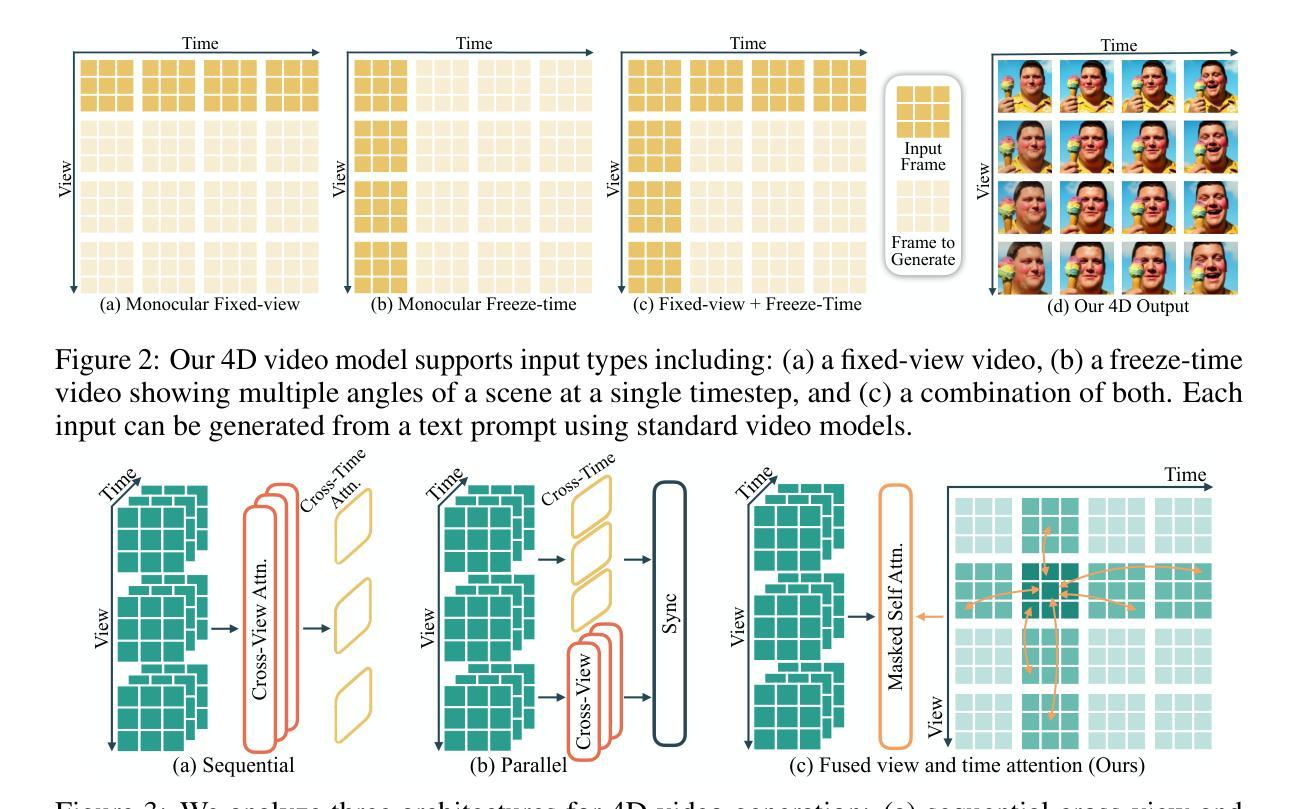
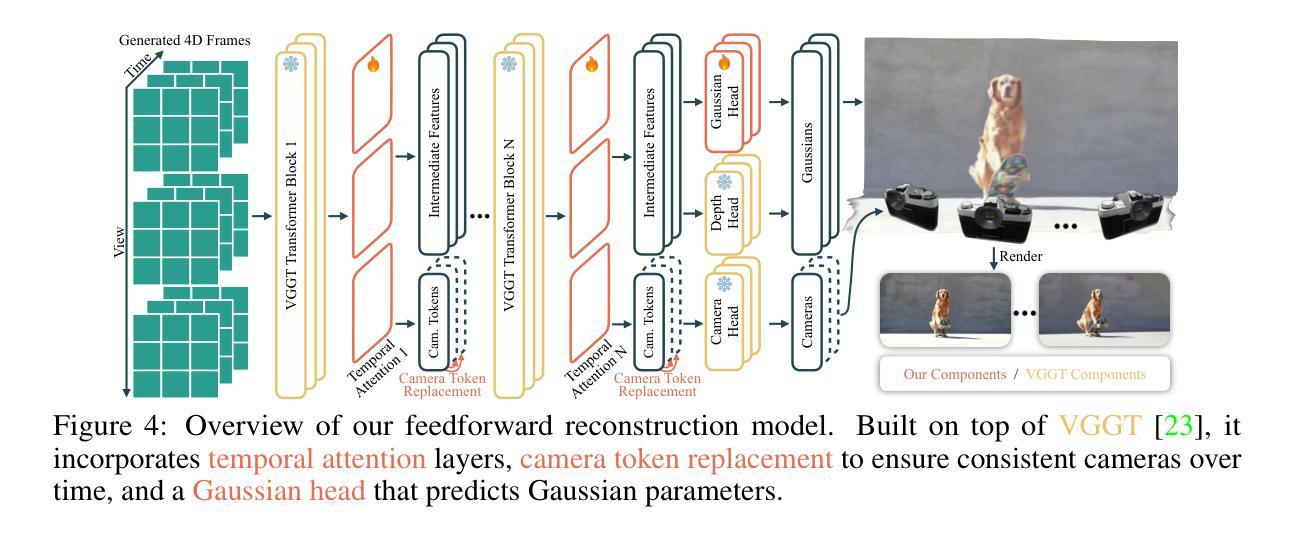
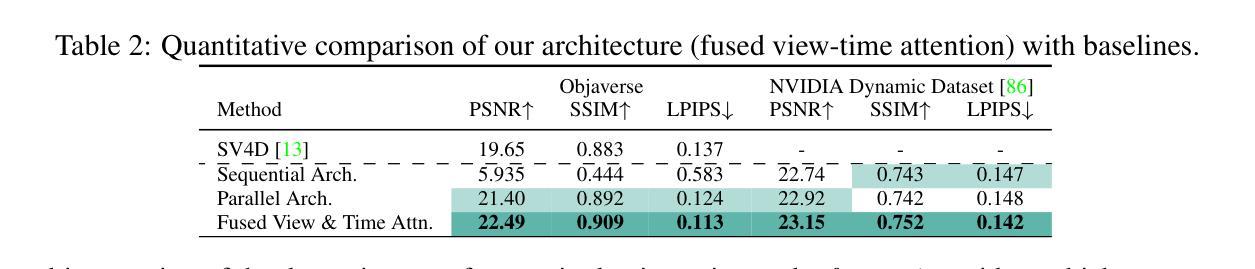
We propose the first framework capable of computing a 4D spatio-temporal grid of video frames and 3D Gaussian particles for each time step using a feed-forward architecture. Our architecture has two main components, a 4D video model and a 4D reconstruction model. In the first part, we analyze current 4D video diffusion architectures that perform spatial and temporal attention either sequentially or in parallel within a two-stream design. We highlight the limitations of existing approaches and introduce a novel fused architecture that performs spatial and temporal attention within a single layer. The key to our method is a sparse attention pattern, where tokens attend to others in the same frame, at the same timestamp, or from the same viewpoint. In the second part, we extend existing 3D reconstruction algorithms by introducing a Gaussian head, a camera token replacement algorithm, and additional dynamic layers and training. Overall, we establish a new state of the art for 4D generation, improving both visual quality and reconstruction capability.
我们提出了一个首创的框架,该框架能够利用前馈架构计算视频帧的4D时空网格和每个时间步的3D高斯粒子。我们的架构主要包括两个部分:4D视频模型和4D重建模型。第一部分,我们分析了当前的4D视频扩散架构,这些架构在两流设计中按顺序或并行执行空间和时间注意力。我们强调了现有方法的局限性,并介绍了一种新型融合架构,该架构能在单个图层内执行空间和时间注意力。我们的方法的关键在于稀疏注意力模式,其中标记会在同一帧、同一时间戳或同一观点中关注其他标记。在第二部分中,我们通过引入高斯头、相机标记替换算法以及额外的动态层和训练,扩展了现有的3D重建算法。总的来说,我们在4D生成方面建立了新的技术标杆,提高了视觉质量和重建能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
点此查看论文截图

ViDAR: Video Diffusion-Aware 4D Reconstruction From Monocular Inputs
Authors:Michal Nazarczuk, Sibi Catley-Chandar, Thomas Tanay, Zhensong Zhang, Gregory Slabaugh, Eduardo Pérez-Pellitero
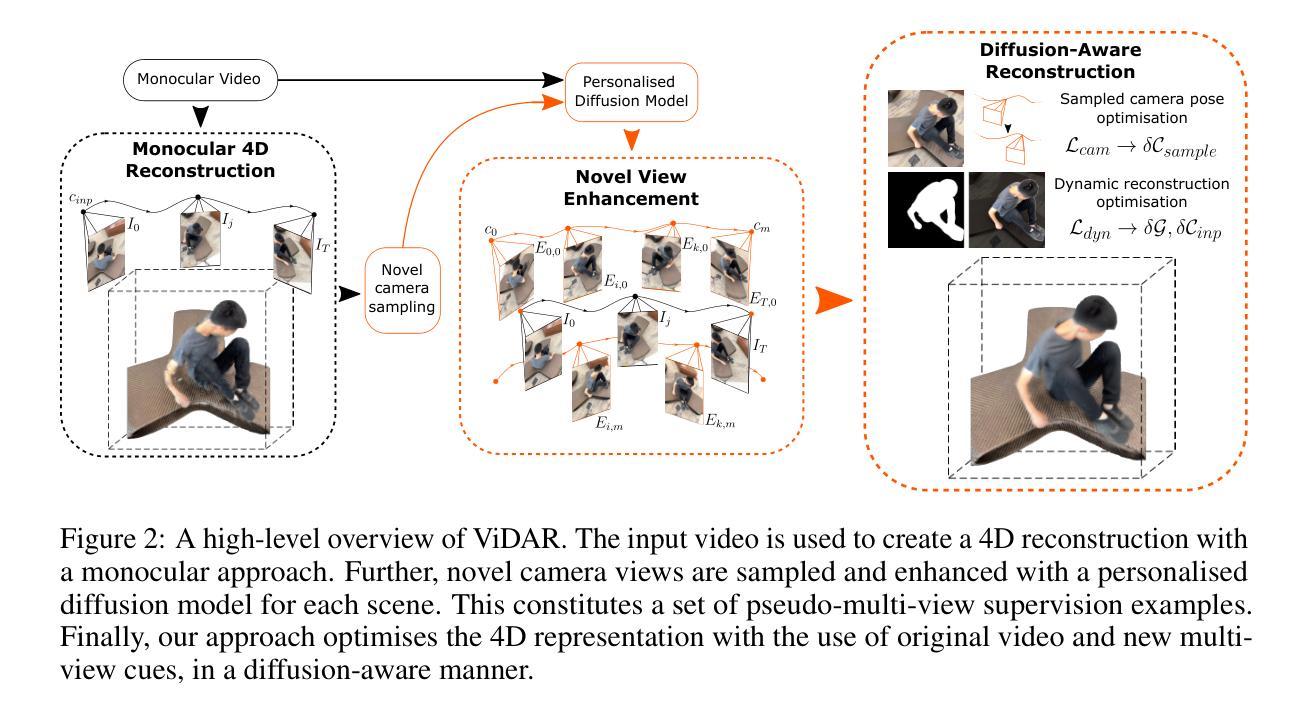
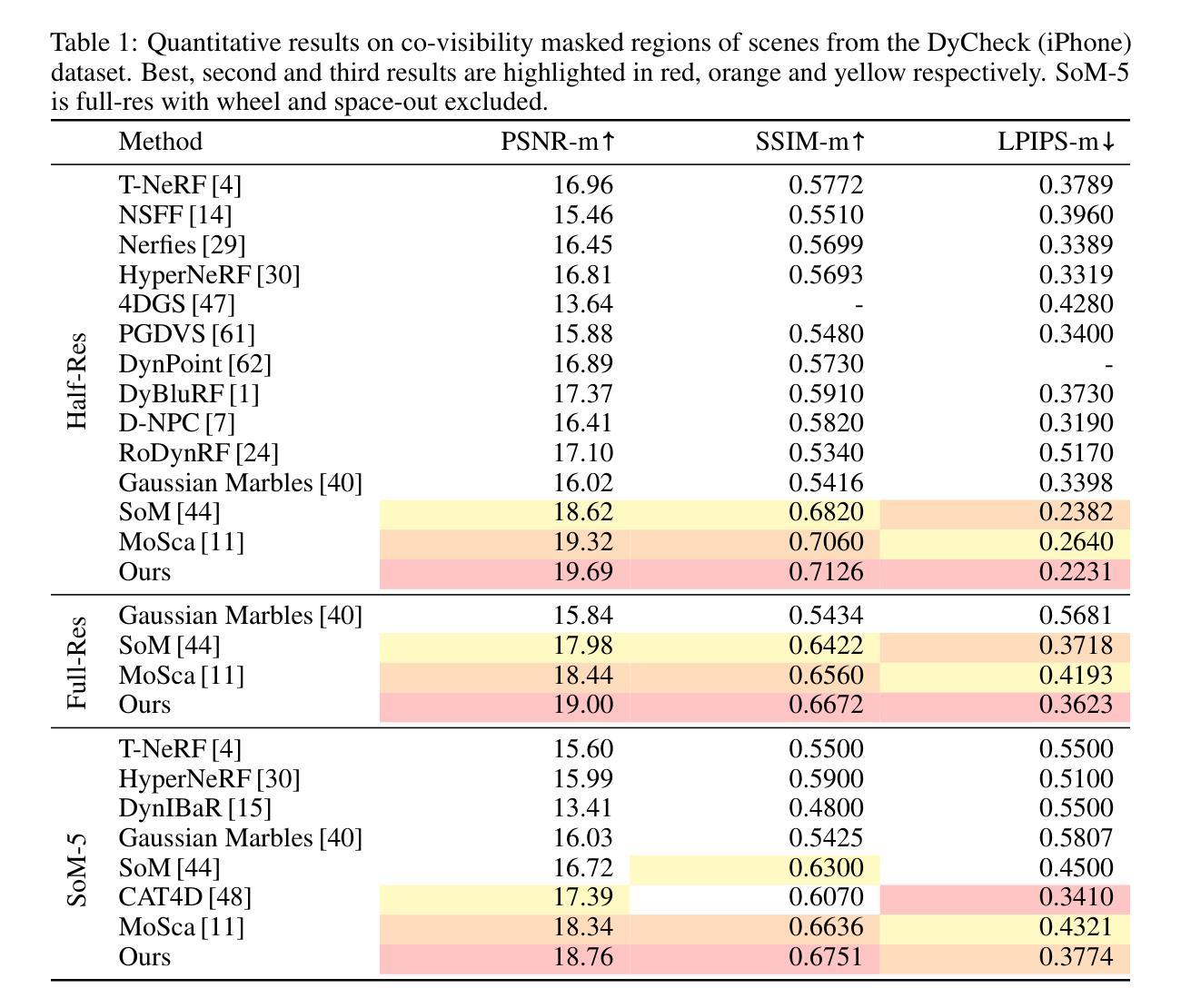
Dynamic Novel View Synthesis aims to generate photorealistic views of moving subjects from arbitrary viewpoints. This task is particularly challenging when relying on monocular video, where disentangling structure from motion is ill-posed and supervision is scarce. We introduce Video Diffusion-Aware Reconstruction (ViDAR), a novel 4D reconstruction framework that leverages personalised diffusion models to synthesise a pseudo multi-view supervision signal for training a Gaussian splatting representation. By conditioning on scene-specific features, ViDAR recovers fine-grained appearance details while mitigating artefacts introduced by monocular ambiguity. To address the spatio-temporal inconsistency of diffusion-based supervision, we propose a diffusion-aware loss function and a camera pose optimisation strategy that aligns synthetic views with the underlying scene geometry. Experiments on DyCheck, a challenging benchmark with extreme viewpoint variation, show that ViDAR outperforms all state-of-the-art baselines in visual quality and geometric consistency. We further highlight ViDAR’s strong improvement over baselines on dynamic regions and provide a new benchmark to compare performance in reconstructing motion-rich parts of the scene. Project page: https://vidar-4d.github.io
动态场景新颖视角合成旨在从任意视角生成动态物体的逼真的视图。当依赖单目视频时,这个任务尤其具有挑战性,因为其中从运动中分离结构的问题表述不清,并且缺乏监督信息。我们引入了视频扩散感知重建(ViDAR)这一新颖的四维重建框架,它利用个性化扩散模型合成一个伪多视角监督信号来训练高斯贴图表示。通过场景特定特征的调节,ViDAR可以恢复精细的外观细节,同时减少由单目模糊性引起的伪影。为了解决基于扩散的监督在时空上不一致的问题,我们提出了一个扩散感知的损失函数和摄像机姿态优化策略,使合成视图与底层场景几何对齐。在具有极端视角变化的挑战基准数据集DyCheck上的实验表明,ViDAR在视觉质量和几何一致性方面均优于所有最新基线技术。我们还重点介绍了ViDAR在动态区域的改进效果,并提供了一个新的基准数据集来比较重建运动丰富场景部分的性能。项目页面:https://vidar-4d.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
动态场景的新型视图合成技术旨在从任意视角生成逼真的移动物体视图。这项任务在依赖单目视频时尤为具有挑战性,因为需要从运动中分离结构是难度很大且缺乏监督。我们引入了Video Diffusion-Aware Reconstruction(ViDAR)这一新型4D重建框架,它利用个性化扩散模型合成伪多视图监督信号来训练高斯展布表示。通过场景特定特征的条件设定,ViDAR在细化纹理细节的同时,减少了因单目歧义产生的伪像。为解决扩散监督的时空不一致问题,我们提出了一种扩散感知的损失函数和相机姿态优化策略,使合成视图与底层场景几何对齐。在具有极端视角变化的DyCheck基准测试上的实验表明,ViDAR在视觉质量和几何一致性方面均优于所有最新基线技术。我们还重点介绍了ViDAR在动态区域的显著改进并提供了一个新基准,以比较重建运动丰富区域性能的比较。
Key Takeaways
- Dynamic Novel View Synthesis 旨在从任意视角生成移动物体的逼真视图。
- Video Diffusion-Aware Reconstruction(ViDAR)是一个新的框架,它解决了单目视频中的结构运动分离问题。
- ViDAR 利用个性化扩散模型合成伪多视图监督信号进行训练。
- 该框架通过特定场景特征的条件设定恢复细节并减少伪像。
- 为解决时空不一致问题,提出了扩散感知损失函数和相机姿态优化策略。
- ViDAR 在DyCheck基准测试上的表现优于其他最新技术。
点此查看论文截图

3D Arena: An Open Platform for Generative 3D Evaluation
Authors:Dylan Ebert
Evaluating Generative 3D models remains challenging due to misalignment between automated metrics and human perception of quality. Current benchmarks rely on image-based metrics that ignore 3D structure or geometric measures that fail to capture perceptual appeal and real-world utility. To address this gap, we present 3D Arena, an open platform for evaluating image-to-3D generation models through large-scale human preference collection using pairwise comparisons. Since launching in June 2024, the platform has collected 123,243 votes from 8,096 users across 19 state-of-the-art models, establishing the largest human preference evaluation for Generative 3D. We contribute the iso3d dataset of 100 evaluation prompts and demonstrate quality control achieving 99.75% user authenticity through statistical fraud detection. Our ELO-based ranking system provides reliable model assessment, with the platform becoming an established evaluation resource. Through analysis of this preference data, we present insights into human preference patterns. Our findings reveal preferences for visual presentation features, with Gaussian splat outputs achieving a 16.6 ELO advantage over meshes and textured models receiving a 144.1 ELO advantage over untextured models. We provide recommendations for improving evaluation methods, including multi-criteria assessment, task-oriented evaluation, and format-aware comparison. The platform’s community engagement establishes 3D Arena as a benchmark for the field while advancing understanding of human-centered evaluation in Generative 3D.
对生成式3D模型的评估仍然具有挑战性,因为自动度量指标与人类对质量的感知之间存在不匹配。目前的基准测试依赖于基于图像的度量指标,这些指标忽略了3D结构或几何度量,而这些度量指标又无法捕捉感知效果和现实世界的实用性。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了名为“三维竞技场”(3D Arena)的开放平台,该平台通过成对的比较来评估图像到三维生成模型的大规模人类偏好收集。自2024年6月上线以来,该平台已从超过八千名用户收集了超过十二万三千二百四十三票的数据,涵盖了十九种最新模型,成为生成式三维领域最大的基于人类偏好的评估。我们贡献了iso3d数据集的一百个评估提示,并通过统计欺诈检测实现了对用户真实性的控制,达到百分之九十九点七五的可靠性。我们的基于ELO的排名系统提供了可靠的模型评估功能,使得该平台成为重要的评估资源。通过对这些偏好数据的分析,我们深入了解了人类偏好模式。我们发现高斯展布输出形式在模型中占据优势地位,拥有高达十六点六的ELO优势,网格形式相较之下逊色不少;纹理模型在无纹理模型中拥有高达一百四十四点一的ELO优势。我们为改进评估方法提供了建议,包括多标准评估、面向任务的评估和格式感知比较等。平台社区参与度提升了三维竞技场在该领域的地位,并推动了生成式三维领域中以人为中心评估的理解和发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文介绍了评估生成式3D模型的挑战,并提出一个开放平台3D Arena来评估图像到3D生成模型。平台通过大规模的人类偏好收集,使用成对比较方式,自2024年6月上线以来,已收集来自8096名用户的123243张投票,建立了最大的生成式3D人类偏好评估数据集。同时,介绍了iso3d数据集和质量控制措施。通过对偏好数据的分析,揭示了人类对视觉呈现特征等的偏好,并为改进评价方法提供了建议。最后,强调了平台作为社区参与者的作用及其对生成式3D领域的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 评估生成式3D模型存在挑战,因为自动化指标与人类感知质量的差异。
- 当前基准测试方法存在缺陷,忽略了3D结构或无法捕捉感知魅力和现实世界的实用性。
- 介绍了新的评估平台3D Arena,通过大规模的人类偏好收集来评估图像到3D的生成模型。
- 平台已收集大量数据,建立了最大的生成式3D人类偏好评估数据集。
- 通过统计欺诈检测实现了用户真实性的高质量控制。
- 平台揭示了人类对视觉呈现特征的偏好,如Gaussian splat输出的优势。
- 平台为改进评价方法提供了建议,如多标准评估、任务导向评估和格式感知比较。
点此查看论文截图

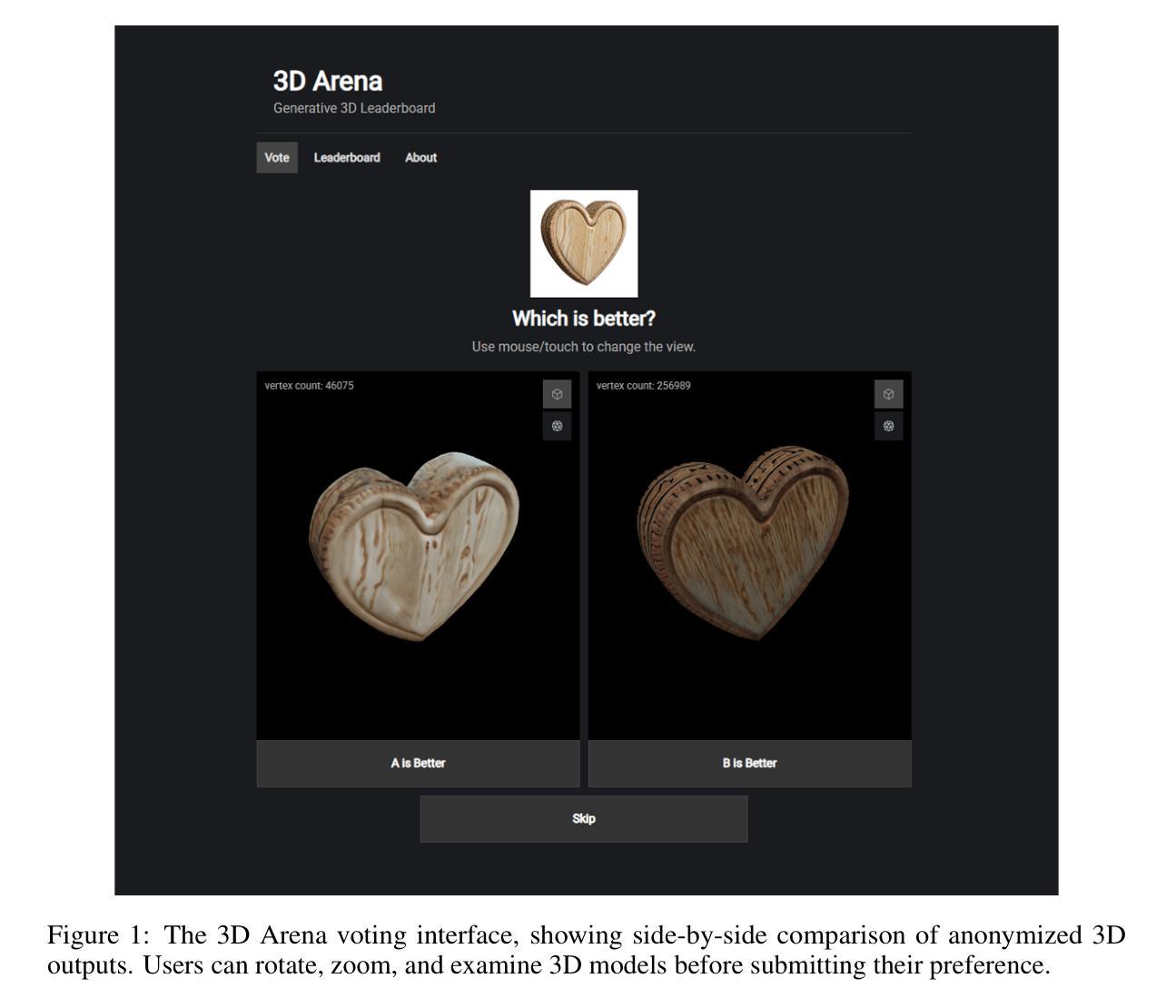
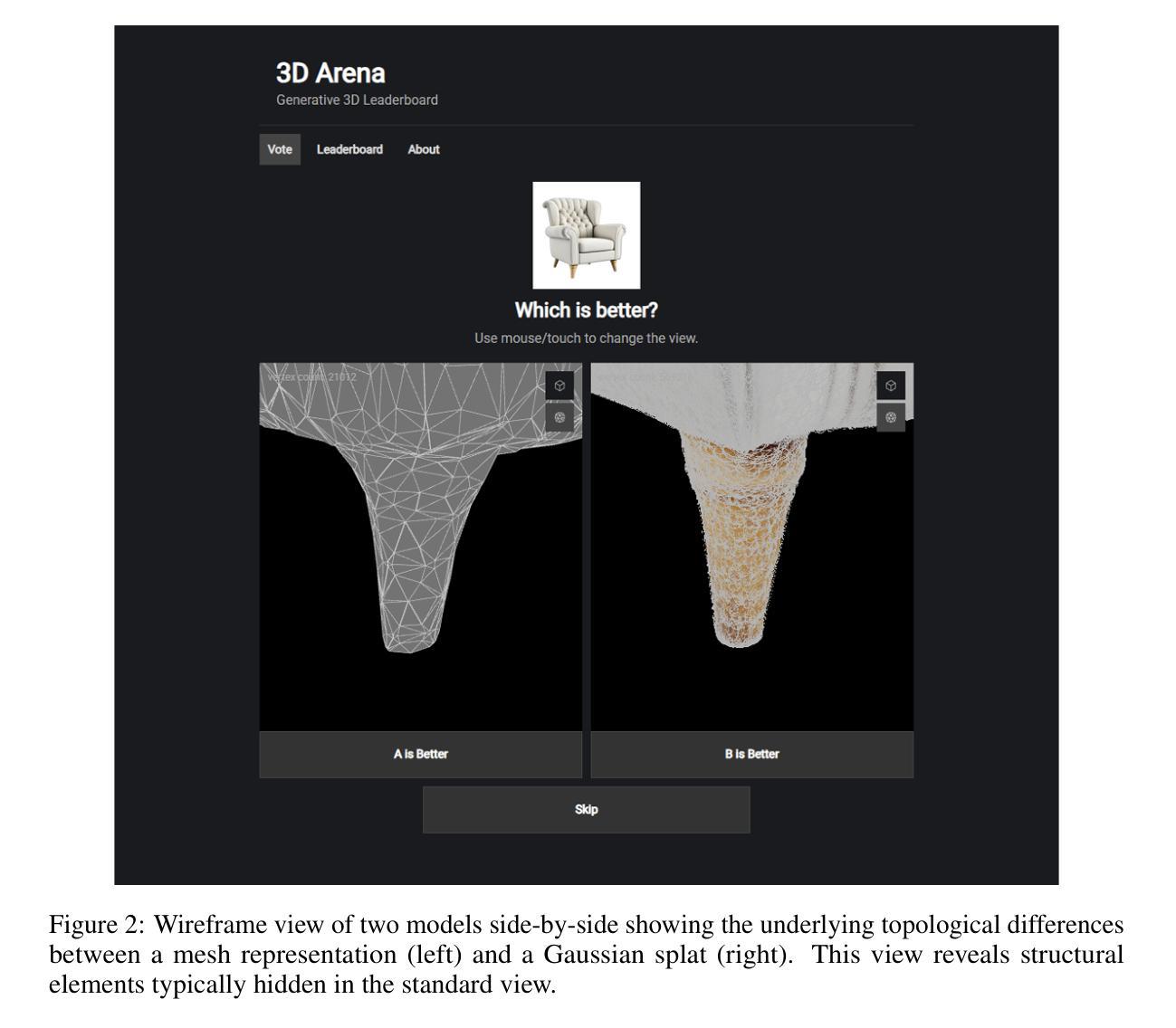
2D Triangle Splatting for Direct Differentiable Mesh Training
Authors:Kaifeng Sheng, Zheng Zhou, Yingliang Peng, Qianwei Wang
Differentiable rendering with 3D Gaussian primitives has emerged as a powerful method for reconstructing high-fidelity 3D scenes from multi-view images. While it offers improvements over NeRF-based methods, this representation still encounters challenges with rendering speed and advanced rendering effects, such as relighting and shadow rendering, compared to mesh-based models. In this paper, we propose 2D Triangle Splatting (2DTS), a novel method that replaces 3D Gaussian primitives with 2D triangle facelets. This representation naturally forms a discrete mesh-like structure while retaining the benefits of continuous volumetric modeling. By incorporating a compactness parameter into the triangle primitives, we enable direct training of photorealistic meshes. Our experimental results demonstrate that our triangle-based method, in its vanilla version (without compactness tuning), achieves higher fidelity compared to state-of-the-art Gaussian-based methods. Furthermore, our approach produces reconstructed meshes with superior visual quality compared to existing mesh reconstruction methods.
使用三维高斯原始数据的可微分渲染已经成为从多视角图像重建高保真三维场景的一种强大方法。虽然它在基于NeRF的方法的基础上有所改进,但这种表示方法仍然面临渲染速度和基于网格模型的先进渲染效果(如重新照明和阴影渲染)的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了二维三角剖分(2DTS)这一新方法,用二维三角形面片代替三维高斯原始数据。这种表示方法能够自然地形成离散网格状结构,同时保留连续体积建模的优点。通过将紧凑参数融入三角形原始数据中,我们能够实现光栅化网格的直接训练。我们的实验结果表明,我们的基于三角形的方法在基础版本(无紧凑性调整)中实现了与最先进的高斯方法相比更高的保真度。此外,我们的方法生成的重建网格在视觉质量上优于现有的网格重建方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures
Summary
基于二维三角剖分技术的可微渲染方法已经展现出强大的能力,能够从多视角图像重建高质量的三维场景。相较于基于高斯原语的方法,该方法在渲染速度和高级渲染效果方面更具优势,如重新打光与阴影渲染等。相较于基于网格的模型,本文提出的基于二维三角剖分(2DTS)的新方法以二维三角面片替代三维高斯原语,既保留了连续体积建模的优势,又自然形成了离散网格结构。实验结果表明,在无需紧凑度调整的情况下,该方法相较于其他基于高斯的方法能够实现更高的保真度,并生成具有优良视觉质量的重建网格。
Key Takeaways
- 可微渲染方法已经发展成为重建高质量三维场景的强大工具,能够使用二维三角剖分技术进行图像渲染和重建。
- 二维三角剖分方法克服了基于高斯原语方法的某些挑战,包括更快的渲染速度和更高级别的渲染效果。
- 与其他网格重建方法相比,二维三角剖分方法生成的重建网格具有更高的视觉质量。
- 通过引入紧凑度参数,该方法能够在保持连续体积建模优势的同时形成离散网格结构。
- 实验结果显示,在不调整紧凑度的情况下,该方法相较于其他基于高斯的方法具有更高的保真度。
- 该方法提供了对传统网格建模方法的改进,实现了更好的图像重建效果。
点此查看论文截图




3D Gaussian Splatting for Fine-Detailed Surface Reconstruction in Large-Scale Scene
Authors:Shihan Chen, Zhaojin Li, Zeyu Chen, Qingsong Yan, Gaoyang Shen, Ran Duan
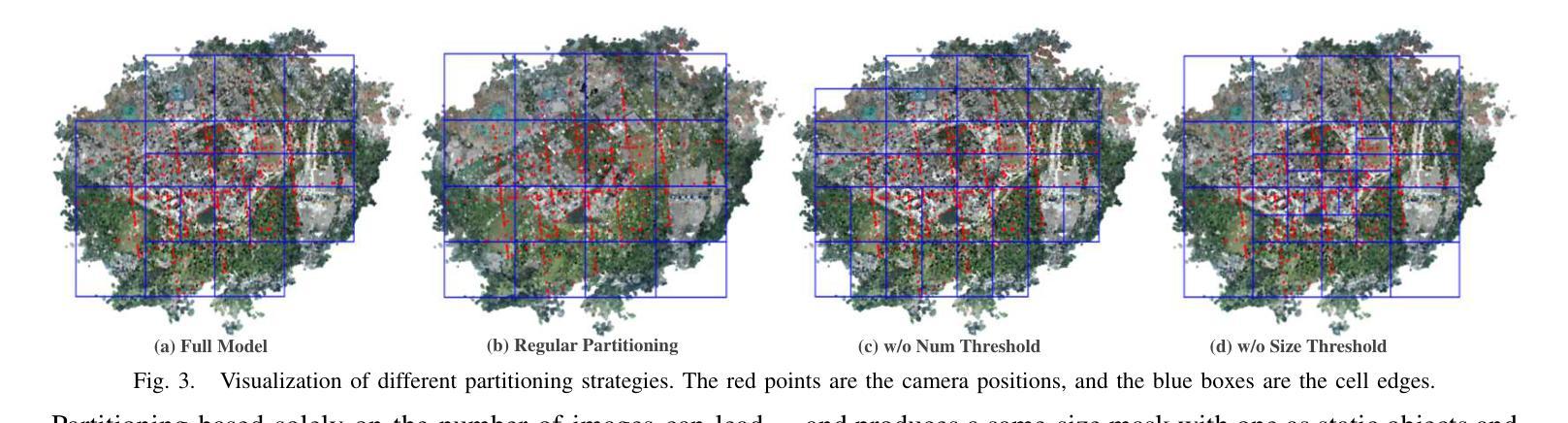
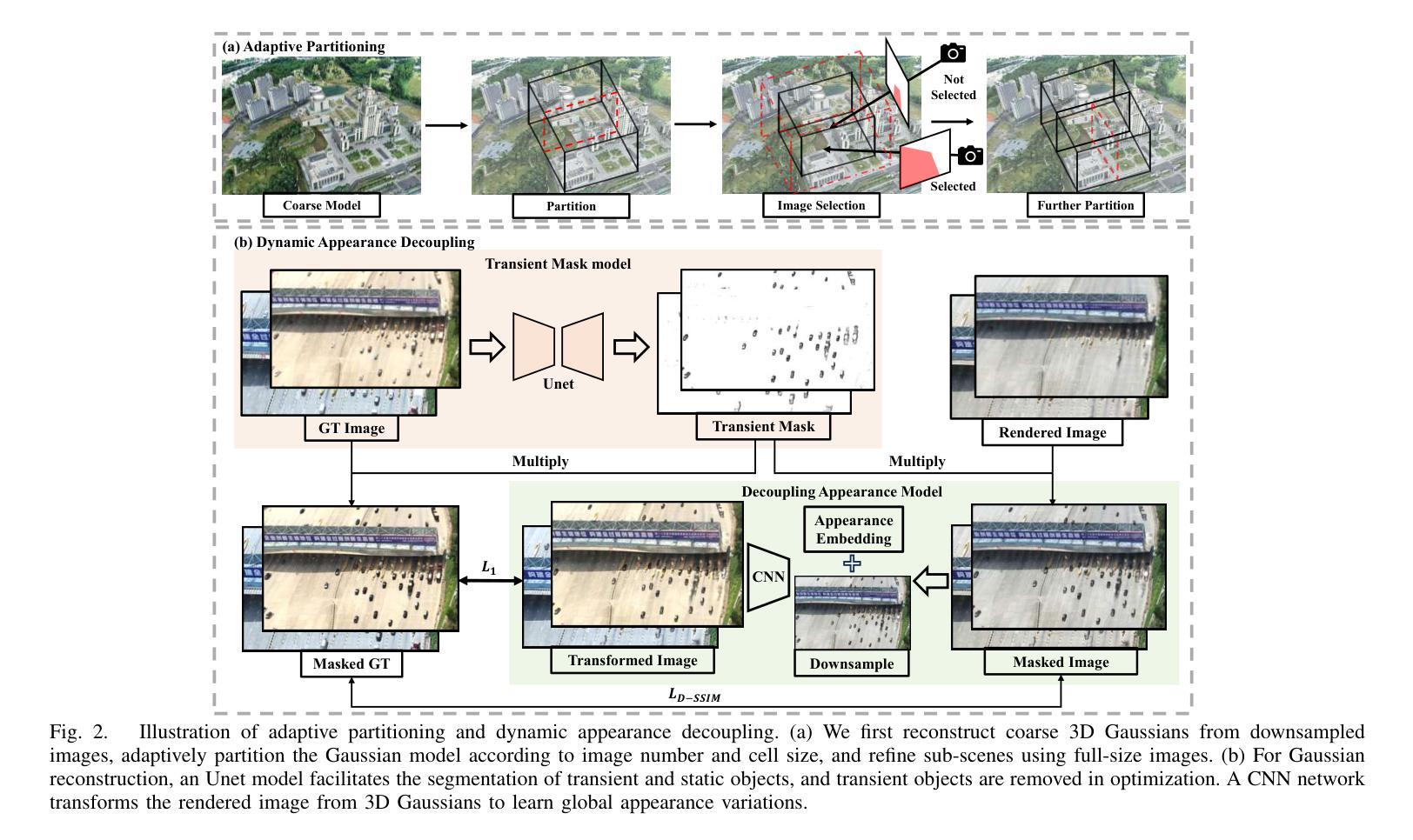
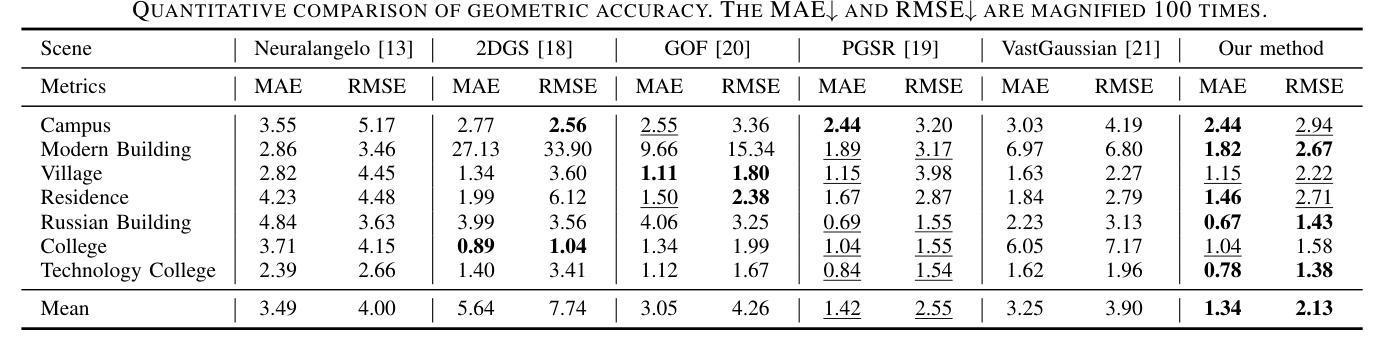
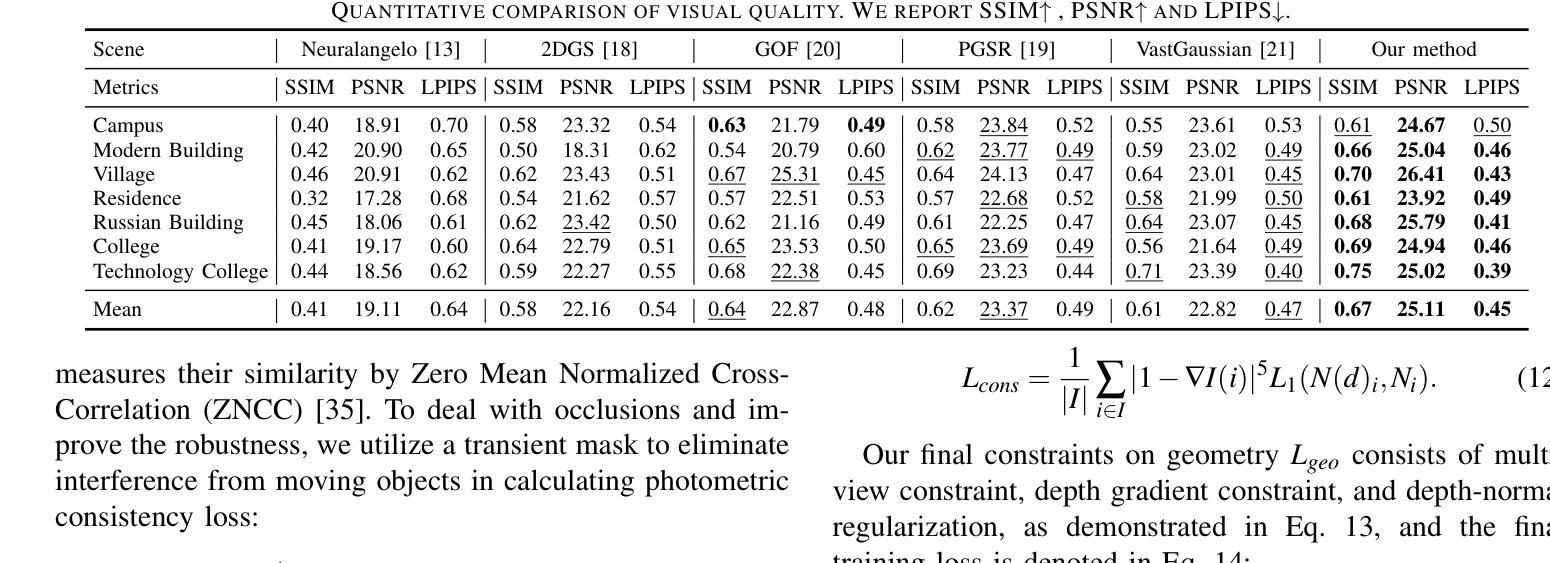
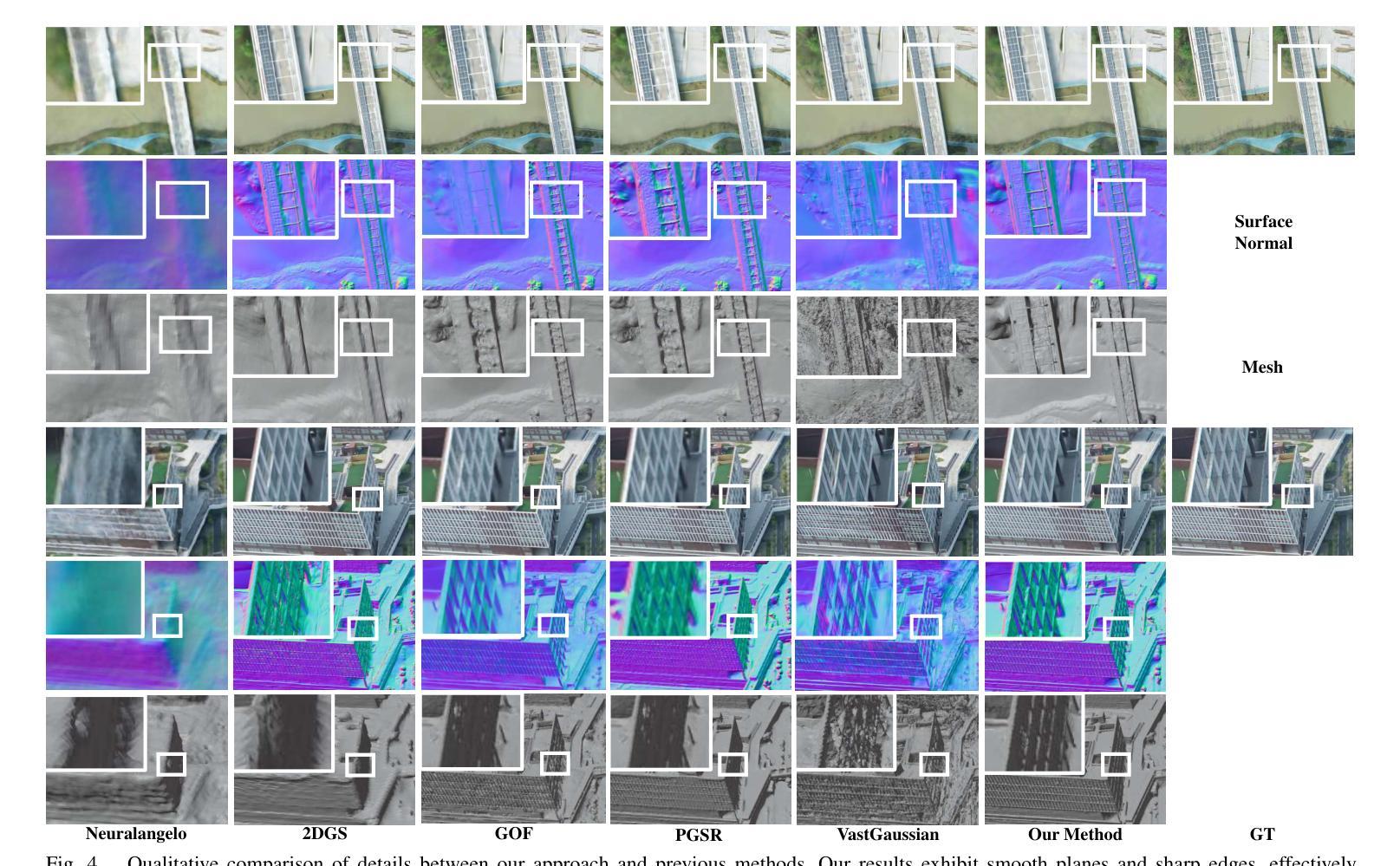
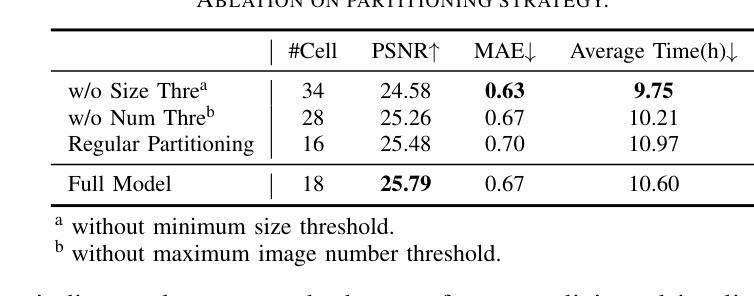
Recent developments in 3D Gaussian Splatting have made significant advances in surface reconstruction. However, scaling these methods to large-scale scenes remains challenging due to high computational demands and the complex dynamic appearances typical of outdoor environments. These challenges hinder the application in aerial surveying and autonomous driving. This paper proposes a novel solution to reconstruct large-scale surfaces with fine details, supervised by full-sized images. Firstly, we introduce a coarse-to-fine strategy to reconstruct a coarse model efficiently, followed by adaptive scene partitioning and sub-scene refining from image segments. Additionally, we integrate a decoupling appearance model to capture global appearance variations and a transient mask model to mitigate interference from moving objects. Finally, we expand the multi-view constraint and introduce a single-view regularization for texture-less areas. Our experiments were conducted on the publicly available dataset GauU-Scene V2, which was captured using unmanned aerial vehicles. To the best of our knowledge, our method outperforms existing NeRF-based and Gaussian-based methods, achieving high-fidelity visual results and accurate surface from full-size image optimization. Open-source code will be available on GitHub.
在三维高斯融合(3D Gaussian Splatting)的最新发展中,表面重建技术取得了重大进展。然而,由于室外环境的高计算需求和复杂的动态外观,将这些方法扩展到大规模场景仍然具有挑战性。这些挑战阻碍了其在航空勘察和自动驾驶中的应用。本文提出了一种由全尺寸图像监督的重建大规模表面细节的新方法。首先,我们采用从粗到细的策略高效重建粗略模型,随后进行自适应场景分割和图像分段的子场景细化。此外,我们集成了一个分离的外观模型来捕捉全局外观变化和一个瞬态掩膜模型来缓解移动物体的干扰。最后,我们扩展了多视角约束,并为无纹理区域引入单视角正则化。我们的实验是在公开可用的GauU-Scene V2数据集上进行的,该数据集是使用无人机捕获的。据我们所知,我们的方法优于现有的基于NeRF和基于高斯的方法,通过全尺寸图像优化实现了高保真视觉结果和精确的表面重建。开源代码将在GitHub上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IROS 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D高斯喷涂技术的最新进展,针对大规模场景表面重建提出了创新解决方案。通过引入从粗到细的重建策略、自适应场景分割、子场景细化以及外观模型与瞬态掩模模型的集成,该方法能够在全尺寸图像监督下重建具有精细细节的大规模场景。实验在公开数据集GauU-Scene V2上进行,该方法优于现有的NeRF和Gaussian方法,实现了高保真视觉结果和准确的表面重建。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的大规模场景表面重建方法,基于3D高斯喷涂技术。
- 提出了一种从粗到细的重建策略,以提高计算效率。
- 通过自适应场景分割和子场景细化,利用图像段进行更精细的重建。
- 采用了脱耦外观模型来捕捉全局外观变化,以及瞬态掩模模型来减轻移动物体的干扰。
- 扩展了多视角约束,为无纹理区域引入了单视角正则化。
- 在公开数据集GauU-Scene V2上进行的实验表明,该方法优于现有的NeRF和Gaussian方法。
点此查看论文截图


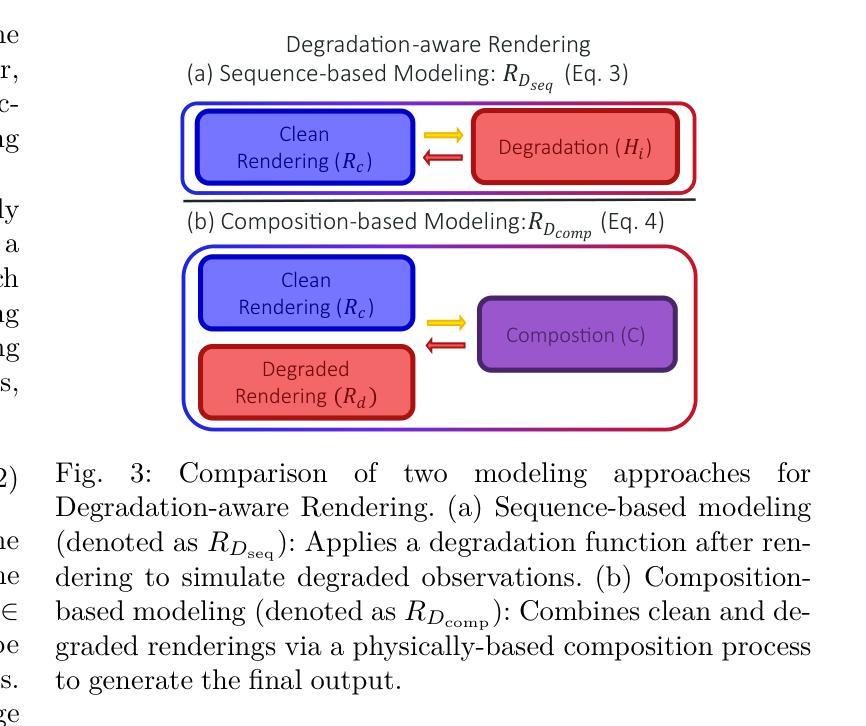
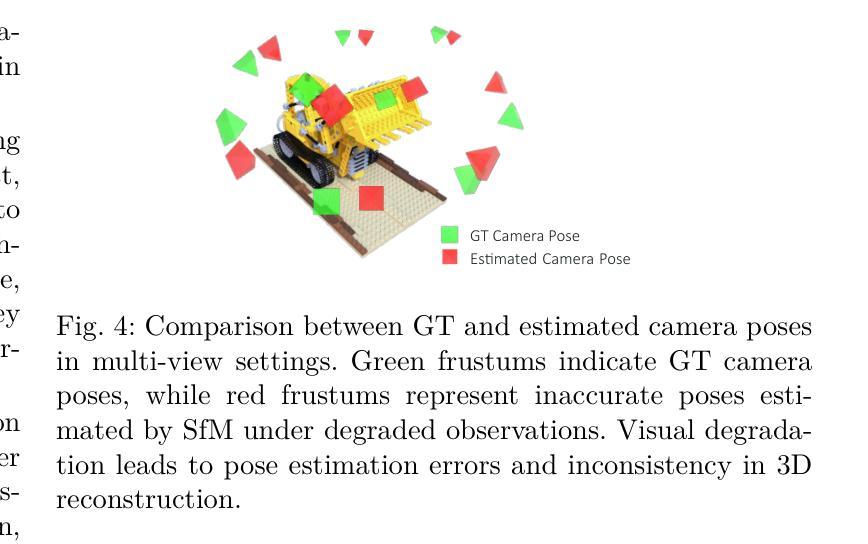
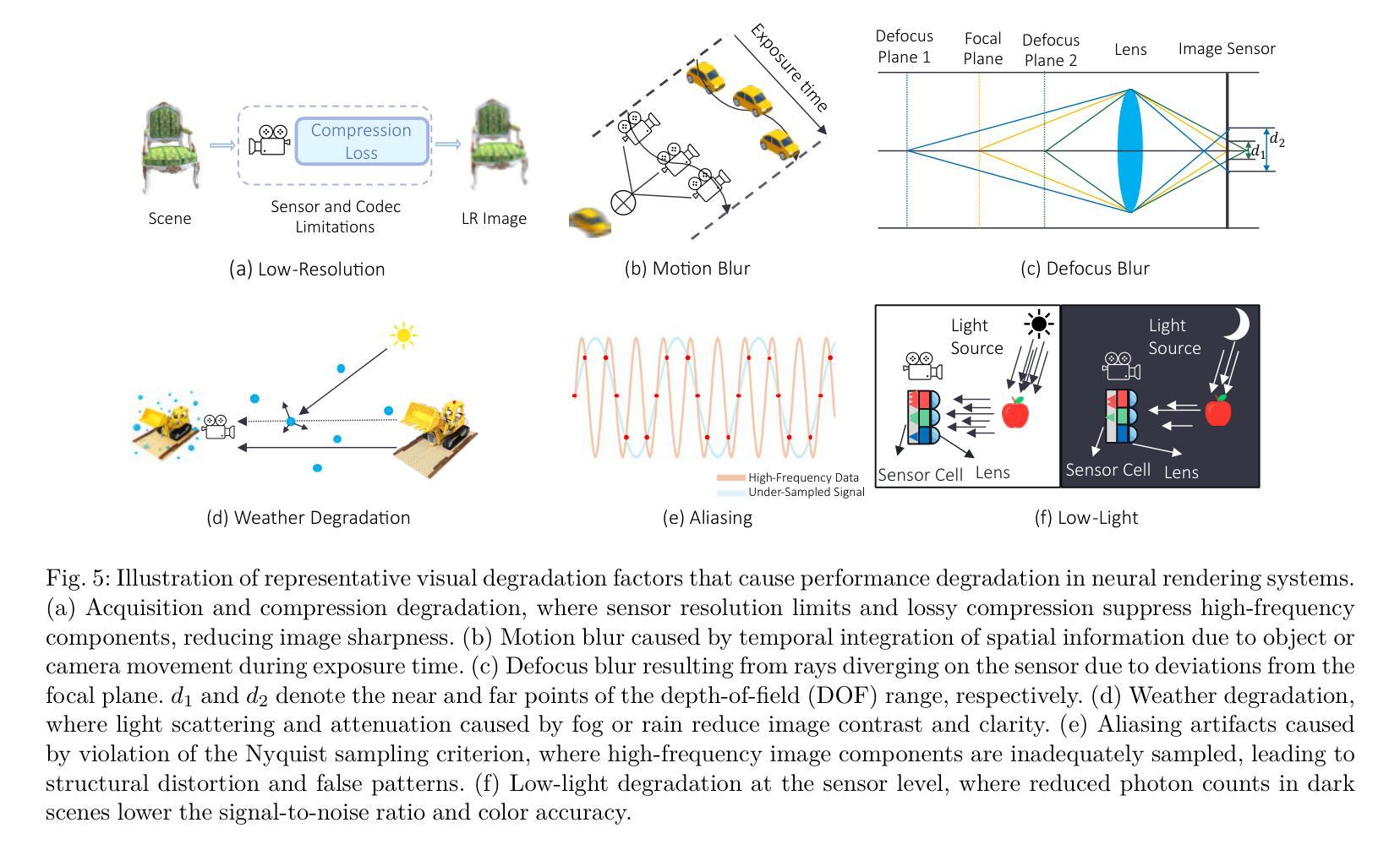
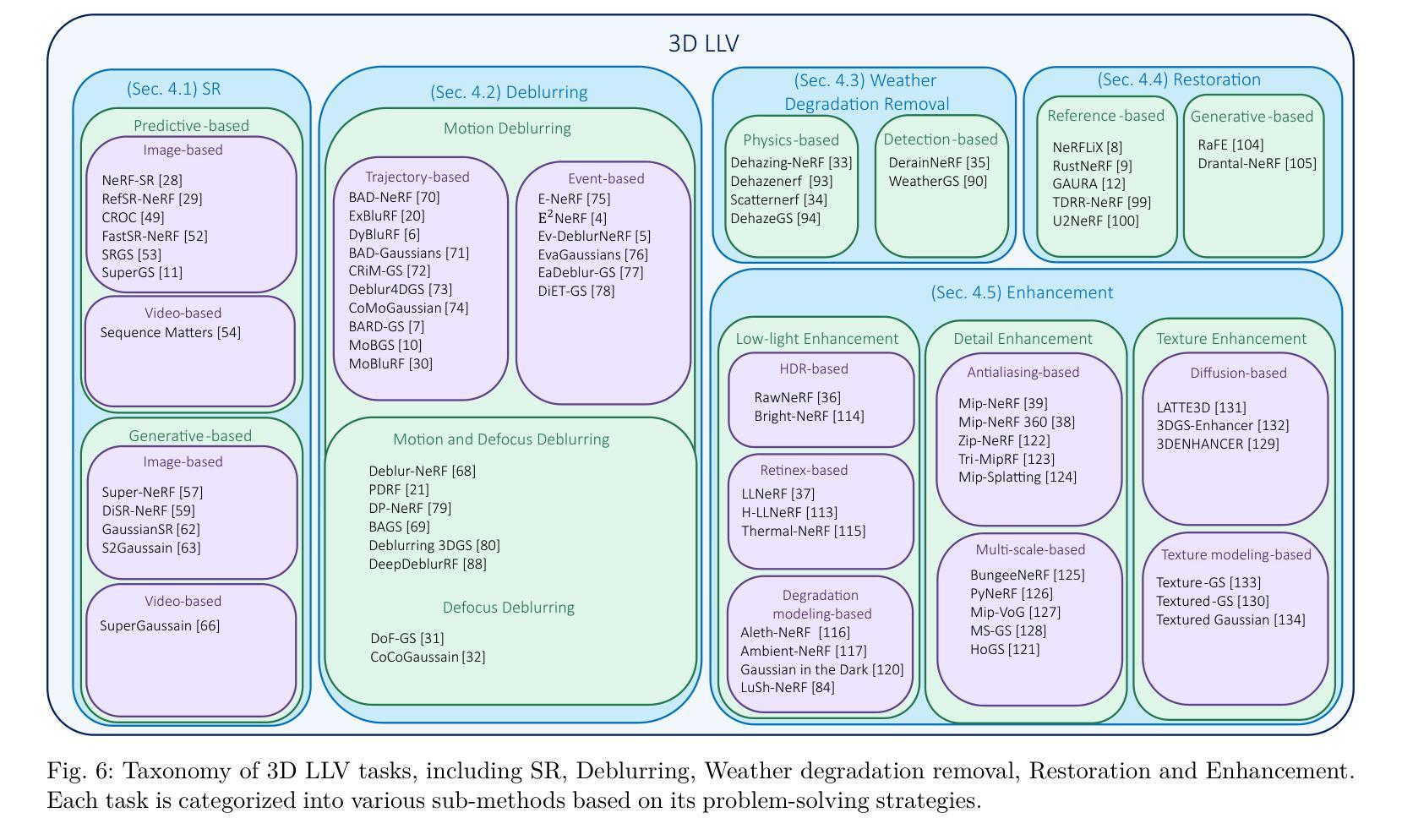
R3eVision: A Survey on Robust Rendering, Restoration, and Enhancement for 3D Low-Level Vision
Authors:Weeyoung Kwon, Jeahun Sung, Minkyu Jeon, Chanho Eom, Jihyong Oh
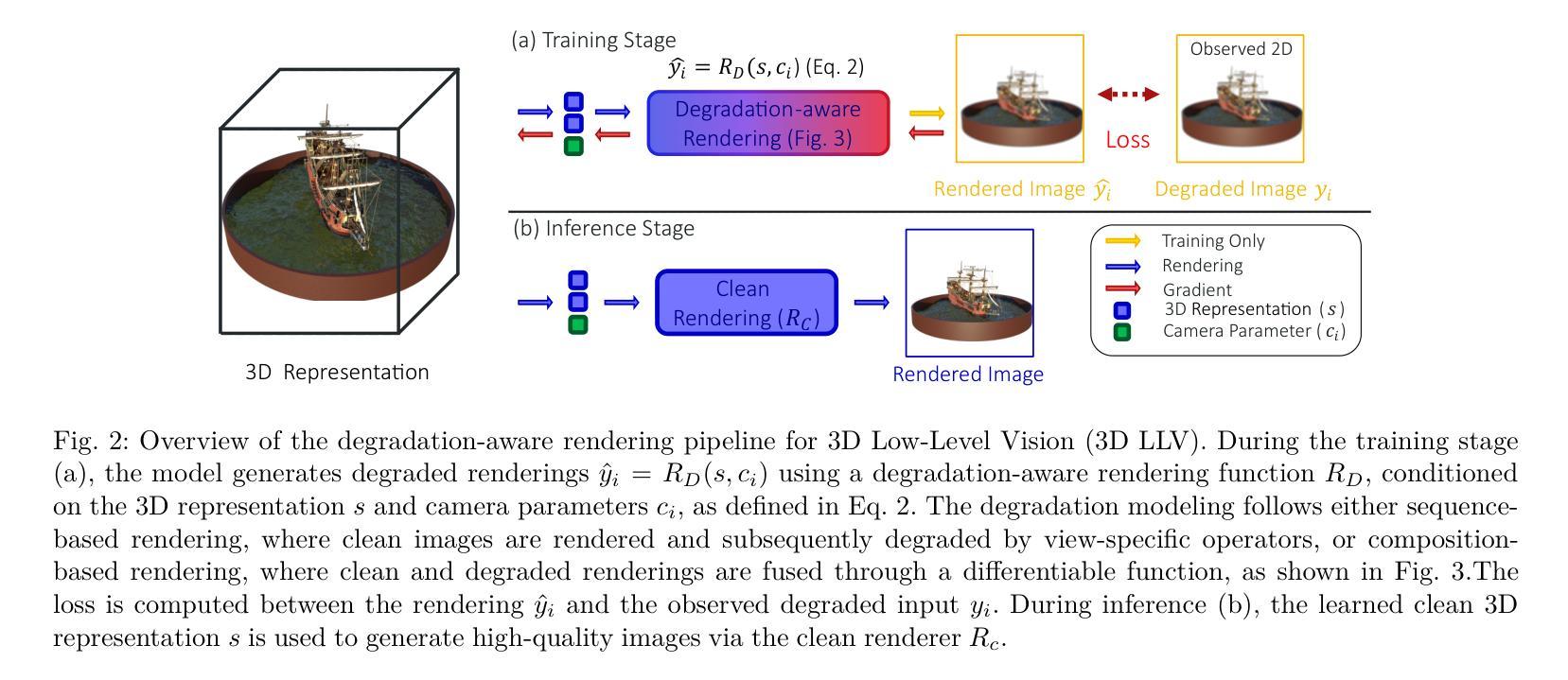
Neural rendering methods such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have achieved significant progress in photorealistic 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, most existing models assume clean and high-resolution (HR) multi-view inputs, which limits their robustness under real-world degradations such as noise, blur, low-resolution (LR), and weather-induced artifacts. To address these limitations, the emerging field of 3D Low-Level Vision (3D LLV) extends classical 2D Low-Level Vision tasks including super-resolution (SR), deblurring, weather degradation removal, restoration, and enhancement into the 3D spatial domain. This survey, referred to as R\textsuperscript{3}eVision, provides a comprehensive overview of robust rendering, restoration, and enhancement for 3D LLV by formalizing the degradation-aware rendering problem and identifying key challenges related to spatio-temporal consistency and ill-posed optimization. Recent methods that integrate LLV into neural rendering frameworks are categorized to illustrate how they enable high-fidelity 3D reconstruction under adverse conditions. Application domains such as autonomous driving, AR/VR, and robotics are also discussed, where reliable 3D perception from degraded inputs is critical. By reviewing representative methods, datasets, and evaluation protocols, this work positions 3D LLV as a fundamental direction for robust 3D content generation and scene-level reconstruction in real-world environments.
神经渲染方法,例如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯延展(3DGS),在逼真三维场景重建和新型视图合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,大多数现有模型假设输入是干净且高分辨率(HR)的多视角,这限制了它们在现实世界退化(例如噪声、模糊、低分辨率(LR)和天气引起的伪影)影响下的稳健性。为了解决这些局限性,新兴的三维低级视觉(3D LLV)领域将传统的二维低级视觉任务,包括超分辨率(SR)、去模糊、去除天气退化、修复和增强任务扩展到三维空间域。这篇综述被称为R\textsuperscript{3}eVision,它为三维LLV的稳健渲染、修复和增强提供了全面的概述,通过形式化退化感知渲染问题并确定与时空一致性和不适定优化相关的关键挑战。将LLV集成到神经渲染框架中的最近的方法被分类,以说明它们在不良条件下实现高保真三维重建的能力。还讨论了自动驾驶、AR/VR和机器人等领域,在这些领域中,从退化输入中进行可靠的3D感知至关重要。通过对代表性方法、数据集和评估协议的回顾,这项工作将3D LLV定位为现实世界中鲁棒三维内容生成和场景级别重建的根本方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Please visit our project page at https://github.com/CMLab-Korea/Awesome-3D-Low-Level-Vision
Summary
基于神经渲染方法如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯涂斑(3DGS)在真实感三维场景重建和新视角合成方面取得了显著进展,但现有模型大多假设干净的高分辨率多视角输入,这在现实世界的噪声、模糊、低分辨率和天气引起的伪影等退化条件下,其稳健性受到限制。为解决这些局限性,新兴的三维低级视觉(3D LLV)领域将传统的二维低级视觉任务扩展到三维空间域,包括超分辨率、去模糊、去除天气退化、修复和增强等。本文综述了R\textsuperscript{3}eVision中的稳健渲染、修复和增强技术,形式化退化感知渲染问题,并识别与时空一致性和病态优化相关的关键挑战。本文还介绍了将LLV集成到神经渲染框架中的最新方法,说明了它们在不良条件下实现高保真三维重建的能力。此外,还讨论了自主驾驶、增强现实/虚拟现实和机器人等领域,在这些领域中,从退化输入实现可靠的三维感知至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 神经渲染方法在三维场景重建和新视角合成方面取得显著进展。
- 现有模型在现实世界退化条件下(如噪声、模糊等)的稳健性受限。
- 三维低级视觉(3D LLV)是扩展传统二维低级视觉任务到三维空间域的新领域。
- R\textsuperscript{3}eVision提供了对3D LLV中稳健渲染、修复和增强的全面概述。
- 退化感知渲染问题被形式化,并识别出与时空一致性和病态优化相关的关键挑战。
- 介绍了将LLV集成到神经渲染框架中的最新方法,以应对不良条件下的高保真三维重建。
点此查看论文截图

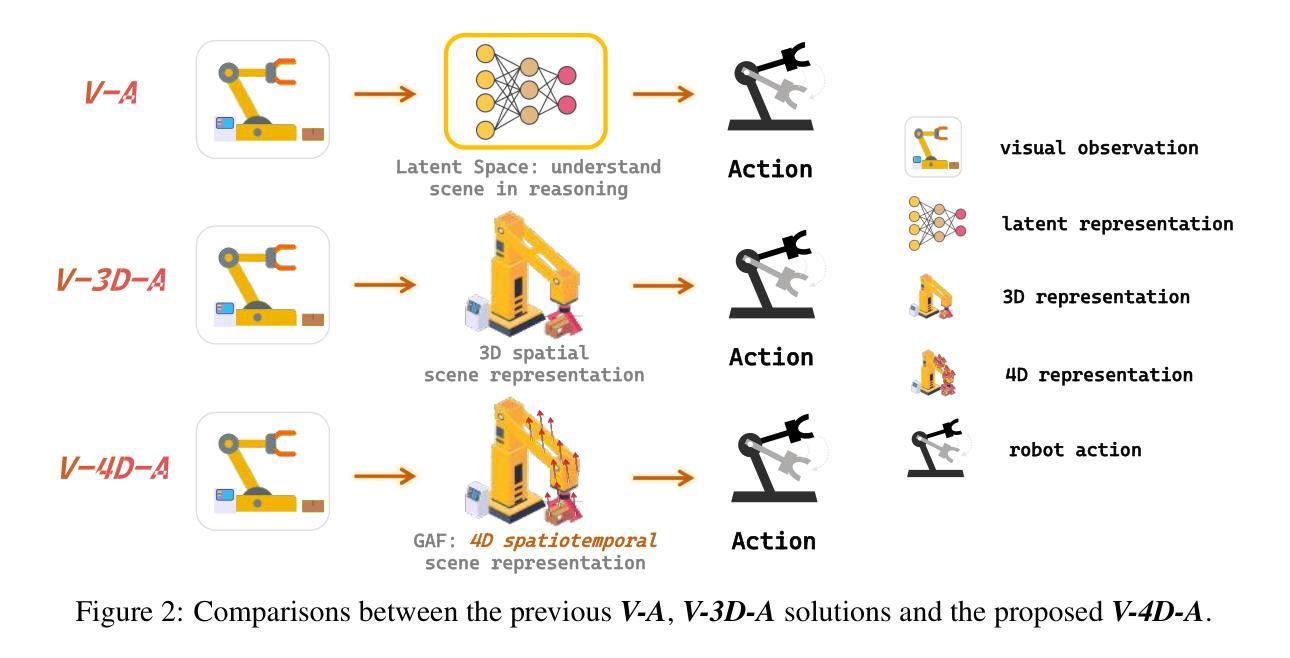
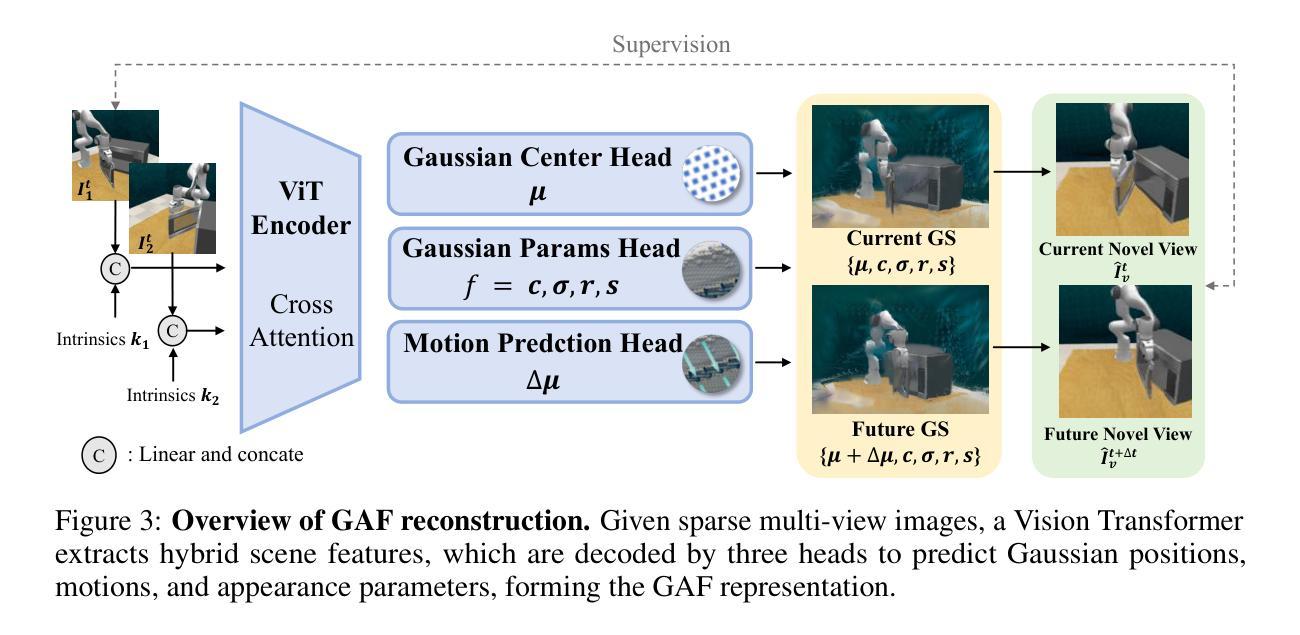
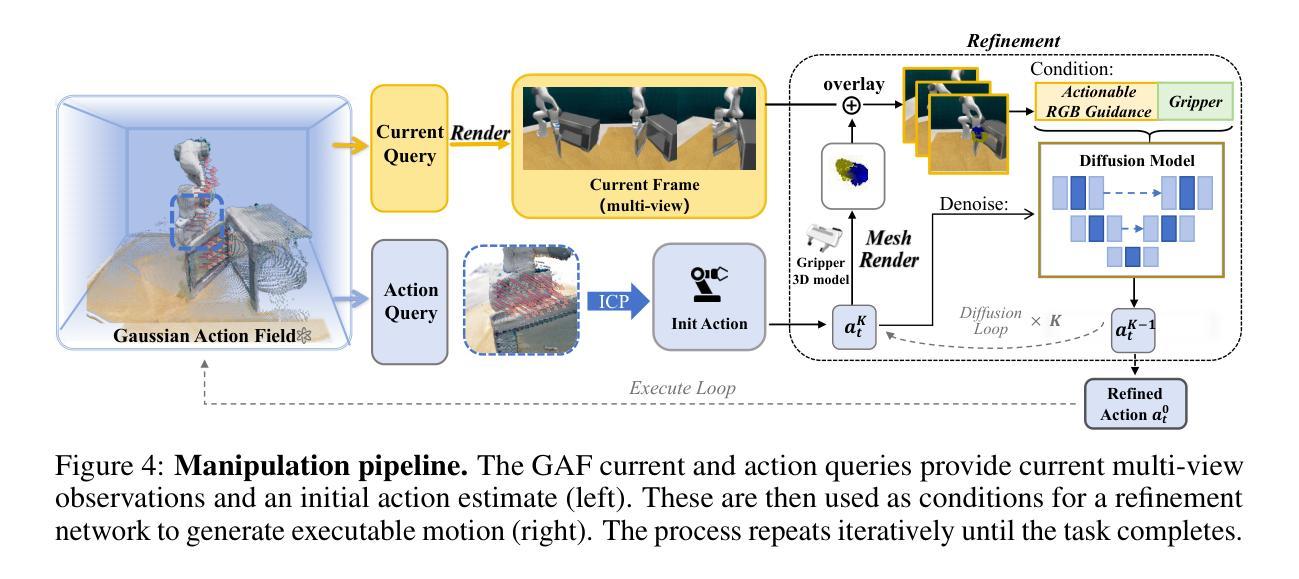
GAF: Gaussian Action Field as a Dynamic World Model for Robotic Manipulation
Authors:Ying Chai, Litao Deng, Ruizhi Shao, Jiajun Zhang, Liangjun Xing, Hongwen Zhang, Yebin Liu
Accurate action inference is critical for vision-based robotic manipulation. Existing approaches typically follow either a Vision-to-Action (V-A) paradigm, predicting actions directly from visual inputs, or a Vision-to-3D-to-Action (V-3D-A) paradigm, leveraging intermediate 3D representations. However, these methods often struggle with action inaccuracies due to the complexity and dynamic nature of manipulation scenes. In this paper, we propose a Vision-to-4D-to-Action (V-4D-A) framework that enables direct action reasoning from motion-aware 4D representations via a Gaussian Action Field (GAF). GAF extends 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) by incorporating learnable motion attributes, allowing simultaneous modeling of dynamic scenes and manipulation actions. To learn time-varying scene geometry and action-aware robot motion, GAF supports three key query types: reconstruction of the current scene, prediction of future frames, and estimation of initial action via robot motion. Furthermore, the high-quality current and future frames generated by GAF facilitate manipulation action refinement through a GAF-guided diffusion model. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements, with GAF achieving +11.5385 dB PSNR and -0.5574 LPIPS improvements in reconstruction quality, while boosting the average success rate in robotic manipulation tasks by 10.33% over state-of-the-art methods. Project page: http://chaiying1.github.io/GAF.github.io/project_page/
在基于视觉的机器人操控中,精确的动作推理至关重要。现有的方法通常采用视觉到动作(V-A)范式,直接从视觉输入预测动作,或者视觉到三维到动作(V-3D-A)范式,利用中间三维表示。然而,这些方法由于操控场景的复杂性和动态性,往往存在动作不准确的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种视觉到四维到动作(V-4D-A)框架,通过高斯动作场(GAF)实现从动态感知的4D表示中直接进行动作推理。GAF通过引入可学习的运动属性扩展了三维高斯拼贴(3DGS),能够实现动态场景和操控动作的同时建模。为了学习随时间变化的场景几何和动作感知的机器人运动,GAF支持三种关键查询类型:重建当前场景、预测未来帧以及通过机器人运动估计初始动作。此外,GAF生成的高质量当前和未来帧通过GAF引导扩散模型促进了操控动作的优化。大量实验表明,GAF在重建质量上实现了+11.5385分贝峰值信噪比(PSNR)和-0.5574图像感知相似度指标(LPIPS)的显著提升,同时在机器人操控任务中将平均成功率提高了10.33%,超过了最新方法。项目页面:http://chaiying1.github.io/GAF.github.io/project_page/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF http://chaiying1.github.io/GAF.github.io/project_page/
Summary
该论文提出了一种基于视觉的机器人操作新框架,即Vision-to-4D-to-Action(V-4D-A)框架,通过高斯动作场(GAF)直接从运动感知的4D表示中进行动作推理。GAF通过引入可学习的运动属性,扩展了3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),能同时建模动态场景和操作动作。
Key Takeaways
现有方法:大多数现有的方法基于视觉进行机器人操作采用Vision-to-Action (V-A) 或 Vision-to-3D-to-Action (V-3D-A) 范式。它们面临着由于操作场景的复杂性和动态性而导致的动作不准确的问题。
新框架提出:论文提出了一个新的框架Vision-to-4D-to-Action (V-4D-A),它利用运动感知的4D表示进行直接动作推理。这个框架通过高斯动作场(GAF)实现,扩展了3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)。
GAF的特点:GAF通过引入可学习的运动属性,能同时建模动态场景和机器人操作动作。它支持三种关键查询类型:当前场景的重建、未来帧的预测以及通过机器人运动对初始动作的估计。
学习和优化:GAF产生的高质量当前和未来帧,通过GAF引导扩散模型,有助于优化机器人操作动作。
实验结果:实验表明,与最新技术相比,GAF在重建质量方面提高了+11.5385 dB PSNR和-0.5574 LPIPS,同时在机器人操作任务中将成功率提高了10.33%。
点此查看论文截图

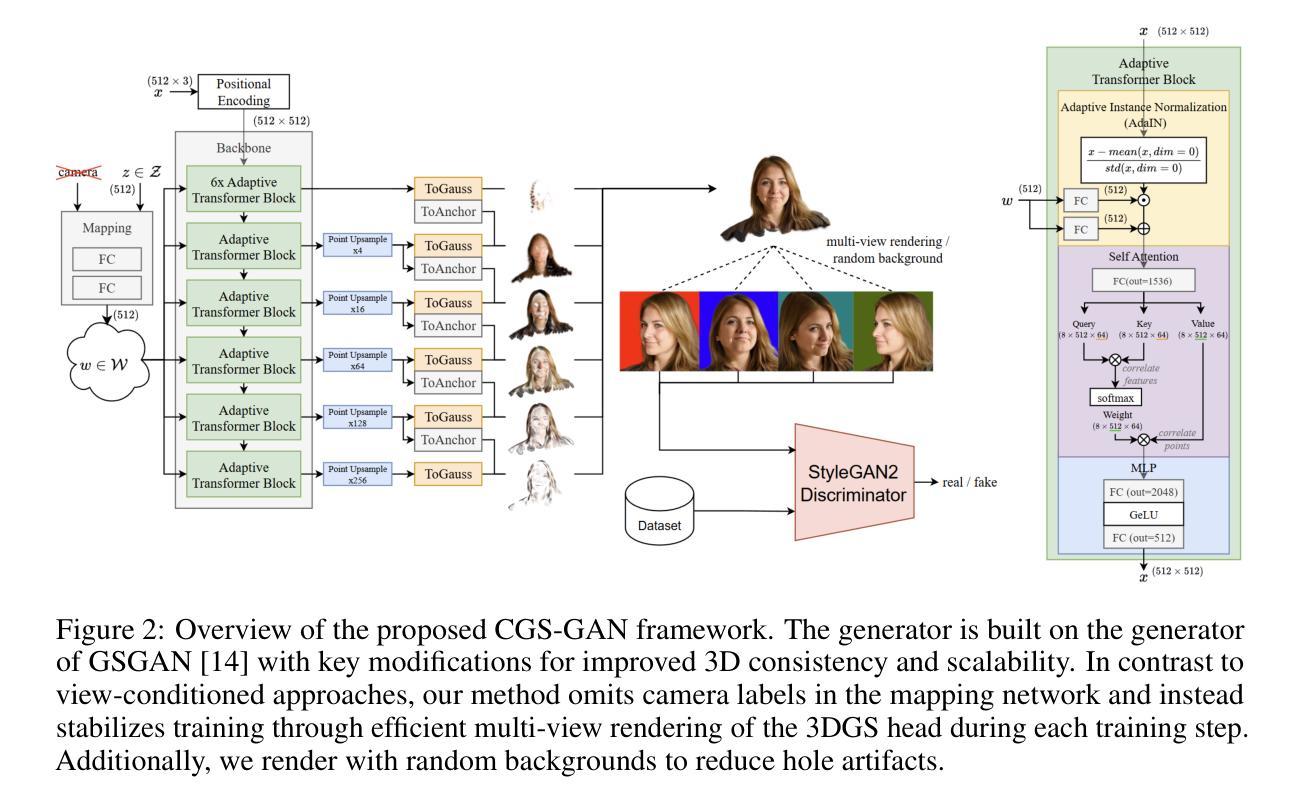
CGS-GAN: 3D Consistent Gaussian Splatting GANs for High Resolution Human Head Synthesis
Authors:Florian Barthel, Wieland Morgenstern, Paul Hinzer, Anna Hilsmann, Peter Eisert
Recently, 3D GANs based on 3D Gaussian splatting have been proposed for high quality synthesis of human heads. However, existing methods stabilize training and enhance rendering quality from steep viewpoints by conditioning the random latent vector on the current camera position. This compromises 3D consistency, as we observe significant identity changes when re-synthesizing the 3D head with each camera shift. Conversely, fixing the camera to a single viewpoint yields high-quality renderings for that perspective but results in poor performance for novel views. Removing view-conditioning typically destabilizes GAN training, often causing the training to collapse. In response to these challenges, we introduce CGS-GAN, a novel 3D Gaussian Splatting GAN framework that enables stable training and high-quality 3D-consistent synthesis of human heads without relying on view-conditioning. To ensure training stability, we introduce a multi-view regularization technique that enhances generator convergence with minimal computational overhead. Additionally, we adapt the conditional loss used in existing 3D Gaussian splatting GANs and propose a generator architecture designed to not only stabilize training but also facilitate efficient rendering and straightforward scaling, enabling output resolutions up to $2048^2$. To evaluate the capabilities of CGS-GAN, we curate a new dataset derived from FFHQ. This dataset enables very high resolutions, focuses on larger portions of the human head, reduces view-dependent artifacts for improved 3D consistency, and excludes images where subjects are obscured by hands or other objects. As a result, our approach achieves very high rendering quality, supported by competitive FID scores, while ensuring consistent 3D scene generation. Check our our project page here: https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/
最近,基于三维高斯贴图的3D GANs已被提出用于高质量的人头合成。然而,现有方法通过根据当前相机位置对随机潜在向量进行条件处理,从而稳定训练并提高了从陡峭视角的呈现质量。这损害了三维一致性,因为我们在重新合成三维头部时观察到身份发生显著变化,每次相机移动时都是如此。相反,将相机固定在一个视角上,可以为该视角产生高质量的渲染,但对于新视角则表现不佳。移除视图条件通常会使GAN训练不稳定,并经常导致训练崩溃。针对这些挑战,我们引入了CGS-GAN,这是一种新型的三维高斯贴图GAN框架,能够在不依赖视图条件的情况下实现稳定训练以及高质量的三维一致人头合成。为了确保训练稳定性,我们引入了一种多视图正则化技术,该技术可增强生成器的收敛性,同时计算开销最小。此外,我们适应了现有三维高斯贴图GAN中的条件损失,并提出了一种设计巧妙的生成器架构,不仅可以稳定训练,还可以促进高效渲染和简洁扩展,支持高达$ 2048^2 $的输出分辨率。为了评估CGS-GAN的能力,我们从FFHQ中整理了一个新的数据集。该数据集可实现非常高的分辨率,侧重于人类头部的大部分区域,减少了视图相关的伪影以改善三维一致性,并排除了主体被手或其他物体遮挡的图像。因此,我们的方法实现了非常高的呈现质量,辅以有竞争力的FID分数,同时确保了一致的三维场景生成。请访问我们的项目页面了解更多信息:https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main paper 12 pages, supplementary materials 8 pages
摘要
本文提出一种新型的三维高斯展平GAN(CGS-GAN)框架,用于解决现有技术中视角调整对训练稳定性和头部渲染质量的影响问题。通过引入多视角正则化技术和改进的条件损失函数,CGS-GAN在不依赖视角调整的情况下实现了稳定的训练和高质量的三维一致性头部合成。此外,还通过优化生成器架构,提高了渲染效率和输出分辨率。实验证明,CGS-GAN在高分辨率渲染质量方面表现出优异的性能,同时保证了三维场景的一致性生成。
关键见解
- 现有基于三维高斯展平的GAN技术在处理头部合成时面临视角调整带来的问题,影响渲染质量和三维一致性。
- CGS-GAN框架被引入以解决这些问题,通过多视角正则化技术确保训练稳定性,同时实现高质量的三维一致性头部合成。
- CGS-GAN改进了现有技术中的条件损失函数,促进生成器的收敛,同时提高渲染效率和输出分辨率。
- 为评估CGS-GAN性能,开发了一个新的数据集,专注于人类头部的大部位,减少视角相关的伪影,并排除被手或其他物体遮挡的图像。
- 实验结果表明,CGS-GAN在高分辨率渲染质量方面具有优异表现,保证三维场景的一致生成。
- CGS-GAN框架具有潜力解决当前技术在头部合成中的关键问题,为未来相关工作提供了有价值的参考。
- 通过引入新型技术和优化策略,CGS-GAN有望推动三维高斯展平GAN的研究进展,并推动相关技术的应用发展。
点此查看论文截图

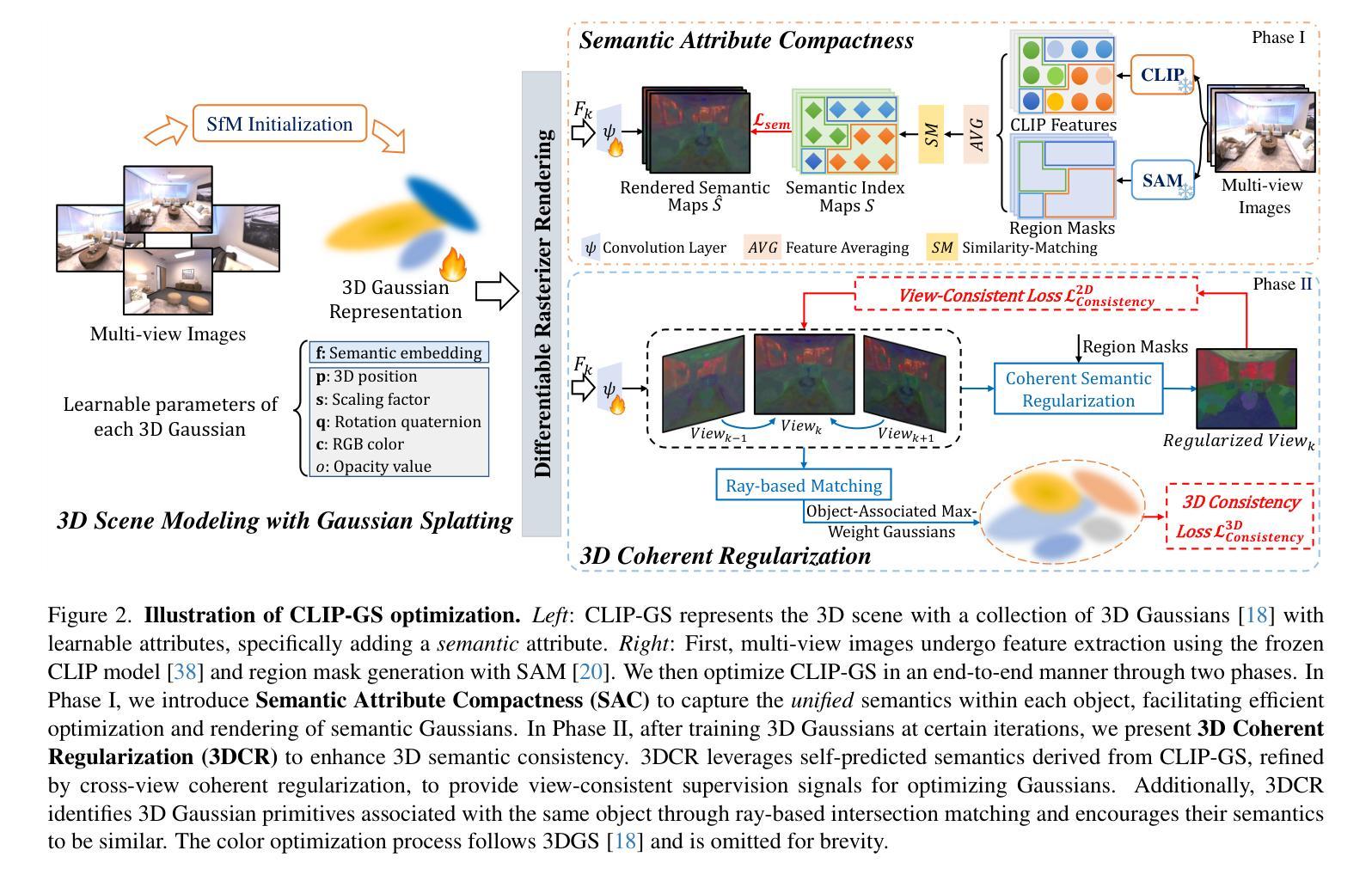
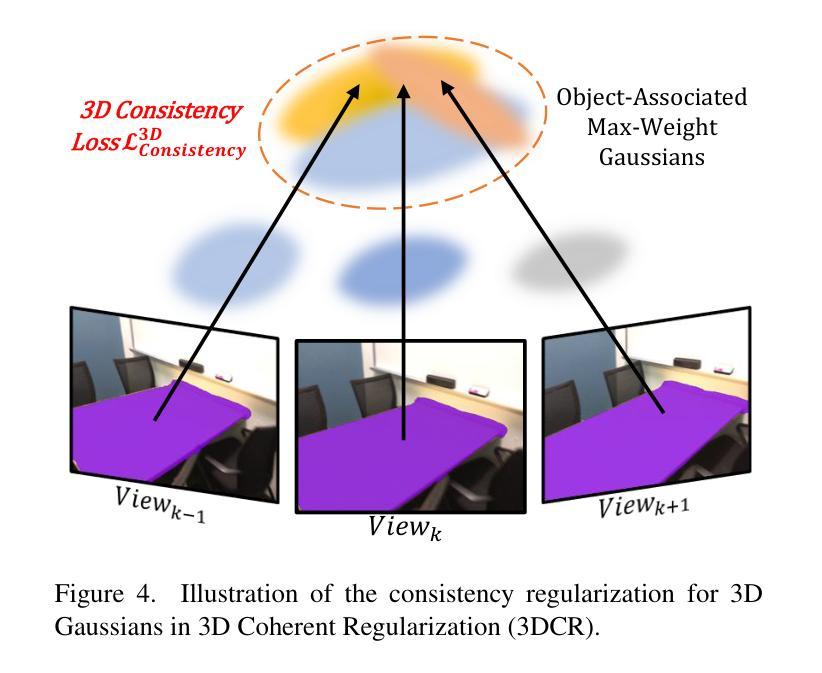
CLIP-GS: CLIP-Informed Gaussian Splatting for View-Consistent 3D Indoor Semantic Understanding
Authors:Guibiao Liao, Jiankun Li, Zhenyu Bao, Xiaoqing Ye, Qing Li, Kanglin Liu
Exploiting 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) models for open-vocabulary 3D semantic understanding of indoor scenes has emerged as an attractive research focus. Existing methods typically attach high-dimensional CLIP semantic embeddings to 3D Gaussians and leverage view-inconsistent 2D CLIP semantics as Gaussian supervision, resulting in efficiency bottlenecks and deficient 3D semantic consistency. To address these challenges, we present CLIP-GS, efficiently achieving a coherent semantic understanding of 3D indoor scenes via the proposed Semantic Attribute Compactness (SAC) and 3D Coherent Regularization (3DCR). SAC approach exploits the naturally unified semantics within objects to learn compact, yet effective, semantic Gaussian representations, enabling highly efficient rendering (>100 FPS). 3DCR enforces semantic consistency in 2D and 3D domains: In 2D, 3DCR utilizes refined view-consistent semantic outcomes derived from 3DGS to establish cross-view coherence constraints; in 3D, 3DCR encourages features similar among 3D Gaussian primitives associated with the same object, leading to more precise and coherent segmentation results. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method remarkably suppresses existing state-of-the-art approaches, achieving mIoU improvements of 21.20% and 13.05% on ScanNet and Replica datasets, respectively, while maintaining real-time rendering speed. Furthermore, our approach exhibits superior performance even with sparse input data, substantiating its robustness.
利用三维高斯映射(3DGS)与对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,实现对室内场景开放词汇表的三维语义理解,已成为一个吸引人的研究焦点。现有方法通常将高维CLIP语义嵌入到三维高斯分布中,并利用视图不一致的二维CLIP语义作为高斯分布的监督信息,从而导致效率瓶颈和三维语义一致性不足。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了CLIP-GS方法,通过提出的语义属性紧凑性(SAC)和三维一致性正则化(3DCR)有效地实现对三维室内场景的一致语义理解。SAC方法利用对象内部的自然统一语义来学习紧凑而有效的语义高斯表示,从而实现高效渲染(>100帧每秒)。3DCR在二维和三维域中强制实施语义一致性:在二维空间中,3DCR利用来自3DGS的精细化视图一致语义结果建立跨视图一致性约束;在三维空间中,3DCR鼓励与同一对象相关的三维高斯基元之间的特征相似性,从而得到更精确和一致的分割结果。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法显著地抑制了现有最先进的方案,在ScanNet和Replica数据集上分别实现了平均交并比(mIoU)的改进为21.20%和13.05%,同时保持实时渲染速度。此外,我们的方法在稀疏输入数据的情况下也表现出卓越的性能,证明了其稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM TOMM 2025
摘要
本文研究了利用三维高斯展开(3DGS)与对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型进行室内场景开放词汇三维语义理解的方法。针对现有方法在处理高维CLIP语义嵌入和视图不一致的2D CLIP语义时出现的效率瓶颈和三维语义一致性不足的问题,本文提出了CLIP-GS方法。该方法通过语义属性紧凑性(SAC)和三维一致正则化(3DCR)实现了对三维室内场景的一致语义理解。SAC方法利用对象内部自然统一的语义来学习紧凑而有效的语义高斯表示,实现了高效渲染(>100帧/秒)。3DCR在二维和三维领域都强制实施语义一致性:在二维空间中,3DCR利用由3DGS派生的精细视图一致语义结果来建立跨视图一致性约束;在三维空间中,3DCR鼓励与同一对象相关的三维高斯原始特征相似,从而获得更精确和一致的分割结果。大量实验结果证明,我们的方法显著优于现有最先进的方法,在ScanNet和Replica数据集上分别实现了mIoU改进21.20%和13.05%,同时保持实时渲染速度。即使在稀疏输入数据下,我们的方法也表现出卓越的性能,证明了其稳健性。
关键见解
- 利用3DGS与CLIP模型结合,实现室内场景开放词汇的三维语义理解。
- 现有方法在处理高维CLIP语义嵌入和视图不一致的2D CLIP语义时存在挑战,导致效率瓶颈和三维语义一致性不足。
- 提出了SAC和3DCR方法来解决上述挑战。SAC实现了紧凑而有效的语义高斯表示,而3DCR在二维和三维空间中强制实施语义一致性。
- SAC方法使高效渲染成为可能(>100帧/秒)。
- 3DCR在跨视图一致性和三维分割精度方面表现出优越性能。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在ScanNet和Replica数据集上显著优于现有方法,同时保持实时渲染速度。
点此查看论文截图