⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-26 更新
Cluster Spin Glass State in Ba$3$Sb${1+x}$Co${2-x}$O${9-δ}$: Cation Disorder and Mixed-Valence Co Dimers
Authors:Anzar Ali, Guratinder Kaur, Lukas Keller, Masahiko Isobe
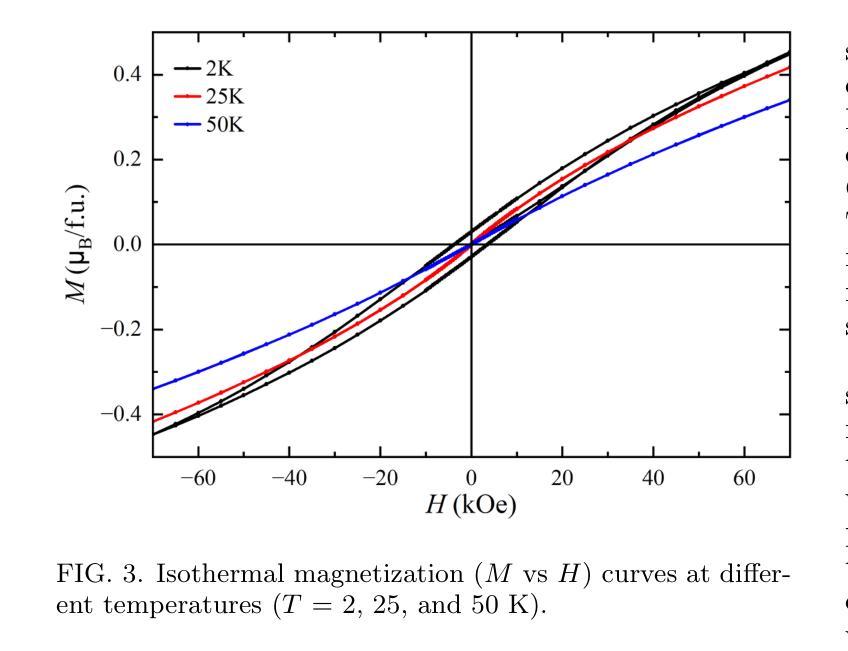
We investigate the structural, magnetic, and thermodynamic properties of \BSCO\ ($x$ = 0.04, $\delta$ = 0.54), a hexagonal perovskite featuring face-sharing CoO$_6$ octahedra that forms Co dimers. DC and AC magnetization measurements reveal a frequency-dependent spin-freezing transition consistent with glassy dynamics. AC susceptibility fits best to the Vogel-Fulcher model, indicating collective freezing of interacting spin clusters. Isothermal magnetization follows the Langevin function, suggesting finite-sized magnetic clusters rather than isolated paramagnetic moments. Non-equilibrium dynamics, evidenced by thermoremanent magnetization and memory effects, further support a spin-glass-like state. Heat capacity shows no sharp anomalies, and neutron powder diffraction confirms the absence of magnetic Bragg peaks down to 1.5K, ruling out long-range magnetic order. Rietveld refinement reveals significant Co/Sb intersite disorder ($\sim$30\pct) and oxygen non-stoichiometry, introducing exchange randomness and frustration that drive the spin-glass-like behavior. Electrical resistivity exhibits Arrhenius-type temperature dependence with an activation energy of 0.173~eV, consistent with semiconducting behavior. Temperature-dependent X-ray diffraction shows no structural phase transitions, confirming that the spin-glass-like state is not lattice-driven. Our results establish \BSCO\ as a cluster spin-glass candidate, where Co dimers, disorder, and geometric frustration prevent long-range order, leading to slow spin dynamics. These findings highlight the role of cation disorder and oxygen vacancies in stabilizing unconventional magnetic states in cobalt-based hexagonal perovskites.
我们对BSCO(x=0.04,δ=0.54)的结构、磁性和热力学性质进行了研究,这是一种具有面共享CoO6八面体的六方钙钛矿结构,形成Co二聚体。直流和交流磁化测量揭示了一种与玻璃态动力学一致的频率依赖性自旋冻结转变。交流磁化率最符合Vogel-Fulcher模型,表明相互作用自旋簇的集体冻结。等温磁化遵循朗之万函数,表明存在有限大小的磁簇,而非孤立的顺磁性矩。热剩余磁化和记忆效应所证明的非平衡动力学进一步支持自旋玻璃态。热容没有显示出尖锐的异常现象,中子粉末衍射确认在1.5K以下没有磁布拉格峰,排除了远程磁序的存在。Rietveld精修揭示出显著的Co/Sb位点间无序(约30%)和氧的非化学计量比,这引入了交换随机性和挫折性,驱动了自旋玻璃态行为。电阻率表现出Arrhenius类型的温度依赖性,活化能为0.173eV,与半导体行为一致。温度依赖的X射线衍射未显示结构相变,证实了自旋玻璃态不是晶格驱动。我们的结果确立了BSCO作为团簇自旋玻璃候选物的地位,其中Co二聚体、无序和几何受挫防止了远程有序性,导致缓慢的自旋动力学。这些发现强调了阳离子无序和氧空位在稳定钴基六方钙钛矿中的非传统磁态中的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文研究了BSCO($x$ = 0.04,$\delta$ = 0.54)的结构、磁性和热力学性质。该材料具有六角形钙钛矿结构,表现为共享面的CoO$_6$八面体形成的Co二聚体。直流和交流磁化测量揭示了一种与玻璃态动力学一致的频率依赖性自旋冻结转变。交流磁化率符合Vogel-Fulcher模型,表明相互作用自旋簇的集体冻结。等温磁化遵循朗之万函数,表明存在有限大小的磁簇,而非孤立的顺磁矩。热残余磁化和记忆效应等非平衡动力学进一步支持自旋玻璃态。热容无尖锐异常,中子粉末衍射证实低温下无磁布拉格峰,排除了远程磁序。Rietveld精炼显示显著的Co/Sb跨位无序和氧的非化学计量,引入交换随机性和挫折,驱动自旋玻璃态行为。电阻率表现出Arrhenius型温度依赖性,具有0.173eV的激活能量,符合半导体行为。温度依赖性X射线衍射未显示结构相变,证实自旋玻璃态不是晶格驱动。本研究结果确认BSCO是一种集群自旋玻璃候选材料,其中Co二聚体、无序和几何受挫防止了远程有序,导致缓慢的自旋动力学。这些发现强调了阳离子无序和氧空位在稳定钴基六角钙钛矿中的不寻常磁态中的作用。
关键见解
- BSCO表现出六角形钙钛矿结构特征,其中包含形成Co二聚体的共享面CoO$_6$八面体。
- 磁化测量揭示了一种频率依赖性的自旋冻结转变,表现出玻璃态动力学特性。
- AC磁化率符合Vogel-Fulcher模型,暗示集体冻结的相互作用自旋簇。
- 等温磁化遵循朗之万函数,表明存在有限大小的磁簇。
- 非平衡动力学证据进一步支持自旋玻璃态的存在。
- 中子粉末衍射和热容测量排除了远程磁序的存在。
点此查看论文截图

UltraAD: Fine-Grained Ultrasound Anomaly Classification via Few-Shot CLIP Adaptation
Authors:Yue Zhou, Yuan Bi, Wenjuan Tong, Wei Wang, Nassir Navab, Zhongliang Jiang
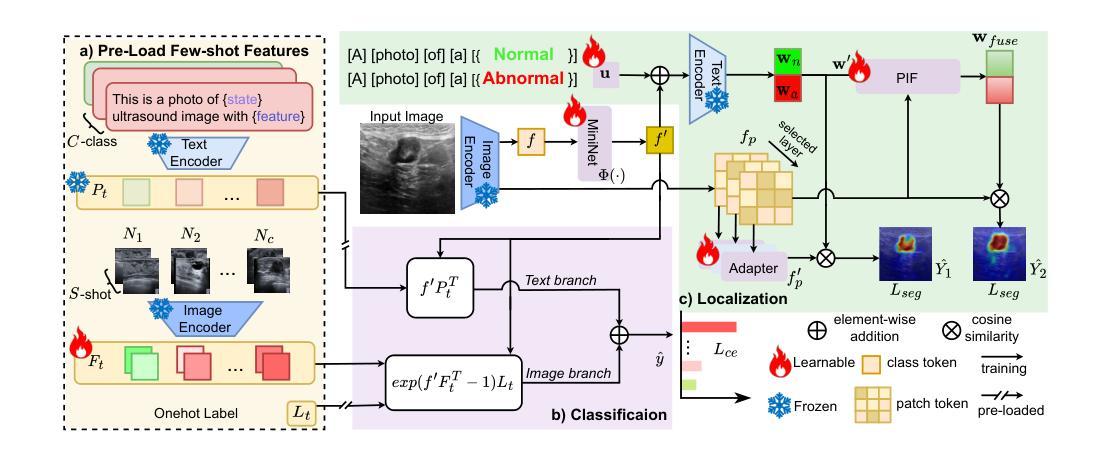
Precise anomaly detection in medical images is critical for clinical decision-making. While recent unsupervised or semi-supervised anomaly detection methods trained on large-scale normal data show promising results, they lack fine-grained differentiation, such as benign vs. malignant tumors. Additionally, ultrasound (US) imaging is highly sensitive to devices and acquisition parameter variations, creating significant domain gaps in the resulting US images. To address these challenges, we propose UltraAD, a vision-language model (VLM)-based approach that leverages few-shot US examples for generalized anomaly localization and fine-grained classification. To enhance localization performance, the image-level token of query visual prototypes is first fused with learnable text embeddings. This image-informed prompt feature is then further integrated with patch-level tokens, refining local representations for improved accuracy. For fine-grained classification, a memory bank is constructed from few-shot image samples and corresponding text descriptions that capture anatomical and abnormality-specific features. During training, the stored text embeddings remain frozen, while image features are adapted to better align with medical data. UltraAD has been extensively evaluated on three breast US datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both lesion localization and fine-grained medical classification. The code will be released upon acceptance.
医学图像中的精确异常检测对于临床决策至关重要。虽然最近的无监督或半监督异常检测方法在大规模正常数据训练上显示出有希望的结果,但它们缺乏精细的差异化,如良性与恶性肿瘤之间的区分。此外,超声(US)成像对设备和采集参数的变化高度敏感,导致超声图像存在显著的域差距。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了UltraAD,这是一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的方法,它利用少量的超声示例进行通用异常定位和精细分类。为了提高定位性能,首先融合查询视觉原型的图像级令牌和可学习的文本嵌入。然后,将图像信息提示特征与补丁级令牌进一步集成,细化局部表示以提高准确性。对于精细分类,从少量图像样本和相应的文本描述中构建了一个内存银行,以捕获特定的解剖和异常特征。在训练过程中,存储的文本嵌入保持不变,而图像特征更好地适应医学数据。UltraAD在三个乳腺超声数据集上进行了广泛评估,在病灶定位和精细医学分类方面均优于最新方法。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像精准检测对临床决策至关重要。针对现有方法的不足,如缺乏精细粒度区分和超声图像领域差异的挑战,我们提出UltraAD模型,采用视觉语言模型(VLM)结合少量超声图像样本进行异常定位与精细分类。通过融合图像级令牌与可学习文本嵌入,增强定位性能。此外,利用记忆库存储少数图像样本及其文本描述,进行精细分类。在三个乳腺超声数据集上的评估表明,UltraAD在病灶定位和精细分类方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像精准检测对临床决策的重要性。
- 当前监督或无监督方法在医学图像异常检测上的不足,尤其是在精细分类方面的挑战。
- UltraAD模型采用视觉语言模型(VLM)解决上述问题。
- UltraAD通过融合图像级令牌与文本嵌入增强异常定位性能。
- 利用记忆库进行精细分类,通过存储少数图像样本及其文本描述来捕捉特定解剖结构和异常特征。
- UltraAD在乳腺超声数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

ReCoGNet: Recurrent Context-Guided Network for 3D MRI Prostate Segmentation
Authors:Ahmad Mustafa, Reza Rastegar, Ghassan AlRegib
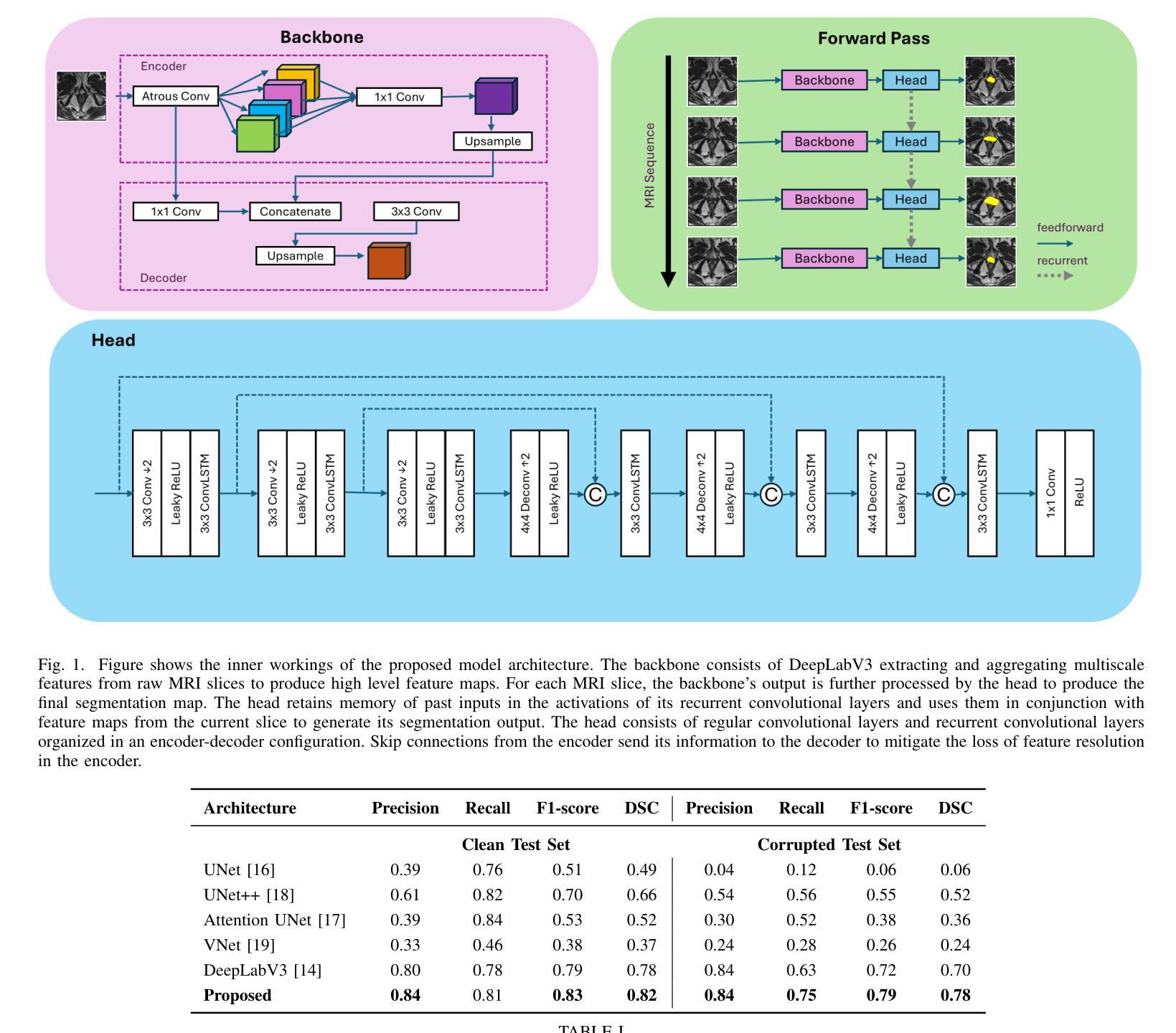
Prostate gland segmentation from T2-weighted MRI is a critical yet challenging task in clinical prostate cancer assessment. While deep learning-based methods have significantly advanced automated segmentation, most conventional approaches-particularly 2D convolutional neural networks (CNNs)-fail to leverage inter-slice anatomical continuity, limiting their accuracy and robustness. Fully 3D models offer improved spatial coherence but require large amounts of annotated data, which is often impractical in clinical settings. To address these limitations, we propose a hybrid architecture that models MRI sequences as spatiotemporal data. Our method uses a deep, pretrained DeepLabV3 backbone to extract high-level semantic features from each MRI slice and a recurrent convolutional head, built with ConvLSTM layers, to integrate information across slices while preserving spatial structure. This combination enables context-aware segmentation with improved consistency, particularly in data-limited and noisy imaging conditions. We evaluate our method on the PROMISE12 benchmark under both clean and contrast-degraded test settings. Compared to state-of-the-art 2D and 3D segmentation models, our approach demonstrates superior performance in terms of precision, recall, Intersection over Union (IoU), and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), highlighting its potential for robust clinical deployment.
前列腺T2加权MRI的腺体分割是临床前列腺癌评估中一项重要且具有挑战性的任务。虽然基于深度学习的方法已经极大地推动了自动分割的进展,但大多数传统方法,特别是二维卷积神经网络(CNN),无法利用切片间的解剖连续性,从而限制了其准确性和稳健性。完全三维模型提供了更好的空间一致性,但需要大量标注数据,这在临床环境中往往不切实际。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种混合架构,该架构将MRI序列建模为时空数据。我们的方法使用深度预训练DeepLabV[精】网络从每个MRI切片中提取高级语义特征,并使用带有ConvLSTM层的递归卷积头来整合切片信息,同时保留空间结构。这种组合可实现具有一致性的上下文感知分割,特别是在数据有限和图像噪声较大的情况下更是如此。我们在干净和对比度降低的测试设置下使用PROMISE12基准数据集评估了我们的方法。与最先进的二维和三维分割模型相比,我们的方法在精确度、召回率、交并比(IoU)和Dice相似系数(DSC)方面表现出卓越的性能,突显了其在临床部署中的稳健潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种混合架构用于前列腺MRI图像的分割,该架构将MRI序列视为时空数据。它结合了DeepLabV3的深度学习特性和ConvLSTM层的卷积头,能在数据有限和噪声干扰的情况下实现上下文感知的分割,提高了分割的一致性和准确性。在PROMISE12基准测试下,该方法相较于其他先进的二维和三维分割模型表现出更高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 前列腺MRI图像分割是临床前列腺癌评估中的关键任务,但具有挑战性。
- 深度学习已显著改善自动化分割方法,但常规方法仍有限制。
- 完全三维模型能提高空间连贯性,但需要大量标注数据,不实用于临床环境。
- 本文提出了一种混合架构,将MRI序列视为时空数据。
- 该架构使用DeepLabV3提取高层次的语义特征,并结合ConvLSTM层整合切片信息,保持空间结构。
- 此方法能在数据有限和噪声干扰的情况下实现上下文感知的分割。
点此查看论文截图

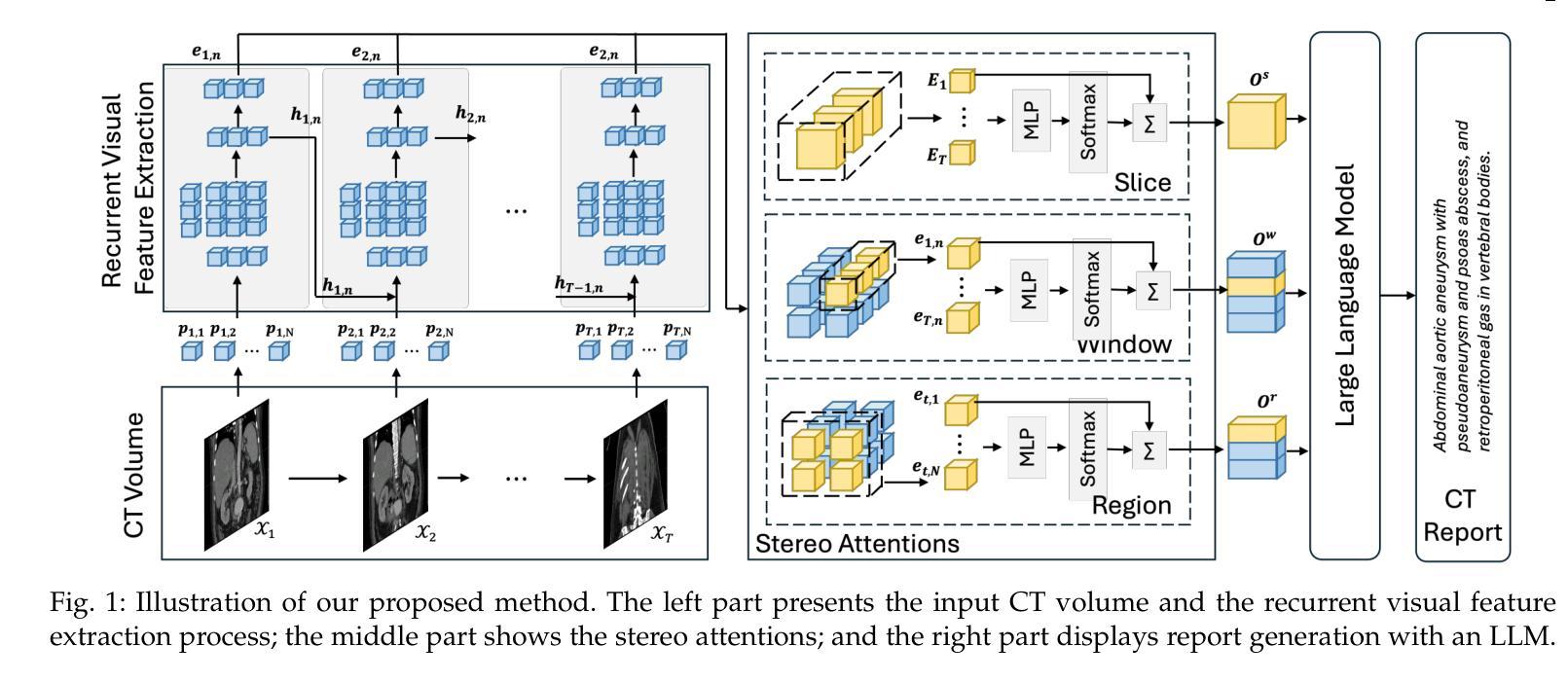
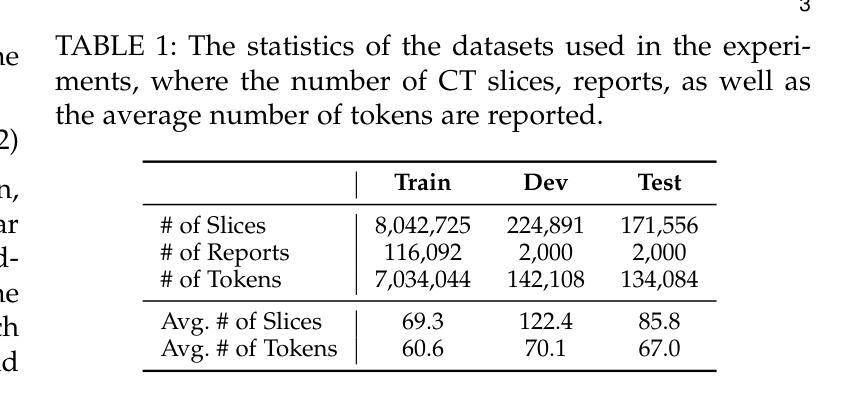
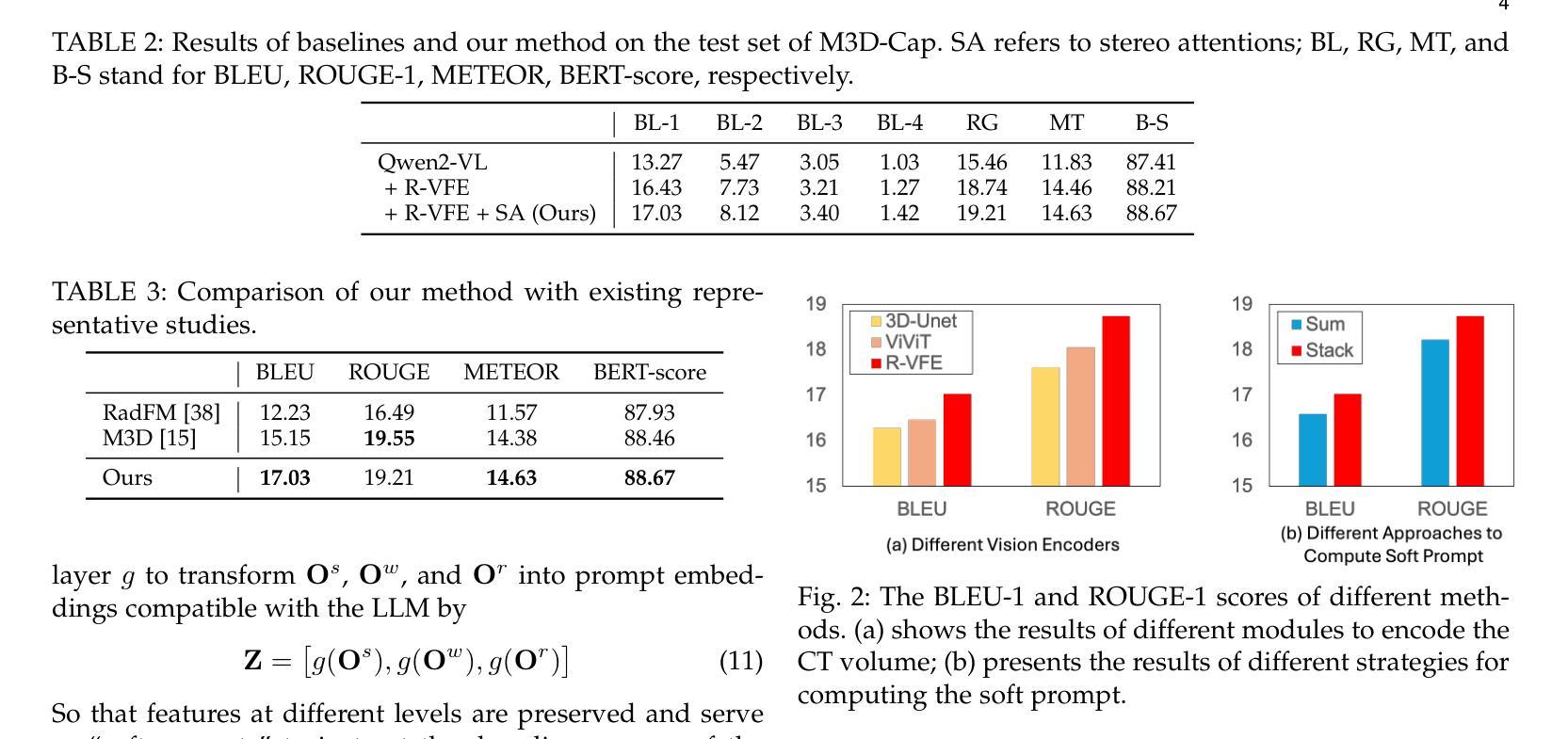
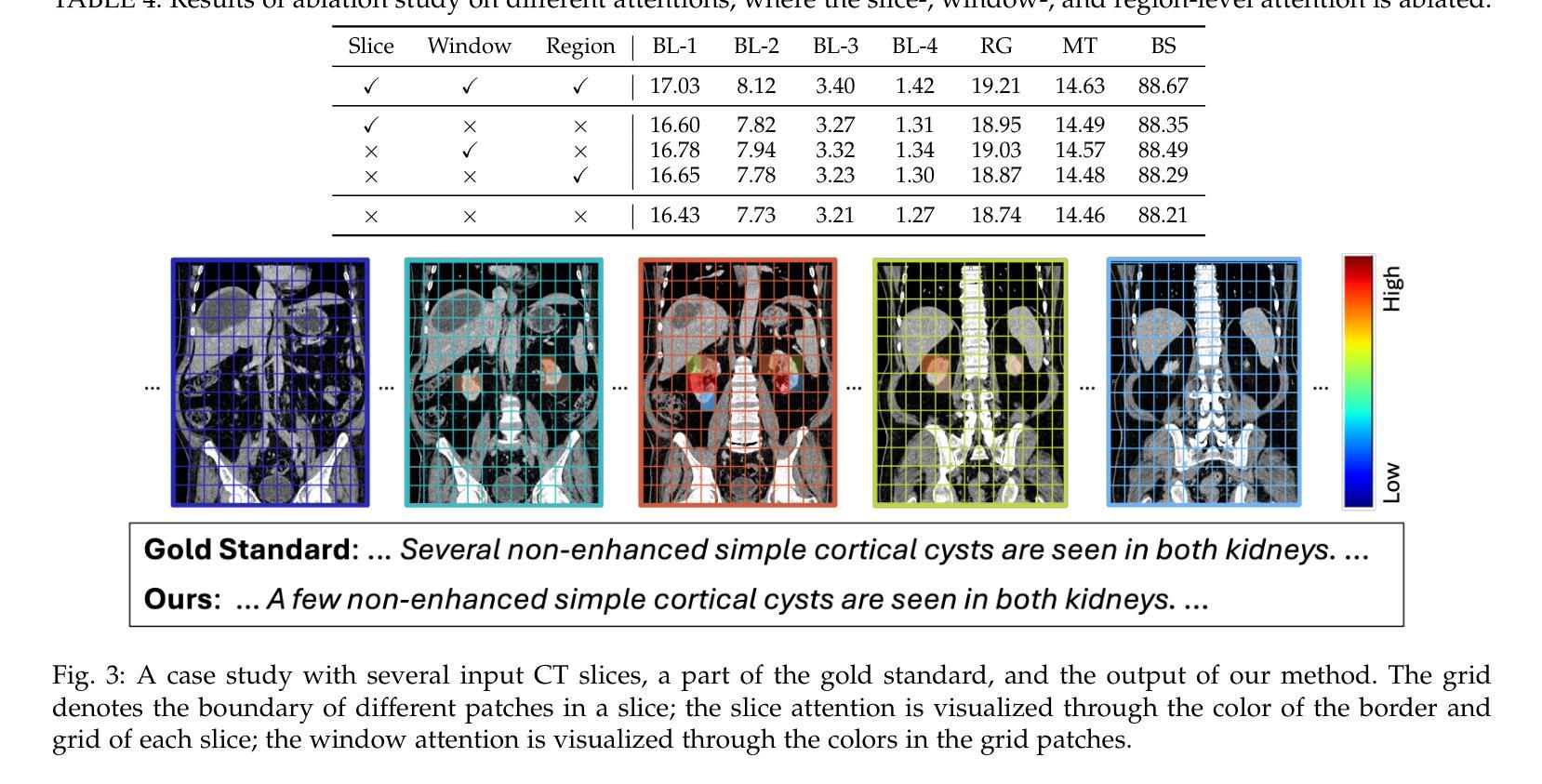
Recurrent Visual Feature Extraction and Stereo Attentions for CT Report Generation
Authors:Yuanhe Tian, Lei Mao, Yan Song
Generating reports for computed tomography (CT) images is a challenging task, while similar to existing studies for medical image report generation, yet has its unique characteristics, such as spatial encoding of multiple images, alignment between image volume and texts, etc. Existing solutions typically use general 2D or 3D image processing techniques to extract features from a CT volume, where they firstly compress the volume and then divide the compressed CT slices into patches for visual encoding. These approaches do not explicitly account for the transformations among CT slices, nor do they effectively integrate multi-level image features, particularly those containing specific organ lesions, to instruct CT report generation (CTRG). In considering the strong correlation among consecutive slices in CT scans, in this paper, we propose a large language model (LLM) based CTRG method with recurrent visual feature extraction and stereo attentions for hierarchical feature modeling. Specifically, we use a vision Transformer to recurrently process each slice in a CT volume, and employ a set of attentions over the encoded slices from different perspectives to selectively obtain important visual information and align them with textual features, so as to better instruct an LLM for CTRG. Experiment results and further analysis on the benchmark M3D-Cap dataset show that our method outperforms strong baseline models and achieves state-of-the-art results, demonstrating its validity and effectiveness.
生成计算机断层扫描(CT)图像的报告是一项具有挑战性的任务。虽然它与现有的医学图像报告生成研究相似,但它具有独特的特性,例如多个图像的空间编码、图像体积与文本之间的对齐等。现有解决方案通常使用通用的二维或三维图像处理技术从CT体积中提取特征,其中他们首先压缩体积,然后将压缩的CT切片分成斑块进行视觉编码。这些方法并没有明确考虑CT切片之间的转换,也没有有效地整合多级图像特征,特别是包含特定器官病变的特征,以指导CT报告生成(CTRG)。考虑到CT扫描中连续切片之间的强烈相关性,本文提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的CTRG方法,该方法具有循环视觉特征提取和立体注意力,用于分层特征建模。具体来说,我们使用视觉Transformer循环处理CT体积中的每个切片,并通过对不同视角的编码切片集注意力来有选择地获取重要的视觉信息,并将其与文本特征对齐,以更好地指导LLM进行CTRG。在基准数据集M3D-Cap上的实验结果和进一步的分析表明,我们的方法优于强大的基线模型,并达到了最先进的性能,证明了其有效性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该文针对计算机断层扫描(CT)图像报告生成任务的独特性,提出一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法,该方法结合递归视觉特征提取和立体注意力进行分层特征建模。通过使用视觉Transformer递归处理CT体积中的每个切片,并从不同角度对编码切片进行注意力集中,选择性获取重要视觉信息并与文本特征对齐,以更好地指导LLM进行CT报告生成。实验结果表明,该方法在M3D-Cap数据集上优于强基线模型,达到先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- CT图像报告生成具有挑战性,需考虑空间编码和多图像对齐等独特特性。
- 现有解决方案通常采用一般的2D或3D图像处理技术从CT体积中提取特征,但缺乏对不同切片间变换的显式考虑以及多级别图像特征的整合。
- 文中提出一种基于大型语言模型的CT报告生成方法,结合递归视觉特征提取和立体注意力进行分层特征建模。
- 使用视觉Transformer递归处理CT体积中的每个切片,以获取更全面的视觉信息。
- 通过不同角度的注意力机制,对编码切片进行注意力集中,选择性获取重要视觉信息并与文本特征对齐。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在M3D-Cap数据集上性能优越,达到先进水平。
点此查看论文截图

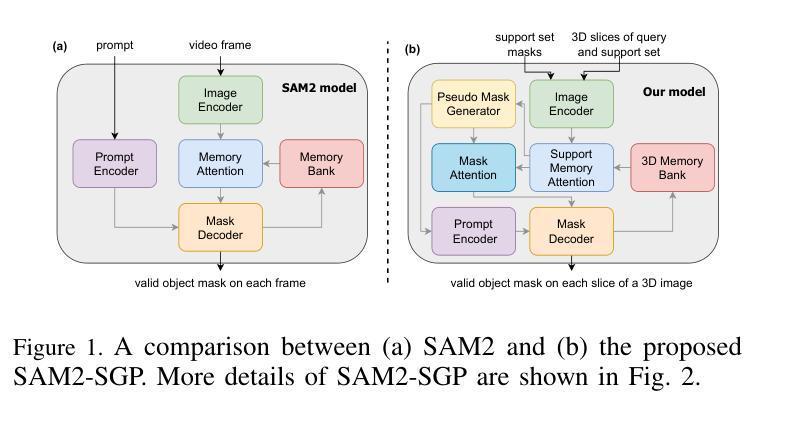
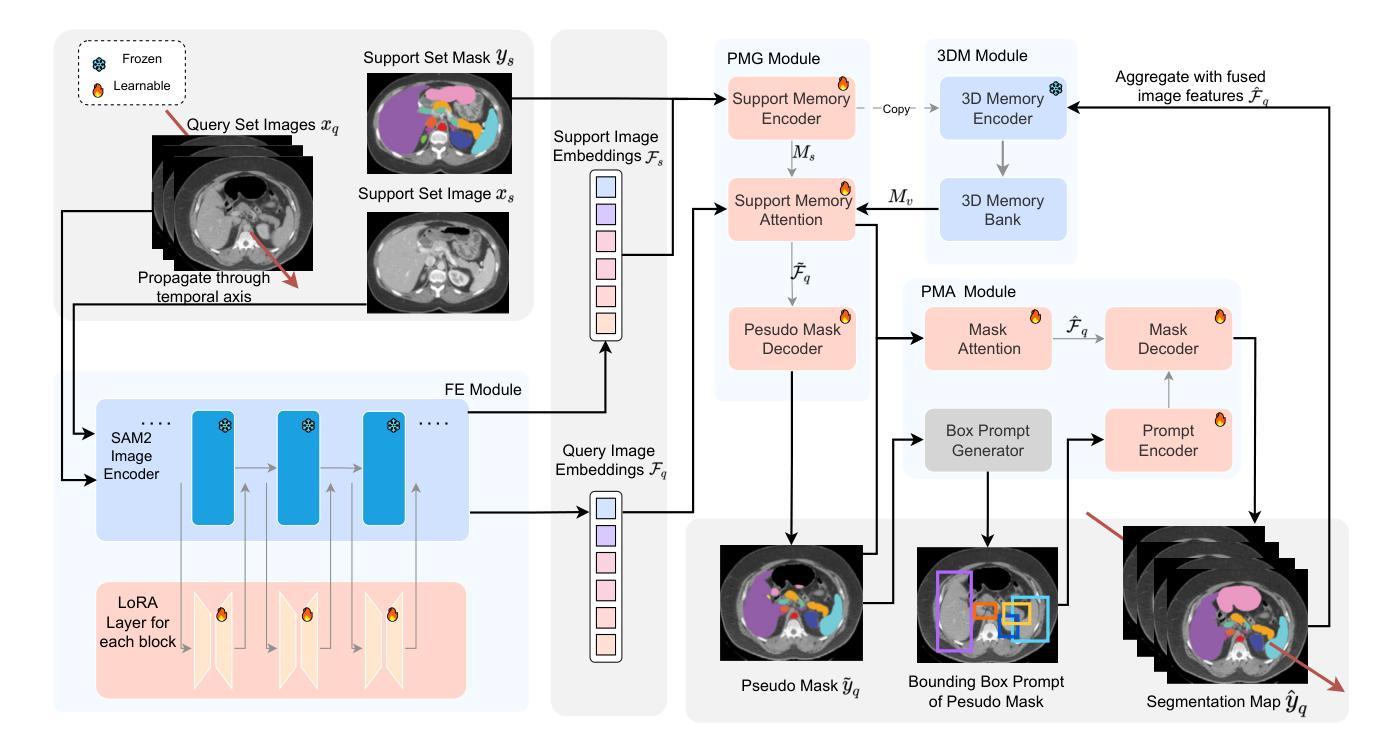
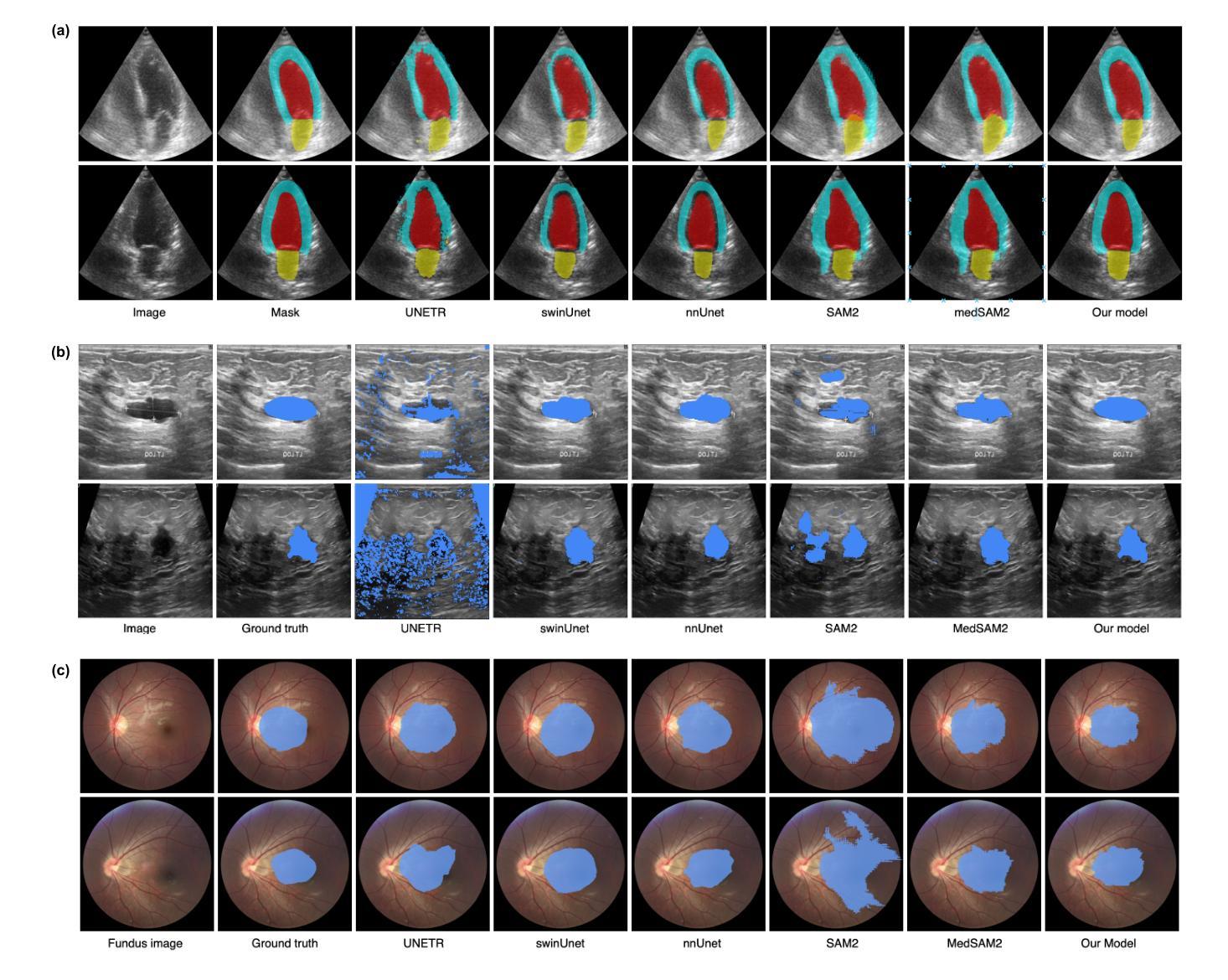
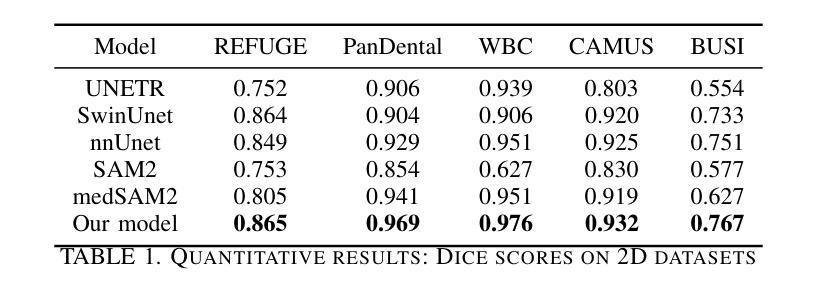
SAM2-SGP: Enhancing SAM2 for Medical Image Segmentation via Support-Set Guided Prompting
Authors:Yang Xing, Jiong Wu, Yuheng Bu, Kuang Gong
Although new vision foundation models such as Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) have significantly enhanced zero-shot image segmentation capabilities, reliance on human-provided prompts poses significant challenges in adapting SAM2 to medical image segmentation tasks. Moreover, SAM2’s performance in medical image segmentation was limited by the domain shift issue, since it was originally trained on natural images and videos. To address these challenges, we proposed SAM2 with support-set guided prompting (SAM2-SGP), a framework that eliminated the need for manual prompts. The proposed model leveraged the memory mechanism of SAM2 to generate pseudo-masks using image-mask pairs from a support set via a Pseudo-mask Generation (PMG) module. We further introduced a novel Pseudo-mask Attention (PMA) module, which used these pseudo-masks to automatically generate bounding boxes and enhance localized feature extraction by guiding attention to relevant areas. Furthermore, a low-rank adaptation (LoRA) strategy was adopted to mitigate the domain shift issue. The proposed framework was evaluated on both 2D and 3D datasets across multiple medical imaging modalities, including fundus photography, X-ray, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and ultrasound. The results demonstrated a significant performance improvement over state-of-the-art models, such as nnUNet and SwinUNet, as well as foundation models, such as SAM2 and MedSAM2, underscoring the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/astlian9/SAM_Support.
尽管Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)等新型视觉基础模型在零样本图像分割能力方面有了显著提升,但它们在医学图像分割任务中依赖人工提示,这带来了很大的挑战。此外,由于SAM2最初是在自然图像和视频上进行训练的,因此在医学图像分割方面存在领域偏移问题,限制了其性能。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了具有支持集引导提示的SAM2(SAM2-SGP)框架,该框架消除了对人工提示的需求。所提出模型利用SAM2的记忆机制,通过伪掩码生成(PMG)模块,使用支持集中的图像-掩码对生成伪掩码。我们还引入了一种新颖的伪掩码注意力(PMA)模块,该模块使用这些伪掩码自动生成边界框,并通过引导注意力关注相关区域来增强局部特征提取。此外,还采用了低秩自适应(LoRA)策略来缓解领域偏移问题。所提出的框架在多个医学成像模态的二维和三维数据集上进行了评估,包括眼底摄影、X射线、计算机断层扫描(CT)、磁共振成像(MRI)、正电子发射断层扫描(PET)和超声。结果表明,与最新模型(如nnUNet和SwinUNet)以及基础模型(如SAM2和MedSAM2)相比,所提出的方法在性能上取得了显著提升,这突显了该方法的有效性。我们的代码已在https://github.com/astlian9/SAM_Support公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)的新视觉基础模型虽然大幅提升了零样本图像分割能力,但在医学图像分割任务中仍面临依赖人工提示的挑战以及领域偏移问题。为解决这个问题,我们提出了SAM2支持集引导提示(SAM2-SGP)框架,无需手动提示即可生成伪掩膜,通过伪掩膜生成(PMG)模块利用支持集中的图像-掩膜对,并通过伪掩膜注意力(PMA)模块自动生成边界框,增强局部特征提取。同时采用低秩适应(LoRA)策略缓解领域偏移问题。在多个医学成像模态的二维和三维数据集上评估表明,该框架较nnUNet、SwinUNet等前沿模型及SAM2等基础模型有显著性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- SAM2在医学图像分割中面临人工提示和领域偏移的挑战。
- SAM2-SGP框架通过支持集自动生成伪掩膜,消除对人工提示的依赖。
- 伪掩膜生成(PMG)模块利用图像-掩膜对产生伪掩膜。
- 伪掩膜注意力(PMA)模块自动生成边界框,增强局部特征提取。
- 低秩适应(LoRA)策略用于缓解领域偏移问题。
- 在多种医学成像模态的数据集上评估,显示SAM2-SGP性能显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

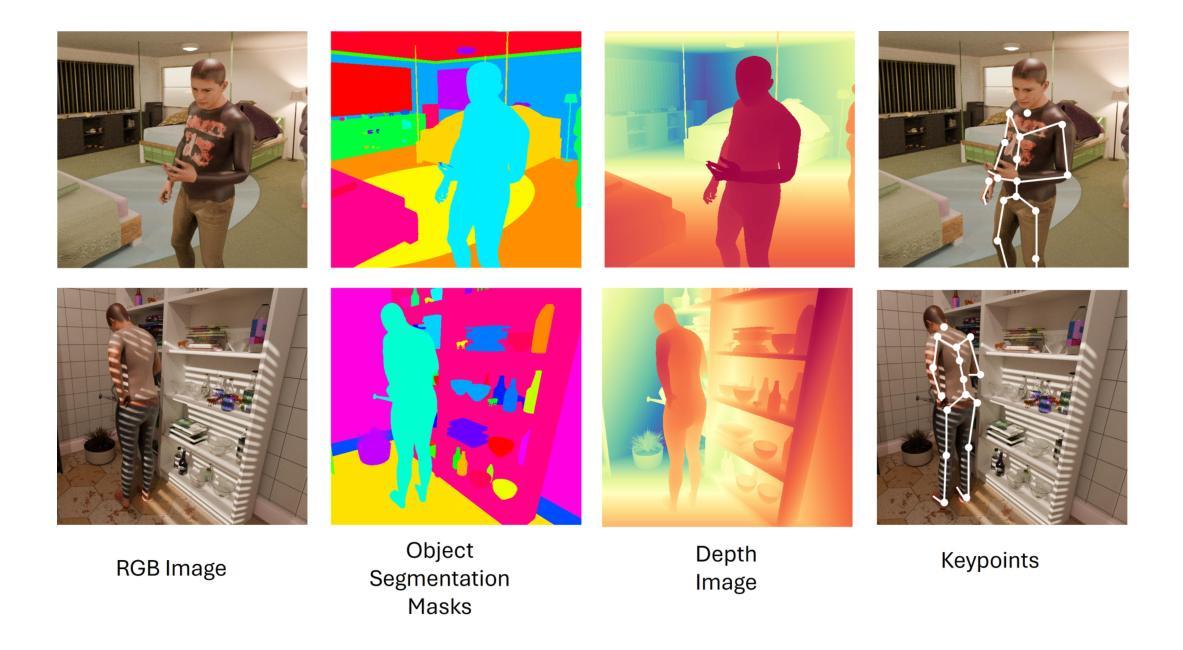
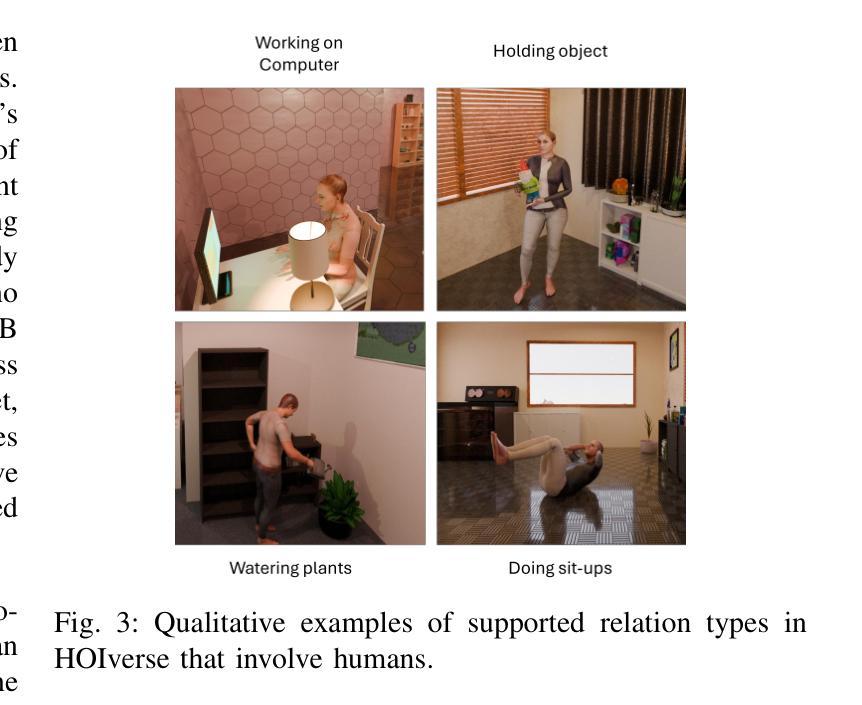
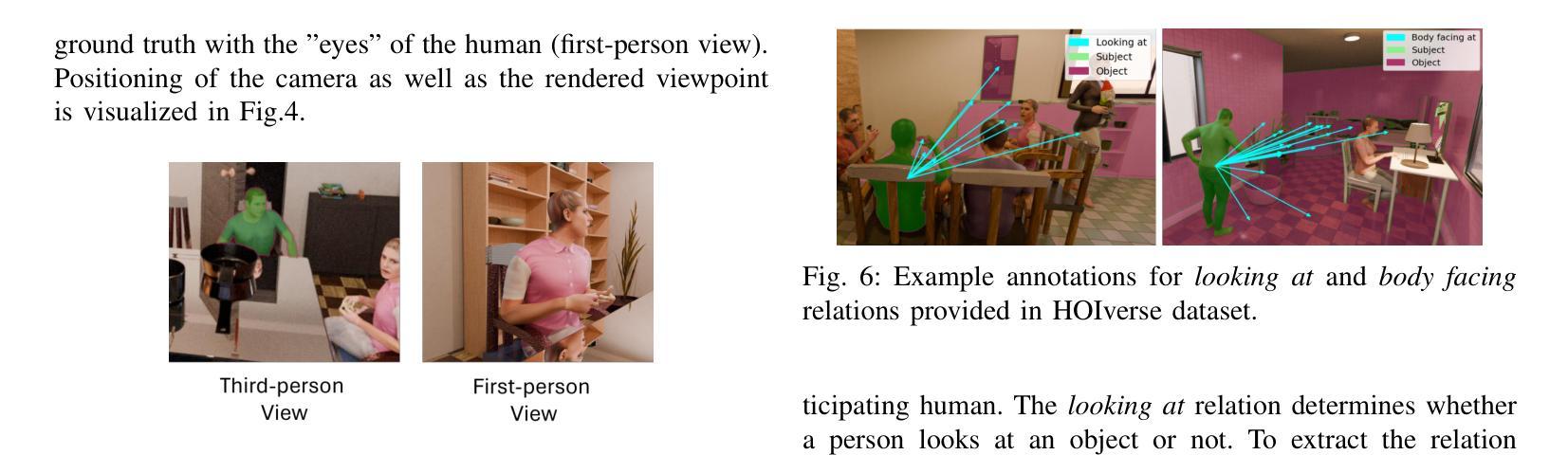
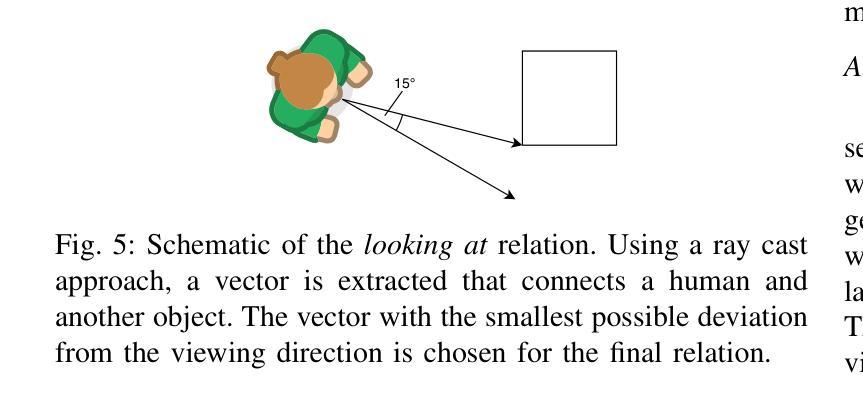
HOIverse: A Synthetic Scene Graph Dataset With Human Object Interactions
Authors:Mrunmai Vivek Phatak, Julian Lorenz, Nico Hörmann, Jörg Hähner, Rainer Lienhart
When humans and robotic agents coexist in an environment, scene understanding becomes crucial for the agents to carry out various downstream tasks like navigation and planning. Hence, an agent must be capable of localizing and identifying actions performed by the human. Current research lacks reliable datasets for performing scene understanding within indoor environments where humans are also a part of the scene. Scene Graphs enable us to generate a structured representation of a scene or an image to perform visual scene understanding. To tackle this, we present HOIverse a synthetic dataset at the intersection of scene graph and human-object interaction, consisting of accurate and dense relationship ground truths between humans and surrounding objects along with corresponding RGB images, segmentation masks, depth images and human keypoints. We compute parametric relations between various pairs of objects and human-object pairs, resulting in an accurate and unambiguous relation definitions. In addition, we benchmark our dataset on state-of-the-art scene graph generation models to predict parametric relations and human-object interactions. Through this dataset, we aim to accelerate research in the field of scene understanding involving people.
当人类和机器人代理共存于同一环境中时,场景理解对于代理执行导航和规划等各种下游任务变得至关重要。因此,代理必须具备定位并识别人类所执行动作的能力。当前的研究缺乏可靠的室内环境数据集来进行场景理解,而人类也是场景的一部分。场景图使我们能够生成场景或图像的结构化表示来进行视觉场景理解。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了HOIverse,这是一个场景图和人机交互之间的合成数据集,包含了人类与周围物体之间准确且密集的关系真实情况,以及相应的RGB图像、分割掩膜、深度图像和人类关键点。我们计算了各物体对以及人机交互对之间的参数关系,从而得到准确且明确的关联定义。此外,我们在最先进的场景图生成模型上对我们的数据集进行了基准测试,以预测参数关系和人机交互。通过此数据集,我们旨在加速涉及人类的场景理解领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
室内环境下人类与机器人协同工作时,场景理解至关重要。当前缺乏可靠数据集支持室内环境下人类参与的场景理解。HOIverse数据集结合场景图和人类物体交互,包含精准密集关系信息以及对应RGB图像等多媒体信息。数据集通过计算物体和人与物体间的参数关系,提供清晰的关系定义,并支持场景图的生成模型预测和人与物体的交互。此数据集旨在加速涉及人类的场景理解研究。
Key Takeaways
- 室内环境下人类与机器人协同工作的场景中,场景理解是完成下游任务如导航和规划的关键。
- 当前缺乏针对室内环境且包含人类在内的可靠数据集支持场景理解研究。
- HOIverse数据集结合了场景图和人类物体交互,提供结构化场景表示。
- HOIverse包含精准密集的关系信息以及多媒体数据如RGB图像等。
- 数据集通过计算参数关系提供清晰的关系定义。
- 数据集支持场景图的生成模型预测和人与物体的交互预测。
点此查看论文截图


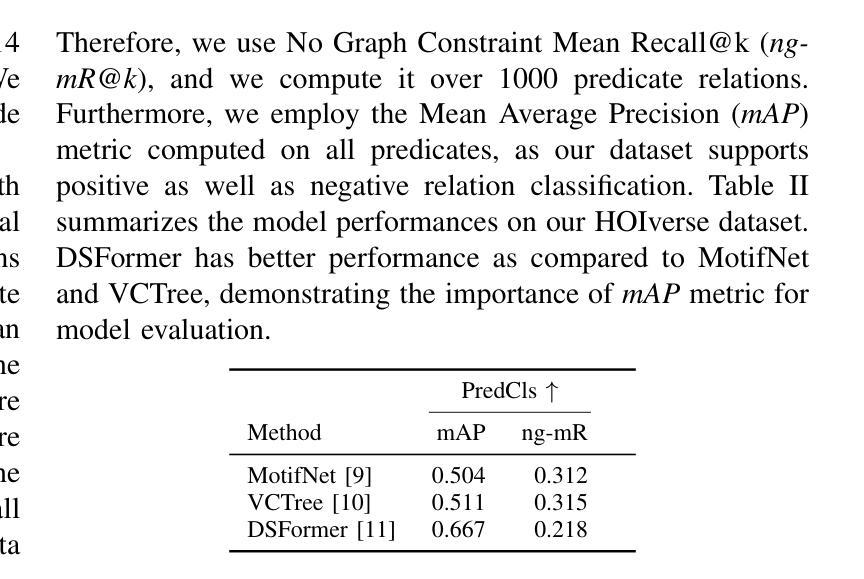
Vision Transformer-Based Time-Series Image Reconstruction for Cloud-Filling Applications
Authors:Lujun Li, Yiqun Wang, Radu State
Cloud cover in multispectral imagery (MSI) poses significant challenges for early season crop mapping, as it leads to missing or corrupted spectral information. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data, which is not affected by cloud interference, offers a complementary solution, but lack sufficient spectral detail for precise crop mapping. To address this, we propose a novel framework, Time-series MSI Image Reconstruction using Vision Transformer (ViT), to reconstruct MSI data in cloud-covered regions by leveraging the temporal coherence of MSI and the complementary information from SAR from the attention mechanism. Comprehensive experiments, using rigorous reconstruction evaluation metrics, demonstrate that Time-series ViT framework significantly outperforms baselines that use non-time-series MSI and SAR or time-series MSI without SAR, effectively enhancing MSI image reconstruction in cloud-covered regions.
在多光谱影像(MSI)中,云覆盖对早期季节作物映射带来了重大挑战,因为它会导致光谱信息丢失或损坏。合成孔径雷达(SAR)数据不受云层干扰的影响,提供了一个补充解决方案,但在精确作物映射方面缺乏足够的光谱细节。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型框架,即利用视觉转换器(ViT)进行时间序列MSI图像重建,通过利用MSI的时间连贯性和来自注意力机制的SAR的补充信息,重建云层覆盖区域中的MSI数据。使用严格的重建评估指标的全面实验表明,时间序列ViT框架显著优于使用非时间序列MSI和SAR或仅使用时间序列MSI的基线方法,有效地提高了云层覆盖区域中MSI图像的重建效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted as a conference paper at the 2025 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS)
Summary
多光谱影像中的云层覆盖对早期农作物制图带来挑战,缺失或损坏的谱信息影响精准度。合成孔径雷达数据不受云层干扰,提供互补解决方案,但缺乏足够的谱细节用于精确农作物制图。为此,我们提出一种新型框架——基于视觉转换器的时序多光谱影像重建(Time-series MSI Image Reconstruction using Vision Transformer,简称ViT),利用多光谱影像的时序连贯性和合成孔径雷达数据的注意力机制中的互补信息,重建云层覆盖区域的多光谱影像数据。实验证明,时序ViT框架显著优于仅使用非时序多光谱影像和SAR或仅使用时序多光谱影像的基线方法,有效提高云层覆盖区域的多光谱影像重建效果。
Key Takeaways
- 云层覆盖在多光谱影像中会对早期农作物制图带来挑战,导致谱信息缺失或损坏。
- 合成孔径雷达数据不受云层干扰,但缺乏足够的谱细节,无法精准进行农作物制图。
- 提出了基于视觉转换器的时序多光谱影像重建框架(Time-series MSI Image Reconstruction using Vision Transformer,简称ViT)。
- 该框架利用多光谱影像的时序连贯性和合成孔径雷达数据的注意力机制中的互补信息。
- 时序ViT框架在重建云层覆盖区域的多光谱影像数据方面表现出显著优势。
- 严谨的实验和重建评估指标证明,时序ViT框架优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

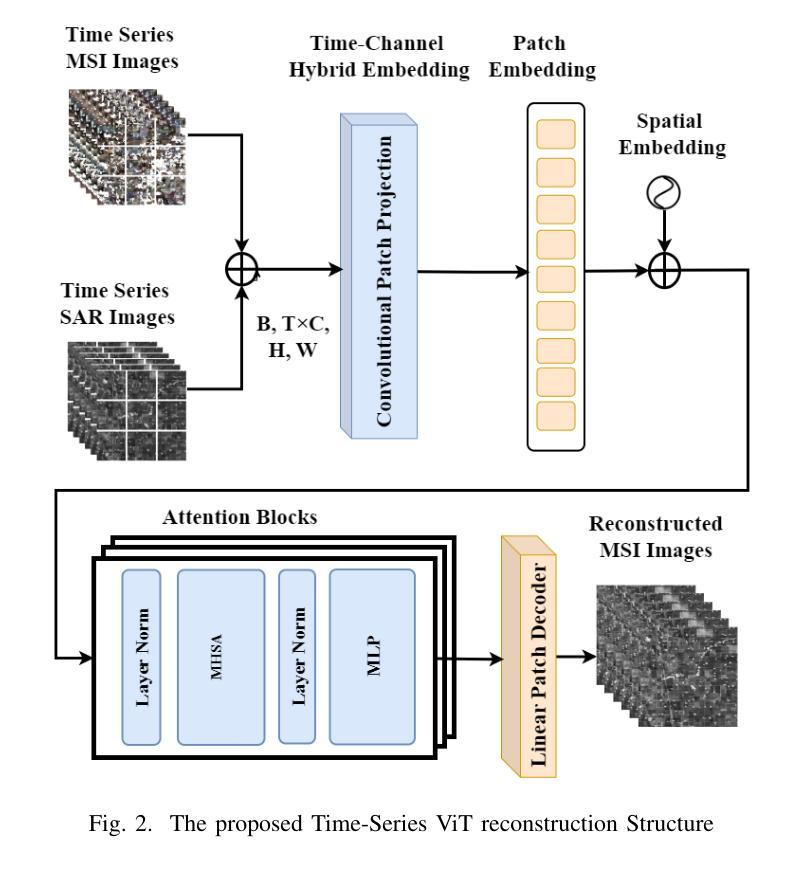
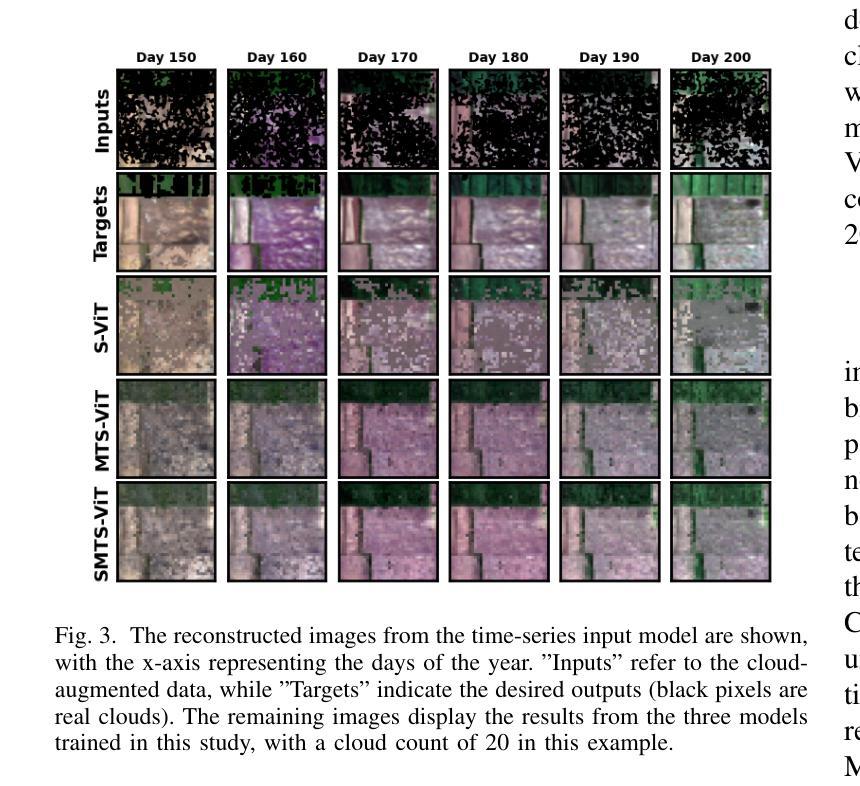
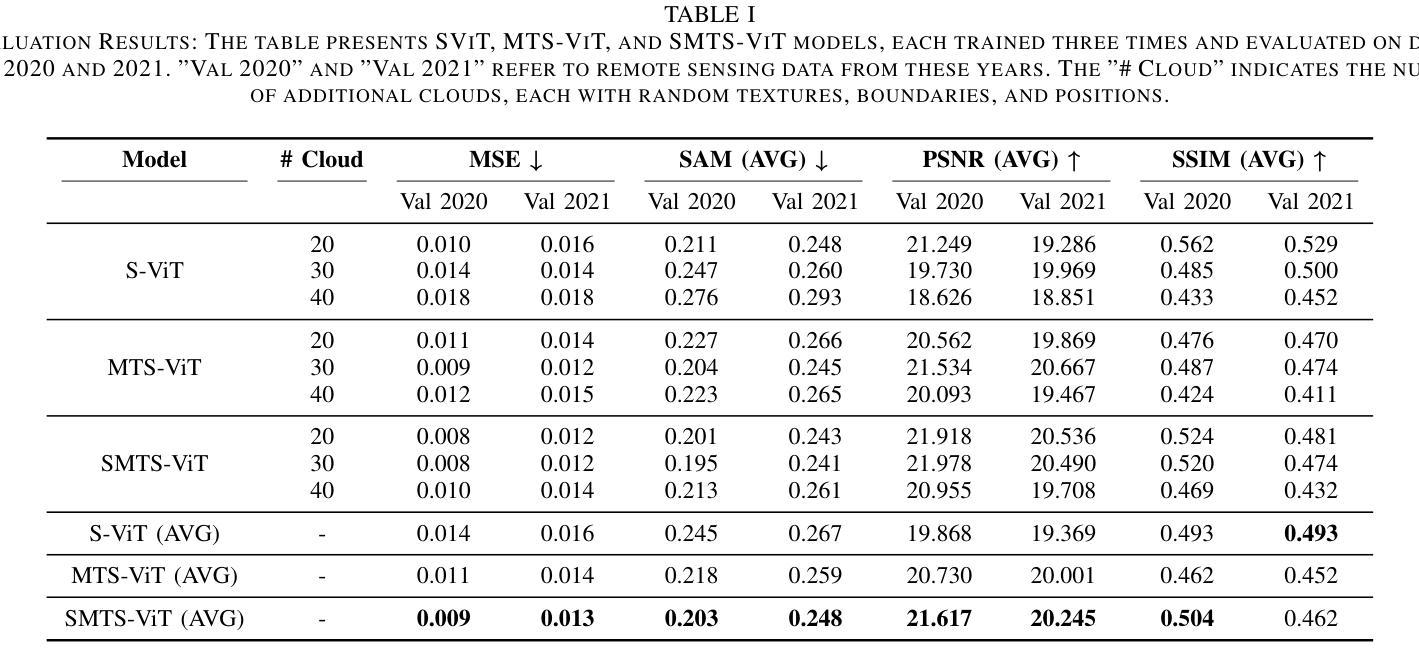
Learning from Anatomy: Supervised Anatomical Pretraining (SAP) for Improved Metastatic Bone Disease Segmentation in Whole-Body MRI
Authors:Joris Wuts, Jakub Ceranka, Nicolas Michoux, Frédéric Lecouvet, Jef Vandemeulebroucke
The segmentation of metastatic bone disease (MBD) in whole-body MRI (WB-MRI) is a challenging problem. Due to varying appearances and anatomical locations of lesions, ambiguous boundaries, and severe class imbalance, obtaining reliable segmentations requires large, well-annotated datasets capturing lesion variability. Generating such datasets requires substantial time and expertise, and is prone to error. While self-supervised learning (SSL) can leverage large unlabeled datasets, learned generic representations often fail to capture the nuanced features needed for accurate lesion detection. In this work, we propose a Supervised Anatomical Pretraining (SAP) method that learns from a limited dataset of anatomical labels. First, an MRI-based skeletal segmentation model is developed and trained on WB-MRI scans from healthy individuals for high-quality skeletal delineation. Then, we compare its downstream efficacy in segmenting MBD on a cohort of 44 patients with metastatic prostate cancer, against both a baseline random initialization and a state-of-the-art SSL method. SAP significantly outperforms both the baseline and SSL-pretrained models, achieving a normalized surface Dice of 0.76 and a Dice coefficient of 0.64. The method achieved a lesion detection F2 score of 0.44, improving on 0.24 (baseline) and 0.31 (SSL). When considering only clinically relevant lesions larger than 1~ml, SAP achieves a detection sensitivity of 100% in 28 out of 32 patients. Learning bone morphology from anatomy yields an effective and domain-relevant inductive bias that can be leveraged for the downstream segmentation task of bone lesions. All code and models are made publicly available.
全身MRI(WB-MRI)中转移性骨病(MBD)的分割是一个具有挑战性的问题。由于病变的外观和解剖位置各异,边界模糊以及类别严重不平衡,要获得可靠的分割结果,需要捕捉病变变异的大而标注良好的数据集。生成这样的数据集需要大量的时间和专业知识,并且容易出错。虽然自监督学习(SSL)可以利用大量未标记的数据集,但所学的通用表示通常难以捕捉准确的病变检测所需的细微特征。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种称为监督解剖预训练(SAP)的方法,该方法从有限的解剖标签数据集中学习。首先,我们开发了一个基于MRI的骨骼分割模型,并使用来自健康个体的WB-MRI扫描进行训练,以进行高质量的骨骼描绘。然后,我们在一组患有转移性前列腺癌的44名患者中,将其下游对MBD分割的有效性与基线随机初始化和最先进的SSL方法进行了比较。SAP显著优于基线模型和SSL预训练模型,实现了归一化表面Dice系数为0.76和Dice系数为0.64。该方法在病变检测方面的F2分数为0.44,优于基线(0.24)和SSL(0.31)。在考虑体积大于1毫升的临床相关病变时,SAP在32名患者中的28名达到了100%的检测灵敏度。从解剖学中学习骨骼形态为下游骨病变分割任务提供了一个有效且相关的先验知识偏见。所有代码和模型都已公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This preprint is currently under review at Computers in Biology and Medicine (Elsevier). This version has not been peer-reviewed
摘要
全身MRI(WB-MRI)中转移性骨病(MBD)的分割是一个具有挑战性的问题。由于病变的外观和位置、边界模糊以及严重的类别不平衡等问题,获得可靠的分割结果需要大规模、标注良好的数据集来捕捉病变的变异性。生成此类数据集需要大量时间和专业知识,并且容易出错。虽然自监督学习(SSL)可以利用大量未标记的数据集,但学到的通用表示通常难以捕捉准确的病变检测所需的细微特征。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种名为Supervised Anatomical Pretraining(SAP)的方法,该方法从有限的解剖标签数据集中学习。首先,开发了一个基于MRI的骨骼分割模型,在来自健康个体的WB-MRI扫描上进行训练,以进行高质量的骨骼描绘。然后,我们将其在患有转移性前列腺癌的44例患者队列中对MBD分割的下游功效与基线随机初始化和最先进的SSL方法进行了比较。SAP显著优于基线模型和SSL预训练模型,达到表面Dice归一化系数为0.76和Dice系数为0.64。该方法在病变检测F2分数方面达到0.44,优于基线(0.24)和SSL(0.31)。当仅考虑大于1毫升的临床相关病变时,SAP在28名患者中的检测灵敏度达到百分之百。从骨骼形态中学习解剖结构为下游的骨骼病变分割任务提供了一个有效的、领域相关的先验知识。所有代码和模型均公开发布。
要点总结
- MBD在WB-MRI中的分割是一个具有挑战性的问题,需要大规模、标注良好的数据集来准确分割病变。
- SAP方法通过利用有限的解剖标签数据集进行预训练,以提高MBD分割的准确性。
- SAP方法显著优于基线和SSL预训练模型,在Dice系数和F2分数方面取得了更好的结果。
- SAP方法对临床相关病变的检测具有较高的灵敏度和准确性。
- SAP方法公开所有代码和模型,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
- 学习骨骼形态和利用解剖结构信息有助于提高MBD分割的准确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

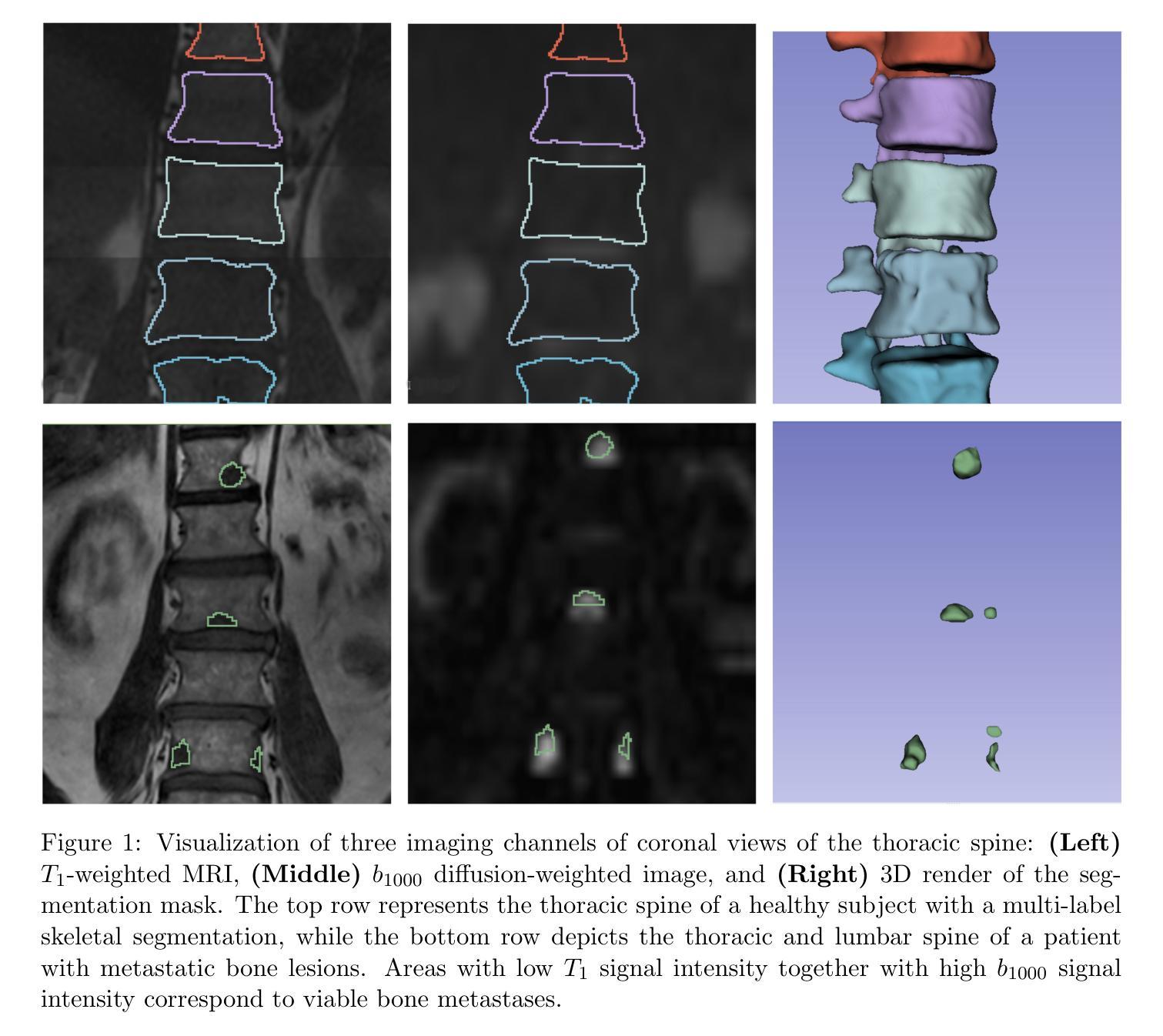
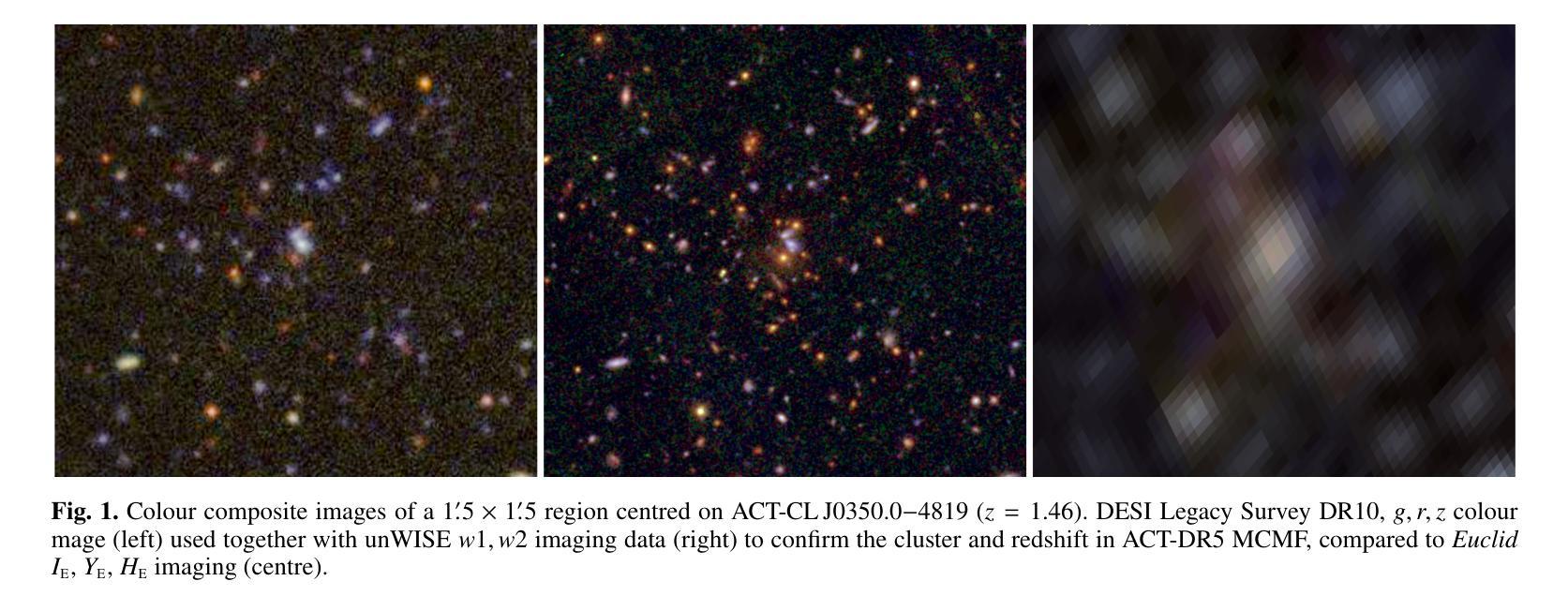
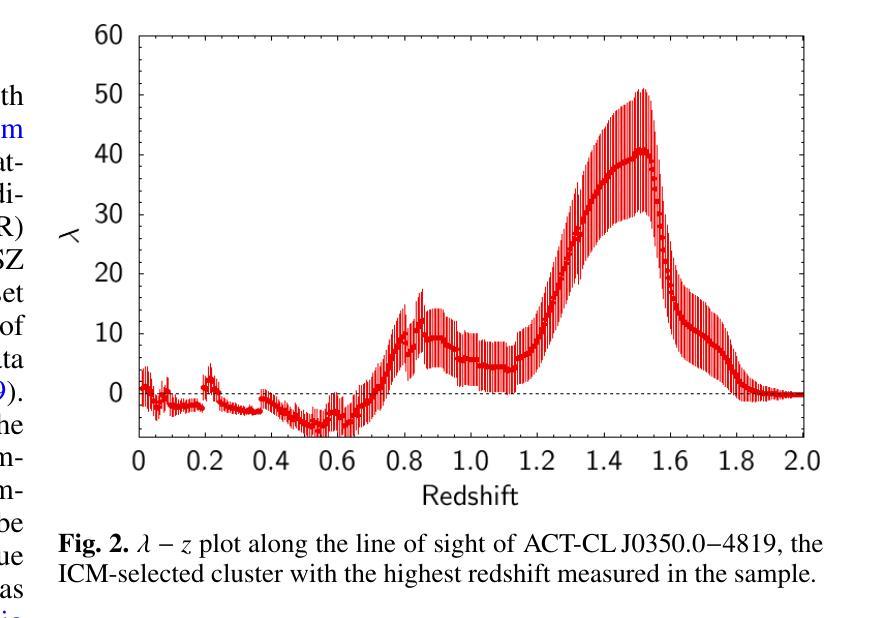
Euclid: Quick Data Release (Q1) – Watching ICM-selected galaxy clusters with Euclid eyes – prospects of Euclid data in the context of large SZ and X-ray based surveys
Authors:M. Klein, K. George, J. J. Mohr, B. Altieri, L. Amendola, S. Andreon, N. Auricchio, C. Baccigalupi, M. Baldi, A. Balestra, S. Bardelli, A. Biviano, E. Branchini, M. Brescia, S. Camera, G. Cañas-Herrera, V. Capobianco, C. Carbone, J. Carretero, S. Casas, M. Castellano, G. Castignani, S. Cavuoti, K. C. Chambers, A. Cimatti, C. Colodro-Conde, G. Congedo, L. Conversi, Y. Copin, F. Courbin, H. M. Courtois, M. Cropper, A. Da Silva, H. Degaudenzi, G. De Lucia, C. Dolding, H. Dole, F. Dubath, F. Ducret, X. Dupac, S. Dusini, M. Farina, R. Farinelli, F. Faustini, S. Ferriol, F. Finelli, M. Frailis, E. Franceschi, M. Fumana, S. Galeotta, B. Gillis, C. Giocoli, J. Gracia-Carpio, A. Grazian, F. Grupp, S. V. H. Haugan, W. Holmes, I. M. Hook, F. Hormuth, A. Hornstrup, K. Jahnke, M. Jhabvala, E. Keihänen, S. Kermiche, B. Kubik, M. Kümmel, M. Kunz, H. Kurki-Suonio, A. M. C. Le Brun, D. Le Mignant, S. Ligori, P. B. Lilje, V. Lindholm, I. Lloro, G. Mainetti, D. Maino, E. Maiorano, O. Mansutti, O. Marggraf, M. Martinelli, N. Martinet, F. Marulli, R. Massey, S. Maurogordato, E. Medinaceli, S. Mei, Y. Mellier, M. Meneghetti, E. Merlin, G. Meylan, L. Moscardini, R. Nakajima, C. Neissner, S. -M. Niemi, C. Padilla, S. Paltani, F. Pasian, K. Pedersen, W. J. Percival, V. Pettorino, S. Pires, G. Polenta, M. Poncet, L. A. Popa, L. Pozzetti, F. Raison, R. Rebolo, A. Renzi, J. Rhodes, G. Riccio, E. Romelli, M. Roncarelli, C. Rosset, H. J. A. Rottgering, R. Saglia, Z. Sakr, D. Sapone, M. Schirmer, P. Schneider, T. Schrabback, A. Secroun, E. Sefusatti, G. Seidel, S. Serrano, C. Sirignano, G. Sirri, L. Stanco, J. Steinwagner, P. Tallada-Crespí, A. N. Taylor, I. Tereno, S. Toft, R. Toledo-Moreo, F. Torradeflot, I. Tutusaus, L. Valenziano, J. Valiviita, T. Vassallo, A. Veropalumbo, Y. Wang, J. Weller, F. M. Zerbi, E. Zucca, C. Burigana, V. Scottez, M. Sereno, M. Viel
Galaxy clusters detected through their X-ray emission or Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect (SZE), both produced by the intra-cluster medium (ICM), are key probes in cosmological and astrophysical studies. To maximise the scientific return of such surveys, complementary data are required for cluster confirmation and redshift estimation. This is typically provided by wide-field optical and infrared surveys, which are increasingly challenged by ongoing and future ICM-selected samples. In particular, at high redshifts ($z>1$) probed by upcoming SZE-selected samples, current large surveys may be insufficient for reliable confirmation. Deep, high-resolution infrared surveys like Euclid will thus be essential for confirming most high-redshift clusters. We present an analysis of the first sizeable Euclid dataset (Q1), overlapping with several ICM-selected cluster samples. We apply an adaptation of the MCMF cluster confirmation tool to estimate key properties, including redshift and richness, and to predict Euclid’s capabilities for high-redshift cluster confirmation. We find promising performance, particularly at high redshifts, while richness estimates at low redshifts ($z<0.4$) are currently limited by Q1 data quality but should improve with future releases. Using MCMF runs on random lines of sight, we predict that Euclid will confirm clusters at $1<z<2$ as effectively as current optical surveys at $z<0.6$, significantly enhancing high-redshift confirmation. SZE-selected samples will thus greatly benefit from Euclid overlap. Among five known high-$z$ SZE clusters in Q1, we identify the highest-redshift jellyfish galaxy candidate to date, EUCLJ035330.86$-$504347.6 in SPT-CLJ0353$-$5043 ($z=1.32$), two massive star-forming galaxies near ACT-CLJ0350.0$-$4819 ($z=1.46$), and strong lensing features in SPT-CLJ0353$-$5043 and SPT-CLJ0421$-$4845.
通过X射线发射或Sunyaev-Zeldovich效应(SZE)检测到的星系团,这两种效应都是由星系团内介质(ICM)产生的,是宇宙学和天体物理学研究中的关键探针。为了最大化此类调查的科学回报,需要补充数据进行集群确认和红移估计。这通常由宽视场光学和红外调查提供,但随着ICM选择的样本的当前和未来挑战,这一任务越来越困难。特别是通过即将出现的SZE选定的高红移(z> 1)样本中,当前的大规模调查可能不足以进行可靠的确认。因此,像Euclid这样深入、高分辨率的红外调查对于确认大多数高红移集群将至关重要。我们分析了首批规模较大的Euclid数据集(Q1),它与多个ICM选定的集群样本重叠。我们应用了MCMF集群确认工具来估计关键属性,包括红移和丰富度,并预测Euclid在高红移集群确认方面的能力。我们发现表现有希望的迹象,特别是在高红移时表现出良好的性能,而低红移(z< 0.4)的丰富度估计目前受到Q1数据质量的限制,但随着未来的发布将会改善。通过在随机视线方向上运行MCMF,我们预计Euclid在确认高红移范围(如确认的集群将像当前光学调查在z < 0.6时一样有效)的效能大大提升),这将对通过SZE选择的样本大有裨益。在Q1中的五个已知高红移SZE集群中,我们确定了迄今为止最高红移的果冻鱼候选者EUCLJ035330.86-504347.6(位于SPT-CLJ0353-5043中)(z= 1.32),ACT-CLJ0350.0-4819附近有两个质量巨大的恒星形成星系(z= 1.46),以及在SPT-CLJ0353-5043和SPT-CLJ0421-4845中出现的强烈透镜特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 10 figures
Summary
欧几里得数据首次大规模分析揭示其在高红移星系团确认中的潜力,与太阳亚-泽尔多维奇效应选定的星系团样本重叠区域表现出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 星系团通过X射线发射和Sunyaev-Zeldovich效应检测是宇宙学和天体物理学研究的关键探针。
- 为最大化此类调查的科研回报,需要宽视场光学和红外调查数据来进行集群确认和红移估计。
- 对于即将出现的SZE选定的样本所探测的高红移($z>1$),当前的大型调查可能不足以进行可靠的确认。
- 深部、高分辨率的红外调查如欧几里得对于确认高红移集群至关重要。
- 对首批大规模欧几里得数据集(Q1)的分析与多个ICM选定集群样本重叠,应用MCMF集群确认工具估计关键属性,包括红移和丰富度。
- 在高红移下的性能表现有前景,尤其是在红移1至2的范围内,欧几里得的确认能力与当前光学调查在红移小于0.6时的效果相当。
点此查看论文截图


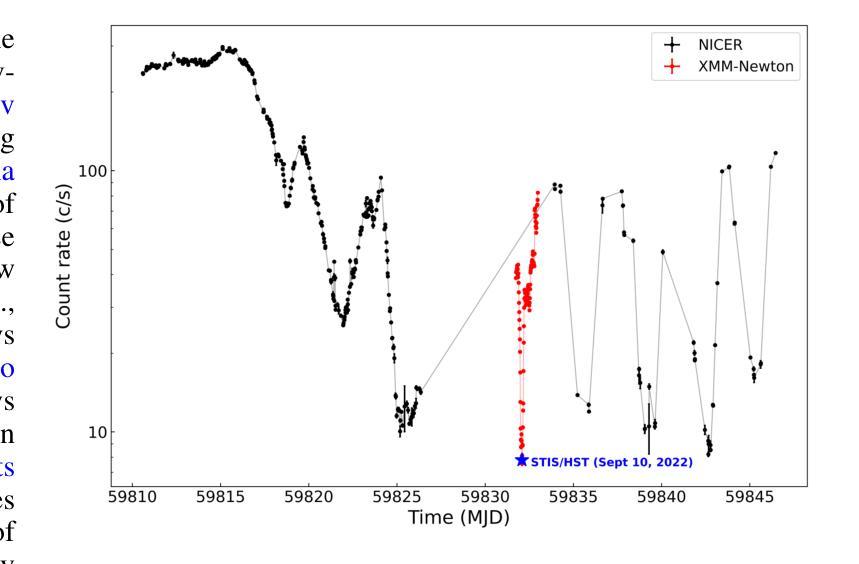
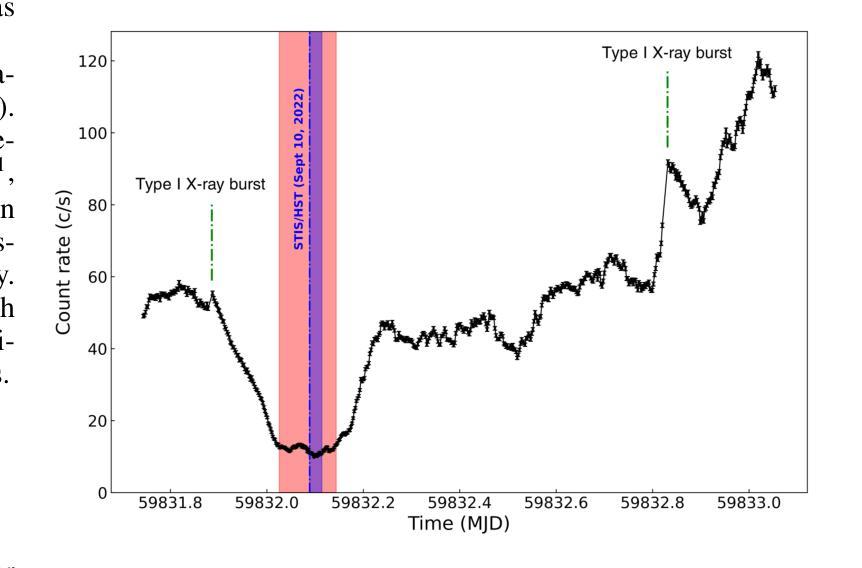
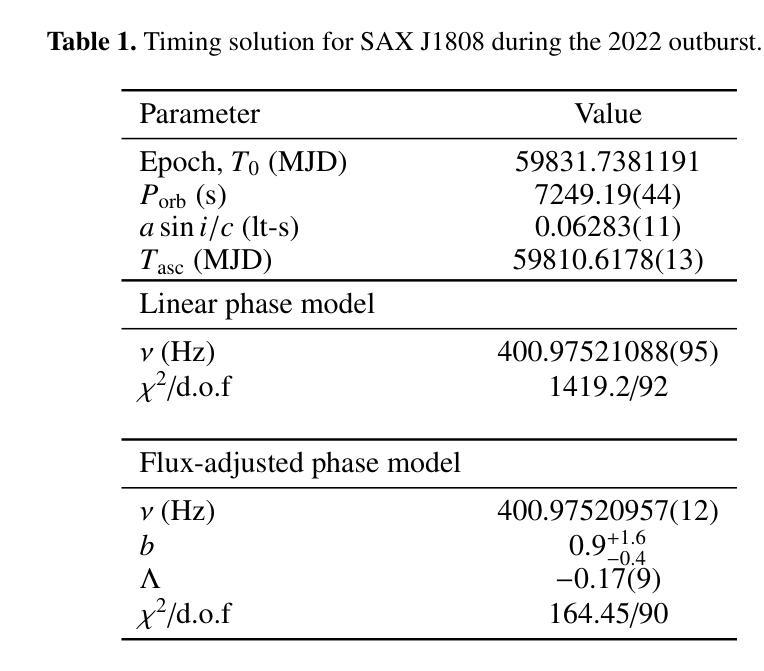
A deep X-ray/UV look into the reflaring stage of the accreting millisecond pulsar SAX J1808.4-3658
Authors:Caterina Ballocco, Alessandro Papitto, Arianna Miraval Zanon, Giulia Illiano, Tiziana Di Salvo, Filippo Ambrosino, Luciano Burderi, Sergio Campana, Francesco Coti Zelati, Alessandro Di Marco, Christian Malacaria, Maura Pilia, Juri Poutanen, Tuomo Salmi, Andrea Sanna
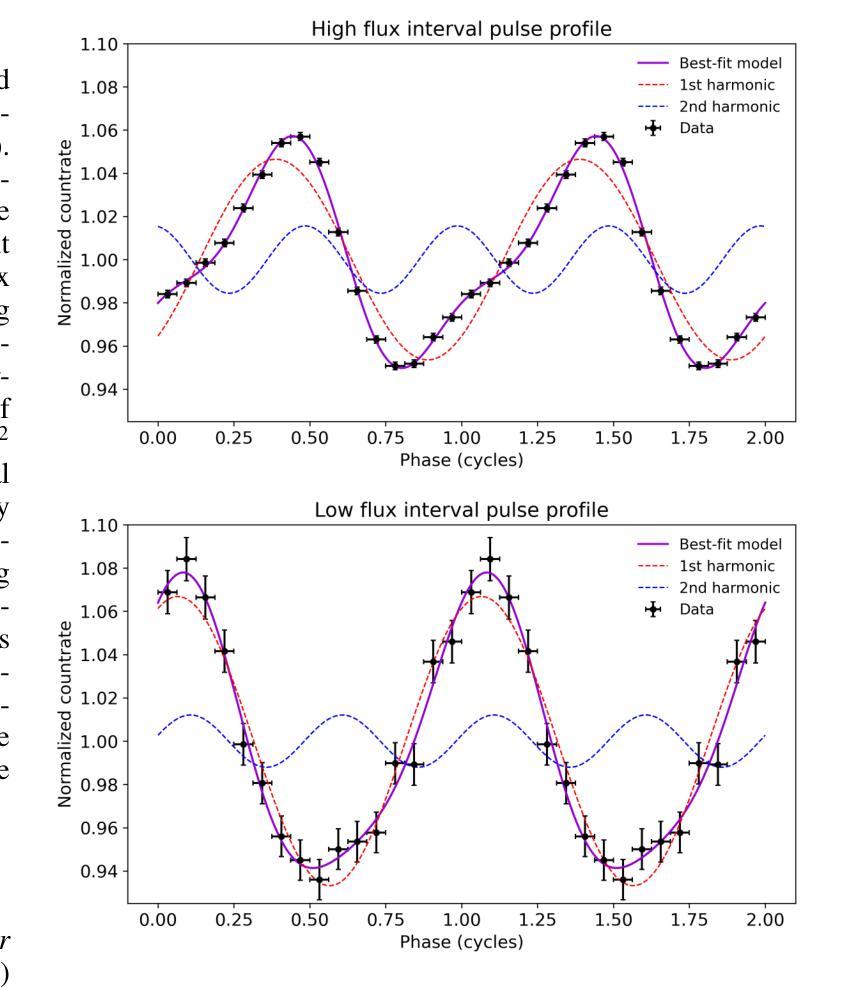
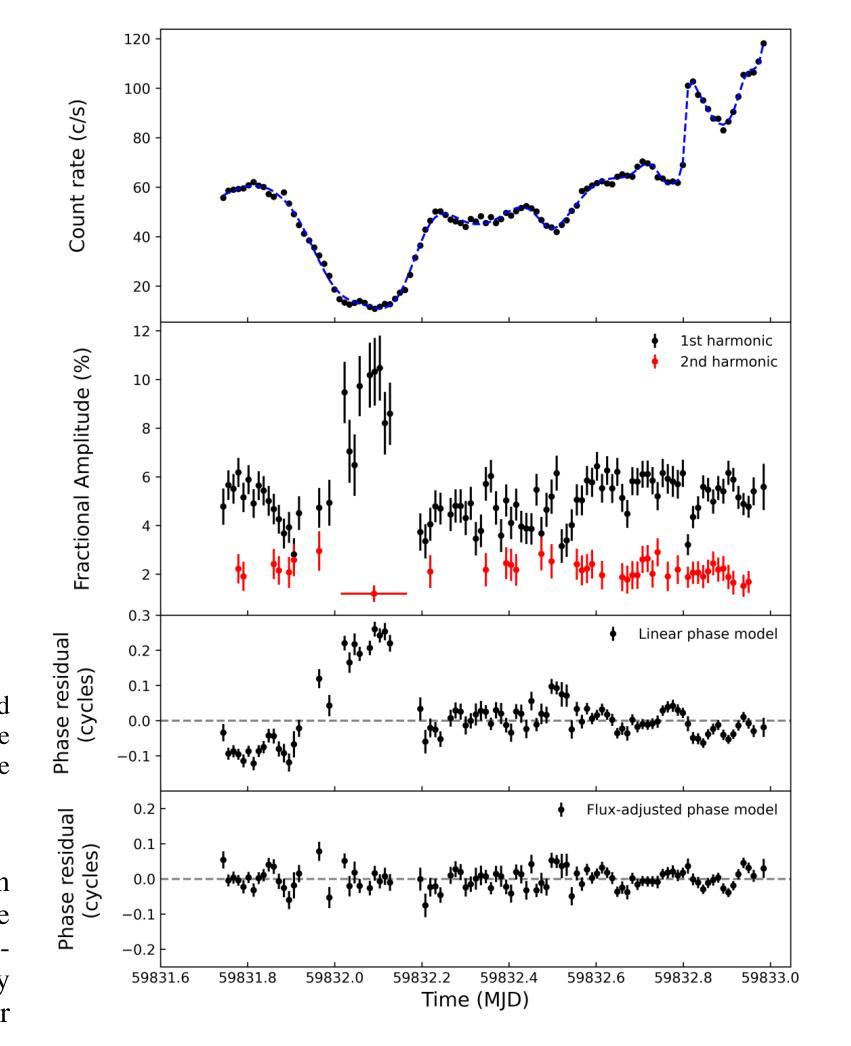
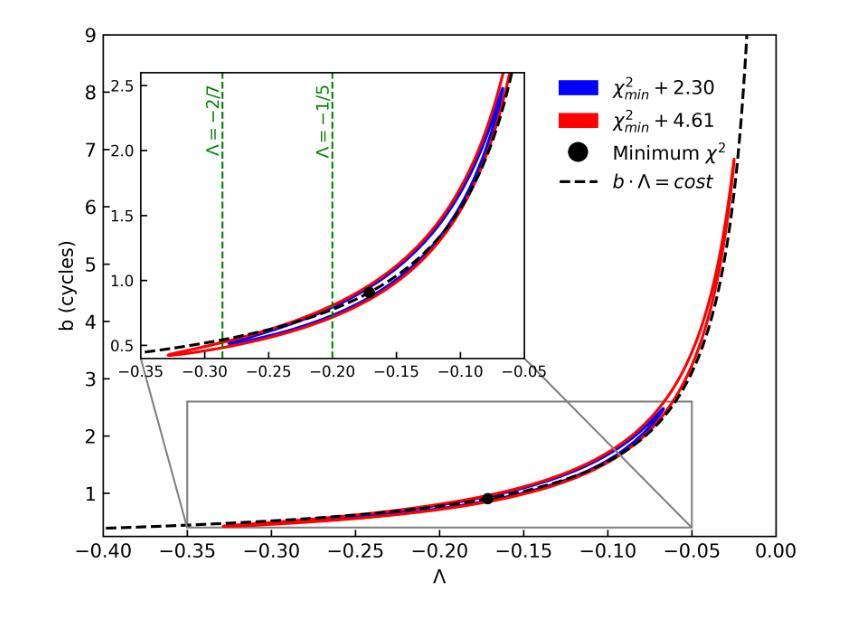
We present a detailed X-ray/UV high-time resolution monitoring of the final reflaring phase of the accreting millisecond pulsar SAXJ1808.4$-$3658. During its 2022 outburst, we obtained simultaneous XMM-Newton and Hubble Space Telescope (HST) observations. We detected coherent X-ray pulsations down to a 0.5-10keV luminosity of $L_{X(low),0.5-10} \simeq 6.21^{+0.20}{-0.15} \times 10^{34} , d^2{3.5},\mathrm{erg , s^{-1}}$, among the lowest ever observed in this source. The uninterrupted coverage provided by XMM-Newton enabled a detailed characterisation of the spectral and temporal evolution of the source X-ray emission as the flux varied by approximately one order of magnitude. At the lowest flux levels, we observed significant variations in pulse amplitude and phase correlated with the X-ray source flux. We found a sharp phase jump of $\sim 0.4$ cycles, accompanied by a doubling of the pulse amplitude and a softening of the X-ray emission. We interpret the changes in the X-ray pulse profiles as drifts of emission regions on the neutron star surface due to an increase of the inner disk radius occurring when the mass accretion rate decreases. The phase evolution was consistent with a magnetospheric radius scaling as $R_{m} \propto \dot{M}^{\Lambda}$, with $\Lambda = -0.17(9)$, in broad agreement with theoretical predictions. Simultaneous HST observations confirmed the presence of significant UV pulsations. The measured pulsed luminosity $-$ $L_{pulsed}^{UV} = (9 \pm 2) \times 10^{31} , \text{erg} , \text{s}^{-1}$ $-$ was approximately half that observed during the 2019 outburst, but the pulsed X-ray to UV luminosity ratio simultaneously measured remained consistent. Yet, such a UV luminosity exceeds the predictions of standard emission models, as further confirmed by the shape of the pulsed spectral energy distribution.
我们对毫秒级脉冲星SAX J1808.4-3658的最终再闪阶段的X射线/紫外高时间分辨率进行了详细监测。在其2022年的爆发期间,我们获得了同时由XMM-牛顿和哈勃太空望远镜(HST)进行的观测。我们检测到相干X射线脉动,其最低能量为Lx(low)0.5− 下的发光度 约为 6.21±××××××××× derg serg serg s,这是在源中观察到的最低值之一。XMM-牛顿提供的连续覆盖使我们能够详细表征源X射线发射的光谱和时间演化,在流量变化约一个数量级的情况下尤为明显。在最低流量水平上,我们观察到脉冲幅度和相位与X射线源流量相关显著变化。我们发现脉冲相位发生了约0.4个周期的跳跃,伴随着脉冲幅度加倍以及X射线发射的软化。我们将X射线脉冲轮廓的变化解释为中子星表面发射区域漂移的结果,这是由于当质量吸积率下降时内部盘半径的增加所导致的。相位演化与磁层半径随质量吸积率的变化而变化的尺度一致,即Rm∝Mḋm的点度 λλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλλ λ,其中Λ=−(反映了当质量吸积率降低时,内盘半径的增加)。这与理论预测大致相符。同时进行的HST观测证实了显著的紫外脉动存在。测得的脉冲发光度约为LpulsedUV=(观察到的峰值)。紫外光度的数值超出了标准发射模型的预测,这与脉冲谱能量分布的形态相符进一步确认了这一点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 13 figures, submitted to A&A
摘要
对SAX J1808.4-3658毫秒脉冲星最终再活跃阶段的X射线和紫外光高时间分辨率监测进行详细呈现。在2022年爆发期间,我们获得了XMM-牛顿和哈勃太空望远镜的同时观测数据。我们在低至Lx(low) 0.5-10 keV的亮度下检测到X射线脉冲,这是该源中观察到的最低亮度之一。XMM-牛顿的无间断覆盖使得我们能够详细表征源X射线发射的谱和时间演化,随着流量变化约一个数量级。在最低流量水平下,我们观察到脉冲振幅和相位与X射线源流量的显著相关性。我们观察到约0.4个周期的突然相位跳跃,伴随着脉冲振幅加倍和X射线发射的软化。我们认为X射线脉冲剖面的变化是由于中子星表面发射区域漂移引起的,这是由于质量吸积率降低时内盘半径的增加所导致的。相位演化与磁层半径与吸积率成比例R_m \propto \dot{M}^{\Lambda},其中Λ=-0.17(9),与理论预测大致相符。同时的轩尼诗天文台观测证实了显著的紫外脉冲的存在。测量的脉冲光度约为标准发射模型预测值的两倍。同时测量的X射线和紫外光脉冲亮度比值保持一致性,但紫外光度超过了标准模型的预测值,这也得到了脉冲光谱能量分布的证实。
关键见解
- 对SAX J1808.4-3658在2022年爆发进行了详细的X射线和紫外线高时间分辨率监测。
- 在低亮度下检测到X射线脉冲,其光谱和时间的演化得到了精细表征。
- 观察到了脉冲振幅和相位与X射线源流量的相关性。
- 中子星表面发射区域的漂移被解释为X射线脉冲剖面的变化原因。
- 磁层半径与吸积率之间的关系得到验证,与理论预测相符。
- 同时的紫外线观测证实了显著的紫外脉冲的存在。
点此查看论文截图

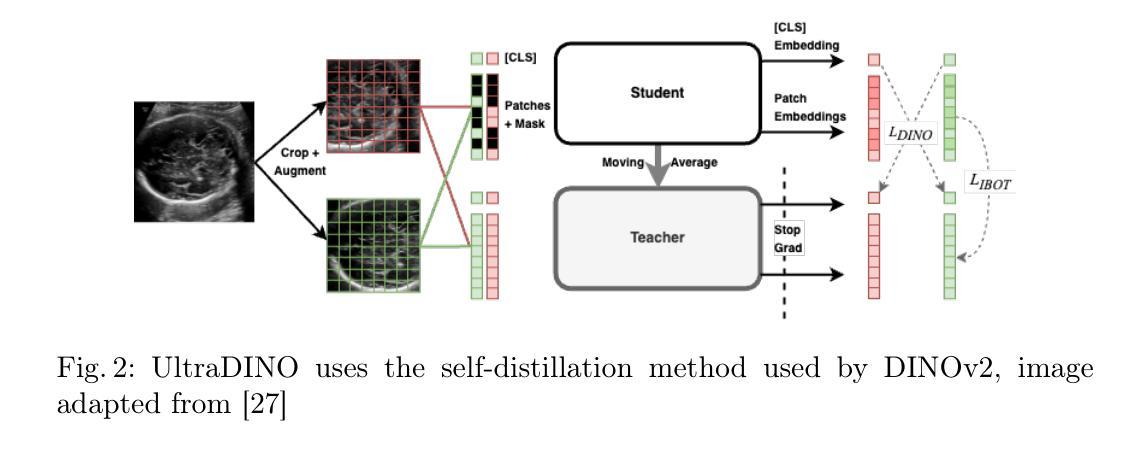
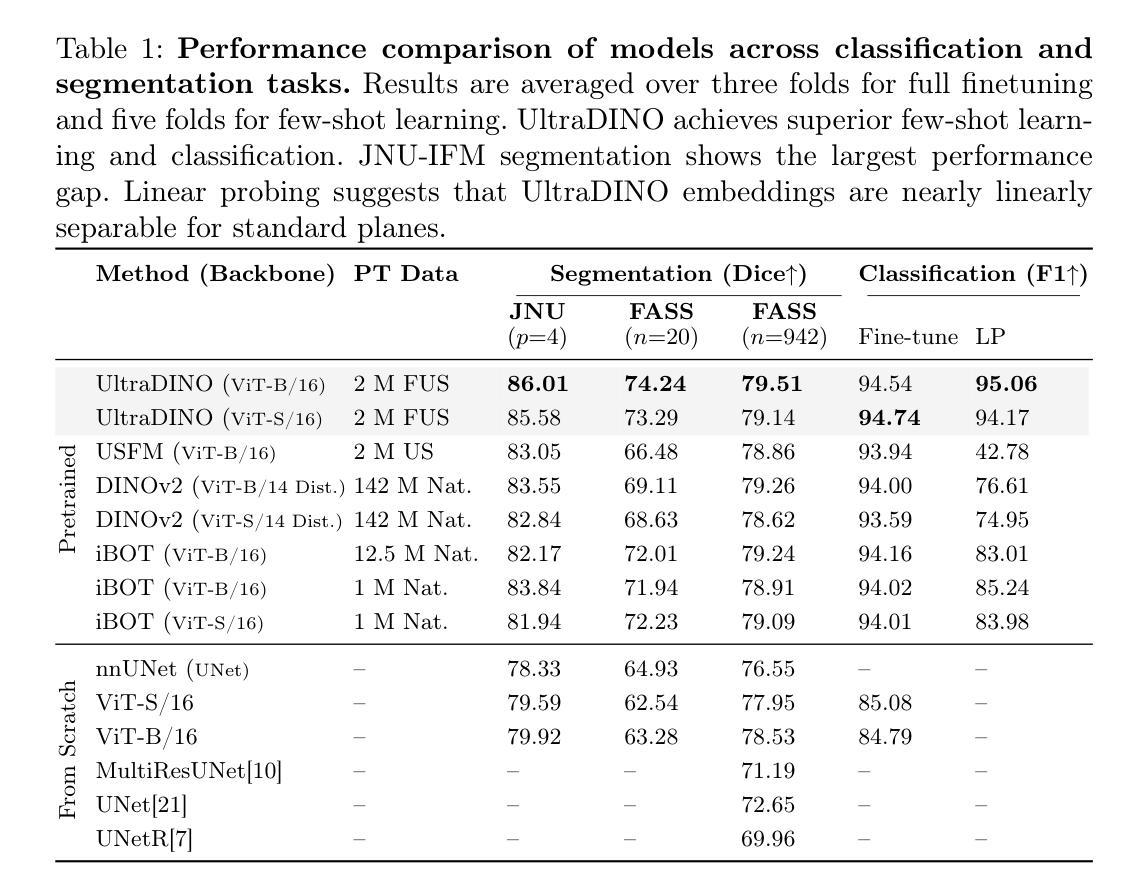
General Methods Make Great Domain-specific Foundation Models: A Case-study on Fetal Ultrasound
Authors:Jakob Ambsdorf, Asbjørn Munk, Sebastian Llambias, Anders Nymark Christensen, Kamil Mikolaj, Randall Balestriero, Martin Tolsgaard, Aasa Feragen, Mads Nielsen
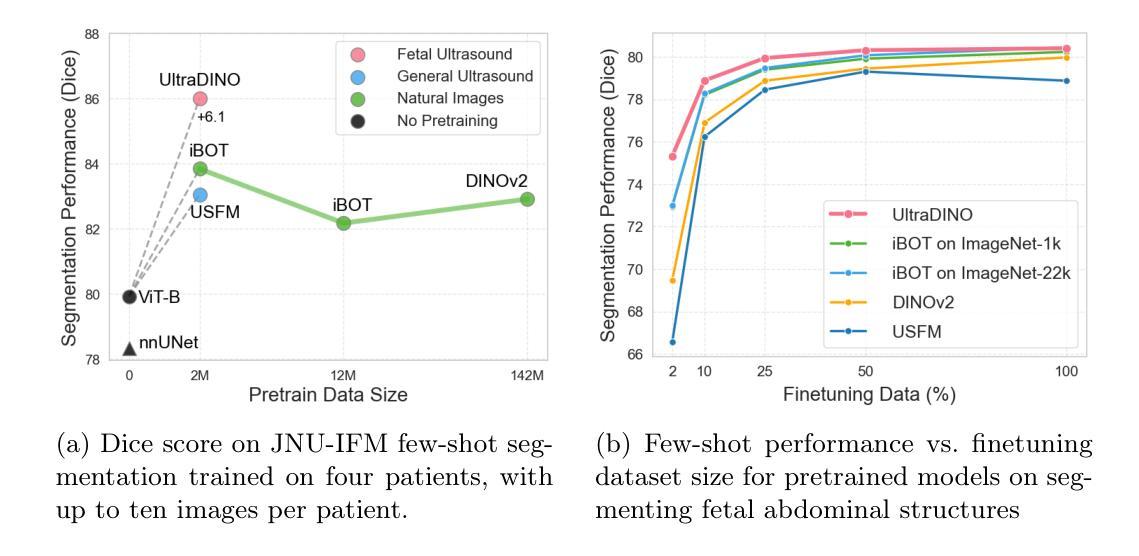
With access to large-scale, unlabeled medical datasets, researchers are confronted with two questions: Should they attempt to pretrain a custom foundation model on this medical data, or use transfer-learning from an existing generalist model? And, if a custom model is pretrained, are novel methods required? In this paper we explore these questions by conducting a case-study, in which we train a foundation model on a large regional fetal ultrasound dataset of 2M images. By selecting the well-established DINOv2 method for pretraining, we achieve state-of-the-art results on three fetal ultrasound datasets, covering data from different countries, classification, segmentation, and few-shot tasks. We compare against a series of models pretrained on natural images, ultrasound images, and supervised baselines. Our results demonstrate two key insights: (i) Pretraining on custom data is worth it, even if smaller models are trained on less data, as scaling in natural image pretraining does not translate to ultrasound performance. (ii) Well-tuned methods from computer vision are making it feasible to train custom foundation models for a given medical domain, requiring no hyperparameter tuning and little methodological adaptation. Given these findings, we argue that a bias towards methodological innovation should be avoided when developing domain specific foundation models under common computational resource constraints.
在获得大规模、未标注的医疗数据集时,研究者将面临两个问题:他们是否应该尝试在此医疗数据上预训练一个自定义基础模型,或者从现有的通用模型中进行迁移学习?如果预训练了自定义模型,是否需要新的方法?在本文中,我们通过进行一项案例研究来探讨这些问题。在该研究中,我们在包含2百万张图像的区域性胎儿超声数据集上训练了一个基础模型。通过选择成熟的DINOv2预训练方法,我们在三个胎儿超声数据集上取得了最新结果,涵盖来自不同国家的数据、分类、分割和少量任务。我们将预训练于自然图像、超声图像和经过监督的基准模型的一系列模型进行了比较。我们的结果展示了两个关键观点:(i)即使在小模型上使用较少数据进行自定义数据预训练也是值得的,因为自然图像预训练的扩展并不能转化为超声性能。(ii)经过良好调整的计算机视觉方法使得为给定医疗领域训练自定义基础模型成为可能,无需进行超参数调整和方法微调。根据这些发现,我们认为在开发特定领域的基础模型时,应避免过分偏向方法创新的倾向,特别是在常见的计算资源约束下。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted version of paper accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了大规模无标签医学数据集的使用问题,研究是否应该使用自定义基础模型进行预训练,还是使用现有通用模型的迁移学习。通过对一个包含2百万张胎儿超声图像的区域数据集进行实证研究,采用成熟的DINOv2预训练法,在三个胎儿超声数据集上取得了最先进的成果。对比在自然图像、超声图像上预训练的模型以及监督学习基线模型,本文发现:一、即使在小数据集上训练小型模型,对自定义数据进行预训练也是值得的;二、在通用计算资源限制下,对于特定医学领域的自定义基础模型开发,应避免过于追求方法创新。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员面临是否使用大规模无标签医学数据集进行自定义基础模型预训练的问题。
- 通过实证研究,发现对自定义医学数据进行预训练值得投入,即使在有限数据集上训练小型模型也是如此。
- 单纯扩大自然图像预训练规模并不等同于超声图像性能的提升。
- 成熟的计算机视觉方法使得针对特定医学领域训练自定义基础模型成为可能,无需进行超参数调整和方法轻微调整。
- 在开发特定领域的医学基础模型时,应避免过于追求方法创新。
- 通过比较研究,使用DINOv2预训练法在胎儿超声图像上取得了最先进成果。
点此查看论文截图

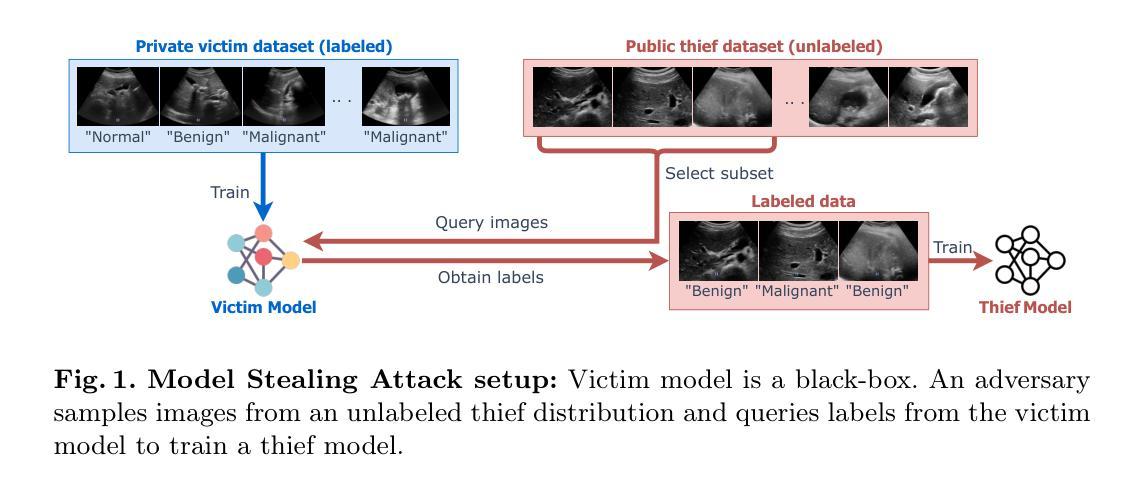
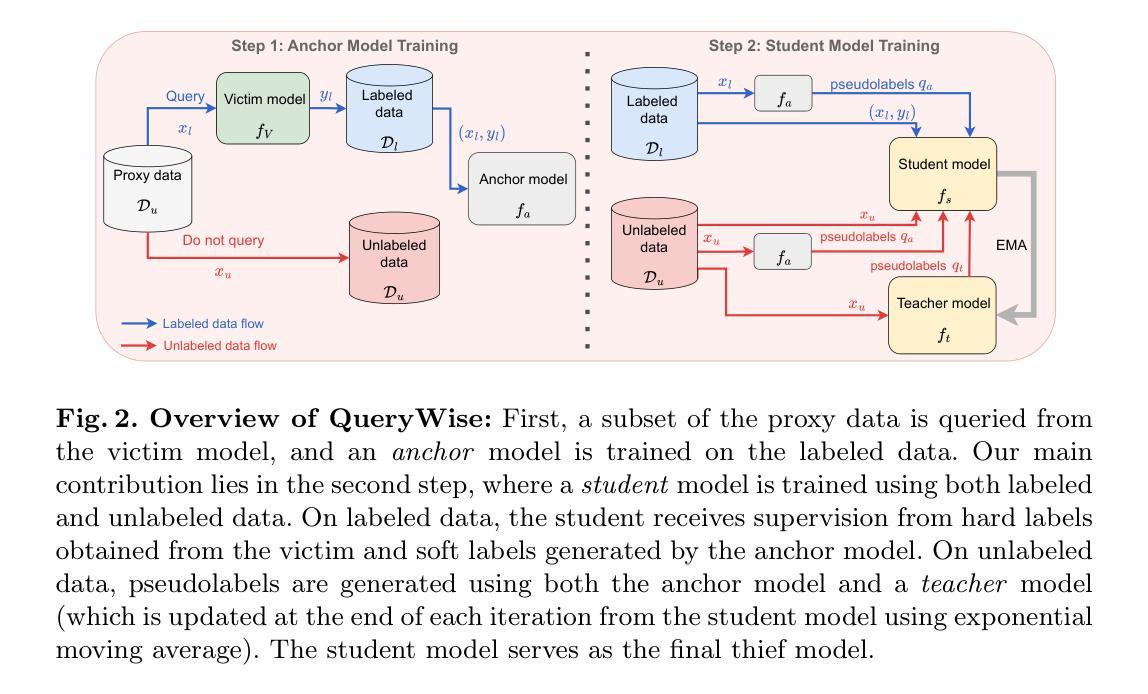
Assessing Risk of Stealing Proprietary Models for Medical Imaging Tasks
Authors:Ankita Raj, Harsh Swaika, Deepankar Varma, Chetan Arora
The success of deep learning in medical imaging applications has led several companies to deploy proprietary models in diagnostic workflows, offering monetized services. Even though model weights are hidden to protect the intellectual property of the service provider, these models are exposed to model stealing (MS) attacks, where adversaries can clone the model’s functionality by querying it with a proxy dataset and training a thief model on the acquired predictions. While extensively studied on general vision tasks, the susceptibility of medical imaging models to MS attacks remains inadequately explored. This paper investigates the vulnerability of black-box medical imaging models to MS attacks under realistic conditions where the adversary lacks access to the victim model’s training data and operates with limited query budgets. We demonstrate that adversaries can effectively execute MS attacks by using publicly available datasets. To further enhance MS capabilities with limited query budgets, we propose a two-step model stealing approach termed QueryWise. This method capitalizes on unlabeled data obtained from a proxy distribution to train the thief model without incurring additional queries. Evaluation on two medical imaging models for Gallbladder Cancer and COVID-19 classification substantiates the effectiveness of the proposed attack. The source code is available at https://github.com/rajankita/QueryWise.
深度学习在医学影像应用中的成功,促使多家公司在诊断工作中部署专有模型,提供收费服务。尽管为了保护服务提供者的知识产权,模型权重是隐藏的,但这些模型仍面临模型窃取(MS)攻击的风险,其中对手可以通过使用代理数据集查询来克隆模型的功能,并在获得的预测上训练窃取模型。虽然在一般视觉任务上进行了广泛的研究,医学影像模型对MS攻击的敏感性仍然没有得到足够的探索。本文研究了在现实世界条件下,黑盒医学影像模型对模型窃取攻击的脆弱性,其中对手无法获得受害者模型的训练数据,并在有限的查询预算下操作。我们证明对手可以使用公开数据集有效地执行MS攻击。为了进一步在有限的查询预算下增强MS能力,我们提出了一种两步模型窃取方法,称为QueryWise。该方法利用从代理分布获得的无标签数据来训练窃取模型,而无需产生额外的查询。对两个用于胆囊癌和COVID-19分类的医学影像模型进行的评估证实了所提出攻击的有效性。源代码可在https://github.com/rajankita/QueryWise找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2024
Summary
深度学习在医学影像应用中的成功促使多家公司在诊断流程中部署专有模型,提供有偿服务。尽管模型权重受到保护以隐藏服务提供商的知识产权,但这些模型仍面临模型窃取(MS)攻击的风险。对手可以通过使用代理数据集查询模型并基于获取的预测训练盗用模型来克隆模型功能。尽管在一般视觉任务上对模型窃取攻击进行了广泛研究,但医学影像模型对其的易感性仍未得到充分探索。本文探讨了在现实条件下,对手无法访问受害模型训练数据且操作受限于查询预算时,黑箱医学影像模型对模型窃取攻击(MS攻击)的脆弱性。我们证明对手可以使用公开数据集有效地执行MS攻击。为了进一步提高有限的查询预算下的模型窃取能力,我们提出了一种名为QueryWise的两步模型窃取方法。该方法利用从代理分布获得的无标签数据来训练盗用模型,无需额外查询。对用于胆囊癌和COVID-19分类的两个医学影像模型进行的评估证实了所提攻击的有效性。源代码可在https://github.com/rajankita/QueryWise找到。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学影像应用中的成功促使公司部署专有模型提供服务,带来知识产权保护的挑战。
- 医学影像模型面临模型窃取攻击的风险,即使模型权重保密,对手仍能通过查询模型和训练盗用模型克隆其功能。
- 尽管对一般视觉任务的模型窃取攻击进行了广泛研究,但医学影像模型的脆弱性仍未得到充分探索。
- 在对手无法访问受害模型的训练数据且查询预算有限的情况下,黑箱医学影像模型易受MS攻击。
- 使用公开数据集可以有效地执行模型窃取攻击。
- 提出了一种名为QueryWise的两步模型窃取方法,该方法利用无标签数据训练盗用模型,无需额外查询。
点此查看论文截图

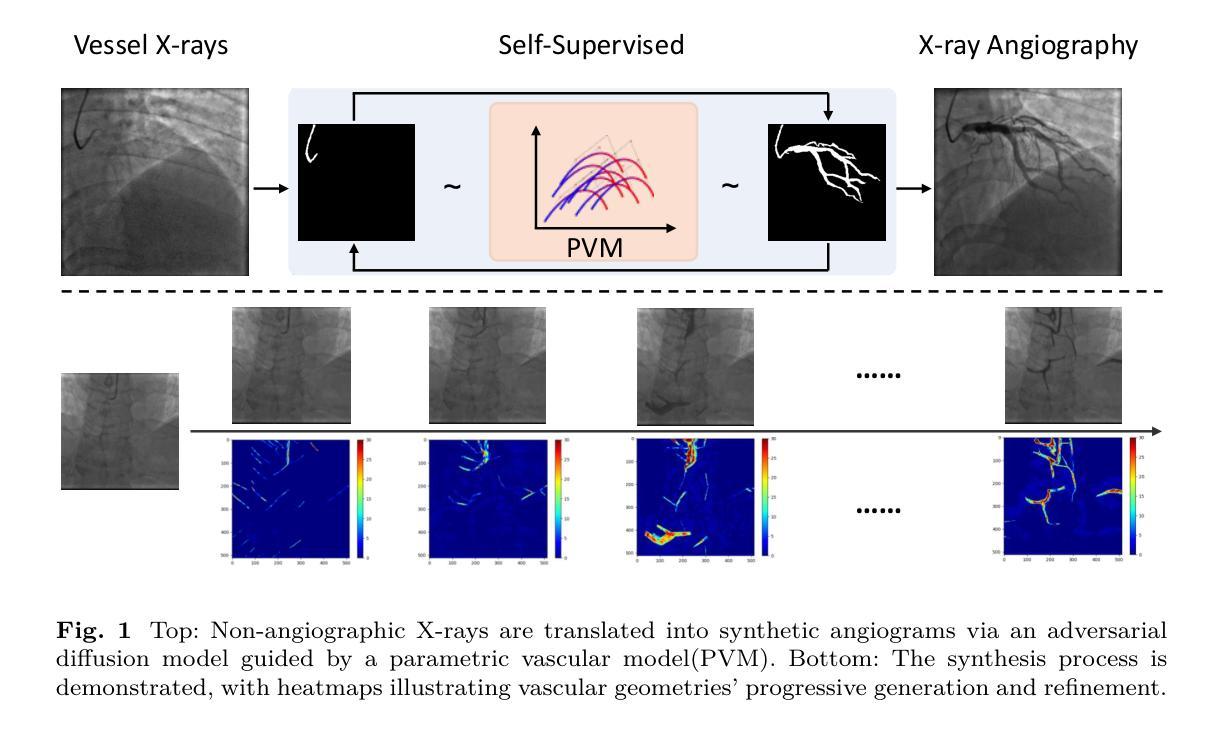
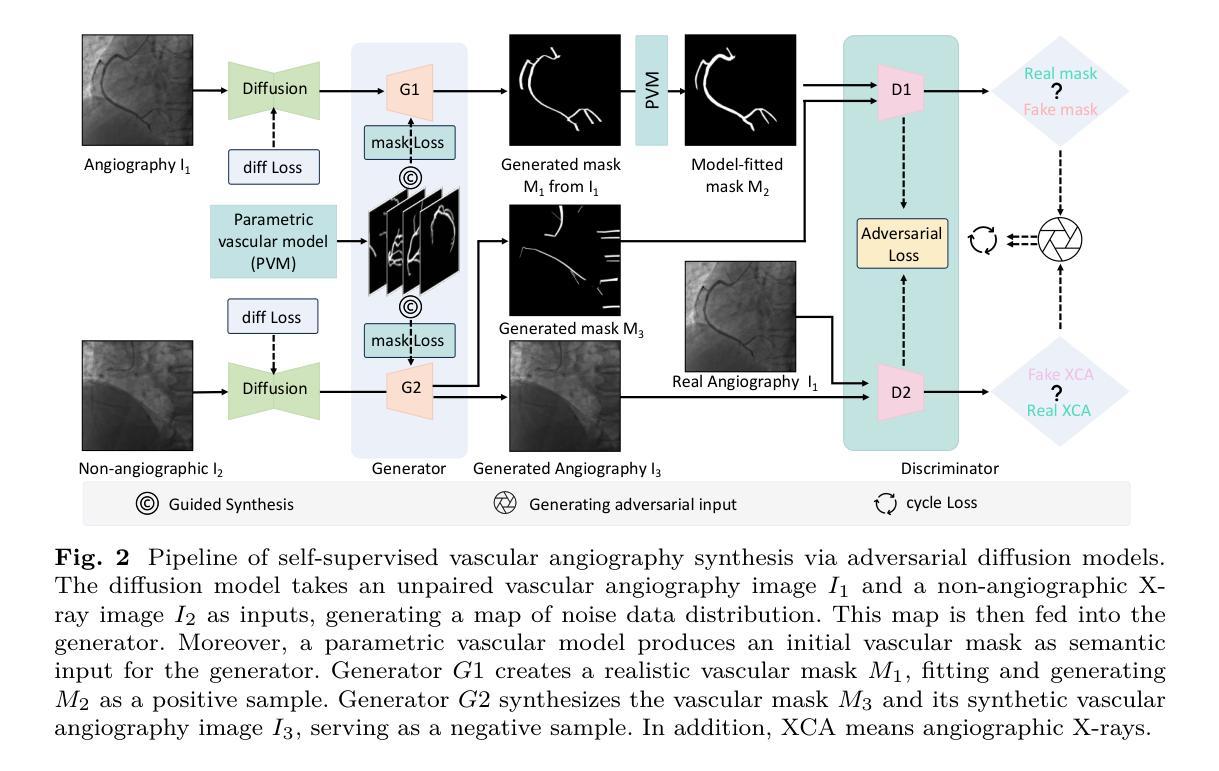
Angio-Diff: Learning a Self-Supervised Adversarial Diffusion Model for Angiographic Geometry Generation
Authors:Zhifeng Wang, Renjiao Yi, Xin Wen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu, Kunlun He
Vascular diseases pose a significant threat to human health, with X-ray angiography established as the gold standard for diagnosis, allowing for detailed observation of blood vessels. However, angiographic X-rays expose personnel and patients to higher radiation levels than non-angiographic X-rays, which are unwanted. Thus, modality translation from non-angiographic to angiographic X-rays is desirable. Data-driven deep approaches are hindered by the lack of paired large-scale X-ray angiography datasets. While making high-quality vascular angiography synthesis crucial, it remains challenging. We find that current medical image synthesis primarily operates at pixel level and struggles to adapt to the complex geometric structure of blood vessels, resulting in unsatisfactory quality of blood vessel image synthesis, such as disconnections or unnatural curvatures. To overcome this issue, we propose a self-supervised method via diffusion models to transform non-angiographic X-rays into angiographic X-rays, mitigating data shortages for data-driven approaches. Our model comprises a diffusion model that learns the distribution of vascular data from diffusion latent, a generator for vessel synthesis, and a mask-based adversarial module. To enhance geometric accuracy, we propose a parametric vascular model to fit the shape and distribution of blood vessels. The proposed method contributes a pipeline and a synthetic dataset for X-ray angiography. We conducted extensive comparative and ablation experiments to evaluate the Angio-Diff. The results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in synthetic angiography image quality and more accurately synthesizes the geometric structure of blood vessels. The code is available at https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff.
血管疾病对人类健康构成重大威胁,X射线血管造影术已确立为诊断的金标准,可以详细观察血管。然而,血管造影X射线使人员和患者暴露于比非血管造影X射线更高的辐射水平,这是人们所不愿意看到的。因此,从非血管造影X射线到血管造影X射线的模态转换是可行的。数据驱动的深度方法由于缺乏配对的大规模X射线血管造影数据集而受到阻碍。尽管进行高质量血管造影合成至关重要,但仍然存在挑战。我们发现当前的医学图像合成主要在像素级别操作,并难以适应血管的复杂几何结构,导致血管图像合成质量不佳,例如断裂或不自然的弯曲。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种通过扩散模型进行非血管造影X射线转换为血管造影X射线的自监督方法,以减轻数据驱动方法的数据短缺问题。我们的模型包括一个从扩散潜在中学习血管数据分布的扩散模型、一个用于血管合成的生成器以及一个基于掩码的对抗模块。为了提高几何精度,我们提出了一种参数化血管模型,以拟合血管的形状和分布。所提出的方法为X射线血管造影提供了一个管道和合成数据集。我们进行了广泛的比较和消融实验来评估Angio-Diff。结果表明,我们的方法在合成血管造影图像质量方面达到了最新性能,并更准确地合成了血管的几何结构。代码可在https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
非血管造影X射线转为血管造影X射线的自监督方法被提出,以克服数据短缺的问题。新方法通过扩散模型学习血管数据的分布,并利用参数化血管模型提升几何精度。此模型提高了合成血管造影图像的质量并更准确地合成血管几何结构。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 血管疾病对人类健康构成重大威胁,X射线血管造影是诊断的金标准,但存在辐射暴露问题。
- 数据驱动的深度学习方法在血管造影图像合成方面面临挑战,缺乏大规模配对X射线血管造影数据集。
- 当前医学图像合成主要在像素层面操作,难以适应血管复杂几何结构,导致血管图像合成质量不佳。
- 提出了一种通过扩散模型进行自监督的方法,将非血管造影X射线转换为血管造影X射线,以缓解数据驱动方法的数据短缺问题。
- 模型包括从扩散潜在学习中血管数据分布的扩散模型、血管合成的生成器以及基于掩膜的对抗模块。
- 为提高几何精度,引入了参数化血管模型来拟合血管的形状和分布。
点此查看论文截图

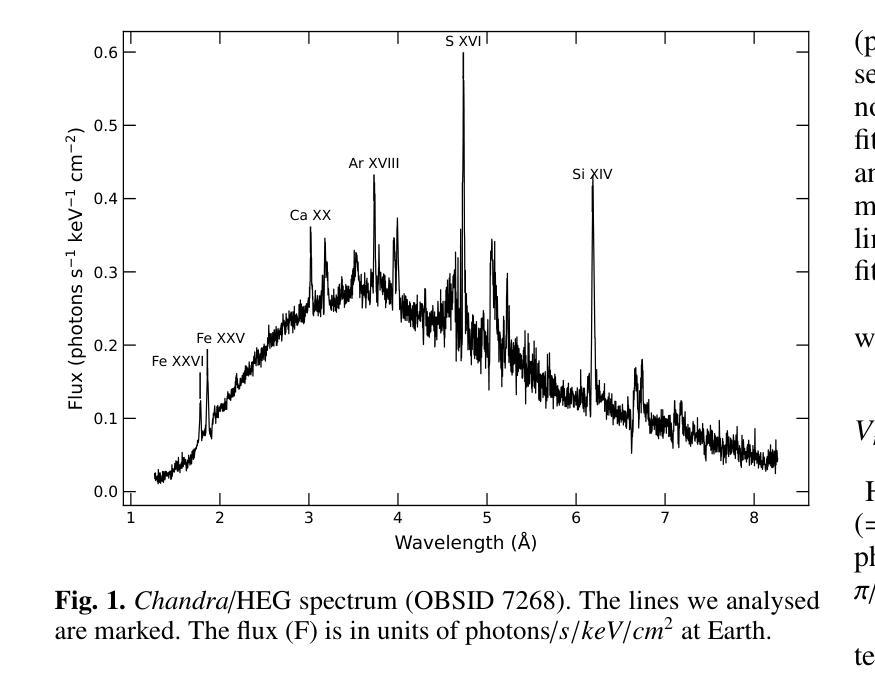
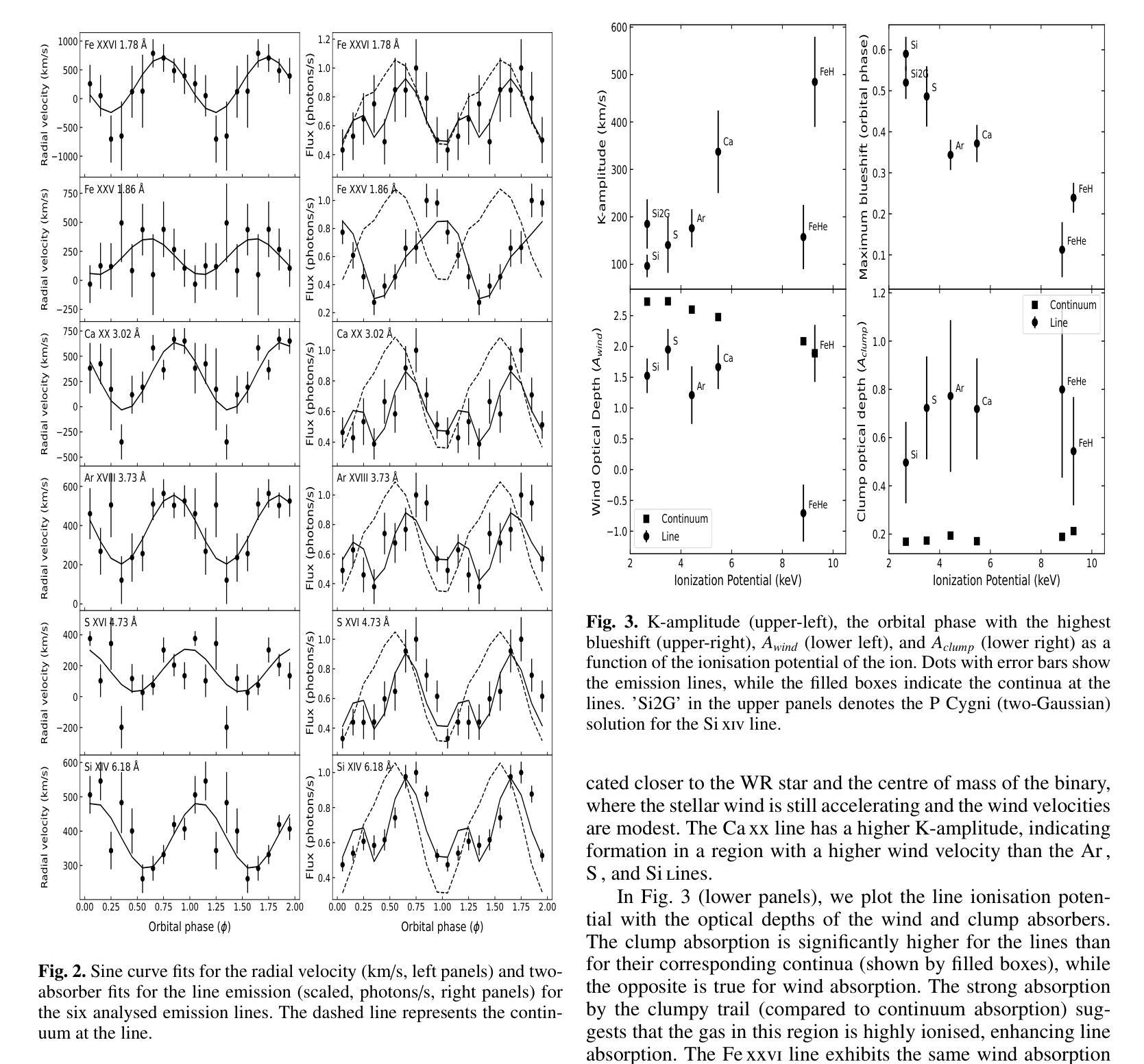
Birthplaces of X-ray emission lines in Cygnus X-3
Authors:Osmi Vilhu, Karri I. I. Koljonen
We investigate the formation of X-ray emission lines in the wind of the Wolf-Rayet (WR) companion in Cyg X-3 by analyzing their orbital dynamics using Chandra High Energy Transmission Grating (HEG) observations during a hypersoft state. Our goal is to constrain the X-ray transparency of the recently discovered funnel-like structure surrounding the compact star, as revealed by X-ray polarimetry. All lines exhibit sinusoidal orbital modulation, with the velocity amplitude generally increasing and the orbital phase with the highest blueshift generally decreasing for ions with a higher ionisation potential. The {Fe}{xxvi}-line displays velocity extremes at phase 0.25 (blueshift) and 0.75 (redshift), indicating that the line-emitting region is close to the compact component (disc or corona) and thus reflects the orbital motion. The {Fe}{xxv}-line shows a complex behaviour that cannot be fully resolved with the Chandra/HEG resolution. Other lines display velocity extremes scattered around phase 0.5 (blueshift) and 0.0 (redshift), with velocity amplitudes of 100–300 km/s, suggesting their origin in the WR stellar wind between the two components along 3D \xi-surfaces. Parts of the emission lines of {Ar}{xviii} and {Ca}{xx} originated around the compact star (disc or corona). The recent polarisation funnel-modelling is consistent with the present results during the hypersoft state.
我们通过对天鹅座X-3中的Wolf-Rayet(WR)伴侣风的X射线发射线的轨道动力学进行分析,利用钱德拉高能传输光栅(HEG)在超软状态下的观测结果,研究其X射线发射线的形成。我们的目标是约束最近发现的围绕致密星的漏斗状结构的X射线透明度,如X射线偏振测量所揭示的。所有发射线都表现出正弦轨道调制,速度振幅一般增加,对于具有较高电离势的离子,具有最高蓝移的轨道相位一般减小。{Fe}{xxvi}线在相位0.25(蓝移)和0.75(红移)时表现出速度极端值,这表明发射线区域靠近致密组件(磁盘或冕),因此反映了轨道运动。{Fe}{xxv}线表现出复杂的行为,无法用钱德拉/HEG分辨率完全解决。其他线路的速度极端值散落在相位0.5(蓝移)和0.0(红移)周围,速度振幅为100-300公里/秒,这表明它们起源于WR恒星风在沿三维ξ表面的两个组件之间。{Ar}{xviii}和{Ca}{xx}的发射线部分起源于致密星(磁盘或冕)。最近的偏振漏斗模型与超软状态下的当前结果一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted 12.6.2025 for A&A, 9 pages 7 figures
摘要
基于Chandra High Energy Transmission Grating(HEG)观测数据,研究Cygnus X-3中的Wolf-Rayet(WR)伴侣星风的X射线发射线形成机制,并分析其轨道动力学特征。目的是通过X射线偏振测量揭示的漏斗状结构约束X射线透明度。所有发射线均表现出正弦轨道调制,对于高电离电位的离子,速度振幅一般增加,而具有最高蓝移的轨道相位一般减小。Fe xxvi线在相位0.25(蓝移)和0.75(红移)时显示出速度极值,表明发射线区域靠近致密成分(磁盘或冕),反映了轨道运动。其他线路的速度极值则分散在相位0.5(蓝移)和0.0(红移),速度振幅为100-300公里/秒,表明它们起源于WR恒星风在两颗恒星之间的三维ξ表面。部分Ar xviii和Ca xx的发射线起源于致密星(磁盘或冕)。最近的偏振漏斗模型与当前处于超软状态的观测结果一致。
关键见解
- 通过分析Chandra HEG观测数据,研究了Cygnus X-3中Wolf-Rayet伴侣星的X射线发射线的轨道动力学特征。
- 所有发射线都表现出轨道调制,反映了WR恒星风的动态变化。
- Fe xxvi线的速度极值与轨道运动紧密相关,表明其发射线区域靠近致密成分(如磁盘或冕)。
- 其他线路的发射源于WR恒星风在两颗恒星之间的三维ξ表面,速度振幅在100-300公里/秒之间。
- 部分Ar xviii和Ca xx的发射线起源于致密星区域。
- X射线偏振测量揭示的漏斗状结构与观测结果一致。
点此查看论文截图

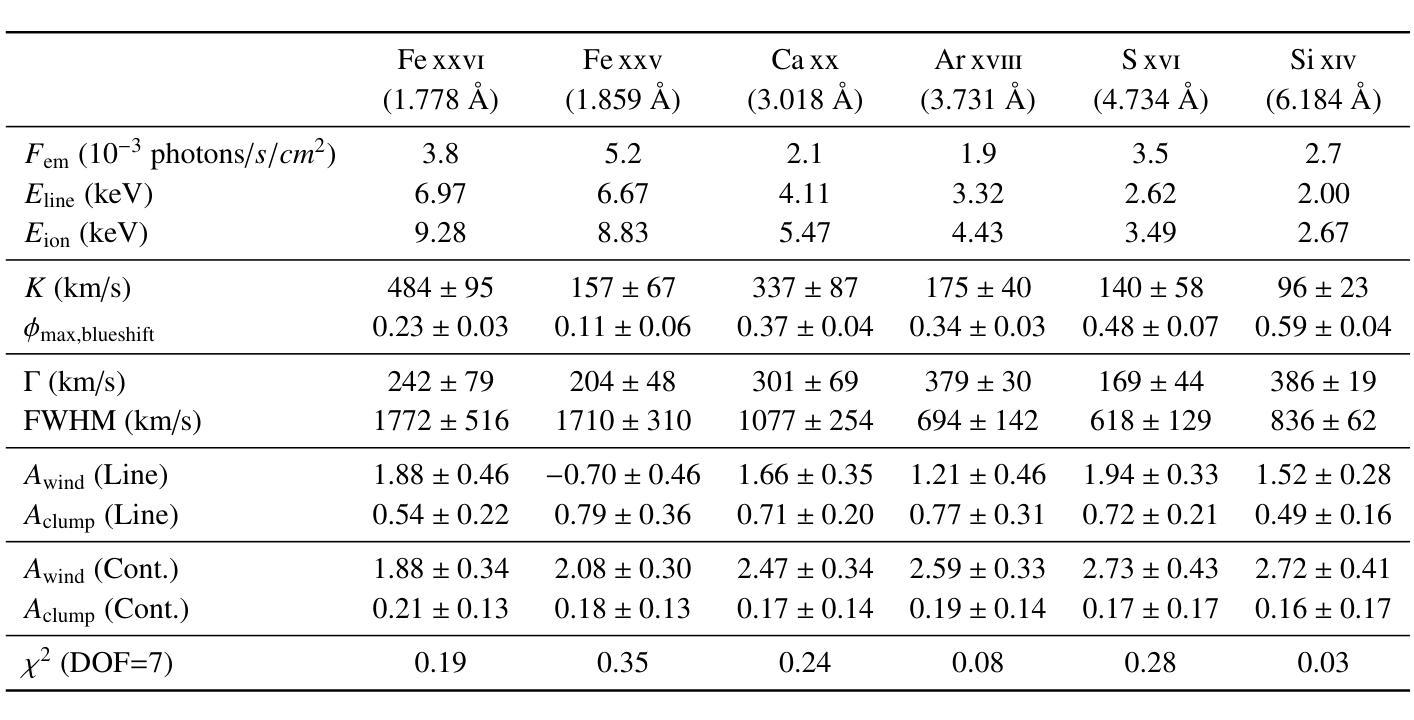
Reconsidering Explicit Longitudinal Mammography Alignment for Enhanced Breast Cancer Risk Prediction
Authors:Solveig Thrun, Stine Hansen, Zijun Sun, Nele Blum, Suaiba A. Salahuddin, Kristoffer Wickstrøm, Elisabeth Wetzer, Robert Jenssen, Maik Stille, Michael Kampffmeyer
Regular mammography screening is essential for early breast cancer detection. Deep learning-based risk prediction methods have sparked interest to adjust screening intervals for high-risk groups. While early methods focused only on current mammograms, recent approaches leverage the temporal aspect of screenings to track breast tissue changes over time, requiring spatial alignment across different time points. Two main strategies for this have emerged: explicit feature alignment through deformable registration and implicit learned alignment using techniques like transformers, with the former providing more control. However, the optimal approach for explicit alignment in mammography remains underexplored. In this study, we provide insights into where explicit alignment should occur (input space vs. representation space) and if alignment and risk prediction should be jointly optimized. We demonstrate that jointly learning explicit alignment in representation space while optimizing risk estimation performance, as done in the current state-of-the-art approach, results in a trade-off between alignment quality and predictive performance and show that image-level alignment is superior to representation-level alignment, leading to better deformation field quality and enhanced risk prediction accuracy. The code is available at https://github.com/sot176/Longitudinal_Mammogram_Alignment.git.
定期乳腺X光摄影筛查对于早期乳腺癌检测至关重要。基于深度学习的风险预测方法引发了针对高风险群体调整筛查间隔的兴趣。早期的方法仅关注当前的乳腺X光摄影,而最近的方法则利用筛查的时间方面来跟踪随时间变化的乳腺组织,这需要跨不同时间点的空间对齐。为此出现了两种主要策略:通过可变形注册进行显式特征对齐和使用变压器技术等隐式学习对齐,前者提供了更多的控制。然而,乳腺X光摄影中显式对齐的最佳方法仍然未得到充分探索。在本研究中,我们提供了关于显式对齐应该发生的位置(输入空间与表示空间)以及是否应该联合优化对齐和风险预测的见解。我们证明了在表示空间中联合学习显式对齐的同时优化风险估计性能(如当前最先进的做法所示),这会导致对齐质量和预测性能之间的权衡,并显示图像级对齐优于表示级对齐,从而提高了变形场的质量和风险预测的准确性。代码可在https://github.com/sot176/Longitudinal_Mammogram_Alignment.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025, early accepted
Summary
本文探讨了在乳腺癌筛查中使用深度学习进行风险预测的方法。研究指出,结合明确特征对齐与风险预测联合优化,在表示空间中进行显式对齐学习,可以在对齐质量和预测性能之间取得平衡。同时,图像级别的对齐优于表示级别的对齐,能提供更好的变形场质量和更高的风险预测准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌筛查中,深度学习用于风险预测已引发关注,尤其是针对高风险群体的筛查间隔调整。
- 现有方法已经从单纯关注当前钼靶图像转向利用时间维度进行屏幕跟踪,以监测乳腺组织随时间的变化。
- 主要有两种策略进行屏幕跟踪:通过可变形注册进行显式特征对齐和使用变压器技术等隐式学习对齐。
- 显式对齐的最优方法对于乳腺癌钼靶图像仍然需要更多的研究。
- 研究提出在表示空间中进行显式对齐,同时优化风险预测性能。
- 通过对齐质量和预测性能之间的权衡,发现图像级别的对齐优于表示级别的对齐。
点此查看论文截图

A Deep Learning Based Method for Fast Registration of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Authors:Benjamin Graham
Image registration is used in many medical image analysis applications, such as tracking the motion of tissue in cardiac images, where cardiac kinematics can be an indicator of tissue health. Registration is a challenging problem for deep learning algorithms because ground truth transformations are not feasible to create, and because there are potentially multiple transformations that can produce images that appear correlated with the goal. Unsupervised methods have been proposed to learn to predict effective transformations, but these methods take significantly longer to predict than established baseline methods. For a deep learning method to see adoption in wider research and clinical settings, it should be designed to run in a reasonable time on common, mid-level hardware. Fast methods have been proposed for the task of image registration but often use patch-based methods which can affect registration accuracy for a highly dynamic organ such as the heart. In this thesis, a fast, volumetric registration model is proposed for the use of quantifying cardiac strain. The proposed Deep Learning Neural Network (DLNN) is designed to utilize an architecture that can compute convolutions incredibly efficiently, allowing the model to achieve registration fidelity similar to other state-of-the-art models while taking a fraction of the time to perform inference. The proposed fast and lightweight registration (FLIR) model is used to predict tissue motion which is then used to quantify the non-uniform strain experienced by the tissue. For acquisitions taken from the same patient at approximately the same time, it would be expected that strain values measured between the acquisitions would have very small differences. Using this metric, strain values computed using the FLIR method are shown to be very consistent.
图像配准在诸多医学图像分析应用中都得到了使用,例如在心脏图像中追踪组织的运动,其中,心脏运动学可以作为组织健康的指标。配准对于深度学习算法来说是一个具有挑战性的问题,因为创建真实的变换基准数据并不可行,而且可能有多重变换会产生与目标图像相关的结果。已有研究者提出了无监督方法用以预测有效变换,但这些方法的预测时间相比传统基线方法明显更长。为了在更广泛的研究和临床环境中采用深度学习方法,应设计能在常见中级硬件上合理运行的方法。虽然已有针对图像配准的快速方法被提出,但这些方法往往采用基于补丁的方式,对于高度动态的组织(如心脏)的配准精度产生影响。在本研究中,提出了一种用于量化心脏应变的快速体积配准模型。所提出深度学习神经网络(DLNN)的设计旨在利用一种可以非常高效地进行卷积的架构,使该模型在推断时间仅需一小部分就能达到与其他最新模型类似的配准保真度。所提出快速轻量级注册(FLIR)模型用于预测组织运动,然后用于量化组织所经历的非均匀应变。对于从同一患者身上大约在同一时间采集的数据,预期在采集数据之间测量的应变值差异会很小。利用这一指标,使用FLIR方法计算的应变值表现出非常一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种快速、轻量级的医学图像配准模型(FLIR模型),用于量化心脏应变。该模型利用深度学习神经网络高效计算卷积,在保证配准精度的同时,提高了推理速度。FLIR模型预测的组织的运动被用来量化组织经历的非均匀应变。对于来自同一患者在大约同一时间采集的采集物,使用FLIR方法计算的应变值表现出非常一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像配准在医学图像分析中有广泛应用,如心脏图像组织运动跟踪,可反映组织健康状况。
- 配准对于深度学习算法是一个挑战,因为难以创建真实的转换,并且可能存在多种产生与目标图像相关的转换。
- 目前存在一些无监督方法预测有效转换,但预测时间较长。
- 论文提出了一种快速、轻量级的配准模型(FLIR),旨在实现在中等硬件上的合理运行时间。
- FLIR模型采用高效卷积计算,实现与最新模型相似的配准精度,同时提高推理速度。
- FLIR模型预测组织运动,用于量化组织的非均匀应变。
点此查看论文截图



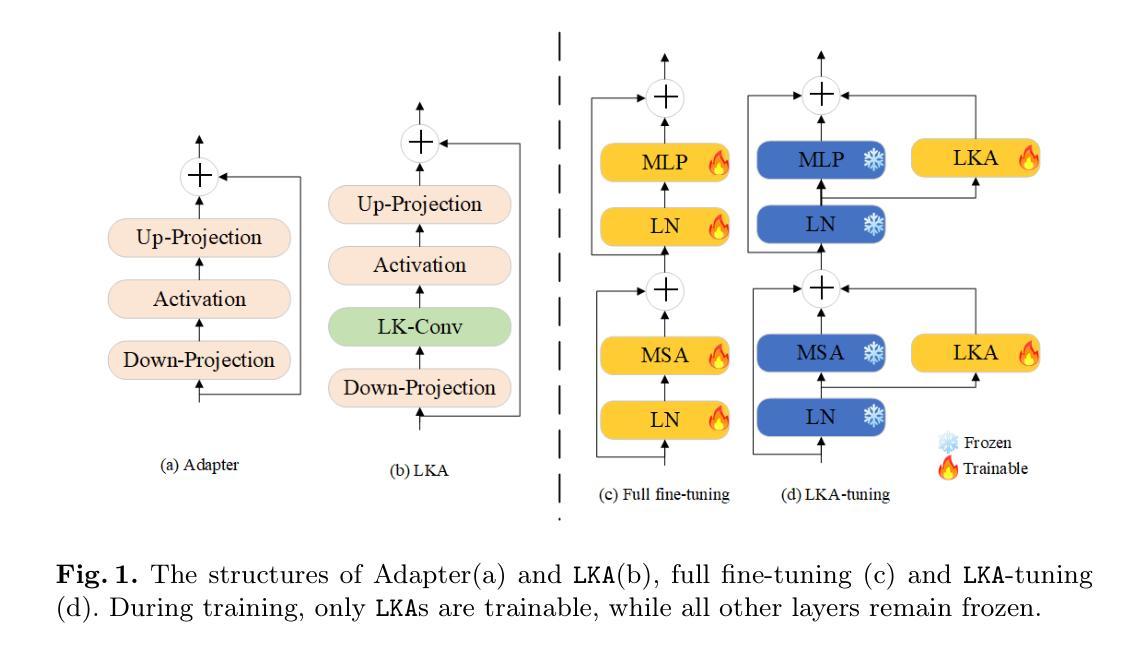
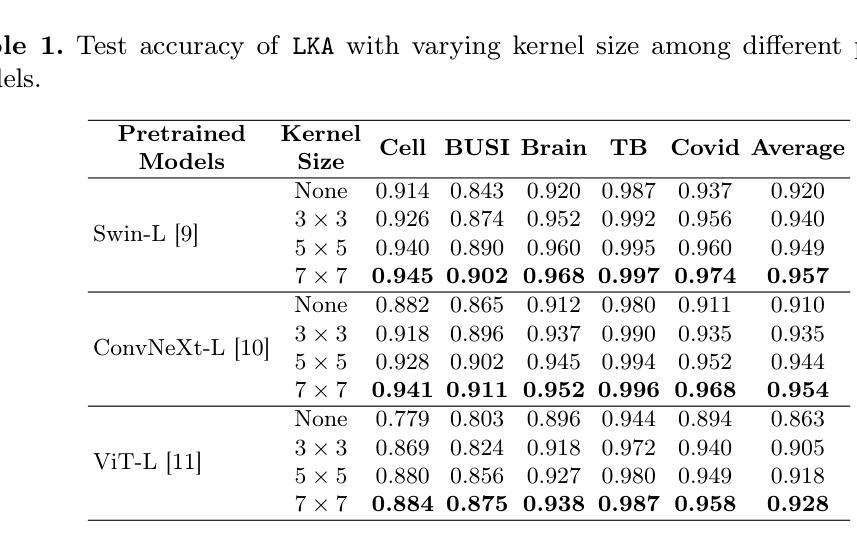
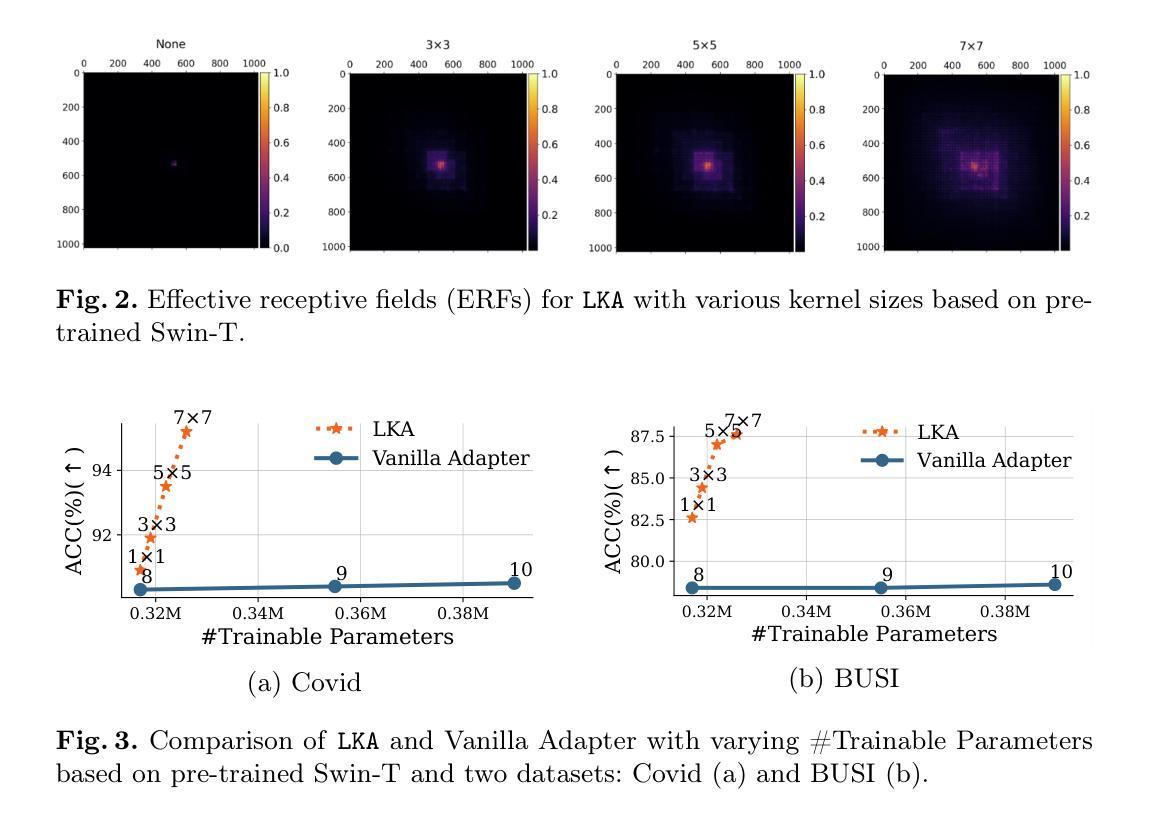
LKA: Large Kernel Adapter for Enhanced Medical Image Classification
Authors:Ziquan Zhu, Si-Yuan Lu, Tianjin Huang, Lu Liu, Zhe Liu
Despite the notable success of current Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods across various domains, their effectiveness on medical datasets falls short of expectations. This limitation arises from two key factors: (1) medical images exhibit extensive anatomical variation and low contrast, necessitating a large receptive field to capture critical features, and (2) existing PEFT methods do not explicitly address the enhancement of receptive fields. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Large Kernel Adapter (LKA), designed to expand the receptive field while maintaining parameter efficiency. The proposed LKA consists of three key components: down-projection, channel-wise large kernel convolution, and up-projection. Through extensive experiments on various datasets and pre-trained models, we demonstrate that the incorporation of a larger kernel size is pivotal in enhancing the adaptation of pre-trained models for medical image analysis. Our proposed LKA outperforms 11 commonly used PEFT methods, surpassing the state-of-the-art by 3.5% in top-1 accuracy across five medical datasets.
尽管当前参数高效微调(PEFT)方法在不同领域取得了显著的成功,它们在医学数据集上的效果却未能达到预期。这一局限性源于两个关键因素:(1)医学图像表现出广泛的解剖变异和低对比度,需要较大的感受野来捕捉关键特征;(2)现有的PEFT方法没有明确解决感受野增强的问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了大型内核适配器(LKA),旨在在保持参数效率的同时扩大感受野。所提出的LKA由三个关键组件组成:下投影、通道大型内核卷积和上投影。通过对各种数据集和预训练模型的广泛实验,我们证明了使用更大的内核尺寸对于增强预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。我们提出的大型内核适配器LKA在五个医学数据集上的前一种精度准确率方面优于常见的PEFT方法中的十一条常规标准流程且超过了当前最佳水平3.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 3 figures, MICCAI
Summary
当前参数高效微调(PEFT)方法在多领域表现出显著的成功,但在医学数据集上的效果不尽如人意。主要由于医学图像存在解剖结构变异大、对比度低的问题,需要较大的感受野来捕捉关键特征,而现有PEFT方法并未明确解决感受野增强问题。为克服这些挑战,提出Large Kernel Adapter(LKA),旨在扩大感受野的同时保持参数效率。通过大量实验验证,更大的卷积核尺寸对提升预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。LKA优于11种常用的PEFT方法,在五套医学数据集上最高精度超过现有最佳水平3.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像存在解剖结构变异大、对比度低的问题,需要更大的感受野捕捉关键特征。
- 当前参数高效微调(PEFT)方法在医学数据集上的效果有限。
- LKA(Large Kernel Adapter)旨在扩大感受野,同时保持参数效率。
- LKA包含三个关键组件:下投影、通道大型卷积核卷积和上投影。
- 实验证明,更大的卷积核尺寸对提升预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。
- LKA在多个数据集和预训练模型上的表现优于11种常用的PEFT方法。
- LKA在五套医学数据集上的最高精度超过现有最佳水平3.5%。
点此查看论文截图

DiffRIS: Enhancing Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation with Pre-trained Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Zhe Dong, Yuzhe Sun, Tianzhu Liu, Yanfeng Gu
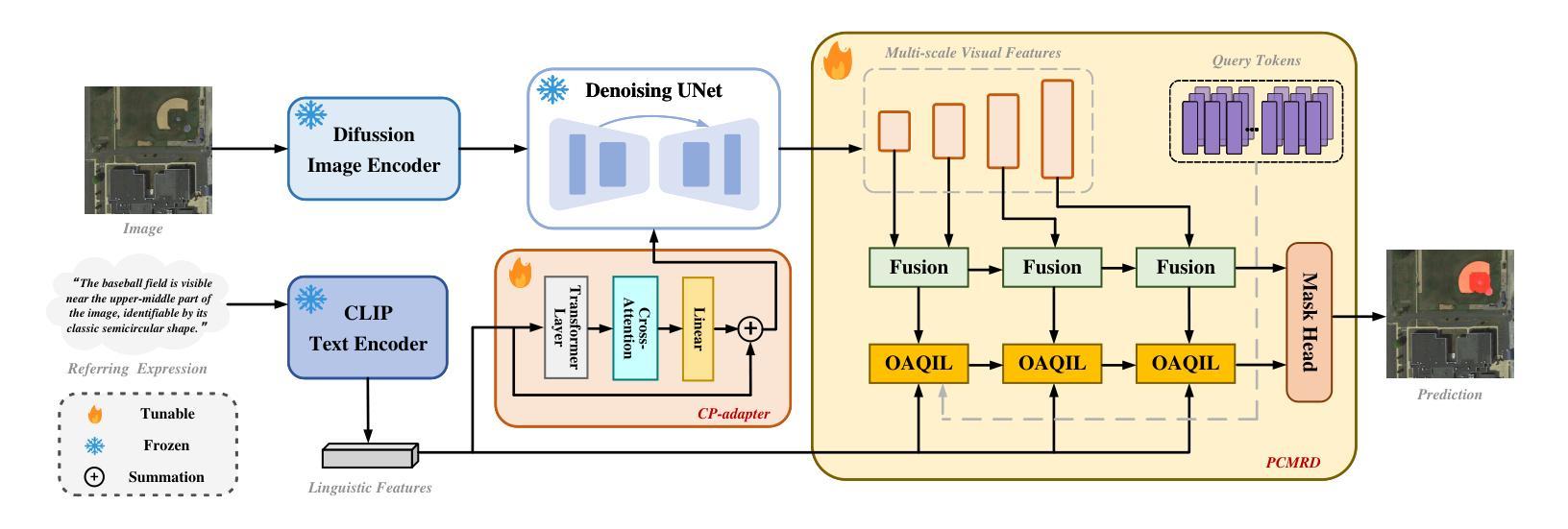
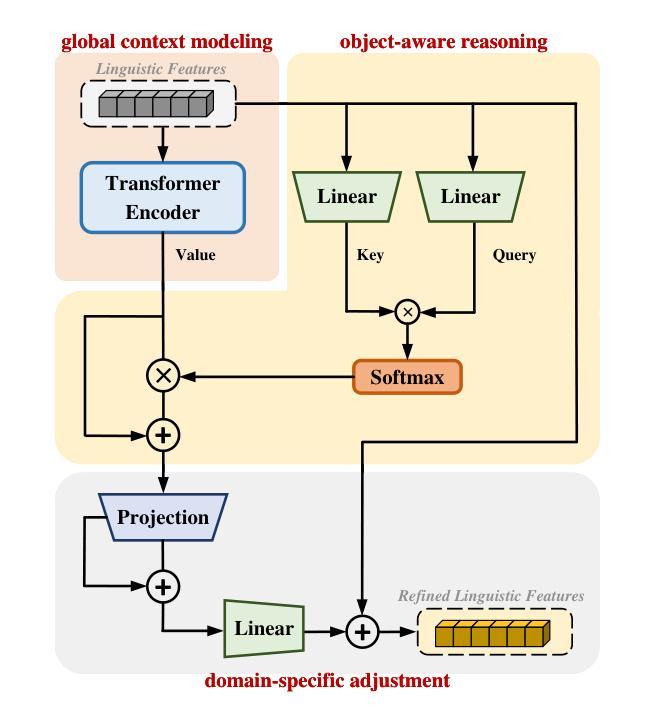
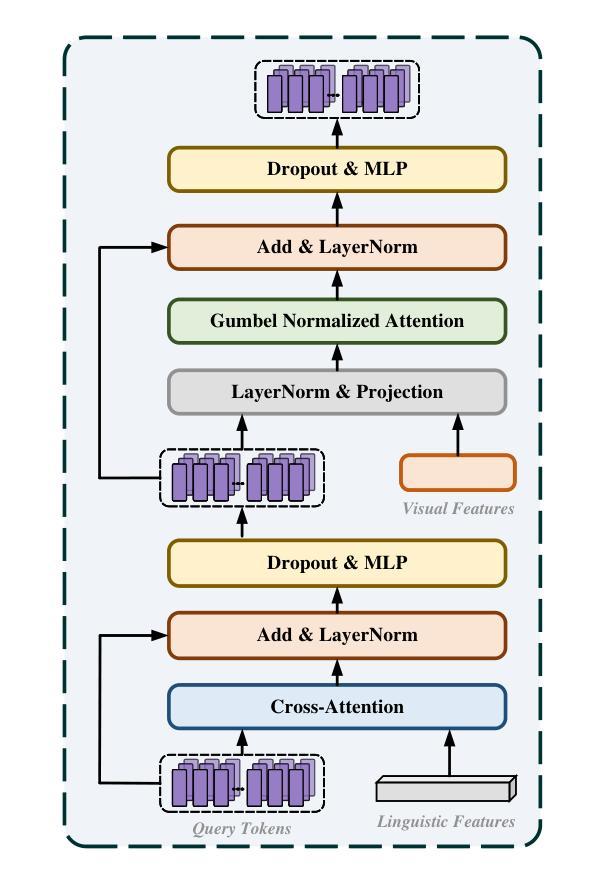
Referring remote sensing image segmentation (RRSIS) enables the precise delineation of regions within remote sensing imagery through natural language descriptions, serving critical applications in disaster response, urban development, and environmental monitoring. Despite recent advances, current approaches face significant challenges in processing aerial imagery due to complex object characteristics including scale variations, diverse orientations, and semantic ambiguities inherent to the overhead perspective. To address these limitations, we propose DiffRIS, a novel framework that harnesses the semantic understanding capabilities of pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models for enhanced cross-modal alignment in RRSIS tasks. Our framework introduces two key innovations: a context perception adapter (CP-adapter) that dynamically refines linguistic features through global context modeling and object-aware reasoning, and a progressive cross-modal reasoning decoder (PCMRD) that iteratively aligns textual descriptions with visual regions for precise segmentation. The CP-adapter bridges the domain gap between general vision-language understanding and remote sensing applications, while PCMRD enables fine-grained semantic alignment through multi-scale feature interaction. Comprehensive experiments on three benchmark datasets-RRSIS-D, RefSegRS, and RISBench-demonstrate that DiffRIS consistently outperforms existing methods across all standard metrics, establishing a new state-of-the-art for RRSIS tasks. The significant performance improvements validate the effectiveness of leveraging pre-trained diffusion models for remote sensing applications through our proposed adaptive framework.
远程遥感图像分割(RRSIS)能够通过自然语言描述精确地界定遥感图像中的区域,在灾害响应、城市发展和环境监测等领域有重要应用。尽管最近有所进展,但由于对象特征的复杂性,包括尺度变化、方向多样以及头顶视角所固有的语义模糊性,当前方法在处理航空图像时仍面临重大挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了DiffRIS这一新型框架,它利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的语义理解能力,增强RRSIS任务的跨模态对齐。我们的框架引入了两个关键创新点:一个是上下文感知适配器(CP-adapter),它通过全局上下文建模和对象感知推理来动态优化语言特征;另一个是渐进式跨模态推理解码器(PCMRD),它通过迭代将文本描述与视觉区域对齐,以实现精确分割。CP-adapter缩小了通用视觉语言理解与遥感应用之间的领域差距,而PCMRD则通过多尺度特征交互实现了精细的语义对齐。在三个基准数据集RRSIS-D、RefSegRS和RISBench上的综合实验表明,DiffRIS在所有标准指标上均优于现有方法,为RRSIS任务建立了新的最先进的性能。显著的性能改进验证了通过我们提出的自适应框架利用预训练扩散模型进行遥感应用的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练文本到图像的扩散模型,提出了一种新的框架DiffRIS,用于解决遥感图像分割中的跨模态对齐问题。该框架引入了两个关键创新点:动态调整语言特征的上下文感知适配器(CP-adapter)和渐进式跨模态推理解码器(PCMRD)。CP-adapter能够缩小通用视觉语言理解与遥感应用之间的领域差距,而PCMRD则通过多尺度特征交互实现精细语义对齐。在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,DiffRIS在标准度量指标上始终优于现有方法,为遥感图像分割任务建立了新的技术标杆。
Key Takeaways
- DiffRIS框架利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型增强遥感图像分割中的跨模态对齐。
- 引入上下文感知适配器(CP-adapter)以动态调整语言特征,并通过全局上下文建模和对象感知推理实现精确分割。
- 渐进式跨模态推理解码器(PCMRD)通过迭代将文本描述与视觉区域对齐,以实现精准分割。
- CP-adapter缩小了通用视觉语言理解与遥感应用之间的领域差距。
- PCMRD通过多尺度特征交互实现精细语义对齐,提高了分割性能。
- 在三个基准数据集上的实验表明,DiffRIS框架在标准度量指标上超越现有方法,表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

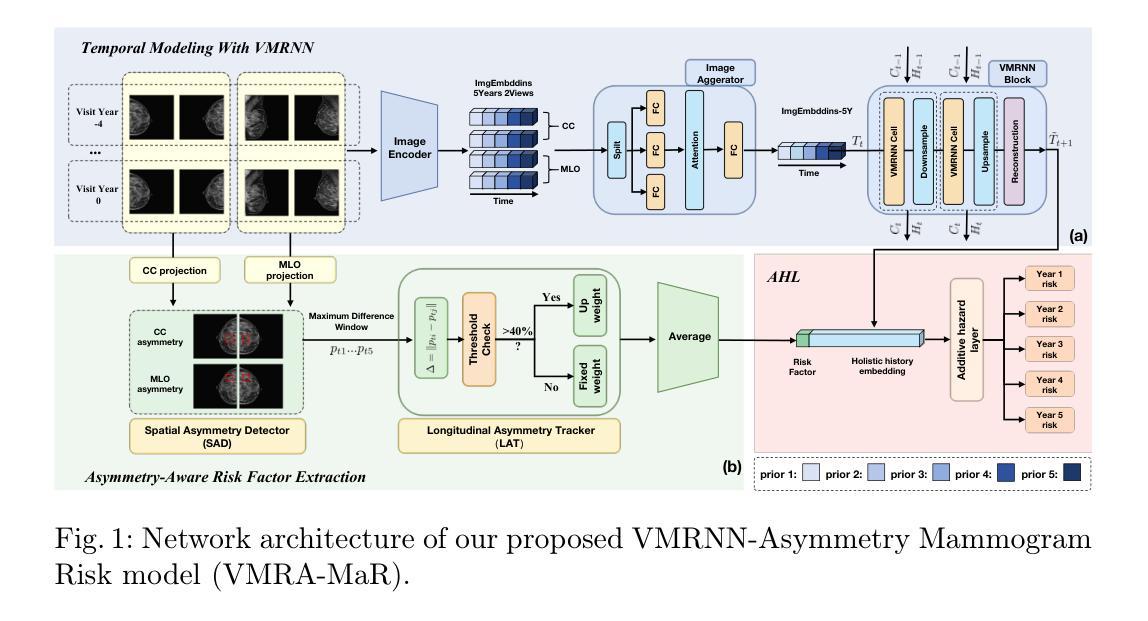
VMRA-MaR: An Asymmetry-Aware Temporal Framework for Longitudinal Breast Cancer Risk Prediction
Authors:Zijun Sun, Solveig Thrun, Michael Kampffmeyer
Breast cancer remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide and is typically detected via screening programs where healthy people are invited in regular intervals. Automated risk prediction approaches have the potential to improve this process by facilitating dynamically screening of high-risk groups. While most models focus solely on the most recent screening, there is growing interest in exploiting temporal information to capture evolving trends in breast tissue, as inspired by clinical practice. Early methods typically relied on two time steps, and although recent efforts have extended this to multiple time steps using Transformer architectures, challenges remain in fully harnessing the rich temporal dynamics inherent in longitudinal imaging data. In this work, we propose to instead leverage Vision Mamba RNN (VMRNN) with a state-space model (SSM) and LSTM-like memory mechanisms to effectively capture nuanced trends in breast tissue evolution. To further enhance our approach, we incorporate an asymmetry module that utilizes a Spatial Asymmetry Detector (SAD) and Longitudinal Asymmetry Tracker (LAT) to identify clinically relevant bilateral differences. This integrated framework demonstrates notable improvements in predicting cancer onset, especially for the more challenging high-density breast cases and achieves superior performance at extended time points (years four and five), highlighting its potential to advance early breast cancer recognition and enable more personalized screening strategies. Our code is available at https://github.com/Mortal-Suen/VMRA-MaR.git.
乳腺癌仍然是全球主要的致死原因之一,通常通过筛查计划(定期邀请健康人群参与)来检测。自动化风险预测方法有望通过动态筛选高风险群体来改善这一流程。虽然大多数模型只关注最近的筛查结果,但临床上越来越有兴趣利用时间信息来捕捉乳腺组织的演变趋势。早期的方法通常依赖于两个时间步骤,尽管最近的研究努力使用Transformer架构将其扩展到多个时间步骤,但仍然存在挑战,即无法充分利用纵向成像数据中的丰富时间动态。在这项工作中,我们提出使用带有状态空间模型(SSM)的Vision Mamba RNN(VMRNN)以及LSTM类记忆机制,以有效捕捉乳腺组织演变的细微趋势。为了进一步改进我们的方法,我们融入了一个不对称模块,该模块利用空间不对称检测器(SAD)和纵向不对称跟踪器(LAT)来识别临床上相关的双侧差异。这一综合框架在预测癌症发生方面显示出显著的改进效果,特别是对高密度乳腺病例更具挑战性,并且在较长时间点(第四年和第五年)实现了卓越的性能,这突显了其推动早期乳腺癌识别并启用更个性化的筛查策略的潜力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Mortal-Suen/VMRA-MaR.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025, Provisional Accept
Summary
乳腺癌仍是全球主要的致死原因,通过筛查程序检测。自动化风险预测方法可通过动态筛选高风险群体改进检测过程。虽然多数模型集中于最新筛查,但临床实践中存在利用时间信息捕捉乳腺组织演变趋势的日益增长的兴趣。早期方法通常依赖于两个时间步骤,尽管近期努力已将其扩展到多个时间步骤,使用Transformer架构,但仍有挑战在于完全利用纵向成像数据的丰富时间动态。本研究提出利用带有状态空间模型的Vision Mamba RNN(VMRNN)和LSTM类记忆机制捕捉乳腺组织演变趋势的微妙变化。为进一步改进方法,结合不对称模块,利用空间不对称检测器(SAD)和纵向不对称跟踪器(LAT)识别临床相关的双侧差异。该综合框架在预测癌症发生方面表现出显著改进,特别是针对密度较高的乳腺病例,且在长期时间点(第四和五年)表现出卓越性能,凸显其推动早期乳腺癌识别和个性化筛查策略的潜力。相关代码可通过链接访问:https://github.com/Mortal-Suen/VMRA-MaR.git。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌仍然是全球主要的死亡原因之一,自动化风险预测方法可以改进检测过程。
- 利用纵向数据的时间信息是临床实践中日益关注的问题。
- Vision Mamba RNN(VMRNN)结合状态空间模型(SSM)和LSTM类记忆机制能有效捕捉乳腺组织演变的微妙趋势。
- 通过结合不对称模块和空间不对称检测器(SAD)及纵向不对称跟踪器(LAT),可识别双侧差异,提高预测准确性。
- 该方法在高密度乳腺病例的癌症预测方面表现优异,并在长期时间点展现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

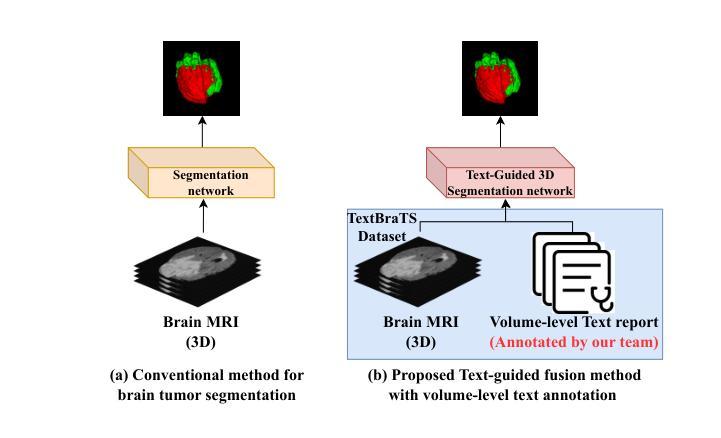
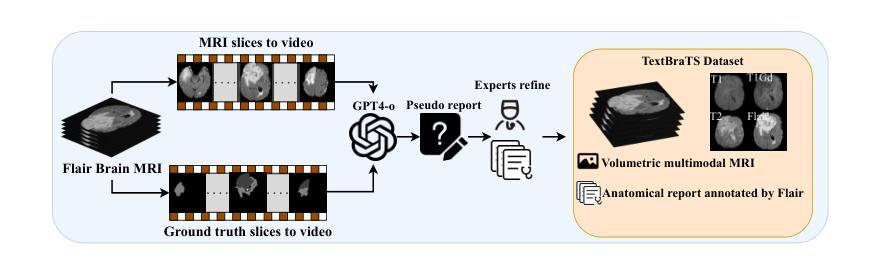
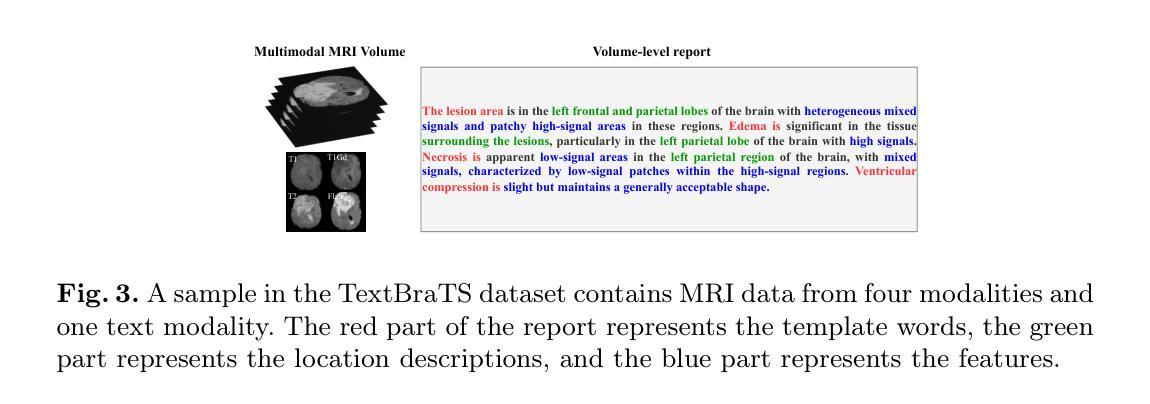
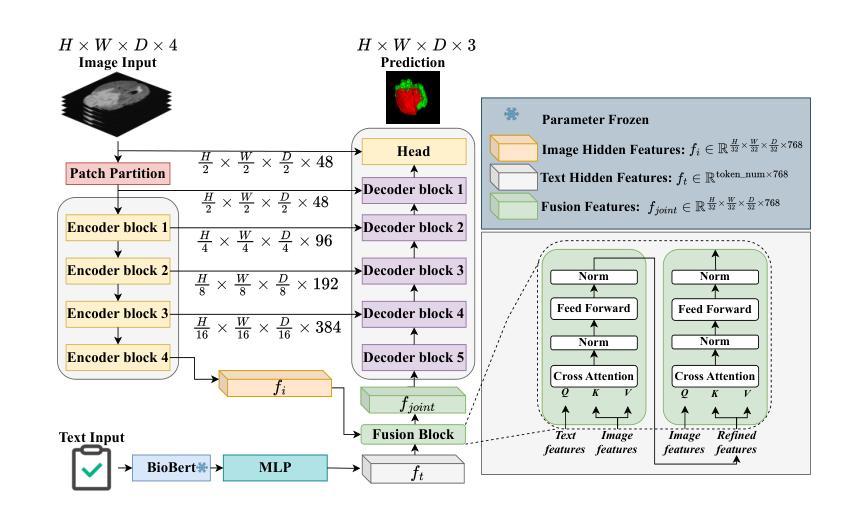
TextBraTS: Text-Guided Volumetric Brain Tumor Segmentation with Innovative Dataset Development and Fusion Module Exploration
Authors:Xiaoyu Shi, Rahul Kumar Jain, Yinhao Li, Ruibo Hou, Jingliang Cheng, Jie Bai, Guohua Zhao, Lanfen Lin, Rui Xu, Yen-wei Chen
Deep learning has demonstrated remarkable success in medical image segmentation and computer-aided diagnosis. In particular, numerous advanced methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance in brain tumor segmentation from MRI scans. While recent studies in other medical imaging domains have revealed that integrating textual reports with visual data can enhance segmentation accuracy, the field of brain tumor analysis lacks a comprehensive dataset that combines radiological images with corresponding textual annotations. This limitation has hindered the exploration of multimodal approaches that leverage both imaging and textual data. To bridge this critical gap, we introduce the TextBraTS dataset, the first publicly available volume-level multimodal dataset that contains paired MRI volumes and rich textual annotations, derived from the widely adopted BraTS2020 benchmark. Building upon this novel dataset, we propose a novel baseline framework and sequential cross-attention method for text-guided volumetric medical image segmentation. Through extensive experiments with various text-image fusion strategies and templated text formulations, our approach demonstrates significant improvements in brain tumor segmentation accuracy, offering valuable insights into effective multimodal integration techniques. Our dataset, implementation code, and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/Jupitern52/TextBraTS.
深度学习在医学图像分割和计算机辅助诊断方面取得了显著的成就。特别是,许多先进的方法在MRI扫描的脑肿瘤分割方面达到了最先进的技术性能。虽然其他医学影像领域的研究表明,将文本报告与视觉数据相结合可以提高分割精度,但脑肿瘤分析领域缺乏一个结合了放射图像和相应文本注释的综合数据集。这一局限性阻碍了利用图像和文本数据的多模式方法的探索。为了弥补这一关键差距,我们推出了TextBraTS数据集,这是第一个公开可用的体积级多模式数据集,包含配对的MRI体积和丰富的文本注释,这些注释来源于广泛采用的BraTS2020基准测试。基于这一新型数据集,我们提出了一种新的基线框架和顺序交叉注意方法,用于文本引导的体积医学图像分割。通过对各种文本图像融合策略和模板文本格式的广泛实验,我们的方法在脑肿瘤分割精度方面取得了显著的提高,为有效的多模式集成技术提供了有价值的见解。我们的数据集、实现代码和预训练模型可在https://github.com/Jupitern52/TextBraTS公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像领域深度学习取得显著成就,尤其在脑肿瘤分割方面。为提高分割精度,有研究融合视觉数据与文本报告。然而,脑肿瘤分析领域缺乏综合数据集,结合影像学图像与相应文本注释。为填补这一空白,推出TextBraTS数据集,包含MRI体积数据与丰富文本注释。基于此数据集,提出基线框架与顺序交叉注意方法,用于文本引导的体积医学图像分割。通过实验验证,该方法显著提高脑肿瘤分割精度,为有效多模式融合技术提供有价值见解。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割和计算机辅助诊断中取得显著成就。
- 脑肿瘤分割是医学图像领域的热点研究课题。
- 融合视觉数据和文本报告能提高分割精度。
- 当前缺乏包含影像学图像和相应文本注释的脑肿瘤分析综合数据集。
- TextBraTS数据集是首个公开的多模式数据集,包含MRI体积数据和文本注释。
- 提出基线框架和顺序交叉注意方法,利用TextBraTS数据集进行文本引导的医学图像体积分割。
点此查看论文截图