⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
Audit & Repair: An Agentic Framework for Consistent Story Visualization in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Kiymet Akdemir, Tahira Kazimi, Pinar Yanardag
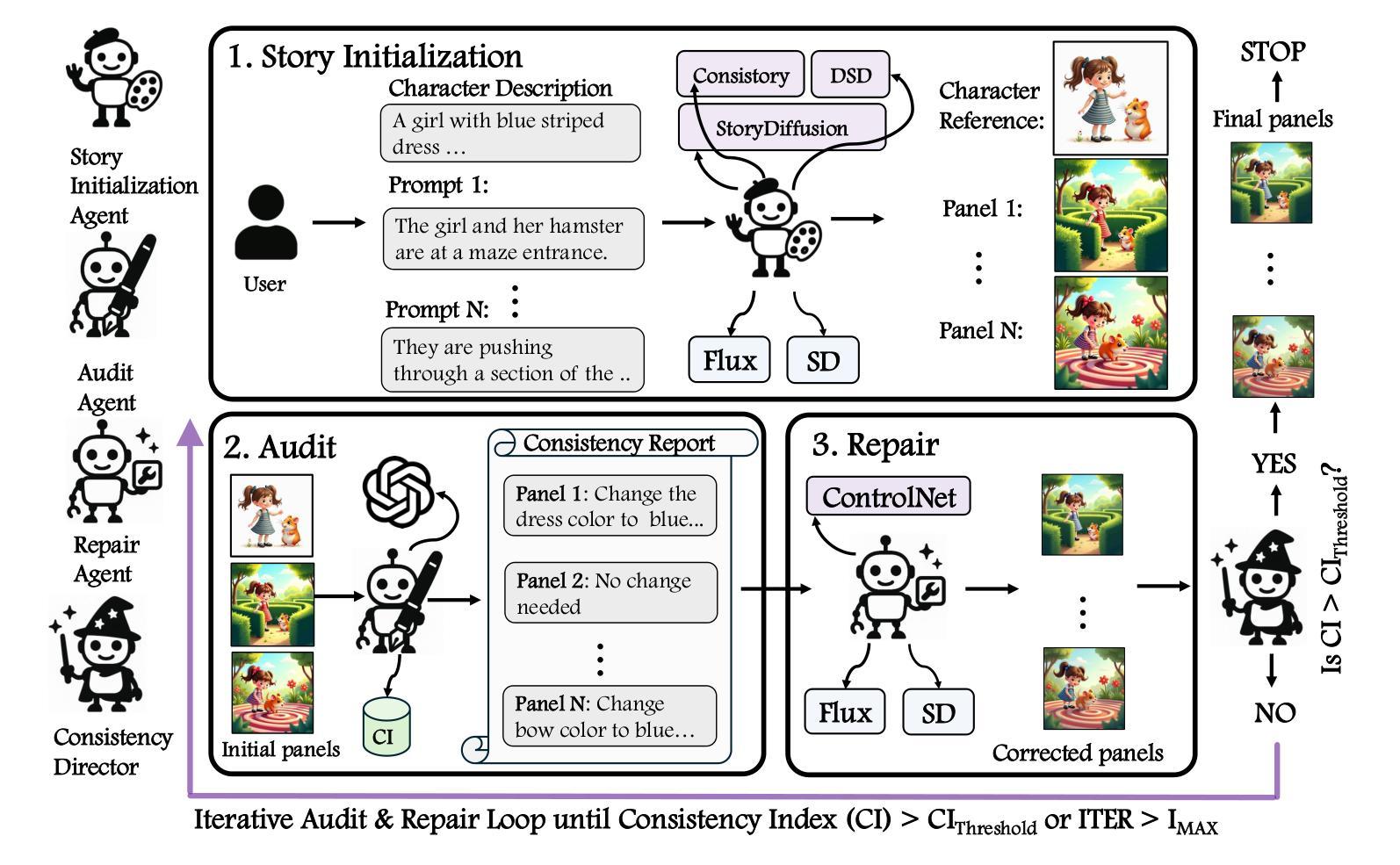
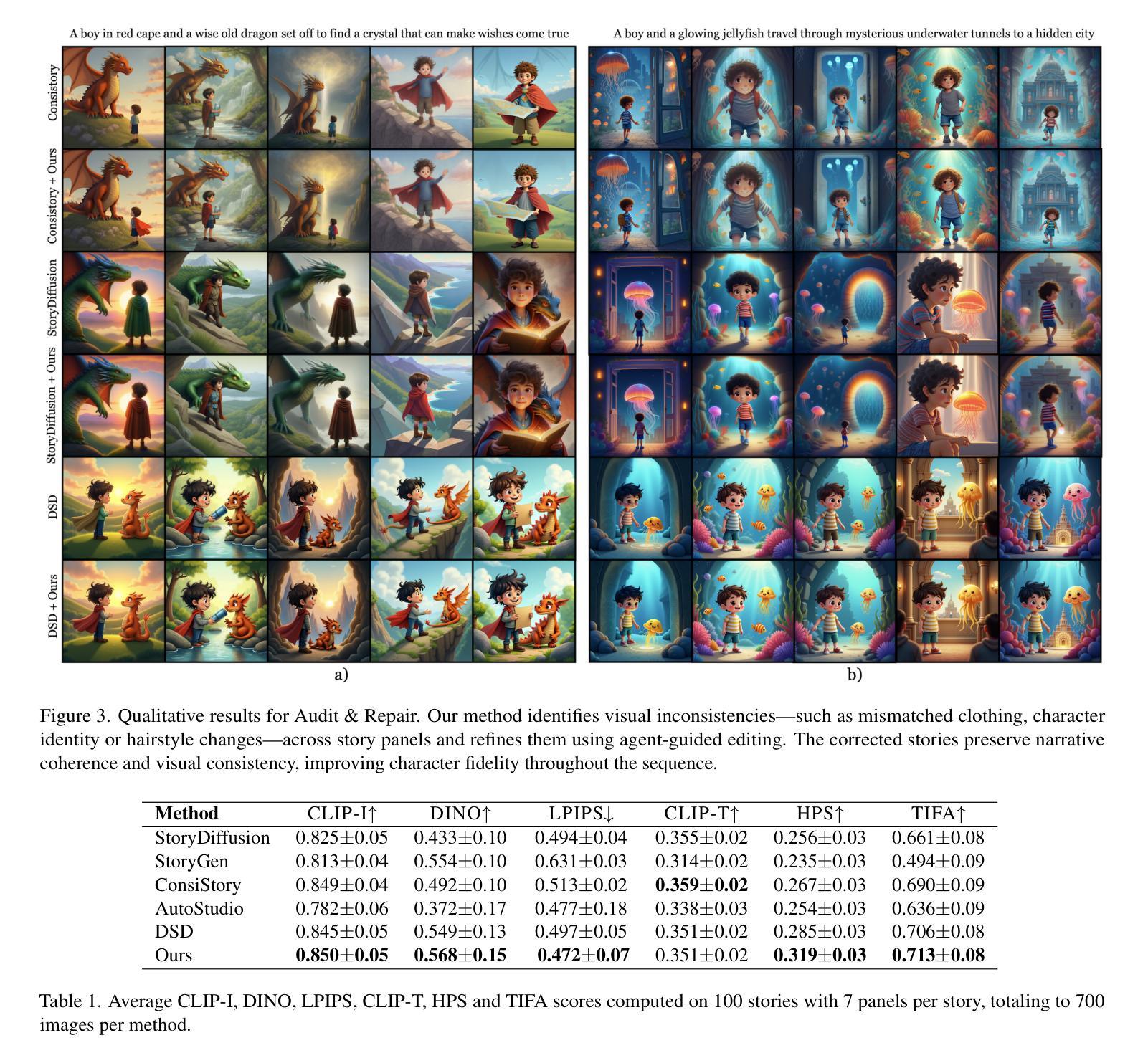
Story visualization has become a popular task where visual scenes are generated to depict a narrative across multiple panels. A central challenge in this setting is maintaining visual consistency, particularly in how characters and objects persist and evolve throughout the story. Despite recent advances in diffusion models, current approaches often fail to preserve key character attributes, leading to incoherent narratives. In this work, we propose a collaborative multi-agent framework that autonomously identifies, corrects, and refines inconsistencies across multi-panel story visualizations. The agents operate in an iterative loop, enabling fine-grained, panel-level updates without re-generating entire sequences. Our framework is model-agnostic and flexibly integrates with a variety of diffusion models, including rectified flow transformers such as Flux and latent diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion. Quantitative and qualitative experiments show that our method outperforms prior approaches in terms of multi-panel consistency.
故事可视化已经成为一项流行的任务,通过生成视觉场景来描绘跨多个面板的叙事。在这个任务中的一个核心挑战是保持视觉一致性,特别是在角色和物体如何在故事中持续和演变方面。尽管扩散模型最近有了一些进展,但当前的方法往往无法保留关键的角色属性,从而导致叙事不一致。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种协作式多智能体框架,该框架能够自主识别、纠正和完善跨多面板故事可视化中的不一致性。智能体在一个迭代循环中运行,能够实现精细的面板级更新,而无需重新生成整个序列。我们的框架与各种扩散模型无关,可以灵活地与多种扩散模型集成,包括经过修正的流变压器(如Flux)和潜在扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)。定量和定性实验表明,我们的方法在跨面板一致性方面优于以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project webpage: https://auditandrepair.github.io/
Summary
故事可视化已成为一个热门任务,旨在生成多个面板来呈现叙事。其中的核心挑战是保持视觉一致性,特别是在角色和物体如何在故事中持续和演变方面。尽管扩散模型最近有所进展,但当前的方法往往无法保留关键角色属性,导致叙事不一致。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种协作的多智能体框架,该框架可自主识别、纠正和完善多面板故事可视化中的不一致性。智能体在迭代循环中运行,可实现精细的面板级更新,而无需重新生成整个序列。我们的框架与各种扩散模型兼容,包括经过修正的流变压器(如Flux)和潜在扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)。定量和定性实验表明,我们的方法在跨面板一致性方面优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 故事可视化旨在通过多个面板呈现叙事,维持视觉一致性是核心挑战。
- 当前方法难以保留关键角色属性,导致叙事不一致。
- 提出了一种协作的多智能体框架来识别和纠正多面板故事可视化中的不一致性。
- 智能体可在迭代循环中运行,实现精细的面板级更新。
- 框架与多种扩散模型兼容,包括流变压器和潜在扩散模型。
- 定量和定性实验证明该方法在跨面板一致性方面优于先前技术。
- 该方法有助于提高故事可视化的质量和观感。
点此查看论文截图

GRAND-SLAM: Local Optimization for Globally Consistent Large-Scale Multi-Agent Gaussian SLAM
Authors:Annika Thomas, Aneesa Sonawalla, Alex Rose, Jonathan P. How
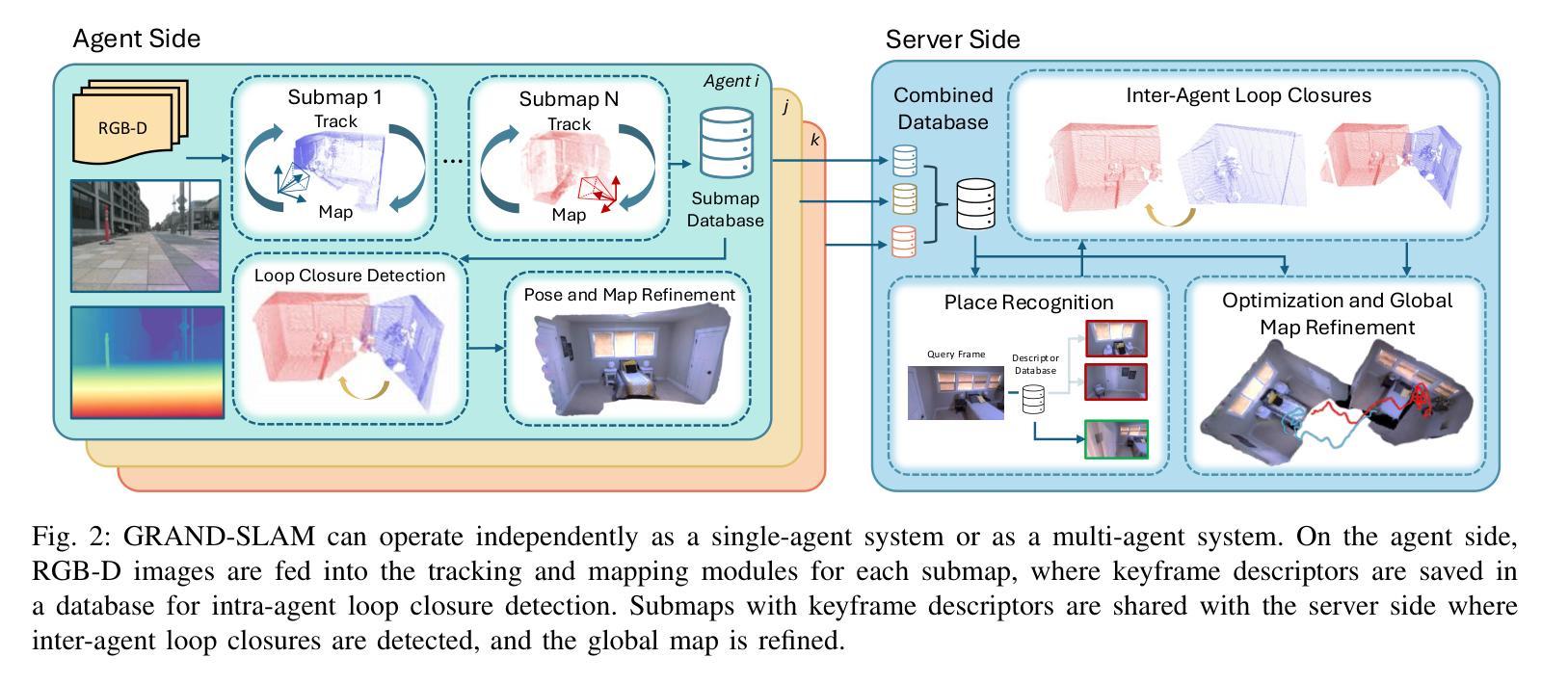
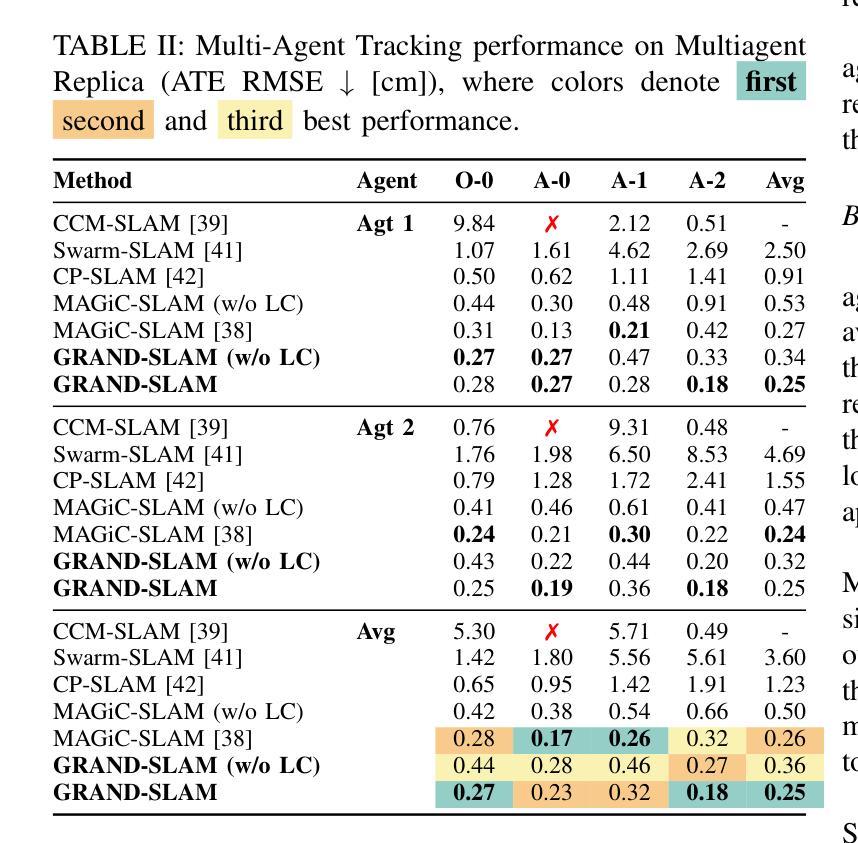
3D Gaussian splatting has emerged as an expressive scene representation for RGB-D visual SLAM, but its application to large-scale, multi-agent outdoor environments remains unexplored. Multi-agent Gaussian SLAM is a promising approach to rapid exploration and reconstruction of environments, offering scalable environment representations, but existing approaches are limited to small-scale, indoor environments. To that end, we propose Gaussian Reconstruction via Multi-Agent Dense SLAM, or GRAND-SLAM, a collaborative Gaussian splatting SLAM method that integrates i) an implicit tracking module based on local optimization over submaps and ii) an approach to inter- and intra-robot loop closure integrated into a pose-graph optimization framework. Experiments show that GRAND-SLAM provides state-of-the-art tracking performance and 28% higher PSNR than existing methods on the Replica indoor dataset, as well as 91% lower multi-agent tracking error and improved rendering over existing multi-agent methods on the large-scale, outdoor Kimera-Multi dataset.
三维高斯喷溅(Gaussian Splatting)技术已成为RGB-D视觉SLAM(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)的场景表示的一种表达方式,但其在大型多智能体室外环境中的应用尚未得到探索。多智能体高斯SLAM(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)是一种有前景的方法,可以快速探索并重建环境,提供可扩展的环境表示,但现有方法仅限于小型室内环境。为此,我们提出了基于多智能体密集SLAM的高斯重建(Gaussian Reconstruction via Multi-Agent Dense SLAM),简称GRAND-SLAM。这是一种协作式高斯喷溅SLAM方法,它集成了i)基于子图局部优化的隐式跟踪模块和ii)一种集成到姿态图优化框架中的机器人内外回路闭合方法。实验表明,GRAND-SLAM在Replica室内数据集上提供了最先进的跟踪性能和比现有方法高出28%的峰值信噪比(PSNR),以及在大型室外Kimera-Multi数据集上实现了91%的多智能体跟踪误差降低和渲染性能的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将多智能体技术应用于大规模户外环境的视觉即时定位与地图构建(SLAM)问题。提出了一种名为GRAND-SLAM的协同高斯融合SLAM方法,通过引入局部优化子图的隐式跟踪模块和集成机器人间与机器人内部的闭环策略,实现了在大型环境中的卓越性能。实验表明,GRAND-SLAM在大型室外环境中的性能优于现有方法。相较于在室内环境中复制的现有数据集,GRAND-SLAM提供出色的追踪性能并实现了较高的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。同时,在大型室外数据集上,其多智能体追踪误差降低了约91%,渲染效果也得到了改善。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了三维高斯融合在大规模多智能体户外环境中的潜在应用。
- 提出了一种新的协同高斯融合SLAM方法——GRAND-SLAM。
- GRAND-SLAM引入了隐式跟踪模块,基于局部优化子图实现。
- GRAND-SLAM集成了机器人间与机器人内部的闭环策略。
- 实验表明GRAND-SLAM在大型室外环境中的性能优于现有方法。相较于室内环境数据集,其追踪性能和PSNR表现优越。
- 在大型室外数据集上,GRAND-SLAM的多智能体追踪误差降低了约91%,渲染效果得到改善。
点此查看论文截图


Understanding Software Engineering Agents: A Study of Thought-Action-Result Trajectories
Authors:Islem Bouzenia, Michael Pradel
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents are increasingly employed to automate complex software engineering tasks such as program repair and issue resolution. These agents operate by autonomously generating natural language thoughts, invoking external tools, and iteratively refining their solutions. Despite their widespread adoption, the internal decision-making processes of these agents remain largely unexplored, limiting our understanding of their operational dynamics and failure modes. In this paper, we present a large-scale empirical study of the thought-action-result trajectories of three state-of-the-art LLM-based agents: \textsc{RepairAgent}, \textsc{AutoCodeRover}, and \textsc{OpenHands}. We unify their interaction logs into a common format, capturing 120 trajectories and 2822 LLM interactions focused on program repair and issue resolution. Our study combines quantitative analyses of structural properties, action patterns, and token usage with qualitative assessments of reasoning coherence and feedback integration. We identify key trajectory characteristics such as iteration counts and token consumption, recurring action sequences, and the semantic coherence linking thoughts, actions, and their results. Our findings reveal behavioral motifs and anti-patterns that distinguish successful from failed executions, providing actionable insights for improving agent design, including prompting strategies, failure diagnosis, and anti-pattern detection. We release our dataset and annotation framework to support further research on transparent and robust autonomous software engineering agents.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理正越来越多地被用于自动化复杂的软件工程任务,如程序修复和问题解析。这些代理通过自主生成自然语言思想、调用外部工具并迭代优化其解决方案来运行。尽管这些代理得到了广泛应用,但其内部决策过程在很大程度上仍未被探索,这限制了我们对它们运行动态和故障模式的了解。在本文中,我们对三种最新基于LLM的代理(RepairAgent、AutoCodeRover和OpenHands)的思想-行动-结果轨迹进行了大规模实证研究。我们将它们的交互日志统一为通用格式,捕获了120条轨迹和2822次专注于程序修复和问题解析的LLM交互。我们的研究结合了结构属性、行动模式和令牌使用量的定量分析,以及对推理连贯性和反馈整合的定性评估。我们确定了关键轨迹特征,如迭代次数和令牌消耗、反复出现的行动序列,以及连接思想、行动和结果之间的语义连贯性。我们的研究结果揭示了区分成功执行和失败执行的行为模式和反模式,为改进代理设计提供了可操作的见解,包括提示策略、故障诊断和反模式检测。我们发布了我们的数据集和注释框架,以支持对透明和稳健的自主软件工程代理的进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理被广泛应用于自动化软件工程的复杂任务,如程序修复和问题解析。然而,它们的内部决策过程尚待探索,限制了我们对它们操作动态和失败模式的理解。本研究对三种最新LLM代理的“思维-行动-结果”轨迹进行了大规模实证研究,并揭示了其行为模式和失败模式的关键特征。研究有助于改进代理设计,并提供关于提示策略、故障诊断和反模式检测的见解。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM代理广泛应用于自动化软件工程的程序修复和问题解析任务。
- LLM代理的内部决策过程尚待探索,限制了对其操作动态和失败模式的理解。
- 本研究对三种LLM代理进行了大规模实证研究,涉及程序修复和问题解析的轨迹分析。
- 研究发现成功与失败执行的关键特征包括迭代次数、令牌消耗、重复的行动序列以及思维与行动之间的语义连贯性。
- 研究揭示了代理的行为模式和反模式,有助于改进代理设计。
- 研究提供了关于提示策略、故障诊断和反模式检测的见解。
点此查看论文截图

MARL-MambaContour: Unleashing Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Active Contour Optimization in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ruicheng Zhang, Yu Sun, Zeyu Zhang, Jinai Li, Xiaofan Liu, Au Hoi Fan, Haowei Guo, Puxin Yan
We introduce MARL-MambaContour, the first contour-based medical image segmentation framework based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). Our approach reframes segmentation as a multi-agent cooperation task focused on generate topologically consistent object-level contours, addressing the limitations of traditional pixel-based methods which could lack topological constraints and holistic structural awareness of anatomical regions. Each contour point is modeled as an autonomous agent that iteratively adjusts its position to align precisely with the target boundary, enabling adaptation to blurred edges and intricate morphologies common in medical images. This iterative adjustment process is optimized by a contour-specific Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm, further enhanced with the Entropy Regularization Adjustment Mechanism (ERAM) which dynamically balance agent exploration with contour smoothness. Furthermore, the framework incorporates a Mamba-based policy network featuring a novel Bidirectional Cross-attention Hidden-state Fusion Mechanism (BCHFM). This mechanism mitigates potential memory confusion limitations associated with long-range modeling in state space models, thereby facilitating more accurate inter-agent information exchange and informed decision-making. Extensive experiments on five diverse medical imaging datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of MARL-MambaContour, highlighting its potential as an accurate and robust clinical application.
我们介绍了MARL-MambaContour,这是基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的首个轮廓基医疗图像分割框架。我们的方法将分割重新构建为一个多智能体合作任务,专注于生成拓扑一致的对象级轮廓,解决了传统像素级方法缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知解剖区域的局限性。每个轮廓点都被建模为自主智能体,可以迭代调整其位置以精确与目标边界对齐,从而适应医疗图像中常见的模糊边缘和复杂形态。这种迭代调整过程通过轮廓特定的柔软演员评论家(SAC)算法优化,进一步增强与熵正则化调整机制(ERAM),动态平衡智能体探索与轮廓平滑。此外,该框架采用基于Mamba的策略网络,并引入了一种新型的双向交叉注意隐藏状态融合机制(BCHFM)。该机制缓解了状态空间模型中长程建模可能带来的潜在内存混淆限制,从而促进了更准确的智能体间信息交换和决策。在五个不同的医学成像数据集上的广泛实验证明了MARL-MambaContour的卓越性能,突显了其在临床应用中作为准确且稳健的潜在优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MARL-MambaContour是一个基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的轮廓基础医学图像分割框架。它将分割视为多智能体合作任务,侧重于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓,解决了传统像素级方法缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知的问题。该框架利用轮廓特定的Soft Actor-Critic算法和熵正则化调整机制,并通过Mamba策略网络和双向交叉关注隐藏状态融合机制提高准确性。在五个不同的医学成像数据集上的实验证明了其卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- MARL-MambaContour是首个基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的轮廓基础医学图像分割框架。
- 该方法将医学图像分割视为多智能体合作任务,侧重于生成拓扑一致的物体级轮廓。
- 解决了传统像素级方法缺乏拓扑约束和整体结构感知的问题。
- 轮廓调整过程中引入了轮廓特定的Soft Actor-Critic算法和熵正则化调整机制(ERAM)。
- 使用了Mamba策略网络来提高性能,包括一个新的双向交叉关注隐藏状态融合机制(BCHFM)。
- 该框架能够在处理医学图像中的模糊边缘和复杂形态时表现出强大的适应性。
点此查看论文截图

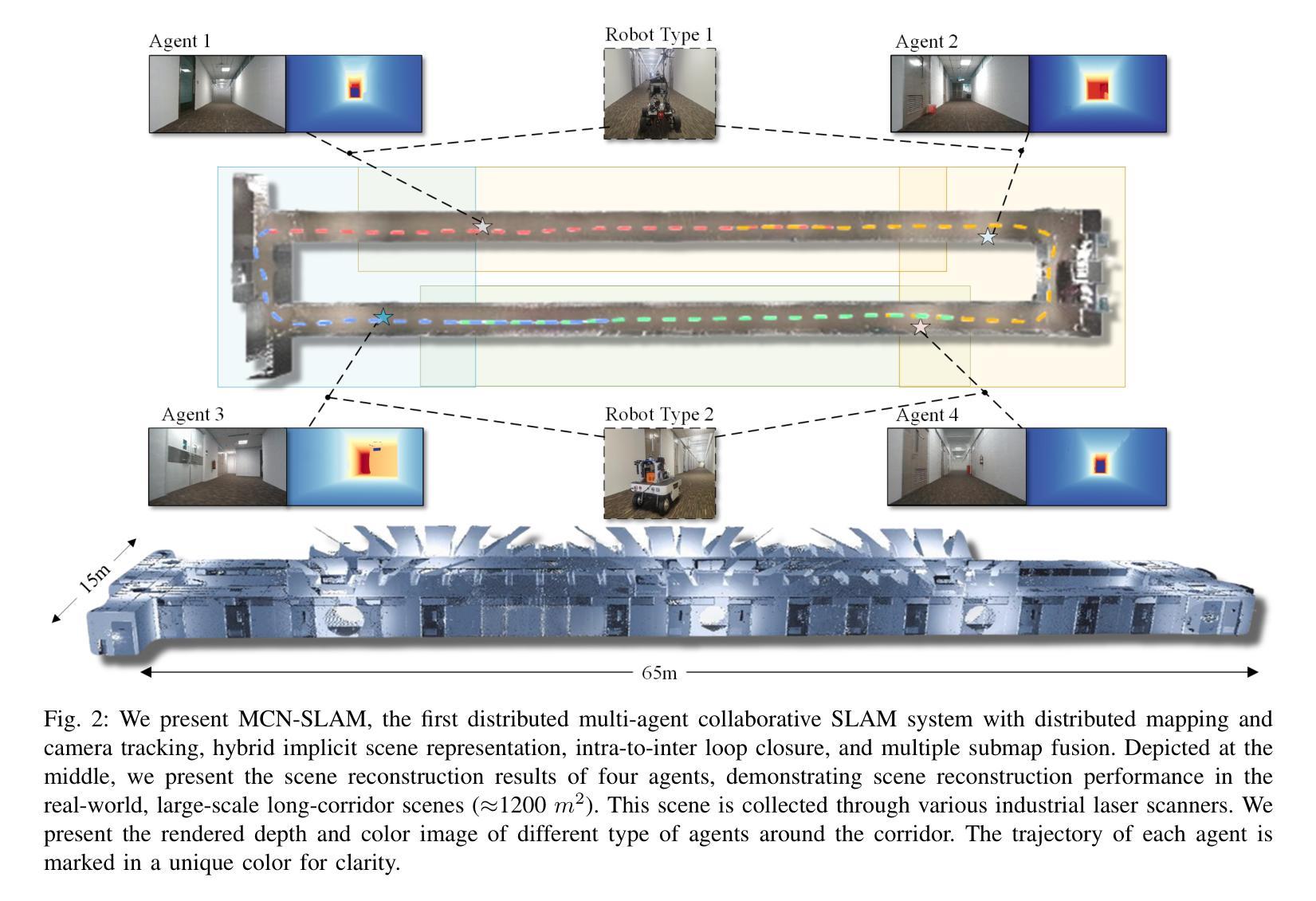
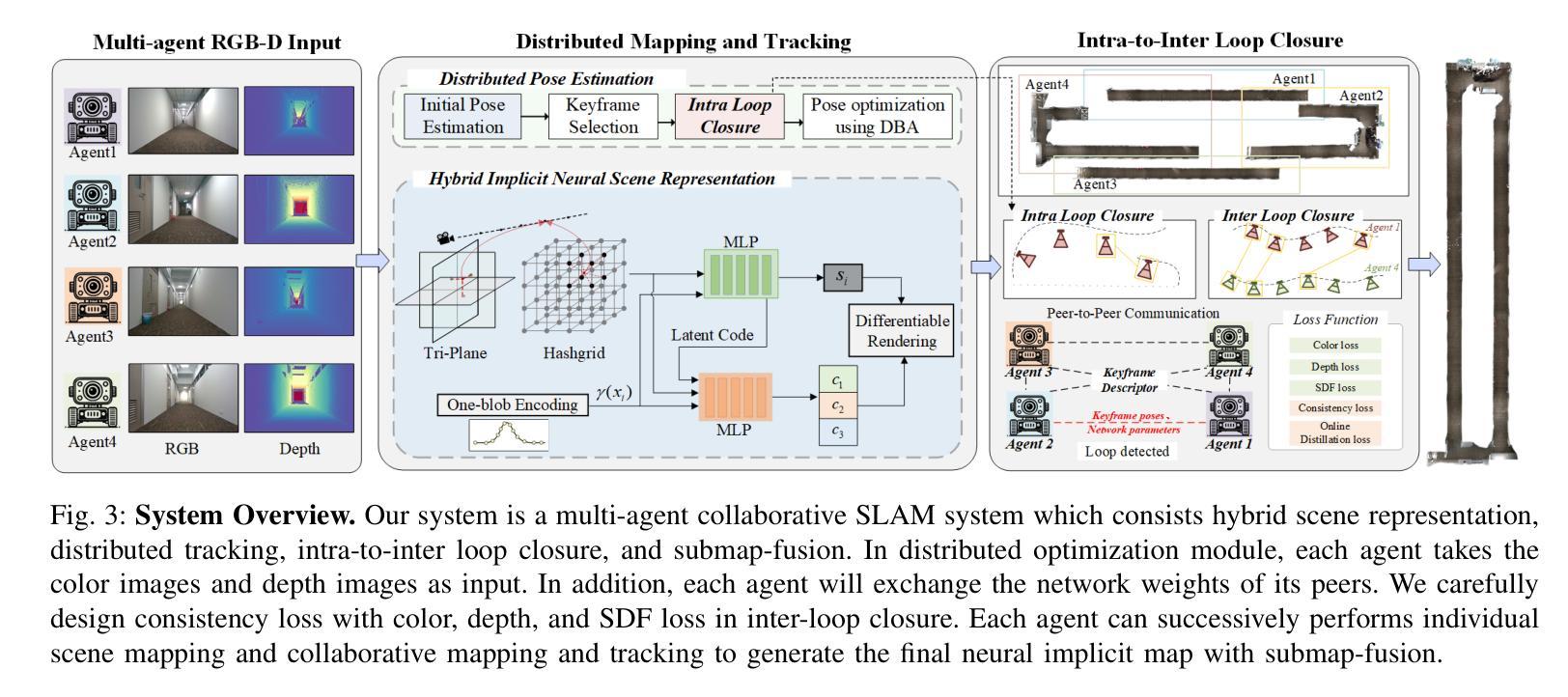
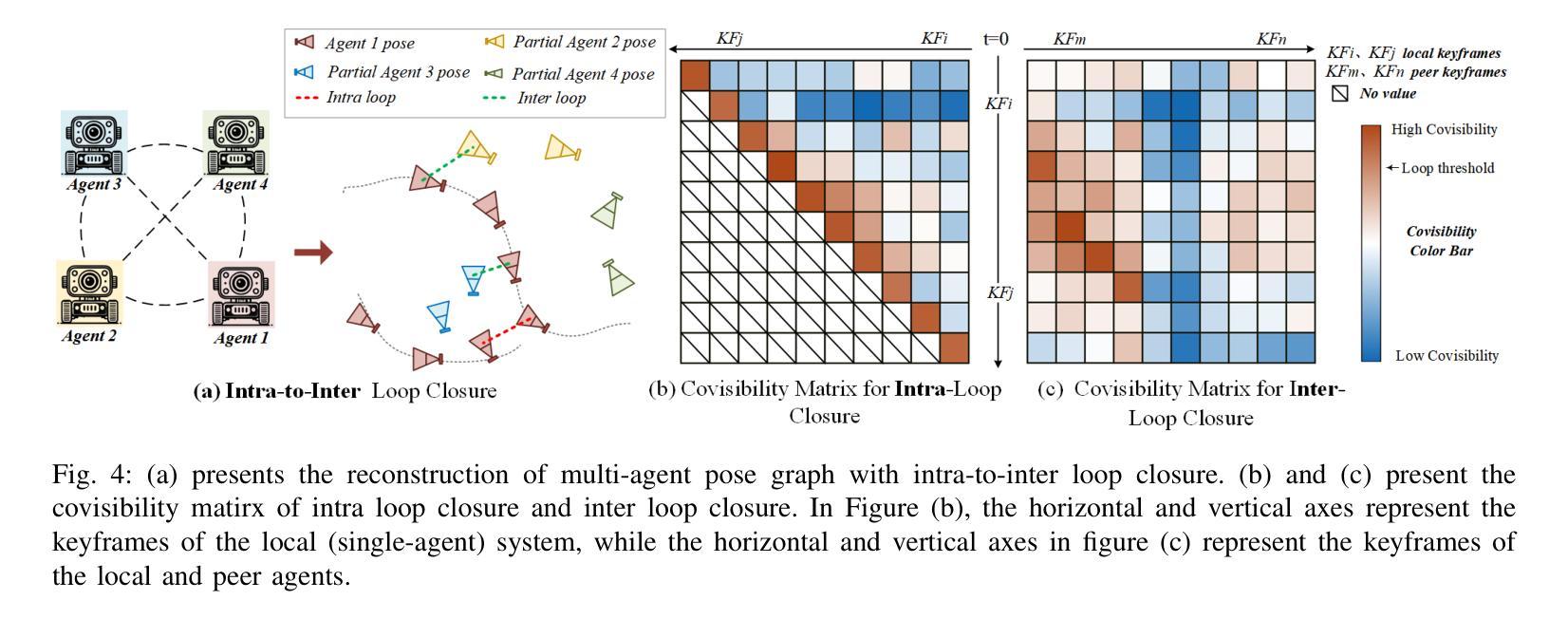
MCN-SLAM: Multi-Agent Collaborative Neural SLAM with Hybrid Implicit Neural Scene Representation
Authors:Tianchen Deng, Guole Shen, Xun Chen, Shenghai Yuan, Hongming Shen, Guohao Peng, Zhenyu Wu, Jingchuan Wang, Lihua Xie, Danwei Wang, Hesheng Wang, Weidong Chen
Neural implicit scene representations have recently shown promising results in dense visual SLAM. However, existing implicit SLAM algorithms are constrained to single-agent scenarios, and fall difficulties in large-scale scenes and long sequences. Existing NeRF-based multi-agent SLAM frameworks cannot meet the constraints of communication bandwidth. To this end, we propose the first distributed multi-agent collaborative neural SLAM framework with hybrid scene representation, distributed camera tracking, intra-to-inter loop closure, and online distillation for multiple submap fusion. A novel triplane-grid joint scene representation method is proposed to improve scene reconstruction. A novel intra-to-inter loop closure method is designed to achieve local (single-agent) and global (multi-agent) consistency. We also design a novel online distillation method to fuse the information of different submaps to achieve global consistency. Furthermore, to the best of our knowledge, there is no real-world dataset for NeRF-based/GS-based SLAM that provides both continuous-time trajectories groundtruth and high-accuracy 3D meshes groundtruth. To this end, we propose the first real-world Dense slam (DES) dataset covering both single-agent and multi-agent scenarios, ranging from small rooms to large-scale outdoor scenes, with high-accuracy ground truth for both 3D mesh and continuous-time camera trajectory. This dataset can advance the development of the research in both SLAM, 3D reconstruction, and visual foundation model. Experiments on various datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in both mapping, tracking, and communication. The dataset and code will open-source on https://github.com/dtc111111/mcnslam.
神经隐式场景表示在密集视觉SLAM中最近显示出有前景的结果。然而,现有的隐式SLAM算法仅限于单智能体场景,在大场景和长序列中遇到困难。基于NeRF的多智能体SLAM框架无法满足通信带宽的限制。为此,我们提出了第一个分布式多智能体协同神经SLAM框架,具有混合场景表示、分布式相机跟踪、内部到跨循环闭合以及多子图融合的在线蒸馏。提出了一种新的triplane网格联合场景表示方法,以提高场景重建的效果。设计了一种新颖的intra-to-inter循环闭合方法,以实现局部(单智能体)和全局(多智能体)的一致性。我们还设计了一种新颖的在线蒸馏方法,以融合不同子图的信息来实现全局一致性。此外,据我们所知,没有基于NeRF或GS的SLAM真实世界数据集能够提供连续时间轨迹的地面真实数据和高精度三维网格地面真实数据。为此,我们提出了第一个真实世界的密集SLAM(DES)数据集,涵盖单智能体和多智能体场景,从小房间到大规模户外场景,同时提供三维网格和连续时间相机轨迹的高精度地面真实数据。该数据集可以促进SLAM、三维重建和视觉基础模型的研究发展。在各种数据集上的实验表明,所提出的方法在映射、跟踪和通信方面都具有优越性。数据集和代码将在https://github.com/dtc111111/mcnslam上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了首个分布式多智能体协同神经网络SLAM框架,该框架具有混合场景表示、分布式相机跟踪、内外环闭合以及在线蒸馏多重子图融合等特点。提出一种新型的三平面网格联合场景表示方法,改进了场景重建。设计了一种新型的内外环闭合方法,实现了局部和全局的一致性。此外,还提出了一种在线蒸馏方法,融合不同子图的信息以实现全局一致性。缺乏针对NeRF或GS的SLAM现实数据集,为此推出了首个密集slam(DES)数据集,包含单智能体和多智能体场景,从小型房间到大型室外场景,同时提供高精度的三维网格和连续时间相机轨迹的真实数据。该数据集推动了SLAM、三维重建和视觉基础模型的研究发展。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了首个分布式多智能体协同神经网络SLAM框架,适用于大规模场景和长序列。
- 采用了混合场景表示、分布式相机跟踪、内外环闭合和在线蒸馏技术,提高了场景重建的精度和效率。
- 提出了一种新型的三平面网格联合场景表示方法,改进了场景细节和连贯性的表现。
- 设计了内外环闭合方法,实现了局部和全局的一致性,提高了智能体之间的协作效率。
- 推出了首个密集slam(DES)数据集,包含多种场景,从小型房间到大型室外场景,同时提供高精度的三维网格和连续时间相机轨迹的真实数据。
- DES数据集能推动SLAM、三维重建和视觉基础模型的研究发展。
点此查看论文截图

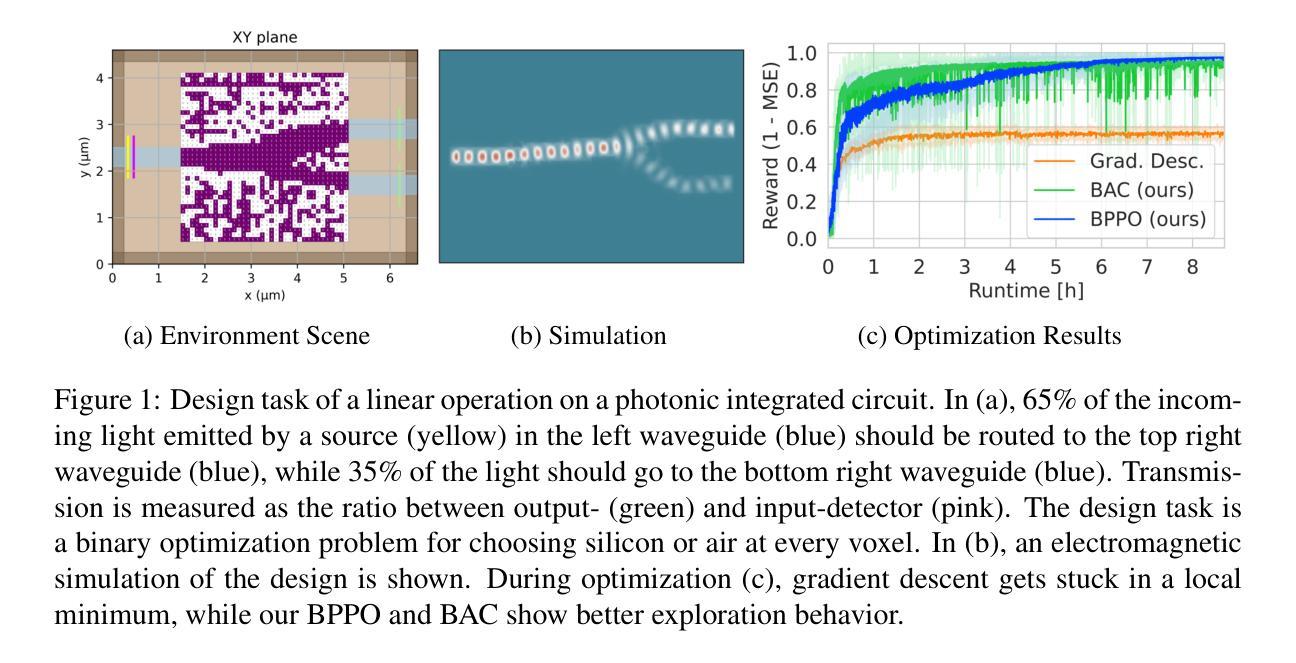
Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Inverse Design in Photonic Integrated Circuits
Authors:Yannik Mahlau, Maximilian Schier, Christoph Reinders, Frederik Schubert, Marco Bügling, Bodo Rosenhahn
Inverse design of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) has traditionally relied on gradientbased optimization. However, this approach is prone to end up in local minima, which results in suboptimal design functionality. As interest in PICs increases due to their potential for addressing modern hardware demands through optical computing, more adaptive optimization algorithms are needed. We present a reinforcement learning (RL) environment as well as multi-agent RL algorithms for the design of PICs. By discretizing the design space into a grid, we formulate the design task as an optimization problem with thousands of binary variables. We consider multiple two- and three-dimensional design tasks that represent PIC components for an optical computing system. By decomposing the design space into thousands of individual agents, our algorithms are able to optimize designs with only a few thousand environment samples. They outperform previous state-of-the-art gradient-based optimization in both twoand three-dimensional design tasks. Our work may also serve as a benchmark for further exploration of sample-efficient RL for inverse design in photonics.
光子集成电路(PIC)的逆向设计传统上依赖于基于梯度的优化。然而,这种方法容易陷入局部最小值,导致设计功能不佳。随着对光子集成电路解决现代硬件需求潜力的兴趣增加,需要通过光学计算来实现更多自适应优化算法的需求也在增加。我们提出了一个强化学习(RL)环境以及用于光子集成电路设计的多智能体强化学习算法。通过将设计空间离散化为网格,我们将设计任务制定为一个具有数千个二进制变量的优化问题。我们考虑多个代表光学计算系统光子集成电路组件的二维和三维设计任务。通过将设计空间分解为数千个独立智能体,我们的算法能够在仅使用数千个环境样本的情况下优化设计。它们在二维和三维设计任务中的表现均优于当前最先进的基于梯度的优化方法。我们的工作也可以作为进一步探索光子学逆向设计的样本高效强化学习的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
逆向设计光子集成电路(PICs)的传统方法主要依赖于基于梯度的优化。然而,这种方法容易陷入局部最小值,导致设计功能次优。随着对PICs兴趣的增加,为适应现代硬件需求并应用于光学计算,需要更多适应性优化算法。本研究提出了用于PIC设计的强化学习环境及多智能体强化学习算法。通过将设计空间离散化为网格,我们将设计任务公式化为具有数千个二进制变量的优化问题。研究考虑了代表光学计算系统组件的多个二维和三维设计任务。通过分解设计空间为数千个独立智能体,我们的算法能够在数千个环境样本中优化设计。它们在二维和三维设计任务中的表现均优于先前的最先进的基于梯度的优化。本研究也可为样本高效的强化学习在光子学逆向设计方面的进一步探索提供参考。
Key Takeaways
- 传统光子集成电路的逆向设计主要依赖基于梯度的优化方法,但易陷入局部最小值。
- 随着光学计算的需求增长,需要更灵活的优化算法来设计光子集成电路。
- 研究人员提出了使用强化学习环境及多智能体强化学习算法进行PIC设计的新方法。
- 设计空间被离散化为网格,将设计任务转化为具有数千个二进制变量的优化问题。
- 该方法适用于多种二维和三维设计任务,代表光学计算系统的组件。
- 通过分解设计空间为独立智能体,该方法能在少量环境样本中优化设计。
点此查看论文截图

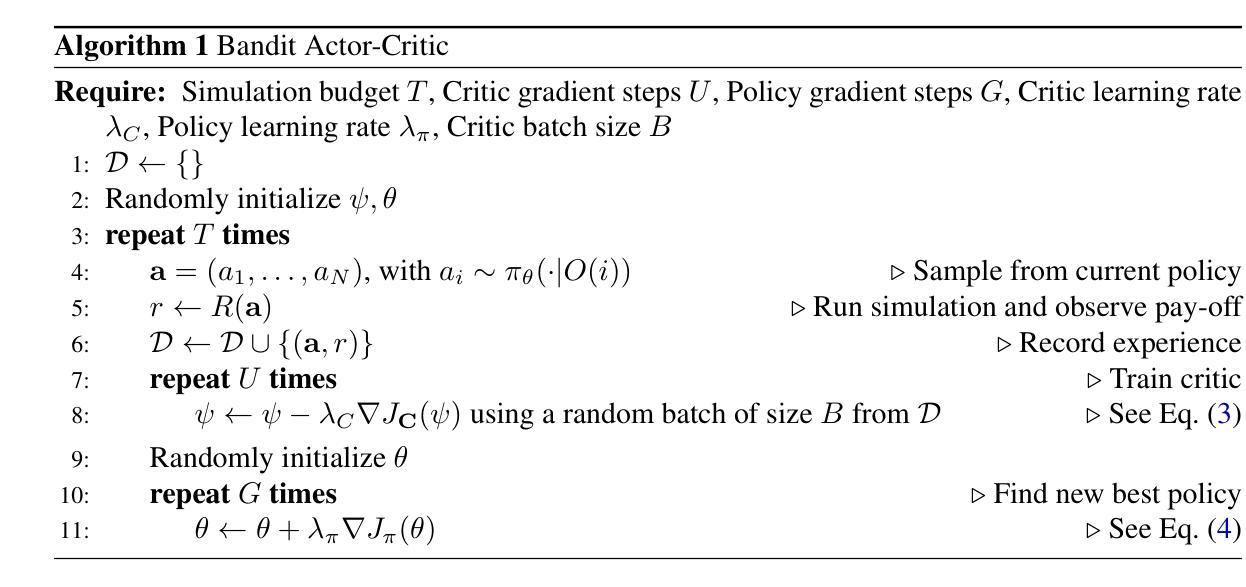
Transformer World Model for Sample Efficient Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Azad Deihim, Eduardo Alonso, Dimitra Apostolopoulou
We present the Multi-Agent Transformer World Model (MATWM), a novel transformer-based world model designed for multi-agent reinforcement learning in both vector- and image-based environments. MATWM combines a decentralized imagination framework with a semi-centralized critic and a teammate prediction module, enabling agents to model and anticipate the behavior of others under partial observability. To address non-stationarity, we incorporate a prioritized replay mechanism that trains the world model on recent experiences, allowing it to adapt to agents’ evolving policies. We evaluated MATWM on a broad suite of benchmarks, including the StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge, PettingZoo, and MeltingPot. MATWM achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming both model-free and prior world model approaches, while demonstrating strong sample efficiency, achieving near-optimal performance in as few as 50K environment interactions. Ablation studies confirm the impact of each component, with substantial gains in coordination-heavy tasks.
我们提出了多智能体Transformer世界模型(MATWM),这是一种基于transformer的新型世界模型,旨在支持向量和图像环境中的多智能体强化学习。MATWM结合了分散式想象框架、半集中式批评家和队友预测模块,使智能体能够在部分可观察的情况下建立他人行为的模型并进行预测。为了解决非平稳性问题,我们采用了优先级回放机制,该机制通过最近的经验训练世界模型,使其能够适应智能体不断变化的策略。我们在一系列基准测试上对MATWM进行了评估,包括星际争霸多智能体挑战、宠物动物园和熔炉。MATWM达到了最先进的技术性能水平,不仅超越了无模型和预先的世界模型方法,而且表现出强大的样本效率,在仅5万次的环境交互中就能达到接近最优的性能。消融研究证实了每个组件的影响,在协调密集的任务中取得了重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer的世界模型在向量和图像环境中的多智能体强化学习应用摘要。提出一种新型的多智能体Transformer世界模型(MATWM),结合了分散式想象框架、半集中式批评家和队友预测模块,以在部分可观察的情况下建模和预测其他智能体的行为。采用优先回放机制应对非平稳性问题,根据最近经验训练世界模型以适应智能体策略的变化。在StarCraft多智能体挑战、PettingZoo和MeltingPot等多个基准测试中表现优异,实现了优于模型免费和先前世界模型的方法的先进性能,并表现出了很强的样本效率,仅在极少数环境交互(例如不到五万次)中实现近优性能。实验显示MATWM在多任务协调中发挥巨大优势。
Key Takeaways
- MATWM是一种基于Transformer的多智能体强化学习世界模型。它将用于解决基于向量和图像环境中的智能体协作任务。此模型可模拟环境并进行自适应训练,以满足快速变化的情境和新的挑战。它结合了多种技术来增强性能,包括分散式想象框架、半集中式批评家和队友预测模块。这些技术使得智能体能够在有限的视野中了解和理解队友行为及行为动机,从而促进多智能体的协调性和交互能力。另外其改进训练算法的性能保证此模型的优秀表现得益于优先回放机制的应用,它使模型能够应对非平稳性问题并适应智能体的策略变化。其在多种任务挑战上展现出极高的性能和出色的样本效率表现突出的是其具备在不同任务上的快速学习和高效适应能力,同时在协调复杂的任务中具有较大优势,有效推进了对新型模型的发展和挑战的态度在不断加剧的世界要求更为精细的任务控制技巧的问题,并取得一系列先进的测试评价表现。
点此查看论文截图

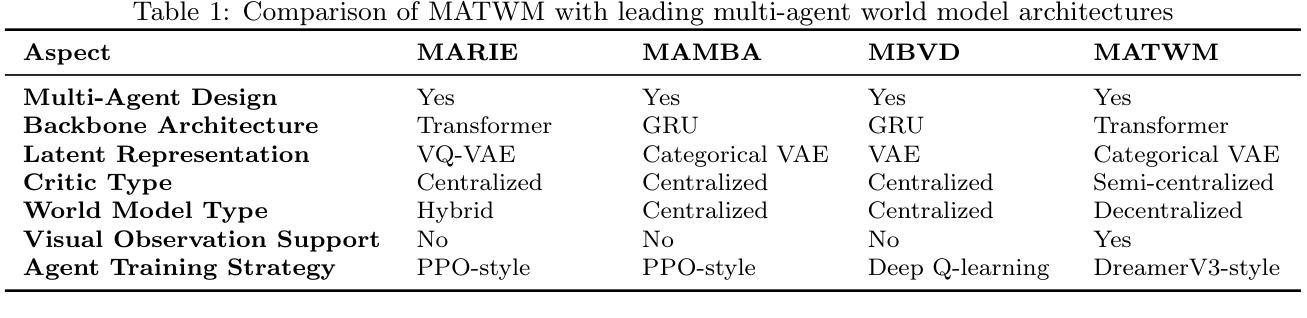
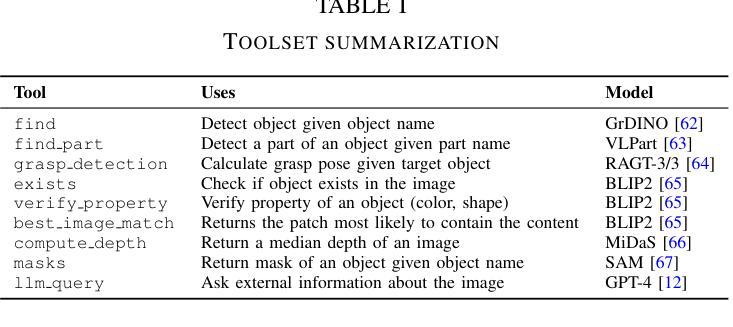
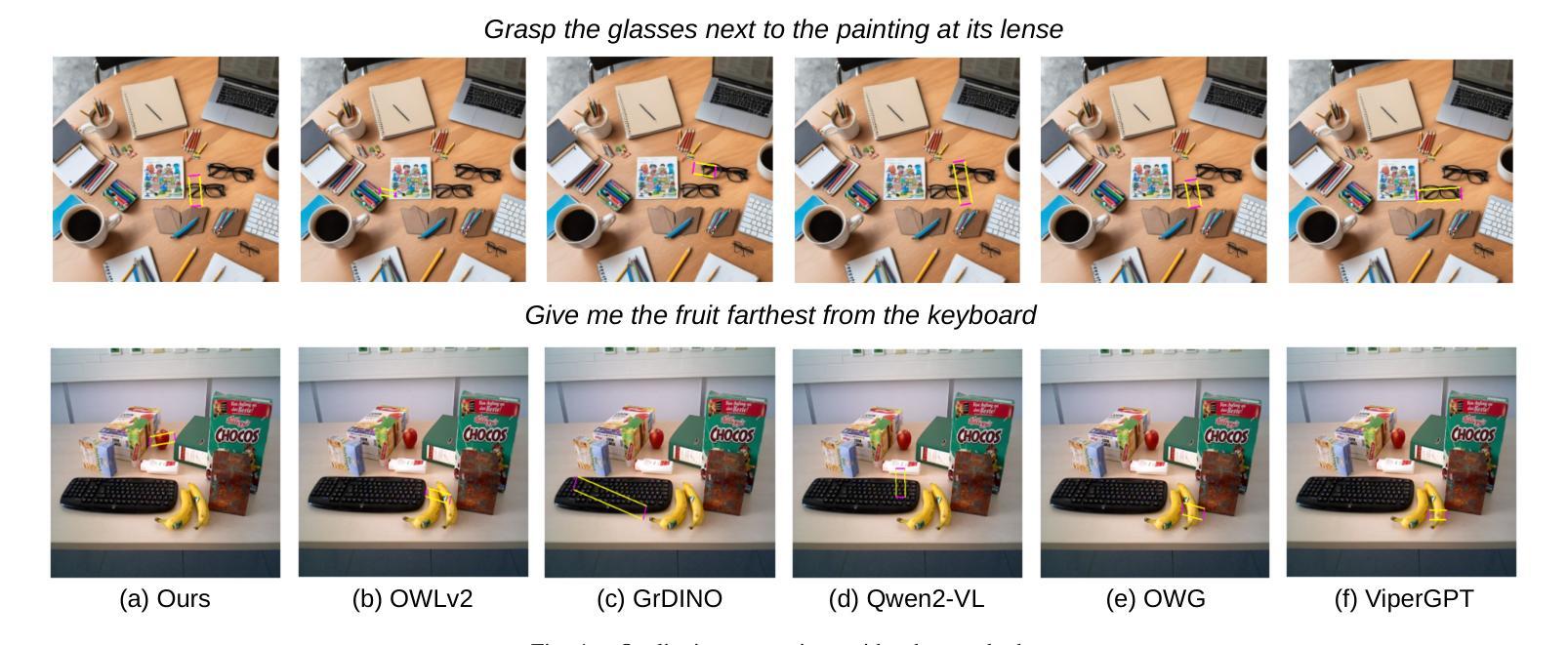
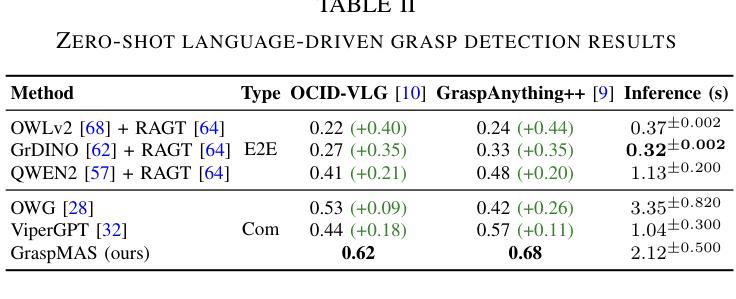
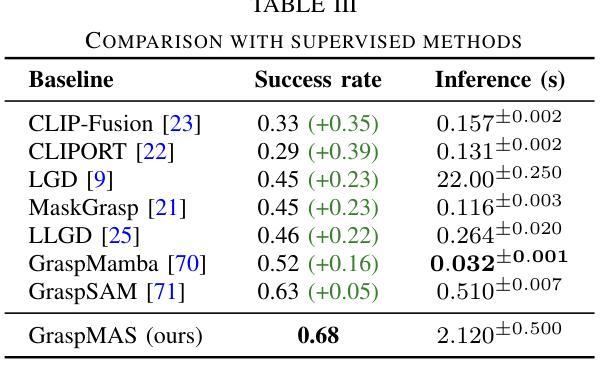
GraspMAS: Zero-Shot Language-driven Grasp Detection with Multi-Agent System
Authors:Quang Nguyen, Tri Le, Huy Nguyen, Thieu Vo, Tung D. Ta, Baoru Huang, Minh N. Vu, Anh Nguyen
Language-driven grasp detection has the potential to revolutionize human-robot interaction by allowing robots to understand and execute grasping tasks based on natural language commands. However, existing approaches face two key challenges. First, they often struggle to interpret complex text instructions or operate ineffectively in densely cluttered environments. Second, most methods require a training or finetuning step to adapt to new domains, limiting their generation in real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce GraspMAS, a new multi-agent system framework for language-driven grasp detection. GraspMAS is designed to reason through ambiguities and improve decision-making in real-world scenarios. Our framework consists of three specialized agents: Planner, responsible for strategizing complex queries; Coder, which generates and executes source code; and Observer, which evaluates the outcomes and provides feedback. Intensive experiments on two large-scale datasets demonstrate that our GraspMAS significantly outperforms existing baselines. Additionally, robot experiments conducted in both simulation and real-world settings further validate the effectiveness of our approach.
语言驱动抓取检测具有通过允许机器人理解和执行基于自然语言命令的抓取任务来革新人机交互的潜力。然而,现有方法面临两大挑战。首先,它们经常难以解释复杂的文本指令或在密集杂乱的环境中操作无效。其次,大多数方法需要一个训练或微调步骤来适应新领域,这限制了它们在现实世界应用中的生成。在本文中,我们介绍了用于语言驱动抓取检测的新型多智能体系统框架GraspMAS。GraspMAS被设计用于解决歧义并改善现实场景中的决策制定。我们的框架包括三个专业智能体:Planner负责策划复杂查询;Coder负责生成并执行源代码;Observer负责评估结果并提供反馈。在两项大规模数据集上的密集实验表明,我们的GraspMAS显著优于现有基线。此外,在模拟和真实环境中进行的机器人实验进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, accepted to IROS 2025
Summary
语言驱动抓取检测有潜力革新人机交互方式,让机器人通过自然语言命令理解和执行抓取任务。现有方法面临两大挑战:一是难以解读复杂文本指令或在密集杂乱环境中操作;二是多数方法需要训练或微调以适应新领域,限制了其在现实世界的广泛应用。本文介绍GraspMAS,一种用于语言驱动抓取检测的新多智能体系统框架。GraspMAS旨在解决歧义问题,提高现实场景中的决策能力。框架包含三个专业智能体:规划者负责策划复杂查询;编码者负责生成并执行源代码;观察者负责评估结果并提供反馈。大规模数据集上的实验显示,GraspMAS显著优于现有基线方法。在模拟和实际机器人实验中的验证也进一步证明了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 语言驱动抓取检测有潜力革新人机交互方式。
- 当前方法面临解读复杂文本指令和杂乱环境操作两大挑战。
- GraspMAS是一种多智能体系统框架,用于语言驱动抓取检测。
- GraspMAS旨在解决歧义问题并提高现实场景中的决策能力。
- GraspMAS包含规划者、编码者和观察者三个专业智能体。
- 实验证明GraspMAS在多个数据集上表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

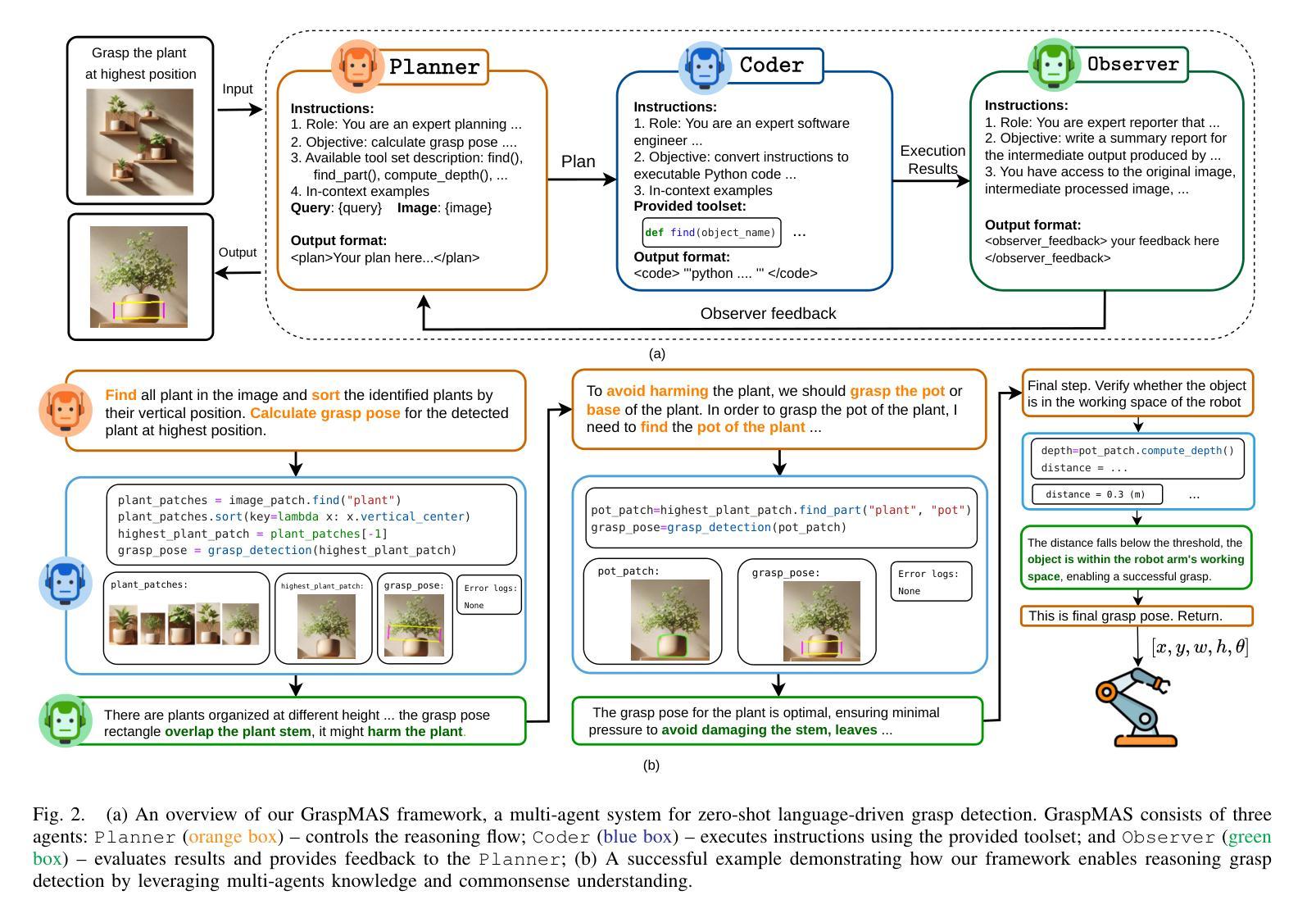
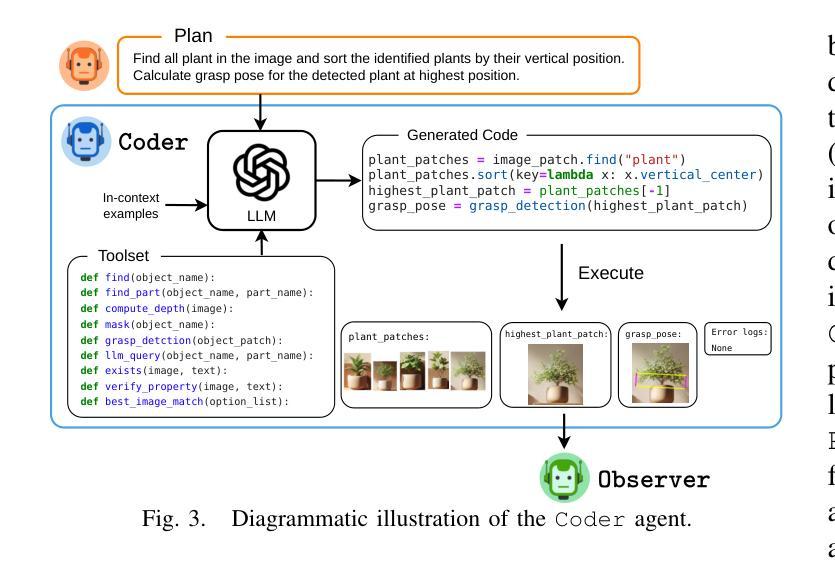

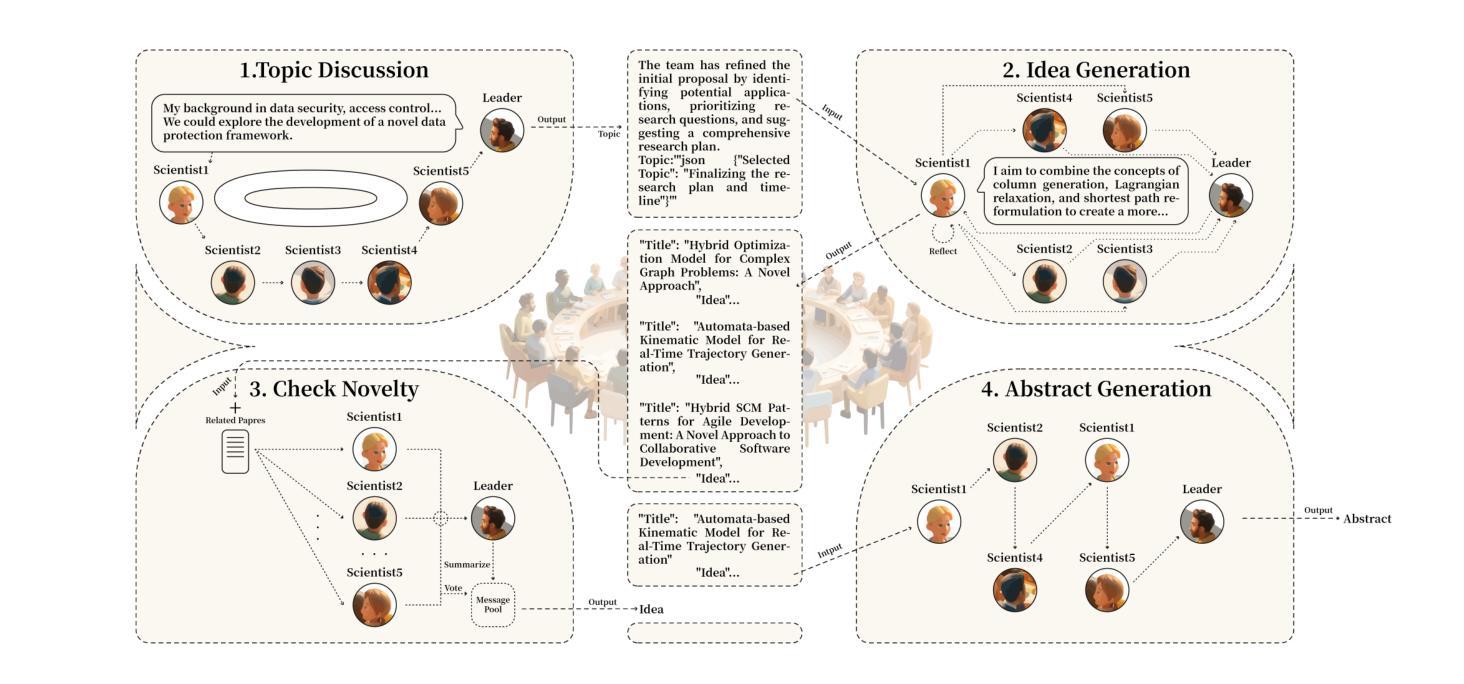
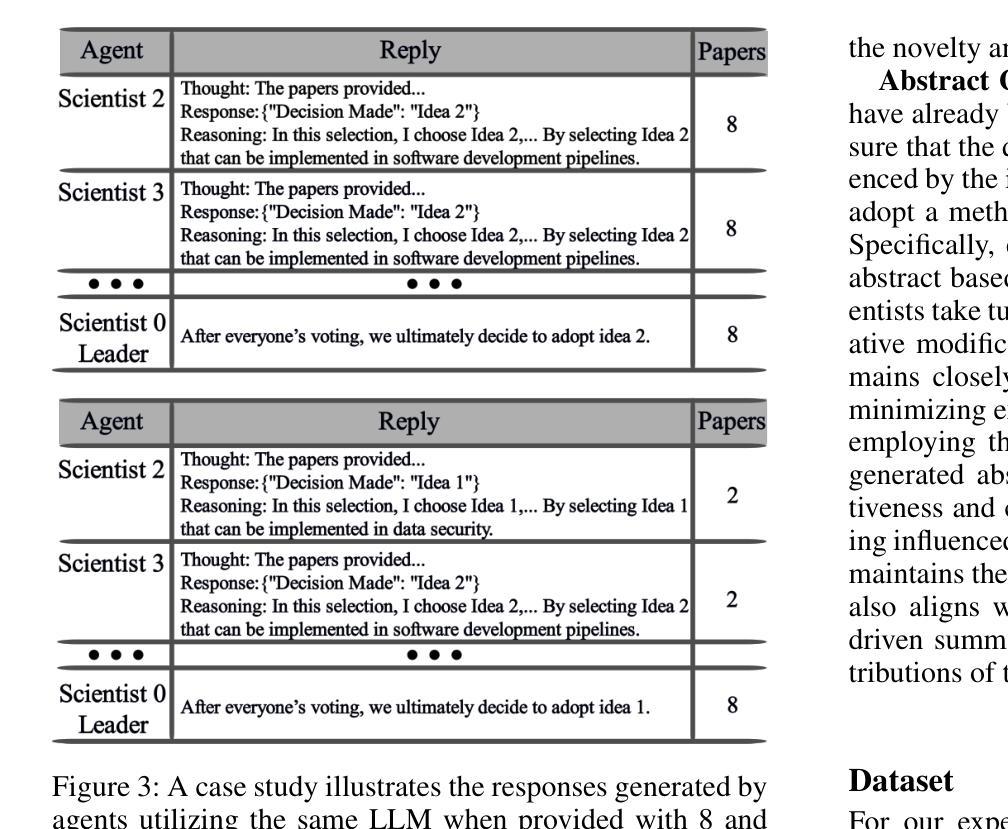
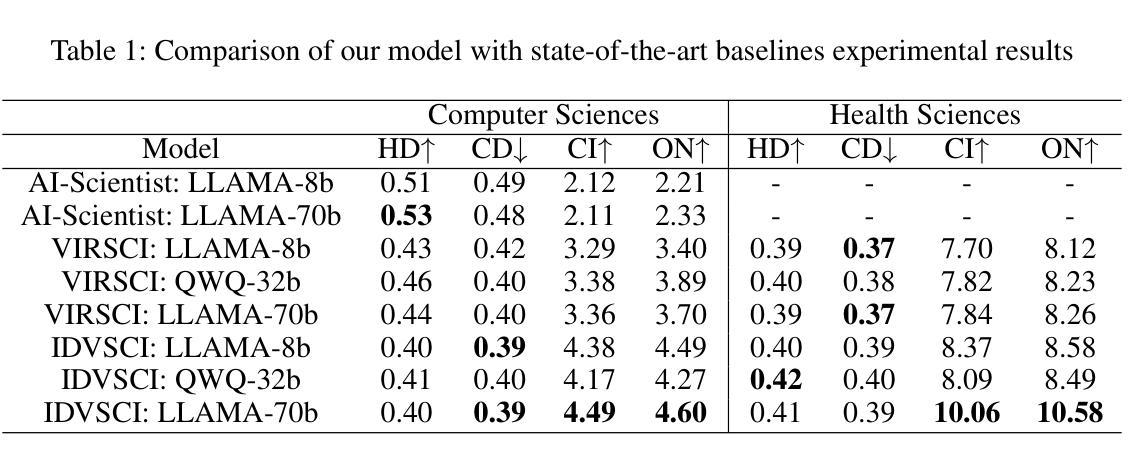
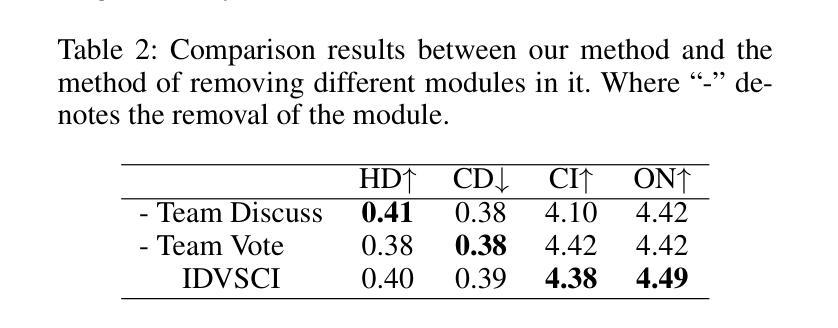
Dynamic Knowledge Exchange and Dual-diversity Review: Concisely Unleashing the Potential of a Multi-Agent Research Team
Authors:Weilun Yu, Shixiang Tang, Yonggui Huang, Nanqing Dong, Li Fan, Honggang Qi, Wei Liu, Xiaoli Diao, Xi Chen, Wanli Ouyang
Scientific progress increasingly relies on effective collaboration among researchers, a dynamic that large language models (LLMs) have only begun to emulate. While recent LLM-based scientist agents show promise in autonomous scientific discovery, they often lack the interactive reasoning and evaluation mechanisms essential to real-world research. We propose IDVSCI (Internal Discussion and Vote SCIentists), a multi-agent framework built on LLMs that incorporates two key innovations: a Dynamic Knowledge Exchange mechanism enabling iterative feedback among agents, and a Dual-Diversity Review paradigm that simulates heterogeneous expert evaluation. These components jointly promote deeper reasoning and the generation of more creative and impactful scientific ideas. To evaluate the effectiveness and generalizability of our approach, we conduct experiments on two datasets: a widely used benchmark in computer science and a new dataset we introduce in the health sciences domain. Results show that IDVSCI consistently achieves the best performance across both datasets, outperforming existing systems such as AI Scientist and VIRSCI. These findings highlight the value of modeling interaction and peer review dynamics in LLM-based autonomous research.
科技进步越来越依赖于研究者之间的有效协作,这一动态是大规模语言模型(LLM)才开始模仿的。虽然基于LLM的科学家代理人在自主科学发现方面显示出前景,但它们通常缺乏现实世界研究中必不可少的交互推理和评估机制。我们提出了IDVSCI(内部讨论与投票科学家),这是一个基于LLM的多代理框架,包含两项关键创新:动态知识交换机制,促进代理之间的迭代反馈;模拟异质专家评估的双重多样性审查范式。这些组件共同促进更深层次的推理和更具创造力和影响力的科学想法的产生。为了评估我们方法的有效性和通用性,我们在两个数据集上进行了实验:一个在计算机科学中广泛使用的基准测试和我们引入的一个健康科学领域的新数据集。结果表明,IDVSCI在两个数据集上均表现最佳,优于现有的AI科学家和VIRSCI系统。这些发现突显了在基于LLM的自主研究中建立交互和同行评审动态的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大语言模型 (LLM) 已开始模拟科学家间的协作方式以促进科学进步。新提出的基于LLM的科学家代理系统在自主科学发现方面显示出前景,但它们通常缺乏重要的交互推理和评估机制。本研究提出IDVSCI(内部讨论与投票科学家)多代理框架,该框架在LLM基础上构建,包含两个关键创新点:动态知识交换机制可实现代理间的迭代反馈,以及模拟不同专家评估的双元评估审查模式。这些共同促进了更深入的推理和更具创造力和影响力的科学想法的产生。通过计算机科学与卫生科学领域的数据集进行的实验表明,IDVSCI的性能表现优于现有系统如AI科学家和VIRSCI,证明了建模交互和同行评审动力学在基于LLM的自主研究中的价值。
关键见解
- 科学进步愈发依赖于研究者间的有效协作,大语言模型开始模拟这种协作方式。
- 基于LLM的科学家代理系统在自主科学发现方面展现潜力,但需加强交互推理和评估机制。
- IDVSCI框架引入动态知识交换机制实现代理间的迭代反馈。
- IDVSCI采用双元评估审查模式,模拟异质专家评估。
- 实验结果显示IDVSCI在多个数据集上的性能优于现有系统。
- IDVSCI建模交互和同行评审动力学对基于LLM的自主研究至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

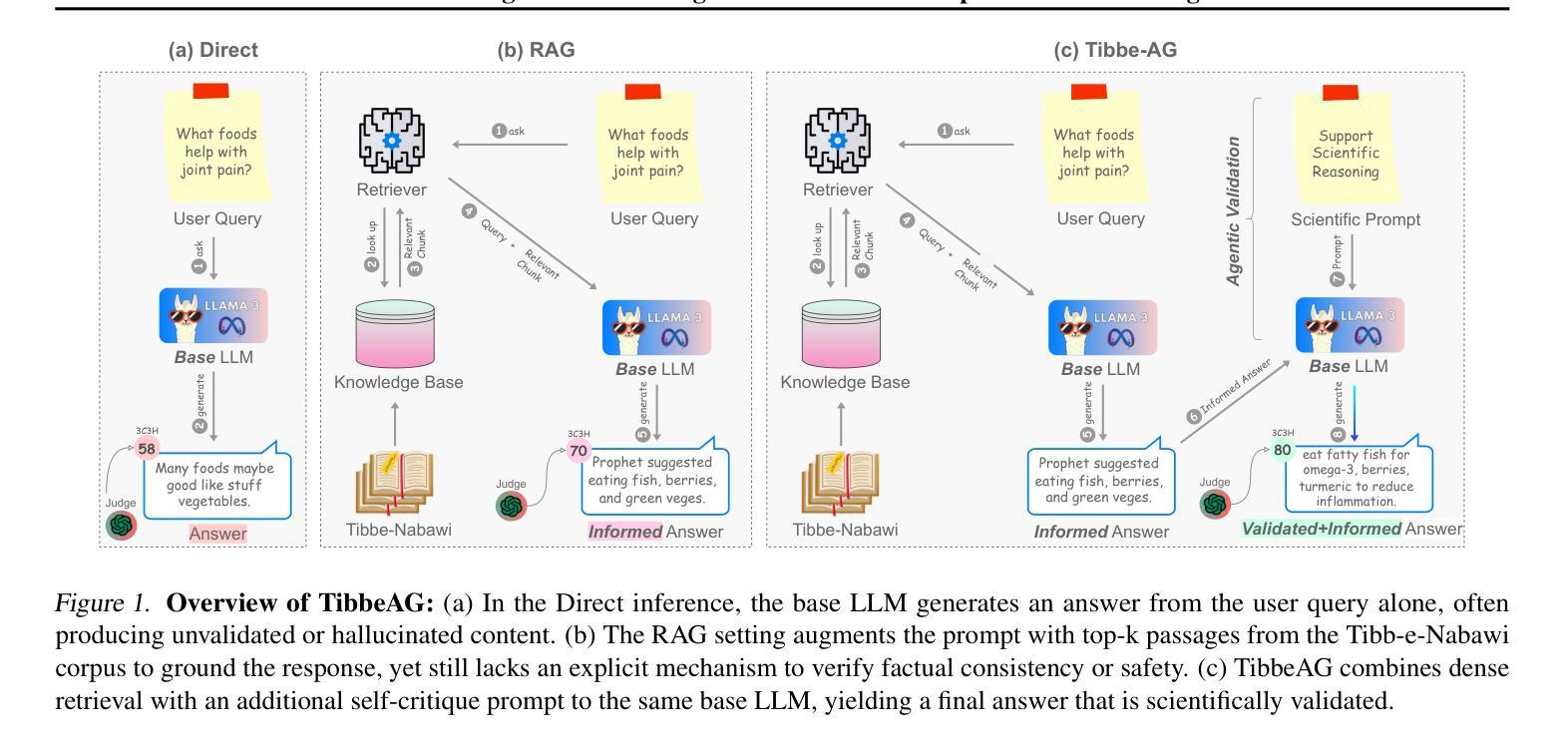
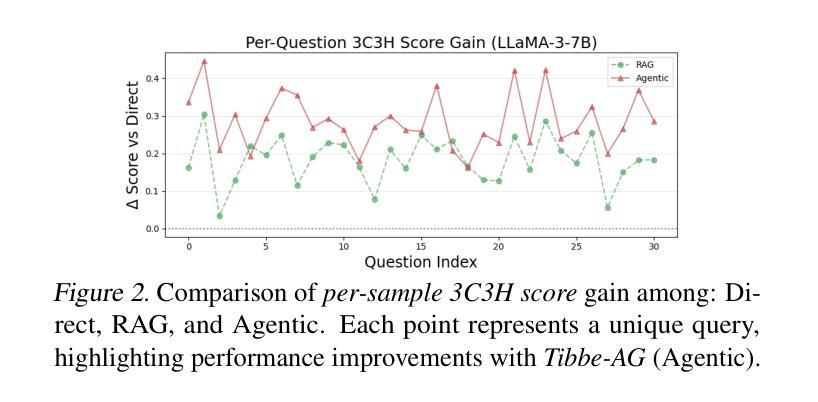
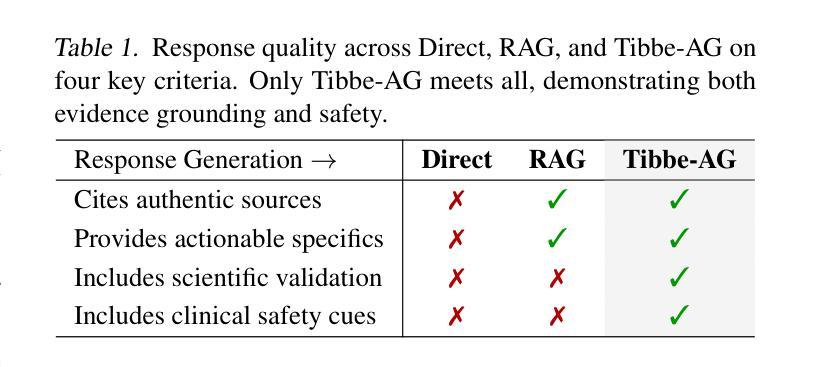
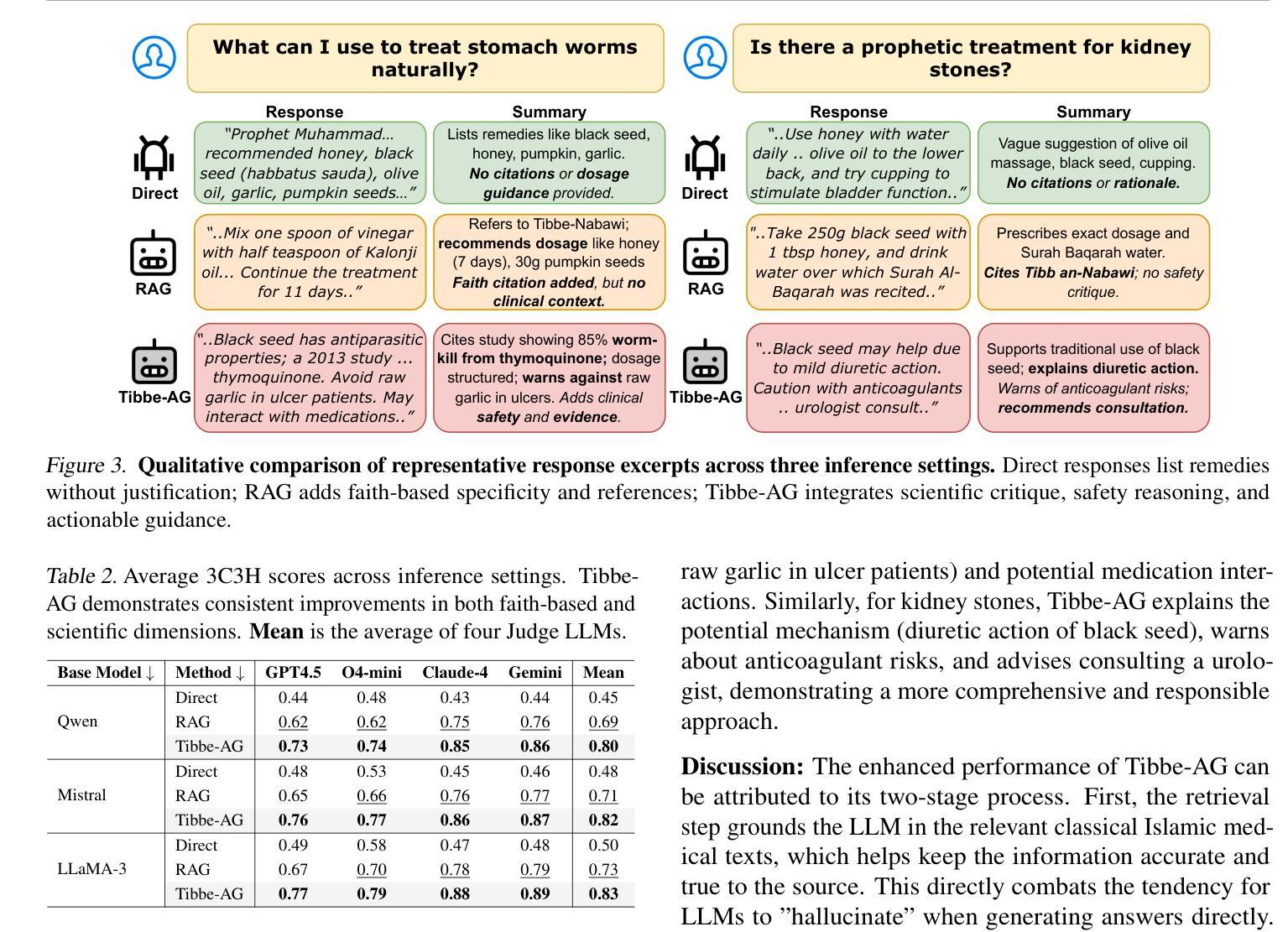
From RAG to Agentic: Validating Islamic-Medicine Responses with LLM Agents
Authors:Mohammad Amaan Sayeed, Mohammed Talha Alam, Raza Imam, Shahab Saquib Sohail, Amir Hussain
Centuries-old Islamic medical texts like Avicenna’s Canon of Medicine and the Prophetic Tibb-e-Nabawi encode a wealth of preventive care, nutrition, and holistic therapies, yet remain inaccessible to many and underutilized in modern AI systems. Existing language-model benchmarks focus narrowly on factual recall or user preference, leaving a gap in validating culturally grounded medical guidance at scale. We propose a unified evaluation pipeline, Tibbe-AG, that aligns 30 carefully curated Prophetic-medicine questions with human-verified remedies and compares three LLMs (LLaMA-3, Mistral-7B, Qwen2-7B) under three configurations: direct generation, retrieval-augmented generation, and a scientific self-critique filter. Each answer is then assessed by a secondary LLM serving as an agentic judge, yielding a single 3C3H quality score. Retrieval improves factual accuracy by 13%, while the agentic prompt adds another 10% improvement through deeper mechanistic insight and safety considerations. Our results demonstrate that blending classical Islamic texts with retrieval and self-evaluation enables reliable, culturally sensitive medical question-answering.
像阿维森纳的《医典》和《先知医学》这样的具有数百年历史的伊斯兰医学文本,蕴含了丰富的预防护理、营养知识和整体疗法,但对许多人来说仍然难以接触和利用,在现代人工智能系统中也是如此。现有的语言模型基准测试主要集中在事实回忆或用户偏好上,从而在验证大规模文化基础的医学指导方面存在差距。我们提出了一种统一的评估流程Tibbe-AG,它将30个精心策划的先知医学问题与人工验证的补救措施相结合,并比较了三种大型语言模型(LLaMA-3、Mistral-7B、Qwen2-7B)在三种配置下的表现:直接生成、检索增强生成和科学自我批判过滤。每个答案然后由第二个大型语言模型作为评判者进行评估,得出一个单一的3C3H质量分数。检索可以提高事实准确性13%,而智能提示通过更深入的机制洞察力和安全考虑增加了额外的10%的改进。我们的结果表明,将古典伊斯兰文本与检索和自我评估相结合,可实现可靠且文化敏感的医疗问题回答。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at the 4th Muslims in Machine Learning (MusIML) Workshop (ICML-25)
Summary
这篇文本讲述了伊斯兰医学古籍如阿维森纳的《医典》和先知医学中的预防保健、营养和整体疗法等内容,强调了这些资源对现代人工智能系统的价值及其可访问性的重要性。文章指出当前语言模型评估基准在事实检索和用户偏好上的局限性,提出一个统一的评估流程Tibbe-AG,将先知医学问题与人工验证的疗法相结合,评估了三个大型语言模型(LLaMA-3、Mistral-7B和Qwen2-7B)的表现。通过增设检索和自我批判过滤器,提高答案的事实准确性和深度机制洞察力。研究结果表明,结合古典伊斯兰文本、检索和自我评估可实现可靠、文化敏感的医疗问答。
Key Takeaways
- 伊斯兰医学古籍包含丰富的预防保健、营养和整体疗法内容,但对许多人来说仍然难以访问并且在现代AI系统中未得到充分利用。
- 当前语言模型评估基准主要关注事实检索和用户偏好,忽视了文化背景下医疗指导的验证。
- 提出的Tibbe-AG评估流程将先知医学问题与人工验证的疗法相结合,评估大型语言模型的表现。
- 检索功能提高了答案的事实准确性。
- 通过增设自我批判过滤器,答案的洞察力和安全性得到提高。
- 结合古典伊斯兰文本与评估流程可实现文化敏感的医疗问答系统。
点此查看论文截图

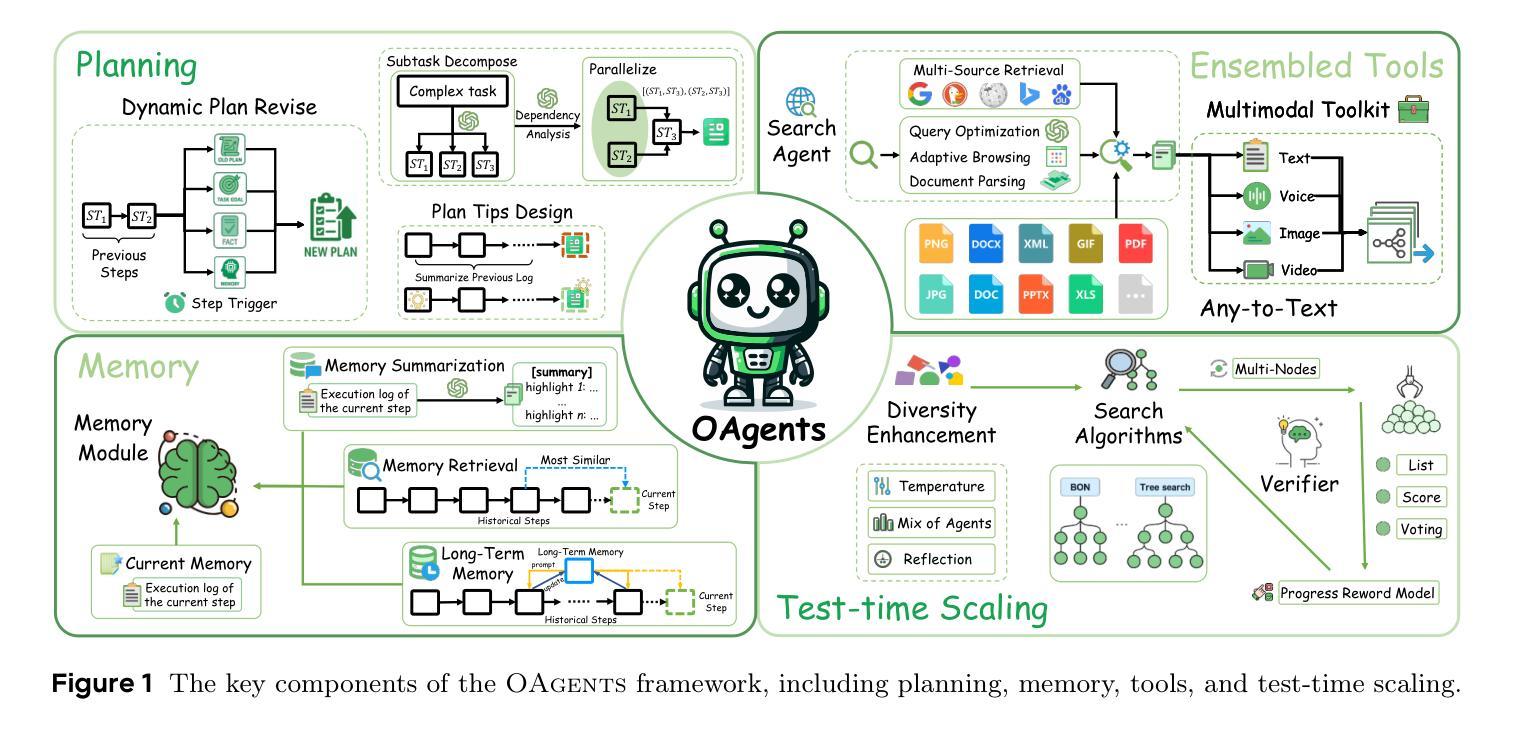
OAgents: An Empirical Study of Building Effective Agents
Authors:He Zhu, Tianrui Qin, King Zhu, Heyuan Huang, Yeyi Guan, Jinxiang Xia, Yi Yao, Hanhao Li, Ningning Wang, Pai Liu, Tianhao Peng, Xin Gui, Xiaowan Li, Yuhui Liu, Yuchen Eleanor Jiang, Jun Wang, Changwang Zhang, Xiangru Tang, Ge Zhang, Jian Yang, Minghao Liu, Xitong Gao, Jiaheng Liu, Wangchunshu Zhou
Recently, Agentic AI has become an increasingly popular research field. However, we argue that current agent research practices lack standardization and scientific rigor, making it hard to conduct fair comparisons among methods. As a result, it is still unclear how different design choices in agent frameworks affect effectiveness, and measuring their progress remains challenging. In this work, we conduct a systematic empirical study on GAIA benchmark and BrowseComp to examine the impact of popular design choices in key agent components in a fair and rigorous manner. We find that the lack of a standard evaluation protocol makes previous works, even open-sourced ones, non-reproducible, with significant variance between random runs. Therefore, we introduce a more robust evaluation protocol to stabilize comparisons. Our study reveals which components and designs are crucial for effective agents, while others are redundant, despite seeming logical. Based on our findings, we build and open-source OAgents, a new foundation agent framework that achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source projects. OAgents offers a modular design for various agent components, promoting future research in Agentic AI.
近期,Agentic AI已成为越来越受欢迎的研究领域。然而,我们认为当前的agent研究实践缺乏标准化和科学严谨性,使得各种方法之间难以进行公平的比较。因此,尚不清楚agent框架中的不同设计选择如何影响效果,衡量其进展仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们对GAIA基准测试和BrowseComp进行了系统的实证研究,以公平严谨的方式检查了关键agent组件中流行设计选择的影响。我们发现,由于缺乏标准的评估协议,以前的工作(即使是开源的)也无法重现,随机运行之间存有明显差异。因此,我们引入了一个更稳健的评估协议来稳定比较。我们的研究表明,哪些组件和设计对于有效的agent至关重要,而其他组件尽管看似逻辑上合理,但却是多余的。基于我们的发现,我们构建并开源了OAgents,这是一个新的基础agent框架,在开源项目中实现了最先进的性能。OAgents为各种agent组件提供了模块化设计,促进了Agentic AI的未来研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages
Summary
近期,Agentic AI成为热门研究领域,但当前研究实践缺乏标准化和科学严谨性,导致方法间难以进行公平比较。本研究通过GAIA基准测试和BrowseComp进行实证研究,探讨关键代理组件中的流行设计选择的影响。研究发现缺乏标准评估协议导致先前工作不可复现,存在随机运行之间的显著差异。因此,我们引入更稳健的评估协议以稳定比较。研究揭示了哪些组件和设计对于有效代理至关重要,哪些虽然看似合理但却是冗余的。基于我们的发现,我们构建并开源了OAgents,一个全新的基础代理框架,在开源项目中实现最先进的性能。OAgents为各种代理组件提供模块化设计,促进Agentic AI的未来研究。
Key Takeaways
- 当前Agentic AI研究领域缺乏标准化和科学严谨性,导致方法比较困难。
- 通过GAIA基准测试和BrowseComp实证研究,探讨了关键代理组件的设计选择的影响。
- 缺乏标准评估协议导致先前的工作不可复现,存在随机运行之间的显著差异。
- 引入更稳健的评估协议以稳定比较不同的代理设计。
- 研究揭示了哪些代理组件和设计至关重要,哪些设计是冗余的。
- 构建并开源了新的基础代理框架OAgents,实现开源项目中的最先进性能。
点此查看论文截图

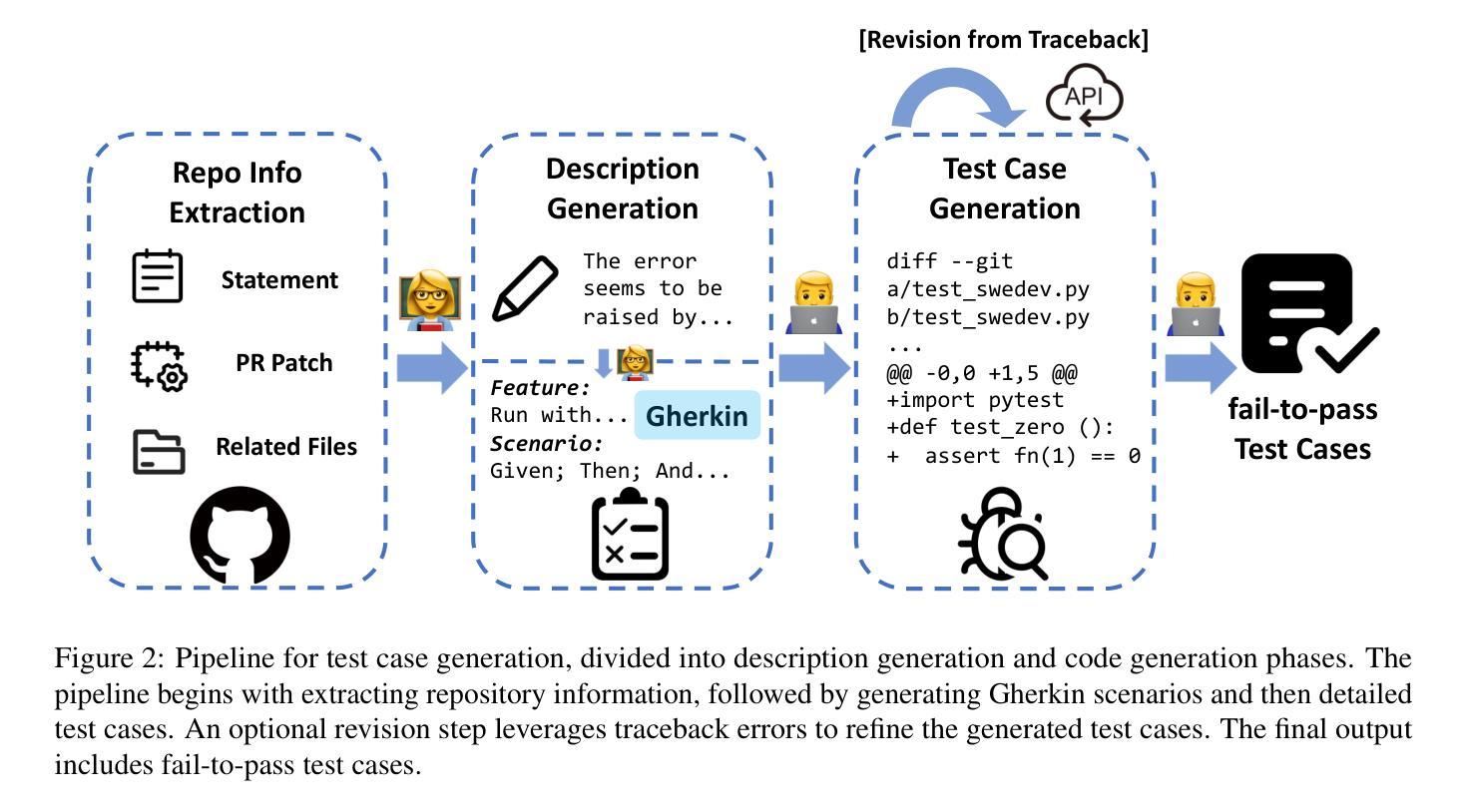
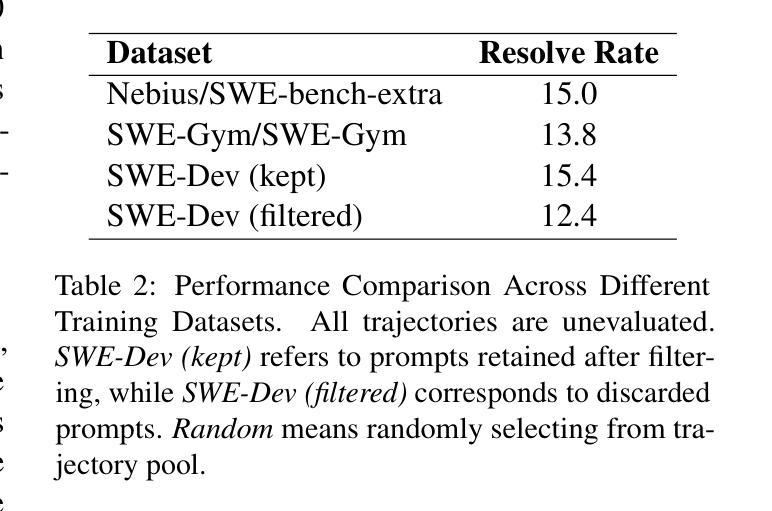
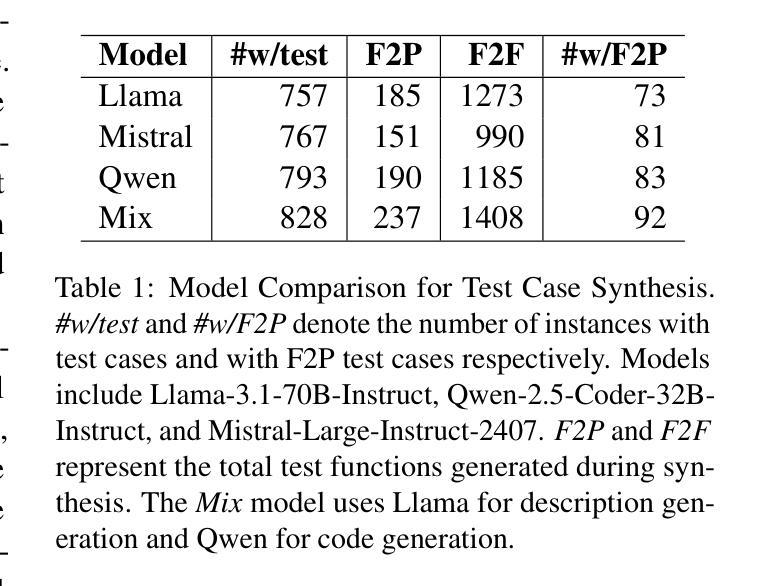
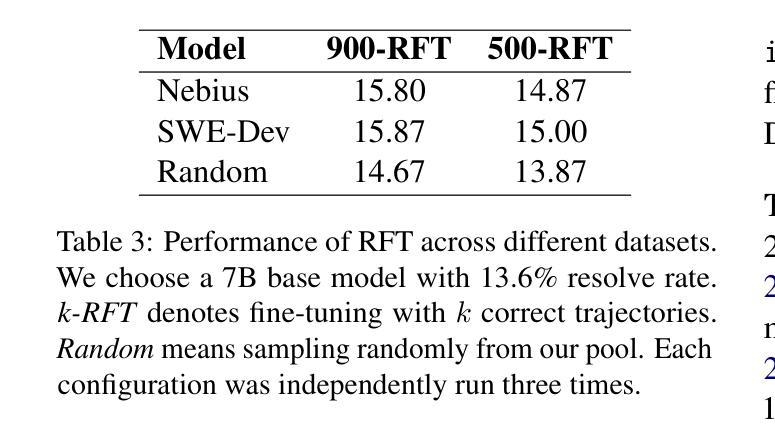
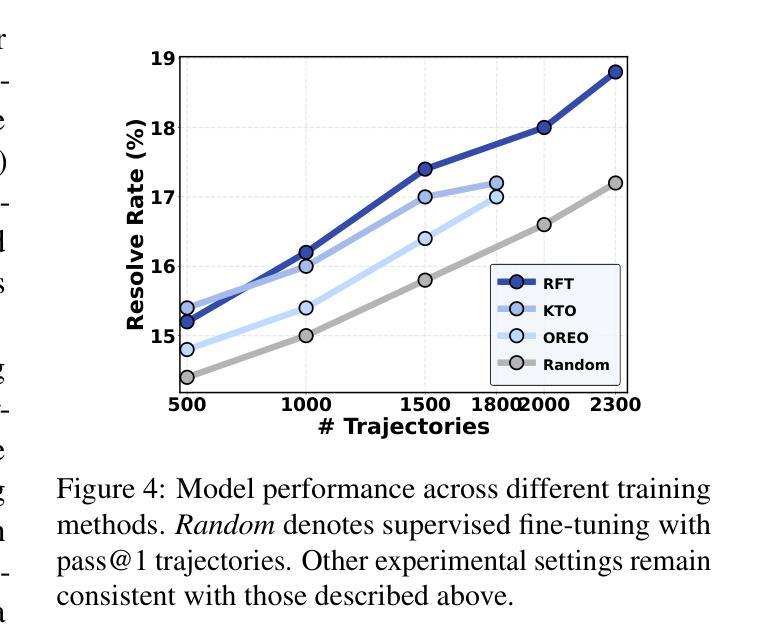
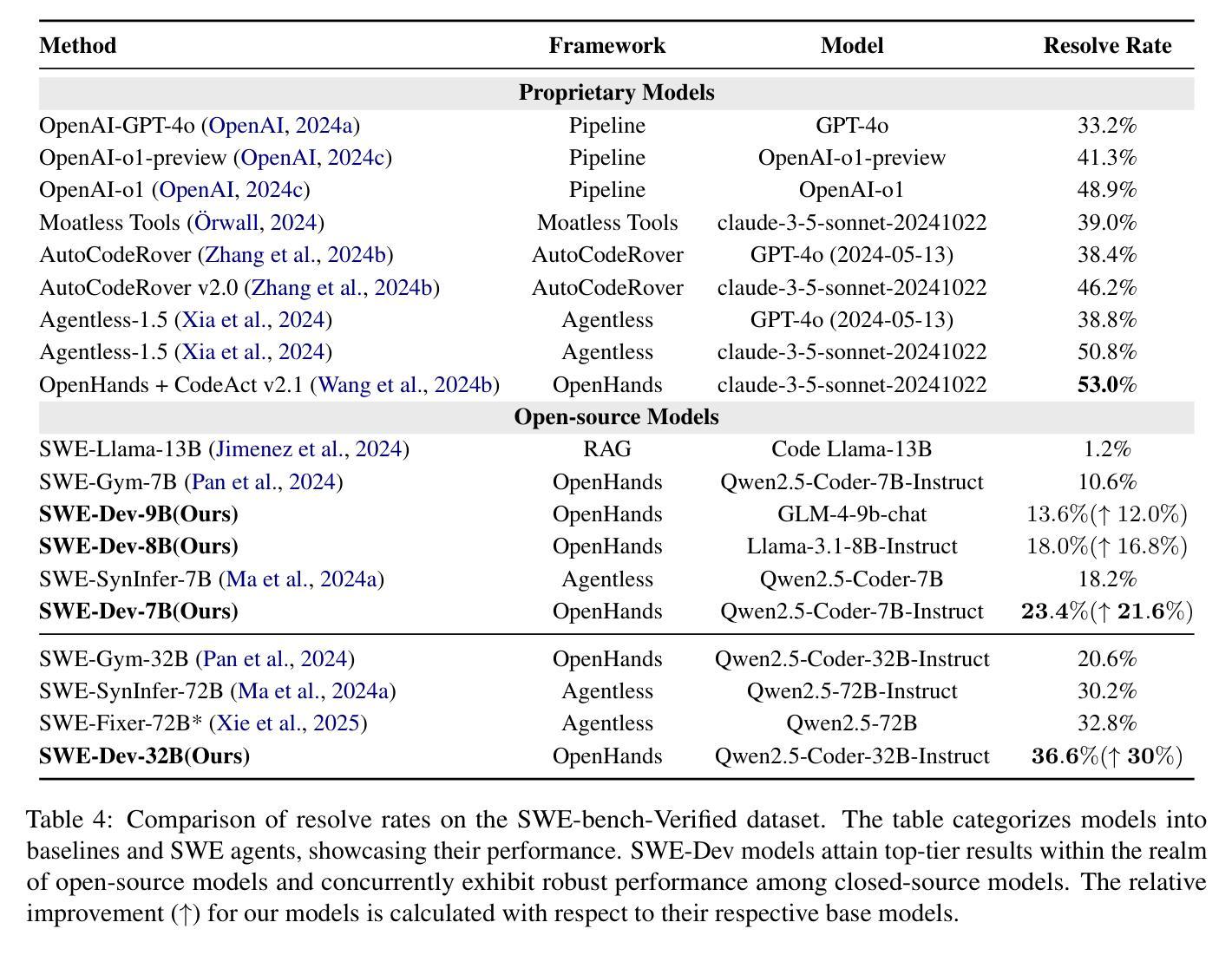
SWE-Dev: Building Software Engineering Agents with Training and Inference Scaling
Authors:Haoran Wang, Zhenyu Hou, Yao Wei, Jie Tang, Yuxiao Dong
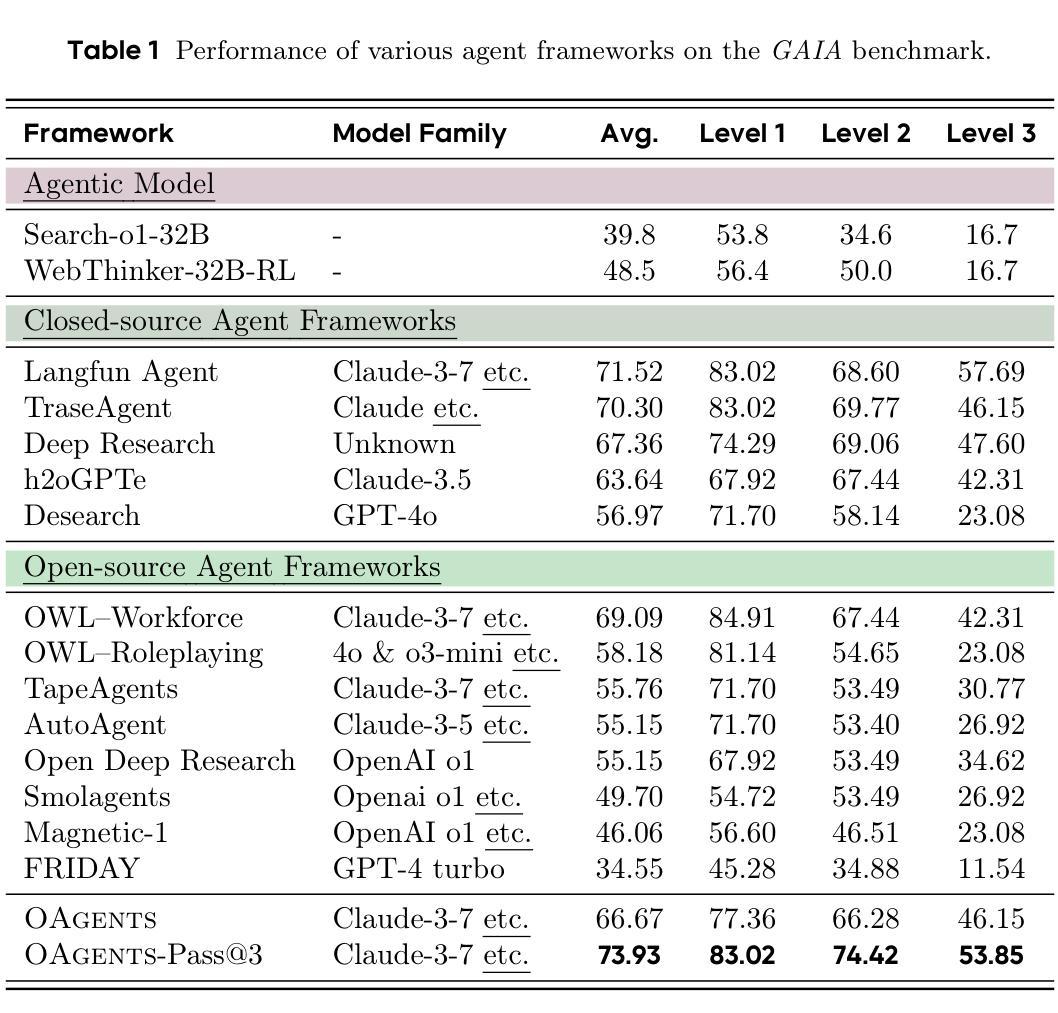
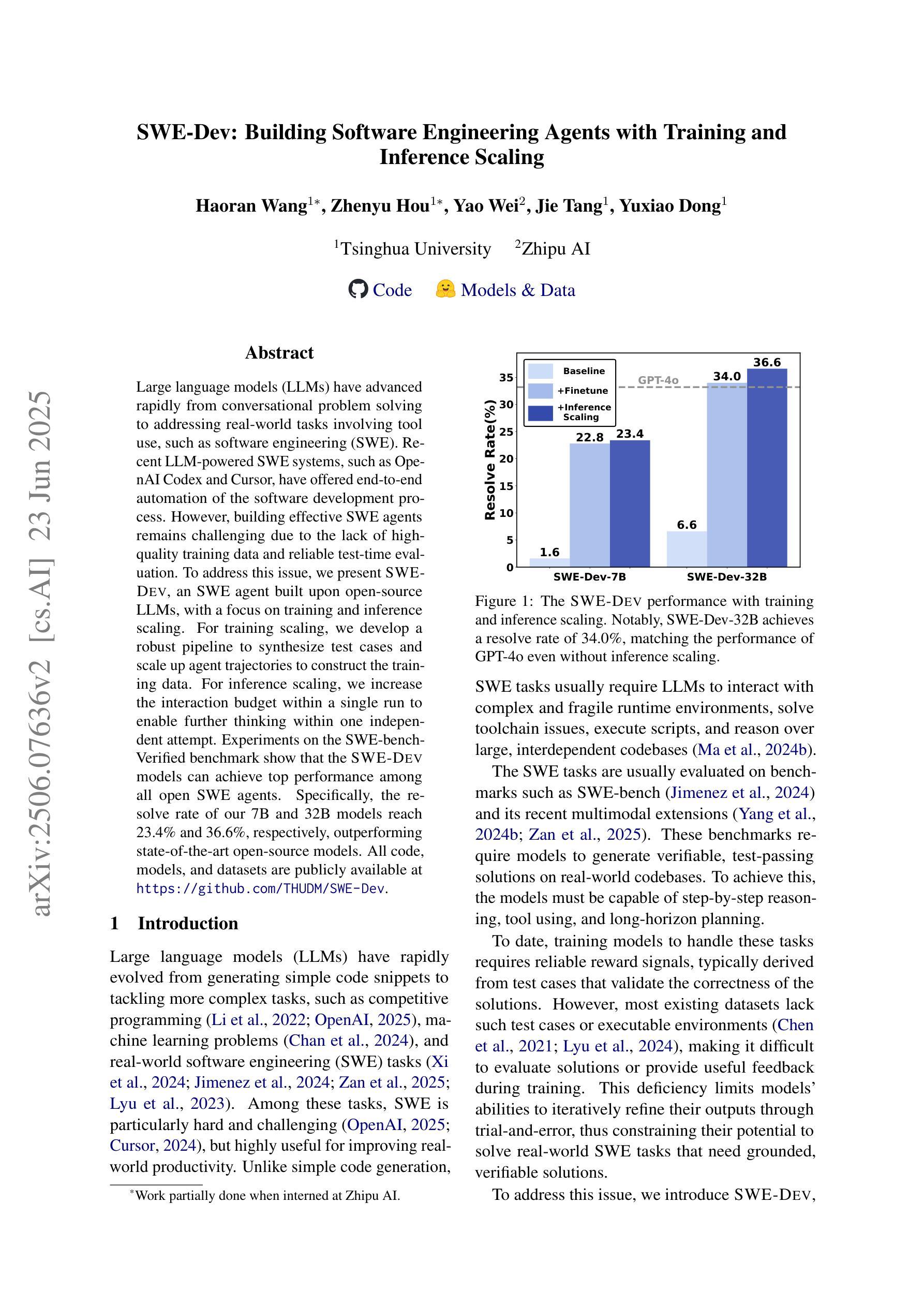
Large language models (LLMs) have advanced rapidly from conversational problem solving to addressing real-world tasks involving tool use, such as software engineering (SWE). Recent LLM-powered toolkits, such as OpenAI Codex and Cursor, have offered end-to-end automation of the software development process. However, building effective SWE agents remains challenging due to the lack of high-quality training data and effective test cases. To address this issue, we present SWE-Dev, an SWE agent built upon open-source LLMs. First, we develop a robust pipeline to synthesize test cases for patch evaluation. Second, we scale up agent trajectories to construct the training data for building SWE-Dev. Experiments on the SWE-bench-Verified benchmark show that the SWE-Dev models can achieve top performance among all open SWE agents. Specifically, the success rates of the SWE-Dev 7B and 32B parameter models reach 23.4% and 36.6%, respectively, outperforming state-of-the-art open-source models. All code, models, and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/THUDM/SWE-Dev.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经从解决对话问题迅速发展到处理涉及工具使用的现实世界任务,如软件工程(SWE)。最近的LLM驱动的工具包,如OpenAI的Codex和Cursor,已经提供了软件开发过程的端到端自动化。然而,由于缺少高质量的训练数据和有效的测试用例,构建有效的SWE代理仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了SWE-Dev,一个基于开源LLM的SWE代理。首先,我们开发了一个稳健的管道来合成测试用例进行评估。其次,我们扩大了代理轨迹以构建SWE-Dev的训练数据。在SWE-bench-Verified基准测试上的实验表明,SWE-Dev模型在所有公开的SWE代理中都能达到顶尖性能。具体来说,SWE-Dev 7B和32B参数模型的成功率分别达到了23.4%和36.6%,超过了最新的开源模型。所有代码、模型和数据集均可在https://github.com/THUDM/SWE-Dev公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Findings of ACL’25
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)已从对话问题解决方案迅速发展到应对涉及工具使用的现实世界任务,如软件工程(SWE)。最近,OpenAI Codex和Cursor等工具包为软件开发流程提供了端到端的自动化。然而,构建有效的SWE代理面临缺乏高质量训练数据和有效测试用例的挑战。为解决此问题,我们推出了基于开源LLM的SWE-Dev代理。首先,我们开发了一个稳健的管道来合成用于补丁评估的测试用例。其次,我们扩大了代理轨迹以构建SWE-Dev的训练数据。在SWE-bench-Verified基准测试上的实验表明,SWE-Dev模型在所有开源SWE代理中名列前茅。特别是,SWE-Dev 7B和32B参数模型的成功率分别达到了23.4%和36.6%,超过了最新的开源模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已扩展到现实世界任务,如软件工程(SWE)。
- 近期LLM工具包如OpenAI Codex和Cursor推动了软件开发的自动化。
- 构建有效的SWE代理面临缺乏高质量训练数据和有效测试用例的挑战。
- 提出了SWE-Dev代理以解决这些问题,该代理基于开源LLM。
- SWE-Dev通过开发用于补丁评估的测试用例的稳健管道来合成测试案例。
- 通过扩大代理轨迹构建了SWE-Dev的训练数据。
点此查看论文截图
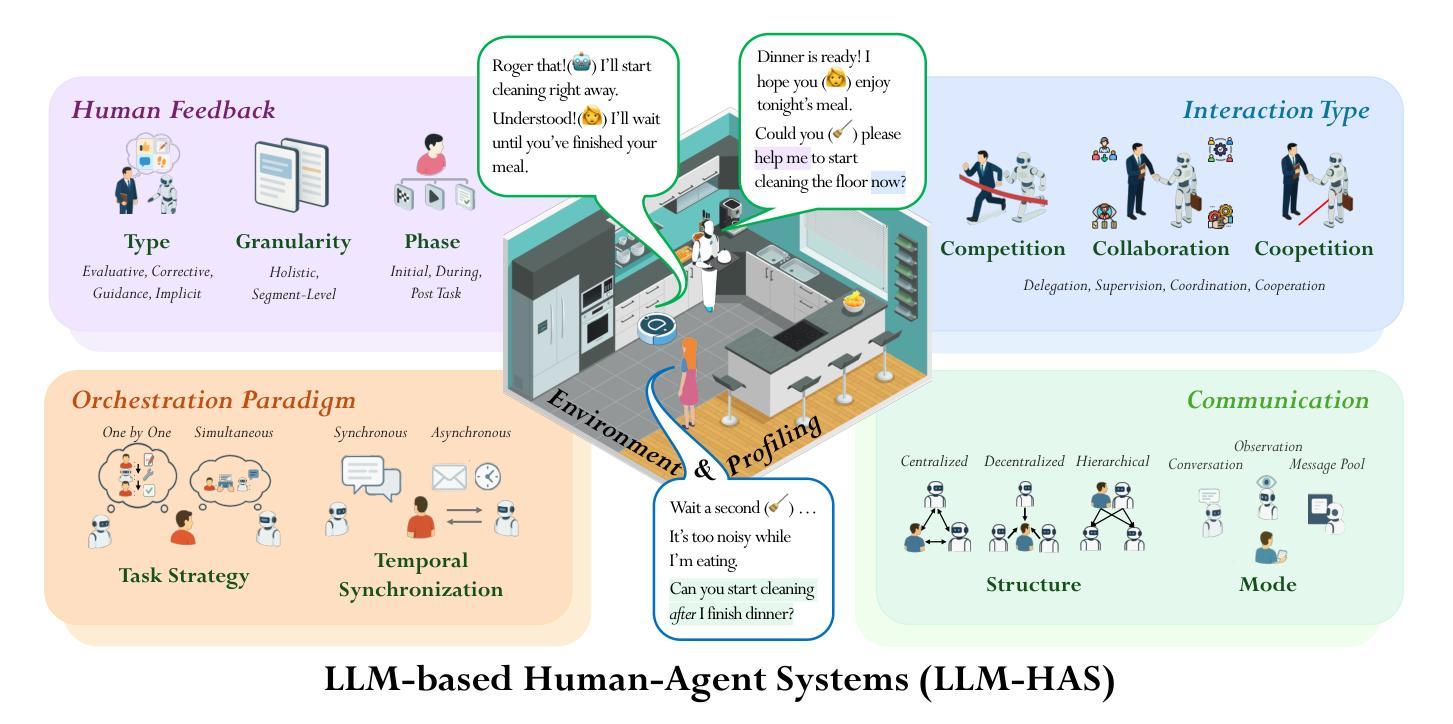
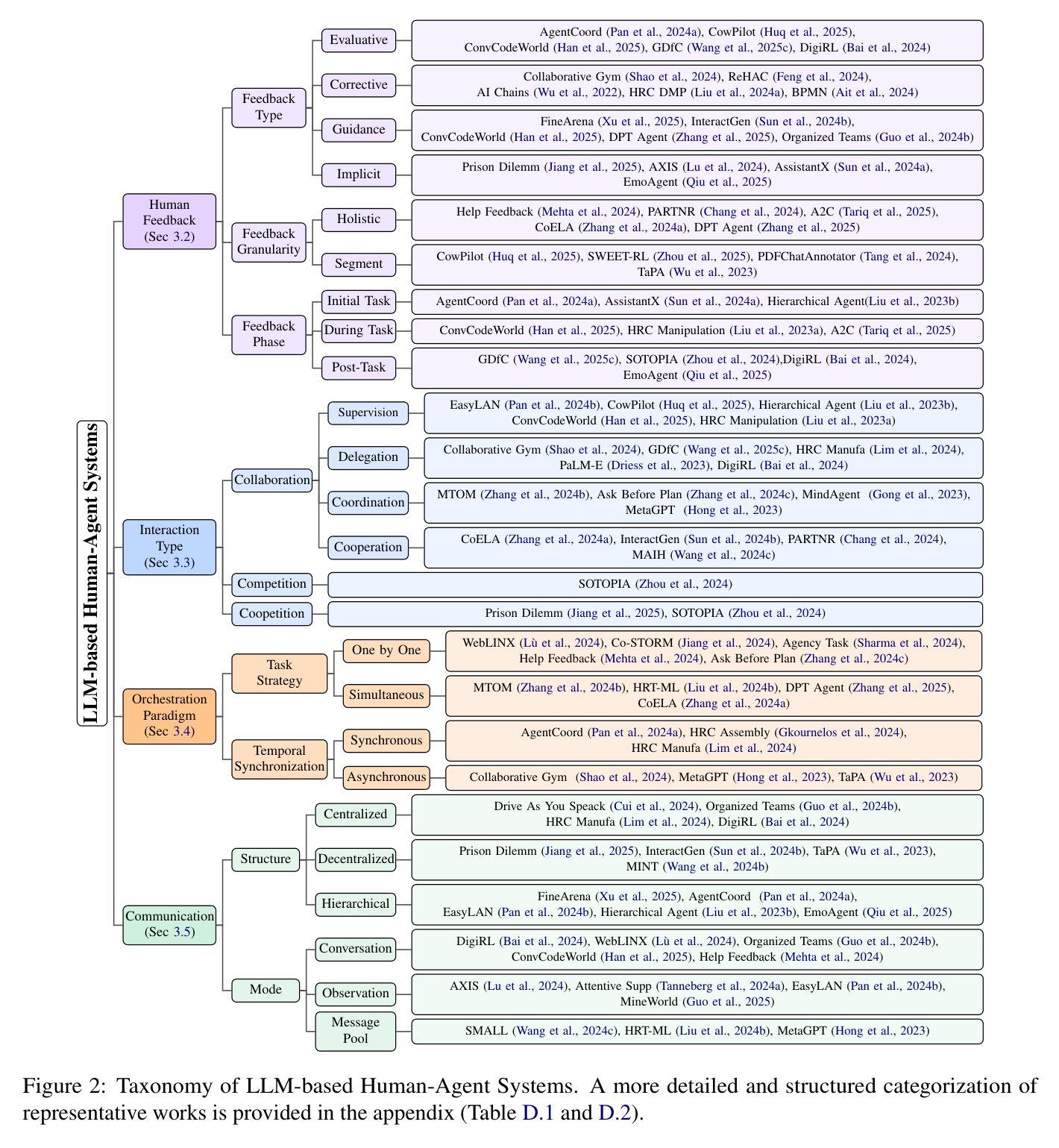
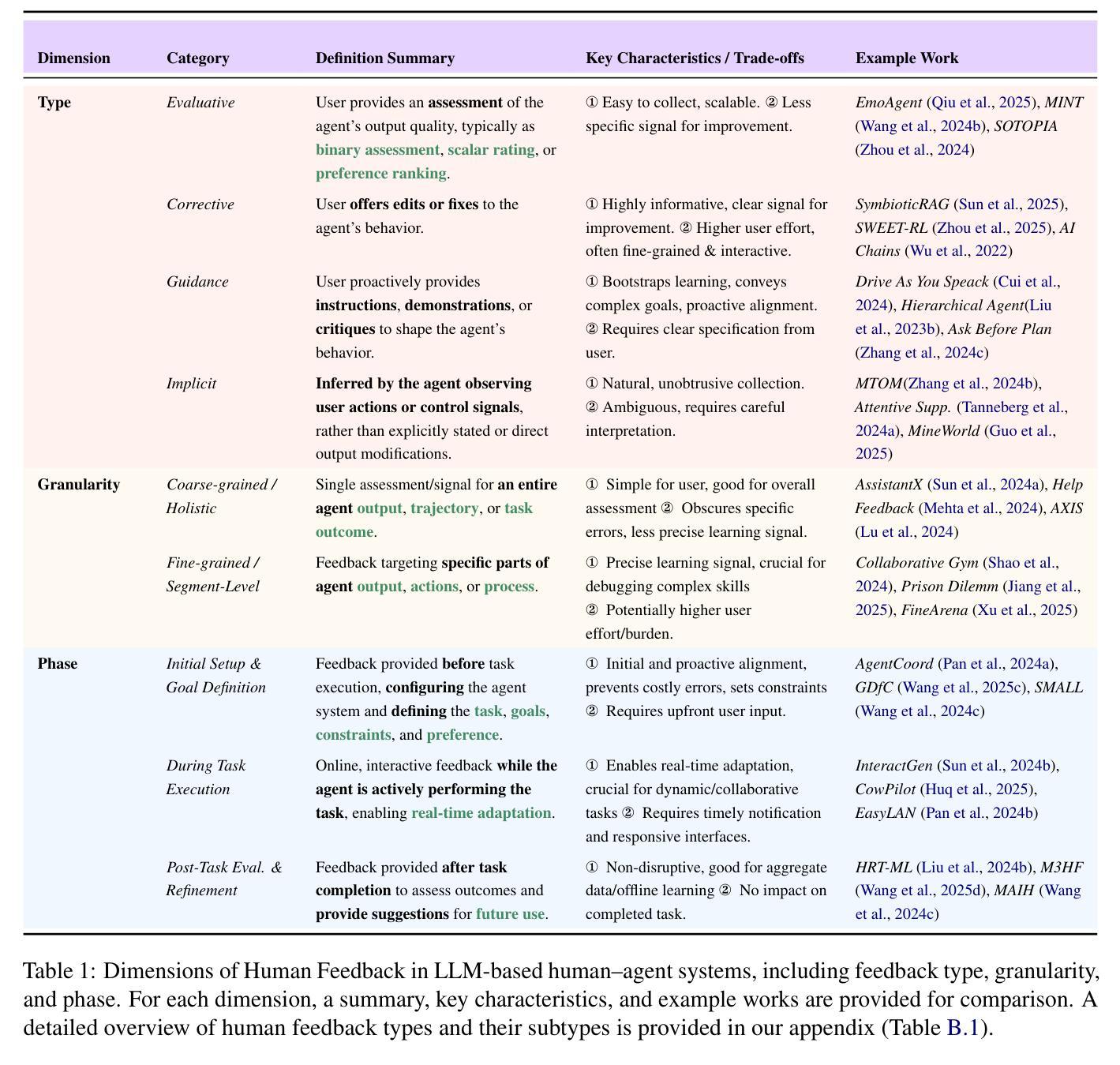
A Survey on Large Language Model based Human-Agent Systems
Authors:Henry Peng Zou, Wei-Chieh Huang, Yaozu Wu, Yankai Chen, Chunyu Miao, Hoang Nguyen, Yue Zhou, Weizhi Zhang, Liancheng Fang, Langzhou He, Yangning Li, Dongyuan Li, Renhe Jiang, Xue Liu, Philip S. Yu
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have sparked growing interest in building fully autonomous agents. However, fully autonomous LLM-based agents still face significant challenges, including limited reliability due to hallucinations, difficulty in handling complex tasks, and substantial safety and ethical risks, all of which limit their feasibility and trustworthiness in real-world applications. To overcome these limitations, LLM-based human-agent systems (LLM-HAS) incorporate human-provided information, feedback, or control into the agent system to enhance system performance, reliability and safety. These human-agent collaboration systems enable humans and LLM-based agents to collaborate effectively by leveraging their complementary strengths. This paper provides the first comprehensive and structured survey of LLM-HAS. It clarifies fundamental concepts, systematically presents core components shaping these systems, including environment & profiling, human feedback, interaction types, orchestration and communication, explores emerging applications, and discusses unique challenges and opportunities arising from human-AI collaboration. By consolidating current knowledge and offering a structured overview, we aim to foster further research and innovation in this rapidly evolving interdisciplinary field. Paper lists and resources are available at https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-Systems.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展引发了人们对构建完全自主代理人的浓厚兴趣。然而,基于LLM的完全自主代理人仍然面临重大挑战,包括由于幻觉导致的可靠性有限、处理复杂任务的困难以及安全和伦理风险较高,所有这些因素都限制了它们在现实世界应用中的可行性和可信度。为了克服这些局限性,基于LLM的人机代理系统(LLM-HAS)将人类提供的信息、反馈或控制纳入代理系统,以提高系统性能、可靠性和安全性。这些人机协作系统通过利用人类和基于LLM的代理人的各自优势,使人类和基于LLM的代理人能够进行有效的协作。本文对LLM-HAS进行了第一次全面和系统的调查。阐明了基本概念,系统地介绍了构成这些系统的核心组件,包括环境分析、人类反馈、交互类型、编排和通信,探讨了新兴应用,并讨论了由人机协作产生的独特挑战和机遇。通过整合当前知识并提供结构化概述,我们的目标是促进这一迅速发展的跨学科领域的进一步研究和创新。论文列表和资源可通过https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-Systems获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper lists and resources are available at https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-Systems
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的全自主代理技术日益受到关注,但仍面临可靠性、处理复杂任务能力、安全和伦理风险等方面的挑战。为了克服这些限制,结合了人类提供的信息、反馈或控制的LLM人机协作系统(LLM-HAS)被提出,通过利用人类和LLM代理的互补优势以实现有效协作。本文是对LLM-HAS的首个全面结构化调查,阐述了基本概念和系统核心组件,包括环境分析、人类反馈、交互类型、协调和通信等。此外,本文探讨了人机协作带来的独特挑战和机遇,并整合了当前知识,为这一迅速发展的跨学科领域的研究和创新提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs面临可靠性、复杂任务处理能力及安全和伦理风险方面的挑战。
- LLM-HAS结合了人类与LLM代理的信息、反馈和控制,以提高系统性能、可靠性和安全性。
- LLM-HAS实现了人类和LLM代理的有效协作,利用双方的互补优势。
- 本文是对LLM-HAS的全面结构化调查,阐述了其基本概念和系统核心组件。
- LLM-HAS的环境分析、人类反馈、交互类型、协调和通信等要素被详细探讨。
- 人机协作带来独特的挑战和机遇。
点此查看论文截图

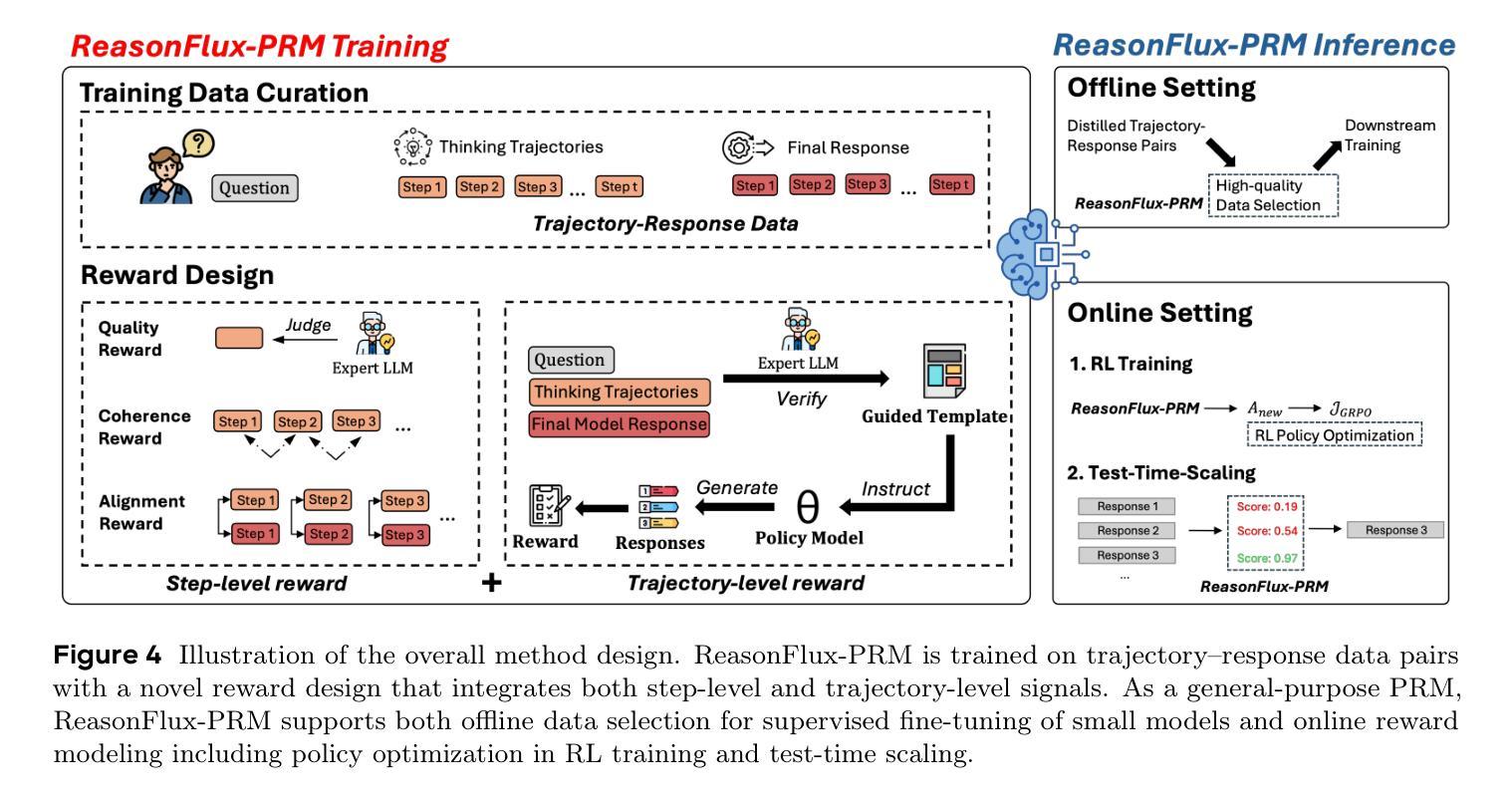
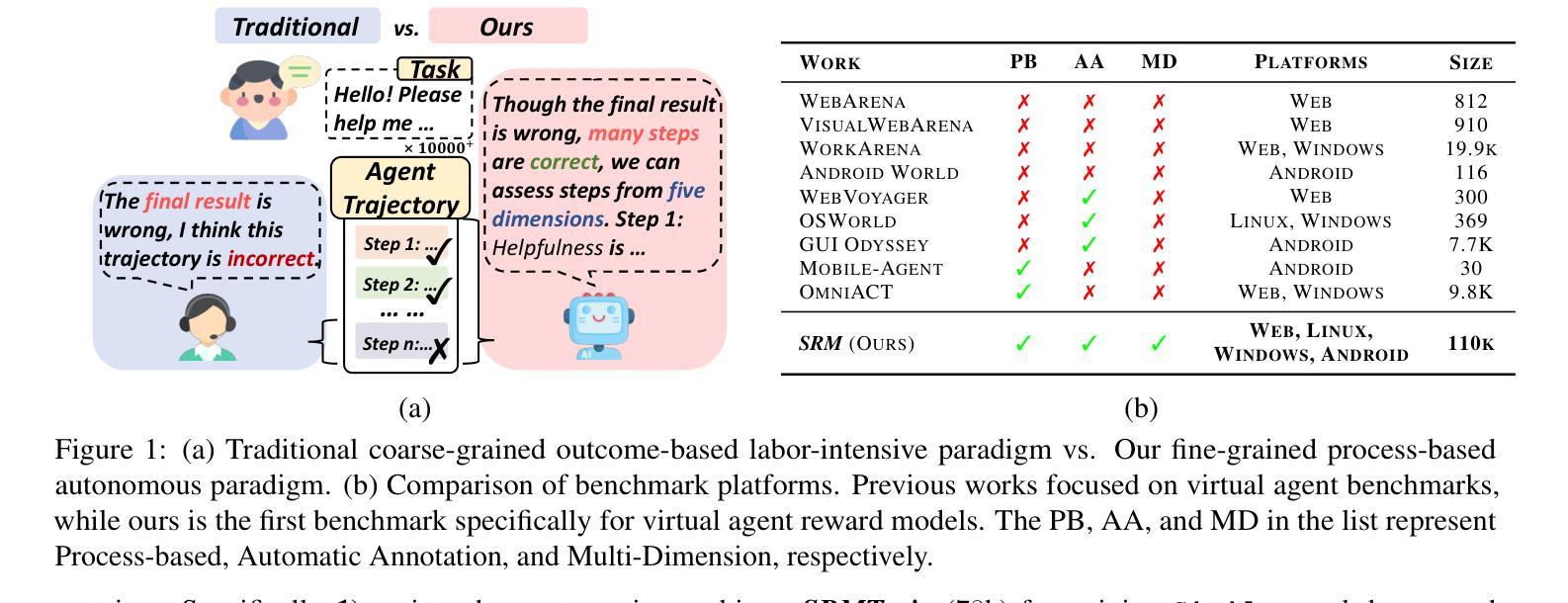
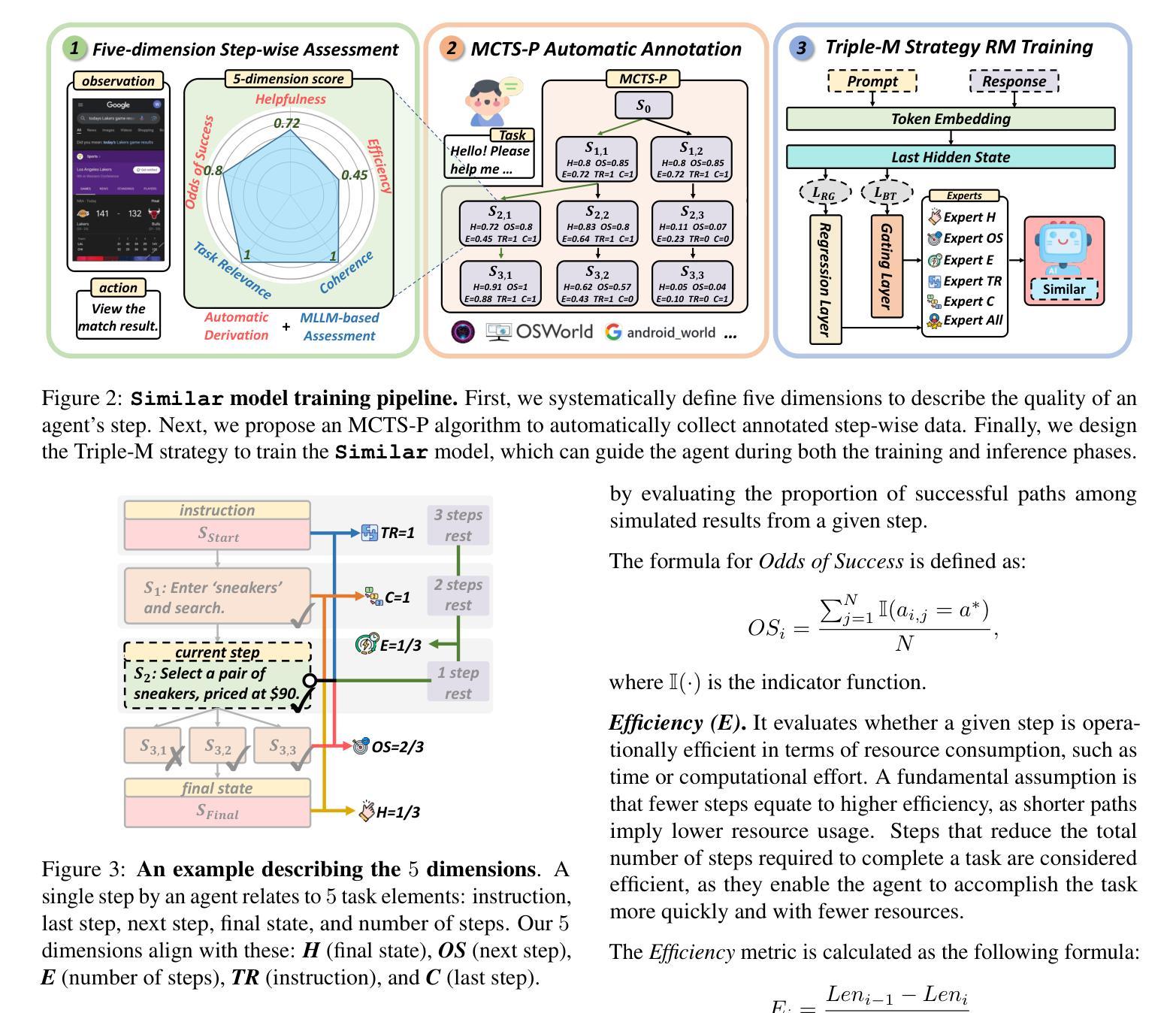
Boosting Virtual Agent Learning and Reasoning: A Step-Wise, Multi-Dimensional, and Generalist Reward Model with Benchmark
Authors:Bingchen Miao, Yang Wu, Minghe Gao, Qifan Yu, Wendong Bu, Wenqiao Zhang, Yunfei Li, Siliang Tang, Tat-Seng Chua, Juncheng Li
The development of Generalist Virtual Agents (GVAs) has shown significant promise in autonomous task execution. However, current training paradigms face critical limitations, including reliance on outcome supervision and labor-intensive human annotations. To address these challenges, we propose Similar, a Step-Wise Multi-Dimensional Generalist Reward Model, which offers fine-grained signals for agent training and can choose better action for inference-time scaling. Specifically, we begin by systematically defining five dimensions for evaluating agent actions. Building on this framework, we design an MCTS-P algorithm to automatically collect and annotate step-wise, five-dimensional agent execution data. Using this data, we train Similar with the Triple-M strategy. Furthermore, we introduce the first benchmark in the virtual agent domain for step-wise, multi-dimensional reward model training and evaluation, named SRM. This benchmark consists of two components: SRMTrain, which serves as the training set for Similar, and SRMEval, a manually selected test set for evaluating the reward model. Experimental results demonstrate that Similar, through its step-wise, multi-dimensional assessment and synergistic gain, provides GVAs with effective intermediate signals during both training and inference-time scaling. The project is available at https://github.com/antgroup/Similar.
通用虚拟智能体(GVAs)的发展在自主任务执行方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,当前的训练模式面临重大局限,包括依赖结果监督和劳动密集型人工标注。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了名为“Similar”的步级多维度通用奖励模型,该模型为智能体训练提供精细的信号,并可以在推理时选择更好的动作进行缩放。具体来说,我们首先系统地定义了五个维度来评估智能体的动作。在此基础上,我们设计了一种基于蒙特卡洛树搜索的算法(MCTS-P),该算法能够自动收集和标注智能体的步级、五维度执行数据。使用这些数据,我们用三重M策略训练Similar模型。此外,我们还引入了虚拟智能体领域首个用于步级多维度奖励模型训练和评价的基准数据集,名为SRM。该基准数据集包含两个组件:用于训练Similar的训练集SRMTrain和用于评估奖励模型的SRMEval手动选择测试集。实验结果表明,通过步级多维评估和协同增益,Similar为GVAs在训练和推理过程中提供了有效的中间信号。该项目可通过https://github.com/antgroup/Similar获取访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Home page is available at https://dcd-ant-similar.github.io
Summary:通用虚拟代理人(GVAs)在自主任务执行方面展现出巨大潜力,但其训练模式仍存在依赖结果监督和劳动密集型人工标注等局限性。为此,本文提出了一种名为Similar的逐步多维通用奖励模型,为代理训练提供精细信号,并在推理时间缩放时选择更好的行动。通过系统地定义五个维度来评估代理行动,设计MCTS-P算法自动收集和标注逐步的五维代理执行数据。使用这种数据,用Triple-M策略训练Similar。此外,本文引入了虚拟代理领域首个用于逐步多维奖励模型训练和评价的基准测试,名为SRM。实验结果表明,Similar通过逐步多维评估和协同增益为GVAs在训练和推理时间缩放期间提供有效的中间信号。
Key Takeaways:
- Generalist Virtual Agents (GVAs) 在自主任务执行方面展现出巨大潜力,但现有训练模式存在局限性。
- 提出了名为Similar的逐步多维通用奖励模型,以精细的方式为代理训练提供信号,并在推理时选择最佳行动。
- 通过系统地定义五个维度来评估代理行动,为代理训练提供更全面的反馈。
- 设计了MCTS-P算法来自动收集和标注逐步的五维代理执行数据,增强训练效率。
- 使用Triple-M策略来训练Similar模型,提高了模型的性能。
- 引入了虚拟代理领域的首个基准测试SRM,用于逐步多维奖励模型训练和评估。
点此查看论文截图

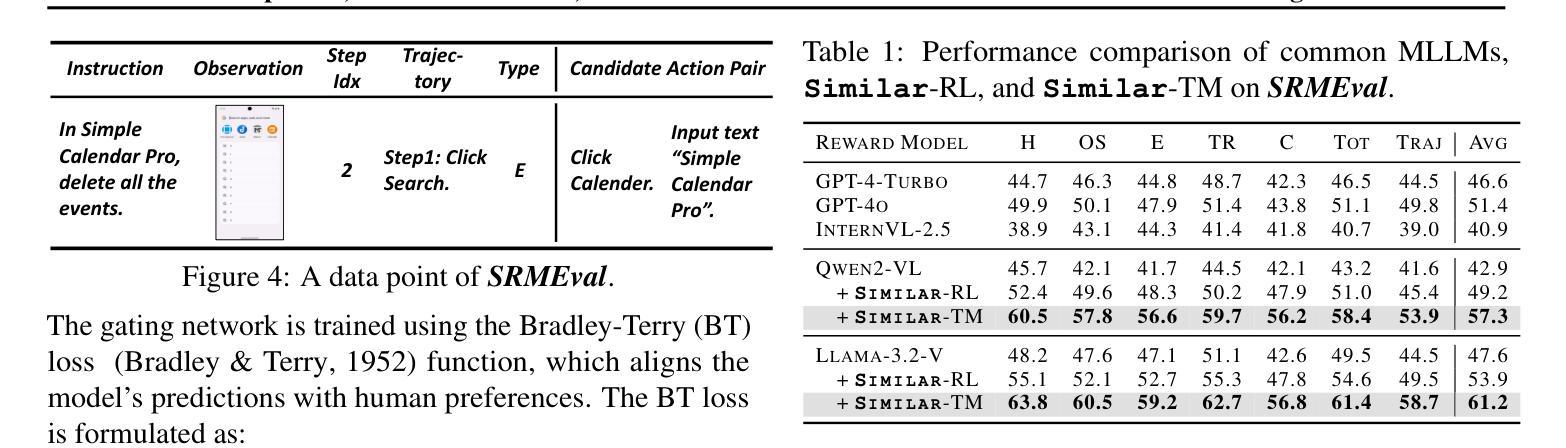
EmoAgent: A Multi-Agent Framework for Diverse Affective Image Manipulation
Authors:Qi Mao, Haobo Hu, Yujie He, Difei Gao, Haokun Chen, Libiao Jin
Affective Image Manipulation (AIM) aims to alter visual elements within an image to evoke specific emotional responses from viewers. However, existing AIM approaches rely on rigid \emph{one-to-one} mappings between emotions and visual cues, making them ill-suited for the inherently subjective and diverse ways in which humans perceive and express emotion.To address this, we introduce a novel task setting termed \emph{Diverse AIM (D-AIM)}, aiming to generate multiple visually distinct yet emotionally consistent image edits from a single source image and target emotion. We propose \emph{EmoAgent}, the first multi-agent framework tailored specifically for D-AIM. EmoAgent explicitly decomposes the manipulation process into three specialized phases executed by collaborative agents: a Planning Agent that generates diverse emotional editing strategies, an Editing Agent that precisely executes these strategies, and a Critic Agent that iteratively refines the results to ensure emotional accuracy. This collaborative design empowers EmoAgent to model \emph{one-to-many} emotion-to-visual mappings, enabling semantically diverse and emotionally faithful edits.Extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that EmoAgent substantially outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both emotional fidelity and semantic diversity, effectively generating multiple distinct visual edits that convey the same target emotion.
情感图像操纵(AIM)旨在改变图像中的视觉元素,以激发观看者特定的情感反应。然而,现有的AIM方法依赖于情感与视觉线索之间的僵化“一对一”映射,这使得它们不适合人类感知和表达情感所具有的固有主观性和多样性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种新型任务设置,称为多样化AIM(D-AIM),旨在从单个源图像和目标情感生成多个视觉上不同但情感上一致的图像编辑。我们提出了专门为D-AIM定制的第一个多代理框架EmoAgent。EmoAgent明确地将操纵过程分解为三个阶段,由协作代理执行:规划代理生成多种情感编辑策略,编辑代理精确执行这些策略,评论家代理迭代优化结果以确保情感准确性。这种协作设计使EmoAgent能够建立“一到多”的情感到视觉映射,从而实现语义多样且情感真实的编辑。广泛定量和定性的评估表明,EmoAgent在情感保真度和语义多样性方面大大优于现有先进技术,能够生成有效传达同一目标情感的多个不同视觉编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
情感图像操作(AIM)旨在改变图像的视觉元素以激发观众特定的情感反应。然而,现有的AIM方法依赖于情绪与视觉线索之间的僵化的一一映射,这使得它们不适合人类感知和表达情绪的固有主观性和多样性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个名为多样化AIM(D-AIM)的新任务设置,旨在从单个源图像和目标情绪生成多个视觉各异但情感一致的图像编辑。我们提出了专门针对D-AIM设计的第一个多代理框架EmoAgent。EmoAgent将操作过程明确分解为三个阶段,由协作代理执行:生成多种情感编辑策略的规划代理、精确执行这些策略编辑代理和不断对结果进行精细化以确保情感准确性的评论家代理。这种协作设计使EmoAgent能够模拟一对一的情绪到视觉映射,实现语义多样且情感真实的编辑。
Key Takeaways:
- 情感图像操作(AIM)通过改变图像的视觉元素来激发特定情感反应。
- 现有方法依赖于僵化的情绪与视觉线索的一一映射,缺乏主观性和多样性。
- 引入多样化AIM(D-AIM)任务设置,旨在从单个源图像生成多个情感一致的图像编辑。
- 提出多代理框架EmoAgent,包括规划、编辑和评论家代理,实现语义多样且情感真实的编辑。
- EmoAgent通过模拟一一对应的情绪到视觉映射,突破现有方法限制。
- EmoAgent在情感保真度和语义多样性方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


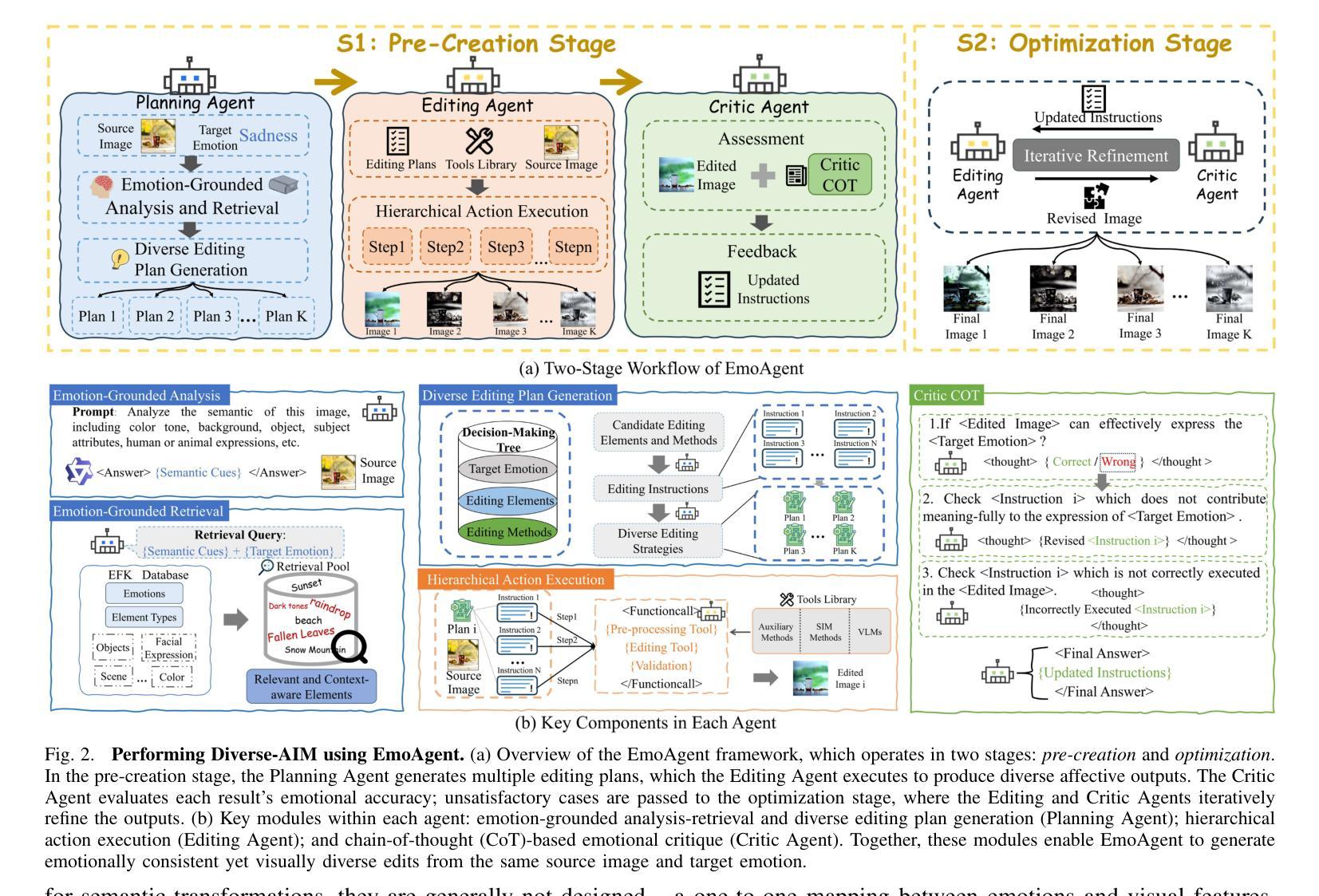
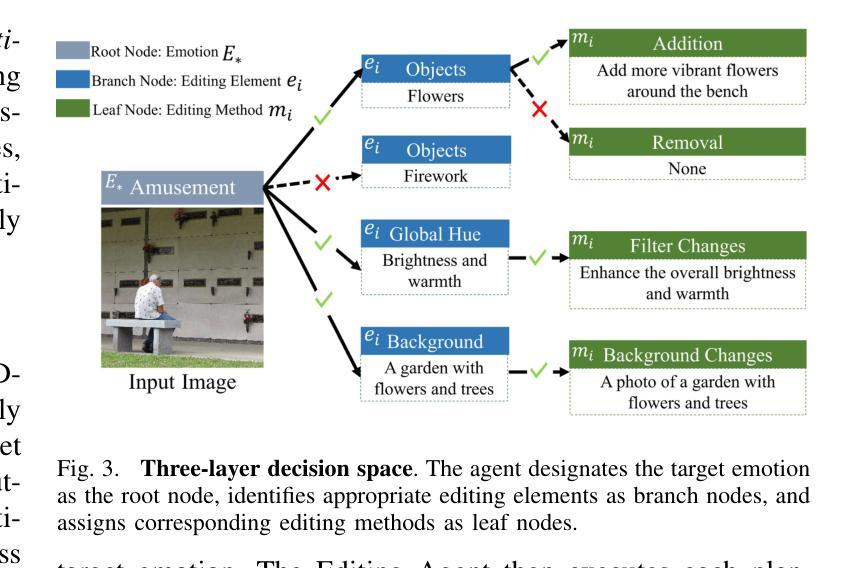
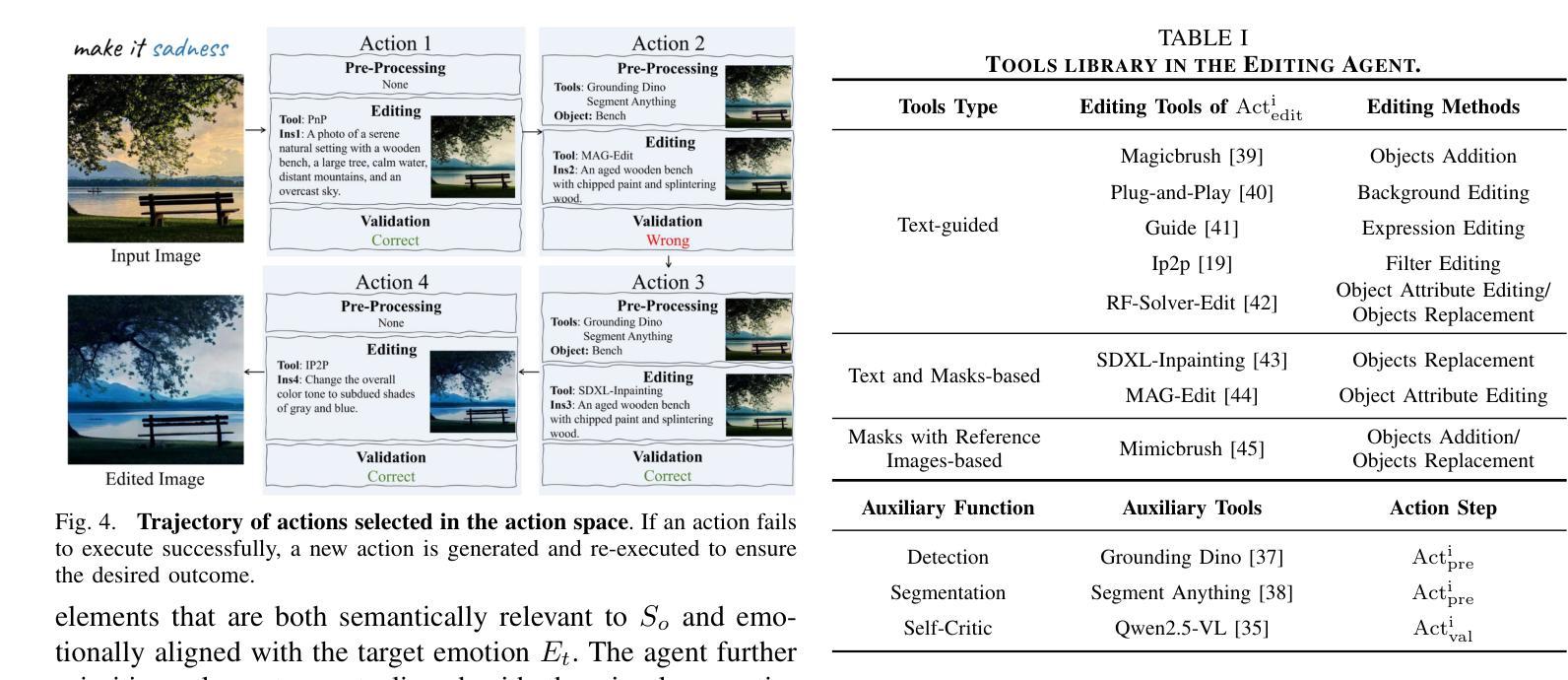
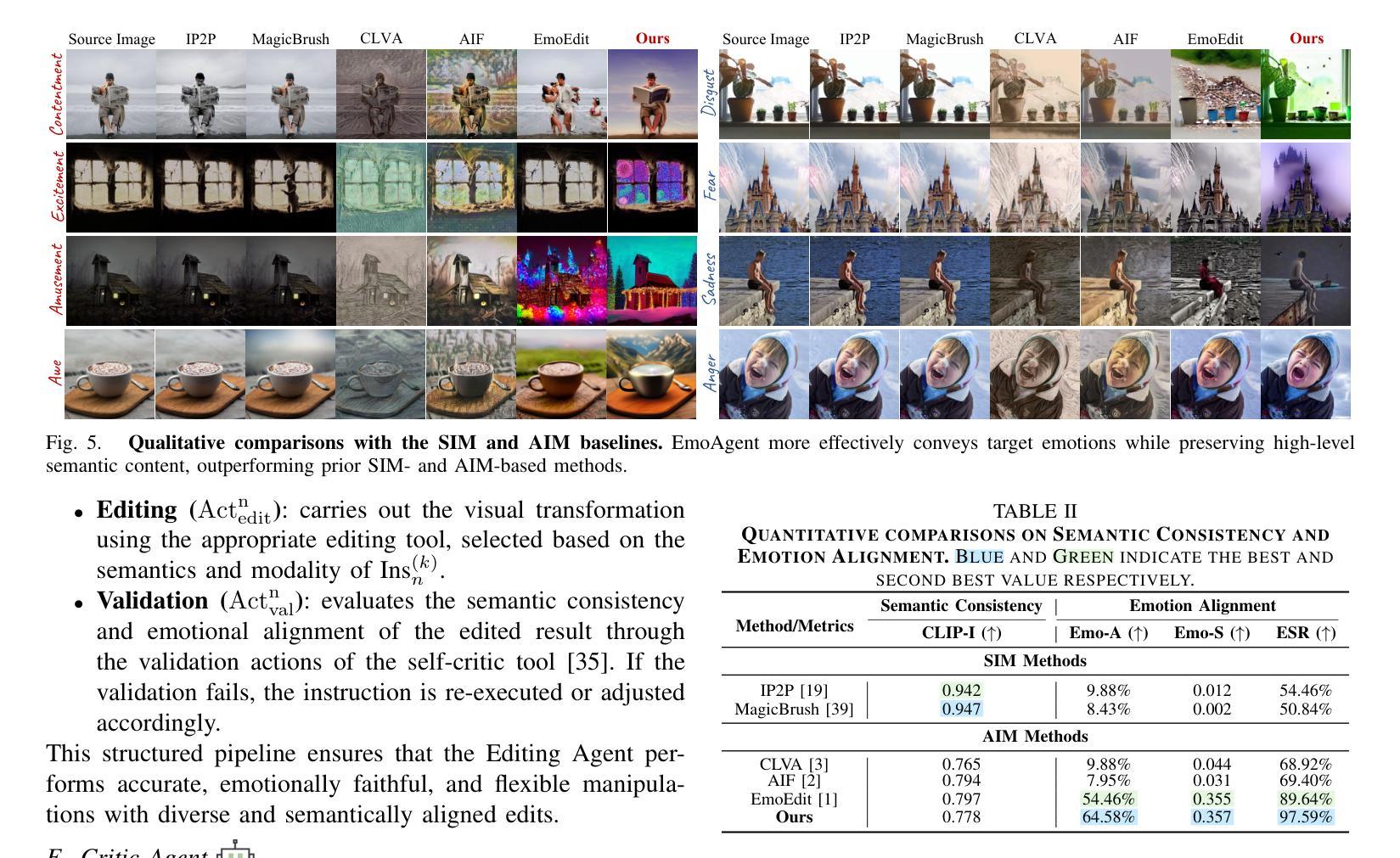
Collaborative Mean Estimation Among Heterogeneous Strategic Agents: Individual Rationality, Fairness, and Truthful Contribution
Authors:Alex Clinton, Yiding Chen, Xiaojin Zhu, Kirthevasan Kandasamy
We study a collaborative learning problem where $m$ agents aim to estimate a vector $\mu =(\mu_1,\ldots,\mu_d)\in \mathbb{R}^d$ by sampling from associated univariate normal distributions ${\mathcal{N}(\mu_k, \sigma^2)}{k\in[d]}$. Agent $i$ incurs a cost $c{i,k}$ to sample from $\mathcal{N}(\mu_k, \sigma^2)$. Instead of working independently, agents can exchange data, collecting cheaper samples and sharing them in return for costly data, thereby reducing both costs and estimation error. We design a mechanism to facilitate such collaboration, while addressing two key challenges: ensuring individually rational (IR) and fair outcomes so all agents benefit, and preventing strategic behavior (e.g. non-collection, data fabrication) to avoid socially undesirable outcomes. We design a mechanism and an associated Nash equilibrium (NE) which minimizes the social penalty-sum of agents’ estimation errors and collection costs-while being IR for all agents. We achieve a $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{m})$-approximation to the minimum social penalty in the worst case and an $\mathcal{O}(1)$-approximation under favorable conditions. Additionally, we establish three hardness results: no nontrivial mechanism guarantees (i) a dominant strategy equilibrium where agents report truthfully, (ii) is IR for every strategy profile of other agents, (iii) or avoids a worst-case $\Omega(\sqrt{m})$ price of stability in any NE. Finally, by integrating concepts from axiomatic bargaining, we demonstrate that our mechanism supports fairer outcomes than one which minimizes social penalty.
我们研究了一个协作学习问题,其中m个代理旨在通过从相关的一元正态分布中采样来估计向量μ=(μ_1,…,μ_d)∈ℝ^d。代理i从N(μk,σ^2)中采样会产生成本c_{i,k}。代理们不必独立工作,他们可以交换数据,收集更便宜的样本并共享昂贵的样本,从而降低成本和估计误差。我们设计了一种机制来促进这种合作,同时解决两个关键挑战:确保个人理性公平的结果使所有代理都能受益,并防止策略性行为(如不收集、制造虚假数据)以避免社会不希望看到的结果。我们设计了一种机制以及相关的纳什均衡(NE),该机制能在最小化代理估计误差和收集成本的社会惩罚的同时,对所有代理实现个体理性。在最坏的情况下,我们实现了对最小社会惩罚的O(√m)近似值,并在有利的条件下实现了O(1)近似值。此外,我们还确定了三个难度结果:没有任何非平凡机制能保证(i)存在一种优势策略均衡让代理人如实报告,(ii)对任何其他代理的策略组合都是个体理性的,(iii)在任何NE中避免最坏情况的Ω(√m)稳定性代价。最后,通过整合原则性谈判的概念,我们证明了我们的机制比最小化社会惩罚的机制更能支持更公平的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
在协作学习问题中,m个代理试图通过从相关的一元正态分布中采样来估计向量μ。代理通过交换数据来降低成本和估计误差。本文设计了一种协作机制,解决了两个关键问题:确保个体理性和公平的结果,防止战略行为。该机制达到了最坏情况下社会惩罚的最小值,并建立了三个难度结果。最后,通过整合公理谈判的概念,证明了该机制支持更公平的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了协作学习问题中m个代理如何估计向量μ的问题。
- 通过数据交换降低采样成本和估计误差。
- 设计了一种协作机制以解决个体理性和公平的问题,同时防止战略行为。
- 该机制达到了最坏情况下社会惩罚的最小值的近似值,并在有利条件下达到了近似值。
- 建立了三个难度结果,表明不存在能保证主导策略均衡、对所有策略组合都是个体理性的机制或避免最坏情况下的稳定性价格的机制。
- 通过整合公理谈判的概念,证明了该机制支持更公平的结果分配。
点此查看论文截图

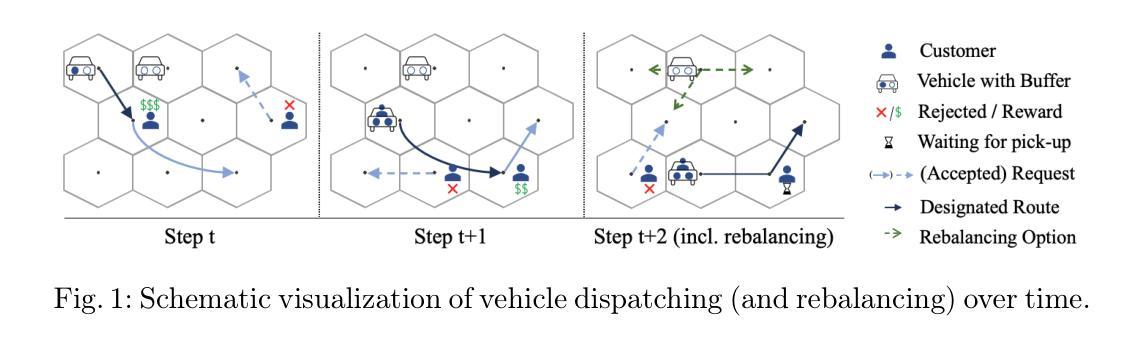
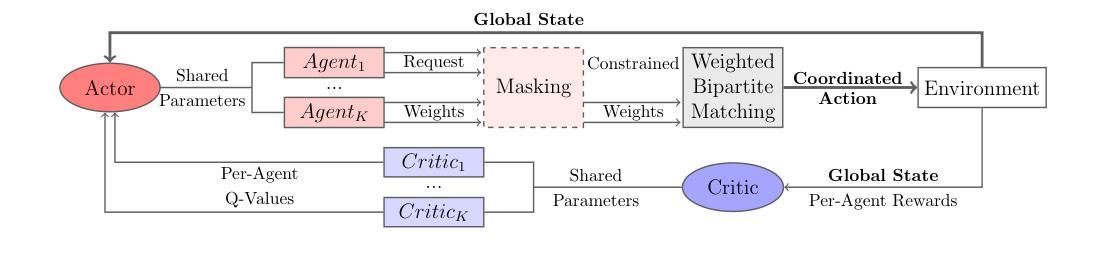
Multi-Agent Soft Actor-Critic with Coordinated Loss for Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand Fleet Control
Authors:Zeno Woywood, Jasper I. Wiltfang, Julius Luy, Tobias Enders, Maximilian Schiffer
We study a sequential decision-making problem for a profit-maximizing operator of an autonomous mobility-on-demand system. Optimizing a central operator’s vehicle-to-request dispatching policy requires efficient and effective fleet control strategies. To this end, we employ a multi-agent Soft Actor-Critic algorithm combined with weighted bipartite matching. We propose a novel vehicle-based algorithm architecture and adapt the critic’s loss function to appropriately consider coordinated actions. Furthermore, we extend our algorithm to incorporate rebalancing capabilities. Through numerical experiments, we show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art benchmarks by up to 12.9% for dispatching and up to 38.9% with integrated rebalancing.
我们对自主按需出行系统中追求利润最大化运营商的连续决策问题进行了研究。优化中心运营商的车辆派遣策略需要高效且有效的车队控制策略。为此,我们采用了一种基于多智能体的Soft Actor-Critic算法,并结合加权二分匹配法。我们提出了一种新型的车辆算法架构,并适应批评者的损失函数以适当考虑协调行动。此外,我们将我们的算法扩展到具备再平衡能力的情况。通过数值实验,我们证明了我们的方法在派遣方面优于最新基准测试达12.9%,在集成再平衡方面提高了高达38.9%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本研究了利润最大化的自主按需出行系统的运营者的顺序决策问题。为了优化中央运营商的车辆对请求派遣政策,需要高效且有效的车队控制策略。为此,采用了一种多代理Soft Actor-Critic算法与加权二分匹配相结合的方法。提出了基于车辆的新型算法架构,并适应了批评者的损失函数以充分考虑协调行动。此外,将算法扩展到纳入再平衡能力。数值实验表明,该方法在派遣方面的性能优于现有基准测试高达12.9%,在集成再平衡方面高达38.9%。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了自主按需出行系统的运营者的顺序决策问题。
- 提出了一种多代理Soft Actor-Critic算法结合加权二分匹配的方法来解决车辆派遣问题。
- 提出了基于车辆的新型算法架构。
- 适应了批评者的损失函数以考虑协调行动。
- 将算法扩展到纳入再平衡能力。
- 数值实验表明,该方法在派遣和集成再平衡方面的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图