⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-25 更新
Selecting N-lowest scores for training MOS prediction models
Authors:Yuto Kondo, Hirokazu Kameoka, Kou Tanaka, Takuhiro Kaneko
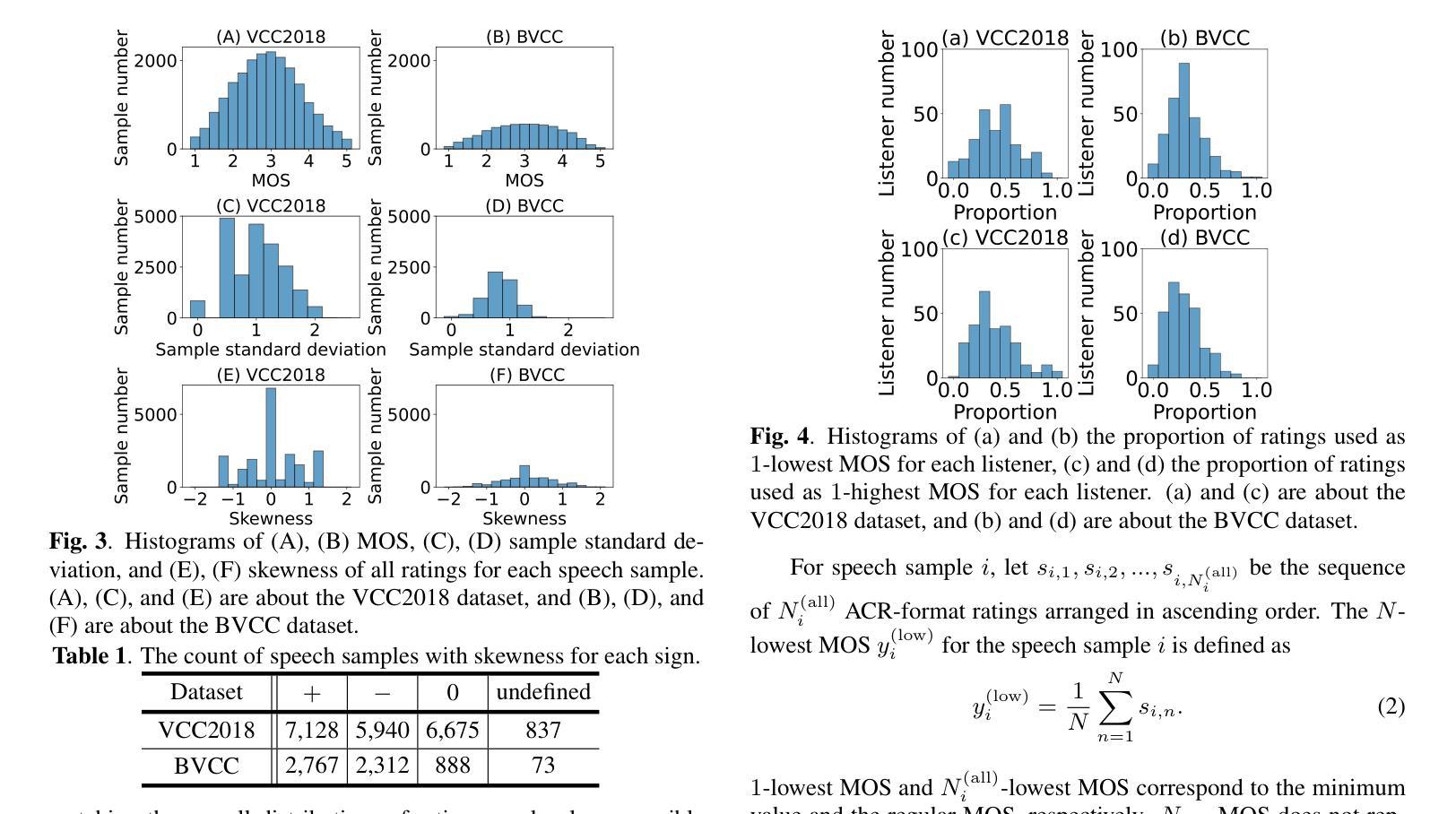
The automatic speech quality assessment (SQA) has been extensively studied to predict the speech quality without time-consuming questionnaires. Recently, neural-based SQA models have been actively developed for speech samples produced by text-to-speech or voice conversion, with a primary focus on training mean opinion score (MOS) prediction models. The quality of each speech sample may not be consistent across the entire duration, and it remains unclear which segments of the speech receive the primary focus from humans when assigning subjective evaluation for MOS calculation. We hypothesize that when humans rate speech, they tend to assign more weight to low-quality speech segments, and the variance in ratings for each sample is mainly due to accidental assignment of higher scores when overlooking the poor quality speech segments. Motivated by the hypothesis, we analyze the VCC2018 and BVCC datasets. Based on the hypothesis, we propose the more reliable representative value N_low-MOS, the mean of the $N$-lowest opinion scores. Our experiments show that LCC and SRCC improve compared to regular MOS when employing N_low-MOS to MOSNet training. This result suggests that N_low-MOS is a more intrinsic representative value of subjective speech quality and makes MOSNet a better comparator of VC models.
自动语音质量评估(SQA)已经被广泛研究,以便在不使用耗时问卷的情况下预测语音质量。最近,基于神经网络的SQA模型得到了积极发展,主要用于文本到语音或语音转换产生的语音样本,主要侧重于训练平均意见得分(MOS)预测模型。每个语音样本的质量在整个时长上可能并不一致,而且对于MOS计算的主观评价,人类主要关注哪些部分仍不清楚。我们假设,当人类对语音进行评分时,他们倾向于给低质量的语音片段分配更多的权重,每个样本评分的差异主要是由于在忽略低质量语音片段时意外分配了较高的分数。受此假设的启发,我们分析了VCC2018和BVCC数据集。基于假设,我们提出了更可靠的代表值N_low-MOS,即最低的N个意见得分的平均值。我们的实验表明,与使用常规MOS相比,在使用N_low-MOS进行MOSNet训练时,LCC和SRCC有所改善。这一结果暗示N_low-MOS是主观语音质量更内在的代表值,使MOSNet成为VC模型更好的比较工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted on ICASSP 2024
Summary
本文探讨了自动语音质量评估(SQA)在预测语音质量方面的应用,重点介绍了基于神经网络的SQA模型在文本转语音或语音转换领域的发展。文章指出,语音样本的质量可能在整个时长中并不一致,而人类在为主观评价分配评分以计算平均意见得分(MOS)时,主要关注哪些部分尚不清楚。研究假设人类在评估语音时,更容易对低质量语音片段赋予更高的权重,并提出了更可靠的代表性值N_low-MOS,即$N$个最低意见得分的平均值。实验表明,使用N_low-MOS进行MOSNet训练时,LCC和SRCC相较于常规MOS有所改善。这表明N_low-MOS是主观语音质量更内在的代表值,使MOSNet成为VC模型更好的比较器。
Key Takeaways
- 自动语音质量评估(SQA)在预测语音质量方面进行了广泛研究,以替代耗时的人力调查问卷。
- 基于神经网络的SQA模型在文本转语音和语音转换领域得到了积极发展。
- 语音样本的质量可能在整个时长中不一致,而人类在评价时的关注重点尚不清楚。
- 人类在评估语音质量时,更容易对低质量片段赋予更高的权重。
- 提出了更可靠的代表性值N_low-MOS,即$N$个最低意见得分的平均值。
- 使用N_low-MOS进行MOSNet训练时,LCC和SRCC有所改善,表明其相较于常规MOS更有效。
点此查看论文截图

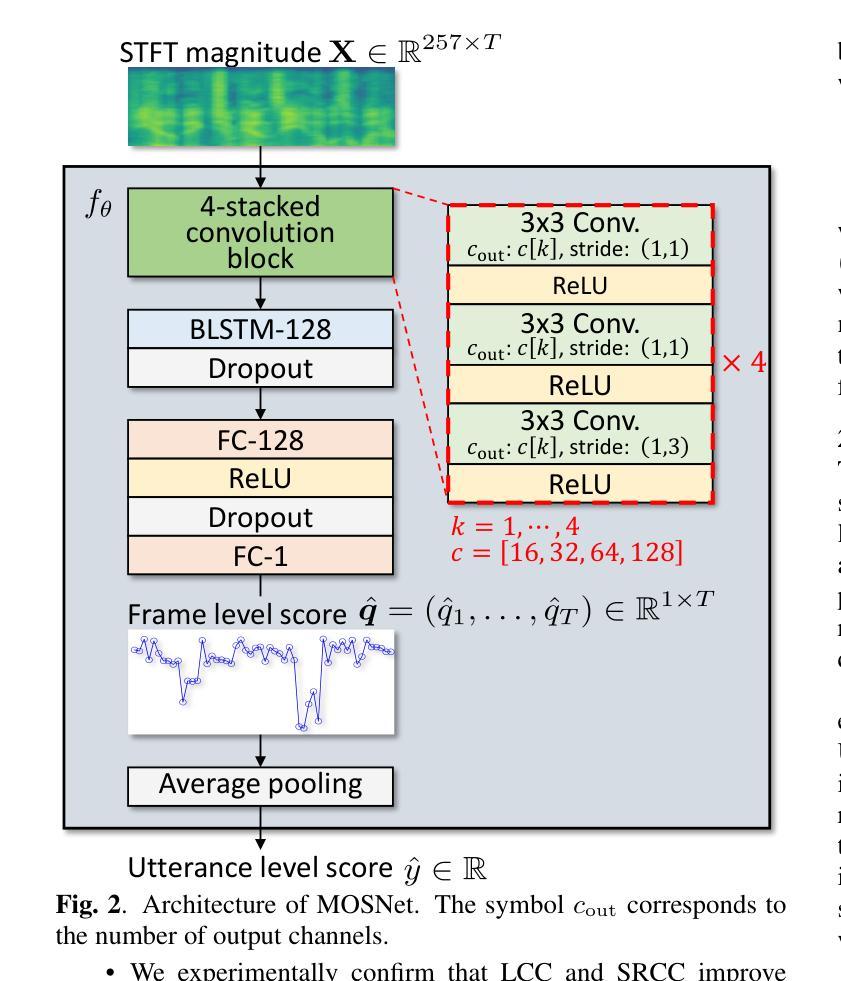
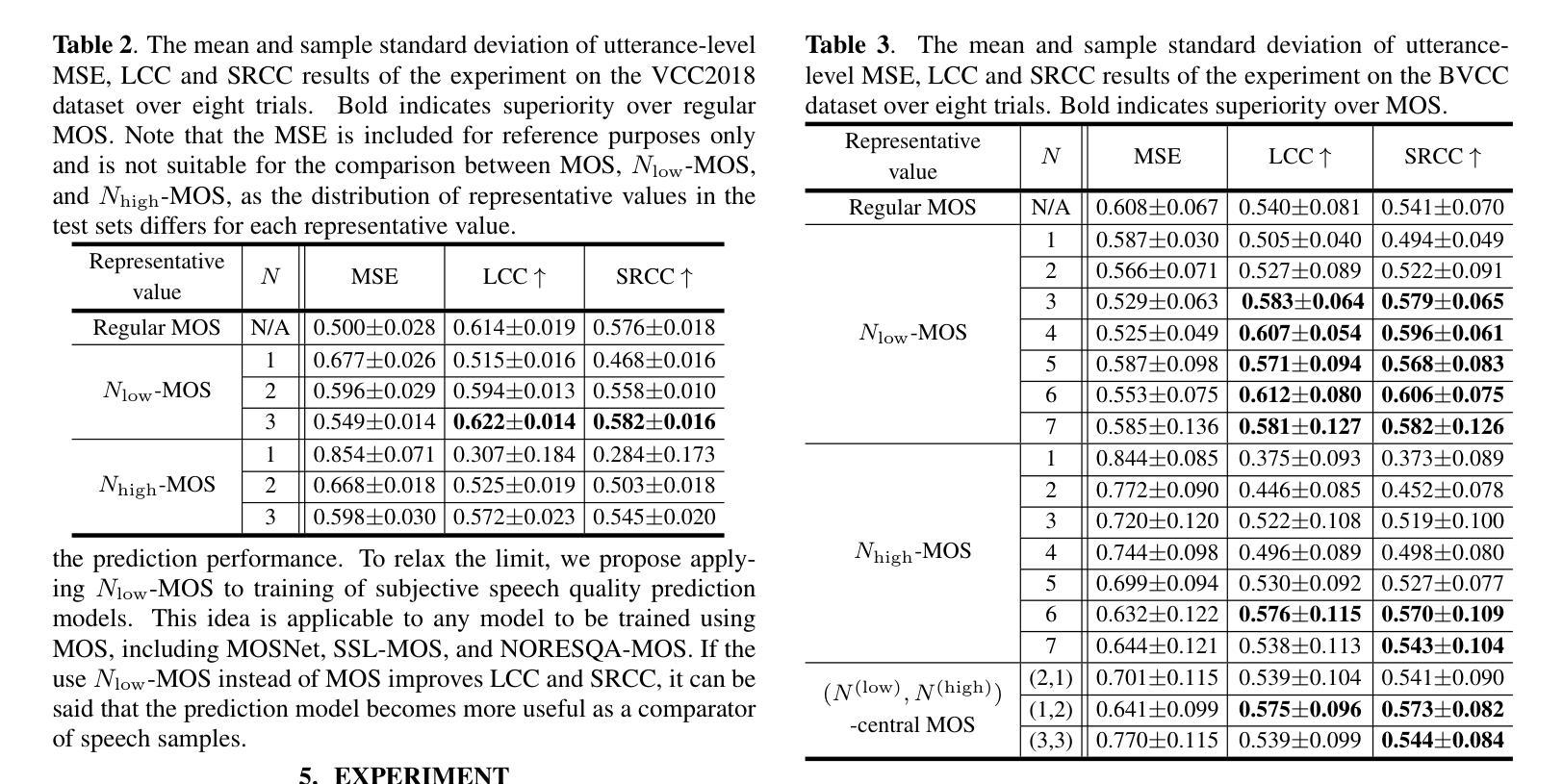
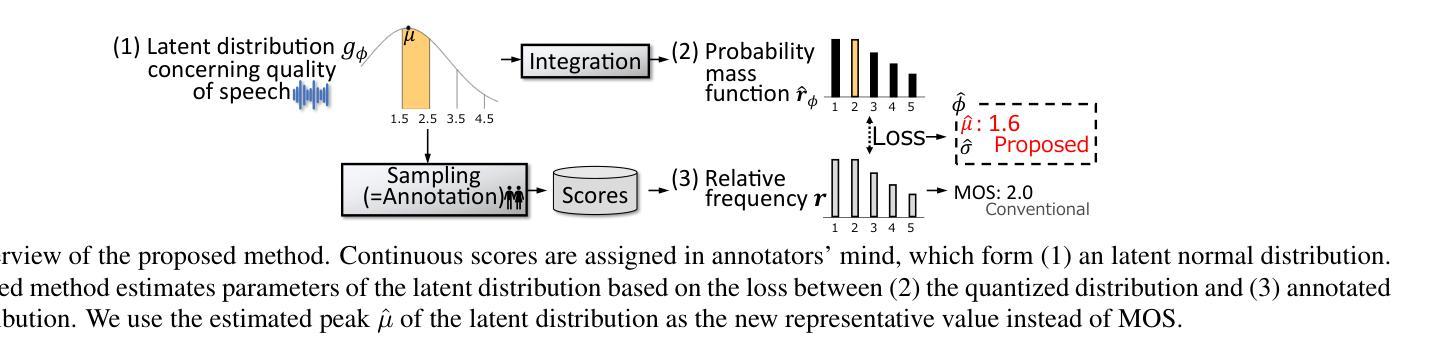
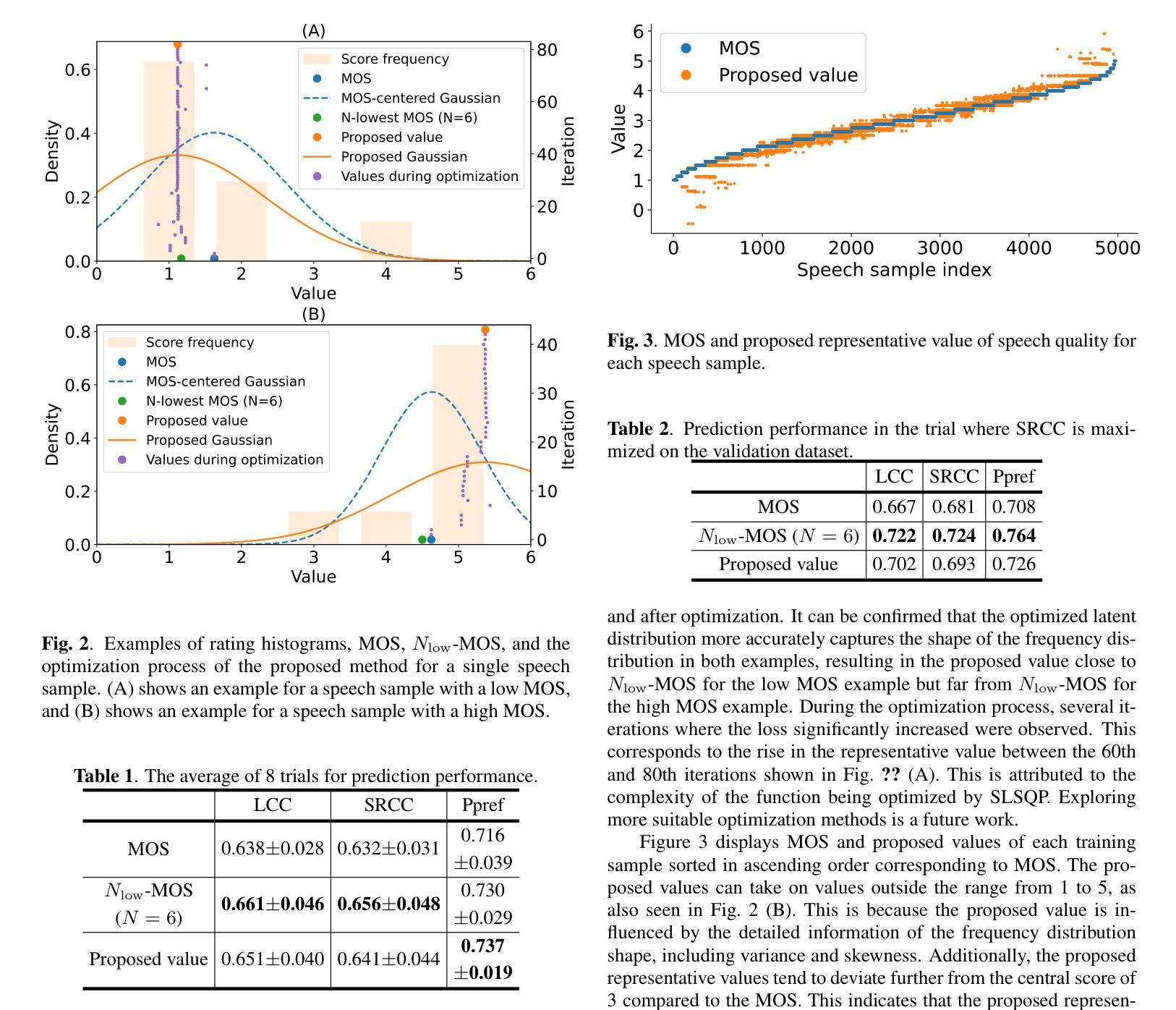
Rethinking Mean Opinion Scores in Speech Quality Assessment: Aggregation through Quantized Distribution Fitting
Authors:Yuto Kondo, Hirokazu Kameoka, Kou Tanaka, Takuhiro Kaneko
Speech quality assessment (SQA) aims to evaluate the quality of speech samples without relying on time-consuming listener questionnaires. Recent efforts have focused on training neural-based SQA models to predict the mean opinion score (MOS) of speech samples produced by text-to-speech or voice conversion systems. This paper targets the enhancement of MOS prediction models’ performance. We propose a novel score aggregation method to address the limitations of conventional annotations for MOS, which typically involve ratings on a scale from 1 to 5. Our method is based on the hypothesis that annotators internally consider continuous scores and then choose the nearest discrete rating. By modeling this process, we approximate the generative distribution of ratings by quantizing the latent continuous distribution. We then use the peak of this latent distribution, estimated through the loss between the quantized distribution and annotated ratings, as a new representative value instead of MOS. Experimental results demonstrate that substituting MOSNet’s predicted target with this proposed value improves prediction performance.
语音质量评估(SQA)旨在评估语音样本的质量,而无需依赖耗时的听众问卷调查。最近的努力主要集中在训练基于神经网络的SQA模型,以预测文本到语音或语音转换系统产生的语音样本的平均意见得分(MOS)。本文旨在提高MOS预测模型的性能。我们提出了一种新的评分聚合方法,以解决传统MOS标注的局限性,传统标注通常涉及从1到5的尺度评分。我们的方法基于这样的假设:评估者在内部考虑连续分数,然后选择最接近的离散评分。通过对这一过程进行建模,我们通过量化潜在的连续分布来近似评分的生成分布。然后,我们通过量化分布和标注评分之间的损失来估计潜在分布的峰值,并将其作为新的代表值来代替MOS。实验结果表明,用该提议值替换MOSNet的预测目标值可以提高预测性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted on ICASSP 2025
摘要
本文主要研究了语音质量评估(SQA)中的平均意见得分(MOS)预测模型的性能提升。针对传统MOS标注方法的局限性,提出了一种新的评分聚合方法。该方法基于标注者实际上考虑的是连续分数,然后选择最接近的离散评分的假设。通过对此过程进行建模,我们量化了潜在连续分布的评分,并使用此潜在分布的峰值作为新的代表值来改进MOS预测模型的性能。实验结果表明,使用该值替代MOSNet的预测目标可以提高预测性能。
要点
- 语音质量评估(SQA)致力于评估语音样本的质量,而不依赖于耗时的听众问卷。
- 近期的研究集中在训练基于神经网络的SQA模型,以预测文本到语音或语音转换系统产生的语音样本的MOS(平均意见得分)。
- 本文旨在提高MOS预测模型的性能。
- 提出了一种新的评分聚合方法,以解决传统MOS标注方法的局限性。
- 该方法基于标注者实际上考虑的是连续分数,然后选择最接近的离散评分进行建模。
- 通过量化潜在连续分布的评分来估算生成评分的分布。
点此查看论文截图

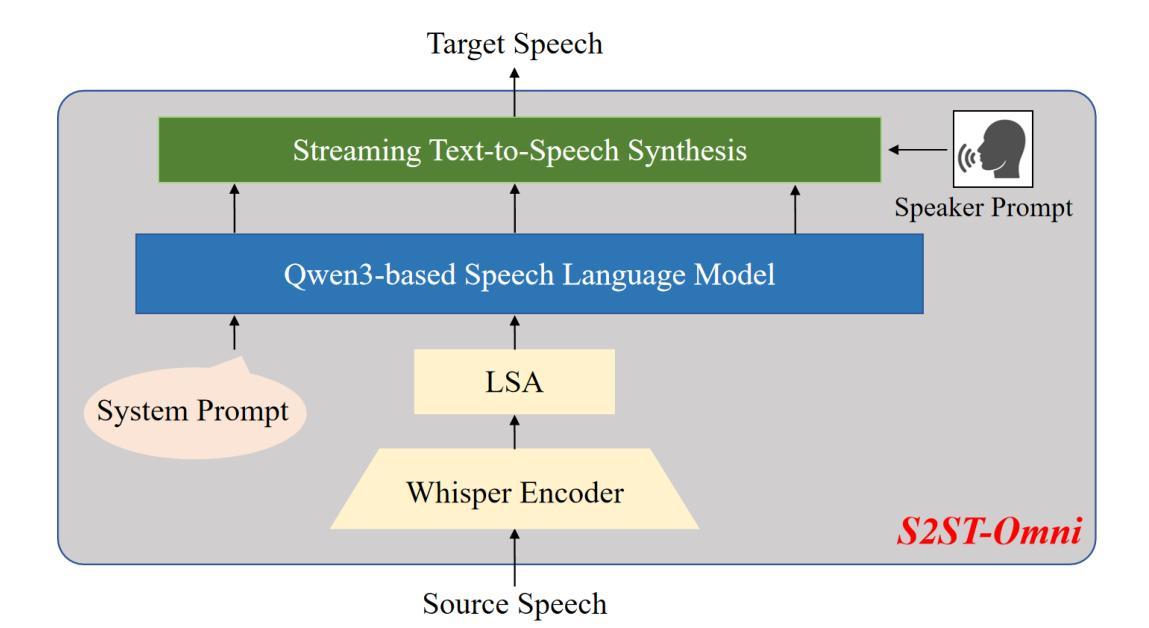
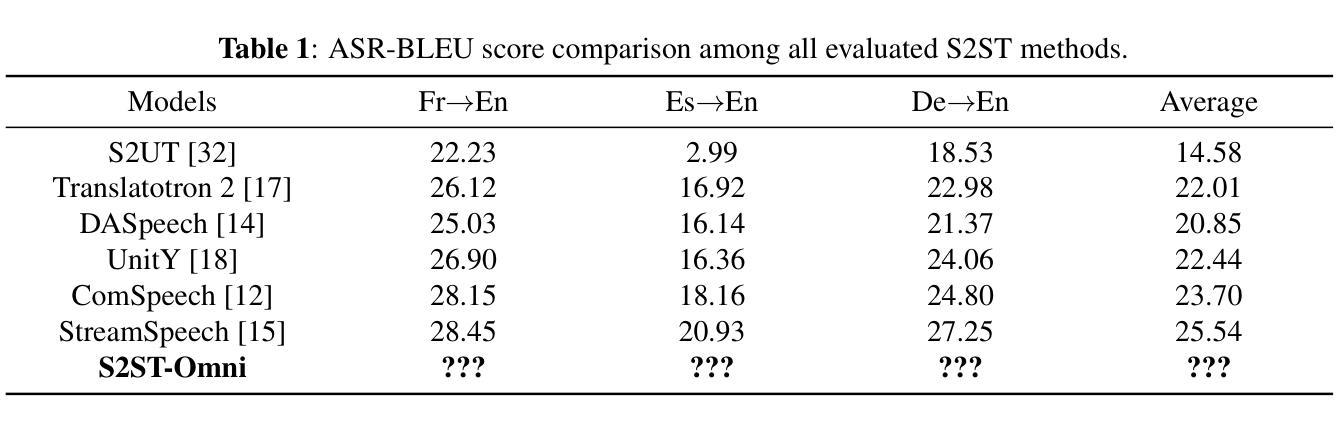
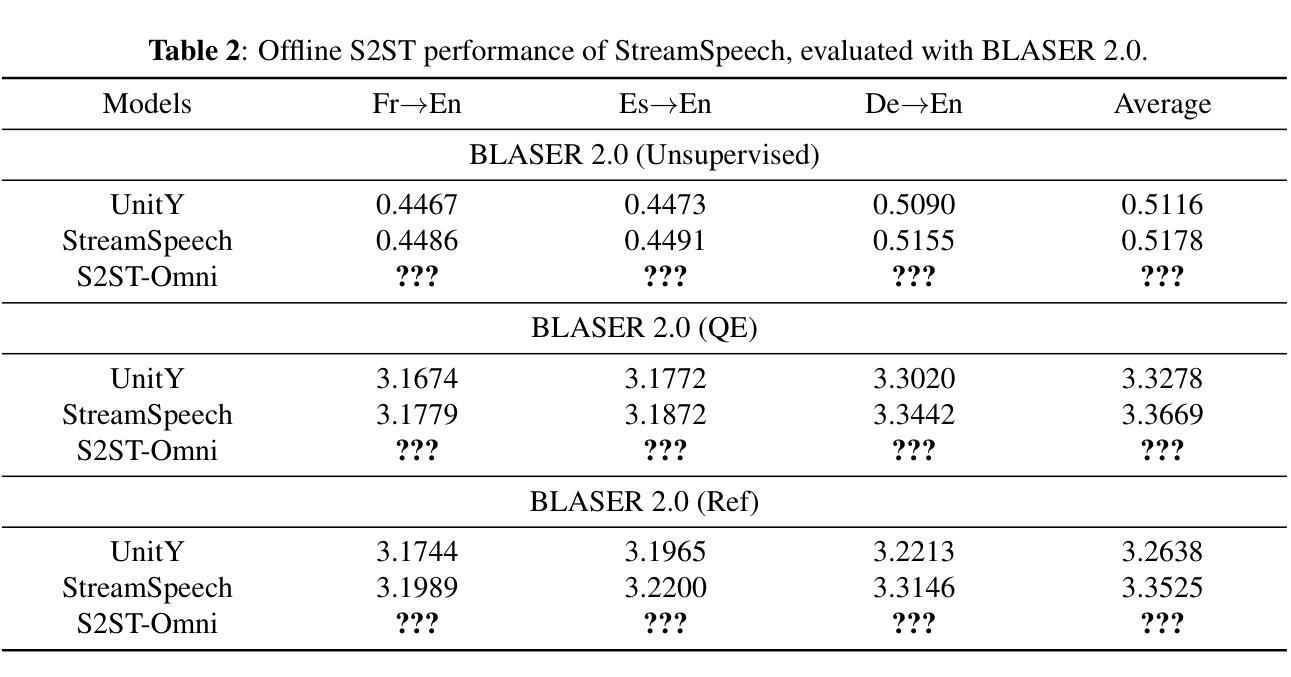
S2ST-Omni: An Efficient and Scalable Multilingual Speech-to-Speech Translation Framework via Seamless Speech-Text Alignment and Streaming Speech Generation
Authors:Yu Pan, Yuguang Yang, Yanni Hu, Jianhao Ye, Xiang Zhang, Hongbin Zhou, Lei Ma, Jianjun Zhao
Multilingual speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) aims to directly convert spoken utterances from multiple source languages into fluent and intelligible speech in a target language. Despite recent progress, several critical challenges persist: 1) achieving high-quality S2ST remains a significant obstacle; 2) most existing S2ST methods rely heavily on large-scale parallel speech corpora, which are difficult and resource-intensive to obtain. To tackle these challenges, we introduce S2ST-Omni, a novel, efficient, and scalable framework tailored for multilingual speech-to-speech translation. Specifically, we decompose S2ST into speech-to-text translation (S2TT) and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). To enable high-quality S2TT while mitigating reliance on large-scale parallel speech corpora, we leverage powerful pretrained models: Whisper for robust audio understanding and Qwen 3.0 for advanced text comprehension. A lightweight speech adapter is introduced to bridge the modality gap between speech and text representations, facilitating effective utilization of pretrained multimodal knowledge. To ensure both translation accuracy and real-time responsiveness, we adopt a streaming speech generation model in the TTS stage, which generates the target speech in an autoregressive manner. Extensive experiments conducted on the CVSS benchmark demonstrate that S2ST-Omni consistently surpasses several state-of-the-art S2ST baselines in translation quality, highlighting its effectiveness and superiority.
多语种语音到语音翻译(S2ST)旨在直接将多种源语言的口语表达翻译成目标语言中的流畅、可理解的语音。尽管最近有所进展,但仍存在几个关键挑战:1)实现高质量的S2ST仍然是一个重大障碍;2)大多数现有的S2ST方法严重依赖于大规模的平行语音语料库,而这些语料库的获取既困难又耗费资源。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了S2ST-Omni,这是一个新颖、高效、可扩展的框架,专为多语种语音到语音翻译而设计。具体来说,我们将S2ST分解为语音到文本翻译(S2TT)和文本到语音合成(TTS)。为了提高S2TT的质量同时减少对大规模平行语音语料库的依赖,我们利用强大的预训练模型:Whisper用于鲁棒音频理解,Qwen 3.0用于高级文本理解。我们引入了一个轻量级的语音适配器来弥合语音和文本表示之间的模态差距,促进预训练多模态知识的有效使用。为了保证翻译准确性和实时响应性,我们在TTS阶段采用了流式语音生成模型,以自回归的方式生成目标语音。在CVSS基准测试上进行的大量实验表明,S2ST-Omni在翻译质量上始终超越了几种最先进的S2ST基准测试,凸显了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF V2 and V3 versions contain experimental errors due to incorrect training data. The results and conclusions are invalid. A corrected version is under preparation and will be uploaded soon. Please do not cite these versions. Working in progress
Summary
针对多语种语音到语音翻译(S2ST)面临的挑战,如高质量翻译和依赖大规模平行语音语料库的问题,提出了S2ST-Omni框架。该框架通过分解为语音到文本翻译(S2TT)和文本到语音合成(TTS)两个阶段,利用预训练模型如Whisper和Qwen 3.0,以高质量和低依赖大规模平行语料库的方式实现S2TT。通过引入轻量级语音适配器,缩小了语音和文本表示之间的模态差距,促进了预训练多模态知识的有效利用。在TTS阶段,采用流式语音生成模型,确保翻译准确性和实时响应性。在CVSS基准测试上的广泛实验表明,S2ST-Omni在翻译质量上超越了几种先进的S2ST基线,突显其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- S2ST-Omni是一个针对多语种语音到语音翻译的新型、高效、可扩展的框架。
- 框架将语音到语音翻译分解为两个主要阶段:语音到文本翻译(S2TT)和文本到语音合成(TTS)。
- 利用预训练模型如Whisper和Qwen 3.0实现高质量S2TT,减少对大规模平行语音语料库的依赖。
- 引入轻量级语音适配器以缩小语音和文本表示之间的模态差距。
- 采用流式语音生成模型确保翻译准确性和实时响应性。
- S2ST-Omni在CVSS基准测试上的表现优于其他先进的S2ST方法。
点此查看论文截图

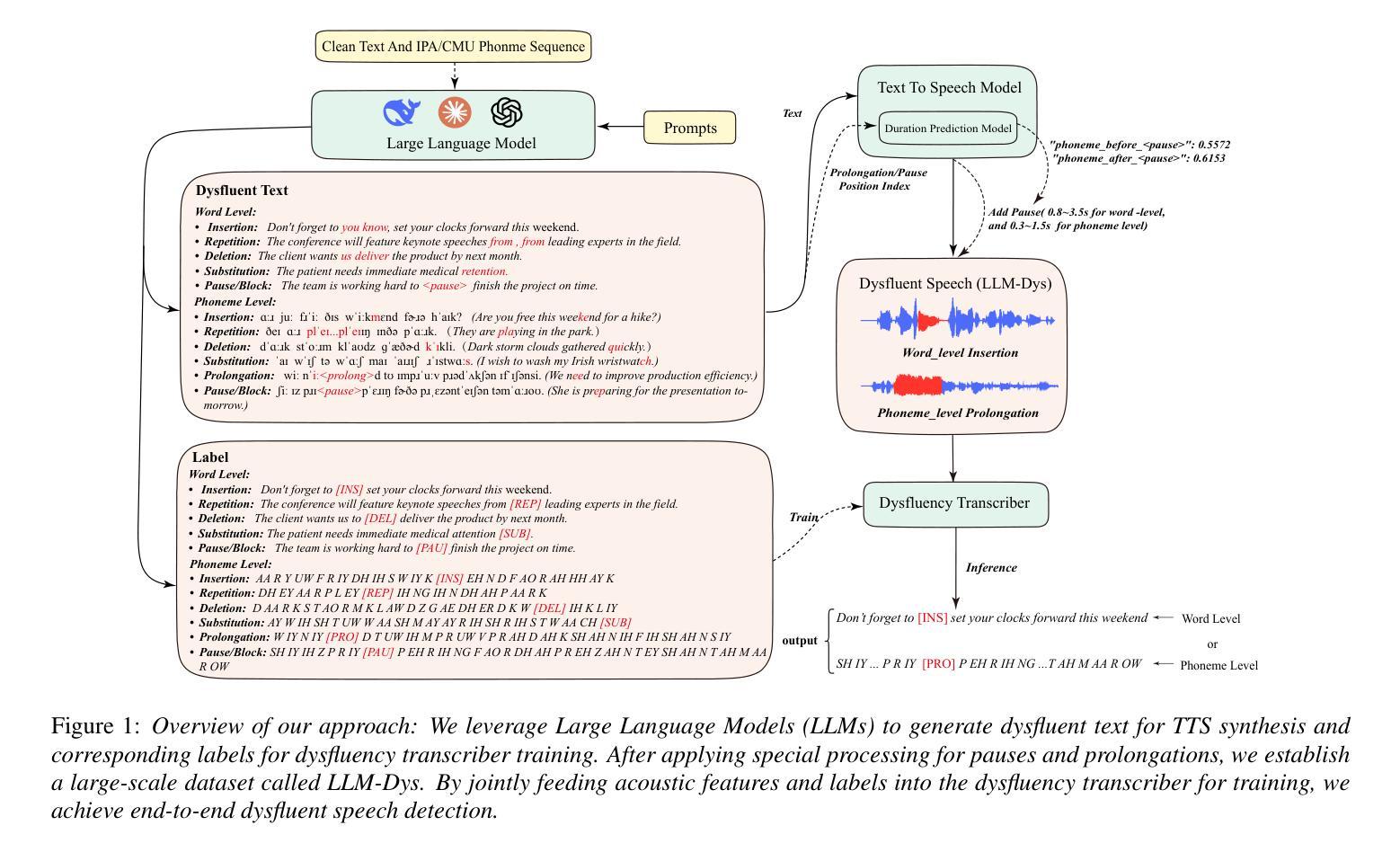
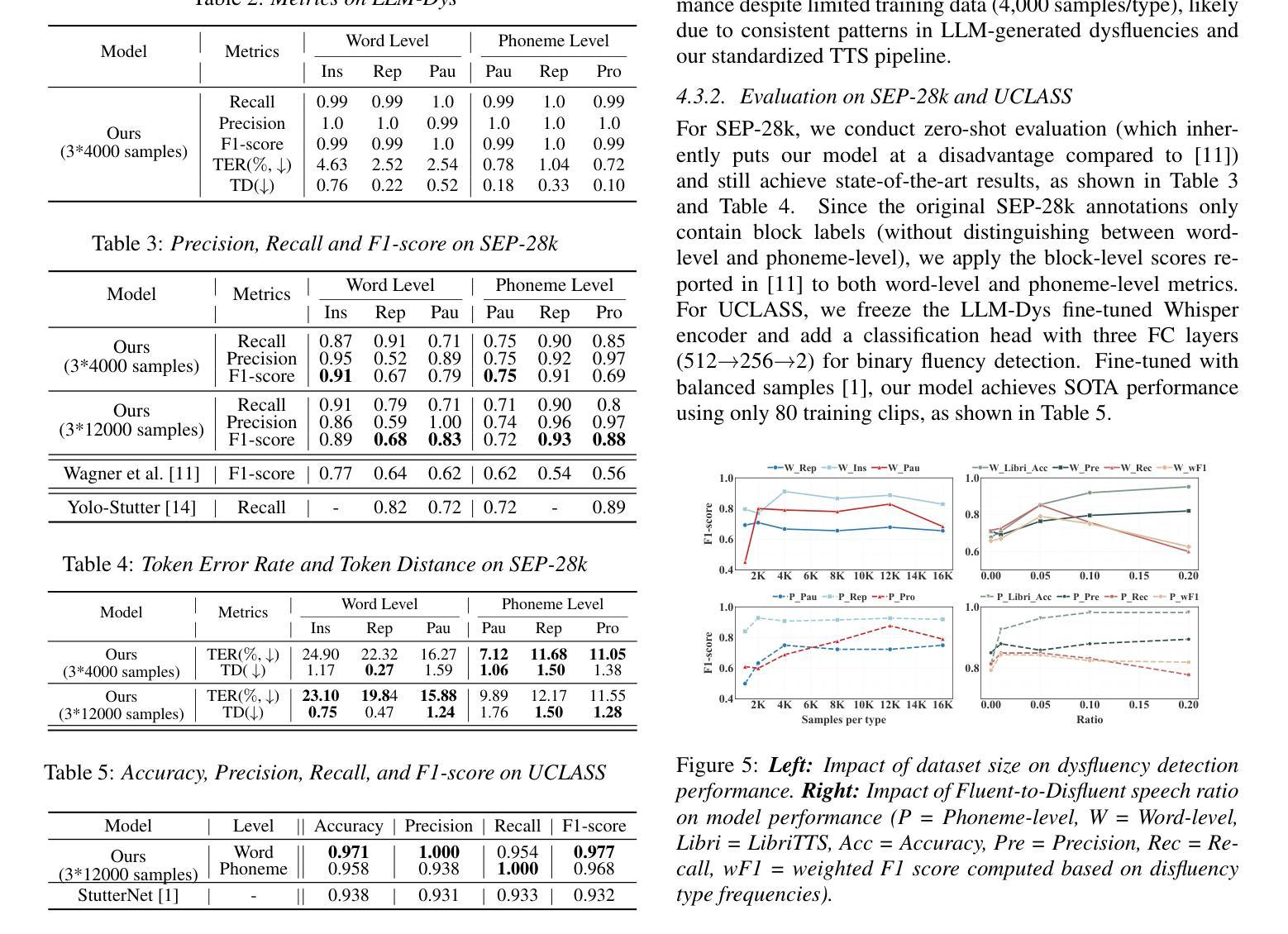
Analysis and Evaluation of Synthetic Data Generation in Speech Dysfluency Detection
Authors:Jinming Zhang, Xuanru Zhou, Jiachen Lian, Shuhe Li, William Li, Zoe Ezzes, Rian Bogley, Lisa Wauters, Zachary Miller, Jet Vonk, Brittany Morin, Maria Gorno-Tempini, Gopala Anumanchipalli
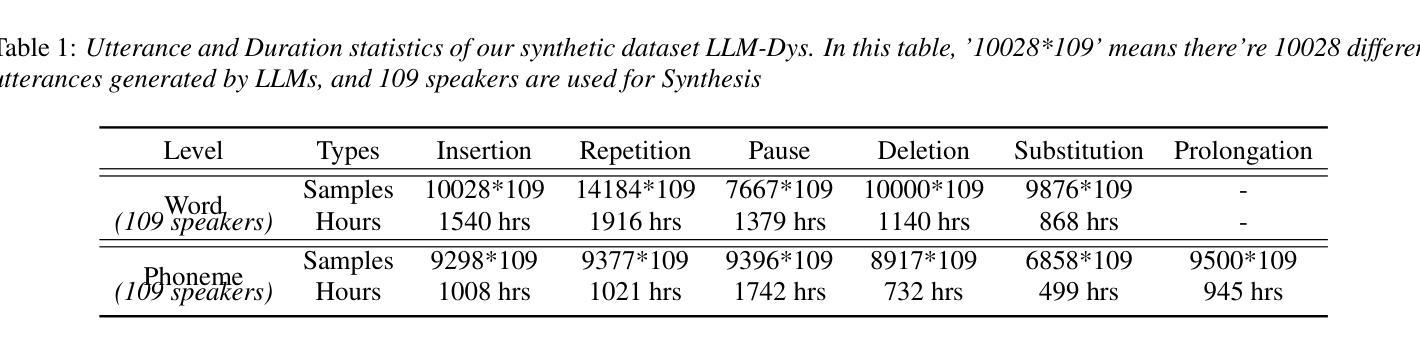
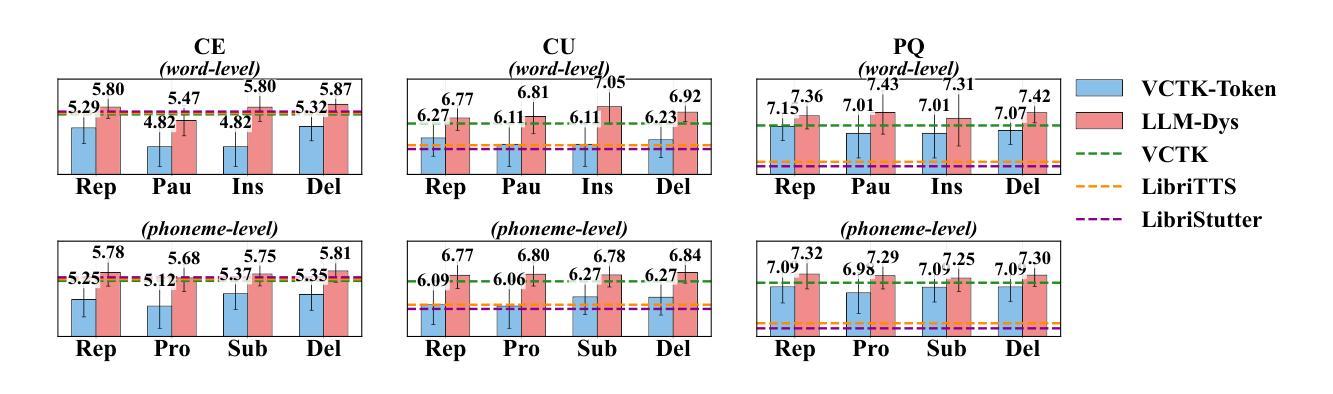
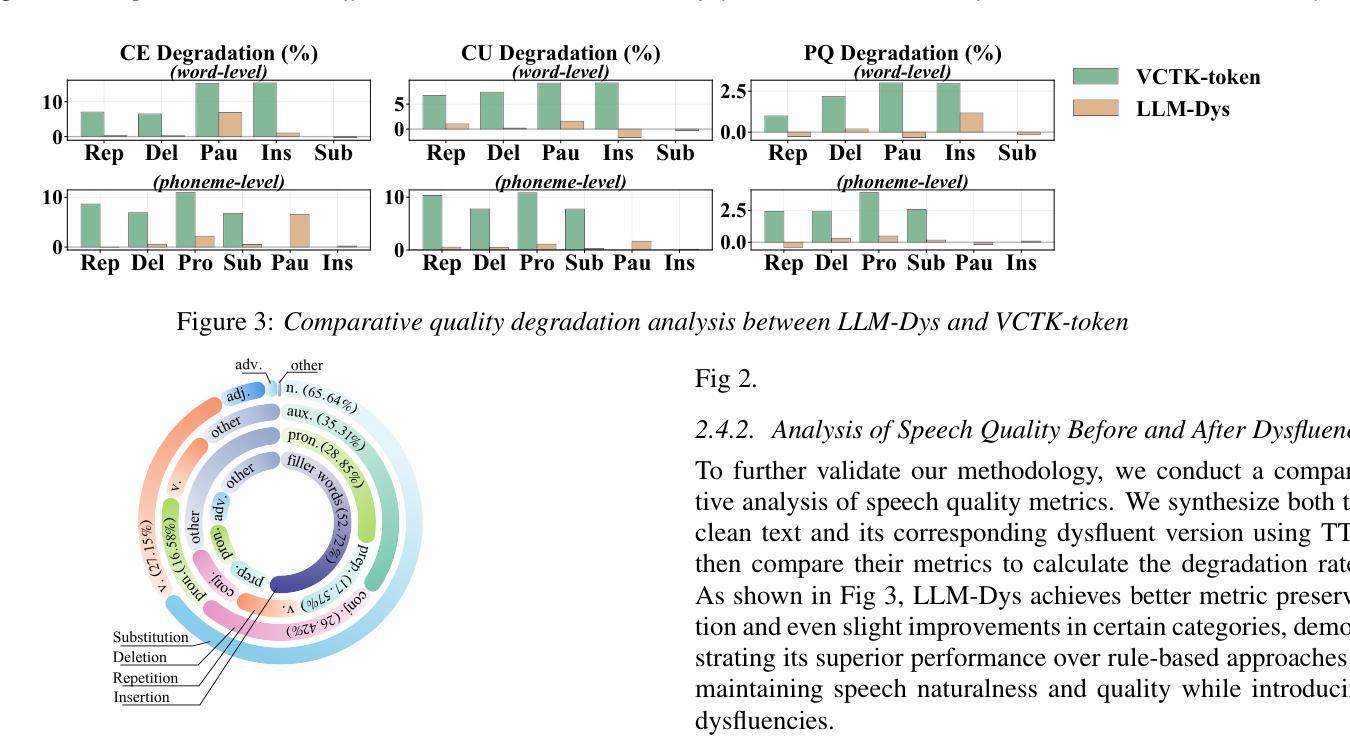
Speech dysfluency detection is crucial for clinical diagnosis and language assessment, but existing methods are limited by the scarcity of high-quality annotated data. Although recent advances in TTS model have enabled synthetic dysfluency generation, existing synthetic datasets suffer from unnatural prosody and limited contextual diversity. To address these limitations, we propose LLM-Dys – the most comprehensive dysfluent speech corpus with LLM-enhanced dysfluency simulation. This dataset captures 11 dysfluency categories spanning both word and phoneme levels. Building upon this resource, we improve an end-to-end dysfluency detection framework. Experimental validation demonstrates state-of-the-art performance. All data, models, and code are open-sourced at https://github.com/Berkeley-Speech-Group/LLM-Dys.
语音流畅性检测对于临床诊断和治疗语言评估至关重要,但现有方法受到高质量注释数据稀缺的限制。尽管最近文本转语音模型的进步已经能够实现合成流畅性生成,但现有合成数据集存在韵律不自然和上下文多样性有限的缺点。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了LLM-Dys——一个由大型语言模型增强流畅性模拟的最全面的流畅性语音语料库。该数据集涵盖了涵盖单词和音素级别的1k种流畅性问题类别。基于此资源,我们改进了一种端到端的流畅性检测框架。实验验证证明了其处于业界前沿的性能。所有数据和代码均已开源,可访问https://github.com/Berkeley-Speech-Group/LLM-Dys。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary
语音流畅性检测对于临床诊断和治疗语言评估至关重要,但高质量标注数据的稀缺性限制了现有方法的性能。最近文本转语音模型的进步已能够实现合成流畅性生成,但现有合成数据集存在韵律不自然和语境多样性有限的问题。为解决这些问题,我们提出了LLM-Dys——一个最全面的流畅性语音语料库,采用LLM增强流畅性模拟。该数据集涵盖了跨越单词和音素级别的11种流畅性问题类别。基于此资源,我们改进了一个端到端的流畅性检测框架,实验验证其性能达到先进水平。所有数据、模型和代码均已开源,地址为:公开链接。
Key Takeaways
- 语音流畅性检测在临床诊断和治疗语言评估中具有重要作用。
- 现有方法受到高质量标注数据稀缺性的限制。
- TTS模型的新进展能够实现合成流畅性的生成。
- 但现有合成数据集存在韵律不自然和语境多样性有限的问题。
- LLM-Dys是最全面的流畅性语音语料库,采用LLM增强模拟技术。
- 该数据集涵盖了跨越单词和音素级别的多种流畅性问题类别。
点此查看论文截图