⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-26 更新
General Methods Make Great Domain-specific Foundation Models: A Case-study on Fetal Ultrasound
Authors:Jakob Ambsdorf, Asbjørn Munk, Sebastian Llambias, Anders Nymark Christensen, Kamil Mikolaj, Randall Balestriero, Martin Tolsgaard, Aasa Feragen, Mads Nielsen
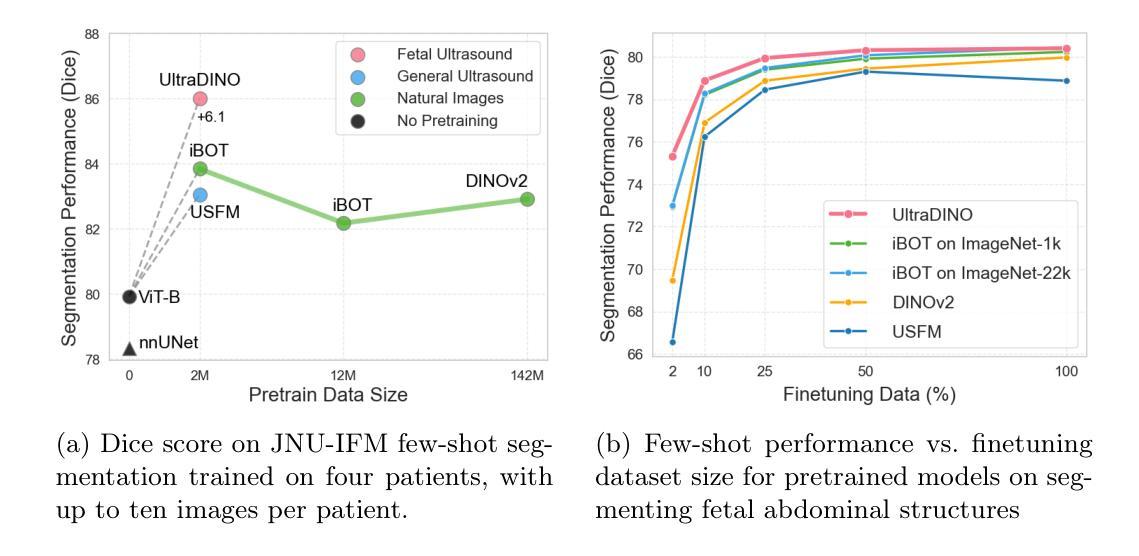
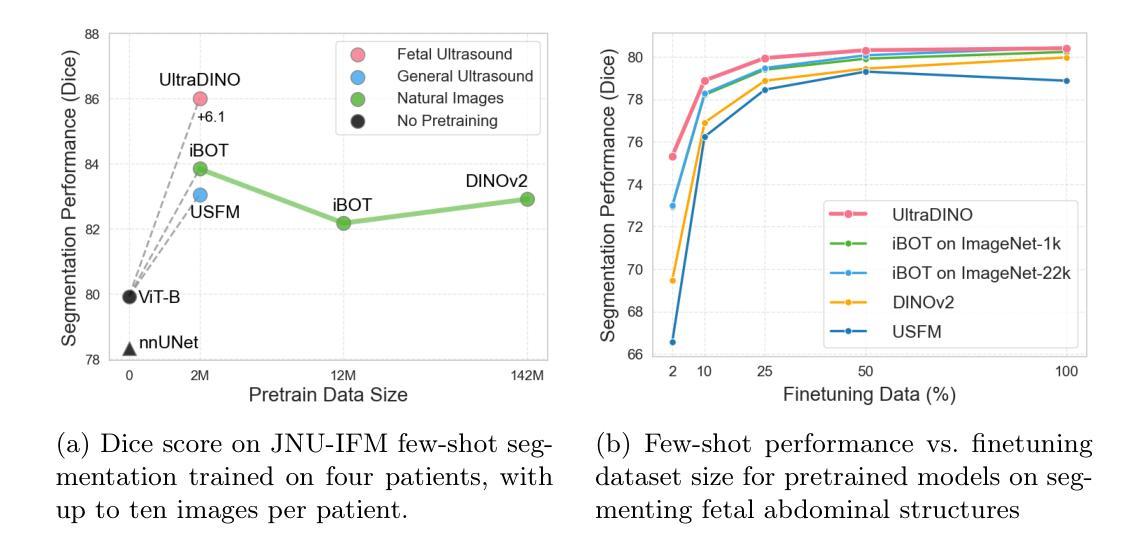
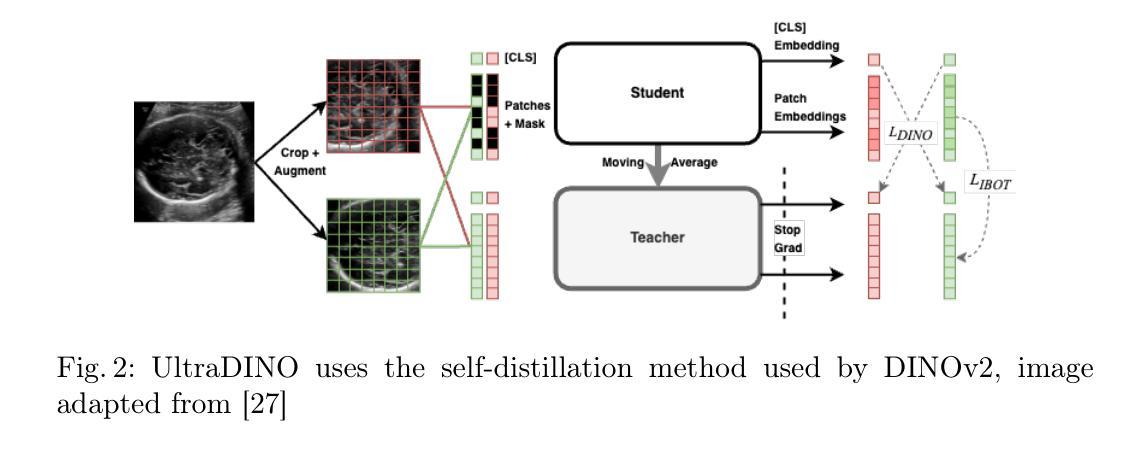
With access to large-scale, unlabeled medical datasets, researchers are confronted with two questions: Should they attempt to pretrain a custom foundation model on this medical data, or use transfer-learning from an existing generalist model? And, if a custom model is pretrained, are novel methods required? In this paper we explore these questions by conducting a case-study, in which we train a foundation model on a large regional fetal ultrasound dataset of 2M images. By selecting the well-established DINOv2 method for pretraining, we achieve state-of-the-art results on three fetal ultrasound datasets, covering data from different countries, classification, segmentation, and few-shot tasks. We compare against a series of models pretrained on natural images, ultrasound images, and supervised baselines. Our results demonstrate two key insights: (i) Pretraining on custom data is worth it, even if smaller models are trained on less data, as scaling in natural image pretraining does not translate to ultrasound performance. (ii) Well-tuned methods from computer vision are making it feasible to train custom foundation models for a given medical domain, requiring no hyperparameter tuning and little methodological adaptation. Given these findings, we argue that a bias towards methodological innovation should be avoided when developing domain specific foundation models under common computational resource constraints.
在获取大规模无标签医疗数据集的情况下,研究人员面临两个问题:他们是否应该尝试在此医疗数据上预训练一个自定义基础模型,或者从现有的通用模型中进行迁移学习?如果预训练了自定义模型,是否需要新颖的方法?在本文中,我们通过进行案例研究来探讨这些问题。我们在一个包含2百万张图像的大规模区域性胎儿超声数据集上训练了一个基础模型。通过选择成熟的DINOv2方法进行预训练,我们在三个胎儿超声数据集上实现了最先进的成果,这些数据集涵盖了不同国家的数据、分类、分割和少量任务。我们将预训练的模型与自然图像、超声图像和监督基准模型的一系列模型进行了比较。我们的结果证明了两个关键观点:(i)即使在较少的数据上训练较小的模型,对自定义数据进行预训练也是值得的,因为自然图像的预训练规模并不能转化为超声性能。(ii)经过良好调整的计算机视觉方法使得为给定医疗领域训练自定义基础模型成为可能,无需进行超参数调整和方法上的轻微适应。根据这些发现,我们认为在开发特定领域的模型时,应在有限的计算资源下避免过于偏向方法创新的基础模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted version of paper accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
大型无标签医学数据集的出现引发了是否需要进行定制化预训练的问题,论文对此进行了深入探讨。通过对包含百万张胎儿超声图像的数据集进行案例研究,使用DINOv2预训练法,论文在多个胎儿超声数据集上取得了突破性成果。对比自然图像预训练模型及监督学习基线模型,论文发现定制化预训练在医学领域表现优越,并证实计算机视觉领域的成熟方法使得训练特定医学领域的定制化基础模型成为可能。因此,在开发特定领域的模型时,应避免过度依赖方法论创新。
Key Takeaways
- 大型无标签医学数据集引发关于是否进行定制化预训练的疑问。
- 通过胎儿超声数据集进行案例研究,使用DINOv2预训练法取得突破性成果。
- 对比多种预训练模型及监督学习基线模型,证实定制化预训练在医学领域的优势。
- 定制化预训练对医学图像的分类、分割和少样本任务有积极影响。
- 预训练在医学数据上的价值得到肯定,即便小规模模型处理少量数据也能取得良好效果。
- 自然图像预训练的规模效应并不适用于超声图像性能的提升。
点此查看论文截图

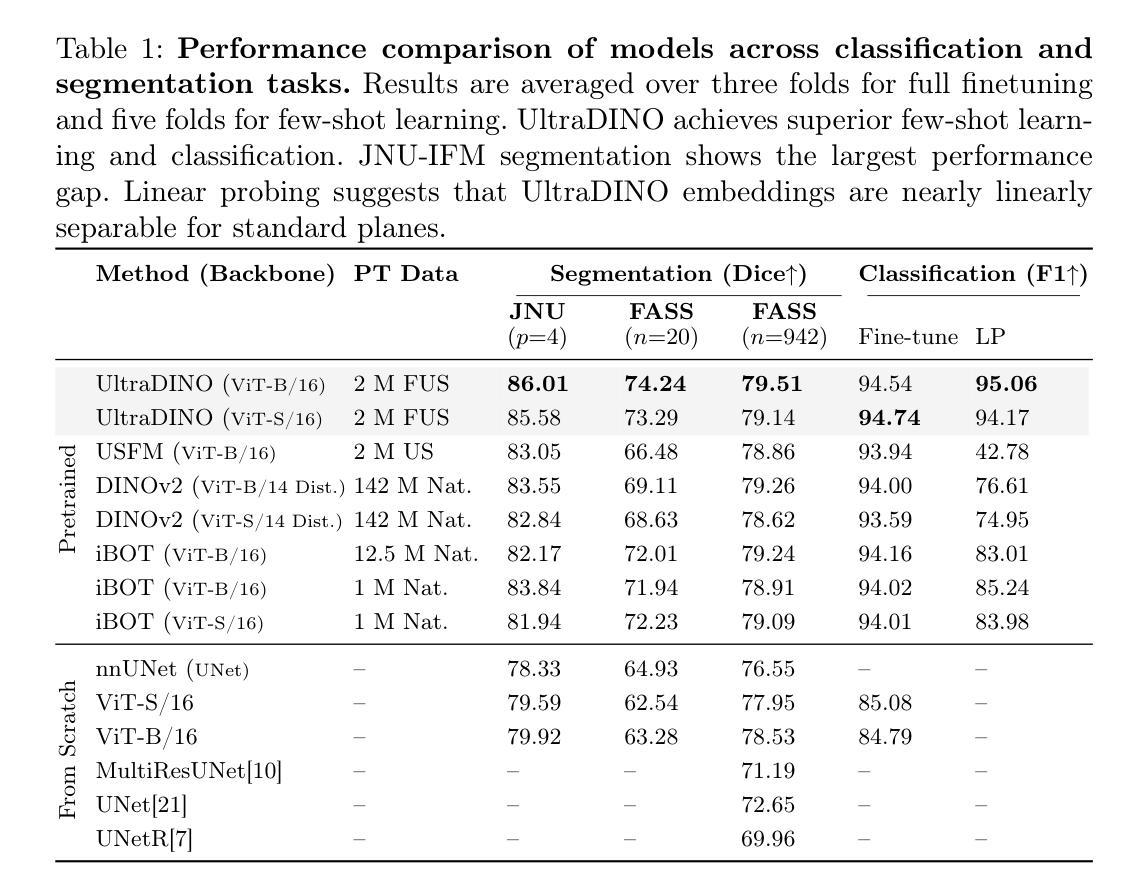
Angio-Diff: Learning a Self-Supervised Adversarial Diffusion Model for Angiographic Geometry Generation
Authors:Zhifeng Wang, Renjiao Yi, Xin Wen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu, Kunlun He
Vascular diseases pose a significant threat to human health, with X-ray angiography established as the gold standard for diagnosis, allowing for detailed observation of blood vessels. However, angiographic X-rays expose personnel and patients to higher radiation levels than non-angiographic X-rays, which are unwanted. Thus, modality translation from non-angiographic to angiographic X-rays is desirable. Data-driven deep approaches are hindered by the lack of paired large-scale X-ray angiography datasets. While making high-quality vascular angiography synthesis crucial, it remains challenging. We find that current medical image synthesis primarily operates at pixel level and struggles to adapt to the complex geometric structure of blood vessels, resulting in unsatisfactory quality of blood vessel image synthesis, such as disconnections or unnatural curvatures. To overcome this issue, we propose a self-supervised method via diffusion models to transform non-angiographic X-rays into angiographic X-rays, mitigating data shortages for data-driven approaches. Our model comprises a diffusion model that learns the distribution of vascular data from diffusion latent, a generator for vessel synthesis, and a mask-based adversarial module. To enhance geometric accuracy, we propose a parametric vascular model to fit the shape and distribution of blood vessels. The proposed method contributes a pipeline and a synthetic dataset for X-ray angiography. We conducted extensive comparative and ablation experiments to evaluate the Angio-Diff. The results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in synthetic angiography image quality and more accurately synthesizes the geometric structure of blood vessels. The code is available at https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff.
血管疾病对人类健康构成重大威胁,X射线血管造影术已确立为诊断的金标准,能够详细观察血管。然而,血管造影X射线使人员和患者暴露在比非血管造影X射线更高的辐射水平下,这是不希望的。因此,从非血管造影X射线转换到血管造影X射线是可取的。数据驱动的深度方法受到配对的大规模X射线血管造影数据集的缺乏的阻碍。尽管合成高质量的血管造影至关重要,但这仍然是一个挑战。我们发现当前的医学图像合成主要操作于像素级别,并难以适应血管的复杂几何结构,导致血管图像合成的质量不佳,例如出现断裂或不规则弯曲。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种通过扩散模型进行非血管造影X射线转换为血管造影X射线的自监督方法,以缓解数据驱动方法的数据短缺问题。我们的模型包括从扩散潜在学习中血管数据分布的扩散模型、用于血管合成的生成器以及基于掩码的对抗模块。为了提高几何精度,我们提出了一种参数化血管模型,以拟合血管的形状和分布。所提出的方法为X射线血管造影提供了一个管道和合成数据集。我们进行了广泛的比较和消融实验来评估Angio-Diff。结果表明,我们的方法在合成血管造影图像质量方面达到了最新性能,并能更准确地合成血管的结构。代码可访问https://github.com/zfw-cv/AngioDiff。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了血管疾病诊断中的X射线血管造影技术存在的问题。由于非血管造影X射线对人体辐射较低,因此转换为血管造影X射线具有重要价值。但由于缺乏大规模的血管造影数据集,数据驱动的深度学习方法面临挑战。本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的自监督方法,将非血管造影X射线转换为血管造影X射线,并利用参数化血管模型提高几何精度。该方法合成高质量血管造影图像并具有领先的性能表现。相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- X射线血管造影是诊断血管疾病的重要技术,但存在辐射风险。
- 非血管造影X射线具有较低的辐射水平,因此转换至血管造影X射线具有重要意义。
- 缺乏大规模的血管造影数据集是数据驱动深度学习方法的难点之一。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的自监督方法,实现了非血管造影X射线到血管造影X射线的转换。
- 利用参数化血管模型提高几何精度,增强图像质量。
- 方法具有良好的性能表现,具备潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

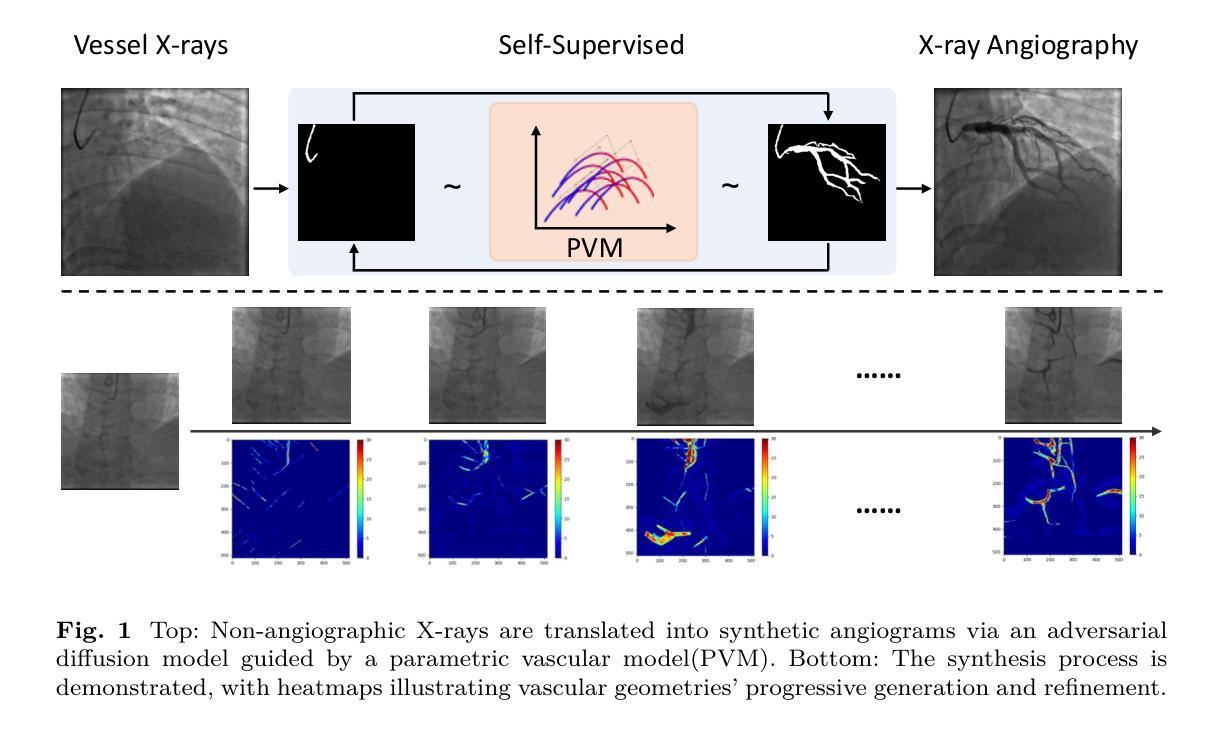
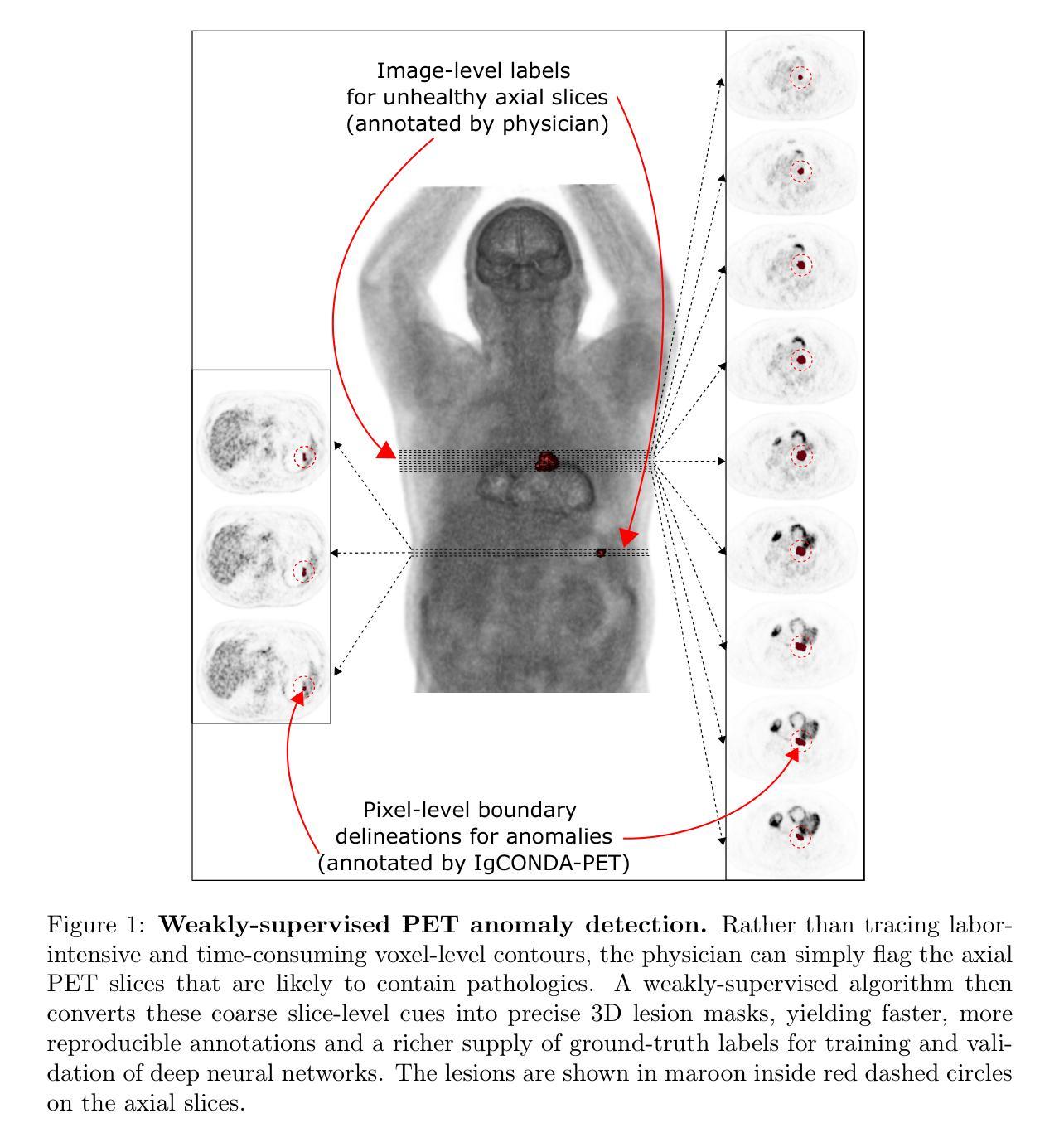
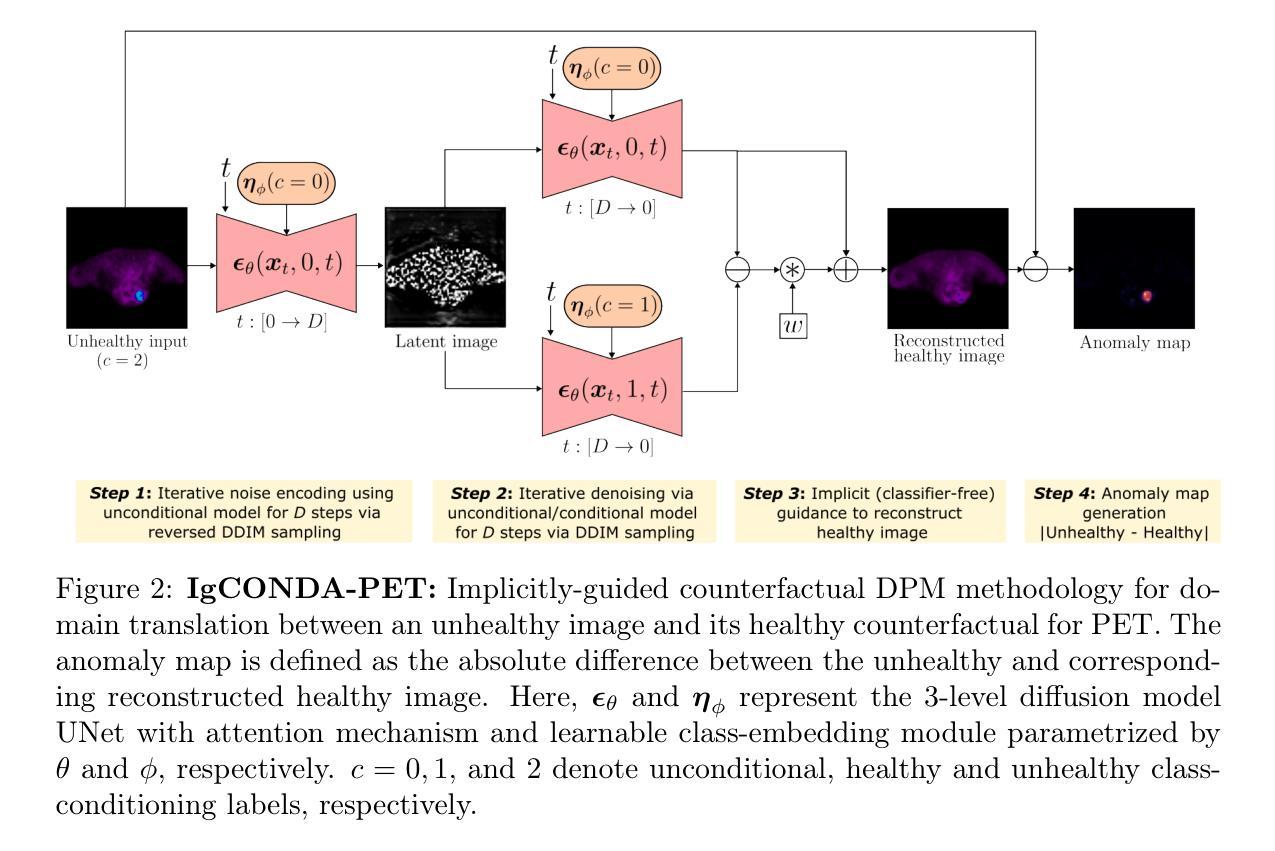
IgCONDA-PET: Weakly-Supervised PET Anomaly Detection using Implicitly-Guided Attention-Conditional Counterfactual Diffusion Modeling – a Multi-Center, Multi-Cancer, and Multi-Tracer Study
Authors:Shadab Ahamed, Arman Rahmim
Minimizing the need for pixel-level annotated data to train PET lesion detection and segmentation networks is highly desired and can be transformative, given time and cost constraints associated with expert annotations. Current unsupervised or weakly-supervised anomaly detection methods rely on autoencoder or generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained only on healthy data. While these approaches reduce annotation dependency, GAN-based methods are notably more challenging to train than non-GAN alternatives (such as autoencoders) due to issues such as the simultaneous optimization of two competing networks, mode collapse, and training instability. In this paper, we present the weakly-supervised $\textbf{I}$mplicitly-$\textbf{g}$uided $\textbf{CO}$u$\textbf{N}$terfactual diffusion model for $\textbf{D}$etecting $\textbf{A}$nomalies in $\textbf{PET}$ images (IgCONDA-PET). The solution is developed and validated using PET scans from six retrospective cohorts consisting of a total of 2652 cases (multi-cancer, multi-tracer) containing both local and public datasets (spanning multiple centers). The training is conditioned on image class labels (healthy vs. unhealthy) via attention modules, and we employ implicit diffusion guidance. We perform counterfactual generation which facilitates “unhealthy-to-healthy” domain translation by generating a synthetic, healthy version of an unhealthy input image, enabling the detection of anomalies through the calculated differences. The performance of our method was compared against several other deep learning based weakly-supervised or unsupervised methods as well as traditional methods like 41% SUV$_\text{max}$ thresholding. We also highlight the importance of incorporating attention modules in our network for the detection of small anomalies. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git.
减少训练PET病变检测与分割网络时对像素级别标注数据的需求是非常理想的选择,考虑到与专家标注相关的时间和成本约束,这可以带来变革。当前的无监督或弱监督异常检测方法依赖于自编码器或生成对抗网络(GANs)进行训练,这些数据仅包含健康数据。虽然这些方法减少了标注的依赖性,但基于GAN的方法相较于非GAN的替代方法(如自编码器)训练起来更具挑战性,这是由于诸如两个竞争网络的同步优化、模式崩溃和训练不稳定等问题。在本文中,我们提出了用于PET图像检测异常的弱监督隐式引导对比扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)。该解决方案是使用来自六个回顾性队列的PET扫描进行开发和验证的,其中包括总共2652例(多癌症、多追踪剂)病例,包含本地和公共数据集(跨多个中心)。训练是通过注意力模块以图像类别标签(健康与否)为条件进行的,我们采用了隐式扩散指导。我们执行了反事实生成,通过生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,促进“不健康到健康”的域转换,并通过计算差异来检测异常。我们的方法与其他的深度学习基于弱监督或无监督的方法以及传统方法(如41% SUVmax阈值法)的性能进行了比较。我们还强调了在网络中融入注意力模块检测小异常的重要性。代码可在https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 13 figures, 4 tables
Summary
在医学图像分析中,针对PET图像的无监督或弱监督异常检测方法受到广泛关注。本文提出了一种基于弱监督的隐式引导对比扩散模型IgCONDA-PET,用于PET图像中的异常检测。该方法通过图像类别标签进行训练,采用隐式扩散引导技术并利用反事实生成来识别异常。其在多种数据集上的表现显著,尤其是对小异常的检测效果良好。模型的代码已公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种名为IgCONDA-PET的弱监督PET图像异常检测模型,通过对比扩散模型实现异常识别。
- 利用图像类别标签(健康与否)进行训练,并利用隐式扩散引导技术辅助识别小异常。
- 采用反事实生成技术,生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,通过计算差异来检测异常。
- 模型在多中心、多种数据集的回顾性研究中得到验证和发展,覆盖多种癌症和追踪剂。
- 与其他深度学习弱监督或无监督方法以及传统方法相比,性能优越。
- 重视在模型中引入注意力模块,提高小异常的检测能力。
点此查看论文截图

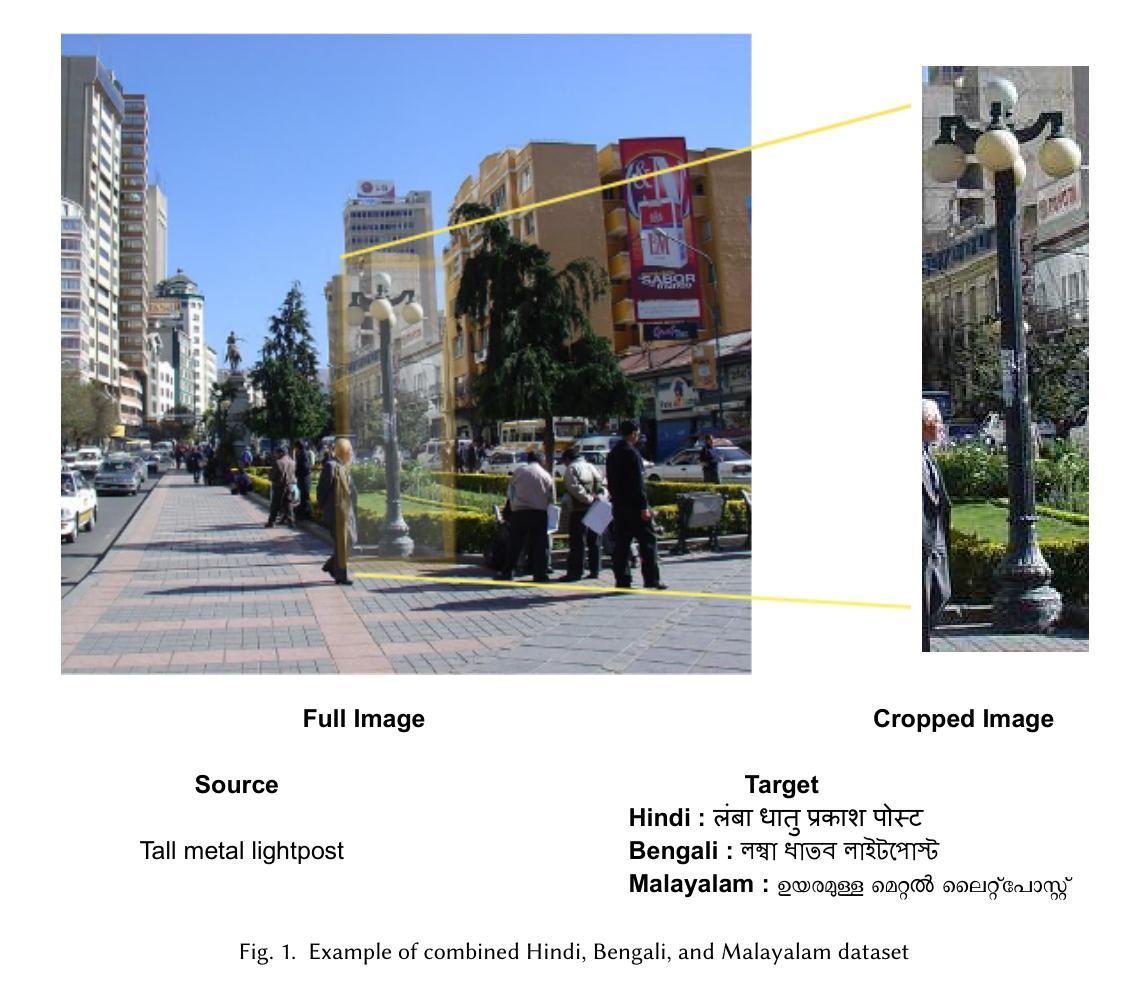
Impact of Visual Context on Noisy Multimodal NMT: An Empirical Study for English to Indian Languages
Authors:Baban Gain, Dibyanayan Bandyopadhyay, Samrat Mukherjee, Chandranath Adak, Asif Ekbal
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) has made remarkable progress using large-scale textual data, but the potential of incorporating multimodal inputs, especially visual information, remains underexplored in high-resource settings. While prior research has focused on using multimodal data in low-resource scenarios, this study examines how image features impact translation when added to a large-scale, pre-trained unimodal NMT system. Surprisingly, the study finds that images might be redundant in this context. Additionally, the research introduces synthetic noise to assess whether images help the model handle textual noise. Multimodal models slightly outperform text-only models in noisy settings, even when random images are used. The study’s experiments translate from English to Hindi, Bengali, and Malayalam, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art benchmarks. Interestingly, the effect of visual context varies with the level of source text noise: no visual context works best for non-noisy translations, cropped image features are optimal for low noise, and full image features perform better in high-noise scenarios. This sheds light on the role of visual context, especially in noisy settings, and opens up a new research direction for Noisy Neural Machine Translation in multimodal setups. The research emphasizes the importance of combining visual and textual information to improve translation across various environments. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/babangain/indicMMT.
神经机器翻译(NMT)在大规模文本数据的应用上取得了显著的进步,但在高资源环境中纳入多模态输入,尤其是视觉信息的潜力,仍然被忽视。虽然之前的研究侧重于在低资源场景中使用多模态数据,但本研究旨在探讨在大型预训练单模态NMT系统中加入图像特征如何影响翻译。令人惊讶的是,该研究认为在这种情况下图像可能是冗余的。此外,该研究引入合成噪声,以评估图像是否有助于模型处理文本噪声。即使在引入随机图像的情况下,多模态模型在噪声环境中也略微优于仅使用文本的模型。该研究的实验涵盖了英语到印地语、孟加拉语和马拉雅拉姆语的翻译,显著优于当前最前沿的基准测试。有趣的是,视觉上下文的影响与源文本噪声水平有关:对于非噪声翻译,没有视觉上下文效果最好,裁剪图像特征适用于低噪声,而完整图像特征在高噪声场景中表现更好。这为理解视觉上下文在噪声环境中的特殊作用提供了新的研究视角,并为多模态设置下的噪声神经机器翻译开启了新的研究方向。该研究强调了结合视觉和文本信息在各种环境中改进翻译的重要性。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/babangain/indicMMT上可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了图像特征对大规模预训练单模态神经机器翻译系统的影响。研究发现,在引入图像特征后,翻译性能有所提升,尤其在处理文本噪声时表现更佳。研究还指出,视觉上下文的作用在不同噪声水平的源文本翻译中有所差异,这为噪声环境下的多模态神经机器翻译研究提供了新的方向。该研究的代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 神经机器翻译在利用大规模文本数据方面取得显著进展,但将多模态输入,特别是视觉信息融入其中的潜力在高资源环境中尚未得到充分探索。
- 图像特征在大型预训练单模态神经机器翻译系统中的加入对翻译性能有积极影响。
- 在处理文本噪声时,多模态模型相较于仅使用文本模型的性能更优,即使使用随机图像也是如此。
- 视觉上下文的作用在源文本噪声水平不同的翻译中有所变化。非噪声翻译中无视觉上下文效果最佳,低噪声情况下裁剪图像特征最优,高噪声场景中完整图像特征表现更好。
- 研究发现在某些情况下,图像可能是冗余的。
- 该研究在英语到印度语(如印地语和马拉雅拉姆语)的翻译上取得了显著超越现有基准测试的成绩。
点此查看论文截图