⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-26 更新
MAM: Modular Multi-Agent Framework for Multi-Modal Medical Diagnosis via Role-Specialized Collaboration
Authors:Yucheng Zhou, Lingran Song, Jianbing Shen
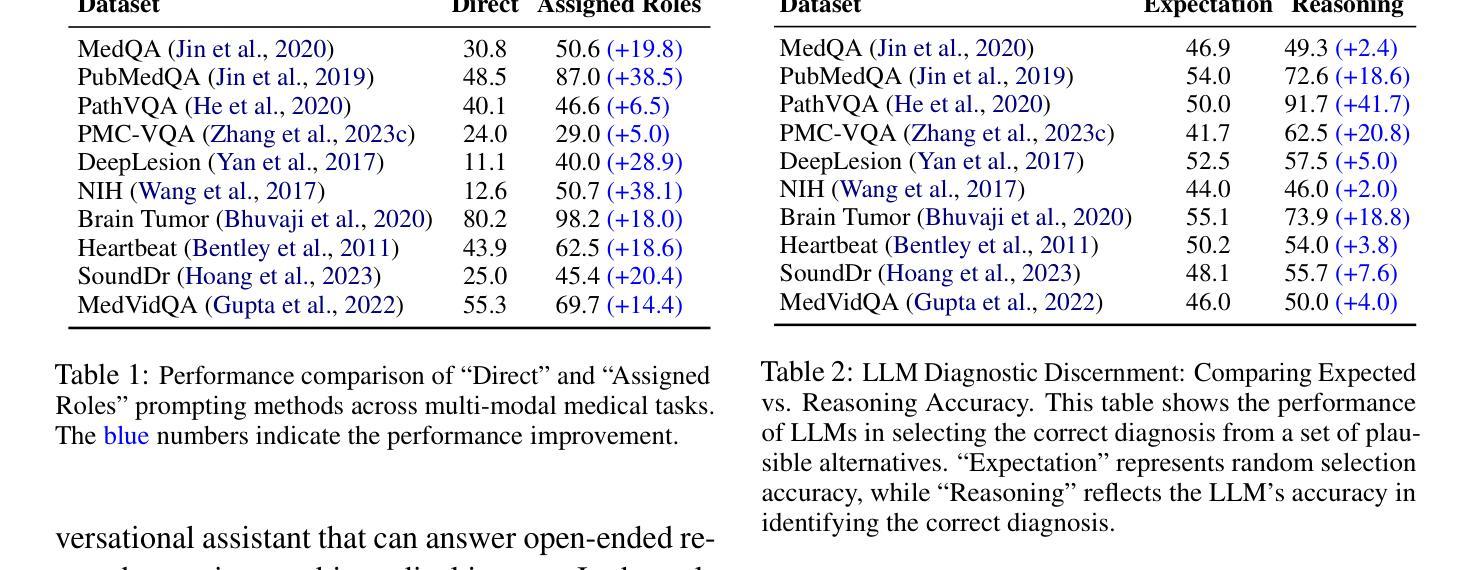
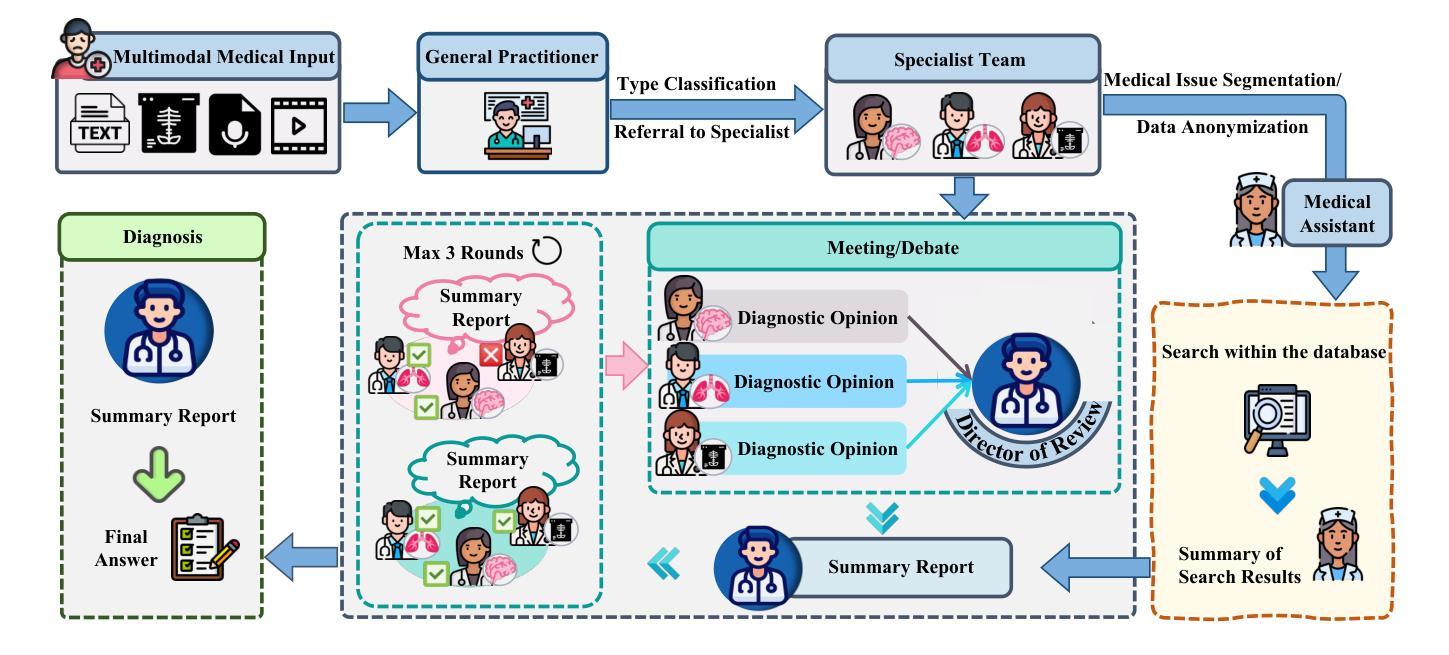
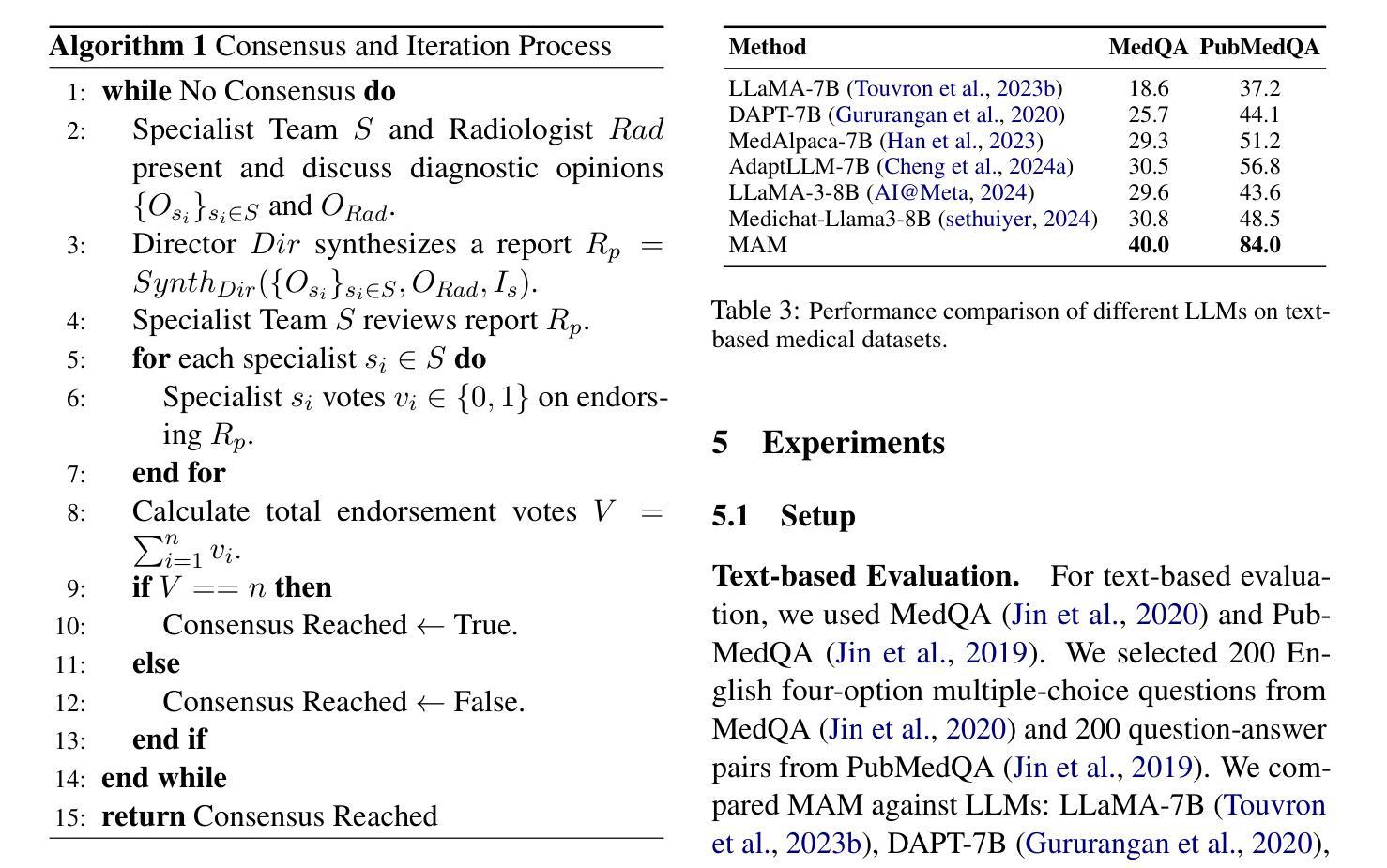
Recent advancements in medical Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased their powerful reasoning and diagnostic capabilities. Despite their success, current unified multimodal medical LLMs face limitations in knowledge update costs, comprehensiveness, and flexibility. To address these challenges, we introduce the Modular Multi-Agent Framework for Multi-Modal Medical Diagnosis (MAM). Inspired by our empirical findings highlighting the benefits of role assignment and diagnostic discernment in LLMs, MAM decomposes the medical diagnostic process into specialized roles: a General Practitioner, Specialist Team, Radiologist, Medical Assistant, and Director, each embodied by an LLM-based agent. This modular and collaborative framework enables efficient knowledge updates and leverages existing medical LLMs and knowledge bases. Extensive experimental evaluations conducted on a wide range of publicly accessible multimodal medical datasets, incorporating text, image, audio, and video modalities, demonstrate that MAM consistently surpasses the performance of modality-specific LLMs. Notably, MAM achieves significant performance improvements ranging from 18% to 365% compared to baseline models. Our code is released at https://github.com/yczhou001/MAM.
医疗领域的大型语言模型(LLM)最近的进展展示出了它们强大的推理和诊断能力。尽管取得了成功,但当前的统一多模式医疗LLM在知识更新成本、全面性和灵活性方面存在局限性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了用于多模式医疗诊断的模块化多智能体框架(MAM)。受我们实证研究的启发,该实证研究突出了角色分配和诊断鉴别在LLM中的优势,MAM将医疗诊断过程分解为专业角色:普通科医生、专家团队、放射科医生、医疗助理和主任,每个角色均由基于LLM的智能体构成。这种模块化和协作的框架能够实现高效的知识更新,并充分利用现有的医疗LLM和知识库。在包含文本、图像、音频和视频模式的公开可访问的多模式医疗数据集上进行的广泛实验评估表明,MAM的性能始终超过了特定模式的LLM。值得注意的是,与基线模型相比,MAM实现了从18%到365%的显著性能提升。我们的代码发布在https://github.com/yczhou001/MAM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Findings
Summary
近期医疗领域的大型语言模型(LLM)展现出强大的推理和诊断能力,但统一的多模态医疗LLM在知识更新成本、全面性和灵活性方面存在局限。为此,我们提出模块化多智能体框架(MAM),将医疗诊断过程分解为不同角色,包括全科医生、专家团队、放射科医生等,每个角色由LLM智能体扮演。该框架可提高知识更新效率并借助现有医疗LLM和知识库。实验证明,MAM在多种公开多模态医疗数据集上的表现优于特定模态的LLM,性能提升幅度从18%至365%。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗LLM展现出强大的推理和诊断能力。
- 统一多模态医疗LLM面临知识更新成本、全面性和灵活性方面的挑战。
- MAM框架通过模块化设计,将医疗诊断过程分解为多个角色,提高知识更新的效率和准确性。
- MAM利用现有医疗LLM和知识库,实现更全面的诊断能力。
- MAM框架在多种公开多模态医疗数据集上表现优异,性能优于特定模态的LLM。
- MAM的性能提升幅度显著,从18%至365%。
点此查看论文截图

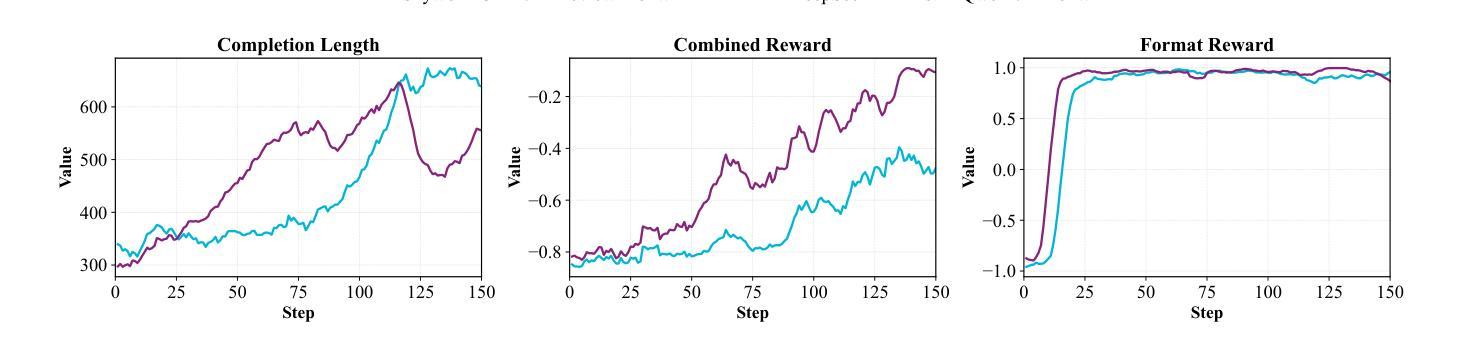
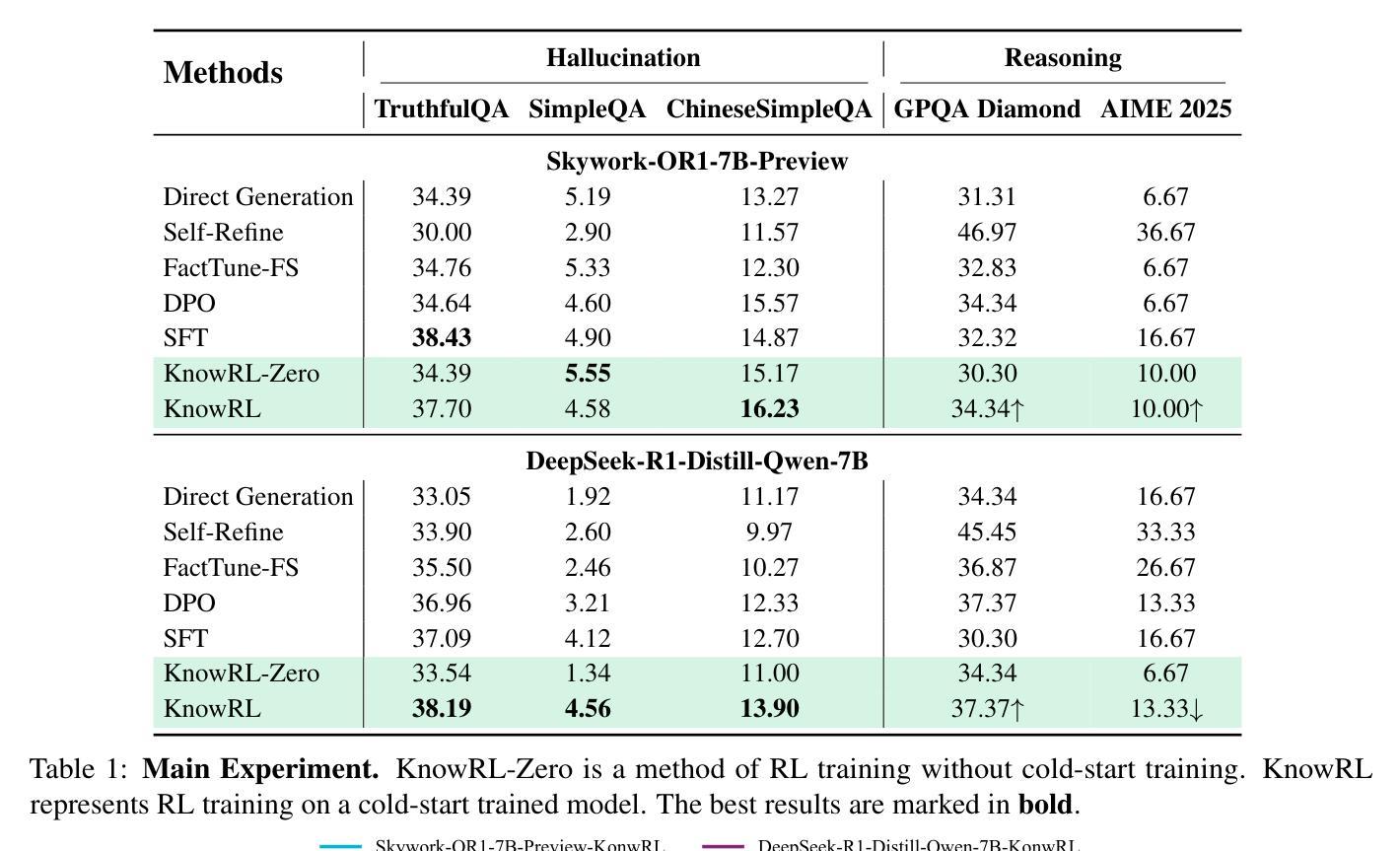
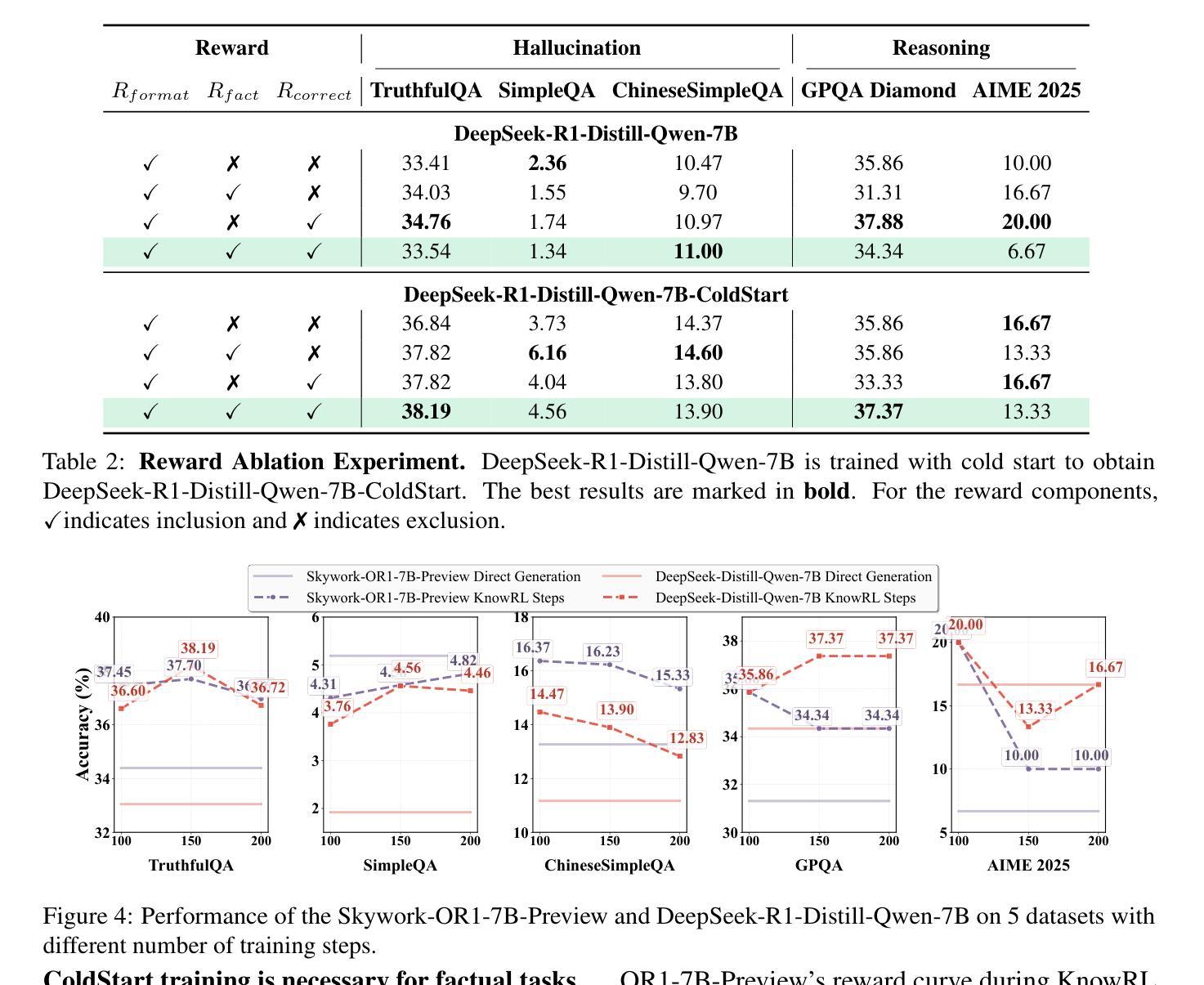
KnowRL: Exploring Knowledgeable Reinforcement Learning for Factuality
Authors:Baochang Ren, Shuofei Qiao, Wenhao Yu, Huajun Chen, Ningyu Zhang
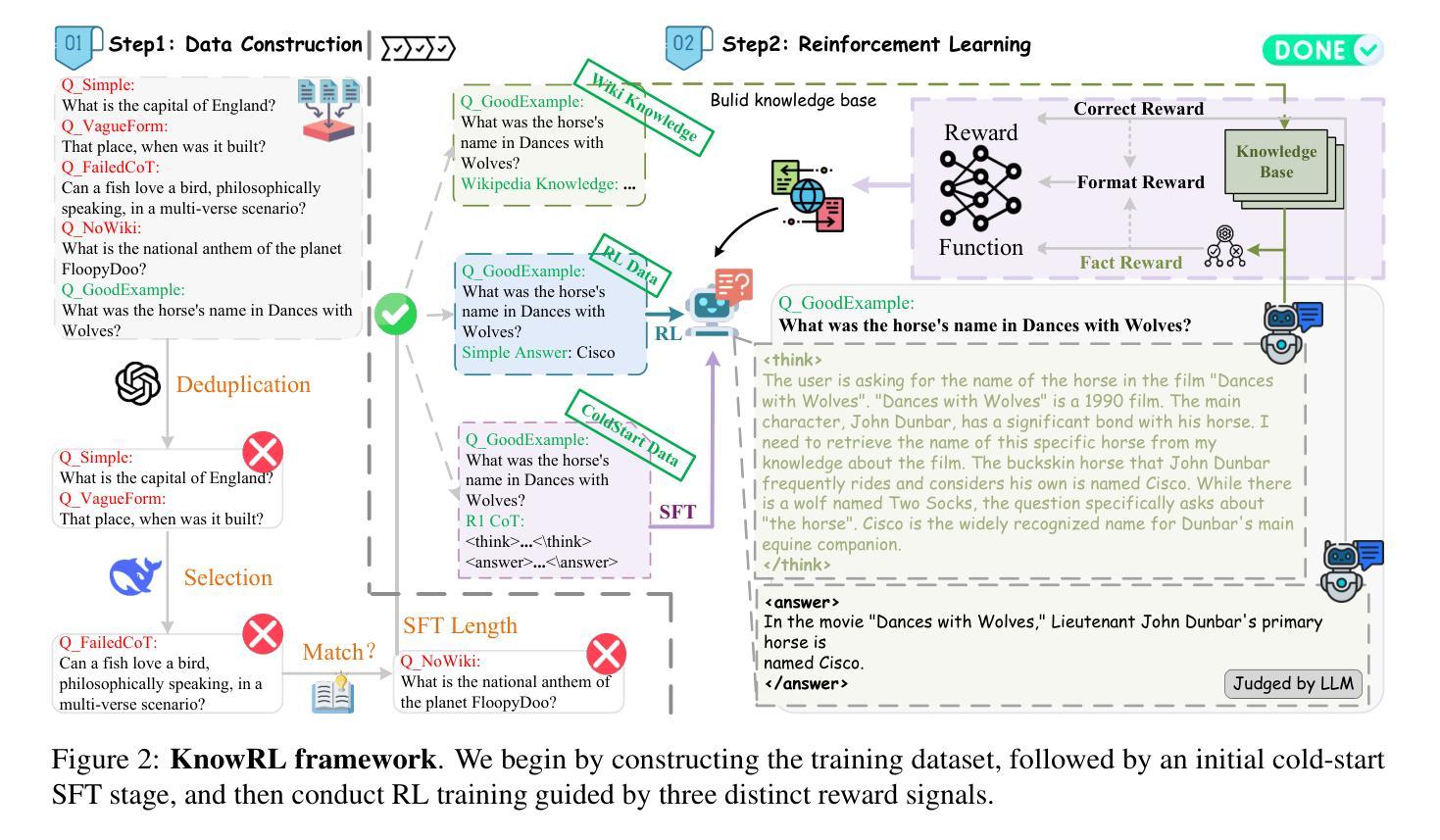
Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly slow-thinking models, often exhibit severe hallucination, outputting incorrect content due to an inability to accurately recognize knowledge boundaries during reasoning. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) can enhance complex reasoning abilities, its outcome-oriented reward mechanism often lacks factual supervision over the thinking process, further exacerbating the hallucination problem. To address the high hallucination in slow-thinking models, we propose Knowledge-enhanced RL, KnowRL. KnowRL guides models to perform fact-based slow thinking by integrating a factuality reward, based on knowledge verification, into the RL training process, helping them recognize their knowledge boundaries. KnowRL guides models to perform fact-based slow thinking by integrating a factuality reward, based on knowledge verification, into the RL training process, helping them recognize their knowledge boundaries. This targeted factual input during RL training enables the model to learn and internalize fact-based reasoning strategies. By directly rewarding adherence to facts within the reasoning steps, KnowRL fosters a more reliable thinking process. Experimental results on three hallucination evaluation datasets and two reasoning evaluation datasets demonstrate that KnowRL effectively mitigates hallucinations in slow-thinking models while maintaining their original strong reasoning capabilities. Our code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/KnowRL.
大型语言模型(LLM),尤其是慢思考模型,常常表现出严重的幻觉,由于推理过程中无法准确识别知识边界,从而输出错误的内容。虽然强化学习(RL)可以提升复杂推理能力,但其以结果为导向的奖励机制往往缺乏对思考过程的真实监督,从而加剧了幻觉问题。为了解决慢思考模型中的高幻觉问题,我们提出了知识增强型RL,即KnowRL。KnowRL通过将基于知识验证的真实性奖励融入RL训练过程,指导模型进行基于事实的慢思考,帮助它们识别自身的知识边界。KnowRL的特色在于,它针对性地在实际推理步骤中奖励对事实的遵循,从而培养模型更可靠的思考过程。在三个幻觉评估数据集和两个推理评估数据集上的实验结果表明,KnowRL有效减轻了慢思考模型中的幻觉问题,同时保持了其原有的强大推理能力。我们的代码可访问https://github.com/zjunlp/KnowRL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
基于知识验证的强化学习训练流程中的事实奖励,帮助大型语言模型进行基于事实的慢速思考,识别知识边界,从而有效缓解慢速思考模型中的严重幻视问题。这一策略的实验结果证明,其在抑制幻视的同时,保持了模型的强推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在推理过程中,由于无法准确识别知识边界,常常出现严重幻视问题。
- 强化学习(RL)虽然能提高复杂推理能力,但其以结果为导向的奖励机制缺乏过程性的事实监督,会加剧幻视问题。
- 针对大型语言模型的幻视问题,提出结合知识验证的事实奖励的强化学习训练方法——KnowRL。
- KnowRL通过将基于知识验证的事实奖励集成到强化学习训练过程中,指导模型进行基于事实的慢速思考,从而帮助模型识别知识边界。
- KnowRL方法通过奖励模型在推理过程中遵循事实的行为,促使模型学习并内化基于事实的推理策略。
- 实验结果表明,KnowRL在抑制幻视的同时,保持了模型的强推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

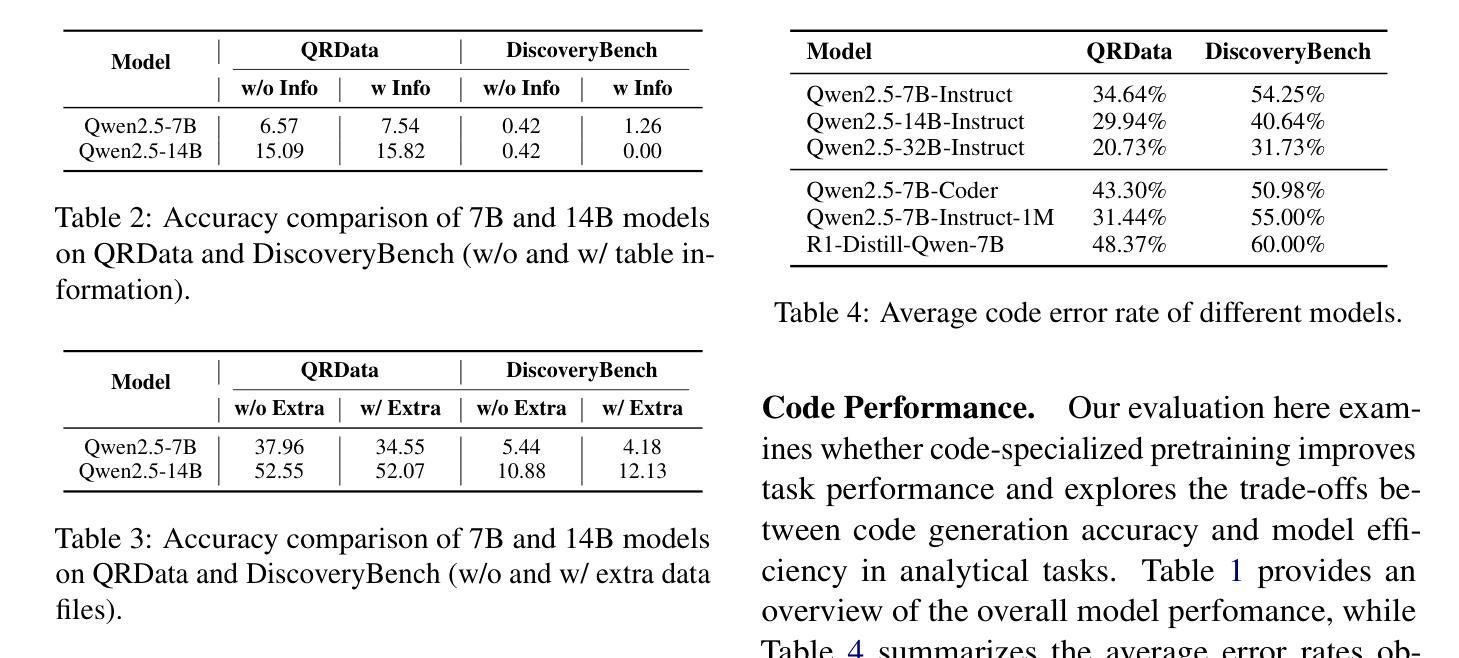
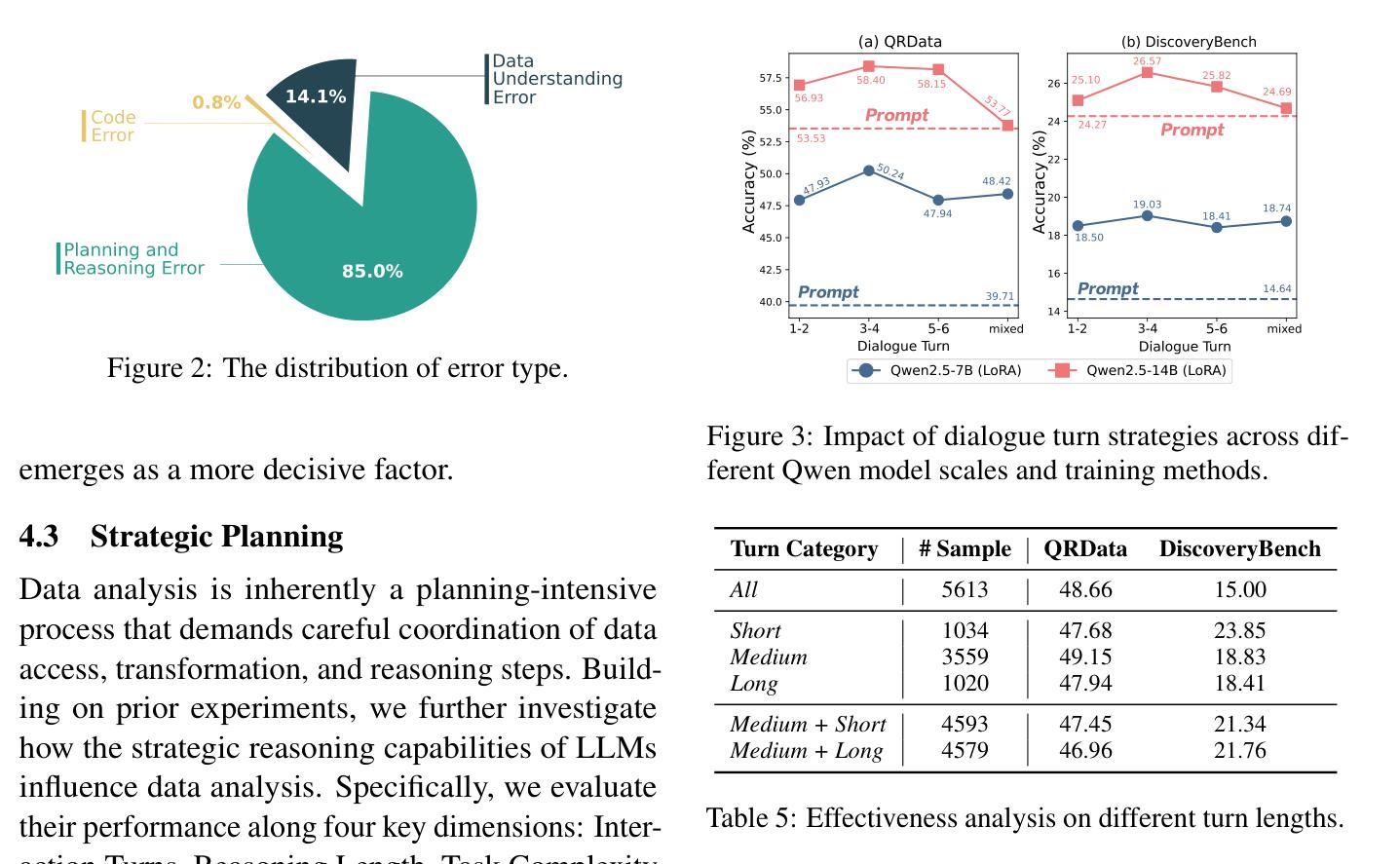
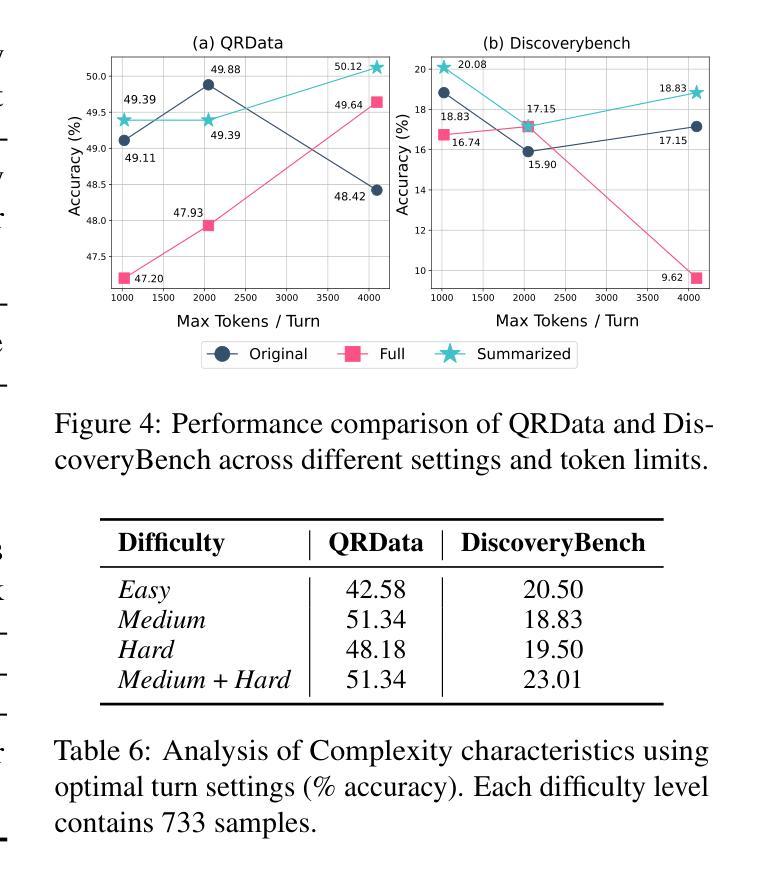
Why Do Open-Source LLMs Struggle with Data Analysis? A Systematic Empirical Study
Authors:Yuqi Zhu, Yi Zhong, Jintian Zhang, Ziheng Zhang, Shuofei Qiao, Yujie Luo, Lun Du, Da Zheng, Huajun Chen, Ningyu Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) hold promise in automating data analysis tasks, yet open-source models face significant limitations in these kinds of reasoning-intensive scenarios. In this work, we investigate strategies to enhance the data analysis capabilities of open-source LLMs. By curating a seed dataset of diverse, realistic scenarios, we evaluate models across three dimensions: data understanding, code generation, and strategic planning. Our analysis reveals three key findings: (1) Strategic planning quality serves as the primary determinant of model performance; (2) Interaction design and task complexity significantly influence reasoning capabilities; (3) Data quality demonstrates a greater impact than diversity in achieving optimal performance. We leverage these insights to develop a data synthesis methodology, demonstrating significant improvements in open-source LLMs’ analytical reasoning capabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化数据分析任务方面显示出巨大的潜力,然而开源模型在面对这些推理密集型的场景时面临着重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们探讨了提高开源LLM数据分析能力的策略。通过筛选多种实际场景的种子数据集,我们从数据理解、代码生成和战略规划三个方面对模型进行了评估。我们的分析揭示了三个关键发现:(1)战略规划质量是模型性能的主要决定因素;(2)交互设计和任务复杂性对推理能力有重大影响;(3)数据质量在实现最佳性能方面的影响大于多样性。我们利用这些见解开发了一种数据合成方法,显著提高了开源LLM的分析推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
在大数据分析中,开源的大型语言模型(LLMs)面临多种能力挑战。本研究通过特定策略来强化LLMs的数据分析性能,采用一个包括多样性和真实场景的种子数据集来评价模型的表现。研究发现了三个关键点:战略规划的质量决定模型性能、交互设计和任务复杂性影响模型的推理能力、数据质量对于达到最佳性能有重要作用。基于此,开发了一种数据合成方法,显著提升了开源LLMs的分析推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 战略规划质量是决定模型性能的主要因素。
- 交互设计和任务复杂性对模型的推理能力有显著影响。
- 数据质量比多样性对实现最佳性能有更重要的作用。
- LLMs在数据合成方法的辅助下,可以提升其分析推理能力。
- 通过特定的种子数据集可以评价模型在数据理解、代码生成和战略规划三个方面的表现。
- 研究中强调真实场景和数据多样性的重要性以提升模型的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

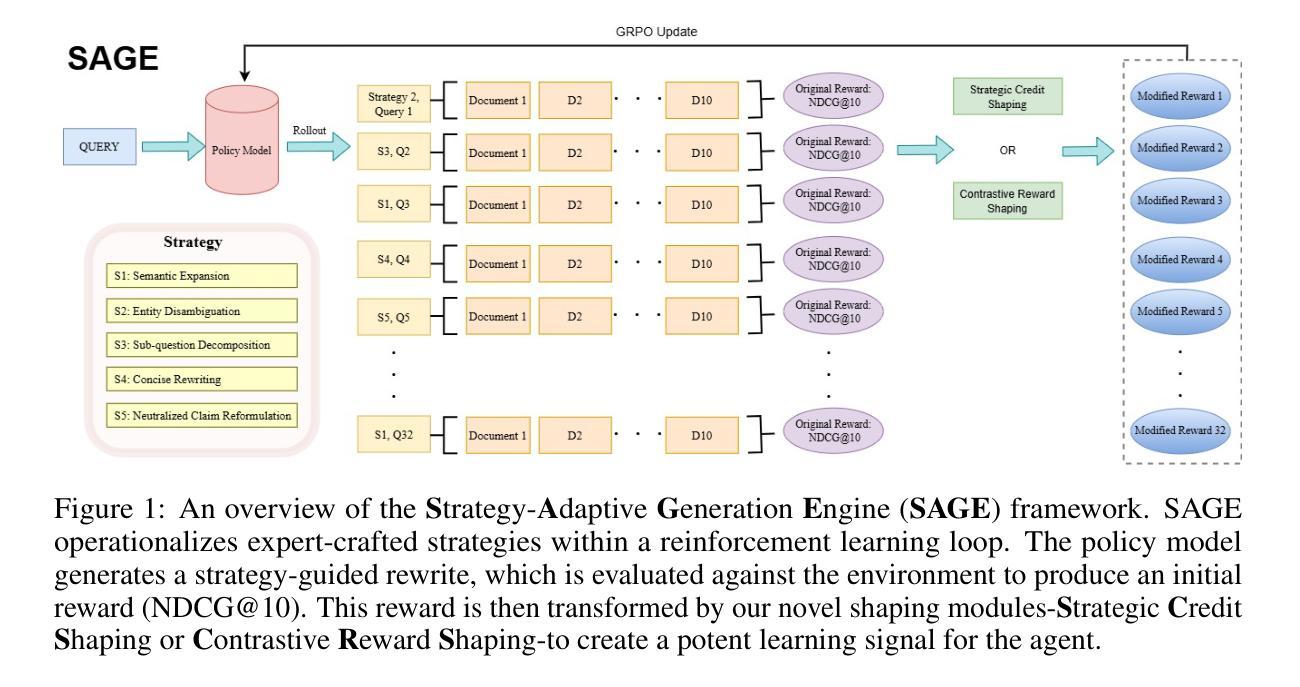
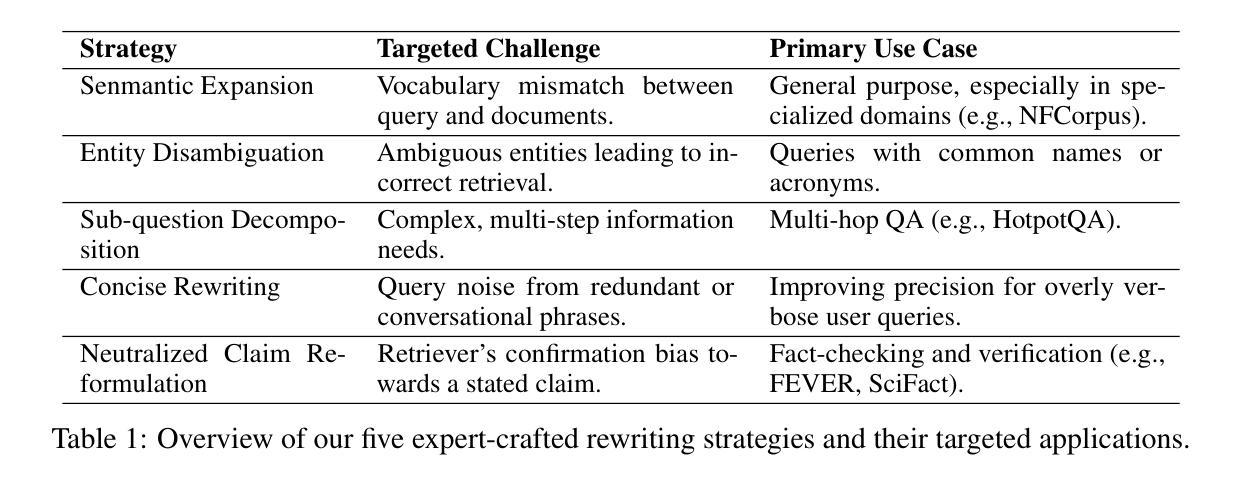
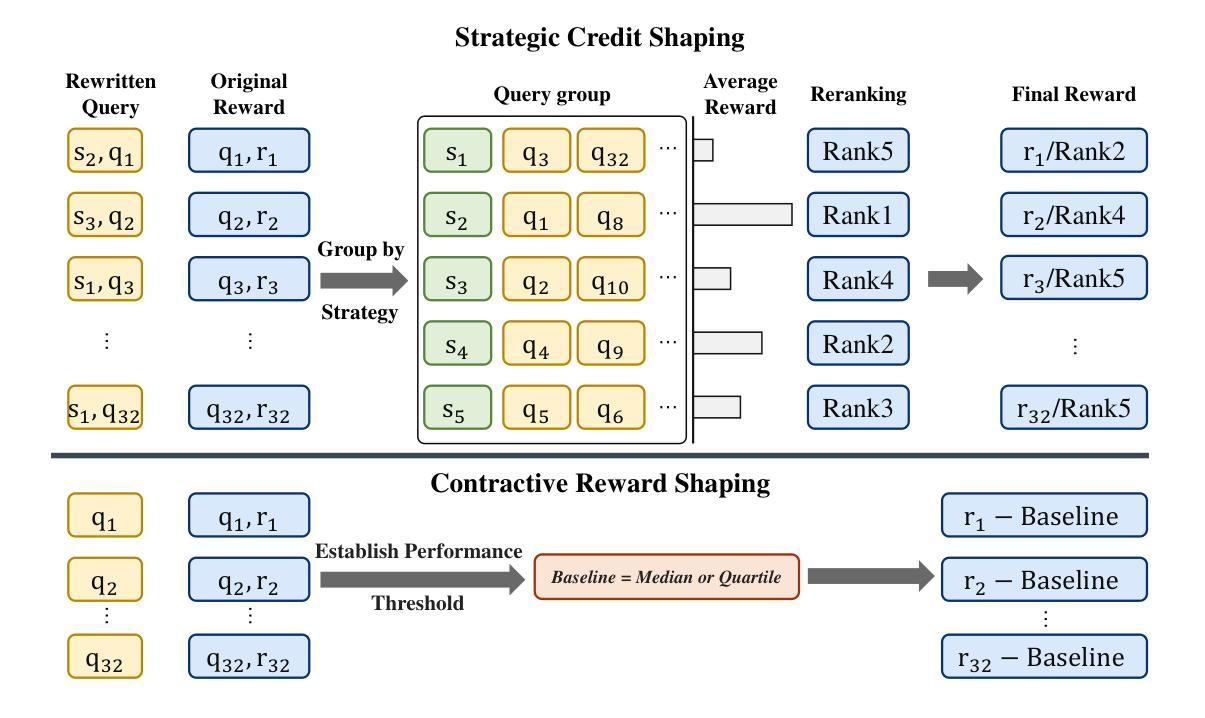
SAGE: Strategy-Adaptive Generation Engine for Query Rewriting
Authors:Teng Wang, Hailei Gong, Changwang Zhang, Jun Wang
Query rewriting is pivotal for enhancing dense retrieval, yet current methods demand large-scale supervised data or suffer from inefficient reinforcement learning (RL) exploration. In this work, we first establish that guiding Large Language Models (LLMs) with a concise set of expert-crafted strategies, such as semantic expansion and entity disambiguation, substantially improves retrieval effectiveness on challenging benchmarks, including HotpotQA, FEVER, NFCorpus, and SciFact. Building on this insight, we introduce the Strategy-Adaptive Generation Engine (SAGE), which operationalizes these strategies in an RL framework. SAGE introduces two novel reward shaping mechanisms-Strategic Credit Shaping (SCS) and Contrastive Reward Shaping (CRS)-to deliver more informative learning signals. This strategy-guided approach not only achieves new state-of-the-art NDCG@10 results, but also uncovers a compelling emergent behavior: the agent learns to select optimal strategies, reduces unnecessary exploration, and generates concise rewrites, lowering inference cost without sacrificing performance. Our findings demonstrate that strategy-guided RL, enhanced with nuanced reward shaping, offers a scalable, efficient, and more interpretable paradigm for developing the next generation of robust information retrieval systems.
查询改写对于提高密集检索至关重要,然而,当前的方法需要大量监督数据,或者面临强化学习(RL)探索效率低下的问题。在这项工作中,我们首先确定,使用一套简洁的专家策略指导大型语言模型(LLM),如语义扩展和实体消歧,可以大大提高在具有挑战性的基准测试集上的检索效果,包括HotpotQA、FEVER、NFCorpus和SciFact。基于这一见解,我们引入了策略自适应生成引擎(SAGE),该引擎在RL框架中实施这些策略。SAGE引入两种新型奖励塑造机制——战略信用塑造(SCS)和对比奖励塑造(CRS),以提供更具信息量的学习信号。这种策略指导的方法不仅实现了新的最先进的NDCG@10结果,还揭示了一个引人注目的新兴行为:代理学会选择最佳策略,减少不必要的探索,并产生简洁的改写,降低推理成本,而不牺牲性能。我们的研究结果表明,以策略为指导的强化学习,通过微妙的奖励塑造增强,为开发下一代稳健的信息检索系统提供了一个可扩展、高效且更具解释性的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了查询重写对于增强密集检索的重要性,并指出当前方法需要大量监督数据或面临强化学习(RL)探索效率低下的问题。研究团队发现,利用简洁的专家策略,如语义扩展和实体消歧,可以显著提高在HotpotQA、FEVER、NFCorpus和SciFact等挑战性基准测试上的检索效果。在此基础上,研究团队提出了策略自适应生成引擎(SAGE),通过强化学习框架实现了这些策略的操作化。SAGE引入两种新型奖励塑造机制——战略信用塑造(SCS)和对比奖励塑造(CRS),以提供更丰富的学习信号。这种策略导向的方法不仅实现了新的NDCG@10结果,还揭示了一个引人注目的新兴行为:代理能够选择最佳策略,减少不必要的探索,并产生简洁的重写,降低了推理成本,不牺牲性能。研究结果表明,策略导向的强化学习结合微妙的奖励塑造为下一代稳健的信息检索系统提供了一个可扩展、高效和更具解释性的范例。
Key Takeaways
- 查询重写对于增强密集检索至关重要。
- 当前查询重写方法存在需要大量监督数据或强化学习探索效率低下的问题。
- 利用专家策略(如语义扩展和实体消歧)可以显著提高检索效果。
- 提出策略自适应生成引擎(SAGE)结合强化学习实现策略操作化。
- SAGE引入战略信用塑造(SCS)和对比奖励塑造(CRS)两种新型奖励塑造机制。
- 策略导向的方法不仅提高了检索效果,还实现了新的NDCG@10结果。
点此查看论文截图

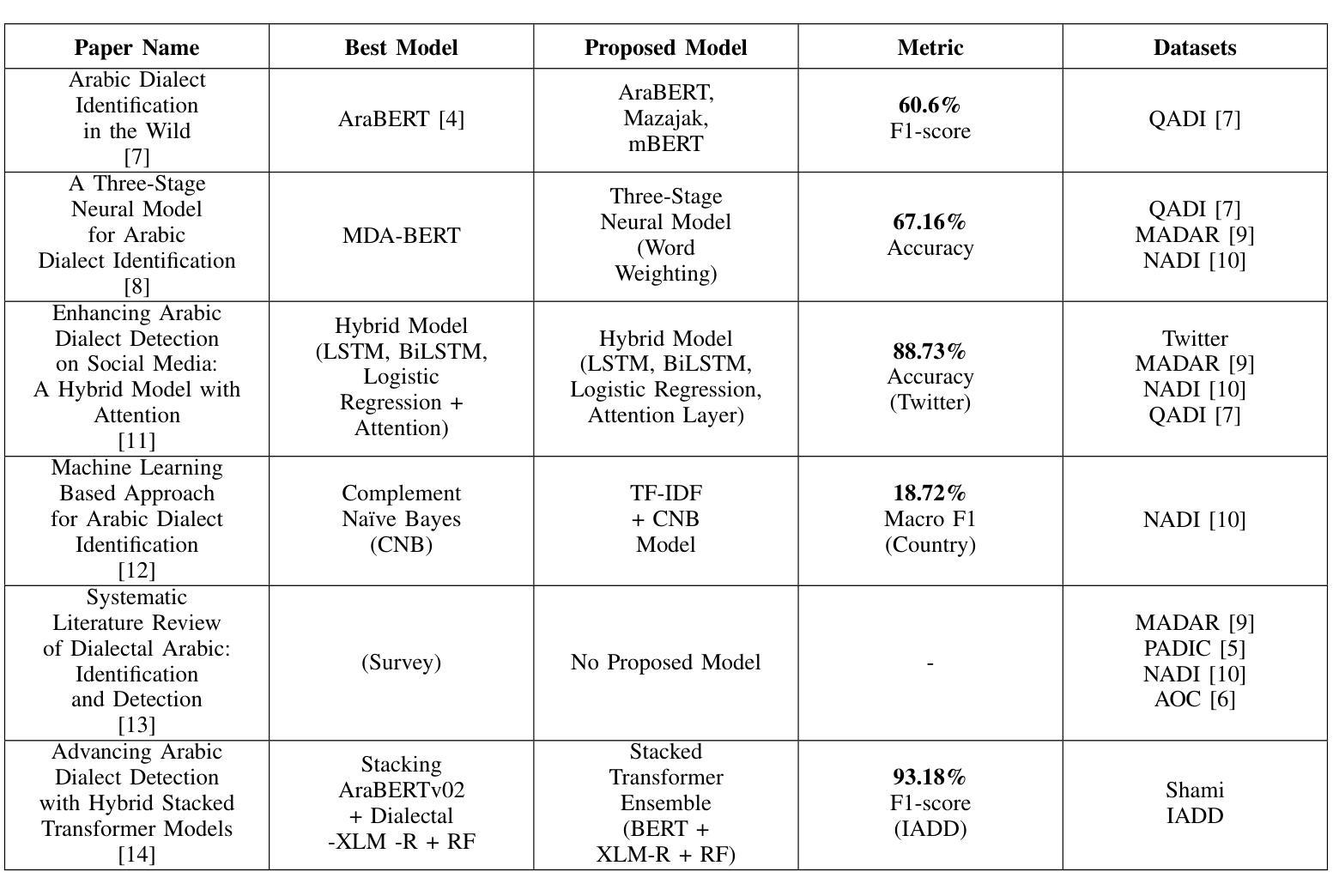
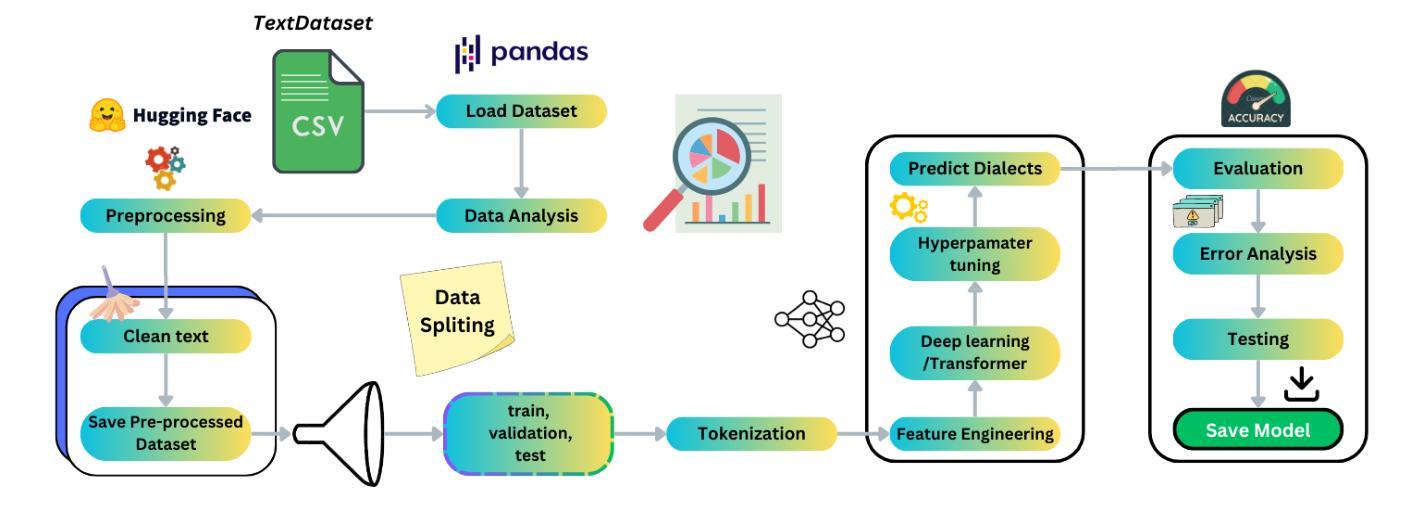
Arabic Dialect Classification using RNNs, Transformers, and Large Language Models: A Comparative Analysis
Authors:Omar A. Essameldin, Ali O. Elbeih, Wael H. Gomaa, Wael F. Elsersy
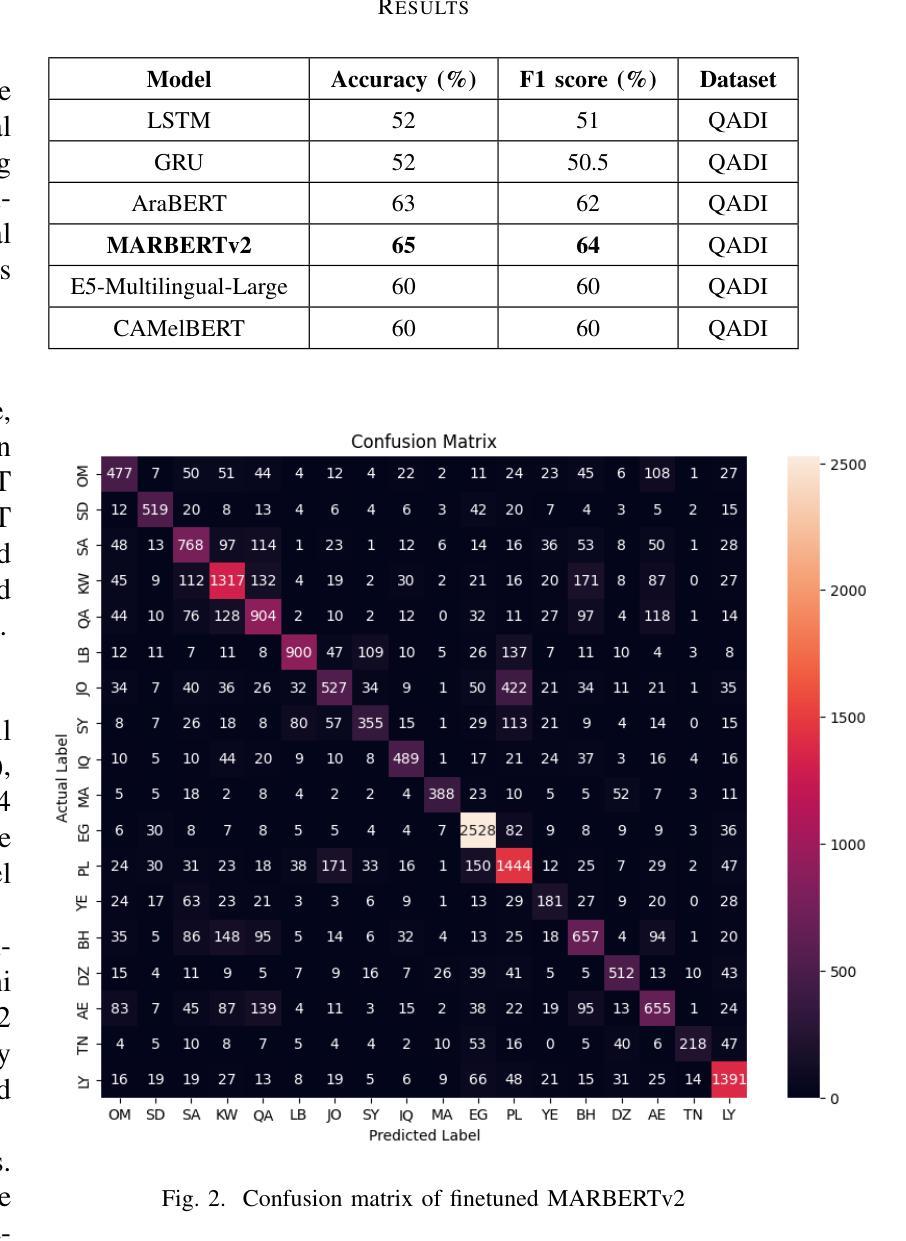
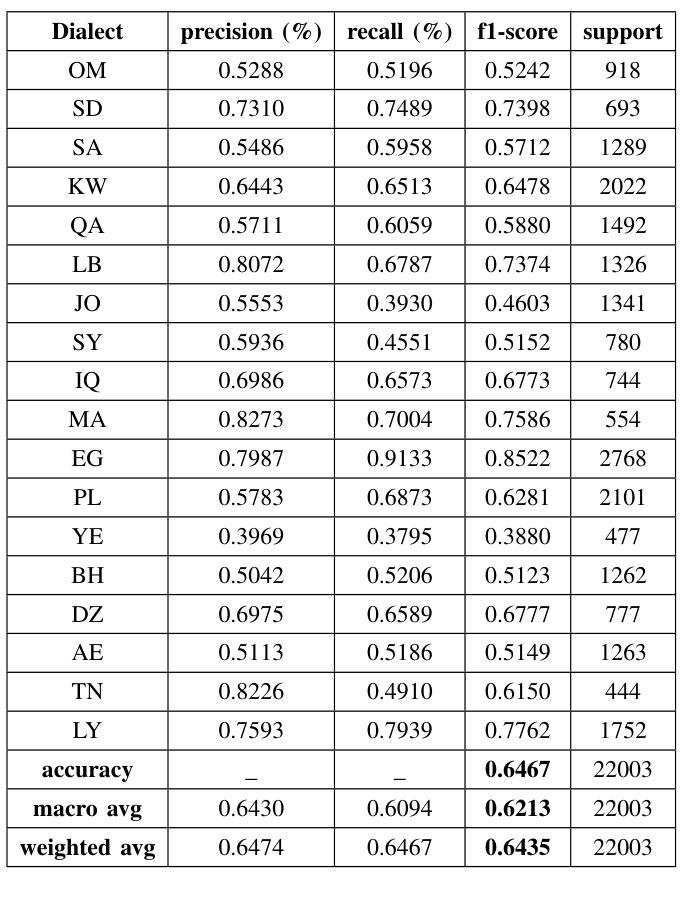
The Arabic language is among the most popular languages in the world with a huge variety of dialects spoken in 22 countries. In this study, we address the problem of classifying 18 Arabic dialects of the QADI dataset of Arabic tweets. RNN models, Transformer models, and large language models (LLMs) via prompt engineering are created and tested. Among these, MARBERTv2 performed best with 65% accuracy and 64% F1-score. Through the use of state-of-the-art preprocessing techniques and the latest NLP models, this paper identifies the most significant linguistic issues in Arabic dialect identification. The results corroborate applications like personalized chatbots that respond in users’ dialects, social media monitoring, and greater accessibility for Arabic communities.
阿拉伯语是世界上使用最广泛的语种之一,在22个国家有众多不同的方言。在这项研究中,我们解决了对阿拉伯推特数据集中的18种阿拉伯语方言进行分类的问题。创建了并测试了RNN模型、Transformer模型以及通过提示工程的大型语言模型(LLM)。其中,MARBERTv2的表现最为出色,准确率为65%,F1分数为64%。通过采用最前沿的预处理技术和最新的自然语言处理模型,本文确定了阿拉伯方言识别中最关键的语言问题。结果证实了个性化聊天机器人响应用户方言、社交媒体监控以及提高阿拉伯社区的访问量等应用的可能性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究关注阿拉伯语的方言分类问题,使用了多种模型包括RNN、Transformer以及大型语言模型(LLM)。通过对QADI数据集阿拉伯推文的实验,发现MARBERTv2模型表现最佳,准确率和F1分数分别为65%和64%。该研究采用先进的预处理技术和最新自然语言处理模型,解决了阿拉伯方言识别中的重大语言问题,并证实了其在个性化聊天机器人、社交媒体监控和增强阿拉伯社区可及性方面的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究针对阿拉伯语的方言分类问题,涵盖了22个国家的多种方言。
- 研究中使用了RNN、Transformer以及大型语言模型(LLM)等模型进行试验。
- MARBERTv2模型在实验中表现最佳,准确率和F1分数分别为65%和64%。
- 先进的预处理技术和最新自然语言处理模型被用于解决阿拉伯方言识别中的语言问题。
- 研究结果证实了模型在个性化聊天机器人、社交媒体监控等应用中的潜力。
- 该研究增强了阿拉伯社区的可及性。
点此查看论文截图
LLM-Driven Medical Document Analysis: Enhancing Trustworthy Pathology and Differential Diagnosis
Authors:Lei Kang, Xuanshuo Fu, Oriol Ramos Terrades, Javier Vazquez-Corral, Ernest Valveny, Dimosthenis Karatzas
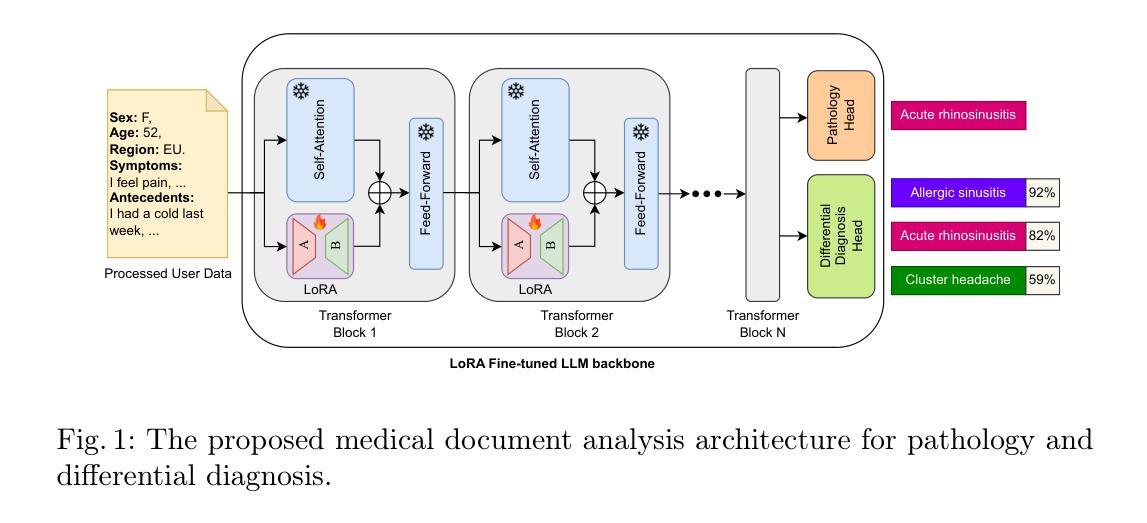
Medical document analysis plays a crucial role in extracting essential clinical insights from unstructured healthcare records, supporting critical tasks such as differential diagnosis. Determining the most probable condition among overlapping symptoms requires precise evaluation and deep medical expertise. While recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced performance in medical document analysis, privacy concerns related to sensitive patient data limit the use of online LLMs services in clinical settings. To address these challenges, we propose a trustworthy medical document analysis platform that fine-tunes a LLaMA-v3 using low-rank adaptation, specifically optimized for differential diagnosis tasks. Our approach utilizes DDXPlus, the largest benchmark dataset for differential diagnosis, and demonstrates superior performance in pathology prediction and variable-length differential diagnosis compared to existing methods. The developed web-based platform allows users to submit their own unstructured medical documents and receive accurate, explainable diagnostic results. By incorporating advanced explainability techniques, the system ensures transparent and reliable predictions, fostering user trust and confidence. Extensive evaluations confirm that the proposed method surpasses current state-of-the-art models in predictive accuracy while offering practical utility in clinical settings. This work addresses the urgent need for reliable, explainable, and privacy-preserving artificial intelligence solutions, representing a significant advancement in intelligent medical document analysis for real-world healthcare applications. The code can be found at \href{https://github.com/leitro/Differential-Diagnosis-LoRA}{https://github.com/leitro/Differential-Diagnosis-LoRA}.
医疗文档分析在从非结构化医疗记录中提取关键临床洞察力方面发挥着至关重要的作用,支持如鉴别诊断等关键任务。在具有重叠症状的情况下确定最可能的疾病需要精确评估和深厚的医学专业知识。虽然最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展已经显著提高了医疗文档分析的性能,但关于敏感患者数据的隐私担忧限制了在线LLM服务在临床环境中的使用。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种可靠的医疗文档分析平台,该平台使用低秩适应技术对LLaMA-v3进行微调,并针对鉴别诊断任务进行了专门优化。我们的方法利用DXPlus数据集(用于鉴别诊断的最大基准数据集),在病理预测和可变长度鉴别诊断方面展示了优于现有方法性能。开发的基于web的平台允许用户提交他们自己的非结构化医疗记录,并获得准确、可解释的诊断结果。通过采用先进的可解释性技术,该系统确保了透明和可靠的预测,增强了用户的信任度。广泛评估证实,所提出的方法在预测精度上超越了当前最先进模型,同时在临床环境中具有实用价值。这项工作满足了人们对可靠、可解释和保护隐私的人工智能解决方案的迫切需求,代表了智能医疗文档分析在真实世界医疗应用中的重大进展。代码可在https://github.com/leitro/Differential-Diagnosis-LoRA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICDAR 2025
Summary:医疗文档分析在提取关键临床信息以支持疾病鉴别诊断等任务中扮演重要角色。本研究提出一种可靠的医疗文档分析平台,采用LLaMA-v3模型进行微调,并利用低秩适应技术进行优化,专门用于鉴别诊断任务。平台使用DDXPlus数据集,展示出色的病理预测和可变长度鉴别诊断性能。此外,平台提供透明的预测结果解释以增强用户信任。此研究解决了临床环境中对可靠、可解释且保护隐私的人工智能解决方案的迫切需求,为医疗文档的智能分析带来了显著进展。
Key Takeaways:
- 医疗文档分析对提取临床洞察至关重要,支持如鉴别诊断等关键任务。
- 提出的医疗文档分析平台基于LLaMA-v3模型,并采用低秩适应技术优化。
- 平台使用DDXPlus数据集,在病理预测和可变长度鉴别诊断方面表现出色。
- 平台提供透明的预测结果解释以增强用户信任和信心。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法在预测准确性方面更胜一筹,并在临床环境中具有实用性。
- 此研究解决了对可靠、可解释且保护隐私的AI解决方案的迫切需求。
- 平台代码可访问[https://github.com/leitro/Differential-Diagnosis-LoRA]。
点此查看论文截图

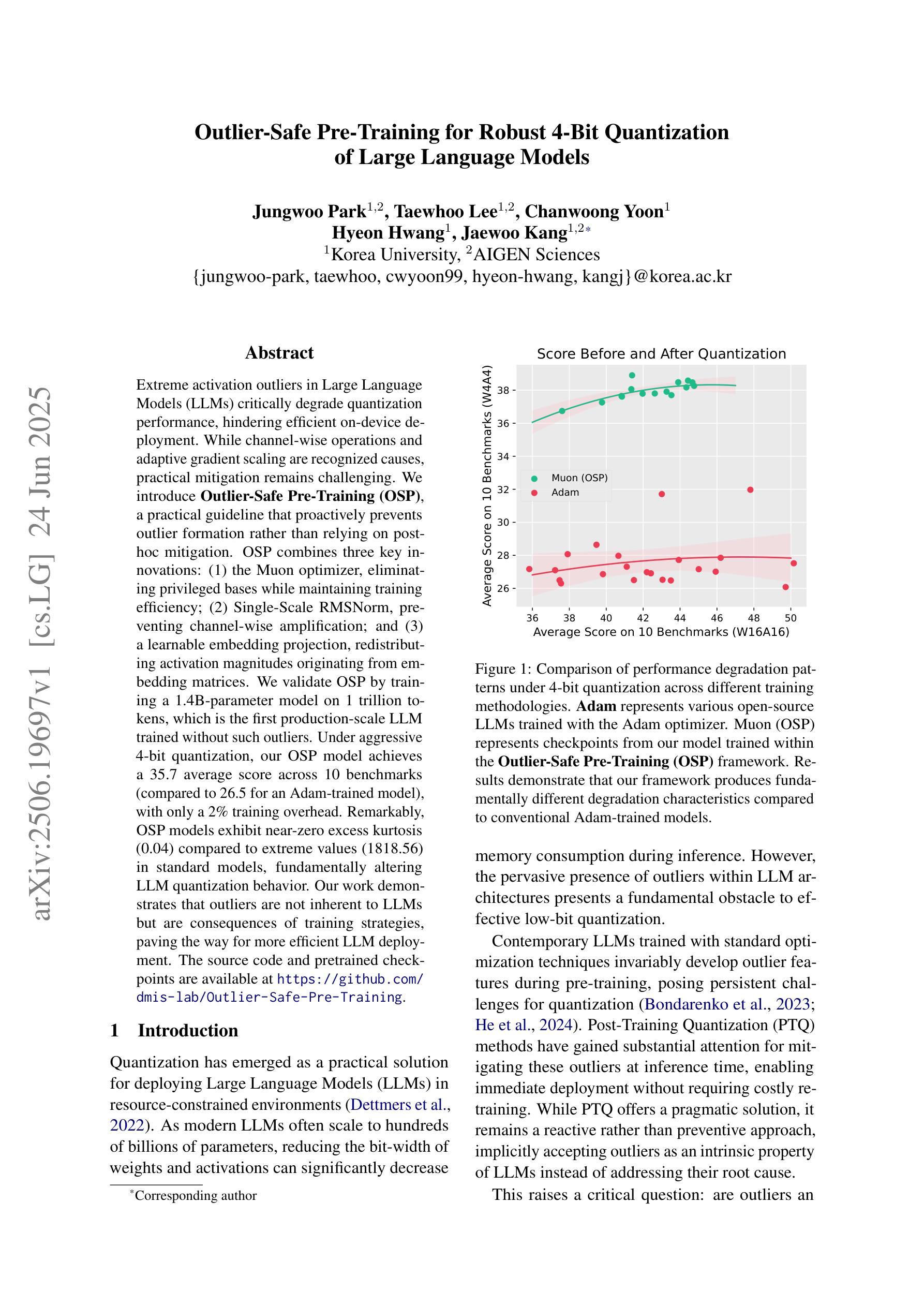
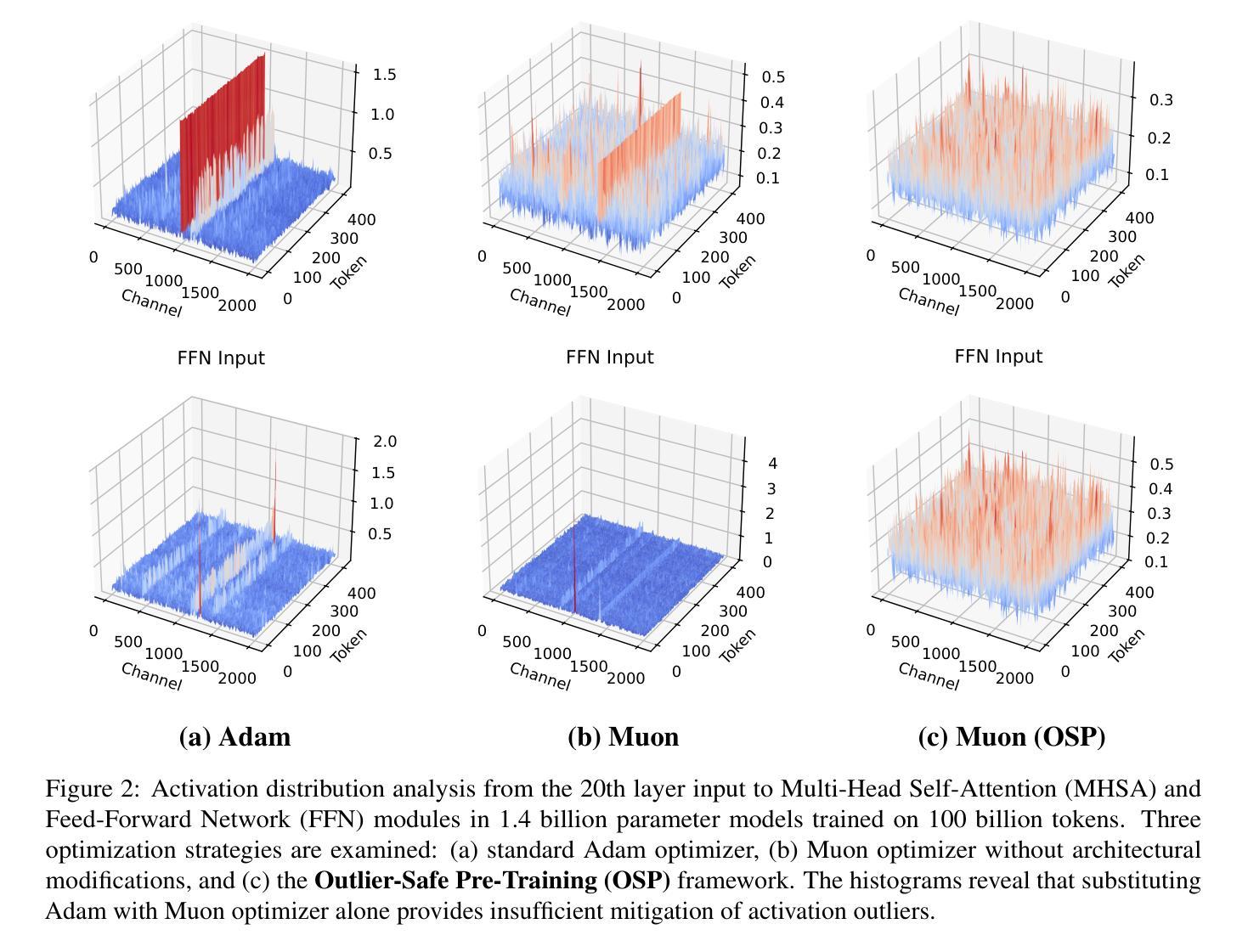
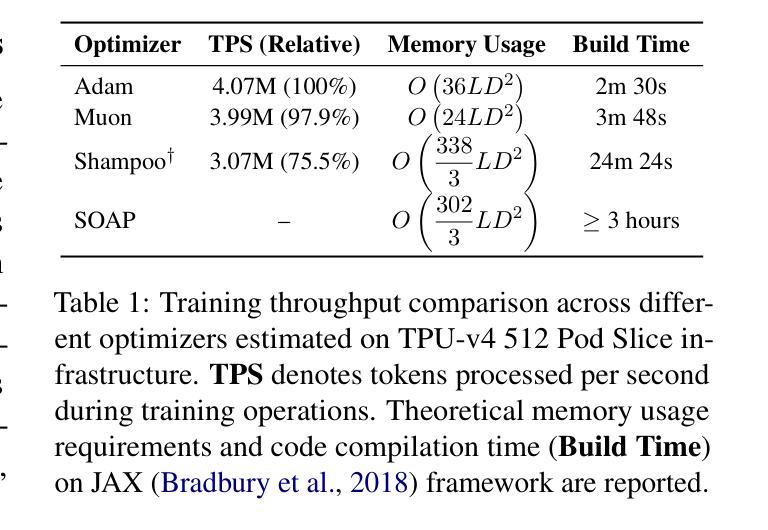
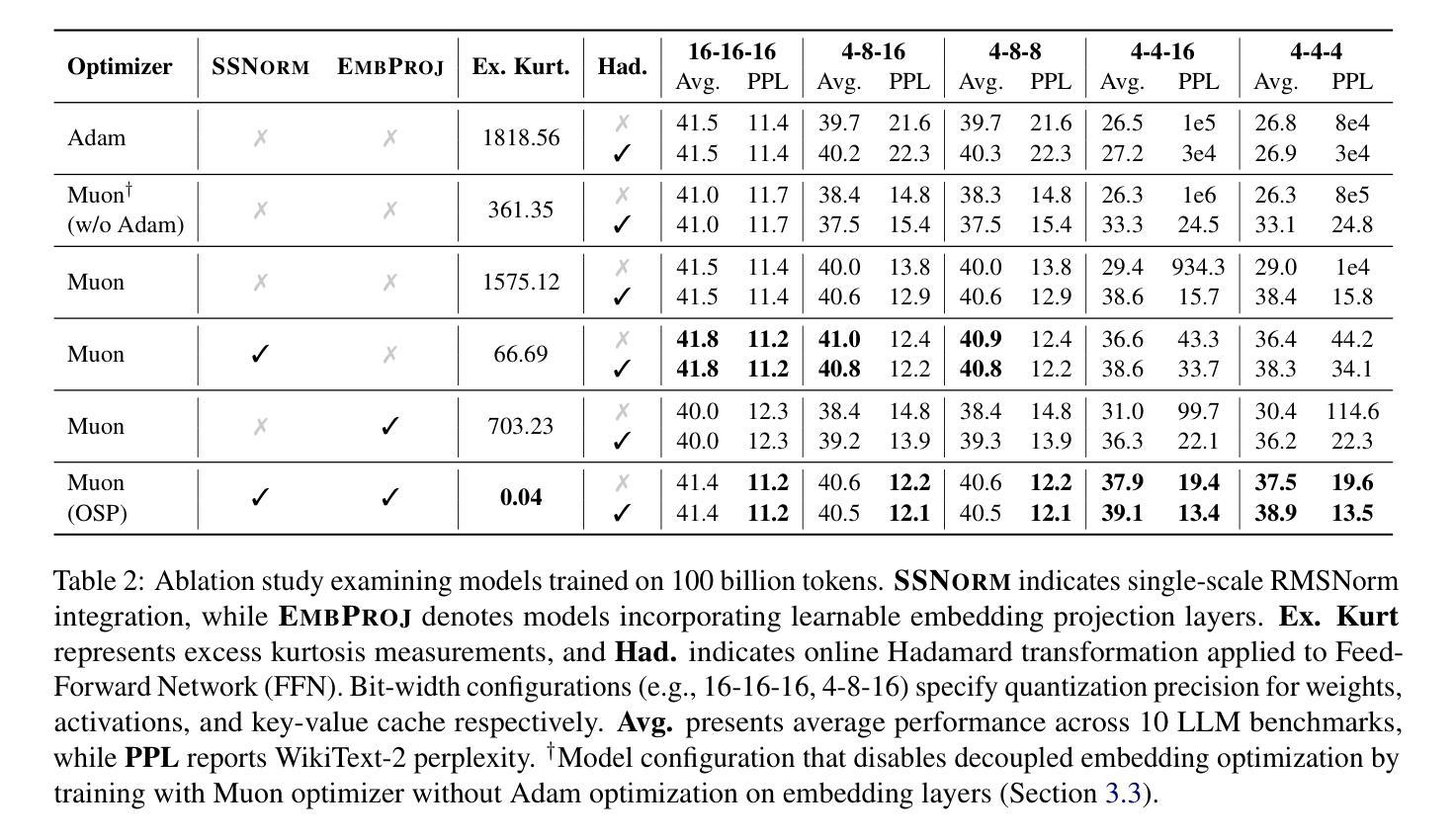
Outlier-Safe Pre-Training for Robust 4-Bit Quantization of Large Language Models
Authors:Jungwoo Park, Taewhoo Lee, Chanwoong Yoon, Hyeon Hwang, Jaewoo Kang
Extreme activation outliers in Large Language Models (LLMs) critically degrade quantization performance, hindering efficient on-device deployment. While channel-wise operations and adaptive gradient scaling are recognized causes, practical mitigation remains challenging. We introduce Outlier-Safe Pre-Training (OSP), a practical guideline that proactively prevents outlier formation rather than relying on post-hoc mitigation. OSP combines three key innovations: (1) the Muon optimizer, eliminating privileged bases while maintaining training efficiency; (2) Single-Scale RMSNorm, preventing channel-wise amplification; and (3) a learnable embedding projection, redistributing activation magnitudes originating from embedding matrices. We validate OSP by training a 1.4B-parameter model on 1 trillion tokens, which is the first production-scale LLM trained without such outliers. Under aggressive 4-bit quantization, our OSP model achieves a 35.7 average score across 10 benchmarks (compared to 26.5 for an Adam-trained model), with only a 2% training overhead. Remarkably, OSP models exhibit near-zero excess kurtosis (0.04) compared to extreme values (1818.56) in standard models, fundamentally altering LLM quantization behavior. Our work demonstrates that outliers are not inherent to LLMs but are consequences of training strategies, paving the way for more efficient LLM deployment. The source code and pretrained checkpoints are available at https://github.com/dmis-lab/Outlier-Safe-Pre-Training.
极端激活值异常在大语言模型(LLM)中会严重降低量化性能,阻碍其在设备上的有效部署。虽然已知通道操作和自适应梯度缩放是原因,但实际的缓解措施仍然具有挑战性。我们引入了异常安全预训练(OSP),这是一种实用的指导方针,能够提前防止异常值形成,而不是依赖后续缓解措施。OSP结合了三个关键创新点:(1)Muon优化器,能够消除特权基同时保持训练效率;(2)单尺度RMSNorm,防止通道放大;(3)可学习嵌入投影,重新分配来自嵌入矩阵的激活值幅度。我们通过训练一个拥有1.4万亿参数的模型在1万亿个令牌上来验证OSP,这是第一个在生产规模上训练的没有此类异常的LLM。在激烈的4位量化下,我们的OSP模型在10个基准测试中达到平均得分35.7(与Adam训练的模型相比为26.5),仅增加了2%的训练开销。值得注意的是,OSP模型的超额峰度接近于零(0.04),与标准模型的极端值(1818.56)相比,从根本上改变了LLM的量化行为。我们的工作表明,异常值并非LLM所固有,而是训练策略的结果,为更高效的LLM部署铺平了道路。源代码和预训练检查点可在https://github.com/dmis-lab/Outlier-Safe-Pre-Training上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在量化过程中存在极端激活异常值问题,严重影响模型在设备上的部署效率。本文提出了Outlier-Safe Pre-Training(OSP)方案,通过引入三种关键创新技术,有效预防异常值产生,提高模型量化性能。实验证明,OSP训练的大型语言模型在极端量化条件下表现优异,且训练开销较小。本文工作表明,大型语言模型中的异常值并非固有,而是训练策略的后果,为更高效部署大型语言模型铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在量化过程中存在极端激活异常值问题,严重影响性能。
- Outlier-Safe Pre-Training(OSP)方案通过引入三种关键创新技术,有效预防异常值产生。
- OSP方案包括:Muon优化器、Single-Scale RMSNorm和可学习嵌入投影。
- OSP训练的大型语言模型在极端量化条件下表现优异,平均得分提升显著。
- OSP模型训练开销较小,仅有2%的额外负担。
- OSP模型的过度峰度值大幅降低,更接近理想模型表现。
点此查看论文截图
Adaptive Request Scheduling for CodeLLM Serving with SLA Guarantees
Authors:Shi Chang, Boyuan Chen, Kishanthan Thangarajah, Hanan Lutfiyya, Ahmed E. Hassan
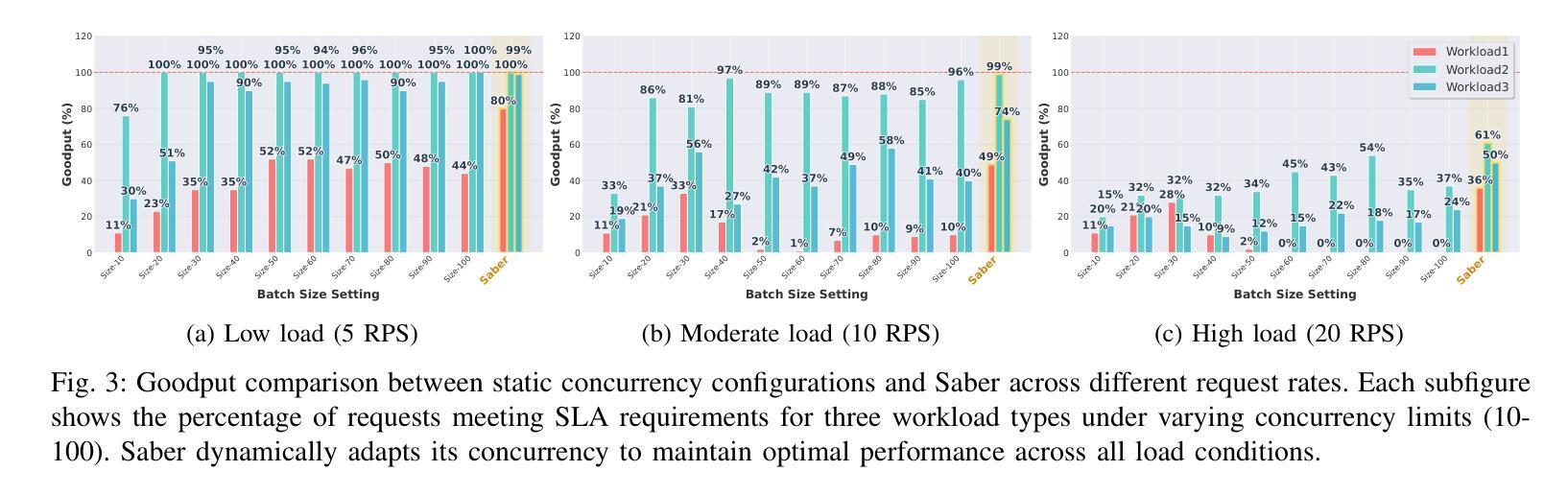
Code Large Language Models (CodeLLMs) are increasingly integrated into modern software development workflows, yet efficiently serving them in resource-constrained, self-hosted environments remains a significant challenge. Existing LLM serving systems employs Continuous Batching for throughput improvement. However, they rely on static batch size configurations that cannot adapt to fluctuating request rates or heterogeneous workloads, leading to frequent SLA (Service Level Agreement) violations and unstable performance. In this study, We propose SABER, a dynamic batching strategy that predicts per-request SLA feasibility and adjusts decisions in real time. SABER improves goodput by up to 26% over the best static configurations and reduces latency variability by up to 45%, all without manual tuning or service restarts. Our results demonstrate that SLA-aware, adaptive scheduling is key to robust, high-performance CodeLLM serving.
代码大语言模型(CodeLLMs)在现代软件开发流程中的集成度越来越高,但在资源受限、自主托管的环境中有效地提供服务仍然是一个重大挑战。现有的LLM服务系统采用连续批处理来提高吞吐量。然而,它们依赖于静态批处理大小配置,无法适应波动的请求率或异构工作量,导致服务等级协议(SLA)频繁违约和性能不稳定。在本研究中,我们提出SABER,这是一种动态批处理策略,可以预测每个请求的SLA可行性并实时调整决策。SABER在最佳静态配置的基础上将goodput提高了高达26%,并将延迟变化减少了高达45%,而且无需手动调整或服务重启。我们的结果表明,了解SLA的自适应调度是稳健、高性能CodeLLM服务的关键。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在软件开发流程中的应用越来越广泛,但在资源受限的自定义托管环境中高效地提供服务仍是一大挑战。现有LLM服务系统采用连续批处理来提高吞吐量,但依赖于无法适应请求率波动或异构工作负载的静态批处理配置,导致服务等级协议(SLA)频繁违规和性能不稳定。本研究提出SABER动态批处理策略,它能预测每个请求的SLA可行性并实时调整决策。SABER在最佳静态配置的基础上将goodput提高了高达26%,并将延迟变化降低了高达45%,且无需手动调整或服务重启。结果证明,基于SLA的调度对于实现稳健、高性能的CodeLLM服务至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- Code Large Language Models (CodeLLMs) 在现代软件开发中的应用及其面临的挑战。
- 现有LLM服务系统主要依赖静态批处理配置,无法适应变化的请求率和异构工作量,导致性能不稳定和SLA违规。
- SABER动态批处理策略被提出以解决上述问题,通过预测每个请求的SLA可行性并实时调整决策来提高性能。
- SABER策略相较于最佳静态配置,在goodput上有显著提升,最多可提高26%,同时降低延迟变化达45%。
- 该策略无需手动调整或服务重启,具有高度的实用性和便捷性。
点此查看论文截图



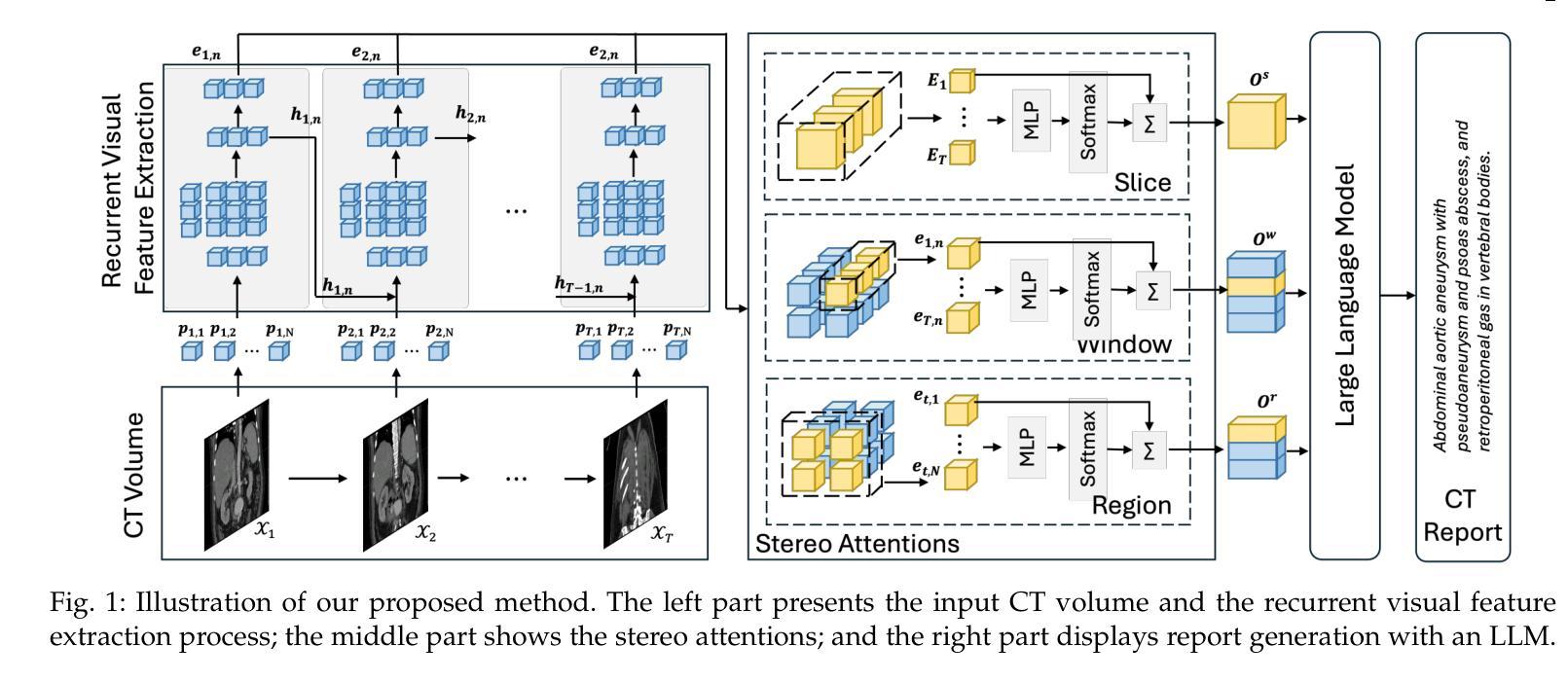
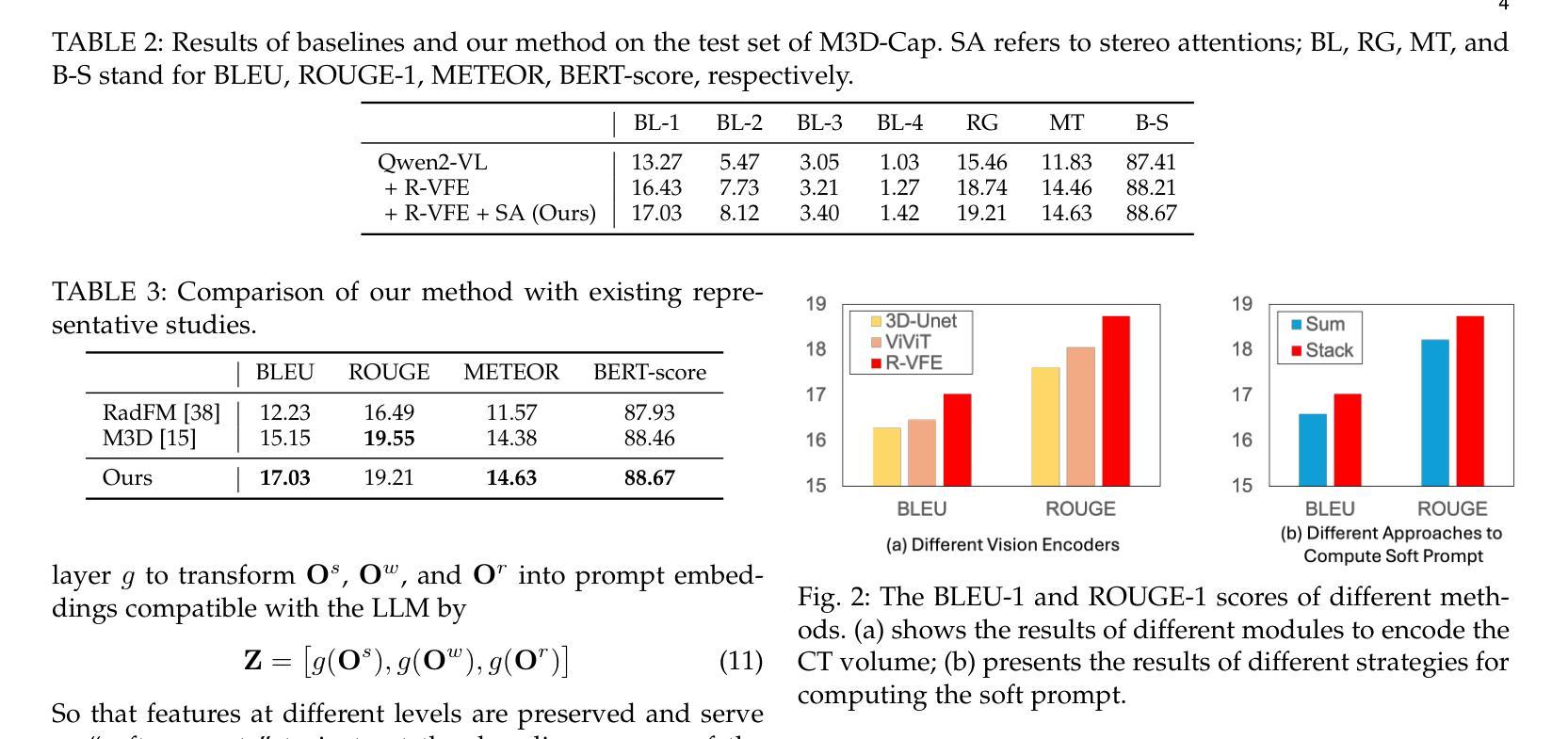
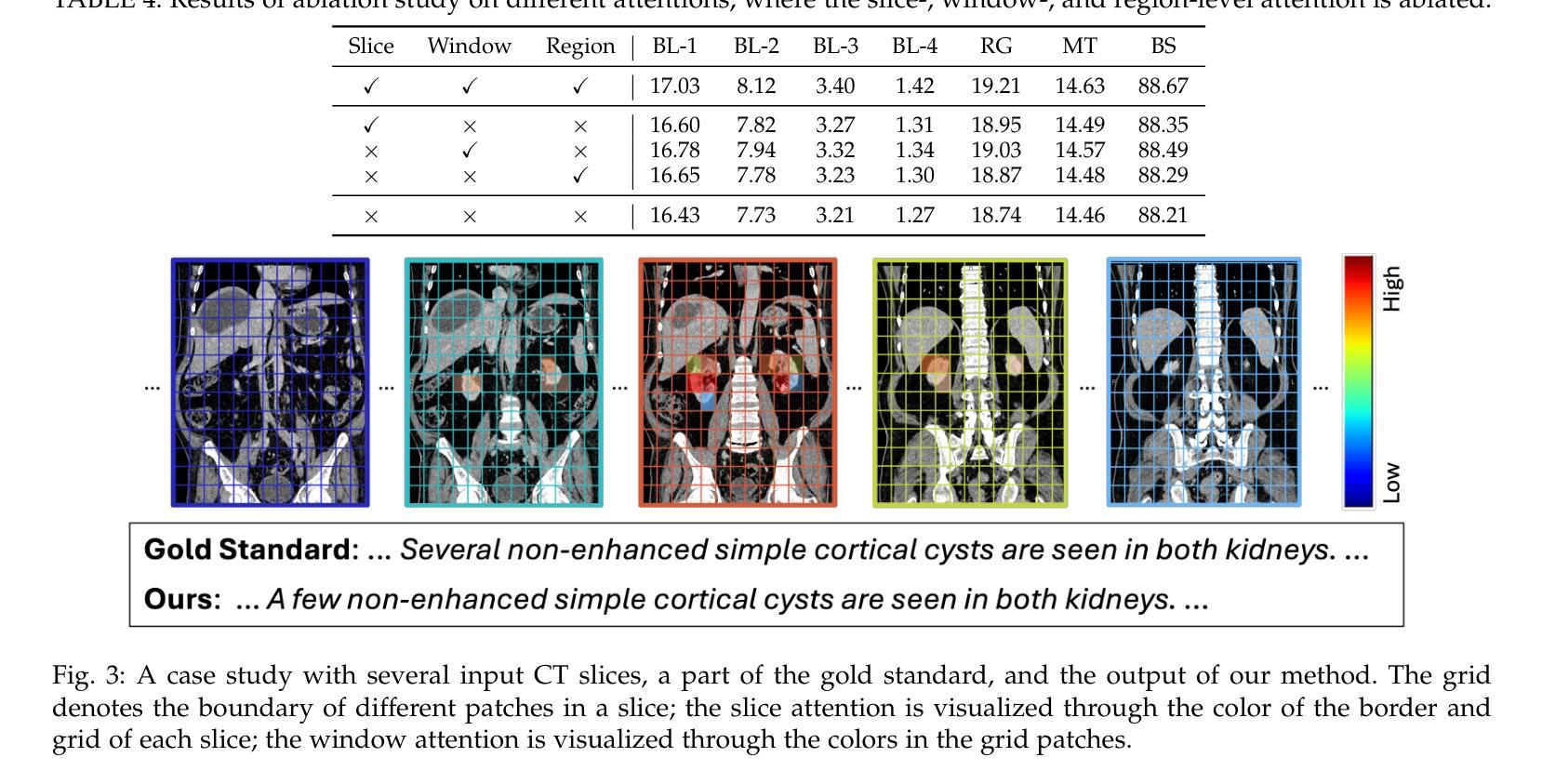
Recurrent Visual Feature Extraction and Stereo Attentions for CT Report Generation
Authors:Yuanhe Tian, Lei Mao, Yan Song
Generating reports for computed tomography (CT) images is a challenging task, while similar to existing studies for medical image report generation, yet has its unique characteristics, such as spatial encoding of multiple images, alignment between image volume and texts, etc. Existing solutions typically use general 2D or 3D image processing techniques to extract features from a CT volume, where they firstly compress the volume and then divide the compressed CT slices into patches for visual encoding. These approaches do not explicitly account for the transformations among CT slices, nor do they effectively integrate multi-level image features, particularly those containing specific organ lesions, to instruct CT report generation (CTRG). In considering the strong correlation among consecutive slices in CT scans, in this paper, we propose a large language model (LLM) based CTRG method with recurrent visual feature extraction and stereo attentions for hierarchical feature modeling. Specifically, we use a vision Transformer to recurrently process each slice in a CT volume, and employ a set of attentions over the encoded slices from different perspectives to selectively obtain important visual information and align them with textual features, so as to better instruct an LLM for CTRG. Experiment results and further analysis on the benchmark M3D-Cap dataset show that our method outperforms strong baseline models and achieves state-of-the-art results, demonstrating its validity and effectiveness.
生成计算机断层扫描(CT)图像的报告是一项具有挑战性的任务。虽然它与医疗图像报告生成领域中的现有研究相似,但它具有独特的特性,例如多个图像的空间编码、图像体积与文本之间的对齐等。现有解决方案通常使用通用的二维或三维图像处理技术从CT体积中提取特征,它们首先压缩体积,然后将压缩的CT切片分成斑块进行视觉编码。这些方法没有明确地考虑到CT切片之间的转换,也没有有效地整合多级图像特征,特别是包含特定器官病变的特征,以指导CT报告生成(CTRG)。考虑到CT扫描中连续切片之间的强烈相关性,本文提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的CTRG方法,该方法具有循环视觉特征提取和立体注意力机制,用于分层特征建模。具体来说,我们使用视觉转换器循环处理CT体积中的每个切片,并从不同角度对编码后的切片集应用一组注意力,以选择性获取重要的视觉信息,并将其与文本特征对齐,从而更好地指导LLM进行CTRG。在基准数据集M3D-Cap上的实验结果和进一步的分析表明,我们的方法优于强大的基线模型,达到了最先进的性能,证明了其有效性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures
Summary
这篇论文提出了使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行CT图像报告生成的方法。针对CT图像的特性,论文使用视觉Transformer对CT体积中的切片进行递归处理,并通过不同角度的注意力机制获取重要的视觉信息,与文本特征对齐,以指导LLM生成报告。实验结果表明,该方法优于基准模型,达到先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- CT图像报告生成是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要处理图像的空间编码和与文本的对齐。
- 现有方法主要使用2D或3D图像处理技术从CT体积中提取特征,但未能充分考虑CT切片间的变换以及多级别图像特征的整合。
- 论文提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的CT图像报告生成方法,结合递归视觉特征提取和立体注意力机制进行分层特征建模。
- 使用视觉Transformer递归处理CT体积中的每个切片。
- 通过不同角度的注意力机制,选择性获取重要的视觉信息,并与文本特征对齐,以指导LLM生成报告。
- 论文在M3D-Cap数据集上进行实验,结果表明该方法优于基准模型,达到先进水平。
点此查看论文截图

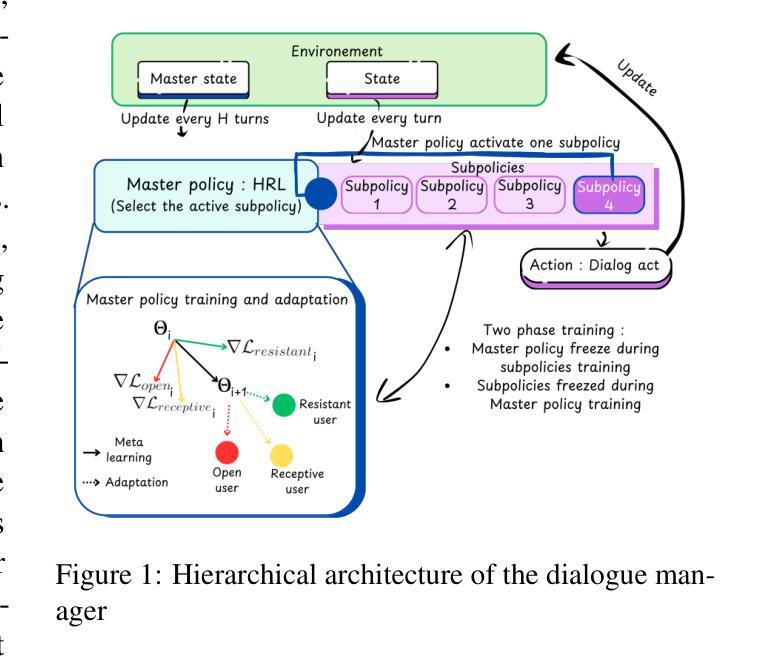
Tailored Conversations beyond LLMs: A RL-Based Dialogue Manager
Authors:Lucie Galland, Catherine Pelachaud, Florian Pecune
In this work, we propose a novel framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) with an RL-based dialogue manager for open-ended dialogue with a specific goal. By leveraging hierarchical reinforcement learning to model the structured phases of dialogue and employ meta-learning to enhance adaptability across diverse user profiles, our approach enhances adaptability and efficiency, enabling the system to learn from limited data, transition fluidly between dialogue phases, and personalize responses to heterogeneous patient needs. We apply our framework to Motivational Interviews, aiming to foster behavior change, and demonstrate that the proposed dialogue manager outperforms a state-of-the-art LLM baseline in terms of reward, showing a potential benefit of conditioning LLMs to create open-ended dialogue systems with specific goals.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架将大型语言模型(LLM)与基于RL的对话管理器集成在一起,用于实现具有特定目标的开放式对话。我们通过利用分层强化学习来模拟对话的结构化阶段,并借助元学习来提高不同用户配置文件之间的适应性,从而提高适应性和效率,使系统能够在有限的数据中学习,在对话阶段之间平稳过渡,并根据不同的患者需求个性化响应。我们将框架应用于动机面试,旨在促进行为改变,并证明所提出的对话管理器在奖励方面优于最先进的大型语言模型基线,显示出将大型语言模型设置为实现具有特定目标的开放式对话系统的潜在优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该工作提出一个新型框架,通过整合大型语言模型(LLMs)和基于强化学习(RL)的对话管理器,实现具有特定目标的开放对话。该框架利用分层强化学习模拟对话的结构化阶段,并通过元学习提高对不同用户特征的适应性,从而提高系统的适应性和效率。系统能够在有限的数据中学习,流畅地转换对话阶段,并对不同患者的需求做出个性化响应。本文在动机访谈方面的应用,旨在促进行为改变,证明提出的对话管理器在奖励方面优于先进LLM基线,展示了为具有特定目标的开放对话系统调节LLM的潜在优势。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的新型框架结合了大型语言模型(LLMs)和强化学习(RL)对话管理器,适用于具有特定目标的开放对话。
- 使用分层强化学习模拟对话的结构化阶段。
- 利用元学习提高系统的适应性,使其能够适应不同的用户特征和对话环境。
- 系统能够在有限数据中学习,流畅转换对话阶段。
- 该框架能够个性化响应不同患者的需求。
- 在动机访谈方面的应用展示了其促进行为改变的能力。
点此查看论文截图


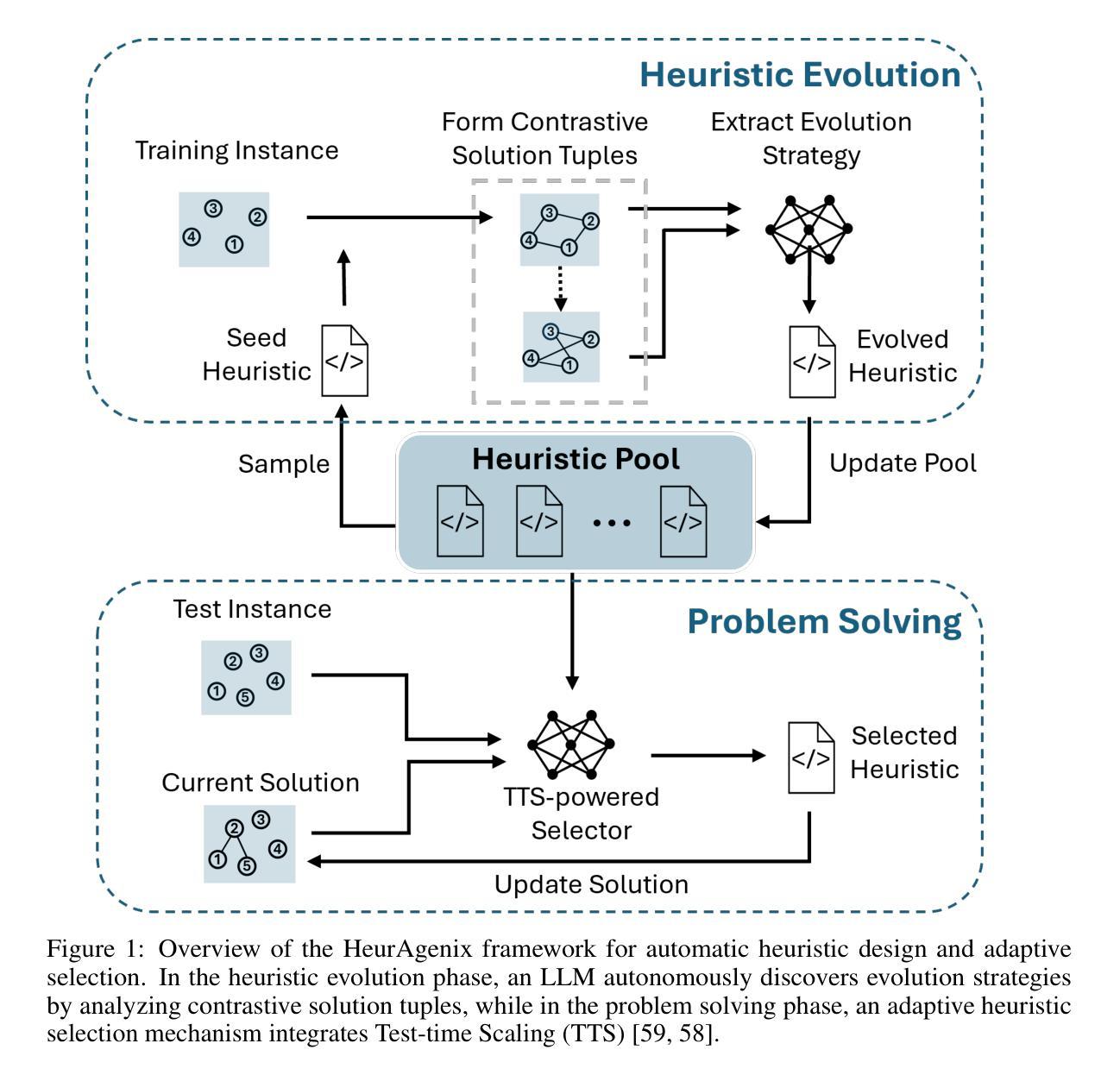
HeurAgenix: Leveraging LLMs for Solving Complex Combinatorial Optimization Challenges
Authors:Xianliang Yang, Ling Zhang, Haolong Qian, Lei Song, Jiang Bian
Heuristic algorithms play a vital role in solving combinatorial optimization (CO) problems, yet traditional designs depend heavily on manual expertise and struggle to generalize across diverse instances. We introduce \textbf{HeurAgenix}, a two-stage hyper-heuristic framework powered by large language models (LLMs) that first evolves heuristics and then selects among them automatically. In the heuristic evolution phase, HeurAgenix leverages an LLM to compare seed heuristic solutions with higher-quality solutions and extract reusable evolution strategies. During problem solving, it dynamically picks the most promising heuristic for each problem state, guided by the LLM’s perception ability. For flexibility, this selector can be either a state-of-the-art LLM or a fine-tuned lightweight model with lower inference cost. To mitigate the scarcity of reliable supervision caused by CO complexity, we fine-tune the lightweight heuristic selector with a dual-reward mechanism that jointly exploits singals from selection preferences and state perception, enabling robust selection under noisy annotations. Extensive experiments on canonical benchmarks show that HeurAgenix not only outperforms existing LLM-based hyper-heuristics but also matches or exceeds specialized solvers. Code is available at https://github.com/microsoft/HeurAgenix.
启发式算法在解决组合优化(CO)问题中发挥着至关重要的作用,然而传统设计严重依赖于人工经验,难以在不同实例之间进行泛化。我们引入了HeurAgenix,这是一个由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的两阶段超启发式框架,首先进化启发式,然后自动从中选择。在启发式进化阶段,HeurAgenix利用LLM比较种子启发式解决方案与高质量解决方案,并提取可重复使用的进化策略。在问题解决过程中,它根据LLM的感知能力,动态选择每个问题状态下最有前途的启发式。为了灵活性,这个选择器可以是最新的大型语言模型,也可以是具有较低推理成本的精细调整轻量级模型。为了缓解由于组合优化复杂性导致的可靠监督数据稀缺问题,我们使用双重奖励机制微调轻量级启发式选择器,该机制联合利用选择偏好和状态感知的信号,实现在嘈杂注释下的稳健选择。在标准基准测试上的广泛实验表明,HeurAgenix不仅优于现有的基于LLM的超启发式,而且与专用求解器相匹配或超越。代码可在https://github.com/microsoft/HeurAgenix获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages,9 figures
Summary
基于启发式算法在解决组合优化问题中的关键作用,我们引入了HeurAgenix,这是一个由大型语言模型驱动的两阶段超启发式框架,能够自动进化并选择合适的启发式算法。它通过LLM比较种子启发式解决方案与高质量解决方案,提取可重复使用的进化策略。在解决问题时,它根据LLM的感知能力动态选择最有前途的启发式方法。为应对复杂性带来的可靠监督不足问题,我们采用双重奖励机制微调轻量级启发式选择器,使其能够从选择偏好和状态感知中联合获取信号,实现噪声标注下的稳健选择。实验表明,HeurAgenix不仅优于现有的LLM超启发式,而且与专用求解器相匹配或超越。
Key Takeaways
- HeurAgenix是一个基于大型语言模型的超启发式框架,旨在解决组合优化问题。
- 它通过进化启发式算法并选择最佳方案来工作,这个过程是自动完成的。
- HeurAgenix利用LLM比较不同的启发式解决方案,并从中提取可重复使用的进化策略。
- 在解决问题时,它会根据LLM的感知能力动态选择最合适的启发式方法。
- 为应对缺乏可靠监督的问题,采用了具有双重奖励机制的轻量级启发式选择器。
- 该框架在标准测试上的表现优于现有的LLM超启发式,并且与专用求解器相当或更好。
- HeurAgenix的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

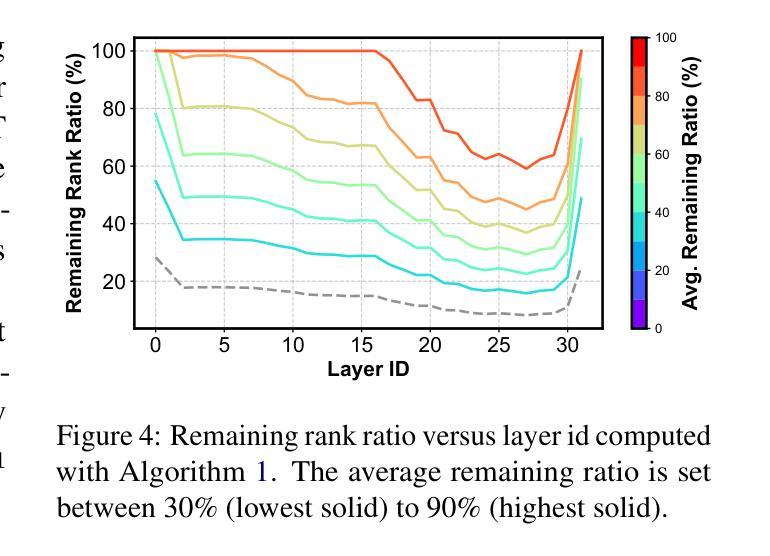
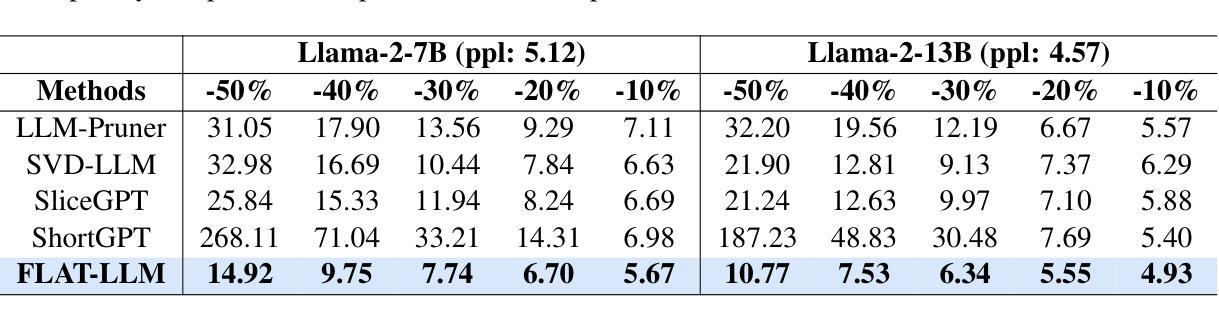
FLAT-LLM: Fine-grained Low-rank Activation Space Transformation for Large Language Model Compression
Authors:Jiayi Tian, Ryan Solgi, Jinming Lu, Yifan Yang, Hai Li, Zheng Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled remarkable progress in natural language processing, yet their high computational and memory demands pose challenges for deployment in resource-constrained environments. Although recent low-rank decomposition methods offer a promising path for structural compression, they often suffer from accuracy degradation, expensive calibration procedures, and result in inefficient model architectures that hinder real-world inference speedups. In this paper, we propose FLAT-LLM, a fast and accurate, training-free structural compression method based on fine-grained low-rank transformations in the activation space. Specifically, we reduce the hidden dimension by transforming the weights using truncated eigenvectors computed via head-wise Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and employ an importance-based metric to adaptively allocate ranks across decoders. FLAT-LLM achieves efficient and effective weight compression without recovery fine-tuning, which could complete the calibration within a few minutes. Evaluated across 4 models and 11 datasets, FLAT-LLM outperforms structural pruning baselines in generalization and downstream performance, while delivering inference speedups over decomposition-based methods.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理方面取得了显著的进步,然而它们的高计算和内存需求对资源受限环境中的部署构成了挑战。尽管最近的低秩分解方法为解决结构压缩问题提供了有前景的路径,但它们经常面临精度下降、校准程序昂贵以及导致阻碍现实世界推理速度提升的低效模型架构的问题。在本文中,我们提出了FLAT-LLM,这是一种快速且准确的无训练结构压缩方法,基于激活空间中的精细粒度低秩转换。具体来说,我们通过头主成分分析(PCA)计算的截断特征向量来转换权重,以降低隐藏维度,并基于重要性的度量来在解码器之间自适应分配等级。FLAT-LLM实现了高效且有效的权重压缩,无需恢复微调,可以在几分钟内完成校准。在4个模型和11个数据集上的评估表明,FLAT-LLM在泛化和下游性能上超过了结构剪枝基线,同时在基于分解的方法上实现了推理速度的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
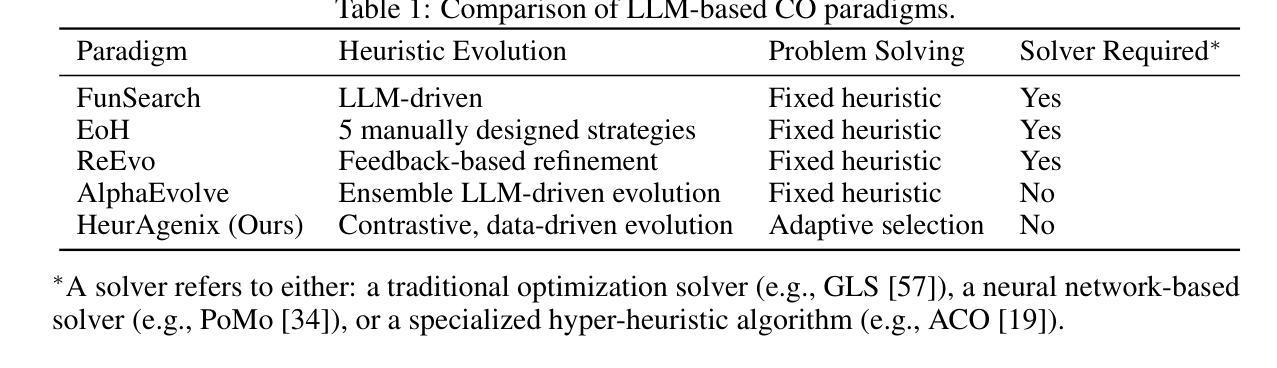
LLM面临计算资源和内存的挑战,现有结构压缩方法存在精度损失、校准繁琐和效率不足的问题。本文提出基于激活空间的精细粒度低秩转换的结构压缩方法FLAT-LLM,采用截断特征值和头主成分分析实现快速部署与性能保证,不需精细训练优化过程,同时提供排名灵活分配的解译能力度量模型性能优势。
在多项模型中实践结果均表明,FLAT-LLM在保证泛化能力和下游性能的同时,实现比现有结构裁剪方法更高的压缩效率,并能显著提升推理速度。
Key Takeaways
- LLM面临资源受限环境中的部署挑战,需要解决计算资源和内存需求高的难题。
- 当前的结构压缩方法存在精度损失和校准过程复杂的问题。
- FLAT-LLM提出一种基于激活空间的低秩转换结构压缩方法,能快速进行结构压缩同时保持准确性。
- 该方法利用头主成分分析进行权重转换,通过截断特征值实现隐藏维度的降低。
- FLAT-LLM采用基于重要性的度量来灵活分配不同解码器的排名。
- 该方法无需恢复精细训练过程,能在几分钟内完成校准过程。
点此查看论文截图
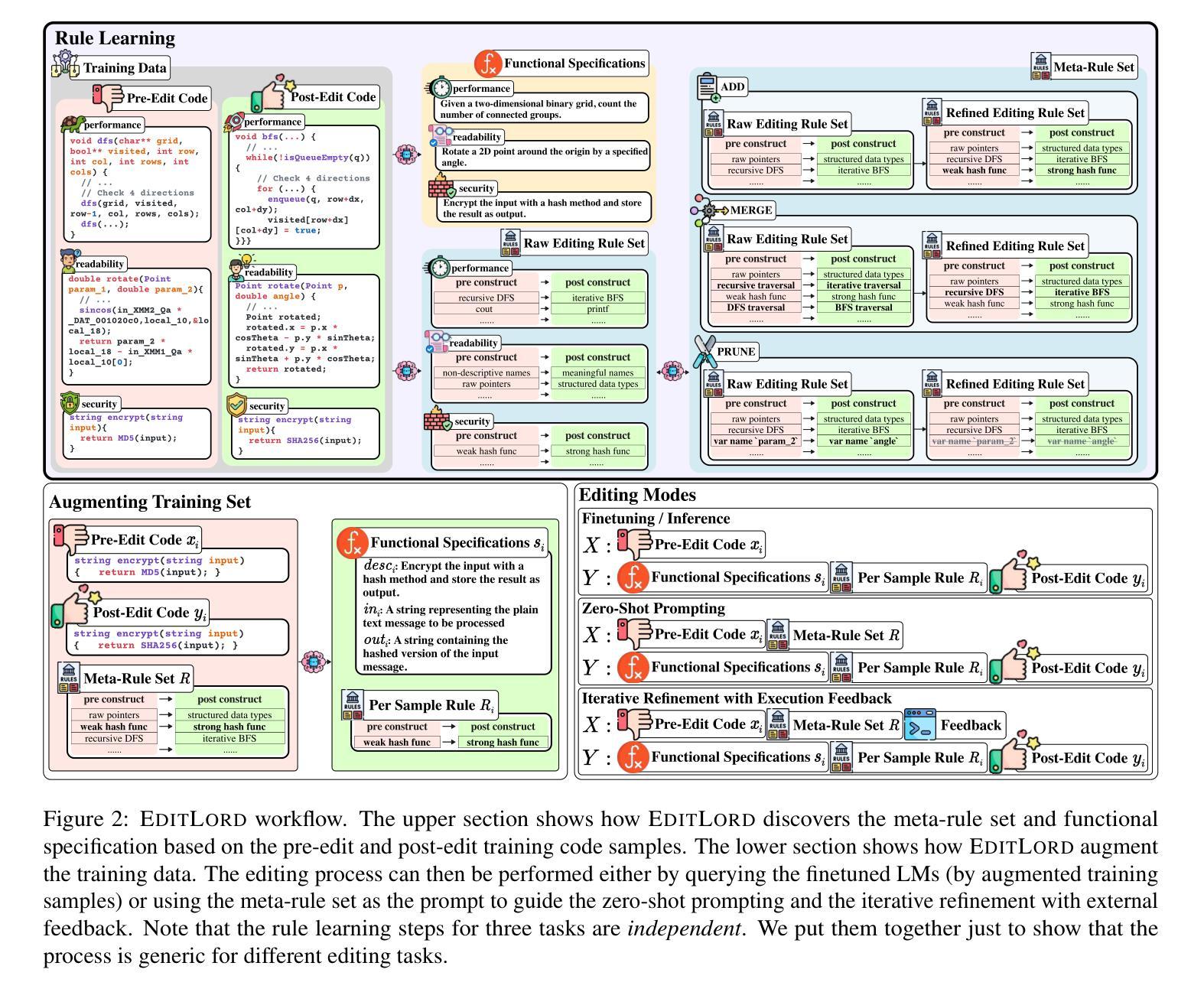
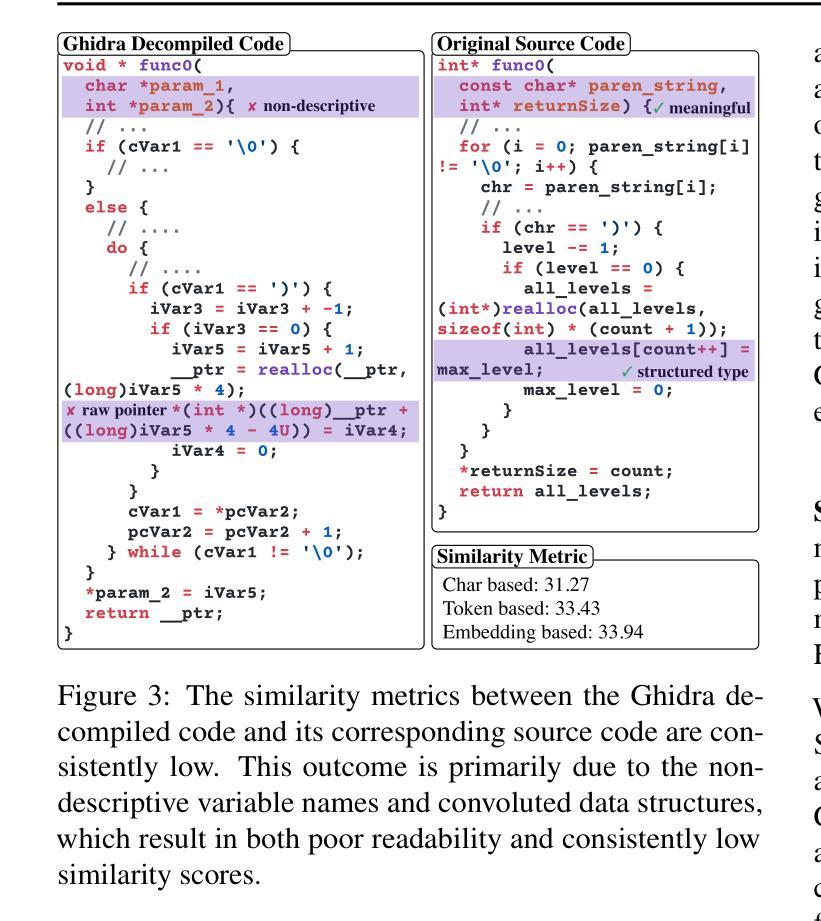
EditLord: Learning Code Transformation Rules for Code Editing
Authors:Weichen Li, Albert Jan, Baishakhi Ray, Junfeng Yang, Chengzhi Mao, Kexin Pei
Code editing is a foundational task in software development, where its effectiveness depends on whether it introduces desired code property changes without changing the original code’s intended functionality. Existing approaches often formulate code editing as an implicit end-to-end task, omitting the fact that code-editing procedures inherently consist of discrete and explicit steps. Thus, they suffer from suboptimal performance and lack of robustness and generalization. We introduce EditLord, a code editing framework that makes the code transformation steps explicit. Our key insight is to employ a language model (LM) as an inductive learner to extract code editing rules from the training code pairs as concise meta-rule sets. Such rule sets will be manifested for each training sample to augment them for finetuning or assist in prompting- and iterative-based code editing. EditLordoutperforms the state-of-the-art by an average of 22.7% in editing performance and 58.1% in robustness while achieving 20.2% higher functional correctness across critical software engineering and security applications, LM models, and editing modes.
代码编辑是软件开发中的基础任务,其有效性取决于是否在不改变原始代码预期功能的情况下引入了所需的代码属性更改。现有方法通常将代码编辑制定为隐式的端到端任务,忽略了代码编辑过程本质上包含离散和明确步骤这一事实。因此,它们面临性能不佳、缺乏稳健性和泛化能力的问题。我们引入了EditLord,这是一个使代码转换步骤明确的代码编辑框架。我们的关键见解是,雇用语言模型(LM)作为归纳学习者,从训练代码对中提取简洁的元规则集作为代码编辑规则。这样的规则集将为每个训练样本提供增强,用于微调或辅助基于提示和迭代的代码编辑。EditLord在编辑性能上平均高出最新技术22.7%,在稳健性上高出58.1%,同时在关键软件工程和安全应用程序、LM模型和编辑模式下实现了20.2%更高的功能正确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
代码编辑是软件开发中的基础任务,其有效性取决于是否能在不改变原始代码预期功能的前提下引入所需的代码属性更改。现有方法常常将代码编辑制定为隐式和端到端的任务,忽略了代码编辑程序本身包含离散和显式步骤的事实。因此,它们存在性能不佳、缺乏稳健性和泛化能力的问题。我们引入了EditLord代码编辑框架,该框架使代码转换步骤显式化。我们的关键见解是,采用语言模型(LM)作为归纳学习器,从训练代码对中提取代码编辑规则,形成简洁的元规则集。这些规则集将为每个训练样本提供支持,用于微调或辅助提示和迭代式代码编辑。EditLord在关键软件工程和安全应用程序中,平均编辑性能提高22.7%,稳健性提高58.1%,功能正确性提高20.2%,优于当前最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- 代码编辑是软件开发中的基础任务,要求在不改变原始代码预期功能的前提下引入所需的代码属性更改。
- 现有方法将代码编辑视为隐式和端到端的任务,忽略了代码编辑的离散和显式步骤,导致性能不佳、缺乏稳健性和泛化能力。
- EditLord框架使代码转换步骤显式化,采用语言模型(LM)作为归纳学习器,从训练代码对中提取代码编辑规则。
- 这些规则集可以用于微调或辅助提示和迭代式代码编辑。
- EditLord通过使编辑步骤显式化,提高了代码编辑的性能、稳健性和功能正确性。
- 在关键软件工程和安全应用程序中,EditLord的表现优于当前最新技术,平均编辑性能提高22.7%,稳健性提高58.1%,功能正确性提高20.2%。
- EditLord框架有望为未来的代码编辑工作提供新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图


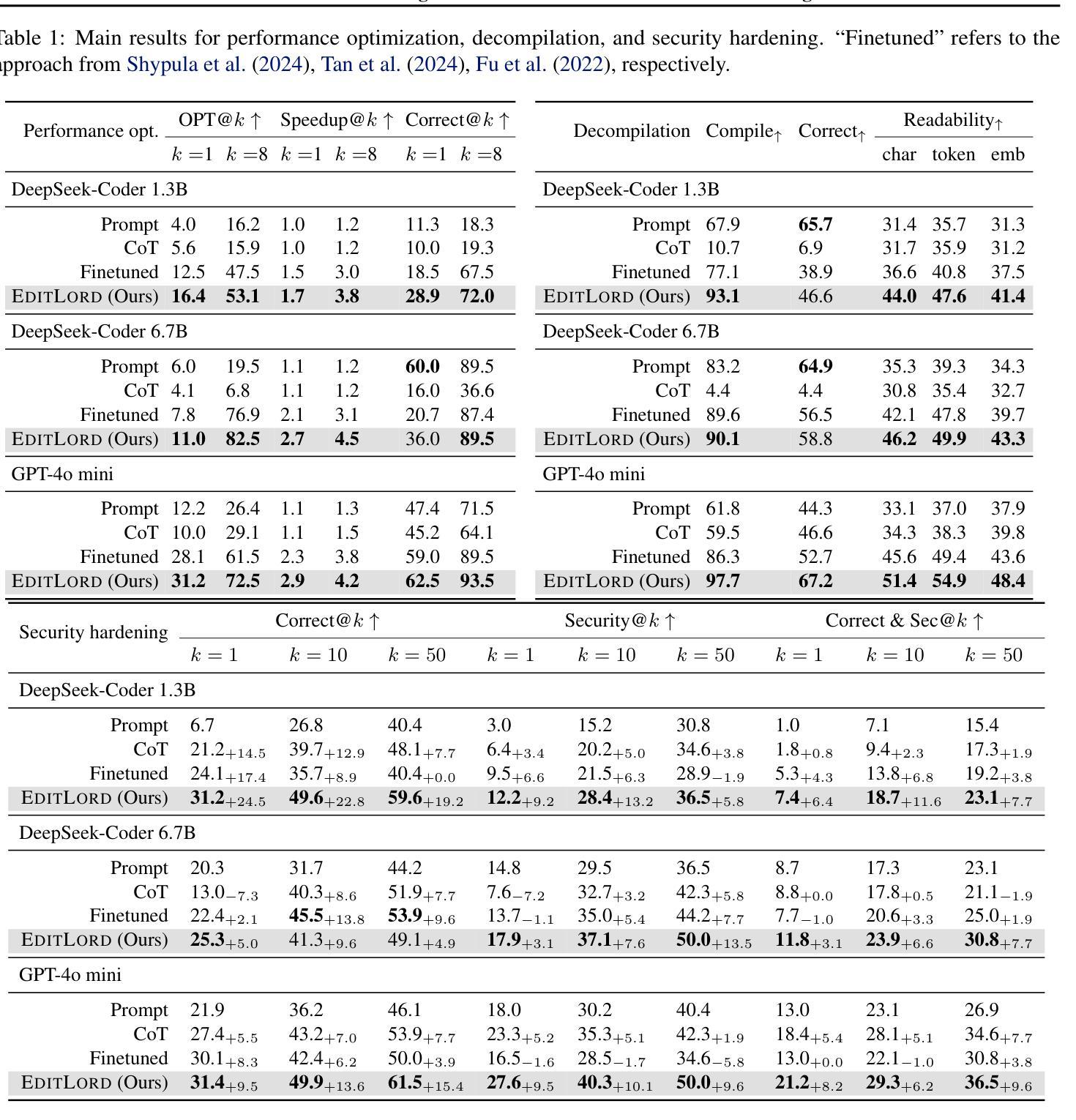
Lemmanaid: Neuro-Symbolic Lemma Conjecturing
Authors:Yousef Alhessi, Sólrún Halla Einarsdóttir, George Granberry, Emily First, Moa Johansson, Sorin Lerner, Nicholas Smallbone
Automatically conjecturing useful, interesting and novel lemmas would greatly improve automated reasoning tools and lower the bar for formalizing mathematics in proof assistants. It is however a very challenging task for both neural and symbolic approaches. We present the first steps towards a practical neuro-symbolic lemma conjecturing tool, Lemmanaid, that combines Large Language Models (LLMs) and symbolic methods, and evaluate it on proof libraries for the Isabelle proof assistant. We train an LLM to generate lemma templates that describe the shape of a lemma, and use symbolic methods to fill in the details. We compare Lemmanaid against an LLM trained to generate complete lemma statements as well as previous fully symbolic conjecturing methods. Lemmanaid outperforms both neural and symbolic methods on test sets from Isabelle’s HOL library and from its Archive of Formal Proofs, discovering between 29-39.5% of the gold standard human written lemmas. This is 8-15% more lemmas than the neural-only method. By leveraging the best of both symbolic and neural methods we can generate useful lemmas for a wide range of input domains, facilitating computer-assisted theory development and formalization.
自动推测有用、有趣和新颖的命题将极大地提高自动化推理工具的性能,降低证明辅助工具中形式化数学的门槛。然而,这对于神经和符号方法来说是一项非常有挑战性的任务。我们迈出了构建实用神经符号命题推测工具的第一步,即结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和符号方法的Lemmanaid,并在针对Isabelle证明助手的证明库中对它进行了评估。我们训练了一个LLM来生成描述命题形状的命题模板,并使用符号方法来填充细节。我们将Lemmanaid与训练生成完整命题陈述的LLM以及以前的完全符号推测方法进行了比较。在Isabelle的HOL库及其形式化证明存档的测试集上,Lemmanaid的表现优于神经和符号方法,发现了黄金标准人类书写命题的29-39.5%。这比仅使用神经方法多出8-15%的命题。通过利用符号方法和神经方法的优点,我们可以为广泛的输入域生成有用的命题,促进计算机辅助理论开发和形式化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇文本介绍了自动推测有用、有趣和新颖命题的工具对自动化推理工具和形式化数学证明助手的重要性。文章提出了首个实用的神经符号命题推测工具Lemmanaid,结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和符号方法,并在Isabelle证明助手的证明库上进行了评估。该工具通过训练LLM生成描述命题形状的模板,并使用符号方法填充细节。比较结果显示,相较于仅使用神经网络或完全符号的推测方法,Lemmanaid在Isabelle的HOL库和形式化证明档案测试集上的表现更优,能够发现人类编写的黄金标准命题的29-39.5%。通过结合符号和神经网络方法的优点,该工具能够为广泛的输入领域生成有用的命题,促进计算机辅助理论发展和形式化。
Key Takeaways
以下是七个关键要点:
- 自动推测有用、有趣和新颖的命题对于改进自动化推理工具和形式化数学证明助手具有重要意义。
- Lemmanaid是首个结合大型语言模型(LLM)和符号方法的实用神经符号命题推测工具。
- Lemmanaid通过在Isabelle证明助手的证明库上训练和评估来表现其有效性。
- LLM被训练生成描述命题形状的模板,而符号方法用于填充细节。
- 与仅使用神经网络或完全符号的推测方法相比,Lemmanaid表现更优。
- Lemmanaid能够发现黄金标准中人类编写的命题的百分比在29-39.5%之间,这比神经网络方法高出8-15%。
点此查看论文截图

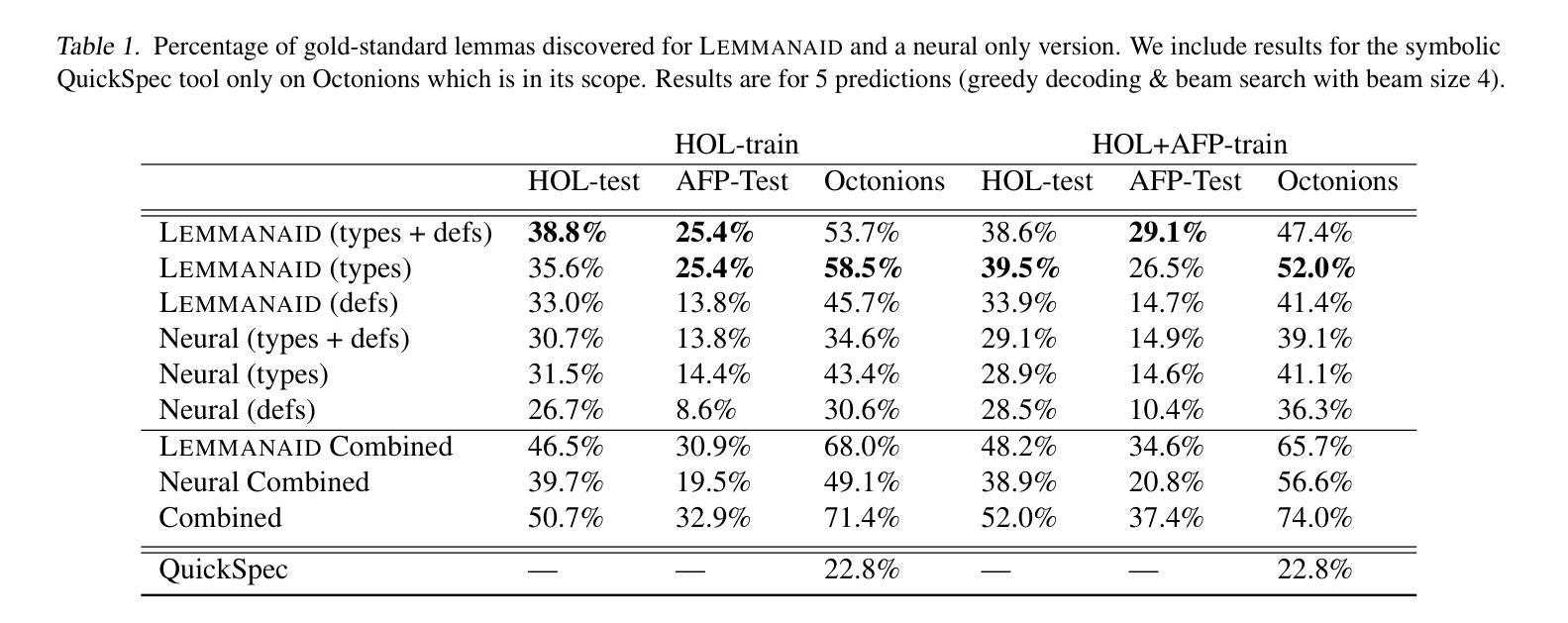
A Foundational individual Mobility Prediction Model based on Open-Source Large Language Models
Authors:Zhenlin Qin, Leizhen Wang, Francisco Camara Pereira, Zhenliang Ma
Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely applied to domain-specific tasks due to their massive general knowledge and remarkable inference capacities. Current studies on LLMs have shown immense potential in applying LLMs to model individual mobility prediction problems. However, most LLM-based mobility prediction models only train on specific datasets or use single well-designed prompts, leading to difficulty in adapting to different cities and users with diverse contexts. To fill these gaps, this paper proposes a unified fine-tuning framework to train a foundational open source LLM-based mobility prediction model. We conducted extensive experiments on six real-world mobility datasets to validate the proposed model. The results showed that the proposed model achieved the best performance in prediction accuracy and transferability over state-of-the-art models based on deep learning and LLMs.
大规模语言模型(LLM)由于其丰富的通用知识和出色的推理能力,被广泛应用于特定领域的任务。当前关于LLM的研究已经显示出将LLM应用于个人出行预测问题的巨大潜力。然而,大多数基于LLM的出行预测模型只在特定数据集上进行训练或使用单一精心设计的提示,这使得它们难以适应不同城市和用户的不同上下文环境。为了填补这些空白,本文提出了一个统一的微调框架来训练一个基于开源LLM的基础出行预测模型。我们在六个真实世界的出行数据集上进行了广泛的实验,以验证所提出模型的效果。结果表明,与基于深度学习和LLM的最先进模型相比,该模型在预测精度和可迁移性方面达到了最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLMs)因其在一般知识方面的优势及强大的推理能力而广泛应用于特定领域的任务。在个体移动预测问题上,LLMs展现出巨大潜力。然而,大多数LLM移动预测模型仅在特定数据集上训练或依赖精心设计的一次性提示,这限制了模型适应不同城市和用户背景的能力。为弥补这些不足,本文提出一个统一的微调框架来训练基于开源LLM的移动预测模型。在六个真实世界移动数据集上的实验表明,该模型在预测精度和迁移能力方面优于基于深度学习和LLM的先进模型。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs被广泛应用于特定领域的任务,得益于其大规模的一般知识和强大的推理能力。
- 在个体移动预测问题上,LLMs具有巨大的潜力。
- 当前LLM移动预测模型主要局限于在特定数据集上训练或依赖一次性提示,缺乏适应不同城市和用户背景的能力。
- 为解决上述问题,本文提出了一个统一的微调框架来训练基于开源LLM的移动预测模型。
- 该框架通过优化模型的训练方式和利用丰富的上下文信息,提高了模型的预测精度和迁移能力。
- 实验结果显示,该模型在六个真实世界移动数据集上的预测性能优于其他先进模型。
点此查看论文截图

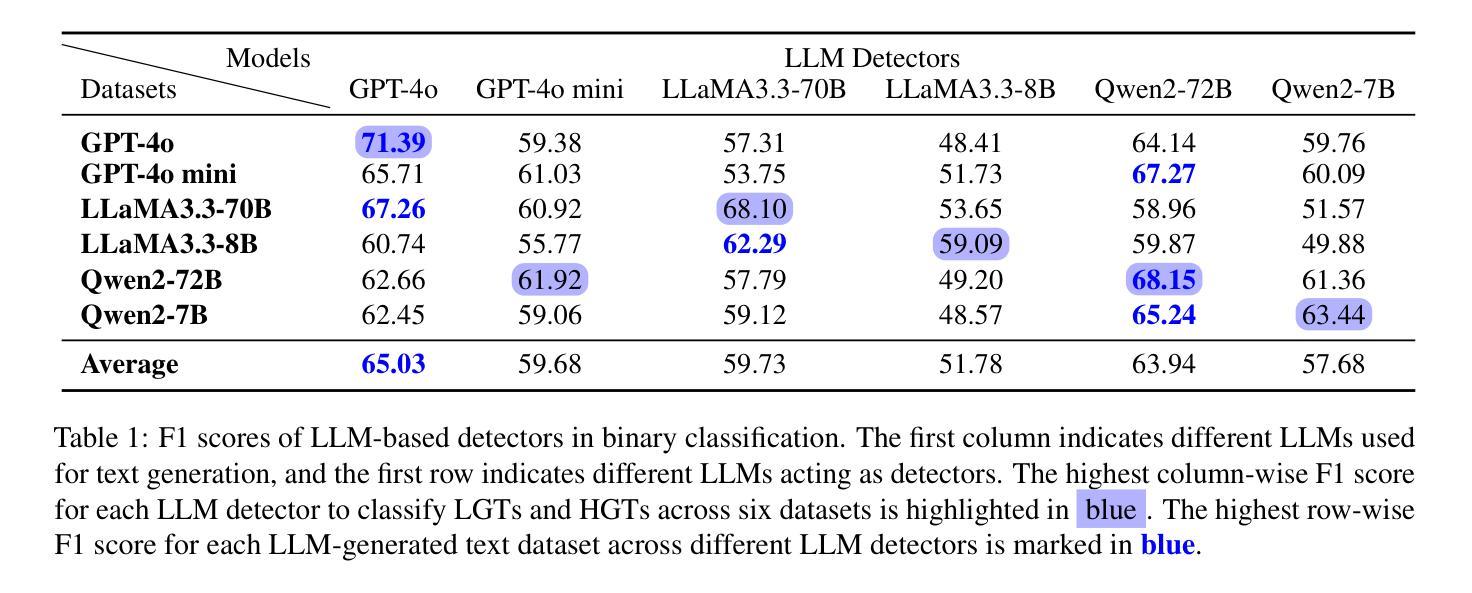
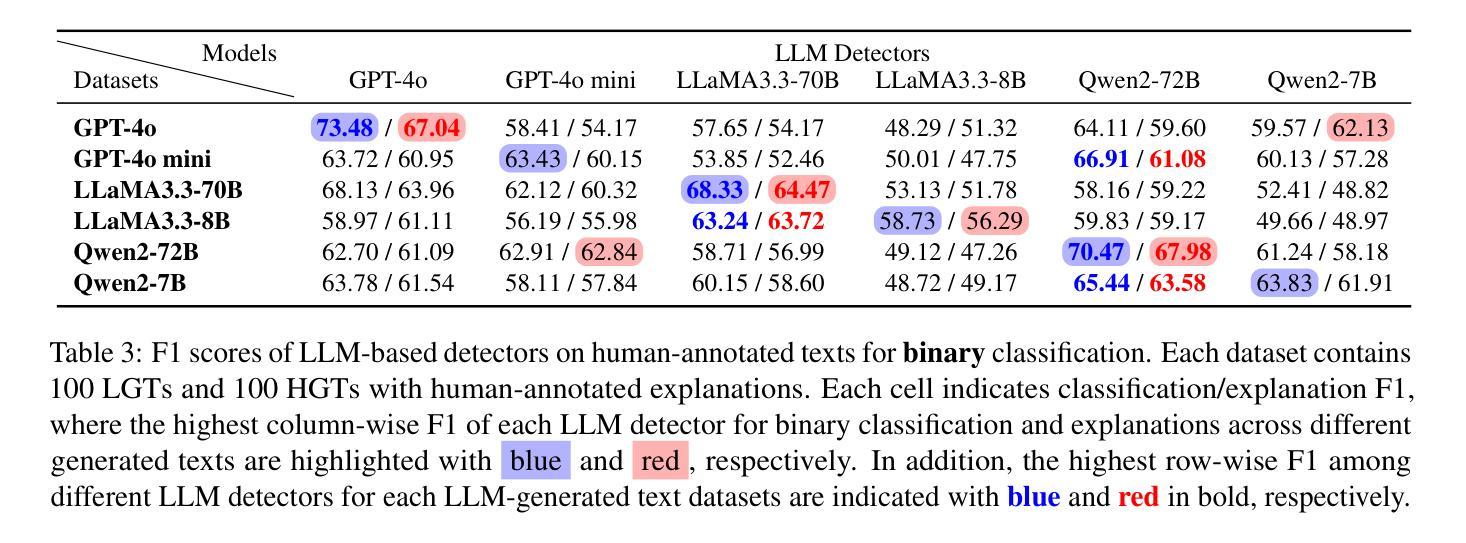
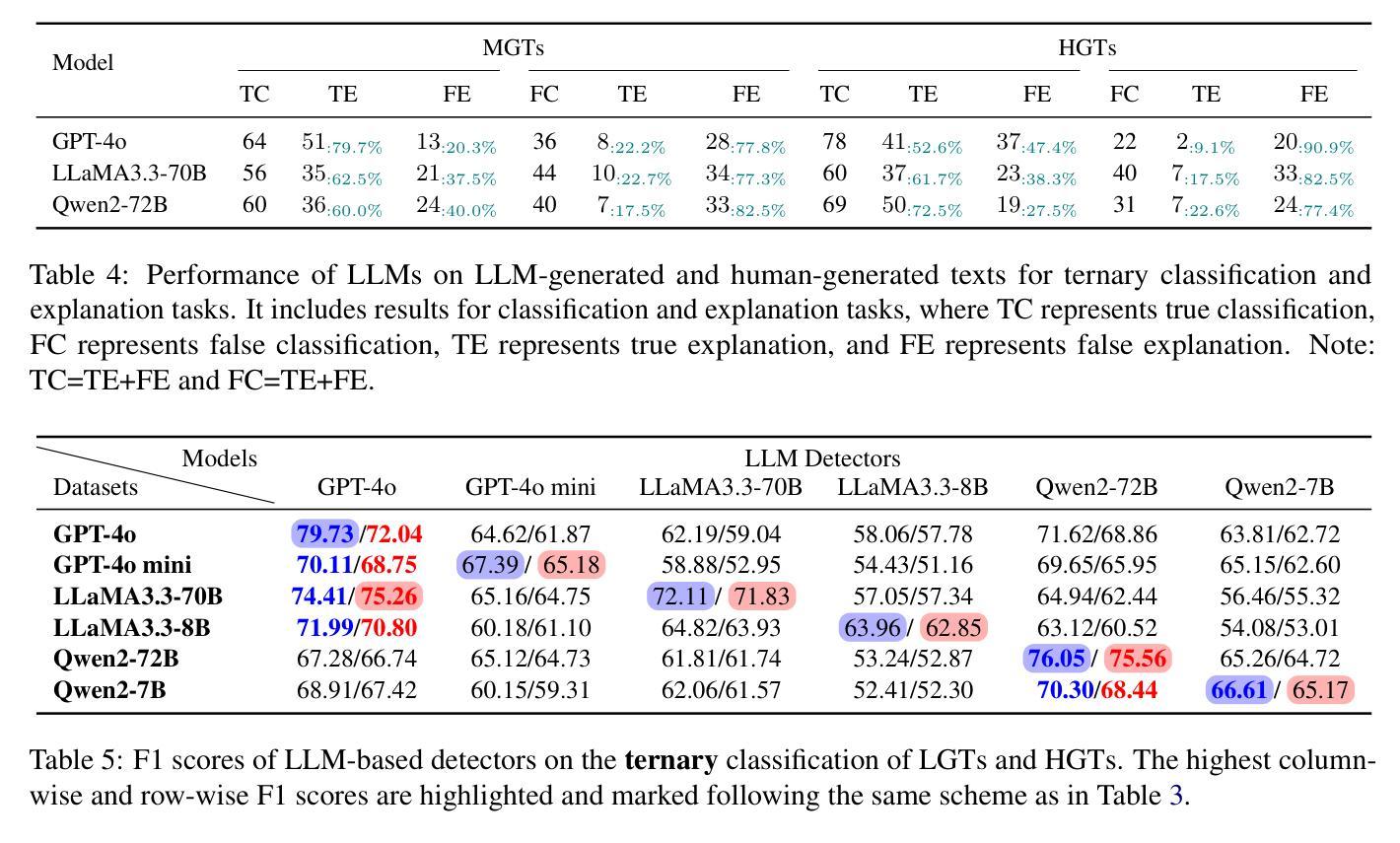
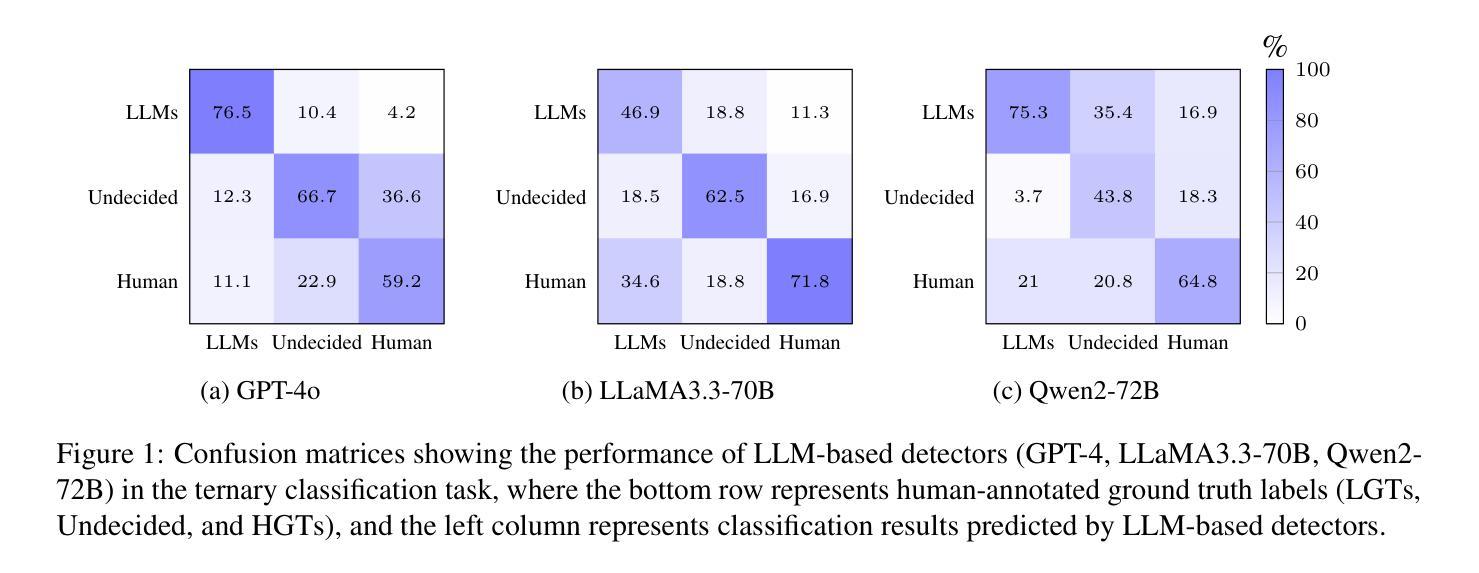
“I know myself better, but not really greatly”: How Well Can LLMs Detect and Explain LLM-Generated Texts?
Authors:Jiazhou Ji, Jie Guo, Weidong Qiu, Zheng Huang, Yang Xu, Xinru Lu, Xiaoyu Jiang, Ruizhe Li, Shujun Li
Distinguishing between human- and LLM-generated texts is crucial given the risks associated with misuse of LLMs. This paper investigates detection and explanation capabilities of current LLMs across two settings: binary (human vs. LLM-generated) and ternary classification (including an ``undecided’’ class). We evaluate 6 close- and open-source LLMs of varying sizes and find that self-detection (LLMs identifying their own outputs) consistently outperforms cross-detection (identifying outputs from other LLMs), though both remain suboptimal. Introducing a ternary classification framework improves both detection accuracy and explanation quality across all models. Through comprehensive quantitative and qualitative analyses using our human-annotated dataset, we identify key explanation failures, primarily reliance on inaccurate features, hallucinations, and flawed reasoning. Our findings underscore the limitations of current LLMs in self-detection and self-explanation, highlighting the need for further research to address overfitting and enhance generalizability.
区分人类和LLM生成文本至关重要,因为滥用LLM存在风险。本文调查了当前LLM的检测和解释能力,涉及两种设置:二元(人类与LLM生成)和三元分类(包括“未决定”类别)。我们评估了6种大小和来源各异的LLM,发现自我检测(LLM识别其自身输出)始终优于交叉检测(识别其他LLM的输出),尽管两者都不够理想。引入三元分类框架提高了所有模型的检测准确性和解释质量。通过使用我们人类注释的数据集进行的综合定量和定性分析,我们确定了主要的解释失败原因,主要是依赖不准确的功能、幻想和有缺陷的推理。我们的研究突出了当前LLM在自我检测和自我解释方面的局限性,强调了需要进一步研究以解决过度拟合问题并增强通用性的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
当前论文探讨了LLM在文本生成中的自我检测与解释能力。研究涉及二元(人类与LLM生成文本)与三元分类(包括“未决定”类别)的场景。评估了不同规模和开源的LLM模型,发现自我检测性能通常优于跨检测,但二者都存在不足。引入三元分类框架有助于提高所有模型的检测准确率和解释质量。通过综合定量和定性分析,研究指出了关键的解释失败原因,如依赖不准确特征、虚构内容和推理缺陷。当前LLM在自我检测和解释方面存在局限性,需要进一步研究以解决过度拟合问题并增强泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在文本生成中的自我检测和解释能力是当前研究的关键领域。
- 二元分类与三元分类是评估LLM检测能力的两种主要场景。
- 自我检测性能通常优于跨检测,但二者都有局限性。
- 引入三元分类框架可以提高检测准确率和解释质量。
- 当前LLM在自我检测方面存在过度拟合和泛化能力不足的局限性。
- LLM在解释失败时,常常依赖于不准确特征、虚构内容和有缺陷的推理。
点此查看论文截图

Exploring the Potential of Encoder-free Architectures in 3D LMMs
Authors:Yiwen Tang, Zoey Guo, Zhuhao Wang, Ray Zhang, Qizhi Chen, Junli Liu, Delin Qu, Zhigang Wang, Dong Wang, Xuelong Li, Bin Zhao
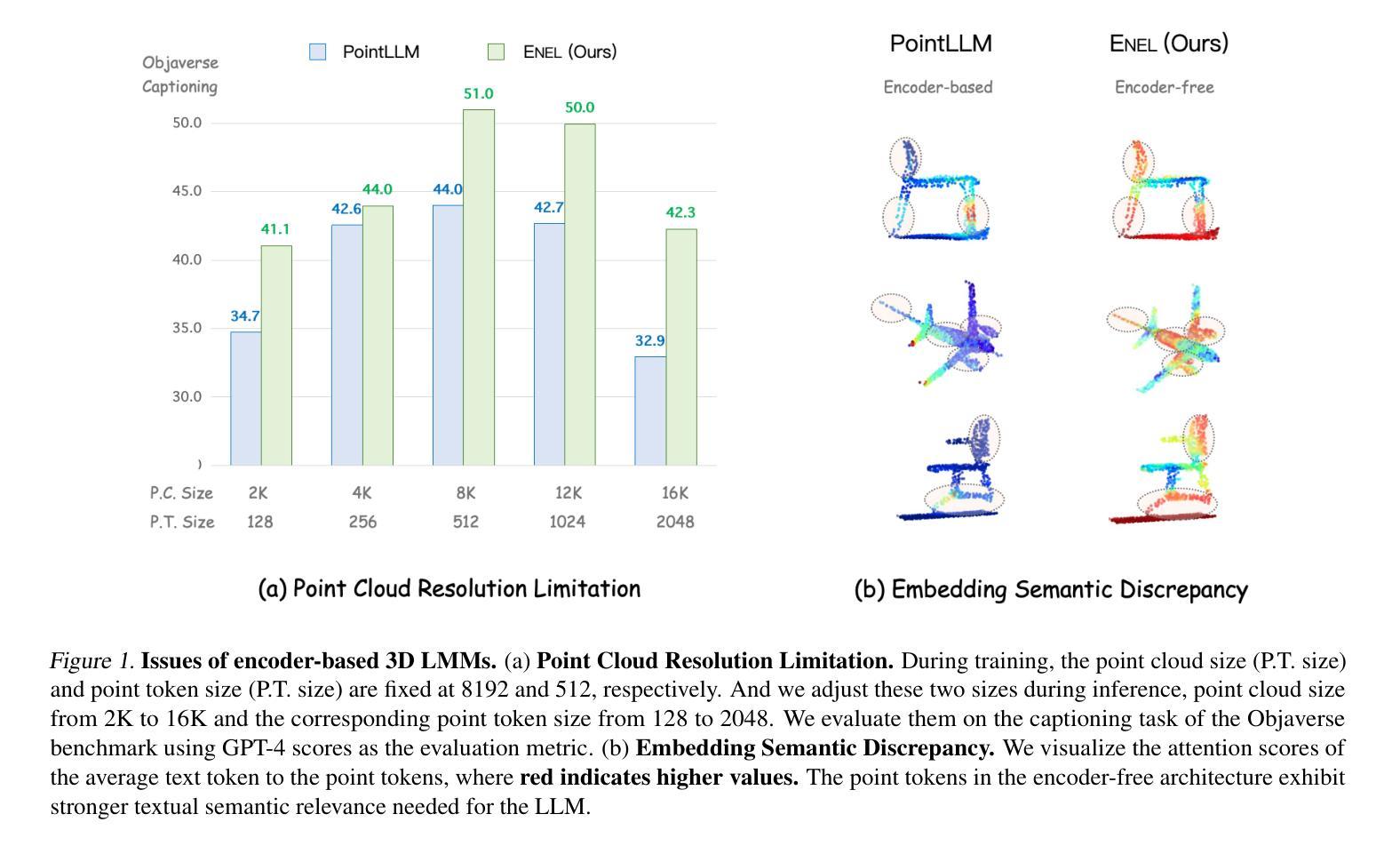
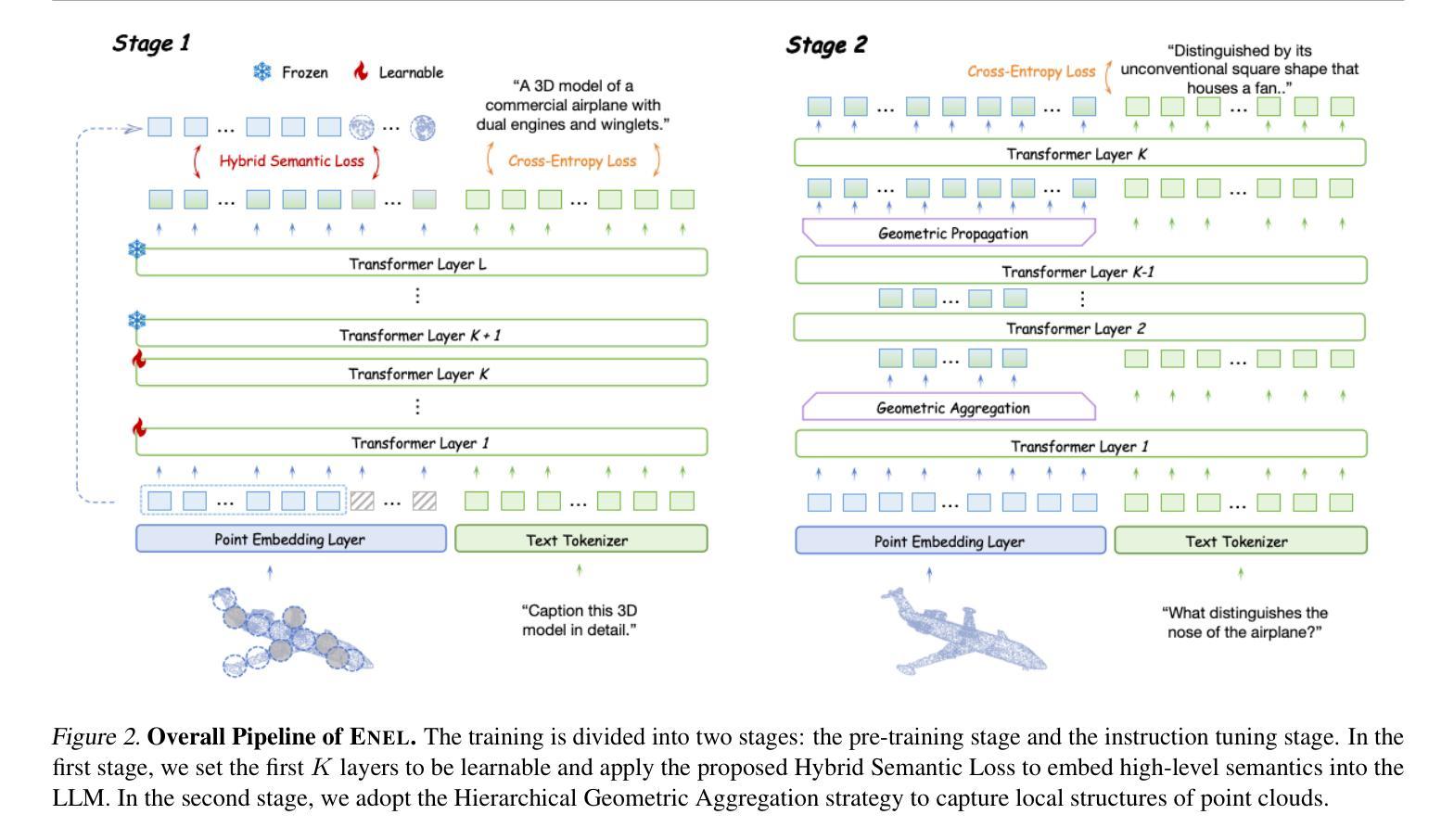
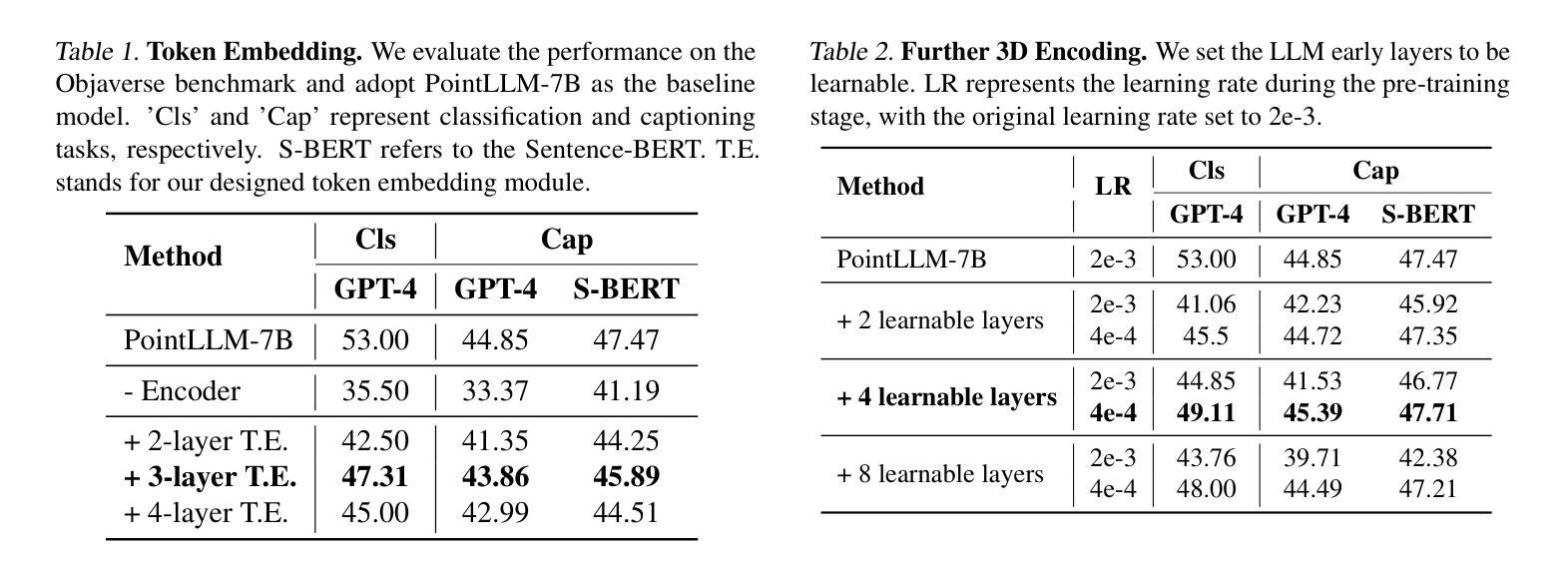
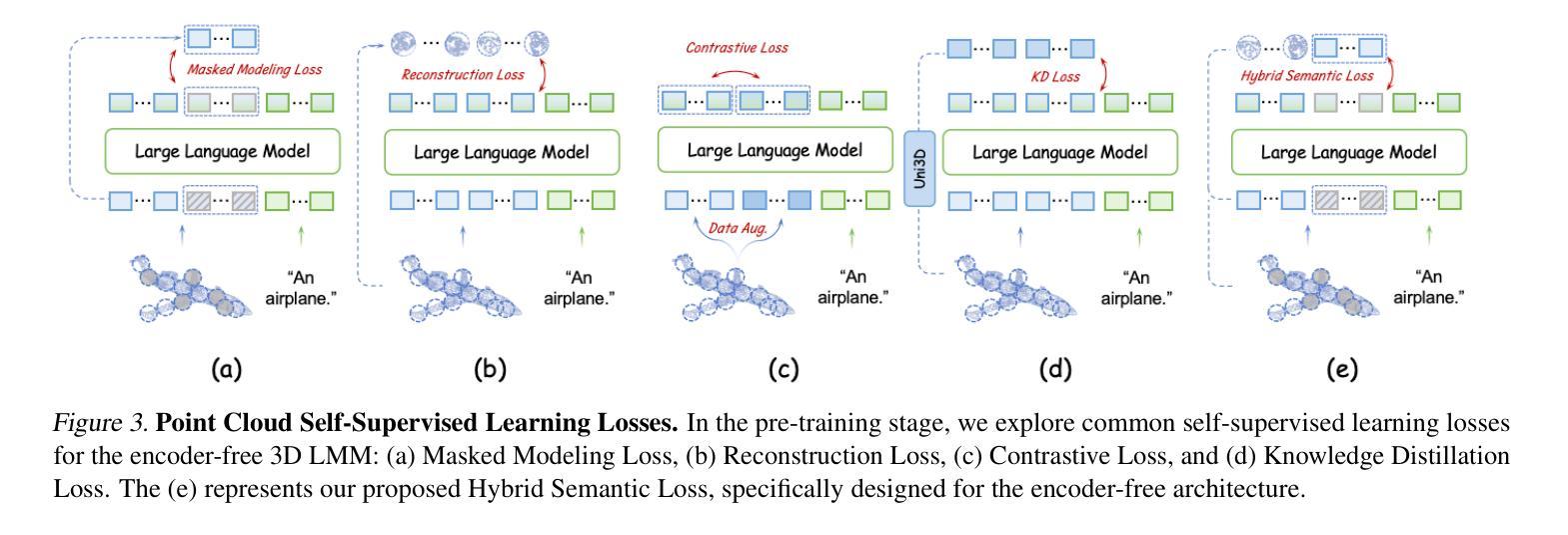
Encoder-free architectures have been preliminarily explored in the 2D visual domain, yet it remains an open question whether they can be effectively applied to 3D understanding scenarios. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive investigation into the potential of encoder-free architectures to alleviate the challenges of encoder-based 3D Large Multimodal Models (LMMs). These challenges include the failure to adapt to varying point cloud resolutions and the point features from the encoder not meeting the semantic needs of Large Language Models (LLMs). We identify key aspects for 3D LMMs to remove the encoder and enable the LLM to assume the role of the 3D encoder: 1) We propose the LLM-embedded Semantic Encoding strategy in the pre-training stage, exploring the effects of various point cloud self-supervised losses. And we present the Hybrid Semantic Loss to extract high-level semantics. 2) We introduce the Hierarchical Geometry Aggregation strategy in the instruction tuning stage. This incorporates inductive bias into the LLM layers to focus on the local details of the point clouds. To the end, we present the first Encoder-free 3D LMM, ENEL. Our 7B model rivals the current state-of-the-art model, ShapeLLM-13B, achieving 55.10%, 50.98%, and 43.10% on the classification, captioning, and VQA tasks, respectively. Our results demonstrate that the encoder-free architecture is highly promising for replacing encoder-based architectures in the field of 3D understanding. The code is released at https://github.com/Ivan-Tang-3D/ENEL
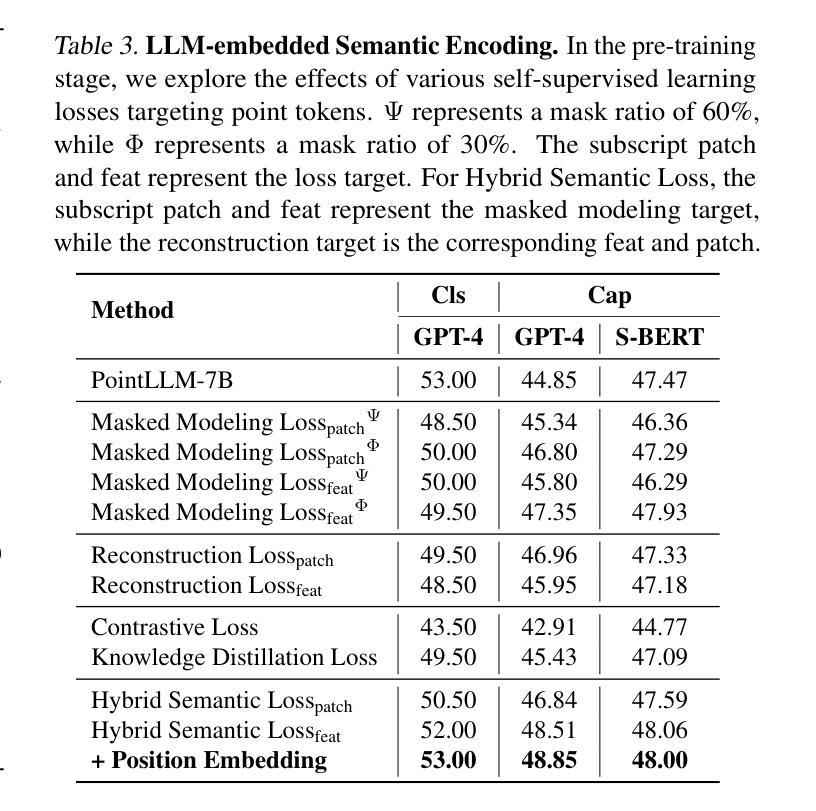
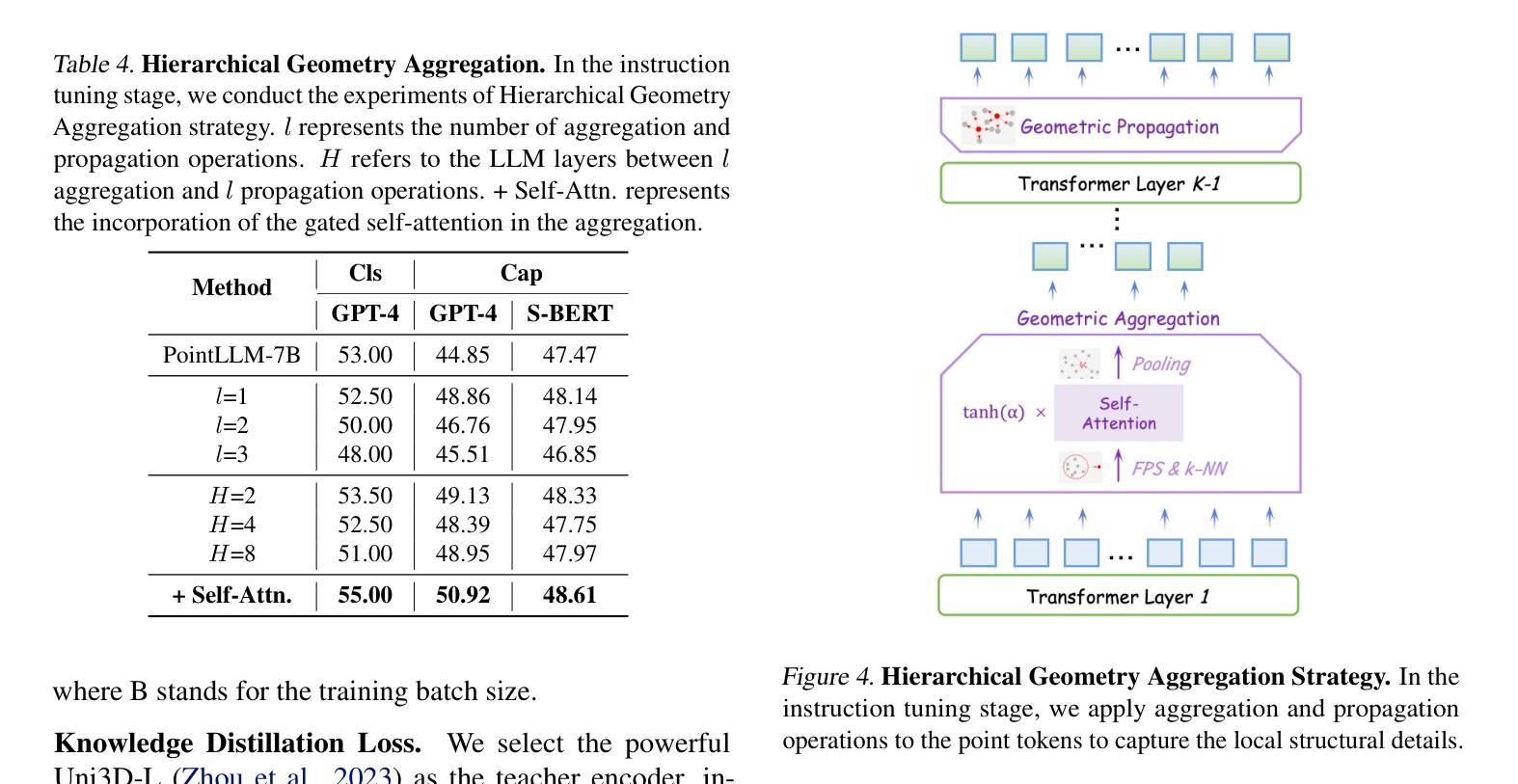
无编码器架构已在2D视觉领域进行了初步探索,但其在3D理解场景中的有效应用仍是开放性问题。本文首次全面探讨了无编码器架构在缓解基于编码器的3D大型多模态模型(LMM)挑战方面的潜力。这些挑战包括无法适应不同的点云分辨率以及编码器中的点特征不符合大型语言模型(LLM)的语义需求。我们确定了使3D LMM去除编码器并允许LLM承担3D编码器角色的关键方面:1)我们在预训练阶段提出了LLM嵌入语义编码策略,探索了各种点云自监督损失的影响。并提出了混合语义损失来提取高级语义。2)我们在指令微调阶段引入了分层几何聚合策略。这将归纳偏置融入LLM层,以关注点云的局部细节。最后,我们提出了首个无编码器3D LMM,ENEL。我们的7B模型与当前最先进的模型ShapeLLM-13B相抗衡,在分类、描述和视觉问答任务上分别实现了55.10%、50.98%和43.10%的性能。我们的结果表明,无编码器架构在3D理解领域替代基于编码器的架构具有巨大潜力。代码已发布在https://github.com/Ivan-Tang-3D/ENEL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF During the review process, we discovered that a portion of the test dataset used in our submission contained content that may have infringed upon the commercial copyrights of others. Due to the conflict regarding these commercial copyrights, we have unfortunately had to retract the submission
摘要
本文首次全面探讨了无编码器架构在缓解基于编码器的三维大型多模态模型(LMM)的挑战方面的潜力。研究解决了适应不同点云分辨率的问题以及编码器点特征不符合大型语言模型(LLM)语义需求的问题。研究提出了在预训练阶段采用LLM嵌入语义编码策略,并探索了各种点云自监督损失的影响,并提出了混合语义损失以提取高级语义。在指令调整阶段引入了分层几何聚合策略,将归纳偏置融入LLM层,以关注点云的局部细节。最终,研究推出了首个无编码器3D LMM,ENEL。该模型的7B性能与当前的先进模型ShapeLLM-13B相当,在分类、描述和视觉问答任务上分别实现了55.10%、50.98%和43.10%的准确率。结果表明,无编码器架构在三维理解领域替代编码器架构具有巨大潜力。
关键见解
- 无编码器架构在三维视觉领域的应用是新颖的,对于解决编码器基于的三维大型多模态模型的挑战具有潜力。
- 研究提出了LLM嵌入语义编码策略,通过在预训练阶段采用自监督损失来优化模型。
- 混合语义损失被用来提取高级语义,这是实现高效三维理解的关键。
- 分层几何聚合策略在指令调整阶段被引入,以关注点云的局部细节,进一步提高模型的性能。
- 推出的无编码器3D LMM,ENEL,在分类、描述和视觉问答任务上取得了显著的成绩,证明了该架构的有效性。
- ENEL的性能与当前最先进的模型相当,展示了无编码器架构在三维理解领域的巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

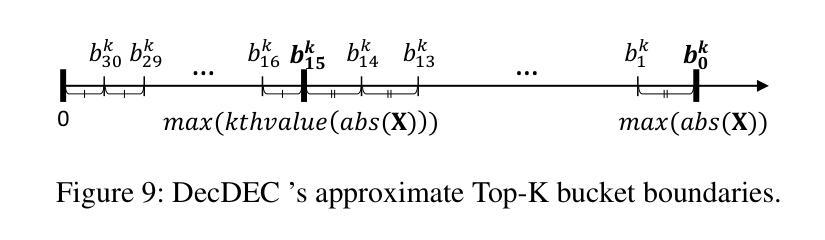
DecDEC: A Systems Approach to Advancing Low-Bit LLM Quantization
Authors:Yeonhong Park, Jake Hyun, Hojoon Kim, Jae W. Lee
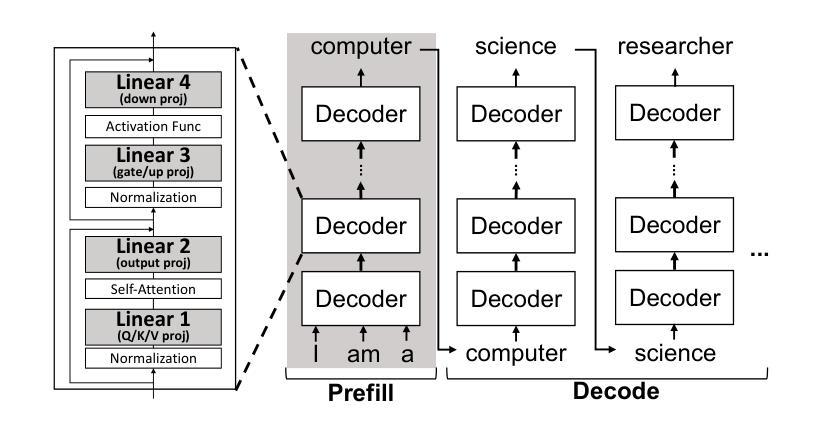
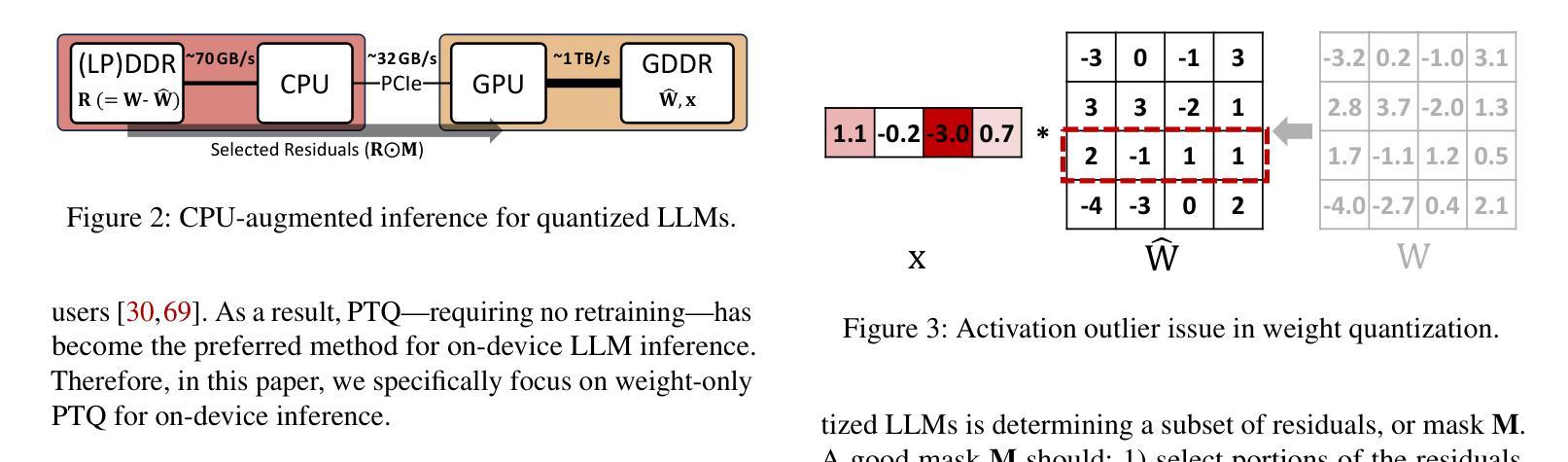
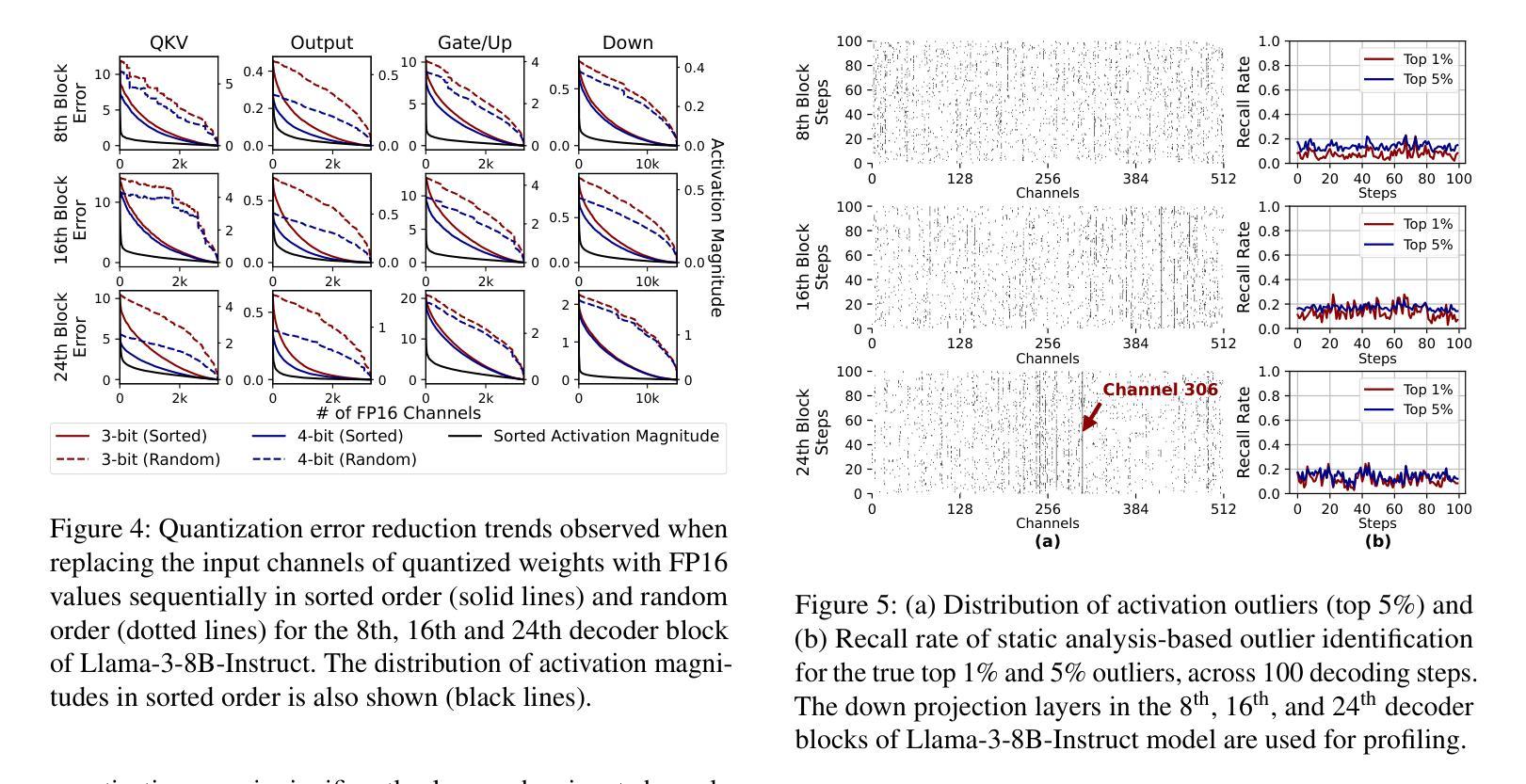
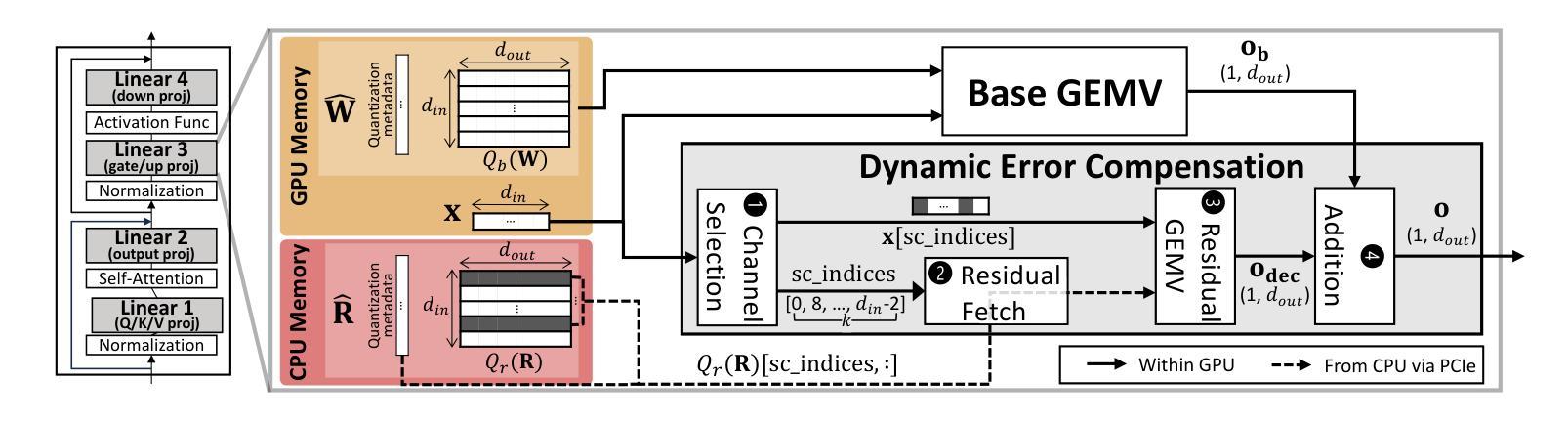
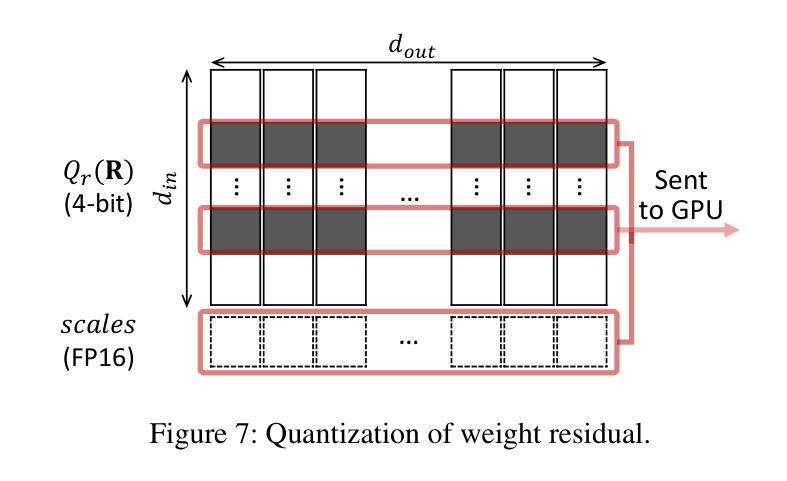
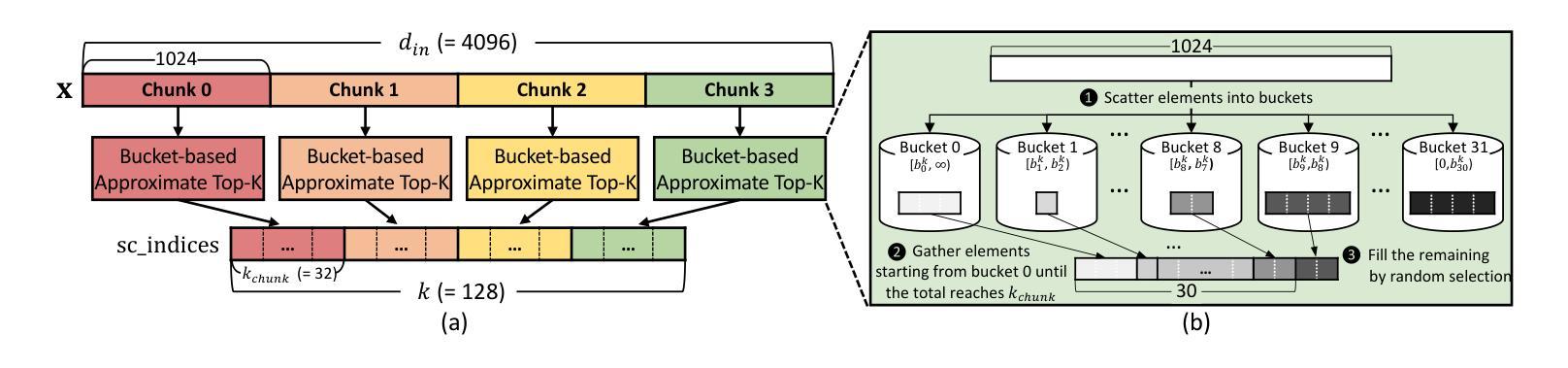
Quantization of Large Language Models (LLMs) has recently gained popularity, particularly for on-device settings with limited hardware resources. While efficient, quantization inevitably degrades model quality, especially in aggressive low-bit settings such as 3-bit and 4-bit precision. In this paper, we propose DecDEC, an inference scheme that improves the quality of low-bit LLMs while preserving the key benefits of quantization: GPU memory savings and latency reduction. DecDEC stores the residual matrix – the difference between full-precision and quantized weights – in CPU, and dynamically fetches the residuals for only a small portion of the weights. This portion corresponds to the salient channels, marked by activation outliers, with the fetched residuals helping to correct quantization errors in these channels. Salient channels are identified dynamically at each decoding step by analyzing the input activations – this enables adaptation to the dynamic nature of activation distribution, thus maximizing the effectiveness of error compensation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of DecDEC by augmenting state-of-the-art quantization methods. For example, DecDEC reduces the perplexity of a 3-bit Llama-3-8B-Instruct model from 10.15 to 9.12 – outperforming its 3.5-bit counterpart – while adding less than 0.0003% to GPU memory usage and incurring only a 1.7% inference slowdown on NVIDIA RTX 4050 Mobile.
大型语言模型(LLM)的量化最近变得流行起来,特别是在硬件资源有限的设备上。虽然效率很高,但量化不可避免地会降低模型质量,特别是在极端的低比特设置(如3位和4位精度)中。在本文中,我们提出了DecDEC,这是一种推理方案,旨在提高低比特LLM的质量,同时保留量化的主要优点:节省GPU内存和减少延迟。DecDEC在CPU中存储残差矩阵(即全精度和量化权重之间的差异),并动态提取权重的小部分残差。这部分对应于显著通道,由激活异常值标记,提取的残差有助于校正这些通道的量化误差。在每个解码步骤中,通过动态分析输入激活来识别显著通道——这有助于适应激活分布的动态特性,从而最大限度地提高误差补偿的有效性。我们通过增强最新的量化方法来证明DecDEC的有效性。例如,DecDEC将3位Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型的困惑度从10.15降低到9.12——超过了其3.5位对应的模型性能——同时GPU内存使用率仅增加不到0.0003%,并且在NVIDIA RTX 4050 Mobile上的推理速度仅下降1.7%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF OSDI 2025
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)的量化近期受到关注,特别是在硬件资源有限的设备上。虽然量化能提高效率,但不可避免地会导致模型质量下降,特别是在3位和4位精度的激进低位设置中。本文提出DecDEC推理方案,旨在提高低位LLM的质量,同时保持量化的主要优势:节省GPU内存和减少延迟。DecDEC将残差矩阵(全精度和量化权重之间的差异)存储在CPU中,并仅动态获取一小部分权重的残差。这部分对应于由激活异常值标记的显著通道,获取的残差有助于校正这些通道中的量化误差。DecDEC通过动态分析输入激活来识别显著通道,这使其能够适应激活分布的动态性质,从而最大限度地提高误差补偿的效果。通过增强最先进量化方法的有效性,DecDEC将3位Llama-3-8B-Instruct模型的困惑度从10.15降低到9.12,超越了其3.5位同行,同时GPU内存使用率仅增加不到0.0003%,并且在NVIDIA RTX 4050 Mobile上的推理速度仅下降1.7%。
关键见解
- LLM量化旨在提高效率和适应硬件资源限制,但会导致模型质量下降。
- DecDEC是一种推理方案,旨在提高低位LLM的质量,同时保持量化的优势。
- DecDEC通过存储和动态获取残差矩阵来提高量化模型的表现。
- 显著通道由激活异常值标记,获取的残差有助于校正这些通道中的量化误差。
- DecDEC能动态适应激活分布的变化,最大限度地提高误差补偿效果。
- DecDEC增强了现有量化方法的效果,降低了模型的困惑度。
点此查看论文截图

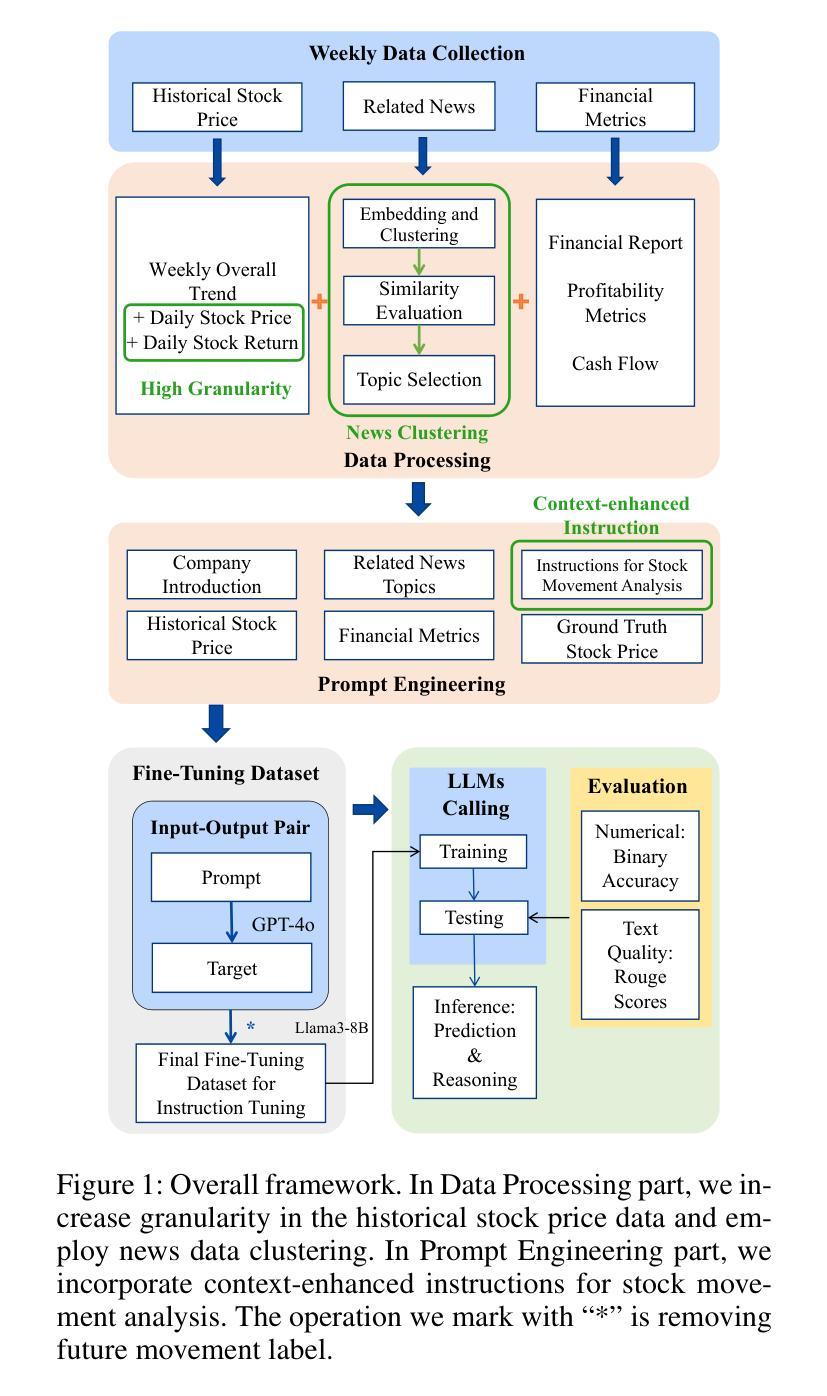
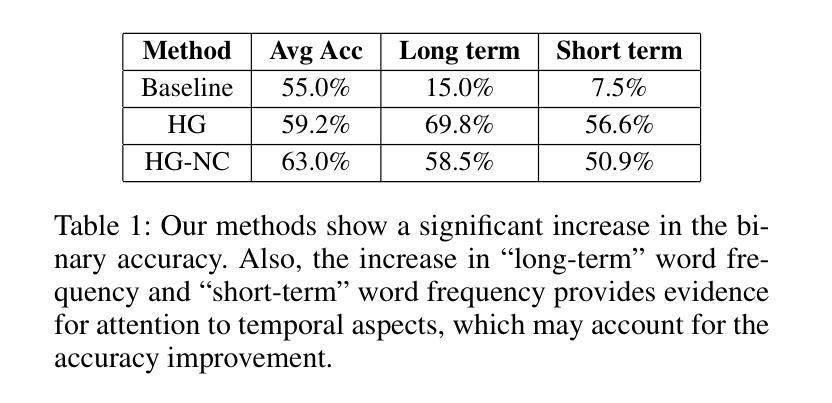
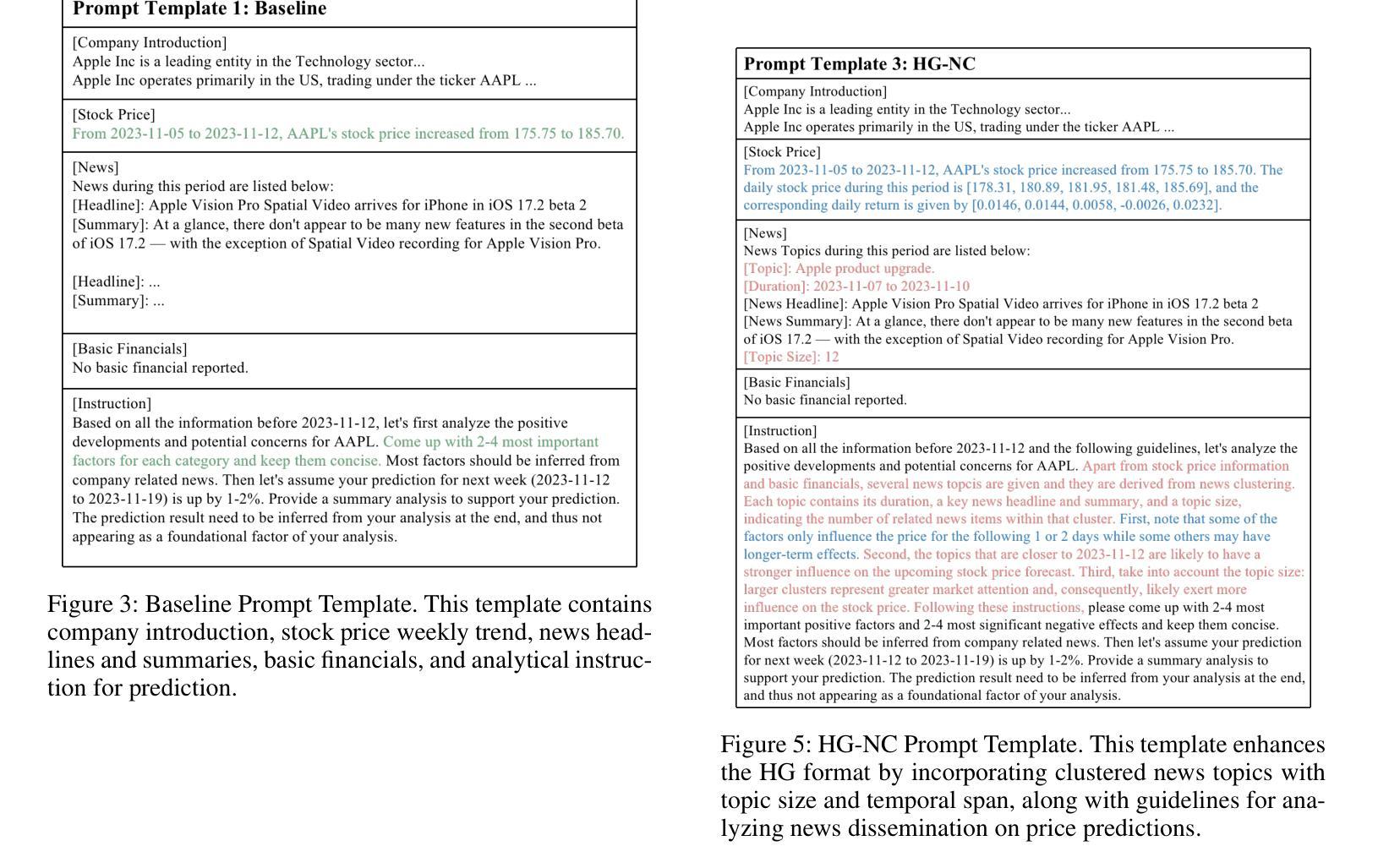
FinGPT: Enhancing Sentiment-Based Stock Movement Prediction with Dissemination-Aware and Context-Enriched LLMs
Authors:Yixuan Liang, Yuncong Liu, Neng Wang, Hongyang Yang, Boyu Zhang, Christina Dan Wang
Financial sentiment analysis is crucial for understanding the influence of news on stock prices. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have been widely adopted for this purpose due to their advanced text analysis capabilities. However, these models often only consider the news content itself, ignoring its dissemination, which hampers accurate prediction of short-term stock movements. Additionally, current methods often lack sufficient contextual data and explicit instructions in their prompts, limiting LLMs’ ability to interpret news. In this paper, we propose a data-driven approach that enhances LLM-powered sentiment-based stock movement predictions by incorporating news dissemination breadth, contextual data, and explicit instructions. We cluster recent company-related news to assess its reach and influence, enriching prompts with more specific data and precise instructions. This data is used to construct an instruction tuning dataset to fine-tune an LLM for predicting short-term stock price movements. Our experimental results show that our approach improves prediction accuracy by 8% compared to existing methods.
金融情感分析对于理解新闻对股票价格的影响至关重要。最近,由于大型语言模型(LLM)具有先进的文本分析能力,因此被广泛应用于此目的。然而,这些模型通常只考虑新闻内容本身,而忽略了其传播情况,这阻碍了短期股票走势的准确预测。此外,当前的方法往往缺乏足够的上下文数据和明确的指令提示,限制了LLM解释新闻的能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种数据驱动的方法,通过结合新闻传播的广度、上下文数据和明确的指令,提高了基于LLM的情感驱动股票走势预测。我们对最近的与公司相关的新闻进行聚类,以评估其传播范围和影响力,并为提示添加了更具体的数据和精确指令。这些数据用于构建指令微调数据集,以微调LLM,以预测短期股票价格走势。我们的实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,我们的方法将预测精度提高了8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 1st Workshop on Preparing Good Data for Generative AI: Challenges and Approaches@ AAAI 2025, ai4finance.org
摘要
金融情感分析对于理解新闻对股票价格的影响至关重要。大型语言模型(LLM)因其先进的文本分析能力而广泛应用于此目的。然而,这些模型通常只考虑新闻内容本身,忽略了新闻的传播情况,这阻碍了短期股票走势的准确预测。本文提出了一种数据驱动的方法,通过结合新闻的传播广度、上下文数据和明确指令,提高基于LLM的情感驱动股票走势预测能力。通过聚类与公司相关的新闻来评估其传播范围和影响力,使用更具体的数据和精确指令丰富提示。该数据用于构建指令微调数据集,微调LLM以预测短期股票价格走势。实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,该方法提高了8%的预测准确性。
要点
- 金融情感分析对于理解新闻对股票价格的影响非常重要。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在情感分析方面具有优势,但存在局限性。
- 现有LLM模型忽略了新闻的传播情况,限制了短期股票预测的准确性。
- 本文提出了一种数据驱动的方法,结合新闻的传播广度、上下文数据和明确指令,提高LLM在情感驱动股票预测方面的性能。
- 通过聚类公司相关新闻来评估其影响力和传播范围。
- 使用更丰富、更具体的数据和精确指令来丰富提示,构建指令微调数据集。
- 实验结果表明,该方法提高了短期股票预测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

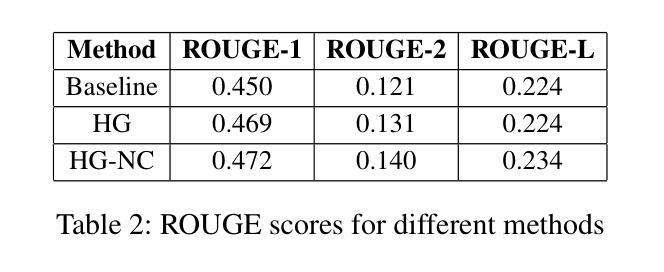

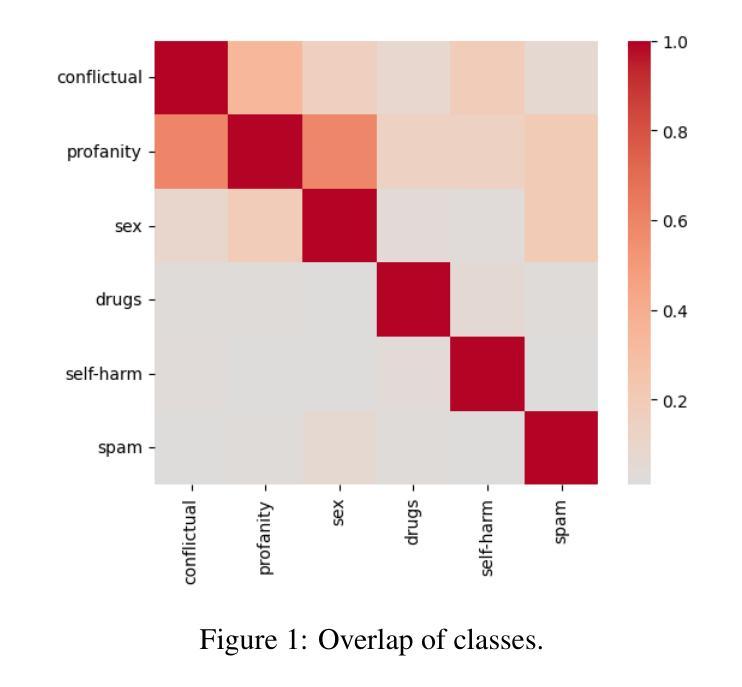
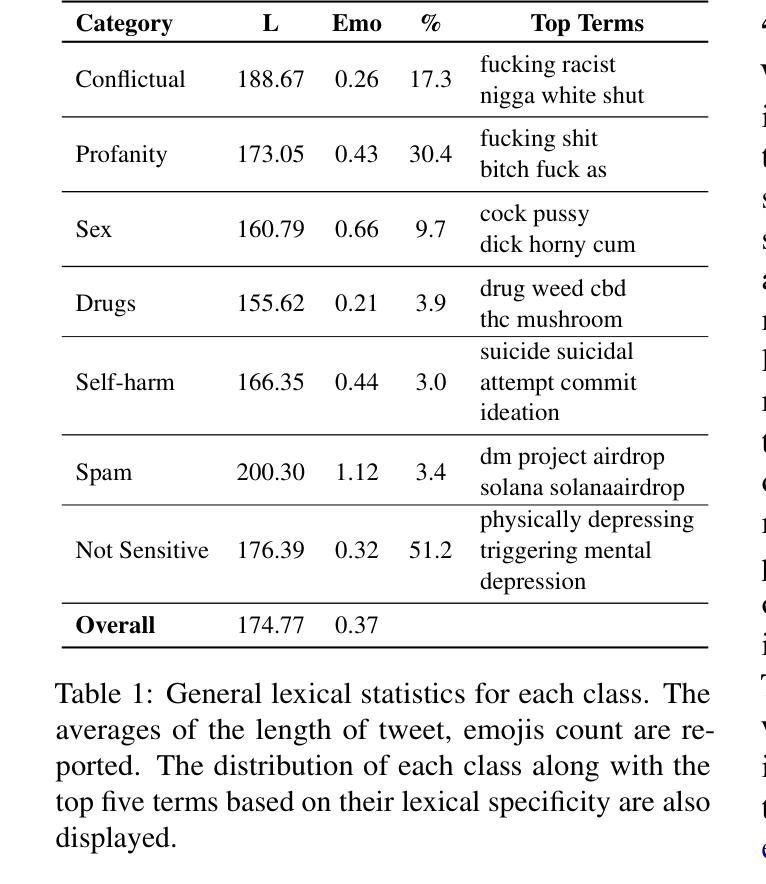
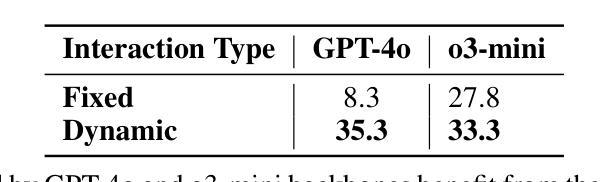
Sensitive Content Classification in Social Media: A Holistic Resource and Evaluation
Authors:Dimosthenis Antypas, Indira Sen, Carla Perez-Almendros, Jose Camacho-Collados, Francesco Barbieri
The detection of sensitive content in large datasets is crucial for ensuring that shared and analysed data is free from harmful material. However, current moderation tools, such as external APIs, suffer from limitations in customisation, accuracy across diverse sensitive categories, and privacy concerns. Additionally, existing datasets and open-source models focus predominantly on toxic language, leaving gaps in detecting other sensitive categories such as substance abuse or self-harm. In this paper, we put forward a unified dataset tailored for social media content moderation across six sensitive categories: conflictual language, profanity, sexually explicit material, drug-related content, self-harm, and spam. By collecting and annotating data with consistent retrieval strategies and guidelines, we address the shortcomings of previous focalised research. Our analysis demonstrates that fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on this novel dataset yields significant improvements in detection performance compared to open off-the-shelf models such as LLaMA, and even proprietary OpenAI models, which underperform by 10-15% overall. This limitation is even more pronounced on popular moderation APIs, which cannot be easily tailored to specific sensitive content categories, among others.
在大规模数据集中检测敏感内容对于确保共享和分析的数据不含有害材料至关重要。然而,当前的审核工具(如外部API)在定制方面存在局限性,对不同敏感类别的准确性也有问题,还引发隐私担忧。此外,现有的数据集和开源模型主要关注有毒语言,在检测其他敏感类别(如滥用物质或自残)方面存在空白。在本文中,我们提出了一个统一的数据集,专为社交媒体内容审核六个敏感类别而设计:冲突语言、粗俗语言、性明确材料、药物相关内容、自残和垃圾广告。我们通过采用一致的数据检索策略和指南来收集和注释数据,解决了以往研究中的不足。我们的分析表明,与市面上的模型(如LLaMA)和表现较差的专有OpenAI模型相比,使用此新型数据集微调大型语言模型(LLM)可显著提高检测性能。总体而言,专有模型的性能不及使用本数据集表现的模型的十分之一到十五分之一。这一局限在流行的审核API上尤其明显,这些API不能轻易针对特定敏感内容进行定制和调整等。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 9th Workshop on Online Abuse and Harms (WOAH)
Summary
在大型数据集中检测敏感内容对于确保共享和分析的数据不包含有害材料至关重要。当前使用的诸如外部API之类的审查工具存在定制化限制、对不同敏感类别的准确性问题以及隐私担忧等局限性。此外,现有数据集和开源模型主要集中在有毒语言上,在检测其他敏感类别(如滥用物质或自我伤害)方面存在空白。本文提出了一种针对社交媒体内容审查的统一数据集,涵盖六大敏感类别:冲突语言、粗鲁语言、性明确材料、与药物相关内容、自我伤害和垃圾邮件。通过采用一致的数据检索策略和标注指南,我们解决了以前聚焦研究的不足。分析表明,与现有的开源模型(如LLaMA)和表现不佳的专有OpenAI模型相比,对此新数据集进行微调的大型语言模型(LLM)在检测性能上有显著改善。这一差距在流行的审查API上尤为突出,这些API难以针对特定敏感类别进行定制。
Key Takeaways
- 检测大型数据集中的敏感内容对于避免共享和分析有害数据至关重要。
- 当前使用的审查工具存在局限性,如定制困难、准确性不足和隐私担忧。
- 现有数据集主要关注有毒语言检测,忽略了其他敏感类别,如滥用物质和自我伤害。
- 论文引入了一个统一数据集,涵盖六大敏感类别,适用于社交媒体内容审查。
- 通过一致的数据检索策略和标注指南,解决了以往研究的不足。
- 相较于现有开源模型和专有模型,微调的大型语言模型(LLM)在敏感内容检测方面表现出更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图