⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
Geometry-aware Distance Measure for Diverse Hierarchical Structures in Hyperbolic Spaces
Authors:Pengxiang Li, Yuwei Wu, Zhi Gao, Xiaomeng Fan, Wei Wu, Zhipeng Lu, Yunde Jia, Mehrtash Harandi
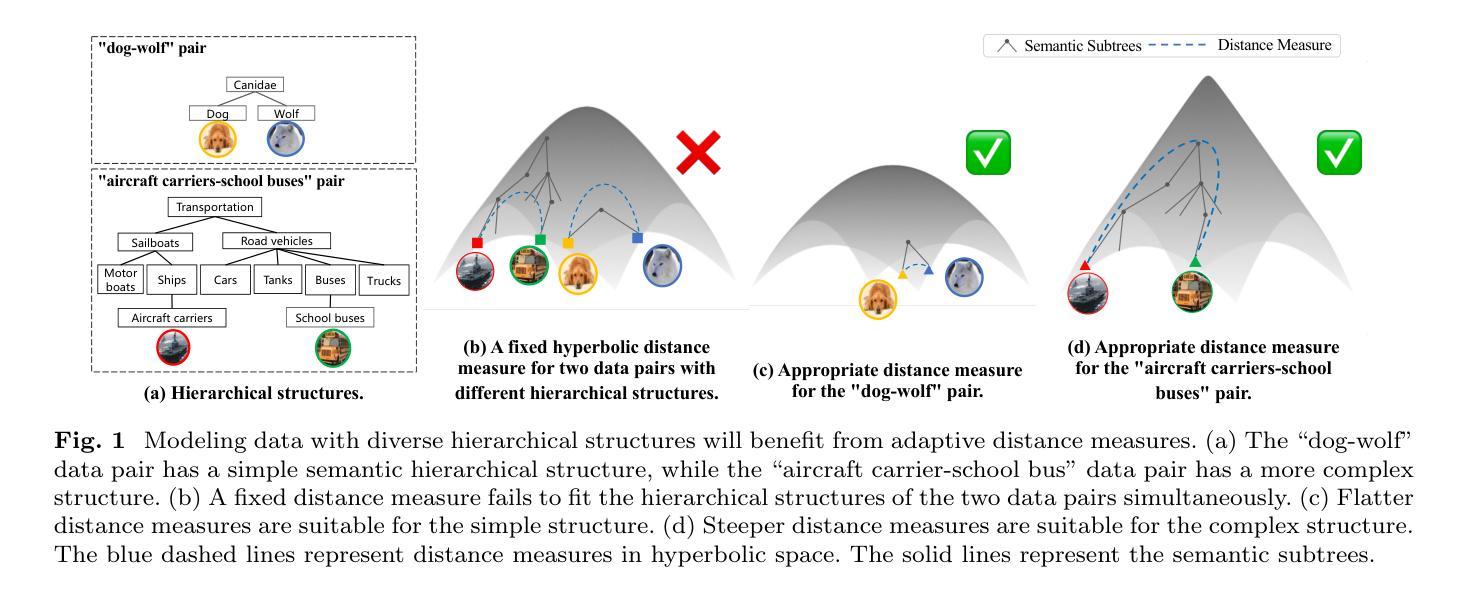
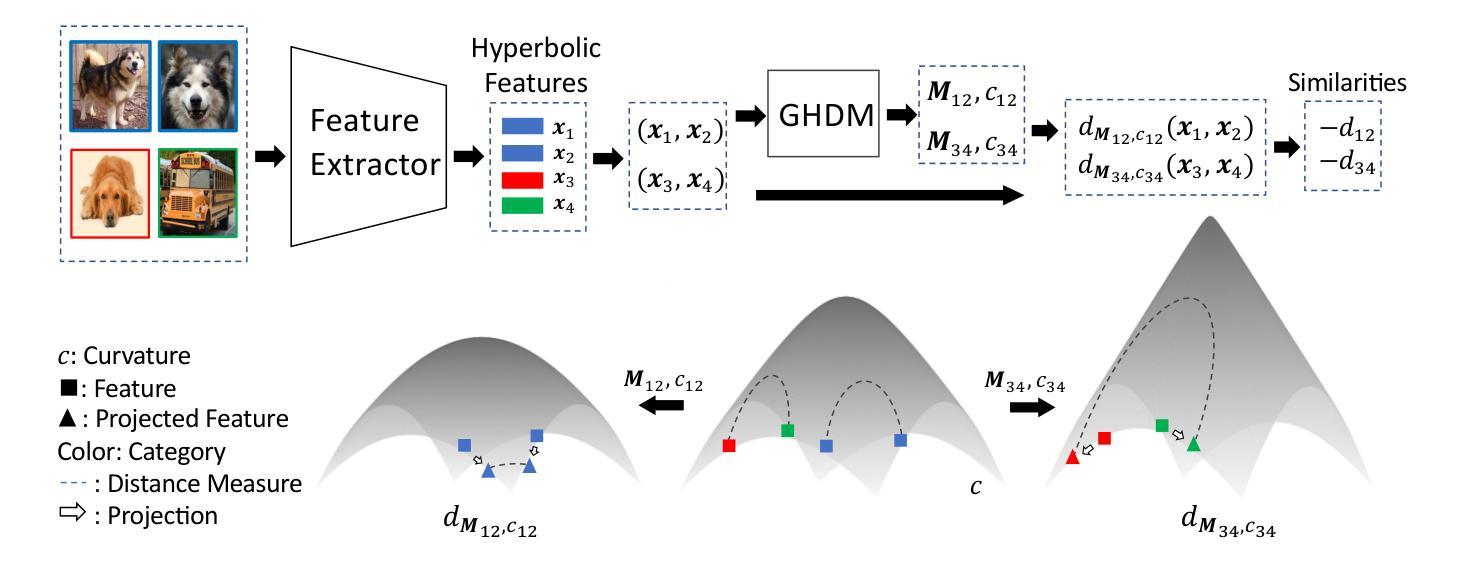
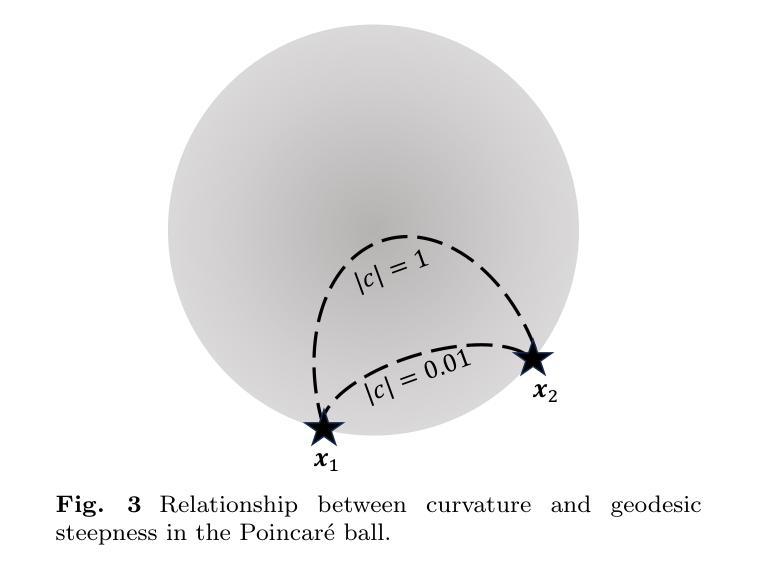
Learning in hyperbolic spaces has attracted increasing attention due to its superior ability to model hierarchical structures of data. Most existing hyperbolic learning methods use fixed distance measures for all data, assuming a uniform hierarchy across all data points. However, real-world hierarchical structures exhibit significant diversity, making this assumption overly restrictive. In this paper, we propose a geometry-aware distance measure in hyperbolic spaces, which dynamically adapts to varying hierarchical structures. Our approach derives the distance measure by generating tailored projections and curvatures for each pair of data points, effectively mapping them to an appropriate hyperbolic space. We introduce a revised low-rank decomposition scheme and a hard-pair mining mechanism to mitigate the computational cost of pair-wise distance computation without compromising accuracy. We present an upper bound on the low-rank approximation error using Talagrand’s concentration inequality, ensuring theoretical robustness. Extensive experiments on standard image classification (MNIST, CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100), hierarchical classification (5-level CIFAR-100), and few-shot learning tasks (mini-ImageNet, tiered-ImageNet) demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our approach consistently outperforms learning methods that use fixed distance measures, with notable improvements on few-shot learning tasks, where it achieves over 5% gains on mini-ImageNet. The results reveal that adaptive distance measures better capture diverse hierarchical structures, with visualization showing clearer class boundaries and improved prototype separation in hyperbolic spaces.
在超几何空间中的学习因其对数据结构层次结构的建模能力而受到越来越多的关注。大多数现有的超几何学习方法对所有数据使用固定的距离度量,假设所有数据点的层次结构是统一的。然而,现实世界的层次结构表现出很大的多样性,使得这个假设过于限制。在本文中,我们提出了一种超几何空间中的几何感知距离度量,它能动态适应不同的层次结构。我们的方法通过为每对数据点生成定制的投影和曲率来推导距离度量,有效地将它们映射到适当的超几何空间。我们引入了一种改进的低秩分解方案和硬对挖掘机制,以减轻成对距离计算的计算成本,同时不损失准确性。我们使用Talagrand的浓度不等式给出了低秩逼近误差的上界,确保了理论上的稳健性。在标准图像分类(MNIST、CIFAR-10和CIFAR-100)、层次分类(5级CIFAR-100)和少样本学习任务(mini-ImageNet、tiered-ImageNet)上的大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的方法始终优于使用固定距离度量的学习方法,在少样本学习任务上有显著改进,在mini-ImageNet上实现了超过5%的增益。结果表明,自适应距离度量能更好地捕捉多样化的层次结构,可视化显示超几何空间中的类边界更清晰,原型分离得到改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages
摘要
学习在双曲空间的方法因其在模拟数据层次结构方面的卓越能力而备受关注。然而,大多数现有方法采用固定距离度量所有数据,假设所有数据点之间存在统一的层次结构,这在现实世界中并不常见。本文提出了一种双曲空间中的几何感知距离度量,能够动态适应不同的层次结构。该方法通过为每对数据点生成定制投影和曲率来推导距离度量,有效地将其映射到适当的双曲空间。同时,我们引入了一种改进的低秩分解方案和硬对挖掘机制,以减轻成对距离计算的计算成本而不损失准确性。利用Talagrand的浓度不等式,我们对低秩近似误差给出了上界,确保理论稳健性。在标准图像分类(MNIST、CIFAR-10和CIFAR-100)、层次分类(5级CIFAR-100)和少镜头学习任务(mini-ImageNet、tiered-ImageNet)上的大量实验表明,我们的方法效果显著。相较于使用固定距离度量的学习方法,我们的方法始终表现出色,特别是在少镜头学习任务上实现了超过5%的增益。结果表明,自适应距离度量能更好地捕捉多样化的层次结构,可视化显示类边界更清晰,双曲空间中的原型分离得到改善。
关键见解
- 双曲空间中的学习因其建模数据层次结构的优势而受到关注。
- 现有方法假定统一距离度量对所有数据有效,这与现实世界的多样性不符。
- 本文提出了一种几何感知距离度量,能动态适应不同的数据层次结构。
- 通过定制投影和曲率为数据点生成适当的双曲空间映射。
- 引入改进的低秩分解和硬对挖掘来平衡计算效率和准确性。
- Talagrand的浓度不等式用于确保理论稳健性并设定低秩近似误差的上限。
点此查看论文截图

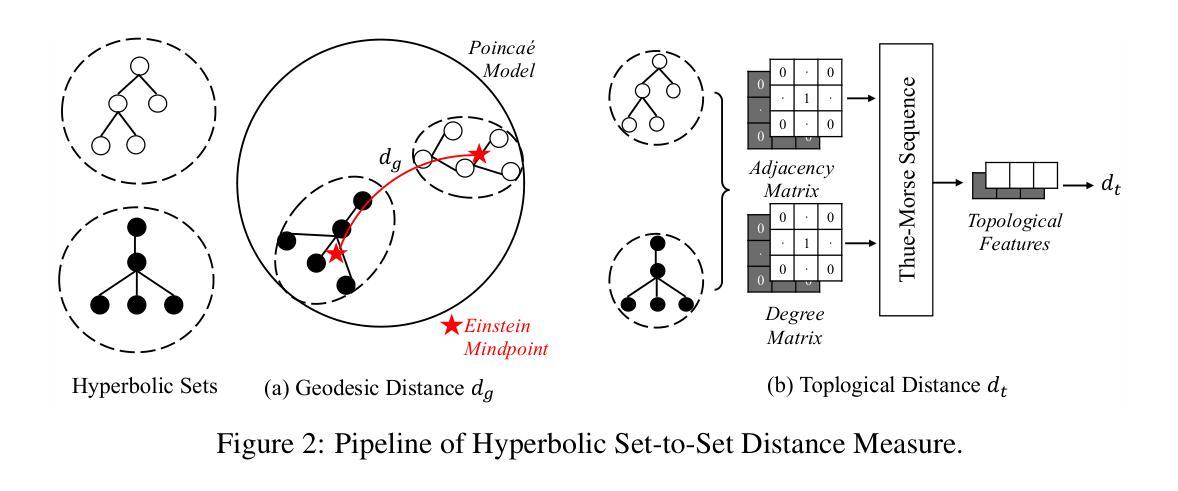
A Set-to-Set Distance Measure in Hyperbolic Space
Authors:Pengxiang Li, Wei Wu, Zhi Gao, Xiaomeng Fan, Peilin Yu, Yuwei Wu, Zhipeng Lu, Yunde Jia, Mehrtash Harandi
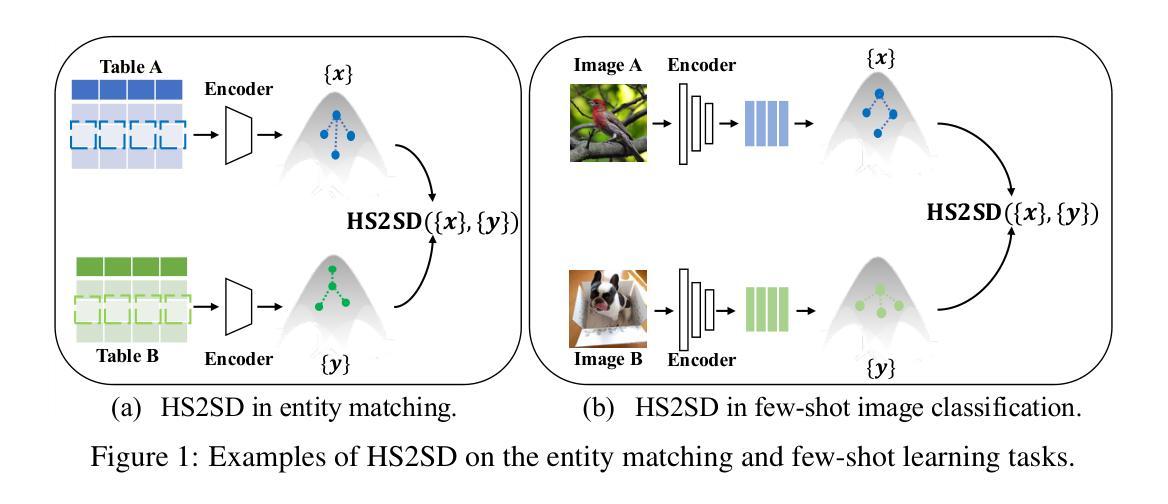
We propose a hyperbolic set-to-set distance measure for computing dissimilarity between sets in hyperbolic space. While point-to-point distances in hyperbolic space effectively capture hierarchical relationships between data points, many real-world applications require comparing sets of hyperbolic data points, where the local structure and the global structure of the sets carry crucial semantic information. The proposed the \underline{h}yperbolic \underline{s}et-\underline{to}-\underline{s}et \underline{d}istance measure (HS2SD) integrates both global and local structural information: global structure through geodesic distances between Einstein midpoints of hyperbolic sets, and local structure through topological characteristics of the two sets. To efficiently compute topological differences, we prove that using a finite Thue-Morse sequence of degree and adjacency matrices can serve as a robust approximation to capture the topological structure of a set. In this case, by considering the topological differences, HS2SD provides a more nuanced understanding of the relationships between two hyperbolic sets. Empirical evaluation on entity matching, standard image classification, and few-shot image classification demonstrates that our distance measure outperforms existing methods by effectively modeling the hierarchical and complex relationships inherent in hyperbolic sets.
我们提出了一种双曲集距离度量方法,用于计算双曲空间中集合之间的不相似性。虽然双曲空间中的点-点距离可以有效地捕获数据点之间的层次关系,但在许多现实世界的应用中需要比较双曲数据点的集合,其中集合的局部结构和全局结构携带重要的语义信息。提出的双曲集距离度量(HS2SD)结合了全局和局部结构信息:通过双曲集合的爱因斯坦中点之间的测地线距离来体现全局结构,并通过两个集合的拓扑特征来体现局部结构。为了有效地计算拓扑差异,我们证明使用有限度的Thue-Morse序列和度与邻接矩阵可以作为一个稳健的近似来捕捉集合的拓扑结构。在这种情况下,通过考虑拓扑差异,HS2SD可以更深入地理解两个双曲集之间的关系。在实体匹配、标准图像分类和少样本图像分类上的实证研究证明,我们的距离度量方法通过有效地建模双曲集中固有的层次和复杂关系,优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages
Summary
本文提出一种基于双曲空间的集合间距离度量方法,用于计算集合之间的不相似性。该方法结合了全局和局部结构信息,通过爱因斯坦中点之间的测地线距离捕捉全局结构,通过集合的拓扑特征捕捉局部结构。通过利用有限度的Thue-Morse序列和邻接矩阵,该方法能够高效计算拓扑差异,更深入地理解两个双曲集合之间的关系。经验评估表明,该方法在实体匹配、标准图像分类和少样本图像分类中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于双曲空间的集合间距离度量方法(HS2SD)。
- HS2SD结合了全局和局部结构信息,通过爱因斯坦中点的测地线距离和集合的拓扑特征来实现。
- 利用有限Thue-Morse序列和邻接矩阵高效计算集合的拓扑差异。
- HS2SD提供了对两个双曲集合之间关系的更深入理解。
- 在实体匹配、标准图像分类和少样本图像分类中进行了经验评估。
- HS2SD在复杂关系的建模中表现优异,尤其是在捕捉数据的层次结构方面。
点此查看论文截图

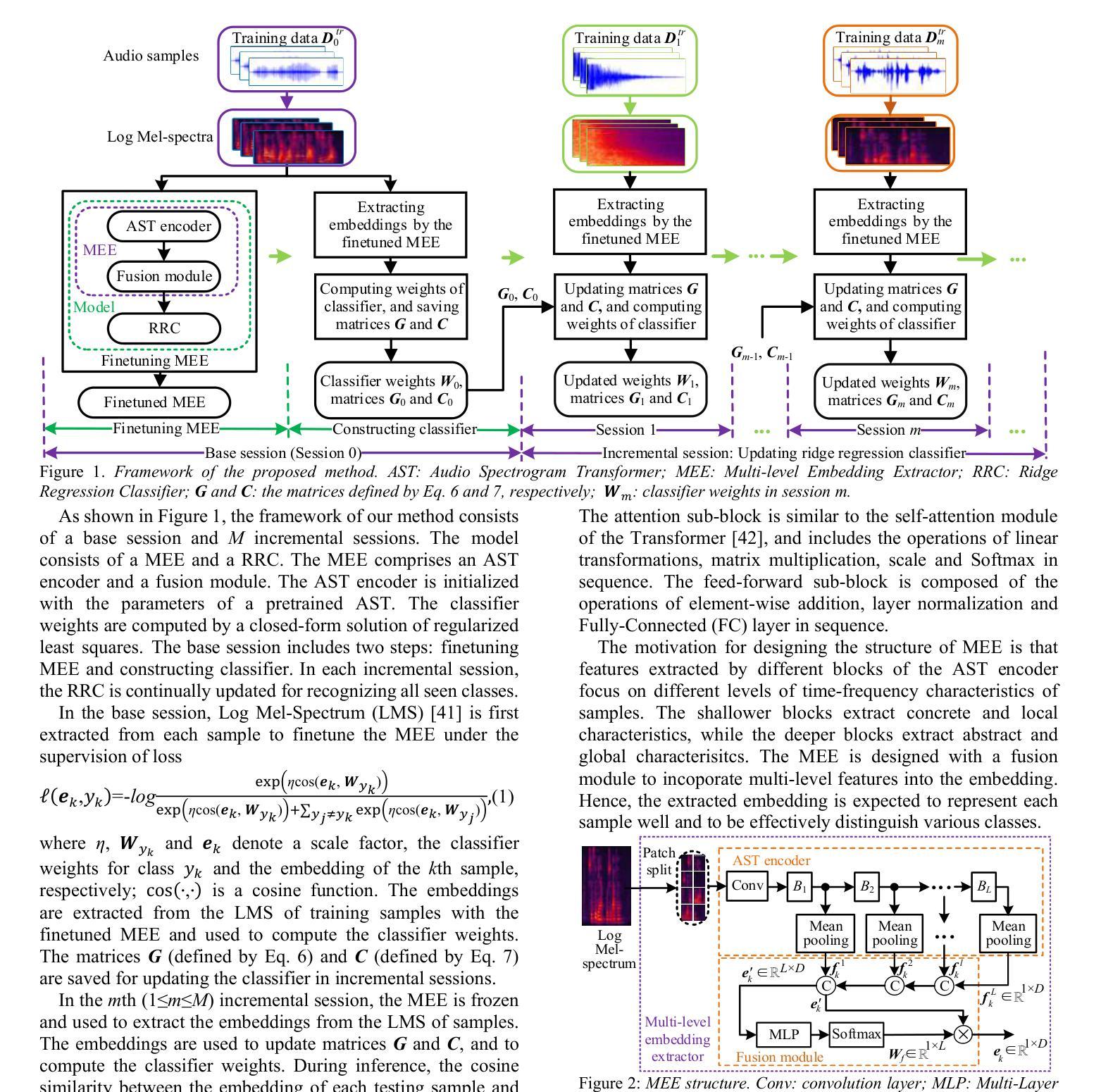
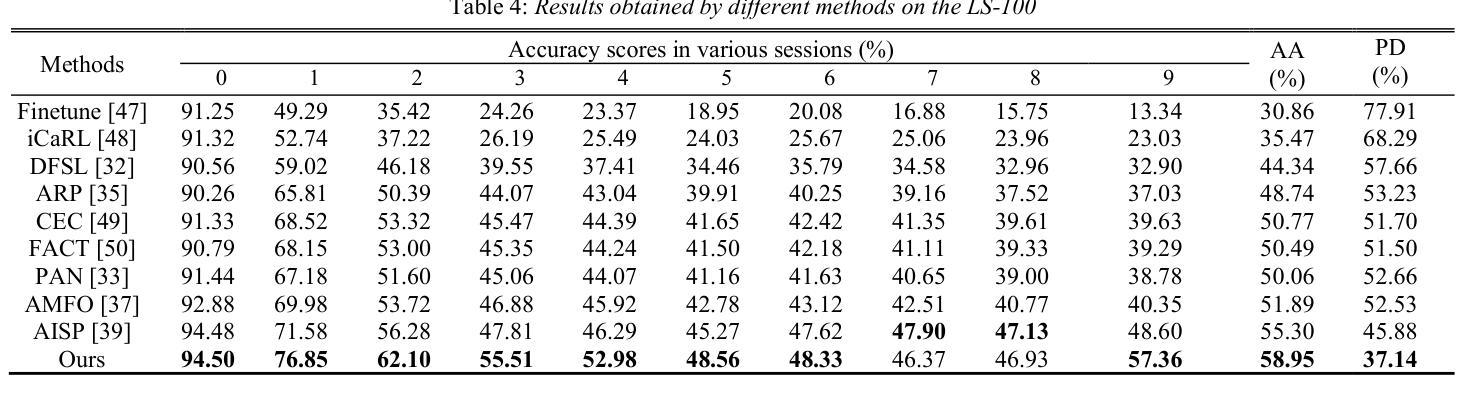
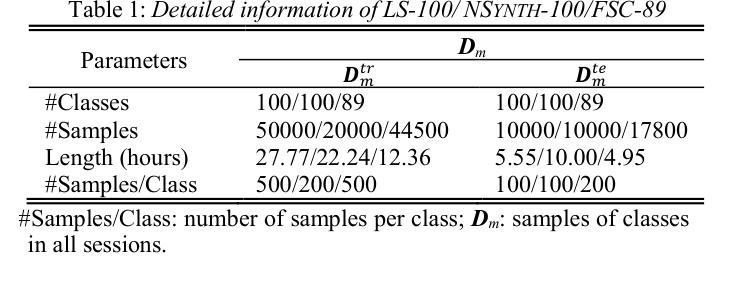
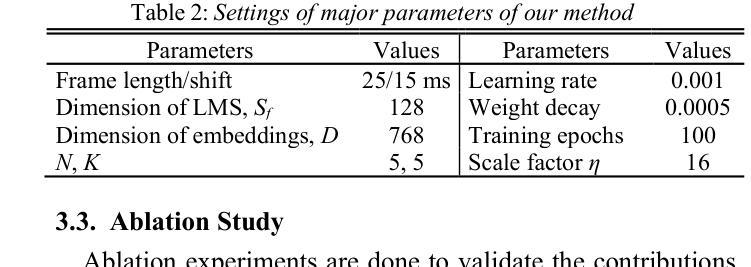
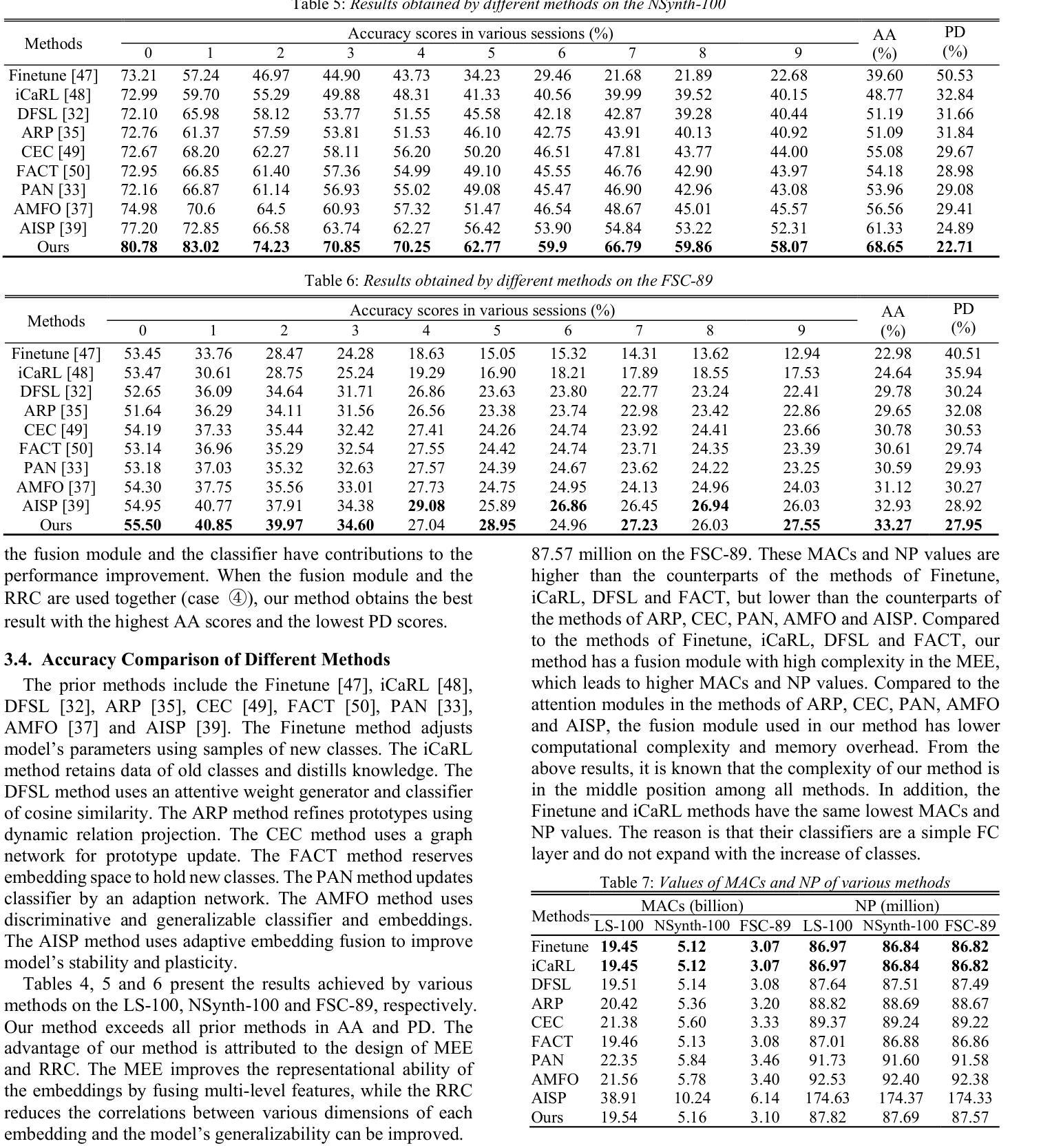
Fully Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification Using Multi-level Embedding Extractor and Ridge Regression Classifier
Authors:Yongjie Si, Yanxiong Li, Jiaxin Tan, Qianhua He, Il-Youp Kwak
In the task of Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification (FCAC), training samples of each base class are required to be abundant to train model. However, it is not easy to collect abundant training samples for many base classes due to data scarcity and high collection cost. We discuss a more realistic issue, Fully FCAC (FFCAC), in which training samples of both base and incremental classes are only a few. Furthermore, we propose a FFCAC method using a model which is decoupled into a multi-level embedding extractor and a ridge regression classifier. The embedding extractor consists of an encoder of audio spectrogram Transformer and a fusion module, and is trained in the base session but frozen in all incremental sessions. The classifier is updated continually in each incremental session. Results on three public datasets show that our method exceeds current methods in accuracy, and has advantage over most of them in complexity. The code is at https://github.com/YongjieSi/MAR.
在Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification(FCAC)任务中,需要各类基础模型的训练样本丰富。然而,由于数据稀缺和收集成本高昂,收集许多基础类的大量训练样本并不容易。我们讨论了一个更实际的问题,即完全FCAC(FFCAC),其中基础类和增量类的训练样本都很少。此外,我们提出了一种FFCAC方法,该方法使用了一个被解耦为多级嵌入提取器和岭回归分类器的模型。嵌入提取器由音频光谱图Transformer的编码器和融合模块组成,它在基础会话中进行训练,但在所有增量会话中被冻结。分类器会在每个增量会话中不断更新。在三个公共数据集上的结果表明,我们的方法在准确度上超过了当前的方法,在复杂性上大多数方法都无法与之匹敌。代码位于https://github.com/YongjieSi 可以通过该链接获取更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication on Interspeech 2025. 5 pages, 6 tables, 7 figures
Summary
针对少样本类增量音频分类任务(FCAC),由于数据稀缺和收集成本高昂,难以收集各类丰富训练样本。研究团队探讨更现实的问题——完全FCAC(FFCAC),其中基础类和增量类的训练样本都很少。他们提出了一种FFCAC方法,使用分离成多级嵌入提取器和岭回归分类器的模型。嵌入提取器由音频频谱图Transformer的编码器和融合模块组成,在基础会话中进行训练,但在所有增量会话中冻结。分类器在每个增量会话中不断更新。在三个公共数据集上的结果表明,该方法在精度上超过了当前的方法,并在复杂性方面的大多数方面都具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- FCAC任务需要为每个基础类提供丰富的训练样本,但由于数据稀缺和收集成本高昂,这一要求难以实现。
- 研究团队引入了完全FCAC(FFCAC)问题,其中基础类和增量类的训练样本都有限。
- 提出了一种FFCAC方法,使用分离的多级嵌入提取器和岭回归分类器。
- 嵌入提取器由音频频谱图Transformer的编码器和融合模块组成,并在基础会话中训练,之后冻结。
- 分类器会在每个增量会话中持续更新。
- 在三个公共数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法在精度上有所超越,并在复杂性方面具优势。
点此查看论文截图

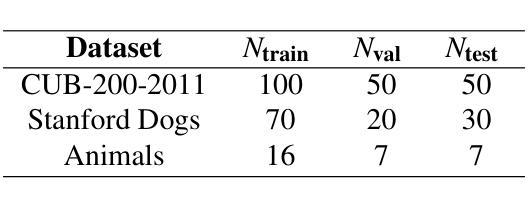
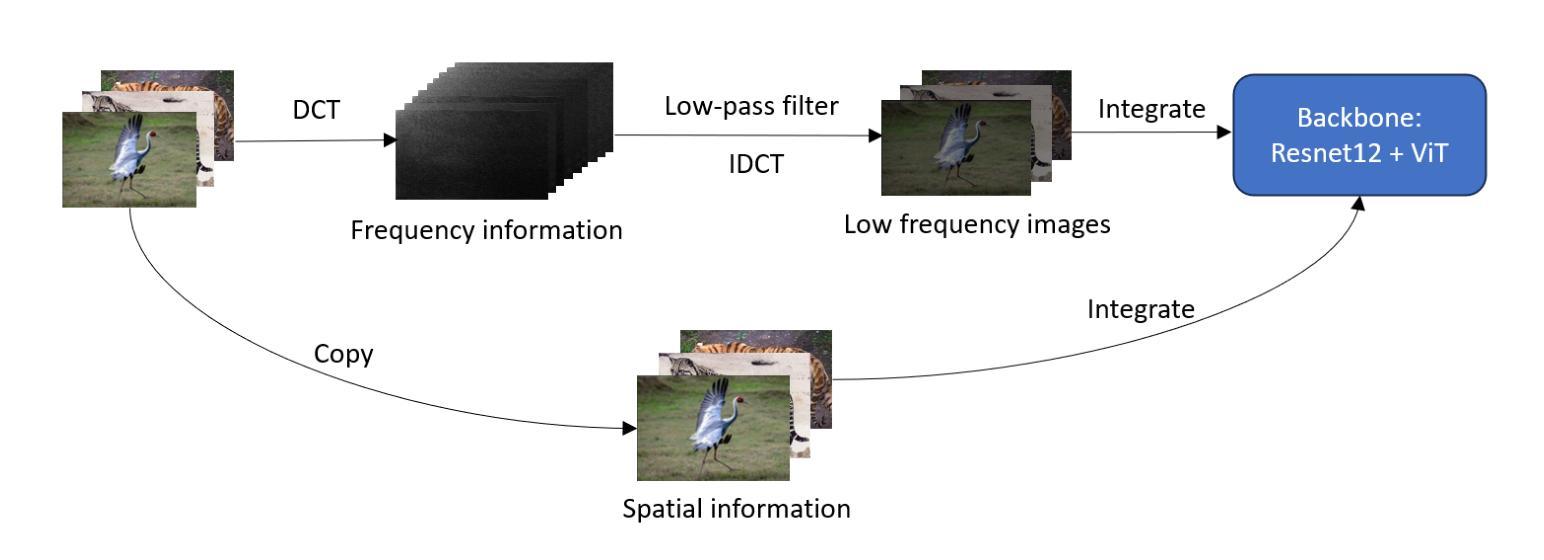
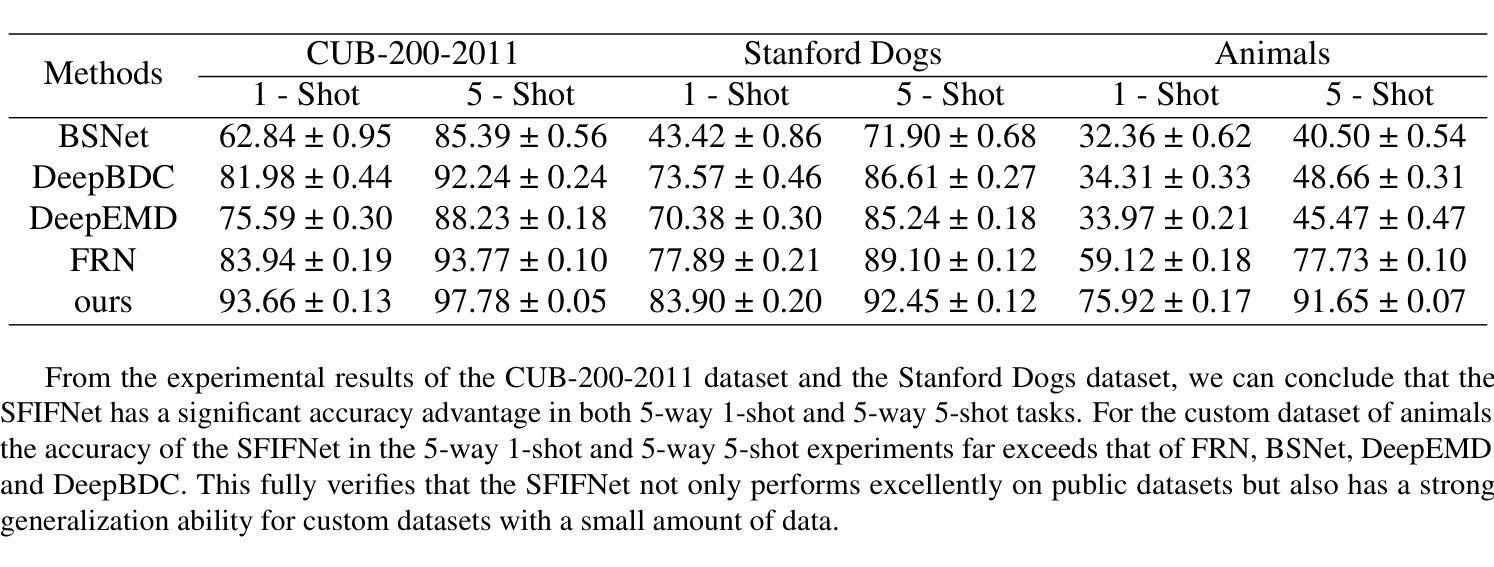
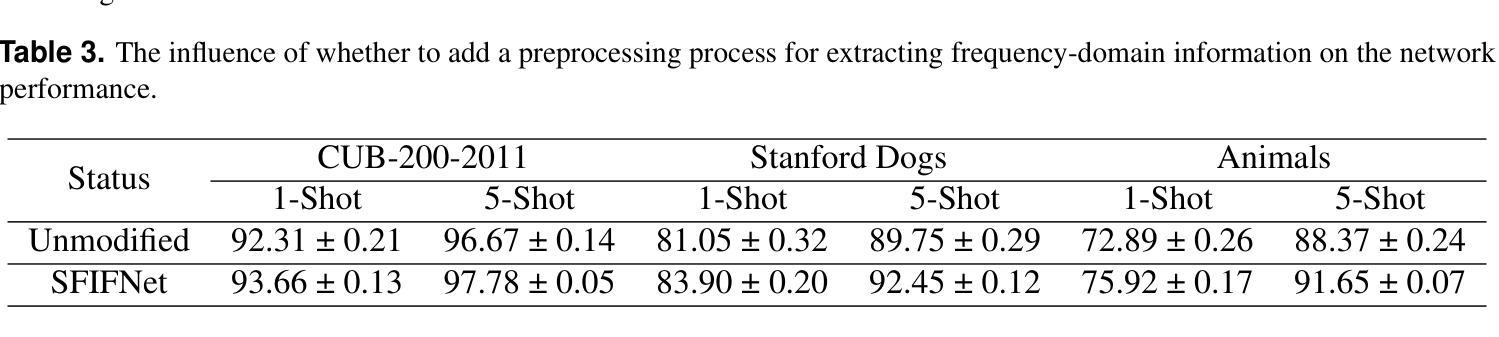
Spatial frequency information fusion network for few-shot learning
Authors:Wenqing Zhao, Guojia Xie, Han Pan, Biao Yang, Weichuan Zhang
The objective of Few-shot learning is to fully leverage the limited data resources for exploring the latent correlations within the data by applying algorithms and training a model with outstanding performance that can adequately meet the demands of practical applications. In practical applications, the number of images in each category is usually less than that in traditional deep learning, which can lead to over-fitting and poor generalization performance. Currently, many Few-shot classification models pay more attention to spatial domain information while neglecting frequency domain information, which contains more feature information. Ignoring frequency domain information will prevent the model from fully exploiting feature information, which would effect the classification performance. Based on conventional data augmentation, this paper proposes an SFIFNet with innovative data preprocessing. The key of this method is enhancing the accuracy of image feature representation by integrating frequency domain information with spatial domain information. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of this method in enhancing classification performance.
少样本学习的目标是充分利用有限的资源数据,通过应用算法训练出性能优异的模型,以满足实际应用的需求,并探索数据中的潜在关联。在实际应用中,每个类别的图像数量通常比传统的深度学习要少,这可能导致过拟合和泛化性能差的问题。目前,许多少样本分类模型过于关注空间域信息而忽略了频率域信息,后者包含了更多的特征信息。忽略频率域信息会阻止模型充分利用特征信息,从而影响分类性能。本文基于传统数据增强技术,提出了一种具有创新数据预处理功能的SFIFNet。该方法的关键是通过整合频率域信息和空间域信息来提高图像特征表示的准确性。实验结果表明,该方法在提高分类性能方面是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Few-shot学习的目标,即利用有限的资源数据探索数据中的潜在关联,并训练出具有良好性能的模型,以满足实际应用的需求。针对实际应用中每类图像数量通常较少的问题,许多Few-shot分类模型更注重空间域信息而忽视频率域信息。本文基于传统数据增强方法提出SFIFNet,通过整合频率域信息和空间域信息提高图像特征表示的准确性,从而提高分类性能。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot学习的目标是利用有限数据资源探索数据中的潜在关联,并训练出高性能模型满足实际应用需求。
- 实际应用中,每类图像数量通常较少,可能导致过拟合和泛化性能差。
- 当前许多Few-shot分类模型更注重空间域信息,而忽视频率域信息,后者包含更多特征信息。
- 忽视频率域信息会阻碍模型充分利用特征信息,影响分类性能。
- 本文提出SFIFNet,结合频率域信息和空间域信息,提高图像特征表示的准确性。
- 基于传统数据增强方法,SFIFNet能有效提高分类性能。
点此查看论文截图

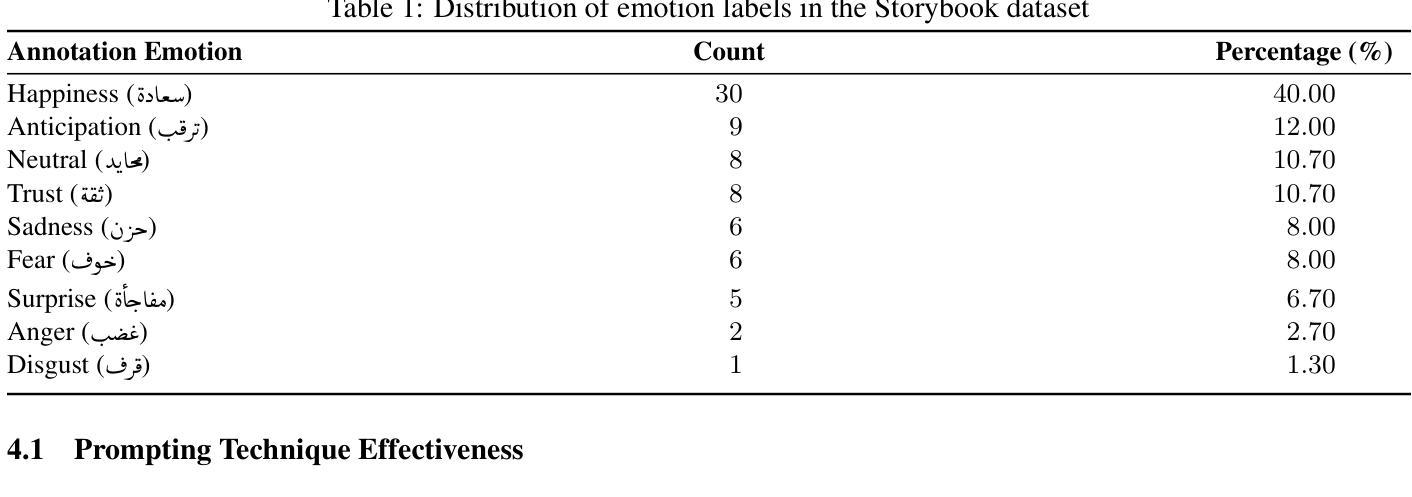
Deciphering Emotions in Children Storybooks: A Comparative Analysis of Multimodal LLMs in Educational Applications
Authors:Bushra Asseri, Estabraq Abdelaziz, Maha Al Mogren, Tayef Alhefdhi, Areej Al-Wabil
Emotion recognition capabilities in multimodal AI systems are crucial for developing culturally responsive educational technologies, yet remain underexplored for Arabic language contexts where culturally appropriate learning tools are critically needed. This study evaluates the emotion recognition performance of two advanced multimodal large language models, GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro, when processing Arabic children’s storybook illustrations. We assessed both models across three prompting strategies (zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought) using 75 images from seven Arabic storybooks, comparing model predictions with human annotations based on Plutchik’s emotional framework. GPT-4o consistently outperformed Gemini across all conditions, achieving the highest macro F1-score of 59% with chain-of-thought prompting compared to Gemini’s best performance of 43%. Error analysis revealed systematic misclassification patterns, with valence inversions accounting for 60.7% of errors, while both models struggled with culturally nuanced emotions and ambiguous narrative contexts. These findings highlight fundamental limitations in current models’ cultural understanding and emphasize the need for culturally sensitive training approaches to develop effective emotion-aware educational technologies for Arabic-speaking learners.
在多模态人工智能系统中,情感识别能力对于开发具有文化回应性的教育技术至关重要。然而,对于阿拉伯语言情境下的情感识别能力的研究仍然不足,而这里恰恰急需开发适合的文化学习工具。本研究旨在评估两种先进的多模态大型语言模型GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5 Pro在处理阿拉伯儿童故事书插图时的情感识别性能。我们使用了来自七本阿拉伯故事书的75张图片,通过三种提示策略(零次射击、少次射击和思维链),对这两种模型进行了评估,并将模型预测与人类基于普特奇情感框架的注释进行了比较。GPT-4o在所有条件下均表现优于Gemini,在思维链提示下达到最高的宏观F1分数为59%,而Gemini的最佳表现仅为43%。误差分析显示,系统存在误分类模式,其中情绪正负颠倒的错误占60.7%,且两个模型在处理具有文化细微差别的情绪和模糊叙事上下文时都遇到了困难。这些发现突显了当前模型在文化理解方面的基本局限性,并强调需要采用文化敏感的训练方法,以开发针对阿拉伯语学习者的有效情感感知教育技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇研究探讨了先进的双模态大型语言模型GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5 Pro在处理阿拉伯儿童故事书插图时的情绪识别性能。该研究在零样本、小样本和思维链三种提示策略下对这两个模型进行了评估,并与人类基于普特契克的情感框架的注释进行了比较。GPT-4o在各种条件下均表现优于Gemini,在思维链提示下达到最高的宏观F1分数为59%,而Gemini的最佳表现仅为43%。分析显示,模型存在系统性误分类模式,情感价值反转的错误占比较高,同时对于文化情感和模糊叙事环境的把握存在困难。这凸显了当前模型在文化理解上的局限性,并强调了为阿拉伯语学习者开发情感感知教育技术的需求,需要采用文化敏感的训练方法。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的多模态语言模型在阿拉伯语境下的情绪识别能力仍待提升。
- GPT-4o在处理阿拉伯儿童故事书插图时的情绪识别性能优于Gemini 1.5 Pro。
- 思维链提示策略对于提高情绪识别性能具有显著效果。
- 模型存在系统性的误分类问题,其中情感价值的反转是主要错误之一。
- 模型在理解和处理文化情感和模糊叙事环境方面存在挑战。
- 当前模型在文化理解上存在局限性,需要采用文化敏感的训练方法。
点此查看论文截图

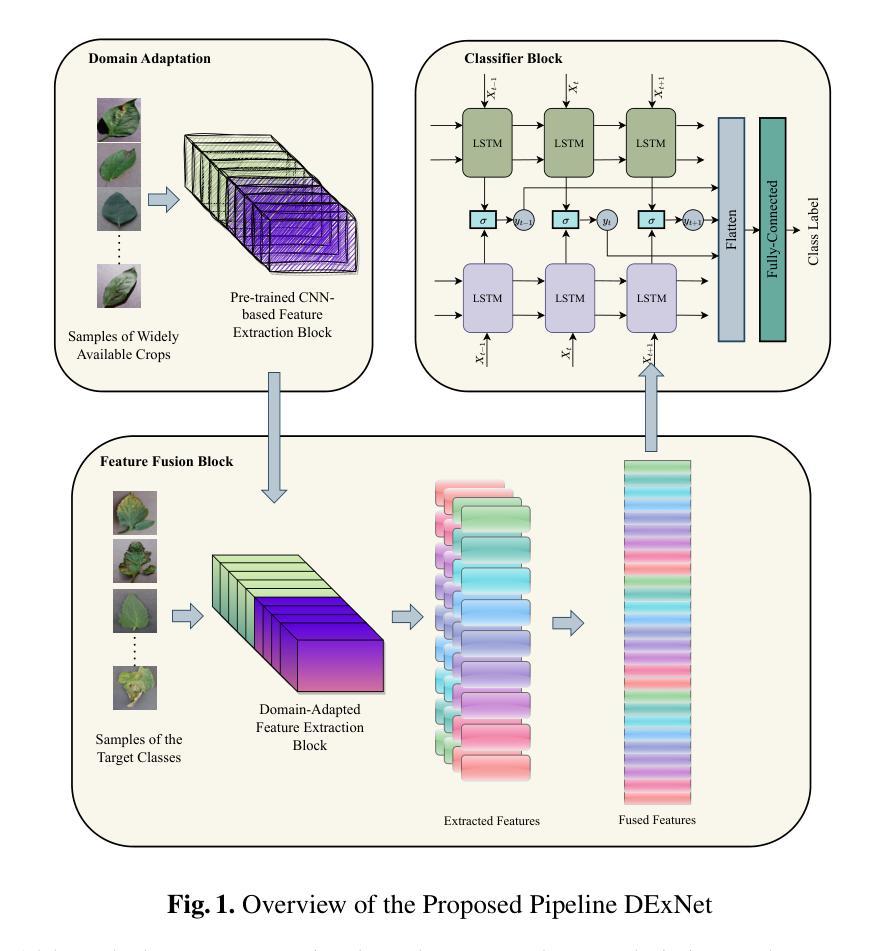
DExNet: Combining Observations of Domain Adapted Critics for Leaf Disease Classification with Limited Data
Authors:Sabbir Ahmed, Md. Bakhtiar Hasan, Tasnim Ahmed, Md. Hasanul Kabir
While deep learning-based architectures have been widely used for correctly detecting and classifying plant diseases, they require large-scale datasets to learn generalized features and achieve state-of-the-art performance. This poses a challenge for such models to obtain satisfactory performance in classifying leaf diseases with limited samples. This work proposes a few-shot learning framework, Domain-adapted Expert Network (DExNet), for plant disease classification that compensates for the lack of sufficient training data by combining observations of a number of expert critics. It starts with extracting the feature embeddings as ‘observations’ from nine ‘critics’ that are state-of-the-art pre-trained CNN-based architectures. These critics are ‘domain adapted’ using a publicly available leaf disease dataset having no overlapping classes with the specific downstream task of interest. The observations are then passed to the ‘Feature Fusion Block’ and finally to a classifier network consisting of Bi-LSTM layers. The proposed pipeline is evaluated on the 10 classes of tomato leaf images from the PlantVillage dataset, achieving promising accuracies of 89.06%, 92.46%, and 94.07%, respectively, for 5-shot, 10-shot, and 15-shot classification. Furthermore, an accuracy of 98.09+-0.7% has been achieved in 80-shot classification, which is only 1.2% less than state-of-the-art, allowing a 94.5% reduction in the training data requirement. The proposed pipeline also outperforms existing works on leaf disease classification with limited data in both laboratory and real-life conditions in single-domain, mixed-domain, and cross-domain scenarios.
虽然基于深度学习的架构已广泛应用于植物病害的准确检测和分类,但它们需要大规模数据集来学习通用特征并实现最先进的性能。这为在样本有限的情况下对叶片病害进行分类获得满意性能的模型带来了挑战。这项工作提出了一个用于植物病害分类的小样本学习框架——Domain-adapted Expert Network(DExNet)。它通过结合多个专业评论家(即疾病分类领域的专家)的观察来弥补缺乏足够训练数据的不足。首先,它从九个最先进的预训练CNN架构中提取特征嵌入作为来自专家的“观察结果”。这些专家通过使用与特定下游任务没有重叠类的公开可用的叶片病害数据集进行“域适应”。这些观察结果然后传递给“特征融合块”,并最终传递给由双向LSTM层组成的分类器网络。该管道在PlantVillage数据集的番茄叶片图像中的十个类别上进行了评估,在5镜头、10镜头和15镜头的分类中分别取得了令人鼓舞的89.06%、92.46%和94.07%的准确率。此外,在拥有更加复杂和多元的疾病类型和条件的实践中或条件特殊的状况下,通过结合多个领域的数据集进行训练,该管道在80镜头分类中实现了高达98.09%±0.7%的准确率,与最新技术相比仅降低了约百分之一点二%,显著减少了高达约百分之九十四点五的训练数据需求。提出的管道也在实验室和实际条件下的单域、混合域和跨域场景中表现优于现有针对叶片病害分类有限数据的现有作品。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ACPR Springer, 15 pages, 1 Figure, 7 Tables, and lots of efforts :)
Summary
本研究提出一种基于小样本学习的Domain-adapted Expert Network(DExNet)框架,用于植物病害分类。该框架通过结合多个专家的观察来弥补训练数据不足的问题。它在公开的植物叶片病害数据集上进行域适应,并使用特征融合块和包含Bi-LSTM层的分类器网络进行分类。在PlantVillage数据集的番茄叶片图像上评估,小样本分类达到较高准确率。此外,在减少训练数据需求的情况下,其性能接近最新技术。该框架在单域、混合域和跨域场景中均优于现有工作在叶片病害分类方面的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究针对植物病害分类提出一种基于小样本学习的DExNet框架。
- DExNet框架通过结合多个专家的观察来弥补训练数据不足的问题。
- DExNet使用了特征融合块和包含Bi-LSTM层的分类器网络进行分类。
- 在PlantVillage数据集的番茄叶片图像上评估,小样本分类达到较高准确率。
- 该框架在减少训练数据需求的情况下性能接近最新技术,并实现了显著的数据效率。
- 该框架在单域、混合域和跨域场景中的叶片病害分类表现均优于现有工作。
点此查看论文截图

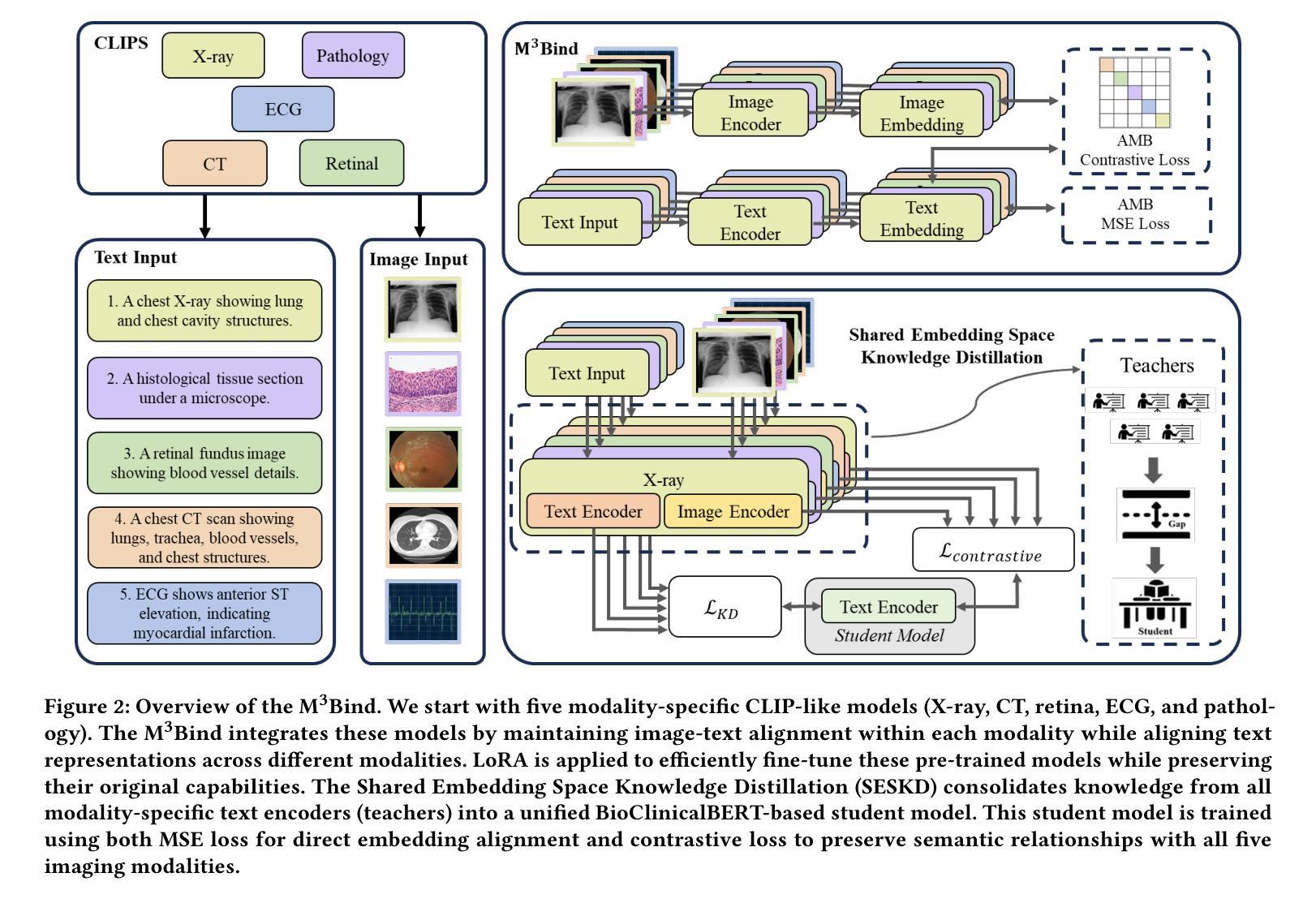
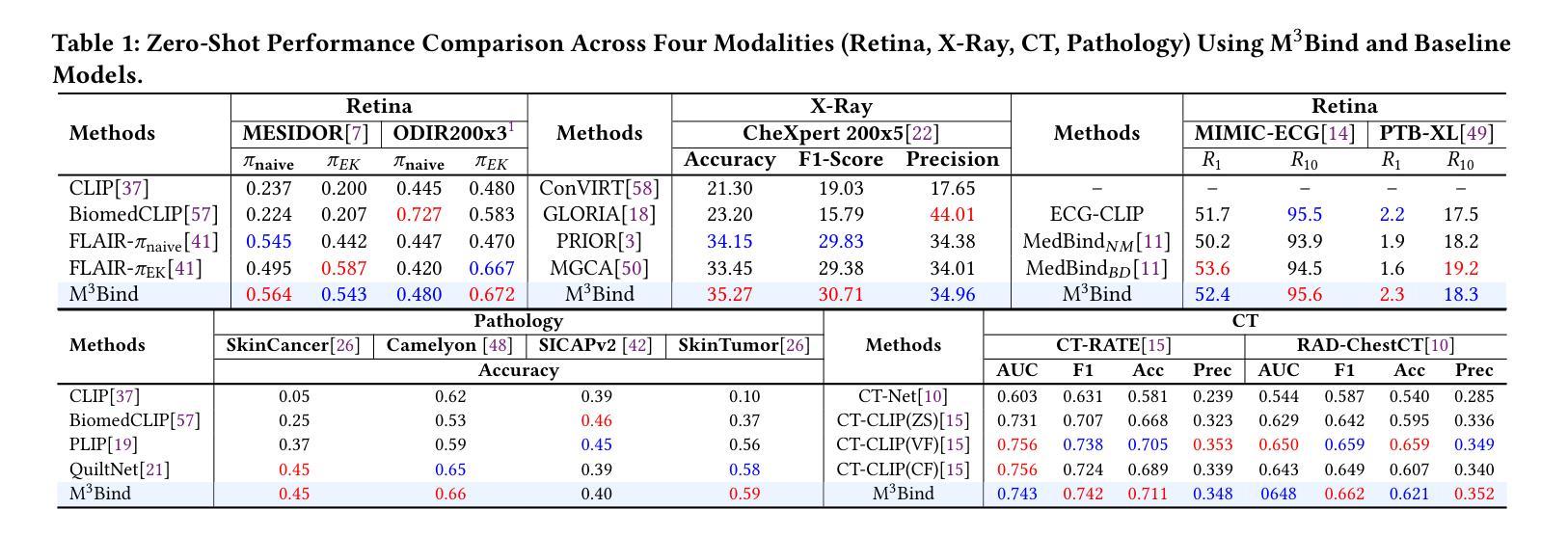
Multimodal Medical Image Binding via Shared Text Embeddings
Authors:Yunhao Liu, Suyang Xi, Shiqi Liu, Hong Ding, Chicheng Jin, Chenxi Yang, Junjun He, Yiqing Shen
Medical image analysis increasingly relies on the integration of multiple imaging modalities to capture complementary anatomical and functional information, enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Achieving aligned feature representations across these diverse modalities is therefore important for effective multimodal analysis. While contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) and its variant have enabled image-text alignments, they require explicitly paired data between arbitrary two modalities, which is difficult to acquire in medical contexts. To address the gap, we present Multimodal Medical Image Binding with Text (M\textsuperscript{3}Bind), a novel pre-training framework that enables seamless alignment of multiple medical imaging modalities through a shared text representation space without requiring explicit paired data between any two medical image modalities. Specifically, based on the insight that different images can naturally bind with text, M\textsuperscript{3}Bind first fine-tunes pre-trained CLIP-like image-text models to align their modality-specific text embedding space while preserving their original image-text alignments. Subsequently, we distill these modality-specific text encoders into a unified model, creating a shared text embedding space. Experiments on X-ray, CT, retina, ECG, and pathological images on multiple downstream tasks demonstrate that M\textsuperscript{3}Bind achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot, few-shot classification and cross-modal retrieval tasks compared to its CLIP-like counterparts. These results validate M\textsuperscript{3}Bind’s effectiveness in achieving cross-image-modal alignment for medical analysis.
医疗图像分析越来越依赖于多种成像模式的集成,以捕获互补的解剖和功能性信息,从而实现更准确的诊断和制定治疗方案。因此,实现这些不同模式之间的对齐特征表示对于有效的多模态分析至关重要。尽管对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)及其变体已经实现了图像文本的对齐,但它们需要任意两个模态之间的明确配对数据,这在医学背景下很难获取。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了基于文本的多模态医学图像绑定(M\textsuperscript{3}Bind),这是一种新的预训练框架,能够通过共享文本表示空间无缝对齐多个医学成像模式,而无需任何两个医学图像模式之间的明确配对数据。具体来说,基于不同图像可以自然绑定文本的见解,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind首先微调预训练的CLIP类似的图像文本模型,以对齐其特定于模态的文本嵌入空间,同时保留其原始的图像文本对齐。随后,我们将这些特定于模态的文本编码器蒸馏到统一模型中,创建一个共享的文本嵌入空间。在X光、CT、视网膜、心电图和病理图像上的多个下游任务进行的实验表明,与CLIP类似的模型相比,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上实现了最先进的性能。这些结果验证了M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在实现医学分析中的跨图像模态对齐方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures
总结
医学图像分析越来越依赖于多种成像方式的融合,捕捉互补的解剖及功能信息,以提供更准确的诊断和更全面的治疗计划。因此,实现在不同模态间的对齐特征表示对多模态分析至关重要。虽然对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)及其变体能够实现图像文本的匹配,但它们需要在两种任意模态之间进行明确配对的数据,这在医学环境中难以获取。为解决这一差距,我们提出了多模态医学图像与文本绑定(M\textsuperscript{3}Bind)的预训练框架,它能够通过共享文本表示空间无缝对齐多个医学成像模态,无需任何两种医学图像模态之间的明确配对数据。具体来说,基于不同图像可以自然绑定文本的见解,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind首先微调预训练的CLIP类图像文本模型,以对齐其模态特定的文本嵌入空间,同时保留其原始的图像文本匹配。随后,我们将这些模态特定的文本编码器蒸馏到统一模型中,创建共享文本嵌入空间。在X光、CT、视网膜、心电图和病理图像上的多项下游任务实验表明,与CLIP类模型相比,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上实现了最先进的性能。这些结果验证了M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在医学分析中实现跨图像模态对齐的有效性。
关键见解
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind是一个用于多模态医学图像分析的新预训练框架。
- 它通过共享文本表示空间实现了不同医学成像模态的无缝对齐。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind不依赖任意两种医学图像模态之间的明确配对数据。
- 该框架通过微调预训练的CLIP类模型并蒸馏模态特定的文本编码器来实现其性能。
- 在多种下游任务上的实验表明,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本和少样本分类以及跨模态检索任务上具有卓越性能。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind的有效性在于其能够实现跨图像模态的对齐,这对于医学分析至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

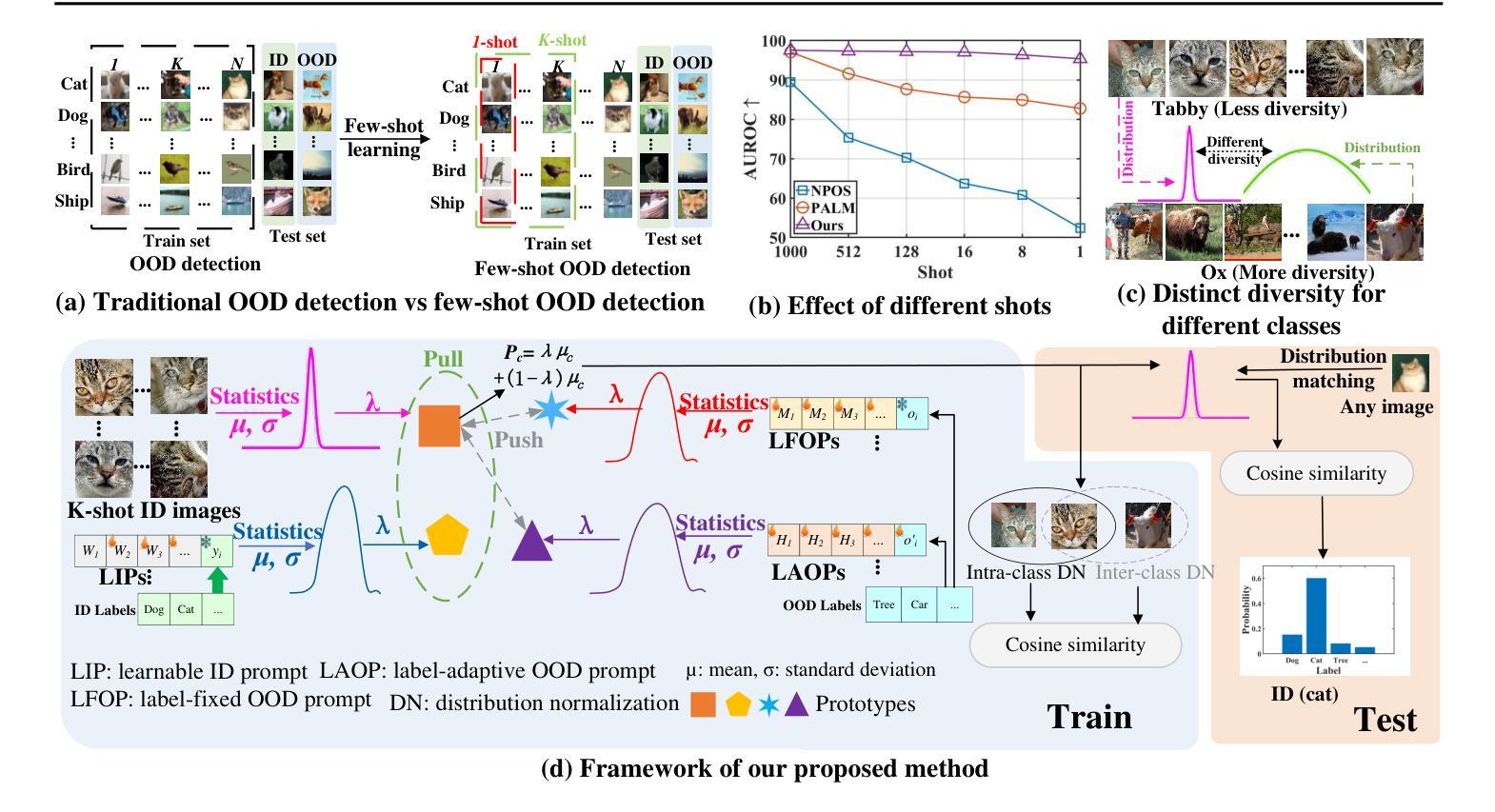
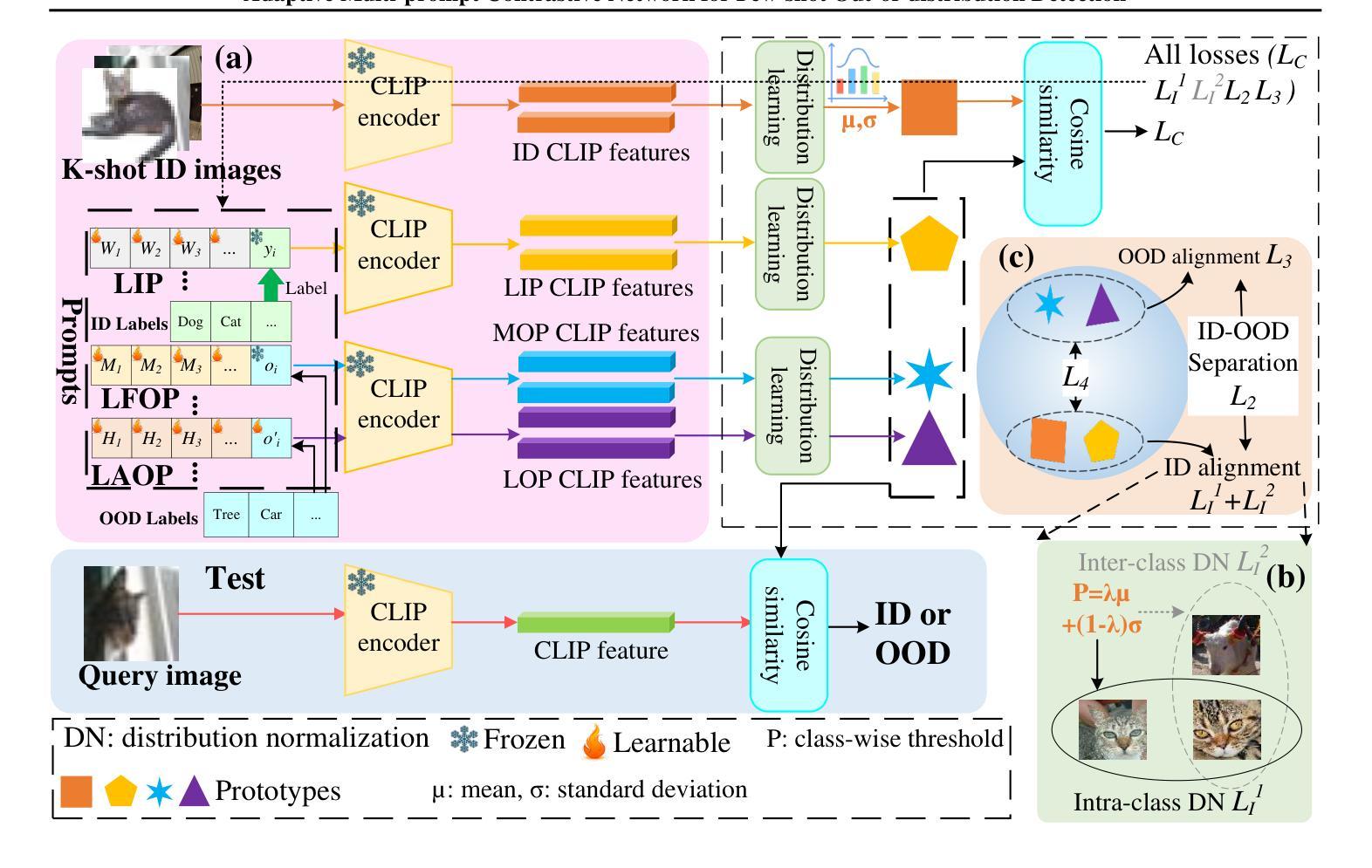
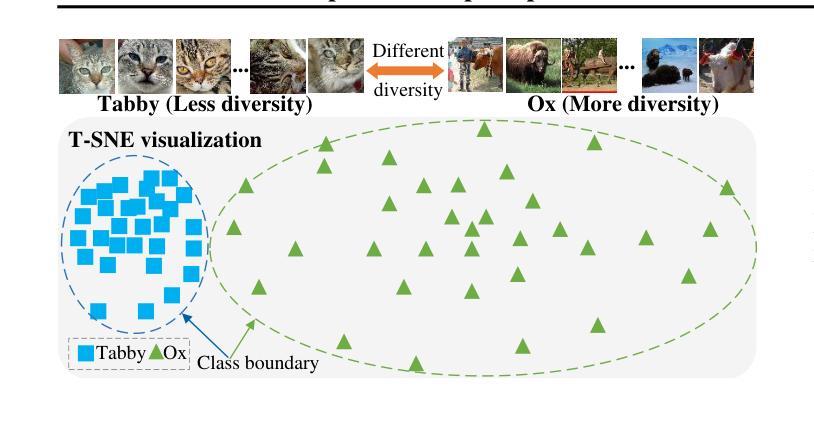
Adaptive Multi-prompt Contrastive Network for Few-shot Out-of-distribution Detection
Authors:Xiang Fang, Arvind Easwaran, Blaise Genest
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection attempts to distinguish outlier samples to prevent models trained on the in-distribution (ID) dataset from producing unavailable outputs. Most OOD detection methods require many IID samples for training, which seriously limits their real-world applications. To this end, we target a challenging setting: few-shot OOD detection, where {Only a few {\em labeled ID} samples are available.} Therefore, few-shot OOD detection is much more challenging than the traditional OOD detection setting. Previous few-shot OOD detection works ignore the distinct diversity between different classes. In this paper, we propose a novel network: Adaptive Multi-prompt Contrastive Network (AMCN), which adapts the ID-OOD separation boundary by learning inter- and intra-class distribution. To compensate for the absence of OOD and scarcity of ID {\em image samples}, we leverage CLIP, connecting text with images, engineering learnable ID and OOD {\em textual prompts}. Specifically, we first generate adaptive prompts (learnable ID prompts, label-fixed OOD prompts and label-adaptive OOD prompts). Then, we generate an adaptive class boundary for each class by introducing a class-wise threshold. Finally, we propose a prompt-guided ID-OOD separation module to control the margin between ID and OOD prompts. Experimental results show that AMCN outperforms other state-of-the-art works.
异常检测(OOD)旨在区分异常样本,以防止对分布内(ID)数据集训练的模型产生不可用输出。大多数OOD检测方法需要大量IID样本进行训练,这严重限制了它们在现实世界中的应用。为此,我们针对一个具有挑战性的场景:少样本异常检测,其中只有少数几个标记的ID样本可用。因此,少样本异常检测比传统的异常检测设置更具挑战性。以前的研究忽略了不同类别之间的明显多样性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型网络:自适应多提示对比网络(AMCN),它通过学习和类内分布来适应ID-OOD分离边界。为了弥补缺少OOD和ID图像样本稀缺的问题,我们利用CLIP技术连接文本和图像,构建可学习的ID和OOD文本提示。具体来说,我们首先生成自适应提示(可学习的ID提示、标签固定的OOD提示和标签自适应的OOD提示)。然后,我们通过引入类别特定的阈值为每个类别生成自适应的类别边界。最后,我们提出了一个提示引导的ID-OOD分离模块来控制ID和OOD提示之间的间隔。实验结果表明,AMCN优于其他最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了自适应多提示对比网络(AMCN),该网络针对少样本的OOD检测问题进行了优化。通过生成自适应提示和类边界,并利用CLIP连接文本和图像,工程学习ID和OOD的文本提示,AMCN能够适应不同类别之间的独特差异,有效区分ID和OOD样本。实验结果表明,AMCN在少样本OOD检测任务上优于其他最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- 本文针对少样本OOD检测问题提出了一种新的网络结构——自适应多提示对比网络(AMCN)。
- AMCN通过生成自适应提示来适应不同类别之间的独特差异,并利用CLIP连接文本和图像,构建学习ID和OOD的文本提示。
- 为了弥补OOD样本的缺乏和ID图像样本的稀缺性,AMCN引入了可学习的ID提示和标签固定的OOD提示以及标签自适应的OOD提示。
- AMC N引入了为每个类别生成的类边界和类别特定的阈值来控制不同类别的分布边界。
点此查看论文截图

Trustworthy Few-Shot Transfer of Medical VLMs through Split Conformal Prediction
Authors:Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Ismail Ben Ayed, Jose Dolz
Medical vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated unprecedented transfer capabilities and are being increasingly adopted for data-efficient image classification. Despite its growing popularity, its reliability aspect remains largely unexplored. This work explores the split conformal prediction (SCP) framework to provide trustworthiness guarantees when transferring such models based on a small labeled calibration set. Despite its potential, the generalist nature of the VLMs’ pre-training could negatively affect the properties of the predicted conformal sets for specific tasks. While common practice in transfer learning for discriminative purposes involves an adaptation stage, we observe that deploying such a solution for conformal purposes is suboptimal since adapting the model using the available calibration data breaks the rigid exchangeability assumptions for test data in SCP. To address this issue, we propose transductive split conformal adaptation (SCA-T), a novel pipeline for transfer learning on conformal scenarios, which performs an unsupervised transductive adaptation jointly on calibration and test data. We present comprehensive experiments utilizing medical VLMs across various image modalities, transfer tasks, and non-conformity scores. Our framework offers consistent gains in efficiency and conditional coverage compared to SCP, maintaining the same empirical guarantees.
医疗视觉语言模型(VLMs)已展现出前所未有的迁移能力,并越来越多地被用于高效图像分类。尽管其越来越受欢迎,但其可靠性方面仍被大量忽视。本研究探讨了分裂顺应性预测(SCP)框架,在基于一小部分标记校准集迁移此类模型时,为其提供可靠性保证。尽管具有潜力,但VLMs的预训练通用性可能会针对特定任务对预测顺应集的属性产生负面影响。在判别目的迁移学习中,常见做法涉及适应阶段,我们观察到针对顺应目的部署这样的解决方案是不理想的,因为使用可用的校准数据适应模型会破坏SCP中测试数据的刚性可交换假设。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了归纳分裂顺应适应(SCA-T),这是一个针对顺应场景迁移学习的新型管道,可在校准和测试数据上联合执行无监督归纳适应。我们进行了全面的实验,利用医疗VLMs跨多种图像模式、迁移任务和非顺应性分数进行研究。我们的框架在效率和有条件覆盖率方面与SCP相比提供了一致的收益,并保持相同的经验保证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025. Code: https://github.com/jusiro/SCA-T
Summary
医学视觉语言模型(VLMs)的迁移能力强大,广泛应用于图像分类领域。但其可靠性方面尚未得到充分探索。本研究采用分裂顺应预测(SCP)框架,为基于少量标注校准集的模型迁移提供可靠性保障。然而,VLMs的预训练通用性可能影响特定任务的预测顺应集属性。虽然迁移学习在判别目的中的常规做法包括适应阶段,但用于顺应目的时效果并不理想。针对这一问题,我们提出了转导分裂顺应适应(SCA-T)这一新型管道,在顺应场景下实现迁移学习,对校准数据和测试数据执行联合的无监督转导适应。经过广泛的医学图像模态实验验证,我们的框架在效率和条件覆盖方面相较于SCP表现出优势,并保持了相同的经验保证。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像分类领域具有强大的迁移能力,但可靠性方面有待探索。
- 分裂顺应预测(SCP)框架用于为基于少量标注校准集的模型迁移提供可靠性保障。
- VLMs预训练的通用性可能影响特定任务的预测顺应集属性。
- 常规迁移学习方法用于顺应目的时效果不理想。
- 提出转导分裂顺应适应(SCA-T)这一新型管道,用于在顺应场景下实现迁移学习,对校准数据和测试数据执行联合的无监督转导适应。
- 综合实验验证SCA-T框架相较于SCP的优势,表现在效率和条件覆盖方面。
点此查看论文截图

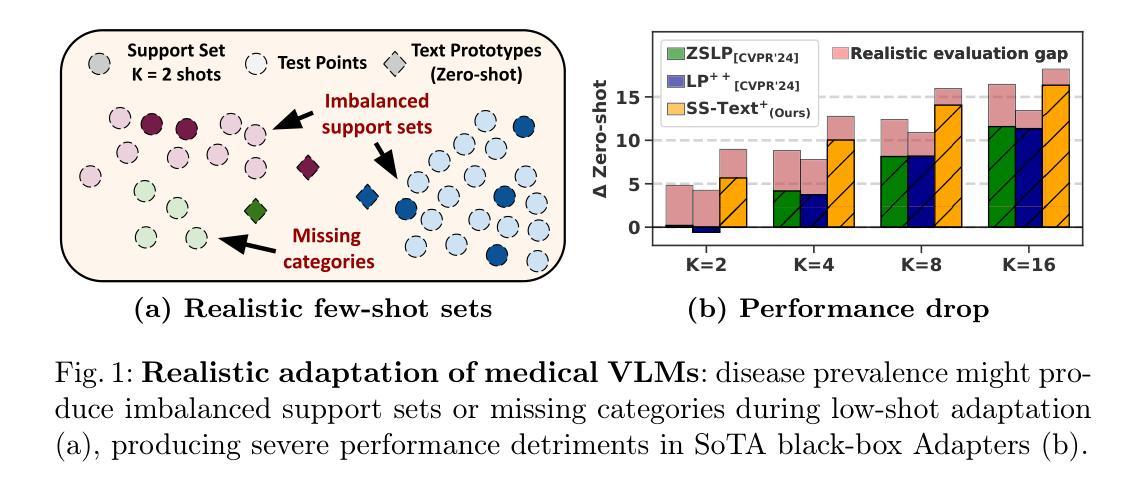
Few-Shot, Now for Real: Medical VLMs Adaptation without Balanced Sets or Validation
Authors:Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Fereshteh Shakeri, Houda Bahig, Jose Dolz, Ismail Ben Ayed
Vision-language models (VLMs) are gaining attention in medical image analysis. These are pre-trained on large, heterogeneous data sources, yielding rich and transferable representations. Notably, the combination of modality-specialized VLMs with few-shot adaptation has provided fruitful results, enabling the efficient deployment of high-performing solutions. However, previous works on this topic make strong assumptions about the distribution of adaptation data, which are unrealistic in the medical domain. First, prior art assumes access to a balanced support set, a condition that breaks the natural imbalance in disease prevalence found in real-world scenarios. Second, these works typically assume the presence of an additional validation set to fix critical hyper-parameters, which is highly data-inefficient. This work challenges these favorable deployment scenarios and introduces a realistic, imbalanced, validation-free adaptation setting. Our extensive benchmark across various modalities and downstream tasks demonstrates that current methods systematically compromise their performance when operating under realistic conditions, occasionally even performing worse than zero-shot inference. Also, we introduce a training-free linear probe that adaptively blends visual and textual supervision. Detailed studies demonstrate that the proposed solver is a strong, efficient baseline, enabling robust adaptation in challenging scenarios.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学图像分析领域越来越受到关注。这些模型在大型、多样化的数据源上进行预训练,产生丰富且可迁移的表示。值得注意的是,模态专用VLMs与少量适应的结合已经产生了富有成果的结果,能够实现高性能解决方案的有效部署。然而,关于该主题的前期研究对适应数据分布做出了强烈的假设,这在医学领域是不现实的。首先,先前技术假定可以访问平衡的支持集,这一条件打破了真实世界场景中疾病发生率存在的自然不平衡。其次,这些工作通常假定存在额外的验证集来修正关键超参数,这在数据使用效率上非常低。这项工作对这些有利的部署场景提出了质疑,并引入了一个现实的、不平衡的、无需验证的适应环境。我们在各种模态和下游任务上的广泛基准测试表明,当前方法在真实条件下运行时,其性能会系统性地受到损害,有时甚至表现得比零射击推理更差。此外,我们还介绍了一种无需训练的线性探测器,它能自适应地融合视觉和文本监督。详细研究表明,所提出的求解器是一个强大且高效的基准,能够在具有挑战性的场景中实现稳健适应。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025. Code: https://github.com/jusiro/SS-Text
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学图像分析领域受到关注。这些模型在大规模、多样化的数据源上进行预训练,产生丰富且可迁移的表示。结合模态专用VLMs进行小样本适应取得了富有成果的结果,可实现高性能解决方案的高效部署。然而,以前的研究对这一主题做出了关于适应数据分布的强烈假设,这在医学领域中是不切实际的。本研究挑战了这些有利的部署场景,并引入了更现实的、不平衡的、无需验证的适应设置。在多种模态和下游任务上的广泛基准测试表明,当前方法在现实条件下的性能会系统性地受到影响,有时甚至不如零样本推理。此外,本研究还提出了一种训练有素的线性探测器,可自适应地融合视觉和文本监督。详细研究表明,该求解器是一个强大且高效的基准,可在具有挑战性的场景中实现稳健适应。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学图像分析领域具有应用价值。
- VLMs通过在大规模、多样化数据源上的预训练,产生丰富且可迁移的表示。
- 模态专用VLMs与小样本适应相结合取得了良好效果。
- 以往研究在适应医学图像分析时存在不切实际的假设,如平衡支持集和额外的验证集。
- 本研究提出了更现实的、无需验证的适应设置,并发现当前方法在现实条件下的性能受影响。
- 引入了一种训练有素的线性探测器,可自适应融合视觉和文本监督。
点此查看论文截图

Learning to Adapt Frozen CLIP for Few-Shot Test-Time Domain Adaptation
Authors:Zhixiang Chi, Li Gu, Huan Liu, Ziqiang Wang, Yanan Wu, Yang Wang, Konstantinos N Plataniotis
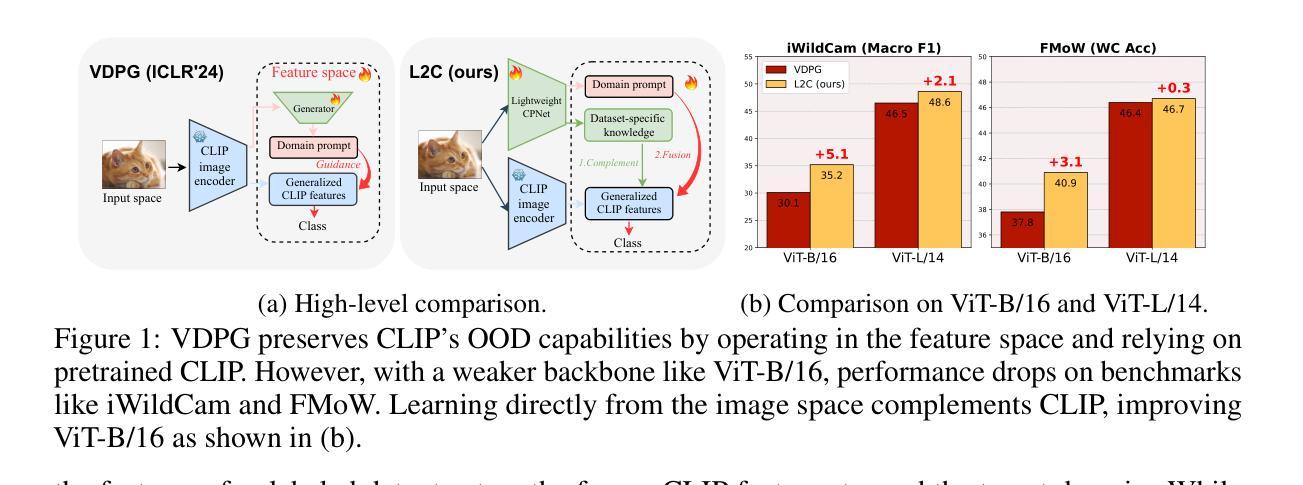
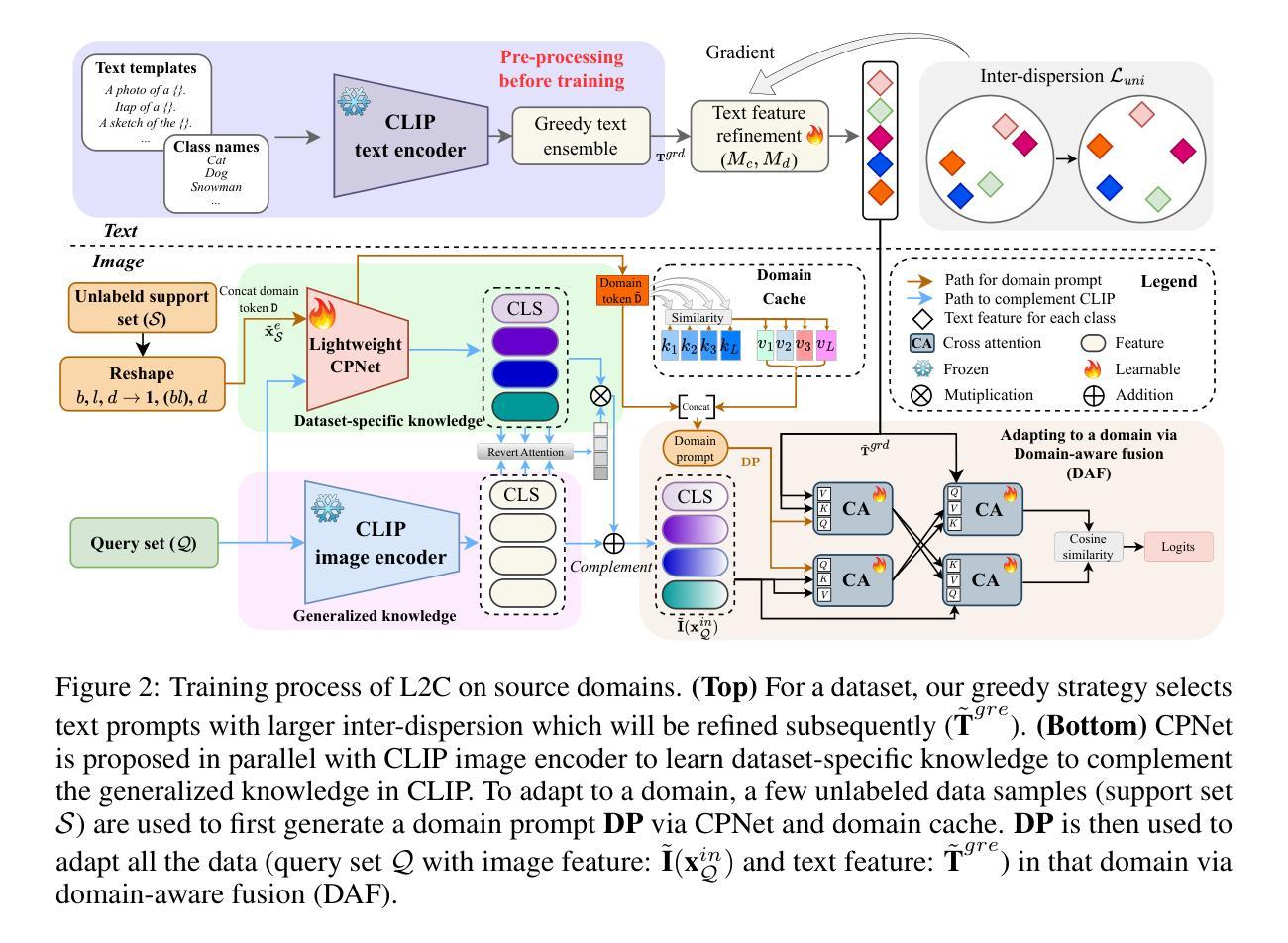
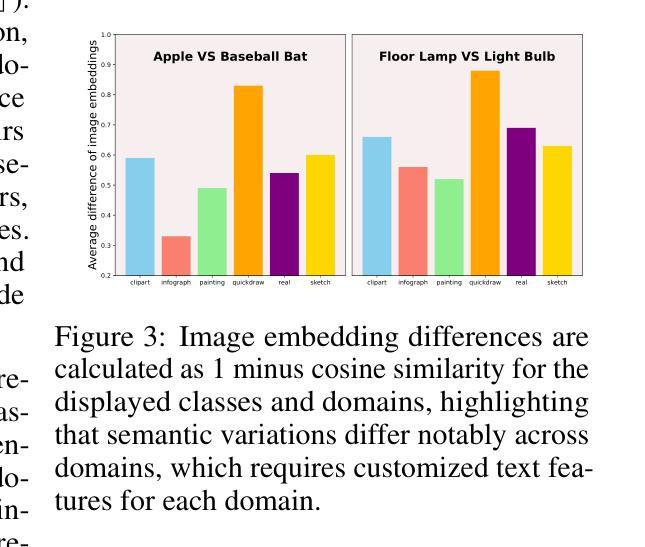
Few-shot Test-Time Domain Adaptation focuses on adapting a model at test time to a specific domain using only a few unlabeled examples, addressing domain shift. Prior methods leverage CLIP’s strong out-of-distribution (OOD) abilities by generating domain-specific prompts to guide its generalized, frozen features. However, since downstream datasets are not explicitly seen by CLIP, solely depending on the feature space knowledge is constrained by CLIP’s prior knowledge. Notably, when using a less robust backbone like ViT-B/16, performance significantly drops on challenging real-world benchmarks. Departing from the state-of-the-art of inheriting the intrinsic OOD capability of CLIP, this work introduces learning directly on the input space to complement the dataset-specific knowledge for frozen CLIP. Specifically, an independent side branch is attached in parallel with CLIP and enforced to learn exclusive knowledge via revert attention. To better capture the dataset-specific label semantics for downstream adaptation, we propose to enhance the inter-dispersion among text features via greedy text ensemble and refinement. The text and visual features are then progressively fused in a domain-aware manner by a generated domain prompt to adapt toward a specific domain. Extensive experiments show our method’s superiority on 5 large-scale benchmarks (WILDS and DomainNet), notably improving over smaller networks like ViT-B/16 with gains of \textbf{+5.1} in F1 for iWildCam and \textbf{+3.1%} in WC Acc for FMoW.
少数样本测试时域适应(Few-Shot Test-Time Domain Adaptation)主要关注在测试阶段使用少数无标签样本对模型进行特定域适应,以解决域偏移问题。先前的方法通过生成特定域的提示来利用CLIP强大的超出分布(OOD)能力,以指导其通用冻结特征。然而,由于下游数据集并未被CLIP显式地看到,仅依赖特征空间的知识受到CLIP先验知识的限制。值得注意的是,当使用不那么稳健的骨干网(如ViT-B/16)时,其在具有挑战性的现实世界基准测试上的性能会显著下降。这项工作摒弃了继承CLIP的内在OOD能力的最新理念,转而直接在输入空间学习,以补充针对冻结CLIP的特定数据集知识。具体来说,一个独立的侧分支与CLIP并行连接,通过反向注意力被强制学习专有知识。为了更好地捕获下游适应的特定数据集标签语义,我们提出通过贪婪文本集合和细化来增强文本特征之间的分散性。然后,文本和视觉特征以领域感知的方式通过生成的领域提示逐步融合,以适应特定领域。大量实验表明,我们的方法在5个大规模基准测试(WILDS和DomainNet)上的表现优于其他方法,尤其是在较小网络(如ViT-B/16)上,在iWildCam的F1得分上提高了+5.1,在FMoW的WC Acc上提高了+3.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR2025,https://github.com/chi-chi-zx/L2C
Summary
该文本介绍了基于Few-Shot的测试时间域自适应技术。传统的方法主要利用CLIP强大的跨域能力生成特定域提示,但这种方法的性能受限于CLIP对下游数据集的知识缺乏。本文引入了在输入空间上直接学习的方法,以补充针对特定数据集的知识。通过引入独立侧分支和反转注意力机制,结合贪婪文本集成和细化策略,实现了对特定域的自适应。实验表明,该方法在大型基准测试上的性能优于现有技术,特别是在较小的网络如ViT-B/16上表现更为突出。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法基于Few-Shot测试时间域自适应技术,针对模型在特定域的适应问题,仅使用少量无标签样本进行适应。
- 传统方法主要利用CLIP的跨域能力生成特定域提示,但受限于CLIP对下游数据集知识的缺乏。
- 引入在输入空间上直接学习的方法,通过独立侧分支和反转注意力机制来补充针对特定数据集的知识。
- 引入贪婪文本集成和细化策略,以更好地捕捉数据集特定的标签语义。
- 使用生成域提示的方式,将文本和视觉特征逐步融合以适应特定域。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Model Guidance to Extract Training Data from Personalized Diffusion Models
Authors:Xiaoyu Wu, Jiaru Zhang, Zhiwei Steven Wu
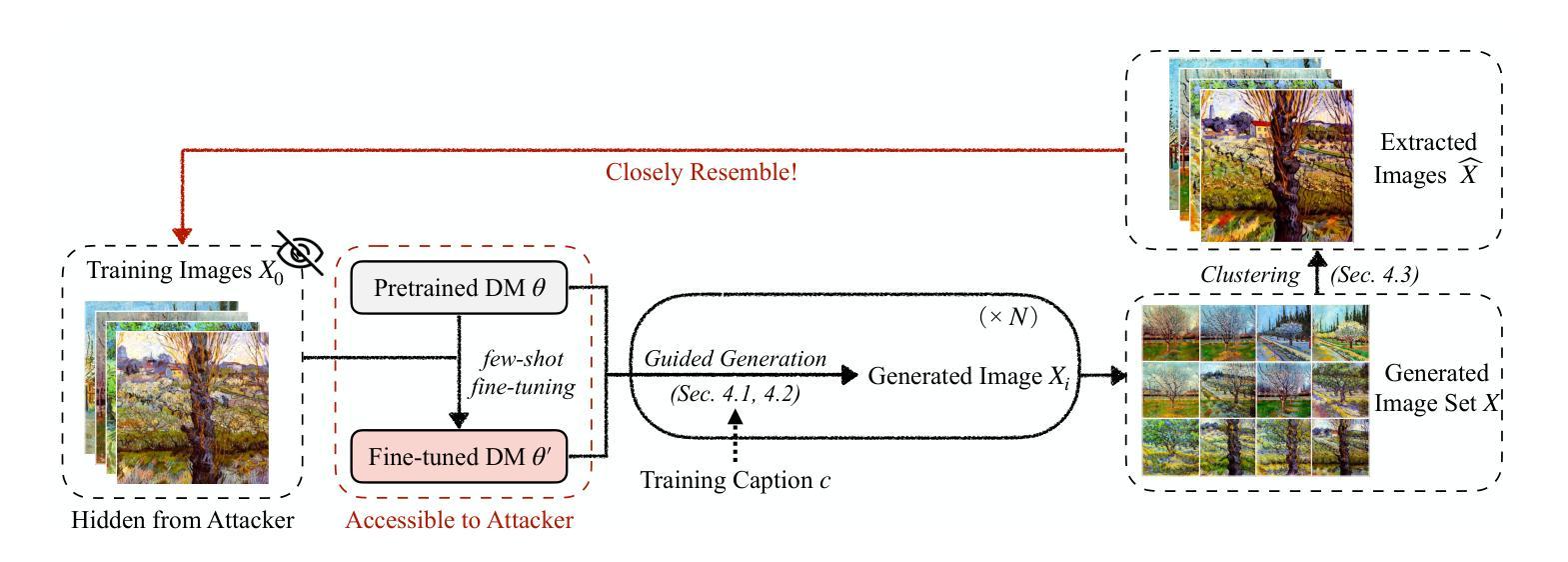
Diffusion Models (DMs) have become powerful image generation tools, especially for few-shot fine-tuning where a pretrained DM is fine-tuned on a small image set to capture specific styles or objects. Many people upload these personalized checkpoints online, fostering communities such as Civitai and HuggingFace. However, model owners may overlook the data leakage risks when releasing fine-tuned checkpoints. Moreover, concerns regarding copyright violations arise when unauthorized data is used during fine-tuning. In this paper, we ask: “Can training data be extracted from these fine-tuned DMs shared online?” A successful extraction would present not only data leakage threats but also offer tangible evidence of copyright infringement. To answer this, we propose FineXtract, a framework for extracting fine-tuning data. Our method approximates fine-tuning as a gradual shift in the model’s learned distribution – from the original pretrained DM toward the fine-tuning data. By extrapolating the models before and after fine-tuning, we guide the generation toward high-probability regions within the fine-tuned data distribution. We then apply a clustering algorithm to extract the most probable images from those generated using this extrapolated guidance. Experiments on DMs fine-tuned with datasets including WikiArt, DreamBooth, and real-world checkpoints posted online validate the effectiveness of our method, extracting about 20% of fine-tuning data in most cases. The code is available https://github.com/Nicholas0228/FineXtract.
扩散模型(DMs)已经成为强大的图像生成工具,特别是在小样本微调领域,其中预训练的DM在小型图像集上进行微调以捕捉特定的风格或对象。许多人在线上传这些个性化的检查点,促进了如Civitai和HuggingFace等社区的发展。然而,在发布微调检查点时,模型所有者可能会忽略数据泄露的风险。此外,当未经授权的数据用于微调时,会出现侵犯版权的问题。在本文中,我们提出的问题是:“这些在线共享经过微调后的DMs能否提取出训练数据?”成功的提取不仅会带来数据泄露的威胁,而且也会提供版权侵权的实际证据。为了回答这个问题,我们提出了FineXtract框架,该框架用于提取微调数据。我们的方法将微调近似为模型学习分布的一个逐渐变化的过程——从原始的预训练DM向微调数据转变。通过对微调前后的模型进行外推,我们引导生成的方向朝向微调数据分布中的高概率区域。然后,我们应用聚类算法从使用这种外推指导生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。在使用WikiArt、DreamBooth以及在线发布的现实世界检查点对DMs进行微调的实验中,验证了我们的方法的有效性,在大多数情况下能够提取约20%的微调数据。代码可用https://github.com/Nicholas0228/FineXtract。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在少量样本微调上展现出强大的图像生成能力,但释放微调后的模型检查点时可能存在数据泄露风险。本文提出“FineXtract”框架,旨在从在线共享的微调DMs中提取训练数据。通过模型微调前后的外推,引导生成图像向微调数据分布的高概率区域靠拢,并应用聚类算法从生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。实验证明该方法在WikiArt、DreamBooth等数据集及在线发布的现实检查点上有效,大多情况下可提取约20%的微调数据。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在少量样本微调上具有强大的图像生成能力。
- 发布微调后的模型检查点时,存在数据泄露风险。
- 本文提出“FineXtract”框架,用于从在线共享的微调DMs中提取训练数据。
- 通过模型微调前后的外推,引导生成图像向高概率区域靠拢。
- 应用聚类算法从生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。
- 实验证明该方法在多个数据集及在线发布的现实检查点上有效。
点此查看论文截图