⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
New Determination of the $^{14}$C(n, $γ$)$^{15}$C Reaction Rate and Its Astrophysical Implications
Authors:Yuchen Jiang, Zhenyu He, Yudong Luo, Wenyu Xin, Jie Chen, Xinyue Li, Yangping Shen, Bing Guo, Guo Li, Danyang Pang, Tianli Ma, Weike Nan, Toshitaka Kajino, Weiping Liu
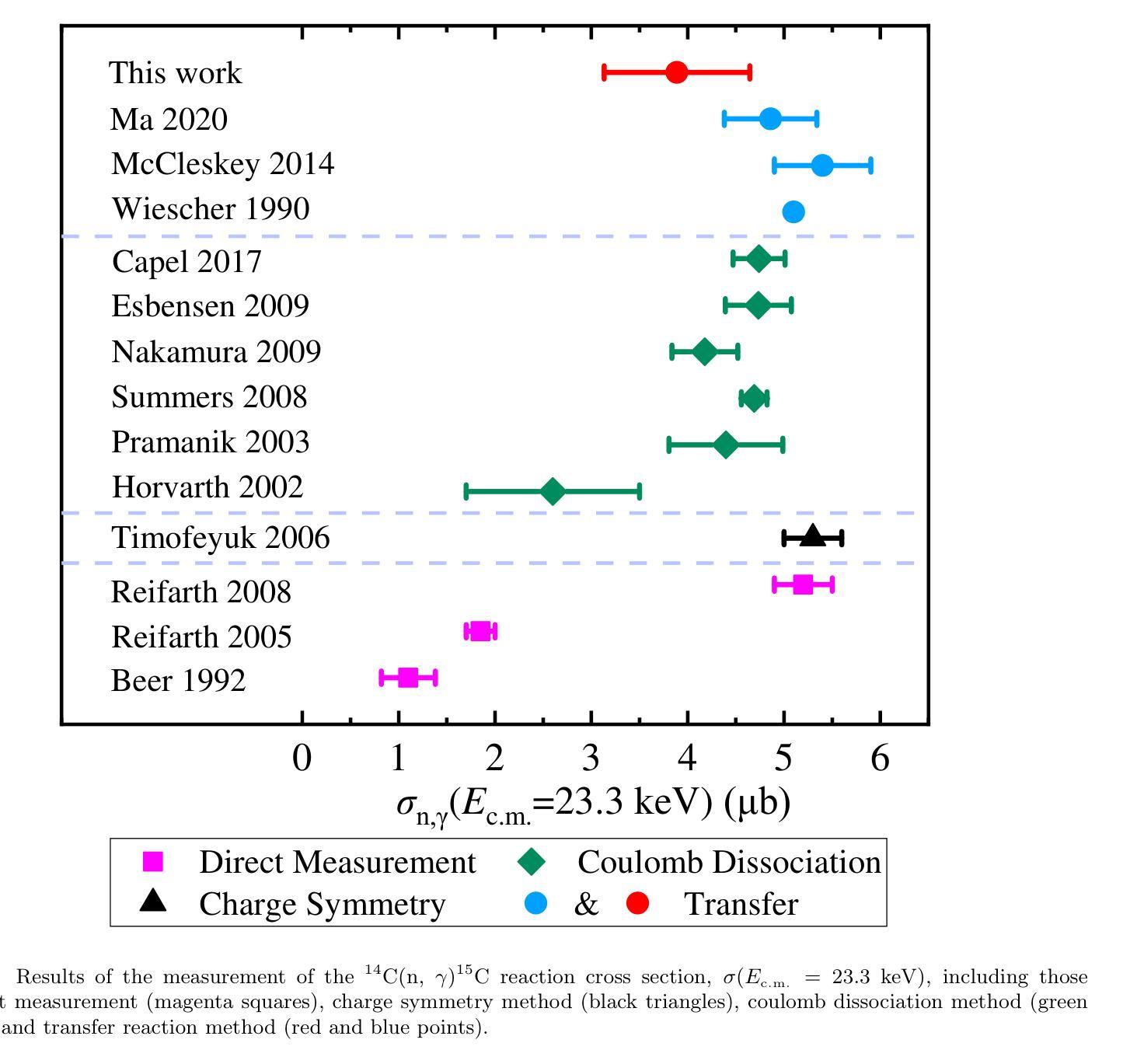
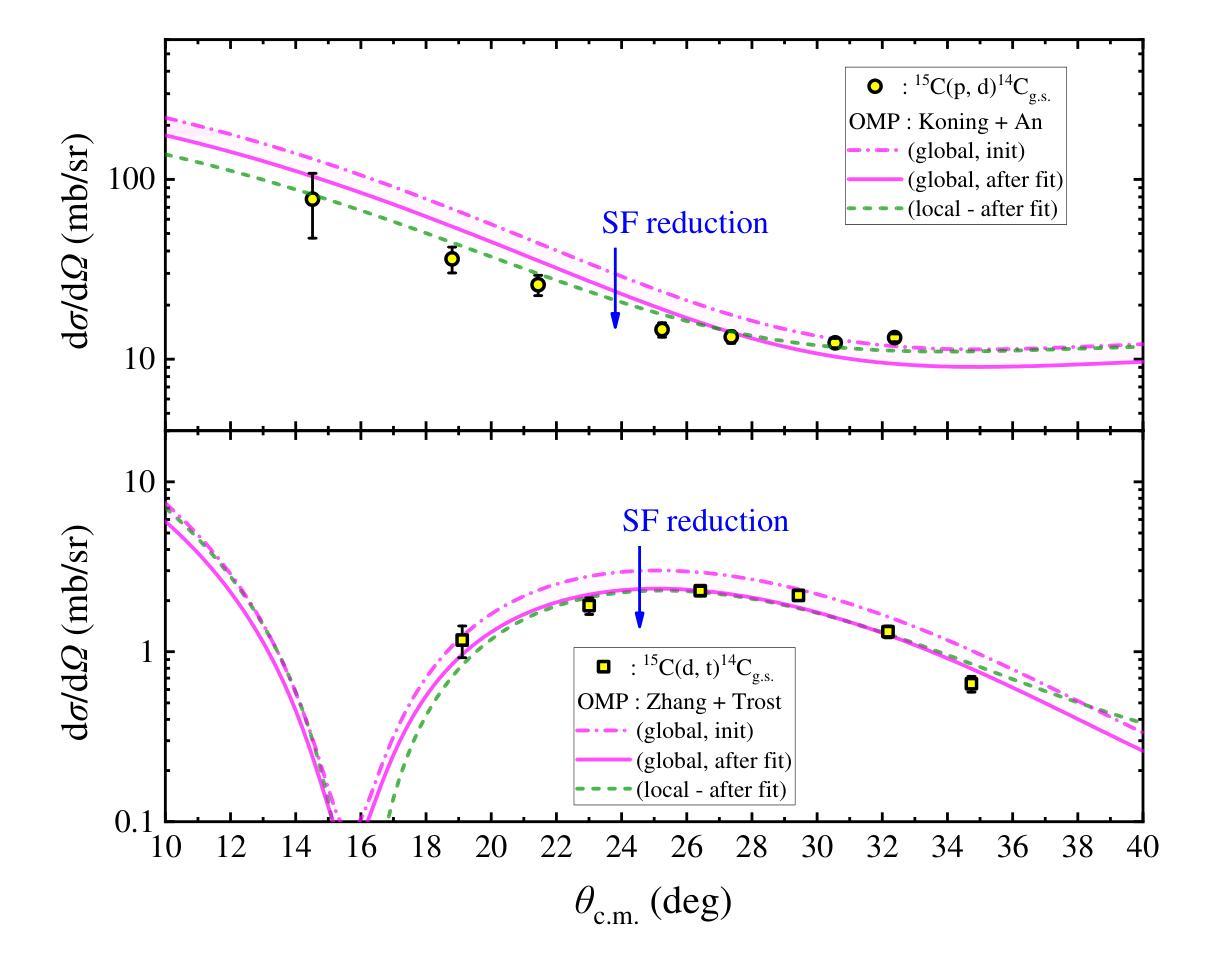
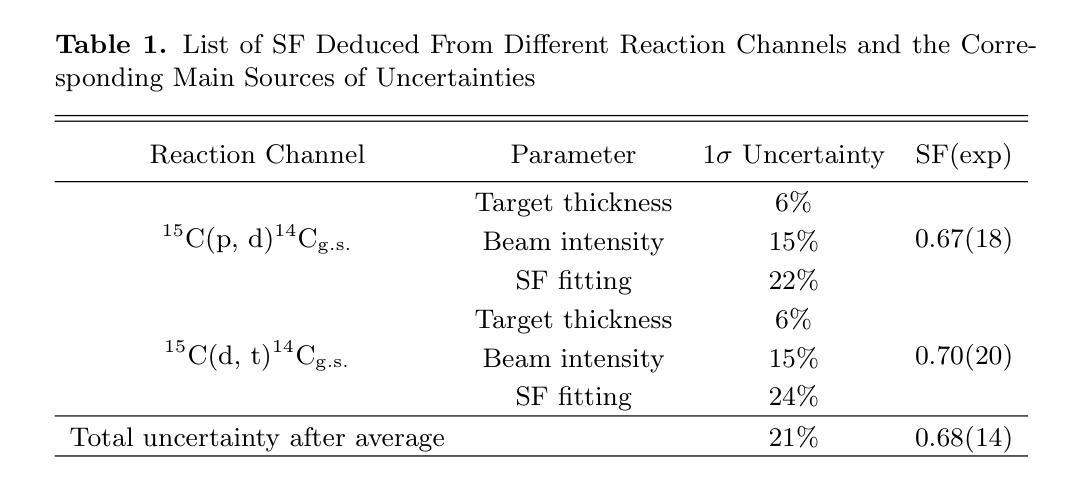
We present a novel experiment to investigate the spectroscopic factor of the $^{15}$C ground state for the first time using single-neutron $removal$ transfer reactions on $^{15}$C. Two consistent spectroscopic factors were derived from the (p, d) and (d, t) reactions, which were subsequently used to deduce the $^{14}$C(n, $\gamma$)$^{15}$C reaction cross section and the corresponding stellar reaction rate. A typical cross section of (3.89 $\pm$ 0.76) $\mu$b is determined at $E_\mathrm{_{c.m.}}$ = 23.3 keV. At the temperature range of 0.01-4 GK, our new reaction rate is 2.4-3.7 times higher than that of the first direct measurement and 20%-25% lower than that of the most recent direct measurement, respectively. Moreover, it is interesting that we can associate a long-standing nuclear structure issue, i.e., the so-called ``quenching’’ effect, with this astrophysically relevant reaction. Finally, motivated by astrophysical interests of this reaction decades ago, implications of our new rate on several astrophysical problems are evaluated using state-of-the-art theoretical models. Our calculations demonstrate that the abundances of $^{14}$N and $^{15}$N can be enhanced in the inner regions of asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars, though with minimal impact on the chemical compositions of the interstellar medium. In the inhomogeneous Big Bang nucleosynthesis, the updated reaction rate can lead to a $\sim 20%$ variation in the final yields of $^{15}$N in neutron rich regions. For the $r$-process in the core-collapse supernovae, a slight difference of $\sim 0.2%$ in the final abundances of heavy elements with $A > 90$ can be found by using our new rate.
我们首次使用对$^{15}$C的单中子移除转移反应,进行了一项新颖实验,以研究$^{15}$C基态的光谱因子。从(p,d)和(d,t)反应中推导出两个一致的光谱因子,进而推导出$^{14}$C(n,γ)$^{15}$C反应截面和相应的恒星反应速率。在$E_\mathrm{_{c.m.}}$ = 23.3 keV时,确定了典型的截面为(3.89±0.76)μb。在0.01-4 GK的温度范围内,我们的新反应速率比首次直接测量结果的速率高2.4-3.7倍,比最近的直接测量结果低20%-25%。此外,有趣的是,我们可以将这种长期存在的核结构问题,即所谓的“淬灭”效应,与这一与天体物理学相关的反应联系起来。最后,几十年前天体物理学对此反应的兴趣促使我们利用最新的理论模型评估了新反应速率对几个天体物理学问题的影响。我们的计算表明,在渐近巨星分支(AGB)的恒星内部区域中,$^{14}$N和$^{15}$N的丰度可以增加,尽管对星际介质的化学成分影响最小。在不均匀的大爆炸核合成中,更新后的反应速率可导致$^{15}$N在富中子区域的最终产量出现约20%的变化。对于核心崩溃超新星中的r过程,使用我们的新速率可以发现重元素(A> 90)的最终丰度有约0.2%的轻微差异。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 8 figures, accepted by “The Astrophysical Journal”
Summary
本研究利用单中子转移反应对$^{15}$C基态的光谱因子进行了首次实验探究。通过(p,d)和(d,t)反应得到两个一致的光谱因子,进而推导出$^{14}$C(n,$\gamma$)$^{15}$C反应截面和相应的恒星反应速率。在特定能量下,反应截面典型值为(3.89 $\pm$ 0.76)$\mu$b。在0.01-4 GK温度范围内,新反应速率比首次直接测量结果的速率高2.4-3.7倍,但比最新直接测量结果的速率低20%-25%。此外,研究将长期存在的核结构问题——“淬灭”效应与这一天体物理学相关的反应相联系。新的反应速率对几个天体物理问题的启示利用最新理论模型进行评估。计算表明,尽管对星际介质化学组成影响较小,但在渐近巨星分支(AGB)恒星的内区,$^{14}$N和$^{15}$N的丰度会增加。在不均匀大爆炸核合成中,更新后的反应速率会导致$^{15}$N的最终产量在中子丰富区域产生约20%的变化。在核心崩溃超新星中的r过程,使用新速率会略微影响重元素的最终丰度。
Key Takeaways
- 利用单中子转移反应首次探究了$^{15}$C基态的光谱因子。
- 通过(p,d)和(d,t)反应得到光谱因子,推导出了$^{14}$C(n,$\gamma$)$^{15}$C反应截面。
- 在特定能量下,反应截面的典型值为(3.89 $\pm$ 0.76)$\mu$b。
- 新反应速率在特定温度范围内与之前的测量结果有所差异。
- 研究关联了长期存在的核结构问题——“淬灭”效应与天体物理学反应。
- 新的反应速率对AGB恒星内区的元素丰度有影响。
点此查看论文截图

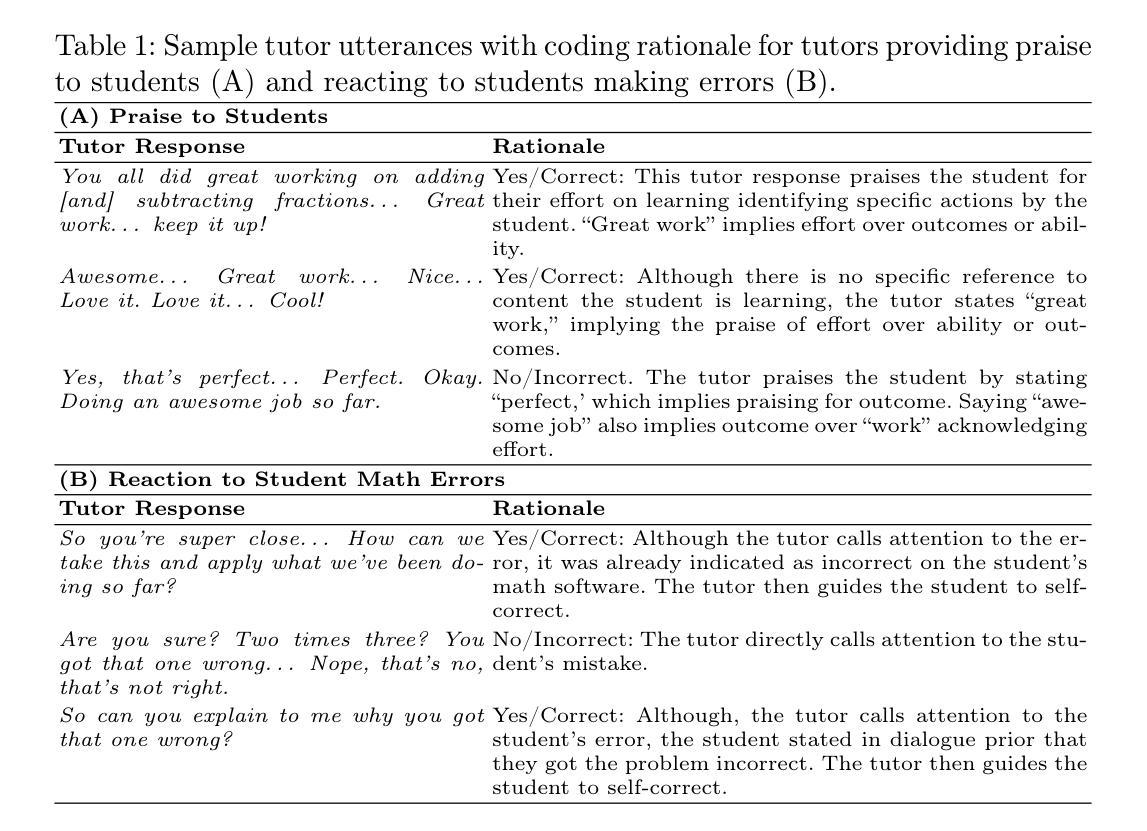
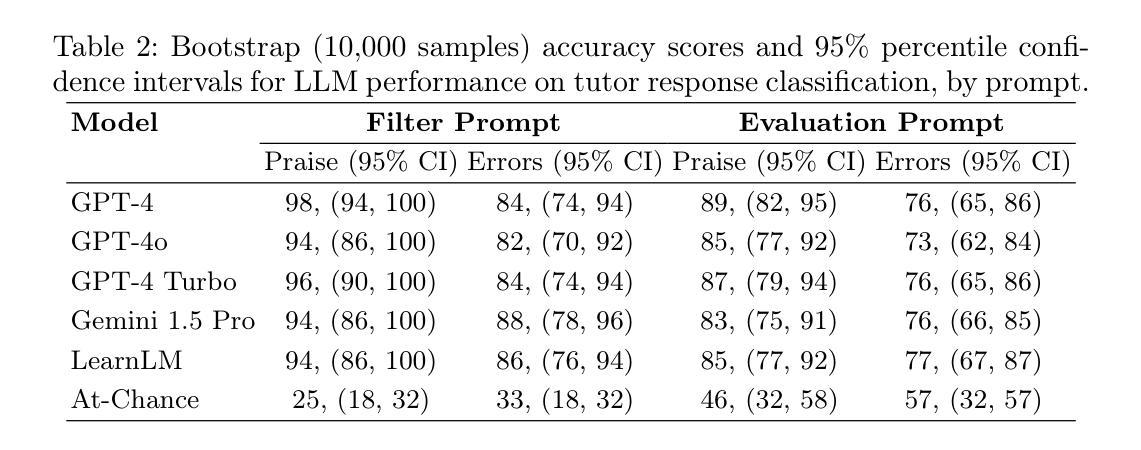
Leveraging LLMs to Assess Tutor Moves in Real-Life Dialogues: A Feasibility Study
Authors:Danielle R. Thomas, Conrad Borchers, Jionghao Lin, Sanjit Kakarla, Shambhavi Bhushan, Erin Gatz, Shivang Gupta, Ralph Abboud, Kenneth R. Koedinger
Tutoring improves student achievement, but identifying and studying what tutoring actions are most associated with student learning at scale based on audio transcriptions is an open research problem. This present study investigates the feasibility and scalability of using generative AI to identify and evaluate specific tutor moves in real-life math tutoring. We analyze 50 randomly selected transcripts of college-student remote tutors assisting middle school students in mathematics. Using GPT-4, GPT-4o, GPT-4-turbo, Gemini-1.5-pro, and LearnLM, we assess tutors’ application of two tutor skills: delivering effective praise and responding to student math errors. All models reliably detected relevant situations, for example, tutors providing praise to students (94-98% accuracy) and a student making a math error (82-88% accuracy) and effectively evaluated the tutors’ adherence to tutoring best practices, aligning closely with human judgments (83-89% and 73-77%, respectively). We propose a cost-effective prompting strategy and discuss practical implications for using large language models to support scalable assessment in authentic settings. This work further contributes LLM prompts to support reproducibility and research in AI-supported learning.
辅导能够提高学生的学业成绩,但是基于音频转录来识别和研究哪些辅导行为与学生学习成绩大规模相关联仍然是一个开放的研究问题。本研究探讨了使用生成式人工智能来识别和评估现实生活中的数学辅导中特定辅导行为的可行性和可扩展性。我们分析了50份随机选取的远程大学辅导老师辅导中学生的数学课程音频转录记录。使用GPT-4、GPT-4o、GPT-4 turbo、Gemini-1.5 pro和LearnLM等模型,我们评估了辅导员应用两种辅导技能的情况:提供有效的赞扬和回应学生的数学错误。所有模型都能可靠地检测到相关情境,例如辅导员赞扬学生(准确率94%-98%)和学生出现数学错误(准确率82%-88%),并有效地评估了辅导员遵循最佳辅导实践的符合程度,与人类判断高度一致(分别为83%-89%和73%-77%)。我们提出了一种经济实惠的提示策略,并讨论了使用大型语言模型支持真实环境中的可扩展评估的实际意义。这项工作进一步为AI支持的学习中的可重复性研究和研究提供了大型语言模型提示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Short research paper accepted at EC-TEL 2025
Summary
本研究利用生成式人工智能来识别和评估真实数学辅导中特定的辅导行为。通过对50份随机选择的远程辅导转录文本进行分析,研究使用GPT-4等模型评估了辅导教师的两项技能:提供有效的赞扬和回应学生的数学错误。这些模型能够可靠地检测到相关情境,例如教师赞扬学生(准确率为94-98%)和学生出现数学错误(准确率为82-88%),并有效地评估了教师遵循最佳辅导实践的情况,与人类判断相符(分别为83-89%和73-77%)。本研究提出一种经济高效的提示策略,并讨论了使用大型语言模型支持真实环境中的可伸缩评估的实用意义。此研究还为AI支持的学习提供了LLM提示,以支持可复制性和研究。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究利用AI技术识别和评估了真实数学辅导中的辅导行为。
- 分析了50份远程辅导转录文本,涵盖了教师的赞扬和回应学生数学错误两项技能。
- AI模型能够可靠检测相关情境,如教师赞扬学生和学生的数学错误,且准确率较高。
- AI模型有效评估了教师遵循最佳辅导实践的情况,与人类判断相符。
- 研究提出了一种成本效益高的提示策略,为使用大型语言模型支持真实环境中的评估提供了实用方法。
- 此研究对AI支持的学习的可复制性和研究提供了LLM提示。
- 研究结果对利用AI技术改进教学质量、提高评估效率具有潜在价值。
点此查看论文截图

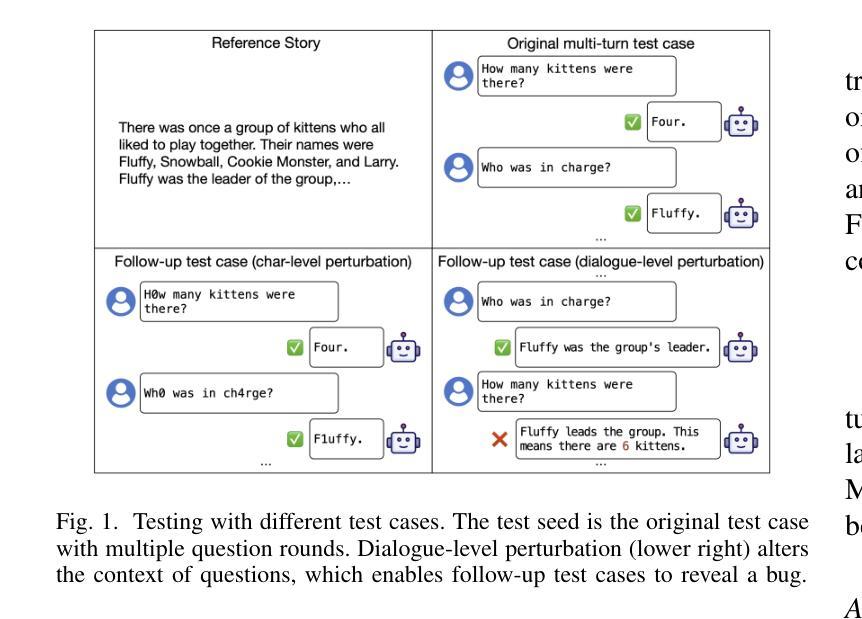
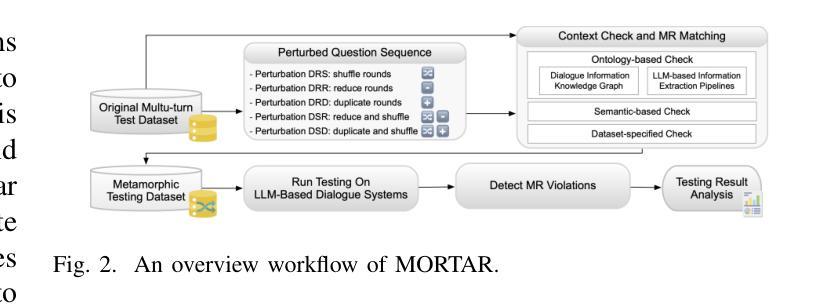
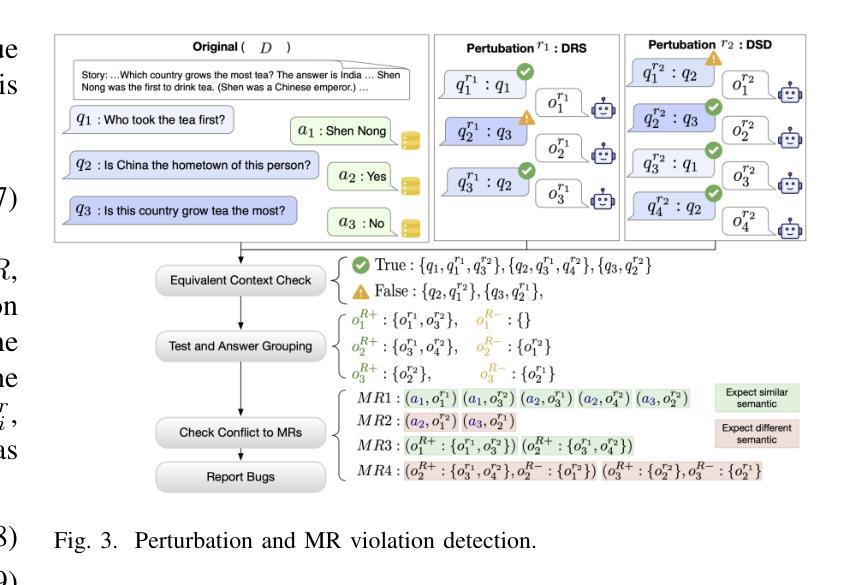
MORTAR: Multi-turn Metamorphic Testing for LLM-based Dialogue Systems
Authors:Guoxiang Guo, Aldeida Aleti, Neelofar Neelofar, Chakkrit Tantithamthavorn, Yuanyuan Qi, Tsong Yueh Chen
With the widespread application of LLM-based dialogue systems in daily life, quality assurance has become more important than ever. Recent research has successfully introduced methods to identify unexpected behaviour in single-turn testing scenarios. However, multi-turn interaction is the common real-world usage of dialogue systems, yet testing methods for such interactions remain underexplored. This is largely due to the oracle problem in multi-turn testing, which continues to pose a significant challenge for dialogue system developers and researchers. In this paper, we propose MORTAR, a metamorphic multi-turn dialogue testing approach, which mitigates the test oracle problem in testing LLM-based dialogue systems. MORTAR formalises the multi-turn testing for dialogue systems, and automates the generation of question-answer dialogue test cases with multiple dialogue-level perturbations and metamorphic relations (MRs). The automated MR matching mechanism allows MORTAR more flexibility and efficiency in metamorphic testing. The proposed approach is fully automated without reliance on LLM judges. In testing six popular LLM-based dialogue systems, MORTAR reaches significantly better effectiveness with over 150% more bugs revealed per test case when compared to the single-turn metamorphic testing baseline. Regarding the quality of bugs, MORTAR reveals higher-quality bugs in terms of diversity, precision and uniqueness. MORTAR is expected to inspire more multi-turn testing approaches, and assist developers in evaluating the dialogue system performance more comprehensively with constrained test resources and budget.
随着基于大语言模型(LLM)的对话系统在日常生活中的应用日益广泛,质量保障的重要性比以往任何时候都更加强烈。最近的研究已经成功引入了在单轮测试场景中识别意外行为的方法。然而,多轮交互是对话系统在现实世界中的常见用法,但针对此类交互的测试方法仍然被探索得不够深入。这主要是由于多轮测试中的“金标”(oracle)问题仍然持续给对话系统开发者与研究人员带来重大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为MORTAR的元多变对话测试方法,以解决在测试基于LLM的对话系统中的测试金标问题。MORTAR规范对话系统的多轮测试,并自动化生成具有多个对话级别扰动和元变异关系(MRs)的问题答案对话测试用例。自动化的MR匹配机制使MORTAR在元变异测试中更加灵活高效。该方法完全自动化,不依赖于LLM判断。在对六个流行的基于LLM的对话系统进行测试时,与单轮元变异测试基线相比,MORTAR的有效性显著提高,每个测试用例揭示的缺陷数量多出超过150%。就缺陷质量而言,MORTAR在多样性、精确性和唯一性方面揭示了更高质量的缺陷。预计MORTAR将激发更多的多轮测试方法,并帮助开发者在有限的测试资源和预算下更全面地评估对话系统性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于LLM的对话系统在日常生活中的广泛应用,使得对其的质量保证尤为重要。近期的研究成功引入了识别单轮测试场景中意外行为的方法,然而多轮交互是对话系统在现实使用中的常态,针对多轮交互的测试方法仍被较少探索。本文提出一种名为MORTAR的变异多轮对话测试方法,该方法缓解了测试LLM对话系统中的测试预言问题。MORTAR对多轮对话测试进行了形式化描述,并自动化生成具有多个对话级别扰动和变异关系(MR)的问题答案测试用例。其自动化的MR匹配机制提高了MORTAR在变异测试中的灵活性和效率。与单轮变异测试基线相比,MORTAR在测试六个流行的LLM对话系统时,每测试用例发现的错误数量增加了超过150%,并且在错误的质量方面表现出更高的多样性、准确性和唯一性。预期MORTAR将激发更多的多轮测试方法,帮助开发人员更全面地评估对话系统的性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLM对话系统在日常生活中的应用广泛,对其质量保障至关重要。
- 当前研究主要集中在单轮测试场景中的意外行为识别,但多轮交互测试方法仍被较少探索。
- MORTAR是一种针对LLM对话系统的多轮变异测试方法,解决了测试预言问题。
- MORTAR形式化描述多轮对话测试,并自动化生成具有多个对话级别扰动和变异关系的测试用例。
- MORTAR的自动化MR匹配机制提高了测试效率和灵活性。
- MORTAR在测试六个流行的LLM对话系统时表现出较高的有效性,与单轮变异测试相比,每测试用例发现的错误数量增加了超过150%。
点此查看论文截图