⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
DIP: Unsupervised Dense In-Context Post-training of Visual Representations
Authors:Sophia Sirko-Galouchenko, Spyros Gidaris, Antonin Vobecky, Andrei Bursuc, Nicolas Thome
We introduce DIP, a novel unsupervised post-training method designed to enhance dense image representations in large-scale pretrained vision encoders for in-context scene understanding. Unlike prior approaches that rely on complex self-distillation architectures, our method trains the vision encoder using pseudo-tasks that explicitly simulate downstream in-context scenarios, inspired by meta-learning principles. To enable post-training on unlabeled data, we propose an automatic mechanism for generating in-context tasks that combines a pretrained diffusion model and the vision encoder itself. DIP is simple, unsupervised, and computationally efficient, requiring less than 9 hours on a single A100 GPU. By learning dense representations through pseudo in-context tasks, it achieves strong performance across a wide variety of downstream real-world in-context scene understanding tasks. It outperforms both the initial vision encoder and prior methods, offering a practical and effective solution for improving dense representations. Code available here: https://github.com/sirkosophia/DIP
我们介绍了DIP,这是一种新型的无监督后训练法,旨在增强大规模预训练视觉编码器的图像密集表示,以实现对上下文场景的理解。不同于依赖复杂自我蒸馏架构的先前方法,我们的方法使用伪任务来明确模拟下游上下文场景,这是受元学习原理的启发。为了在无标签数据上进行后训练,我们提出了一种自动生成上下文任务的机制,它结合了预训练的扩散模型和视觉编码器本身。DIP简单、无监督、计算高效,在单个A100 GPU上耗时不到9小时。它通过伪上下文任务学习密集表示,在多种下游现实场景理解任务中表现出强大的性能。它优于初始的视觉编码器和先前的方法,为改进密集表示提供了实用有效的解决方案。代码可在https://github.com/sirkosophia/DIP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种新型无监督后训练法DIP,旨在增强大规模预训练视觉编码器的密集图像表示,以提升对上下文场景的理解。该方法通过模拟下游上下文场景生成伪任务,受元学习原理启发,训练视觉编码器。使用预训练的扩散模型和视觉编码器本身生成上下文任务,实现无监督的后训练。DIP方法简单、高效,在单个A100 GPU上不到9小时即可完成。通过学习密集表示,在多种下游现实场景理解任务中表现优异,优于初始视觉编码器和先前方法。
Key Takeaways
- DIP是一种新型无监督后训练法,旨在增强视觉编码器的密集图像表示,提升对上下文场景的理解。
- 该方法通过模拟下游上下文场景生成伪任务进行训练,受元学习原理启发。
- DIP使用预训练的扩散模型和视觉编码器本身结合,自动生成上下文任务,实现无监督的后训练。
- DIP具有简单、高效的特点,计算成本低,适用于大规模图像数据处理。
- DIP在多种下游现实场景理解任务中表现优异,包括图像分类、目标检测等。
- DIP方法优于初始视觉编码器和先前方法,为改善密集表示提供了实用有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

CPAM: Context-Preserving Adaptive Manipulation for Zero-Shot Real Image Editing
Authors:Dinh-Khoi Vo, Thanh-Toan Do, Tam V. Nguyen, Minh-Triet Tran, Trung-Nghia Le
Editing natural images using textual descriptions in text-to-image diffusion models remains a significant challenge, particularly in achieving consistent generation and handling complex, non-rigid objects. Existing methods often struggle to preserve textures and identity, require extensive fine-tuning, and exhibit limitations in editing specific spatial regions or objects while retaining background details. This paper proposes Context-Preserving Adaptive Manipulation (CPAM), a novel zero-shot framework for complicated, non-rigid real image editing. Specifically, we propose a preservation adaptation module that adjusts self-attention mechanisms to preserve and independently control the object and background effectively. This ensures that the objects’ shapes, textures, and identities are maintained while keeping the background undistorted during the editing process using the mask guidance technique. Additionally, we develop a localized extraction module to mitigate the interference with the non-desired modified regions during conditioning in cross-attention mechanisms. We also introduce various mask-guidance strategies to facilitate diverse image manipulation tasks in a simple manner. Extensive experiments on our newly constructed Image Manipulation BenchmArk (IMBA), a robust benchmark dataset specifically designed for real image editing, demonstrate that our proposed method is the preferred choice among human raters, outperforming existing state-of-the-art editing techniques.
在文本到图像的扩散模型中,使用文本描述编辑自然图像仍然是一个重大挑战,特别是在实现一致生成和处理复杂、非刚性物体方面。现有方法往往难以保留纹理和身份,需要大量微调,并且在编辑特定空间区域或物体时保留背景细节方面存在局限性。本文提出了上下文保留自适应操作(CPAM),这是一种用于复杂、非刚性的真实图像编辑的新型零样本框架。具体来说,我们提出了一个保留适应模块,该模块调整自注意力机制,以有效地保留并独立控制物体和背景。这确保了物体的形状、纹理和身份得以保持,同时在编辑过程中使用遮罩指导技术保持背景不变形。此外,我们开发了一个局部提取模块,以减轻交叉注意力机制中条件设置时非期望修改区域的干扰。我们还介绍了各种遮罩指导策略,以简单的方式促进各种图像操作任务。在我们新构建的图像操作基准测试(IMBA)上的大量实验表明,与人类评估者相比,我们提出的方法是首选,超越了现有的先进编辑技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为CPAM的零样本框架,用于复杂、非刚性的真实图像编辑。该框架通过调整自我关注机制,实现了对象与背景的有效独立控制,从而在编辑过程中保持对象和背景的一致性。使用mask指导技术,能够在保持背景不变的同时,保持对象的形状、纹理和身份。此外,还引入了多种mask指导策略,以简化各种图像操作任务。在专门设计的真实图像编辑基准数据集IMBA上进行的大量实验表明,该方法在人类评估中表现优异,超越了现有的先进编辑技术。
Key Takeaways
- CPAM是一个用于复杂、非刚性真实图像编辑的零样本框架。
- 框架通过调整自我关注机制,实现了对象和背景的有效独立控制。
- 使用mask指导技术,能够在编辑过程中保持对象的形状、纹理和身份。
- 引入了多种mask指导策略,以简化图像操作任务。
- 提出了一个新建的真实图像编辑基准数据集IMBA。
- 实验结果表明,CPAM在人类评估中表现优异。
- CPAM超越了现有的先进编辑技术。
点此查看论文截图



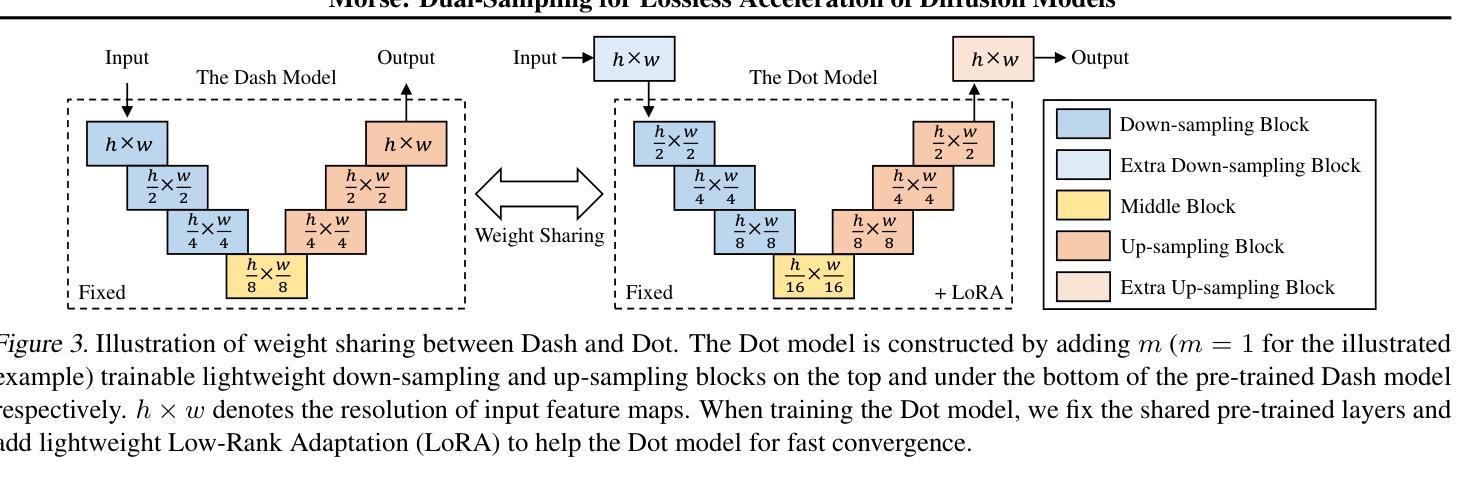
Morse: Dual-Sampling for Lossless Acceleration of Diffusion Models
Authors:Chao Li, Jiawei Fan, Anbang Yao
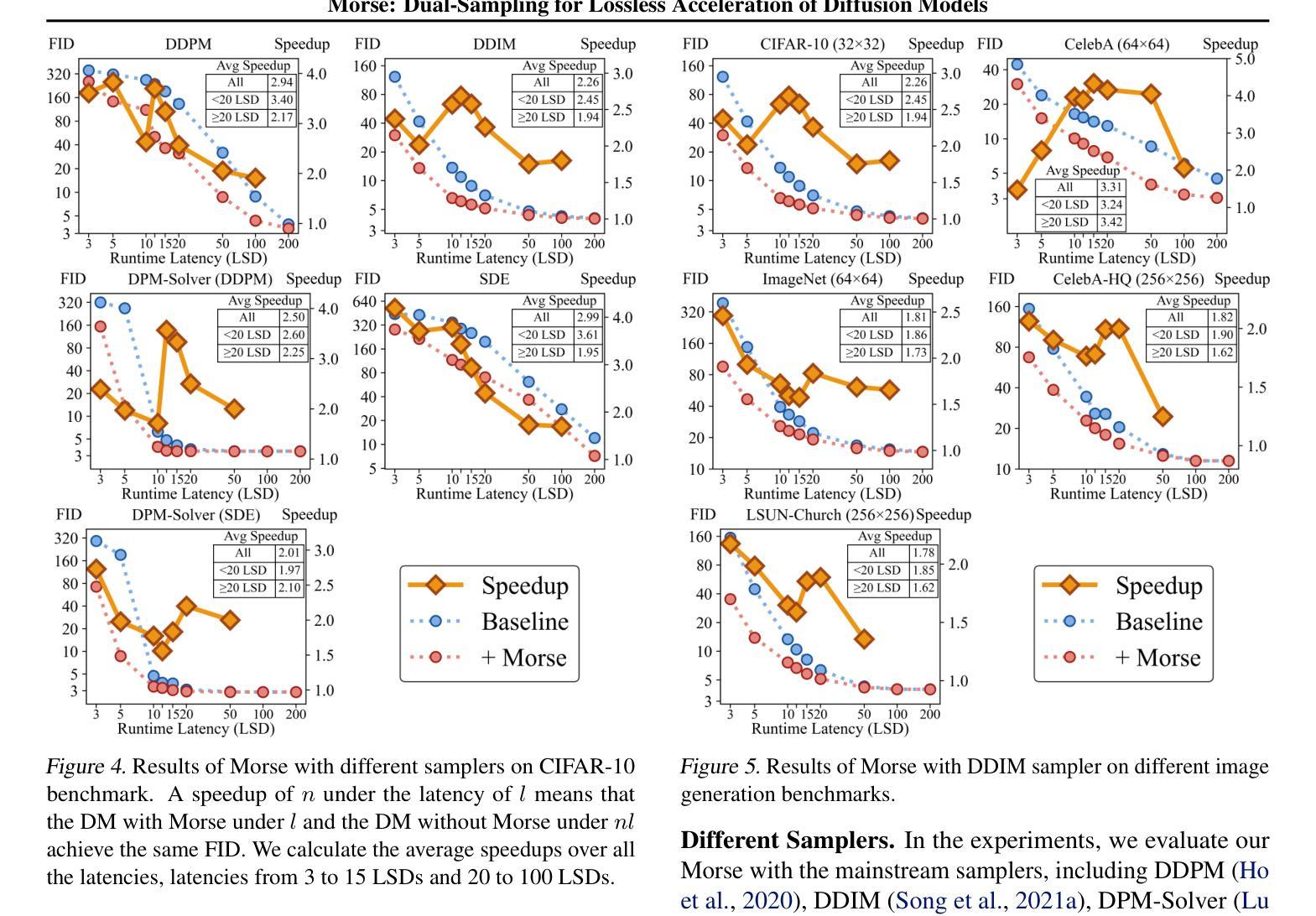
In this paper, we present Morse, a simple dual-sampling framework for accelerating diffusion models losslessly. The key insight of Morse is to reformulate the iterative generation (from noise to data) process via taking advantage of fast jump sampling and adaptive residual feedback strategies. Specifically, Morse involves two models called Dash and Dot that interact with each other. The Dash model is just the pre-trained diffusion model of any type, but operates in a jump sampling regime, creating sufficient space for sampling efficiency improvement. The Dot model is significantly faster than the Dash model, which is learnt to generate residual feedback conditioned on the observations at the current jump sampling point on the trajectory of the Dash model, lifting the noise estimate to easily match the next-step estimate of the Dash model without jump sampling. By chaining the outputs of the Dash and Dot models run in a time-interleaved fashion, Morse exhibits the merit of flexibly attaining desired image generation performance while improving overall runtime efficiency. With our proposed weight sharing strategy between the Dash and Dot models, Morse is efficient for training and inference. Our method shows a lossless speedup of 1.78X to 3.31X on average over a wide range of sampling step budgets relative to 9 baseline diffusion models on 6 image generation tasks. Furthermore, we show that our method can be also generalized to improve the Latent Consistency Model (LCM-SDXL, which is already accelerated with consistency distillation technique) tailored for few-step text-to-image synthesis. The code and models are available at https://github.com/deep-optimization/Morse.
本文介绍了Morse,这是一个简单的高效无损扩散模型双采样框架。Morse的关键洞察力是通过利用快速跳跃采样和自适应残差反馈策略来重新制定迭代生成(从噪声到数据)过程。具体来说,Morse包含两个相互作用的模型,称为Dash和Dot。Dash模型只是任何类型的预训练扩散模型,但在跳跃采样机制下运行,为采样效率改进创造了足够空间。Dot模型显著快于Dash模型,它学会根据Dash模型轨迹当前跳跃采样点的观察生成残差反馈,将噪声估计提升到无需跳跃采样的下一步估计,与Dash模型的估计相匹配。通过以时间交错方式链接Dash和Dot模型的输出,Morse在灵活实现所需的图像生成性能的同时,提高了总体运行效率。通过我们在Dash和Dot模型之间提出的权重共享策略,Morse在训练和推理方面都很高效。我们的方法在采样步骤预算方面相对于9个基线扩散模型在6个图像生成任务上平均无损加速1.78X至3.31X。此外,我们还证明了我们方法可以推广到改进针对少步骤文本到图像合成的Latent Consistency Model(LCM-SDXL,已经使用一致性蒸馏技术加速)。代码和模型可在https://github.com/deep-optimization/Morse获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work is accepted to ICML 2025. The project page: https://github.com/deep-optimization/Morse
Summary
本文介绍了名为Morse的加速扩散模型框架,它通过采用双采样策略和自适应残差反馈策略来优化迭代生成过程。Morse包含两个相互作用的模型:Dash和Dot。Dash模型是任何类型的预训练扩散模型,采用跳跃采样机制以提高采样效率。Dot模型比Dash模型更快,学会根据Dash模型的当前跳跃采样点生成残差反馈,从而更容易匹配下一步估计。通过交替使用Dash和Dot模型的输出,Morse在提高运行效率的同时灵活实现图像生成性能。此外,Morse还采用权重共享策略,提高了训练和推理效率。在广泛的采样步长预算范围内,相对于9种基线扩散模型,Morse在6项图像生成任务上的平均无损加速达到1.78X至3.31X。此外,该方法还可以推广到用于少步骤文本到图像合成的LCM-SDXL模型的加速。
Key Takeaways
- Morse是一个用于加速扩散模型的简单双采样框架,能无损地提高图像生成效率。
- Morse包含两个模型:Dash和Dot,分别负责不同的采样和反馈生成任务。
- Morse利用跳跃采样和自适应残差反馈策略优化迭代生成过程。
- Morse通过交替使用Dash和Dot模型的输出,实现了图像生成性能和运行效率的提升。
- Morse采用权重共享策略,提高了训练和推理效率。
- Morse相对于多种基线扩散模型,在多项图像生成任务上实现了平均无损加速。
点此查看论文截图


CDG-MAE: Learning Correspondences from Diffusion Generated Views
Authors:Varun Belagali, Pierre Marza, Srikar Yellapragada, Zilinghan Li, Tarak Nath Nandi, Ravi K Madduri, Joel Saltz, Stergios Christodoulidis, Maria Vakalopoulou, Dimitris Samaras
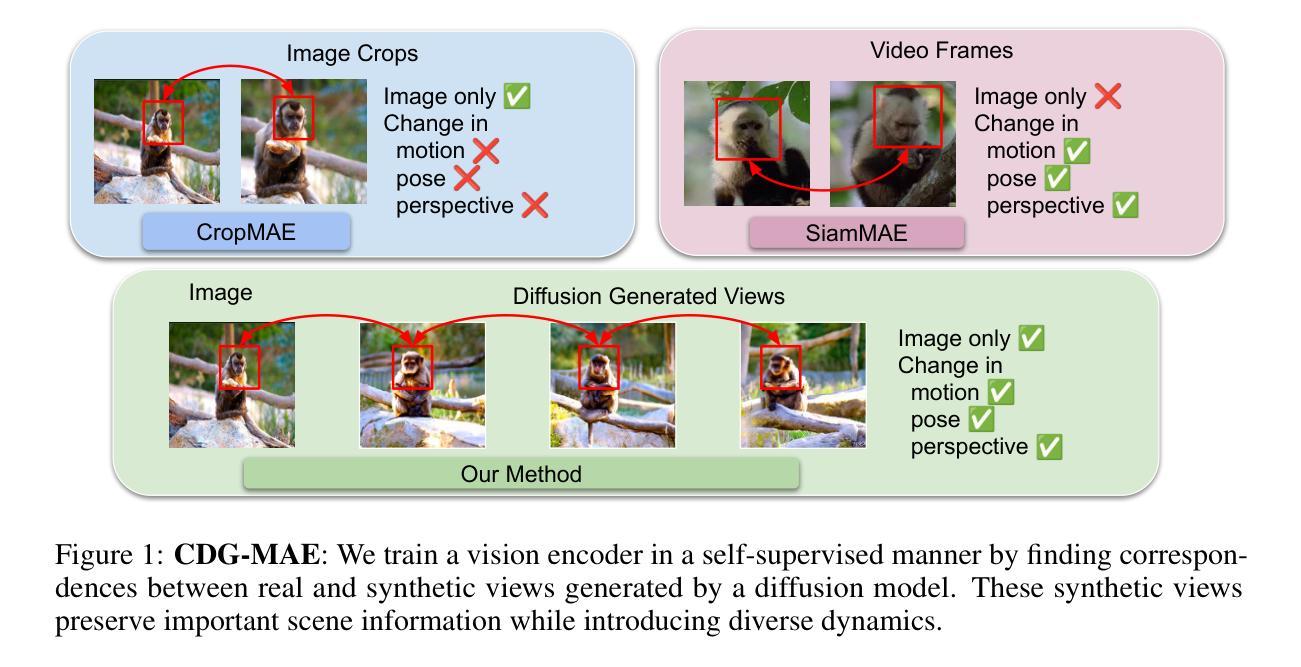
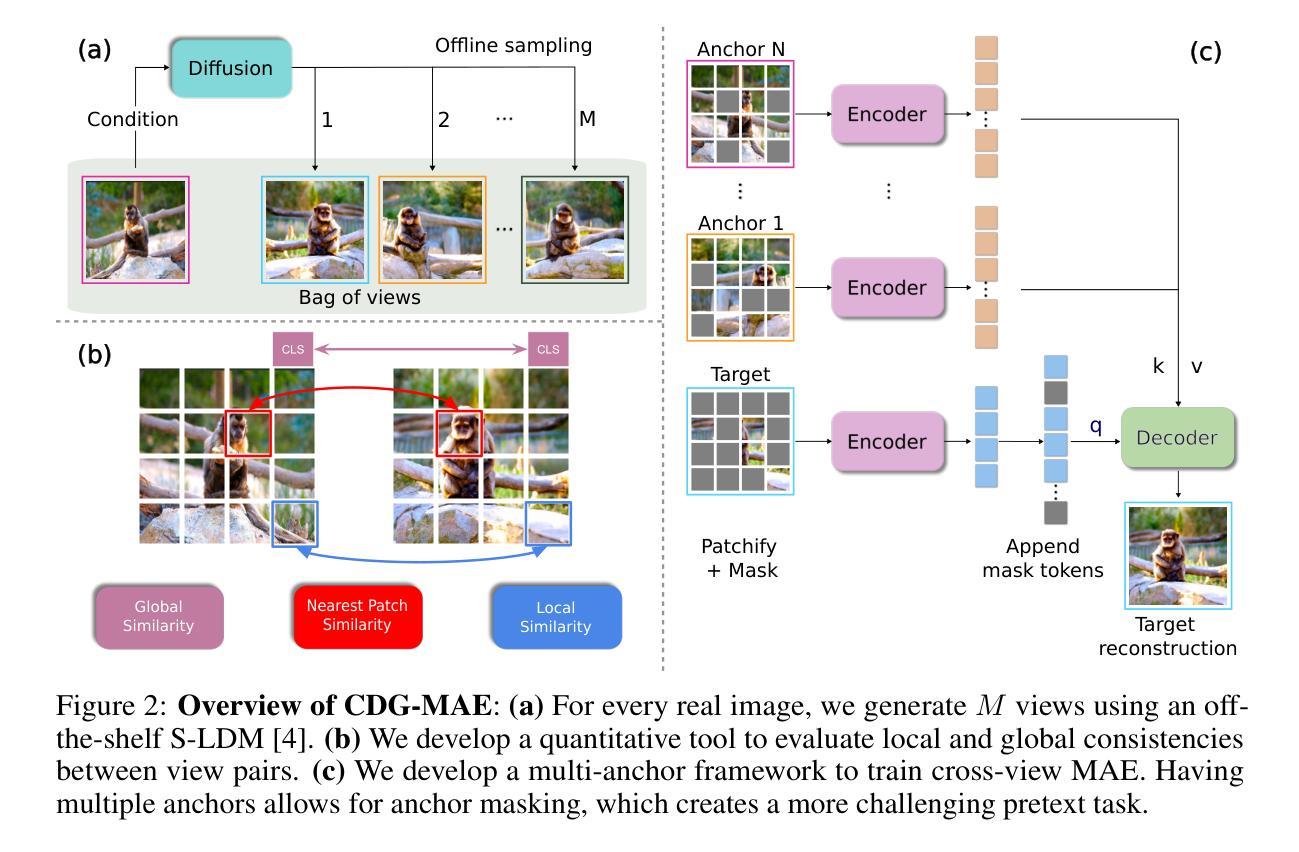
Learning dense correspondences, critical for application such as video label propagation, is hindered by tedious and unscalable manual annotation. Self-supervised methods address this by using a cross-view pretext task, often modeled with a masked autoencoder, where a masked target view is reconstructed from an anchor view. However, acquiring effective training data remains a challenge - collecting diverse video datasets is difficult and costly, while simple image crops lack necessary pose variations. This paper introduces CDG-MAE, a novel MAE-based self-supervised method that uses diverse synthetic views generated from static images via an image-conditioned diffusion model. These generated views exhibit substantial changes in pose and perspective, providing a rich training signal that overcomes the limitations of video and crop-based anchors. We present a quantitative method to evaluate local and global consistency of generated images, discussing their use for cross-view self-supervised pretraining. Furthermore, we enhance the standard single-anchor MAE setting to a multi-anchor strategy to effectively modulate the difficulty of pretext task. CDG-MAE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art MAE methods reliant only on images and substantially narrows the performance gap to video-based approaches.
学习密集对应关系对于视频标签传播等应用至关重要,但繁琐且不可扩展的手动注释阻碍了其学习。自监督方法通过使用跨视图预训练任务来解决这个问题,通常使用掩码自动编码器进行建模,其中从锚视图重建掩码的目标视图。然而,获取有效的训练数据仍然是一个挑战——收集多样化的视频数据集既困难又成本高昂,而简单的图像裁剪缺乏必要的姿势变化。本文介绍了CDG-MAE,这是一种基于MAE的新型自监督方法,它使用图像条件扩散模型从静态图像生成多样化的合成视图。这些生成的视图在姿势和视角上表现出重大变化,提供了丰富的训练信号,克服了基于视频和裁剪锚点的局限性。我们提出了一种定量方法,以评估生成图像的地方和全球一致性,并讨论它们在跨视图自监督预训练中的使用。此外,我们将标准单锚点MAE设置增强为多锚点策略,以有效地调节预训练任务的难度。CDG-MAE显著优于仅依赖图像的最新MAE方法,并大幅缩小了与基于视频的方法的性能差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于自监督学习的密集对应学习方法CDG-MAE,通过图像条件扩散模型生成多样的合成视图,解决了视频标签传播等应用中手动标注的繁琐和不可扩展的问题。该方法利用静态图像生成具有显著姿势和视角变化的视图,提供丰富的训练信号,克服了视频和基于裁剪的锚点方法的局限性。同时,本文还提出了一种评估生成图像局部和全局一致性的定量方法,并讨论了它们在跨视图自监督预训练中的应用。此外,还增强了标准单锚点MAE设置,采用多锚点策略,以有效调整先验任务的难度。CDG-MAE显著优于仅依赖图像的最新MAE方法,并大大缩小了与基于视频的方法之间的性能差距。
Key Takeaways
- CDG-MAE是一种基于自监督学习的密集对应学习方法,解决了视频标签传播中的繁琐手动标注问题。
- 利用图像条件扩散模型生成多样合成视图,这些视图具有显著变化的姿势和视角。
- 生成图像具有丰富训练信号,克服视频和基于裁剪锚点的局限性。
- 提出一种定量评估生成图像局部和全局一致性的方法。
- 讨论了生成图像在跨视图自监督预训练中的应用。
- 增强了标准单锚点MAE设置,采用多锚点策略以有效调整先验任务难度。
点此查看论文截图

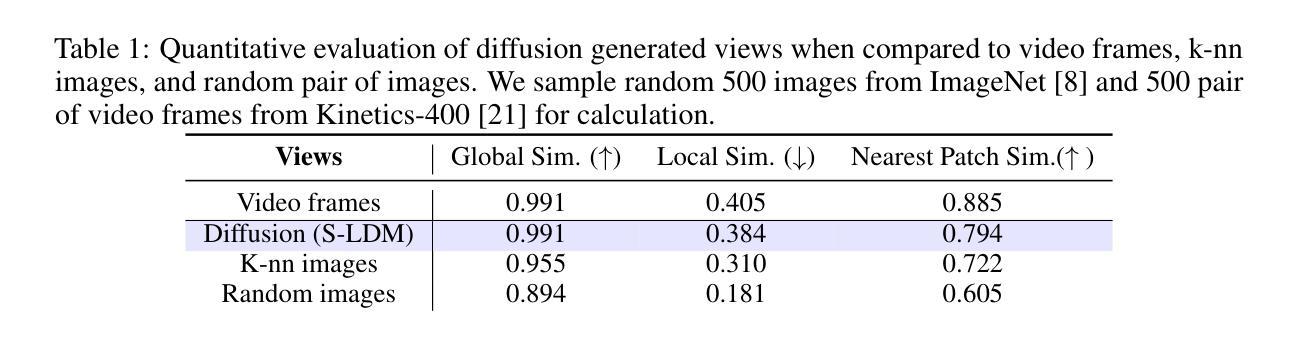
Enabling PSO-Secure Synthetic Data Sharing Using Diversity-Aware Diffusion Models
Authors:Mischa Dombrowski, Bernhard Kainz
Synthetic data has recently reached a level of visual fidelity that makes it nearly indistinguishable from real data, offering great promise for privacy-preserving data sharing in medical imaging. However, fully synthetic datasets still suffer from significant limitations: First and foremost, the legal aspect of sharing synthetic data is often neglected and data regulations, such as the GDPR, are largley ignored. Secondly, synthetic models fall short of matching the performance of real data, even for in-domain downstream applications. Recent methods for image generation have focused on maximising image diversity instead of fidelity solely to improve the mode coverage and therefore the downstream performance of synthetic data. In this work, we shift perspective and highlight how maximizing diversity can also be interpreted as protecting natural persons from being singled out, which leads to predicate singling-out (PSO) secure synthetic datasets. Specifically, we propose a generalisable framework for training diffusion models on personal data which leads to unpersonal synthetic datasets achieving performance within one percentage point of real-data models while significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods that do not ensure privacy. Our code is available at https://github.com/MischaD/Trichotomy.
合成数据最近已经达到了视觉保真度的水平,使其几乎无法与真实数据区分开,这在医学影像的隐私保护数据共享方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,完全合成数据集仍存在重大局限性:首先,合成数据的共享方面的法律常常被忽视,数据法规(如GDPR)在很大程度上被忽略。其次,合成模型在匹配真实数据性能方面还存在不足,即使在域内下游应用中也是如此。最近的图像生成方法主要关注最大化图像多样性而非仅仅提高保真度,以此来提高合成数据的模式覆盖率和下游性能。在这项工作中,我们改变了视角并强调了如何最大化多样性也可以被解释为保护自然人免受个别对待,从而导致谓语单一化(PSO)安全的合成数据集。具体来说,我们提出了一个通用的训练扩散模型个人数据的框架,该框架生成的无个人信息的合成数据集的性能与真实数据模型相差不到一个百分点,同时显著优于不能保证隐私的最新方法。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/MischaD/Trichotomy 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出合成数据在视觉保真度方面已经达到近乎无法分辨真伪的水平,对于医学影像等隐私保护领域的数据共享具有巨大潜力。然而,合成数据集仍存在法律忽视和数据性能匹配不足等局限性。研究团队提出了一种基于扩散模型的通用框架,旨在训练个人数据上的合成数据集,在保护个人隐私的同时实现与真实数据模型相近的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 合成数据在视觉保真度上已接近真实数据水平,为隐私保护领域的数据共享带来巨大潜力。
- 目前合成数据集面临法律和性能匹配问题,例如忽视数据法规(如GDPR)以及模型性能与真实数据存在差距。
- 近期图像生成方法侧重于最大化图像多样性以提高合成数据的下游性能,但可能忽视了保真度的重要性。
- 研究团队提出了一个基于扩散模型的通用框架,该框架旨在训练合成数据集以实现隐私保护。
- 该框架在保护个人隐私的同时,实现了与真实数据模型相近的性能表现,且在性能上显著优于未确保隐私的现有方法。
- 合成数据在确保隐私的同时可以提升模型性能,对医学影像等领域的数据共享具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

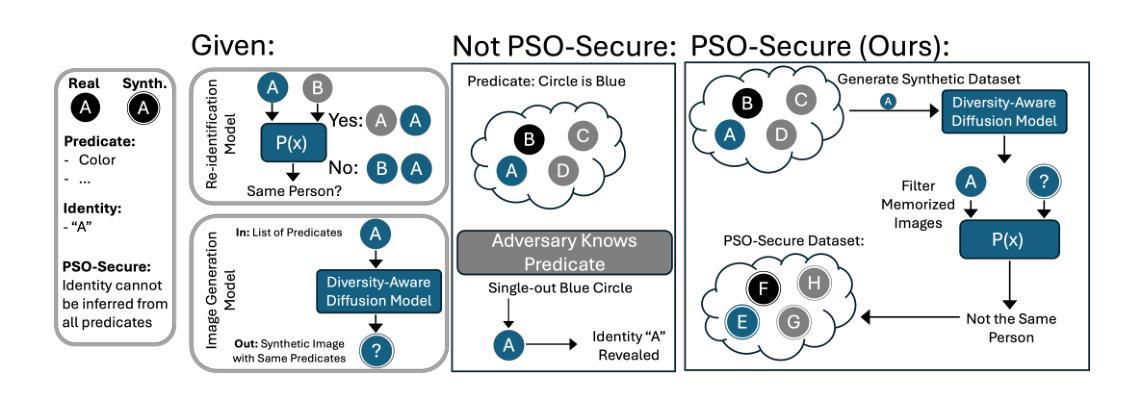
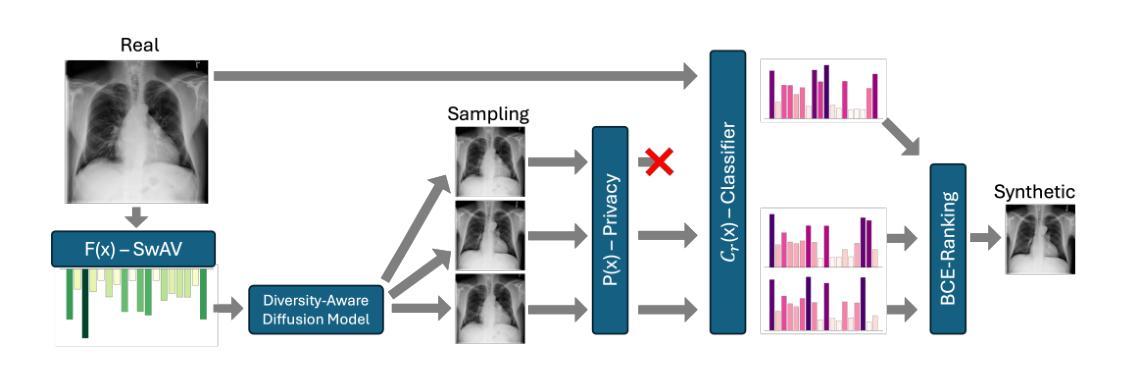
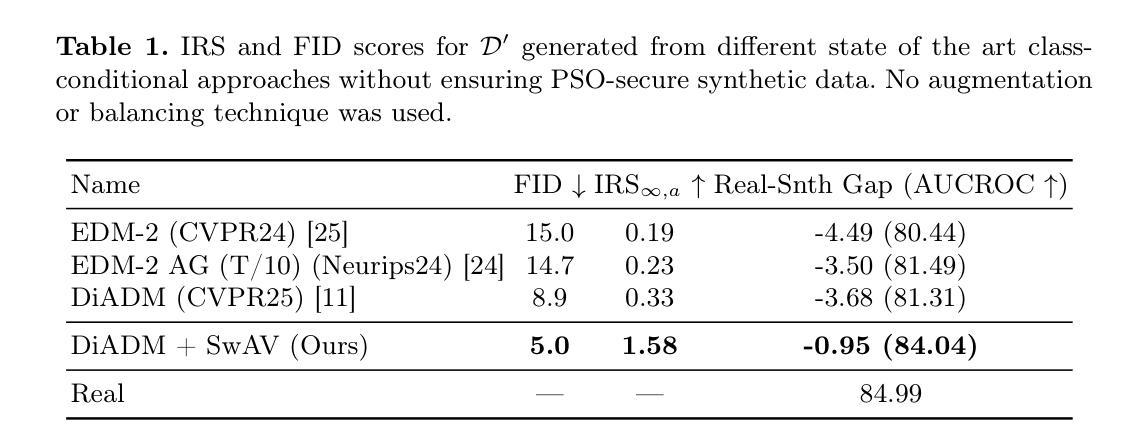
Programmable-Room: Interactive Textured 3D Room Meshes Generation Empowered by Large Language Models
Authors:Jihyun Kim, Junho Park, Kyeongbo Kong, Suk-Ju Kang
We present Programmable-Room, a framework which interactively generates and edits a 3D room mesh, given natural language instructions. For precise control of a room’s each attribute, we decompose the challenging task into simpler steps such as creating plausible 3D coordinates for room meshes, generating panorama images for the texture, constructing 3D meshes by integrating the coordinates and panorama texture images, and arranging furniture. To support the various decomposed tasks with a unified framework, we incorporate visual programming (VP). VP is a method that utilizes a large language model (LLM) to write a Python-like program which is an ordered list of necessary modules for the various tasks given in natural language. We develop most of the modules. Especially, for the texture generating module, we utilize a pretrained large-scale diffusion model to generate panorama images conditioned on text and visual prompts (i.e., layout, depth, and semantic map) simultaneously. Specifically, we enhance the panorama image generation quality by optimizing the training objective with a 1D representation of a panorama scene obtained from bidirectional LSTM. We demonstrate Programmable-Room’s flexibility in generating and editing 3D room meshes, and prove our framework’s superiority to an existing model quantitatively and qualitatively. Project page is available in https://jihyun0510.github.io/Programmable_Room_Page/.
我们推出了Programmable-Room,这是一个框架,可以根据自然语言指令交互地生成和编辑3D房间网格。为了精确控制房间的每个属性,我们将复杂的任务分解为更简单的步骤,例如为房间网格创建合理的3D坐标、为纹理生成全景图像、通过整合坐标和全景纹理图像构建3D网格,以及布置家具。为了用一个统一的框架来支持各种分解任务,我们引入了可视化编程(VP)。VP是一种利用大型语言模型(LLM)来编写类似于Python的程序的方法,该程序是根据自然语言给出的各种任务所需的必要模块的有序列表。我们开发了大部分的模块。特别是纹理生成模块,我们利用预训练的大型扩散模型来根据文本和视觉提示(即布局、深度和语义地图)同时生成全景图像。具体来说,我们通过优化训练目标,使用一个从双向LSTM获得的全景场景的一维表示,提高了全景图像生成的品质。我们展示了Programmable-Room在生成和编辑3D房间网格方面的灵活性,并从定量和定性的角度证明了我们的框架对现有模型的优越性。项目页面可在https://jihyun0510.github.io/Programmable_Room_Page/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Summary
该程序提出了一个名为Programmable-Room的框架,该框架能够根据自然语言指令交互式地生成和编辑3D房间网格。通过分解任务,实现对房间每个属性的精确控制,如生成房间网格的3D坐标、纹理的全景图像生成、结合坐标和全景纹理图像构建3D网格以及家具布置等。为支持各项分解任务,该程序结合了可视化编程(VP)技术。VP利用大型语言模型(LLM)编写Python类程序,以有序列表的形式呈现各种任务所需的模块,并根据自然语言进行划分。该程序大部分模块为自主开发,其中纹理生成模块利用预训练的大型扩散模型,根据文本和视觉提示(如布局、深度和语义地图)生成全景图像。通过优化训练目标,提高了全景图像生成质量。Programmable-Room展现了生成和编辑3D房间网格的灵活性,并在定量和定性方面证明了其框架的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Programmable-Room框架能基于自然语言指令生成和编辑3D房间网格。
- 通过分解任务,框架能精确控制房间的每个属性,包括3D坐标、纹理全景图像、3D网格构建和家具布局。
- 框架结合了可视化编程技术,利用大型语言模型处理自然语言指令。
- 纹理生成模块采用预训练的大型扩散模型,能基于文本和视觉提示生成全景图像。
- 通过优化训练目标,提高了全景图像生成的品质。
- Programmable-Room展现了生成和编辑3D房间网格的灵活性。
- 与现有模型相比,Programmable-Room框架在定量和定性方面表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

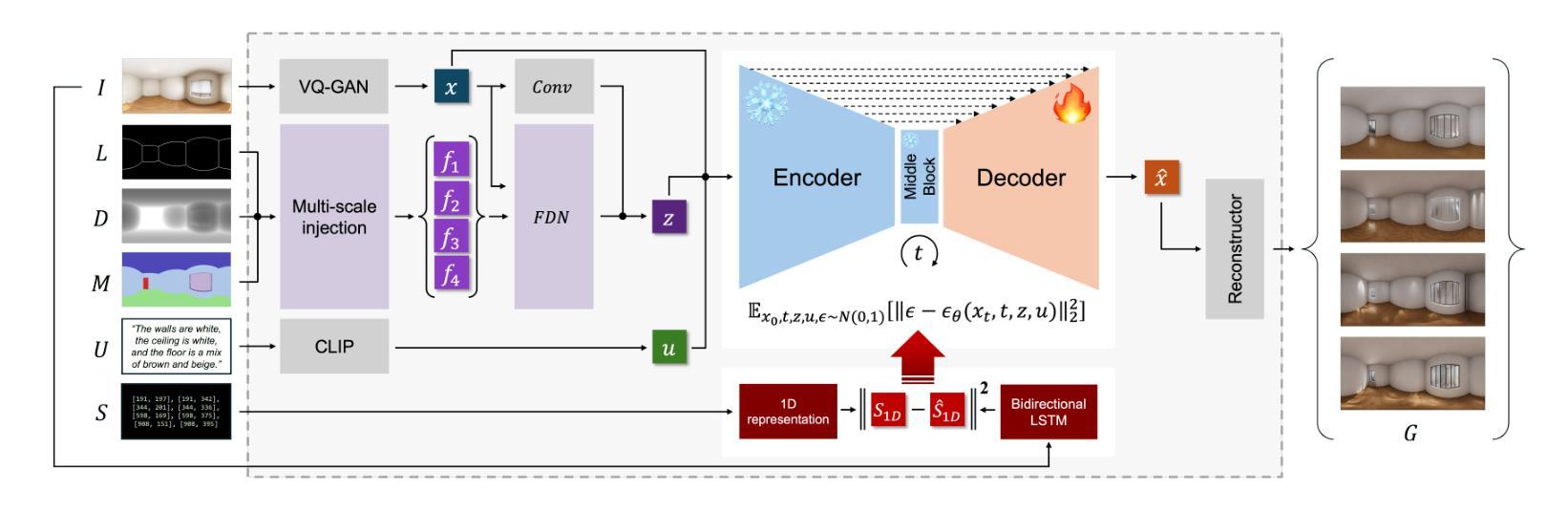
DreamJourney: Perpetual View Generation with Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Bo Pan, Yang Chen, Yingwei Pan, Ting Yao, Wei Chen, Tao Mei
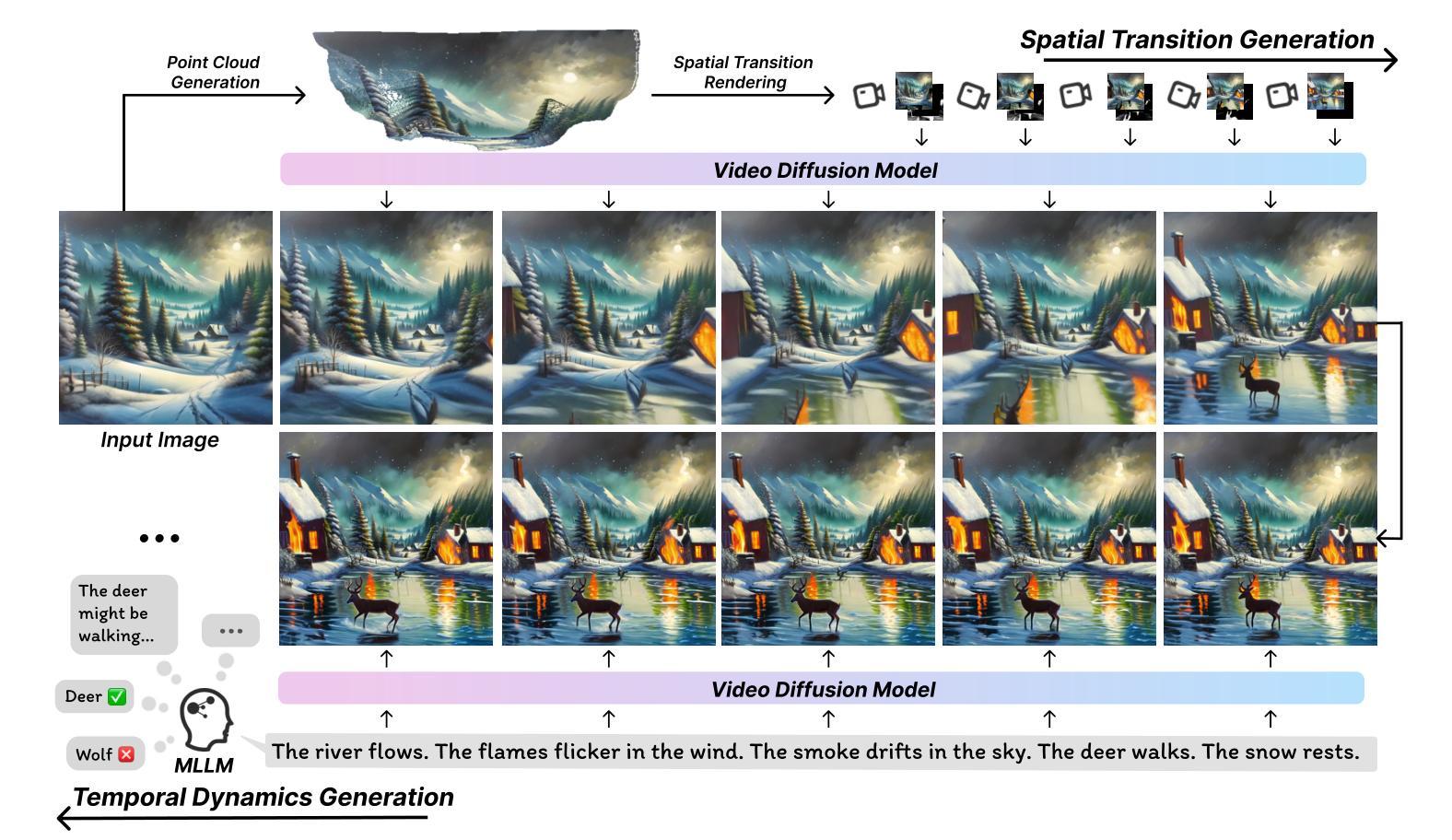
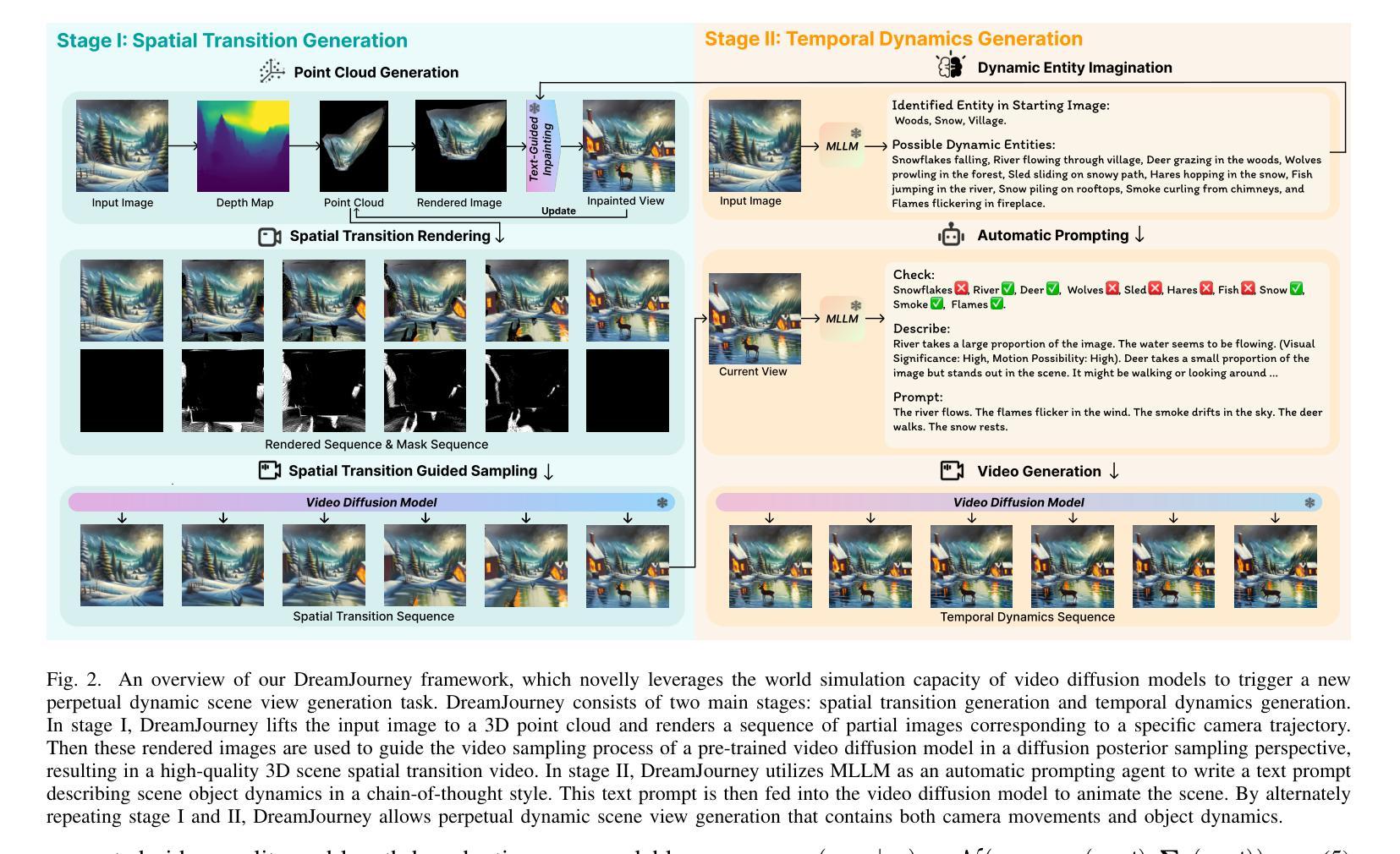
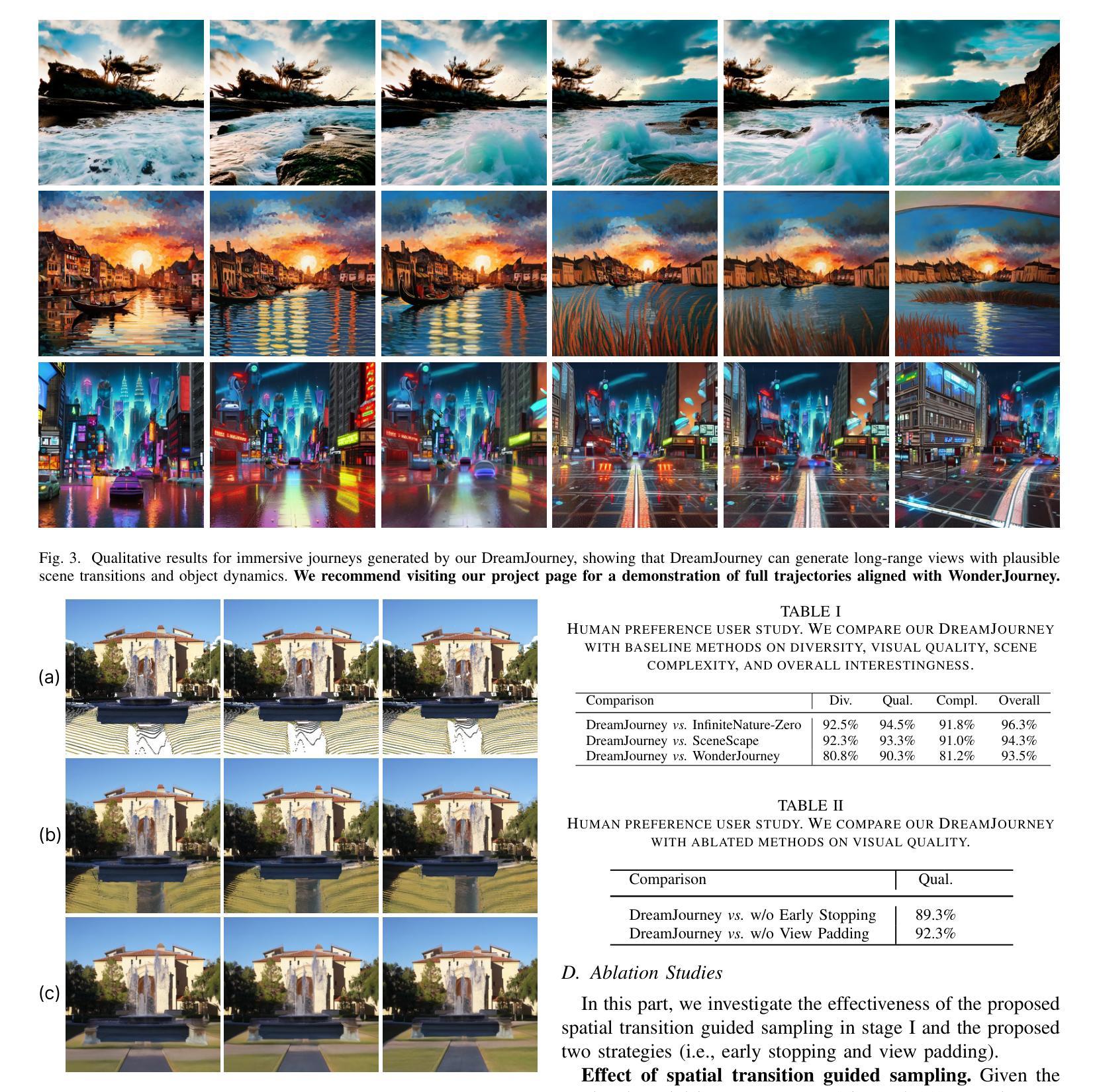
Perpetual view generation aims to synthesize a long-term video corresponding to an arbitrary camera trajectory solely from a single input image. Recent methods commonly utilize a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model to synthesize new content of previously unseen regions along camera movement. However, the underlying 2D diffusion model lacks 3D awareness and results in distorted artifacts. Moreover, they are limited to generating views of static 3D scenes, neglecting to capture object movements within the dynamic 4D world. To alleviate these issues, we present DreamJourney, a two-stage framework that leverages the world simulation capacity of video diffusion models to trigger a new perpetual scene view generation task with both camera movements and object dynamics. Specifically, in stage I, DreamJourney first lifts the input image to 3D point cloud and renders a sequence of partial images from a specific camera trajectory. A video diffusion model is then utilized as generative prior to complete the missing regions and enhance visual coherence across the sequence, producing a cross-view consistent video adheres to the 3D scene and camera trajectory. Meanwhile, we introduce two simple yet effective strategies (early stopping and view padding) to further stabilize the generation process and improve visual quality. Next, in stage II, DreamJourney leverages a multimodal large language model to produce a text prompt describing object movements in current view, and uses video diffusion model to animate current view with object movements. Stage I and II are repeated recurrently, enabling perpetual dynamic scene view generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our DreamJourney over state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively. Our project page: https://dream-journey.vercel.app.
持续视图生成旨在从单个输入图像合成与任意相机轨迹相对应的长视频。最近的方法通常利用预先训练的文本到图像的扩散模型,来合成相机移动时先前未见区域的新内容。然而,基本的二维扩散模型缺乏三维意识,导致失真伪影。此外,它们仅限于生成静态三维场景的观点,忽略了捕捉动态四维世界中的物体运动。为了缓解这些问题,我们推出了DreamJourney,这是一个两阶段框架,利用视频扩散模型的世界模拟能力,触发新的持续场景视图生成任务,包括相机运动和物体动力学。具体来说,在第一阶段,DreamJourney首先将输入图像提升到三维点云,并从特定的相机轨迹渲染一系列部分图像。视频扩散模型被用作生成先验,以完成缺失的区域,增强序列中的视觉连贯性,产生符合三维场景和相机轨迹的跨视图一致视频。同时,我们引入了两个简单有效的策略(早期停止和视图填充)来进一步稳定生成过程,提高视觉质量。接下来,在第二阶段,DreamJourney利用多模态大型语言模型生成描述当前视图中物体运动的文本提示,并使用视频扩散模型使当前视图与物体运动相结合。阶段一和阶段二反复进行,实现了持续的动态场景视图生成。大量实验表明,我们的DreamJourney在定量和定性上均优于最先进的方法。我们的项目页面:https://dream-journey.vercel.app。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了利用视频扩散模型进行无限动态场景视图生成的技术。首先通过阶段一将输入图像提升到三维点云,并从特定相机轨迹渲染一系列部分图像,使用视频扩散模型完成缺失区域并增强序列的视觉连贯性,产生遵循三维场景和相机轨迹的跨视图一致视频。阶段二则利用多模态大型语言模型生成描述当前视图对象运动的文本提示,并使用视频扩散模型进行动画生成。两个阶段的重复进行,实现了持续的动态场景视图生成。
Key Takeaways
- 该技术利用视频扩散模型合成与相机轨迹相对应的长视频,仅从单张输入图像开始。
- 现有方法主要使用预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型来合成新的内容,但缺乏三维意识,导致失真和忽略对象动态的问题。
- 提出的DreamJourney框架包含两个阶段,第一阶段将输入图像提升到三维点云并渲染一系列部分图像,然后使用视频扩散模型完成缺失区域并增强视觉连贯性。
- 第二阶段利用多模态大型语言模型和视频扩散模型来生成和动画化当前视图的对象运动。
- 通过重复两个阶段,DreamJourney能实现持续的动态场景视图生成。
- 引入两种策略(早期停止和视图填充)来进一步稳定生成过程并提高视觉质量。
点此查看论文截图

Exploring Strategies for Personalized Radiation Therapy Part II Predicting Tumor Drift Patterns with Diffusion Models
Authors:Hao Peng, Steve Jiang, Robert Timmerman
Radiation therapy outcomes are decided by two key parameters, dose and timing, whose best values vary substantially across patients. This variability is especially critical in the treatment of brain cancer, where fractionated or staged stereotactic radiosurgery improves safety compared to single fraction approaches, but complicates the ability to predict treatment response. To address this challenge, we employ Personalized Ultra-fractionated Stereotactic Adaptive Radiotherapy (PULSAR), a strategy that dynamically adjusts treatment based on how each tumor evolves over time. However, the success of PULSAR and other adaptive approaches depends on predictive tools that can guide early treatment decisions and avoid both overtreatment and undertreatment. However, current radiomics and dosiomics models offer limited insight into the evolving spatial and temporal patterns of tumor response. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel framework using Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM), which learns data-driven mappings from pre to post treatment imaging. In this study, we developed single step and iterative denoising strategies and compared their performance. The results show that diffusion models can effectively simulate patient specific tumor evolution and localize regions associated with treatment response. The proposed strategy provides a promising foundation for modeling heterogeneous treatment response and enabling early, adaptive interventions, paving the way toward more personalized and biologically informed radiotherapy.
放疗效果由剂量和时间两个关键参数决定,最佳值在不同患者之间有很大的差异。这种差异在脑癌的治疗中尤其关键,分段或分期立体定向放射手术与单次分割方法相比提高了安全性,但预测治疗反应的难度增加。为了应对这一挑战,我们采用了个性化超分段立体定向自适应放疗(PULSAR)策略,该策略根据每个肿瘤的随时间演变情况动态调整治疗。然而,PULSAR和其他自适应方法的成功取决于能够指导早期治疗决策并避免过度治疗和不足治疗的预测工具。然而,当前的放射组学和剂量组学模型对肿瘤反应不断变化的时空模式提供的洞察有限。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了一种使用去噪扩散隐式模型(DDIM)的新框架,该框架学习从治疗前到治疗后的成像数据驱动映射。在这项研究中,我们开发了单步和迭代去噪策略,并比较了它们的性能。结果表明,扩散模型可以有效地模拟患者特定的肿瘤演变,并定位与治疗反应相关的区域。所提出的策略为模拟异质治疗反应和实现早期自适应干预提供了有前途的基础,为更个性化和生物学信息驱动的放射治疗铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
辐射治疗结果取决于剂量和时间两个关键参数,其最佳值在不同患者间差异显著。在治疗脑癌时,这种差异性尤为关键。为应对挑战,我们采用个性化超分割立体定向自适应放疗(PULSAR)策略,根据肿瘤随时间的变化动态调整治疗。但PULSAR等自适应策略的成功取决于能指导早期治疗决策、避免过度或不足治疗的预测工具。当前放射组学和剂量组学模型对肿瘤反应的空间和时间模式了解有限。为克服这些局限,我们提出使用去噪扩散隐模型(DDIM)的新框架,学习从治疗前到治疗后的成像数据驱动映射。研究结果显示,扩散模型能有效模拟患者特定肿瘤演变,定位与治疗反应相关的区域。该策略为实现个性化、生物学信息支持的放射治疗铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways:
- 辐射治疗结果受剂量和时间参数影响,最佳值因患者而异。
- 在脑癌治疗中,分割或分期立体定向放射手术提高了安全性,但预测治疗反应的能力复杂化。
- PULSAR策略根据肿瘤变化动态调整治疗。
- 当前放射组学和剂量组学模型对肿瘤反应的空间和时间模式了解有限。
- 去噪扩散隐模型(DDIM)能有效模拟患者特定肿瘤演变。
- 扩散模型能定位与治疗反应相关的区域。
点此查看论文截图

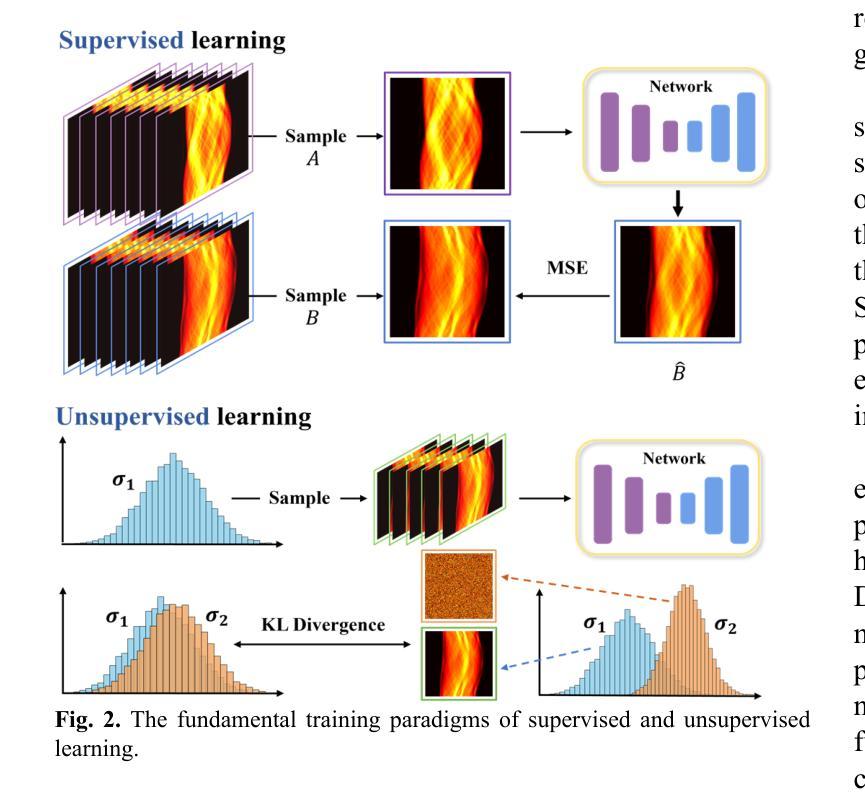
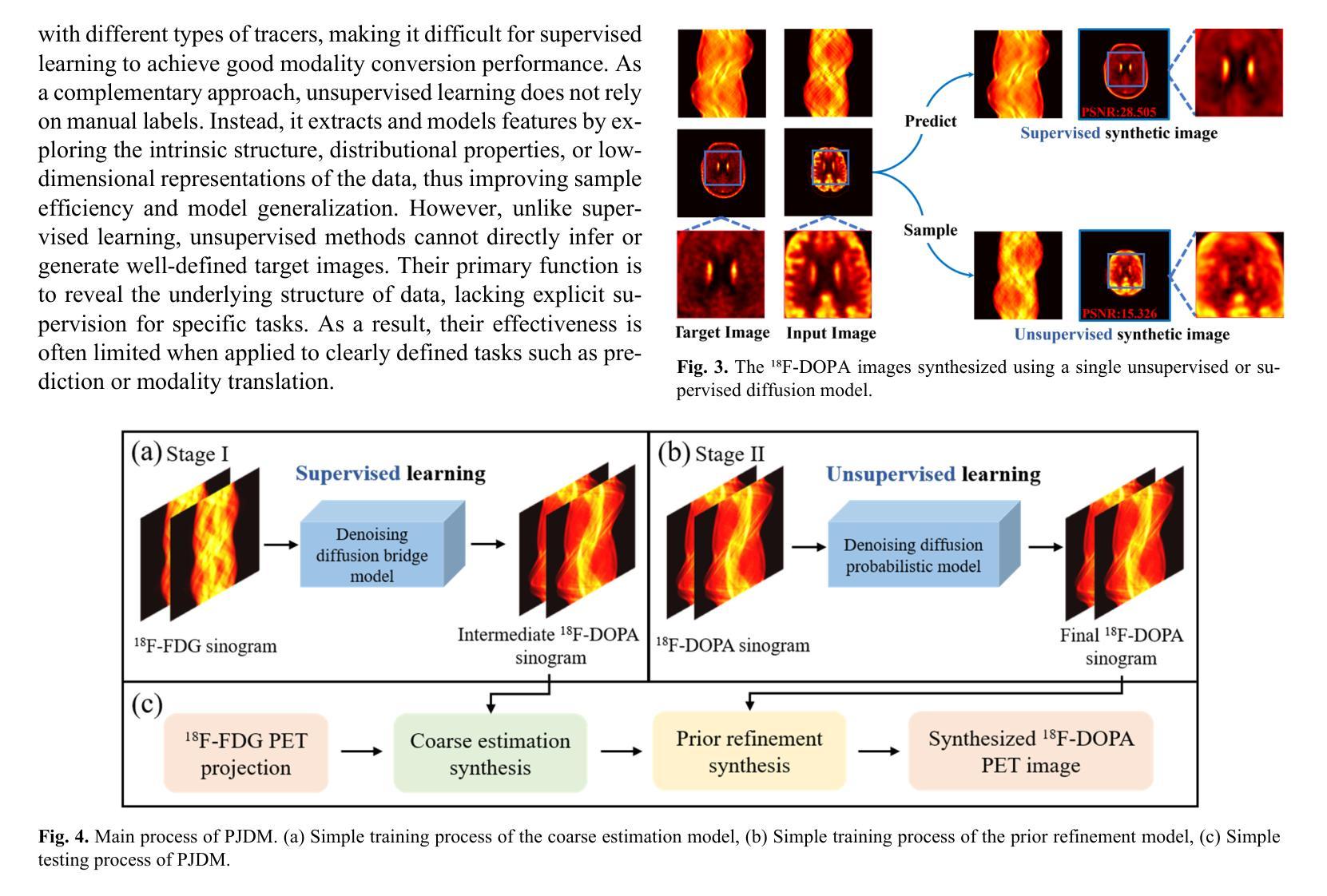
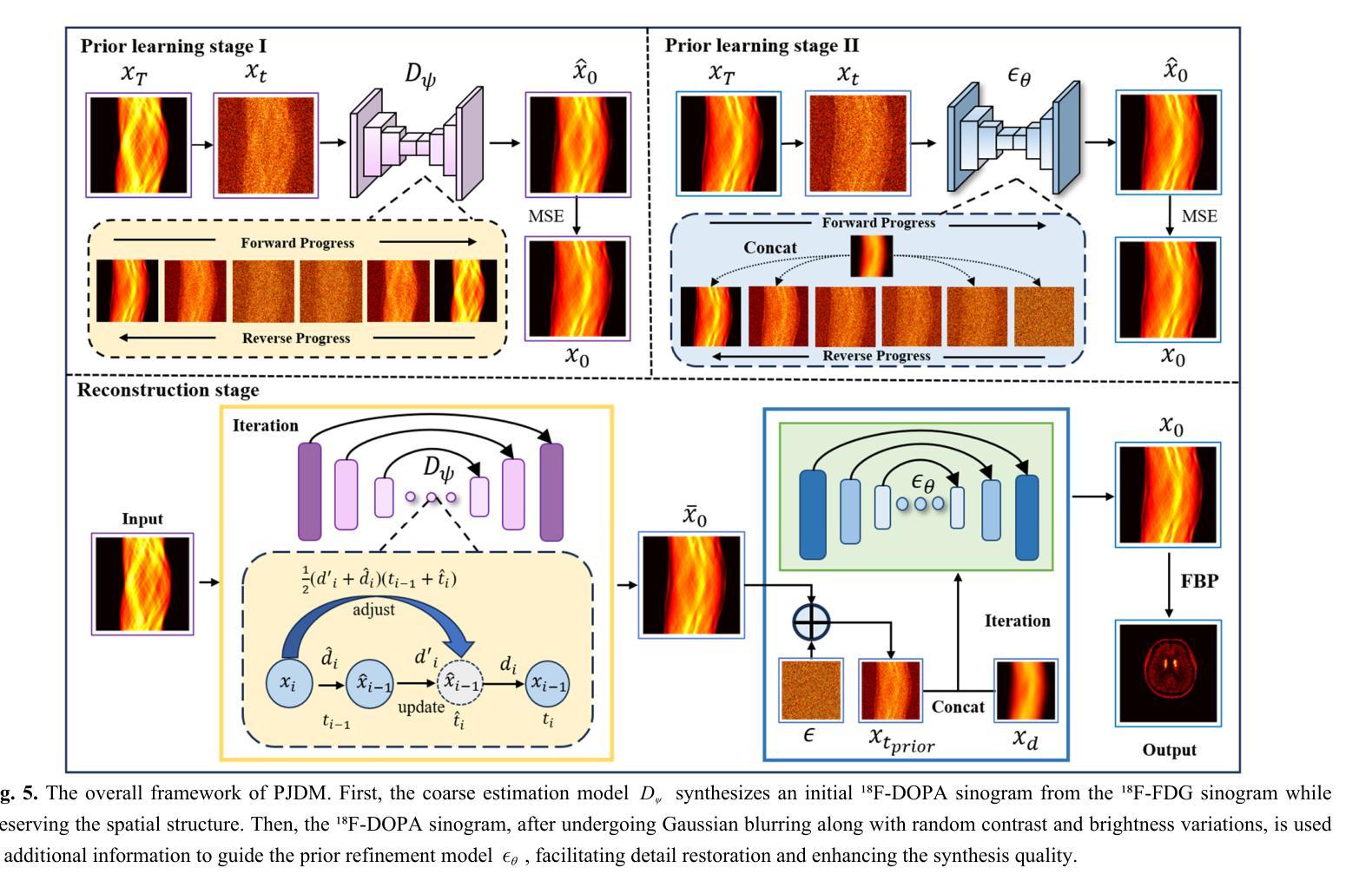
A Prior-Guided Joint Diffusion Model in Projection Domain for PET Tracer Conversion
Authors:Fang Chen, Weifeng Zhang, Xingyu Ai, BingXuan Li, An Li, Qiegen Liu
Positron emission tomography (PET) is widely used to assess metabolic activity, but its application is limited by the availability of radiotracers. 18F-labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) is the most commonly used tracer but shows limited effectiveness for certain tumors. In contrast, 6-18F-fluoro-3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (18F-DOPA) offers higher specificity for neuroendocrine tumors and neurological disorders. However, the complexity of its synthesis process and constraints on transportation time have limited its clinical application. Among different forms of raw data acquired by the scanner, sinogram is a commonly used representation in PET imaging. Therefore, modeling in projection domain enables more direct utilization of the original information, potentially reducing the accumulation errors during the image reconstruction process. Inspired by these factors, this study proposes a prior-guided joint diffusion model (PJDM) for transforming 18F-FDG PET sinograms into 18F-DOPA PET sinograms. During inference, an initial synthetic 18F-DOPA PET sinogram is first generated using a higher-order hybrid sampler. This sinogram is then degraded and serves as an additional condition to guide the iterative refinement process. Experimental results demonstrated that PJDM effectively improved both sinogram quality and the final synthetic outcomes. The code is available at: https://github.com/yqx7150/PJDM.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)广泛用于评估代谢活性,但其应用受到放射性示踪剂可用性的限制。18F标记的氟脱氧葡萄糖(18F-FDG)是最常用的示踪剂,但对于某些肿瘤,其效果有限。相比之下,6-18F-氟-3,4-二羟基-L-苯丙氨酸(18F-DOPA)对神经内分泌肿瘤和神经性疾病具有更高的特异性。然而,其合成过程的复杂性和运输时间的限制阻碍了其临床应用的广泛实施。在众多由扫描仪获得的不同形式的原始数据中,辛格拉姆(sinogram)是PET成像中常用的表示方法。因此,投影域的建模能够更直接地利用原始信息,从而可能减少图像重建过程中的累积误差。受这些因素启发,本研究提出了一种先验引导联合扩散模型(PJDM),用于将18F-FDG PET辛格拉姆转换为18F-DOPA PET辛格拉姆。在推理过程中,首先使用高阶混合采样器生成初始合成18F-DOPA PET辛格拉姆。然后将其退化并作为附加条件来引导迭代优化过程。实验结果表明,PJDM有效提高辛格拉姆的质量和最终合成结果。相关代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/yqx7150/PJDM 。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文本介绍了一种基于先验知识的联合扩散模型(PJDM),用于将18F-FDG PET正弦图转换为18F-DOPA PET正弦图。PJDM在投影域进行建模,直接利用原始信息,减少图像重建过程中的累积误差。通过初始合成18F-DOPA PET正弦图,然后将其退化并作为迭代优化过程的附加条件进行引导。实验结果表明,PJDM能有效提高正弦图和最终合成结果的质量。相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
关键见解
- PET在评估代谢活性方面应用广泛,但受限于放射性示踪剂的可用性。
- 18F-FDG是最常用的示踪剂,但对某些肿瘤的效用有限。
- 相比之下,18F-DOPA对神经内分泌肿瘤和神经系统疾病具有更高的特异性,但由于合成过程复杂及运输时间限制,其临床应用受限。
- 研究提出了一种基于先验知识的联合扩散模型(PJDM),用于转换PET正弦图数据,从18F-FDG转换至18F-DOPA。
- 该模型直接在投影域建模,有效利用原始信息,减少图像重建过程中的误差积累。
- 通过初始合成并退化正弦图来引导迭代优化过程。
- 实验结果表明PJDM对提高正弦图和最终合成图像质量有效,相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图


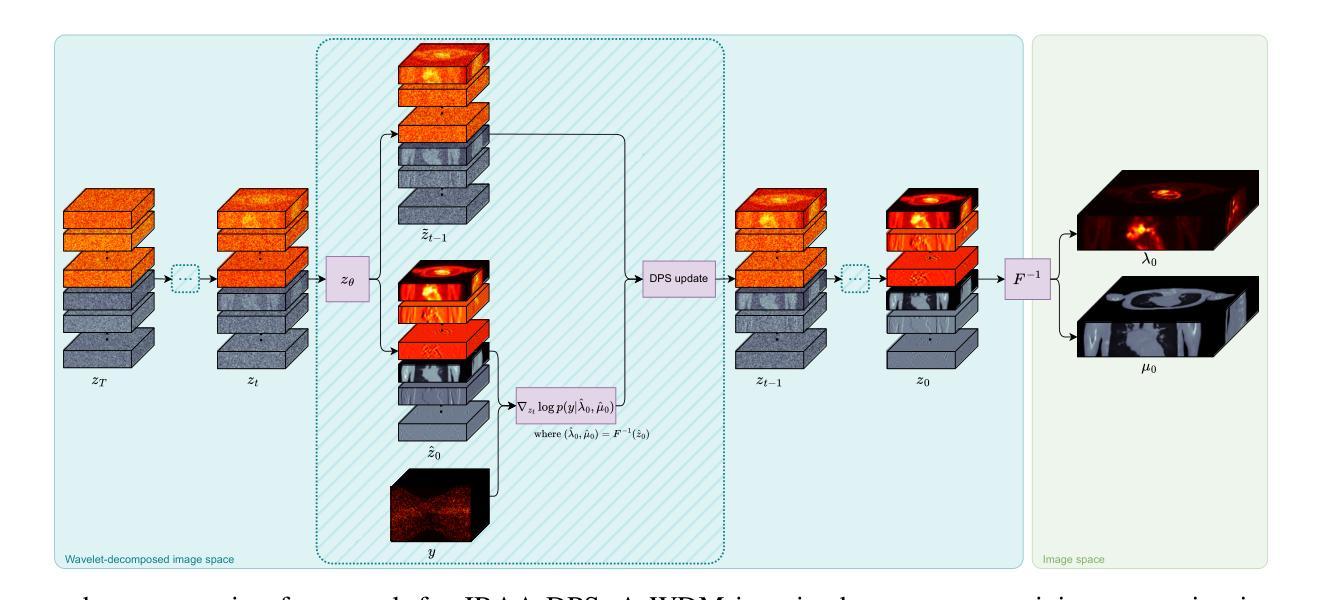
Joint Reconstruction of Activity and Attenuation in PET by Diffusion Posterior Sampling in Wavelet Coefficient Space
Authors:Clémentine Phung-Ngoc, Alexandre Bousse, Antoine De Paepe, Hong-Phuong Dang, Olivier Saut, Dimitris Visvikis
Attenuation correction (AC) is necessary for accurate activity quantification in positron emission tomography (PET). Conventional reconstruction methods typically rely on attenuation maps derived from a co-registered computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging scan. However, this additional scan may complicate the imaging workflow, introduce misalignment artifacts and increase radiation exposure. In this paper, we propose a joint reconstruction of activity and attenuation (JRAA) approach that eliminates the need for auxiliary anatomical imaging by relying solely on emission data. This framework combines wavelet diffusion model (WDM) and diffusion posterior sampling (DPS) to reconstruct fully three-dimensional (3-D) data. Experimental results show our method outperforms maximum likelihood activity and attenuation (MLAA) and MLAA with UNet-based post processing, and yields high-quality noise-free reconstructions across various count settings when time-of-flight (TOF) information is available. It is also able to reconstruct non-TOF data, although the reconstruction quality significantly degrades in low-count (LC) conditions, limiting its practical effectiveness in such settings. This approach represents a step towards stand-alone PET imaging by reducing the dependence on anatomical modalities while maintaining quantification accuracy, even in low-count scenarios when TOF information is available.
衰减校正(AC)在正电子发射断层扫描(PET)的准确活性定量中必不可少。传统重建方法通常依赖于由共注册的计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像扫描得到的衰减图。然而,这种额外的扫描可能会使成像工作流程复杂化,引入错位伪影并增加辐射暴露。在本文中,我们提出了一种联合重建活动和衰减(JRAA)的方法,该方法仅依靠发射数据,无需辅助解剖成像。该框架结合了小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS)来重建全三维(3-D)数据。实验结果表明,我们的方法在有时间飞行(TOF)信息的情况下,性能优于最大似然活动和衰减(MLAA)以及基于UNet的后处理的MLAA,并在各种计数设置下实现了高质量的无噪声重建。尽管在低计数条件下重建质量有所降低,但该方法在无TOF数据的情况下也能进行重建,这在实践中具有一定的有效性。这种方法通过减少对解剖模态的依赖,即使在有时间飞行信息的情况下低计数场景中也能保持量化精度,代表了实现独立PET成像的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文提出一种联合重建活动度和衰减(JRAA)的方法,该方法利用发射数据,无需辅助的解剖学成像。通过结合小波扩散模型(WDM)和扩散后采样(DPS),重建出全三维数据。实验表明,该方法在有时间飞行(TOF)信息的情况下,在多种计数设置下表现出优于最大似然活动度和衰减(MLAA)及其UNet后处理的方法的性能,且能得到高质量的无噪声重建。尽管该方法能重建非TOF数据,但在低计数条件下重建质量显著降低,限制了其在这些场景中的实际应用效果。此方法为实现独立PET成像提供了可能性,降低了对解剖学模态的依赖,同时保持了量化准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 衰减校正(AC)对于正电子发射断层扫描(PET)中的活动量化至关重要。
- 传统重建方法依赖于从合并的计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像扫描得到的衰减图。
- 提出的联合重建活动度和衰减(JRAA)方法消除了对辅助解剖学成像的需求,仅依赖发射数据。
- JRAA方法结合小波扩散模型和扩散后采样进行全三维数据重建。
- 在有时间飞行(TOF)信息的情况下,JRAA方法在各种计数设置下表现出优越性能。
- JRAA方法在非TOF数据的重建中也能应用,但在低计数条件下重建质量下降。
点此查看论文截图

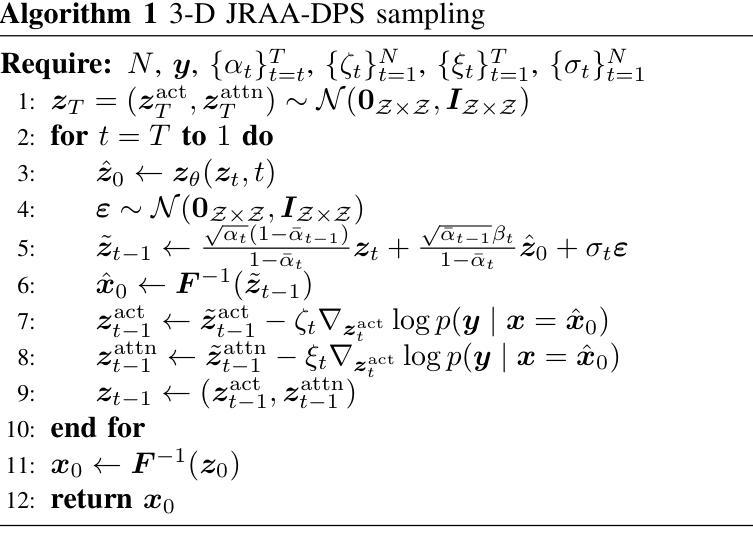
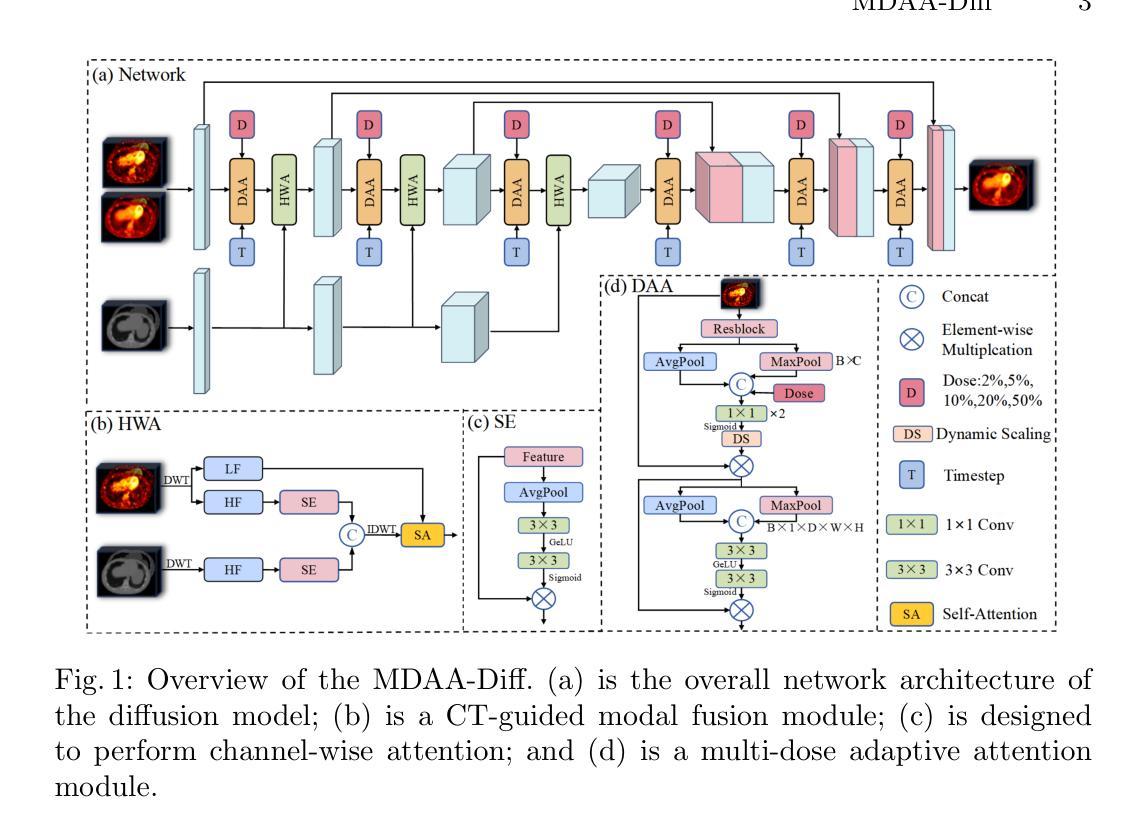
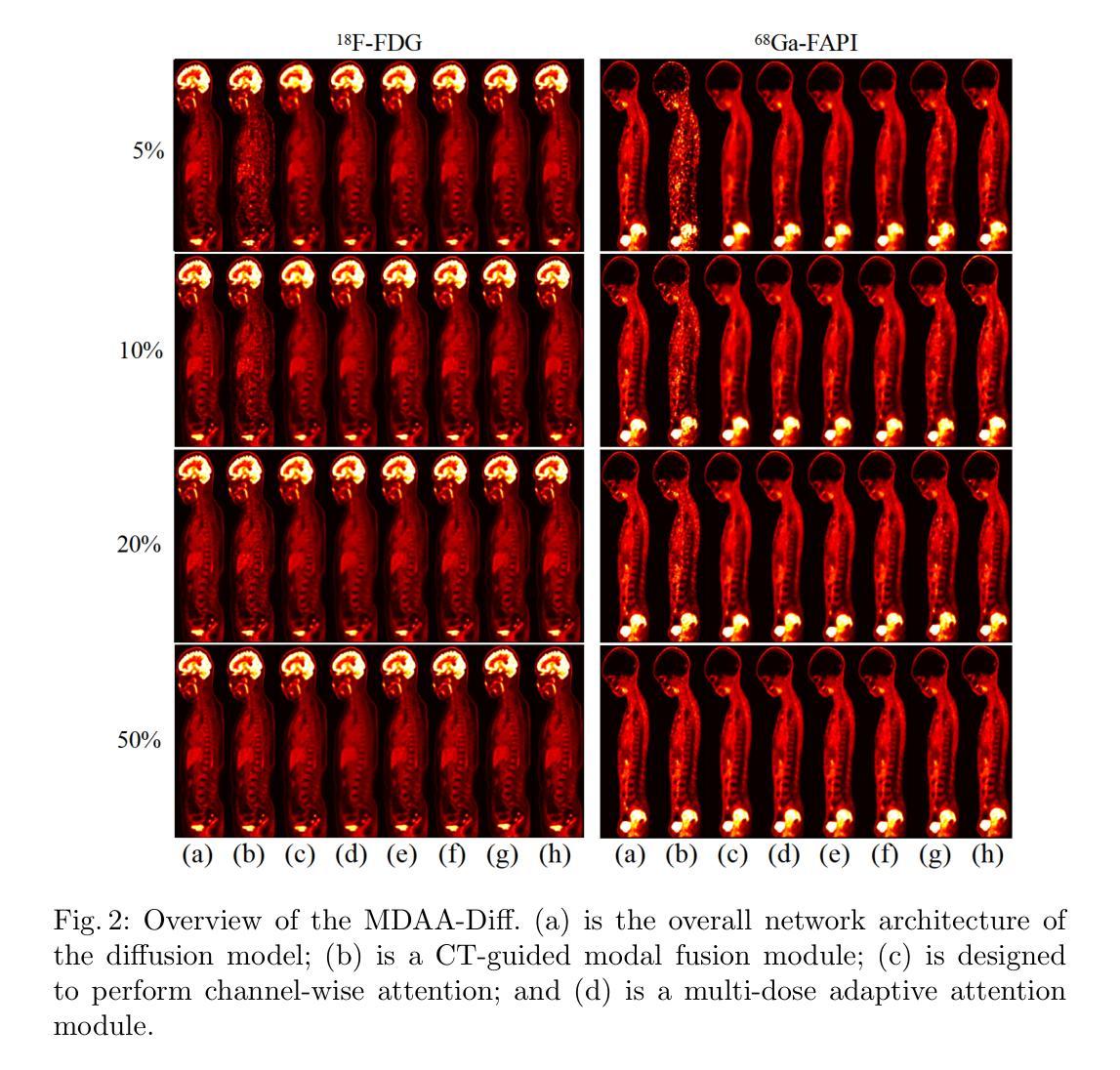
MDAA-Diff: CT-Guided Multi-Dose Adaptive Attention Diffusion Model for PET Denoising
Authors:Xiaolong Niu, Zanting Ye, Xu Han, Yanchao Huang, Hao Sun, Hubing Wu, Lijun Lu
Acquiring high-quality Positron Emission Tomography (PET) images requires administering high-dose radiotracers, which increases radiation exposure risks. Generating standard-dose PET (SPET) from low-dose PET (LPET) has become a potential solution. However, previous studies have primarily focused on single low-dose PET denoising, neglecting two critical factors: discrepancies in dose response caused by inter-patient variability, and complementary anatomical constraints derived from CT images. In this work, we propose a novel CT-Guided Multi-dose Adaptive Attention Denoising Diffusion Model (MDAA-Diff) for multi-dose PET denoising. Our approach integrates anatomical guidance and dose-level adaptation to achieve superior denoising performance under low-dose conditions. Specifically, this approach incorporates a CT-Guided High-frequency Wavelet Attention (HWA) module, which uses wavelet transforms to separate high-frequency anatomical boundary features from CT images. These extracted features are then incorporated into PET imaging through an adaptive weighted fusion mechanism to enhance edge details. Additionally, we propose the Dose-Adaptive Attention (DAA) module, a dose-conditioned enhancement mechanism that dynamically integrates dose levels into channel-spatial attention weight calculation. Extensive experiments on 18F-FDG and 68Ga-FAPI datasets demonstrate that MDAA-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in preserving diagnostic quality under reduced-dose conditions. Our code is publicly available.
获取高质量的正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像需要给予高剂量放射性示踪剂,这增加了辐射暴露风险。从低剂量PET(LPET)生成标准剂量PET(SPET)已成为一种可能的解决方案。然而,以往的研究主要集中在单一低剂量PET去噪上,忽略了两个关键因素:由患者间差异引起的剂量反应差异,以及从CT图像中得到的互补解剖约束。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff)用于多剂量PET去噪。我们的方法结合了解剖指导和剂量水平适应,以在低剂量条件下实现卓越的去噪性能。具体来说,该方法采用CT引导的高频小波注意力(HWA)模块,利用小波变换从CT图像中分离出高频解剖边界特征。这些提取的特征然后通过自适应加权融合机制融入到PET成像中,以增强边缘细节。此外,我们提出了剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,这是一种剂量调节增强机制,动态地将剂量水平集成到通道空间注意力权重计算中。在18F-FDG和68Ga-FAPI数据集上的大量实验表明,MDAA-Diff在降低剂量条件下保持诊断质量方面优于最先进的方法。我们的代码公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
获取高质量的发射型计算机断层扫描(PET)图像需要给予大剂量放射性示踪剂,从而增加了辐射暴露风险。低剂量PET(LPET)生成标准剂量PET(SPET)已成为一种可能的解决方案。然而,以前的研究主要集中在单剂量PET去噪上,忽略了由患者间差异引起的剂量反应差异以及来自CT图像的互补解剖约束这两个关键因素。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff),用于多剂量PET去噪。我们的方法结合了解剖指导和剂量水平自适应,以实现低剂量条件下的卓越去噪性能。具体来说,该方法采用CT引导的高频小波注意力(HWA)模块,利用小波变换从CT图像中分离出高频解剖边界特征。这些提取的特征通过自适应加权融合机制融入到PET成像中,以增强边缘细节。此外,我们还提出了剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,这是一种根据剂量条件增强的机制,动态地将剂量水平纳入通道空间注意力权重计算。在18F-FDG和68Ga-FAPI数据集上的大量实验表明,MDAA-Diff在降低剂量条件下保留诊断质量方面优于现有技术。我们的代码已公开可用。
关键见解
- 高剂量放射性示踪剂在PET成像中的使用增加了辐射暴露风险,提出通过生成标准剂量PET(SPET)来解决这一问题。
- 现有研究主要关注单一低剂量PET去噪,忽略了患者间差异引起的剂量反应差异和CT图像的解剖约束。
- 提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff),结合了解剖指导和剂量水平自适应。
- 采用CT引导的高频小波注意力(HWA)模块,通过小波变换提取CT图像中的高频解剖边界特征,并将其融入PET成像中增强边缘细节。
- 提出剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,动态结合剂量水平进行计算,增强去噪效果。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,MDAA-Diff在降低剂量条件下能保留诊断质量,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

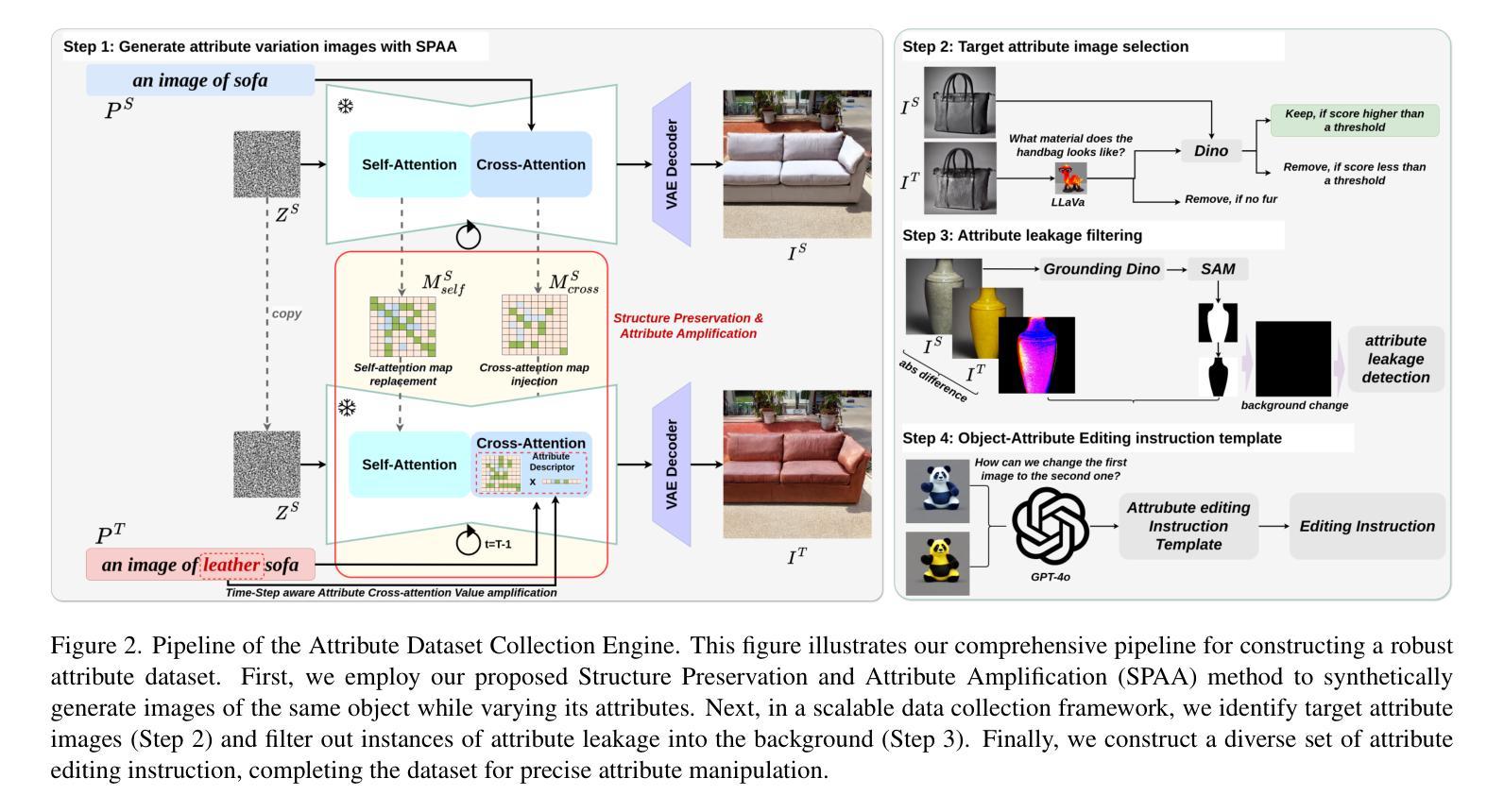
InstructAttribute: Fine-grained Object Attributes editing with Instruction
Authors:Xingxi Yin, Jingfeng Zhang, Yue Deng, Zhi Li, Yicheng Li, Yin Zhang
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models are widely used in image editing due to their powerful generative capabilities. However, achieving fine-grained control over specific object attributes, such as color and material, remains a considerable challenge. Existing methods often fail to accurately modify these attributes or compromise structural integrity and overall image consistency. To fill this gap, we introduce Structure Preservation and Attribute Amplification (SPAA), a novel training-free framework that enables precise generation of color and material attributes for the same object by intelligently manipulating self-attention maps and cross-attention values within diffusion models. Building on SPAA, we integrate multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to automate data curation and instruction generation. Leveraging this object attribute data collection engine, we construct the Attribute Dataset, encompassing a comprehensive range of colors and materials across diverse object categories. Using this generated dataset, we propose InstructAttribute, an instruction-tuned model that enables fine-grained and object-level attribute editing through natural language prompts. This capability holds significant practical implications for diverse fields, from accelerating product design and e-commerce visualization to enhancing virtual try-on experiences. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InstructAttribute outperforms existing instruction-based baselines, achieving a superior balance between attribute modification accuracy and structural preservation.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型由于其强大的生成能力而在图像编辑中得到了广泛应用。然而,实现对特定对象属性(如颜色和材质)的精细控制仍然是一个巨大的挑战。现有方法往往无法准确修改这些属性,或者会损害结构完整性和整体图像一致性。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了无训练框架——结构保留与属性放大(SPAA),通过智能操作扩散模型中的自注意力图和跨注意力值,实现对同一对象的颜色和材质属性的精确生成。基于SPAA,我们集成了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来自动进行数据整理和指令生成。利用该对象属性数据收集引擎,我们构建了属性数据集,涵盖了各类对象中的多种颜色和材质。使用这个生成的数据集,我们提出了指令属性模型InstructAttribute,这是一个通过自然语言提示实现精细粒度和对象级别的属性编辑的指令调优模型。这种能力对于加速产品设计、电子商务可视化以及增强虚拟试穿体验等多个领域都具有重要的实际意义。大量实验表明,InstructAttribute在属性修改精度和结构保留之间取得了出色的平衡,超越了现有的指令基准模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了针对文本转图像(T2I)扩散模型的一项新技术——结构保留与属性放大(SPAA)。该技术解决了现有方法在修改特定对象属性(如颜色和材质)时面临的挑战,能够在不损害结构完整性和整体图像一致性的情况下,精确生成颜色和材质属性。此外,该研究还结合了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)构建了属性数据集,并提出了基于指令调校的模型InstructAttribute,可实现通过自然语言提示进行精细化和对象级的属性编辑。这项技术在产品设计、电子商务可视化以及虚拟试穿体验等领域具有实际意义,并在实验中表现出优于现有指令基准的性能。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型广泛应用于图像编辑,但在精细控制特定对象属性方面存在挑战。
- SPAA框架解决了现有方法在修改颜色和材质属性方面的不足,通过智能操作扩散模型中的自注意力图和跨注意力值,实现精确生成属性。
- 结合MLLMs构建属性数据集,用于自动化数据整理和指令生成。
- 提出InstructAttribute模型,通过自然语言提示实现精细化和对象级的属性编辑。
- InstructAttribute在平衡属性修改准确性和结构保留方面表现出优异性能。
- 该技术对于产品设计、电子商务可视化及虚拟试穿体验等领域具有实际意义。
点此查看论文截图




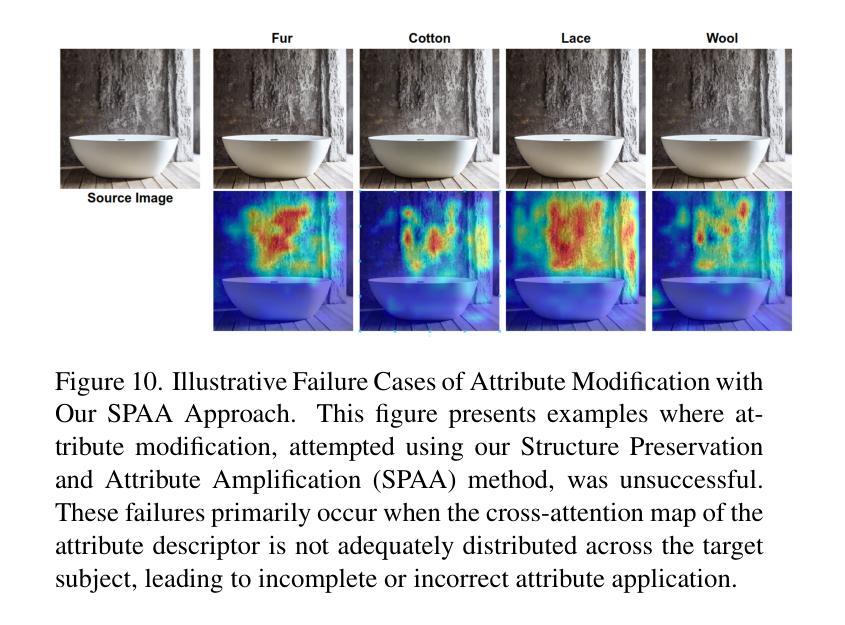

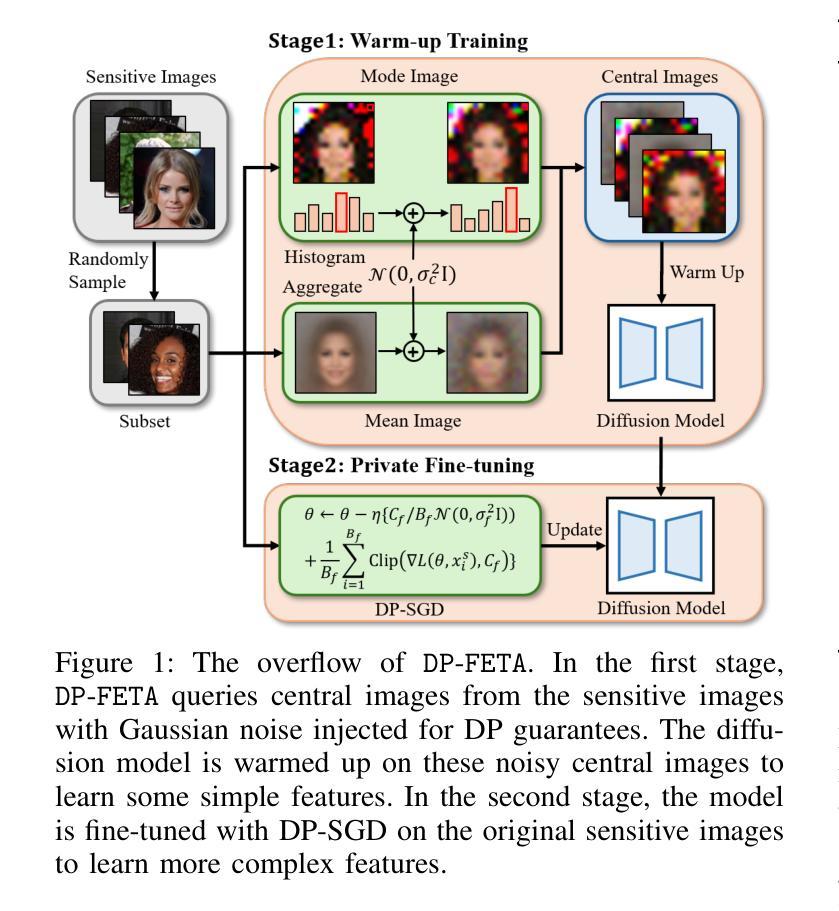
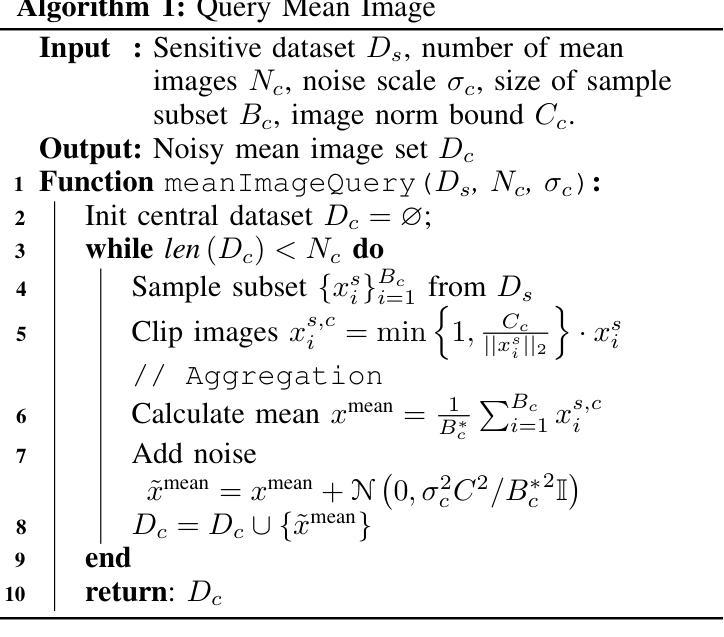
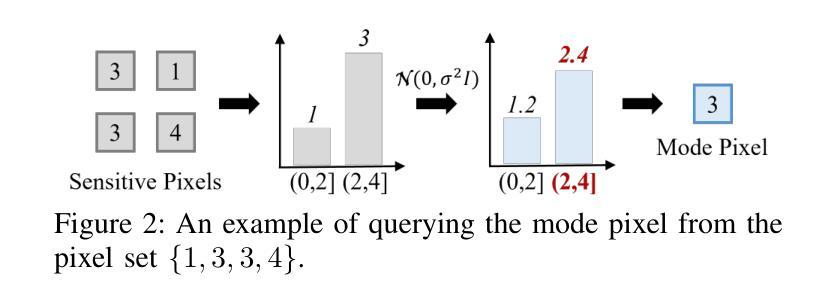
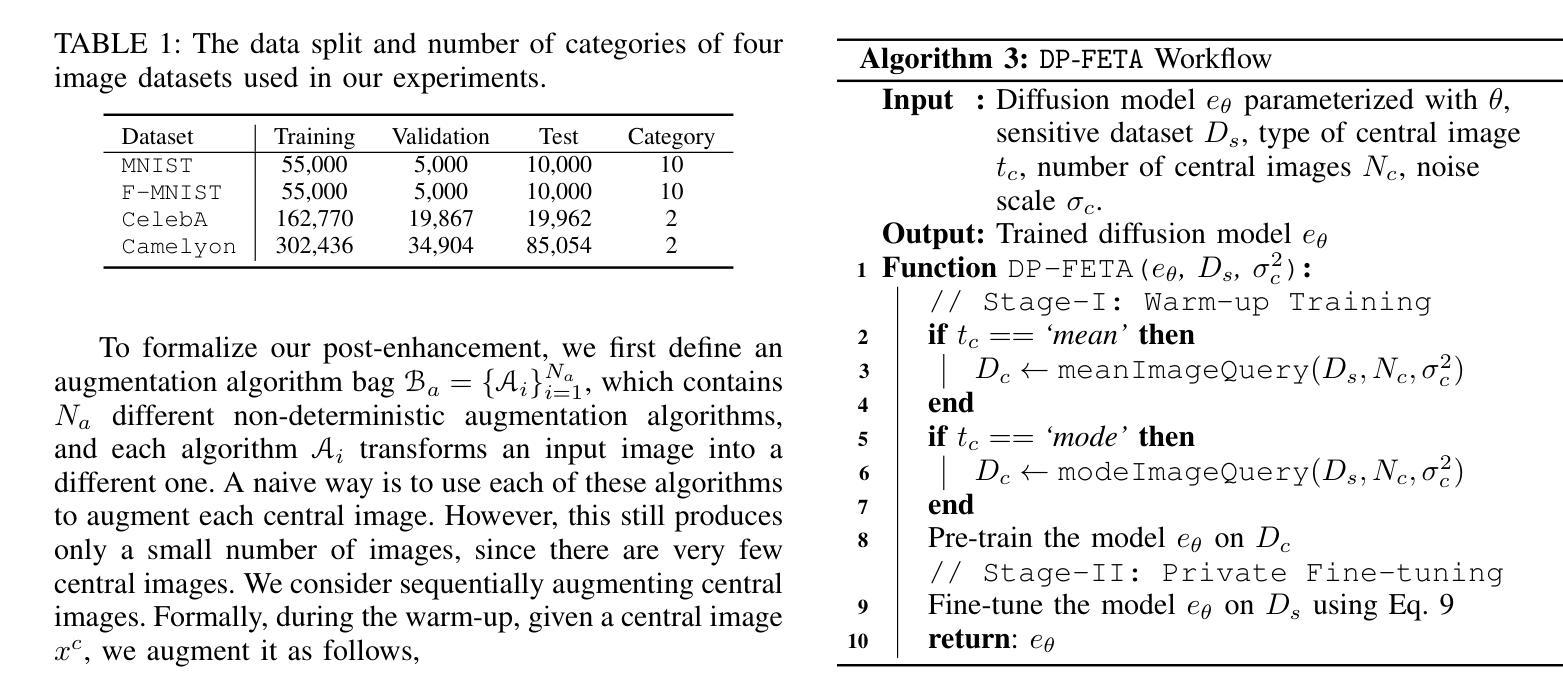
From Easy to Hard: Building a Shortcut for Differentially Private Image Synthesis
Authors:Kecen Li, Chen Gong, Xiaochen Li, Yuzhong Zhao, Xinwen Hou, Tianhao Wang
Differentially private (DP) image synthesis aims to generate synthetic images from a sensitive dataset, alleviating the privacy leakage concerns of organizations sharing and utilizing synthetic images. Although previous methods have significantly progressed, especially in training diffusion models on sensitive images with DP Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD), they still suffer from unsatisfactory performance. In this work, inspired by curriculum learning, we propose a two-stage DP image synthesis framework, where diffusion models learn to generate DP synthetic images from easy to hard. Unlike existing methods that directly use DP-SGD to train diffusion models, we propose an easy stage in the beginning, where diffusion models learn simple features of the sensitive images. To facilitate this easy stage, we propose to use `central images’, simply aggregations of random samples of the sensitive dataset. Intuitively, although those central images do not show details, they demonstrate useful characteristics of all images and only incur minimal privacy costs, thus helping early-phase model training. We conduct experiments to present that on the average of four investigated image datasets, the fidelity and utility metrics of our synthetic images are 33.1% and 2.1% better than the state-of-the-art method.
差分隐私(DP)图像合成旨在从敏感数据集中生成合成图像,从而减轻组织和机构共享和利用合成图像时的隐私泄露担忧。尽管之前的方法已经有了显著进展,特别是在使用差分隐私随机梯度下降法(DP-SGD)对敏感图像进行扩散模型训练方面,但它们仍然存在性能不佳的问题。在这项工作中,我们受到课程学习的启发,提出了一个两阶段的差分隐私图像合成框架,其中扩散模型从易到难学习生成差分隐私合成图像。与现有方法直接使用DP-SGD训练扩散模型不同,我们在开始时提出了一个简单阶段,让扩散模型学习敏感图像的简单特征。为了促进这一简单阶段,我们建议使用“中心图像”,即敏感数据集随机样本的简单集合。直观地看,虽然这些中心图像不显示细节,但它们展示了所有图像的有用特征并且只产生微小的隐私成本,从而有助于早期模型训练。我们进行实验表明,在调查的四个图像数据集的平均值上,我们的合成图像的保真度和效用指标比现有最先进的方法分别提高了33.1%和2.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE S&P (Oakland) 2025; code available at https://github.com/SunnierLee/DP-FETA; revised proofs in App.A
Summary
差分隐私(DP)图像合成旨在从敏感数据集中生成合成图像,以缓解组织和公众对共享和利用合成图像时的隐私泄露担忧。尽管之前的方法,特别是在使用DP随机梯度下降(DP-SGD)训练扩散模型方面取得了显著进展,但它们仍然表现不佳。在这项工作中,受到课程学习的启发,我们提出了一个两阶段的DP图像合成框架,其中扩散模型从易到难学习生成DP合成图像。与现有方法直接使用DP-SGD训练扩散模型不同,我们在开始时加入了一个简单的阶段,让扩散模型学习敏感图像的简单特征。为了促进这一简单阶段,我们建议使用“中心图像”,即敏感数据集的随机样本的集合。尽管这些中心图像不显示细节,但它们展示了所有图像的有用特征并且只产生最小的隐私成本,从而有助于早期阶段的模型训练。实验表明,在调查的四个图像数据集上,我们生成的合成图像的保真度和效用指标均优于现有最佳方法,分别提高了33.1%和2.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 差分隐私(DP)图像合成旨在解决共享和利用合成图像时的隐私泄露问题。
- 现有方法在DP图像合成方面的表现仍有待提升。
- 提出了一个两阶段的DP图像合成框架,从简单到复杂训练扩散模型。
- 在早期阶段,使用“中心图像”促进模型学习敏感图像的简单特征。
- 中心图像能够展示数据集的有用特征且对隐私影响较小。
- 实验结果显示,在多个图像数据集上,该方法生成的合成图像优于现有最佳方法。
点此查看论文截图


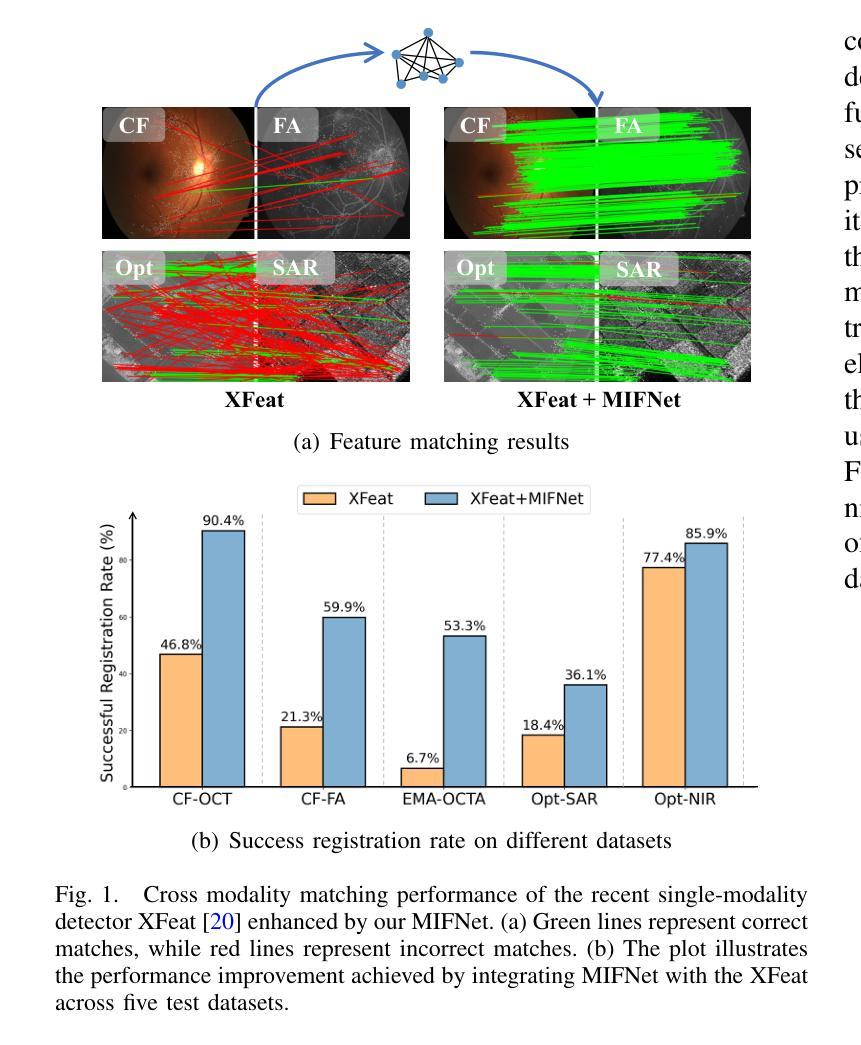
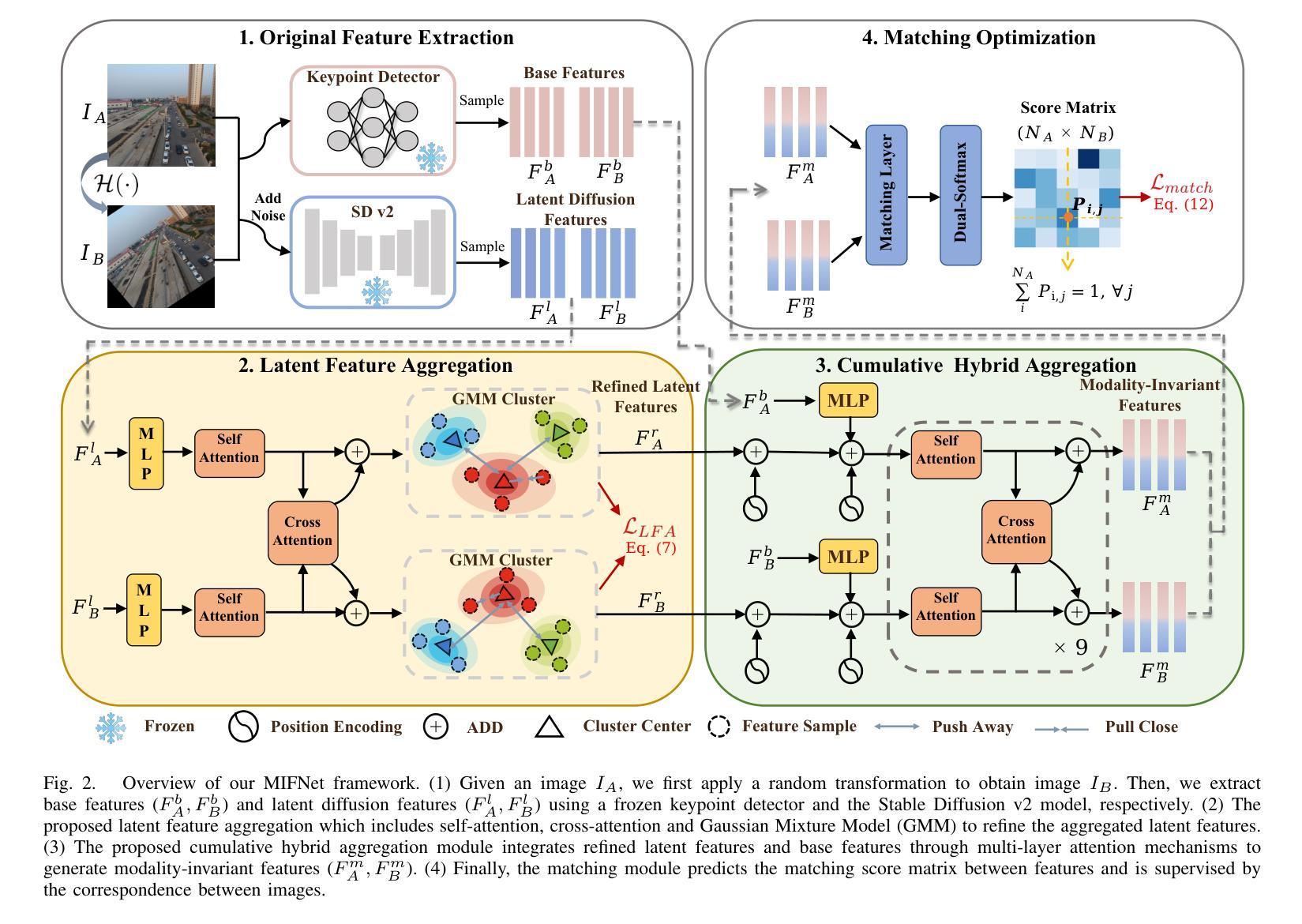
MIFNet: Learning Modality-Invariant Features for Generalizable Multimodal Image Matching
Authors:Yepeng Liu, Zhichao Sun, Baosheng Yu, Yitian Zhao, Bo Du, Yongchao Xu, Jun Cheng
Many keypoint detection and description methods have been proposed for image matching or registration. While these methods demonstrate promising performance for single-modality image matching, they often struggle with multimodal data because the descriptors trained on single-modality data tend to lack robustness against the non-linear variations present in multimodal data. Extending such methods to multimodal image matching often requires well-aligned multimodal data to learn modality-invariant descriptors. However, acquiring such data is often costly and impractical in many real-world scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a modality-invariant feature learning network (MIFNet) to compute modality-invariant features for keypoint descriptions in multimodal image matching using only single-modality training data. Specifically, we propose a novel latent feature aggregation module and a cumulative hybrid aggregation module to enhance the base keypoint descriptors trained on single-modality data by leveraging pre-trained features from Stable Diffusion models. %, our approach generates robust and invariant features across diverse and unknown modalities. We validate our method with recent keypoint detection and description methods in three multimodal retinal image datasets (CF-FA, CF-OCT, EMA-OCTA) and two remote sensing datasets (Optical-SAR and Optical-NIR). Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed MIFNet is able to learn modality-invariant feature for multimodal image matching without accessing the targeted modality and has good zero-shot generalization ability. The code will be released at https://github.com/lyp-deeplearning/MIFNet.
针对图像匹配或注册,已经提出了许多关键点检测与描述方法。虽然这些方法在单模态图像匹配上表现出有前景的性能,但它们通常在多模态数据上表现挣扎,因为那些在单模态数据上训练的描述符往往缺乏对多模态数据中存在的非线性变异的稳健性。将这些方法扩展到多模态图像匹配通常需要精准对齐的多模态数据来学习模态不变描述符。然而,在现实的许多场景中,获取这样的数据往往成本高昂且不切实际。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种模态不变特征学习网络(MIFNet),仅使用单模态训练数据,为多模态图像匹配中的关键点描述计算模态不变特征。具体来说,我们提出了一种新型潜在特征聚合模块和累积混合聚合模块,以利用来自Stable Diffusion模型的预训练特征,增强在单模态数据上训练的基准关键点描述符。我们的方法能够在多样且未知的模式下生成稳健和不变的特征。我们在三个多模态视网膜图像数据集(CF-FA、CF-OCT、EMA-OCTA)和两个遥感数据集(Optical-SAR和Optical-NIR)上与最近的关键点检测和描述方法进行验证。大量实验表明,所提出的MIFNet能够在不接触目标模态的情况下学习多模态图像匹配的模态不变特征,并具有良好的零样本泛化能力。代码将发布在https://github.com/lyp-deeplearning/MIFNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by IEEE TIP 2025
Summary
针对多模态图像匹配中的挑战,提出一种模态不变特征学习网络(MIFNet),利用单模态训练数据计算关键点的模态不变特征。通过新型潜在特征聚合模块和累积混合聚合模块增强基于单模态数据训练的基础关键描述符,并借助Stable Diffusion模型的预训练特征。实验验证,MIFNet在多种模态视网膜图像数据集和遥感数据集中表现出良好的零样本泛化能力和模态不变特征学习能力,无需访问目标模态。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态图像匹配面临挑战:现有方法在单模态图像匹配上表现良好,但在多模态数据上缺乏鲁棒性。
- MIFNet被提出以解决此挑战:计算关键点的模态不变特征,适用于多模态图像匹配。
- MIFNet利用单模态训练数据:不需要多模态对齐数据,降低了获取成本。
- 新型潜在特征聚合模块和累积混合聚合模块:增强基于单模态数据训练的基础关键描述符。
- 利用Stable Diffusion模型的预训练特征:提升特征的质量和泛化能力。
- 在多个数据集上的实验验证:显示MIFNet的零样本泛化能力和模态不变特征学习能力。
点此查看论文截图

CDI: Copyrighted Data Identification in Diffusion Models
Authors:Jan Dubiński, Antoni Kowalczuk, Franziska Boenisch, Adam Dziedzic
Diffusion Models (DMs) benefit from large and diverse datasets for their training. Since this data is often scraped from the Internet without permission from the data owners, this raises concerns about copyright and intellectual property protections. While (illicit) use of data is easily detected for training samples perfectly re-created by a DM at inference time, it is much harder for data owners to verify if their data was used for training when the outputs from the suspect DM are not close replicas. Conceptually, membership inference attacks (MIAs), which detect if a given data point was used during training, present themselves as a suitable tool to address this challenge. However, we demonstrate that existing MIAs are not strong enough to reliably determine the membership of individual images in large, state-of-the-art DMs. To overcome this limitation, we propose CDI, a framework for data owners to identify whether their dataset was used to train a given DM. CDI relies on dataset inference techniques, i.e., instead of using the membership signal from a single data point, CDI leverages the fact that most data owners, such as providers of stock photography, visual media companies, or even individual artists, own datasets with multiple publicly exposed data points which might all be included in the training of a given DM. By selectively aggregating signals from existing MIAs and using new handcrafted methods to extract features for these datasets, feeding them to a scoring model, and applying rigorous statistical testing, CDI allows data owners with as little as 70 data points to identify with a confidence of more than 99% whether their data was used to train a given DM. Thereby, CDI represents a valuable tool for data owners to claim illegitimate use of their copyrighted data. We make the code available at https://github.com/sprintml/copyrighted_data_identification
扩散模型(DMs)受益于大规模、多样化的数据集进行训练。由于这些数据通常未经数据所有者许可就从互联网上抓取,这引发了关于版权和知识产权保护的担忧。虽然(非法)使用数据很容易检测到训练样本被扩散模型在推理时完美重建的情况,但当怀疑的扩散模型输出不是紧密副本时,数据所有者很难验证其数据是否用于训练。从概念上讲,成员推理攻击(MIAs)能够检测给定数据点是否用于训练,似乎是一个解决这一挑战的合理工具。然而,我们证明现有的MIAs不足以可靠地确定大型、最先进的DM中个别图像的会员身份。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了CDI,一个数据所有者用来判断其数据集是否用于训练特定扩散模型的框架。CDI依赖于数据集推理技术,即不是使用单个数据点的成员信号,而是利用大多数数据所有者(如库存照片提供商、视觉媒体公司甚至个人艺术家)拥有多个可能包含在特定扩散模型训练中的公开数据点这一事实。通过有选择地聚合现有MIAs的信号,并使用新的手工方法来提取这些数据集的特征,将其输入评分模型并进行严格的统计测试,CDI允许数据所有者使用至少70个数据点以超过99%的置信度来识别他们的数据是否用于训练特定的扩散模型。因此,CDI是数据所有者要求制止对其版权数据的非法使用的一种有价值工具。我们在https://github.com/sprintml/copyrighted_data_identification上提供了代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR2025 (Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition) Code available at https://github.com/sprintml/copyrighted_data_identification
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)训练受益于大规模、多样化的数据集,但这些数据往往未经数据所有者许可从互联网抓取,引发版权和知识产权保护的担忧。对于训练样本的非法使用,如果DM在推理阶段完美复现这些样本,则容易检测。然而,当输出并非精确复制时,数据所有者难以证明其数据是否被用于训练。成员推理攻击(MIAs)作为一种检测给定数据点是否用于训练的工具,对此挑战具有概念上的适用性。但研究指出现有MIAs不足以可靠判断大型前沿DM中单个图像的成员身份。为解决此局限性,我们提出CDI框架,帮助数据所有者判断其数据集是否被用于训练特定DM。CDI依赖数据集推理技术,即并非使用单个数据点的成员信号,而是利用大多数数据所有者(如库存照片提供商、视觉媒体公司或个人艺术家)拥有多个可能包含在特定DM训练中的公开数据点这一事实。通过有选择地聚合来自现有MIAs的信号,并使用新的手工方法提取这些数据集的特征,将其输入评分模型并进行严格的统计测试,CDI允许拥有仅70个数据点的数据所有者以超过99%的置信度判断其数据是否被用于训练特定DM。因此,CDI是数据所有者主张其版权数据被非法使用时的宝贵工具。我们已将代码公开在https://github.com/sprintml/copyrighted_data_identification。
关键见解
- 扩散模型(DMs)经常从互联网抓取大规模、多样化的数据集进行训练,引发版权问题。
- 当DM输出并非精确复制训练样本时,数据所有者难以证明其数据是否被用于训练DM。
- 成员推理攻击(MIAs)在判断DM是否使用了特定数据方面具有一定价值,但现有MIAs不足以进行可靠判断。
- 提出的CDI框架基于数据集推理技术,利用数据所有者的多个公开数据点来识别其数据集是否被用于训练DM。
- CDI通过结合现有MIAs的信号和新的手工方法提取数据集特征,进行严格的统计测试。
- 仅需70个数据点,CDI便能以超过99%的置信度判断数据是否被用于训练特定DM。
- CDI工具对于数据所有者主张其版权数据被非法使用具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

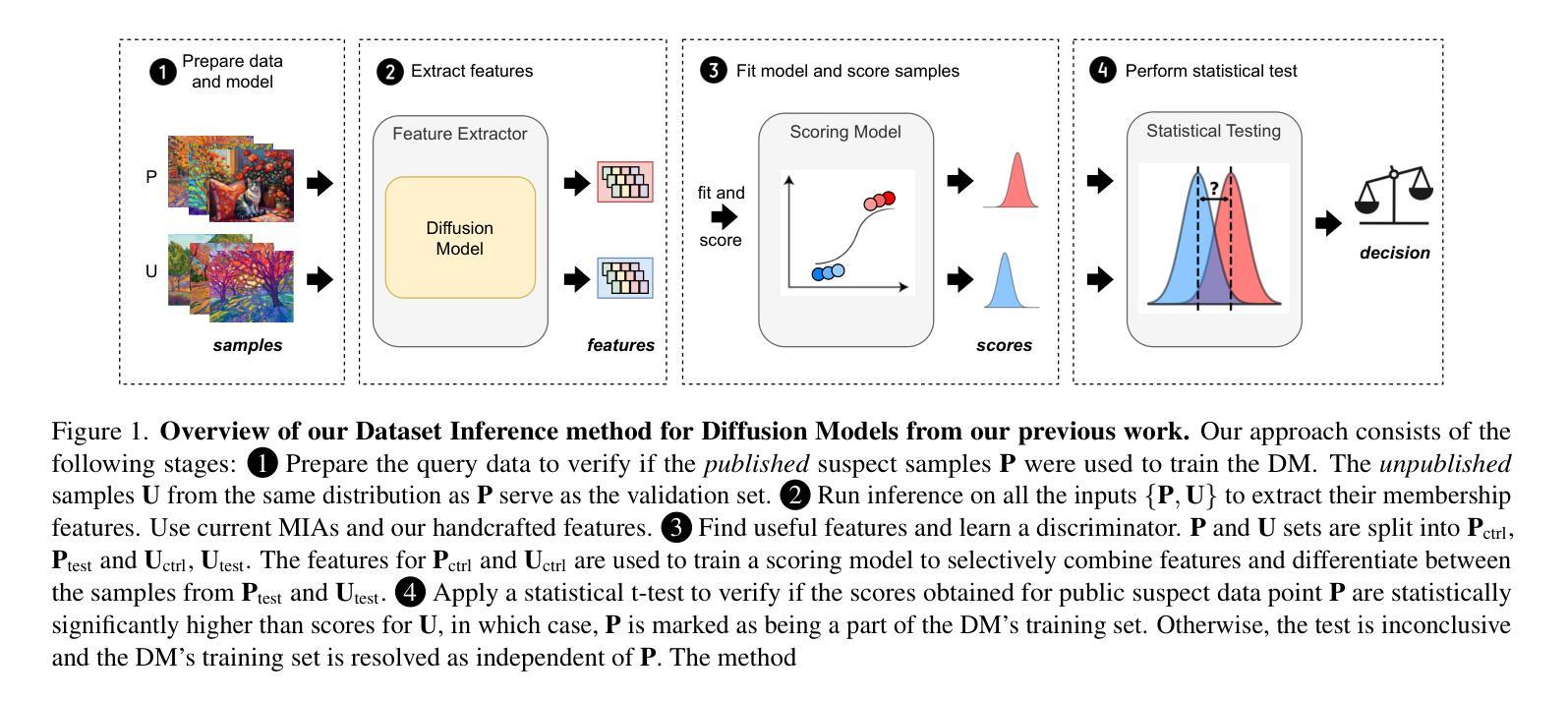
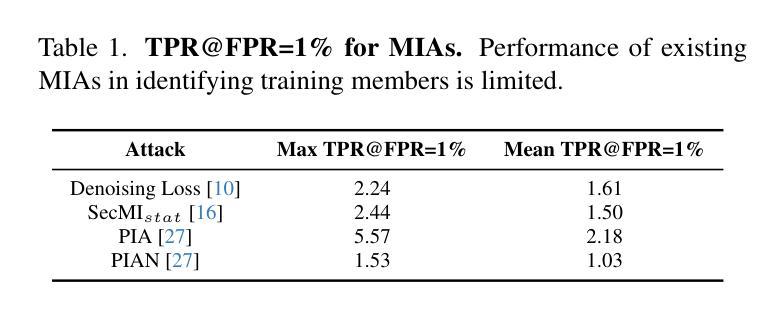
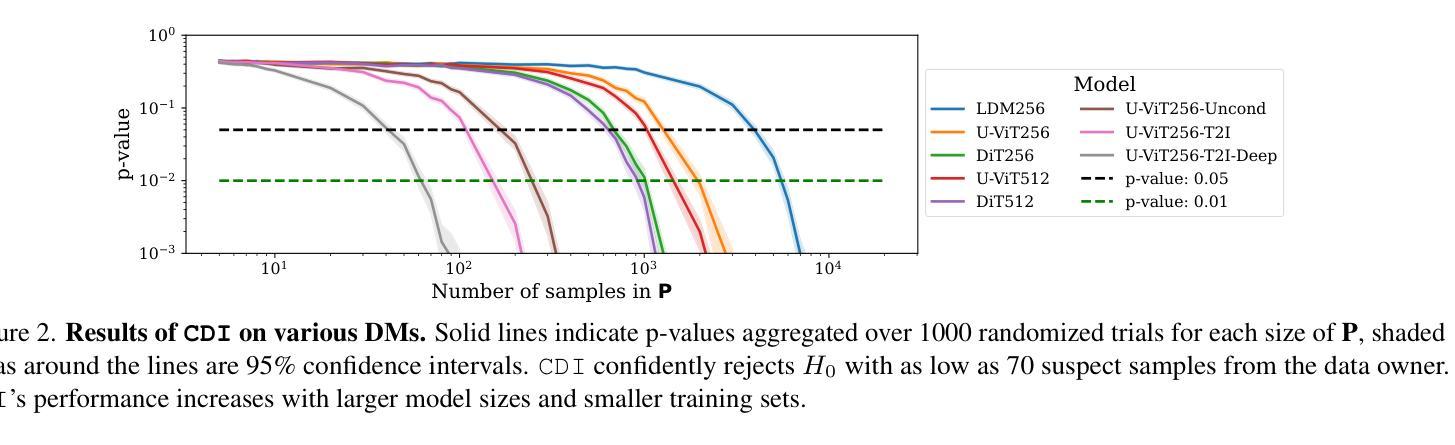
Leveraging Model Guidance to Extract Training Data from Personalized Diffusion Models
Authors:Xiaoyu Wu, Jiaru Zhang, Zhiwei Steven Wu
Diffusion Models (DMs) have become powerful image generation tools, especially for few-shot fine-tuning where a pretrained DM is fine-tuned on a small image set to capture specific styles or objects. Many people upload these personalized checkpoints online, fostering communities such as Civitai and HuggingFace. However, model owners may overlook the data leakage risks when releasing fine-tuned checkpoints. Moreover, concerns regarding copyright violations arise when unauthorized data is used during fine-tuning. In this paper, we ask: “Can training data be extracted from these fine-tuned DMs shared online?” A successful extraction would present not only data leakage threats but also offer tangible evidence of copyright infringement. To answer this, we propose FineXtract, a framework for extracting fine-tuning data. Our method approximates fine-tuning as a gradual shift in the model’s learned distribution – from the original pretrained DM toward the fine-tuning data. By extrapolating the models before and after fine-tuning, we guide the generation toward high-probability regions within the fine-tuned data distribution. We then apply a clustering algorithm to extract the most probable images from those generated using this extrapolated guidance. Experiments on DMs fine-tuned with datasets including WikiArt, DreamBooth, and real-world checkpoints posted online validate the effectiveness of our method, extracting about 20% of fine-tuning data in most cases. The code is available https://github.com/Nicholas0228/FineXtract.
扩散模型(DMs)已成为强大的图像生成工具,特别是在小样本微调中,预训练的DM被微调以捕捉特定风格或对象的小图像集。许多人在线上传这些个性化的检查点,促进了如Civitai和HuggingFace等社区的发展。然而,在发布微调检查点时,模型所有者可能会忽略数据泄露的风险。此外,当微调过程中使用未经授权的数据时,会出现版权违规的担忧。在本文中,我们提出的问题是:“可以从在线共享的这些微调后的DMs中提取训练数据吗?”成功的提取不仅会带来数据泄露的威胁,而且提供了版权侵权的切实证据。为了回答这个问题,我们提出了FineXtract,一个用于提取微调数据的框架。我们的方法将微调近似为模型学习分布的一个逐渐变化——从原始的预训练DM向微调数据变化。通过外推微调前后的模型,我们引导生成进入微调数据分布内的概率较高的区域。然后,我们应用聚类算法从使用这种外推指导生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。在使用WikiArt、DreamBooth和在线发布的现实世界检查点对DMs进行微调的实验验证了我们的方法的有效性,在大多数情况下,我们能够提取约20%的微调数据。代码可在此链接找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)已成为强大的图像生成工具,特别是在小样数据微调中,预训练的DM通过微调少量的图像集来捕捉特定的风格或对象。本文探讨了从在线共享的微调扩散模型中提取训练数据的问题。我们提出FineXtract框架来提取微调数据,通过外推模型在微调前后的变化,引导生成向微调数据分布的高概率区域,并应用聚类算法从生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。实验证明,该方法在大多数情况下可有效提取约20%的微调数据。
关键见解
- 扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成领域表现出强大的能力,尤其在小样数据微调方面。
- 人们会在网上上传个性化的检查点,从而促进了社区的发展,但也带来了数据泄露风险。
- 存在对版权侵犯的担忧,当未经授权的数据用于微调时。
- FineXtract框架被提出来提取微调数据,通过将微调视为模型学习分布的一个渐变变化来实现。
- 通过外推模型在微调前后的变化,可以引导生成向微调数据分布的高概率区域。
- 应用聚类算法可以从生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。
- 实验证明,该方法在提取在线共享的微调扩散模型的训练数据方面是有效的,提取的数据量约为20%。
点此查看论文截图


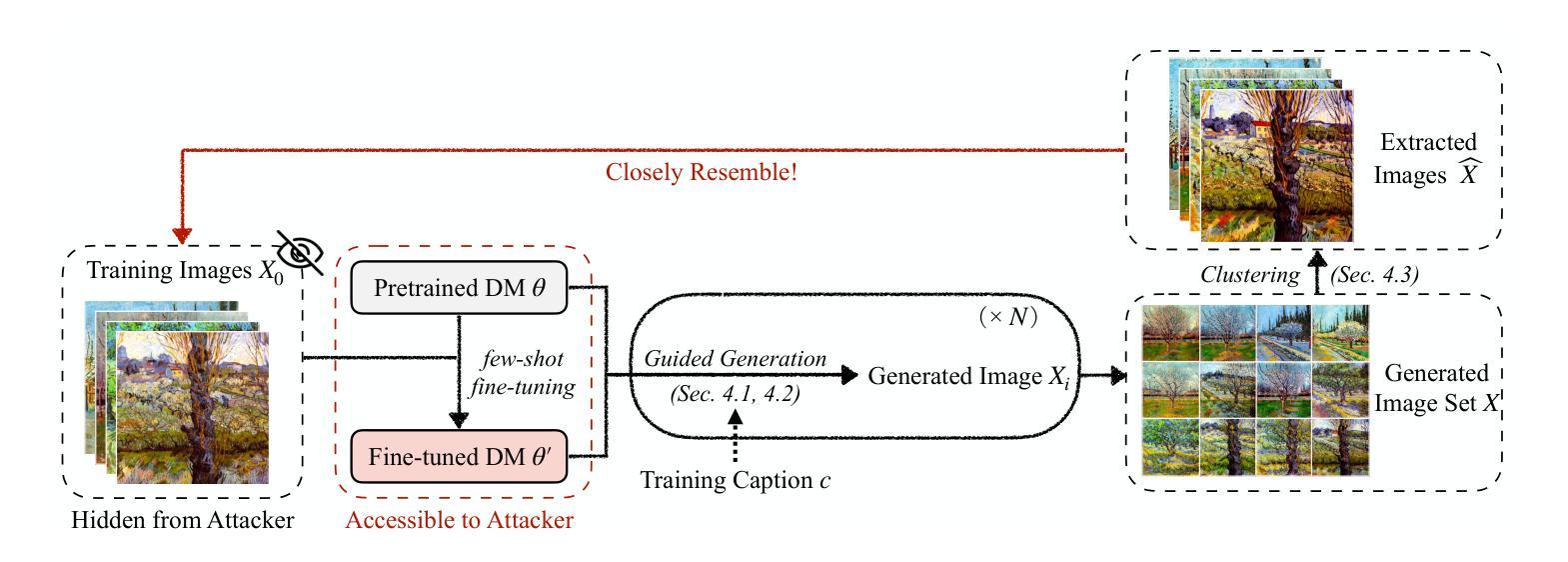
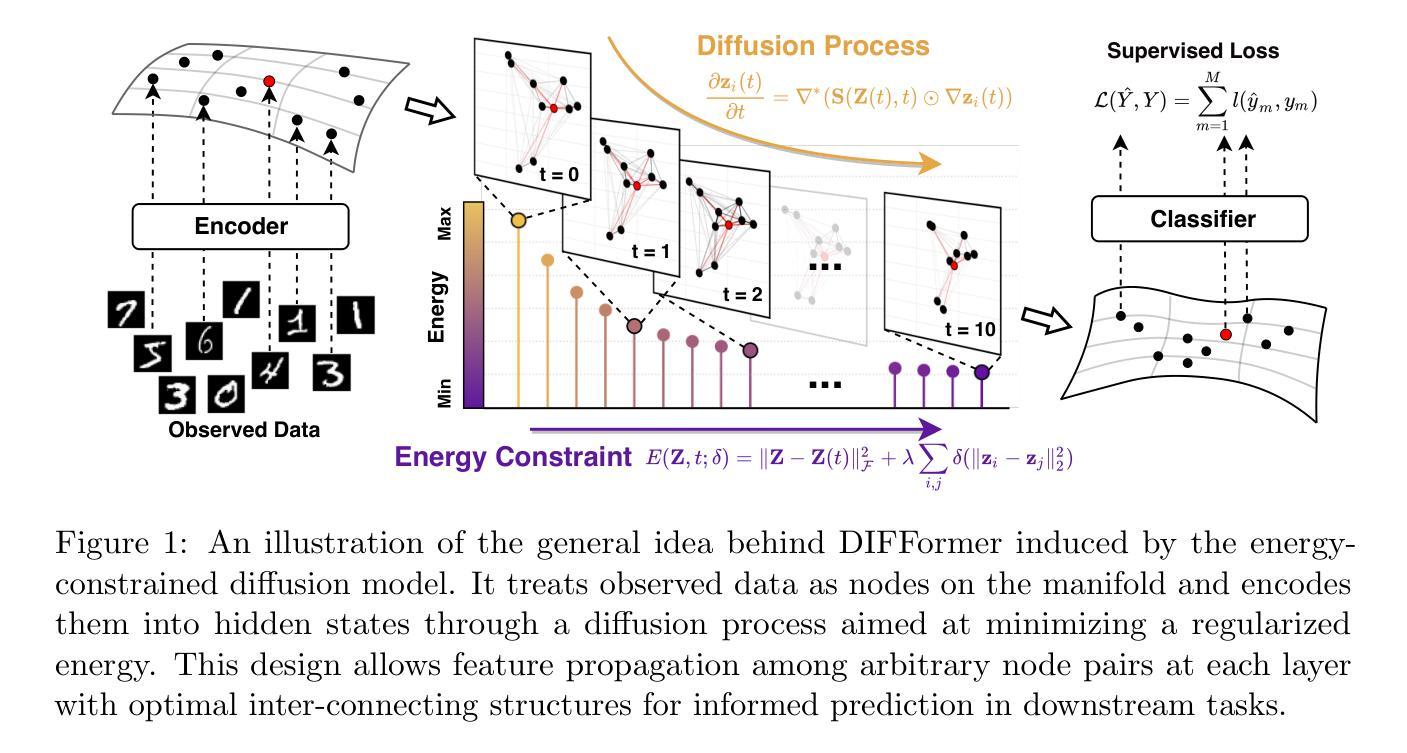
Bridging Geometric Diffusion and Energy Minimization: A Unified Framework for Neural Message Passing
Authors:Qitian Wu, David Wipf, Junchi Yan
Learning representations for structured data with certain geometries (e.g., observed or unobserved) is a fundamental challenge, wherein message passing neural networks (MPNNs) have become a de facto class of model solutions. In this paper, we propose an energy-constrained diffusion model as a principled mathematical framework for understanding the mechanism of MPNNs and navigating novel architectural designs. Inspired by physical systems, the model combines the inductive bias of diffusion on manifolds with layer-wise constraints of energy minimization. We identify that the diffusion operators have a one-to-one correspondence with the energy functions implicitly descended by the diffusion process, and the finite-difference iteration for solving the energy-constrained diffusion system induces the propagation layers of various types of MPNNs operating on observed or latent structures. This leads to a unified perspective on common neural architectures whose computational flows can be cast as message passing (or its special case), including MLP, GCN, GIN, APPNP, GCNII, GAT, and Transformers. Building on these insights, we devise a new class of neural message passing models, dubbed diffusion-inspired Transformers, whose global attention layers are derived from the principled energy-constrained diffusion framework. Across diverse datasets, ranging from real-world networks to images, texts, and physical particles, we demonstrate that the new model achieves promising performance in scenarios where the data structures are observed (as a graph), partially observed, or entirely unobserved.
对于具有特定几何结构(无论是观察到的还是未观察到的)的结构化数据的学习表示是一个基本挑战,其中消息传递神经网络(MPNNs)已成为一种模型解决方案的实际类别。在本文中,我们提出了一种能量约束扩散模型,作为理解MPNN机制并探索新型架构设计的基本原则数学框架。该模型受到物理系统的启发,结合了流形上扩散的归纳偏见和能量最小化的逐层约束。我们发现扩散算子与扩散过程隐含下降的能函数之间存在一一对应关系,解决能量约束扩散系统的有限差分迭代引发了各种类型的MPNN传播层,这些层在观察到的或潜在的结构上运行。这为常见的神经网络架构提供了一个统一的视角,其计算流程可以转换为消息传递(或其特殊情况),包括MLP、GCN、GIN、APPNP、GCNII、GAT和Transformer。基于这些见解,我们开发了一类新的神经网络消息传递模型,称为“扩散启发式Transformer”,其全局注意力层源于有原则的能量约束扩散框架。在真实世界网络、图像、文本和物理粒子等多种数据集上,我们证明了新模型在处理观察到的(作为图形)、部分观察到的或完全未观察到的数据结构场景中均取得了有前景的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). Extended version from DIFFormer in ICLR 2023
Summary
本文提出一种能量约束扩散模型,作为理解消息传递神经网络(MPNNs)机制的原则性数学框架,并探索新型架构设计。模型结合流形上的扩散归纳偏见与能量最小化的逐层约束。扩散算子与能量函数有一一对应关系,通过求解能量约束扩散系统的有限差分迭代,诱导各种MPNNs的传播层在观测或潜在结构上进行操作。这提供了一个统一视角,重新审视计算流可转换为消息传递或其特殊情况的常见神经网络架构。基于这些见解,我们设计了一种新型的神经网络消息传递模型——扩散启发式Transformer,其全局注意力层源于原则性的能量约束扩散框架。在多种数据集上,无论是网络、图像、文本还是物理粒子,新模型在数据结构被观测、部分观测或完全未被观测的场景中均表现出良好性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出一种基于能量约束扩散模型的数学框架,用以理解消息传递神经网络(MPNNs)的工作原理。
- 模型结合了流形上的扩散归纳偏见和能量最小化的逐层约束,为新型神经网络架构设计提供灵感。
- 论文揭示了扩散算子与能量函数之间的对应关系,并通过有限差分迭代模拟扩散过程,从而理解不同类型的MPNNs传播层。
- 模型提供了一个统一视角,涵盖多种计算流可转换为消息传递或其特殊情况的神经网络架构。
- 基于该框架,论文设计了一种新型的神经网络消息传递模型——扩散启发式Transformer,其全局注意力层源于能量约束扩散原理。
- 新模型在多种数据集上表现出良好性能,包括网络、图像、文本和物理粒子等。
点此查看论文截图

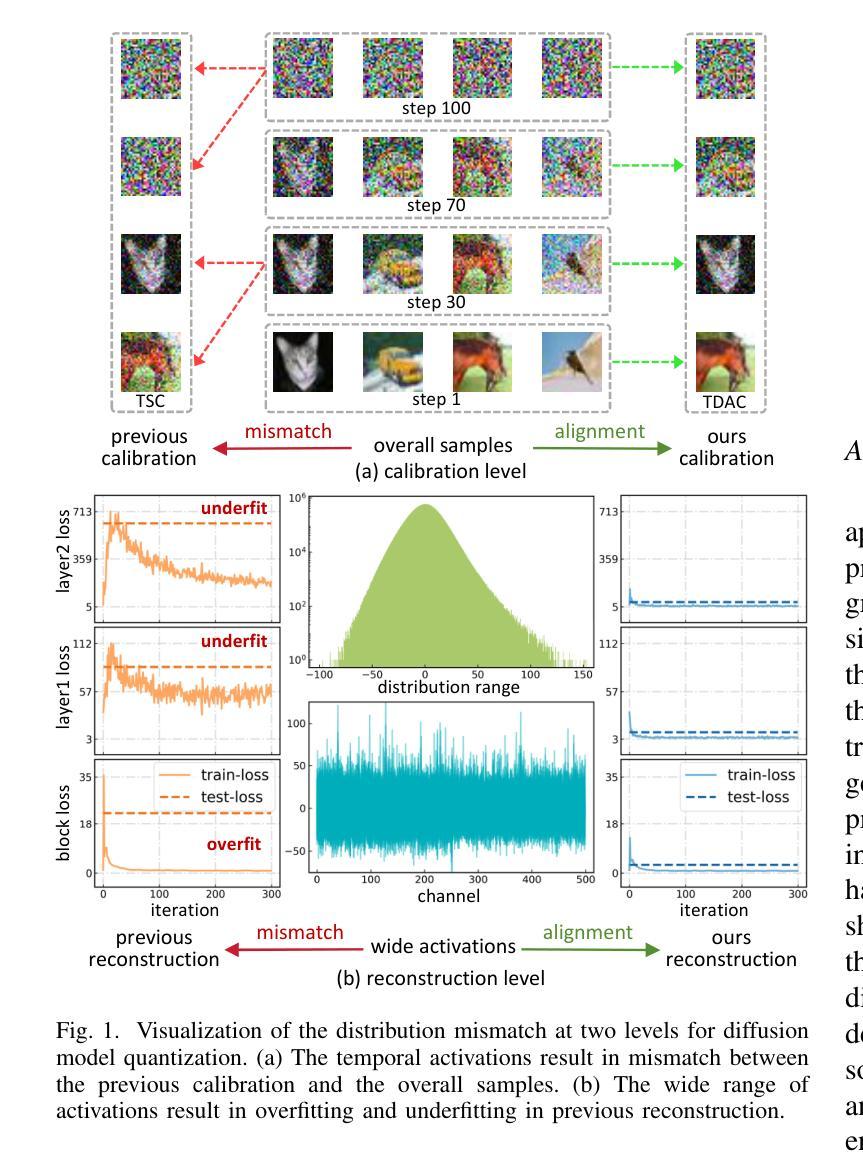
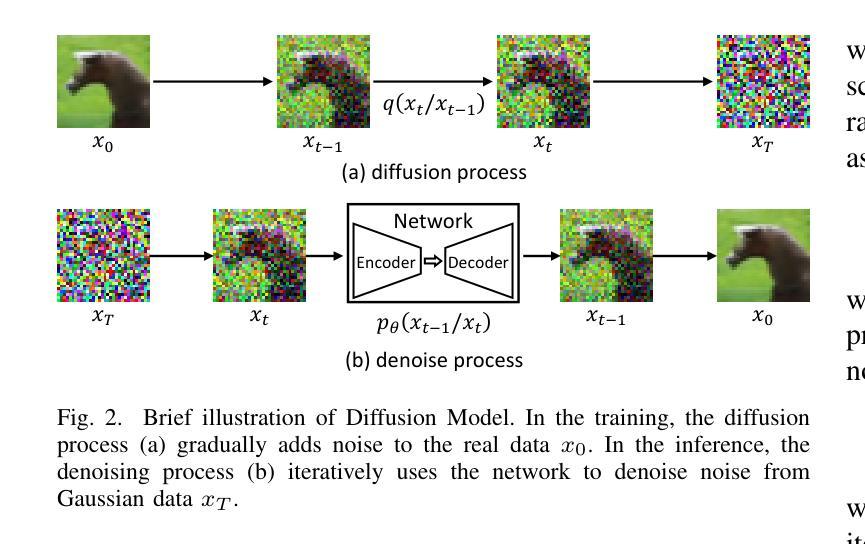
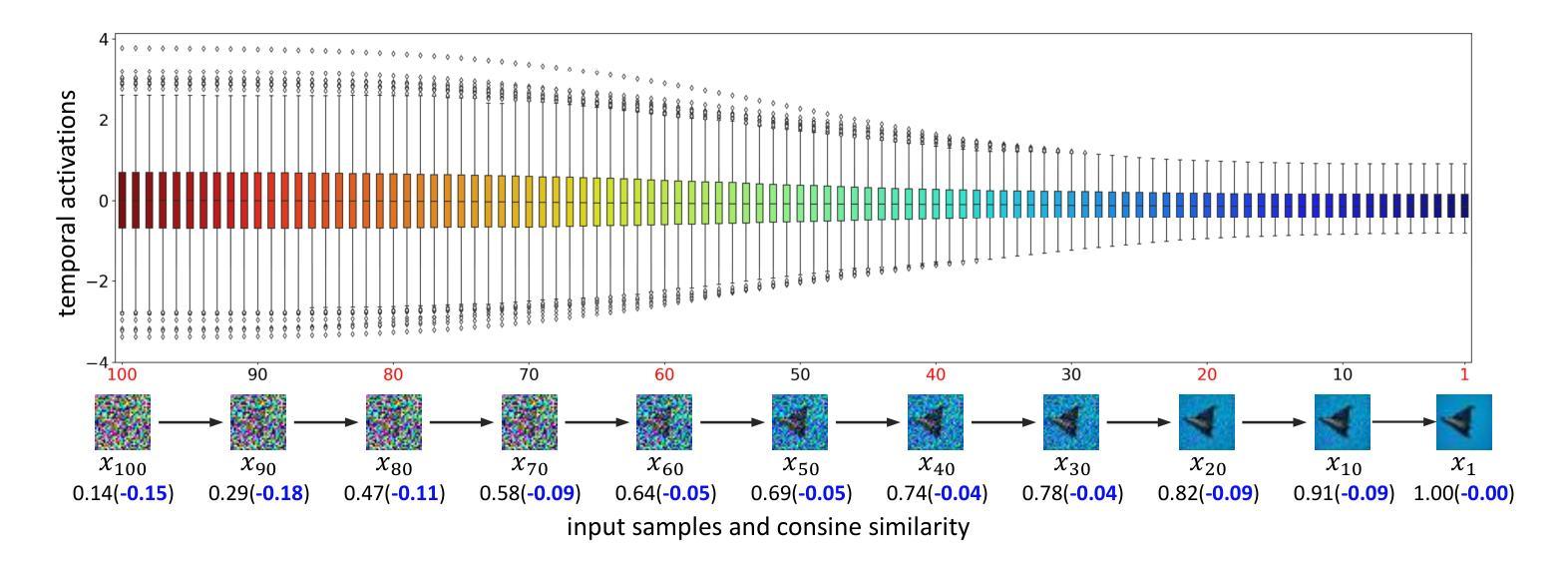
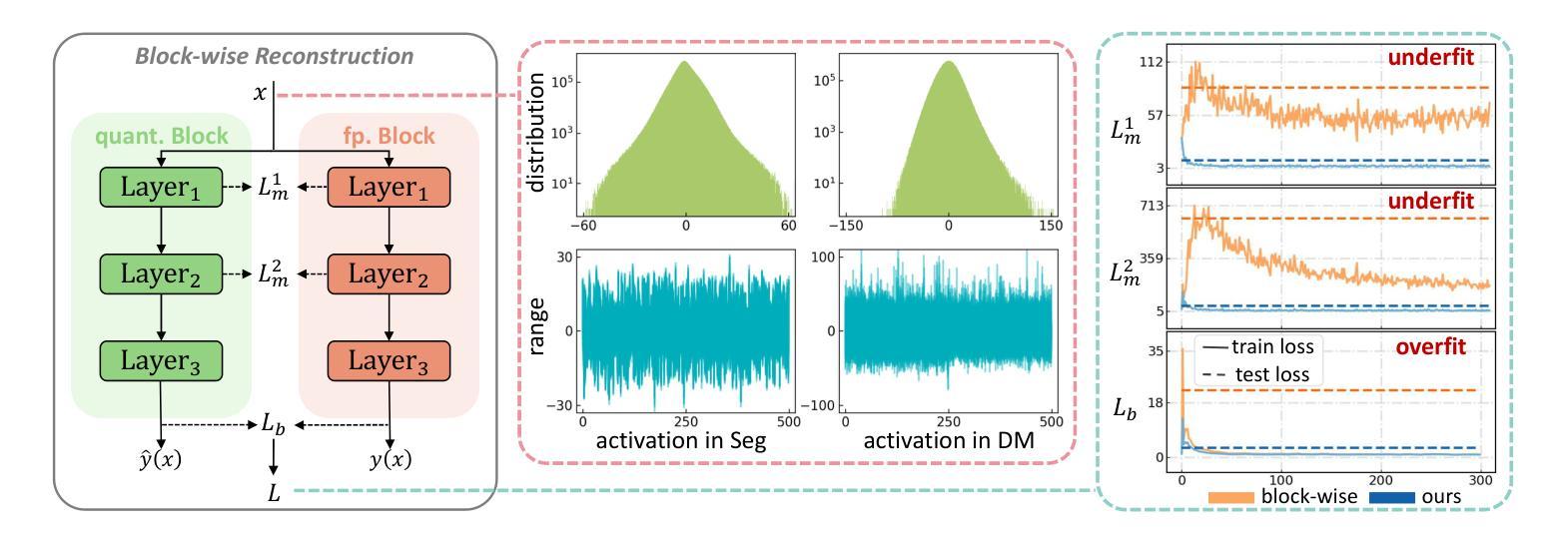
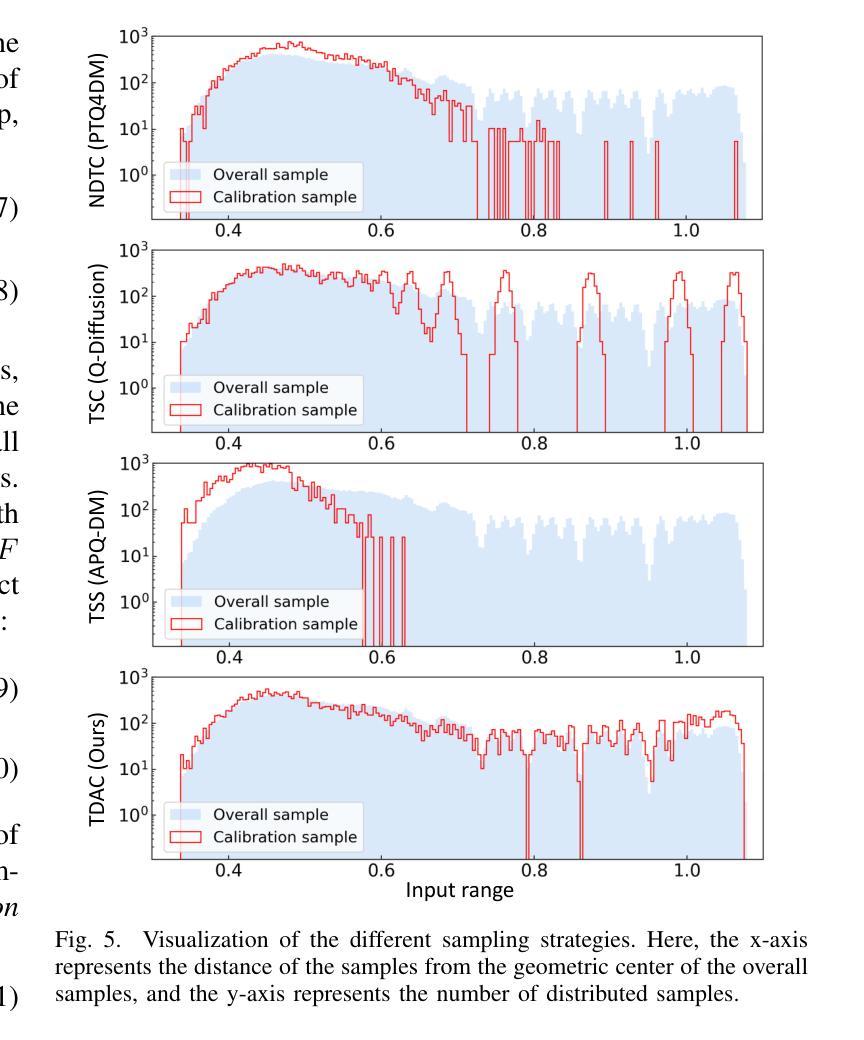
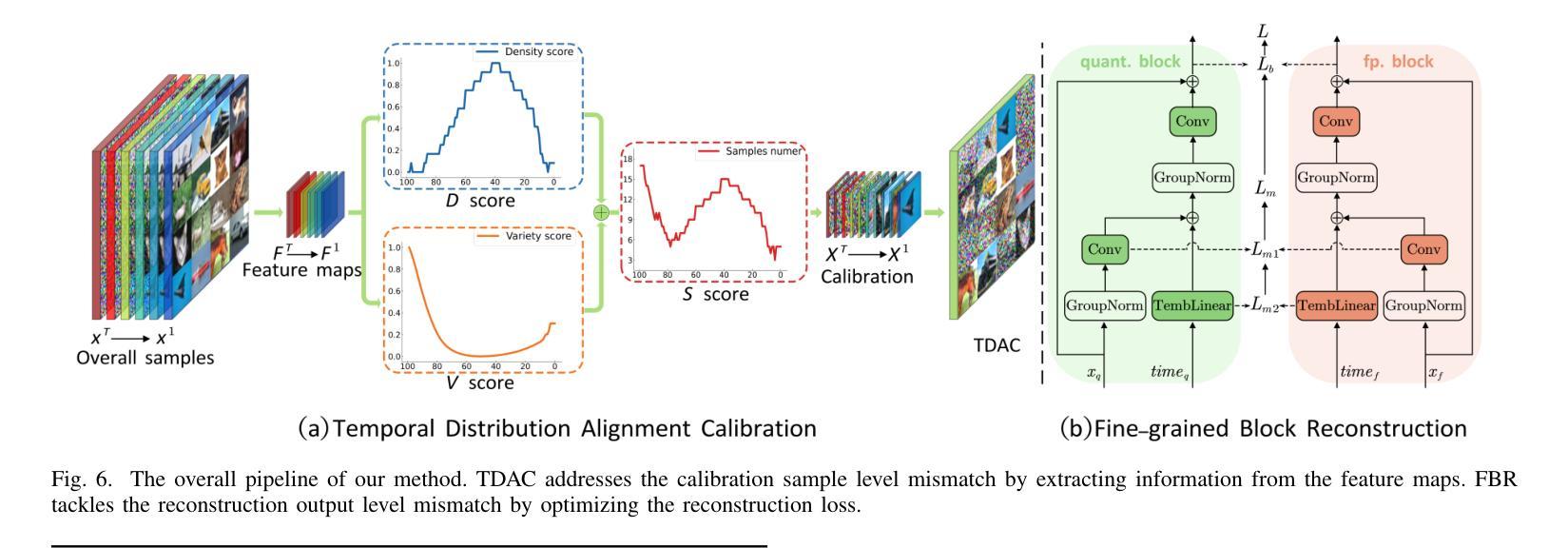
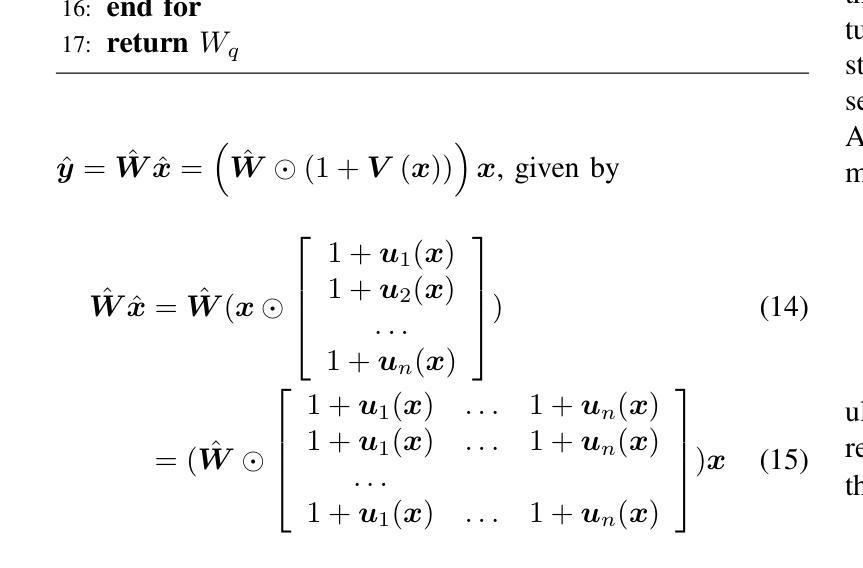
EDA-DM: Enhanced Distribution Alignment for Post-Training Quantization of Diffusion Models
Authors:Xuewen Liu, Zhikai Li, Junrui Xiao, Mengjuan Chen, Jianquan Li, Qingyi Gu
Diffusion models have achieved great success in image generation tasks. However, the lengthy denoising process and complex neural networks hinder their low-latency applications in real-world scenarios. Quantization can effectively reduce model complexity, and post-training quantization (PTQ), which does not require fine-tuning, is highly promising for compressing and accelerating diffusion models. Unfortunately, we find that due to the highly dynamic activations, existing PTQ methods suffer from distribution mismatch issues at both calibration sample level and reconstruction output level, which makes the performance far from satisfactory. In this paper, we propose EDA-DM, a standardized PTQ method that efficiently addresses the above issues. Specifically, at the calibration sample level, we extract information from the density and diversity of latent space feature maps, which guides the selection of calibration samples to align with the overall sample distribution; and at the reconstruction output level, we theoretically analyze the reasons for previous reconstruction failures and, based on this insight, optimize block reconstruction using the Hessian loss of layers, aligning the outputs of quantized model and full-precision model at different network granularity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EDA-DM significantly outperforms the existing PTQ methods across various models and datasets. Our method achieves a 1.83 times speedup and 4 times compression for the popular Stable-Diffusion on MS-COCO, with only a 0.05 loss in CLIP score. Code is available at http://github.com/BienLuky/EDA-DM .
扩散模型在图像生成任务中取得了巨大成功。然而,漫长的去噪过程和复杂的神经网络阻碍了其在现实场景中的低延迟应用。量化可以有效地降低模型复杂度,而不需要微调的后训练量化(PTQ)在压缩和加速扩散模型方面前景广阔。然而,我们发现由于激活高度动态,现有的PTQ方法在校准样本级别和重建输出级别都存在分布不匹配问题,这使得性能远不能令人满意。在本文中,我们提出了EDA-DM,一种标准化的PTQ方法,有效地解决了上述问题。具体而言,在校准样本级别,我们从潜在空间特征图的密度和多样性中提取信息,这有助于选择校准样本以符合总体样本分布;在重建输出级别,我们分析了之前重建失败的原因,并在此基础上,利用层的高斯损失优化块重建,使量化模型和全精度模型在不同网络粒度上的输出保持一致。大量实验表明,在各种模型和数据集上,EDA-DM显著优于现有的PTQ方法。我们的方法在MS-COCO上的流行Stable-Diffusion上实现了1.83倍的速度提升和4倍的压缩,同时CLIP分数只损失了0.05。相关代码可访问http://github.com/BienLuky/EDA-DM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: http://github.com/BienLuky/EDA-DM
摘要
扩散模型在图像生成任务中取得了巨大成功,但其去噪过程冗长、神经网络复杂,限制了其在现实场景中的低延迟应用。量化可以有效降低模型复杂度,后训练量化(PTQ)在不需微调的情况下展现出对压缩和加速扩散模型的巨大潜力。然而,由于激活高度动态,现有PTQ方法在校准样本级和重建输出级存在分布不匹配问题,性能难以令人满意。本文提出EDA-DM,一种标准化的PTQ方法,有效解决上述问题。在校准样本级,我们从潜在空间特征图的密度和多样性中提取信息,指导校准样本的选择,以与整体样本分布对齐;在重建输出级,我们分析以往重建失败的原因,基于此优化块重建,使用层的高斯损失,在不同网络粒度上对齐量化模型和全精度模型的输出。大量实验表明,EDA-DM在多种模型和数据集上显著优于现有PTQ方法。我们的方法为流行的Stable-Diffusion在MS-COCO上实现了1.83倍加速和4倍压缩,CLIP分数仅下降0.05。相关代码可通过http://github.com/BienLuky/EDA-DM获取。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在图像生成中表现优秀,但在实际低延迟应用中因过程冗长和神经网络复杂而受到限制。
- 量化是降低模型复杂度的一种有效方法,后训练量化(PTQ)为扩散模型的压缩和加速提供巨大潜力。
- 现有PTQ方法面临校准样本级和重建输出级的分布不匹配问题。
- EDA-DM是一种标准化的PTQ方法,通过提取潜在空间特征图的信息来解决分布不匹配问题,并在重建输出级进行优化。
- EDA-DM在多种模型和数据集上表现优于其他PTQ方法。
- 在MS-COCO上的Stable-Diffusion实验表明,EDA-DM实现了加速和压缩的同时,仅牺牲了微小的CLIP分数。
- 相关研究代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图