⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
Transforming H&E images into IHC: A Variance-Penalized GAN for Precision Oncology
Authors:Sara Rehmat, Hafeez Ur Rehman
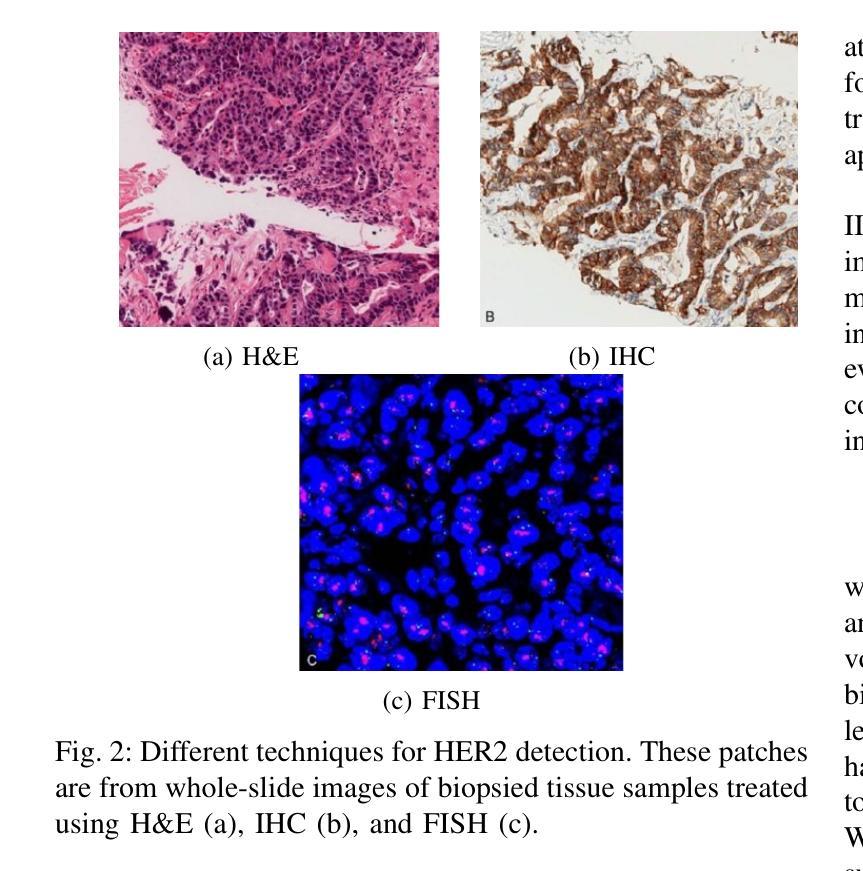
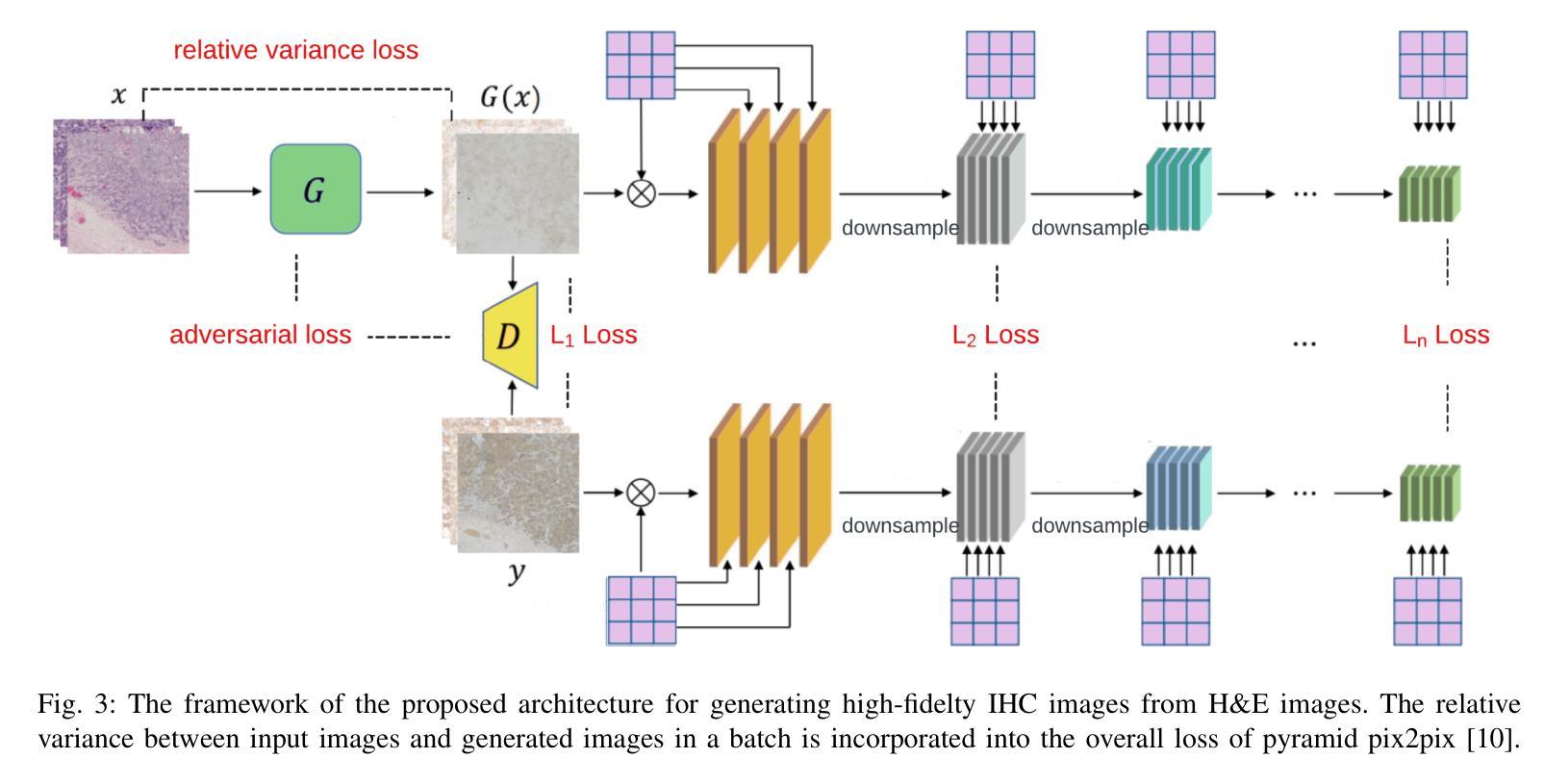
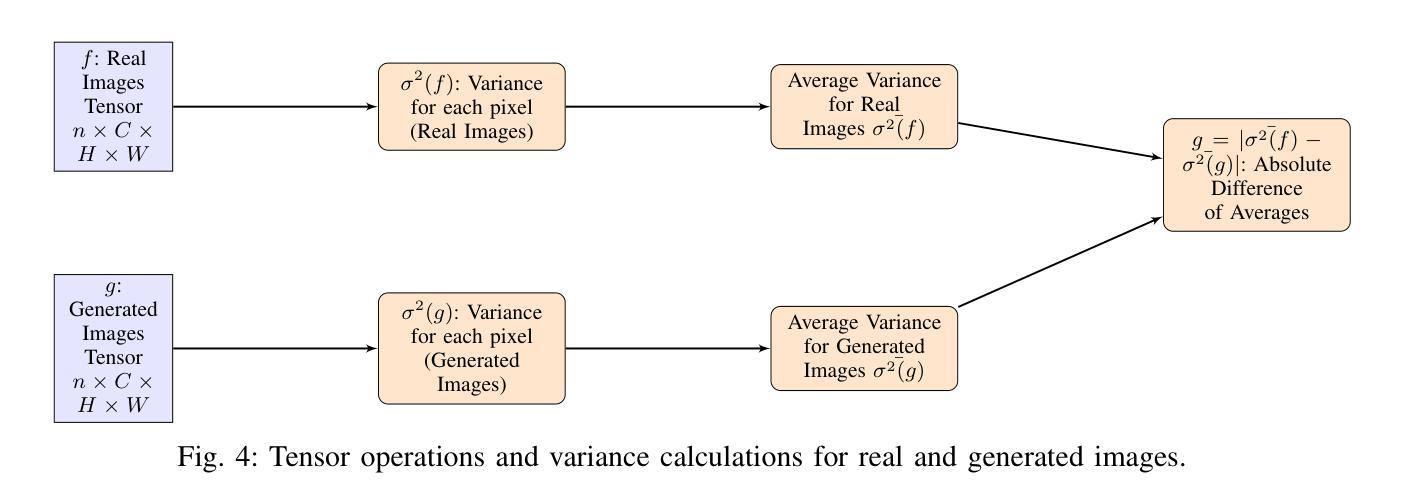
The overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in breast cells is a key driver of HER2-positive breast cancer, a highly aggressive subtype requiring precise diagnosis and targeted therapy. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the standard technique for HER2 assessment but is costly, labor-intensive, and highly dependent on antibody selection. In contrast, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, a routine histopathological procedure, offers broader accessibility but lacks HER2 specificity. This study proposes an advanced deep learning-based image translation framework to generate highfidelity IHC images from H&E-stained tissue samples, enabling cost-effective and scalable HER2 assessment. By modifying the loss function of pyramid pix2pix, we mitigate mode collapse, a fundamental limitation in generative adversarial networks (GANs), and introduce a novel variance-based penalty that enforces structural diversity in generated images. Our model particularly excels in translating HER2-positive (IHC 3+) images, which have remained challenging for existing methods due to their complex morphological variations. Extensive evaluations on the BCI histopathological dataset demonstrate that our model surpasses state-of-the-art methods in terms of peak signal-tonoise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), and Frechet Inception Distance (FID), particularly in accurately translating HER2-positive (IHC 3+) images. Beyond medical imaging, our model exhibits superior performance in general image-to-image translation tasks, showcasing its potential across multiple domains. This work marks a significant step toward AI-driven precision oncology, offering a reliable and efficient alternative to traditional HER2 diagnostics.
人类表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)在乳腺细胞中的过度表达是HER2阳性乳腺癌的关键驱动因素,这是一种高度侵袭性的亚型,需要精确诊断和靶向治疗。免疫组织化学(IHC)是评估HER2的标准技术,但成本高昂、劳动强度高,并且高度依赖于抗体选择。相比之下,苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色是一种常规的病理程序,具有更广泛的可及性,但缺乏HER2特异性。本研究提出了一种先进的基于深度学习的图像翻译框架,能够从H&E染色的组织样本生成高保真的IHC图像,从而实现经济高效且可扩展的HER2评估。通过修改金字塔pix2pix的损失函数,我们缓解了模式崩溃问题,这是生成对抗网络(GANs)的一个基本局限,并引入了一种新型基于方差的惩罚措施,以加强生成图像的结构多样性。我们的模型在翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面特别出色,由于复杂的形态变化,现有方法一直难以处理这类图像。在BCI病理数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的模型在峰值信号与噪声比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)等方面超越了最先进的方法,特别是在准确翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面。除了医学成像外,我们的模型在一般的图像到图像翻译任务中也表现出卓越的性能,展示了其在多个领域的潜力。这项工作标志着人工智能驱动的精准肿瘤学的重要一步,为传统的HER 结诊断提供了可靠高效的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用深度学习的图像翻译框架,从H&E染色组织样本生成高保真IHC图像,提出一种成本效益高且可扩展的HER2评估方法。通过改进金字塔pix2pix的损失函数,该模型成功解决了生成对抗网络(GANs)的基本限制——模式崩溃问题,并引入基于方差的新罚项以确保生成图像的结构多样性。在BCI病理数据集上的广泛评估表明,该研究模型在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)和弗雷歇特入门距离(FID)等方面均优于现有方法,特别是在翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面表现优异。此工作标志着人工智能驱动的精准肿瘤学的重大进展,为传统的HER2诊断提供了可靠且高效的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- HER2在乳腺癌细胞中的过度表达是HER2阳性乳腺癌的关键驱动因素,需要精确诊断和针对性治疗。
- 免疫组化(IHC)是评估HER2的标准技术,但成本高昂、劳动密集,且高度依赖于抗体选择。
- 本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的图像翻译框架,能从H&E染色组织样本生成高保真IHC图像。
- 通过改进金字塔pix2pix的损失函数,成功解决了模式崩溃问题,并引入了基于方差的新罚项来确保图像结构多样性。
- 该模型在BCI病理数据集上的表现优于现有方法,特别是在翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面。
- 此技术为传统HER2诊断提供了可靠且高效的替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

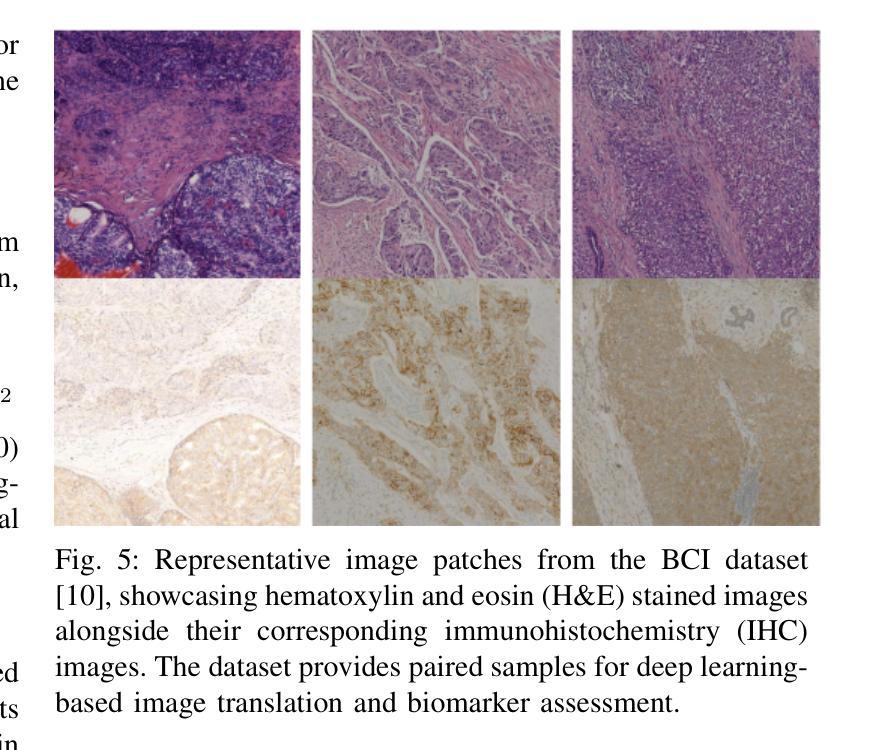
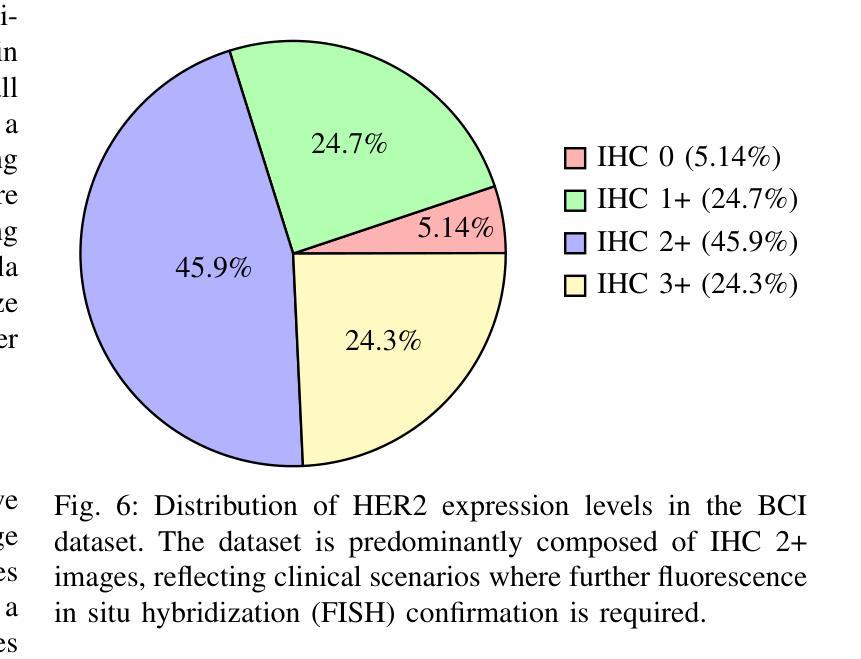
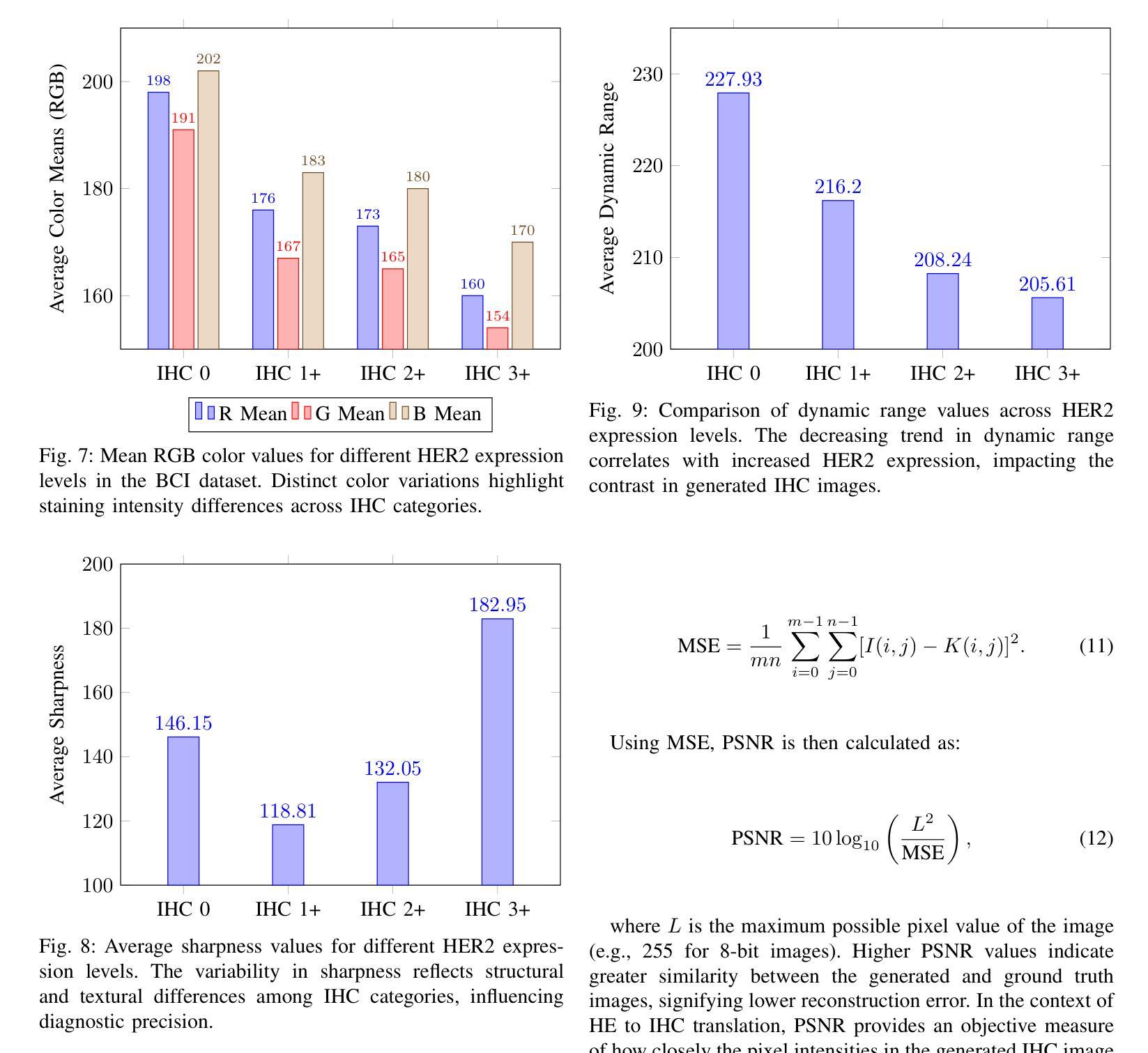
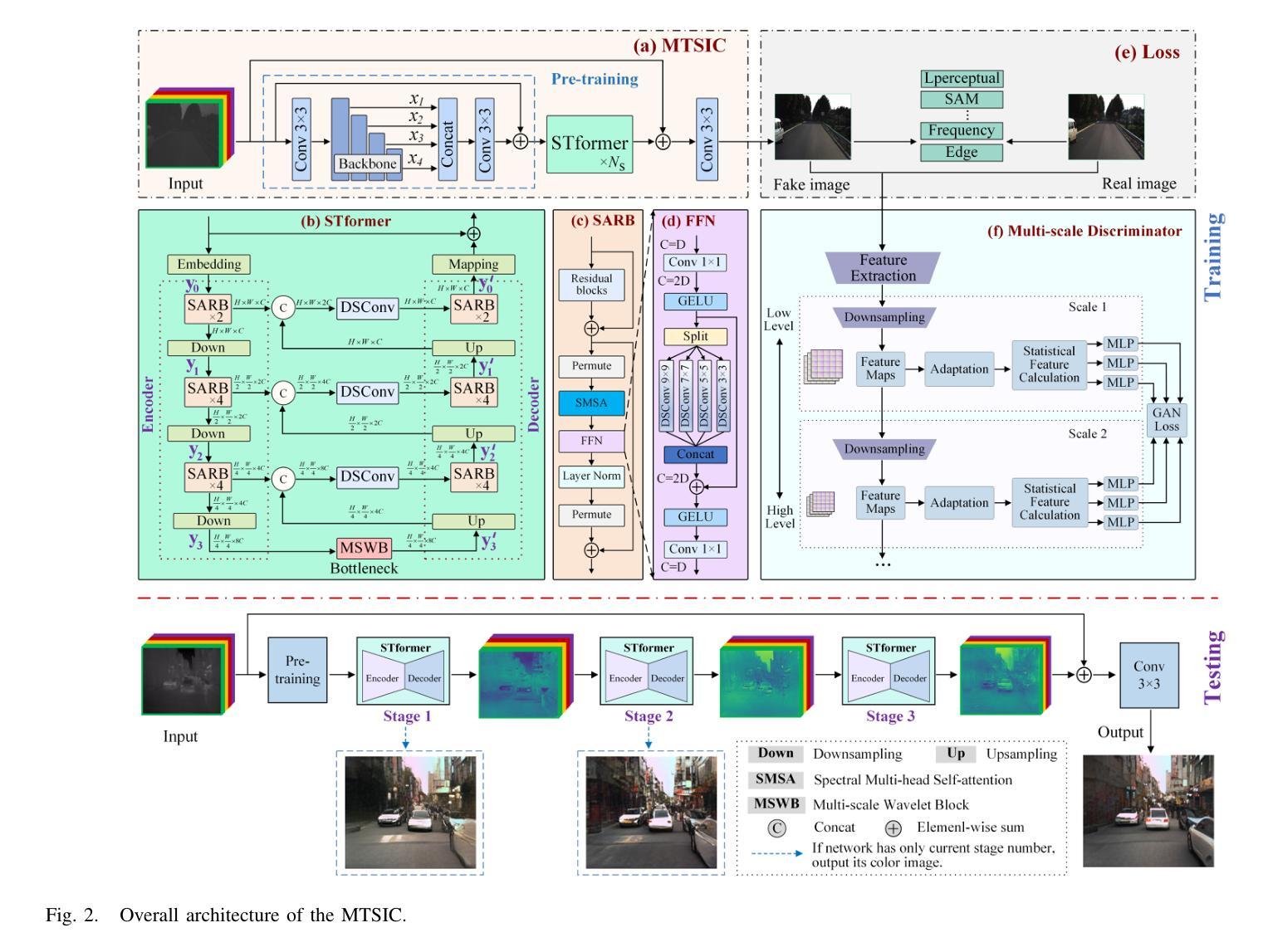
MTSIC: Multi-stage Transformer-based GAN for Spectral Infrared Image Colorization
Authors:Tingting Liu, Yuan Liu, Jinhui Tang, Liyin Yuan, Chengyu Liu, Chunlai Li, Xiubao Sui, Qian Chen
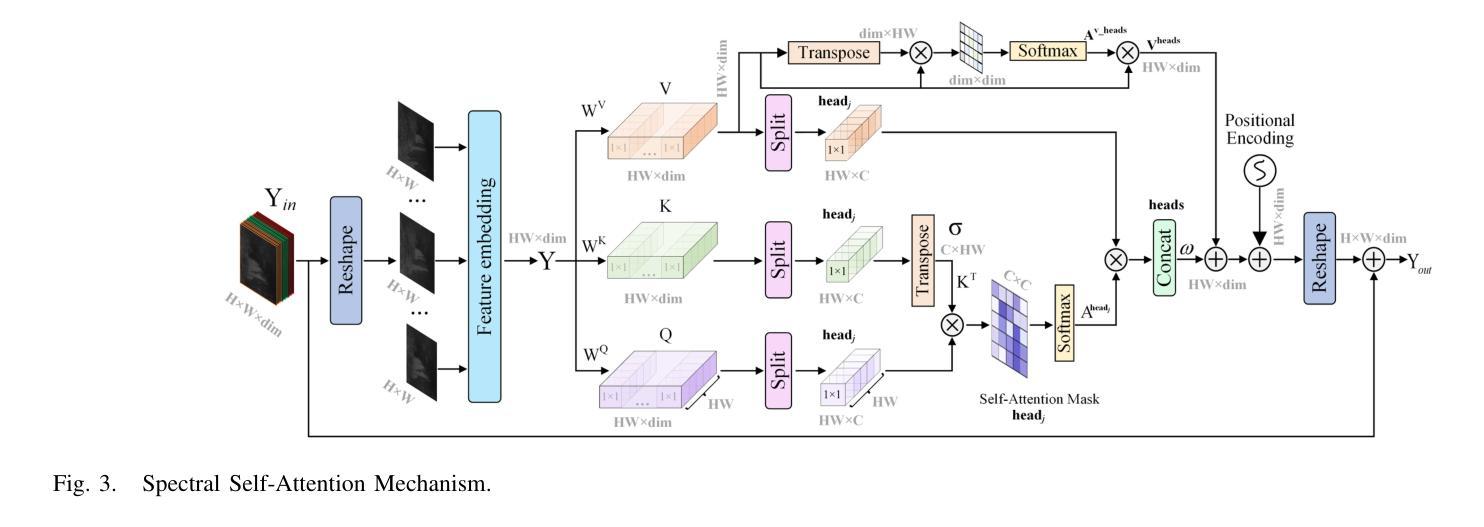
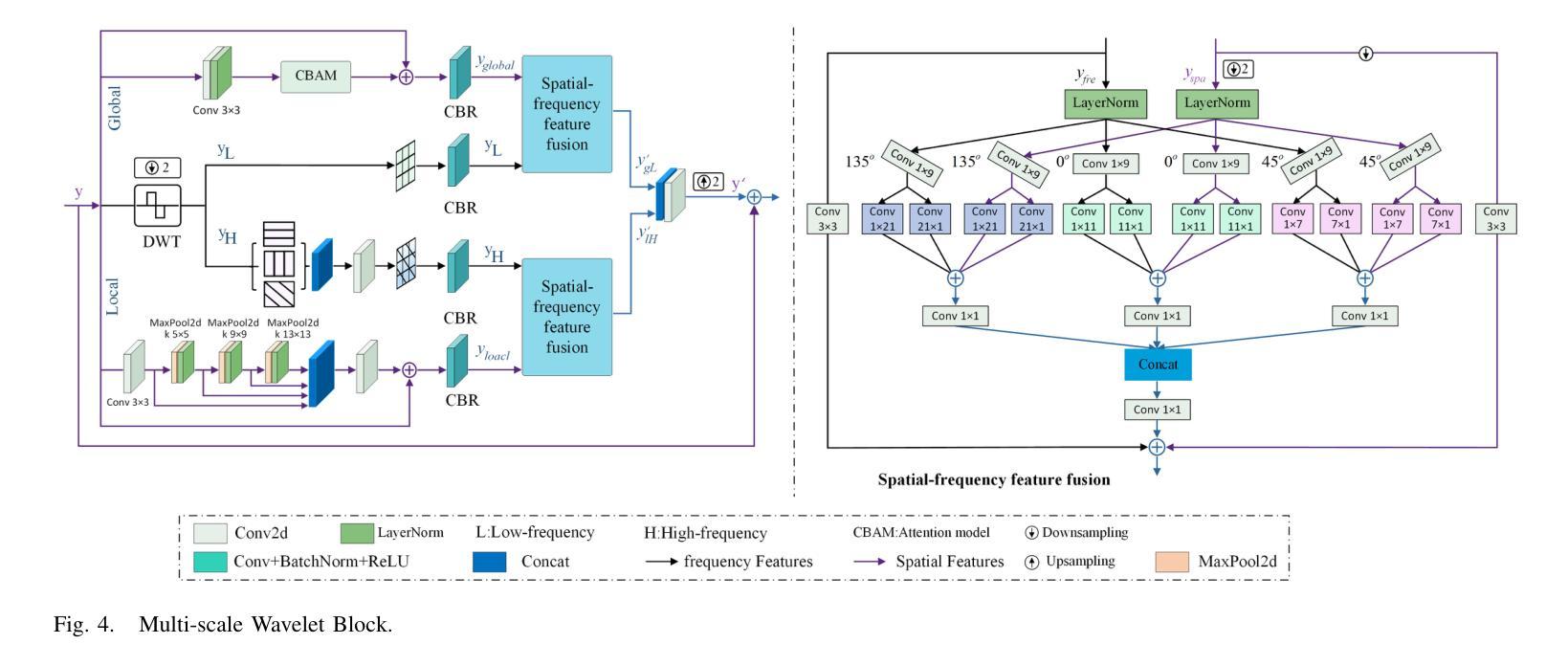
Thermal infrared (TIR) images, acquired through thermal radiation imaging, are unaffected by variations in lighting conditions and atmospheric haze. However, TIR images inherently lack color and texture information, limiting downstream tasks and potentially causing visual fatigue. Existing colorization methods primarily rely on single-band images with limited spectral information and insufficient feature extraction capabilities, which often result in image distortion and semantic ambiguity. In contrast, multiband infrared imagery provides richer spectral data, facilitating the preservation of finer details and enhancing semantic accuracy. In this paper, we propose a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based framework designed to integrate spectral information to enhance the colorization of infrared images. The framework employs a multi-stage spectral self-attention Transformer network (MTSIC) as the generator. Each spectral feature is treated as a token for self-attention computation, and a multi-head self-attention mechanism forms a spatial-spectral attention residual block (SARB), achieving multi-band feature mapping and reducing semantic confusion. Multiple SARB units are integrated into a Transformer-based single-stage network (STformer), which uses a U-shaped architecture to extract contextual information, combined with multi-scale wavelet blocks (MSWB) to align semantic information in the spatial-frequency dual domain. Multiple STformer modules are cascaded to form MTSIC, progressively optimizing the reconstruction quality. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms traditional techniques and effectively enhances the visual quality of infrared images.
热红外(TIR)图像是通过热辐射成像获得的,不受光照条件和大气雾的影响。然而,TIR图像本身缺乏颜色和纹理信息,这限制了下游任务并可能导致视觉疲劳。现有的彩色化方法主要依赖于具有有限光谱信息的单波段图像和特征提取能力不足的图像,这通常会导致图像失真和语义模糊。相比之下,多波段红外图像提供了更丰富光谱数据,有利于保留更精细的细节并增强语义准确性。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的框架,旨在整合光谱信息以提高红外图像的彩色化质量。该框架采用多阶段光谱自注意力Transformer网络(MTSIC)作为生成器。将每个光谱特征视为自注意力计算中的标记,多头自注意力机制形成空间光谱注意力残差块(SARB),实现多波段特征映射并减少语义混淆。多个SARB单元被集成到基于Transformer的单阶段网络(STformer)中,该网络采用U形架构来提取上下文信息,并结合多尺度小波块(MSWB)在空间频率双域中对齐语义信息。多个STformer模块级联形成MTSIC,逐步优化重建质量。实验结果表明,所提出的方法显著优于传统技术,并有效提高红外图像的可视质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的框架,用于集成光谱信息,提高红外图像的颜色化质量。采用多阶段光谱自注意力Transformer网络(MTSIC)作为生成器,通过自我注意力计算和采用多头自注意力机制实现多波段特征映射,减少语义混淆,提升红外图像的颜色表现和细节质量。
Key Takeaways
- TIR图像不受光照和大气雾霾影响,但缺乏颜色和纹理信息。
- 现有颜色化方法主要依赖单波段图像,存在光谱信息不足和特征提取能力有限的问题。
- 多波段红外图像提供丰富的光谱数据,有助于保留细节并提高语义准确性。
- 提出的GAN框架集成光谱信息以增强红外图像的颜色化。
- 采用多阶段光谱自注意力Transformer网络(MTSIC)作为生成器,实现多波段特征映射,减少语义混淆。
- MTSIC结合U型架构和多尺度小波块(MSWB)提取上下文信息,并在空间频率双域中对齐语义信息。
点此查看论文截图


CGS-GAN: 3D Consistent Gaussian Splatting GANs for High Resolution Human Head Synthesis
Authors:Florian Barthel, Wieland Morgenstern, Paul Hinzer, Anna Hilsmann, Peter Eisert
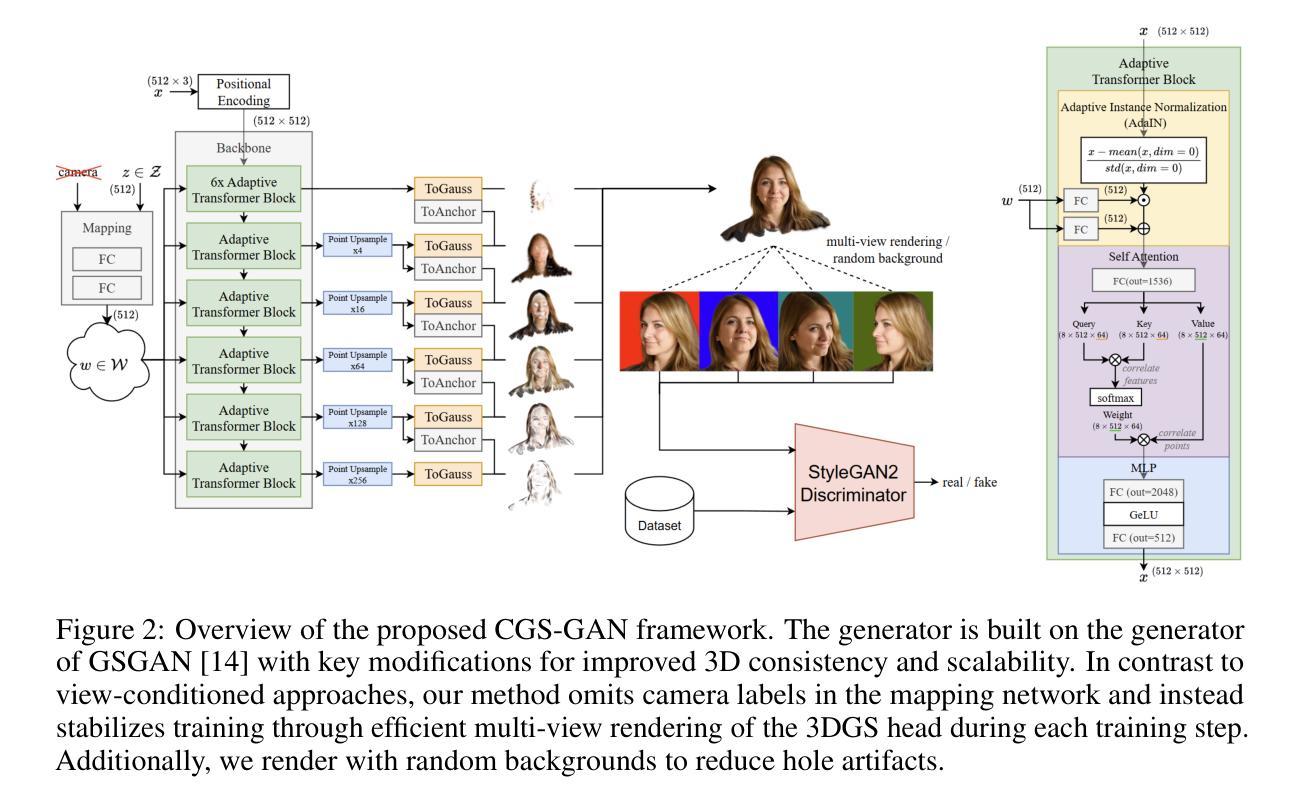
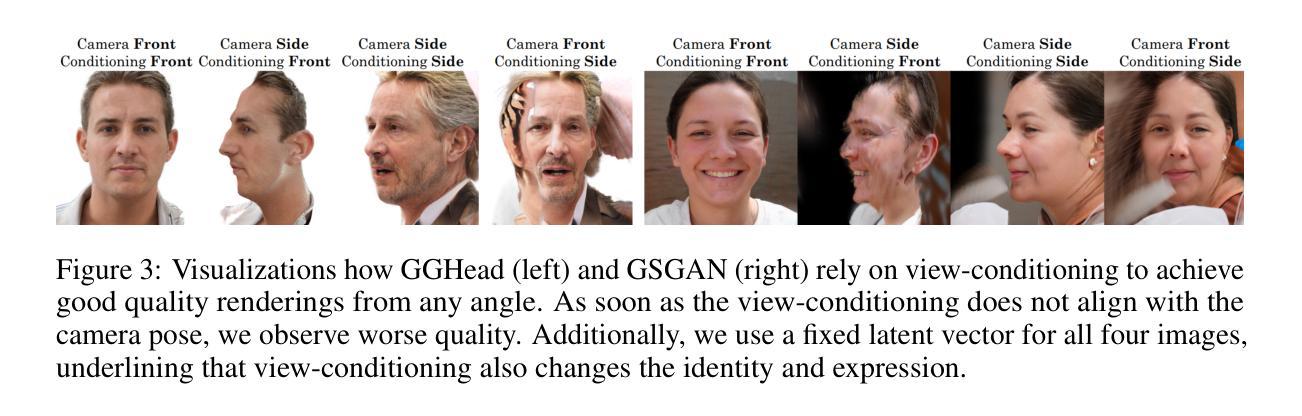
Recently, 3D GANs based on 3D Gaussian splatting have been proposed for high quality synthesis of human heads. However, existing methods stabilize training and enhance rendering quality from steep viewpoints by conditioning the random latent vector on the current camera position. This compromises 3D consistency, as we observe significant identity changes when re-synthesizing the 3D head with each camera shift. Conversely, fixing the camera to a single viewpoint yields high-quality renderings for that perspective but results in poor performance for novel views. Removing view-conditioning typically destabilizes GAN training, often causing the training to collapse. In response to these challenges, we introduce CGS-GAN, a novel 3D Gaussian Splatting GAN framework that enables stable training and high-quality 3D-consistent synthesis of human heads without relying on view-conditioning. To ensure training stability, we introduce a multi-view regularization technique that enhances generator convergence with minimal computational overhead. Additionally, we adapt the conditional loss used in existing 3D Gaussian splatting GANs and propose a generator architecture designed to not only stabilize training but also facilitate efficient rendering and straightforward scaling, enabling output resolutions up to $2048^2$. To evaluate the capabilities of CGS-GAN, we curate a new dataset derived from FFHQ. This dataset enables very high resolutions, focuses on larger portions of the human head, reduces view-dependent artifacts for improved 3D consistency, and excludes images where subjects are obscured by hands or other objects. As a result, our approach achieves very high rendering quality, supported by competitive FID scores, while ensuring consistent 3D scene generation. Check our our project page here: https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/
最近,基于三维高斯展开技术的三维生成对抗网络(GAN)已被提出用于高质量的人头合成。然而,现有方法通过使随机潜在向量适应当前相机位置来稳定训练并提高从陡峭视角的渲染质量。这损害了三维一致性,因为我们在重新合成三维头部时观察到身份随着每次相机移动而显著改变。相反,将相机固定在单一视角会产生高质量的该视角的渲染结果,但对于新颖视角表现不佳。移除视角条件通常会使GAN训练不稳定,并经常导致训练崩溃。针对这些挑战,我们引入了CGS-GAN,这是一种新型的三维高斯展开GAN框架,可在不依赖视角条件的情况下实现稳定训练和高质量的三维一致的人头合成。为确保训练稳定性,我们引入了一种多视角正则化技术,该技术可在最小计算开销的情况下增强生成器收敛。此外,我们适应了现有三维高斯展开GAN中的条件损失,并提出了一种设计巧妙的生成器架构,不仅可稳定训练,还可实现高效渲染和直观缩放,支持高达$ 2048^2 $的输出分辨率。为了评估CGS-GAN的能力,我们从FFHQ中整理了一个新的数据集。该数据集可实现超高分辨率,侧重于人类头部较大的部分,减少了视角相关的伪影以改善三维一致性,并排除了主体被手或其他物体遮挡的图像。因此,我们的方法在保证三维场景一致生成的同时,达到了很高的渲染质量,并且FID得分具有竞争力。请访问我们的项目页面了解更多信息:https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main paper 12 pages, supplementary materials 8 pages
Summary
基于3D高斯贴图技术的3D GANs已用于高质量合成人类头部。但现有方法通过当前相机位置调整随机潜在向量,以实现从陡峭视角的稳定训练和增强渲染质量,这会影响3D一致性。为解决这些挑战,我们推出CGS-GAN,一个无需依赖视角调节即可实现稳定训练和高质量3D一致性的新型人类头部合成框架。通过引入多视角正则化技术和改良的条件损失和生成器架构,确保训练稳定性并提升渲染效率。评估CGS-GAN能力的新数据集已准备就绪,支持高分辨率并改进3D一致性。点击访问项目页面了解更多:https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于3D高斯贴图的GAN技术在合成人类头部时面临视角相关的挑战。
- CGS-GAN框架解决了这些问题,实现了稳定训练和高质量、高分辨率的3D一致合成。
- 通过引入多视角正则化技术确保训练稳定性。
- 改良的条件损失和生成器架构提升了渲染效率并改善了输出质量。
点此查看论文截图

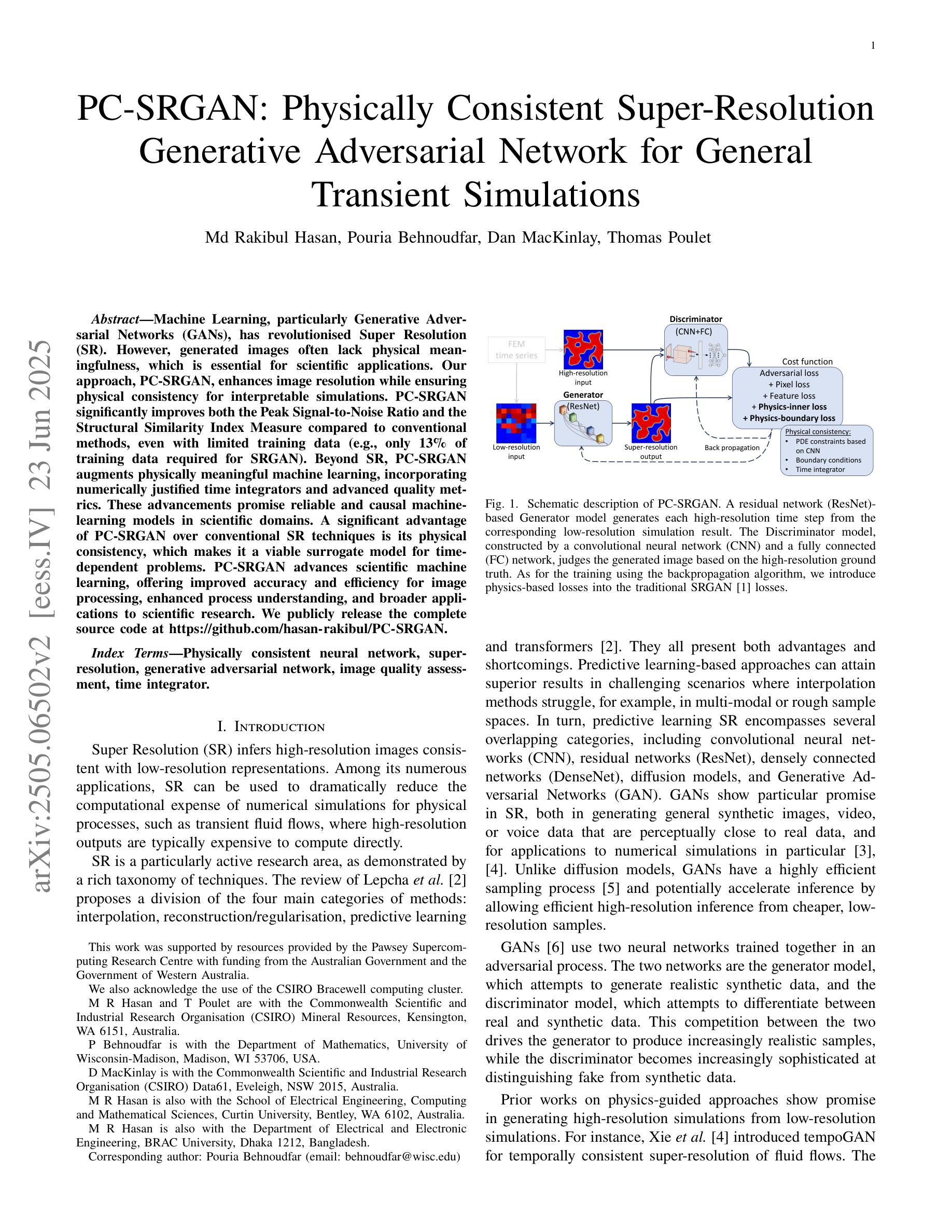
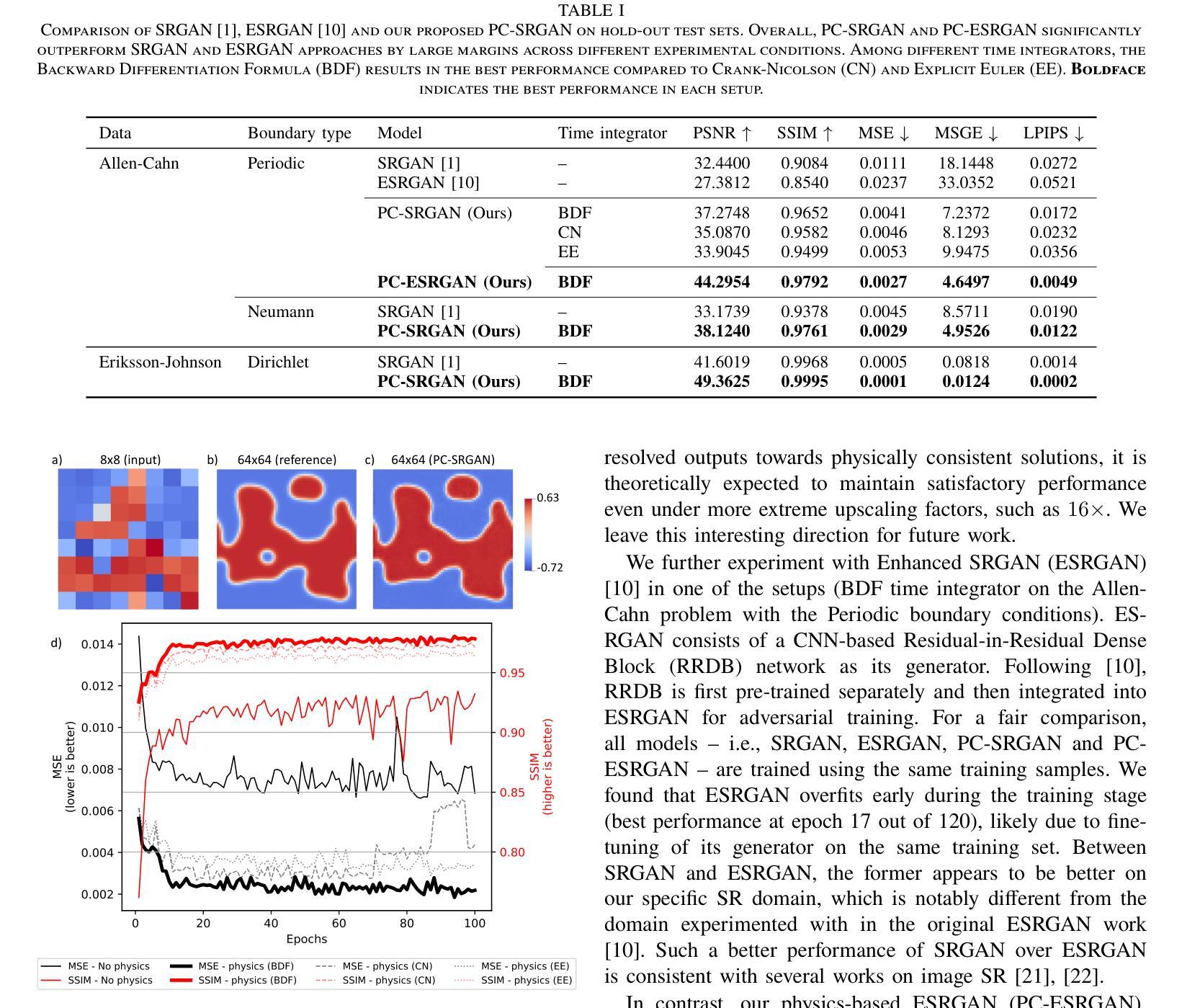
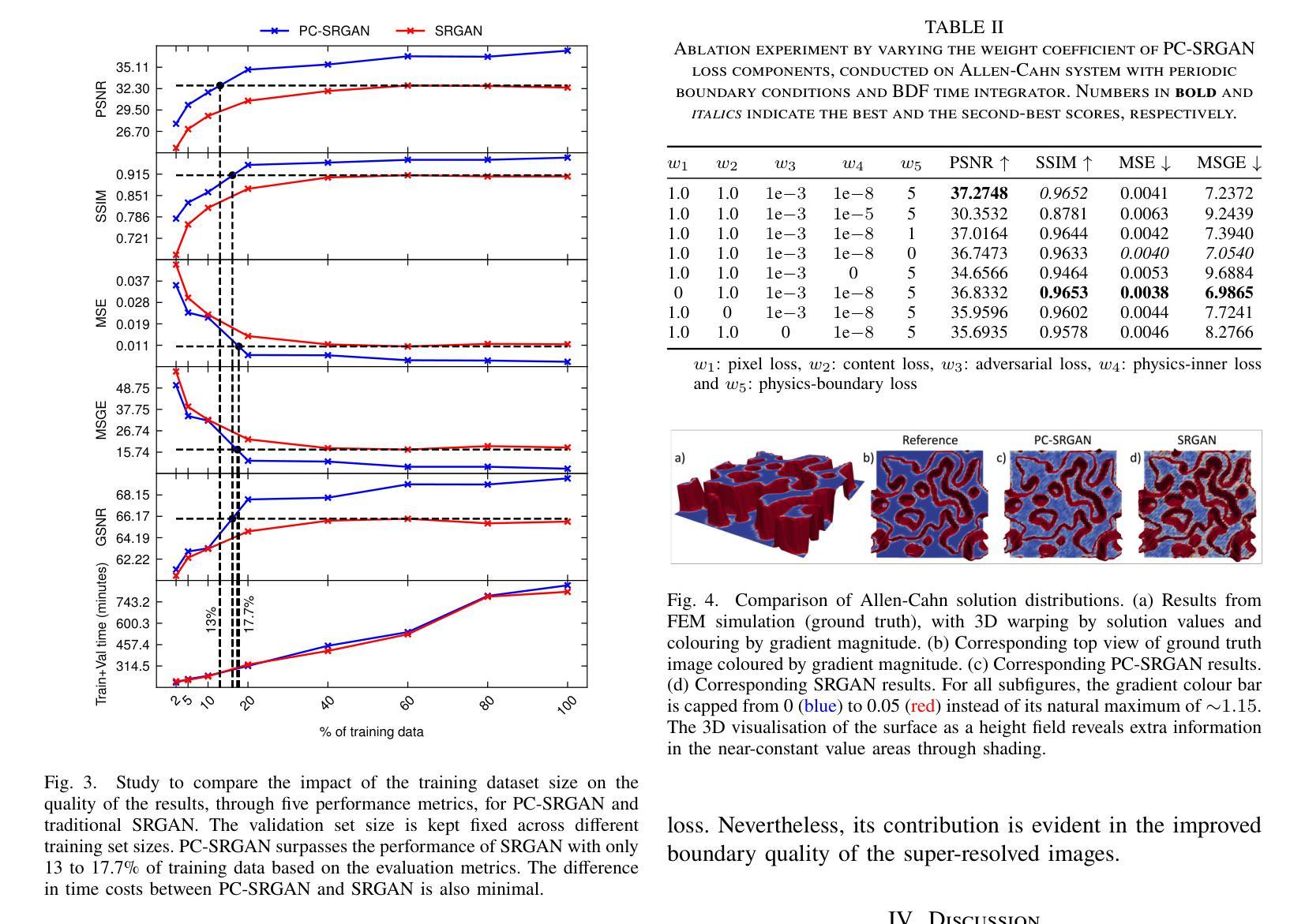
PC-SRGAN: Physically Consistent Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for General Transient Simulations
Authors:Md Rakibul Hasan, Pouria Behnoudfar, Dan MacKinlay, Thomas Poulet
Machine Learning, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), has revolutionised Super Resolution (SR). However, generated images often lack physical meaningfulness, which is essential for scientific applications. Our approach, PC-SRGAN, enhances image resolution while ensuring physical consistency for interpretable simulations. PC-SRGAN significantly improves both the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio and the Structural Similarity Index Measure compared to conventional methods, even with limited training data (e.g., only 13% of training data required for SRGAN). Beyond SR, PC-SRGAN augments physically meaningful machine learning, incorporating numerically justified time integrators and advanced quality metrics. These advancements promise reliable and causal machine-learning models in scientific domains. A significant advantage of PC-SRGAN over conventional SR techniques is its physical consistency, which makes it a viable surrogate model for time-dependent problems. PC-SRGAN advances scientific machine learning, offering improved accuracy and efficiency for image processing, enhanced process understanding, and broader applications to scientific research. We publicly release the complete source code at https://github.com/hasan-rakibul/PC-SRGAN.
机器学习,特别是生成对抗网络(GANs),已经对超分辨率(SR)领域产生了革命性的影响。然而,生成的图像通常缺乏物理意义,这对于科学应用至关重要。我们的PC-SRGAN方法在提升图像分辨率的同时,确保了物理一致性,为可解释的模拟提供了支持。相较于传统方法,PC-SRGAN在峰值信噪比(Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio)和结构相似性指数度量(Structural Similarity Index Measure)上有了显著提升,即使在有限的训练数据下(例如,仅需SRGAN的13%的训练数据)。除了超分辨率应用外,PC-SRGAN还增强了具有物理意义的机器学习,融入了经过数值验证的时间积分器和高级质量指标。这些进步为科学领域带来了可靠且因果关系的机器学习模型。与传统超分辨率技术相比,PC-SRGAN的一大优势在于其物理一致性,使其成为时间依赖问题的可行替代模型。PC-SRGAN推动了科学机器学习的发展,为图像处理提供了更高的准确性和效率,增强了过程理解,并扩展了其在科学研究中的广泛应用。我们已在https://github.com/hasan-rakibul/PC-SRGAN上公开发布了完整的源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PC-SRGAN通过结合机器学习和物理规律,革命性地改进了超分辨率(SR)技术。该方法在生成图像时保证了物理一致性,增强了图像分辨率,适用于可解释的模拟。与传统方法相比,PC-SRGAN在峰值信噪比和结构相似性指数度量方面表现出显著优势,甚至在训练数据量有限的情况下也是如此。此外,PC-SRGAN还促进了物理意义丰富的机器学习的发展,并公开了完整的源代码。
Key Takeaways
- PC-SRGAN结合了机器学习和物理规律,改进了超分辨率技术。
- 该方法在生成图像时保证了物理一致性,增强了图像分辨率。
- PC-SRGAN适用于可解释的模拟,促进了科学应用的发展。
- 与传统方法相比,PC-SRGAN在峰值信噪比和结构相似性指数度量方面表现出显著优势。
- PC-SRGAN在训练数据量有限的情况下也能表现出良好的性能。
- PC-SRGAN促进了物理意义丰富的机器学习的发展。
点此查看论文截图
PotatoGANs: Utilizing Generative Adversarial Networks, Instance Segmentation, and Explainable AI for Enhanced Potato Disease Identification and Classification
Authors:Fatema Tuj Johora Faria, Mukaffi Bin Moin, Mohammad Shafiul Alam, Ahmed Al Wase, Md. Rabius Sani, Khan Md Hasib
Numerous applications have resulted from the automation of agricultural disease segmentation using deep learning techniques. However, when applied to new conditions, these applications frequently face the difficulty of overfitting, resulting in lower segmentation performance. In the context of potato farming, where diseases have a large influence on yields, it is critical for the agricultural economy to quickly and properly identify these diseases. Traditional data augmentation approaches, such as rotation, flip, and translation, have limitations and frequently fail to provide strong generalization results. To address these issues, our research employs a novel approach termed as PotatoGANs. In this novel data augmentation approach, two types of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are utilized to generate synthetic potato disease images from healthy potato images. This approach not only expands the dataset but also adds variety, which helps to enhance model generalization. Using the Inception score as a measure, our experiments show the better quality and realisticness of the images created by PotatoGANs, emphasizing their capacity to resemble real disease images closely. The CycleGAN model outperforms the Pix2Pix GAN model in terms of image quality, as evidenced by its higher IS scores CycleGAN achieves higher Inception scores (IS) of 1.2001 and 1.0900 for black scurf and common scab, respectively. This synthetic data can significantly improve the training of large neural networks. It also reduces data collection costs while enhancing data diversity and generalization capabilities. Our work improves interpretability by combining three gradient-based Explainable AI algorithms (GradCAM, GradCAM++, and ScoreCAM) with three distinct CNN architectures (DenseNet169, Resnet152 V2, InceptionResNet V2) for potato disease classification.
采用深度学习技术实现农业病害分割自动化已经产生了许多应用。然而,当应用于新条件时,这些应用经常面临过拟合的困难,导致分割性能下降。在土豆种植业中,病害对产量有很大影响,因此快速正确地识别这些病害对农业经济至关重要。传统的数据增强方法,如旋转、翻转和翻译,都有局限性,往往不能提供强有力的泛化结果。为了解决这些问题,我们的研究采用了一种新颖的方法,称为PotatoGANs。在这种新型数据增强方法中,利用两种生成对抗网络(GANs)从健康土豆图像生成合成土豆病害图像。这种方法不仅扩大了数据集,还增加了多样性,有助于增强模型的泛化能力。我们的实验采用Inception分数作为衡量标准,显示了PotatoGANs创建的图像具有更好的质量和逼真度,强调它们模拟真实病害图像的能力。在图像质量方面,CycleGAN模型优于Pix2Pix GAN模型,CycleGAN实现了黑腐病和普通疮痂病的Inception分数(IS)分别为1.2001和1.0900。这种合成数据可以显著改善大型神经网络的训练。它还可以降低数据收集成本,同时提高数据多样性和泛化能力。我们的工作通过结合三种基于梯度的可解释人工智能算法(GradCAM、GradCAM++和ScoreCAM)与三种不同的CNN架构(DenseNet169、Resnet152 V2、InceptionResNet V2)进行土豆病害分类,提高了可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的农业病害分割自动化应用广泛,但在新条件下应用时常常面临过拟合问题,影响分割性能。本研究采用名为PotatoGANs的新型数据增强方法,利用两种生成对抗网络(GANs)从健康土豆图像生成合成病害图像,不仅扩充数据集,还增加多样性,提高模型泛化能力。实验表明,CycleGAN模型在图像质量上表现更佳,能更真实地模拟真实病害图像。合成的数据能显著改善大型神经网络的训练,降低数据收集成本,提高数据多样性和泛化能力。结合三种解释性AI算法和三种CNN架构,提高了土豆病害分类的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法在农业病害分割中应用广泛,但面临新条件下的过拟合问题。
- PotatoGANs方法利用生成对抗网络(GANs)从健康土豆图像生成合成病害图像,有效扩充数据集并增加多样性。
- CycleGAN模型在模拟真实病害图像方面表现优于Pix2Pix GAN模型。
- 合成数据能显著改善神经网络训练,降低数据收集成本,提高泛化能力。
- 结合解释性AI算法和CNN架构,提高了土豆病害分类的可解释性。
- PotatoGANs方法具有潜力解决农业中快速准确识别病害的关键问题,对农业经济发展具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图