⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-26 更新
Style Transfer: A Decade Survey
Authors:Tianshan Zhang, Hao Tang
The revolutionary advancement of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) has fundamentally transformed the landscape of visual content creation and artistic expression. While remarkable progress has been made in image generation and style transfer, the underlying mechanisms and aesthetic implications of these technologies remain insufficiently understood. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of AIGC technologies in visual arts, tracing their evolution from early algorithmic frameworks to contemporary deep generative models. We identify three pivotal paradigms: Variational Autoencoders (VAE), Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Diffusion Models, and examine their roles in bridging the gap between human creativity and machine synthesis. To support our analysis, we systematically review over 500 research papers published in the past decade, spanning both foundational developments and state-of-the-art innovations. Furthermore, we propose a multidimensional evaluation framework that incorporates Technical Innovation, Artistic Merit, Visual Quality, Computational Efficiency, and Creative Potential. Our findings reveal both the transformative capacities and current limitations of AIGC systems, emphasizing their profound impact on the future of creative practices. Through this extensive synthesis, we offer a unified perspective on the convergence of artificial intelligence and artistic expression, while outlining key challenges and promising directions for future research in this rapidly evolving field.
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的革命性进步从根本上改变了视觉内容创作和艺术表达领域的格局。虽然图像生成和风格转换取得了显著的进展,但这些技术的基础机制和美学影响尚未得到充分理解。本文对AIGC技术在视觉艺术领域进行了全面综述,追溯了从早期算法框架到当前深度生成模型的演变过程。我们确定了三个关键范式:变分自编码器(VAE)、生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型,并研究了它们在弥合人类创造力和机器合成之间的差距方面的作用。为了支持我们的分析,我们系统地回顾了过去十年发表的500多篇研究论文,这些论文涵盖了基础发展以及最新创新技术。此外,我们提出了一个多维度的评估框架,其中包括技术创新、艺术价值、视觉质量、计算效率和创造潜力。我们的研究结果揭示了AIGC系统的变革能力和当前局限性,强调了其对未来创作实践的深远影响。通过这篇综合评述,我们对人工智能和艺术表达的融合提供了统一的视角,同时概述了未来在这一快速演变领域进行研究的关键挑战和具有前景的研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages
Summary
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的革命性进展从根本上改变了视觉内容创作和艺术表达领域的格局。本文全面概述了AIGC技术在视觉艺术中的应用,从早期算法框架到当前深度生成模型的演变。通过审查500多篇研究论文,本文分析了三种关键范式:变分自编码器(VAE)、生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型,及其在弥合人类创造力和机器合成之间的差距方面的作用。本文还提出了一个多维评估框架,包括技术创新、艺术价值、视觉质量、计算效率和创造潜力,揭示了AIGC系统的变革潜力和当前局限,强调了其对未来创作实践的深远影响。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能生成内容(AIGC)在视觉内容创作和艺术表达上带来了革命性变化。
- 本文全面介绍了AIGC技术在视觉艺术中的应用,从早期算法到现代深度生成模型的演变。
- 分析了三种关键技术范式:变分自编码器(VAE)、生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型。
- 通过审查500多篇研究论文,本文深入研究了这些技术在弥合人类创造力和机器合成之间的差距方面的作用。
- 提出了一个多维评估框架,包括技术创新、艺术价值、视觉质量、计算效率和创造潜力,以全面评估AIGC技术。
- 揭示了AIGC系统的变革潜力和当前局限。
点此查看论文截图


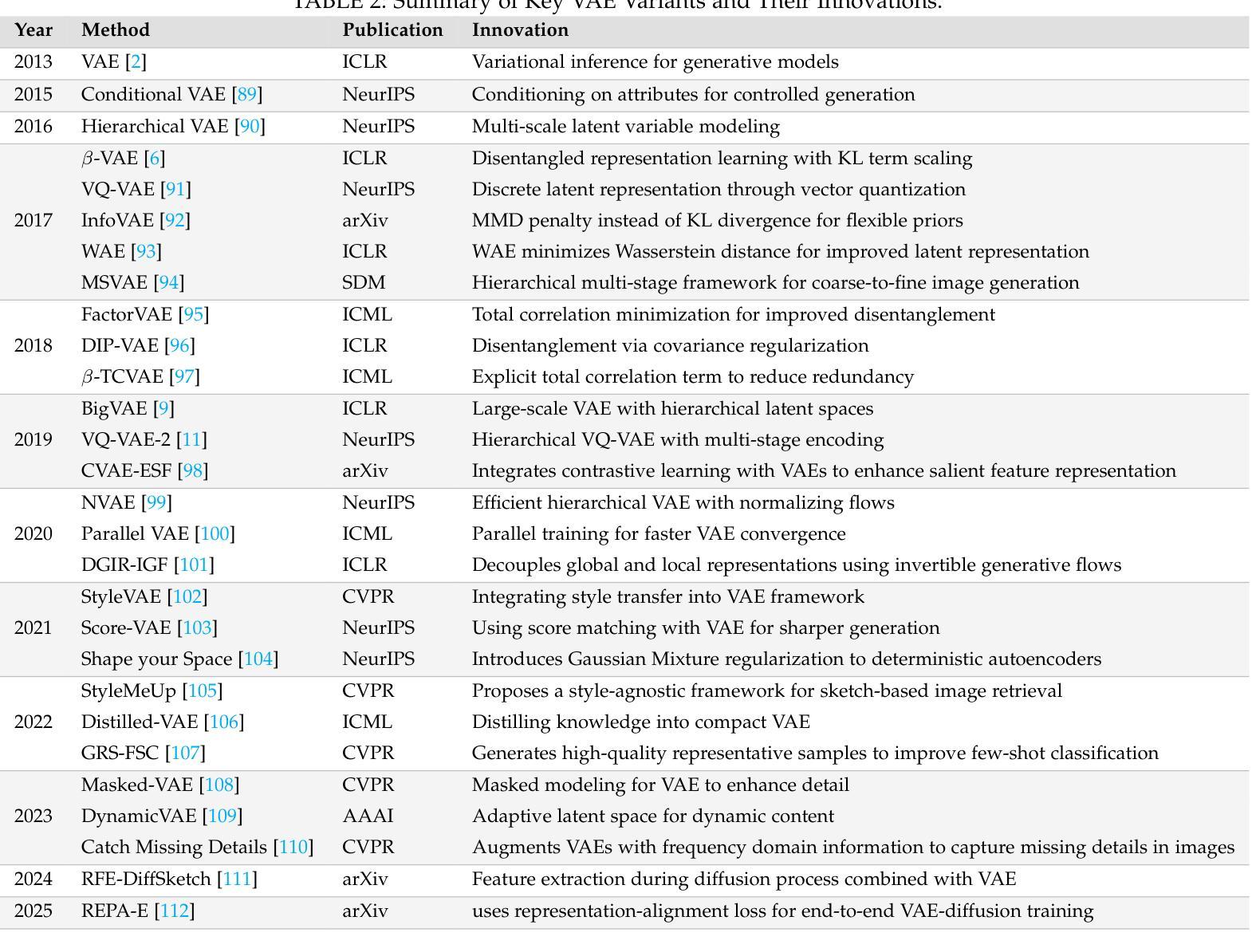
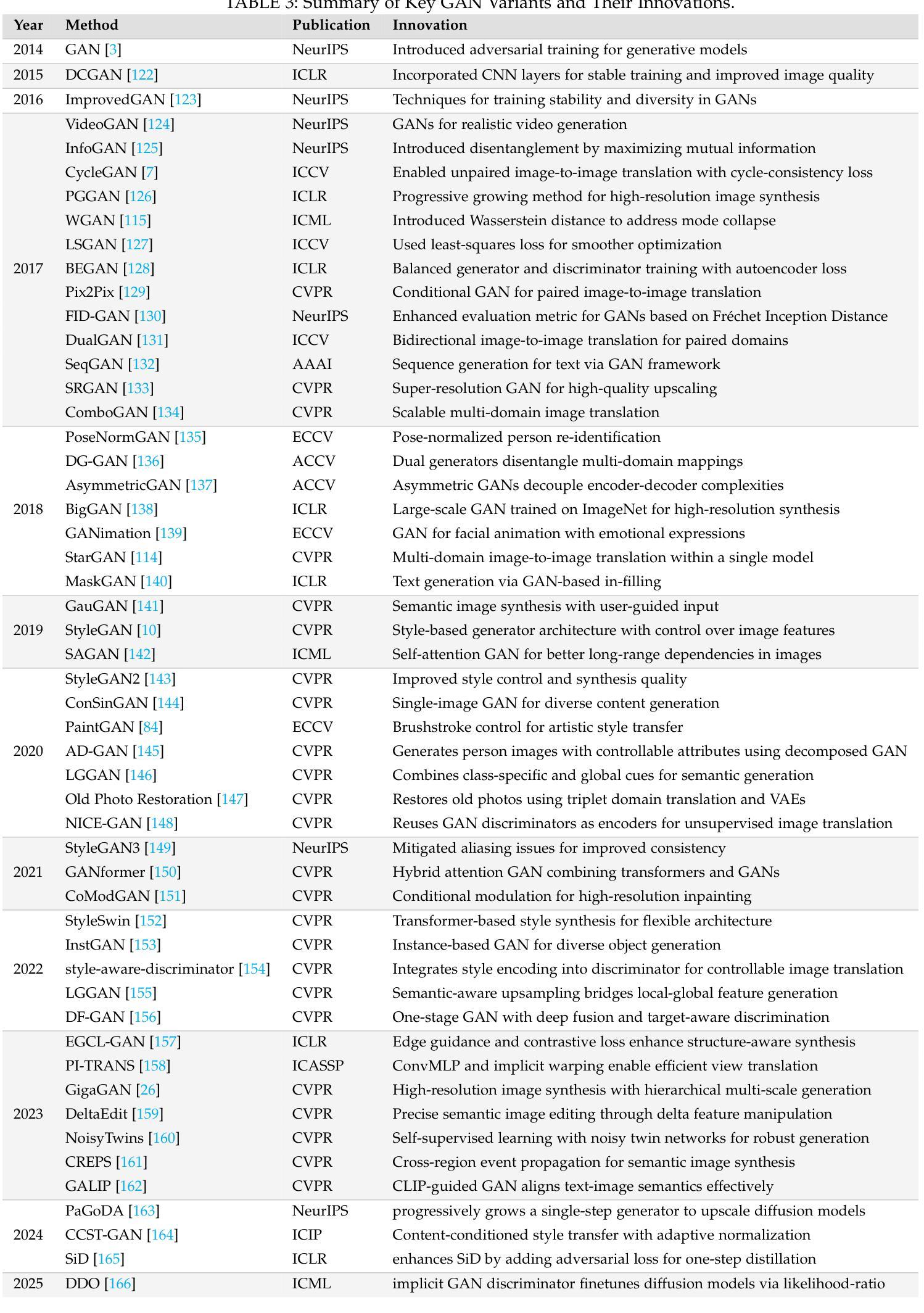
IgCONDA-PET: Weakly-Supervised PET Anomaly Detection using Implicitly-Guided Attention-Conditional Counterfactual Diffusion Modeling – a Multi-Center, Multi-Cancer, and Multi-Tracer Study
Authors:Shadab Ahamed, Arman Rahmim
Minimizing the need for pixel-level annotated data to train PET lesion detection and segmentation networks is highly desired and can be transformative, given time and cost constraints associated with expert annotations. Current unsupervised or weakly-supervised anomaly detection methods rely on autoencoder or generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained only on healthy data. While these approaches reduce annotation dependency, GAN-based methods are notably more challenging to train than non-GAN alternatives (such as autoencoders) due to issues such as the simultaneous optimization of two competing networks, mode collapse, and training instability. In this paper, we present the weakly-supervised $\textbf{I}$mplicitly-$\textbf{g}$uided $\textbf{CO}$u$\textbf{N}$terfactual diffusion model for $\textbf{D}$etecting $\textbf{A}$nomalies in $\textbf{PET}$ images (IgCONDA-PET). The solution is developed and validated using PET scans from six retrospective cohorts consisting of a total of 2652 cases (multi-cancer, multi-tracer) containing both local and public datasets (spanning multiple centers). The training is conditioned on image class labels (healthy vs. unhealthy) via attention modules, and we employ implicit diffusion guidance. We perform counterfactual generation which facilitates “unhealthy-to-healthy” domain translation by generating a synthetic, healthy version of an unhealthy input image, enabling the detection of anomalies through the calculated differences. The performance of our method was compared against several other deep learning based weakly-supervised or unsupervised methods as well as traditional methods like 41% SUV$_\text{max}$ thresholding. We also highlight the importance of incorporating attention modules in our network for the detection of small anomalies. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git.
最小化对像素级标注数据的需求以训练PET病变检测与分割网络是非常理想的,考虑到与专家标注相关的时间和成本约束,这具有变革性。当前的无监督或弱监督异常检测方法依赖于仅对健康数据进行训练的自动编码器或生成对抗网络(GANs)。虽然这些方法减少了标注依赖性,但基于GAN的方法与非GAN替代方案(如自动编码器)相比,训练难度更大,因为存在诸如两个竞争网络的同步优化、模式崩溃和训练不稳定等问题。在本文中,我们提出了用于PET图像检测异常的弱监督隐式引导对比扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)。该解决方案是使用来自六个回顾性队列的PET扫描开发并验证的,其中包括总共2652个病例(多癌种、多追踪器),包含本地和公共数据集(跨多个中心)。训练是通过注意力模块以图像类别标签(健康与非健康)为条件进行的,我们采用了隐式扩散指导。我们执行了反事实生成,通过生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,促进了“不健康到健康”的领域转换,通过计算差异来实现异常检测。我们的方法与其他基于深度学习的弱监督或无监督方法以及传统的如41% SUVmax阈值方法进行了比较。我们还强调了在网络中融入注意力模块检测小异常的重要性。代码公开在:https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 13 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种基于弱监督的隐含引导计数扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET),用于PET图像中的异常检测。该方法利用条件扩散模型进行图像转换,生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,并通过计算差异来检测异常。该模型具有优越的性能,可广泛应用于多种癌症和多追踪器的PET扫描数据。模型代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于弱监督的PET图像异常检测新方法——IgCONDA-PET模型。
- 该模型利用条件扩散模型进行图像转换,实现“不健康到健康”的域翻译。
- 通过生成合成健康图像,计算与健康图像的差异来检测异常。
- 模型在多种癌症和多追踪器的PET扫描数据上进行了开发和验证。
- 相比其他深度学习方法及传统方法,IgCONDA-PET模型表现出优越性能。
- 强调了注意力模块在网络中检测小异常的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

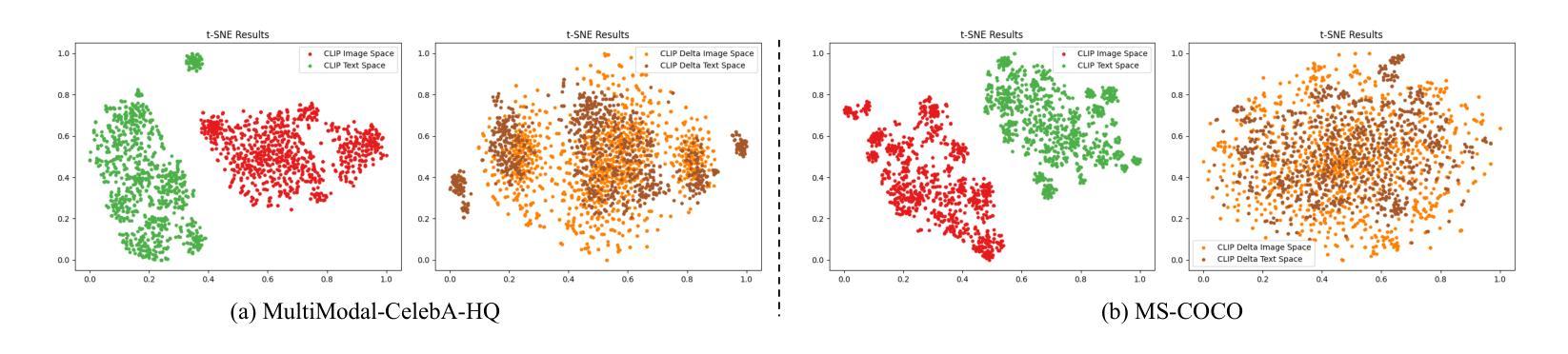
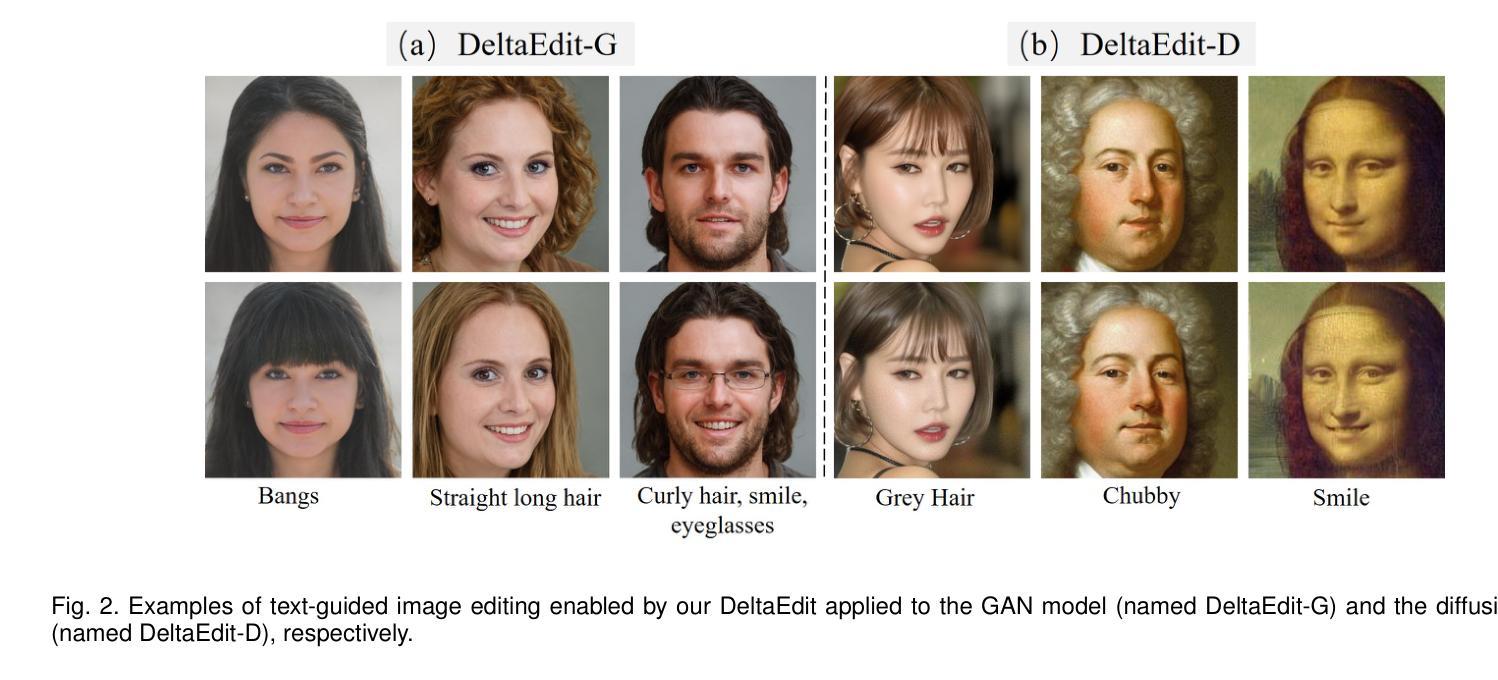
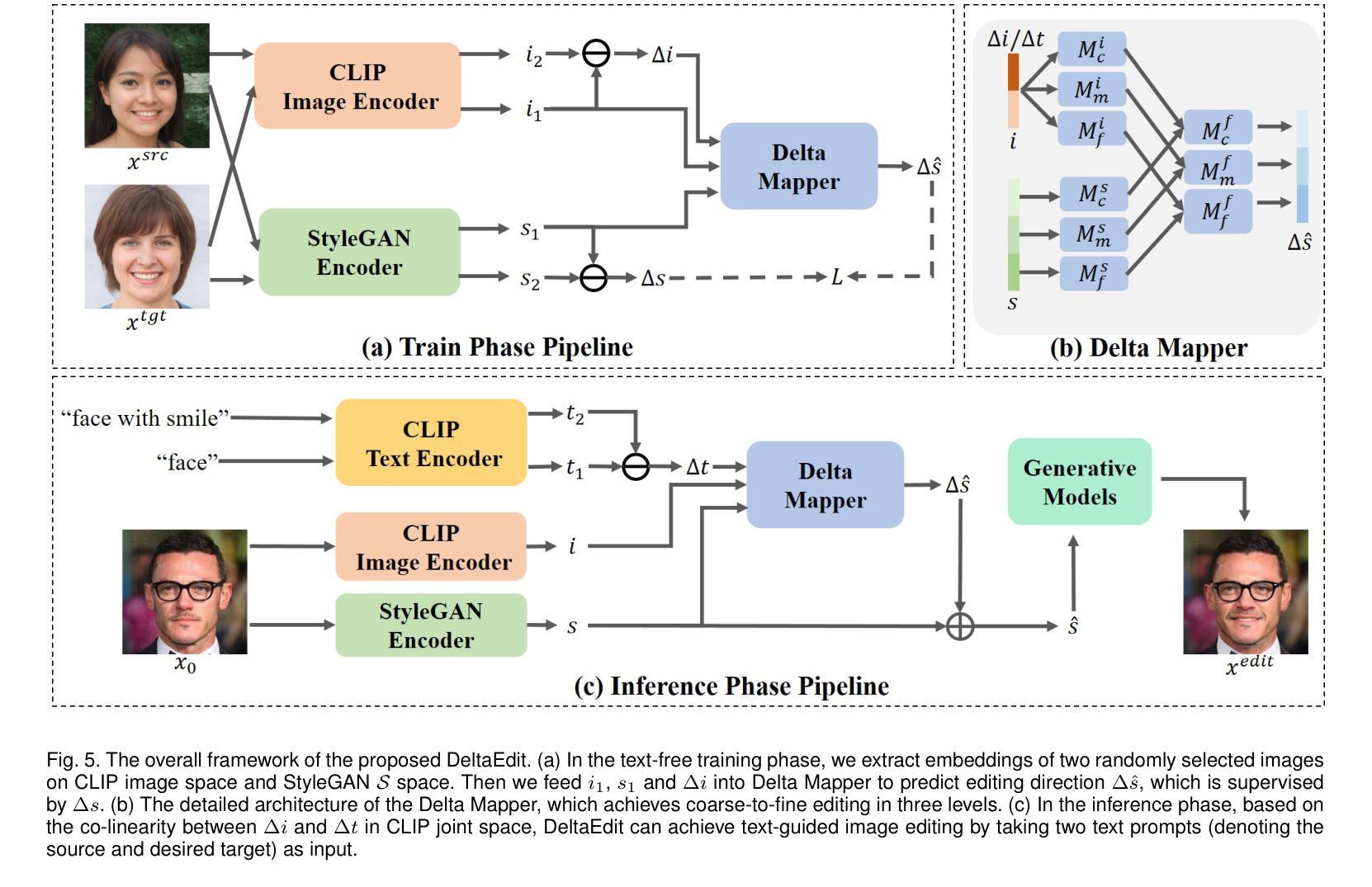
DeltaSpace: A Semantic-aligned Feature Space for Flexible Text-guided Image Editing
Authors:Yueming Lyu, Kang Zhao, Bo Peng, Huafeng Chen, Yue Jiang, Yingya Zhang, Jing Dong, Caifeng Shan
Text-guided image editing faces significant challenges when considering training and inference flexibility. Much literature collects large amounts of annotated image-text pairs to train text-conditioned generative models from scratch, which is expensive and not efficient. After that, some approaches that leverage pre-trained vision-language models have been proposed to avoid data collection, but they are limited by either per text-prompt optimization or inference-time hyper-parameters tuning. To address these issues, we investigate and identify a specific space, referred to as CLIP DeltaSpace, where the CLIP visual feature difference of two images is semantically aligned with the CLIP textual feature difference of their corresponding text descriptions. Based on DeltaSpace, we propose a novel framework called DeltaEdit, which maps the CLIP visual feature differences to the latent space directions of a generative model during the training phase, and predicts the latent space directions from the CLIP textual feature differences during the inference phase. And this design endows DeltaEdit with two advantages: (1) text-free training; (2) generalization to various text prompts for zero-shot inference. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and versatility of DeltaEdit with different generative models, including both the GAN model and the diffusion model, in achieving flexible text-guided image editing. Code is available at https://github.com/Yueming6568/DeltaEdit.
文本引导的图像编辑在考虑训练和推理灵活性时面临重大挑战。许多文献收集了大量的带注释的图像文本对,以从头开始训练文本条件生成模型,这既昂贵又低效。之后,一些利用预训练的语言视觉模型的方法被提出来避免数据收集,但它们受到文本提示优化或推理时间超参数调整的限制。为了解决这些问题,我们研究和确定了特定的空间,称为CLIP DeltaSpace,在该空间中,两个图像的CLIP视觉特征差异与其对应的文本描述的CLIP文本特征差异语义对齐。基于DeltaSpace,我们提出了一种新的框架,称为DeltaEdit。在训练阶段,DeltaEdit将CLIP视觉特征差异映射到生成模型的潜在空间方向,并在推理阶段预测CLIP文本特征差异的潜在空间方向。这种设计赋予了DeltaEdit两个优点:(1)无需文本的训练;(2)对各种文本提示进行零样本推理的泛化能力。大量实验验证了DeltaEdit在不同生成模型(包括GAN模型和扩散模型)中的有效性和通用性,可实现灵活的文本引导图像编辑。代码可在https://github.com/Yueming6568/DeltaEdit找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2303.06285
Summary:针对文本指导的图像编辑面临的挑战,如训练与推理的灵活性问题,本文提出了DeltaEdit框架。该框架利用CLIP视觉特征差异与对应文本描述的CLIP文本特征差异之间的语义对齐,实现文本无关的训练和零样本推理。通过映射CLIP视觉特征差异到生成模型的潜在空间方向,并在训练阶段进行预测,DeltaEdit框架具有文本无关的训练和对各种文本提示的通用性,可在不同生成模型(包括GAN模型和扩散模型)中实现灵活的文本指导图像编辑。
Key Takeaways:
- 文本指导的图像编辑面临训练与推理灵活性的挑战。
- 大量文献采用收集大量标注的图像-文本对来训练文本条件生成模型,但这种方法成本高昂且效率低下。
- 现有方法利用预训练的视觉语言模型避免数据收集,但受限于文本提示优化或推理时超参数调整。
- 本文通过识别CLIP DeltaSpace空间,实现CLIP视觉特征差异与文本特征差异的语义对齐。
- 提出的DeltaEdit框架利用这一空间,在训练阶段将CLIP视觉特征差异映射到生成模型的潜在空间方向。
- DeltaEdit具有文本无关的训练和对各种文本提示的通用性,适用于不同生成模型。
点此查看论文截图