⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-26 更新
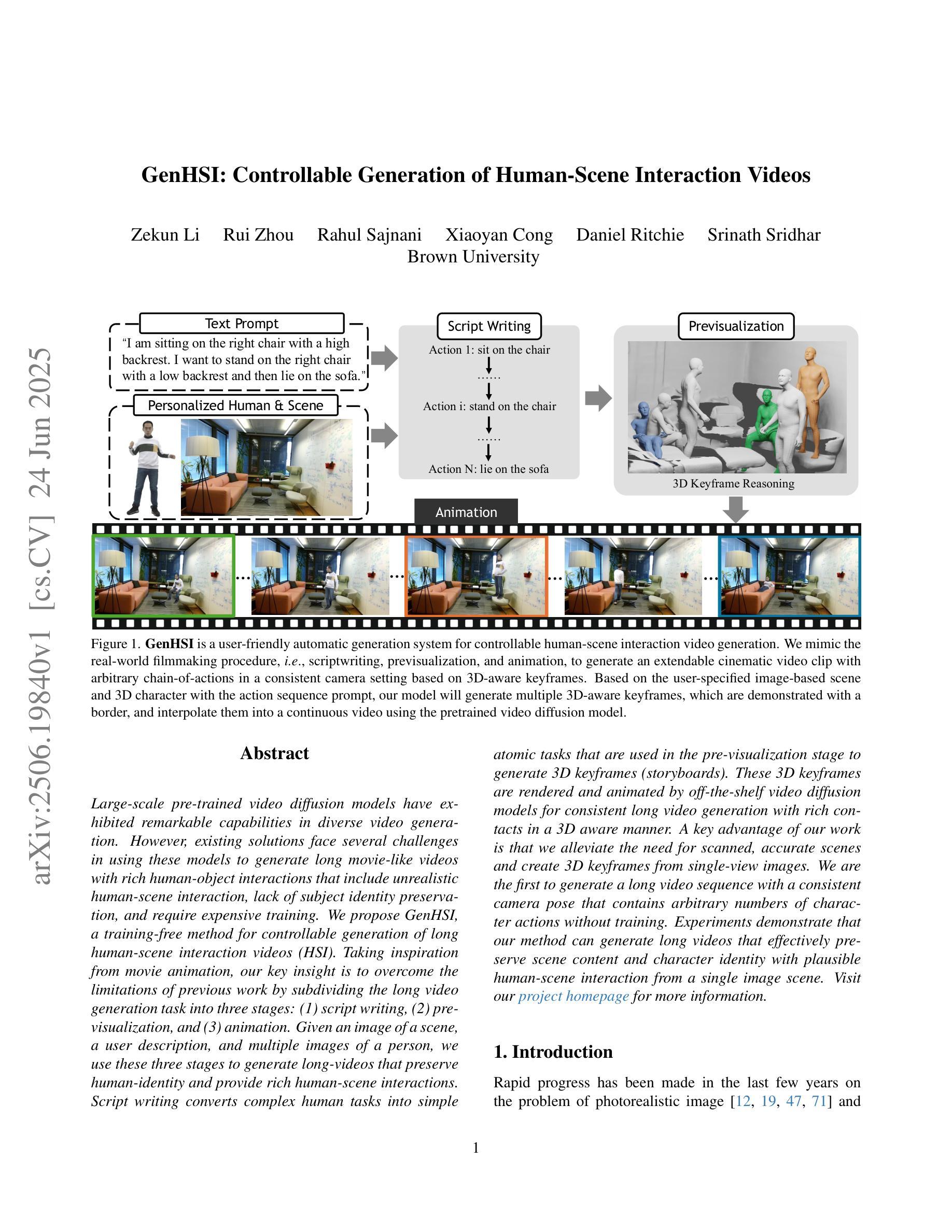
GenHSI: Controllable Generation of Human-Scene Interaction Videos
Authors:Zekun Li, Rui Zhou, Rahul Sajnani, Xiaoyan Cong, Daniel Ritchie, Srinath Sridhar
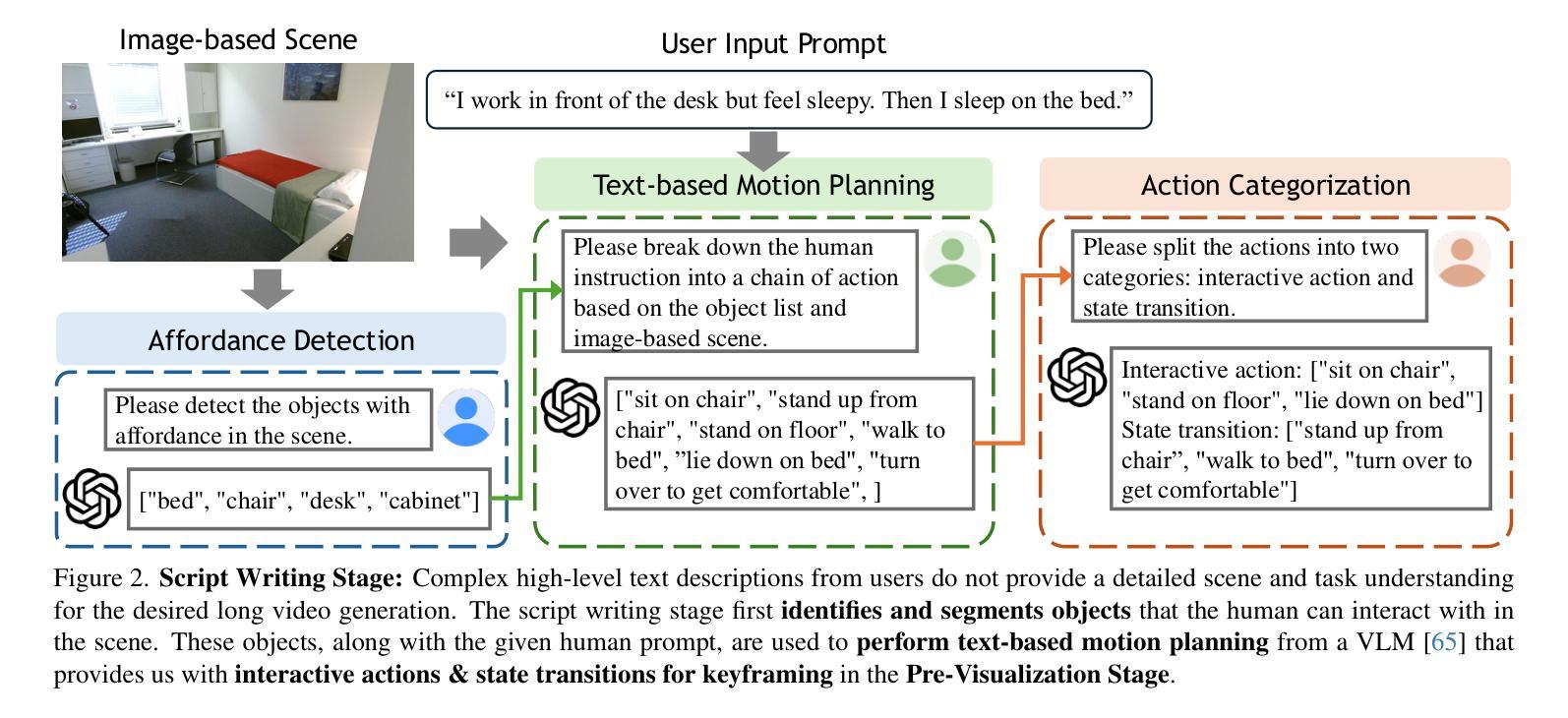
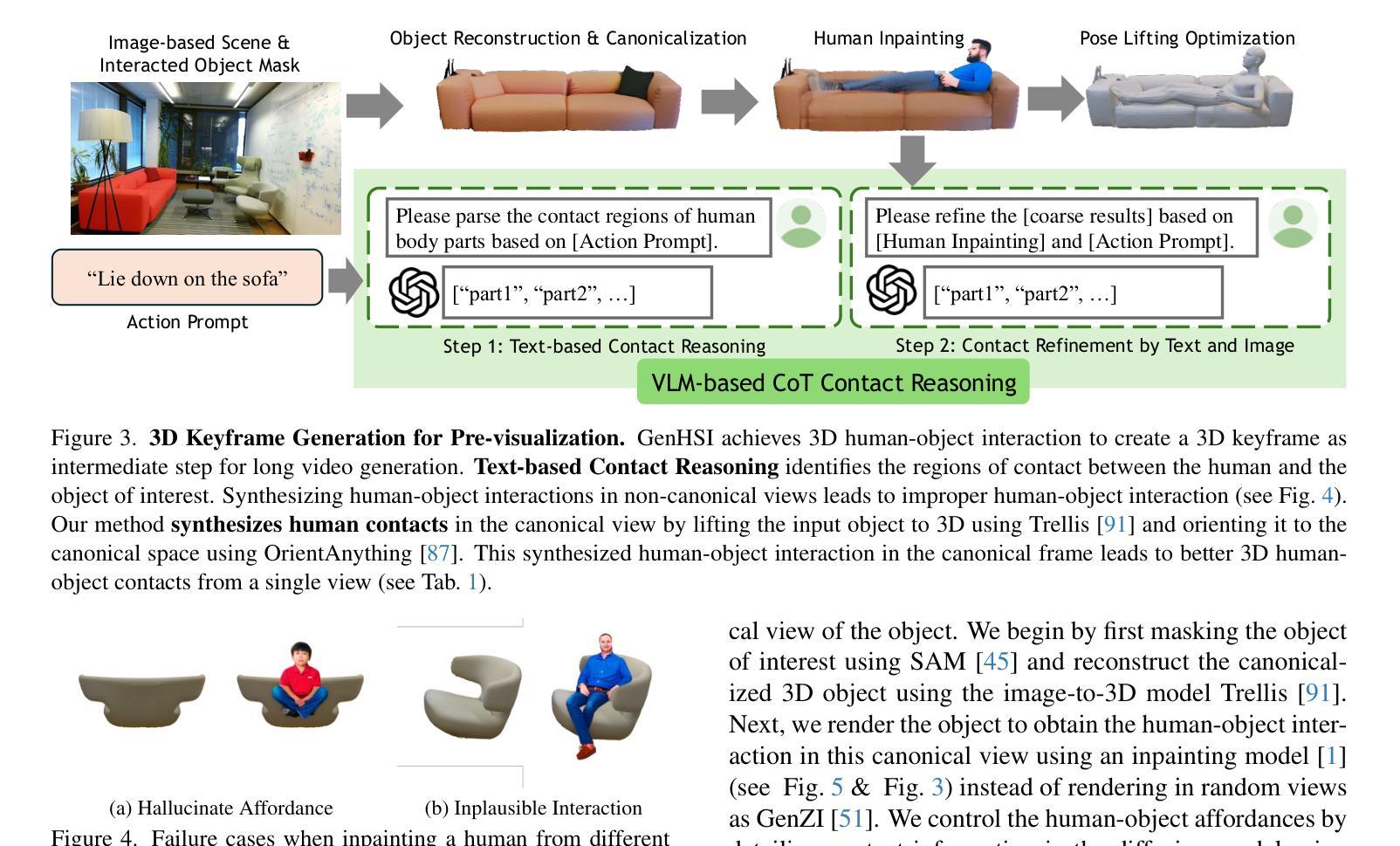
Large-scale pre-trained video diffusion models have exhibited remarkable capabilities in diverse video generation. However, existing solutions face several challenges in using these models to generate long movie-like videos with rich human-object interactions that include unrealistic human-scene interaction, lack of subject identity preservation, and require expensive training. We propose GenHSI, a training-free method for controllable generation of long human-scene interaction videos (HSI). Taking inspiration from movie animation, our key insight is to overcome the limitations of previous work by subdividing the long video generation task into three stages: (1) script writing, (2) pre-visualization, and (3) animation. Given an image of a scene, a user description, and multiple images of a person, we use these three stages to generate long-videos that preserve human-identity and provide rich human-scene interactions. Script writing converts complex human tasks into simple atomic tasks that are used in the pre-visualization stage to generate 3D keyframes (storyboards). These 3D keyframes are rendered and animated by off-the-shelf video diffusion models for consistent long video generation with rich contacts in a 3D-aware manner. A key advantage of our work is that we alleviate the need for scanned, accurate scenes and create 3D keyframes from single-view images. We are the first to generate a long video sequence with a consistent camera pose that contains arbitrary numbers of character actions without training. Experiments demonstrate that our method can generate long videos that effectively preserve scene content and character identity with plausible human-scene interaction from a single image scene. Visit our project homepage https://kunkun0w0.github.io/project/GenHSI/ for more information.
大规模预训练视频扩散模型在多种视频生成方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,现有解决方案在使用这些模型生成包含丰富人机互动的长电影式视频时面临诸多挑战,包括不真实的人景互动、缺乏主题身份保留以及训练成本高昂。我们提出了GenHSI,这是一种无需训练即可控制长人机互动视频(HSI)生成的方法。我们从电影动画中汲取灵感,通过将长视频生成任务细分为三个阶段来克服以前工作的局限性:(1)剧本编写、(2)预可视化、(3)动画制作。给定场景图像、用户描述以及多个人物图像,我们利用这三个阶段来生成保留人物身份并提供丰富人机互动的长视频。剧本编写将复杂的人物任务转换为简单的原子任务,用于在预可视化阶段生成3D关键帧(故事板)。这些3D关键帧由现成的视频扩散模型进行渲染和动画处理,以在3D感知方式下生成连贯的长视频,其中包含丰富的接触。我们工作的一个关键优势是,我们减轻了对扫描精确场景的需求,并能从单视图图像创建3D关键帧。我们是首个能够生成具有一致相机姿态的长视频序列的团队,该序列包含任意数量的人物动作而无需进行训练。实验表明,我们的方法可以从单个图像场景中生成有效保留场景内容和人物身份、具有合理人机互动的长视频。更多信息请访问我们的项目主页https://kunkun0w0.github.io/project/GenHSI/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种无需训练的大型预训练视频扩散模型GenHSI,用于可控地生成长视频的人机交互(HSI)。通过将长视频生成任务分为剧本创作、预可视化和动画制作三个阶段,GenHSI能够从场景图像、用户描述和人物多张图像中生成保持人物身份、提供丰富人机交互的长视频。实验证明,该方法能够生成有效保留场景内容和人物身份、具有合理人机交互的长视频。
Key Takeaways
- GenHSI是一种无需训练的大型预训练视频扩散模型,用于生成长视频的人机交互。
- GenHSI通过将长视频生成任务分为剧本创作、预可视化和动画制作三个阶段,克服现有解决方案的挑战。
- GenHSI能够从场景图像、用户描述和人物多张图像中生成保持人物身份、提供丰富人机交互的长视频。
- GenHSI通过利用现成的视频扩散模型,以3D感知的方式生成一致的长视频,具有丰富的内容接触。
- GenHSI不需要精确的扫描场景,能够从单视图图像创建3D关键帧。
- GenHSI能够生成具有一致摄像机姿态的长视频序列,包含任意数量的人物动作,无需训练。
点此查看论文截图
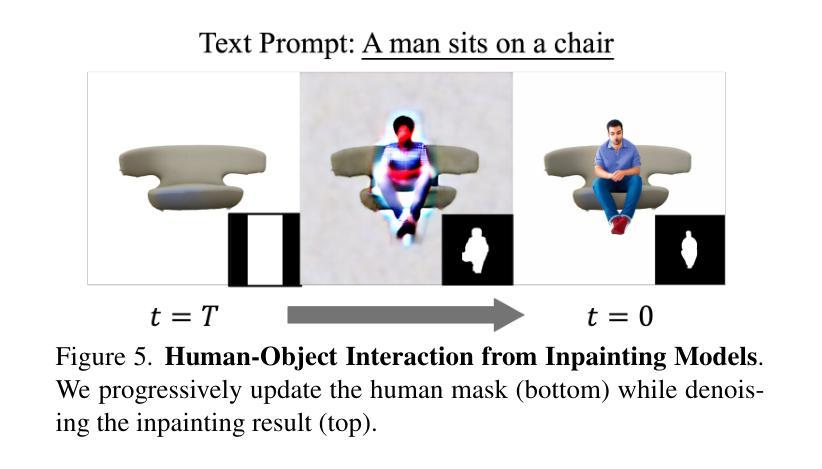
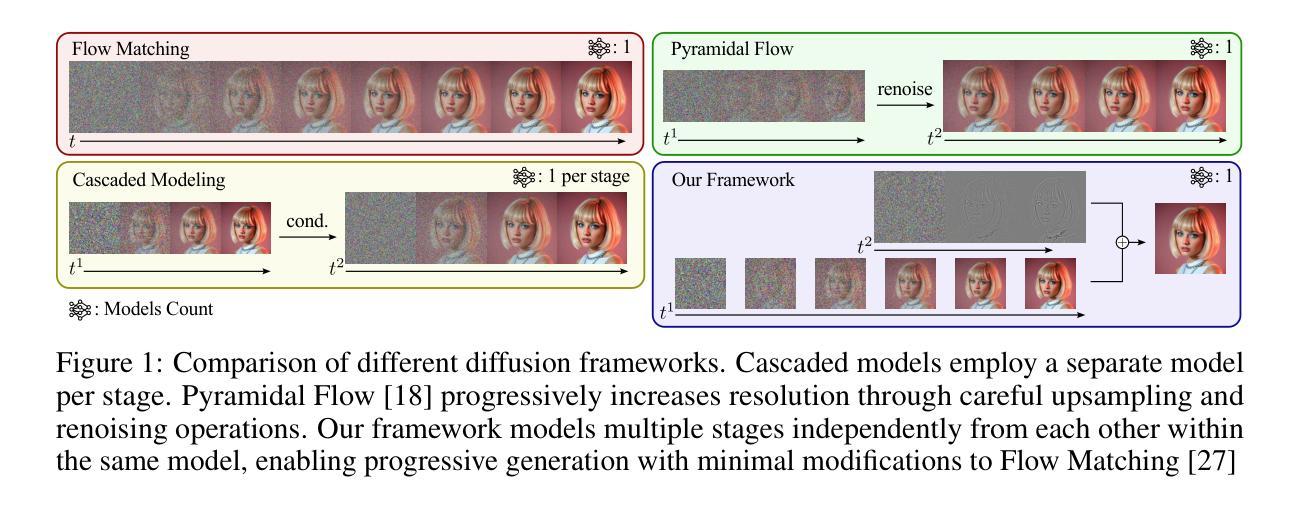
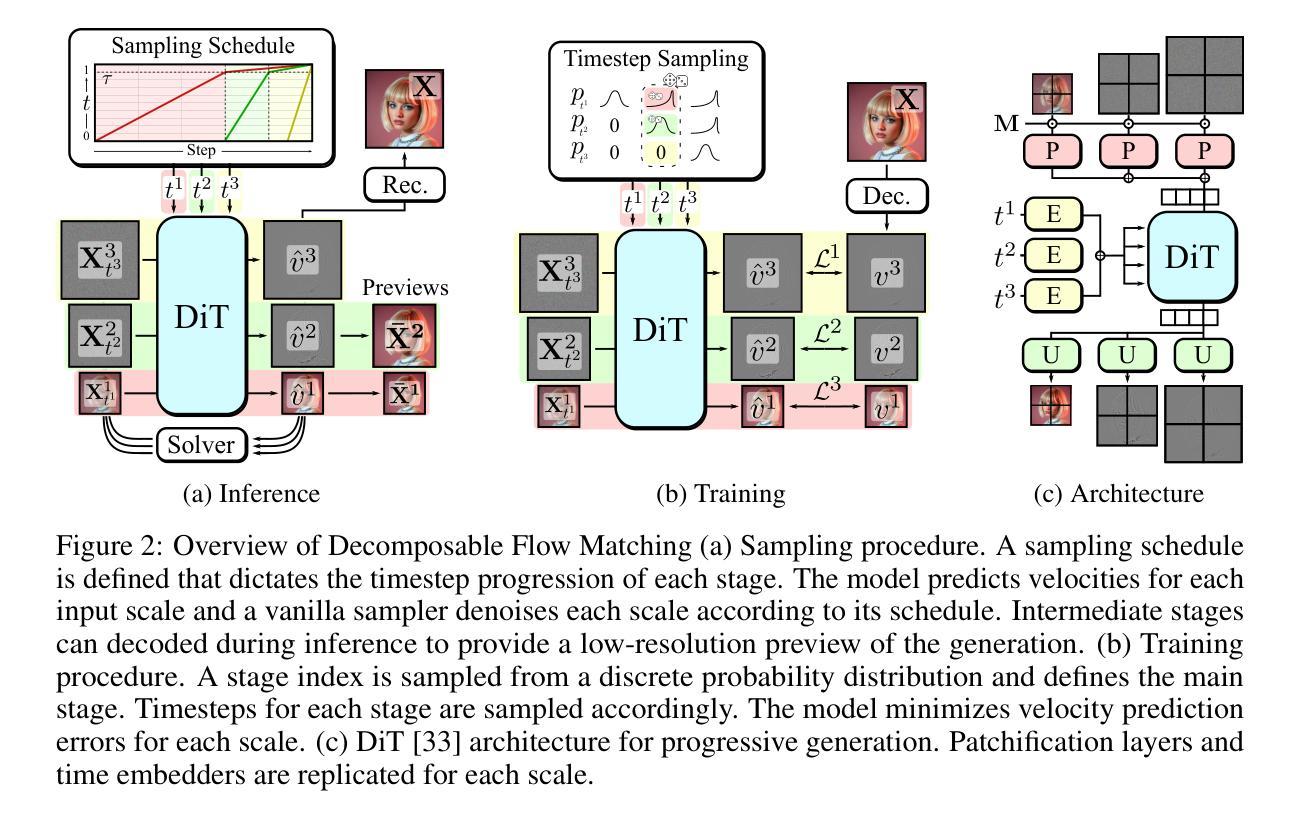
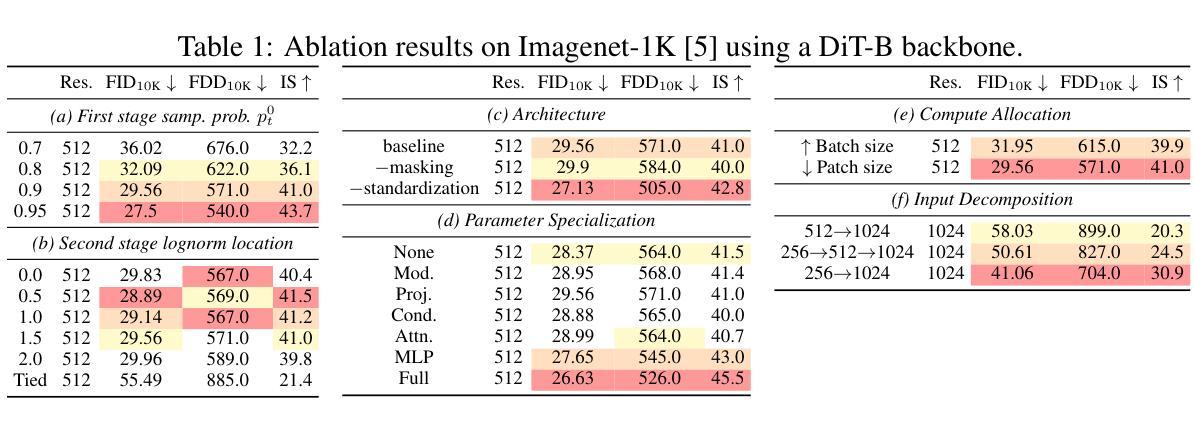
Improving Progressive Generation with Decomposable Flow Matching
Authors:Moayed Haji-Ali, Willi Menapace, Ivan Skorokhodov, Arpit Sahni, Sergey Tulyakov, Vicente Ordonez, Aliaksandr Siarohin
Generating high-dimensional visual modalities is a computationally intensive task. A common solution is progressive generation, where the outputs are synthesized in a coarse-to-fine spectral autoregressive manner. While diffusion models benefit from the coarse-to-fine nature of denoising, explicit multi-stage architectures are rarely adopted. These architectures have increased the complexity of the overall approach, introducing the need for a custom diffusion formulation, decomposition-dependent stage transitions, add-hoc samplers, or a model cascade. Our contribution, Decomposable Flow Matching (DFM), is a simple and effective framework for the progressive generation of visual media. DFM applies Flow Matching independently at each level of a user-defined multi-scale representation (such as Laplacian pyramid). As shown by our experiments, our approach improves visual quality for both images and videos, featuring superior results compared to prior multistage frameworks. On Imagenet-1k 512px, DFM achieves 35.2% improvements in FDD scores over the base architecture and 26.4% over the best-performing baseline, under the same training compute. When applied to finetuning of large models, such as FLUX, DFM shows faster convergence speed to the training distribution. Crucially, all these advantages are achieved with a single model, architectural simplicity, and minimal modifications to existing training pipelines.
生成高维视觉模式是一项计算密集型的任务。常见的解决方案是渐进生成,其中输出以由粗到细的频谱自回归方式合成。虽然扩散模型受益于去噪的由粗到细的特性,但明确的多阶段架构很少被采用。这些架构增加了整体方法的复杂性,需要自定义的扩散公式、依赖于分解的阶段转换、专门的采样器或模型级联。我们的贡献是提出可分解流匹配(DFM),这是一个简单有效的视觉媒体渐进生成框架。DFM在用户定义的多尺度表示(如拉普拉斯金字塔)的每一级独立应用流匹配。我们的实验表明,该方法在图像和视频方面提高了视觉质量,与先前的多阶段框架相比,结果更为优越。在Imagenet-1k 512px上,DFM在FDD得分上较基础架构提高了35.2%,在相同训练计算下较最佳基线提高了26.4%。当应用于大型模型的微调(如FLUX)时,DFM显示出更快的收敛速度以达到训练分布。关键的是,所有这些优势都是用一个单一模型实现的,具有架构简单性,对现有训练管道进行了最少的修改。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Webpage: https://snap-research.github.io/dfm/
Summary
该文介绍了生成高维视觉模态的计算密集型任务中,一种名为可分解流匹配(DFM)的渐进生成视觉媒体的简单有效框架。DFM在用户定义的多尺度表示(如拉普拉斯金字塔)的每个级别上独立应用流匹配,提高了图像和视频的视觉质量,并在Imagenet-1k 512px上实现了对基础架构的35.2%的FDD分数改进,以及对最佳基准的26.4%改进。同时,应用于大型模型的微调时,DFM展现了更快的收敛速度。关键是,所有这些优势都通过一个简单的模型、最少的架构改动和现有的训练管道实现。
Key Takeaways
- 生成高维视觉模态是计算密集型的任务,通常采用渐进生成的方法。
- 扩散模型受益于从粗糙到精细的降噪特性,但多阶段架构的复杂性限制了其应用。
- 可分解流匹配(DFM)是一个简单有效的渐进生成视觉媒体的框架。
- DFM在用户定义的多尺度表示的每个级别上独立应用流匹配。
- DFM提高了图像和视频的视觉质量,并在Imagenet-1k 512px上实现了显著的改进。
- DFM可应用于大型模型的微调,并展现更快的收敛速度。
- DFM的实现具有简单的模型、最少的架构改动和现有的训练管道需求。
点此查看论文截图

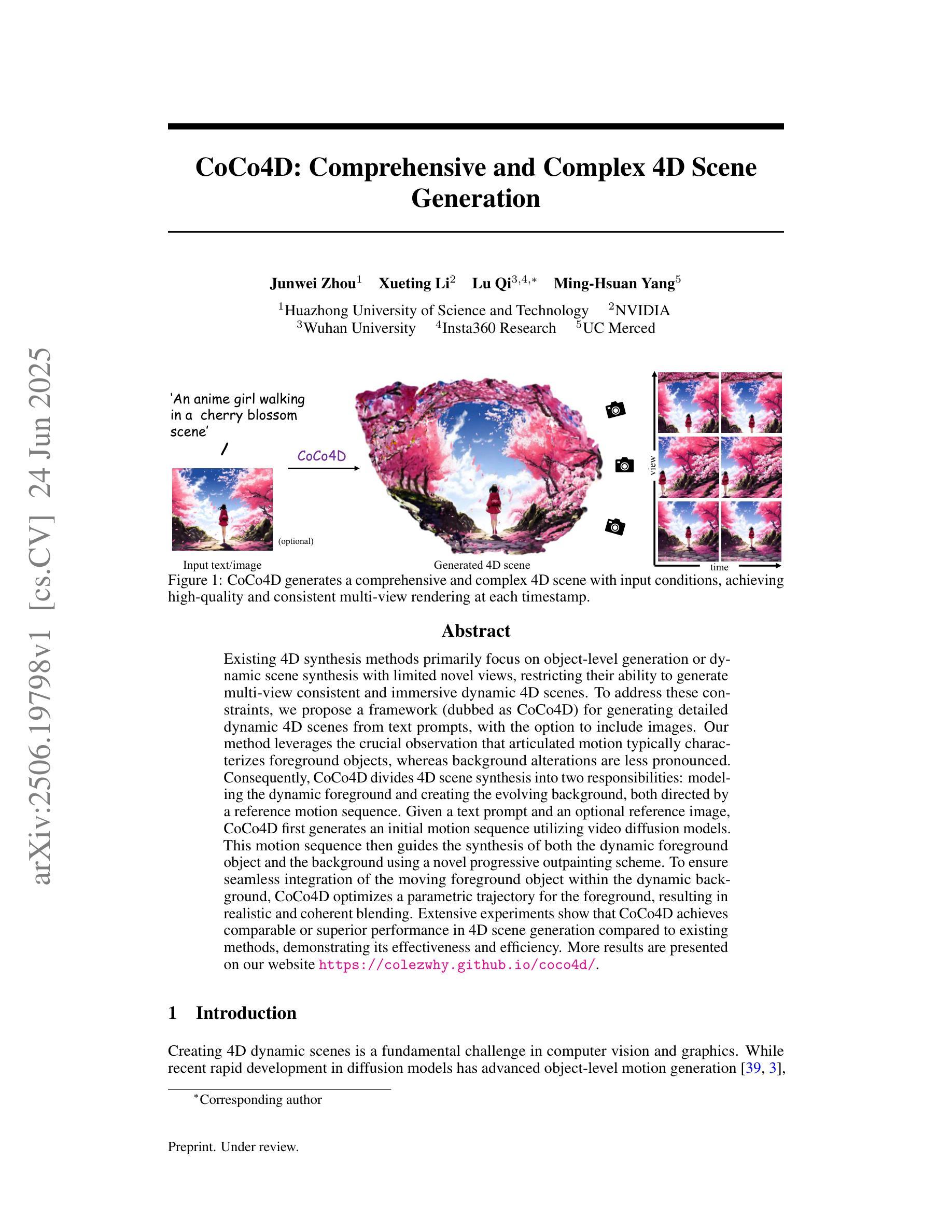
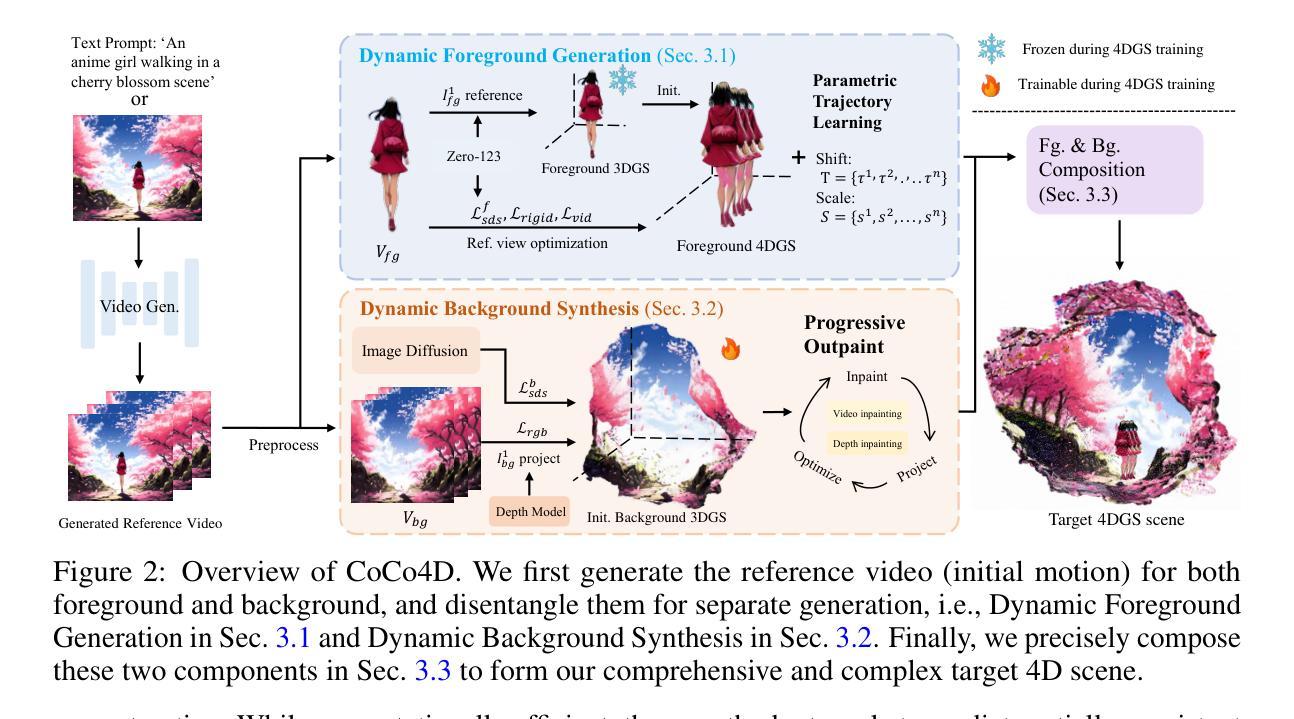
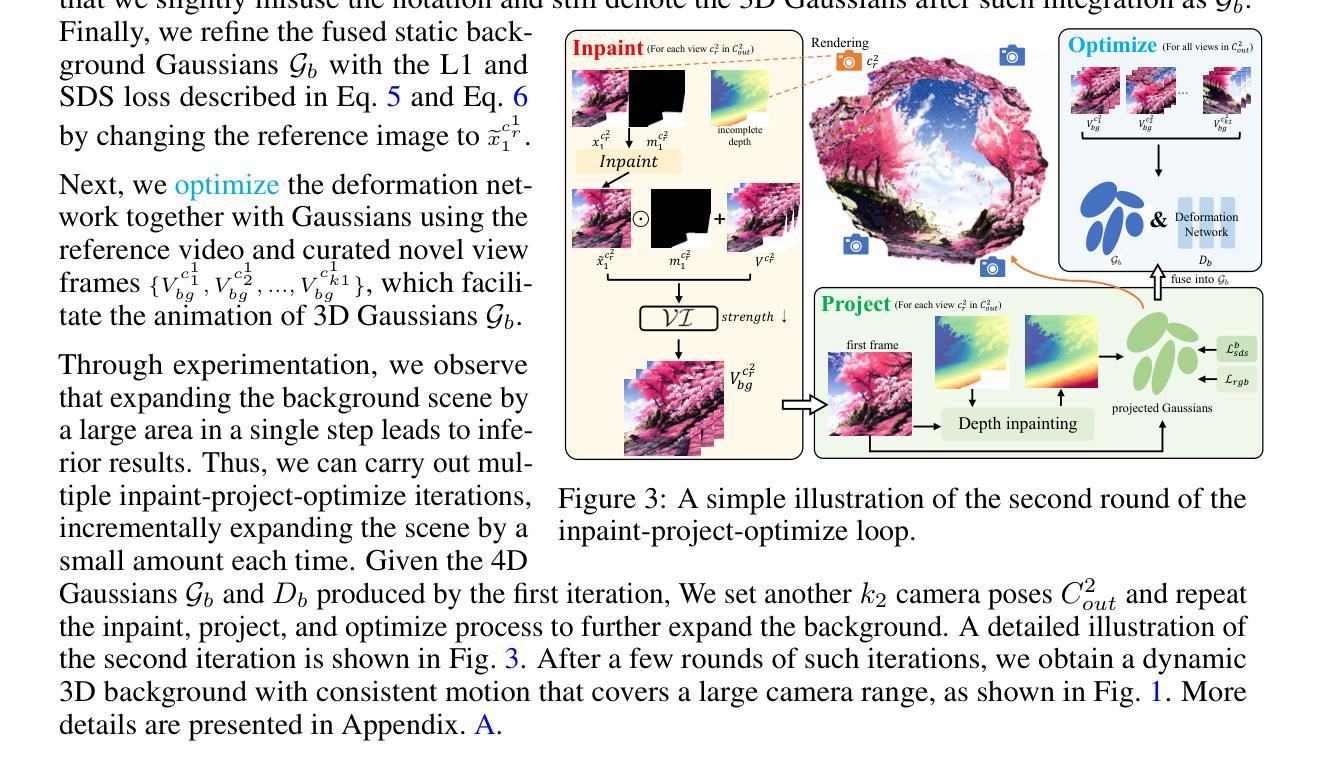
CoCo4D: Comprehensive and Complex 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Junwei Zhou, Xueting Li, Lu Qi, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Existing 4D synthesis methods primarily focus on object-level generation or dynamic scene synthesis with limited novel views, restricting their ability to generate multi-view consistent and immersive dynamic 4D scenes. To address these constraints, we propose a framework (dubbed as CoCo4D) for generating detailed dynamic 4D scenes from text prompts, with the option to include images. Our method leverages the crucial observation that articulated motion typically characterizes foreground objects, whereas background alterations are less pronounced. Consequently, CoCo4D divides 4D scene synthesis into two responsibilities: modeling the dynamic foreground and creating the evolving background, both directed by a reference motion sequence. Given a text prompt and an optional reference image, CoCo4D first generates an initial motion sequence utilizing video diffusion models. This motion sequence then guides the synthesis of both the dynamic foreground object and the background using a novel progressive outpainting scheme. To ensure seamless integration of the moving foreground object within the dynamic background, CoCo4D optimizes a parametric trajectory for the foreground, resulting in realistic and coherent blending. Extensive experiments show that CoCo4D achieves comparable or superior performance in 4D scene generation compared to existing methods, demonstrating its effectiveness and efficiency. More results are presented on our website https://colezwhy.github.io/coco4d/.
当前存在的四维合成方法主要聚焦于物体级别的生成或动态场景合成,并且具有有限的视角范围,这限制了它们在生成多视角一致且沉浸式动态四维场景方面的能力。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种名为CoCo4D的框架,用于从文本提示生成详细的动态四维场景,并且可以选择包含图像。我们的方法利用了关键观察结果,即关节运动通常表征前景物体,而背景变化则不太明显。因此,CoCo4D将四维场景合成分为两个任务:对动态前景进行建模并创建不断变化的背景,两者均由参考运动序列控制。给定文本提示和可选的参考图像,CoCo4D首先利用视频扩散模型生成初始运动序列。然后,此运动序列通过一种新颖的进步式外推方案来指导动态前景物体和背景的合成。为了确保移动前景物体在动态背景中的无缝集成,CoCo4D优化了前景的参数轨迹,从而实现真实且连贯的融合。大量实验表明,在四维场景生成方面,CoCo4D与现有方法相比达到了相当或更优的性能,证明了其有效性和高效性。更多结果请参见我们的网站:https://colezwhy.github.io/coco4d/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages,10 figures
Summary
动态四维度场景生成新方法,从文本提示出发并可选择包含图像。通过理解前景与背景动态变化的差异,分为模拟动态前景和创建变化背景两部分。采用视频扩散模型生成初始运动序列,通过渐进式扩展方案合成动态前景和背景。优化前景参数轨迹,实现无缝集成。在四维度场景生成上表现卓越,详情请见网站。
Key Takeaways
- 现有四维度(4D)合成方法主要关注对象级别的生成或动态场景合成,具有局限性。
- 提出名为CoCo4D的框架,可从文本提示生成详细动态4D场景,并可选择包含图像。
- CoCo4D利用前景和背景动态变化差异进行建模,分为模拟动态前景和创建背景两部分。
- 通过视频扩散模型生成初始运动序列,引导前景和背景的合成。
- 采用渐进式扩展方案实现场景合成。
- 优化前景参数轨迹,确保无缝集成动态前景于背景中。
点此查看论文截图
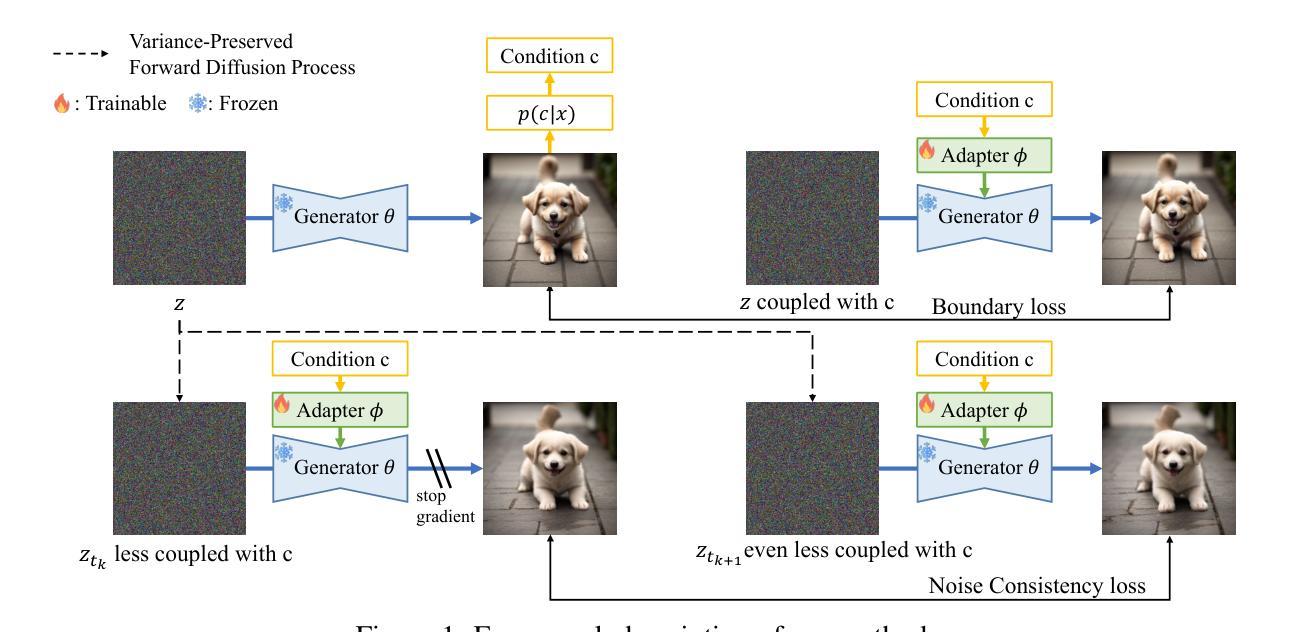
Noise Consistency Training: A Native Approach for One-Step Generator in Learning Additional Controls
Authors:Yihong Luo, Shuchen Xue, Tianyang Hu, Jing Tang
The pursuit of efficient and controllable high-quality content generation remains a central challenge in artificial intelligence-generated content (AIGC). While one-step generators, enabled by diffusion distillation techniques, offer excellent generation quality and computational efficiency, adapting them to new control conditions–such as structural constraints, semantic guidelines, or external inputs–poses a significant challenge. Conventional approaches often necessitate computationally expensive modifications to the base model and subsequent diffusion distillation. This paper introduces Noise Consistency Training (NCT), a novel and lightweight approach to directly integrate new control signals into pre-trained one-step generators without requiring access to original training images or retraining the base diffusion model. NCT operates by introducing an adapter module and employs a noise consistency loss in the noise space of the generator. This loss aligns the adapted model’s generation behavior across noises that are conditionally dependent to varying degrees, implicitly guiding it to adhere to the new control. Theoretically, this training objective can be understood as minimizing the distributional distance between the adapted generator and the conditional distribution induced by the new conditions. NCT is modular, data-efficient, and easily deployable, relying only on the pre-trained one-step generator and a control signal model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that NCT achieves state-of-the-art controllable generation in a single forward pass, surpassing existing multi-step and distillation-based methods in both generation quality and computational efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/Luo-Yihong/NCT
在人工智能生成内容(AIGC)领域,追求高效且可控的高质量内容生成仍然是一个核心挑战。一步生成器通过扩散蒸馏技术实现了出色的生成质量和计算效率,但将其适应新的控制条件(如结构约束、语义指南或外部输入)却是一个巨大的挑战。传统方法通常需要对基础模型进行昂贵的修改和随后的扩散蒸馏。本文介绍了噪声一致性训练(NCT)这一新颖而轻量级的方法,它可以直接将新的控制信号集成到预训练的一步生成器中,无需访问原始训练图像或重新训练基础扩散模型。NCT通过引入适配器模块并采用生成器噪声空间中的噪声一致性损失来运行。这种损失会调整适应模型的生成行为,使其在不同程度的条件噪声之间保持一致,从而隐式地指导其适应新的控制。从理论上讲,这种训练目标可以理解为最小化适应生成器与由新条件引起的条件分布之间的分布距离。NCT具有模块化、数据高效、易于部署等特点,仅依赖于预训练的一步生成器和控制信号模型。大量实验表明,NCT在单次前向传递中实现了最先进的可控生成,在生成质量和计算效率方面都超越了现有的多步骤和基于蒸馏的方法。相关代码可通过https://github.com/Luo-Yihong/NCT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种新颖且轻量级的方法——噪声一致性训练(NCT),用于将新的控制信号直接集成到预训练的一步生成器中,实现高效可控的高质量内容生成。该方法无需访问原始训练图像或重新训练基础扩散模型,通过引入适配器模块和噪声空间中的噪声一致性损失,使适应模型的生成行为在不同条件下保持一致,从而实现控制。实验证明,NCT在单次前向传递中实现可控生成,达到最新技术水平,在生成质量和计算效率上均超越了现有的多步骤和基于蒸馏的方法。
Key Takeaways
- NCT是一种用于适应预训练的一步生成器以响应新控制条件的方法。
- 通过引入适配器模块和噪声一致性损失,NCT能够在不需要原始训练图像或重新训练基础扩散模型的情况下集成新的控制信号。
- NCT方法实现了在噪声空间中的一致性,使适应模型的生成行为在不同条件下保持一致。
- NCT通过最小化适应生成器与由新条件引起的条件分布之间的分布距离,实现了理论上的训练目标。
- NCT具有模块化、数据高效和易于部署的特点,仅依赖于预训练的一步生成器和控制信号模型。
- 实验证明,NCT在单次前向传递中实现了可控生成,达到或超越了现有方法的生成质量和计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

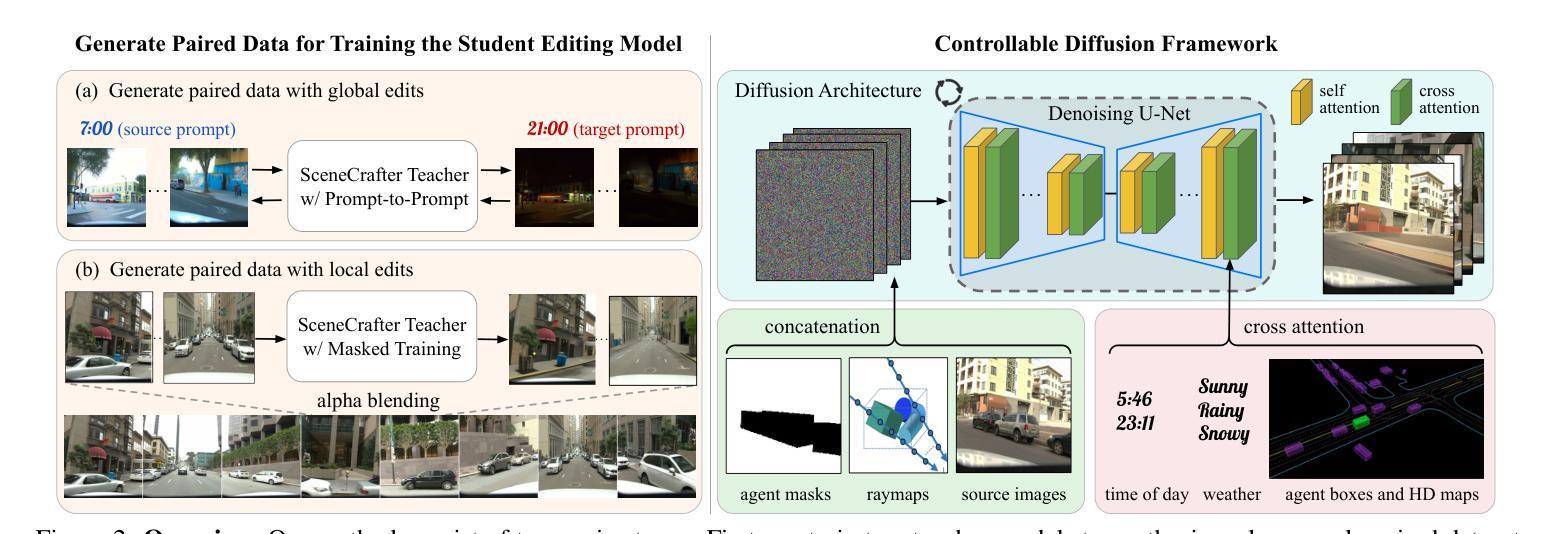
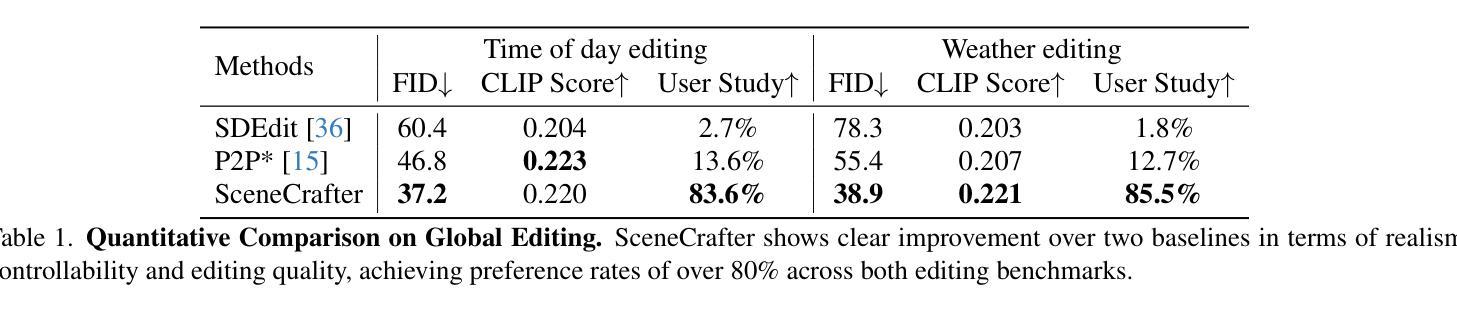
SceneCrafter: Controllable Multi-View Driving Scene Editing
Authors:Zehao Zhu, Yuliang Zou, Chiyu Max Jiang, Bo Sun, Vincent Casser, Xiukun Huang, Jiahao Wang, Zhenpei Yang, Ruiqi Gao, Leonidas Guibas, Mingxing Tan, Dragomir Anguelov
Simulation is crucial for developing and evaluating autonomous vehicle (AV) systems. Recent literature builds on a new generation of generative models to synthesize highly realistic images for full-stack simulation. However, purely synthetically generated scenes are not grounded in reality and have difficulty in inspiring confidence in the relevance of its outcomes. Editing models, on the other hand, leverage source scenes from real driving logs, and enable the simulation of different traffic layouts, behaviors, and operating conditions such as weather and time of day. While image editing is an established topic in computer vision, it presents fresh sets of challenges in driving simulation: (1) the need for cross-camera 3D consistency, (2) learning ``empty street” priors from driving data with foreground occlusions, and (3) obtaining paired image tuples of varied editing conditions while preserving consistent layout and geometry. To address these challenges, we propose SceneCrafter, a versatile editor for realistic 3D-consistent manipulation of driving scenes captured from multiple cameras. We build on recent advancements in multi-view diffusion models, using a fully controllable framework that scales seamlessly to multi-modality conditions like weather, time of day, agent boxes and high-definition maps. To generate paired data for supervising the editing model, we propose a novel framework on top of Prompt-to-Prompt to generate geometrically consistent synthetic paired data with global edits. We also introduce an alpha-blending framework to synthesize data with local edits, leveraging a model trained on empty street priors through novel masked training and multi-view repaint paradigm. SceneCrafter demonstrates powerful editing capabilities and achieves state-of-the-art realism, controllability, 3D consistency, and scene editing quality compared to existing baselines.
模拟对于开发和评估自动驾驶(AV)系统至关重要。最近的研究文献建立在一代新的生成模型上,合成高度逼真的图像,用于全栈模拟。然而,纯粹合成生成的场景并没有实际基础,且难以激发对其结果相关性的信心。另一方面,编辑模型则利用来自真实驾驶日志的源场景,能够模拟不同的交通布局、行为和操作条件,例如天气和一天中的时间。虽然图像编辑是计算机视觉中的一个既定主题,但它给驾驶模拟带来了新的挑战:(1)需要跨相机3D一致性,(2)从带有前景遮挡的驾驶数据中学习“空街”先验,以及(3)在保持一致布局和几何结构的同时,获取具有不同编辑条件的配对图像元组。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SceneCrafter,这是一个通用的编辑器,可以对从多个相机捕获的驾驶场景进行逼真的3D一致操作。我们建立在最新的多视角扩散模型进展之上,使用完全可控的框架,无缝扩展到多模式条件,如天气、一天中的时间、代理框和高清晰度地图。为了生成用于监督编辑模型的数据对,我们在Prompt-to-Prompt之上提出了一个新的框架,以生成具有全局编辑的几何一致合成数据对。我们还引入了一个alpha混合框架,以合成具有局部编辑的数据,利用一个通过新颖掩膜训练和多元视图重绘范式训练的空街先验模型。SceneCrafter展现出强大的编辑能力,并在现实感、可控性、3D一致性和场景编辑质量方面达到了现有基准的最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
摘要
新一代生成模型在合成高度逼真的图像以进行全堆栈模拟方面有着广泛的应用,这对于开发和评估自动驾驶系统至关重要。然而,纯粹的合成场景缺乏现实基础,难以让人信服其结果的现实性。因此,编辑模型应运而生,它利用真实驾驶日志的场景作为来源,并模拟不同的交通布局、行为和操作条件,如天气和时间。然而,驾驶模拟中的图像编辑虽然带来了许多新挑战,例如需要跨相机进行三维一致性处理、学习存在前景遮挡的“空街”先验知识,以及在保持一致的布局和几何的同时获得配对图像的不同编辑条件等。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SceneCrafter,这是一个用于从多个相机捕获的驾驶场景进行现实三维一致性操作的通用编辑器。借助最新的多视角扩散模型,我们构建了一个可完全控制的框架,可无缝扩展到多模式条件下,如天气、时间、代理框和高精度地图等。为了生成用于监督编辑模型的数据对,我们在Prompt-to-Prompt的基础上提出了一个新型框架来生成具有全局编辑的几何一致性合成数据对。我们还引入了一个alpha混合框架来合成具有局部编辑的数据,并利用新型掩膜训练和跨视图重绘范式来训练一个空街先验模型。SceneCrafter展示了强大的编辑能力,并在现实感、可控性、三维一致性和场景编辑质量方面达到了最新水平。
关键见解
- 新一代生成模型在自动驾驶车辆模拟中发挥着重要作用,能够合成高度逼真的图像。
- 纯粹合成场景由于缺乏现实基础,在评估自动驾驶系统时难以建立信心。
- 编辑模型利用真实驾驶日志的场景,能够模拟不同的交通条件,如天气和时间。
- 驾驶模拟中的图像编辑面临挑战,包括跨相机的三维一致性、学习空街先验知识等。
- SceneCrafter是一个强大的编辑工具,能够实现现实三维一致的驾驶场景操作。
- SceneCrafter利用多视角扩散模型,可无缝适应多种模式条件,如天气、时间等。
点此查看论文截图


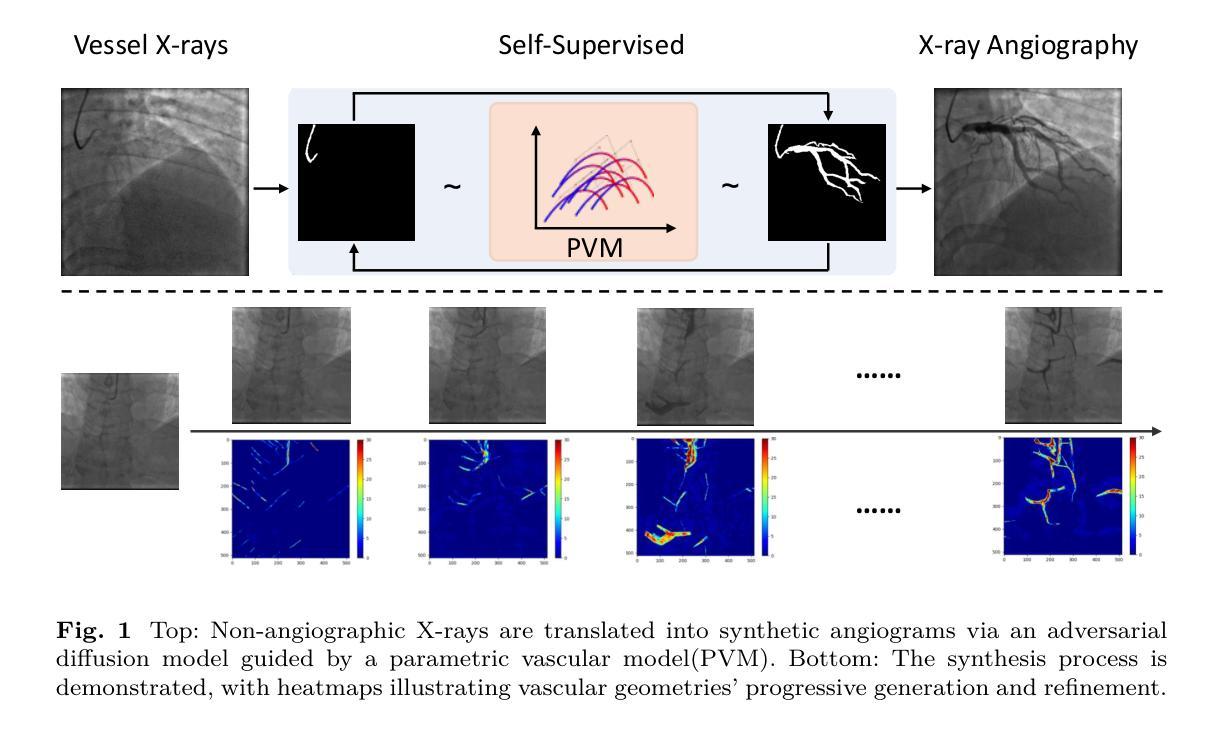
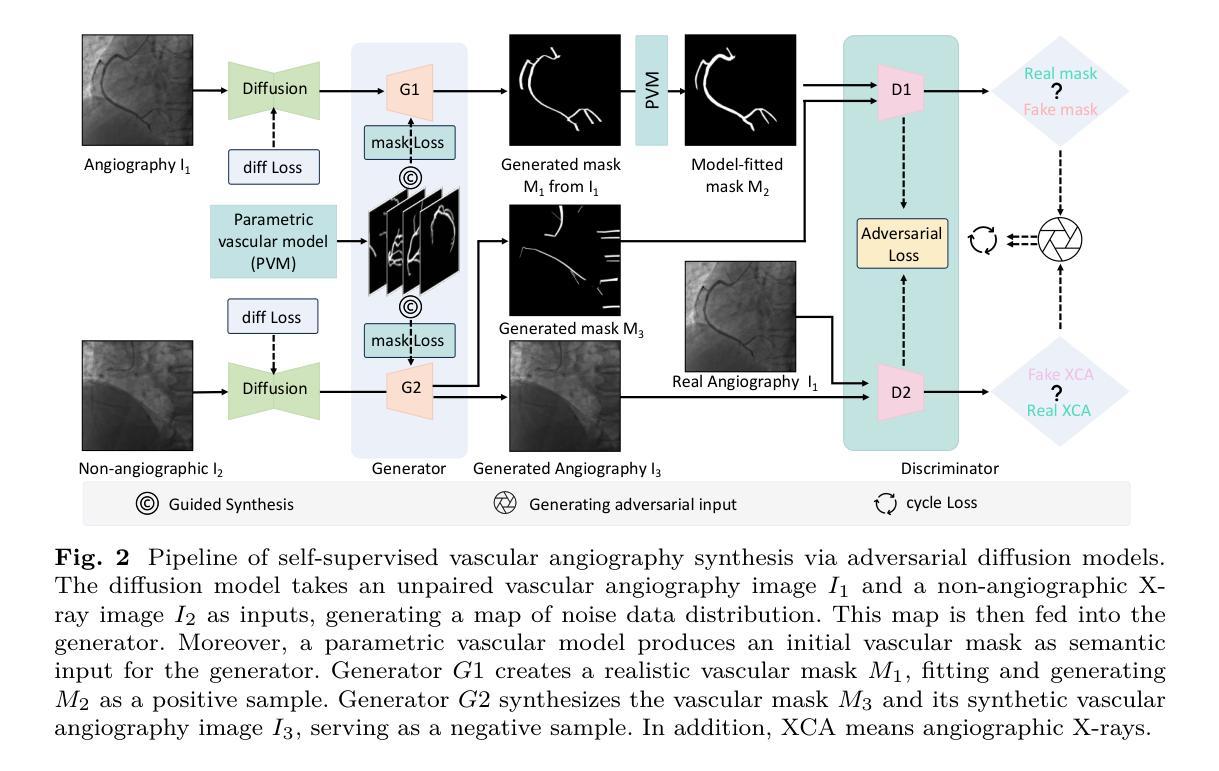
Angio-Diff: Learning a Self-Supervised Adversarial Diffusion Model for Angiographic Geometry Generation
Authors:Zhifeng Wang, Renjiao Yi, Xin Wen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu, Kunlun He
Vascular diseases pose a significant threat to human health, with X-ray angiography established as the gold standard for diagnosis, allowing for detailed observation of blood vessels. However, angiographic X-rays expose personnel and patients to higher radiation levels than non-angiographic X-rays, which are unwanted. Thus, modality translation from non-angiographic to angiographic X-rays is desirable. Data-driven deep approaches are hindered by the lack of paired large-scale X-ray angiography datasets. While making high-quality vascular angiography synthesis crucial, it remains challenging. We find that current medical image synthesis primarily operates at pixel level and struggles to adapt to the complex geometric structure of blood vessels, resulting in unsatisfactory quality of blood vessel image synthesis, such as disconnections or unnatural curvatures. To overcome this issue, we propose a self-supervised method via diffusion models to transform non-angiographic X-rays into angiographic X-rays, mitigating data shortages for data-driven approaches. Our model comprises a diffusion model that learns the distribution of vascular data from diffusion latent, a generator for vessel synthesis, and a mask-based adversarial module. To enhance geometric accuracy, we propose a parametric vascular model to fit the shape and distribution of blood vessels. The proposed method contributes a pipeline and a synthetic dataset for X-ray angiography. We conducted extensive comparative and ablation experiments to evaluate the Angio-Diff. The results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in synthetic angiography image quality and more accurately synthesizes the geometric structure of blood vessels. The code is available at https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff.
血管疾病对人类健康构成重大威胁,X线血管造影术已确立为诊断的金标准,能够详细观察血管。然而,血管造影X线使人员和患者暴露在比非血管造影X线更高的辐射水平下,这是不必要的。因此,从非血管造影X线到血管造影X线的模态转换是可行的。数据驱动的深度方法因缺乏配套的大规模X线血管造影数据集而受到阻碍。尽管进行高质量的血管造影合成至关重要,但仍然存在挑战。我们发现当前的医学图像合成主要停留在像素层面,难以适应血管的复杂几何结构,导致血管图像合成的质量不佳,如断裂或不自然的弯曲。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的白监督方法,将非血管造影X线转化为血管造影X线,缓解数据驱动方法的短缺数据问题。我们的模型包括一个从扩散潜在学习中血管数据分布的扩散模型、一个血管合成生成器和一个基于遮罩的对抗模块。为了提高几何精度,我们提出了一个参数化血管模型,以拟合血管的形状和分布。所提出的方法为X线血管造影贡献了一条管道和合成数据集。我们进行了广泛的比较和消融实验来评估Angio-Diff。结果表明,我们的方法在合成血管造影图像质量方面达到最新性能,并更准确地合成血管的几何结构。代码可在https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
非血管造影X射线因辐射水平较低而更受欢迎,但其对血管疾病的诊断效果不如血管造影X射线。由于缺乏大规模配对血管造影X射线数据集,数据驱动的深度学习方法受限。当前医学图像合成主要在像素层面操作,难以适应血管复杂几何结构,导致血管图像合成质量不佳。本研究提出一种基于扩散模型的自监督方法,将非血管造影X射线转化为血管造影X射线,解决数据短缺问题。该方法包括扩散模型、血管合成生成器和基于掩膜的对抗模块,并提出参数化血管模型提高几何准确性。实验结果显示,该方法在合成血管造影图像质量和血管几何结构合成准确性方面达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 血管疾病诊断中,X射线血管造影仍是金标准,但其较高的辐射暴露成为痛点。
- 数据驱动方法受限于缺乏配对的大规模血管造影X射线数据集。
- 当前医学图像合成方法在适应血管复杂几何结构方面存在挑战,导致合成质量不佳。
- 提出一种基于扩散模型的自监督方法,实现从非血管造影X射线到血管造影X射线的转换。
- 方法包括扩散模型、血管合成生成器和基于掩膜的对抗模块,以确保图像质量。
- 引入参数化血管模型以提高几何准确性。
- 实验结果显示该方法在合成血管造影图像质量和准确性方面领先。
点此查看论文截图

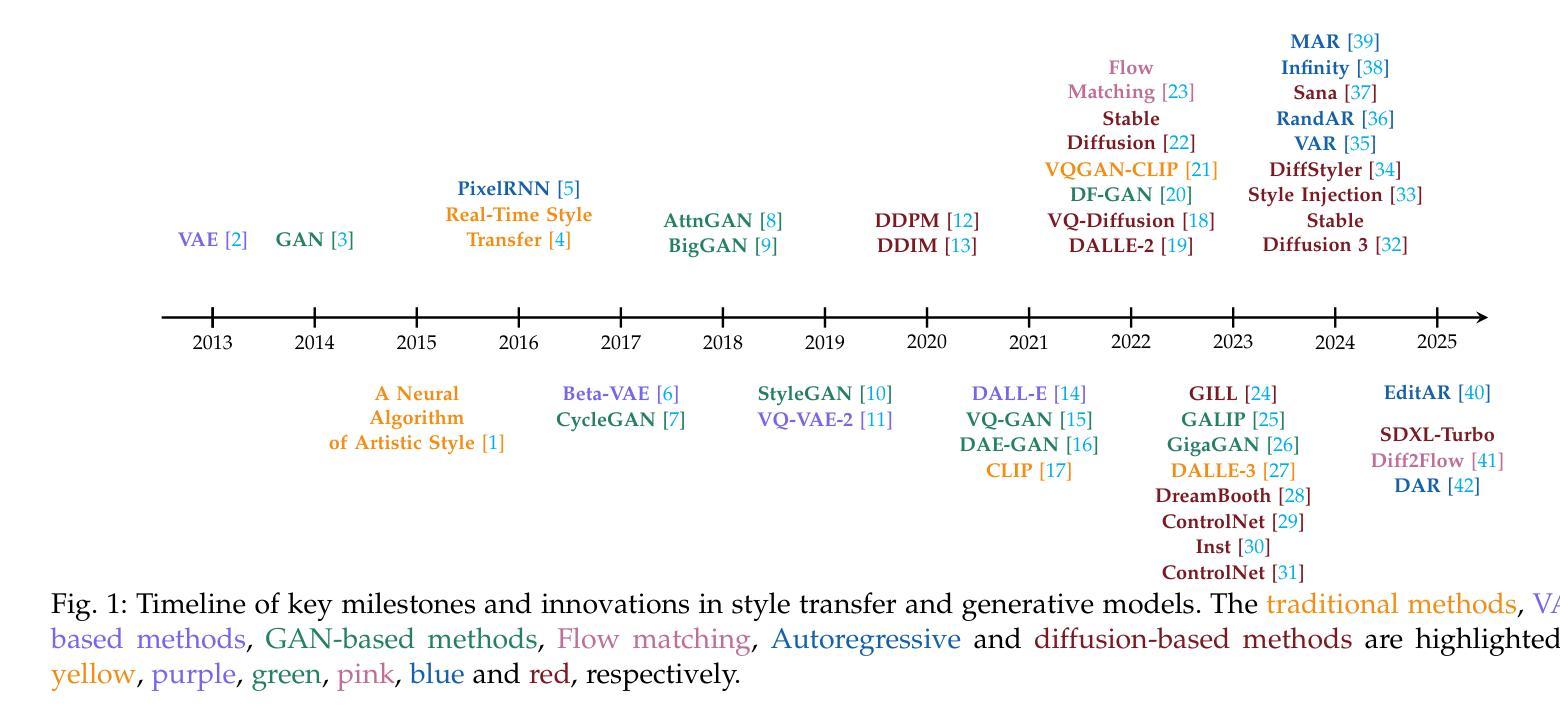
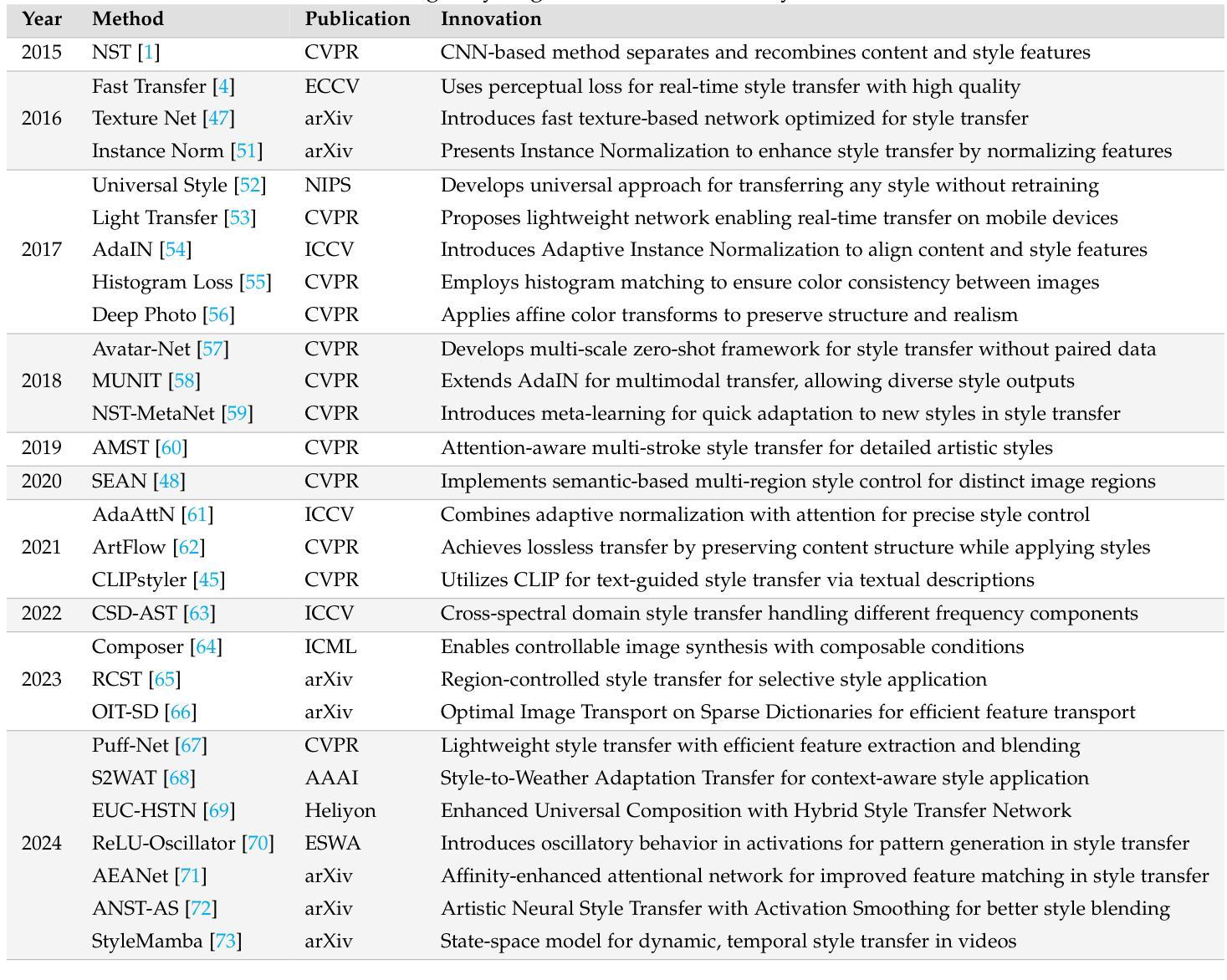
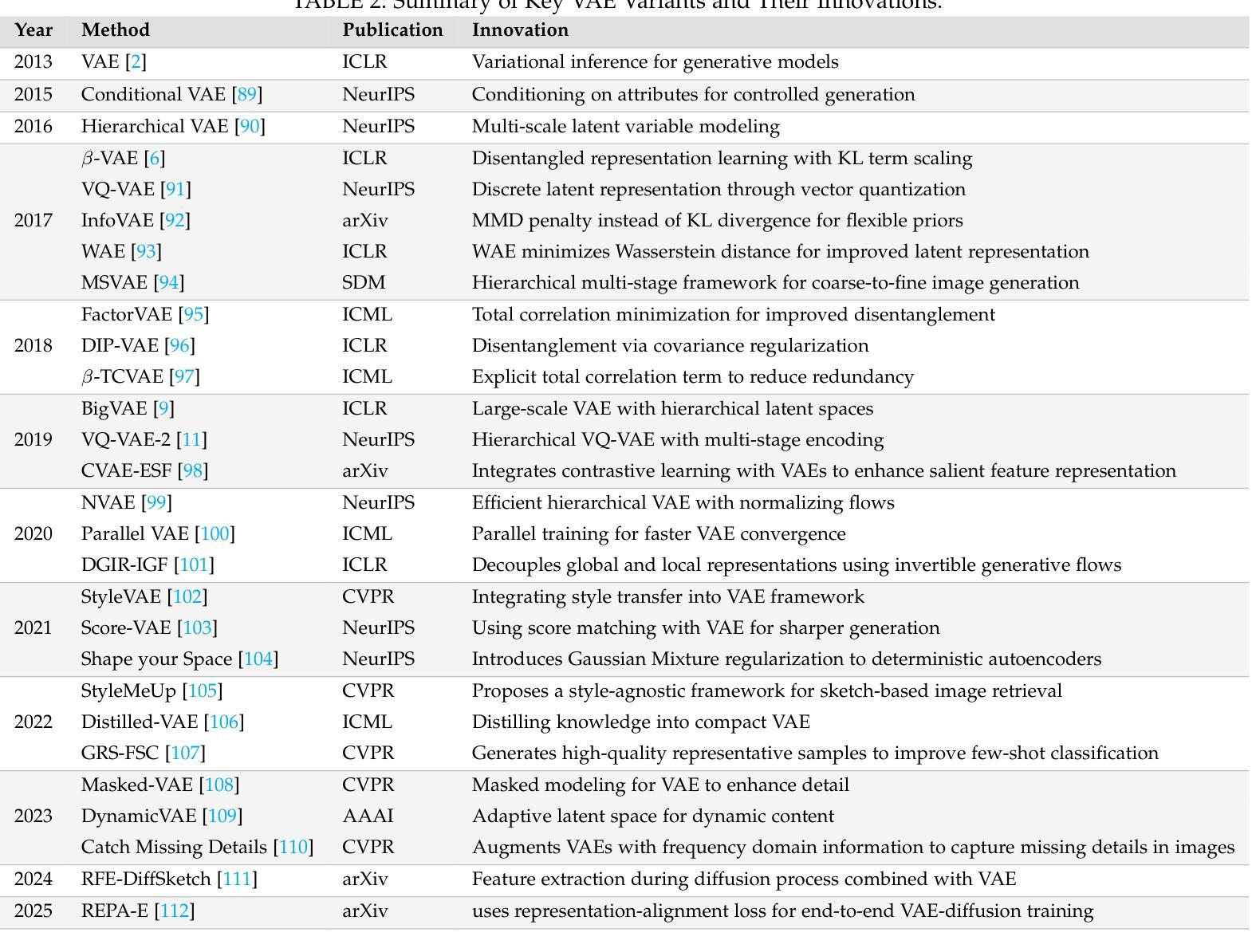
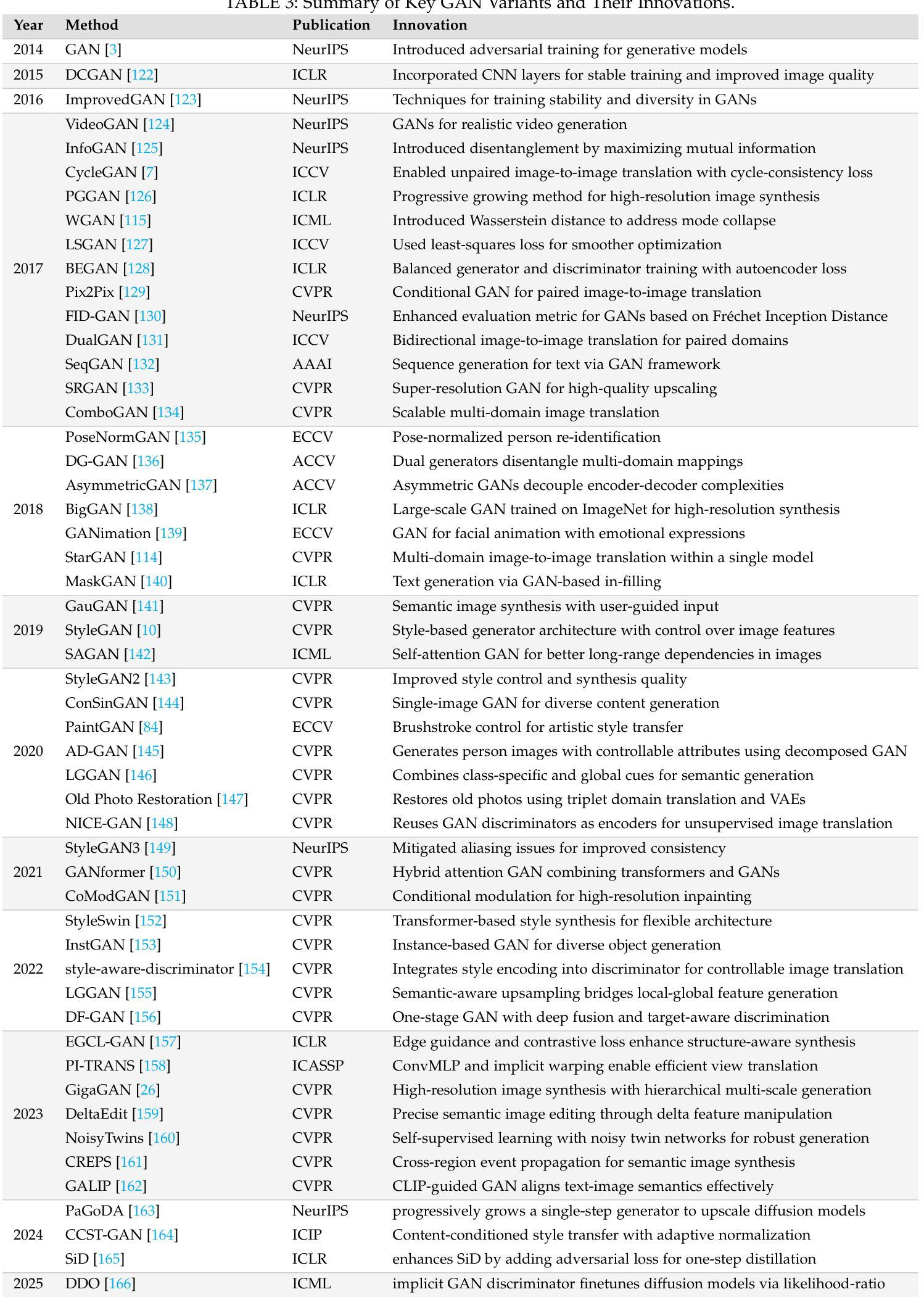
Style Transfer: A Decade Survey
Authors:Tianshan Zhang, Hao Tang
The revolutionary advancement of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) has fundamentally transformed the landscape of visual content creation and artistic expression. While remarkable progress has been made in image generation and style transfer, the underlying mechanisms and aesthetic implications of these technologies remain insufficiently understood. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of AIGC technologies in visual arts, tracing their evolution from early algorithmic frameworks to contemporary deep generative models. We identify three pivotal paradigms: Variational Autoencoders (VAE), Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Diffusion Models, and examine their roles in bridging the gap between human creativity and machine synthesis. To support our analysis, we systematically review over 500 research papers published in the past decade, spanning both foundational developments and state-of-the-art innovations. Furthermore, we propose a multidimensional evaluation framework that incorporates Technical Innovation, Artistic Merit, Visual Quality, Computational Efficiency, and Creative Potential. Our findings reveal both the transformative capacities and current limitations of AIGC systems, emphasizing their profound impact on the future of creative practices. Through this extensive synthesis, we offer a unified perspective on the convergence of artificial intelligence and artistic expression, while outlining key challenges and promising directions for future research in this rapidly evolving field.
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的革命性进步从根本上改变了视觉内容创作和艺术表达领域的格局。虽然在图像生成和风格转换方面取得了显著进展,但这些技术的基础机制和美学影响尚未得到充分理解。本文全面概述了AIGC技术在视觉艺术领域的应用,追溯了从早期算法框架到当前深度生成模型的演变过程。我们确定了三个关键范式:变分自编码器(VAE)、生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型,并探讨了它们在弥合人类创造力和机器合成之间的差距方面的作用。为了支持我们的分析,我们系统地回顾了过去十年发表的500多篇研究论文,包括基础发展和最新创新。此外,我们提出了一个多维评价框架,纳入技术创新、艺术价值、视觉质量、计算效率和创意潜力。我们的研究结果表明,人工智能生成内容系统的变革能力和当前局限性,并强调了它对未来创作实践的深远影响。通过这一综合综述,我们对人工智能和艺术表达的融合提供了统一的视角,同时概述了未来在这一快速发展领域研究的关键挑战和前景方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages
Summary
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)在视觉艺术领域带来了革命性的进展,改变了视觉内容创作和艺术表达的方式。本文从算法框架到当前深度生成模型全面回顾了AIGC技术在视觉艺术领域的发展,并指出了三种关键范式:变分自编码器(VAE)、生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型。通过对超过500篇研究论文的系统回顾和分析,本文提出了一个多维度的评估框架,涵盖了技术创新、艺术价值、视觉质量、计算效率和创意潜力等方面。研究揭示了AIGC系统的变革潜力和当前局限,强调了其对未来艺术创作实践的深远影响。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能生成内容(AIGC)在视觉艺术领域带来革命性进展。
- AIGC技术从早期算法框架发展到当前深度生成模型。
- 文中指出了三种关键范式:变分自编码器(VAE)、生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型。
- 系统回顾了超过500篇研究论文,包括基础发展及最新创新。
- 提出了一个多维度的评估框架,包括技术创新、艺术价值、视觉质量等方面。
- 研究揭示了AIGC系统的变革潜力和当前局限。
点此查看论文截图


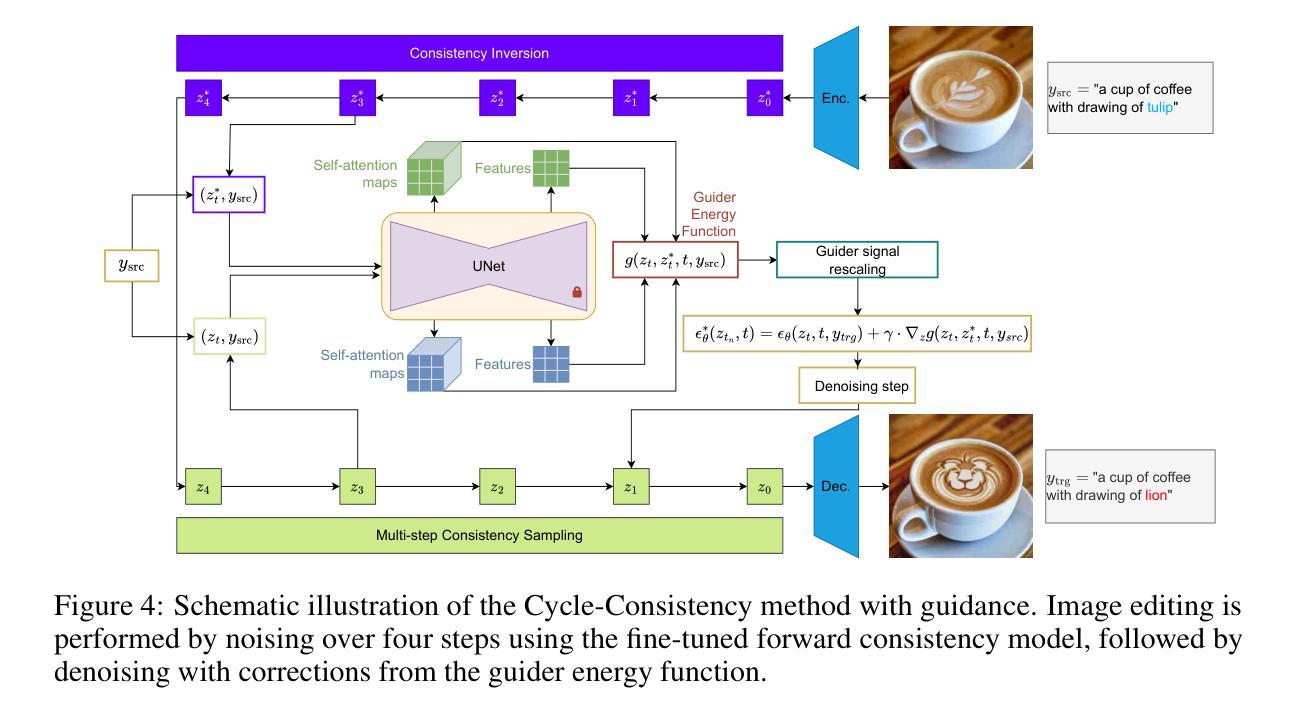
Inverse-and-Edit: Effective and Fast Image Editing by Cycle Consistency Models
Authors:Ilia Beletskii, Andrey Kuznetsov, Aibek Alanov
Recent advances in image editing with diffusion models have achieved impressive results, offering fine-grained control over the generation process. However, these methods are computationally intensive because of their iterative nature. While distilled diffusion models enable faster inference, their editing capabilities remain limited, primarily because of poor inversion quality. High-fidelity inversion and reconstruction are essential for precise image editing, as they preserve the structural and semantic integrity of the source image. In this work, we propose a novel framework that enhances image inversion using consistency models, enabling high-quality editing in just four steps. Our method introduces a cycle-consistency optimization strategy that significantly improves reconstruction accuracy and enables a controllable trade-off between editability and content preservation. We achieve state-of-the-art performance across various image editing tasks and datasets, demonstrating that our method matches or surpasses full-step diffusion models while being substantially more efficient. The code of our method is available on GitHub at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/Inverse-and-Edit.
在扩散模型图像编辑方面的最新进展取得了令人印象深刻的结果,对生成过程进行了精细控制。然而,由于这些方法的迭代性质,计算量很大。尽管蒸馏扩散模型能够实现更快的推理,但其编辑功能仍然有限,主要是因为反转质量较差。高保真反转和重建对于精确图像编辑至关重要,因为它们保留了源图像的结构和语义完整性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种利用一致性模型增强图像反转的新型框架,只需四个步骤即可实现高质量编辑。我们的方法引入了一种循环一致性优化策略,显著提高了重建精度,并在可编辑性和内容保留之间实现了可控的权衡。我们在各种图像编辑任务和数据集上实现了最先进的性能,证明我们的方法在匹配或超越全步扩散模型的同时,效率更高。我们的方法的代码可以在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/ControlGenAI/Inverse-and-Edit。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code of our method is available on GitHub at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/Inverse-and-Edit
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的图像编辑技术的新进展。文章指出,虽然扩散模型能够提供精细的生成过程控制,但它们计算量大且迭代性质导致计算效率低下。为了解决这个问题,研究者提出了一种使用一致性模型(Consistency Models)增强图像反转(inversion)的新框架,实现了高质量编辑仅需四步完成。新方法引入了循环一致性优化策略,显著提高重建精度,可在编辑和内容保留之间实现可控权衡。实验结果表明,该方法在不同图像编辑任务和数据集上达到领先水平,相比全步扩散模型更高效,代码已开源于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像编辑领域取得显著进展,但计算量大仍是挑战。
- 现有蒸馏扩散模型虽加快推理速度,但编辑能力受限,主要因为反转质量不佳。
- 高保真反转和重建对于精确图像编辑至关重要,能保留源图像的结构和语义完整性。
- 研究者提出了一种新的框架,利用一致性模型增强图像反转。
- 新方法引入循环一致性优化策略,显著提高了重建精度。
- 该方法实现了编辑和内容保留之间的可控权衡,在各种图像编辑任务和数据集上表现优秀。
点此查看论文截图



When Diffusion Models Memorize: Inductive Biases in Probability Flow of Minimum-Norm Shallow Neural Nets
Authors:Chen Zeno, Hila Manor, Greg Ongie, Nir Weinberger, Tomer Michaeli, Daniel Soudry
While diffusion models generate high-quality images via probability flow, the theoretical understanding of this process remains incomplete. A key question is when probability flow converges to training samples or more general points on the data manifold. We analyze this by studying the probability flow of shallow ReLU neural network denoisers trained with minimal $\ell^2$ norm. For intuition, we introduce a simpler score flow and show that for orthogonal datasets, both flows follow similar trajectories, converging to a training point or a sum of training points. However, early stopping by the diffusion time scheduler allows probability flow to reach more general manifold points. This reflects the tendency of diffusion models to both memorize training samples and generate novel points that combine aspects of multiple samples, motivating our study of such behavior in simplified settings. We extend these results to obtuse simplex data and, through simulations in the orthogonal case, confirm that probability flow converges to a training point, a sum of training points, or a manifold point. Moreover, memorization decreases when the number of training samples grows, as fewer samples accumulate near training points.
尽管扩散模型通过概率流生成高质量图像,但对此过程的理论理解仍然不完整。一个关键的问题是概率流何时收敛于训练样本或数据流形上的更一般点。我们通过研究用最小l²范数训练的浅层ReLU神经网络去噪器的概率流来分析这个问题。为了直观理解,我们引入了一个更简单的分数流,并表明对于正交数据集,两种流遵循相似的轨迹,收敛到训练点或训练点的和。然而,扩散时间调度器的提前停止允许概率流达到更一般的流形点。这反映了扩散模型既会记住训练样本,又会生成结合多个样本方面的新点的趋势,这促使我们在简化环境中研究这种行为。我们将这些结果扩展到晦涩的单纯形数据,并通过正交情况的模拟证实,概率流收敛于训练点、训练点的和或流形点。此外,当训练样本的数量增加时,记忆会减少,因为较少的样本在训练点附近积累。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Forty-second International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025)
Summary
扩散模型通过概率流生成高质量图像,但其理论理解尚不完全。本文通过分析浅层ReLU神经网络去噪器在最小二范数下的概率流来探究概率流何时收敛于训练样本或数据流形上的更一般点。引入更简单的分数流,对于正交数据集,两种流遵循相似的轨迹,收敛到训练点或训练点的组合。但扩散时间调度器的提前停止允许概率流达到更一般的流形点。这反映了扩散模型既会记忆训练样本,也会生成结合多个样本方面的新点,激励我们在简化环境中研究这种行为。本文将这些结果扩展到复杂的数据集,并通过正交情况的模拟证实概率流收敛于训练点、训练点的组合或流形点。此外,随着训练样本数量的增长,记忆会逐渐减少。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过概率流生成高质量图像,但其理论理解尚未完全成熟。
- 扩散模型中的概率流收敛问题被研究,特别是在浅层ReLU神经网络去噪器的上下文中。
- 引入更简单分数流的概念,其与概率流的轨迹在正交数据集上相似。
- 扩散时间调度器的提前停止允许概率流探索数据空间中的更广泛区域。
- 扩散模型既会记忆训练样本,也能生成结合多个样本特征的新点。
- 在模拟的正交情况下,概率流被观察到收敛于训练点、训练点的组合或流形点。
点此查看论文截图

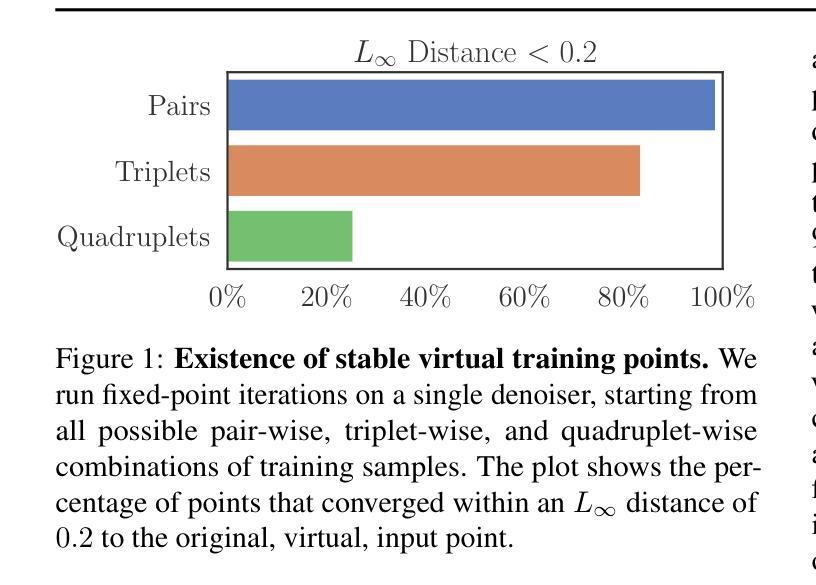
LoRA-Edit: Controllable First-Frame-Guided Video Editing via Mask-Aware LoRA Fine-Tuning
Authors:Chenjian Gao, Lihe Ding, Xin Cai, Zhanpeng Huang, Zibin Wang, Tianfan Xue
Video editing using diffusion models has achieved remarkable results in generating high-quality edits for videos. However, current methods often rely on large-scale pretraining, limiting flexibility for specific edits. First-frame-guided editing provides control over the first frame, but lacks flexibility over subsequent frames. To address this, we propose a mask-based LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) tuning method that adapts pretrained Image-to-Video (I2V) models for flexible video editing. Our approach preserves background regions while enabling controllable edits propagation. This solution offers efficient and adaptable video editing without altering the model architecture. To better steer this process, we incorporate additional references, such as alternate viewpoints or representative scene states, which serve as visual anchors for how content should unfold. We address the control challenge using a mask-driven LoRA tuning strategy that adapts a pre-trained image-to-video model to the editing context. The model must learn from two distinct sources: the input video provides spatial structure and motion cues, while reference images offer appearance guidance. A spatial mask enables region-specific learning by dynamically modulating what the model attends to, ensuring that each area draws from the appropriate source. Experimental results show our method achieves superior video editing performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project Page: https://cjeen.github.io/LoraEditPaper
使用扩散模型进行视频编辑已经在生成高质量视频编辑方面取得了显著成果。然而,当前的方法通常依赖于大规模预训练,这限制了特定编辑的灵活性。虽然基于首帧引导编辑可以控制首帧,但对于后续帧的控制却不足。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种基于掩码的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,该方法可适应预训练图像到视频(I2V)模型,实现灵活的视频编辑。我们的方法能够在保留背景区域的同时,实现可控的编辑传播。这种解决方案在不改变模型架构的情况下,实现了高效且可适应的视频编辑。为了更好地引导这一过程,我们引入了额外的参考,如不同的视角或具有代表性的场景状态,它们作为内容展开的可视锚点。我们使用掩膜驱动的LoRA调优策略来解决控制挑战,该策略使预训练的图像到视频模型适应编辑上下文。模型必须从两个独特的信息源中学习:输入视频提供空间结构和运动线索,而参考图像提供外观指导。空间掩膜通过动态调制模型关注的区域来实现特定区域的学习,确保每个区域都能从适当的源中获取。实验结果表明,我们的方法达到了先进的视频编辑性能水平。项目页面:https://cjeen.github.io/LoraEditPaper
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
基于扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的视频编辑技术已生成高质量的视频编辑效果。为提升视频编辑的灵活性和可控性,提出了一种基于掩膜(mask-based)的LoRA(低秩适应,Low-Rank Adaptation)调参方法,适用于预训练图像到视频(I2V)模型的灵活视频编辑。通过引入额外参考图像作为视觉锚点,解决了控制难题。使用掩膜驱动的LoRA调参策略,使模型能够在编辑环境中适应学习。实验结果显示,该方法相较于现有技术,视频编辑性能更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于视频编辑取得了显著成果。
- 当前方法依赖大规模预训练,缺乏特定编辑的灵活性。
- 提出基于掩膜的LoRA调参方法,用于适应预训练图像到视频模型进行灵活视频编辑。
- 方法能保留背景区域,实现可控的编辑传播。
- 方法高效且可适应视频编辑,无需改变模型架构。
- 引入额外参考图像作为视觉锚点,以更好地引导编辑过程。
点此查看论文截图


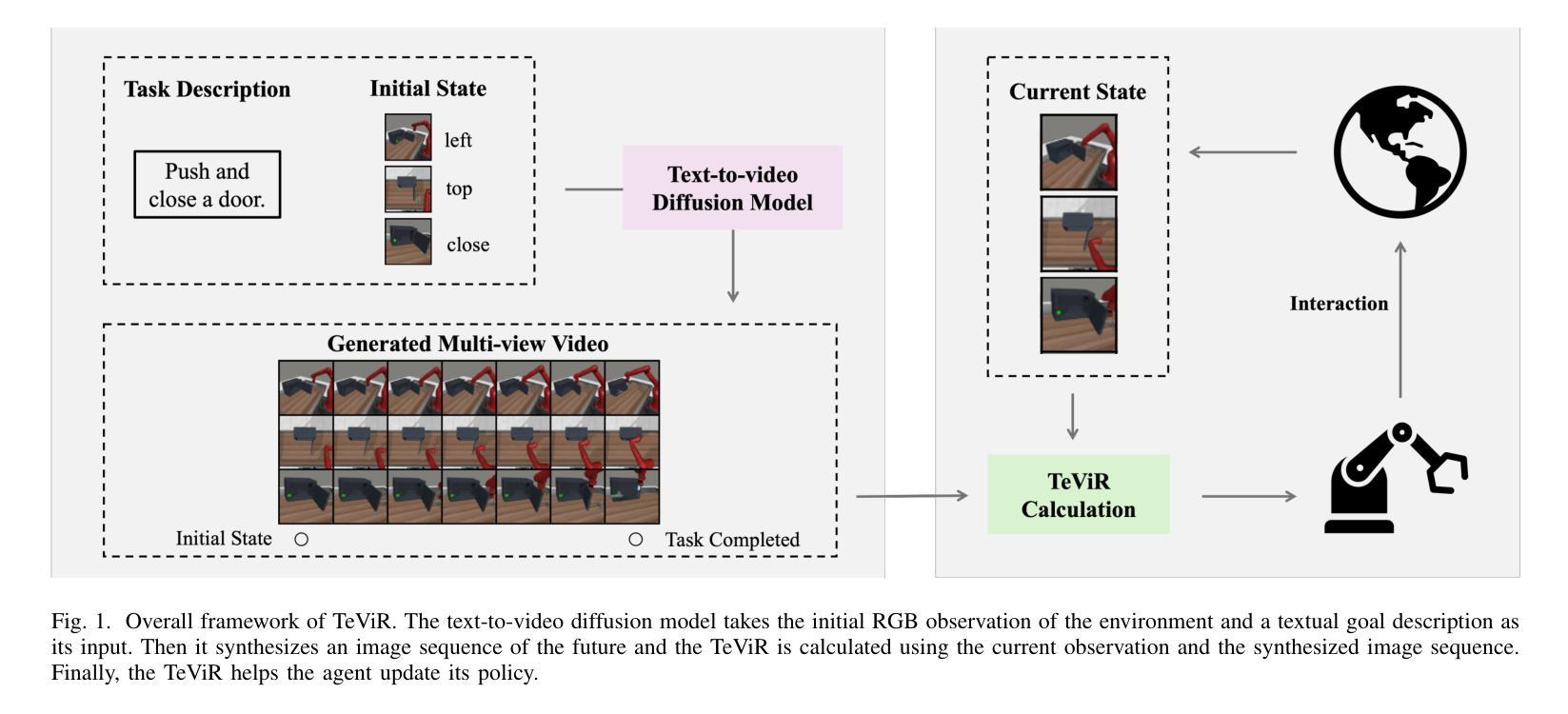
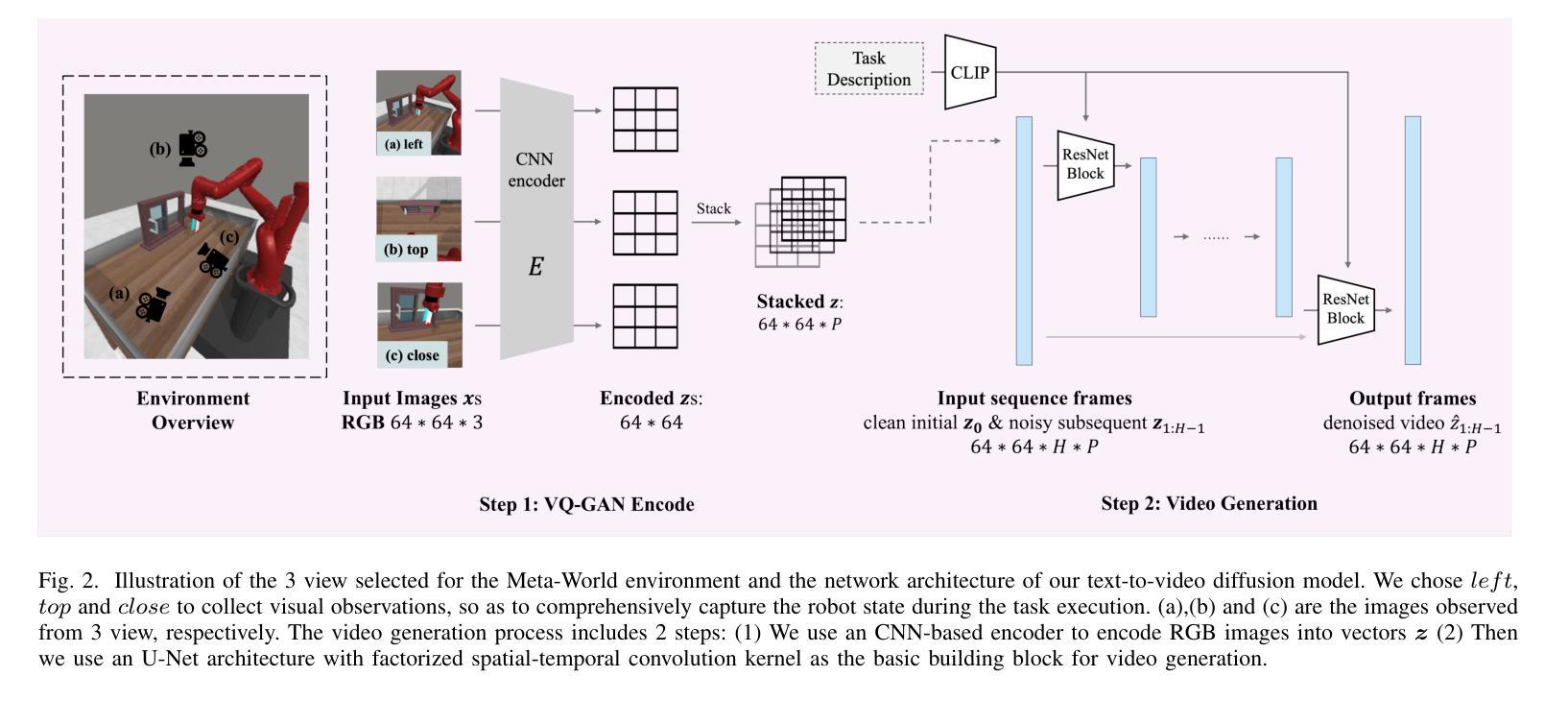
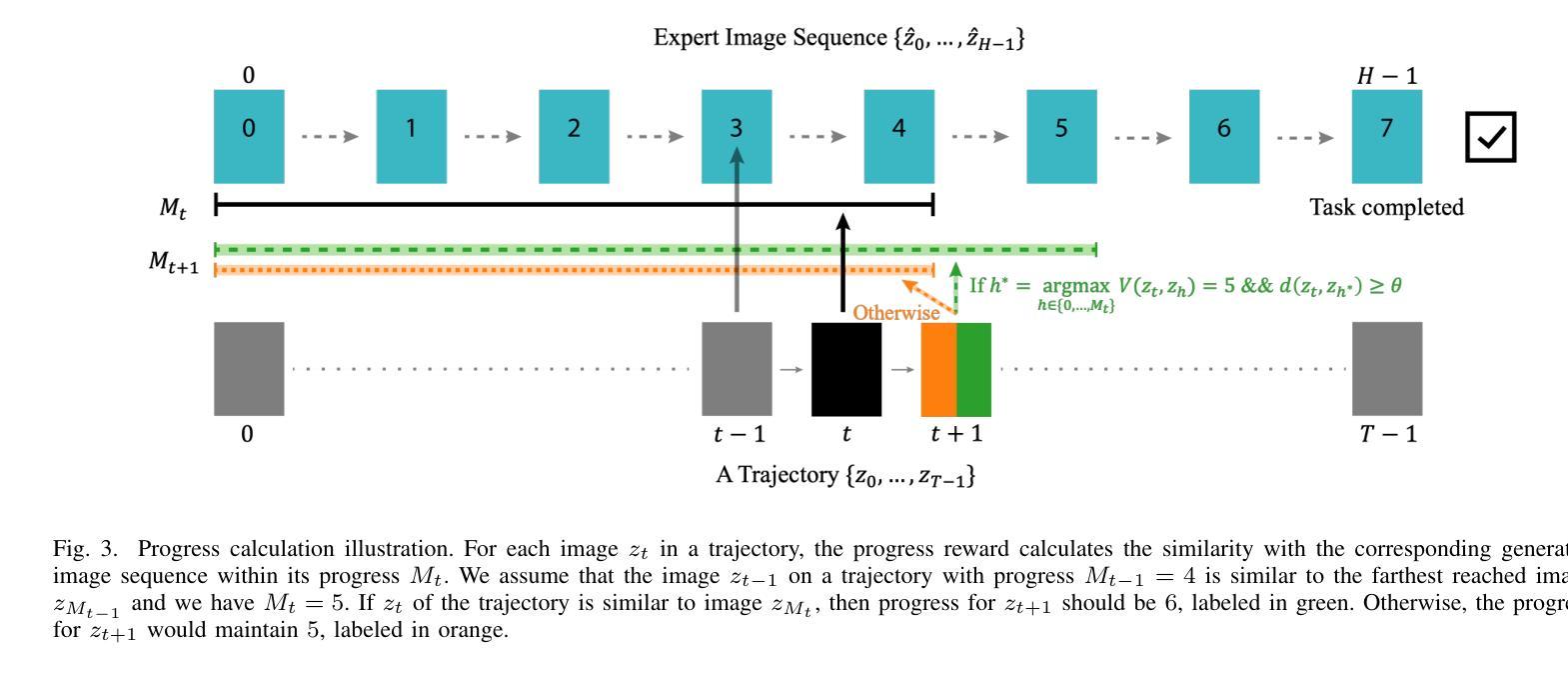
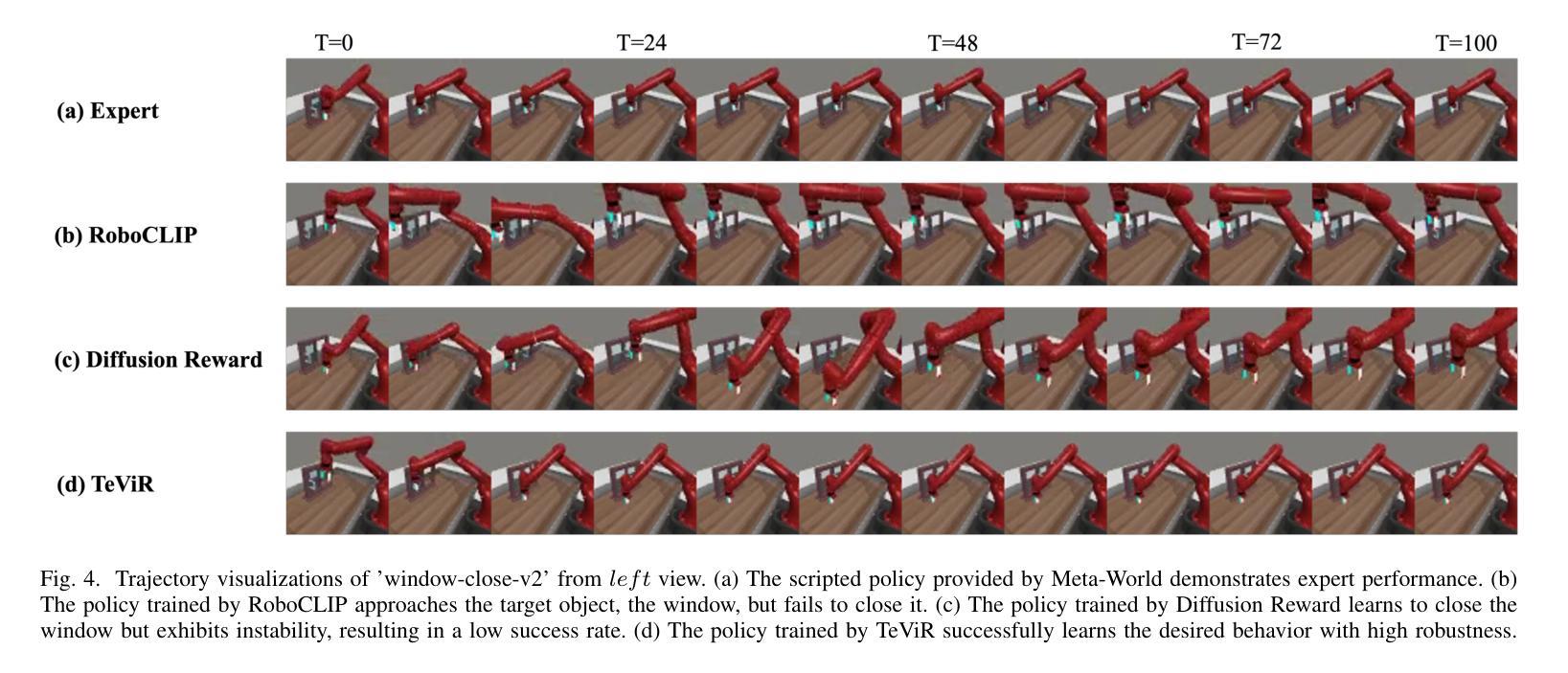
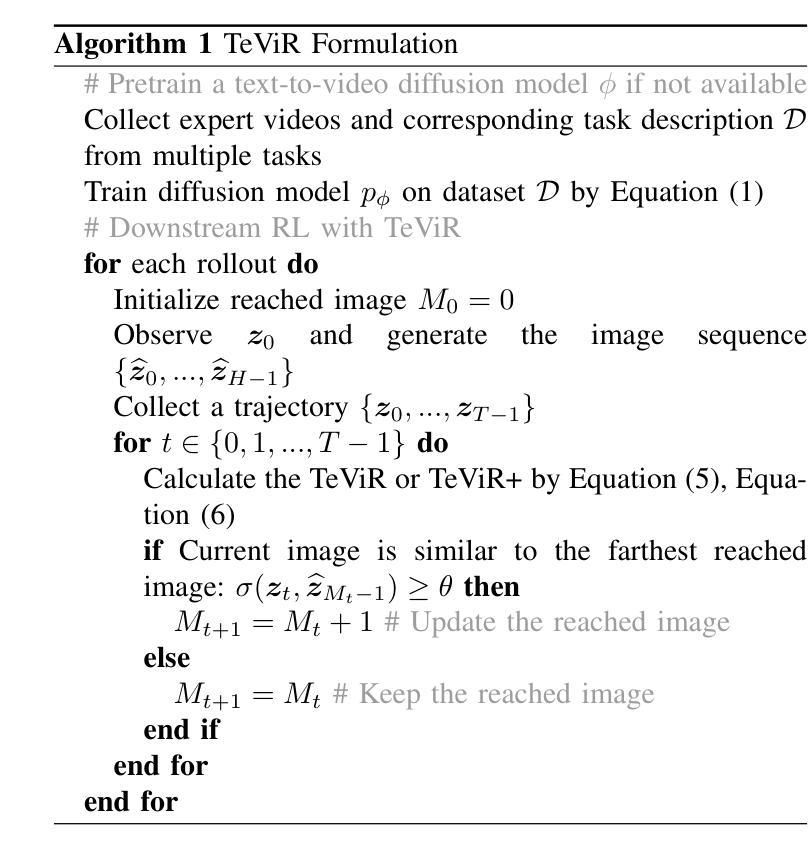
TeViR: Text-to-Video Reward with Diffusion Models for Efficient Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yuhui Chen, Haoran Li, Zhennan Jiang, Haowei Wen, Dongbin Zhao
Developing scalable and generalizable reward engineering for reinforcement learning (RL) is crucial for creating general-purpose agents, especially in the challenging domain of robotic manipulation. While recent advances in reward engineering with Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown promise, their sparse reward nature significantly limits sample efficiency. This paper introduces TeViR, a novel method that leverages a pre-trained text-to-video diffusion model to generate dense rewards by comparing the predicted image sequence with current observations. Experimental results across 11 complex robotic tasks demonstrate that TeViR outperforms traditional methods leveraging sparse rewards and other state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, achieving better sample efficiency and performance without ground truth environmental rewards. TeViR’s ability to efficiently guide agents in complex environments highlights its potential to advance reinforcement learning applications in robotic manipulation.
开发可扩展且可通用的强化学习(RL)奖励工程对于创建通用智能体至关重要,特别是在机器人操纵等具有挑战性的领域中。虽然最近使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的奖励工程进展显示出了一定的前景,但其稀疏奖励的特性极大地限制了样本效率。本文介绍了一种新方法TeViR,它利用预训练的文本到视频扩散模型,通过比较预测的图像序列与当前观察结果来生成密集奖励。在跨越1e个复杂机器人任务的实验中,TeViR的表现优于利用稀疏奖励的传统方法和其它最新技术方法,能够在无需真实环境奖励的情况下实现更高的样本效率和性能。TeViR在复杂环境中有效指导智能体的能力突显了其在机器人操纵的强化学习应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本到视频的预训练扩散模型TeViR,通过对比预测图像序列与当前观测值来生成密集奖励,提高了样本效率,在复杂的机器人操作任务中表现出卓越性能。与传统使用稀疏奖励的方法以及其他先进方法相比,TeViR在不依赖环境真实奖励的情况下实现了更高的样本效率和性能。这显示出TeViR在复杂环境中有效指导智能体的潜力,有望推动机器人在强化学习领域的发展。
Key Takeaways
- TeViR利用预训练的文本到视频扩散模型生成密集奖励。
- 对比预测图像序列与当前观测值以提高样本效率。
- 在11个复杂的机器人任务中,TeViR表现出卓越性能。
- TeViR与传统方法和其它先进方法相比,实现了更高的样本效率和性能。
- TeViR在不依赖环境真实奖励的情况下表现出强大的潜力。
- TeViR能有效指导智能体在复杂环境中的行为。
点此查看论文截图
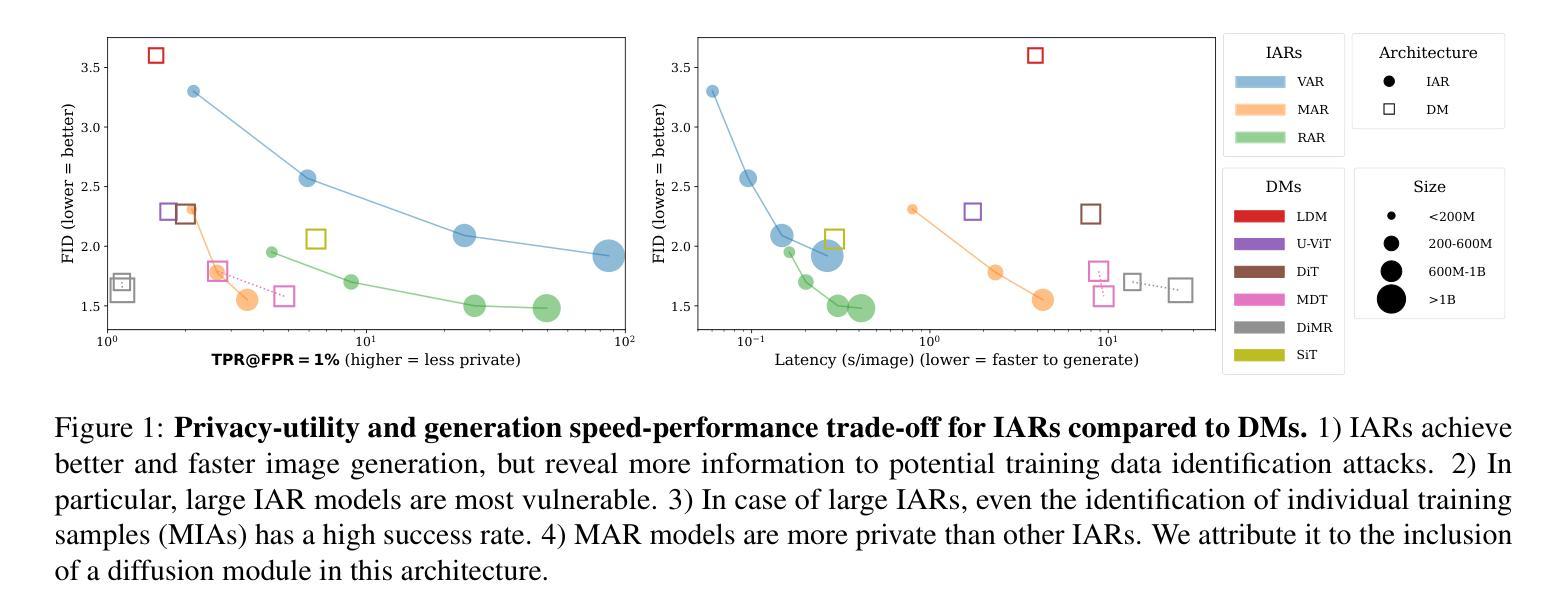
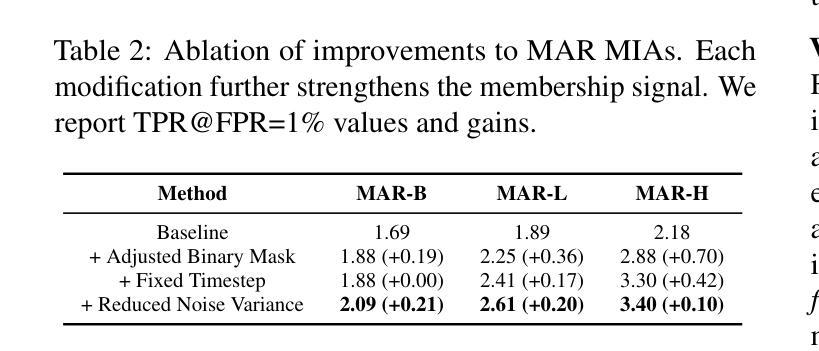
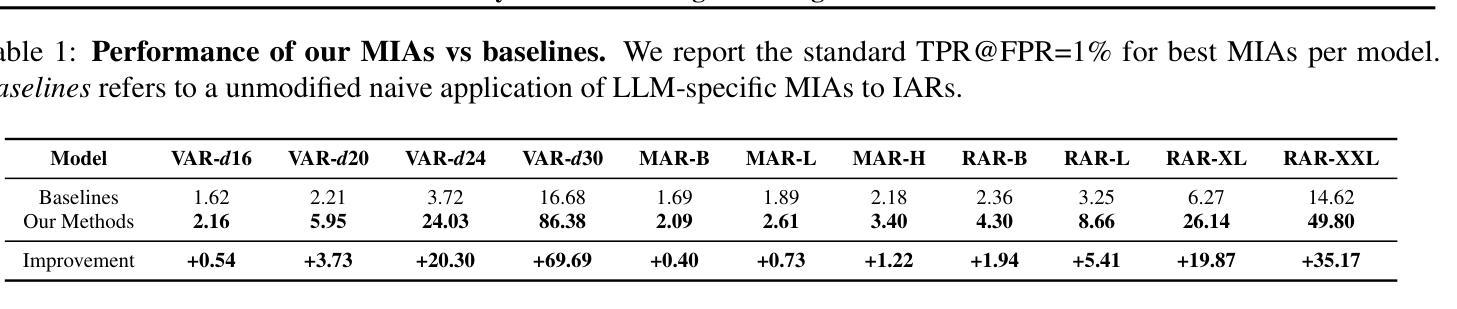
Privacy Attacks on Image AutoRegressive Models
Authors:Antoni Kowalczuk, Jan Dubiński, Franziska Boenisch, Adam Dziedzic
Image AutoRegressive generation has emerged as a new powerful paradigm with image autoregressive models (IARs) matching state-of-the-art diffusion models (DMs) in image quality (FID: 1.48 vs. 1.58) while allowing for a higher generation speed. However, the privacy risks associated with IARs remain unexplored, raising concerns regarding their responsible deployment. To address this gap, we conduct a comprehensive privacy analysis of IARs, comparing their privacy risks to the ones of DMs as reference points. Concretely, we develop a novel membership inference attack (MIA) that achieves a remarkably high success rate in detecting training images (with a True Positive Rate at False Positive Rate = 1% of 86.38% vs. 6.38% for DMs with comparable attacks). We leverage our novel MIA to provide dataset inference (DI) for IARs, and show that it requires as few as 6 samples to detect dataset membership (compared to 200 for DI in DMs), confirming a higher information leakage in IARs. Finally, we are able to extract hundreds of training data points from an IAR (e.g., 698 from VAR-d30). Our results suggest a fundamental privacy-utility trade-off: while IARs excel in image generation quality and speed, they are empirically significantly more vulnerable to privacy attacks compared to DMs that achieve similar performance. We release the code at https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars for reproducibility.
图像自回归生成已经成为一种新型强大的范式,图像自回归模型(IAR)在图像质量方面与最先进的扩散模型(DM)相匹配(FID:1.48与DM的FID为1.58),同时生成速度更快。然而,与IAR相关的隐私风险尚未得到探索,这引发了人们对它们负责部署的担忧。为了弥补这一空白,我们对IAR进行了全面的隐私分析,并将其隐私风险与DM作为参考点进行比较。具体来说,我们开发了一种新型成员推理攻击(MIA),在检测训练图像方面取得了非常高的成功率(在假阳性率为百分之一的情况下,真正阳性率为百分之八十六点三八,相比之下,DM面临类似攻击时的真正阳性率为百分之六点三八)。我们利用新型MIA为IAR提供数据集推理(DI),并表明仅需六个样本即可检测数据集成员身份(相比之下,DM中的DI需要二百个样本),证实了IAR存在更高的信息泄露。最后,我们能够从一个IAR中提取数百个训练数据点(例如从VAR-d30中提取了六百九十八个)。我们的结果表明存在一个基本的隐私效用权衡:虽然IAR在图像生成质量和速度方面表现出色,但与实现类似性能的DM相比,它们在实证上更容易受到隐私攻击。我们发布代码于https://github.com/sprintml/privacy_attacks_against_iars以促进重复实验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML2025
Summary
图像自回归生成模型(IARs)作为一种新兴的强大范式,在图像质量上与最先进的扩散模型(DMs)相匹配,同时生成速度更快。然而,IARs的隐私风险尚未被探索,这引发了对其负责任部署的担忧。本研究对IARs进行了全面的隐私分析,并与DMs进行了比较。我们开发了一种新型成员推理攻击(MIA),在检测训练图像方面取得了非常高的成功率。此外,我们的研究证实IARs的信息泄露更高,只需少数样本即可进行数据集推断(DI)。最后,我们能够从IAR中提取大量训练数据点。研究结果表明,IARs在隐私保护方面存在明显的弱点,尽管它们在图像生成质量和速度上表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 图像自回归生成模型(IARs)与扩散模型(DMs)在图像质量上表现相近,但生成速度更快。
- IARs的隐私风险尚未得到充分探索,需要进行全面的隐私分析。
- 新型成员推理攻击(MIA)在检测IARs的训练图像方面取得了非常高的成功率。
- IARs的信息泄露较高,只需少数样本即可进行数据集推断(DI)。
- IARs在隐私保护方面存在明显的弱点,相比DMs更容易受到隐私攻击。
- 研究结果揭示了隐私保护与实用性之间的权衡:尽管IARs在图像生成质量和速度上表现出色,但在隐私保护方面存在明显不足。
点此查看论文截图

MIFNet: Learning Modality-Invariant Features for Generalizable Multimodal Image Matching
Authors:Yepeng Liu, Zhichao Sun, Baosheng Yu, Yitian Zhao, Bo Du, Yongchao Xu, Jun Cheng
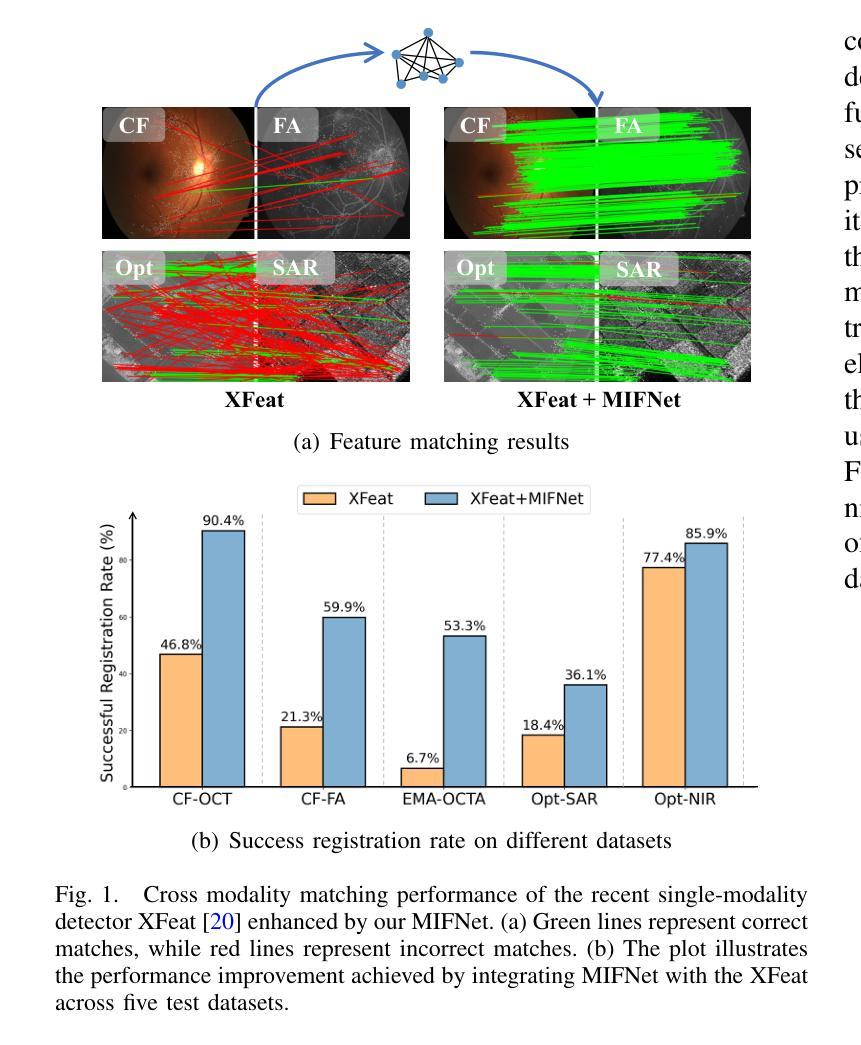
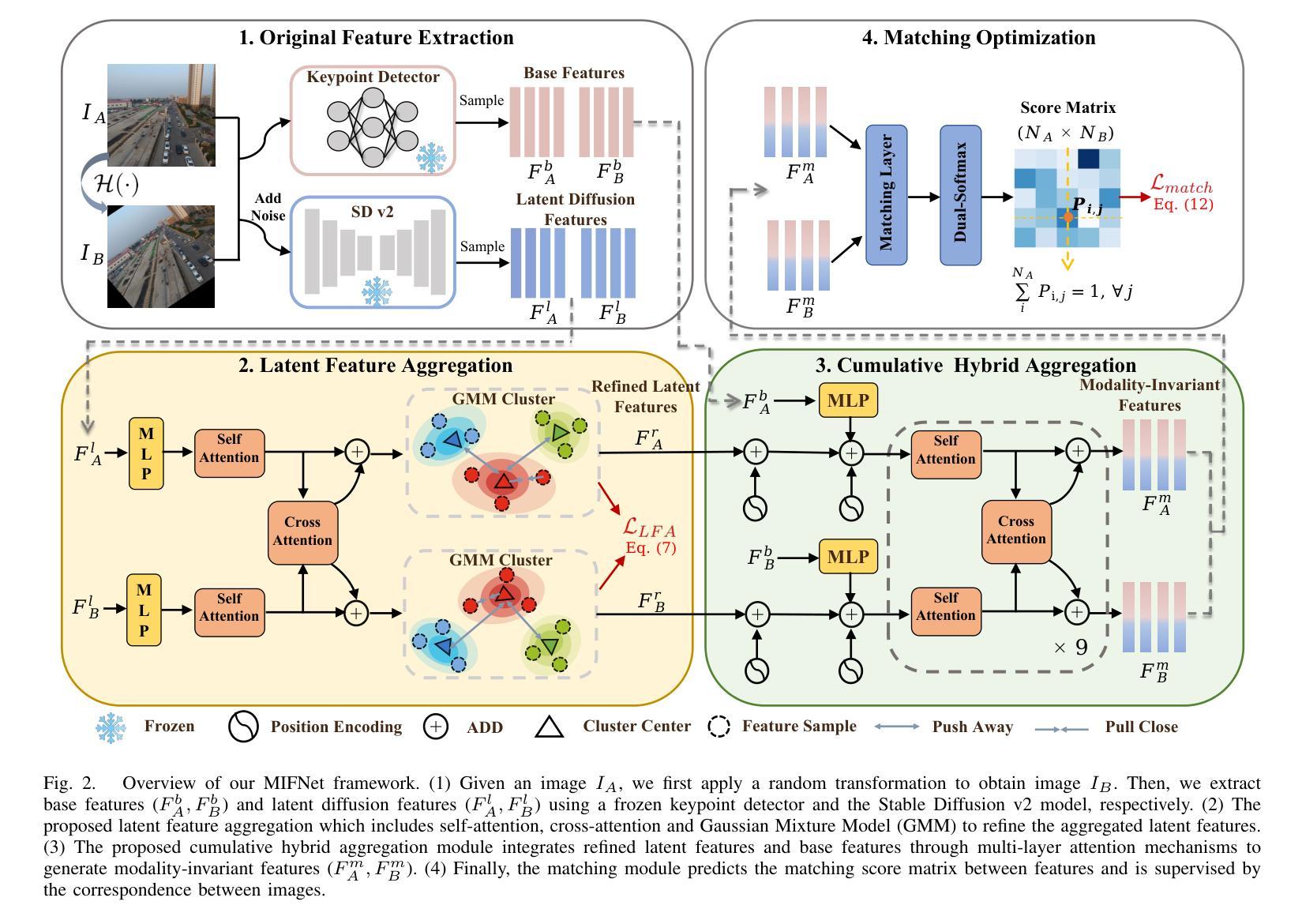
Many keypoint detection and description methods have been proposed for image matching or registration. While these methods demonstrate promising performance for single-modality image matching, they often struggle with multimodal data because the descriptors trained on single-modality data tend to lack robustness against the non-linear variations present in multimodal data. Extending such methods to multimodal image matching often requires well-aligned multimodal data to learn modality-invariant descriptors. However, acquiring such data is often costly and impractical in many real-world scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a modality-invariant feature learning network (MIFNet) to compute modality-invariant features for keypoint descriptions in multimodal image matching using only single-modality training data. Specifically, we propose a novel latent feature aggregation module and a cumulative hybrid aggregation module to enhance the base keypoint descriptors trained on single-modality data by leveraging pre-trained features from Stable Diffusion models. %, our approach generates robust and invariant features across diverse and unknown modalities. We validate our method with recent keypoint detection and description methods in three multimodal retinal image datasets (CF-FA, CF-OCT, EMA-OCTA) and two remote sensing datasets (Optical-SAR and Optical-NIR). Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed MIFNet is able to learn modality-invariant feature for multimodal image matching without accessing the targeted modality and has good zero-shot generalization ability. The code will be released at https://github.com/lyp-deeplearning/MIFNet.
针对图像匹配或注册,已经提出了许多关键点检测与描述方法。虽然这些方法在单模态图像匹配上表现出有前景的性能,但它们通常难以处理多模态数据,因为那些在单模态数据上训练的描述符往往缺乏对多模态数据中存在的非线性变异的稳健性。将这些方法扩展到多模态图像匹配通常需要对齐良好的多模态数据来学习模态不变描述符。然而,在许多真实场景中,获取这样的数据通常成本高昂且不切实际。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种模态不变特征学习网络(MIFNet),该网络仅使用单模态训练数据,为多模态图像匹配中的关键点描述计算模态不变特征。具体来说,我们提出了一种新型潜在特征聚合模块和累积混合聚合模块,以利用来自Stable Diffusion模型的预训练特征,增强在单模态数据上训练的基准关键点描述符。我们的方法在多样且未知的模式下生成稳健且不变的特征。我们在三个多模态视网膜图像数据集(CF-FA、CF-OCT、EMA-OCTA)和两个遥感数据集(Optical-SAR和Optical-NIR)中验证了我们的方法与最新的关键点检测和描述方法。大量实验表明,所提出的MIFNet能够在不访问目标模态的情况下学习模态不变特征,并具有良好的零样本泛化能力。代码将发布在https://github.com/lyp-deeplearning/MIFNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by IEEE TIP 2025
摘要
基于多模态图像匹配挑战,提出了模态无关特征学习网络(MIFNet),用于计算关键点的模态无关特征描述。通过使用仅单模态训练数据,增强基于单模态数据训练的基准关键点描述符,并借助预训练的Stable Diffusion模型特征。实验证明,MIFNet在多种模态图像匹配中具有良好的零样本泛化能力,无需访问目标模态即可学习模态无关特征。代码将发布在相应链接。
关键见解
- 针对多模态图像匹配,现有的基于单模态的方法通常缺乏稳健性以应对非线性的多模态数据变化。
- 提出了一种新的模态无关特征学习网络(MIFNet),旨在解决多模态图像匹配中的关键问题。
- 利用潜在特征聚合模块和累积混合聚合模块,增强基于单模态数据训练的基准关键点描述符。
- 使用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型特征进一步强化了描述子。
- MIFNet具有良好的零样本泛化能力,能够在不接触目标模态的情况下学习模态无关特征。
点此查看论文截图

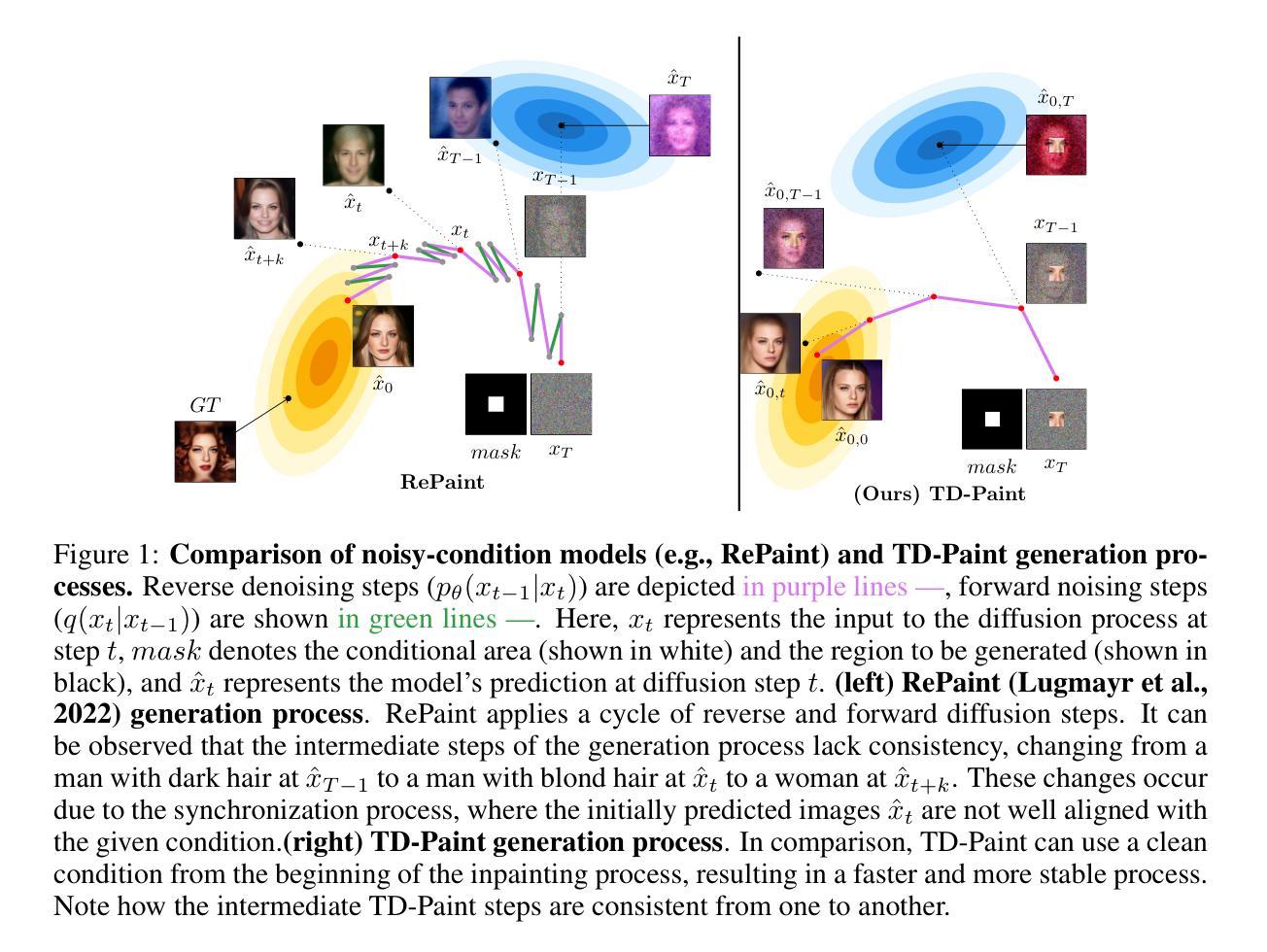
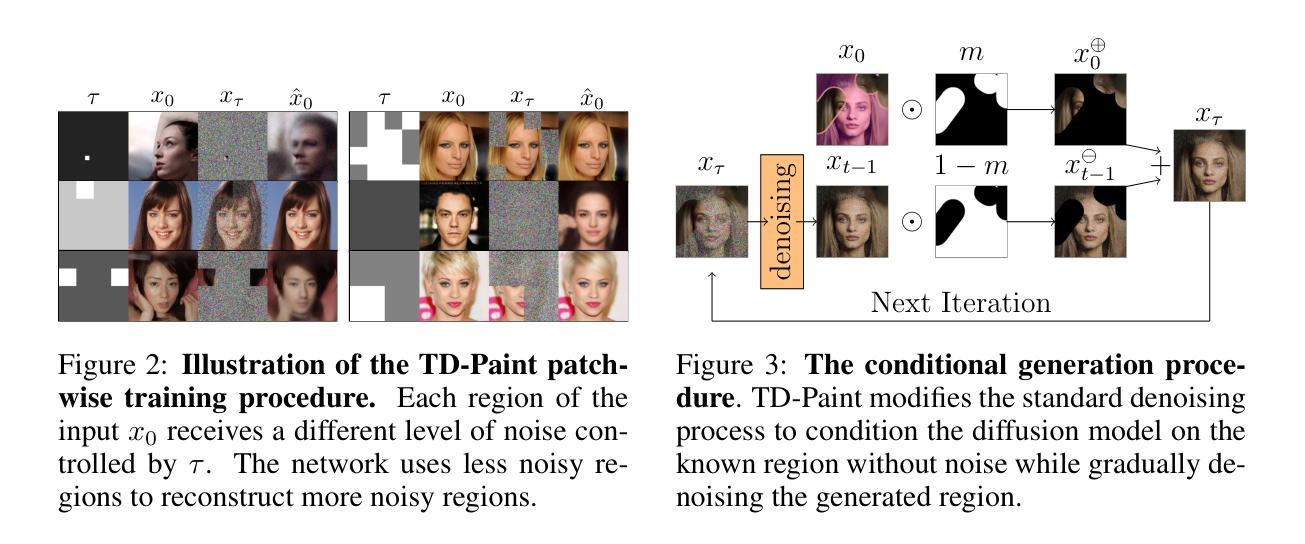
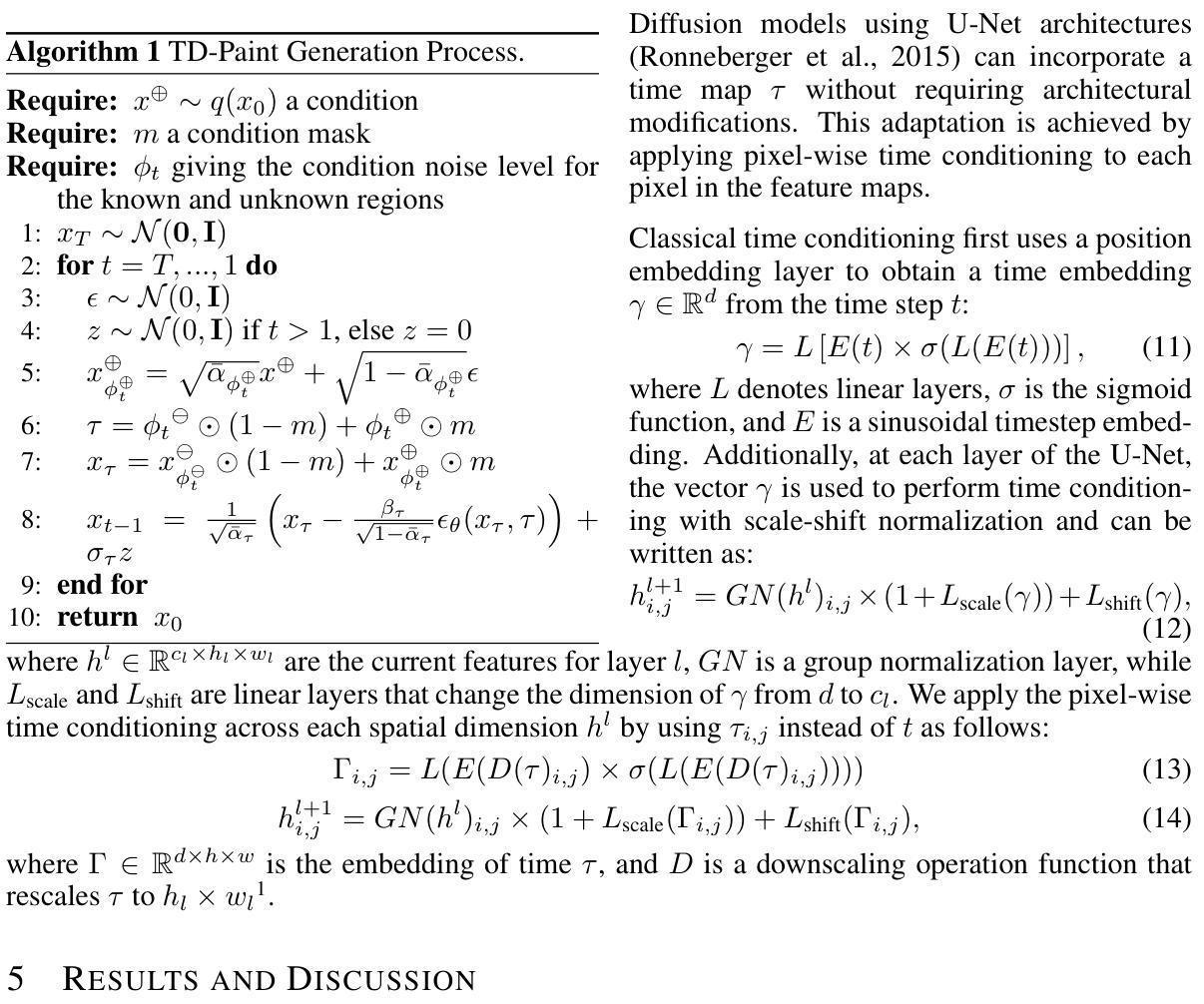
TD-Paint: Faster Diffusion Inpainting Through Time Aware Pixel Conditioning
Authors:Tsiry Mayet, Pourya Shamsolmoali, Simon Bernard, Eric Granger, Romain Hérault, Clement Chatelain
Diffusion models have emerged as highly effective techniques for inpainting, however, they remain constrained by slow sampling rates. While recent advances have enhanced generation quality, they have also increased sampling time, thereby limiting scalability in real-world applications. We investigate the generative sampling process of diffusion-based inpainting models and observe that these models make minimal use of the input condition during the initial sampling steps. As a result, the sampling trajectory deviates from the data manifold, requiring complex synchronization mechanisms to realign the generation process. To address this, we propose Time-aware Diffusion Paint (TD-Paint), a novel approach that adapts the diffusion process by modeling variable noise levels at the pixel level. This technique allows the model to efficiently use known pixel values from the start, guiding the generation process toward the target manifold. By embedding this information early in the diffusion process, TD-Paint significantly accelerates sampling without compromising image quality. Unlike conventional diffusion-based inpainting models, which require a dedicated architecture or an expensive generation loop, TD-Paint achieves faster sampling times without architectural modifications. Experimental results across three datasets show that TD-Paint outperforms state-of-the-art diffusion models while maintaining lower complexity.
扩散模型已经在图像修复中展现出高效的技术特性,然而它们仍然受到采样速率较慢的限制。尽管最近的进展提高了生成质量,但也增加了采样时间,从而限制了在现实世界应用中的可扩展性。我们研究了基于扩散的图像修复模型的生成采样过程,并观察到这些模型在初始采样步骤中对输入条件的利用微乎其微。因此,采样轨迹偏离了数据流形,需要复杂的同步机制来重新对齐生成过程。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了时间感知扩散绘图(TD-Paint),这是一种通过像素级可变噪声水平对扩散过程进行建模的新方法。该技术允许模型从起始阶段就有效地使用已知的像素值,引导生成过程朝着目标流形进行。通过在扩散过程中尽早嵌入这些信息,TD-Paint可以在不损害图像质量的情况下显著加速采样。与传统的基于扩散的图像修复模型不同,TD-Paint无需专门的架构或昂贵的生成循环,即可实现更快的采样速度。在三个数据集上的实验结果表明,TD-Paint在保持较低复杂度的同时,优于最先进的扩散模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像修复中表现出高效性,但采样速率较慢限制了其在现实世界应用中的可扩展性。研究团队探究了基于扩散的修复模型的生成采样过程,发现这些模型在初始采样步骤中对输入条件的利用甚微,导致采样轨迹偏离数据流形。为此,团队提出了时间感知扩散涂料(TD-Paint)方法,通过像素级可变噪声水平对扩散过程进行适应。此方法使模型从一开始就能有效利用已知像素值,引导生成过程朝向目标流形。将信息嵌入扩散过程的早期阶段,TD-Paint可显著加速采样而不损害图像质量。与需要专门架构或昂贵生成循环的传统扩散修复模型不同,TD-Paint在不进行架构修改的情况下实现了更快的采样时间。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像修复中表现出高效性,但采样速率较慢。
- 现有扩散模型在初始采样阶段对输入条件的利用不足,导致采样轨迹偏离数据流形。
- 提出了一种新的方法TD-Paint,通过像素级的可变噪声水平适应扩散过程。
- TD-Paint允许模型从开始就有效利用已知像素值,引导生成过程向目标流形。
- TD-Paint将信息嵌入扩散过程的早期阶段,能显著加速采样过程。
- TD-Paint在不进行架构修改的情况下实现了更快的采样时间。
点此查看论文截图

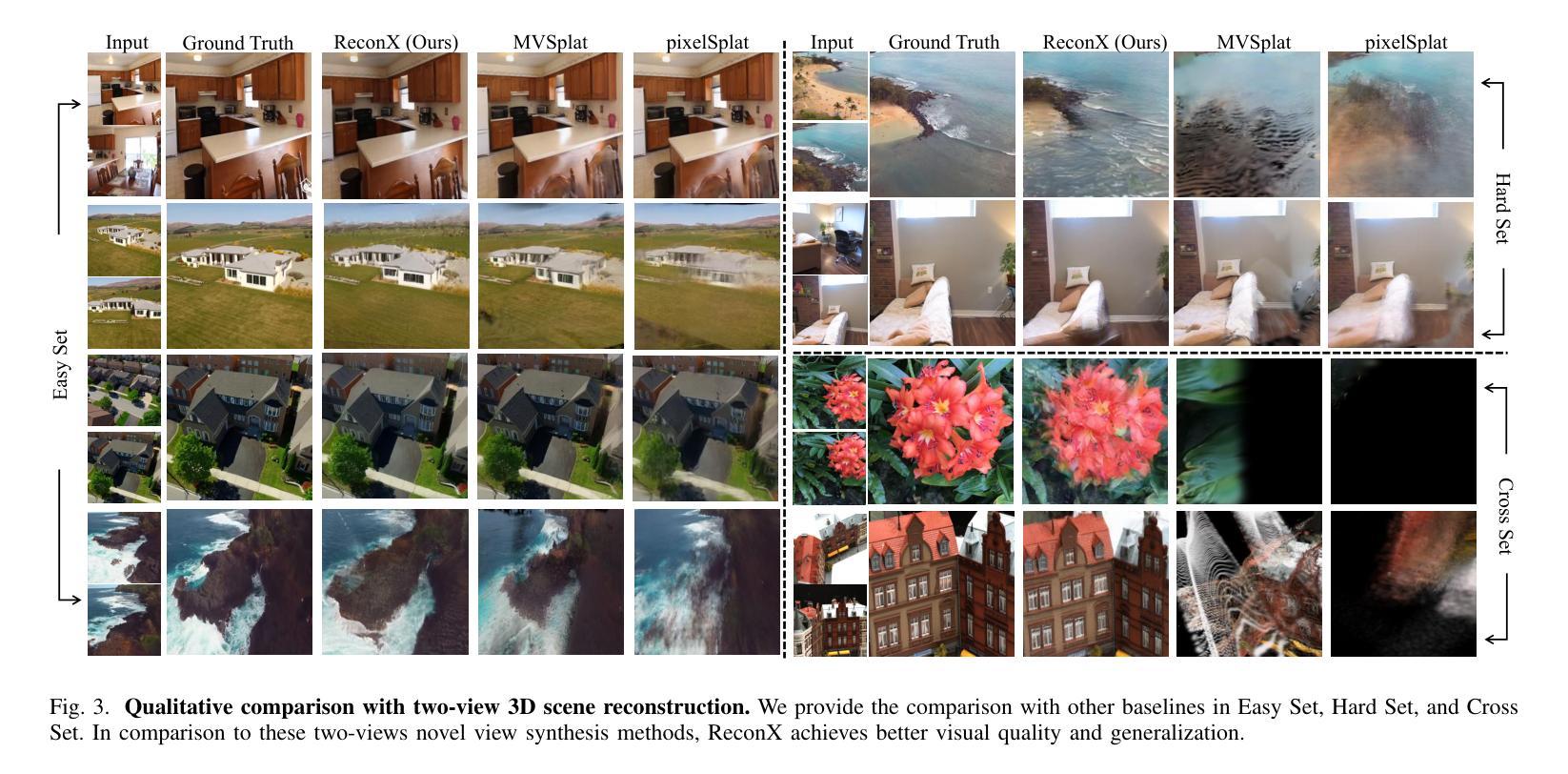
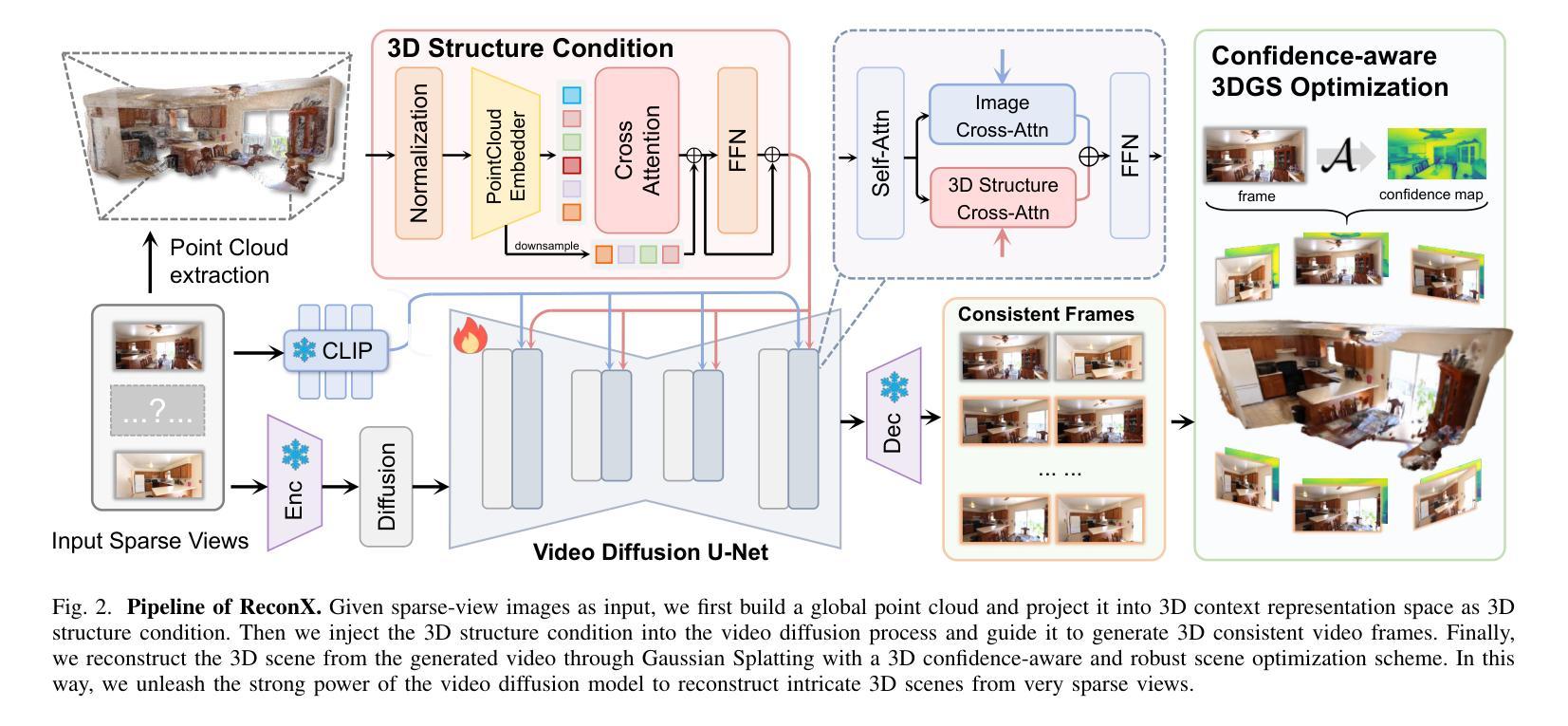
ReconX: Reconstruct Any Scene from Sparse Views with Video Diffusion Model
Authors:Fangfu Liu, Wenqiang Sun, Hanyang Wang, Yikai Wang, Haowen Sun, Junliang Ye, Jun Zhang, Yueqi Duan
Advancements in 3D scene reconstruction have transformed 2D images from the real world into 3D models, producing realistic 3D results from hundreds of input photos. Despite great success in dense-view reconstruction scenarios, rendering a detailed scene from insufficient captured views is still an ill-posed optimization problem, often resulting in artifacts and distortions in unseen areas. In this paper, we propose ReconX, a novel 3D scene reconstruction paradigm that reframes the ambiguous reconstruction challenge as a temporal generation task. The key insight is to unleash the strong generative prior of large pre-trained video diffusion models for sparse-view reconstruction. However, 3D view consistency struggles to be accurately preserved in directly generated video frames from pre-trained models. To address this, given limited input views, the proposed ReconX first constructs a global point cloud and encodes it into a contextual space as the 3D structure condition. Guided by the condition, the video diffusion model then synthesizes video frames that are both detail-preserved and exhibit a high degree of 3D consistency, ensuring the coherence of the scene from various perspectives. Finally, we recover the 3D scene from the generated video through a confidence-aware 3D Gaussian Splatting optimization scheme. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets show the superiority of our ReconX over state-of-the-art methods in terms of quality and generalizability.
随着三维场景重建技术的进步,能够将来自现实世界的二维图像转化为三维模型,并从数百张输入照片中生成逼真的三维结果。虽然在密集视图重建场景中取得了巨大成功,但从不足够的捕获视角渲染详细场景仍然是一个不适定的优化问题,这常常导致在看不见的区域出现伪影和失真。在本文中,我们提出了名为ReconX的新型三维场景重建范式,它将模糊的重建挑战重新构建为时间生成任务,其关键见解是释放大型预训练视频扩散模型的强大生成先验,用于稀疏视图重建。然而,直接从预训练模型生成的视频帧中准确保持三维视图的一致性是一项挑战。为了解决这一问题,给定有限的输入视角,所提出ReconX首先构建全局点云并将其编码为上下文空间作为三维结构条件。在条件的引导下,视频扩散模型随后合成既保留细节又展现高度三维一致性的视频帧,确保从不同角度的场景连贯性。最后,我们通过信心感知的三维高斯拼贴优化方案,从生成的视频中恢复三维场景。在多种真实世界数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的ReconX在质量和通用性方面优于现有先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://liuff19.github.io/ReconX
Summary
提出一种新型的三维场景重建方法ReconX,将稀疏视角下的重建挑战转化为时间生成任务,利用预训练的视频扩散模型的强生成先验。通过构建全局点云并将其编码为三维结构条件,指导扩散模型生成细节丰富且三维一致性高的视频帧。最后,通过置信度感知的3D高斯拼贴优化方案,从生成的视频中恢复三维场景。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种新型的三维场景重建方法ReconX,该方法利用视频扩散模型的生成先验来解决稀疏视角下的重建问题。
- ReconX将重建问题转化为时间生成任务,通过构建全局点云并将其编码为三维结构条件,以提高生成视频帧的详细性和三维一致性。
- 为了确保场景从不同角度的一致性,论文使用了条件引导的视频扩散模型来合成视频帧。
- 该方法利用置信度感知的3D高斯拼贴优化方案从生成的视频中恢复三维场景。
- 实验结果表明,ReconX在质量和泛化性方面优于现有最先进的重建方法。
- ReconX能处理从不同视角拍摄的不足照片,并通过构建全局点云来解决这一问题。
点此查看论文截图



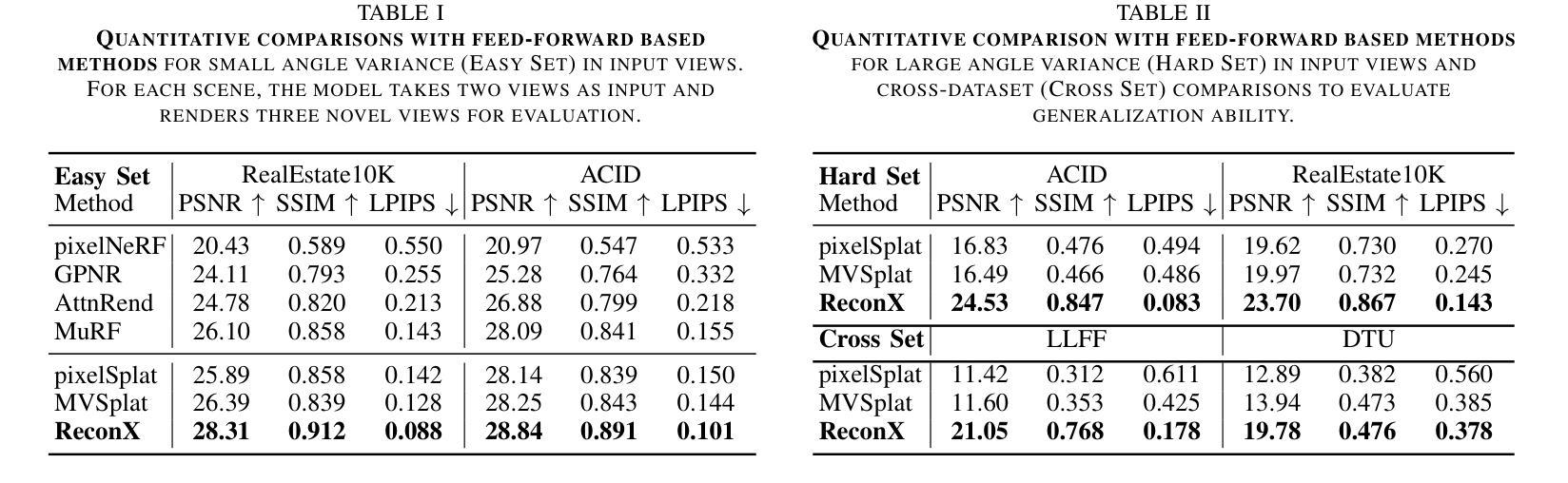
IgCONDA-PET: Weakly-Supervised PET Anomaly Detection using Implicitly-Guided Attention-Conditional Counterfactual Diffusion Modeling – a Multi-Center, Multi-Cancer, and Multi-Tracer Study
Authors:Shadab Ahamed, Arman Rahmim
Minimizing the need for pixel-level annotated data to train PET lesion detection and segmentation networks is highly desired and can be transformative, given time and cost constraints associated with expert annotations. Current unsupervised or weakly-supervised anomaly detection methods rely on autoencoder or generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained only on healthy data. While these approaches reduce annotation dependency, GAN-based methods are notably more challenging to train than non-GAN alternatives (such as autoencoders) due to issues such as the simultaneous optimization of two competing networks, mode collapse, and training instability. In this paper, we present the weakly-supervised $\textbf{I}$mplicitly-$\textbf{g}$uided $\textbf{CO}$u$\textbf{N}$terfactual diffusion model for $\textbf{D}$etecting $\textbf{A}$nomalies in $\textbf{PET}$ images (IgCONDA-PET). The solution is developed and validated using PET scans from six retrospective cohorts consisting of a total of 2652 cases (multi-cancer, multi-tracer) containing both local and public datasets (spanning multiple centers). The training is conditioned on image class labels (healthy vs. unhealthy) via attention modules, and we employ implicit diffusion guidance. We perform counterfactual generation which facilitates “unhealthy-to-healthy” domain translation by generating a synthetic, healthy version of an unhealthy input image, enabling the detection of anomalies through the calculated differences. The performance of our method was compared against several other deep learning based weakly-supervised or unsupervised methods as well as traditional methods like 41% SUV$_\text{max}$ thresholding. We also highlight the importance of incorporating attention modules in our network for the detection of small anomalies. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git.
减少训练PET病变检测与分割网络时对像素级别标注数据的需求是非常理想的,考虑到与专家标注相关的时间和成本约束,这可能会带来变革。当前的无监督或弱监督异常检测方法依赖于自编码器或生成对抗网络(GANs)的训练,这些网络仅在健康数据上进行训练。虽然这些方法减少了标注的依赖性,但基于GAN的方法与基于非GAN的替代方法(如自编码器)相比,训练难度更大,因为存在诸如两个竞争网络的同步优化、模式崩溃和训练不稳定等问题。在本文中,我们提出了用于PET图像检测异常的弱监督隐式引导对比扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)。该解决方案是使用来自六个回顾性队列的PET扫描进行开发和验证的,这些队列共有2652个病例(多癌症、多追踪剂),包含本地和公共数据集(跨越多个中心)。训练是通过注意力模块对图像类别标签(健康与非健康)进行条件化,我们采用隐式扩散指导。我们执行反事实生成,通过生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,促进“不健康到健康”的领域转换,通过计算差异来实现异常检测。我们的方法与基于深度学习的其他弱监督或无监督方法以及传统的如SUVmax阈值方法进行了比较。我们还强调了在网络中融入注意力模块检测小异常的重要性。代码公开在:https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 13 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种基于弱监督的隐式引导扩散模型IgCONDA-PET,用于PET图像中的异常检测。该模型利用注意力模块和隐式扩散指导,通过生成合成健康图像来检测异常。在多个回顾性队列的PET扫描数据上进行了训练和验证,表现出良好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- IgCONDA-PET模型是一种基于弱监督的PET图像异常检测方法。
- 该模型利用扩散模型进行图像生成,通过生成合成健康图像来检测异常。
- 模型通过注意力模块进行训练,可检测小到大的异常。
- 模型在多个回顾性队列的PET扫描数据上进行了验证,包括本地和公开数据集。
- 与其他深度学习和传统方法相比,IgCONDA-PET模型表现出良好的性能。
- 模型代码已公开可用,方便进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

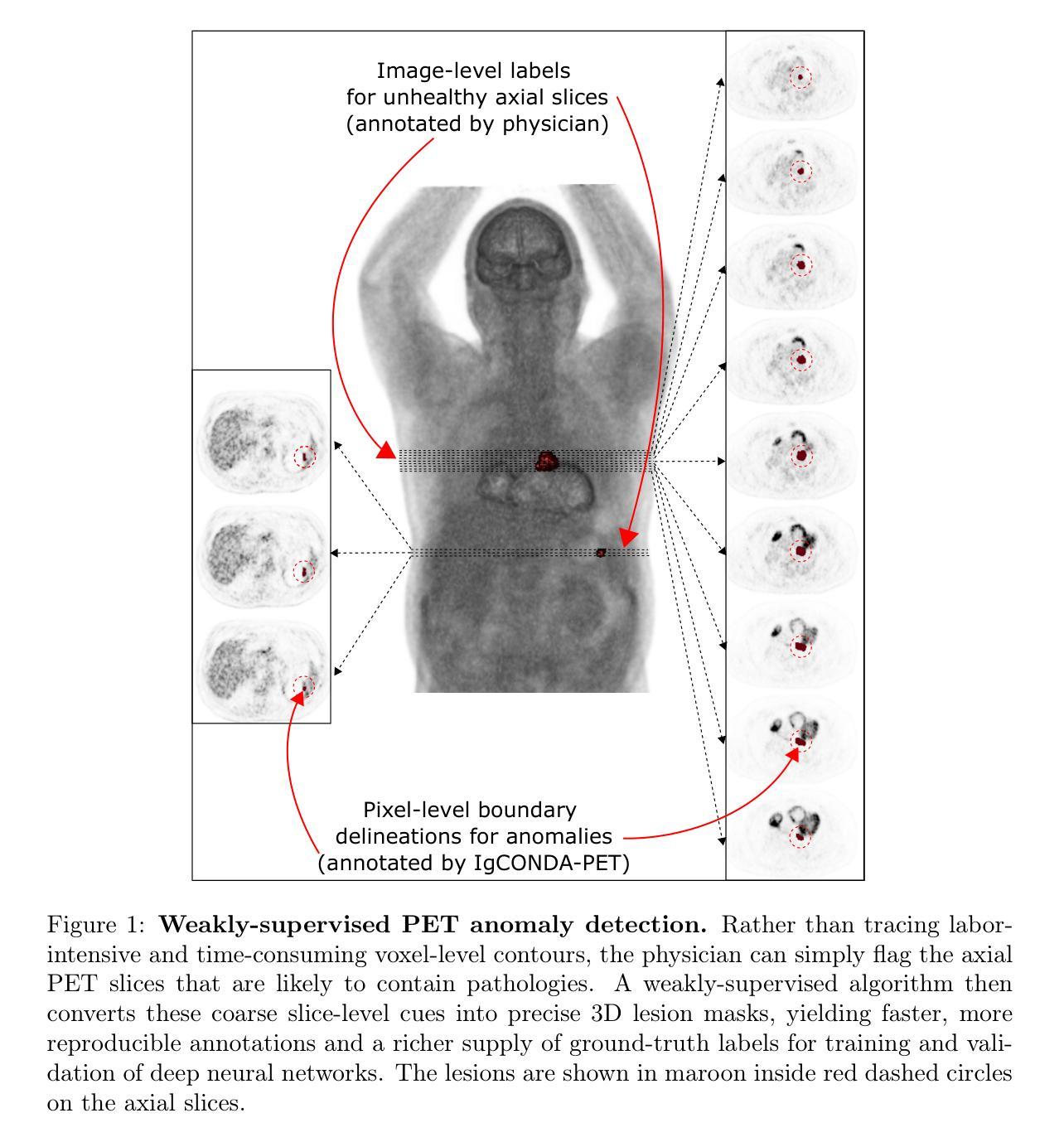
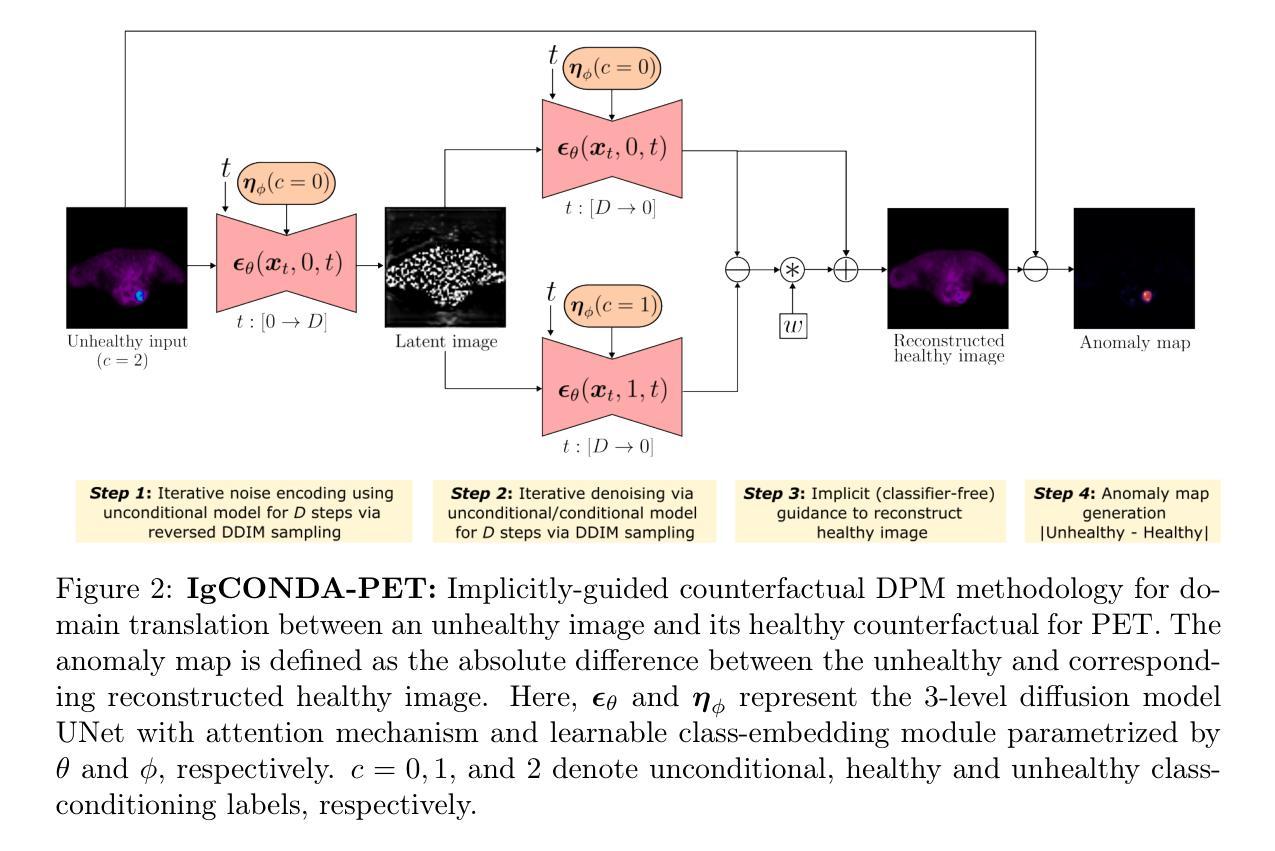
Diff-Def: Diffusion-Generated Deformation Fields for Conditional Atlases
Authors:Sophie Starck, Vasiliki Sideri-Lampretsa, Bernhard Kainz, Martin J. Menten, Tamara T. Mueller, Daniel Rueckert
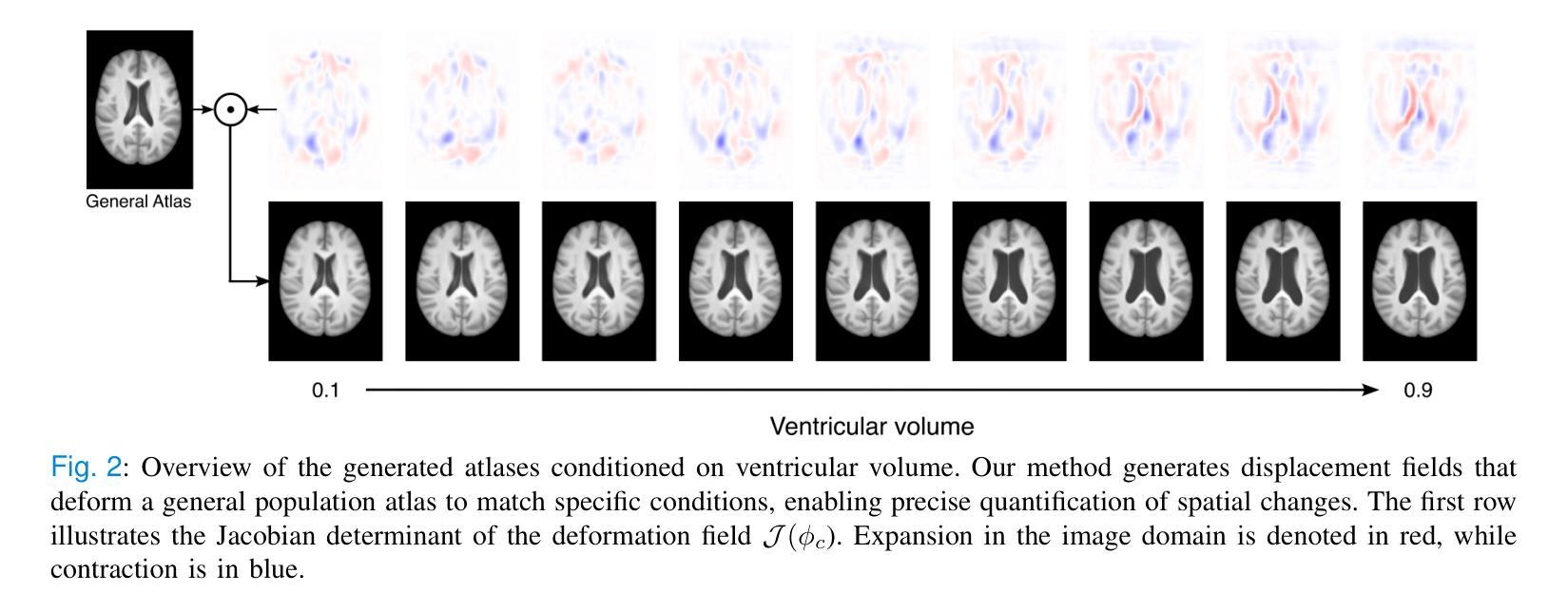
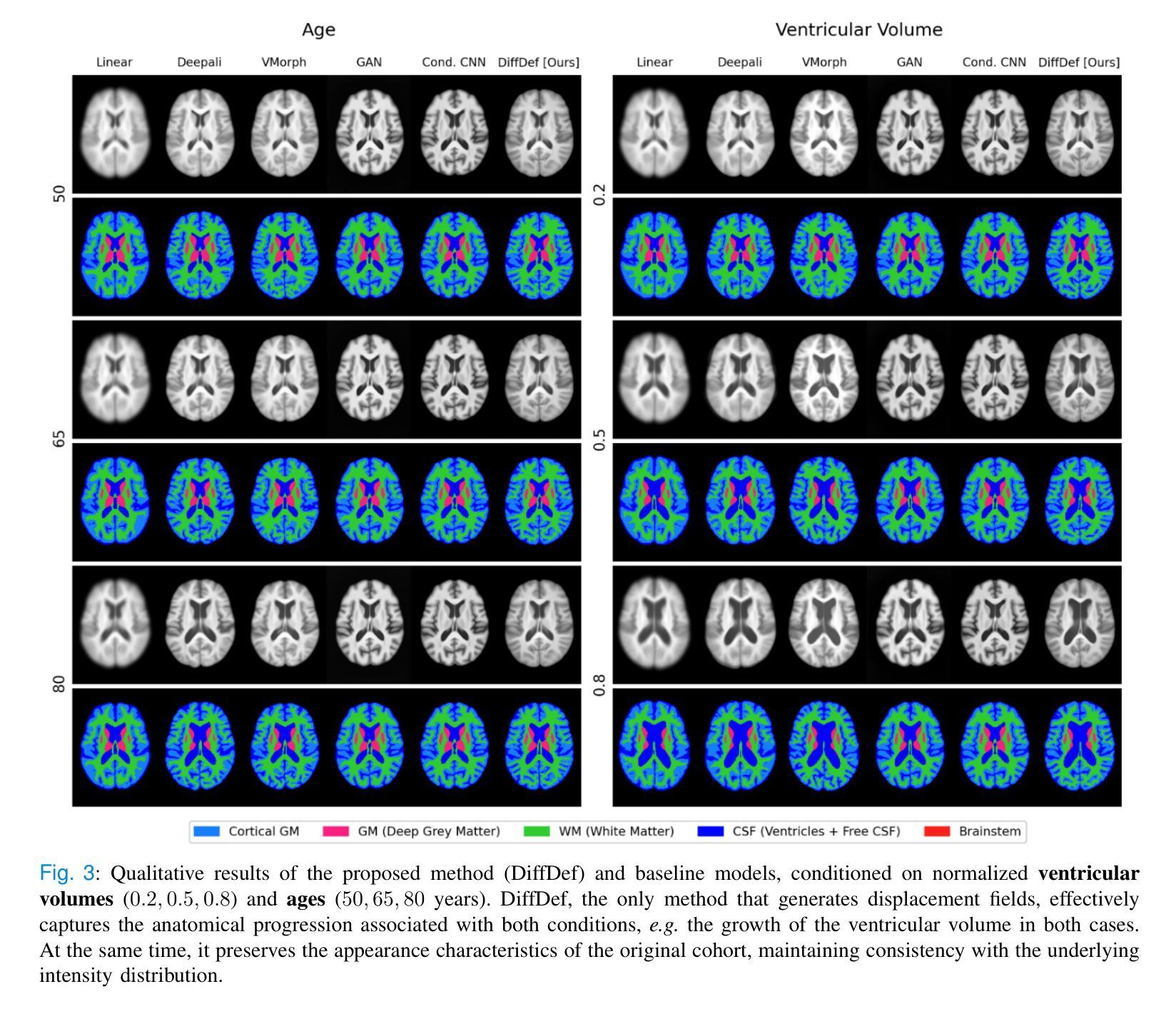
Anatomical atlases are widely used for population studies and analysis. Conditional atlases target a specific sub-population defined via certain conditions, such as demographics or pathologies, and allow for the investigation of fine-grained anatomical differences like morphological changes associated with ageing or disease. Existing approaches use either registration-based methods that are often unable to handle large anatomical variations or generative adversarial models, which are challenging to train since they can suffer from training instabilities. Instead of generating atlases directly in as intensities, we propose using latent diffusion models to generate deformation fields, which transform a general population atlas into one representing a specific sub-population. Our approach ensures structural integrity, enhances interpretability and avoids hallucinations that may arise during direct image synthesis by generating this deformation field and regularising it using a neighbourhood of images. We compare our method to several state-of-the-art atlas generation methods using brain MR images from the UK Biobank. Our method generates highly realistic atlases with smooth transformations and high anatomical fidelity, outperforming existing baselines. We demonstrate the quality of these atlases through comprehensive evaluations, including quantitative metrics for anatomical accuracy, perceptual similarity, and qualitative analyses displaying the consistency and realism of the generated atlases.
解剖图谱在人群研究和分析中得到了广泛应用。条件图谱针对通过特定条件(如人口统计学或病理学)定义的具体亚群体,并允许研究精细的解剖差异,例如与衰老或疾病相关的形态变化。现有方法使用基于注册的方法,这些方法通常无法处理较大的解剖变异,或使用生成对抗模型,由于训练不稳定性的挑战,这些模型的训练具有挑战性。我们并不直接生成强度图谱,而是建议使用潜在扩散模型来生成变形场,该变形场将一个通用人群图谱转变为代表特定亚人群的图谱。我们的方法确保了结构的完整性,提高了可解释性,并且通过在图像邻域生成并正则化这个变形场,避免了在直接图像合成过程中可能出现的幻觉。我们使用英国生物银行的大脑MRI图像将我们的方法与几种最先进的图谱生成方法进行比较。我们的方法生成了高度逼真的图谱,具有平滑的变换和高度的解剖保真度,超过了现有的基线。我们通过综合评估证明了这些图谱的质量,包括用于解剖精度的定量指标、感知相似性,以及显示生成图谱的一致性和真实性的定性分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了使用潜在扩散模型生成特定子人群解剖图谱的变形场的方法。该方法通过变换通用人群图谱来反映特定子人群特征,确保了结构完整性、提高了可解释性,避免了直接图像合成中可能出现的幻觉。在UK Biobank的脑MRI图像上,该方法生成的高度逼真的图谱具有平滑变换和高解剖学保真度,优于现有基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 条件性图谱针对特定子人群,通过特定条件(如人口统计学或病理学)进行研究。
- 现有方法存在难以处理大解剖学变异或训练不稳定的问题。
- 本研究使用潜在扩散模型生成变形场,将通用图谱转换为特定子人群图谱。
- 通过图像邻域进行正则化,确保结构完整性、提高可解释性并避免幻觉。
- 在UK Biobank的脑MRI图像上进行了方法比较,表现出高度逼真、平滑变换和高解剖学保真度。
- 通过定量指标(解剖学准确性、感知相似性)和定性分析验证了生成图谱的质量。
点此查看论文截图

DeltaSpace: A Semantic-aligned Feature Space for Flexible Text-guided Image Editing
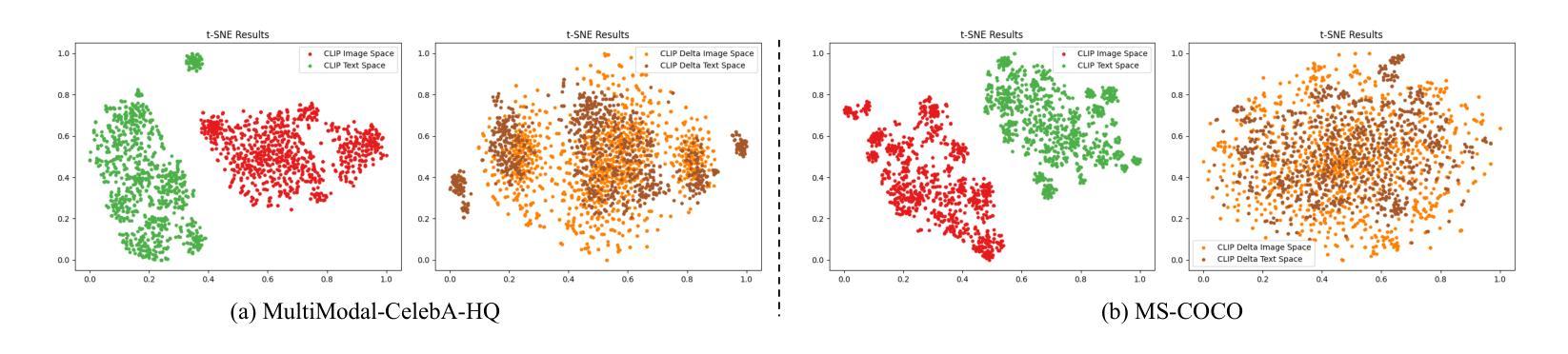
Authors:Yueming Lyu, Kang Zhao, Bo Peng, Huafeng Chen, Yue Jiang, Yingya Zhang, Jing Dong, Caifeng Shan
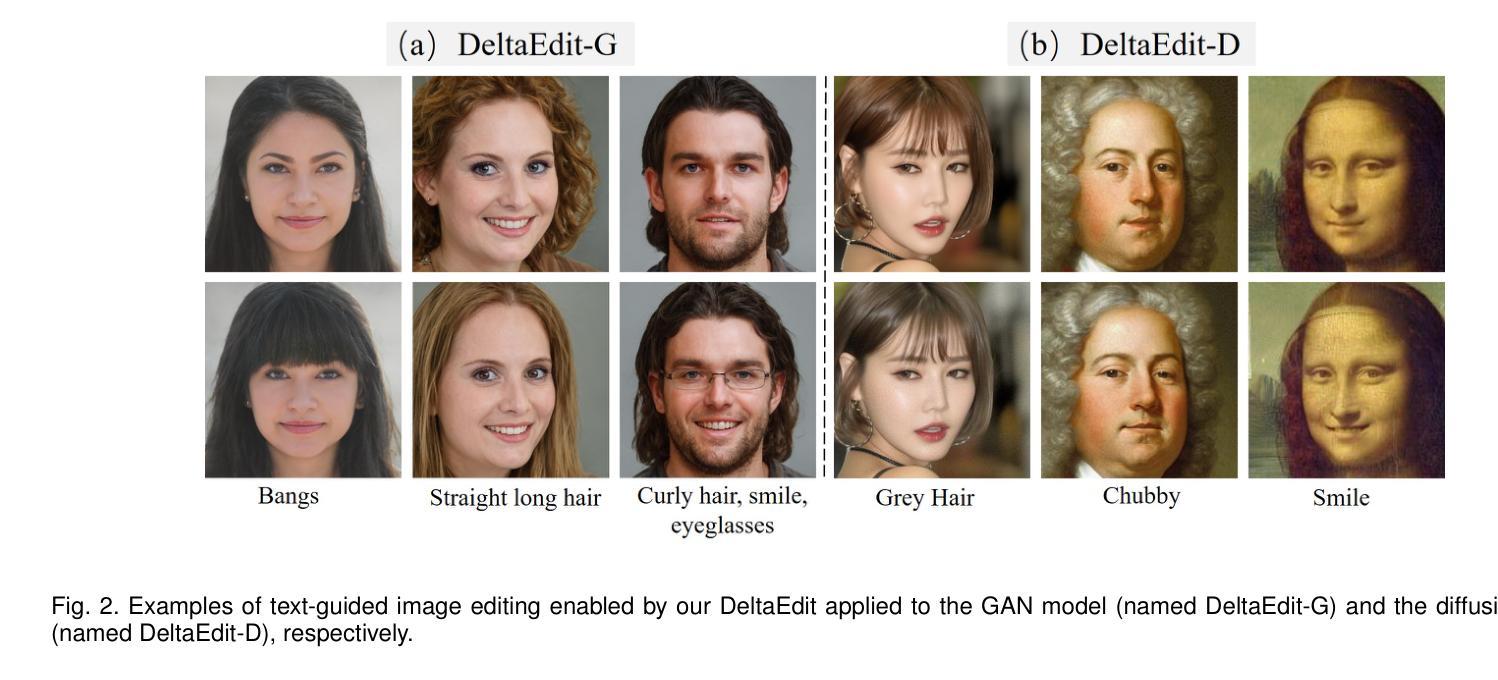
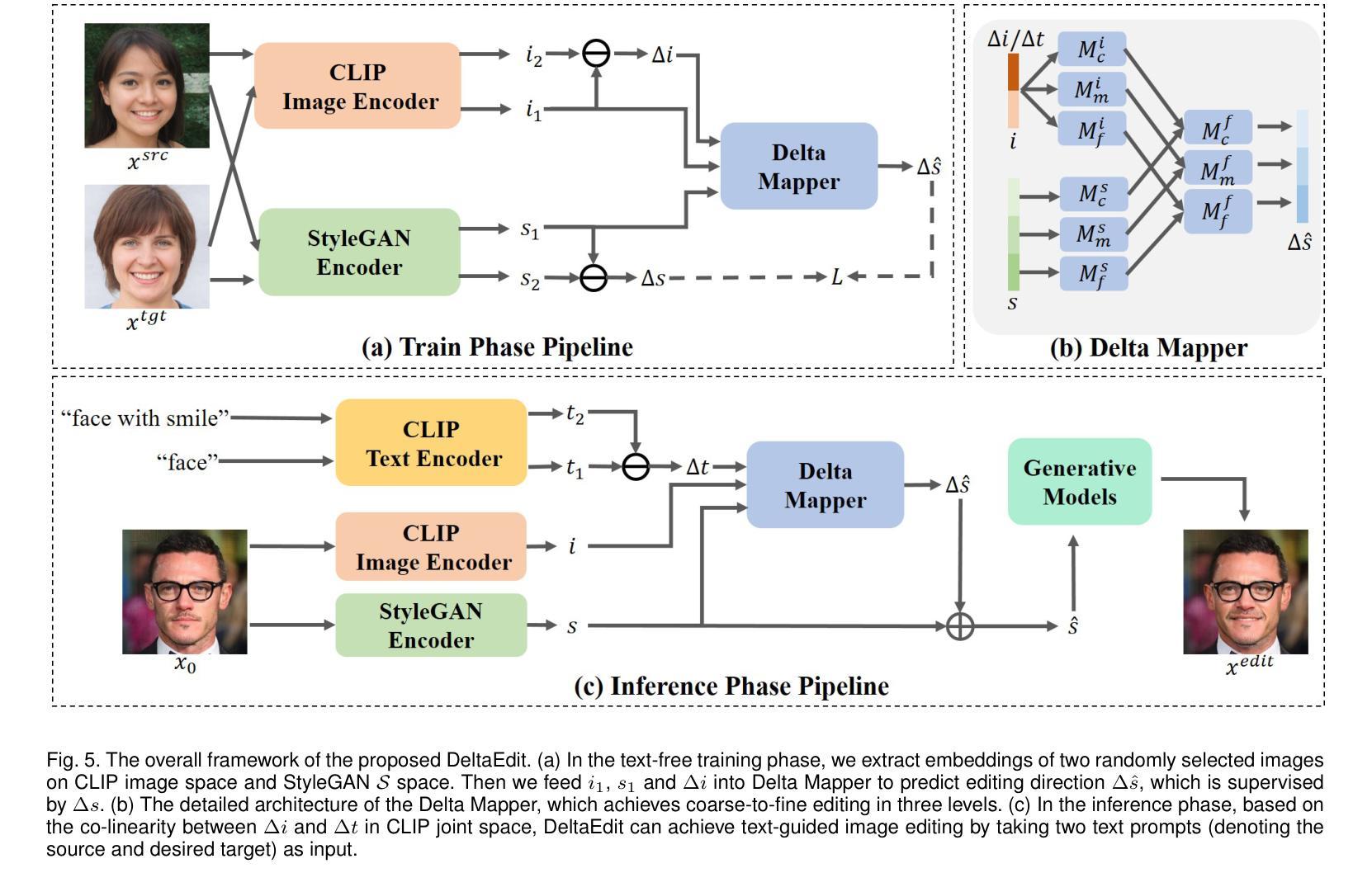
Text-guided image editing faces significant challenges when considering training and inference flexibility. Much literature collects large amounts of annotated image-text pairs to train text-conditioned generative models from scratch, which is expensive and not efficient. After that, some approaches that leverage pre-trained vision-language models have been proposed to avoid data collection, but they are limited by either per text-prompt optimization or inference-time hyper-parameters tuning. To address these issues, we investigate and identify a specific space, referred to as CLIP DeltaSpace, where the CLIP visual feature difference of two images is semantically aligned with the CLIP textual feature difference of their corresponding text descriptions. Based on DeltaSpace, we propose a novel framework called DeltaEdit, which maps the CLIP visual feature differences to the latent space directions of a generative model during the training phase, and predicts the latent space directions from the CLIP textual feature differences during the inference phase. And this design endows DeltaEdit with two advantages: (1) text-free training; (2) generalization to various text prompts for zero-shot inference. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and versatility of DeltaEdit with different generative models, including both the GAN model and the diffusion model, in achieving flexible text-guided image editing. Code is available at https://github.com/Yueming6568/DeltaEdit.
文本引导的图像编辑在考虑训练和推理灵活性时面临重大挑战。大量文献收集了大量的带注释的图像-文本对来从头训练文本条件生成模型,这既昂贵又无效。之后,一些利用预训练的语言视觉模型的方法被提出来避免数据收集,但它们受限于文本提示优化或推理时间超参数调整。为了解决这些问题,我们研究和确定了一个特定空间,称为CLIP DeltaSpace,在该空间中,两张图像之间的CLIP视觉特征差异与其对应文本描述的CLIP文本特征差异在语义上对齐。基于DeltaSpace,我们提出了一种新的框架,称为DeltaEdit,它在训练阶段将CLIP视觉特征差异映射到生成模型的潜在空间方向,并在推理阶段从CLIP文本特征差异预测潜在空间方向。这种设计赋予了DeltaEdit两个优点:(1)无文本训练;(2)泛化到各种文本提示进行零样本推理。大量实验验证了DeltaEdit在不同生成模型中的有效性和通用性,包括GAN模型和扩散模型,在实现灵活的文本引导图像编辑方面都有很好的表现。代码可在https://github.com/Yueming6568/DeltaEdit找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2303.06285
Summary
文本指导的图像编辑在考虑训练和推理灵活性时面临重大挑战。现有文献大多收集大量的图文配对进行文本控制的生成模型训练,成本高昂且效率低下。虽有利用预训练的视觉语言模型来避免数据收集的方法,但它们受限于文本提示优化或推理时间超参数调整。为解决这个问题,本文探索并确定了一个特定空间,称为CLIP DeltaSpace,其中CLIP图像特征差异与其对应文本描述的特征差异语义对齐。基于此,提出了名为DeltaEdit的新框架,在训练阶段将CLIP视觉特征差异映射到生成模型的潜在空间方向,并在推理阶段预测CLIP文本特征差异对应的潜在空间方向。此设计使DeltaEdit具有两大优势:(1)无需文本训练;(2)能够针对各种文本提示进行零样本推理。实验证明,DeltaEdit在不同生成模型(包括GAN模型和扩散模型)上均能有效实现灵活文本引导的图像编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 训练与推理的灵活性是文本引导的图像编辑的主要挑战。
- 收集大量标注的图文配对进行训练成本高且效率低下。
- CLIP DeltaSpace被发现,其中CLIP图像和文本特征的差异在此空间内语义对齐。
- 基于DeltaSpace,提出了名为DeltaEdit的新框架,该框架在训练和推理阶段利用视觉和文本特征差异。
- DeltaEdit具有两大优势:无需文本训练,并能针对多种文本提示进行零样本推理。
点此查看论文截图