⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
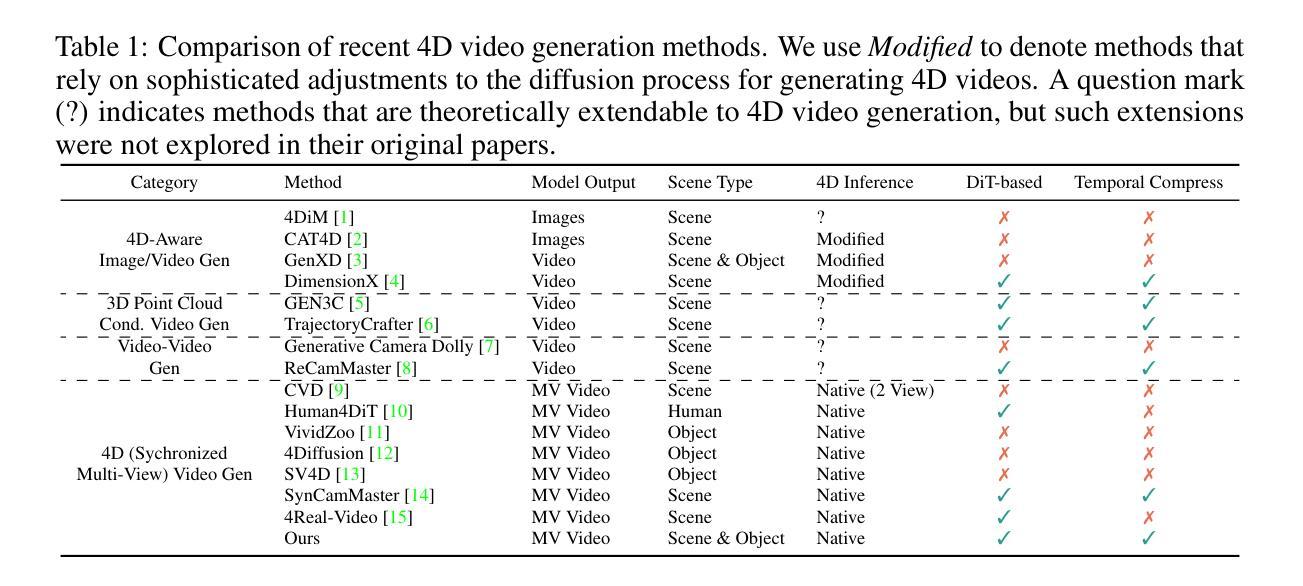
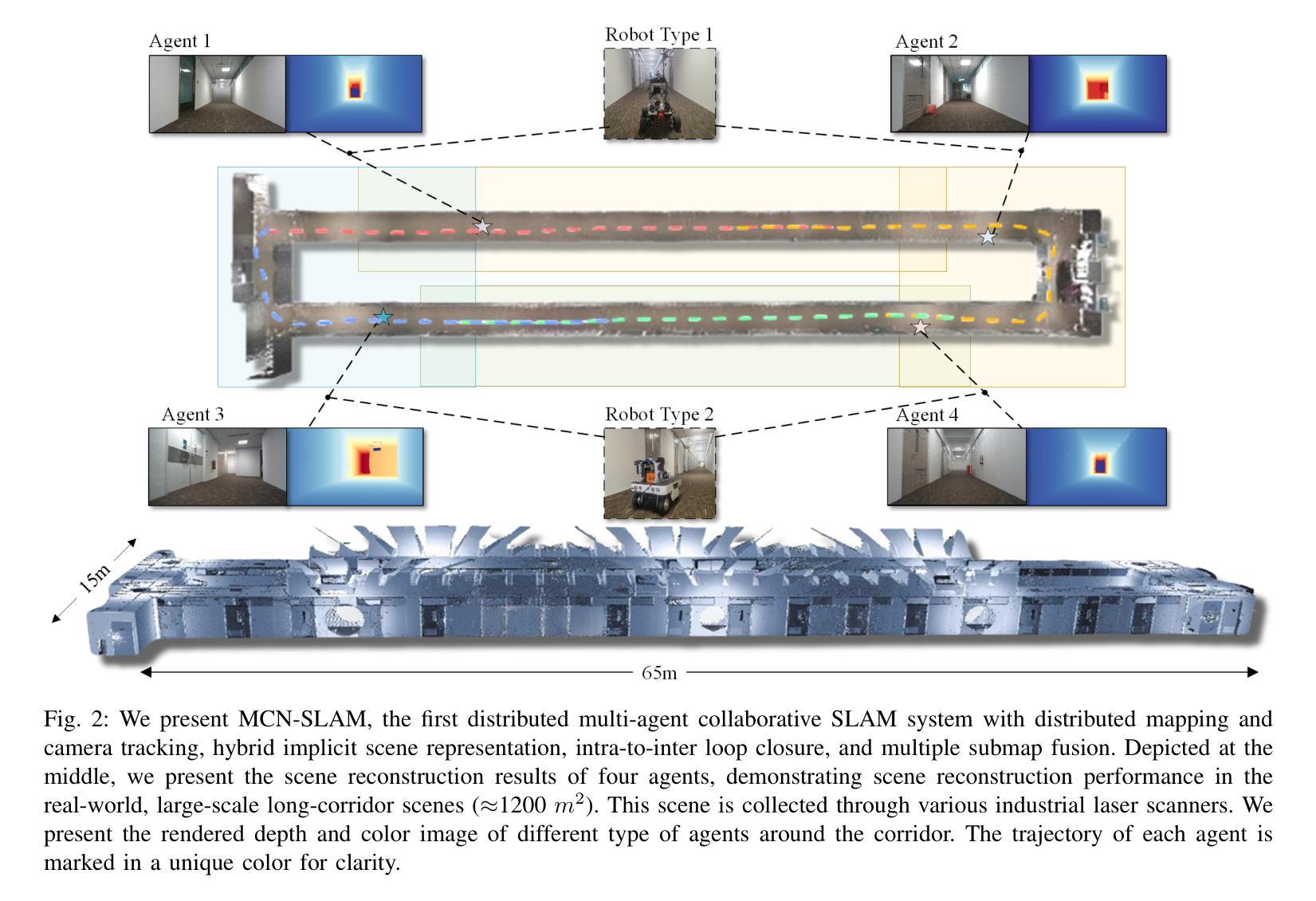
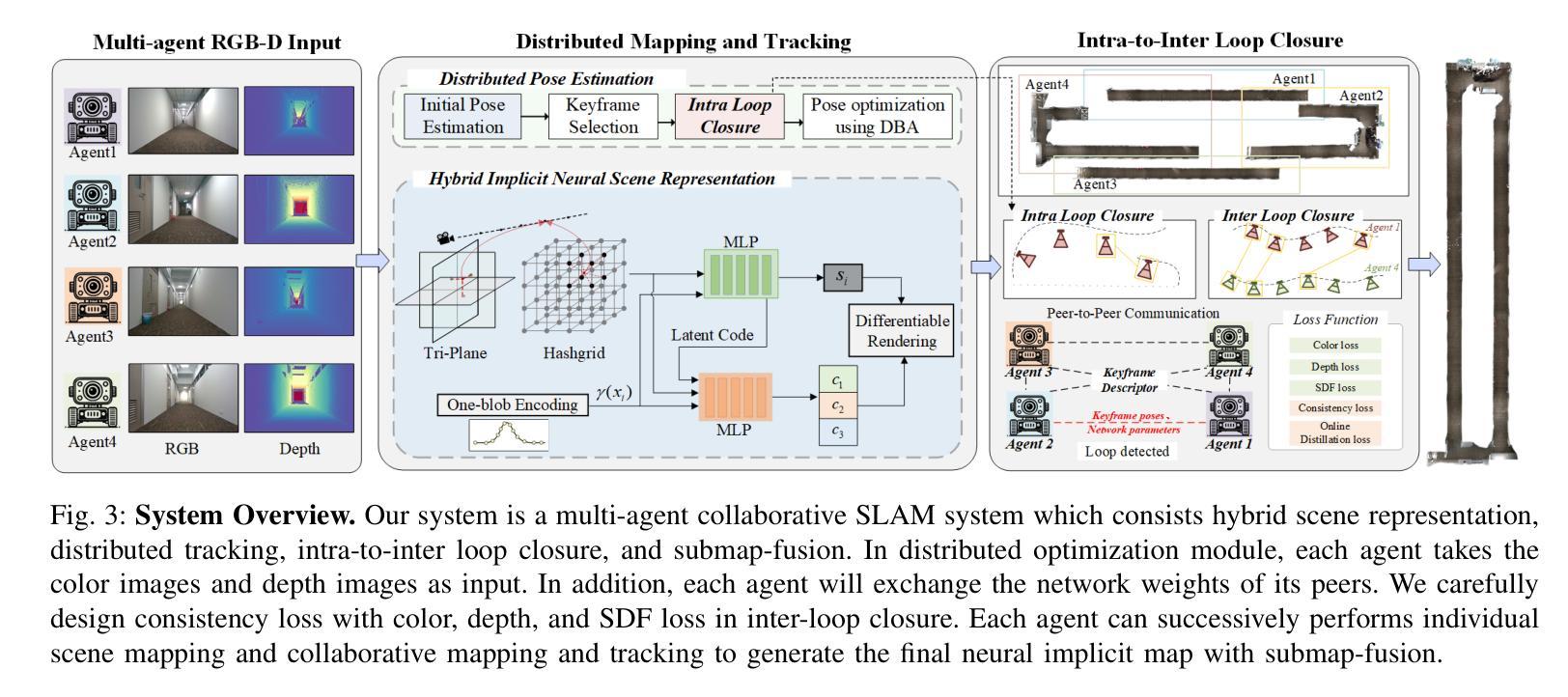
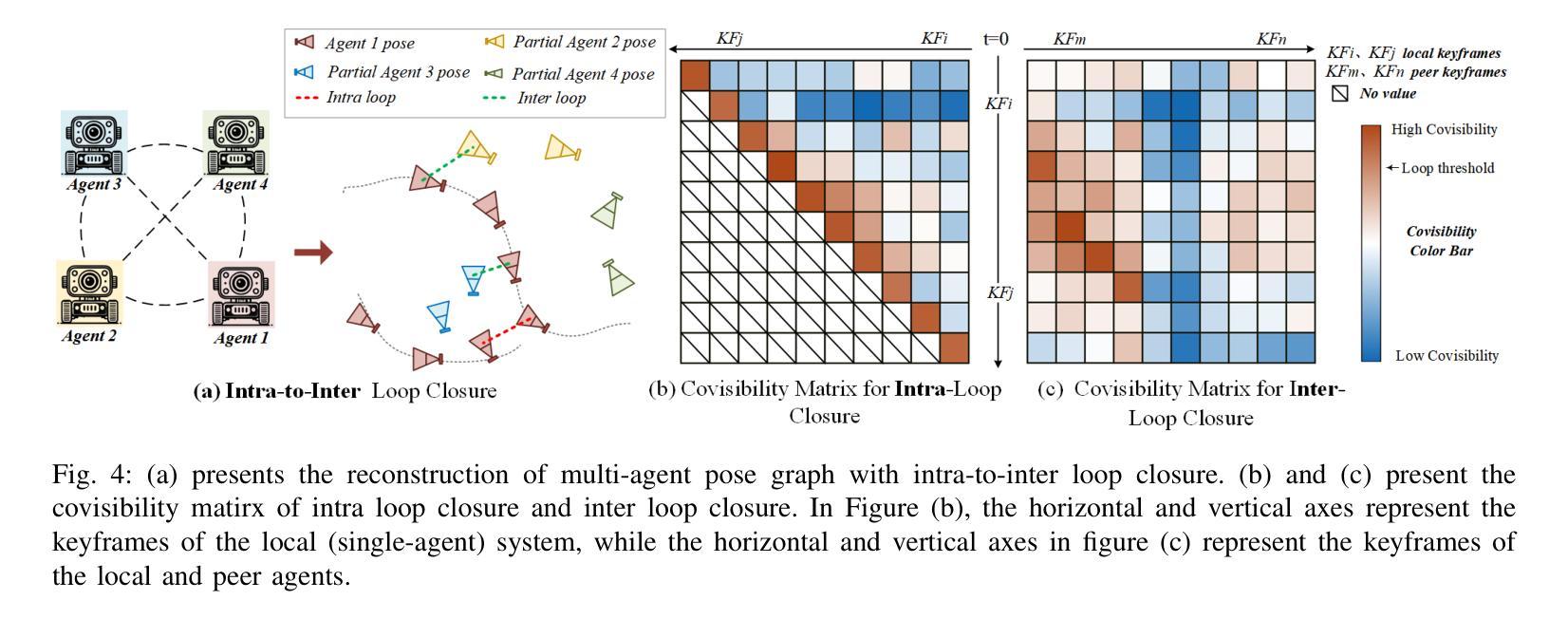
MCN-SLAM: Multi-Agent Collaborative Neural SLAM with Hybrid Implicit Neural Scene Representation
Authors:Tianchen Deng, Guole Shen, Xun Chen, Shenghai Yuan, Hongming Shen, Guohao Peng, Zhenyu Wu, Jingchuan Wang, Lihua Xie, Danwei Wang, Hesheng Wang, Weidong Chen
Neural implicit scene representations have recently shown promising results in dense visual SLAM. However, existing implicit SLAM algorithms are constrained to single-agent scenarios, and fall difficulties in large-scale scenes and long sequences. Existing NeRF-based multi-agent SLAM frameworks cannot meet the constraints of communication bandwidth. To this end, we propose the first distributed multi-agent collaborative neural SLAM framework with hybrid scene representation, distributed camera tracking, intra-to-inter loop closure, and online distillation for multiple submap fusion. A novel triplane-grid joint scene representation method is proposed to improve scene reconstruction. A novel intra-to-inter loop closure method is designed to achieve local (single-agent) and global (multi-agent) consistency. We also design a novel online distillation method to fuse the information of different submaps to achieve global consistency. Furthermore, to the best of our knowledge, there is no real-world dataset for NeRF-based/GS-based SLAM that provides both continuous-time trajectories groundtruth and high-accuracy 3D meshes groundtruth. To this end, we propose the first real-world Dense slam (DES) dataset covering both single-agent and multi-agent scenarios, ranging from small rooms to large-scale outdoor scenes, with high-accuracy ground truth for both 3D mesh and continuous-time camera trajectory. This dataset can advance the development of the research in both SLAM, 3D reconstruction, and visual foundation model. Experiments on various datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in both mapping, tracking, and communication. The dataset and code will open-source on https://github.com/dtc111111/mcnslam.
神经隐式场景表示在密集视觉SLAM中最近显示出有前途的结果。然而,现有的隐式SLAM算法仅限于单智能体场景,在大场景和长序列中面临困难。基于NeRF的多智能体SLAM框架无法满足通信带宽的限制。为此,我们提出了第一个分布式多智能体协同神经SLAM框架,具有混合场景表示、分布式相机跟踪、内外环闭合以及用于多个子图融合的在线蒸馏。提出了一种新型的三平面网格联合场景表示方法,以改进场景重建。设计了一种新型的内外环闭合方法,以实现局部(单智能体)和全局(多智能体)的一致性。我们还设计了一种新的在线蒸馏方法,以融合不同子图的信息,实现全局一致性。此外,据我们所知,没有基于NeRF或GS的SLAM真实世界数据集能够提供连续时间轨迹的高精度3D网格地面真实情况。为此,我们提出了第一个真实世界的Dense slam(DES)数据集,涵盖单智能体和多智能体场景,从小房间到大型室外场景,同时提供3D网格和连续时间相机轨迹的高精度地面真实情况。该数据集可以促进SLAM、3D重建和视觉基础模型的研究发展。在各种数据集上的实验证明了所提出方法在映射、跟踪和通信方面的优越性。数据集和代码将在https://github.com/dtc111111/mcnslam上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出首个分布式多智能体协同神经网络SLAM框架,解决现有隐式SLAM算法在大型场景和长序列中的困难,以及NeRF基多智能体SLAM框架通信带宽的限制。提出新型场景表示方法、分布式相机跟踪、环路闭合技术及在线蒸馏融合多子图信息。同时,发布首个真实世界Dense slam(DES)数据集,推动SLAM、3D重建和视觉基础模型的发展。实验证明该方法和数据集在映射、追踪和通信方面的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出首个分布式多智能体协同神经网络SLAM框架,适用于大型场景和长序列。
- 引入新型场景表示方法,如triplane-grid联合场景表示法,改善场景重建。
- 设计分布式相机跟踪、环路闭合方法,实现局部和全局一致性。
- 创新在线蒸馏方法融合不同子图信息,保障全局一致性。
- 公开首个真实世界的Dense slam(DES)数据集,包含单智能体和多智能体场景,提供高精度3D网格和连续时间相机轨迹的地面真实数据。
- 该数据集推动SLAM、3D重建和视觉基础模型的研究发展。
点此查看论文截图

2D Triangle Splatting for Direct Differentiable Mesh Training
Authors:Kaifeng Sheng, Zheng Zhou, Yingliang Peng, Qianwei Wang
Differentiable rendering with 3D Gaussian primitives has emerged as a powerful method for reconstructing high-fidelity 3D scenes from multi-view images. While it offers improvements over NeRF-based methods, this representation still encounters challenges with rendering speed and advanced rendering effects, such as relighting and shadow rendering, compared to mesh-based models. In this paper, we propose 2D Triangle Splatting (2DTS), a novel method that replaces 3D Gaussian primitives with 2D triangle facelets. This representation naturally forms a discrete mesh-like structure while retaining the benefits of continuous volumetric modeling. By incorporating a compactness parameter into the triangle primitives, we enable direct training of photorealistic meshes. Our experimental results demonstrate that our triangle-based method, in its vanilla version (without compactness tuning), achieves higher fidelity compared to state-of-the-art Gaussian-based methods. Furthermore, our approach produces reconstructed meshes with superior visual quality compared to existing mesh reconstruction methods.
使用3D高斯原始数据的可微渲染已经成为一种强大的方法,可以从多视角图像重建高保真度的3D场景。虽然相较于基于NeRF的方法有所提升,但这种表示形式在渲染速度和高级渲染效果(如重新照明和阴影渲染)方面仍然面临挑战,特别是在与基于网格的模型比较时。在本文中,我们提出了二维三角拼贴(2DTS)这种新型方法,它用二维三角形面片替代了原始的3D高斯数据。这种表示形式自然地形成了一个离散网格状结构,同时保留了连续体积建模的优点。通过将紧凑参数融入三角形原始数据中,我们可以直接训练逼真的网格。我们的实验结果表明,我们基于三角形的原生版本方法(无需紧凑度调整)相较于最先进的基于高斯的方法达到了更高的保真度。此外,我们的方法产生的重建网格在视觉质量上相较于现有的网格重建方法更为优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures
摘要
以二维三角剖分(2DTS)为表现方法的可微分渲染技术,为从多视角图像重建高保真三维场景提供了一种新的有力手段。相较于基于NeRF的方法,此方法虽有所改进,但在渲染速度及高级渲染效果(如重新照明和阴影渲染)方面仍面临挑战。本文提出一种新型方法,以二维三角面片替代三维高斯原始单元。这种表现方法既能形成离散网格结构,同时保留连续体积建模的优势。通过引入紧凑参数,我们能直接训练具有逼真感的网格模型。实验结果显示,在未经紧凑度调整的基础三角剖分方法,其保真度已超越当前主流的高斯基础方法。此外,我们的方法生成的重建网格在视觉质量上优于现有的网格重建方法。
要点提炼
- 论文提出了二维三角剖分(2DTS)技术,该技术使用二维三角面片替代三维高斯原始单元进行可微分渲染。
- 相较于基于NeRF的方法,虽然有所改进,但在渲染速度和高级渲染效果方面仍存在挑战。
- 二维三角剖分技术能够形成离散网格结构,同时保留连续体积建模的优势。
- 通过引入紧凑参数,该方法的三角原始单元能用于直接训练具有逼真感的网格模型。
- 实验结果显示,基础三角剖分方法在未经紧凑度调整的情况下已超越主流的高斯基础方法。
- 该方法生成的重建网格在视觉质量上优于现有的网格重建方法。
点此查看论文截图




GANs vs. Diffusion Models for virtual staining with the HER2match dataset
Authors:Pascal Klöckner, José Teixeira, Diana Montezuma, Jaime S. Cardoso, Hugo M. Horlings, Sara P. Oliveira
Virtual staining is a promising technique that uses deep generative models to recreate histological stains, providing a faster and more cost-effective alternative to traditional tissue chemical staining. Specifically for H&E-HER2 staining transfer, despite a rising trend in publications, the lack of sufficient public datasets has hindered progress in the topic. Additionally, it is currently unclear which model frameworks perform best for this particular task. In this paper, we introduce the HER2match dataset, the first publicly available dataset with the same breast cancer tissue sections stained with both H&E and HER2. Furthermore, we compare the performance of several Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs), and implement a novel Brownian Bridge Diffusion Model for H&E-HER2 translation. Our findings indicate that, overall, GANs perform better than DMs, with only the BBDM achieving comparable results. Furthermore, we emphasize the importance of data alignment, as all models trained on HER2match produced vastly improved visuals compared to the widely used consecutive-slide BCI dataset. This research provides a new high-quality dataset ([available upon publication acceptance]), improving both model training and evaluation. In addition, our comparison of frameworks offers valuable guidance for researchers working on the topic.
虚拟染色是一种有前途的技术,它利用深度生成模型重新创建组织染色,为传统的组织化学染色提供了更快、更经济的替代方案。对于H&E-HER2染色转移而言,尽管相关文献呈上升趋势,但缺乏足够的公共数据集阻碍了该主题的研究进展。此外,目前尚不清楚哪些模型框架特别适用于这一任务。在本文中,我们介绍了HER2match数据集,这是第一个公开可用的同时具有H&E和HER2染色的乳腺癌组织切片的公共数据集。此外,我们比较了几种生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)的性能,并实现了用于H&E-HER2翻译的新型布朗桥扩散模型(BBDM)。我们的研究结果表明,总体而言,GANs的表现优于DMs,只有BBDM取得了相当的结果。此外,我们强调了数据对齐的重要性,因为在HER2match数据集上训练的所有模型产生的视觉效果都大大优于广泛使用的连续切片BCI数据集。该研究提供了一个新的高质量数据集(在论文被接受后即可获得),提高了模型训练和评估的效果。此外,我们对框架的比较为从事这一领域的研究人员提供了宝贵的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出并引入了HER2match数据集,它是第一个公开可用的、同时含有H&E和HER2染色的乳腺癌组织切片数据集。论文比较了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)的性能,并实现了针对H&E-HER2翻译的布朗桥扩散模型(BBDM)。研究结果显示,GANs整体表现优于DMs,其中BBDM取得了相当的结果。此外,论文强调了数据对齐的重要性,所有在HER2match上训练的模型都比广泛使用的连续切片BCI数据集产生了更好的视觉效果。该研究提供了高质量的新数据集,改进了模型训练和评估,并为相关研究提供了有价值的指导。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟染色技术利用深度生成模型重新创建组织化学染色的过程,为更快、更经济的染色方式带来希望。
- 对于H&E-HER2染色转移任务,缺乏公共数据集限制了研究进展。
- 论文首次引入了HER2match数据集,包含相同的乳腺癌组织切片H&E和HER2染色结果。
- 比较了多种生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)的性能。
- 新提出的布朗桥扩散模型(BBDM)在H&E-HER2翻译任务上取得了良好效果。
- GANs在整体性能上优于DMs,其中BBDM表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图

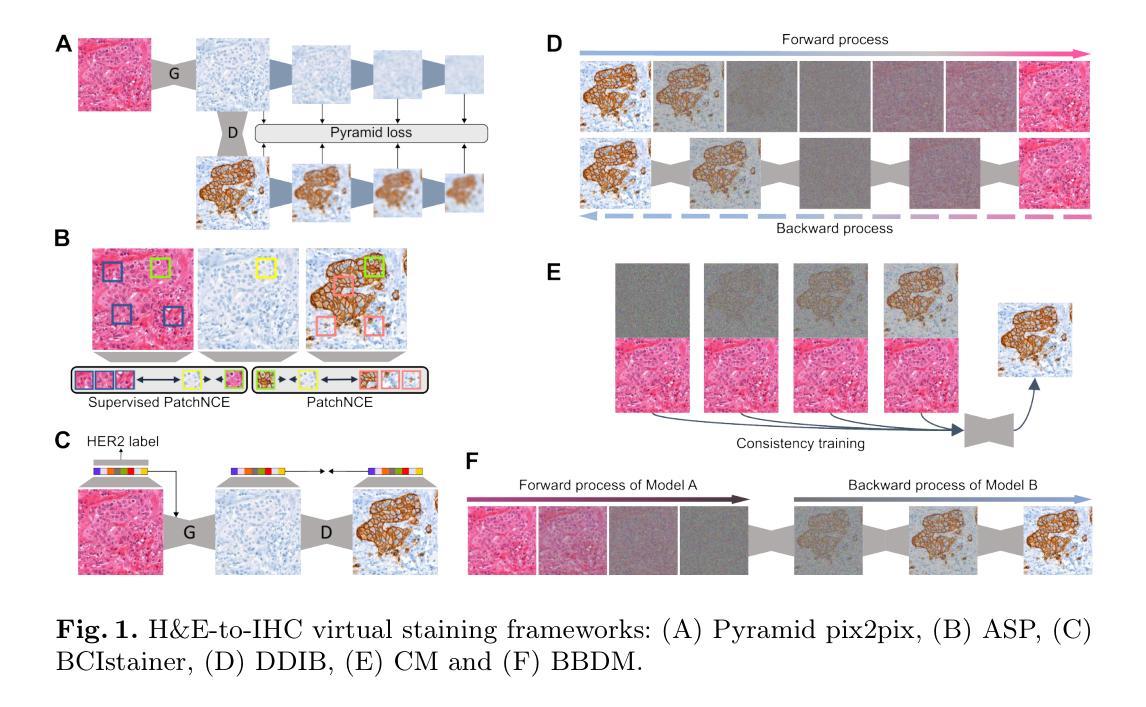
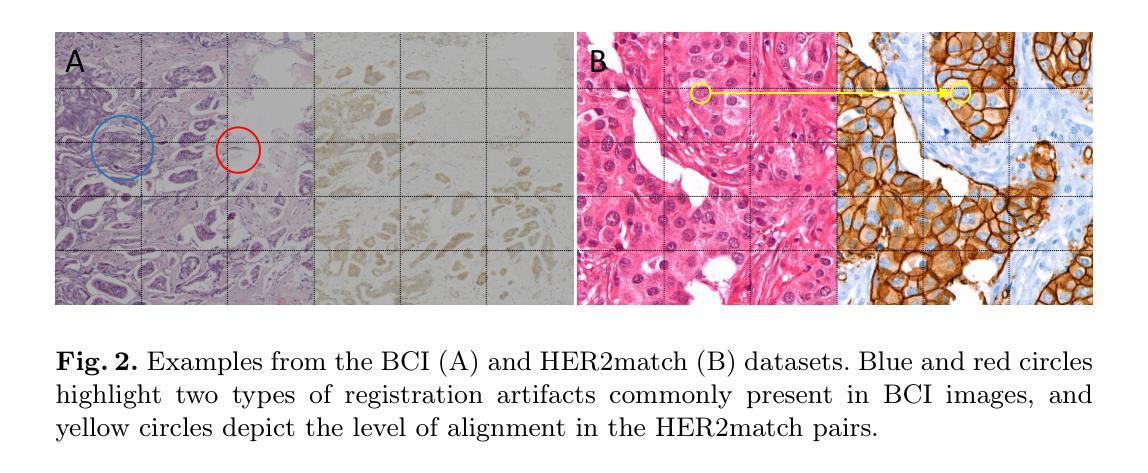
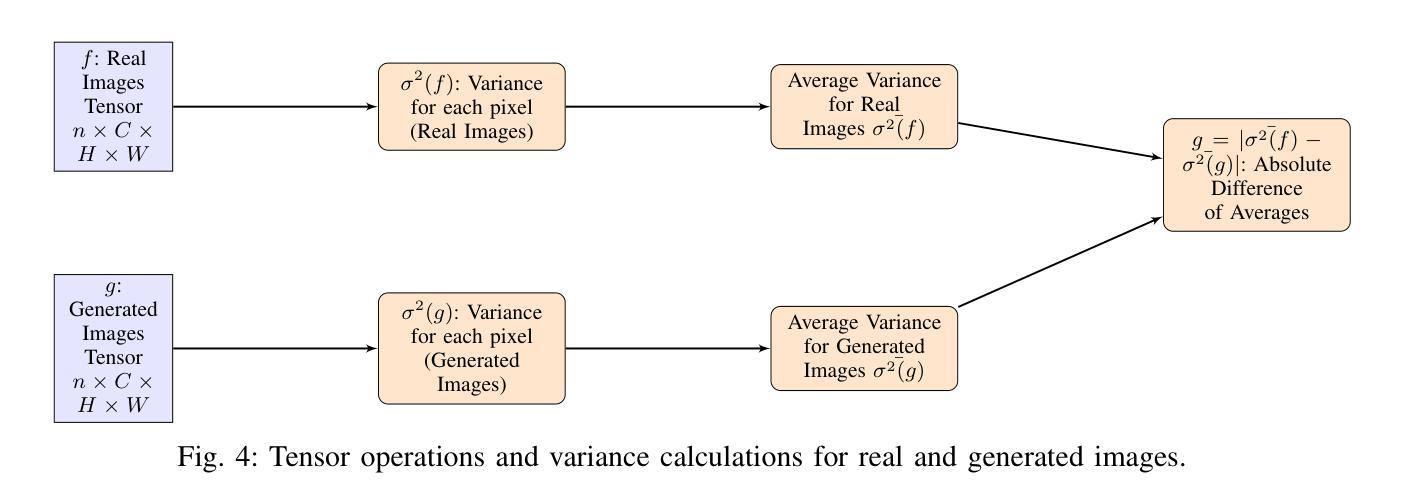
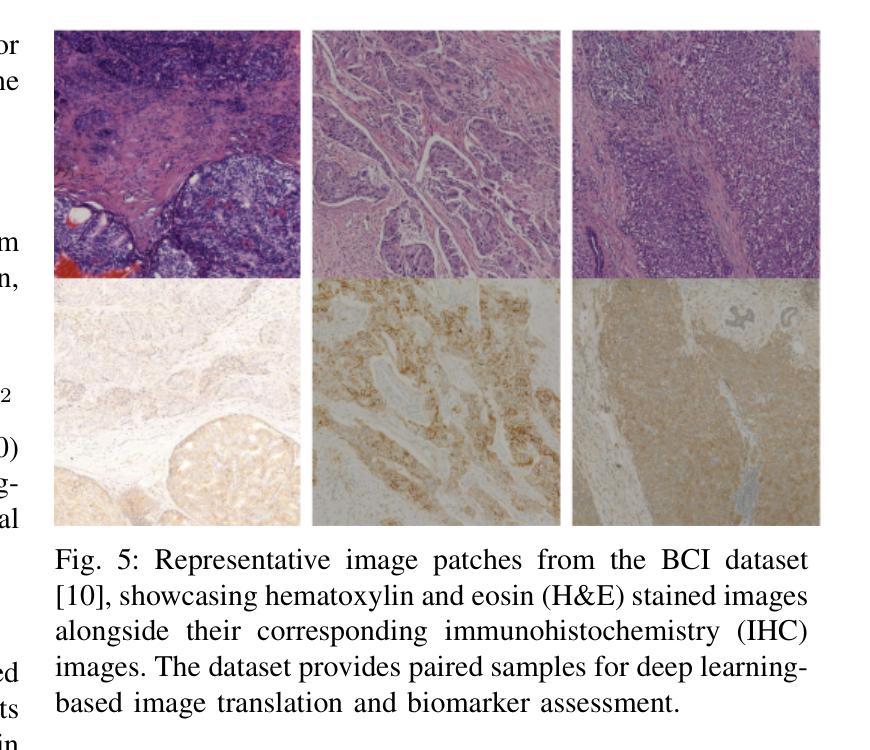
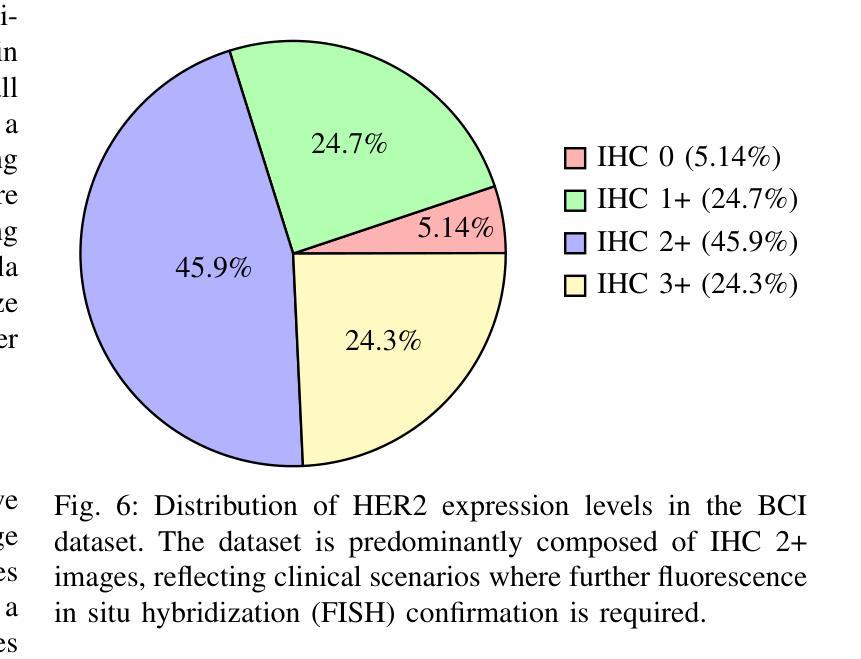
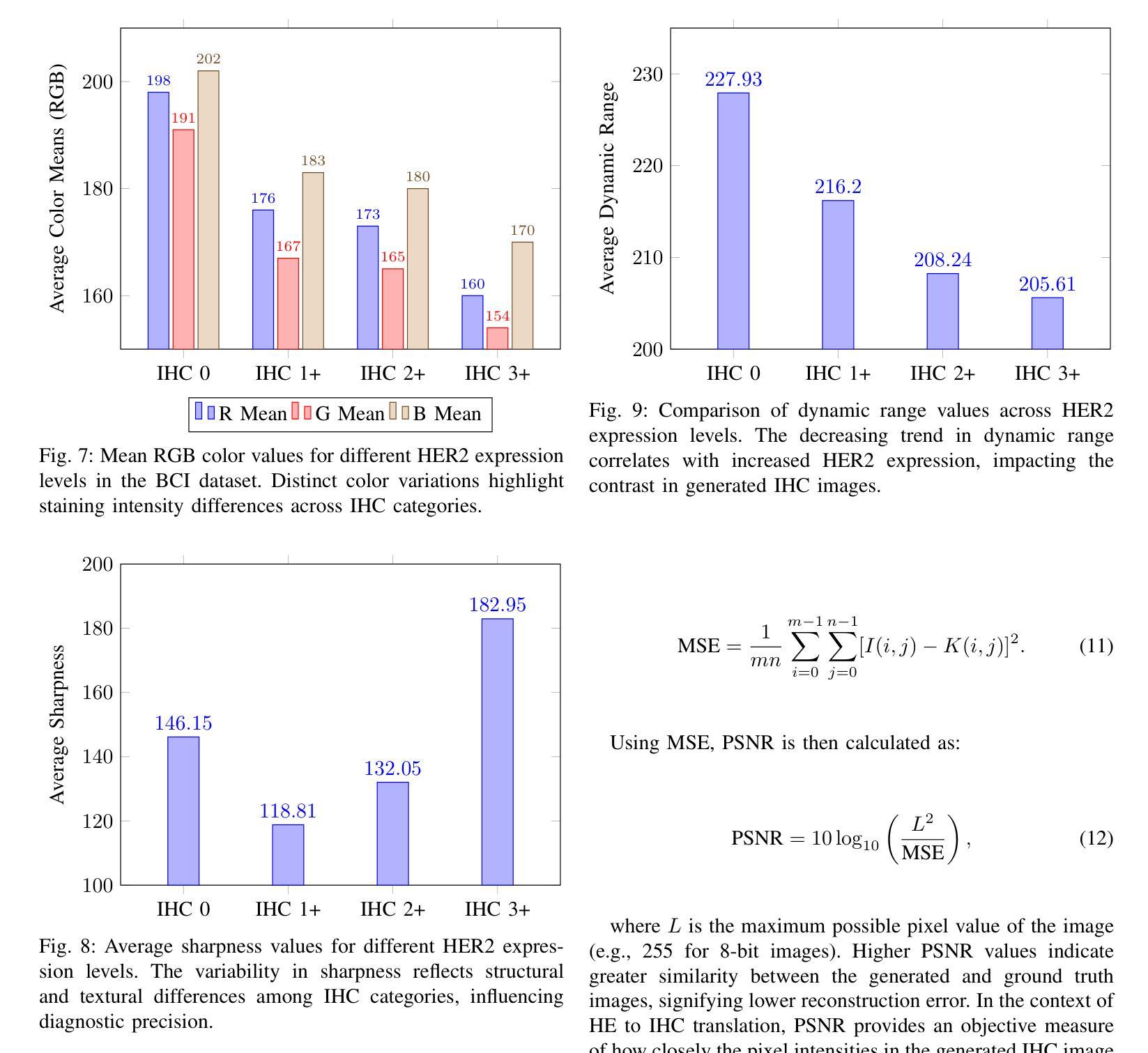
Transforming H&E images into IHC: A Variance-Penalized GAN for Precision Oncology
Authors:Sara Rehmat, Hafeez Ur Rehman
The overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in breast cells is a key driver of HER2-positive breast cancer, a highly aggressive subtype requiring precise diagnosis and targeted therapy. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the standard technique for HER2 assessment but is costly, labor-intensive, and highly dependent on antibody selection. In contrast, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, a routine histopathological procedure, offers broader accessibility but lacks HER2 specificity. This study proposes an advanced deep learning-based image translation framework to generate highfidelity IHC images from H&E-stained tissue samples, enabling cost-effective and scalable HER2 assessment. By modifying the loss function of pyramid pix2pix, we mitigate mode collapse, a fundamental limitation in generative adversarial networks (GANs), and introduce a novel variance-based penalty that enforces structural diversity in generated images. Our model particularly excels in translating HER2-positive (IHC 3+) images, which have remained challenging for existing methods due to their complex morphological variations. Extensive evaluations on the BCI histopathological dataset demonstrate that our model surpasses state-of-the-art methods in terms of peak signal-tonoise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), and Frechet Inception Distance (FID), particularly in accurately translating HER2-positive (IHC 3+) images. Beyond medical imaging, our model exhibits superior performance in general image-to-image translation tasks, showcasing its potential across multiple domains. This work marks a significant step toward AI-driven precision oncology, offering a reliable and efficient alternative to traditional HER2 diagnostics.
人类表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)在乳腺细胞中的过度表达是HER2阳性乳腺癌的关键驱动因素,这是一种高度侵袭性的亚型,需要精确诊断和治疗。免疫组织化学(IHC)是评估HER2的标准技术,但成本高昂、劳动强度大,且高度依赖于抗体选择。相比之下,苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色是一种常规的病理组织学程序,具有更广泛的可及性,但缺乏HER2特异性。本研究提出了一种先进的基于深度学习的图像翻译框架,能够从H&E染色组织样本生成高保真IHC图像,从而实现经济高效的HER2评估。通过修改金字塔pix2pix的损失函数,我们减轻了模式崩溃这一生成对抗网络(GANs)的基本局限性,并引入了一种基于方差的新型惩罚机制,以在生成的图像中实施结构多样性。我们的模型在翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面表现出色,由于复杂的形态变化,这些图像对于现有方法来说一直具有挑战性。在BCI病理数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的模型在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)和弗雷歇特Inception距离(FID)等方面超过了最先进的方法,特别是在准确翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面。除了医学成像外,我们的模型在一般的图像到图像翻译任务中也表现出卓越的性能,展示了其在多个领域的潜力。这项工作标志着人工智能驱动精准肿瘤学的重大进展,为传统的HER2诊断提供了可靠高效的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文关注人表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)在乳腺癌细胞中的过度表达,这是HER2阳性乳腺癌的关键驱动因素。该研究提出了一种基于深度学习的图像翻译框架,能够从H&E染色组织样本生成高保真IHC图像,实现了成本效益高且可扩展的HER2评估。该研究通过改进金字塔pix2pix的损失函数,缓解了生成对抗网络(GANs)的根本局限性——模式崩溃,并引入了一种新型方差惩罚,以加强生成图像的结构多样性。在BCI病理数据集上的全面评估表明,该研究提出的模型在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)等方面超越了现有最先进的方法,特别是在翻译HER2阳性(IHC 3+)图像方面。此外,该模型在一般图像到图像的翻译任务中也表现出卓越性能,展示了其在多个领域的潜力。这项研究是迈向人工智能驱动的精准肿瘤学的重大一步,为传统的HER2诊断提供了可靠高效的替代方案。
关键见解
- HER2在乳腺癌细胞中的过度表达是HER2阳性乳腺癌的关键驱动因素,需要精确诊断和治疗。
- 免疫组织化学(IHC)是评估HER2的标准技术,但成本高、劳动密集且依赖于抗体选择。
- 常规病理程序H&E染色方法更广泛可用,但缺乏HER2特异性。
- 本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的图像翻译框架,能够从H&E染色生成高保真IHC图像,以实现成本效益高且可扩展的HER2评估。
- 通过改进损失函数和引入方差惩罚,该模型在BCI数据集上超越了现有方法,特别是在翻译HER2阳性图像方面。
- 该模型在一般图像到图像的翻译任务中也表现出卓越性能,具有跨多个领域的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

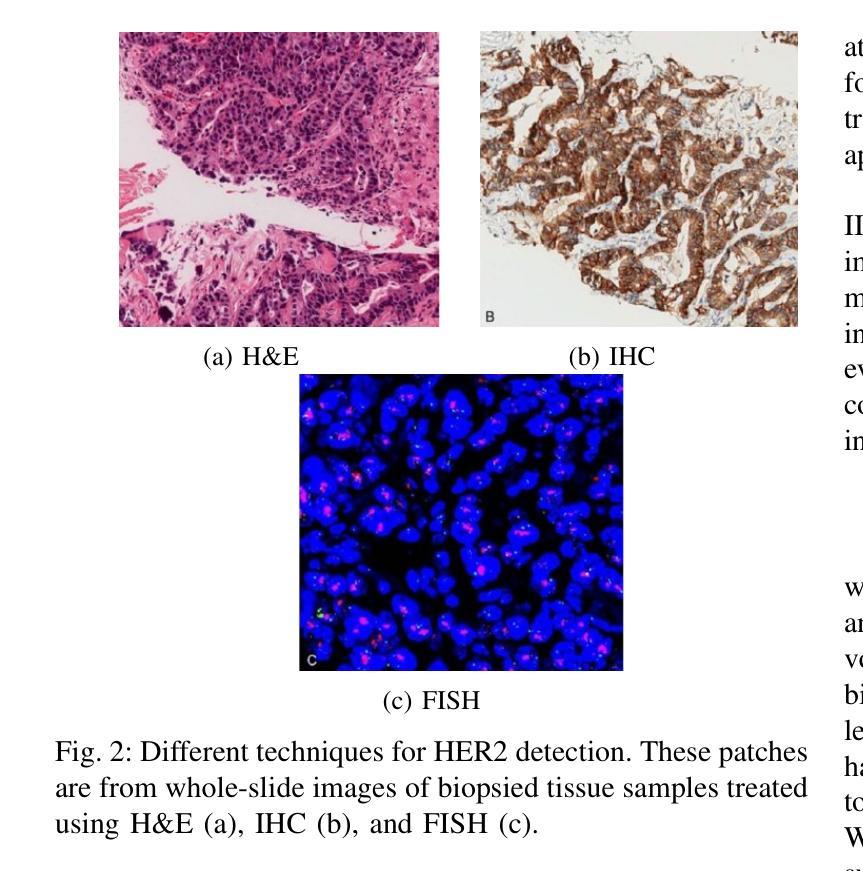
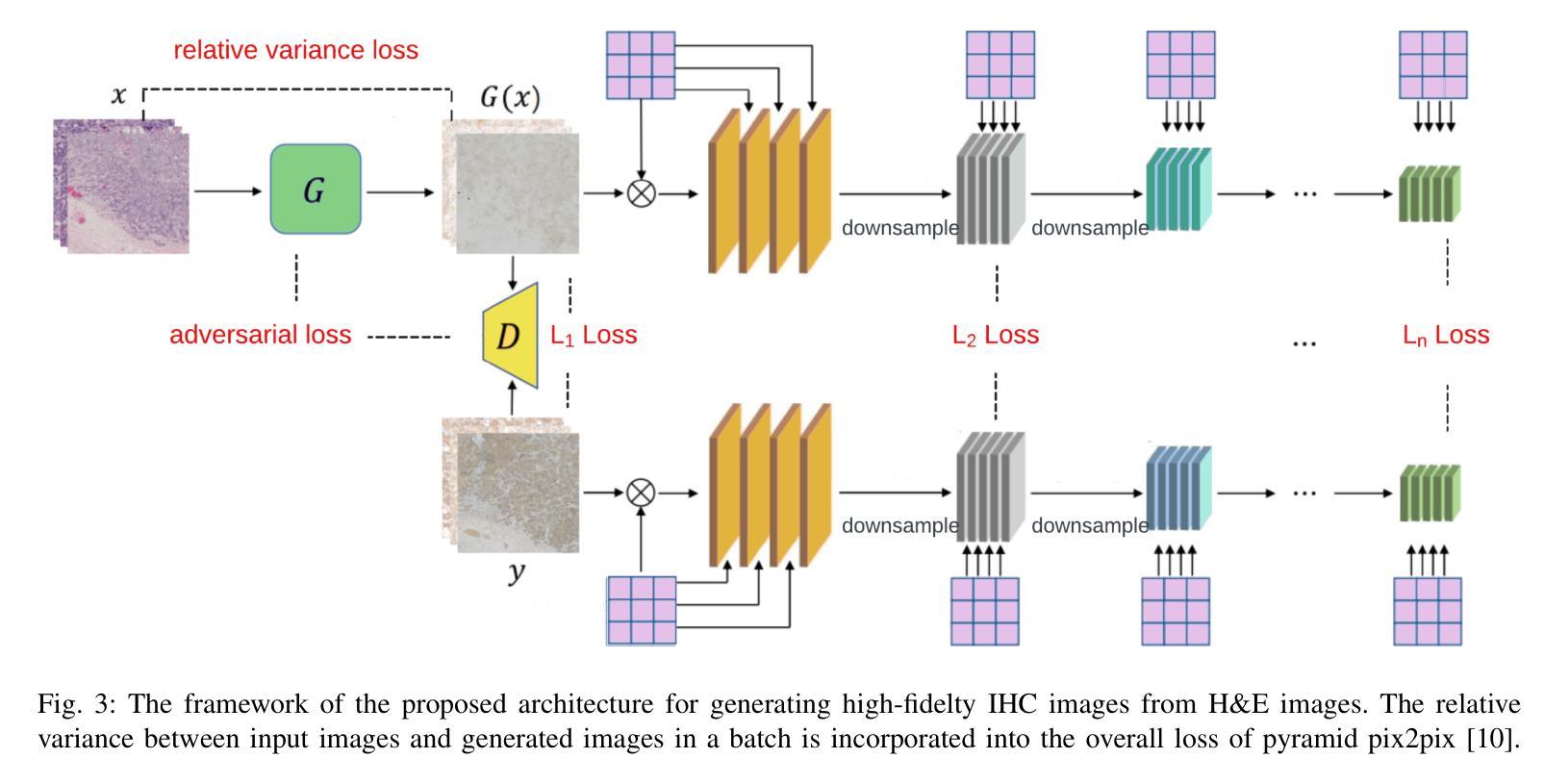
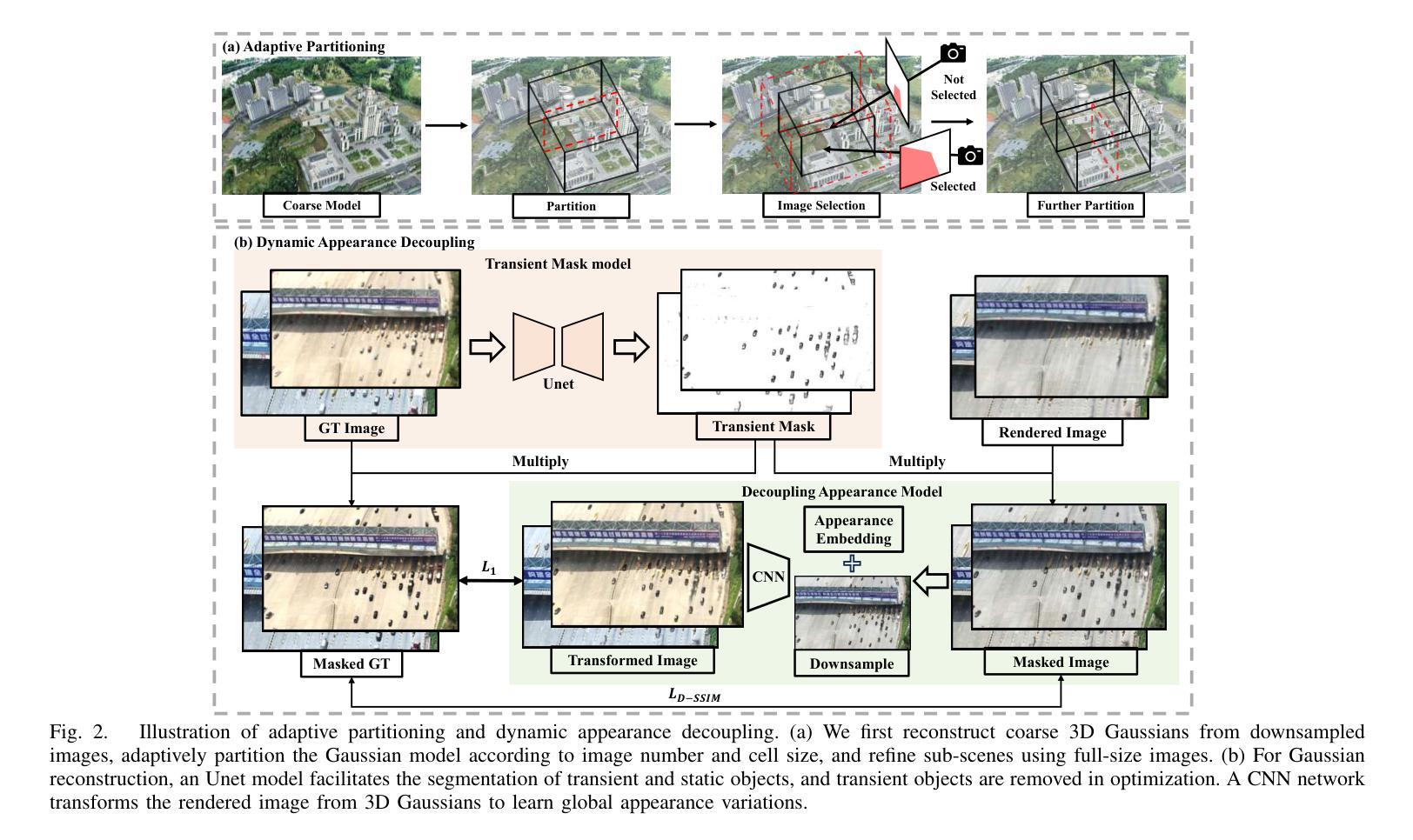
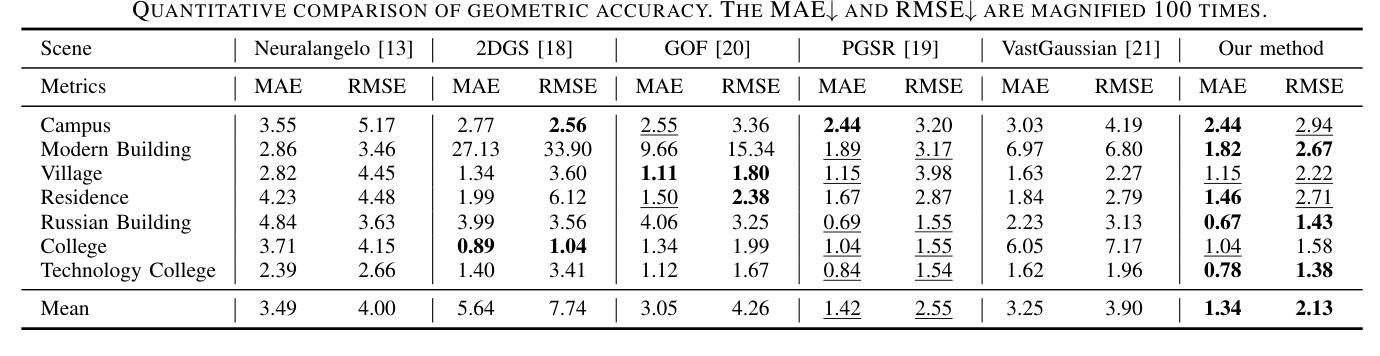
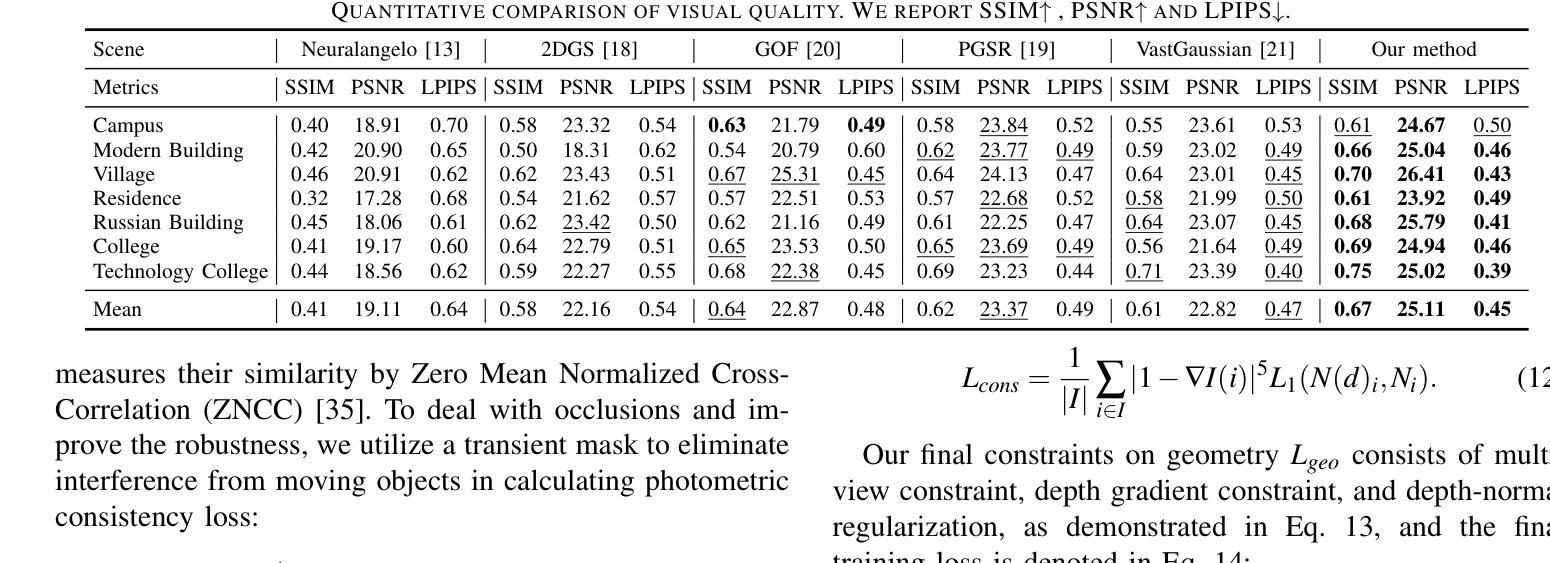
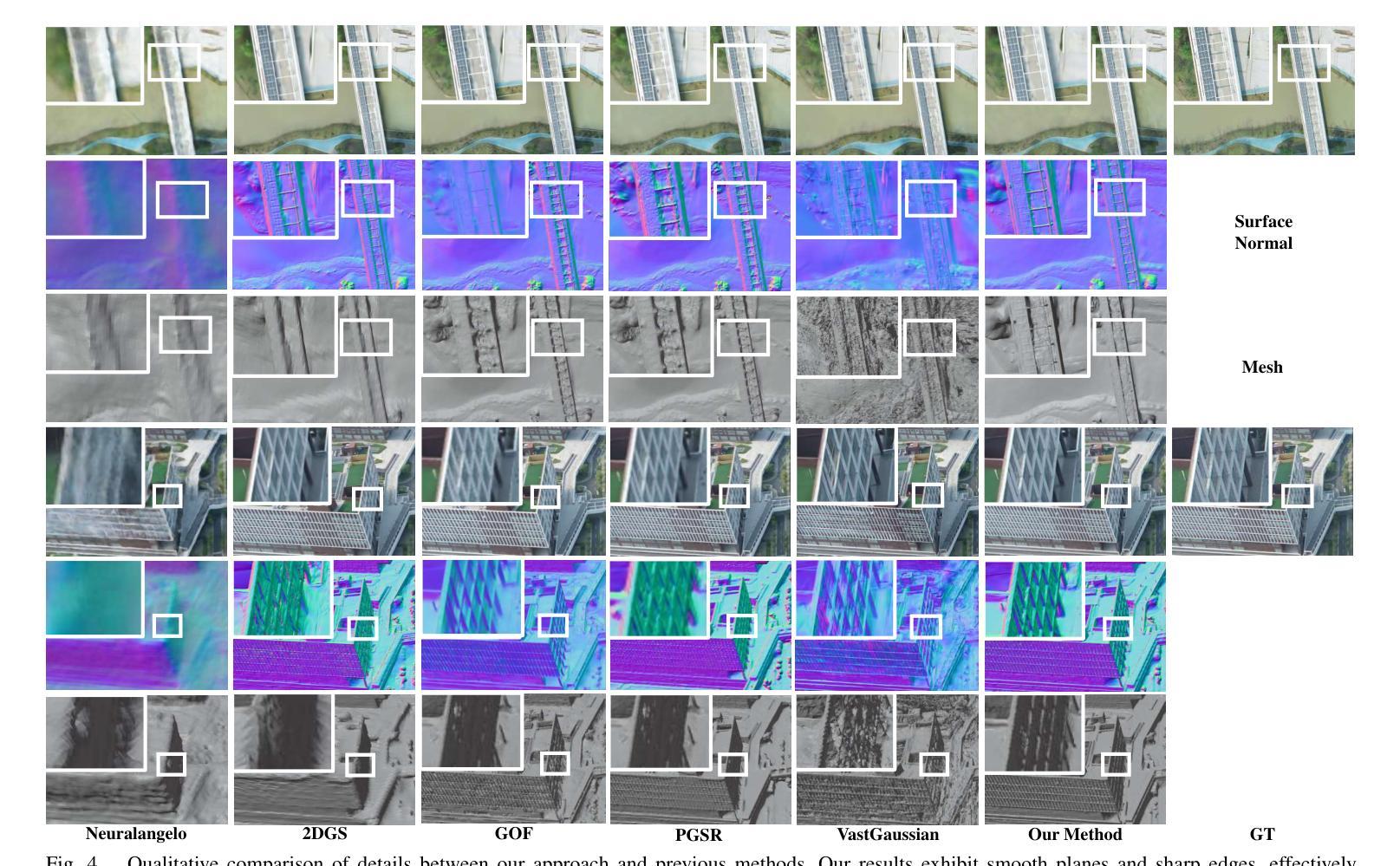
3D Gaussian Splatting for Fine-Detailed Surface Reconstruction in Large-Scale Scene
Authors:Shihan Chen, Zhaojin Li, Zeyu Chen, Qingsong Yan, Gaoyang Shen, Ran Duan
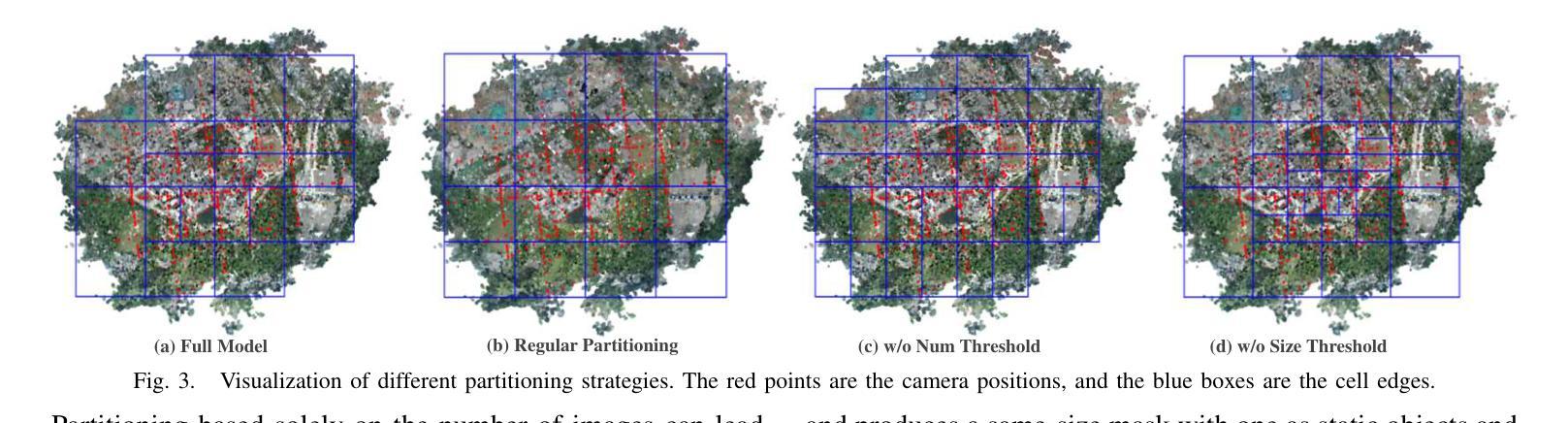
Recent developments in 3D Gaussian Splatting have made significant advances in surface reconstruction. However, scaling these methods to large-scale scenes remains challenging due to high computational demands and the complex dynamic appearances typical of outdoor environments. These challenges hinder the application in aerial surveying and autonomous driving. This paper proposes a novel solution to reconstruct large-scale surfaces with fine details, supervised by full-sized images. Firstly, we introduce a coarse-to-fine strategy to reconstruct a coarse model efficiently, followed by adaptive scene partitioning and sub-scene refining from image segments. Additionally, we integrate a decoupling appearance model to capture global appearance variations and a transient mask model to mitigate interference from moving objects. Finally, we expand the multi-view constraint and introduce a single-view regularization for texture-less areas. Our experiments were conducted on the publicly available dataset GauU-Scene V2, which was captured using unmanned aerial vehicles. To the best of our knowledge, our method outperforms existing NeRF-based and Gaussian-based methods, achieving high-fidelity visual results and accurate surface from full-size image optimization. Open-source code will be available on GitHub.
近期3D高斯贴图技术的进展在表面重建方面取得了重大突破。然而,由于高计算需求和户外环境的复杂动态外观,将这些方法扩展到大规模场景仍然具有挑战性。这些挑战阻碍了其在航空测量和自动驾驶中的应用。本文提出了一种由全尺寸图像监督的,带有精细细节的大规模表面重建的新解决方案。首先,我们采用从粗到细的策略高效重建粗模型,随后进行自适应场景分割和来自图像段的子场景细化。此外,我们集成了一个分离的外观模型来捕捉全局外观变化,并引入了一个瞬态掩膜模型来减轻移动物体的干扰。最后,我们扩展了多视角约束,并为无纹理区域引入了单视角正则化。我们的实验是在公开可用的GauU-Scene V2数据集上进行的,该数据集是使用无人机捕获的。据我们所知,我们的方法在NeRF基和基于高斯的方法中表现最佳,通过全尺寸图像优化实现了高保真视觉结果和精确的表面重建。开源代码将在GitHub上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IROS 2025
Summary
大规模场景的三维高斯融合技术虽然取得了进展,但其在复杂动态室外环境中的应用仍存在计算量大和细节缺失的挑战。本文提出一种新型方法,利用全尺寸图像监督重建具有精细细节的大规模场景表面。通过由粗到细的重建策略,结合自适应场景分割和子场景细化,以及解耦外观模型和瞬态掩模模型,该方法实现了高效准确的重建。在公开数据集GauU-Scene V2上的实验表明,该方法优于现有的NeRF和高斯方法,实现了高保真视觉结果和从全尺寸图像优化的准确表面重建。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模场景的三维重建在复杂动态室外环境中存在计算量大和细节缺失的挑战。
- 提出了一种新的重建方法,通过全尺寸图像监督实现大规模场景的精细细节重建。
- 采用由粗到细的重建策略,首先构建粗略模型,再进行细化。
- 利用自适应场景分割和子场景细化技术,提高重建效率。
- 引入解耦外观模型和瞬态掩模模型,以捕捉全局外观变化和减轻移动物体的干扰。
- 扩展了多视角约束,并为无纹理区域引入了单视角正则化。
点此查看论文截图


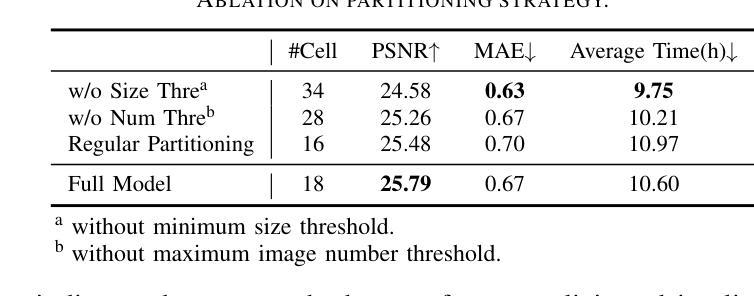
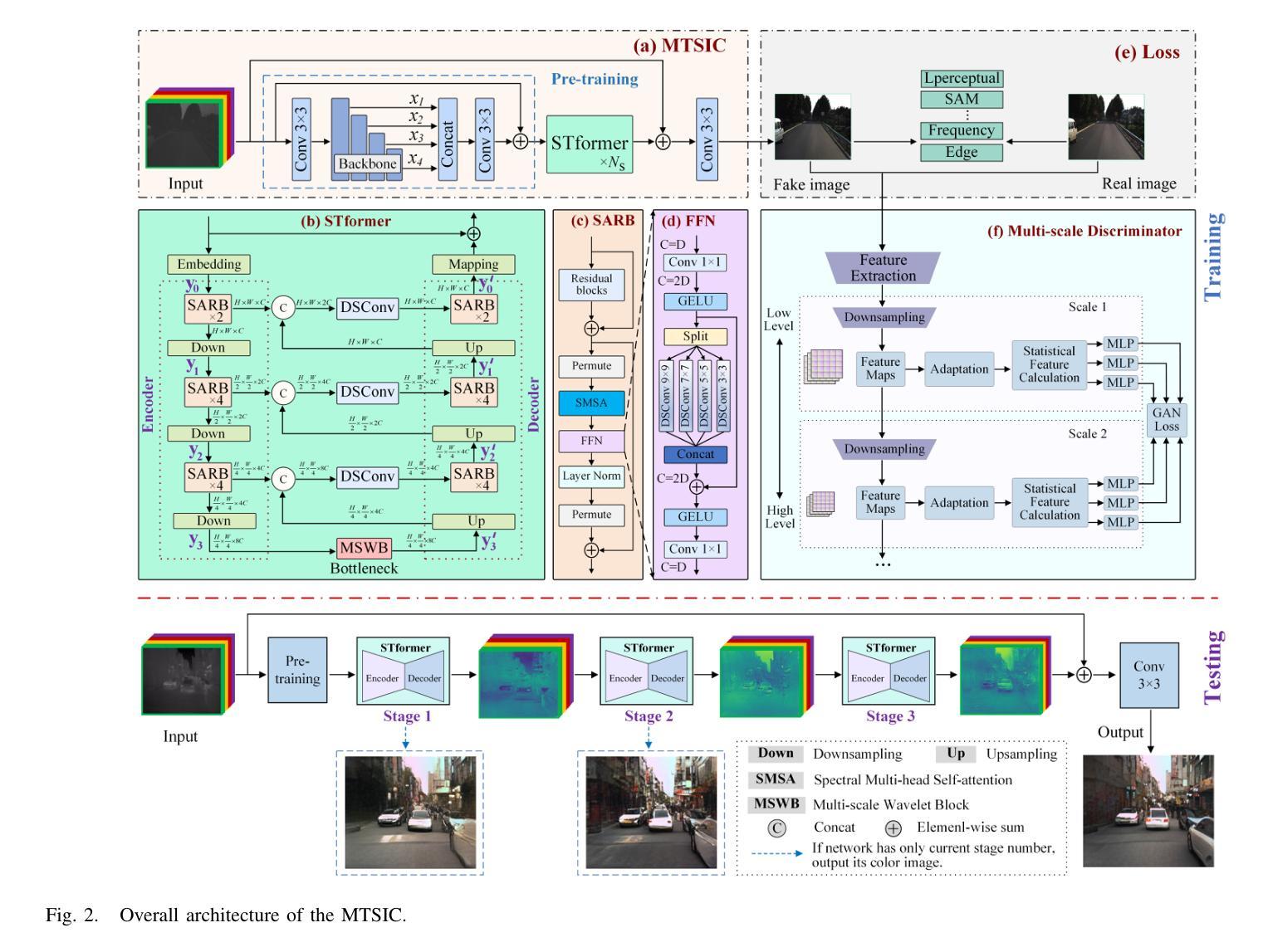
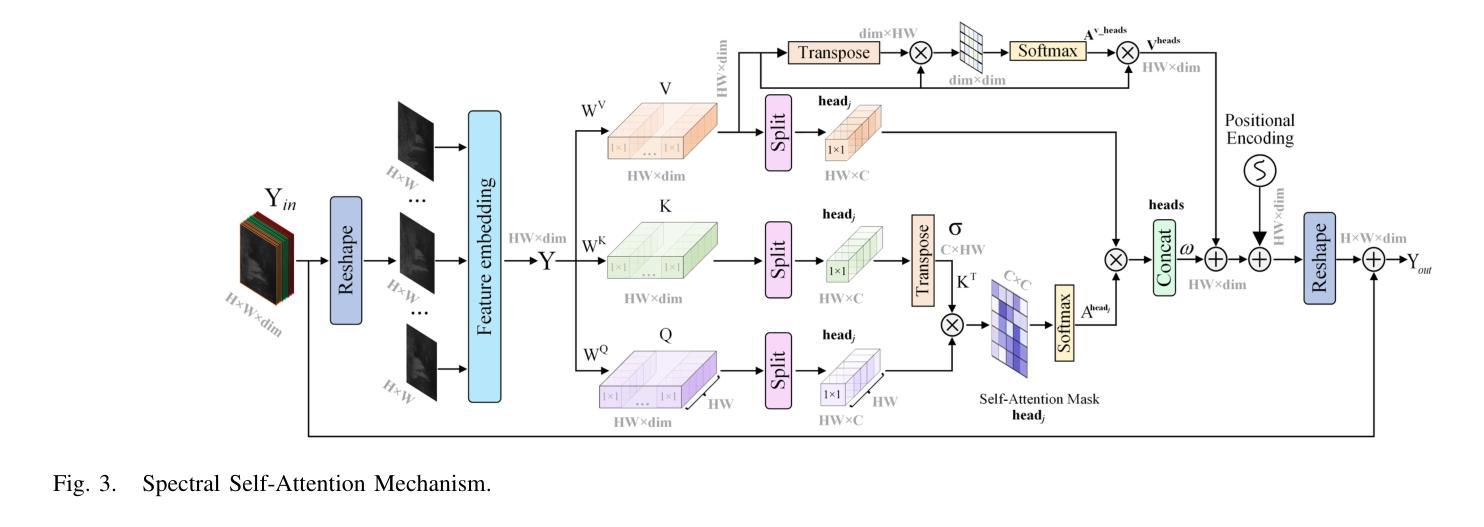
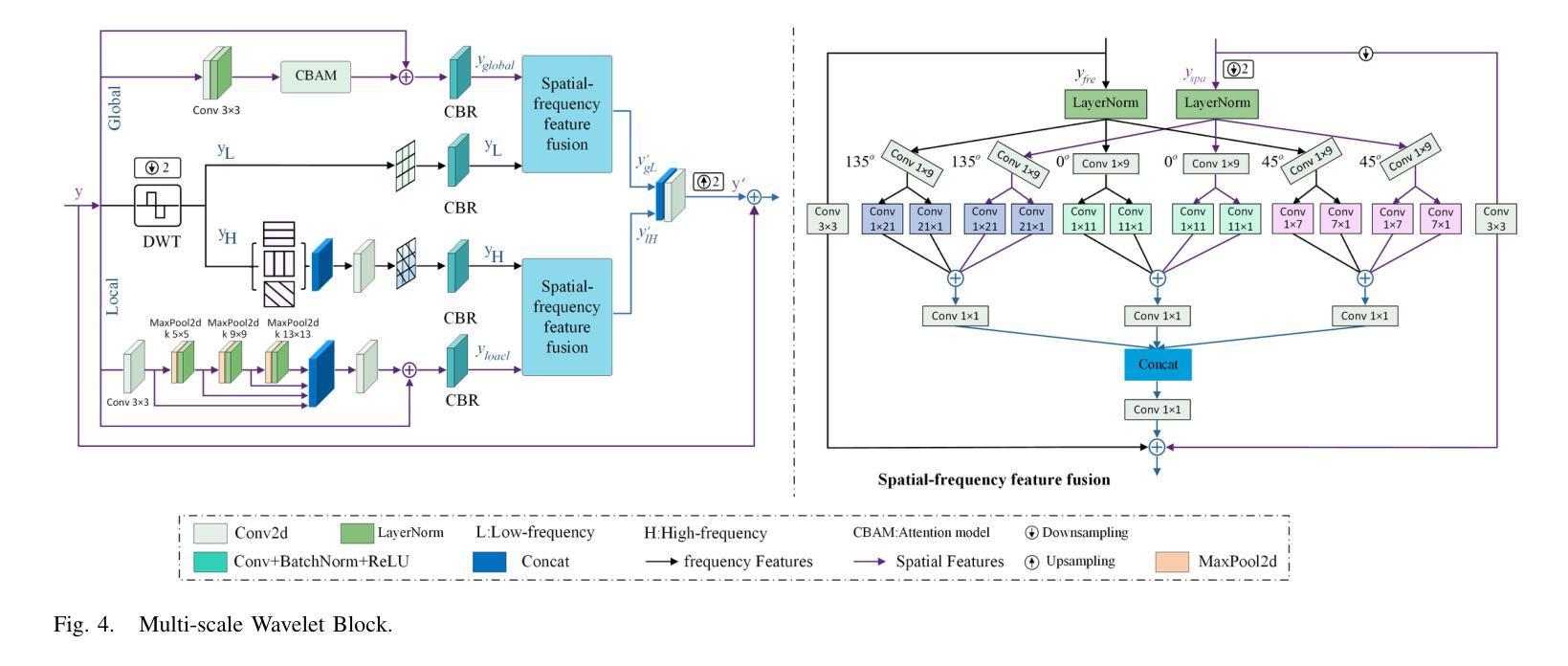
MTSIC: Multi-stage Transformer-based GAN for Spectral Infrared Image Colorization
Authors:Tingting Liu, Yuan Liu, Jinhui Tang, Liyin Yuan, Chengyu Liu, Chunlai Li, Xiubao Sui, Qian Chen
Thermal infrared (TIR) images, acquired through thermal radiation imaging, are unaffected by variations in lighting conditions and atmospheric haze. However, TIR images inherently lack color and texture information, limiting downstream tasks and potentially causing visual fatigue. Existing colorization methods primarily rely on single-band images with limited spectral information and insufficient feature extraction capabilities, which often result in image distortion and semantic ambiguity. In contrast, multiband infrared imagery provides richer spectral data, facilitating the preservation of finer details and enhancing semantic accuracy. In this paper, we propose a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based framework designed to integrate spectral information to enhance the colorization of infrared images. The framework employs a multi-stage spectral self-attention Transformer network (MTSIC) as the generator. Each spectral feature is treated as a token for self-attention computation, and a multi-head self-attention mechanism forms a spatial-spectral attention residual block (SARB), achieving multi-band feature mapping and reducing semantic confusion. Multiple SARB units are integrated into a Transformer-based single-stage network (STformer), which uses a U-shaped architecture to extract contextual information, combined with multi-scale wavelet blocks (MSWB) to align semantic information in the spatial-frequency dual domain. Multiple STformer modules are cascaded to form MTSIC, progressively optimizing the reconstruction quality. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms traditional techniques and effectively enhances the visual quality of infrared images.
热红外(TIR)图像是通过热辐射成像获得的,不受光照条件和大气雾影响。然而,由于本身缺乏色彩和纹理信息,这些图像会给后续任务带来潜在问题,并且可能会导致视觉疲劳。现有的彩色化方法主要依赖于具有有限光谱信息的单波段图像,并且特征提取能力不足以满足需求,这往往会导致图像失真和语义模糊。相比之下,多波段红外图像提供了更丰富光谱数据,有助于保留更精细的细节并提高语义准确性。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的框架,旨在融合光谱信息来提高红外图像的彩色化效果。该框架采用多阶段光谱自注意力Transformer网络(MTSIC)作为生成器。将每个光谱特征视为自注意力计算的标记,利用多头自注意力机制构建空间光谱注意力残差块(SARB),实现多波段特征映射并减少语义混淆。多个SARB单元被集成到基于Transformer的单阶段网络(STformer)中,该网络采用U型结构来提取上下文信息,并结合多尺度小波块(MSWB)在空间频率双域中对齐语义信息。多个STformer模块级联形成MTSIC,逐步优化重建质量。实验结果表明,所提出的方法在性能上大大优于传统技术,有效地提高了红外图像的可视质量。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的框架,旨在整合光谱信息提升红外图像的彩色化。采用多阶段光谱自注意力Transformer网络(MTSIC)作为生成器,将每个光谱特征视为自注意力的标记,并通过多头自注意力机制形成空间光谱注意力残差块(SARB),实现多频段特征映射,减少语义混淆。实验结果表明,该方法显著优于传统技术,有效提高红外图像视觉质量。
关键见解
- 红外图像在多种光照和大气条件下表现稳定,但其本身缺乏颜色和纹理信息,限制后续任务和视觉感受。
- 传统颜色化方法依赖单一频带图像,存在信息提取能力不足的问题,可能导致图像失真和语义模糊。
- 多频带红外成像提供丰富的光谱数据,有助于保留更精细的细节并增强语义准确性。
- 本文提出一种基于GAN的框架,整合光谱信息以提升红外图像的颜色化质量。
- 采用多头自注意力机制形成SARB,实现多频段特征映射,减少语义混淆。
- 通过结合多个STformer模块形成MTSIC,逐步优化重建质量。
点此查看论文截图


R3eVision: A Survey on Robust Rendering, Restoration, and Enhancement for 3D Low-Level Vision
Authors:Weeyoung Kwon, Jeahun Sung, Minkyu Jeon, Chanho Eom, Jihyong Oh
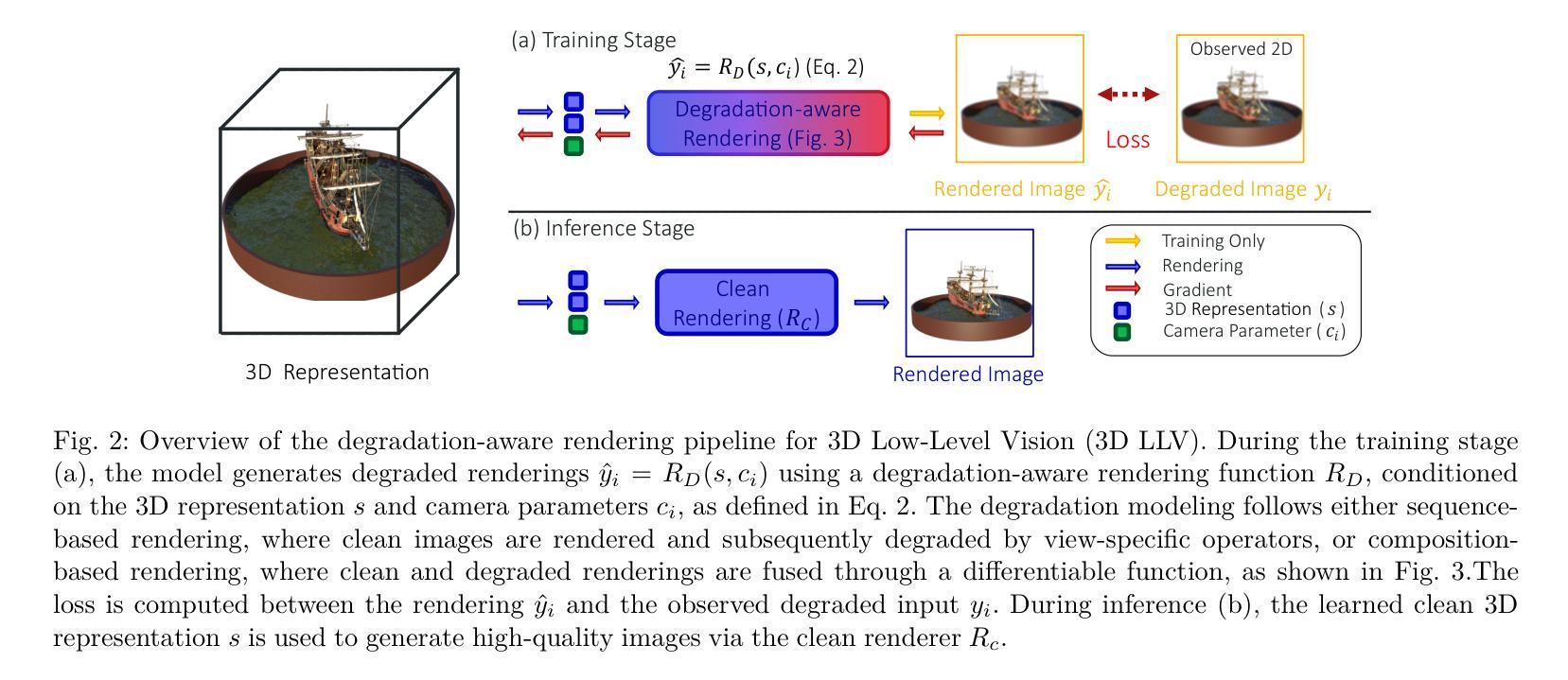
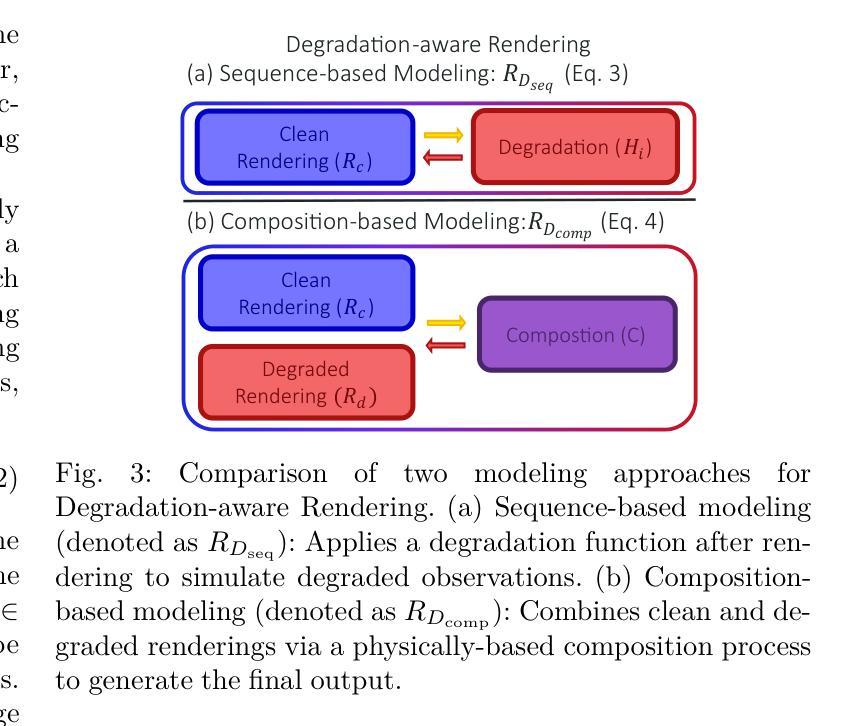
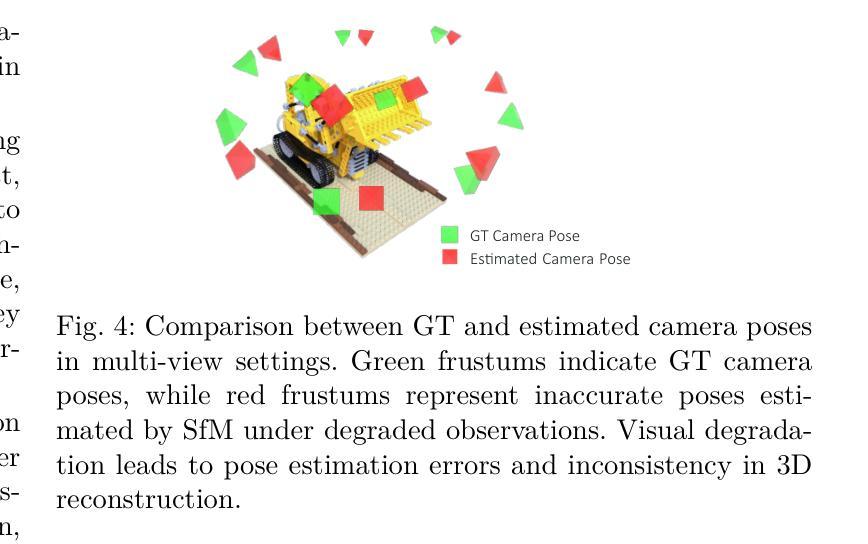
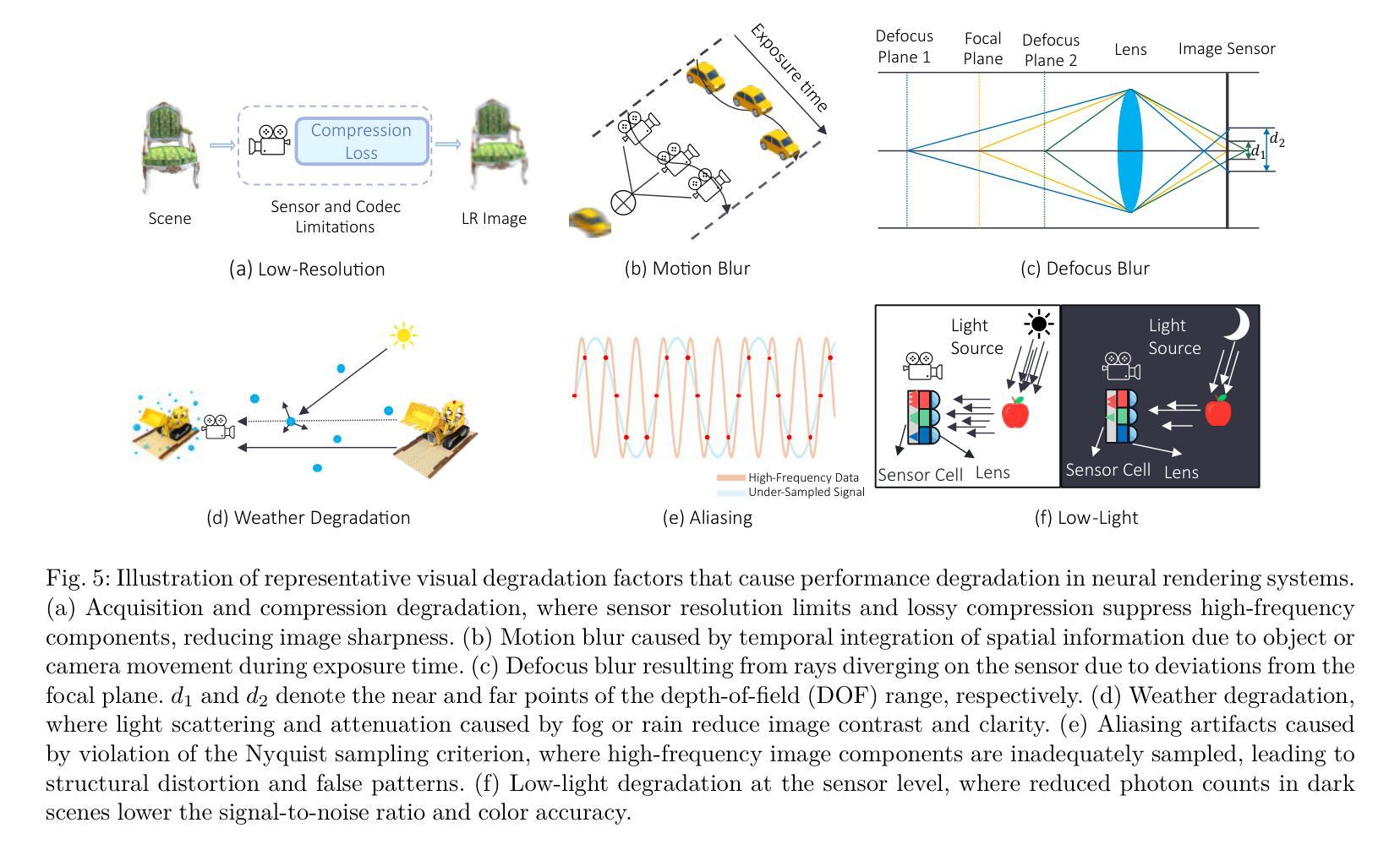
Neural rendering methods such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have achieved significant progress in photorealistic 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, most existing models assume clean and high-resolution (HR) multi-view inputs, which limits their robustness under real-world degradations such as noise, blur, low-resolution (LR), and weather-induced artifacts. To address these limitations, the emerging field of 3D Low-Level Vision (3D LLV) extends classical 2D Low-Level Vision tasks including super-resolution (SR), deblurring, weather degradation removal, restoration, and enhancement into the 3D spatial domain. This survey, referred to as R\textsuperscript{3}eVision, provides a comprehensive overview of robust rendering, restoration, and enhancement for 3D LLV by formalizing the degradation-aware rendering problem and identifying key challenges related to spatio-temporal consistency and ill-posed optimization. Recent methods that integrate LLV into neural rendering frameworks are categorized to illustrate how they enable high-fidelity 3D reconstruction under adverse conditions. Application domains such as autonomous driving, AR/VR, and robotics are also discussed, where reliable 3D perception from degraded inputs is critical. By reviewing representative methods, datasets, and evaluation protocols, this work positions 3D LLV as a fundamental direction for robust 3D content generation and scene-level reconstruction in real-world environments.
神经渲染方法,例如神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯喷绘(3DGS),在真实感3D场景重建和新型视图合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,大多数现有模型假设清晰且高分辨率(HR)的多视角输入,这限制了它们在现实世界退化(例如噪声、模糊、低分辨率(LR)和天气引起的伪影)影响下的稳健性。为了解决这些局限性,新兴的3D低级视觉(3D LLV)领域将传统的2D低级视觉任务(包括超分辨率(SR)、去模糊、去除天气退化、恢复和增强)扩展到3D空间域。这篇综述被称为R\textsuperscript{3}eVision,通过对退化感知渲染问题进行形式化并确定与时空一致性和不适定优化相关的关键挑战,全面概述了3D LLV的稳健渲染、恢复和增强。将LLV集成到神经渲染框架中的最近方法被分类,以说明它们在不利条件下实现高保真3D重建的能力。还讨论了自动驾驶、AR/VR和机器人等领域,在这些领域中,从退化输入中可靠地获取3D感知至关重要。通过回顾代表性方法、数据集和评估协议,这项工作将3D LLV定位为在真实世界环境中进行稳健的3D内容生成和场景级重建的基本方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Please visit our project page at https://github.com/CMLab-Korea/Awesome-3D-Low-Level-Vision
摘要
NeRF与相关技术如3DGS在三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了显著进展,但现有模型大多依赖干净、高清的多视角输入,这在现实世界中容易受到噪声、模糊、低分辨率和天气影响。为解决这些问题,3D低层次视觉(LLV)领域将超分辨率、去模糊等任务扩展到三维空间域。这篇综述介绍了面向恶劣环境的稳健渲染、恢复和增强技术,强调对感知退化感知的渲染问题的重视并总结了相关的挑战。集成LLV到神经渲染框架的方法也被分类讨论,展示了它们在恶劣条件下实现高质量三维重建的能力。应用领域如自动驾驶、AR/VR和机器人技术也受到了关注,其中从退化输入中进行可靠的3D感知至关重要。本文总结了代表性方法、数据集和评估协议,将3D LLV定位为现实环境中鲁棒三维内容生成和场景级重建的基本方向。
关键见解
- NeRF等神经渲染技术在三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得显著进展,但对输入数据的质量和数量有较高要求。
- 现有模型在面临现实世界中的噪声、模糊、低分辨率和天气影响时表现受限。
- 3D低层次视觉(LLV)领域扩展了传统的二维低层次视觉任务到三维空间域,以解决上述问题。
- R\textsuperscript{3}eVision综述介绍了面向恶劣环境的稳健渲染、恢复和增强技术,并强调了感知退化感知的渲染问题的严重性。
- 此领域面临的关键挑战包括时空一致性和病态优化问题。
- 集成LLV到神经渲染框架的方法能够在恶劣条件下实现高质量的三维重建。
点此查看论文截图

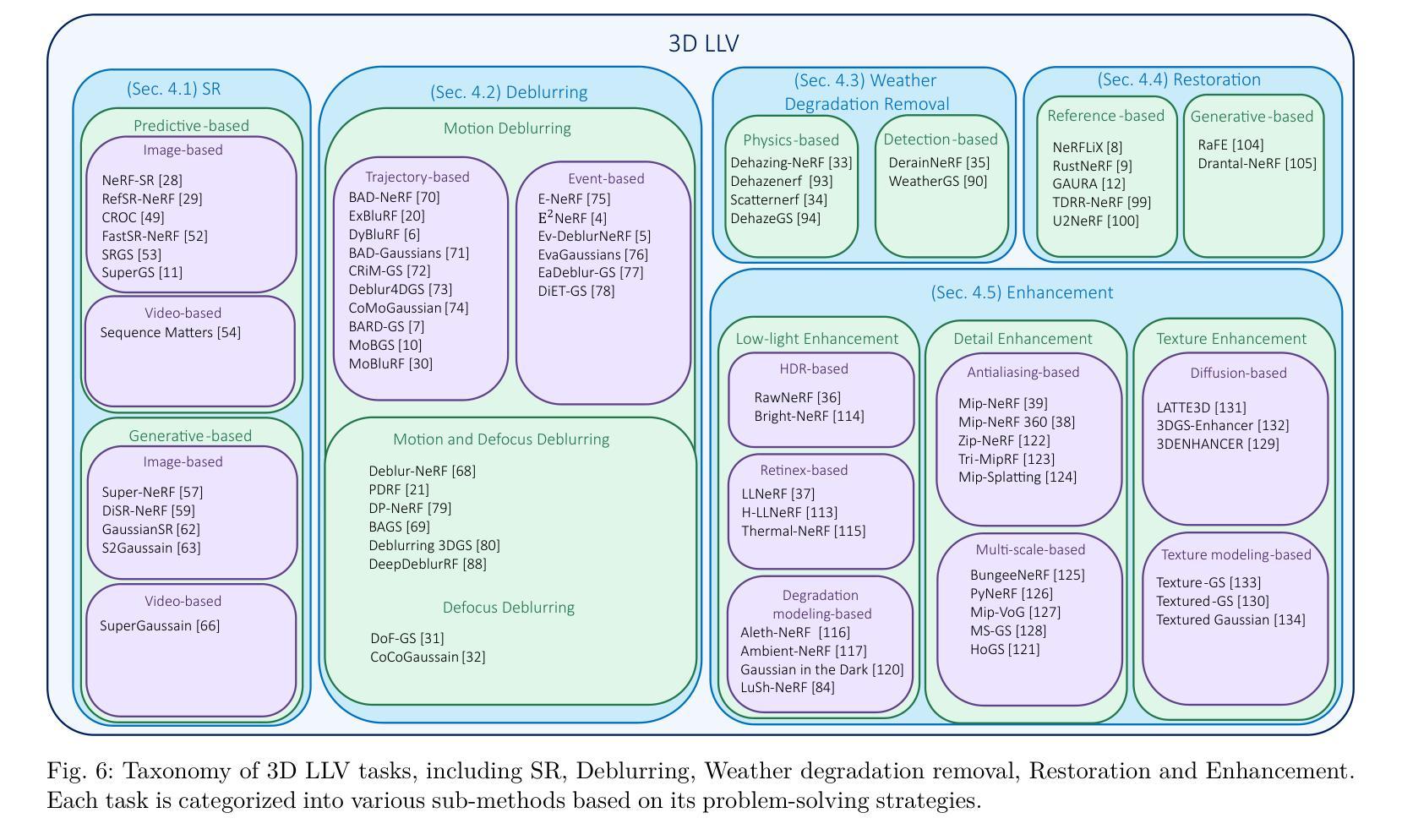
Layered Motion Fusion: Lifting Motion Segmentation to 3D in Egocentric Videos
Authors:Vadim Tschernezki, Diane Larlus, Iro Laina, Andrea Vedaldi
Computer vision is largely based on 2D techniques, with 3D vision still relegated to a relatively narrow subset of applications. However, by building on recent advances in 3D models such as neural radiance fields, some authors have shown that 3D techniques can at last improve outputs extracted from independent 2D views, by fusing them into 3D and denoising them. This is particularly helpful in egocentric videos, where the camera motion is significant, but only under the assumption that the scene itself is static. In fact, as shown in the recent analysis conducted by EPIC Fields, 3D techniques are ineffective when it comes to studying dynamic phenomena, and, in particular, when segmenting moving objects. In this paper, we look into this issue in more detail. First, we propose to improve dynamic segmentation in 3D by fusing motion segmentation predictions from a 2D-based model into layered radiance fields (Layered Motion Fusion). However, the high complexity of long, dynamic videos makes it challenging to capture the underlying geometric structure, and, as a result, hinders the fusion of motion cues into the (incomplete) scene geometry. We address this issue through test-time refinement, which helps the model to focus on specific frames, thereby reducing the data complexity. This results in a synergy between motion fusion and the refinement, and in turn leads to segmentation predictions of the 3D model that surpass the 2D baseline by a large margin. This demonstrates that 3D techniques can enhance 2D analysis even for dynamic phenomena in a challenging and realistic setting.
计算机视觉在很大程度上基于二维技术,而三维视觉仍然局限于相对较少的应用领域。然而,一些作者通过建立基于神经网络辐射场等三维模型的最新进展,展示了三维技术最终可以通过融合独立二维视图并对其进行去噪,来改善提取的输出。这在以自我为中心的视频中特别有帮助,其中相机运动显著,但假设场景本身是静态的。事实上,正如EPIC Fields的最新分析所示,当涉及到动态现象,特别是分割移动物体时,三维技术并不有效。在本文中,我们将更详细地探讨这个问题。首先,我们提出通过融合基于二维模型的动态分割预测结果到分层辐射场(Layered Motion Fusion)来改善三维中的动态分割。然而,长动态视频的复杂性使得捕捉其底层几何结构具有挑战性,并因此阻碍了将运动线索融合到(不完整)场景几何中。我们通过测试时改进来解决这个问题,这有助于模型专注于特定帧,从而降低数据复杂性。这导致了运动融合和细化之间的协同作用,并进而实现了对三维模型的分割预测,大幅超越了二维基准测试。这表明,即使在具有挑战性和现实性的设置中,三维技术也可以增强二维分析,甚至用于动态现象。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready for CVPR25
摘要
本文探讨了计算机视觉领域中3D技术与动态现象分析的问题。虽然计算机视觉主要基于2D技术,但近年来在3D模型上的进展表明,将独立2D视角融合到3D并进行去噪可以提高输出质量。特别是在以自我为中心的视频中,当场景本身静态时,这种技术尤其有用。然而,EPIC Fields的近期分析显示,对于动态现象的研究,尤其是分割移动物体时,3D技术并不有效。本文旨在解决这一问题,通过提出将基于二维模型的动态分割预测融合到分层辐射场(Layered Motion Fusion)中改进动态场景的分割问题。然而,处理长动态视频的高复杂性使其难以捕捉底层几何结构,阻碍了运动线索融入(不完整)场景几何的融合。本文通过测试时修正解决了这一问题,帮助模型专注于特定帧,降低数据复杂性,实现运动融合与修正之间的协同作用,进而提高三维模型的分割预测结果,大幅超越二维基线,证明了三维技术即使在挑战性和现实场景中也能提高二维分析对动态现象的分析效果。
关键见解
- 计算机视觉主要依赖2D技术,但3D技术在特定领域如视频处理中展现出优势。
- 融合独立2D视角到3D并去噪可以提高输出质量,尤其在场景静态时效果显著。
- 对于动态现象和移动物体分割,尤其是长视频,传统的3D技术存在局限性。
- 本研究旨在通过Layered Motion Fusion方法改进动态场景的分割问题。
- 处理复杂动态视频时面临底层几何结构捕捉的挑战。
- 测试时修正方法帮助模型专注于特定帧,提高运动融合与修正之间的协同作用。
点此查看论文截图

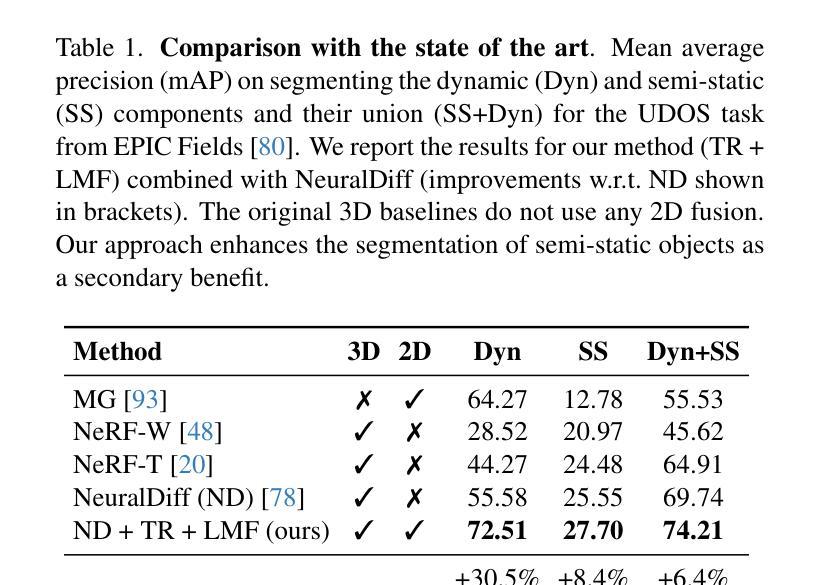
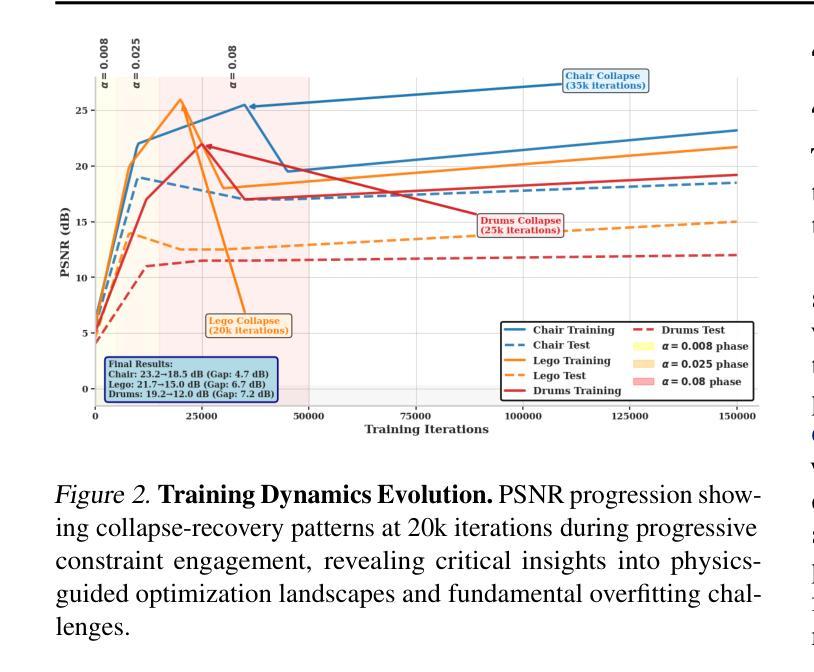
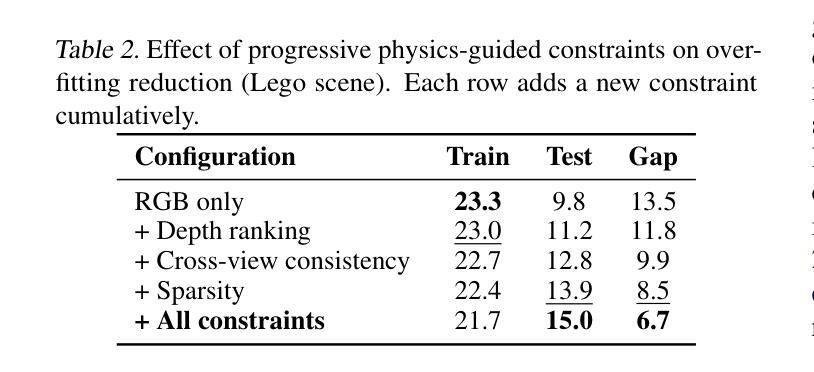
PhysicsNeRF: Physics-Guided 3D Reconstruction from Sparse Views
Authors:Mohamed Rayan Barhdadi, Hasan Kurban, Hussein Alnuweiri
PhysicsNeRF is a physically grounded framework for 3D reconstruction from sparse views, extending Neural Radiance Fields with four complementary constraints: depth ranking, RegNeRF-style consistency, sparsity priors, and cross-view alignment. While standard NeRFs fail under sparse supervision, PhysicsNeRF employs a compact 0.67M-parameter architecture and achieves 21.4 dB average PSNR using only 8 views, outperforming prior methods. A generalization gap of 5.7-6.2 dB is consistently observed and analyzed, revealing fundamental limitations of sparse-view reconstruction. PhysicsNeRF enables physically consistent, generalizable 3D representations for agent interaction and simulation, and clarifies the expressiveness-generalization trade-off in constrained NeRF models.
PhysicsNeRF是一个基于物理的框架,用于从稀疏视角进行3D重建,它扩展了Neural Radiance Fields,包含四种互补约束:深度排序、RegNeRF风格的一致性、稀疏先验和跨视图对齐。虽然标准NeRF在稀疏监督下会失效,但PhysicsNeRF采用紧凑的0.67M参数架构,仅使用8个视角就实现了21.4 dB的平均PSNR,优于先前的方法。观察到并分析了5.7-6.2 dB的泛化差距,揭示了稀疏视图重建的根本局限性。PhysicsNeRF能够实现物理上一致的、可泛化的3D表示,用于代理交互和模拟,并明确了受限NeRF模型的表达力-泛化能力之间的权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables. Appearing in Building Physically Plausible World Models at the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025), Vancouver, Canada
Summary
PhysicsNeRF是一种基于物理的三维重建框架,它通过四个互补约束扩展了神经辐射场,包括深度排序、RegNeRF风格的一致性、稀疏先验和跨视图对齐。在稀疏监督下,标准NeRF表现不佳,而PhysicsNeRF采用紧凑的0.67M参数架构,仅使用8个视图就实现了平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)为21.4 dB的高性能表现,优于现有方法。此外,研究团队发现了一致的泛化差距为5.7~6.2 dB,揭示了稀疏视图重建的根本局限性。PhysicsNeRF可实现物理一致性强的通用三维表示,适用于代理交互和模拟,并明确了约束NeRF模型的表达性与泛化之间的权衡。
Key Takeaways
- PhysicsNeRF是一种基于物理的三维重建框架,用于解决稀疏视图下的重建问题。
- 它通过四个互补约束扩展了神经辐射场:深度排序、RegNeRF风格的一致性、稀疏先验和跨视图对齐。
- 与标准NeRF相比,PhysicsNeRF在稀疏监督下表现更优秀,使用紧凑的架构实现了高PSNR值。
- 研究团队发现PhysicsNeRF相较于其他方法的平均泛化差距为5~6dB。
- PhysicsNeRF可实现物理一致性强的通用三维表示,适用于多种应用场景如代理交互和模拟。
- PhysicsNeRF强调了约束NeRF模型的表达性与泛化之间的权衡。
点此查看论文截图

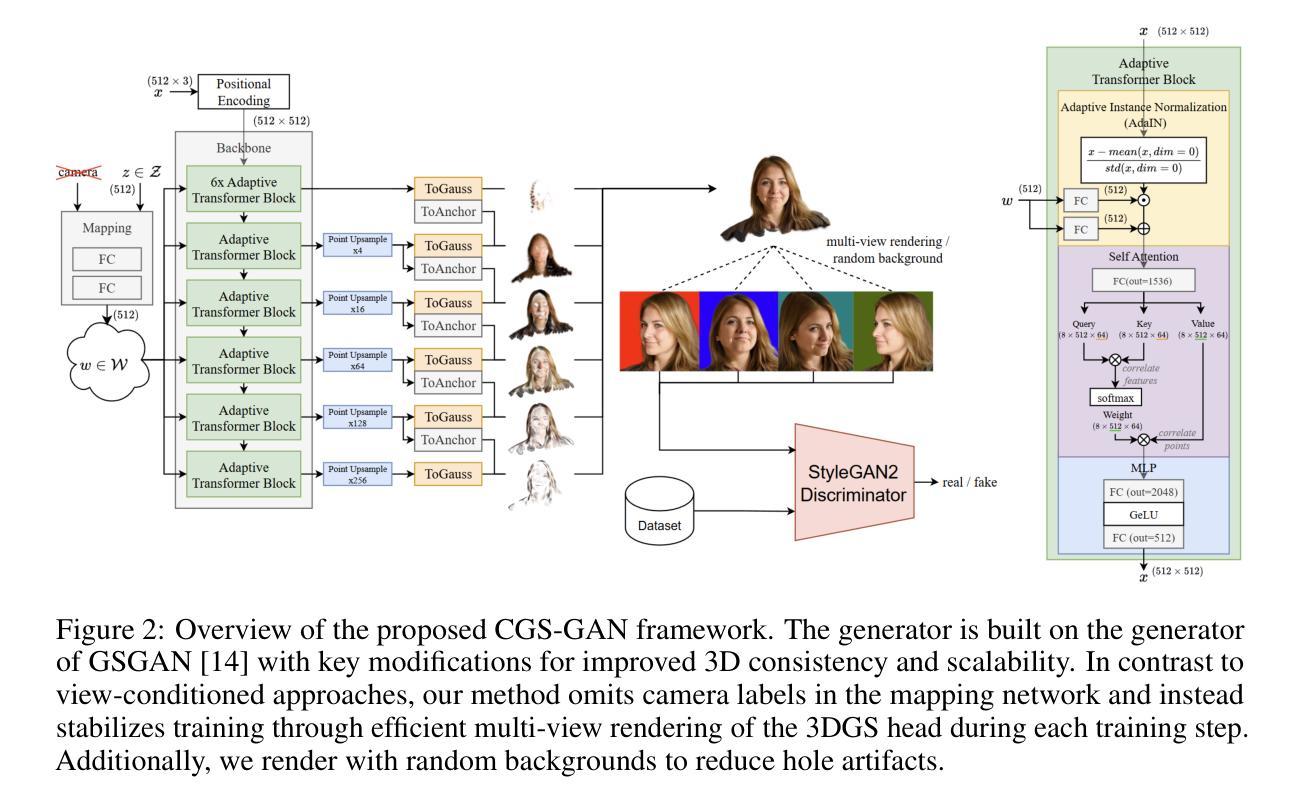
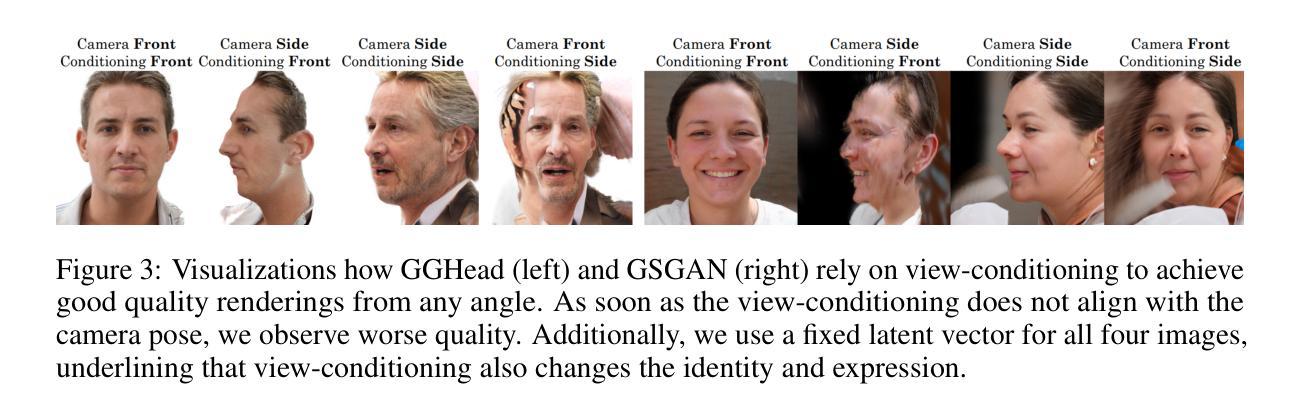
CGS-GAN: 3D Consistent Gaussian Splatting GANs for High Resolution Human Head Synthesis
Authors:Florian Barthel, Wieland Morgenstern, Paul Hinzer, Anna Hilsmann, Peter Eisert
Recently, 3D GANs based on 3D Gaussian splatting have been proposed for high quality synthesis of human heads. However, existing methods stabilize training and enhance rendering quality from steep viewpoints by conditioning the random latent vector on the current camera position. This compromises 3D consistency, as we observe significant identity changes when re-synthesizing the 3D head with each camera shift. Conversely, fixing the camera to a single viewpoint yields high-quality renderings for that perspective but results in poor performance for novel views. Removing view-conditioning typically destabilizes GAN training, often causing the training to collapse. In response to these challenges, we introduce CGS-GAN, a novel 3D Gaussian Splatting GAN framework that enables stable training and high-quality 3D-consistent synthesis of human heads without relying on view-conditioning. To ensure training stability, we introduce a multi-view regularization technique that enhances generator convergence with minimal computational overhead. Additionally, we adapt the conditional loss used in existing 3D Gaussian splatting GANs and propose a generator architecture designed to not only stabilize training but also facilitate efficient rendering and straightforward scaling, enabling output resolutions up to $2048^2$. To evaluate the capabilities of CGS-GAN, we curate a new dataset derived from FFHQ. This dataset enables very high resolutions, focuses on larger portions of the human head, reduces view-dependent artifacts for improved 3D consistency, and excludes images where subjects are obscured by hands or other objects. As a result, our approach achieves very high rendering quality, supported by competitive FID scores, while ensuring consistent 3D scene generation. Check our our project page here: https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/
最近,基于三维高斯拼贴技术的三维GAN已被提出用于高质量的人头合成。然而,现有方法通过根据当前相机位置对随机潜在向量进行条件处理,从而稳定训练并从陡峭视角增强渲染质量。这会影响三维一致性,因为我们在重新合成三维头部时观察到身份的重大变化会随着每次相机移动而改变。相反,将相机固定在单一视角会产生高质量的该视角的渲染效果,但对于新颖视角的效果不佳。移除视角条件通常会破坏GAN的训练稳定性,经常导致训练崩溃。针对这些挑战,我们引入了CGS-GAN,这是一种新型的三维高斯拼贴GAN框架,可在不依赖视角条件的情况下实现稳定训练和高质量的三维一致人头合成。为确保训练稳定性,我们引入了一种多视角正则化技术,该技术可在最小计算开销的情况下增强生成器的收敛性。此外,我们适应了现有三维高斯拼贴GAN中的条件损失,并设计了一种旨在稳定训练并促进高效渲染和简便扩展的生成器架构,可实现高达$ 2048^2 $的输出分辨率。为了评估CGS-GAN的能力,我们从FFHQ中筛选出了一个新的数据集。该数据集可实现极高分辨率,侧重于人类头部的大部分区域,减少了视角相关的伪影以改善三维一致性,并排除了主体被手或其他物体遮挡的图像。因此,我们的方法在保证三维场景一致性生成的同时,实现了非常高的渲染质量并得到有竞争力的FID分数。请访问我们的项目页面了解更多信息:https://fraunhoferhhi.github.io/cgs-gan/ 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main paper 12 pages, supplementary materials 8 pages
Summary
近日,提出了基于3D高斯贴图的3D GANs用于高质量的人头合成。现有方法通过当前相机位置对随机潜在向量进行条件化,以实现训练稳定性和从陡峭视角提高渲染质量,但这会损害3D一致性。为解决这一问题,提出CGS-GAN框架,无需依赖视角条件化即可实现稳定训练和高质量、一致的3D人头合成。通过多视角正则化技术确保训练稳定性,并改进现有条件损失和生成器架构,以提高渲染效率和分辨率。评估CGS-GAN能力的新数据集已问世,更专注于大头部分的高分辨率,减少视角相关的伪影和遮挡物。该方法的渲染质量高,保证一致的3D场景生成。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于3D高斯贴图的3D GANs方法在合成高质量的人头时面临挑战,如训练稳定性和视角相关的渲染质量。
- CGS-GAN框架被引入以解决这些问题,无需依赖视角条件化即可实现稳定训练和高质量、一致的3D人头合成。
- 通过多视角正则化技术确保训练稳定性,提高生成器收敛性。
- 改进了现有条件损失和生成器架构,以提高渲染效率和分辨率,支持高达$2048^2$的输出分辨率。
- 新数据集问世以评估CGS-GAN的能力,专注于大头部分的高分辨率,减少视角相关的伪影和遮挡物的影响。
- CGS-GAN实现了高渲染质量和一致的3D场景生成,具有竞争力的FID分数。
点此查看论文截图

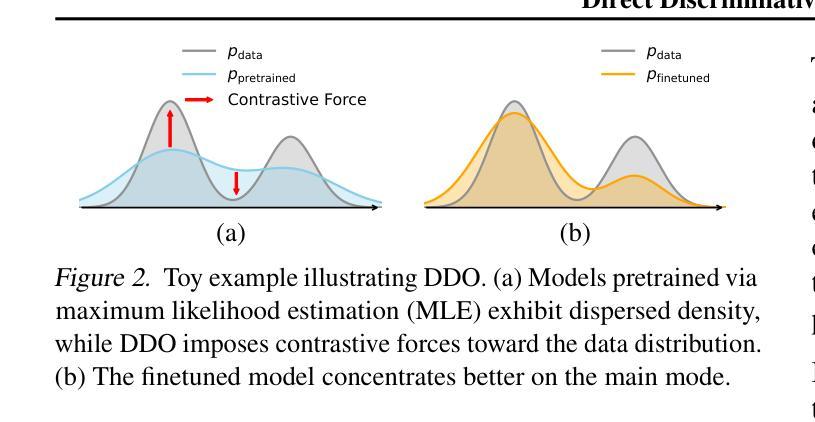
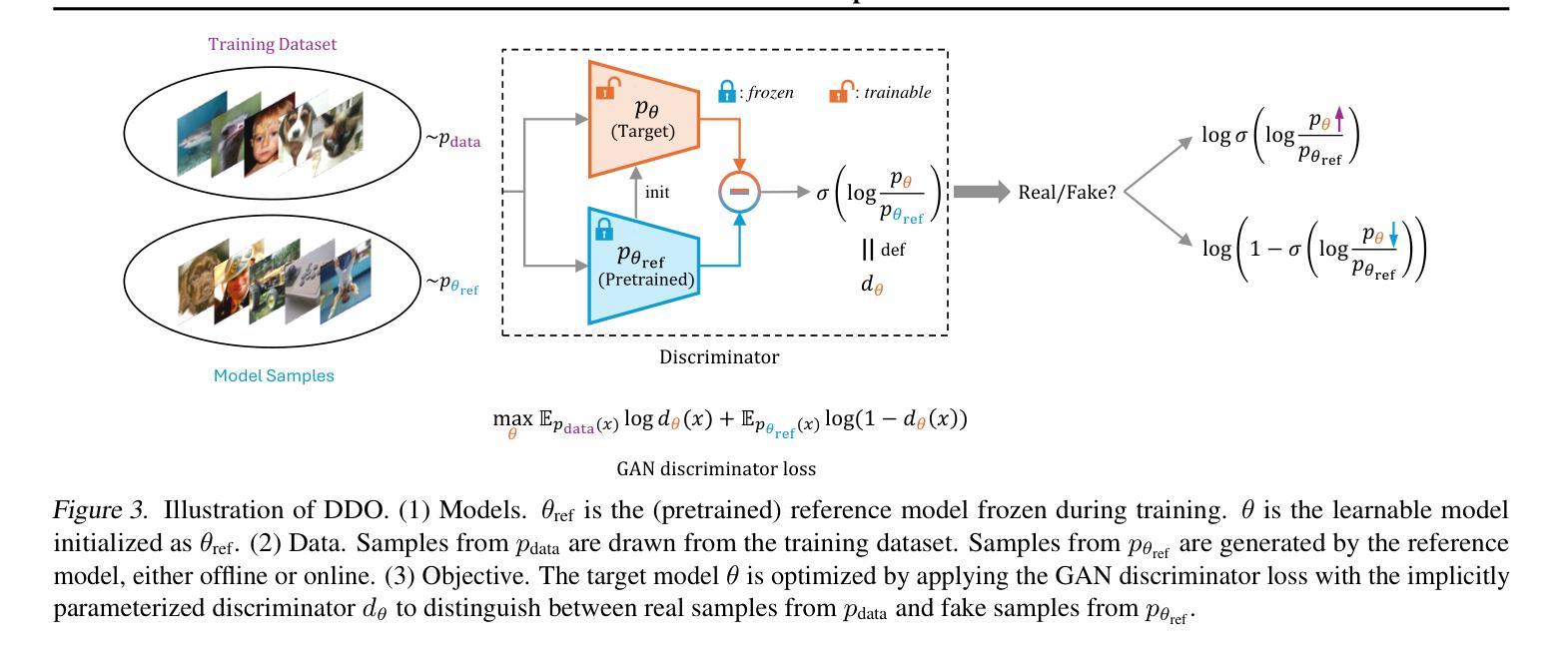
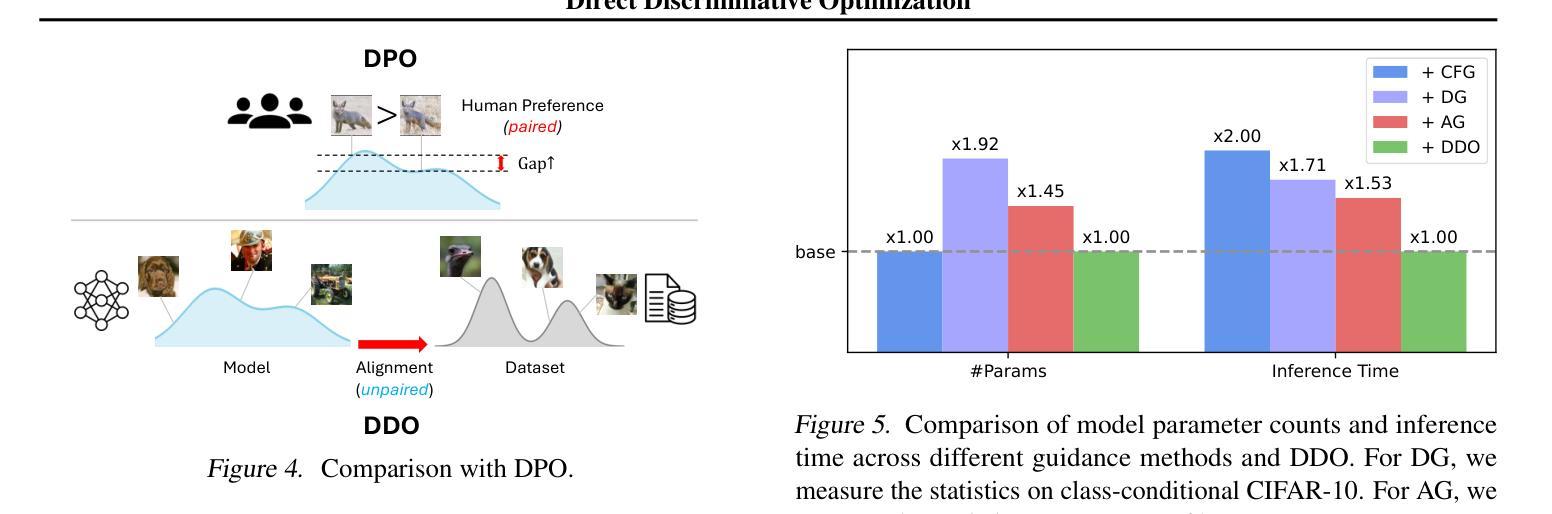
Direct Discriminative Optimization: Your Likelihood-Based Visual Generative Model is Secretly a GAN Discriminator
Authors:Kaiwen Zheng, Yongxin Chen, Huayu Chen, Guande He, Ming-Yu Liu, Jun Zhu, Qinsheng Zhang
While likelihood-based generative models, particularly diffusion and autoregressive models, have achieved remarkable fidelity in visual generation, the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) objective, which minimizes the forward KL divergence, inherently suffers from a mode-covering tendency that limits the generation quality under limited model capacity. In this work, we propose Direct Discriminative Optimization (DDO) as a unified framework that integrates likelihood-based generative training and GAN-type discrimination to bypass this fundamental constraint by exploiting reverse KL and self-generated negative signals. Our key insight is to parameterize a discriminator implicitly using the likelihood ratio between a learnable target model and a fixed reference model, drawing parallels with the philosophy of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). Unlike GANs, this parameterization eliminates the need for joint training of generator and discriminator networks, allowing for direct, efficient, and effective finetuning of a well-trained model to its full potential beyond the limits of MLE. DDO can be performed iteratively in a self-play manner for progressive model refinement, with each round requiring less than 1% of pretraining epochs. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DDO by significantly advancing the previous SOTA diffusion model EDM, reducing FID scores from 1.79/1.58/1.96 to new records of 1.30/0.97/1.26 on CIFAR-10/ImageNet-64/ImageNet 512x512 datasets without any guidance mechanisms, and by consistently improving both guidance-free and CFG-enhanced FIDs of visual autoregressive models on ImageNet 256x256.
基于概率的生成模型,特别是扩散和自回归模型,在视觉生成方面取得了显著的保真度。最大似然估计(MLE)目标通过最小化正向KL散度,固有地遭受模式覆盖的倾向,这限制了有限的模型容量下的生成质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了直接判别优化(DDO)作为一个统一的框架,它将基于概率的生成训练和GAN类型的判别结合起来,通过利用反向KL和自我生成的负信号绕过这个基本约束。我们的关键见解是,使用一个判别器隐式地参数化目标模型和一个固定参考模型之间的概率比率,这与直接偏好优化(DPO)的理念相平行。不同于生成对抗网络(GANs),这种参数化消除了生成器和判别器网络联合训练的需要,允许对良好训练的模型进行直接、高效和有效的微调,充分发挥其潜力,超越MLE的限制。DDO可以以一种自我对抗的方式迭代进行模型的渐进优化,每一轮所需的预训练周期不到1%。我们的实验通过显著地提升先前的最佳扩散模型EDM,在无需任何指导机制的情况下,在CIFAR-10、ImageNet-64和ImageNet 512x512数据集上将FID得分从1.79/1.58/1.96降低到新的记录1.30/0.97/1.26,证明了DDO的有效性。同时,它在无需指导和CFG增强的条件下,对ImageNet 256x256的视觉自回归模型的FID进行了持续不断的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Spotlight Project Page: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/ddo/ Code: https://github.com/NVlabs/DDO
摘要
基于似然生成模型,特别是扩散和自回归模型,在视觉生成方面取得了显著的保真度。然而,最大似然估计(MLE)目标通过最小化正向KL散度,存在模式覆盖倾向,限制了有限模型容量下的生成质量。本研究提出直接判别优化(DDO)作为统一框架,融合基于似然的生成训练和GAN型判别,通过反向KL和自我生成的负信号绕过这一基本约束。我们的关键见解是利用可学习的目标模型和固定参考模型之间的似然比来隐含地参数化判别器,这与直接偏好优化(DPO)的理念相契合。不同于GANs,这种参数化方式无需生成器和判别器的联合训练,能够直接、高效且有效地对预训练良好的模型进行微调,充分发挥其潜力,突破MLE的限制。DDO可以自我迭代的方式进行渐进模型优化,每轮所需预训练周期不到1%。实验证明DDO的有效性,显著提升了之前的SOTA扩散模型EDM,在无需任何引导机制的情况下,将CIFAR-10/ImageNet-64/ImageNet 512x512数据集的FID分数从1.79/1.58/1.96降至新纪录的1.30/0.97/1.26。同时,对于ImageNet 256x256的视觉自回归模型,在无引导和CFG增强的情况下,也实现了FID的持续改善。
关键见解
- 基于似然生成模型在视觉生成方面的优异表现,但存在模式覆盖的固有缺陷。
- 提出直接判别优化(DDO)框架,结合似然生成训练和GAN型判别,绕过模式覆盖问题。
- 利用可学习的目标模型和固定参考模型之间的似然比参数化判别器,与直接偏好优化(DPO)理念相似。
- DDO不需要生成器和判别器的联合训练,能够直接微调预训练模型。
- DDO可实现渐进模型优化,每轮预训练周期少。
- DDO显著提升了扩散模型的性能,降低了FID分数。
- DDO对无引导和带CFG增强的视觉自回归模型也有改善效果。
点此查看论文截图