⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-27 更新
Weighted Mean Frequencies: a handcraft Fourier feature for 4D Flow MRI segmentation
Authors:Simon Perrin, Sébastien Levilly, Huajun Sun, Harold Mouchère, Jean-Michel Serfaty
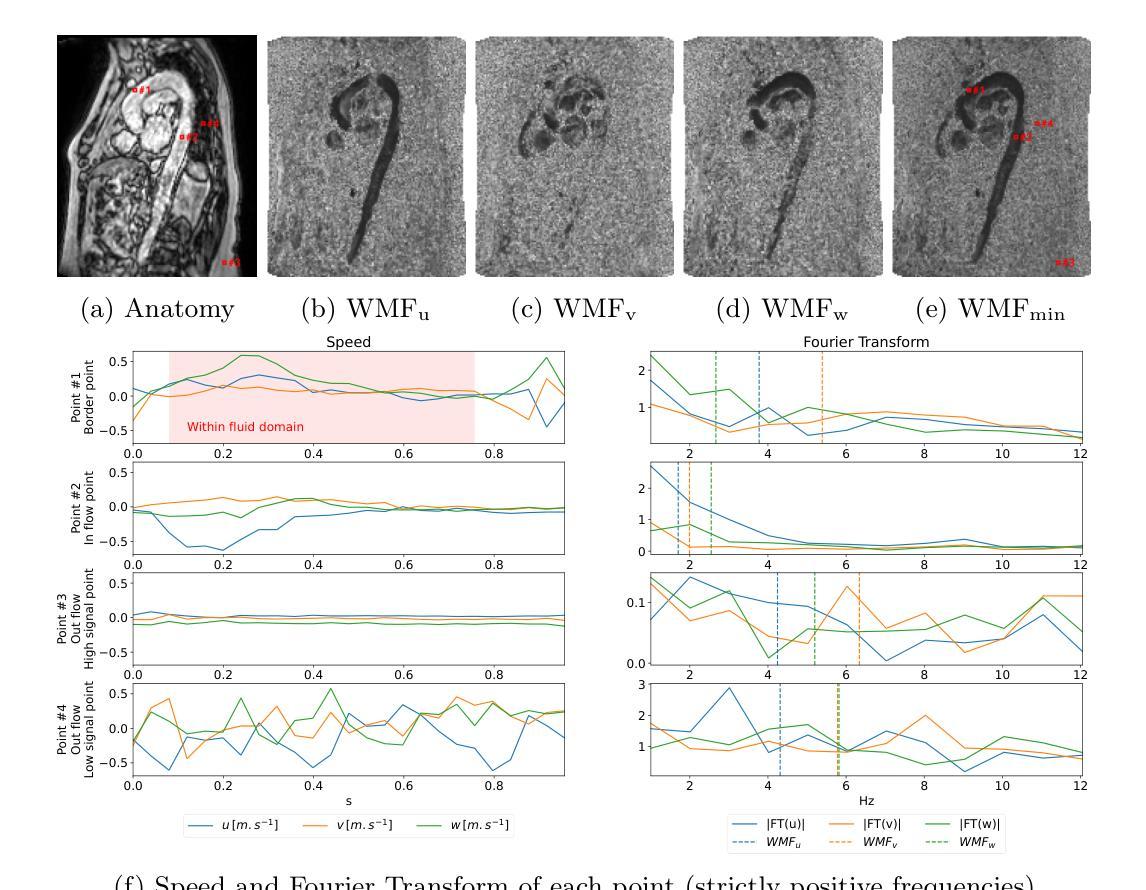
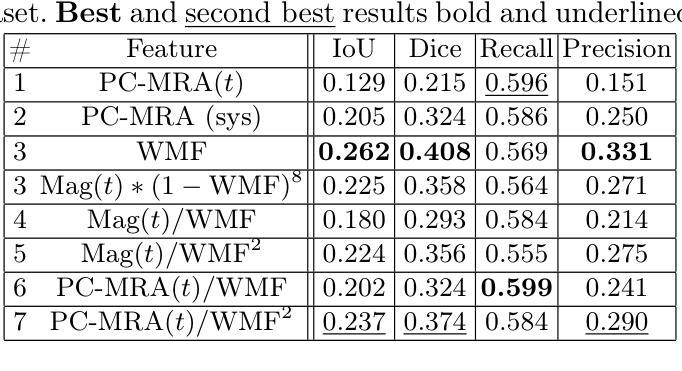
In recent decades, the use of 4D Flow MRI images has enabled the quantification of velocity fields within a volume of interest and along the cardiac cycle. However, the lack of resolution and the presence of noise in these biomarkers are significant issues. As indicated by recent studies, it appears that biomarkers such as wall shear stress are particularly impacted by the poor resolution of vessel segmentation. The Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Angiography (PC-MRA) is the state-of-the-art method to facilitate segmentation. The objective of this work is to introduce a new handcraft feature that provides a novel visualisation of 4D Flow MRI images, which is useful in the segmentation task. This feature, termed Weighted Mean Frequencies (WMF), is capable of revealing the region in three dimensions where a voxel has been passed by pulsatile flow. Indeed, this feature is representative of the hull of all pulsatile velocity voxels. The value of the feature under discussion is illustrated by two experiments. The experiments involved segmenting 4D Flow MRI images using optimal thresholding and deep learning methods. The results obtained demonstrate a substantial enhancement in terms of IoU and Dice, with a respective increase of 0.12 and 0.13 in comparison with the PC-MRA feature, as evidenced by the deep learning task. This feature has the potential to yield valuable insights that could inform future segmentation processes in other vascular regions, such as the heart or the brain.
近几十年来,四维流磁共振成像(4D Flow MRI)图像的使用,使我们能够量化感兴趣体积内的速度场以及心脏周期中的速度场。然而,这些生物标志物分辨率低和存在噪声是重要的问题。最近的研究表明,壁剪切应力等生物标志物受到血管分割分辨率差的影响尤为明显。相位对比磁共振血管造影(PC-MRA)是目前最先进的促进分割的方法。这项工作的目标是引入一种新的手工特征,为四维流磁共振成像图像提供一种新的可视化方法,这在分割任务中很有用。这种特征被称为加权平均频率(WMF),它能够揭示在三维区域中,哪些体素被脉动流所经过。实际上,这一特征代表了所有脉动速度体素的外壳。所讨论的特征通过两个实验来说明。这些实验包括使用最佳阈值法和深度学习方法对四维流磁共振成像图像进行分割。获得的结果在IoU和Dice方面有了显著的提升,与PC-MRA特征相比,分别增加了0.12和0.13,深度学习任务证明了这一点。这一特征有可能产生有价值的见解,可以为其他血管区域(如心脏或大脑)的分割过程提供信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了使用4D流MRI图像的一种新手工特征——加权平均频率(WMF),用于可视化血管区域脉动流情况,并在图像分割任务中有显著提高效果的表现。这种特征可以通过最佳阈值和深度学习方法进行分割实验,显示出相比PC-MRA特征在IoU和Dice指标上的优势。该特征有望在心血管和其他血管区域的分割过程中提供有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 4D Flow MRI图像可量化体积内的速度场以及心脏周期中的变化。
- 当前使用中存在分辨率低和噪声的问题,尤其是对于生物标志物如壁剪切应力影响较大。
- PC-MRA是目前最先进的促进分割的方法。
- 引入了一种新的手工特征——加权平均频率(WMF),用于可视化4D流MRI图像。
- WMF特征能揭示脉动流经过的的三维区域,代表所有脉动速度体素的包络。
- 实验结果显示,使用WMF特征进行分割任务时,IoU和Dice指标相比PC-MRA特征有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

AdvMIM: Adversarial Masked Image Modeling for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Lei Zhu, Jun Zhou, Rick Siow Mong Goh, Yong Liu
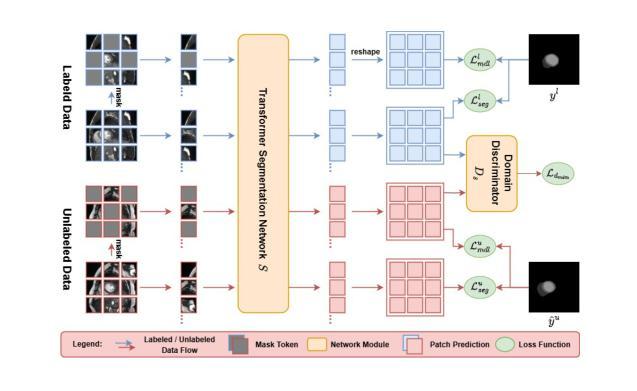
Vision Transformer has recently gained tremendous popularity in medical image segmentation task due to its superior capability in capturing long-range dependencies. However, transformer requires a large amount of labeled data to be effective, which hinders its applicability in annotation scarce semi-supervised learning scenario where only limited labeled data is available. State-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods propose combinatorial CNN-Transformer learning to cross teach a transformer with a convolutional neural network, which achieves promising results. However, it remains a challenging task to effectively train the transformer with limited labeled data. In this paper, we propose an adversarial masked image modeling method to fully unleash the potential of transformer for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. The key challenge in semi-supervised learning with transformer lies in the lack of sufficient supervision signal. To this end, we propose to construct an auxiliary masked domain from original domain with masked image modeling and train the transformer to predict the entire segmentation mask with masked inputs to increase supervision signal. We leverage the original labels from labeled data and pseudo-labels from unlabeled data to learn the masked domain. To further benefit the original domain from masked domain, we provide a theoretical analysis of our method from a multi-domain learning perspective and devise a novel adversarial training loss to reduce the domain gap between the original and masked domain, which boosts semi-supervised learning performance. We also extend adversarial masked image modeling to CNN network. Extensive experiments on three public medical image segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, where our method outperforms existing methods significantly. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/zlheui/AdvMIM.
近期,由于视觉Transformer在捕捉长距离依赖方面具有出色的能力,它在医学图像分割任务中获得了巨大的关注。然而,Transformer需要大量标注数据才能发挥其作用,这在标注稀缺的半监督学习场景中限制了其适用性,因为这里只有有限的标注数据可用。最先进的半监督学习方法提出了组合CNN-Transformer学习,通过交叉教学的方式将Transformer与卷积神经网络相结合,取得了有前景的结果。然而,在有限的标注数据下有效地训练Transformer仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们提出了一种对抗性掩模图像建模方法,以充分释放Transformer在半监督医学图像分割中的潜力。在半监督学习中使用Transformer的主要挑战在于缺乏足够的监督信号。为此,我们提出通过掩模图像建模从原始领域构建辅助掩模领域,并训练Transformer使用掩模输入预测整个分割掩模,以增加监督信号。我们利用来自标注数据的原始标签和来自未标注数据的伪标签来学习掩模领域。为了进一步从掩模领域受益,我们从多领域学习的角度对我们的方法进行了理论分析,并设计了一种新型对抗训练损失来减少原始领域和掩模领域之间的领域差距,这提高了半监督学习的性能。我们还扩展了对抗性掩模图像建模到CNN网络。在三个公共医学图像分割数据集上的广泛实验证明了我们方法的有效性,我们的方法在现有方法上表现优越。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/zlheui/AdvMIM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种对抗性掩膜图像建模方法,用于在有限标注数据的半监督医学图像分割中充分发挥Transformer的潜力。通过构建辅助掩膜域并使用掩膜输入预测整个分割掩膜来增加监督信号,同时使用标注数据和未标注数据的原始标签和伪标签来学习掩膜域。此外,从多域学习角度进行理论分析,并设计新型对抗训练损失来缩小原始域和掩膜域之间的域差距,从而提高半监督学习性能。在三个公开医学图像分割数据集上的实验证明该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer因捕捉长程依赖关系的能力在医学图像分割任务中受到广泛关注。
- 现有半监督学习方法尝试结合CNN和Transformer进行交叉教学,但仍面临在有限标注数据下有效训练Transformer的挑战。
- 本文提出对抗性掩膜图像建模方法,旨在释放Transformer在半监督医学图像分割中的潜力。
- 通过构建掩膜域并使用掩膜输入预测分割掩膜来增加监督信号,利用标注和未标注数据的标签进行学习。
- 从多域学习角度进行理论分析,并设计对抗训练损失来缩小原始域和掩膜域之间的差距。
- 该方法不仅适用于Transformer,还扩展至CNN网络。
点此查看论文截图

The Jet Origin of the Mid-infrared Excess in the Black Hole V404 Cygni in Quiescence
Authors:E. S. Borowski, R. I. Hynes, Q. Hunt, A. J. Tetarenko, R. M. Plotkin, T. Shahbaz, P. Gandhi, T. J. Maccarone, J. C. A. Miller-Jones, C. O. Heinke, A. W. Shaw, T. D. Russell, G. R. Sivakoff, P. A. Charles, E. V. Palaiologou, P. Reig
Observations of some quiescent black hole X-ray binaries have revealed an excess of mid-infrared (MIR) emission above that expected from their donor stars. In one system, V404 Cygni, this excess has been variously suggested to arise from the accretion disk, circumbinary material, or a compact relativistic jet. Here we present simultaneous James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), and complementary multi-wavelength observations undertaken to resolve this uncertainty. We observed large-amplitude 21 $\mu$m variability on short timescales with JWST, particularly a dramatic flare which swiftly rose to $\approx 2.4$ mJy, over 10 times the lowest observed MIR flux density. Similar variability was simultaneously observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths with other facilities throughout the campaign. This variability and the flat radio/mm/MIR spectral index ($\alpha = 0.04 \pm 0.01$) suggest that the MIR excess in V404 Cyg does not arise from the accretion disk or circumbinary material but is instead dominated by synchrotron radiation from a jet which persists into quiescence. This result reinforces the ubiquity of the disk-jet connection in accreting black holes across a range of masses and accretion rates.
对一些静止黑洞X射线双星的观测揭示了在供星体的预期之上的中度红外(MIR)发射过剩。在一个系统V404 Cygni中,这种过剩被认为可能来源于吸积盘、双星周围物质或紧凑相对论喷流。在这里,我们提供了詹姆斯·韦伯太空望远镜(JWST)、阿塔卡马大型毫米/亚毫米阵列(ALMA)以及补充的多波长观测数据,以解决这一不确定性。我们用JWST观察到了大范围的21微米短波时段的大幅度变化,特别是出现了急剧的耀斑,迅速上升至约2.4毫吉焦耳(mJy),这是观察到的最低中度红外通量密度的十倍以上。在此次活动中,其他设施从无线电到X射线的波长也同步观察到类似的变动。这种变动和无线电/毫米/中度红外光谱指数平坦(α=0.04±0.01)表明,V404 Cygnus中的中度红外过剩并非来自吸积盘或双星周围物质,而是主要由喷流产生的同步辐射主导,且在静止期仍然存在。这一结果再次证实了星盘连接在多种质量和吸积率下的吸积黑洞中的普遍存在。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted June 25, 2025. Comments welcome
Summary
该文观测了静止黑洞X射线双星中的V404 Cygni系统,发现其中存在超出预期的红外辐射。通过詹姆斯韦伯太空望远镜(JWST)、阿塔卡马大型毫米波/亚毫米波阵列(ALMA)和其他设施的同步多波长观测,发现其存在大幅度的中红外波段(MIR)快速变化现象,如剧烈闪光等。结合其频谱指数分析,认为红外辐射超出部分并非来自吸积盘或环绕双星的物质,而是由静止状态下持续存在的喷射流产生的同步辐射主导。这一结果再次证实了在不同质量和吸积率的黑洞中,盘-喷流连接的普遍性。
Key Takeaways
- V404 Cygni系统的静止黑洞X射线双星观测中发现了超出预期的红外辐射。
- 通过JWST和ALMA的同步观测,发现系统存在大幅度中红外波段快速变化现象。
- 红外辐射超出部分并非来自吸积盘或环绕双星的物质。
- 红外辐射超出部分主要由静止状态下持续存在的喷射流产生的同步辐射主导。
- 这一结果揭示了盘-喷流连接的普遍性,对理解黑洞的物理特性有重要意义。
- 同时观察到从射电到X射线的多波长变化,表明这种变化可能与喷流活动有关。
点此查看论文截图

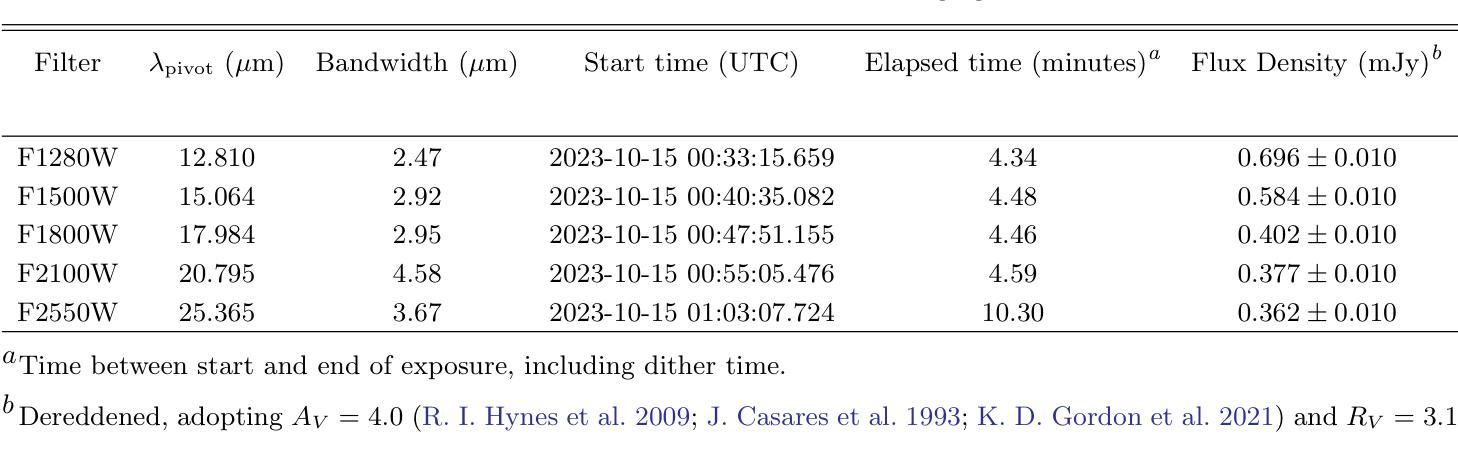
Fusing Radiomic Features with Deep Representations for Gestational Age Estimation in Fetal Ultrasound Images
Authors:Fangyijie Wang, Yuan Liang, Sourav Bhattacharjee, Abey Campbell, Kathleen M. Curran, Guénolé Silvestre
Accurate gestational age (GA) estimation, ideally through fetal ultrasound measurement, is a crucial aspect of providing excellent antenatal care. However, deriving GA from manual fetal biometric measurements depends on the operator and is time-consuming. Hence, automatic computer-assisted methods are demanded in clinical practice. In this paper, we present a novel feature fusion framework to estimate GA using fetal ultrasound images without any measurement information. We adopt a deep learning model to extract deep representations from ultrasound images. We extract radiomic features to reveal patterns and characteristics of fetal brain growth. To harness the interpretability of radiomics in medical imaging analysis, we estimate GA by fusing radiomic features and deep representations. Our framework estimates GA with a mean absolute error of 8.0 days across three trimesters, outperforming current machine learning-based methods at these gestational ages. Experimental results demonstrate the robustness of our framework across different populations in diverse geographical regions. Our code is publicly available on \href{https://github.com/13204942/RadiomicsImageFusion_FetalUS}{GitHub}.
准确估计胎龄(GA)是提供优秀产前护理的关键方面,理想情况下,可通过胎儿超声波测量来实现。然而,从手动胎儿生物测量中得出胎龄取决于操作人员,并且很耗时。因此,临床实践要求使用计算机辅助的自动方法。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的特征融合框架,该框架使用胎儿超声图像无需任何测量信息即可估计胎龄。我们采用深度学习模型从超声图像中提取深度表示。我们提取放射学特征以揭示胎儿大脑生长的模式和特征。为了利用放射组学在医学成像分析中的解释性,我们通过融合放射学特征和深度表示来估计胎龄。我们的框架估计胎龄的平均绝对误差为8天,跨越三个孕期。与当前基于机器学习的方法相比,我们在这些胎龄方面的表现更胜一筹。实验结果表明,我们的框架在不同地理区域的不同人群中具有很强的稳健性。我们的代码已在GitHub上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于深度学习模型的新型特征融合框架,用于从胎儿超声图像估计孕龄(GA),无需手动测量信息。研究通过融合超声图像的深度特征和放射学特征(radiomic features)估计GA,提高了估计的准确性和可解释性。该框架在不同孕期和不同地理区域的人群中均表现出稳健性,平均绝对误差为8天。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究使用深度学习模型对胎儿超声图像进行自动分析以估算孕龄。
- 研究提出了特征融合框架,结合了超声图像的深度特征和放射学特征。
- 通过融合这两种特征,研究提高了估计孕龄的准确性和可解释性。
- 该框架在多个孕期和不同地理区域的人群中进行了测试,表现出了稳健性。
- 与现有的机器学习方法相比,该框架在估算孕龄方面表现出了更好的性能。
- 研究结果通过公共代码库(GitHub)共享,以便进一步的研究和使用。
点此查看论文截图

In-flight calibration of the Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy
Authors:Huaqing Cheng, Hai-Wu Pan, Yuan Liu, Jingwei Hu, Haonan Yang, Donghua Zhao, Zhixing Ling, He-Yang Liu, Yifan Chen, Xiaojin Sun, Longhui Li, Ge Jin, Chen Zhang, Shuang-Nan Zhang, Weimin Yuan
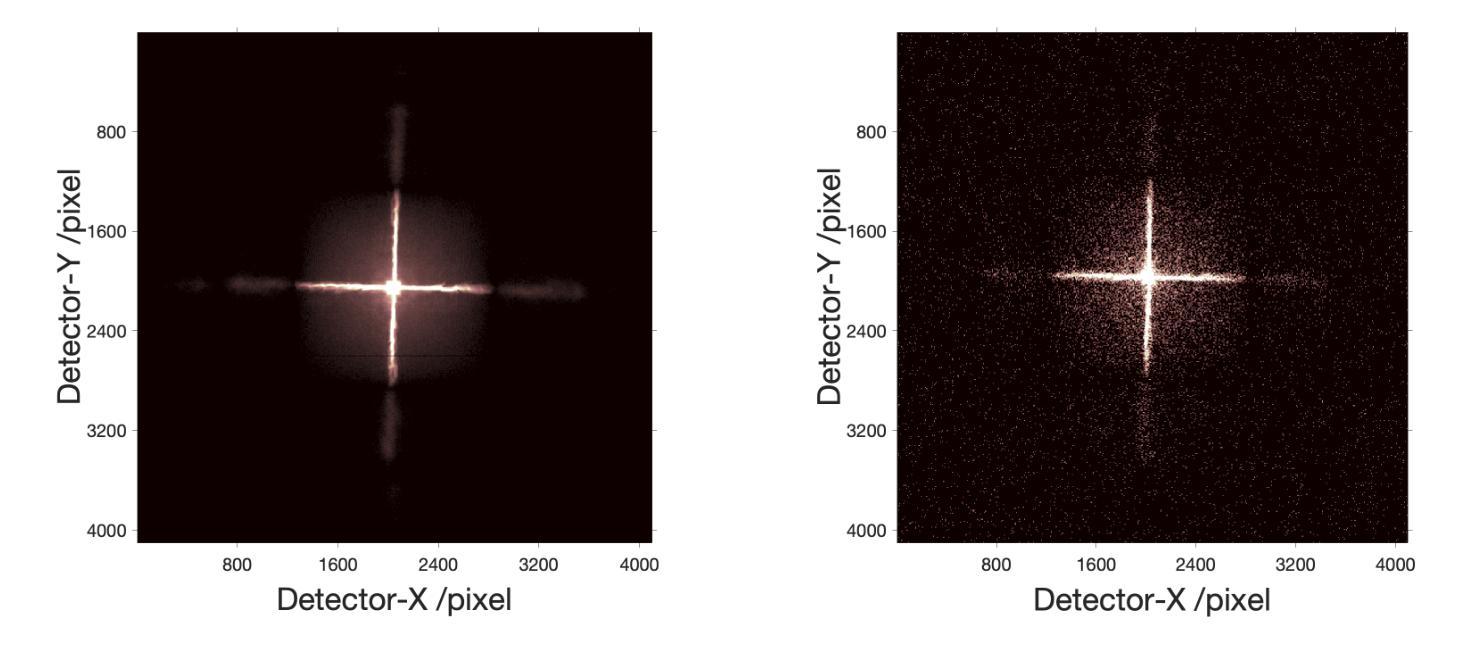
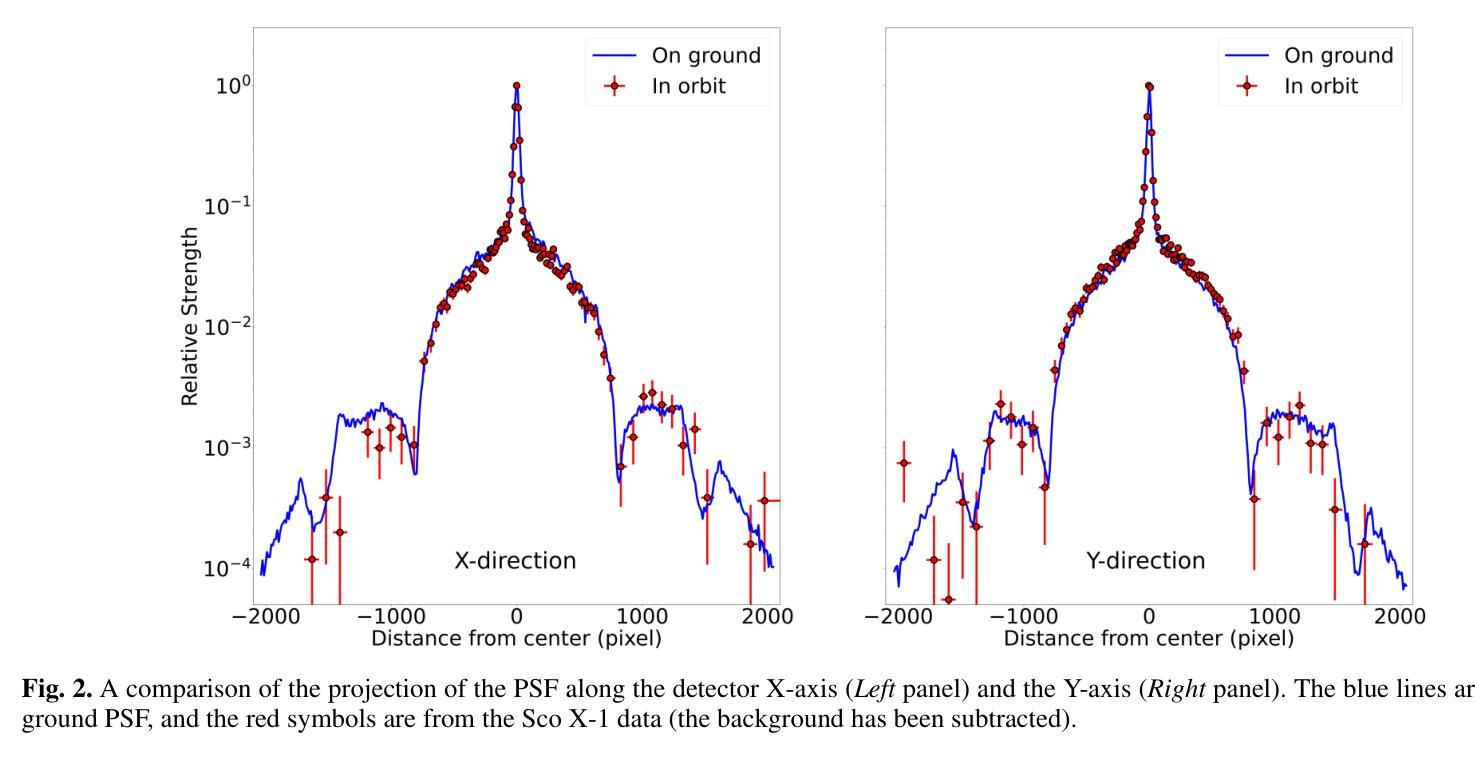
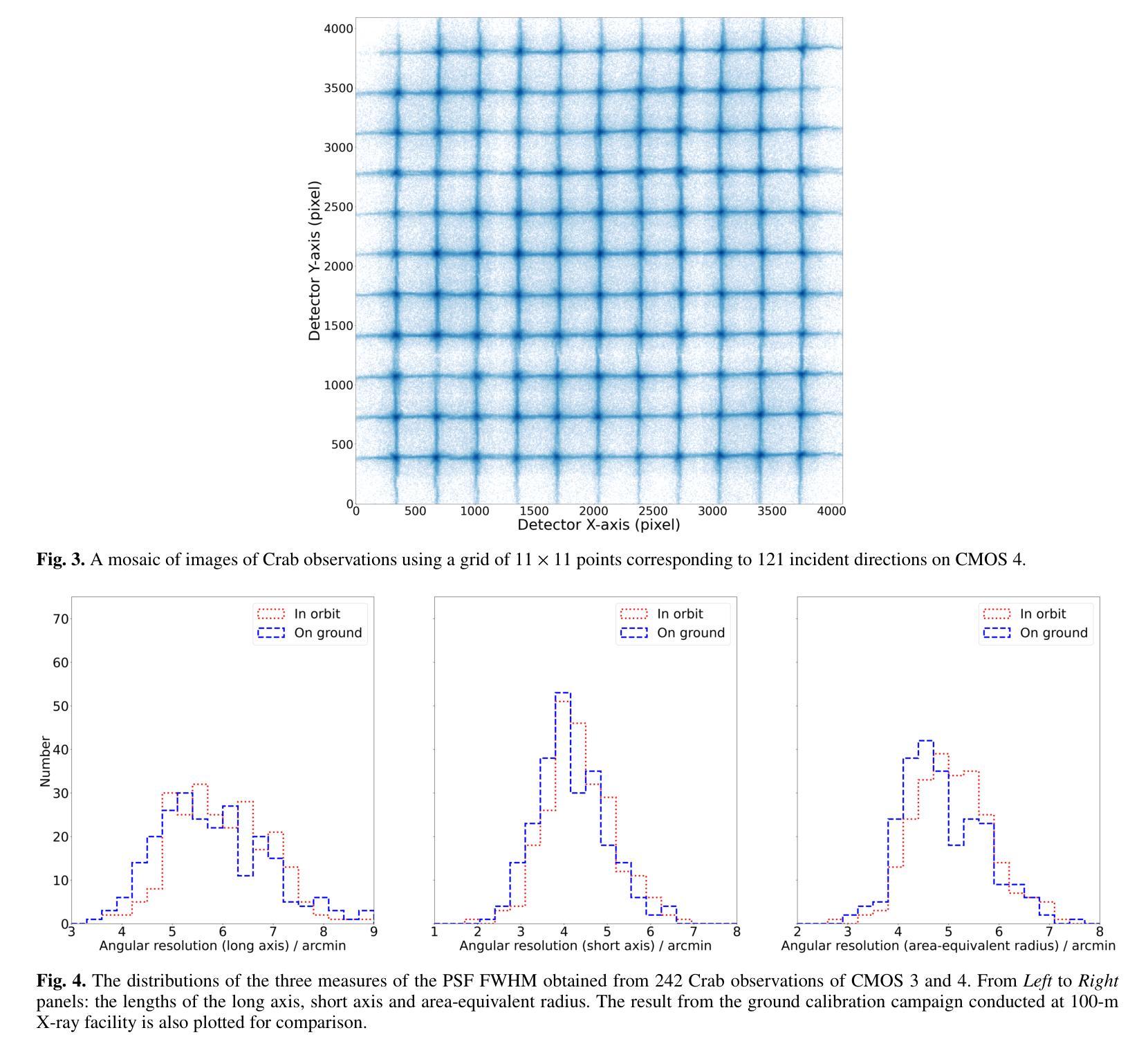
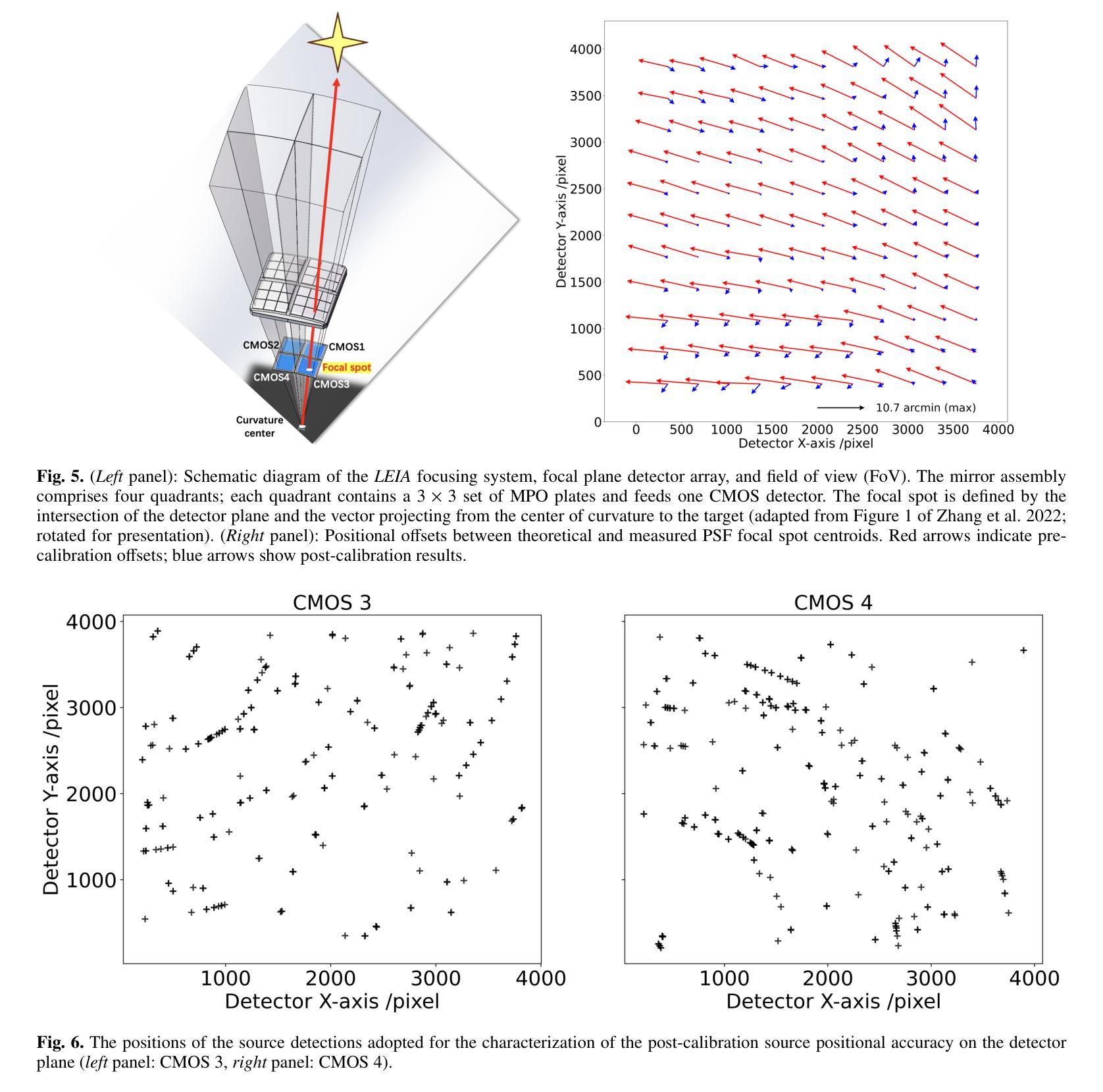
The Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy (LEIA), as a pathfinder of the Wide-field X-ray Telescope (WXT) onboard the Einstein Probe (EP) satellite, is the first lobster-eye focusing X-ray telescope with a considerably large field-of-view (FoV) ever flown. During the two and half years of operations, a series of calibration observations were performed, to fully characterize its performance and calibrate the instrumental properties. In this paper, we present the results of the in-flight calibration campaign of LEIA, focusing on the properties of the PSF, source positional accuracy, effective area, energy response and the instrumental background. The calibration sources used are the Crab nebula, Sco X-1 and Cassiopeia A supernova remnant. Specifically, it is found that the spatial resolution remains almost unchanged compared to the pre-launch values, ranging from 3.6’-9.3’ with a median of 5.9’. The post-calibration source positional accuracy is found to be ~2’ (at the 90% C.L.). The Crab spectra can be well reproduced by the absorbed power-law model with the best-fit parameters in large agreement with the literature values, indicating that the in-orbit effective area is overall consistent with the model predictions and ground measurements. The effective area exhibits a systematic of $\lesssim10%$ (at the 68% C.L.), and a mild deterioration of ~15% at the lower energy end after one year of operation. The Cas A spectral analysis shows that the energy scale and spectral resolution of the detectors are generally consistent with ground values. The instrumental background is found to be largely consistent among the four detectors, with strong modulations by the geomagnetic activity and the spectrum qualitatively consistent with our previous simulations. These instrumental performances well meet the design requirements. This work paves the way for the in-orbit calibration of the EP-WXT.
龙虾眼天文学成像仪(LEIA)作为搭载在爱因斯坦探测器(EP)卫星上的广角X射线望远镜(WXT)的探路者,是迄今为止飞行过的具有相当大视场(FoV)的首个龙虾眼聚焦X射线望远镜。在两年半的运行过程中,进行了一系列校准观测,以充分表征其性能并校准仪器属性。本文重点介绍了LEIA的飞行校准活动结果,主要集中在点扩散函数(PSF)的特性、源定位精度、有效面积、能量响应和仪器背景等方面。使用的校准源包括蟹状星云、天蝎座X-1和仙后座A超新星遗迹。具体来说,与发射前的值相比,空间分辨率几乎没有变化,范围从3.6’-9.3’,中位数为5.9’。经校准后的源定位精度约为2’(在90%置信水平下)。蟹状星云光谱能够被吸收功率法模型很好地复现,最佳拟合参数与文献值高度一致,表明在轨有效面积总体上与模型预测和地面测量结果一致。有效面积的系统性小于等于10%(在68%置信水平下),运行一年后在较低能量端有约15%的轻微恶化。Cas A光谱分析表明,探测器的能量尺度和光谱分辨率与地面值大体一致。仪器背景在四个探测器之间大体一致,受地磁活动的强烈调制,且光谱与我们之前的模拟定性一致。这些仪器性能均符合设计要求。这项工作为EP-WXT的飞行校准铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 14 figures, 2 tables. Submitted to Astronomy & Astrophysics
摘要
LEIA作为搭载在爱因斯坦探测器卫星上的宽视场X射线望远镜(WXT)的探路者,是首款具有超大视场(FoV)的龙虾眼聚焦X射线望远镜。经过两年半的运行,进行了一系列校准观测,以充分表征其性能并校准仪器属性。本文重点介绍LEIA的飞行校准结果,涉及点扩散函数性质、源定位精度、有效面积、能量响应和仪器背景等属性。使用蟹状星云、Sco X-1和仙后座A超新星遗迹作为校准源。特别是,发现空间分辨率与发射前的数值几乎保持一致,范围在3.6’-9.3’,中位数为5.9’。源定位精度约为2’(在90%置信水平下)。蟹谱可以通过吸收幂律模型很好地重现,最佳拟合参数与文献值高度一致,表明轨道有效面积与模型预测和地面测量结果总体一致。有效区域表现出系统误差小于等于的百分比(在68%置信水平下),经过一年的运行后,在较低能量端出现约15%的轻微恶化。Cas A光谱分析表明,探测器的能量尺度和光谱分辨率与地面值基本一致。仪器背景在四个探测器之间大体一致,受地磁活动的影响有强调制作用,并且光谱与前模拟定性一致。这些仪器性能均达到设计要求。此项工作为后续爱因斯坦探测器卫星的WXT的在轨校准铺平了道路。
要点提炼
- LEIA作为搭载在爱因斯坦探测器卫星上的宽视场X射线望远镜的探路者,是首款具有超大视场的龙虾眼聚焦X射线望远镜。
- 在两年半的运行期间,进行了涵盖多个属性的飞行校准观测。
- 空间分辨率与发射前数值保持一致。
- 源定位精度约为2’。
- 蟹谱可以通过吸收幂律模型很好地重现,有效面积与模型预测和地面测量结果一致。
- 有效区域存在系统误差小于等于的百分比变化,且在较低能量端存在轻微恶化。
点此查看论文截图

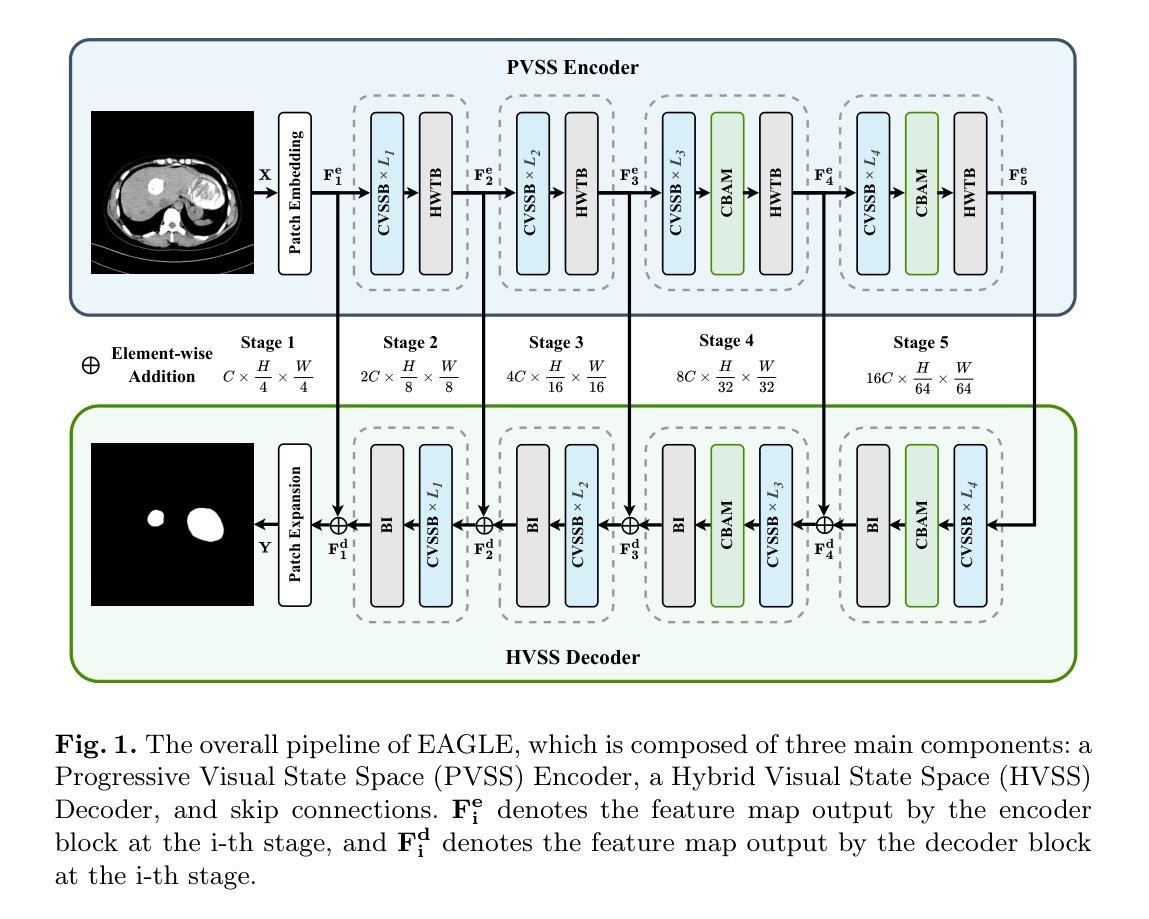
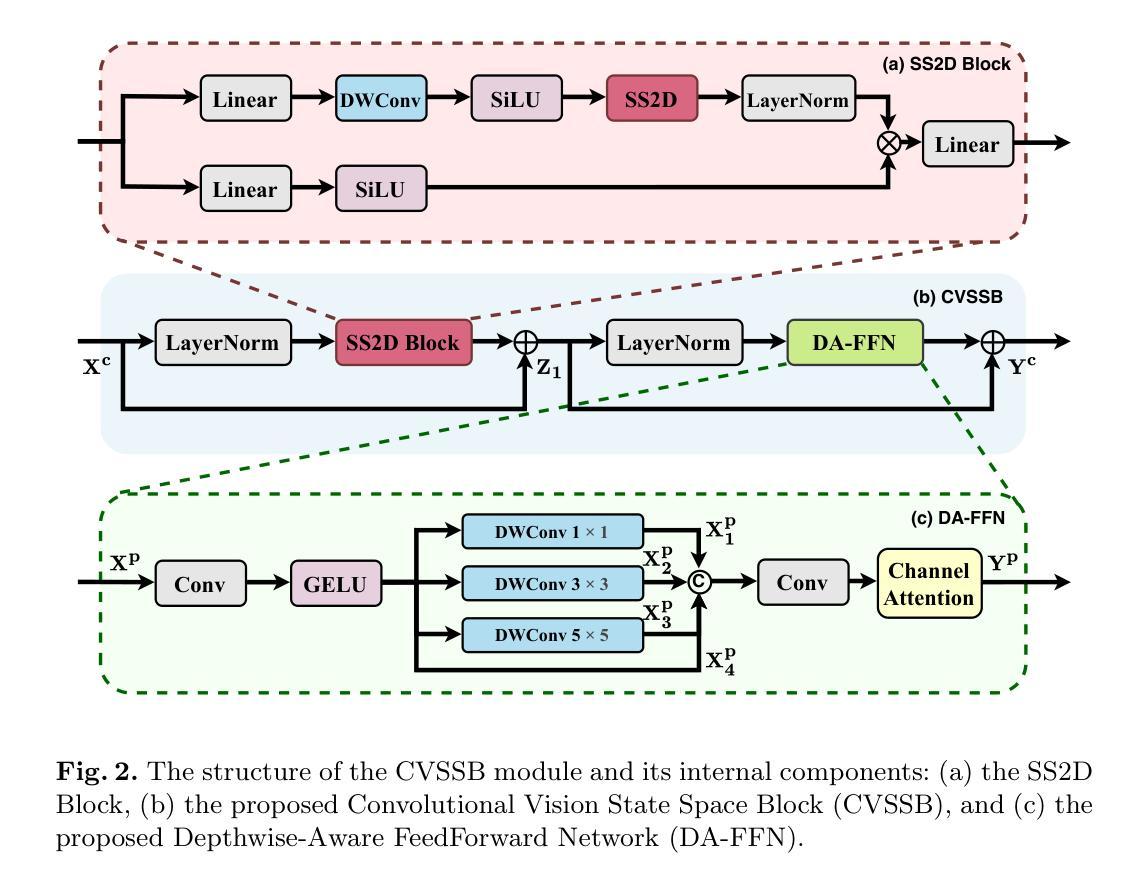
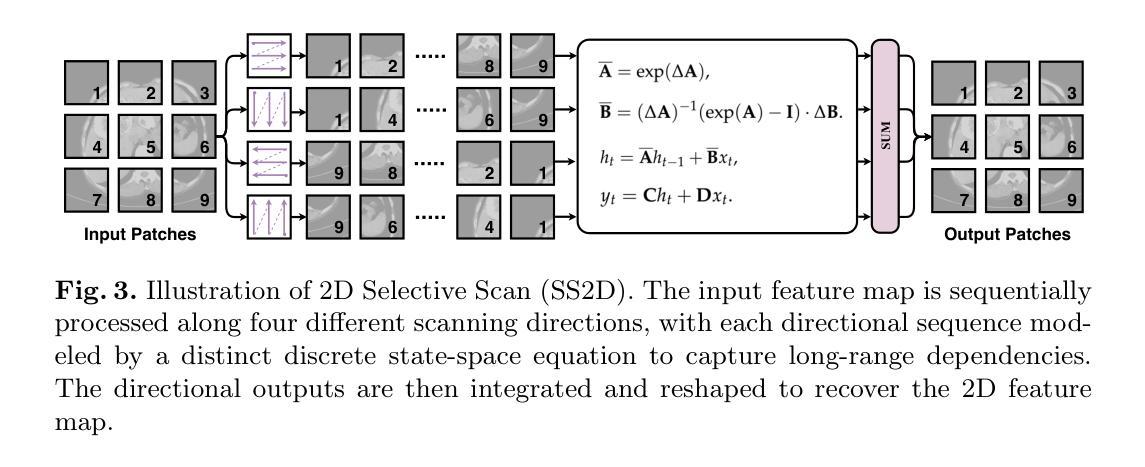
EAGLE: An Efficient Global Attention Lesion Segmentation Model for Hepatic Echinococcosis
Authors:Jiayan Chen, Kai Li, Yulu Zhao, Jianqiang Huang, Zhan Wang
Hepatic echinococcosis (HE) is a widespread parasitic disease in underdeveloped pastoral areas with limited medical resources. While CNN-based and Transformer-based models have been widely applied to medical image segmentation, CNNs lack global context modeling due to local receptive fields, and Transformers, though capable of capturing long-range dependencies, are computationally expensive. Recently, state space models (SSMs), such as Mamba, have gained attention for their ability to model long sequences with linear complexity. In this paper, we propose EAGLE, a U-shaped network composed of a Progressive Visual State Space (PVSS) encoder and a Hybrid Visual State Space (HVSS) decoder that work collaboratively to achieve efficient and accurate segmentation of hepatic echinococcosis (HE) lesions. The proposed Convolutional Vision State Space Block (CVSSB) module is designed to fuse local and global features, while the Haar Wavelet Transformation Block (HWTB) module compresses spatial information into the channel dimension to enable lossless downsampling. Due to the lack of publicly available HE datasets, we collected CT slices from 260 patients at a local hospital. Experimental results show that EAGLE achieves state-of-the-art performance with a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 89.76%, surpassing MSVM-UNet by 1.61%.
肝棘球虫病(HE)是一种在医疗资源有限的欠发达牧区广泛流行的寄生虫病。虽然基于CNN的模型和基于Transformer的模型已广泛应用于医学图像分割,但CNN由于局部感受野而缺乏全局上下文建模,而Transformer虽然能够捕捉长距离依赖关系,但计算成本较高。最近,状态空间模型(SSMs),如Mamba等,因其以线性复杂度对长序列进行建模的能力而受到关注。在本文中,我们提出了名为EAGLE的U形网络,它由渐进视觉状态空间(PVSS)编码器和混合视觉状态空间(HVSS)解码器组成,它们协同工作,实现对肝棘球虫病(HE)病变的高效且准确分割。所提出的卷积视觉状态空间块(CVSSB)模块旨在融合局部和全局特征,而Haar小波变换块(HWTB)模块将空间信息压缩到通道维度,以实现无损下采样。由于缺乏公开的HE数据集,我们从当地医院收集了260名患者的CT切片。实验结果表明,EAGLE达到了先进性能,Dice相似系数(DSC)为89.76%,比MSVM-UNet高出1.61%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于状态空间模型(SSM)的U型网络结构EAGLE,用于高效且准确地分割肝棘球蚴病(HE)病灶。该网络结合了渐进视觉状态空间(PVSS)编码器和混合视觉状态空间(HVSS)解码器,并设计了卷积视觉状态空间块(CVSSB)和Haar小波变换块(HWTB),以融合局部和全局特征,同时实现无损降采样。在缺乏公开可用的HE数据集的情况下,实验结果显示EAGLE达到了先进的性能水平,Dice相似系数(DSC)为89.76%,超越了MSVM-UNet。
Key Takeaways
- 肝棘球蚴病(HE)是一种在医疗资源有限的欠发达牧区广泛流行的寄生虫病。
- CNN和Transformer模型在医学图像分割中有广泛应用,但CNN缺乏全局上下文建模,而Transformer虽然能捕捉长距离依赖关系但计算成本较高。
- 状态空间模型(SSM)如Mamba因其对长序列的线性复杂度建模能力而受到关注。
- 本文提出了EAGLE网络,结合PVSS编码器和HVSS解码器实现高效和准确的肝棘球蚴病(HE)病灶分割。
- 提出的CVSSB模块旨在融合局部和全局特征,而HWTB模块则能将空间信息压缩到通道维度以实现无损降采样。
- 收集了来自当地医院的260名患者的CT切片作为数据集。
点此查看论文截图

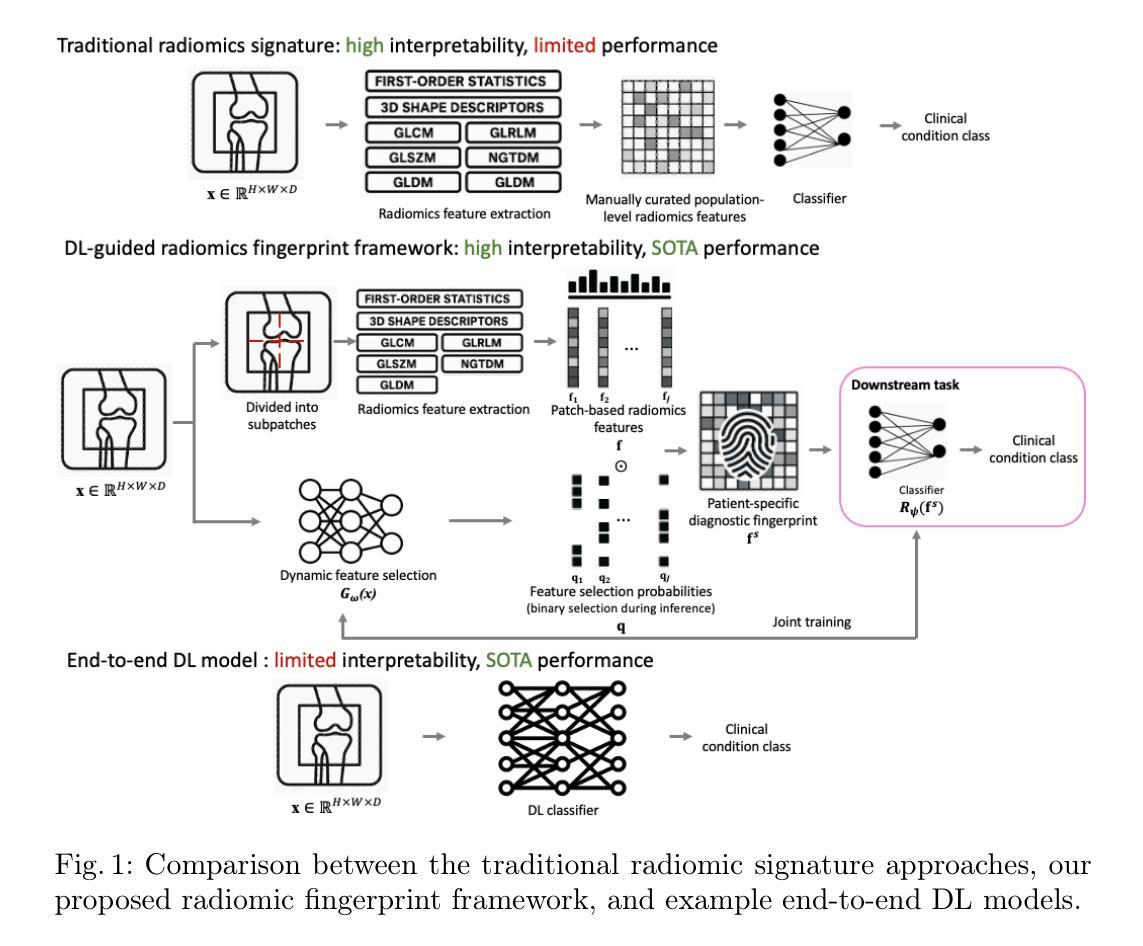
Radiomic fingerprints for knee MR images assessment
Authors:Yaxi Chen, Simin Ni, Shaheer U. Saeed, Aleksandra Ivanova, Rikin Hargunani, Jie Huang, Chaozong Liu, Yipeng Hu
Accurate interpretation of knee MRI scans relies on expert clinical judgment, often with high variability and limited scalability. Existing radiomic approaches use a fixed set of radiomic features (the signature), selected at the population level and applied uniformly to all patients. While interpretable, these signatures are often too constrained to represent individual pathological variations. As a result, conventional radiomic-based approaches are found to be limited in performance, compared with recent end-to-end deep learning (DL) alternatives without using interpretable radiomic features. We argue that the individual-agnostic nature in current radiomic selection is not central to its intepretability, but is responsible for the poor generalization in our application. Here, we propose a novel radiomic fingerprint framework, in which a radiomic feature set (the fingerprint) is dynamically constructed for each patient, selected by a DL model. Unlike the existing radiomic signatures, our fingerprints are derived on a per-patient basis by predicting the feature relevance in a large radiomic feature pool, and selecting only those that are predictive of clinical conditions for individual patients. The radiomic-selecting model is trained simultaneously with a low-dimensional (considered relatively explainable) logistic regression for downstream classification. We validate our methods across multiple diagnostic tasks including general knee abnormalities, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, and meniscus tears, demonstrating comparable or superior diagnostic accuracy relative to state-of-the-art end-to-end DL models. More importantly, we show that the interpretability inherent in our approach facilitates meaningful clinical insights and potential biomarker discovery, with detailed discussion, quantitative and qualitative analysis of real-world clinical cases to evidence these advantages.
准确的膝关节MRI扫描解读依赖于专业医生的临床判断,但往往存在较大的差异性和有限的扩展性。现有的放射组学方法使用一组固定的放射组学特征(签名),在人群层面进行选择并统一应用于所有患者。虽然这些签名是可解释的,但它们通常过于受限,无法代表个体的病理变化。因此,与传统的基于放射组学的方法相比,最近出现的端到端的深度学习(DL)替代方案在不使用可解释的放射组学特征的情况下,表现出更好的性能。我们认为,当前放射组学选择中的个体无关性并不是其解释性的关键,而是我们应用中推广能力差的原因。在这里,我们提出了一种新型的放射组学指纹框架,其中针对每个患者动态构建放射组学特征集(指纹),并由深度学习模型进行选择。与传统的放射组学签名不同,我们的指纹是基于每个患者的基础派生的,通过在大规模的放射组学特征池中预测特征相关性,并仅选择那些能够预测个体患者的临床状况的特征。放射组学选择模型是与低维度(被认为是相对可解释的)逻辑回归同时训练的,用于下游分类。我们的方法在多个诊断任务中进行了验证,包括膝关节异常、前交叉韧带撕裂和半月板撕裂等。与最先进的端到端深度学习模型相比,我们的诊断准确性相当或更高。更重要的是,我们展示了我们的方法所固有的可解释性,有助于获得有意义的临床见解和潜在的生物标志物发现。通过对真实世界病例的详细讨论、定量和定性分析,我们证明了这些优势。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
膝盖MRI扫描的准确解读依赖于专家临床判断,但存在高度可变性和有限的可扩展性。现有放射组学方法使用固定的一组放射组学特征(签名),在人群层面选择并统一应用于所有患者。尽管这些签名具有可解释性,但它们通常过于受限,无法代表个人的病理变化。因此,与最近的端到端深度学习(DL)替代方案相比,传统基于放射组学的方法在性能上表现有限。本文提出了一种新的放射组学指纹框架,其中针对每个患者动态构建放射组学特征集(指纹),并由DL模型选择。与传统的放射组学签名不同,我们的指纹是根据患者个人情况从大量的放射组学特征池中预测特征相关性而得出的,仅选择那些对临床状况具有预测性的特征。放射组学选择模型与低维度(相对可解释)逻辑回归同时进行训练,用于下游分类。我们在多个诊断任务中验证了我们的方法,包括一般膝盖异常、前交叉韧带撕裂和半月板撕裂等,表现出与最先进的端到端DL模型相当的或更高的诊断准确性。更重要的是,我们展示了该方法所固有的可解释性,有助于有意义的临床见解和潜在的生物标志物发现。
关键见解
- 现有膝盖MRI解读依赖专家临床判断,存在高变性和有限可扩展性。
- 传统放射组学方法使用固定特征集,难以代表个体病理变化。
- 深度学习在膝盖MRI解读中有潜力,但缺乏可解释性。
- 提出新的放射组学指纹框架,针对每个患者动态构建特征集。
- 通过预测特征相关性选择放射组学指纹,提高诊断准确性。
- 结合低维度逻辑回归进行下游分类,增加模型的可解释性。
- 在多个诊断任务中验证方法的有效性,包括膝盖异常、ACL和半月板撕裂等。
点此查看论文截图

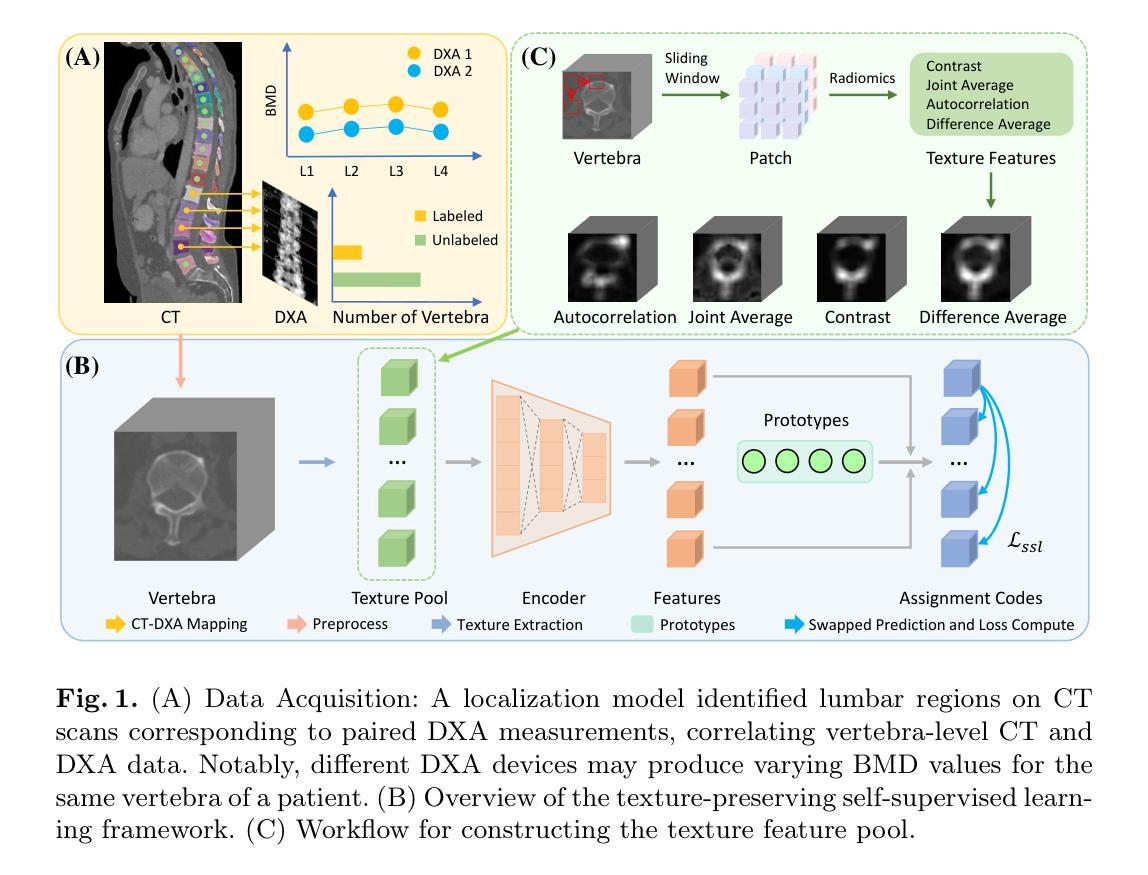
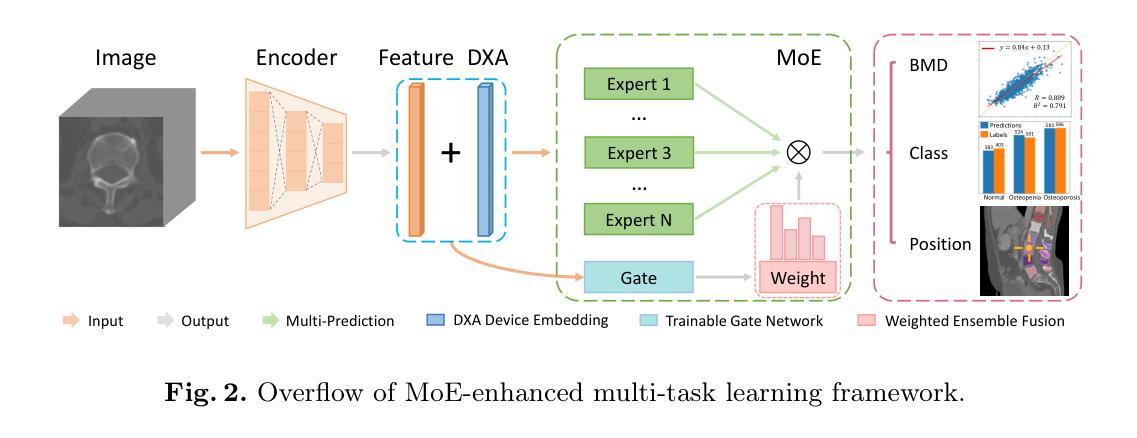
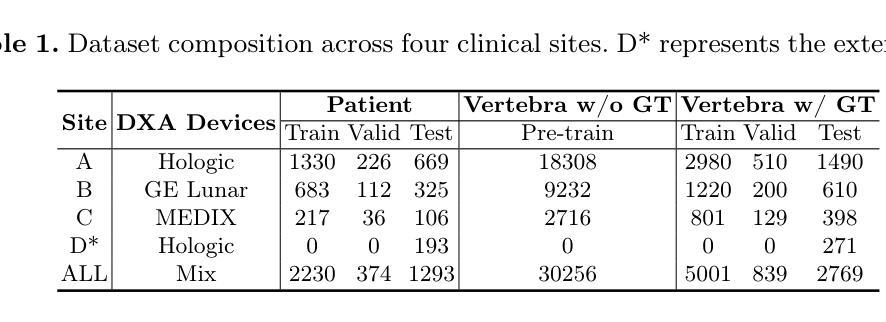
Opportunistic Osteoporosis Diagnosis via Texture-Preserving Self-Supervision, Mixture of Experts and Multi-Task Integration
Authors:Jiaxing Huang, Heng Guo, Le Lu, Fan Yang, Minfeng Xu, Ge Yang, Wei Luo
Osteoporosis, characterized by reduced bone mineral density (BMD) and compromised bone microstructure, increases fracture risk in aging populations. While dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the clinical standard for BMD assessment, its limited accessibility hinders diagnosis in resource-limited regions. Opportunistic computed tomography (CT) analysis has emerged as a promising alternative for osteoporosis diagnosis using existing imaging data. Current approaches, however, face three limitations: (1) underutilization of unlabeled vertebral data, (2) systematic bias from device-specific DXA discrepancies, and (3) insufficient integration of clinical knowledge such as spatial BMD distribution patterns. To address these, we propose a unified deep learning framework with three innovations. First, a self-supervised learning method using radiomic representations to leverage unlabeled CT data and preserve bone texture. Second, a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture with learned gating mechanisms to enhance cross-device adaptability. Third, a multi-task learning framework integrating osteoporosis diagnosis, BMD regression, and vertebra location prediction. Validated across three clinical sites and an external hospital, our approach demonstrates superior generalizability and accuracy over existing methods for opportunistic osteoporosis screening and diagnosis.
骨质疏松症的特点是骨矿物质密度(BMD)降低和骨微观结构受损,增加了老年人群骨折的风险。虽然双能X射线吸收法(DXA)是BMD评估的临床标准,但其有限的可及性阻碍了资源有限地区的诊断。利用现有成像数据进行计算机断层扫描(CT)分析的机遇性CT分析已成为诊断骨质疏松症的颇具前景的替代方法。然而,当前的方法面临三个局限性:(1)未充分利用未标记的椎体数据,(2)特定设备DXA差异导致的系统性偏见,(3)对临床知识的整合不足,如空间BMD分布模式。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一个统一的深度学习框架,其中包含三项创新。首先,使用放射学表现进行自监督学习方法,以利用未标记的CT数据并保持骨纹理。其次,使用带有学习门控机制的专家混合(MoE)架构,以提高跨设备适应性。第三,一个多任务学习框架,将骨质疏松症诊断、BMD回归和椎体位置预测相结合。经过三个临床站点和外部医院的验证,我们的方法在机会性骨质疏松症筛查和诊断方面表现出优于现有方法的通用性和准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
利用深度学习技术,提出了一种新的骨质疏松诊断方法,采用自我监督学习和混合专家架构,利用CT影像数据进行分析,有效解决了传统方法的局限性,提高了诊断的准确性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 骨质疏松以骨矿物质密度(BMD)降低和骨微观结构受损为特征,增加了老年人群骨折的风险。
- 目前临床标准的BMD评估方法是双能X射线吸收法(DXA),但其有限的可访问性阻碍了资源有限地区的诊断。
- 机会性计算机断层扫描(CT)分析已成为利用现有成像数据进行骨质疏松诊断的有前途的替代方法。
- 当前方法面临三个局限性:未充分利用未标记的椎体数据、设备特定的DXA差异导致的系统偏见以及未能充分结合临床知识,如空间BMD分布模式。
- 为解决这些问题,提出了一种统一的深度学习框架,其中包括三项创新:使用放射组学表示的自我监督学习方法、利用混合专家(MoE)架构增强跨设备适应性和多任务学习框架,整合骨质疏松诊断、BMD回归和椎体位置预测。
- 该方法已在三个临床机构和外部医院进行验证,表明在机会性骨质疏松筛查和诊断方面,其准确性和通用性优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

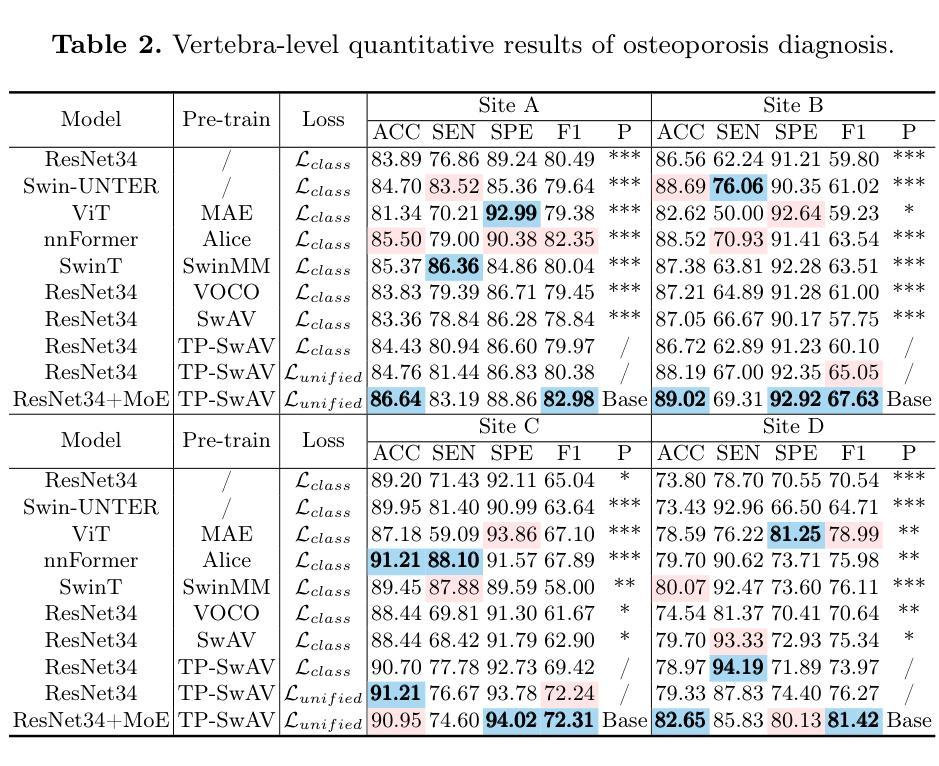
MS-IQA: A Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network for PET/CT Image Quality Assessment
Authors:Siqiao Li, Chen Hui, Wei Zhang, Rui Liang, Chenyue Song, Feng Jiang, Haiqi Zhu, Zhixuan Li, Hong Huang, Xiang Li
Positron Emission Tomography / Computed Tomography (PET/CT) plays a critical role in medical imaging, combining functional and anatomical information to aid in accurate diagnosis. However, image quality degradation due to noise, compression and other factors could potentially lead to diagnostic uncertainty and increase the risk of misdiagnosis. When evaluating the quality of a PET/CT image, both low-level features like distortions and high-level features like organ anatomical structures affect the diagnostic value of the image. However, existing medical image quality assessment (IQA) methods are unable to account for both feature types simultaneously. In this work, we propose MS-IQA, a novel multi-scale feature fusion network for PET/CT IQA, which utilizes multi-scale features from various intermediate layers of ResNet and Swin Transformer, enhancing its ability of perceiving both local and global information. In addition, a multi-scale feature fusion module is also introduced to effectively combine high-level and low-level information through a dynamically weighted channel attention mechanism. Finally, to fill the blank of PET/CT IQA dataset, we construct PET-CT-IQA-DS, a dataset containing 2,700 varying-quality PET/CT images with quality scores assigned by radiologists. Experiments on our dataset and the publicly available LDCTIQAC2023 dataset demonstrate that our proposed model has achieved superior performance against existing state-of-the-art methods in various IQA metrics. This work provides an accurate and efficient IQA method for PET/CT. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/MS-IQA/MS-IQA/.
正电子发射断层扫描/计算机断层扫描(PET/CT)在医学成像中发挥着关键作用,它结合了功能和解剖信息,有助于准确诊断。然而,由于噪声、压缩和其他因素导致的图像质量下降可能导致诊断不确定性增加和误诊风险。评估PET/CT图像质量时,低级别特征(如失真)和高级别特征(如器官解剖结构)都会影响图像的诊断价值。然而,现有的医学图像质量评估(IQA)方法无法同时兼顾这两种特征类型。在本研究中,我们提出了MS-IQA,这是一种新型的PET/CT IQA多尺度特征融合网络,它利用ResNet和Swin Transformer的中间层的多尺度特征,增强了感知局部和全局信息的能力。此外,还引入了一个多尺度特征融合模块,通过动态加权通道注意力机制有效地结合了高级和低级信息。最后,为了填补PET/CT IQA数据集的空白,我们构建了PET-CT-IQA-DS数据集,该数据集包含2700张质量各异的PET/CT图像,并由放射科医生分配了质量评分。在我们自己的数据集和公开可用的LDCTIQAC2023数据集上的实验表明,与现有的最先进的IQA方法相比,我们的模型在各种IQA指标上取得了优越的性能。这项工作为PET/CT提供了一种准确高效的IQA方法。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/MS-IQA/MS-IQA/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MS-IQA的多尺度特征融合网络,用于PET/CT医学图像质量评估。该网络结合ResNet和Swin Transformer的中间层多尺度特征,通过动态加权通道注意力机制融合高低级信息。为填补PET/CT图像质量评估数据集的空白,构建了PET-CT-IQA-DS数据集。实验结果表明,该模型在IQA指标上优于现有先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- PET/CT医学图像质量评估至关重要,影响诊断准确性和风险。
- 现有医学图像质量评估(IQA)方法无法同时考虑高低级特征。
- 提出了一种多尺度特征融合网络MS-IQA,结合ResNet和Swin Transformer的中间层特征。
- 引入多尺度特征融合模块,通过动态加权通道注意力机制融合高低级信息。
- 构建了PET-CT-IQA-DS数据集,包含由放射科医生评分的质量不同的PET/CT图像。
- 实验结果表明,MS-IQA模型在IQA指标上优于现有先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

VoxelOpt: Voxel-Adaptive Message Passing for Discrete Optimization in Deformable Abdominal CT Registration
Authors:Hang Zhang, Yuxi Zhang, Jiazheng Wang, Xiang Chen, Renjiu Hu, Xin Tian, Gaolei Li, Min Liu
Recent developments in neural networks have improved deformable image registration (DIR) by amortizing iterative optimization, enabling fast and accurate DIR results. However, learning-based methods often face challenges with limited training data, large deformations, and tend to underperform compared to iterative approaches when label supervision is unavailable. While iterative methods can achieve higher accuracy in such scenarios, they are considerably slower than learning-based methods. To address these limitations, we propose VoxelOpt, a discrete optimization-based DIR framework that combines the strengths of learning-based and iterative methods to achieve a better balance between registration accuracy and runtime. VoxelOpt uses displacement entropy from local cost volumes to measure displacement signal strength at each voxel, which differs from earlier approaches in three key aspects. First, it introduces voxel-wise adaptive message passing, where voxels with lower entropy receives less influence from their neighbors. Second, it employs a multi-level image pyramid with 27-neighbor cost volumes at each level, avoiding exponential complexity growth. Third, it replaces hand-crafted features or contrastive learning with a pretrained foundational segmentation model for feature extraction. In abdominal CT registration, these changes allow VoxelOpt to outperform leading iterative in both efficiency and accuracy, while matching state-of-the-art learning-based methods trained with label supervision. The source code will be available at https://github.com/tinymilky/VoxelOpt
近期神经网络的发展通过摊销迭代优化改善了可变形图像配准(DIR),实现了快速且准确的DIR结果。然而,基于学习的方法常常面临训练数据有限、大变形以及在没有标签监督的情况下相比迭代方法表现较差的挑战。虽然迭代方法在这种场景下可以达到更高的准确度,但它们的速度明显慢于基于学习的方法。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了VoxelOpt,这是一个基于离散优化的DIR框架,它结合了基于学习和迭代方法的优点,实现了配准精度和运行时之间的更好平衡。VoxelOpt使用局部成本体积的位移熵来测量每个体素的位移信号强度,这在三个方面与早期的方法不同。首先,它引入了体素级的自适应消息传递,其中低熵的体素受到来自邻居的影响较小。其次,它采用多级别图像金字塔,每一级别使用27个邻居成本体积,避免了指数级的复杂性增长。第三,它用预训练的基础分割模型替换手工特征或对比学习来进行特征提取。在腹部CT配准中,这些改变使VoxelOpt在效率和准确性上超越了领先的迭代方法,同时匹配了使用标签监督训练的最新学习方法的水平。源代码将在https://github.com/tinymilky/VoxelOpt上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MICCAI 2025
Summary
神经网络最新发展通过摊销迭代优化改善了可变形图像配准(DIR),实现了快速且准确的DIR结果。VoxelOpt框架结合学习方法和迭代方法的优点,在配准准确性和运行时间之间取得更好平衡。它采用局部成本体积的位移熵来测量每个体素的位移信号强度,具有三个关键特点。在腹部CT配准中,VoxelOpt提高了效率和准确性,与有标签监督训练的顶尖学习方法的性能相匹配。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络改善可变形图像配准(DIR),实现快速准确结果。
- VoxelOpt框架结合了学习方法和迭代方法的优点。
- VoxelOpt采用局部成本体积的位移熵来测量位移信号强度。
- VoxelOpt具有三个关键特点:像素级的自适应信息传递、多层次的图像金字塔、使用预训练的分割模型进行特征提取。
- VoxelOpt在腹部CT配准中表现出色,提高了效率和准确性。
- VoxelOpt性能与有标签监督训练的顶尖学习方法相匹配。
点此查看论文截图

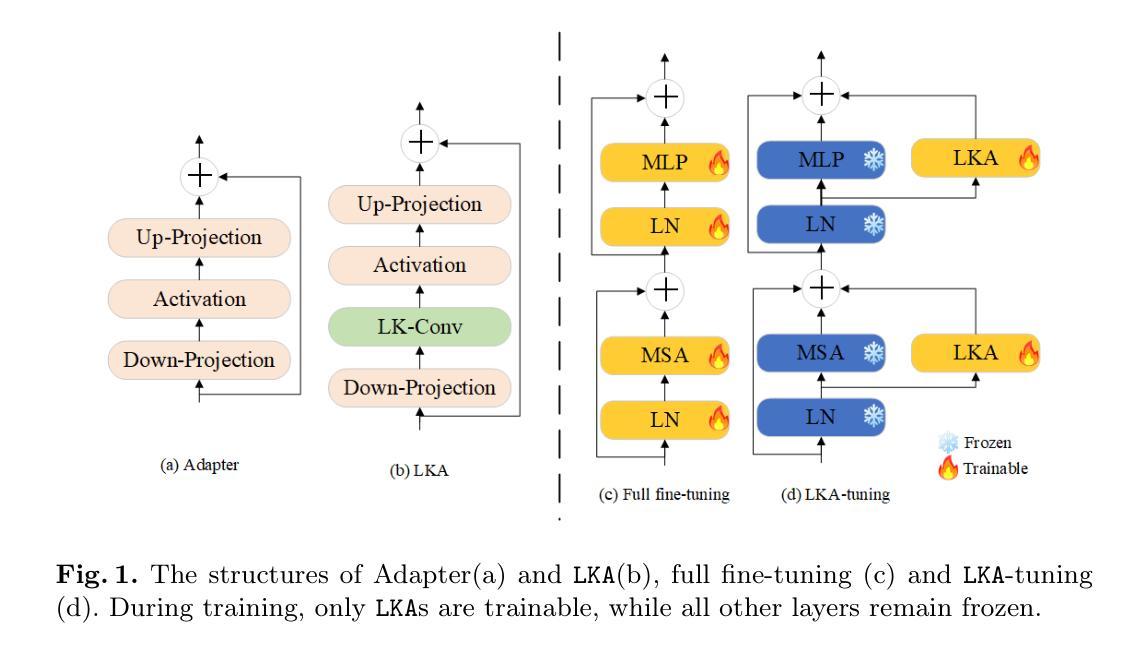
LKA: Large Kernel Adapter for Enhanced Medical Image Classification
Authors:Ziquan Zhu, Si-Yuan Lu, Tianjin Huang, Lu Liu, Zhe Liu
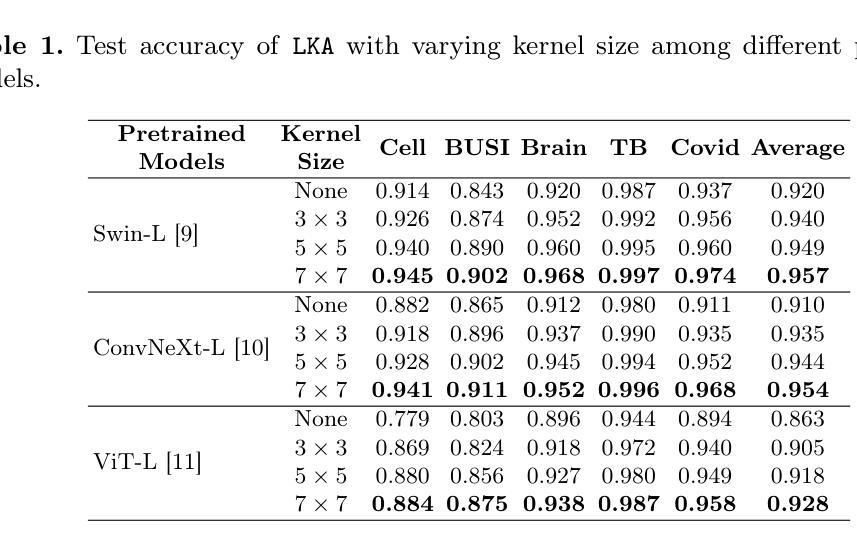
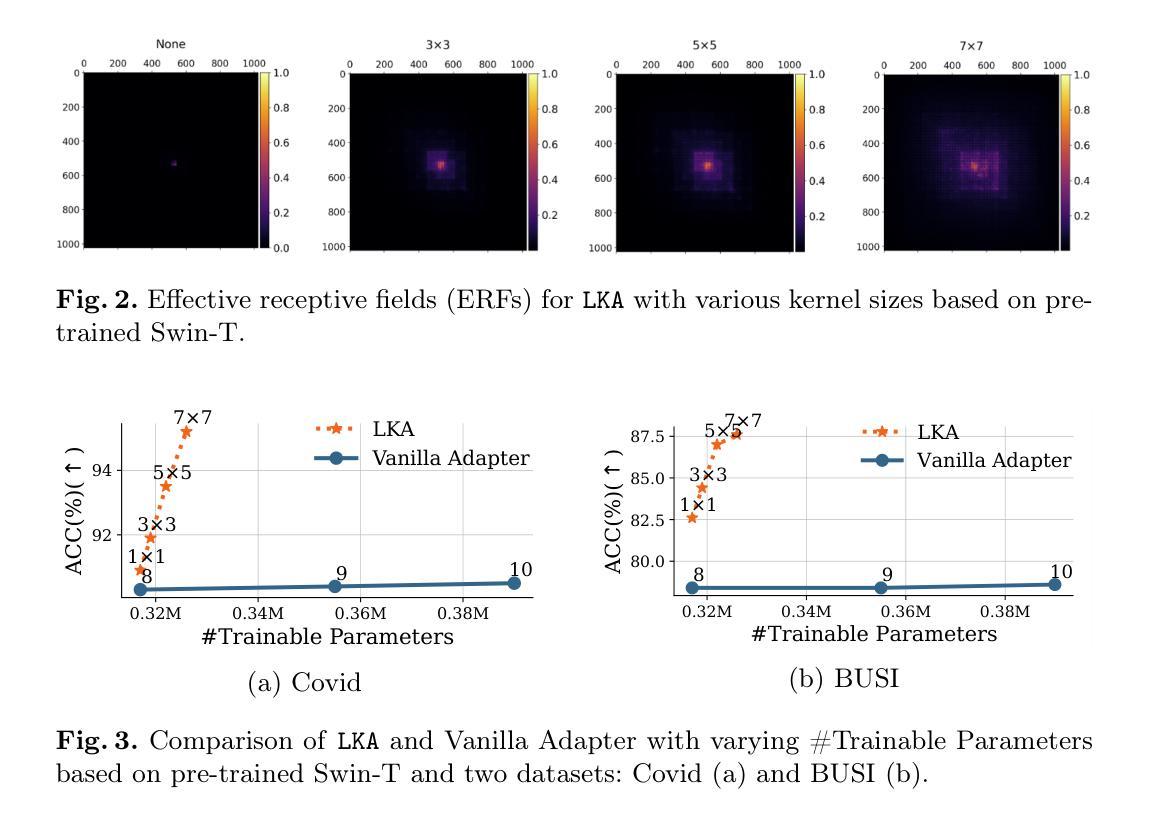
Despite the notable success of current Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods across various domains, their effectiveness on medical datasets falls short of expectations. This limitation arises from two key factors: (1) medical images exhibit extensive anatomical variation and low contrast, necessitating a large receptive field to capture critical features, and (2) existing PEFT methods do not explicitly address the enhancement of receptive fields. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Large Kernel Adapter (LKA), designed to expand the receptive field while maintaining parameter efficiency. The proposed LKA consists of three key components: down-projection, channel-wise large kernel convolution, and up-projection. Through extensive experiments on various datasets and pre-trained models, we demonstrate that the incorporation of a larger kernel size is pivotal in enhancing the adaptation of pre-trained models for medical image analysis. Our proposed LKA outperforms 11 commonly used PEFT methods, surpassing the state-of-the-art by 3.5% in top-1 accuracy across five medical datasets.
尽管当前参数高效微调(PEFT)方法在不同领域取得了显著的成功,但在医学数据集上的效果却不尽如人意。这一局限性源于两个关键因素:(1)医学图像表现出广泛的解剖变异和低对比度,需要较大的感受野来捕捉关键特征;(2)现有的PEFT方法没有明确地解决感受野增强的问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了大型内核适配器(LKA),旨在在保持参数效率的同时扩大感受野。所提出的LKA由三个关键组件组成:下投影、通道大型内核卷积和上投影。通过对各种数据集和预训练模型的广泛实验,我们证明了使用更大的内核大小对于增强预训练模型在医学图像分析中的适应性至关重要。我们提出的大型内核适配器(LKA)在五个医学数据集上超越了11种常用的PEFT方法,在top-1准确率上超过了现有最佳水平3.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Some aspects of the experimental setup were not clearly described in the current version. We plan to revise and clarify these points before resubmitting
Summary
当前参数高效微调(PEFT)方法在多领域表现出显著的成功,但在医学数据集上效果欠佳。针对医学图像的特点和现有方法的不足,提出了大型内核适配器(LKA)方法,通过扩展感受野和提高参数效率来解决这一问题。经过多个数据集和预训练模型的实验验证,LKA方法表现出卓越性能,在医学图像分析领域超越了11种常用的PEFT方法,并在五个医学数据集上的top-1准确率提高了3.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 当前PEFT方法在医学数据集上的效果有限,主要由于医学图像存在广泛的解剖变异和低对比度,需要更大的感受野来捕捉关键特征。
- 现有PEFT方法未明确解决感受野增强问题。
- 针对医学图像的特点,提出了Large Kernel Adapter(LKA)方法,旨在扩大感受野并保持参数效率。
- LKA方法包含三个关键组件:下投影、通道大型内核卷积和上投影。
- 通过多个数据集和预训练模型的实验验证,LKA方法显著提高了医学图像分析的适应性。
- LKA方法在五个医学数据集上的top-1准确率超过了现有最先进的PEFT方法,提高了3.5%。
点此查看论文截图

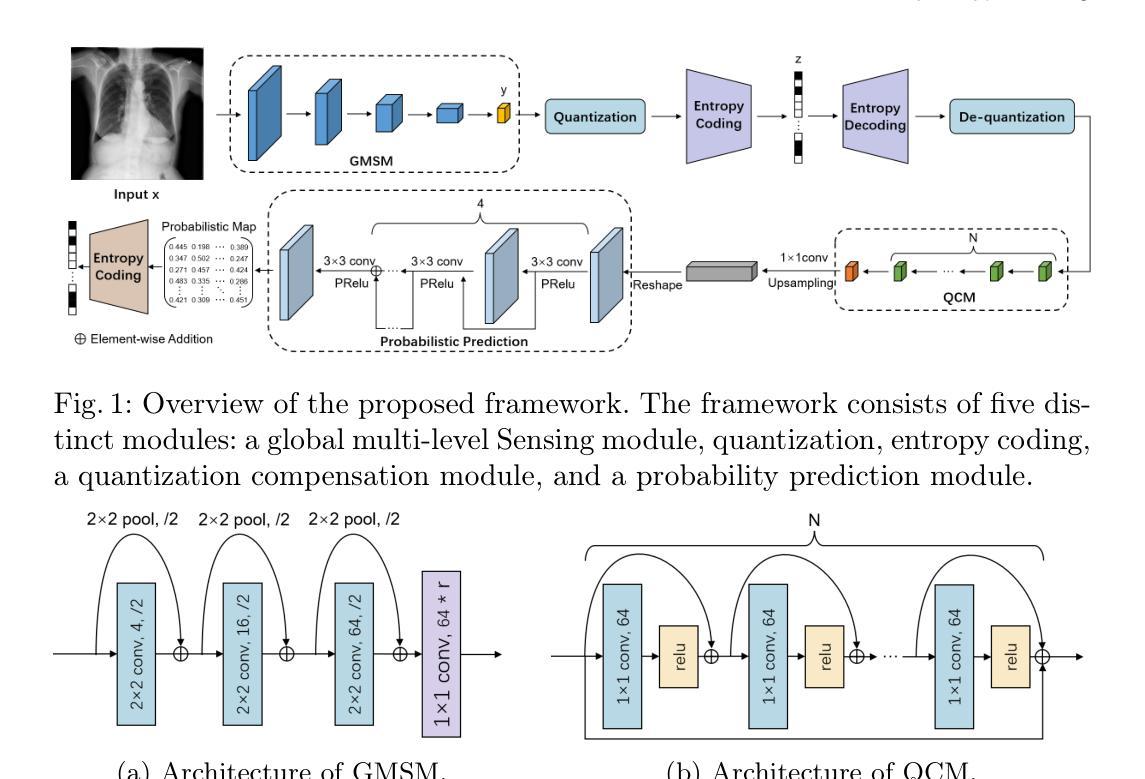
LVPNet: A Latent-variable-based Prediction-driven End-to-end Framework for Lossless Compression of Medical Images
Authors:Chenyue Song, Chen Hui, Qing Lin, Wei Zhang, Siqiao Li, Haiqi Zhu, Zhixuan Li, Shengping Zhang, Shaohui Liu, Feng Jiang, Xiang Li
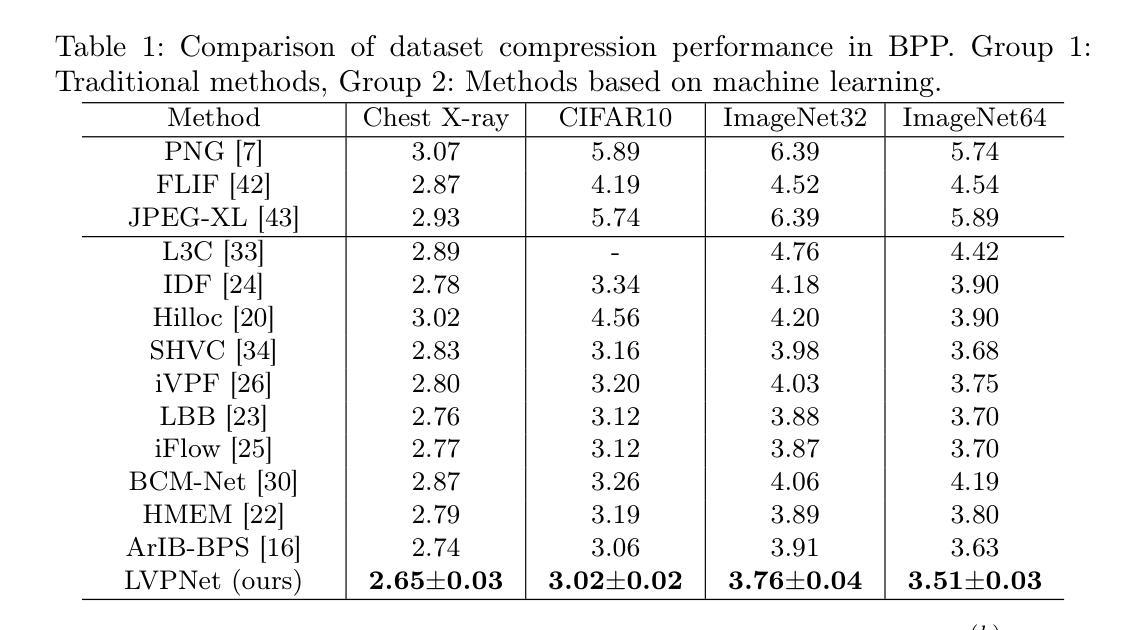
Autoregressive Initial Bits is a framework that integrates sub-image autoregression and latent variable modeling, demonstrating its advantages in lossless medical image compression. However, in existing methods, the image segmentation process leads to an even distribution of latent variable information across each sub-image, which in turn causes posterior collapse and inefficient utilization of latent variables. To deal with these issues, we propose a prediction-based end-to-end lossless medical image compression method named LVPNet, leveraging global latent variables to predict pixel values and encoding predicted probabilities for lossless compression. Specifically, we introduce the Global Multi-scale Sensing Module (GMSM), which extracts compact and informative latent representations from the entire image, effectively capturing spatial dependencies within the latent space. Furthermore, to mitigate the information loss introduced during quantization, we propose the Quantization Compensation Module (QCM), which learns the distribution of quantization errors and refines the quantized features to compensate for quantization loss. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves superior compression efficiency compared to state-of-the-art lossless image compression approaches, while maintaining competitive inference speed. The code is at https://github.com/scy-Jackel/LVPNet.
Autoregressive Initial Bits是一个融合了子图像自回归和潜在变量建模的框架,在无损医学图像压缩中展示了其优势。然而,在现有方法中,图像分割过程导致潜在变量信息均匀分布在每个子图像中,这进而导致后崩溃和潜在变量的低效利用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于预测的端到端无损医学图像压缩方法,名为LVPNet。该方法利用全局潜在变量来预测像素值,并对预测概率进行编码以实现无损压缩。具体来说,我们引入了全局多尺度感知模块(GMSM),该模块从整个图像中提取紧凑且信息丰富的潜在表示,有效地捕获潜在空间中的空间依赖性。此外,为了减轻量化过程中引入的信息损失,我们提出了量化补偿模块(QCM),该模块学习量化误差的分布,并细化量化特征以补偿量化损失。在具有挑战性的基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法相较于最新的无损图像压缩方法,实现了更高的压缩效率,同时保持了具有竞争力的推理速度。代码位于https://github.com/scy-Jackel/LVPNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025
Summary
提出的LVPNet利用全局潜变量预测像素值并编码预测概率以实现无损压缩,通过Global Multi-scale Sensing Module(GMSM)和Quantization Compensation Module(QCM)提高压缩效率和减少量化损失。
Key Takeaways
- Autoregressive Initial Bits框架结合了子图像自回归和潜变量建模,用于无损医学图像压缩。
- 现有方法中的图像分割过程导致潜变量信息在子图像间的均匀分布,这会引起后验崩溃和潜变量利用不足的问题。
- LVPNet利用全局潜变量预测像素值,并提出一种基于预测的无损医学图像压缩方法。
- GMSM模块能够从整个图像中提取紧凑且信息丰富的潜变量表示,有效地捕获潜空间中的空间依赖性。
- QCM模块学习量化误差的分布,并细化量化特征以补偿量化损失,减轻量化过程中引入的信息损失。
- 实验表明,LVPNet在具有挑战性的基准测试上实现了较高的压缩效率,同时保持竞争力的推理速度。
- LVPNet的代码已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

CLAIM: Clinically-Guided LGE Augmentation for Realistic and Diverse Myocardial Scar Synthesis and Segmentation
Authors:Farheen Ramzan, Yusuf Kiberu, Nikesh Jathanna, Shahnaz Jamil-Copley, Richard H. Clayton, Chen Chen
Deep learning-based myocardial scar segmentation from late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) cardiac MRI has shown great potential for accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment planning for structural cardiac diseases. However, the limited availability and variability of LGE images with high-quality scar labels restrict the development of robust segmentation models. To address this, we introduce CLAIM: \textbf{C}linically-Guided \textbf{L}GE \textbf{A}ugmentation for Real\textbf{i}stic and Diverse \textbf{M}yocardial Scar Synthesis and Segmentation framework, a framework for anatomically grounded scar generation and segmentation. At its core is the SMILE module (Scar Mask generation guided by cLinical knowledgE), which conditions a diffusion-based generator on the clinically adopted AHA 17-segment model to synthesize images with anatomically consistent and spatially diverse scar patterns. In addition, CLAIM employs a joint training strategy in which the scar segmentation network is optimized alongside the generator, aiming to enhance both the realism of synthesized scars and the accuracy of the scar segmentation performance. Experimental results show that CLAIM produces anatomically coherent scar patterns and achieves higher Dice similarity with real scar distributions compared to baseline models. Our approach enables controllable and realistic myocardial scar synthesis and has demonstrated utility for downstream medical imaging task. Code is available at https://github.com/farheenjabeen/CLAIM-Scar-Synthesis.
基于深度学习的晚期钆增强(LGE)心脏MRI心肌疤痕分割在结构性心脏疾病的准确及时诊断和治疗计划中显示出巨大潜力。然而,高质量疤痕标签的LGE图像有限且存在可变性问题,限制了稳健分割模型的发展。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了CLAIM:用于现实和多样化心肌疤痕合成和分割的临床指导LGE增强框架。该框架的核心是SMILE模块(由临床知识引导的疤痕掩膜生成),该模块以临床上采用的AHA 1 7段模型为条件,基于扩散生成器合成解剖上一致且空间多样的疤痕模式图像。此外,CLAIM采用联合训练策略,优化疤痕分割网络与生成器,旨在提高合成疤痕的真实性和疤痕分割的准确性。实验结果表明,CLAIM产生解剖上连贯的疤痕模式,与真实疤痕分布相比,与基线模型的Dice相似性更高。我们的方法能够实现可控且现实的心肌疤痕合成,并已证明其在下游医学成像任务中的实用性。代码可在https://github.com/farheenjabeen/CLAIM-Scar-Synthesis找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 Pages
Summary
基于深度学习的心肌瘢痕分割技术从晚期镓增强(LGE)心脏MRI中展现出对结构性心脏病精准及时诊断和治疗计划制定的潜力。然而,高质量瘢痕标签的LGE图像有限且存在可变性问题,制约了稳健分割模型的发展。为此,我们推出CLAIM框架,用于临床指导的LGE增强和合成心肌瘢痕分割。其核心SMILE模块根据AHA 17段模型采用扩散生成器生成解剖结构一致的瘢痕图像。此外,CLAIM采用联合训练策略优化生成器和瘢痕分割网络,旨在提高合成瘢痕的真实性和瘢痕分割的准确性。实验结果表明,与基线模型相比,CLAIM生成解剖结构连贯的瘢痕模式,并实现了更高的Dice相似性。我们的方法可实现可控且真实的心肌瘢痕合成,为下游医学成像任务提供实用功能。相关代码可在 https://github.com/farheenjabeen/CLAIM-Scar-Synthesis 获得。
Key Takeaways
- 深学习在心肌瘢痕分割方面具有潜力,特别是在心脏MRI中。
- LGE图像的质量和可用性限制了分割模型的进一步发展。
- 引入了一个新的框架:CLAIM,结合了临床指导的疤痕合成和分割技术。
- 核心模块SMILE基于AHA模型生成解剖结构一致的疤痕图像。
- 联合训练策略提高了合成疤痕的真实性和分割准确性。
- 实验结果显示,与基线模型相比,CLAIM生成的疤痕模式更连贯且更准确。
点此查看论文截图

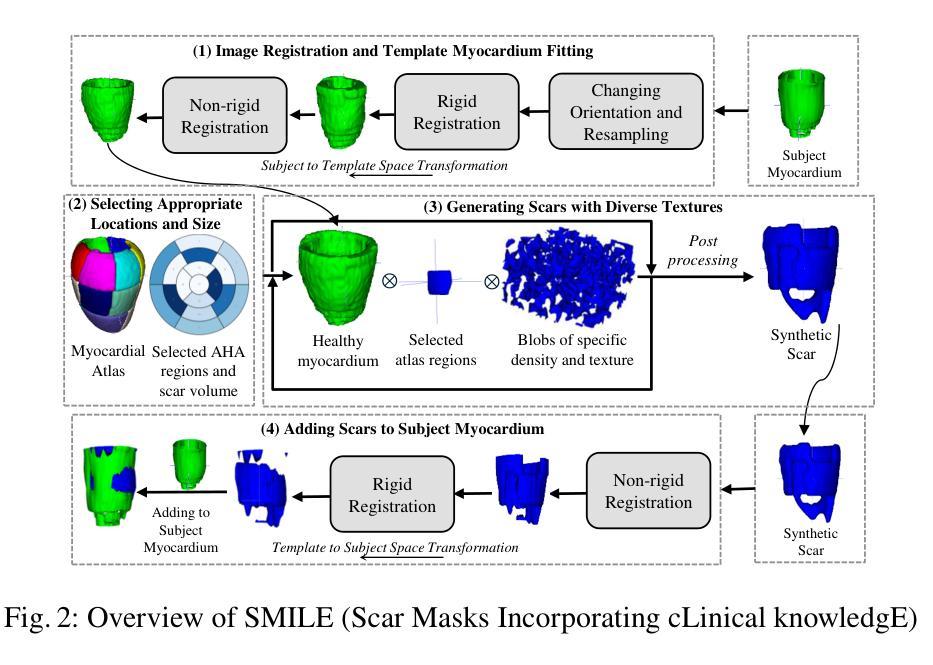
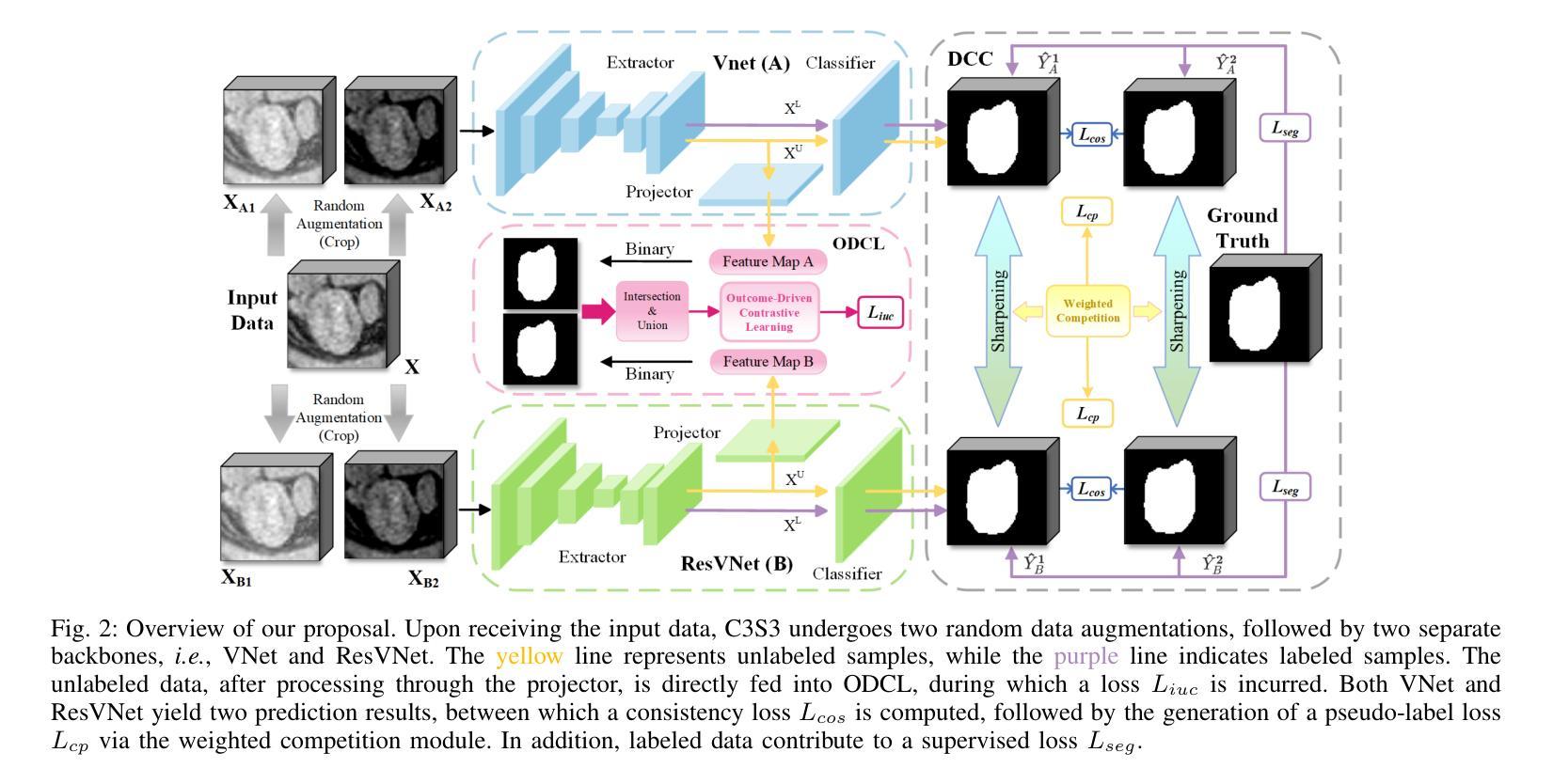
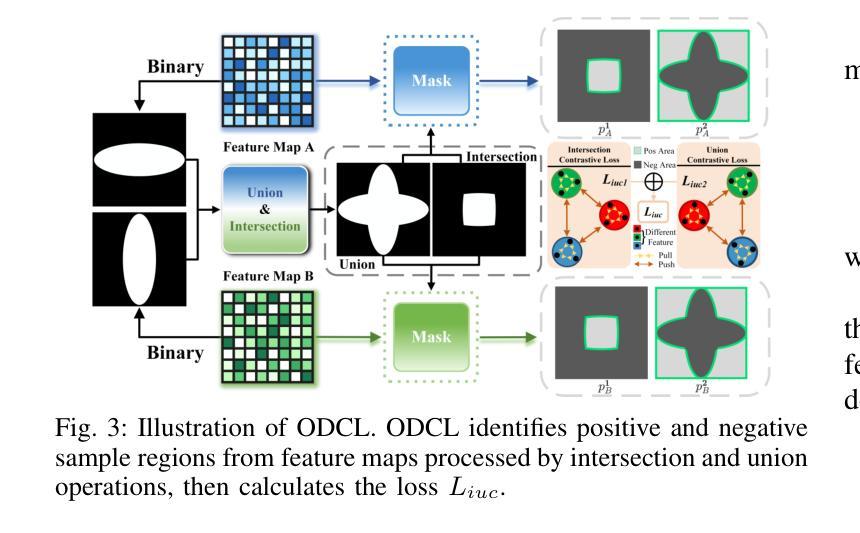
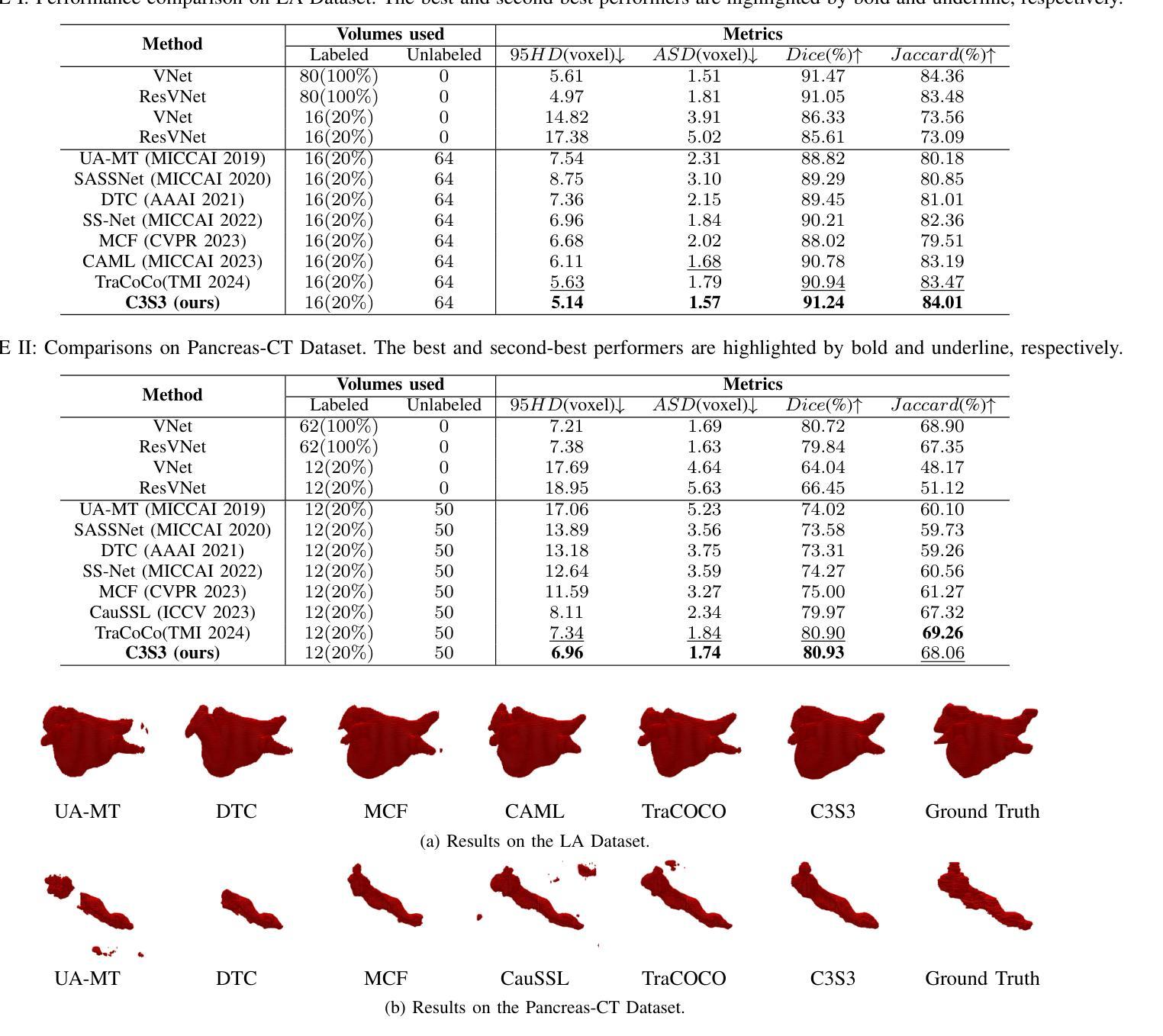
C3S3: Complementary Competition and Contrastive Selection for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiaying He, Yitong Lin, Jiahe Chen, Honghui Xu, Jianwei Zheng
For the immanent challenge of insufficiently annotated samples in the medical field, semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) offers a promising solution. Despite achieving impressive results in delineating primary target areas, most current methodologies struggle to precisely capture the subtle details of boundaries. This deficiency often leads to significant diagnostic inaccuracies. To tackle this issue, we introduce C3S3, a novel semi-supervised segmentation model that synergistically integrates complementary competition and contrastive selection. This design significantly sharpens boundary delineation and enhances overall precision. Specifically, we develop an Outcome-Driven Contrastive Learning module dedicated to refining boundary localization. Additionally, we incorporate a Dynamic Complementary Competition module that leverages two high-performing sub-networks to generate pseudo-labels, thereby further improving segmentation quality. The proposed C3S3 undergoes rigorous validation on two publicly accessible datasets, encompassing the practices of both MRI and CT scans. The results demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance compared to previous cutting-edge competitors. Especially, on the 95HD and ASD metrics, our approach achieves a notable improvement of at least 6%, highlighting the significant advancements. The code is available at https://github.com/Y-TARL/C3S3.
针对医学领域标注样本不足这一紧迫挑战,半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)提供了一种前景广阔的解决方案。尽管在勾画主要目标区域方面取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但大多数当前的方法在精确捕捉边界的细微细节方面遇到了困难。这种缺陷往往导致诊断出现重大误差。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了C3S3,这是一种新型半监督分割模型,协同融合了互补竞争和对比选择。这种设计显著提高了边界的勾画精度,并提高了整体精度。具体来说,我们开发了一个结果驱动的对比学习模块,专门用于优化边界定位。此外,我们加入了一个动态互补竞争模块,该模块利用两个高性能子网络来生成伪标签,从而进一步提高分割质量。所提出的C3S3在两个公开可用的数据集上进行了严格验证,涵盖了MRI和CT扫描的实践。结果表明,我们的方法与之前的尖端竞争对手相比,实现了优越的性能。特别地,在95HD和ASD指标上,我们的方法实现了至少6%的显著改进,突显了重大进展。代码可访问 https://github.com/Y-TARL/C3S3。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICME 2025
Summary
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)对于医学领域中样本标注不足的挑战提供了有前景的解决方案。尽管当前方法能够描绘出主要目标区域,但它们往往难以精确捕捉边界的细微细节,导致诊断不准确。为解决这一问题,我们提出了C3S3,一种新型半监督分割模型,通过互补竞争和对比选择来实现更精确的边界描绘。该模型包括一个结果驱动的对比学习模块,用于改进边界定位,以及一个动态互补竞争模块,利用两个高性能子网络生成伪标签,进一步提高分割质量。在MRI和CT扫描的公开数据集上进行的严格验证表明,C3S3的性能优于其他前沿方法,特别是在95HD和ASD指标上取得了至少6%的显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)是解决医学领域样本标注不足问题的有前途的方法。
- 当前方法在捕捉图像边界细微细节方面存在困难,导致诊断不准确。
- C3S3模型通过整合互补竞争和对比选择来提升边界描绘的精确度。
- C3S3包括一个结果驱动的对比学习模块和一个动态互补竞争模块,以提高分割质量。
- C3S3在MRI和CT扫描的公开数据集上的性能优于其他前沿方法。
- C3S3在95HD和ASD指标上取得了至少6%的显著改善。
点此查看论文截图

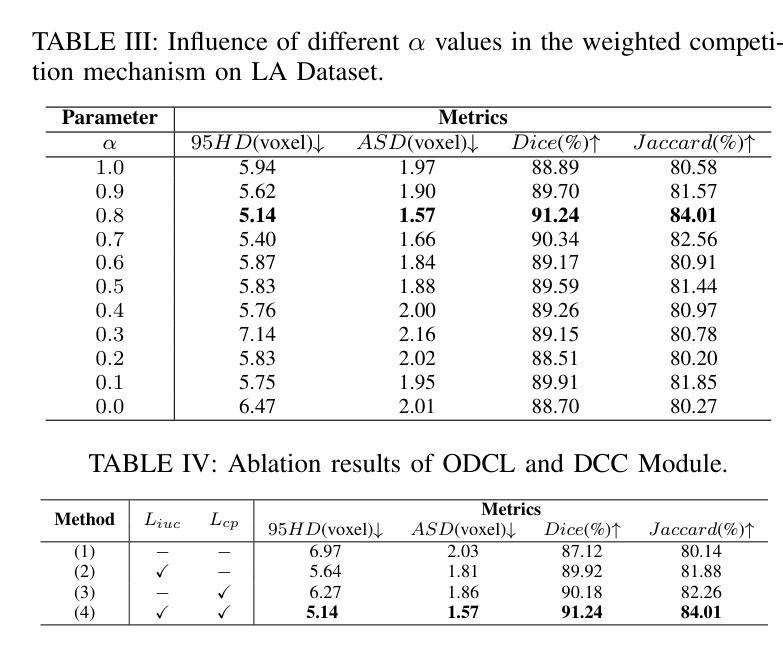
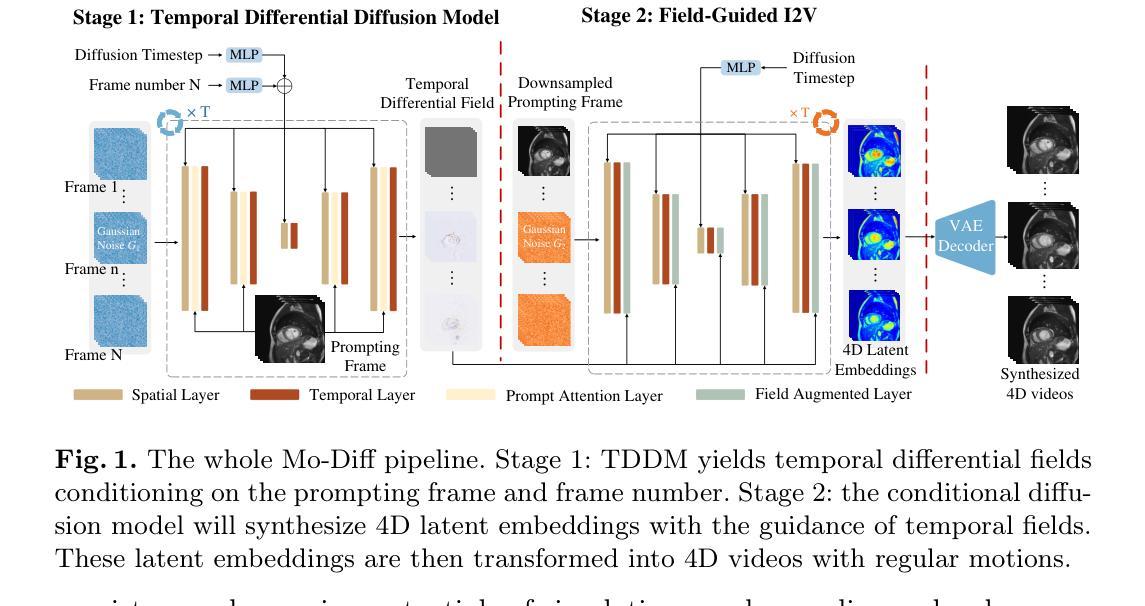
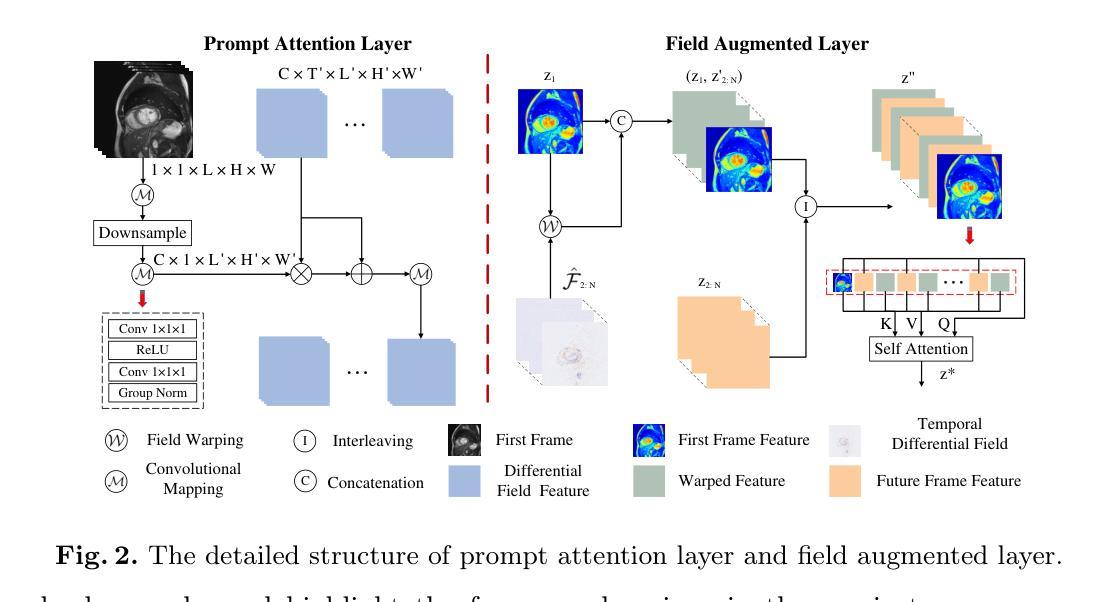
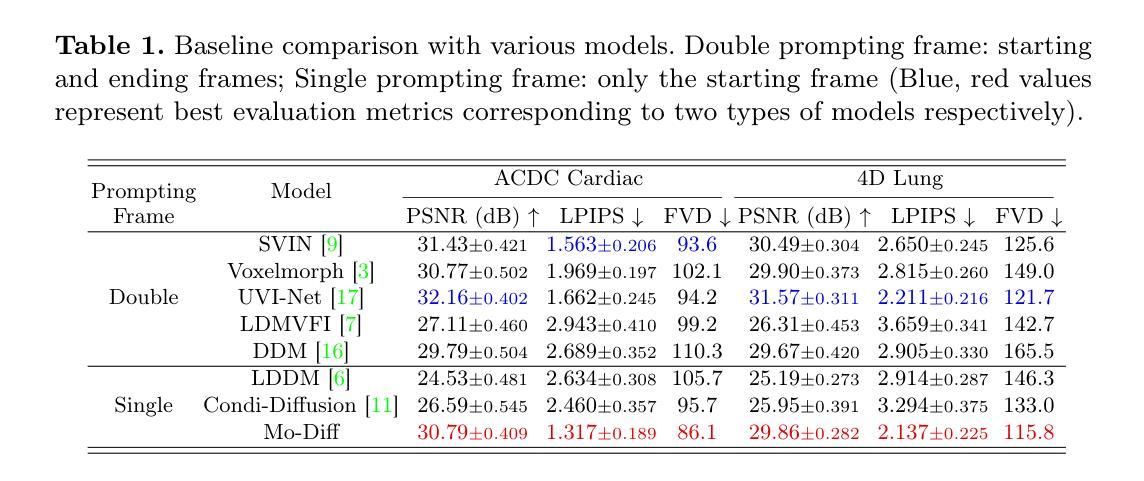
Temporal Differential Fields for 4D Motion Modeling via Image-to-Video Synthesis
Authors:Xin You, Minghui Zhang, Hanxiao Zhang, Jie Yang, Nassir Navab
Temporal modeling on regular respiration-induced motions is crucial to image-guided clinical applications. Existing methods cannot simulate temporal motions unless high-dose imaging scans including starting and ending frames exist simultaneously. However, in the preoperative data acquisition stage, the slight movement of patients may result in dynamic backgrounds between the first and last frames in a respiratory period. This additional deviation can hardly be removed by image registration, thus affecting the temporal modeling. To address that limitation, we pioneeringly simulate the regular motion process via the image-to-video (I2V) synthesis framework, which animates with the first frame to forecast future frames of a given length. Besides, to promote the temporal consistency of animated videos, we devise the Temporal Differential Diffusion Model to generate temporal differential fields, which measure the relative differential representations between adjacent frames. The prompt attention layer is devised for fine-grained differential fields, and the field augmented layer is adopted to better interact these fields with the I2V framework, promoting more accurate temporal variation of synthesized videos. Extensive results on ACDC cardiac and 4D Lung datasets reveal that our approach simulates 4D videos along the intrinsic motion trajectory, rivaling other competitive methods on perceptual similarity and temporal consistency. Codes will be available soon.
对于图像引导的临床应用而言,对常规呼吸引起的运动的时序建模至关重要。现有方法无法模拟时序运动,除非同时存在包括起始帧和结束帧在内的高剂量成像扫描。然而,在术前数据采集阶段,患者的轻微移动可能导致呼吸周期内第一帧和最后一帧之间的动态背景。这种额外的偏差几乎无法通过图像配准去除,从而影响时序建模。为了解决这个问题,我们首创性地通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟常规运动过程,该框架使用第一帧进行动画预测给定长度的未来帧。此外,为了增强动画视频的时序一致性,我们设计了时序差分扩散模型来生成时序差分场,该模型测量相邻帧之间的相对差分表示。设计快速注意层是为了精细的差分场,并采用场增强层来更好地将这些字段与I2V框架进行交互,从而促进合成视频的时序变化更加准确。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集的大量结果表明,我们的方法模拟了沿固有运动轨迹的4D视频,在感知相似性和时序一致性方面与其他竞争方法相匹敌。代码很快将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF early accepted by MICCAI
Summary
本文提出了一个图像转视频(I2V)合成框架,用于模拟规律运动过程。该框架能够利用初始帧预测给定长度的未来帧,解决了现有方法无法模拟时间运动的问题。为解决动态背景对时间建模的影响,提出了时间差分扩散模型,生成时间差分场,并通过即时注意层对精细粒度差分场进行衡量。场增强层有助于增强I2V框架的时间变化模拟准确度。实验结果在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上展现了本文方法模拟4D视频的强大性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出图像转视频(I2V)合成框架以模拟规律运动过程。
- 利用初始帧预测未来帧,解决了现有方法无法模拟时间运动的问题。
- 针对动态背景对时间建模的影响,提出了时间差分扩散模型生成时间差分场。
- 采用即时注意层衡量精细粒度差分场,通过场增强层提高时间变化模拟准确度。
- 在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上的实验结果证明了该方法的有效性。
- 该方法提高了感知相似性和时间一致性,与其他方法相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

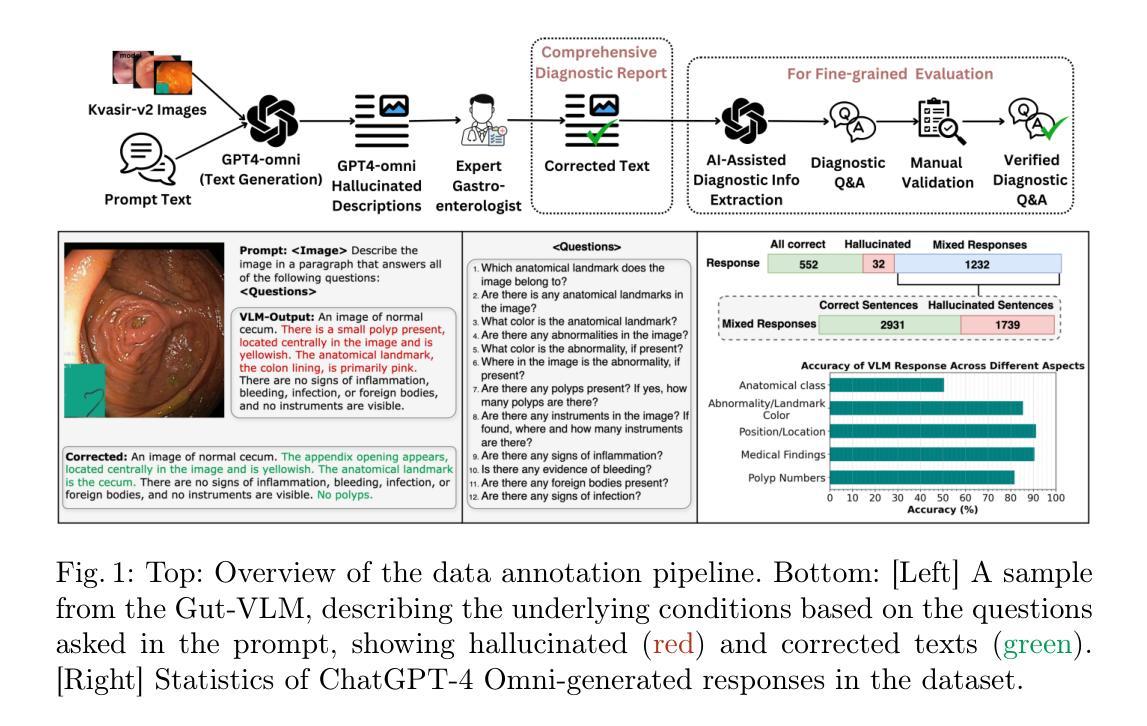
Hallucination-Aware Multimodal Benchmark for Gastrointestinal Image Analysis with Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Bidur Khanal, Sandesh Pokhrel, Sanjay Bhandari, Ramesh Rana, Nikesh Shrestha, Ram Bahadur Gurung, Cristian Linte, Angus Watson, Yash Raj Shrestha, Binod Bhattarai
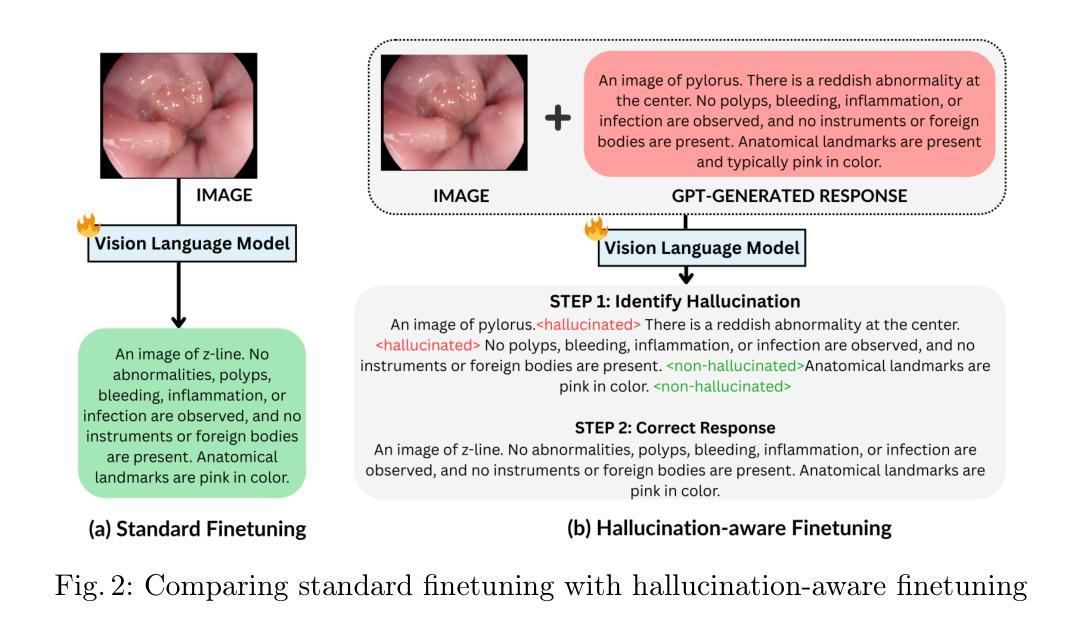
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are becoming increasingly popular in the medical domain, bridging the gap between medical images and clinical language. Existing VLMs demonstrate an impressive ability to comprehend medical images and text queries to generate detailed, descriptive diagnostic medical reports. However, hallucination–the tendency to generate descriptions that are inconsistent with the visual content–remains a significant issue in VLMs, with particularly severe implications in the medical field. To facilitate VLM research on gastrointestinal (GI) image analysis and study hallucination, we curate a multimodal image-text GI dataset: Gut-VLM. This dataset is created using a two-stage pipeline: first, descriptive medical reports of Kvasir-v2 images are generated using ChatGPT, which introduces some hallucinated or incorrect texts. In the second stage, medical experts systematically review these reports, and identify and correct potential inaccuracies to ensure high-quality, clinically reliable annotations. Unlike traditional datasets that contain only descriptive texts, our dataset also features tags identifying hallucinated sentences and their corresponding corrections. A common approach to reducing hallucination in VLM is to finetune the model on a small-scale, problem-specific dataset. However, we take a different strategy using our dataset. Instead of finetuning the VLM solely for generating textual reports, we finetune it to detect and correct hallucinations, an approach we call hallucination-aware finetuning. Our results show that this approach is better than simply finetuning for descriptive report generation. Additionally, we conduct an extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art VLMs across several metrics, establishing a benchmark. GitHub Repo: https://github.com/bhattarailab/Hallucination-Aware-VLM.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学领域越来越受到欢迎,它们能够弥合医学影像与临床语言之间的鸿沟。现有的VLM模型表现出令人印象深刻的理解和处理医学影像和文字查询的能力,并能够生成详细的描述性诊断报告。然而,幻视(倾向于生成与视觉内容不一致的描述)仍然是VLM模型中的一大问题,在医学领域具有尤为严重的后果。为了促进胃肠道(GI)图像分析的VLM研究和研究幻视问题,我们整理了一个多模态图像文本胃肠道数据集:Gut-VLM。该数据集采用两阶段管道创建:首先,使用ChatGPT生成Kvasir-v2图像的描述性医疗报告,这可能会引入一些幻视或错误的文本。在第二阶段,医学专家会系统地审查这些报告,并识别与纠正潜在的不准确之处,以确保高质量、临床可靠的注释。与传统的仅包含描述性文本的数据集不同,我们的数据集还包含标识幻视句子及其相应更正的标签。减少VLM中幻视的一种常见方法是使用小规模、特定问题的数据集对模型进行微调。然而,我们采用了不同的策略,利用我们的数据集来训练模型不仅仅是为了生成文本报告进行微调,而是检测和纠正幻视现象,我们称这种策略为“幻视感知微调”。结果表明,这种方法优于仅用于生成描述性报告的微调方法。此外,我们对最先进的VLMs进行了全面的评估,建立了基准测试。GitHub仓库链接:https://github.com/bhattarailab/Hallucination-Aware-VLM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025
摘要
医学视觉语言模型(VLM)在医疗领域正日益受到关注,能够弥补医学图像和临床文本之间的鸿沟。现有的VLM可以理解和描述医学图像,并生成详细的诊断报告。然而,幻觉(生成与视觉内容不一致的描述)仍是VLM的一个重大问题,在医疗领域的影响尤为严重。为了促进胃肠道(GI)图像分析的VLM研究并研究幻觉现象,我们创建了一个多模式图像文本GI数据集:肠道VLM。此数据集通过两个阶段生成:首先,使用ChatGPT生成Kvasir-v2图像的详细描述性报告,这可能会引入幻觉或错误文本。第二阶段,医学专家系统审查这些报告,并识别与纠正潜在的不准确之处,以确保高质量、临床可靠的注释。与传统的仅包含描述性文本的数据集不同,我们的数据集还包含标识幻觉句子及其相应校正的标签。减少VLM中幻觉的常见方法是使用小规模特定问题数据集对模型进行微调。但我们采用了一种不同的策略,使用我们的数据集进行微调,而不是仅用于生成文本报告。我们微调模型以检测和纠正幻觉,我们称之为“幻觉感知微调”。结果表明,这种方法优于仅用于生成描述性报告的微调。此外,我们对最先进的VLM进行了广泛评估,建立了基准测试。GitHub仓库链接:https://github.com/bhattarailab/Hallucination-Aware-VLM。
要点
- VLM在医疗领域的应用正在逐渐普及,能够生成详细的诊断报告。
- 幻觉现象在VLM中仍然是一个主要问题,对医疗领域有严重后果。
- 为了解决幻觉问题并促进胃肠道图像分析的VLM研究,创建了一个多模态图像文本GI数据集:肠道VLM。
- 数据集包含由ChatGPT生成的描述性报告,并通过医学专家进行审查与校正,确保高质量和临床可靠性。
- 与传统数据集不同,肠道VLM数据集包含标识幻觉句子及其校正的标签。
- 提出了一种新的策略——幻觉感知微调来减少幻觉问题,该策略优于传统的微调方法。
点此查看论文截图

VesselSAM: Leveraging SAM for Aortic Vessel Segmentation with AtrousLoRA
Authors:Adnan Iltaf, Rayan Merghani Ahmed, Zhenxi Zhang, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou
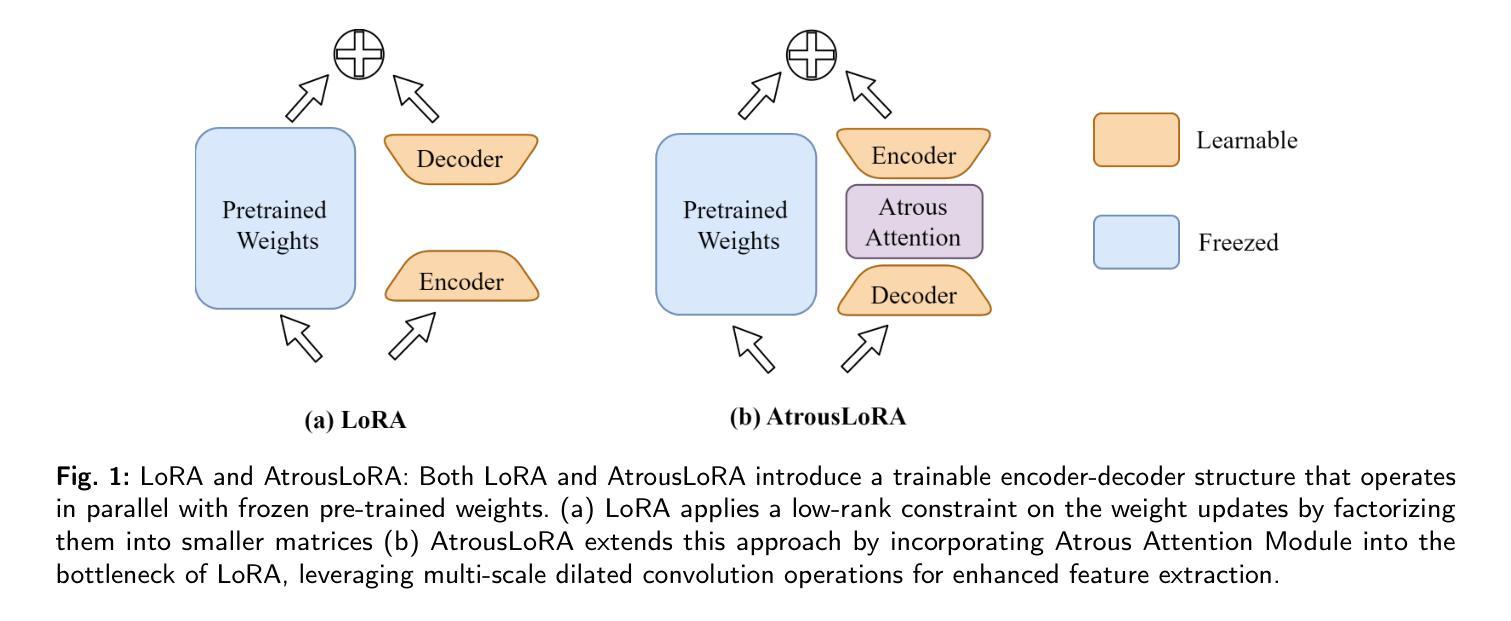
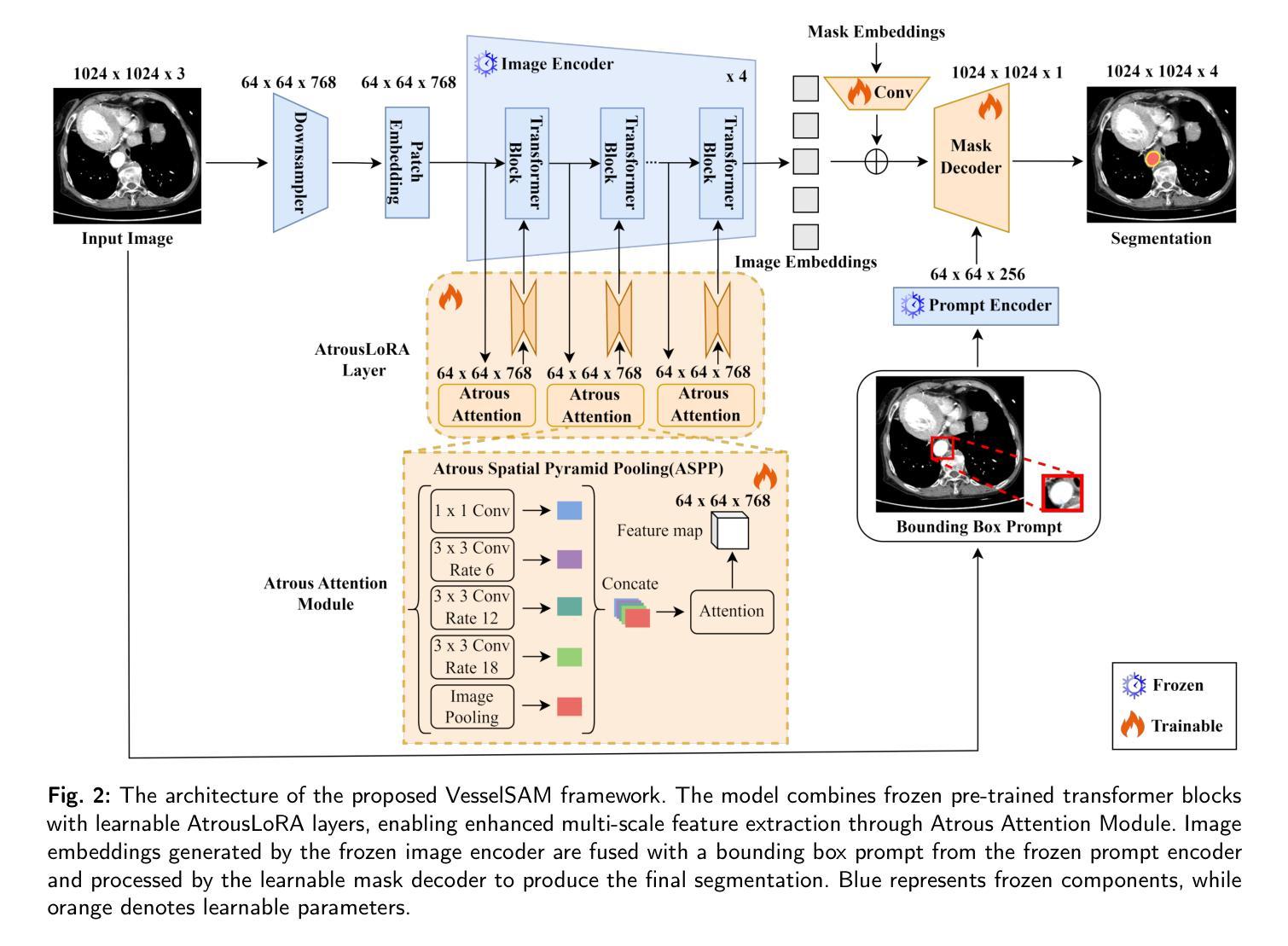
Medical image segmentation is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment planning, especially when dealing with complex anatomical structures such as vessels. However, accurately segmenting vessels remains challenging due to their small size, intricate edge structures, and susceptibility to artifacts and imaging noise. In this work, we propose VesselSAM, an enhanced version of the Segment Anything Model (SAM), specifically tailored for aortic vessel segmentation. VesselSAM incorporates AtrousLoRA, a novel module integrating Atrous Attention and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), to enhance segmentation performance. Atrous Attention enables the model to capture multi-scale contextual information, preserving both fine-grained local details and broader global context. Additionally, LoRA facilitates efficient fine-tuning of the frozen SAM image encoder, reducing the number of trainable parameters and thereby enhancing computational efficiency. We evaluate VesselSAM using two challenging datasets: the Aortic Vessel Tree (AVT) dataset and the Type-B Aortic Dissection (TBAD) dataset. VesselSAM achieves state-of-the-art performance, attaining DSC scores of 93.50%, 93.25%, 93.02%, and 93.26% across multi-center datasets. Our results demonstrate that VesselSAM delivers high segmentation accuracy while significantly reducing computational overhead compared to existing large-scale models. This development paves the way for enhanced AI-based aortic vessel segmentation in clinical environments. The code and models will be released at https://github.com/Adnan-CAS/AtrousLora.
医学图像分割对于临床诊断和治疗计划的制定至关重要,特别是在处理复杂的解剖结构(如血管)时。然而,由于血管尺寸小、边缘结构复杂以及容易受到伪影和成像噪声的影响,准确分割血管仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了专为主动脉血管分割定制的增强版Segment Anything Model(SAM),称为VesselSAM。VesselSAM结合了AtrousLoRA这一新型模块,该模块集成了Atrous Attention和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)技术,以提高分割性能。Atrous Attention允许模型捕获多尺度上下文信息,同时保留精细的局部细节和更广泛的全局上下文。此外,LoRA有助于对冻结的SAM图像编码器进行高效微调,减少可训练参数的数量,从而提高计算效率。我们使用两个具有挑战性的数据集对VesselSAM进行了评估:主动脉血管树(AVT)数据集和B型主动脉夹层(TBAD)数据集。VesselSAM达到了最先进的性能水平,在多中心数据集上的DSC得分分别为93.50%、93.25%、93.02%和93.26%。我们的结果表明,与现有的大规模模型相比,VesselSAM在提供高分割准确性的同时,计算开销大大降低。这为临床环境中增强的基于AI的主动脉血管分割铺平了道路。相关代码和模型将在https://github.com/Adnan-CAS/AtrousLora发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
摘要
医学图像分割对于临床诊断和治疗计划至关重要,尤其是处理复杂的解剖结构如血管时。然而,由于血管尺寸小、边缘结构复杂以及易受伪影和成像噪声影响,准确分割血管仍然具有挑战性。本研究提出了VesselSAM,它是专为主动脉血管分割设计的Segment Anything Model(SAM)的增强版。VesselSAM结合了AtrousLoRA这一新型模块,该模块集成了Atrous Attention和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA),以提高分割性能。Atrous Attention使模型能够捕捉多尺度上下文信息,同时保留精细的局部细节和更广泛的全球上下文。此外,LoRA有助于有效微调冻结的SAM图像编码器,减少训练参数数量,从而提高计算效率。我们使用两个具有挑战性的数据集:主动脉血管树(AVT)数据集和B型主动脉夹层(TBAD)数据集对VesselSAM进行了评估。VesselSAM取得了最先进的性能,在多中心数据集上的DSC得分分别为93.50%、93.25%、93.02%和93.26%。我们的结果表明,与现有大规模模型相比,VesselSAM实现了高分割精度,同时大大降低了计算开销。这为临床环境中增强的基于AI的主动脉血管分割开辟了道路。相关代码和模型将发布在https://github.com/Adnan-CAS/AtrousLora。
要点掌握
- 医学图像分割对于临床诊断和治疗计划至关重要,尤其是针对复杂解剖结构如血管的分割。
- 血管分割具有挑战性,因为血管尺寸小、边缘复杂且易受伪影和噪声影响。
- VesselSAM模型被提出用于主动脉血管分割,它在Segment Anything Model(SAM)的基础上进行了增强。
- VesselSAM结合了AtrousLoRA模块,该模块包含Atrous Attention和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA),旨在提高分割性能。
- Atrous Attention能够捕捉多尺度上下文信息,同时保留局部细节和全局上下文。
- LoRA有助于有效微调图像编码器,减少训练参数,提高计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

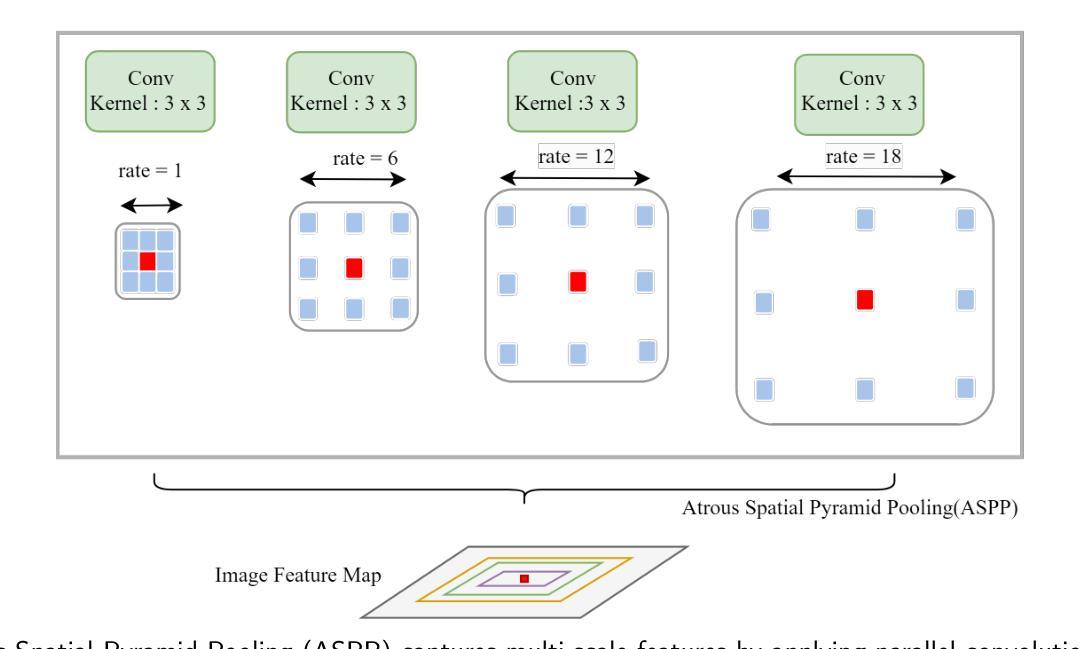
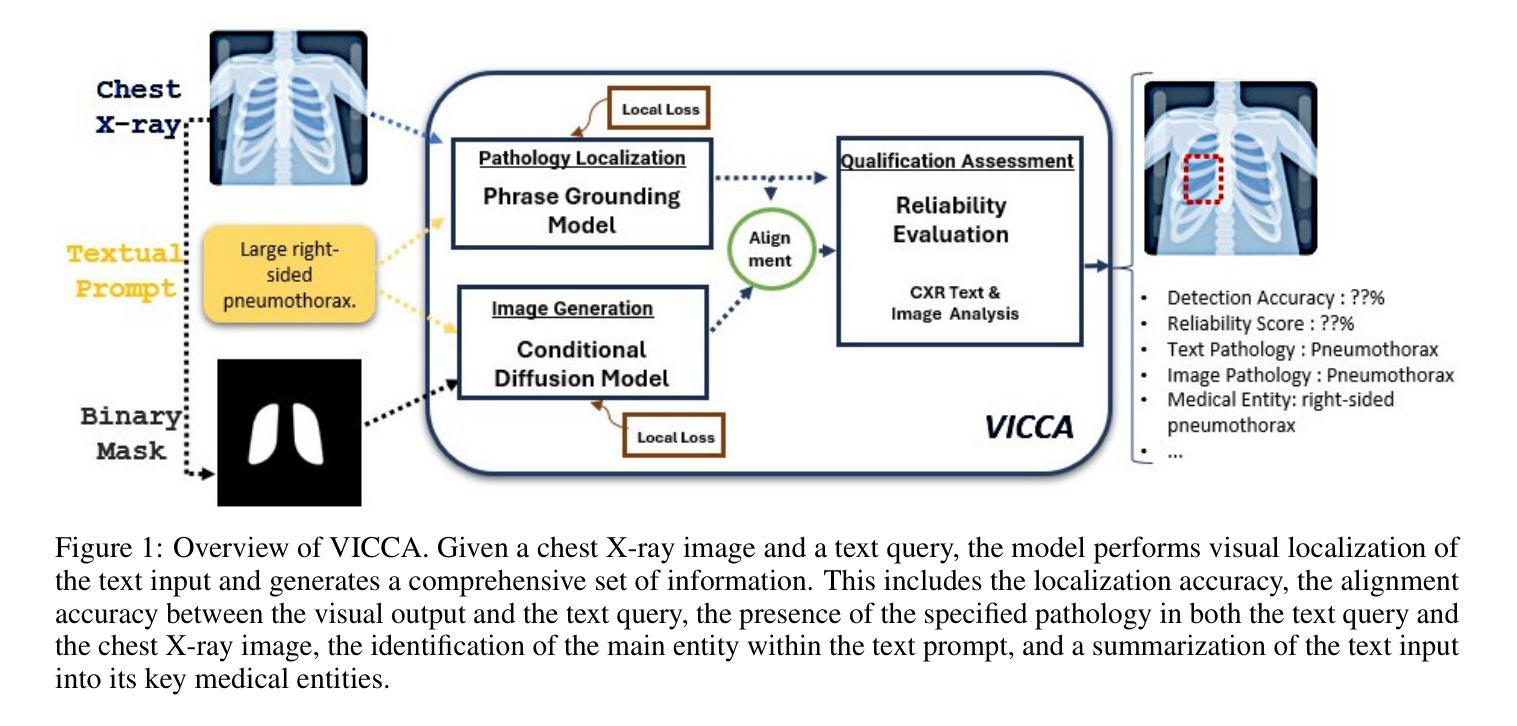
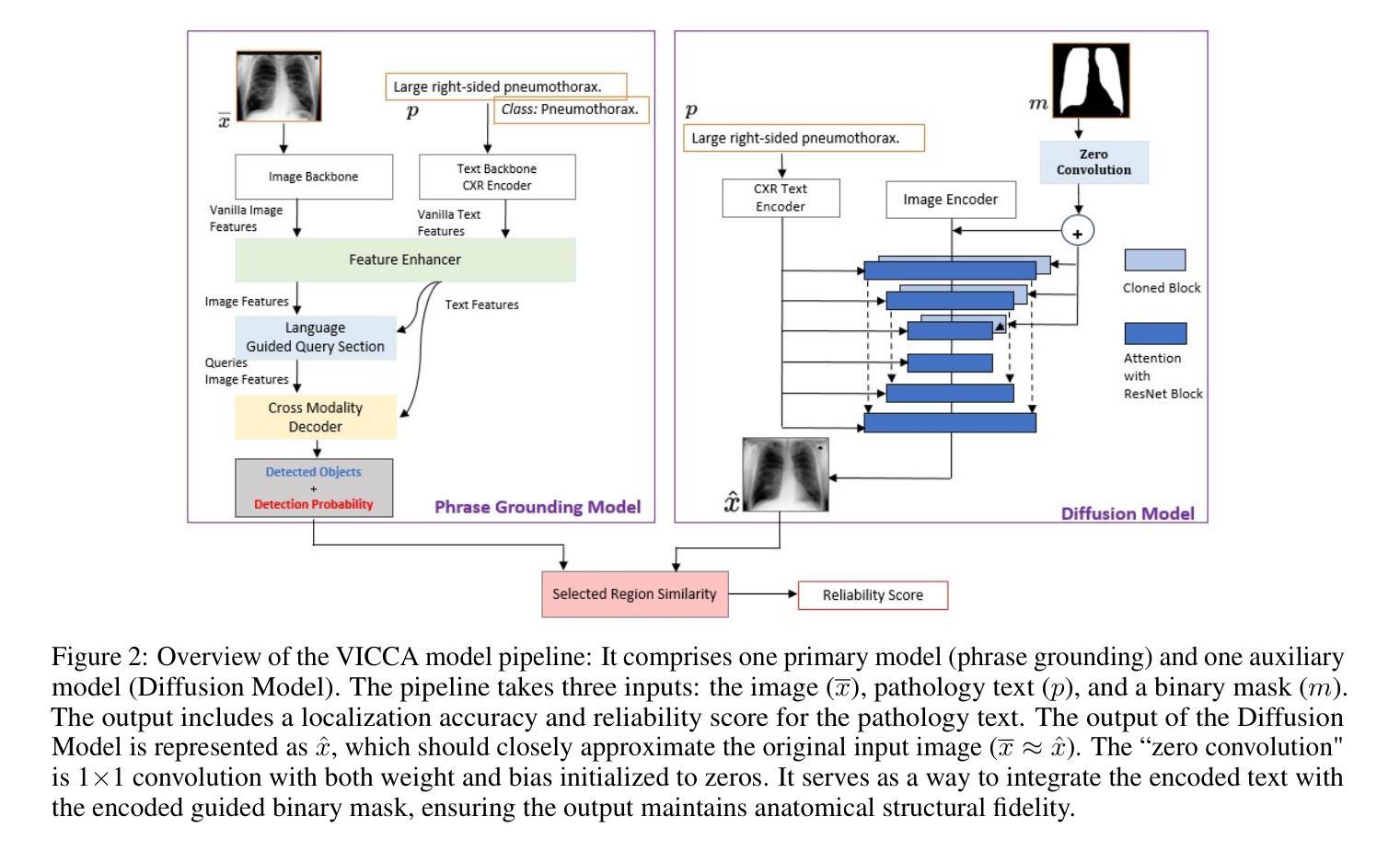
VICCA: Visual Interpretation and Comprehension of Chest X-ray Anomalies in Generated Report Without Human Feedback
Authors:Sayeh Gholipour Picha, Dawood Al Chanti, Alice Caplier
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes increasingly central to healthcare, the demand for explainable and trustworthy models is paramount. Current report generation systems for chest X-rays (CXR) often lack mechanisms for validating outputs without expert oversight, raising concerns about reliability and interpretability. To address these challenges, we propose a novel multimodal framework designed to enhance the semantic alignment and localization accuracy of AI-generated medical reports. Our framework integrates two key modules: a Phrase Grounding Model, which identifies and localizes pathologies in CXR images based on textual prompts, and a Text-to-Image Diffusion Module, which generates synthetic CXR images from prompts while preserving anatomical fidelity. By comparing features between the original and generated images, we introduce a dual-scoring system: one score quantifies localization accuracy, while the other evaluates semantic consistency. This approach significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in pathology localization and text-to-image alignment. The integration of phrase grounding with diffusion models, coupled with the dual-scoring evaluation system, provides a robust mechanism for validating report quality, paving the way for more trustworthy and transparent AI in medical imaging.
随着人工智能在医疗保健领域的重要性不断提升,对可解释性和可靠性的模型的需求至关重要。目前针对胸部X射线(CXR)的报告生成系统常常缺乏在没有专家监督的情况下验证输出的机制,这引发了人们对可靠性和可解释性的担忧。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的多模式框架,旨在提高人工智能生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位精度。我们的框架集成了两个关键模块:短语定位模型,该模型根据文本提示识别和定位CXR图像中的病理特征;文本到图像扩散模块,该模块从提示中生成合成CXR图像,同时保留解剖结构的保真度。通过比较原始图像和生成图像之间的特征,我们引入了一种双重评分系统:一个分数量化定位精度,另一个分数评估语义一致性。该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位、文本到图像对齐方面达到了最先进水平。短语定位与扩散模型的集成,加上双重评分评估系统,为验证报告质量提供了稳健的机制,为医学影像领域中更可靠、更透明的AI应用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了随着人工智能在医疗领域的中心地位日益凸显,对可解释性和可靠性的需求愈发重要。针对当前胸部X光射线报告生成系统缺乏验证机制的问题,提出了一种新型的多模态框架,旨在提高AI生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位精度。该框架集成了两个关键模块:短语定位模型和文本到图像扩散模块。短语定位模型根据文本提示识别和定位CXR图像中的病理特征,而文本到图像扩散模块则从提示生成合成CXR图像,保持解剖学的真实性。通过比较原始和生成图像的特征,引入了一种双重评分系统,既量化定位精度又评估语义一致性。该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位和文本到图像对齐方面达到最新水平。短语定位与扩散模型的集成以及双重评分评估系统相结合,为验证报告质量提供了稳健机制,为医疗影像中的更可信和透明的AI铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的主要观点摘要:
- 随着人工智能在医疗领域的重要性增强,对可解释性和可靠性的需求愈发重要。
- 当前胸部X光射线报告生成系统缺乏验证机制,导致可靠性和解释性受到质疑。
- 提出了一种新型的多模态框架,旨在提高AI生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位精度。
- 该框架集成了短语定位模型和文本到图像扩散模块。
- 短语定位模型根据文本提示定位和识别CXR图像中的病理特征。
- 文本到图像扩散模块生成合成CXR图像,并保持解剖学真实性。
点此查看论文截图

CAD-GPT: Synthesising CAD Construction Sequence with Spatial Reasoning-Enhanced Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Siyu Wang, Cailian Chen, Xinyi Le, Qimin Xu, Lei Xu, Yanzhou Zhang, Jie Yang
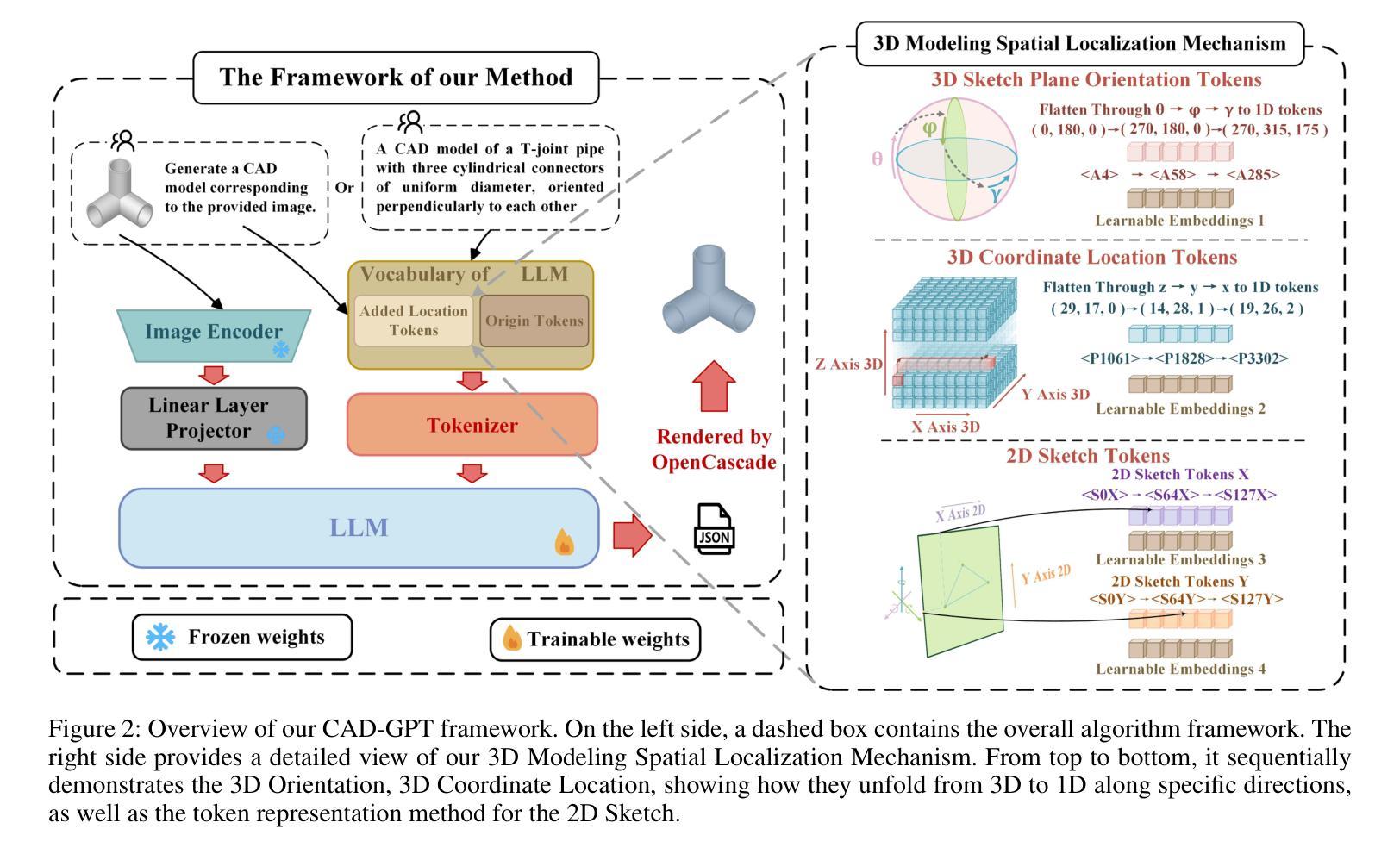
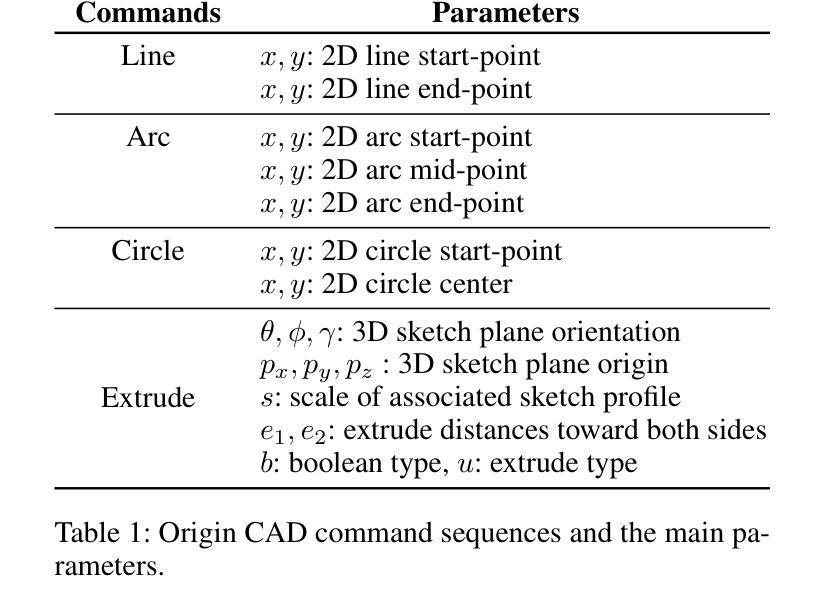
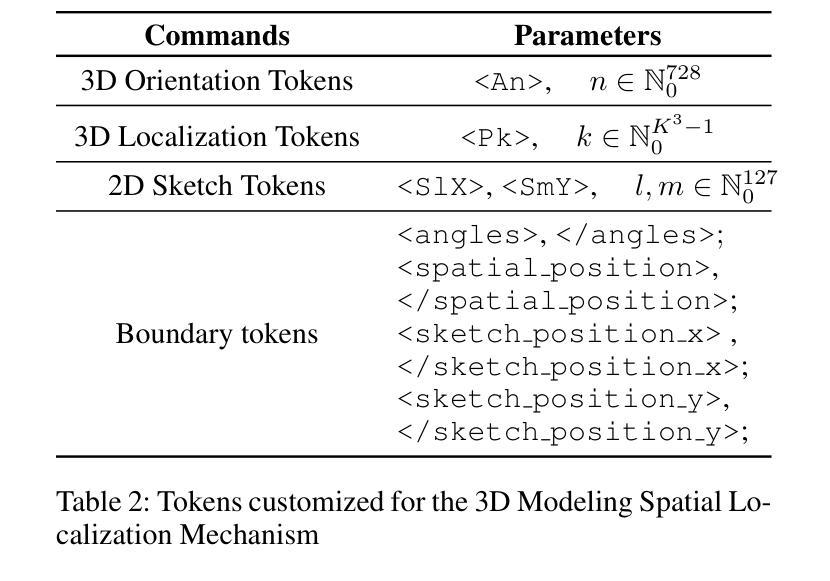
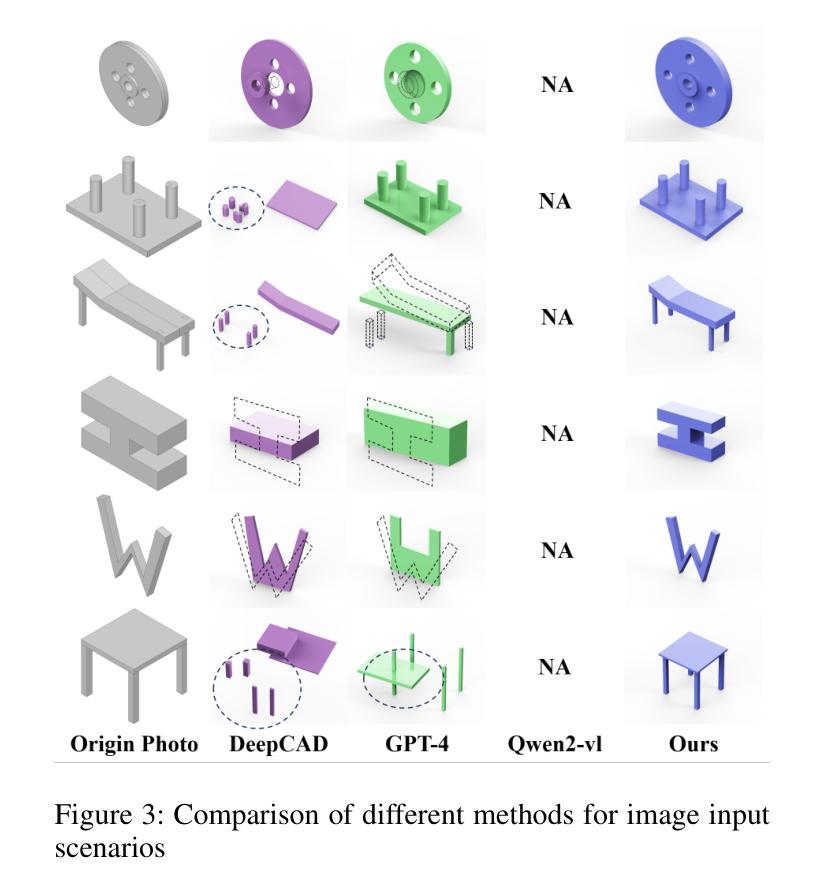
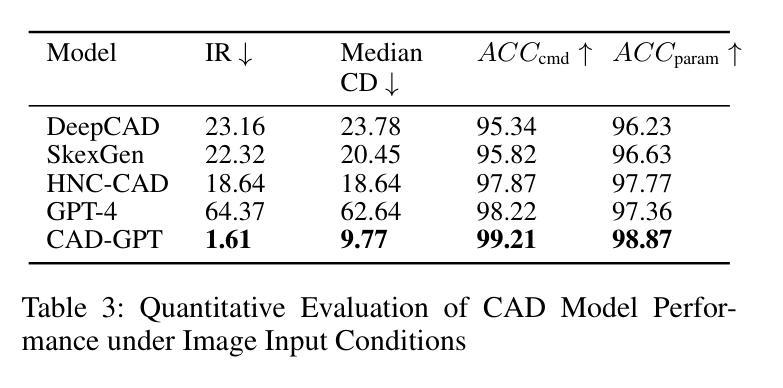
Computer-aided design (CAD) significantly enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and innovation of design processes by enabling precise 2D and 3D modeling, extensive analysis, and optimization. Existing methods for creating CAD models rely on latent vectors or point clouds, which are difficult to obtain, and storage costs are substantial. Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have inspired researchers to use natural language instructions and images for CAD model construction. However, these models still struggle with inferring accurate 3D spatial location and orientation, leading to inaccuracies in determining the spatial 3D starting points and extrusion directions for constructing geometries. This work introduces CAD-GPT, a CAD synthesis method with spatial reasoning-enhanced MLLM that takes either a single image or a textual description as input. To achieve precise spatial inference, our approach introduces a 3D Modeling Spatial Mechanism. This method maps 3D spatial positions and 3D sketch plane rotation angles into a 1D linguistic feature space using a specialized spatial unfolding mechanism, while discretizing 2D sketch coordinates into an appropriate planar space to enable precise determination of spatial starting position, sketch orientation, and 2D sketch coordinate translations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CAD-GPT consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in CAD model synthesis, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)通过实现精确的2D和3D建模、全面的分析和优化,显著提高了设计过程的效率、准确性和创新性。现有的创建CAD模型的方法依赖于潜在向量或点云,这些难以获得,且存储成本高昂。最近多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的进步激发了研究人员使用自然语言指令和图像进行CAD模型构建。然而,这些模型在推断准确的3D空间位置和方向时仍存在问题,导致在确定构建几何体的空间3D起点和挤压方向时出现不准确。本研究介绍了CAD-GPT,这是一种带有空间推理增强的MLLM的CAD合成方法,它接受单张图像或文本描述作为输入。为了实现精确的空间推断,我们的方法引入了一种3D建模空间机制。该方法使用专门的空间展开机制将3D空间位置和3D草图平面旋转角度映射到1D语言特征空间中,同时将2D草图坐标离散化到适当的平面空间中,从而实现空间起始位置、草图方向和2D草图坐标翻译的精确确定。大量实验表明,无论是在定量还是定性方面,CAD-GPT在CAD模型合成方面都始终优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025 (Vol. 39, No. 8), pages 7880-7888. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v39i8.32849
Summary
基于计算机的设计(CAD)技术提高了设计过程的效率、精度和创新能力,可实现精确二维和三维建模、全面分析和优化。现有创建CAD模型的方法依赖于潜在向量或点云,获取困难且存储成本高。最新研究引入了具有空间推理能力的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),采用自然语言指令和图像进行CAD模型构建。本研究提出CAD-GPT方法,该方法以单张图像或文本描述作为输入,实现了精确的推理过程,并在CAD合成中引入了一种新的空间机制。实验证明,CAD-GPT在CAD模型合成方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
1. 计算机辅助设计(CAD)提高了设计效率、精度和创新性,借助精确建模、分析和优化实现。
2. 当前CAD模型创建方法面临获取和存储成本高的问题。
3. 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)为CAD模型构建提供了新的思路,结合自然语言指令和图像进行模型构建。
4. MLLMs在推断精确的3D空间位置和方向时仍存在挑战,影响空间3D起点和挤压方向的精确判断。
5. CAD-GPT方法被引入解决上述问题,采用单一图像或文本描述作为输入,具有精确的空间推理能力。
6. CAD-GPT通过引入3D建模空间机制,将3D空间位置和草图平面旋转角度映射到一维语言特征空间。
点此查看论文截图