⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-26 更新
UltraAD: Fine-Grained Ultrasound Anomaly Classification via Few-Shot CLIP Adaptation
Authors:Yue Zhou, Yuan Bi, Wenjuan Tong, Wei Wang, Nassir Navab, Zhongliang Jiang
Precise anomaly detection in medical images is critical for clinical decision-making. While recent unsupervised or semi-supervised anomaly detection methods trained on large-scale normal data show promising results, they lack fine-grained differentiation, such as benign vs. malignant tumors. Additionally, ultrasound (US) imaging is highly sensitive to devices and acquisition parameter variations, creating significant domain gaps in the resulting US images. To address these challenges, we propose UltraAD, a vision-language model (VLM)-based approach that leverages few-shot US examples for generalized anomaly localization and fine-grained classification. To enhance localization performance, the image-level token of query visual prototypes is first fused with learnable text embeddings. This image-informed prompt feature is then further integrated with patch-level tokens, refining local representations for improved accuracy. For fine-grained classification, a memory bank is constructed from few-shot image samples and corresponding text descriptions that capture anatomical and abnormality-specific features. During training, the stored text embeddings remain frozen, while image features are adapted to better align with medical data. UltraAD has been extensively evaluated on three breast US datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both lesion localization and fine-grained medical classification. The code will be released upon acceptance.
精确医学图像异常检测对于临床决策至关重要。虽然最近基于大规模正常数据的无监督或半监督异常检测方法显示出有前景的结果,但它们缺乏精细的区分,如良性与恶性肿瘤等。此外,超声(US)成像对设备和采集参数的变化高度敏感,导致超声图像存在显著的域差异。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了UltraAD,一种基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的方法,利用少量超声图像例子进行通用异常定位和精细分类。为了提高定位性能,首先融合查询视觉原型的图像级令牌和可学习的文本嵌入。然后,将图像信息提示特征与补丁级令牌进一步集成,以细化局部表示并提高准确性。对于精细分类,从少量图像样本和相应的文本描述中构建了一个内存银行,以捕获解剖结构和异常特定的特征。在训练过程中,存储的文本嵌入保持不变,而图像特征更好地适应医学数据。UltraAD在三个乳腺超声数据集上进行了广泛评估,在病灶定位和精细医学分类方面都优于最新方法。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医疗图像精准异常检测的重要性,针对现有方法缺乏精细粒度区分(如良性与恶性肿瘤)以及超声成像中的设备与采集参数变化带来的领域差距问题,提出了基于视觉语言模型的UltraAD方法。该方法利用少量超声图像样本进行通用异常定位和精细粒度分类。通过融合图像级令牌与可学习文本嵌入,提高定位性能。同时,利用记忆库存储少量图像样本及其文本描述,进行精细粒度分类。在三个乳腺超声数据集上的评估表明,UltraAD在病灶定位与精细粒度医学分类方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像精准异常检测对临床决策至关重要。
- 现有方法缺乏精细粒度区分,如良性与恶性肿瘤的区分。
- UltraAD方法基于视觉语言模型,利用少量超声图像样本进行通用异常定位和精细粒度分类。
- UltraAD通过融合图像级令牌与可学习文本嵌入提高定位性能。
- 利用记忆库存储图像样本及其文本描述,进行精细粒度分类。
- UltraAD在病灶定位与精细粒度医学分类方面均表现出优异性能。
点此查看论文截图

Correcting Hallucinations in News Summaries: Exploration of Self-Correcting LLM Methods with External Knowledge
Authors:Juraj Vladika, Ihsan Soydemir, Florian Matthes
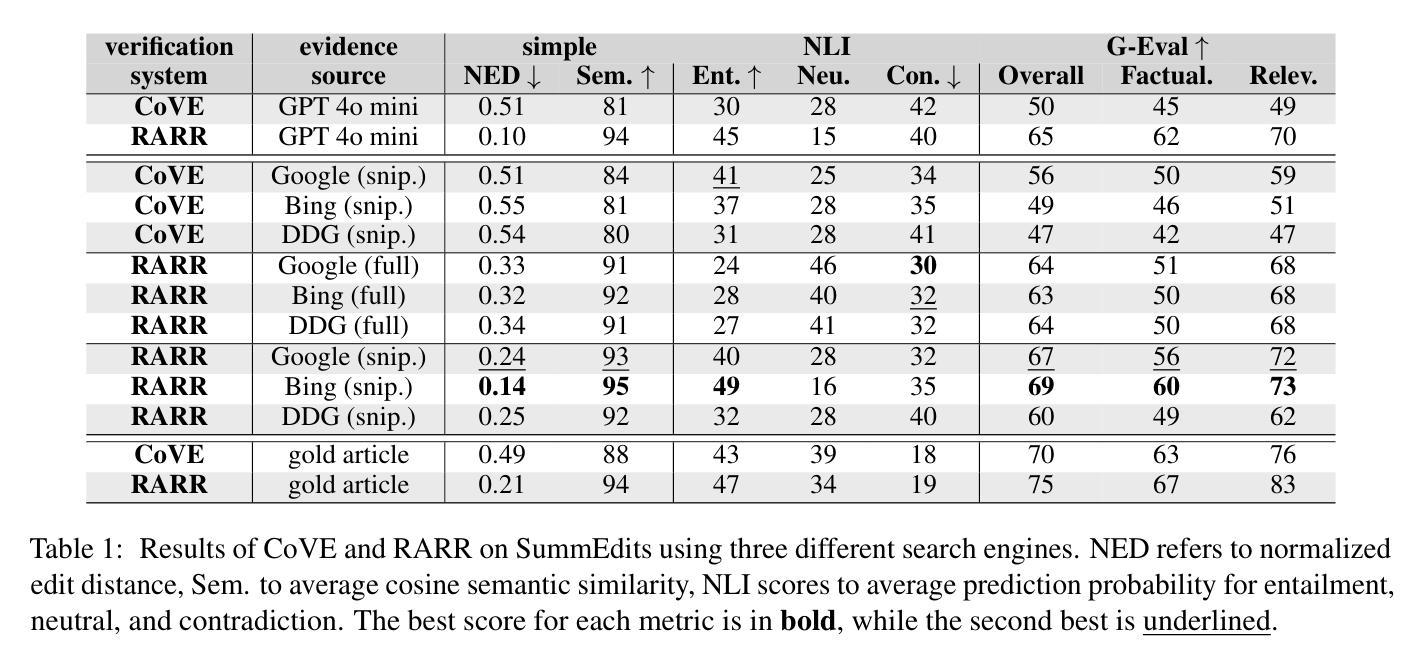
While large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities to generate coherent text, they suffer from the issue of hallucinations – factually inaccurate statements. Among numerous approaches to tackle hallucinations, especially promising are the self-correcting methods. They leverage the multi-turn nature of LLMs to iteratively generate verification questions inquiring additional evidence, answer them with internal or external knowledge, and use that to refine the original response with the new corrections. These methods have been explored for encyclopedic generation, but less so for domains like news summarization. In this work, we investigate two state-of-the-art self-correcting systems by applying them to correct hallucinated summaries using evidence from three search engines. We analyze the results and provide insights into systems’ performance, revealing interesting practical findings on the benefits of search engine snippets and few-shot prompts, as well as high alignment of G-Eval and human evaluation.
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在生成连贯文本方面表现出了显著的能力,但它们存在虚构问题,即事实上不准确的说法。在解决虚构问题的众多方法中,特别有前景的是自我校正方法。它们利用LLM的多轮对话性质来生成验证问题,询问额外的证据,用内部或外部知识回答问题,并利用这些新修正来完善原始回答。这些方法在百科全书生成方面已被探索过,但在新闻摘要等领域则较少探索。在这项工作中,我们通过将两种最先进的自我校正系统应用于使用来自三个搜索引擎的证据来纠正虚构摘要,从而进行研究。我们分析了结果,并深入了解了系统的性能,揭示了关于搜索引擎片段和少量提示的实际好处的一些有趣发现,以及G-Eval与人类评估的高度一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to FEVER @ ACL 2025
Summary:
大型语言模型在生成连贯文本方面表现出显著的能力,但它们存在事实不准确的问题。自我校正方法通过利用LLM的多轮特性生成验证问题、寻找额外证据来回答问题,并使用这些来修正原始响应。尽管这些方法在百科全书生成方面得到了探索,但在新闻摘要等领域的应用较少。本研究将两种先进的自我校正系统应用于纠正因幻觉产生的摘要,并利用来自三个搜索引擎的证据。我们分析了结果,并深入了解了系统的性能,发现了搜索引擎片段和少量提示的实用优势,以及G-Eval与人类评价的极高一致性。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型虽然能生成连贯文本,但存在事实不准确的问题,即“幻觉”。
- 自我校正方法通过生成验证问题、寻找额外证据来修正原始响应,是解决幻觉问题的有前途的方法。
- 自我校正方法在百科全书生成方面得到了探索,但在新闻摘要等领域的应用较少。
- 研究中,两种先进的自我校正系统被应用于纠正因幻觉产生的摘要。
- 利用来自三个搜索引擎的证据来提高校正效果。
- 分析结果显示搜索引擎片段和少量提示具有实用优势。
点此查看论文截图


FAF: A Feature-Adaptive Framework for Few-Shot Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Pengpeng Ouyang, Dong Chen, Tong Yang, Shuo Feng, Zhao Jin, Mingliang Xu
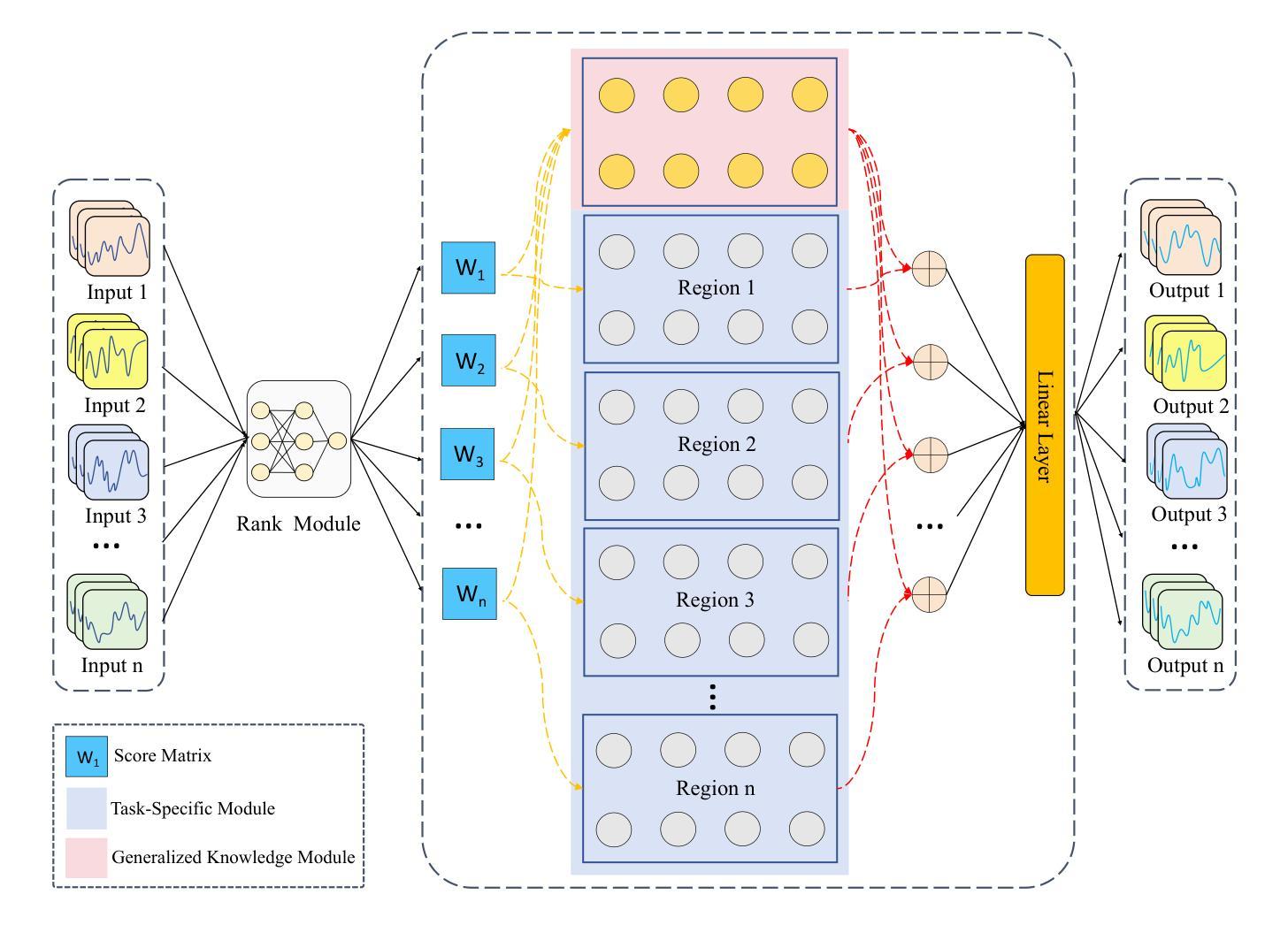
Multi-task and few-shot time series forecasting tasks are commonly encountered in scenarios such as the launch of new products in different cities. However, traditional time series forecasting methods suffer from insufficient historical data, which stems from a disregard for the generalized and specific features among different tasks. For the aforementioned challenges, we propose the Feature-Adaptive Time Series Forecasting Framework (FAF), which consists of three key components: the Generalized Knowledge Module (GKM), the Task-Specific Module (TSM), and the Rank Module (RM). During training phase, the GKM is updated through a meta-learning mechanism that enables the model to extract generalized features across related tasks. Meanwhile, the TSM is trained to capture diverse local dynamics through multiple functional regions, each of which learns specific features from individual tasks. During testing phase, the RM dynamically selects the most relevant functional region from the TSM based on input sequence features, which is then combined with the generalized knowledge learned by the GKM to generate accurate forecasts. This design enables FAF to achieve robust and personalized forecasting even with sparse historical observations We evaluate FAF on five diverse real-world datasets under few-shot time series forecasting settings. Experimental results demonstrate that FAF consistently outperforms baselines that include three categories of time series forecasting methods. In particular, FAF achieves a 41.81% improvement over the best baseline, iTransformer, on the CO$_2$ emissions dataset.
多任务与少样本时间序列预测任务在诸如不同城市推出新产品等场景中经常遇到。然而,传统的时间序列预测方法面临历史数据不足的问题,这源于它们忽视了不同任务之间的通用和特定特征。针对上述挑战,我们提出了特征自适应时间序列预测框架(FAF),它包括三个关键组件:通用知识模块(GKM)、任务特定模块(TSM)和排名模块(RM)。在训练阶段,GKM通过元学习机制进行更新,使模型能够在相关任务中提取通用特征。同时,TSM经过训练,通过多个功能区域捕捉不同的局部动态,每个功能区域都从单个任务中学习特定特征。在测试阶段,RM根据输入序列特征动态选择最相关的功能区域,然后将其与GKM中学习的通用知识相结合,生成准确的预测。这种设计使FAF即使在稀疏的历史观测下也能实现稳健和个性化的预测。我们在五个不同的真实数据集上评估了FAF在少样本时间序列预测设置下的表现。实验结果表明,FAF持续优于包括三类时间序列预测方法在内的基线模型。特别地,FAF在二氧化碳排放数据集上相较于最佳基线模型iTransformer实现了41.81%的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages,4 figures, 8 tables
Summary
在推出新产品于不同城市的情境中,经常遇到多任务与少样本时间序列预测任务。传统的时间序列预测方法因缺乏历史数据而受限,忽视了不同任务间的通用和特定特征。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了特征自适应时间序列预测框架(FAF),包含三个关键组件:通用知识模块(GKM)、任务特定模块(TSM)和排名模块(RM)。在训练阶段,GKM通过元学习机制更新,使模型能够提取相关任务间的通用特征。TSM则训练以捕捉不同功能区域的局部动态,每个区域从个别任务中学习特定特征。在测试阶段,RM根据输入序列特征动态选择最相关的功能区域,并与GKM学到的通用知识结合,生成准确预测。即使历史观测数据稀疏,这种设计也使FAF能够实现稳健和个性化的预测。在五个真实世界数据集上进行少样本时间序列预测设置评估,实验结果表明,FAF持续优于基线,特别是在二氧化碳排放数据集上,相对于最佳基线iTransformer,FAF实现了41.81%的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 多任务与少样本时间序列预测在实际场景中很常见,特别是在新产品在不同城市的推广过程中。
- 传统的时间序列预测方法存在对历史数据不足的问题,这主要源于它们忽视了不同任务之间的通用和特定特征。
- 提出的特征自适应时间序列预测框架(FAF)包括三个核心组件:用于提取通用特征的广义知识模块(GKM),用于捕捉特定任务的特定特征的任务特定模块(TSM),以及根据输入选择相关功能的排名模块(RM)。
- 在训练阶段,FAF通过元学习更新GKM,并训练TSM以捕捉不同功能区域的局部动态。
- 在测试阶段,RM动态选择功能区域,结合GKM的通用知识做出预测。
- FAF框架对于历史数据稀疏的情况依然有效,能够实现稳健和个性化的预测。
点此查看论文截图

ConCM: Consistency-Driven Calibration and Matching for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:QinZhe Wang, Zixuan Chen, Keke Huang, Xiu Su, Chunhua Yang, Chang Xu
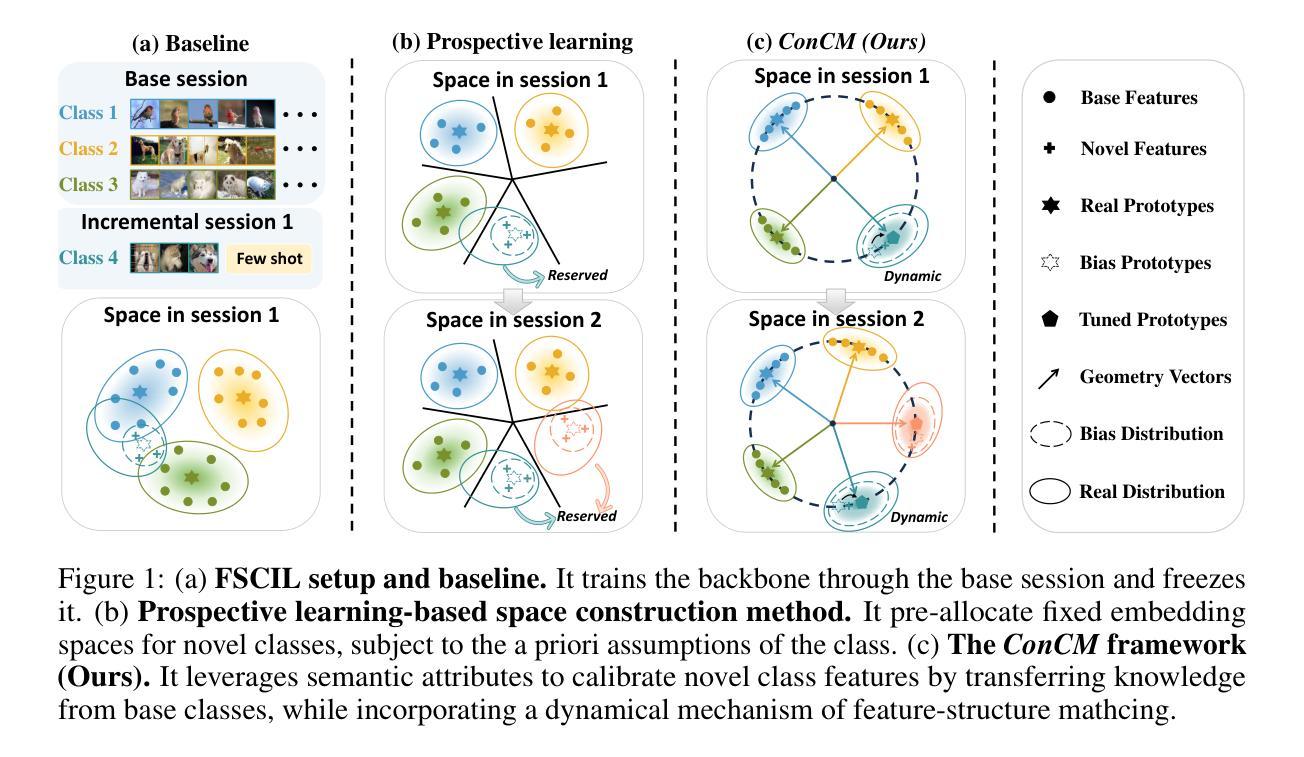
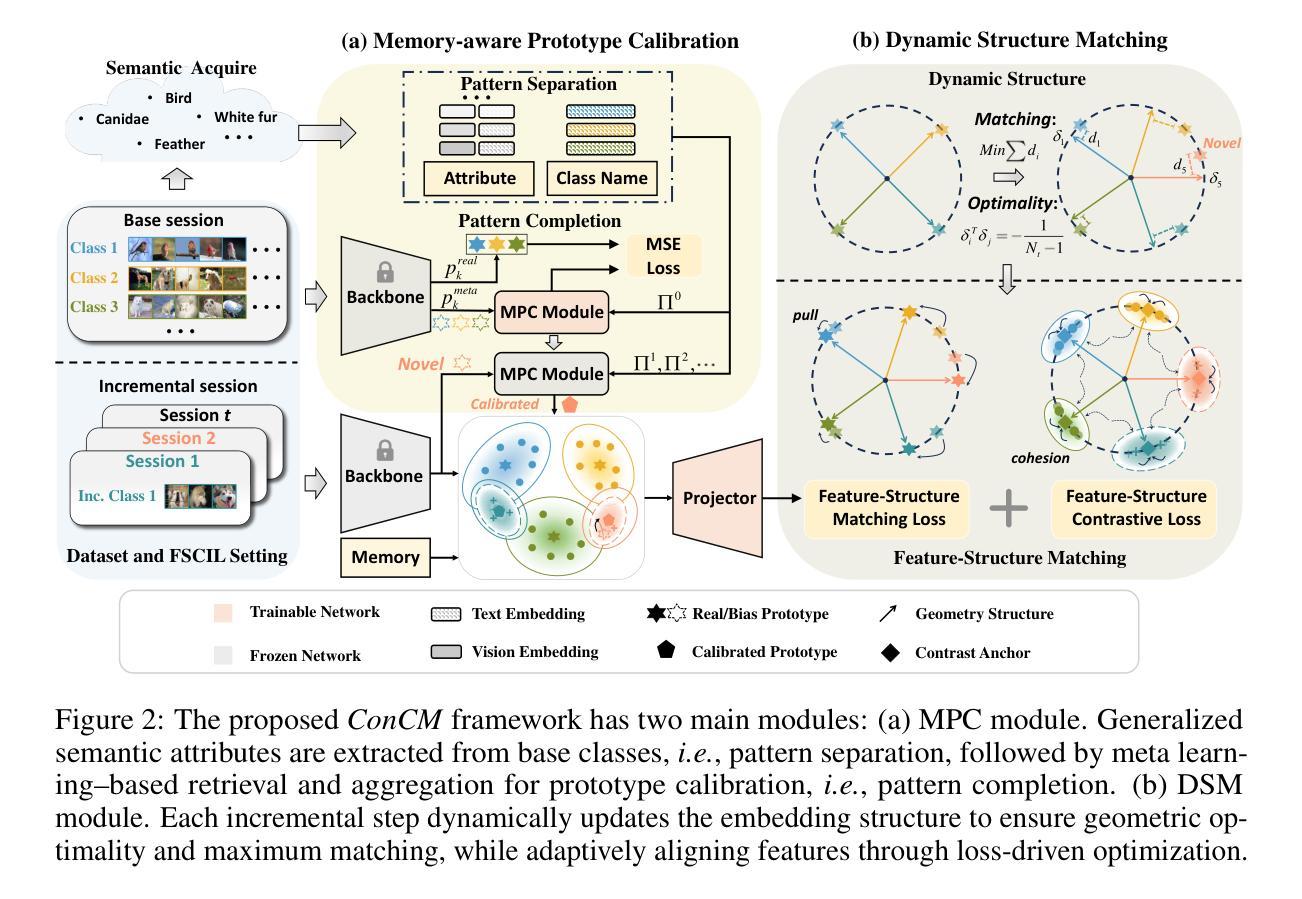
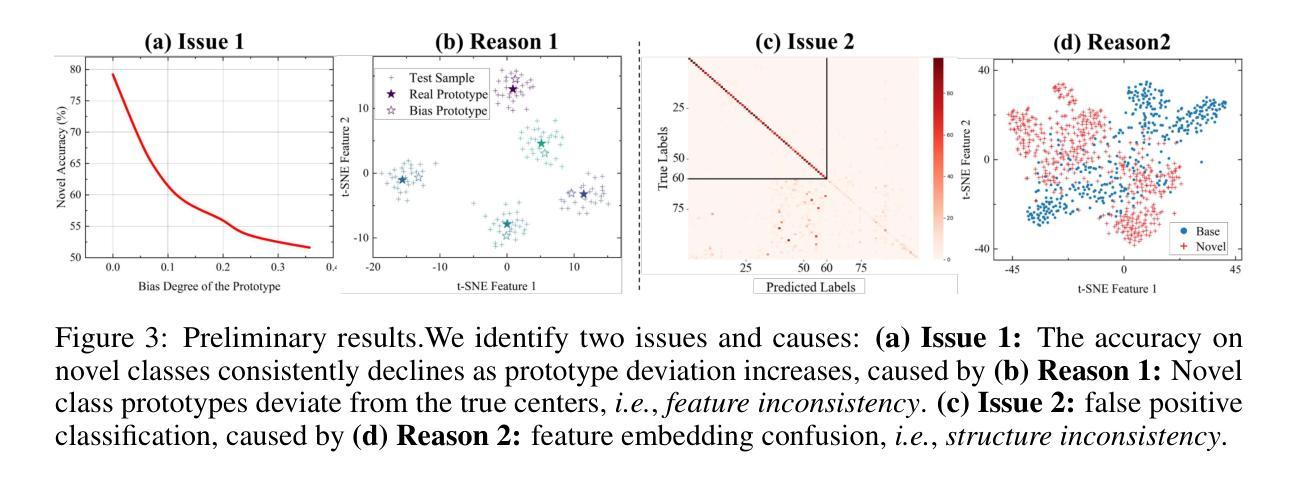
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) requires models to adapt to novel classes with limited supervision while preserving learned knowledge. Existing prospective learning-based space construction methods reserve space to accommodate novel classes. However, prototype deviation and structure fixity limit the expressiveness of the embedding space. In contrast to fixed space reservation, we explore the optimization of feature-structure dual consistency and propose a Consistency-driven Calibration and Matching Framework (ConCM) that systematically mitigate the knowledge conflict inherent in FSCIL. Specifically, inspired by hippocampal associative memory, we design a memory-aware prototype calibration that extracts generalized semantic attributes from base classes and reintegrates them into novel classes to enhance the conceptual center consistency of features. Further, we propose dynamic structure matching, which adaptively aligns the calibrated features to a session-specific optimal manifold space, ensuring cross-session structure consistency. Theoretical analysis shows that our method satisfies both geometric optimality and maximum matching, thereby overcoming the need for class-number priors. On large-scale FSCIL benchmarks including mini-ImageNet and CUB200, ConCM achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing current optimal method by 3.20% and 3.68% in harmonic accuracy of incremental sessions.
少量类别增量学习(FSCIL)要求模型在有限监督下适应新类别,同时保留已学习的知识。现有的基于前瞻性学习空间构建的方法保留空间来容纳新类别。然而,原型偏差和结构固定性限制了嵌入空间的表达能力。与固定空间预留相反,我们探索特征结构双重一致性的优化,并提出一种一致性驱动校准和匹配框架(ConCM),系统地减轻FSCIL中固有的知识冲突。具体来说,受到海马体关联记忆的启发,我们设计了一种记忆感知原型校准,从基础类别中提取通用语义属性,并将其重新整合到新类别中,以增强特征的概念中心一致性。此外,我们提出了动态结构匹配,自适应地将校准后的特征对齐到会话特定的最优流形空间,确保跨会话结构一致性。理论分析表明,我们的方法满足几何最优性和最大匹配度,从而不需要类别数量先验。在包括mini-ImageNet和CUB200的大规模FSCIL基准测试中,ConCM实现了最先进的性能,在增量会话的调和准确性上分别比当前最优方法高出3.20%和3.68%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures(Excluding the appendix)
Summary
本文探讨了Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)中的嵌入空间构建方法的问题。现有方法主要通过固定空间预留来适应新类,但存在原型偏差和结构固定性,限制了表达性。本文提出了一个一致性驱动校准和匹配框架(ConCM),通过优化特征结构一致性来解决FSCIL中的知识冲突问题。该框架包含记忆感知原型校准和动态结构匹配,分别在特征的概念中心一致性和跨会话结构一致性上实现优化。在大型FSCIL基准测试上,ConCM实现了最先进的性能,超越了当前最优方法。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)要求模型在有限监督下适应新类,同时保留已学习知识。
- 现有基于空间的构建方法主要通过固定空间预留来适应新类,但存在原型偏差和结构固定性的限制。
- ConCM框架通过优化特征结构一致性来解决FSCIL中的知识冲突问题。
- ConCM包含记忆感知原型校准,从基础类中提取广义语义属性并重新集成到新类中,以增强特征的概念中心一致性。
- 动态结构匹配技术被提出,以自适应地对齐校准特征到会话特定的最优流形空间,确保跨会话的结构一致性。
- ConCM在大型FSCIL基准测试上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

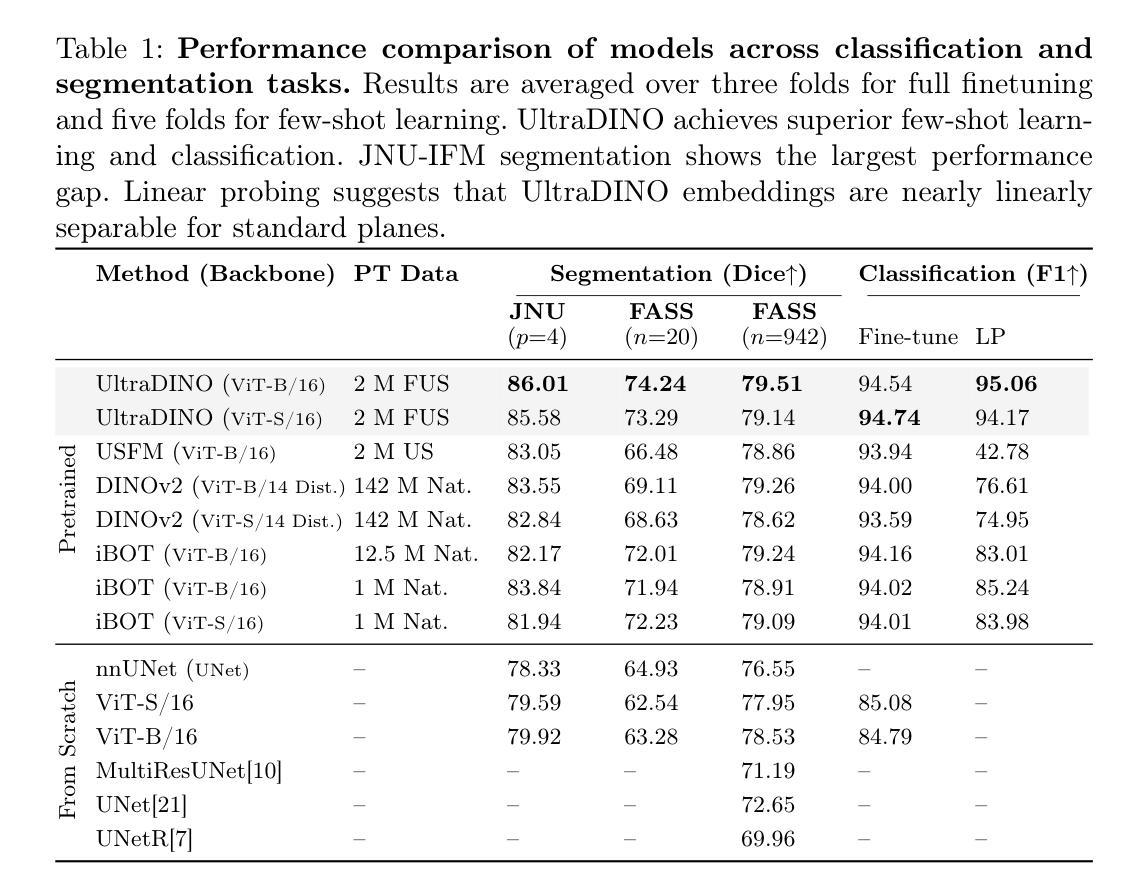
General Methods Make Great Domain-specific Foundation Models: A Case-study on Fetal Ultrasound
Authors:Jakob Ambsdorf, Asbjørn Munk, Sebastian Llambias, Anders Nymark Christensen, Kamil Mikolaj, Randall Balestriero, Martin Tolsgaard, Aasa Feragen, Mads Nielsen
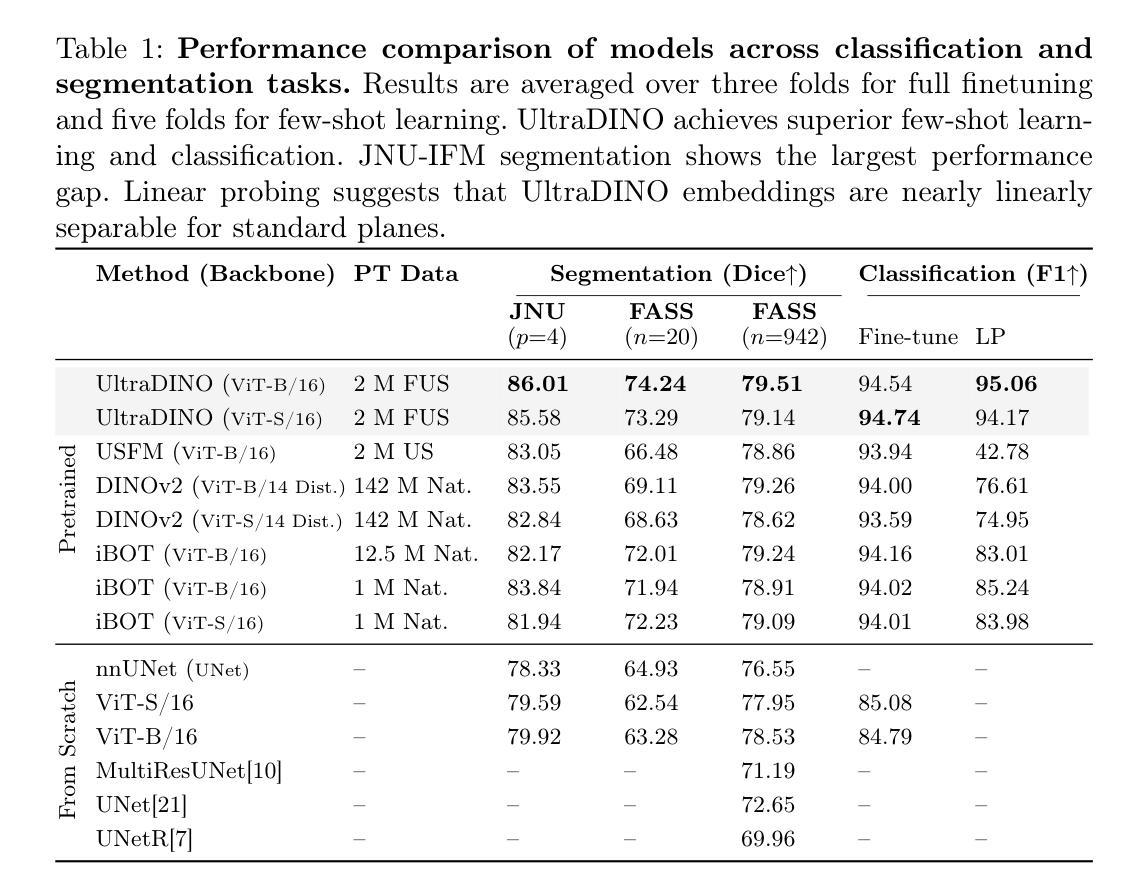
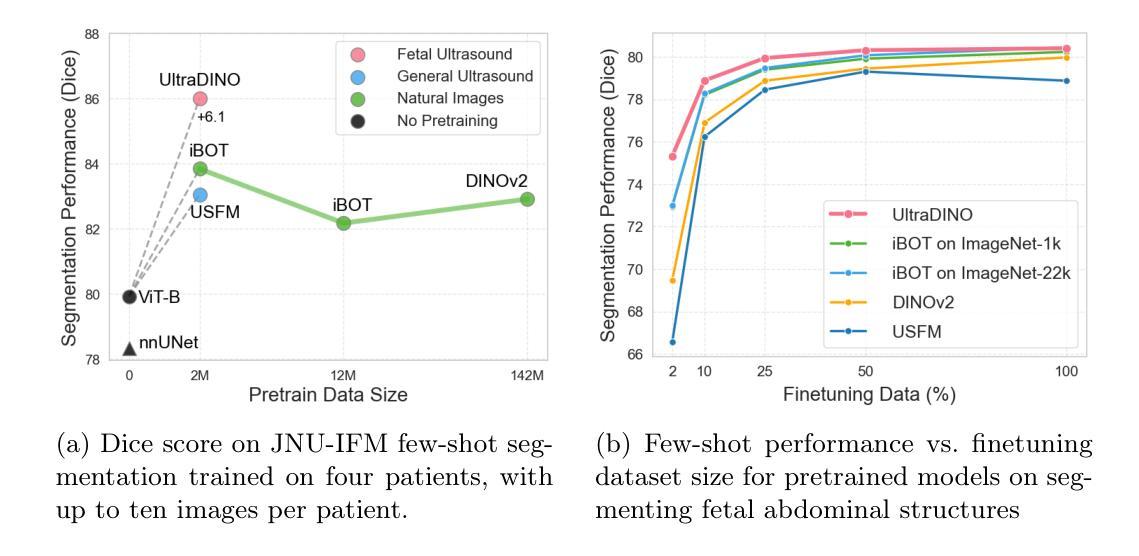
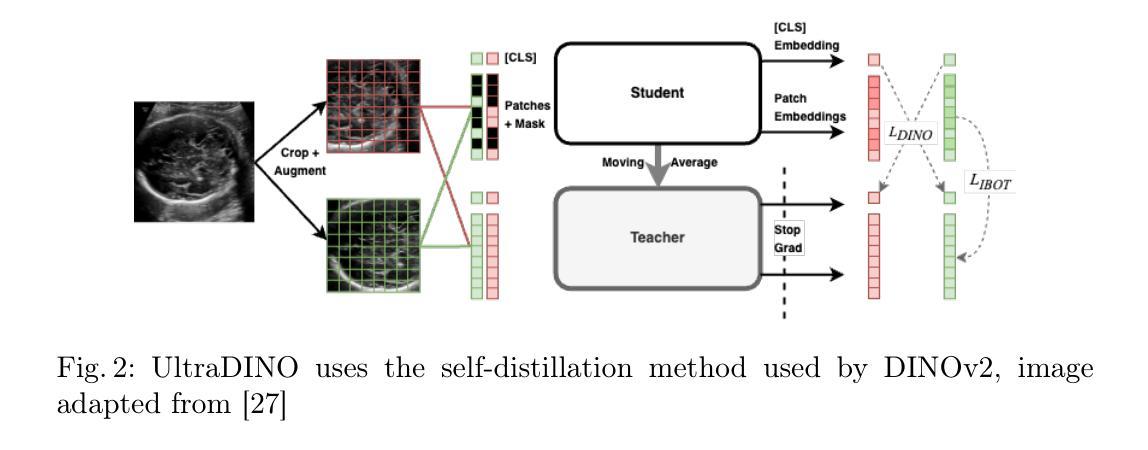
With access to large-scale, unlabeled medical datasets, researchers are confronted with two questions: Should they attempt to pretrain a custom foundation model on this medical data, or use transfer-learning from an existing generalist model? And, if a custom model is pretrained, are novel methods required? In this paper we explore these questions by conducting a case-study, in which we train a foundation model on a large regional fetal ultrasound dataset of 2M images. By selecting the well-established DINOv2 method for pretraining, we achieve state-of-the-art results on three fetal ultrasound datasets, covering data from different countries, classification, segmentation, and few-shot tasks. We compare against a series of models pretrained on natural images, ultrasound images, and supervised baselines. Our results demonstrate two key insights: (i) Pretraining on custom data is worth it, even if smaller models are trained on less data, as scaling in natural image pretraining does not translate to ultrasound performance. (ii) Well-tuned methods from computer vision are making it feasible to train custom foundation models for a given medical domain, requiring no hyperparameter tuning and little methodological adaptation. Given these findings, we argue that a bias towards methodological innovation should be avoided when developing domain specific foundation models under common computational resource constraints.
在面对大规模的无标签医疗数据集时,研究人员面临两个问题:他们是否应该尝试在此医疗数据上预训练一个自定义基础模型,还是使用从现有通用模型进行迁移学习?如果预训练了自定义模型,是否需要新颖的方法?在本文中,我们通过进行案例研究来探讨这些问题。我们在一个包含2百万图像的大规模区域性胎儿超声数据集上训练了一个基础模型。通过选择成熟的DINOv2方法进行预训练,我们在三个胎儿超声数据集上实现了最新结果,这些数据集涵盖了不同国家的数据、分类、分割和少量任务。我们将预训练在自然图像、超声图像上的模型以及与监督基准模型进行了一系列比较。我们的结果证明了两个关键见解:(i)即使在较少的数据上训练较小的模型,对自定义数据进行预训练也是值得的,因为自然图像预训练的扩展并不等同于超声性能。(ii)经过良好调整的计算视觉方法使得训练针对给定医疗领域的自定义基础模型成为可能,无需调整超参数和少量的方法论适应。根据这些发现,我们认为在开发特定领域的模型时,应尽量避免倾向于方法创新的偏见,尤其是在常见的计算资源约束下。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted version of paper accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
大型无标签医学数据集的使用面临选择:是尝试预训练一个定制的基础模型,还是使用从现有通用模型进行的迁移学习?本文通过一个案例研究探讨了这些问题。我们在一个包含2百万张胎儿超声图像的大型区域超声数据集上训练了一个基础模型,并使用成熟的DINOv2预训练技术取得了最先进的成果。我们的研究结果显示,针对特定医学领域的定制基础模型预训练是值得的,即使使用较小的模型处理较少的数据。此外,计算机视觉领域的良好调整方法使得训练针对特定医学领域的定制基础模型成为可能,无需进行超参数调整和方法轻微调整。因此,在开发特定领域的基础模型时,应避免偏向方法创新的倾向。
Key Takeaways
- 面对大型无标签医学数据集,应探讨是否预训练定制基础模型或采用迁移学习。
- 在胎儿超声数据集上预训练的定制基础模型取得了先进成果。
- 预训练在特定医学领域值得投入,即使处理数据量和模型规模相对较小。
- 自然图像预训练的可扩展性并不等同于超声性能的提升。
- 计算机视觉领域的方法使得训练特定医学领域的定制基础模型成为可能。
- 训练这样的模型无需大量超参数调整和方法适应。
点此查看论文截图

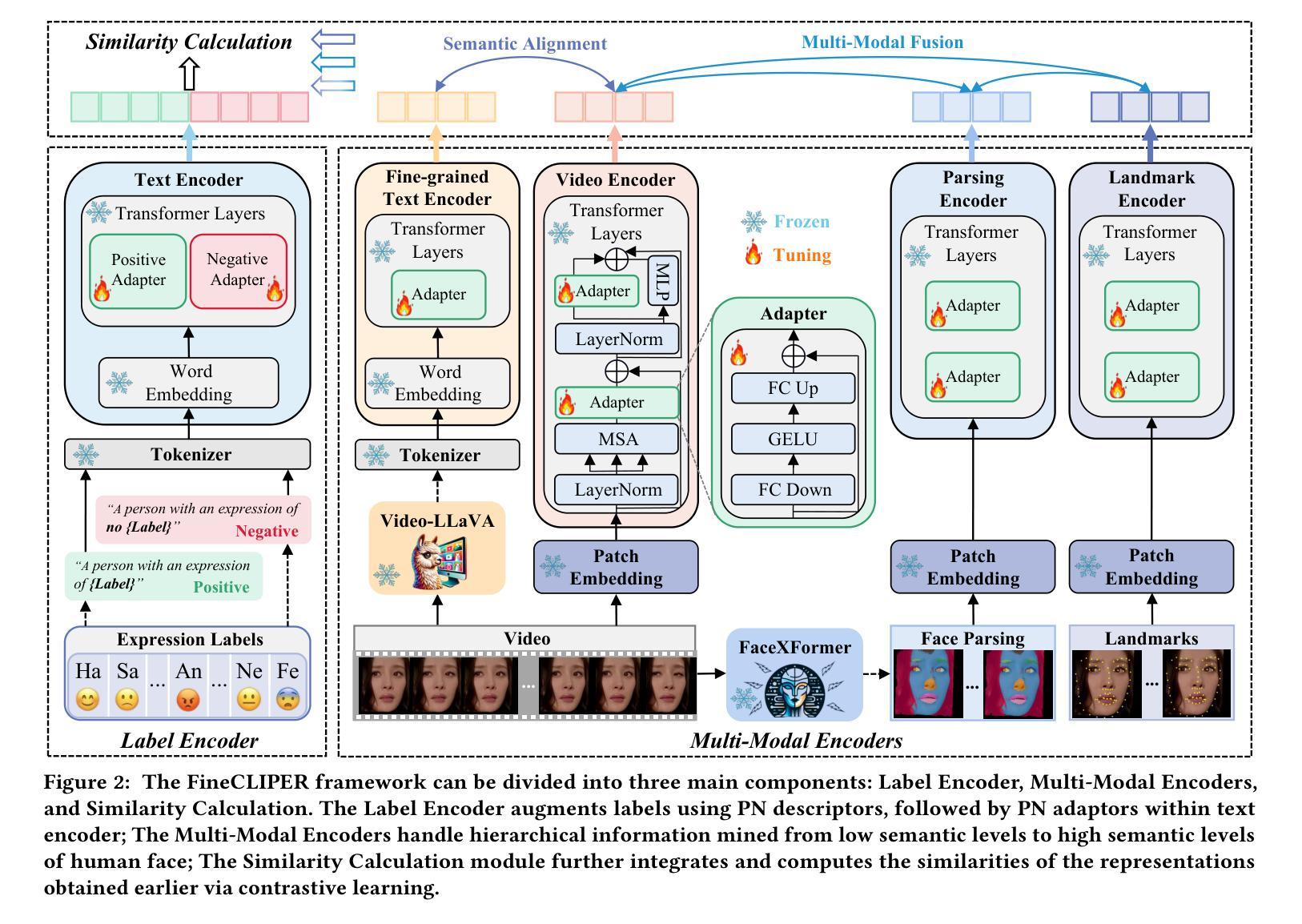
FineCLIPER: Multi-modal Fine-grained CLIP for Dynamic Facial Expression Recognition with AdaptERs
Authors:Haodong Chen, Haojian Huang, Junhao Dong, Mingzhe Zheng, Dian Shao
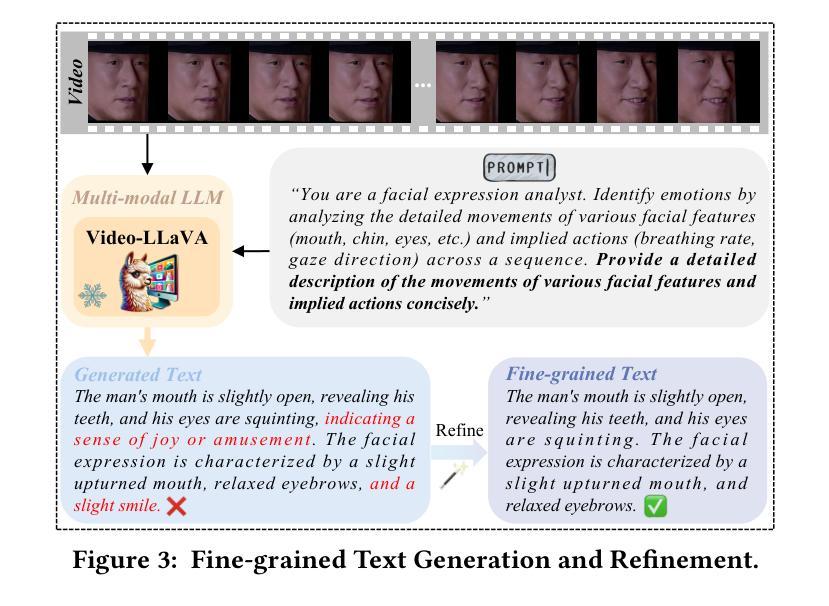
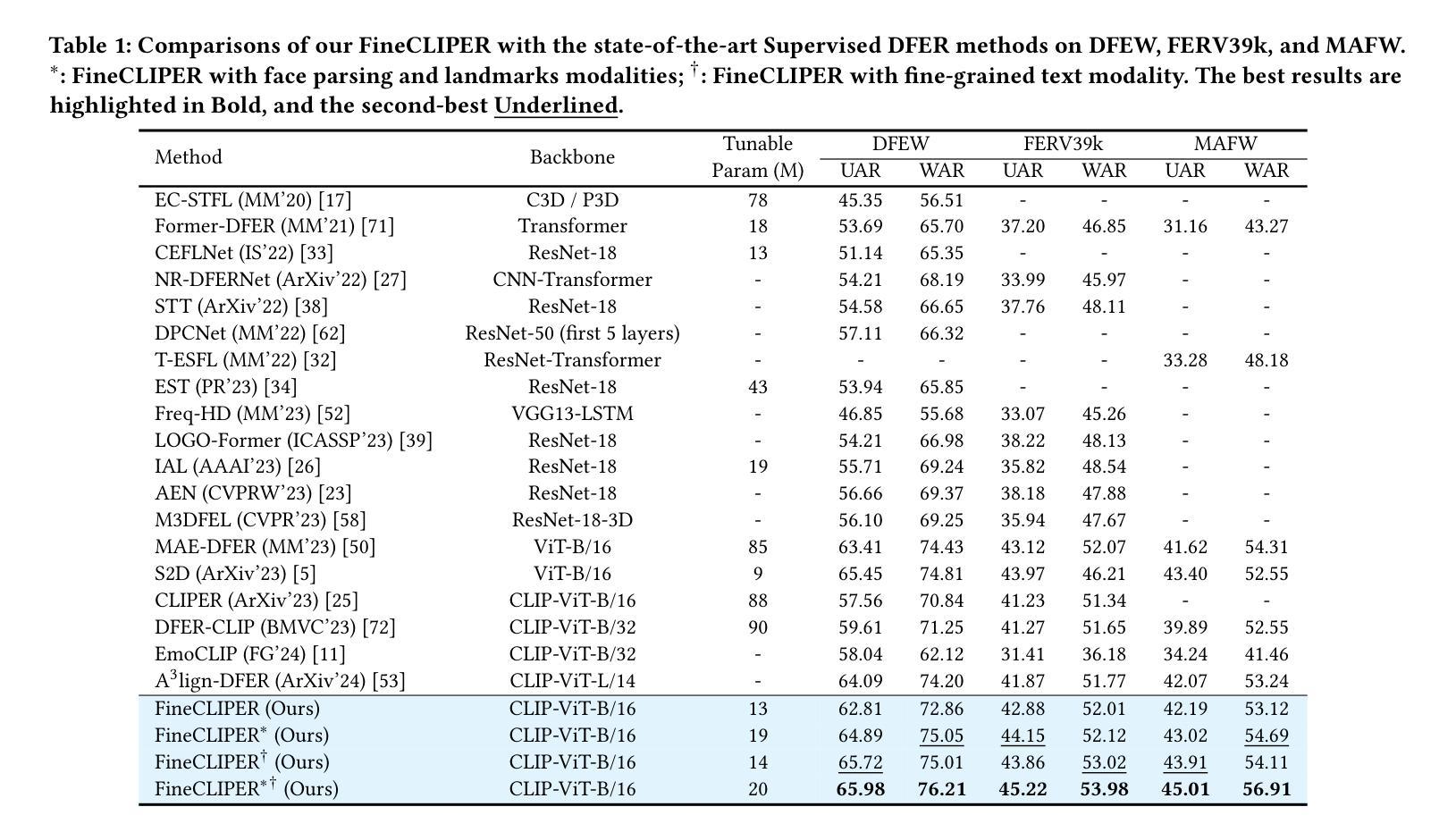
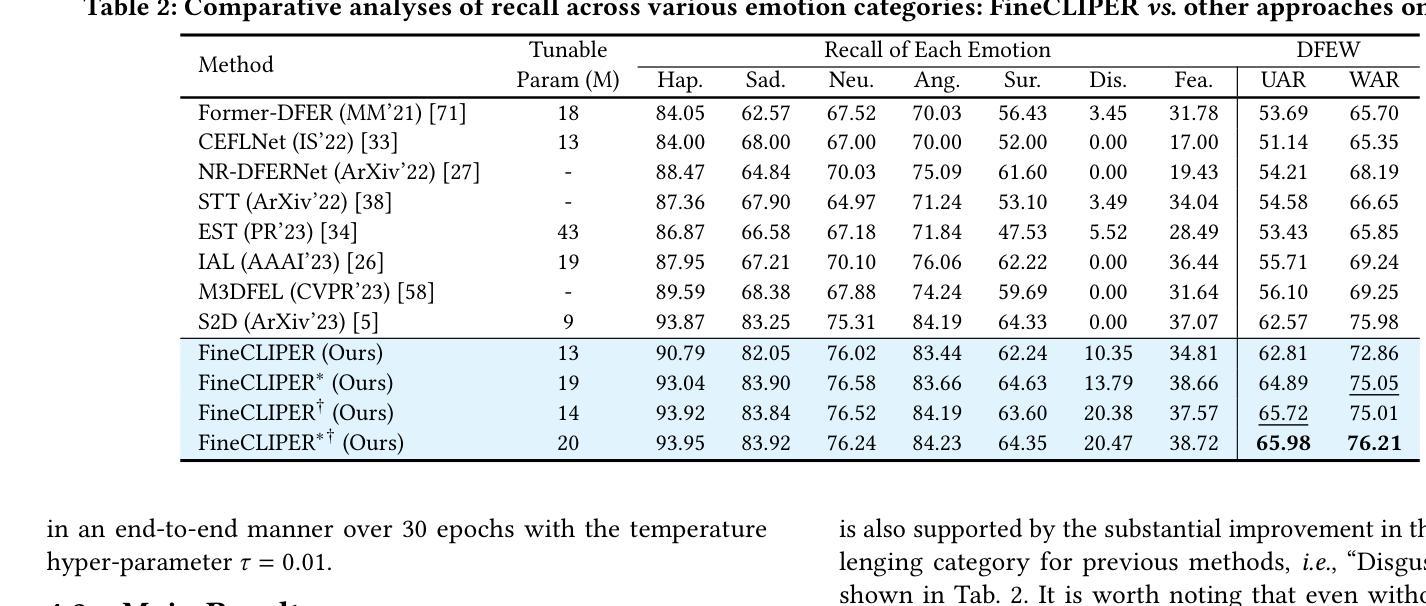
Dynamic Facial Expression Recognition (DFER) is crucial for understanding human behavior. However, current methods exhibit limited performance mainly due to the scarcity of high-quality data, the insufficient utilization of facial dynamics, and the ambiguity of expression semantics, etc. To this end, we propose a novel framework, named Multi-modal Fine-grained CLIP for Dynamic Facial Expression Recognition with AdaptERs (FineCLIPER), incorporating the following novel designs: 1) To better distinguish between similar facial expressions, we extend the class labels to textual descriptions from both positive and negative aspects, and obtain supervision by calculating the cross-modal similarity based on the CLIP model; 2) Our FineCLIPER adopts a hierarchical manner to effectively mine useful cues from DFE videos. Specifically, besides directly embedding video frames as input (low semantic level), we propose to extract the face segmentation masks and landmarks based on each frame (middle semantic level) and utilize the Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) to further generate detailed descriptions of facial changes across frames with designed prompts (high semantic level). Additionally, we also adopt Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) to enable efficient adaptation of large pre-trained models (i.e., CLIP) for this task. Our FineCLIPER achieves SOTA performance on the DFEW, FERV39k, and MAFW datasets in both supervised and zero-shot settings with few tunable parameters. Project Page: https://haroldchen19.github.io/FineCLIPER-Page/
动态面部表情识别(DFER)对于理解人类行为至关重要。然而,当前的方法表现有限,主要是由于高质量数据的稀缺、面部动态利用不足以及表达语义的模糊等原因。为此,我们提出了一种名为Multi-modal Fine-grained CLIP for Dynamic Facial Expression Recognition with AdaptERs(FineCLIPER)的新型框架,并融入了以下新颖设计:1)为了更好地区分相似的面部表情,我们将类别标签扩展到正面和负面方面的文本描述,并通过基于CLIP模型的跨模态相似性计算来获得监督;2)我们的FineCLIPER采用分层方式,有效地从DFE视频中挖掘有用线索。具体来说,除了直接将视频帧嵌入作为输入(低语义级别)外,我们还提议基于每帧提取面部分割掩码和地标(中级语义级别),并利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来进一步生成跨帧面部变化的详细描述(高级语义级别)。此外,我们还采用参数高效微调(PEFT)技术,使大型预训练模型(例如CLIP)能够高效适应此任务。我们的FineCLIPER在DFEW、FERV39k和MAFW数据集上实现了监督学习和零样本设置下的最佳性能,并且只需要调整很少的参。项目页面:https://haroldchen19.github.io/FineCLIPER-Page/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM 2024
Summary:基于多模态精细粒度CLIP模型的动态面部表情识别新方法FineCLIPER,通过结合跨模态相似性进行标签扩展,并采用层次化方式挖掘DFE视频中的有用线索,实现面部表情识别的优异性能。同时,通过参数高效微调技术适应大型预训练模型,可在监督学习和零样本设置下实现SOTA性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 动态面部表情识别(DFER)对于理解人类行为至关重要。
- 当前方法性能受限,主要由于高质量数据稀缺、面部动态利用不足和表情语义模糊等原因。
- FineCLIPER框架通过结合多模态信息提高DFER性能。
- 采用标签扩展方法,通过计算跨模态相似性进行正面和负面方面的文本描述监督。
- FineCLIPER采用层次化方式挖掘DFE视频中的有用线索,包括直接嵌入视频帧、提取面部分割掩膜和地标,以及利用多模态大型语言模型生成面部变化详细描述。
- 采用参数高效微调(PEFT)技术,使大型预训练模型适应此任务。
- FineCLIPER在DFEW、FERV39k和MAFW数据集上实现监督学习和零样本设置下的SOTA性能。
点此查看论文截图