⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-27 更新
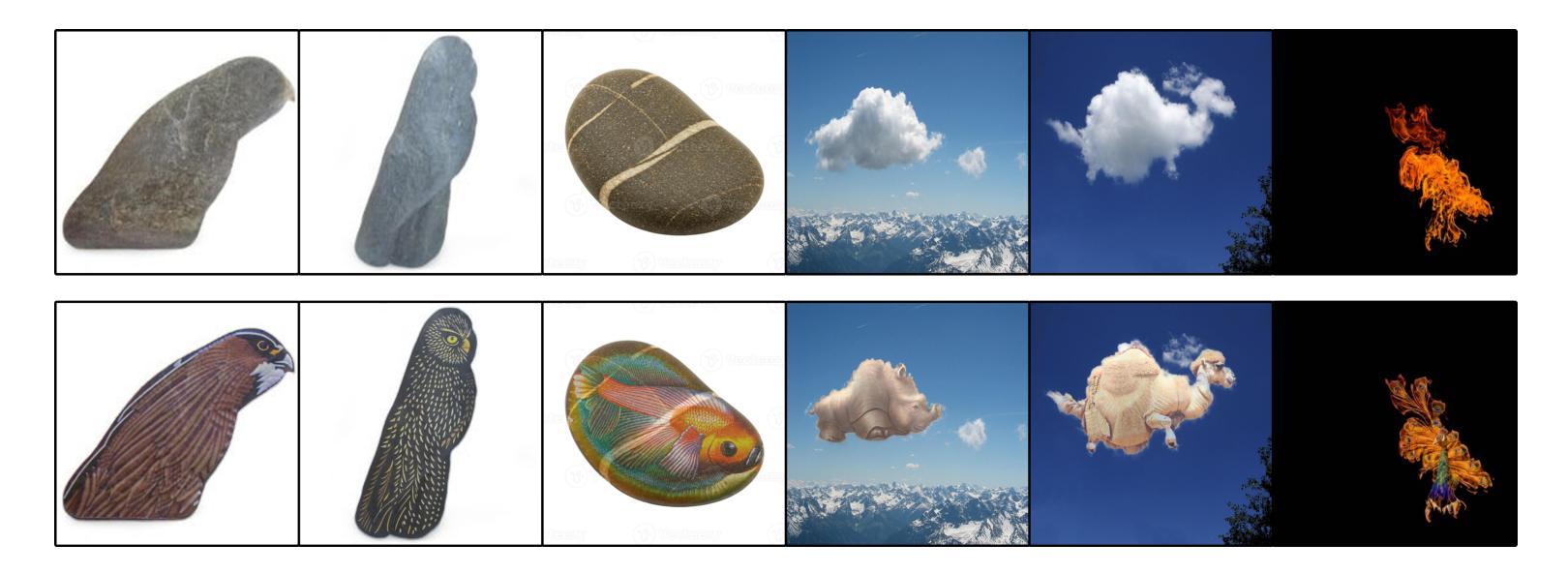
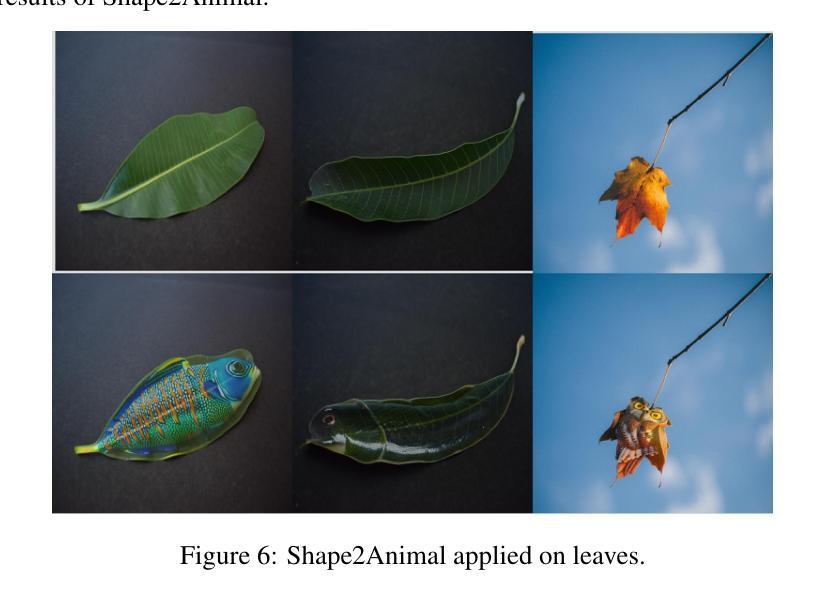
Shape2Animal: Creative Animal Generation from Natural Silhouettes
Authors:Quoc-Duy Tran, Anh-Tuan Vo, Dinh-Khoi Vo, Tam V. Nguyen, Minh-Triet Tran, Trung-Nghia Le
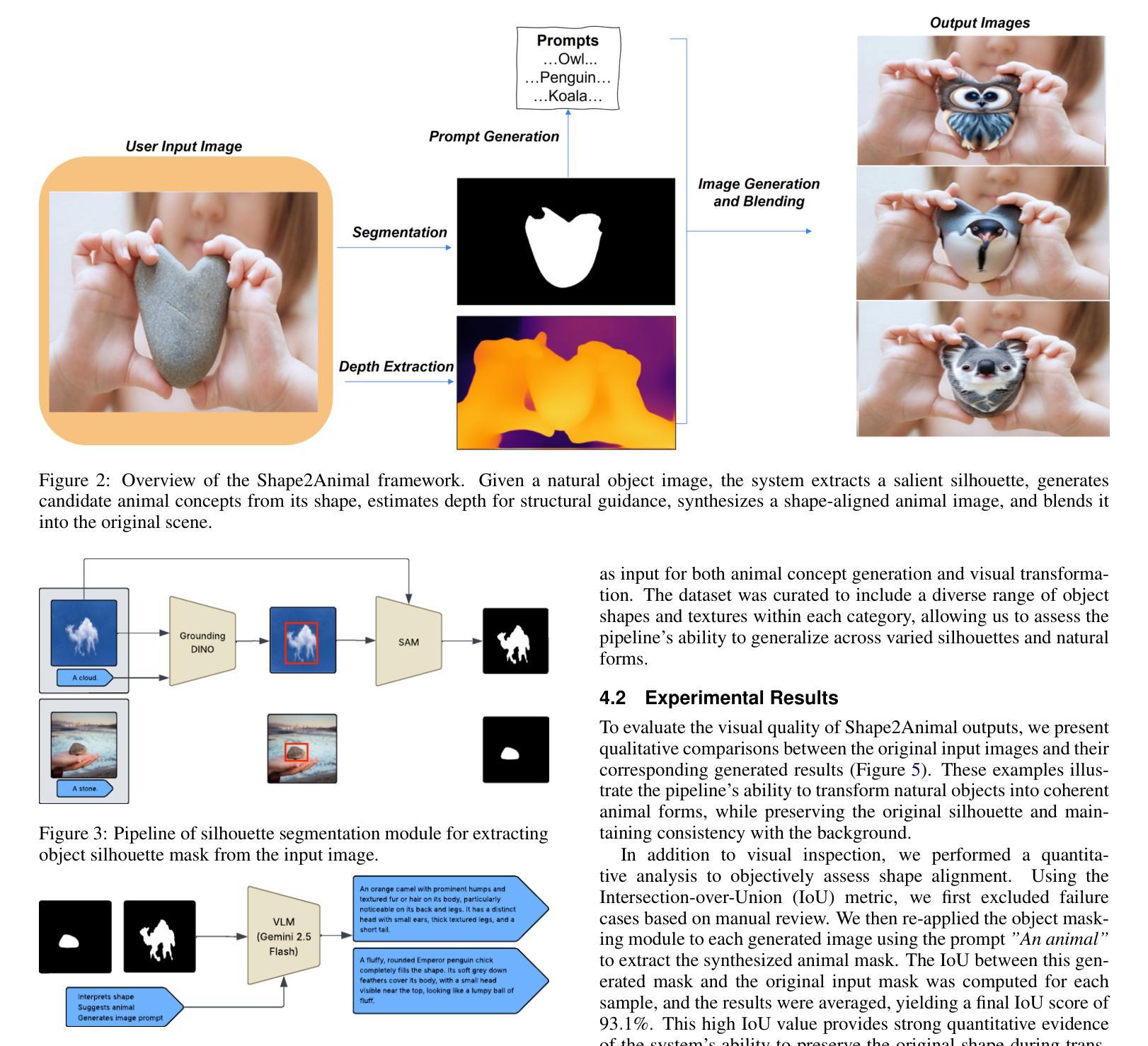
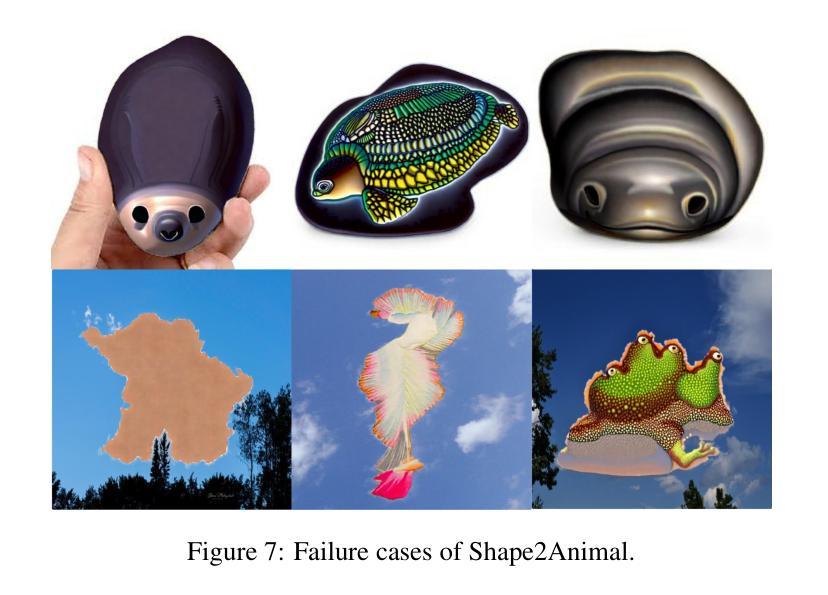
Humans possess a unique ability to perceive meaningful patterns in ambiguous stimuli, a cognitive phenomenon known as pareidolia. This paper introduces Shape2Animal framework to mimics this imaginative capacity by reinterpreting natural object silhouettes, such as clouds, stones, or flames, as plausible animal forms. Our automated framework first performs open-vocabulary segmentation to extract object silhouette and interprets semantically appropriate animal concepts using vision-language models. It then synthesizes an animal image that conforms to the input shape, leveraging text-to-image diffusion model and seamlessly blends it into the original scene to generate visually coherent and spatially consistent compositions. We evaluated Shape2Animal on a diverse set of real-world inputs, demonstrating its robustness and creative potential. Our Shape2Animal can offer new opportunities for visual storytelling, educational content, digital art, and interactive media design. Our project page is here: https://shape2image.github.io
人类拥有在模糊刺激中感知有意义模式的能力,这是一种称为“帕里多利现象”的认知现象。本文介绍了Shape2Animal框架,它通过重新解释自然物体的轮廓(如云彩、石头或火焰)来模仿这种想象力能力,将这些轮廓转化为合理的动物形态。我们的自动化框架首先执行开放词汇分割技术,以提取物体轮廓并使用视觉语言模型解释语义上适当的动物概念。然后,它利用文本到图像的扩散模型合成符合输入形状的动物图像,并将其无缝融合到原始场景中,生成视觉连贯且空间一致的构图。我们在各种真实世界的输入上对Shape2Animal进行了评估,证明了其稳健性和创造力潜力。Shape2Animal为视觉故事叙述、教育内容、数字艺术和交互式媒体设计提供了新的机会。我们的项目页面位于:https://shape2image.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人类拥有在模糊刺激中感知有意义模式的能力,称为帕里多利现象。本文介绍的Shape2Animal框架模拟了这一想象力,重新解释自然物体的轮廓,如云彩、石头或火焰,作为合理的动物形态。该自动化框架首先进行开放词汇分割以提取物体轮廓,并使用视觉语言模型解释语义上适当的动物概念。然后,它利用文本到图像的扩散模型合成符合输入形状的动物图像,并将其无缝融合到原始场景中,以产生视觉连贯且空间一致的构图。在多种真实世界输入上评估了Shape2Animal的稳健性和创造性潜力。Shape2Animal可为视觉叙事、教育内容、数字艺术和交互式媒体设计提供新机会。我们的项目页面位于:https://shape2image.github.io。简而言之,这是一个以Shape2Animal框架展示人造智能对人类视觉创意的模仿能力的研究。框架可以将自然物体的轮廓转化为动物形态,具有强大的稳健性和创造性潜力。该技术在视觉叙事、教育等领域有广泛应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- Shape2Animal框架模拟人类的帕里多利现象能力,即把自然物体的轮廓解释为动物形态的能力。
- 框架包含开放词汇分割技术以提取物体轮廓和视觉语言模型解释动物概念。
- 利用文本到图像的扩散模型合成符合输入形状的动物图像,并与原始场景无缝融合。
- Shape2Animal在多种真实世界输入上表现出稳健性和创造性潜力。
- Shape2Animal框架在视觉叙事、教育内容、数字艺术和交互式媒体设计等领域具有广泛应用前景。
- 项目页面提供了关于Shape2Animal框架的详细信息和技术实现。
点此查看论文截图



Pay Less Attention to Deceptive Artifacts: Robust Detection of Compressed Deepfakes on Online Social Networks
Authors:Manyi Li, Renshuai Tao, Yufan Liu, Chuangchuang Tan, Haotong Qin, Bing Li, Yunchao Wei, Yao Zhao
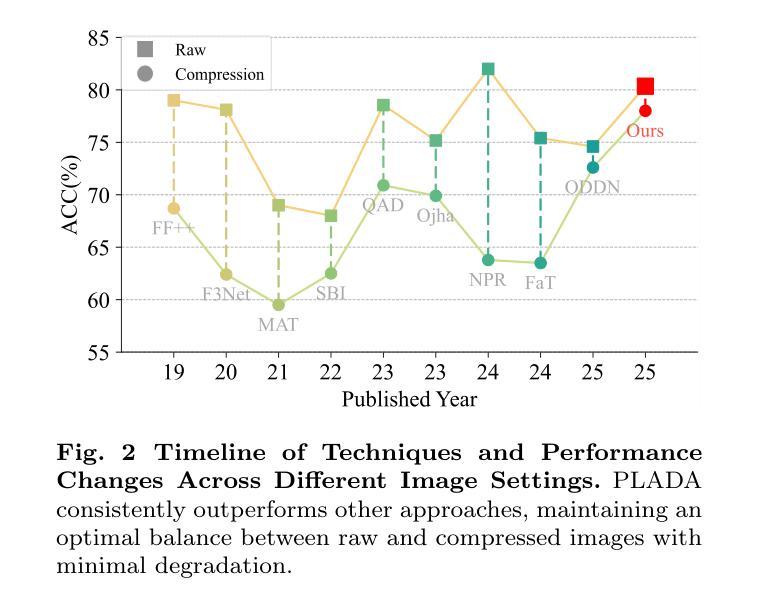
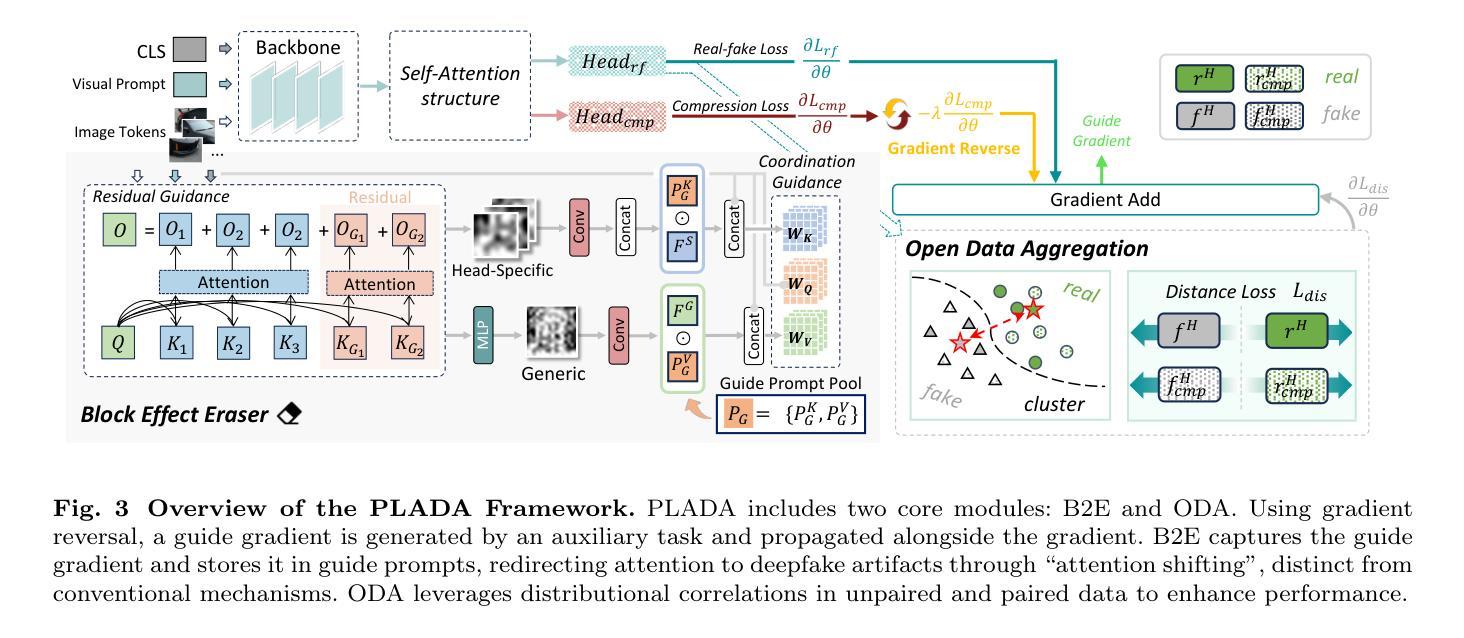
With the rapid advancement of deep learning, particularly through generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models (DMs), AI-generated images, or deepfakes", have become nearly indistinguishable from real ones. These images are widely shared across Online Social Networks (OSNs), raising concerns about their misuse. Existing deepfake detection methods overlook the block effects” introduced by compression in OSNs, which obscure deepfake artifacts, and primarily focus on raw images, rarely encountered in real-world scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose PLADA (Pay Less Attention to Deceptive Artifacts), a novel framework designed to tackle the lack of paired data and the ineffective use of compressed images. PLADA consists of two core modules: Block Effect Eraser (B2E), which uses a dual-stage attention mechanism to handle block effects, and Open Data Aggregation (ODA), which processes both paired and unpaired data to improve detection. Extensive experiments across 26 datasets demonstrate that PLADA achieves a remarkable balance in deepfake detection, outperforming SoTA methods in detecting deepfakes on OSNs, even with limited paired data and compression. More importantly, this work introduces the ``block effect” as a critical factor in deepfake detection, providing a robust solution for open-world scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/ManyiLee/PLADA.
随着深度学习的快速发展,特别是通过生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs),AI生成的图像,或称为“深度伪造”,已经变得几乎与真实的图像无法区分。这些图像在在线社交网络(OSNs)上被广泛共享,引发了关于其误用的担忧。现有的深度伪造检测方法忽略了OSN中压缩引入的“块效应”,这掩盖了深度伪造的痕迹,并且主要关注原始图像,在现实世界场景中很少遇到。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了PLADA(少关注欺骗性人工制品),这是一个新颖的框架,旨在解决配对数据的缺乏以及压缩图像的有效使用问题。PLADA由两个核心模块组成:块效应消除器(B2E),它使用两阶段注意力机制来处理块效应;开放数据聚合(ODA),它处理配对和非配对数据以提高检测能力。在26个数据集上的大量实验表明,PLADA在深度伪造检测方面取得了令人瞩目的平衡,即使在有限的配对数据和压缩情况下,也能在OSN上检测深度伪造方面优于最先进的方法。更重要的是,这项工作将“块效应”作为深度伪造检测的关键因素,为开放世界场景提供了稳健的解决方案。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ManyiLee/PLADA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 10 figures
Summary
随着深度学习,特别是生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)的快速发展,AI生成的图像,即所谓的“深度伪造”(deepfakes)图像,已经变得与真实图像难以区分。这些图像在在线社交网络(OSNs)上被广泛共享,引发了关于其误用的担忧。现有的深度伪造检测方法忽视了OSN中的压缩引入的“块效应”,该效应掩盖了深度伪造的痕迹,并且主要关注原始图像,这在现实场景中很少见。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了PLADA(少关注欺骗性人工制品),一个新颖的设计框架,旨在解决配对数据缺乏和压缩图像使用无效的问题。PLADA由两个核心模块组成:块效应消除器(B2E),使用两阶段注意力机制处理块效应;开放数据聚合(ODA),处理配对和非配对数据以提高检测能力。在26个数据集上的广泛实验表明,PLADA在OSN上的深度伪造检测中实现了出色的平衡,即使在配对数据有限和压缩的情况下也优于最新方法。更重要的是,这项工作将“块效应”作为深度伪造检测的关键因素,为开放世界场景提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的图像(深度伪造)与真实图像难以区分,已在在线社交网络(OSN)上广泛共享,引发误用担忧。
- 现有深度伪造检测方法主要关注原始图像,忽视OSN中的图像压缩所引入的“块效应”。
- PLADA框架提出解决上述挑战,包含处理块效应的核心模块B2E和处理配对及非配对数据的ODA。
- PLADA通过广泛实验证明其在OSN上的深度伪造检测中的出色性能,尤其是在配对数据有限和图像压缩的情况下。
- PLADA引入“块效应”作为深度伪造检测的关键因素,为现实场景提供稳健解决方案。
- PLADA的代码已公开可供使用。
点此查看论文截图


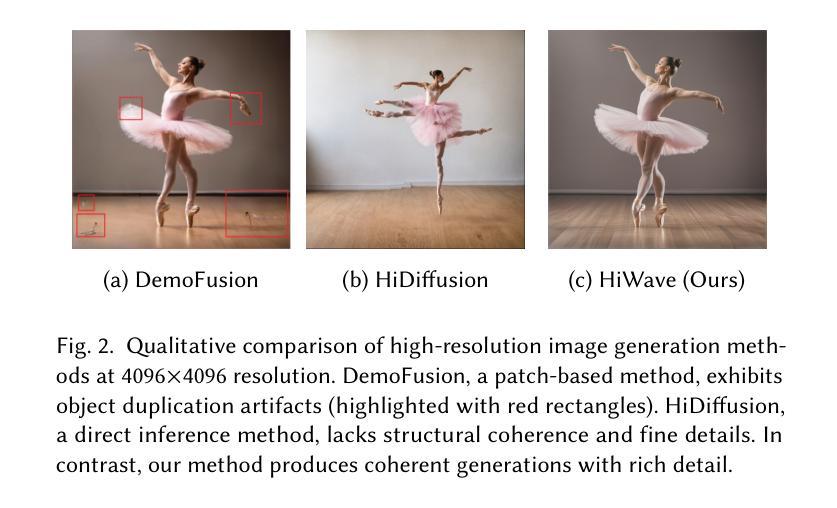
HiWave: Training-Free High-Resolution Image Generation via Wavelet-Based Diffusion Sampling
Authors:Tobias Vontobel, Seyedmorteza Sadat, Farnood Salehi, Romann M. Weber
Diffusion models have emerged as the leading approach for image synthesis, demonstrating exceptional photorealism and diversity. However, training diffusion models at high resolutions remains computationally prohibitive, and existing zero-shot generation techniques for synthesizing images beyond training resolutions often produce artifacts, including object duplication and spatial incoherence. In this paper, we introduce HiWave, a training-free, zero-shot approach that substantially enhances visual fidelity and structural coherence in ultra-high-resolution image synthesis using pretrained diffusion models. Our method employs a two-stage pipeline: generating a base image from the pretrained model followed by a patch-wise DDIM inversion step and a novel wavelet-based detail enhancer module. Specifically, we first utilize inversion methods to derive initial noise vectors that preserve global coherence from the base image. Subsequently, during sampling, our wavelet-domain detail enhancer retains low-frequency components from the base image to ensure structural consistency, while selectively guiding high-frequency components to enrich fine details and textures. Extensive evaluations using Stable Diffusion XL demonstrate that HiWave effectively mitigates common visual artifacts seen in prior methods, achieving superior perceptual quality. A user study confirmed HiWave’s performance, where it was preferred over the state-of-the-art alternative in more than 80% of comparisons, highlighting its effectiveness for high-quality, ultra-high-resolution image synthesis without requiring retraining or architectural modifications.
扩散模型已经成为图像合成的领先方法,表现出了非凡的逼真度和多样性。然而,在高分辨率下训练扩散模型仍然计算上是不现实的,并且现有的零射击生成技术对于合成超出训练分辨率的图像通常会产生伪影,包括对象重复和空间不一致性。在本文中,我们介绍了HiWave,这是一种无需训练、零射击的方法,使用预训练的扩散模型进行超高分辨率图像合成,极大地提高了视觉保真度和结构一致性。我们的方法采用两阶段管道:首先从预训练模型生成基础图像,然后进行分块DDIM反转和基于新型小波的细节增强模块。具体来说,我们首先使用反转方法推导出初始噪声向量,从基础图像中保留全局一致性。随后,在采样过程中,我们的小波域细节增强器保留基础图像的低频成分以确保结构一致性,同时有选择地引导高频成分以丰富细节和纹理。使用Stable Diffusion XL的广泛评估表明,HiWave有效减轻了先前方法中常见的视觉伪影,实现了更高的感知质量。用户研究证实了HiWave的性能,在超过80%的比较中,它比最先进的替代品更受欢迎,这突出了其在无需重新训练或修改架构的情况下进行高质量、超高分辨率图像合成的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了HiWave,这是一种无需训练、零射击的方法,使用预训练的扩散模型进行超高分辨率图像合成,显著提高了视觉保真度和结构连贯性。HiWave采用两阶段管道,首先生成基础图像,然后进行斑片状DDIM反转和基于小波的细节增强模块。它通过保留基础图像的低频成分确保结构一致性,同时选择性引导高频成分丰富细节和纹理。使用Stable Diffusion XL的广泛评估证明,HiWave有效减轻了先前方法中常见的视觉伪影,实现了优越的感知质量。用户研究证实,HiWave在超过80%的比较中优于最新技术替代方案,突显其在无需重新训练或修改架构的情况下实现高质量、超高分辨率图像合成的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为图像合成的领先方法,展现出卓越的逼真度和多样性。
- 训练扩散模型进行高分辨率图像合成计算量大,现有零射击生成技术在合成超过训练分辨率的图像时会产生伪影。
- HiWave是一种无需训练的零射击方法,用于超高分辨率图像合成,提高了视觉保真度和结构连贯性。
- HiWave采用两阶段管道:生成基础图像,然后进行斑片状DDIM反转和基于小波的细节增强。
- HiWave通过保留基础图像的低频成分来确保结构一致性,同时引导高频成分丰富细节和纹理。
- 使用Stable Diffusion XL的广泛评估证明HiWave方法有效减轻伪影,实现优越感知质量。
点此查看论文截图


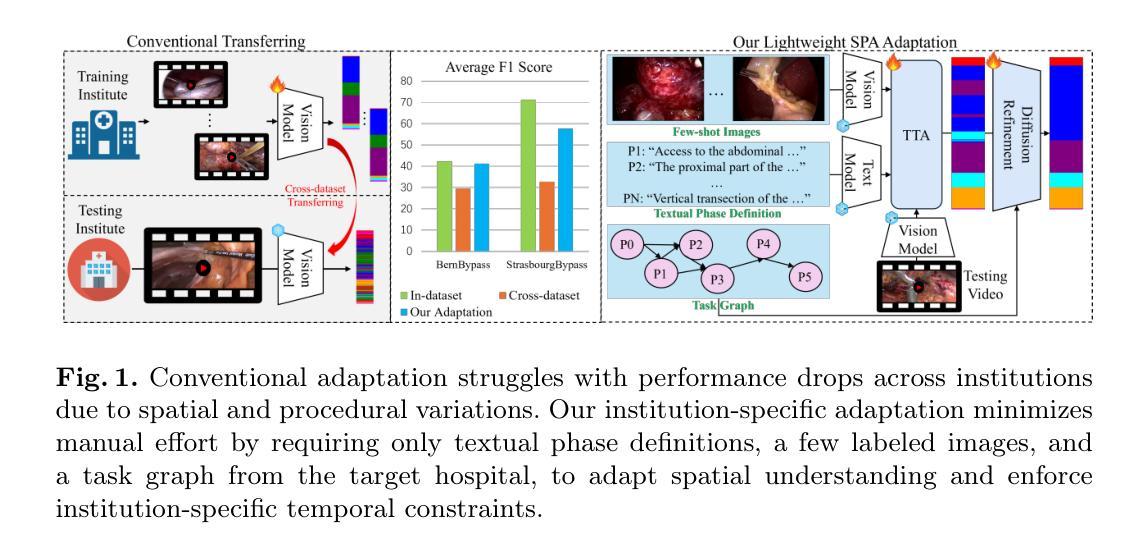
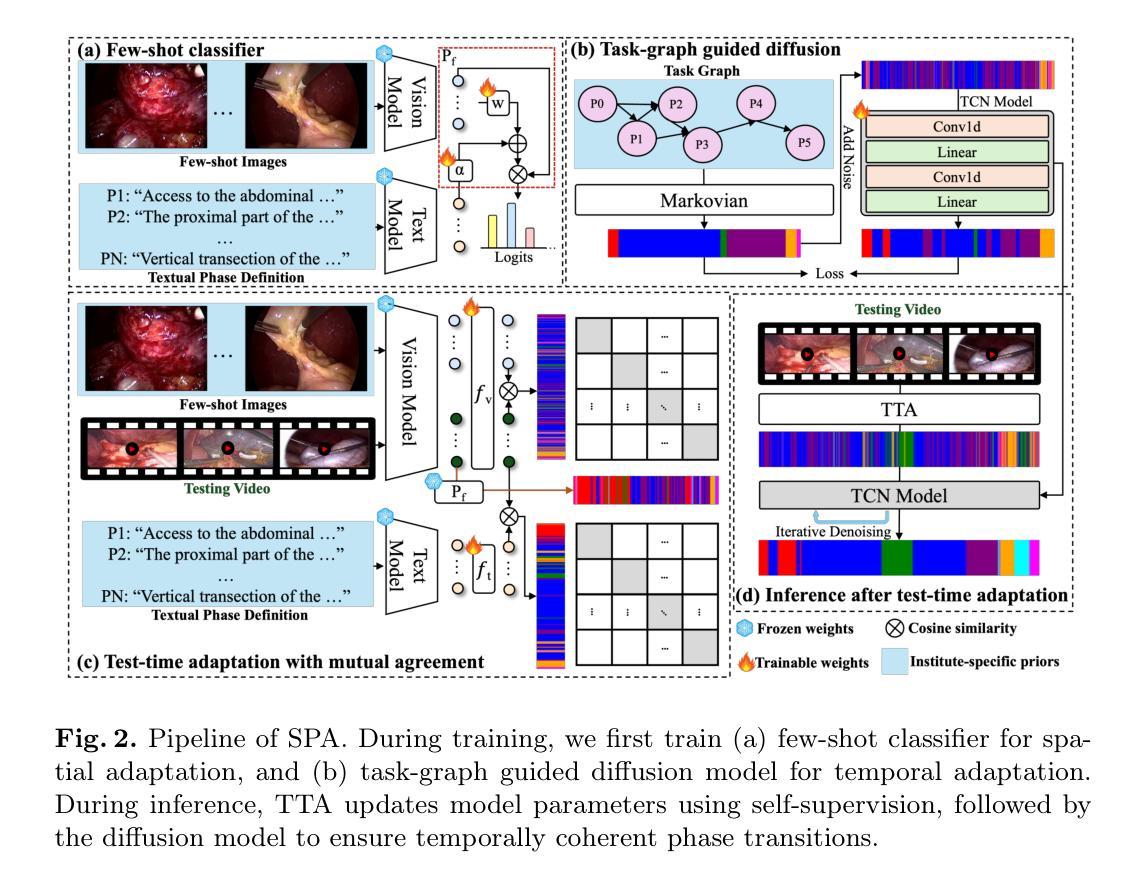
Recognizing Surgical Phases Anywhere: Few-Shot Test-time Adaptation and Task-graph Guided Refinement
Authors:Kun Yuan, Tingxuan Chen, Shi Li, Joel L. Lavanchy, Christian Heiliger, Ege Özsoy, Yiming Huang, Long Bai, Nassir Navab, Vinkle Srivastav, Hongliang Ren, Nicolas Padoy
The complexity and diversity of surgical workflows, driven by heterogeneous operating room settings, institutional protocols, and anatomical variability, present a significant challenge in developing generalizable models for cross-institutional and cross-procedural surgical understanding. While recent surgical foundation models pretrained on large-scale vision-language data offer promising transferability, their zero-shot performance remains constrained by domain shifts, limiting their utility in unseen surgical environments. To address this, we introduce Surgical Phase Anywhere (SPA), a lightweight framework for versatile surgical workflow understanding that adapts foundation models to institutional settings with minimal annotation. SPA leverages few-shot spatial adaptation to align multi-modal embeddings with institution-specific surgical scenes and phases. It also ensures temporal consistency through diffusion modeling, which encodes task-graph priors derived from institutional procedure protocols. Finally, SPA employs dynamic test-time adaptation, exploiting the mutual agreement between multi-modal phase prediction streams to adapt the model to a given test video in a self-supervised manner, enhancing the reliability under test-time distribution shifts. SPA is a lightweight adaptation framework, allowing hospitals to rapidly customize phase recognition models by defining phases in natural language text, annotating a few images with the phase labels, and providing a task graph defining phase transitions. The experimental results show that the SPA framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot surgical phase recognition across multiple institutions and procedures, even outperforming full-shot models with 32-shot labeled data. Code is available at https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SPA
手术工作流的复杂性和多样性,受到手术室设置、机构协议和解剖结构差异的影响,为开发用于跨机构和跨程序手术理解的通用模型带来了重大挑战。虽然最近基于大规模视觉语言数据的预训练手术基础模型显示出有希望的迁移性,但它们的零样本性能仍然受到领域偏移的限制,在未见过的手术环境中效用有限。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了手术阶段无处不在(SPA),这是一个轻量级的手术工作流程理解框架,能够适应机构设置,并且需要的标注很少。SPA利用少数空间适应技术,使多模式嵌入与机构特定的手术场景和阶段保持一致。它还通过扩散模型保证时间一致性,该模型编码来自机构程序协议的任务图先验。最后,SPA采用动态测试时间适应,利用多模式阶段预测流之间的相互一致性,以自我监督的方式适应给定的测试视频,增强测试时分布变化的可靠性。SPA是一个轻量级的适应框架,允许医院通过用自然语言文本定义阶段、对少数图像进行阶段标签注释以及提供定义阶段转换的任务图来快速定制阶段识别模型。实验结果表明,SPA框架在多机构和程序中的少数手术阶段识别中实现了最佳性能,甚至在32次标注数据的全镜头模型中也是如此。代码可在https://github.com/CAMMA-public/SPA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对手术流程理解的挑战,提出了一种新的轻量级框架——Surgical Phase Anywhere (SPA)。SPA利用大型跨视图语言数据的预训练模型,通过少样本空间适应、扩散建模和动态测试时间适应等技术,实现了对特定机构手术环境的快速自定义模型适应。实验结果表明,SPA框架在多个机构和手术过程中的少样本手术阶段识别中取得了最佳性能,甚至在标注数据只有全量的三十二分之一的情况下也表现优秀。相关代码已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 手术流程的复杂性和多样性给跨机构和跨程序的手术理解模型开发带来了挑战。
- 现有预训练模型虽然具有良好的迁移性,但在未见过的手术环境中的零样本性能仍然受限。
- SPA框架通过少样本空间适应技术,使多模态嵌入与特定机构的手术场景和阶段对齐。
- 扩散建模技术确保了SPA的时间一致性,并编码了来自机构程序协议的任务图先验。
- SPA采用动态测试时间适应,通过多模态阶段预测流的相互一致性,以自我监督的方式适应给定的测试视频,提高了测试时分布变化的可靠性。
- SPA框架允许医院通过自然语言文本定义阶段、对少量图像进行阶段标签注释以及提供定义阶段转换的任务图,来快速定制阶段识别模型。
点此查看论文截图

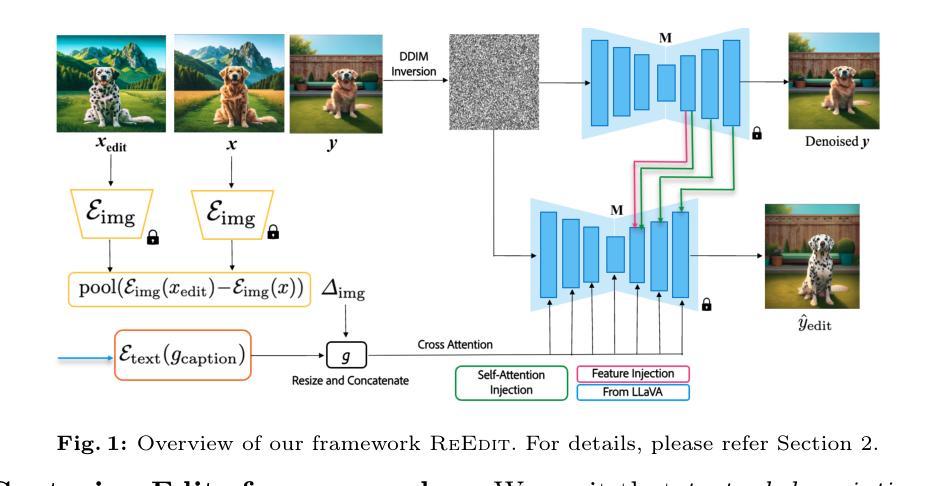
Towards Efficient Exemplar Based Image Editing with Multimodal VLMs
Authors:Avadhoot Jadhav, Ashutosh Srivastava, Abhinav Java, Silky Singh, Tarun Ram Menta, Surgan Jandial, Balaji Krishnamurthy
Text-to-Image Diffusion models have enabled a wide array of image editing applications. However, capturing all types of edits through text alone can be challenging and cumbersome. The ambiguous nature of certain image edits is better expressed through an exemplar pair, i.e., a pair of images depicting an image before and after an edit respectively. In this work, we tackle exemplar-based image editing – the task of transferring an edit from an exemplar pair to a content image(s), by leveraging pretrained text-to-image diffusion models and multimodal VLMs. Even though our end-to-end pipeline is optimization-free, our experiments demonstrate that it still outperforms baselines on multiple types of edits while being ~4x faster.
文本到图像的扩散模型已经启用了多种图像编辑应用程序。然而,仅通过文本捕捉所有类型的编辑可能具有挑战性和繁琐性。某些图像编辑的模糊性质通过示例对(即分别描绘编辑前和编辑后的图像对)来表达更好。在这项工作中,我们解决了基于示例的图像编辑问题——将从示例对到内容图像(们)的编辑任务转移,利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型和跨模态VLMs。尽管我们的端到端管道无需优化,但实验表明,它在多种类型的编辑方面仍优于基线,同时速度提高了约4倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECCV 2024 (AI4VA Workshop)
Summary
本文介绍了基于文本到图像扩散模型(Text-to-Image Diffusion models)的范例图像编辑技术。该技术通过利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型和多媒体视觉语言模型(multimodal VLMs),实现了从范例图像对到内容图像(s)的编辑转移。尽管该端到端的管道无需优化,实验证明其在多种类型的编辑上仍优于基线,且速度提高了约4倍。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型已经启用了广泛的图像编辑应用。
- 仅通过文本捕获所有类型的编辑具有挑战性和繁琐性。
- 某些图像编辑的模糊性更适合通过示例图像对来表达,即展示图像编辑前后的对比。
- 本文解决了基于范例的图像编辑问题,即通过范例图像对将编辑转移到内容图像上。
- 利用了预训练的文本到图像扩散模型和多媒体视觉语言模型来实现这一技术。
- 该端到端的范例图像编辑管道无需优化,但实验证明其性能优于多种基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

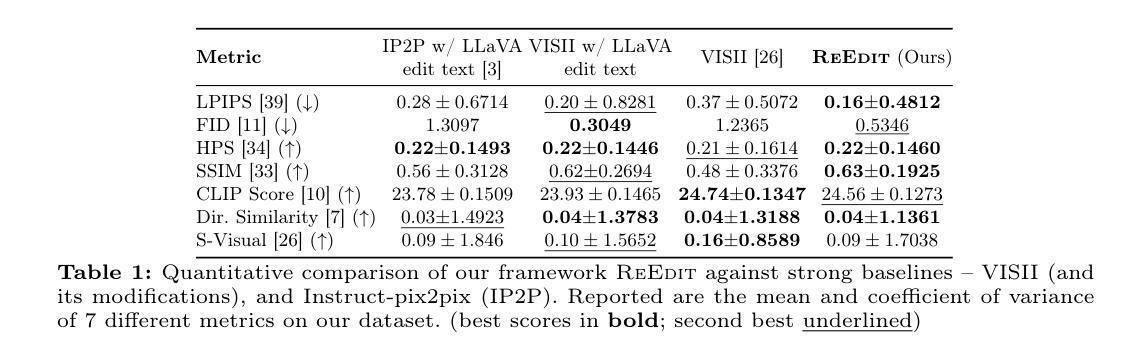

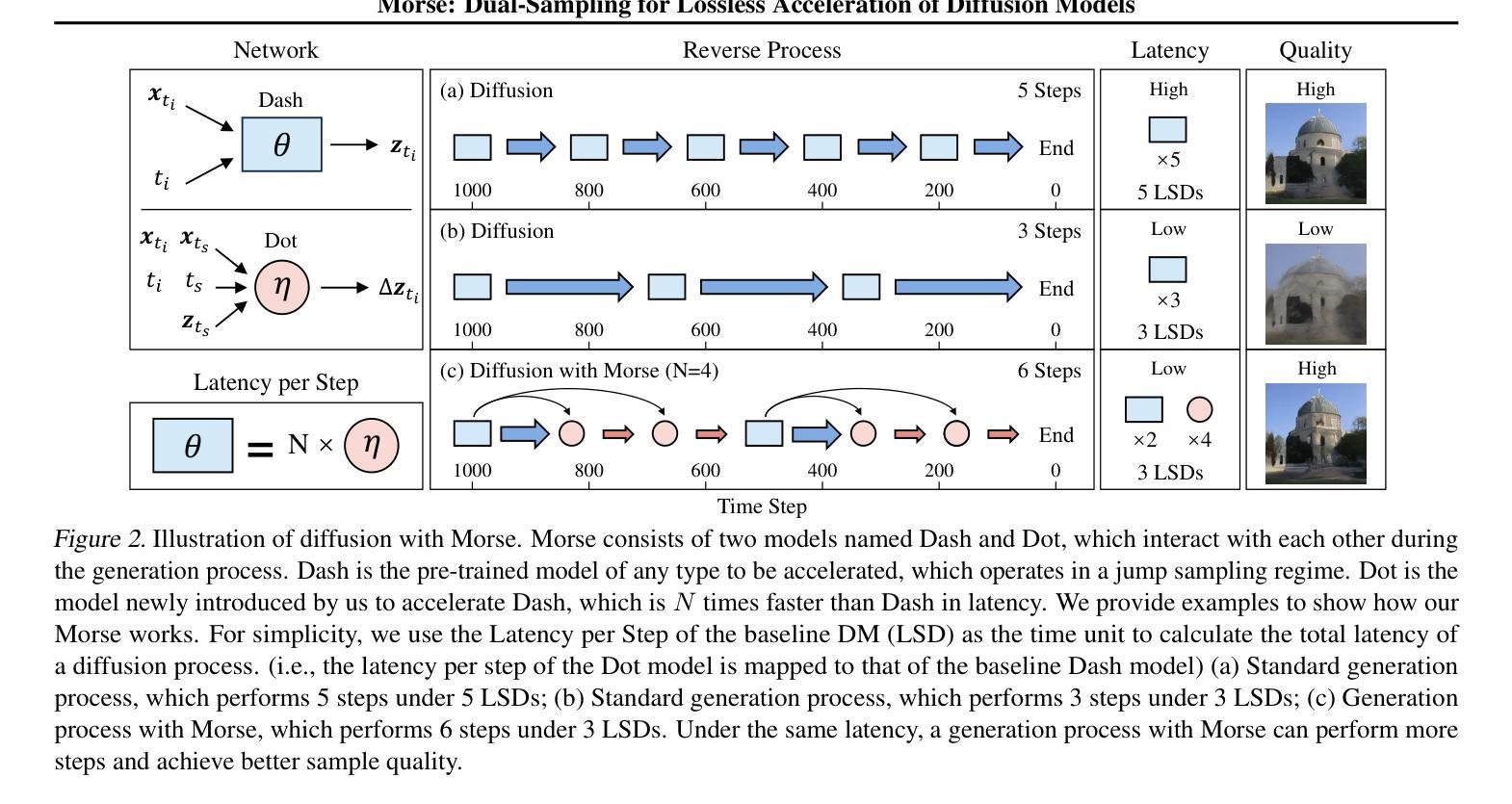
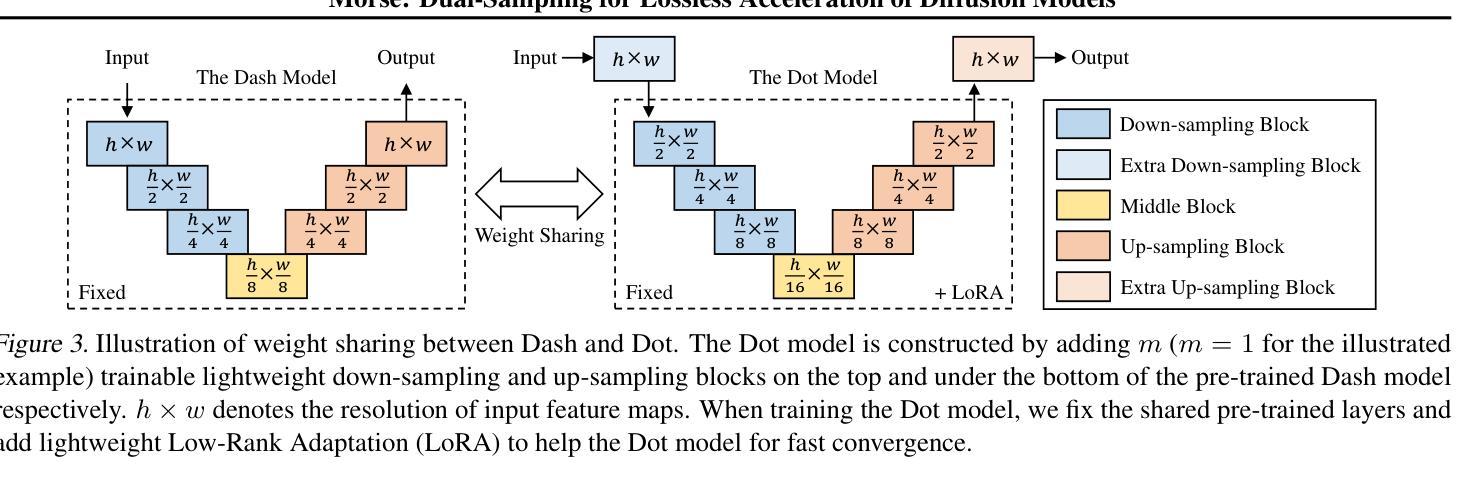
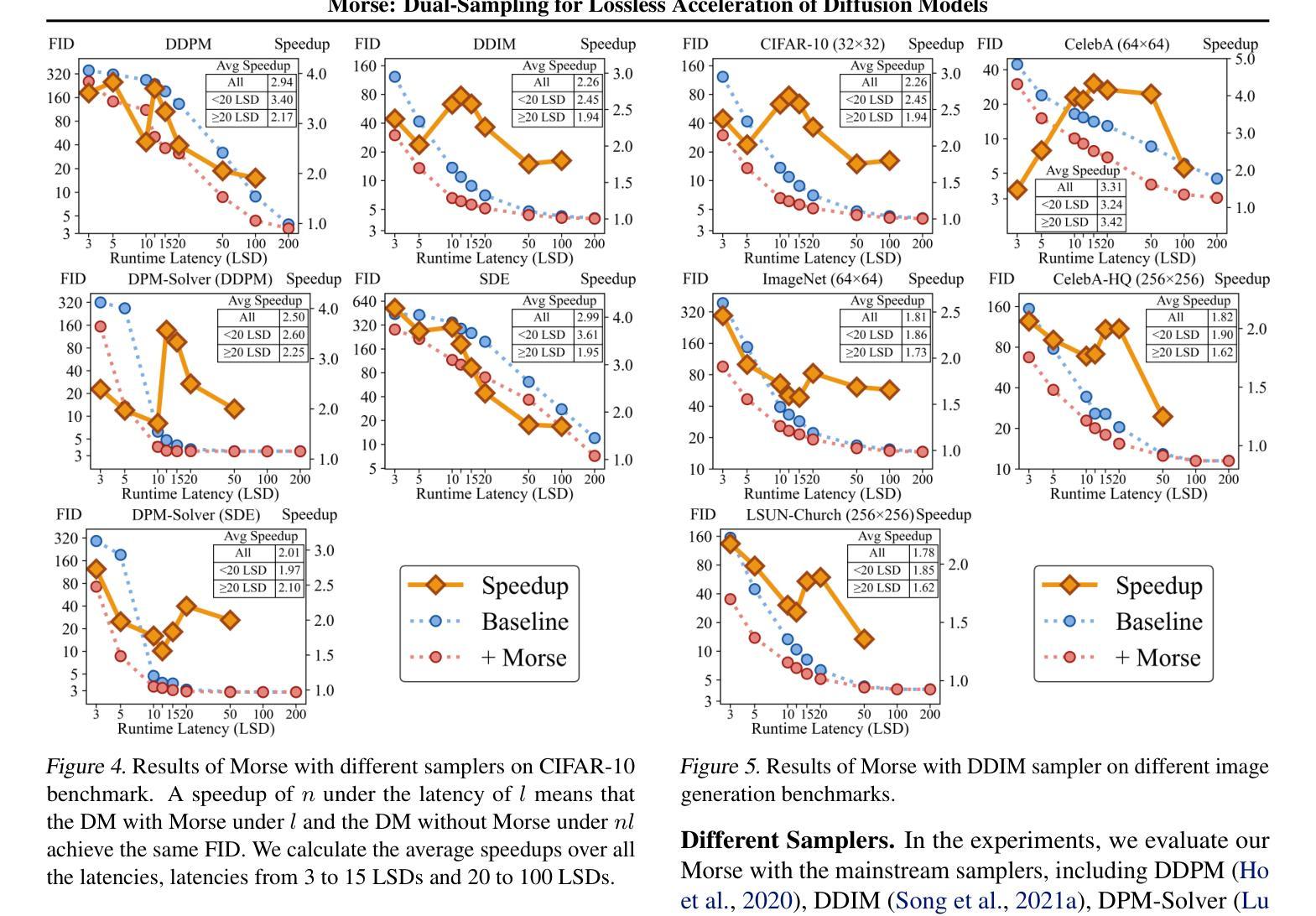
Morse: Dual-Sampling for Lossless Acceleration of Diffusion Models
Authors:Chao Li, Jiawei Fan, Anbang Yao
In this paper, we present Morse, a simple dual-sampling framework for accelerating diffusion models losslessly. The key insight of Morse is to reformulate the iterative generation (from noise to data) process via taking advantage of fast jump sampling and adaptive residual feedback strategies. Specifically, Morse involves two models called Dash and Dot that interact with each other. The Dash model is just the pre-trained diffusion model of any type, but operates in a jump sampling regime, creating sufficient space for sampling efficiency improvement. The Dot model is significantly faster than the Dash model, which is learnt to generate residual feedback conditioned on the observations at the current jump sampling point on the trajectory of the Dash model, lifting the noise estimate to easily match the next-step estimate of the Dash model without jump sampling. By chaining the outputs of the Dash and Dot models run in a time-interleaved fashion, Morse exhibits the merit of flexibly attaining desired image generation performance while improving overall runtime efficiency. With our proposed weight sharing strategy between the Dash and Dot models, Morse is efficient for training and inference. Our method shows a lossless speedup of 1.78X to 3.31X on average over a wide range of sampling step budgets relative to 9 baseline diffusion models on 6 image generation tasks. Furthermore, we show that our method can be also generalized to improve the Latent Consistency Model (LCM-SDXL, which is already accelerated with consistency distillation technique) tailored for few-step text-to-image synthesis. The code and models are available at https://github.com/deep-optimization/Morse.
本文介绍了Morse,一个简单用于无损加速扩散模型的双重采样框架。Morse的关键见解在于通过利用快速跳跃采样和自适应残差反馈策略来重新制定迭代生成(从噪声到数据)过程。具体来说,Morse包含两个相互作用的模型,称为Dash和Dot。Dash模型只是任何类型的预训练扩散模型,但在跳跃采样机制下运行,为采样效率提升创造了足够空间。Dot模型显著快于Dash模型,它学会在Dash模型的轨迹当前跳跃采样点处生成基于观察的残差反馈,将噪声估计提升到轻松匹配Dash模型下一步估计而无需跳跃采样。通过以时间交错方式运行Dash和Dot模型的输出链接,Morse在灵活实现所需的图像生成性能的同时提高了总体运行效率。通过我们在Dash和Dot模型之间提出的权重共享策略,Morse在训练和推理方面都非常高效。我们的方法在6项图像生成任务上相对于9个基线扩散模型在广泛的采样步骤预算范围内平均实现了无损加速1.78倍至3.31倍。此外,我们还证明了我们的方法可以推广到改进针对少步骤文本到图像合成的Latent Consistency Model(LCM-SDXL,已使用一致性蒸馏技术加速)。代码和模型可在https://github.com/deep-optimization/Morse获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Fixed a prompt typo in Figure 18 of the Appendix. This work is accepted to ICML 2025. The project page: https://github.com/deep-optimization/Morse
Summary
本文提出了名为Morse的简单双采样框架,用于加速扩散模型而无损。其关键见解是通过利用快速跳跃采样和自适应残差反馈策略来改革迭代生成过程。Morse包含两个相互作用的模型:Dash和Dot。Dash模型是任何类型的预训练扩散模型,但在跳跃采样体制下运行,为采样效率改进提供了充足的空间。Dot模型比Dash模型更快,它学习在Dash模型的轨迹当前跳跃采样点生成残差反馈,将噪声估计提升到与Dash模型的下一步估计相匹配,无需跳跃采样。通过以时间交错方式运行Dash和Dot模型的输出链,Morse能够在提高运行效率的同时灵活地实现所需的图像生成性能。通过提出Dash和Dot模型之间的权重共享策略,Morse在训练和推理方面都是高效的。该方法相对于9种基线扩散模型在6种图像生成任务上平均实现了无损加速比,为压缩步数较少的文本到图像合成提供了良好的改进方向。其代码和模型已公开在GitHub上分享。
Key Takeaways
- Morse是一个用于加速扩散模型的简单双采样框架,旨在提高图像生成的效率。
- Morse包含两个模型:Dash和Dot,它们相互协作以改进采样过程。
- Dash模型采用跳跃采样机制,为采样效率提供了提升空间。
- Dot模型快速生成残差反馈,以改善基于Dash模型的噪声估计。
- 通过结合Dash和Dot模型的输出,Morse实现了灵活的图像生成性能,同时提高了运行效率。
- Morse通过权重共享策略在训练和推理过程中展现出高效性。
点此查看论文截图


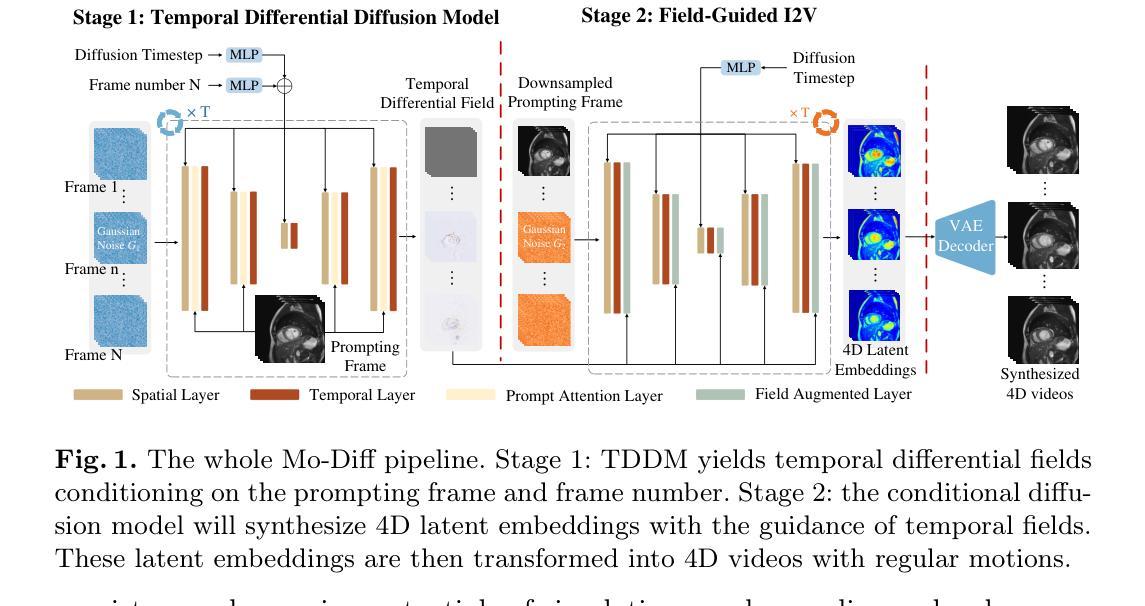
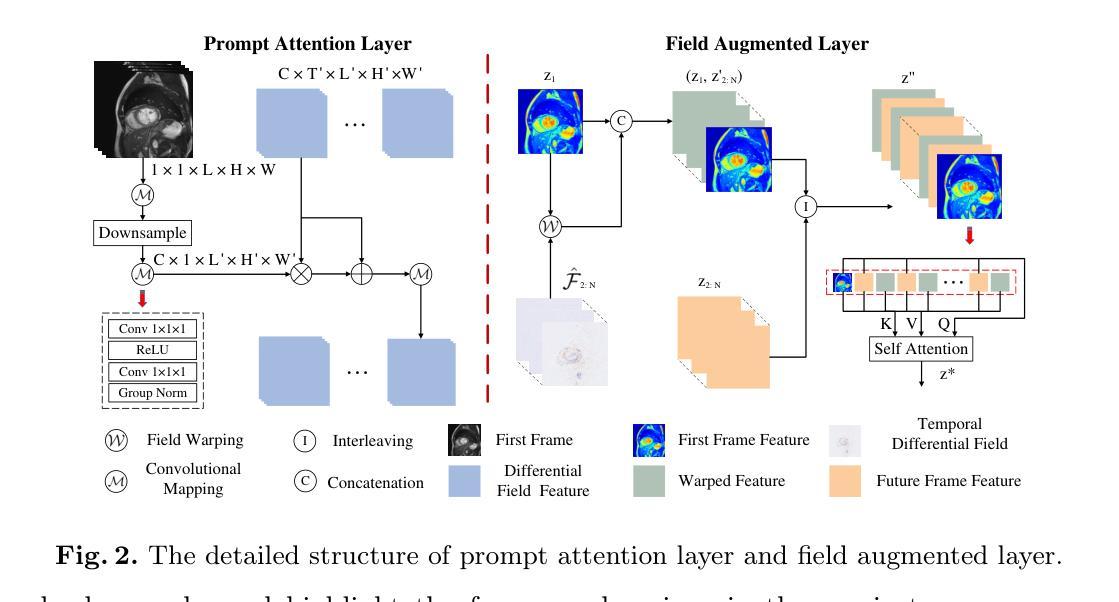
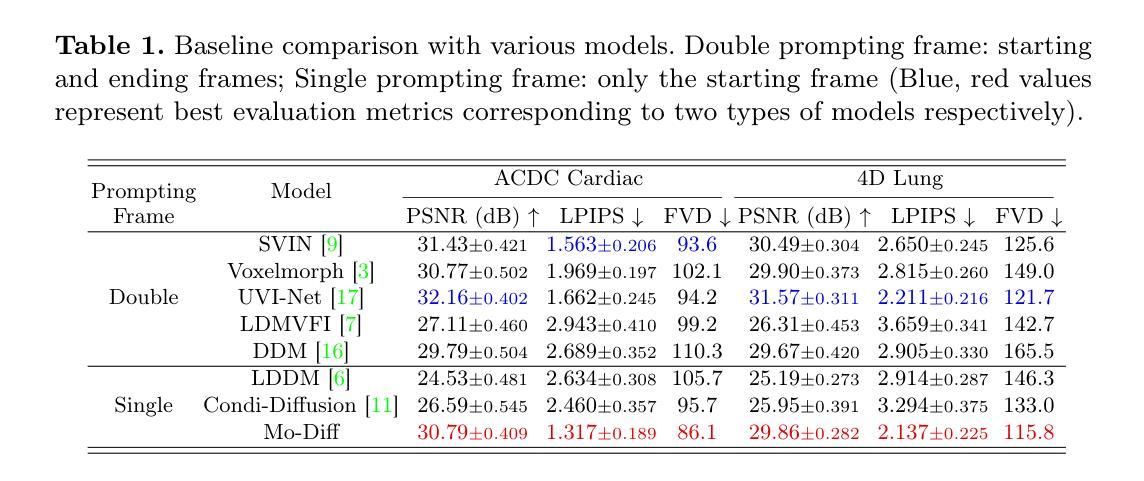
Temporal Differential Fields for 4D Motion Modeling via Image-to-Video Synthesis
Authors:Xin You, Minghui Zhang, Hanxiao Zhang, Jie Yang, Nassir Navab
Temporal modeling on regular respiration-induced motions is crucial to image-guided clinical applications. Existing methods cannot simulate temporal motions unless high-dose imaging scans including starting and ending frames exist simultaneously. However, in the preoperative data acquisition stage, the slight movement of patients may result in dynamic backgrounds between the first and last frames in a respiratory period. This additional deviation can hardly be removed by image registration, thus affecting the temporal modeling. To address that limitation, we pioneeringly simulate the regular motion process via the image-to-video (I2V) synthesis framework, which animates with the first frame to forecast future frames of a given length. Besides, to promote the temporal consistency of animated videos, we devise the Temporal Differential Diffusion Model to generate temporal differential fields, which measure the relative differential representations between adjacent frames. The prompt attention layer is devised for fine-grained differential fields, and the field augmented layer is adopted to better interact these fields with the I2V framework, promoting more accurate temporal variation of synthesized videos. Extensive results on ACDC cardiac and 4D Lung datasets reveal that our approach simulates 4D videos along the intrinsic motion trajectory, rivaling other competitive methods on perceptual similarity and temporal consistency. Codes will be available soon.
对常规呼吸引起的运动进行时间建模对图像引导的临床应用至关重要。现有方法无法模拟时间运动,除非同时存在包括起始帧和结束帧在内的高剂量成像扫描。然而,在术前数据采集阶段,患者的轻微移动可能会导致一个呼吸周期内第一帧和最后一帧之间的动态背景。这种额外的偏差几乎无法通过图像注册去除,从而影响时间建模。为了解决这个问题,我们首创性地通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟常规运动过程,该框架以第一帧为动画预测给定长度的未来帧。此外,为了提高动画视频的时间一致性,我们设计了时间差分扩散模型来生成时间差分场,该模型测量相邻帧之间的相对差分表示。设计了即时注意层用于精细差分场,并采用场增强层来更好地将这些字段与I2V框架进行交互,促进合成视频的时间变化更加准确。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集的大量结果表明,我们的方法模拟了沿内在运动轨迹的4D视频,在感知相似性和时间一致性方面与其他竞争方法相当。代码很快就会提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF early accepted by MICCAI
Summary
本文解决了在图像引导的临床应用中,关于规律呼吸运动的时间建模问题。现有方法需要在开始和结束帧同时存在的条件下才能模拟时序运动。但患者术前数据获取阶段的轻微移动可能导致呼吸周期内首尾帧之间的动态背景差异,难以通过图像注册技术消除,从而影响时序建模。为解决这一问题,本文首次通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟常规运动过程,从首帧生成给定长度的未来帧动画。为提高动画视频的时序一致性,本文提出了时序差分扩散模型,生成时序差分场来衡量相邻帧间的相对差异表示。设计了即时注意层用于精细差分场,并采用场增强层改善其与I2V框架的交互,提高合成视频的准确时序变化。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上的大量结果表明,该方法模拟的4D视频沿内在运动轨迹进行,在感知相似性和时序一致性方面与其他方法竞争并展现出优势。代码即将开放使用。
Key Takeaways
- 解决现有方法无法模拟患者呼吸运动时序变化的问题,特别是在术前数据获取阶段存在的动态背景差异问题。
- 提出图像到视频(I2V)合成框架,模拟规律运动过程,从首帧预测未来帧。
- 引入时序差分扩散模型,生成时序差分场以提高动画视频的时序一致性。
- 设计即时注意层和场增强层,改善模型性能,提高合成视频的准确度和质量。
- 在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在感知相似性和时序一致性方面表现优异。
- 代码即将开放使用,便于其他研究者进行进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Models Through a Global Lens: Are They Culturally Inclusive?
Authors:Zahra Bayramli, Ayhan Suleymanzade, Na Min An, Huzama Ahmad, Eunsu Kim, Junyeong Park, James Thorne, Alice Oh
Text-to-image diffusion models have recently enabled the creation of visually compelling, detailed images from textual prompts. However, their ability to accurately represent various cultural nuances remains an open question. In our work, we introduce CultDiff benchmark, evaluating state-of-the-art diffusion models whether they can generate culturally specific images spanning ten countries. We show that these models often fail to generate cultural artifacts in architecture, clothing, and food, especially for underrepresented country regions, by conducting a fine-grained analysis of different similarity aspects, revealing significant disparities in cultural relevance, description fidelity, and realism compared to real-world reference images. With the collected human evaluations, we develop a neural-based image-image similarity metric, namely, CultDiff-S, to predict human judgment on real and generated images with cultural artifacts. Our work highlights the need for more inclusive generative AI systems and equitable dataset representation over a wide range of cultures.
文本到图像的扩散模型最近能够从文本提示中生成视觉吸引力强、细节丰富的图像。然而,它们准确表现各种文化细微差别的能力仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在我们的工作中,我们引入了CultDiff基准测试,评估最先进的扩散模型是否能生成涵盖十个国家的文化特定图像。我们通过对不同相似方面的精细分析发现,这些模型在生成建筑、服装和食品等文化文物时经常失败,尤其是对代表性不足的国家地区更是如此。与真实世界参考图像相比,在文化的相关性、描述的保真度和逼真度方面存在显著差异。通过收集的人类评估数据,我们开发了一种基于神经的图像图像相似性度量指标,即CultDiff-S,用于预测人类对带有文化文物的真实和生成图像的判断。我们的工作强调了需要更多包容性的生成人工智能系统和在广泛文化背景下均衡数据集表示的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 17 figures, 3 tables
摘要
近期文本到图像扩散模型能够从文本提示生成视觉上吸引人的、详细的图像。然而,这些模型在准确表现不同文化细微差别方面的能力仍存在疑问。我们的工作中,推出了CultDiff基准测试,评估先进扩散模型是否能生成涵盖十个国家的文化特定图像。我们发现这些模型在生成建筑、服饰和食物等文化产物方面常常失败,尤其是对代表性不足的国家地区。通过对不同相似性的精细分析,我们揭示了与文化相关性、描述保真度和现实感与真实世界参考图像相比存在的显著差距。结合收集的人类评估数据,我们开发了一种基于神经的图像-图像相似性度量标准CultDiff-S,以预测包含文化产物的真实和生成图像的逼真度。我们的研究强调了更包容的生成性人工智能系统和广泛文化均衡数据集表示的必要性。
要点
- 文本到图像扩散模型能生成详细的图像,但其在表现文化细微差别方面的能力有待提升。
- CultDiff基准测试用于评估扩散模型在生成涵盖多国文化特定图像方面的性能。
- 现有模型在生成建筑、服饰和食物等文化产物方面存在缺陷,特别是在代表性不足的国家地区。
- 模型在文化相关性、描述保真度和现实感方面与真实图像存在差距。
- 通过人类评估数据,开发出基于神经的图像-图像相似性度量标准CultDiff-S。
- CultDiff-S能有效预测包含文化产物的真实和生成图像的逼真度。
点此查看论文截图

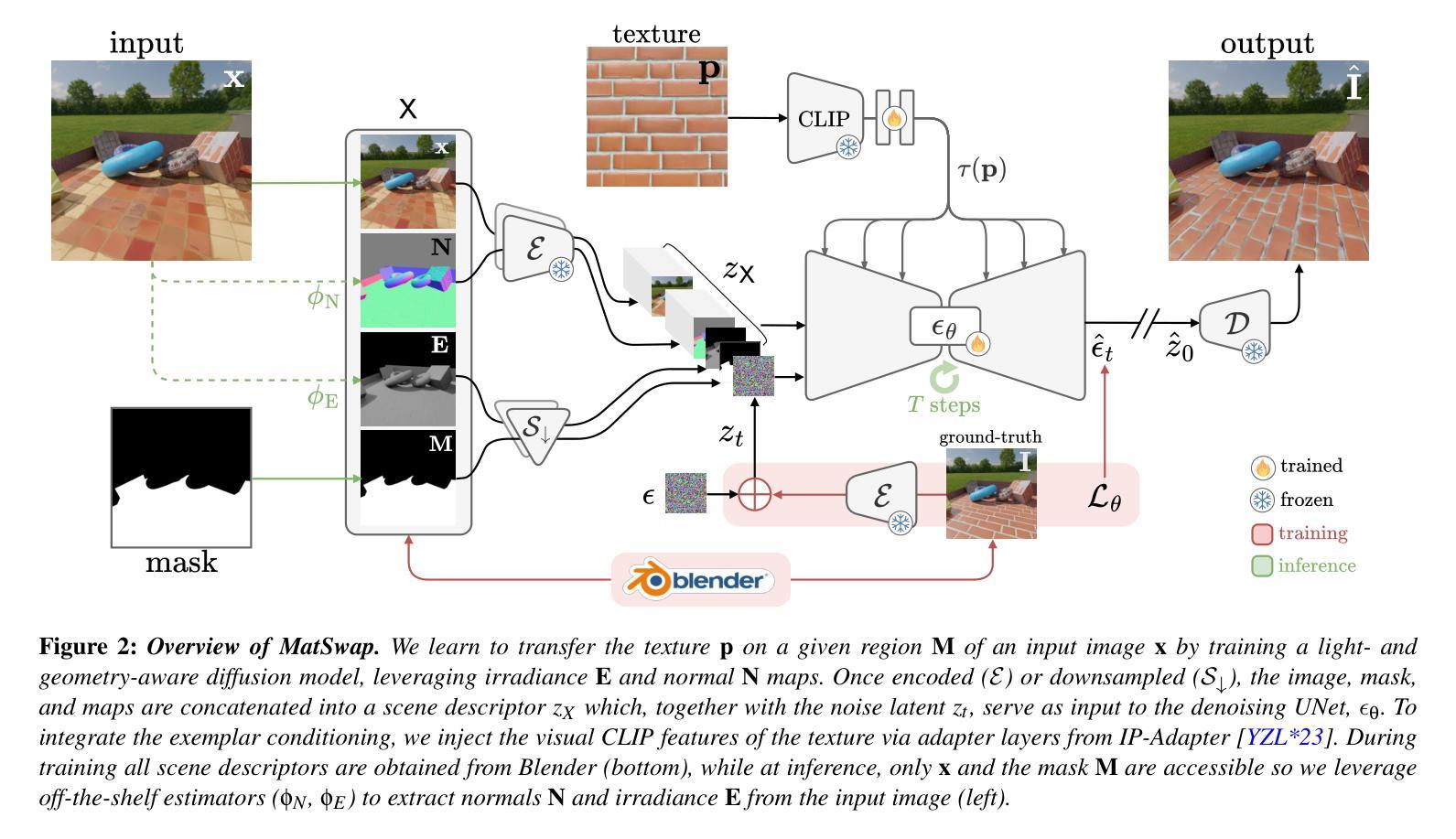
MatSwap: Light-aware material transfers in images
Authors:Ivan Lopes, Valentin Deschaintre, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Raoul de Charette
We present MatSwap, a method to transfer materials to designated surfaces in an image photorealistically. Such a task is non-trivial due to the large entanglement of material appearance, geometry, and lighting in a photograph. In the literature, material editing methods typically rely on either cumbersome text engineering or extensive manual annotations requiring artist knowledge and 3D scene properties that are impractical to obtain. In contrast, we propose to directly learn the relationship between the input material – as observed on a flat surface – and its appearance within the scene, without the need for explicit UV mapping. To achieve this, we rely on a custom light- and geometry-aware diffusion model. We fine-tune a large-scale pre-trained text-to-image model for material transfer using our synthetic dataset, preserving its strong priors to ensure effective generalization to real images. As a result, our method seamlessly integrates a desired material into the target location in the photograph while retaining the identity of the scene. We evaluate our method on synthetic and real images and show that it compares favorably to recent work both qualitatively and quantitatively. We release our code and data on https://github.com/astra-vision/MatSwap
我们提出了MatSwap方法,这是一种以摄影写实的方式将材料转移到图像指定表面的方法。由于照片中材料外观、几何形状和光照的复杂纠缠,这一任务非常困难。在文献中,材料编辑方法通常依赖于繁琐的文本工程或需要大量手动注释,这需要艺术家的知识和不切实际的3D场景属性。相比之下,我们提出直接在平面表面上观察到的输入材料与其在场景中的外观之间建立关系,而无需明确的UV映射。为了实现这一点,我们依赖于一个自定义的轻量级和几何感知的扩散模型。我们使用合成数据集对大规模预训练文本到图像模型进行微调,以进行材料转移,同时保留其强大的先验知识,以确保有效泛化到真实图像。因此,我们的方法能够无缝地将所需材料集成到照片的目标位置,同时保留场景的身份。我们在合成图像和真实图像上评估了我们的方法,并定性定量地展示了它与最新工作的比较结果。我们在https://github.com/astra-vision/MatSwap上发布了我们的代码和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to EGSR, journal track to appear in Computer Graphics Forum
摘要
我们提出了MatSwap方法,可以在图像中以逼真的方式将材料转移到指定表面。由于照片中材料外观、几何形状和光照之间的复杂纠缠,这一任务非常困难。现有的材料编辑方法通常依赖于繁琐的文本工程或需要大量手动注释,这需要艺术家的知识和不切实际的3D场景属性。相比之下,我们提出直接学习输入材料(在平面表面上观察到的)与其在场景中的外观之间的关系,无需明确的UV映射。为此,我们依赖于一个自定义的轻量级和几何感知扩散模型。我们使用合成数据集微调大规模预训练文本到图像模型,用于材料转移,保留其强大的先验知识,以确保有效地推广到真实图像。因此,我们的方法能够无缝地将所需材料集成到照片的目标位置,同时保留场景的标识。我们在合成图像和真实图像上评估了我们的方法,并展示了与最新工作的比较结果既有定性也有定量。我们将代码和数据发布在https://github.com/astra-vision/MatSwap。
关键见解
- 提出了MatSwap方法,可在图像中逼真地将材料转移到指定表面。
- 解决了材料外观、几何形状和光照之间的复杂纠缠问题。
- 与现有方法不同,无需繁琐的文本工程或大量手动注释。
- 利用自定义的轻量级和几何感知扩散模型实现材料转移。
- 通过合成数据集微调大规模预训练文本到图像模型,确保有效推广到真实图像。
- 方法能够无缝集成所需材料到照片的目标位置,同时保留场景的标识。
点此查看论文截图




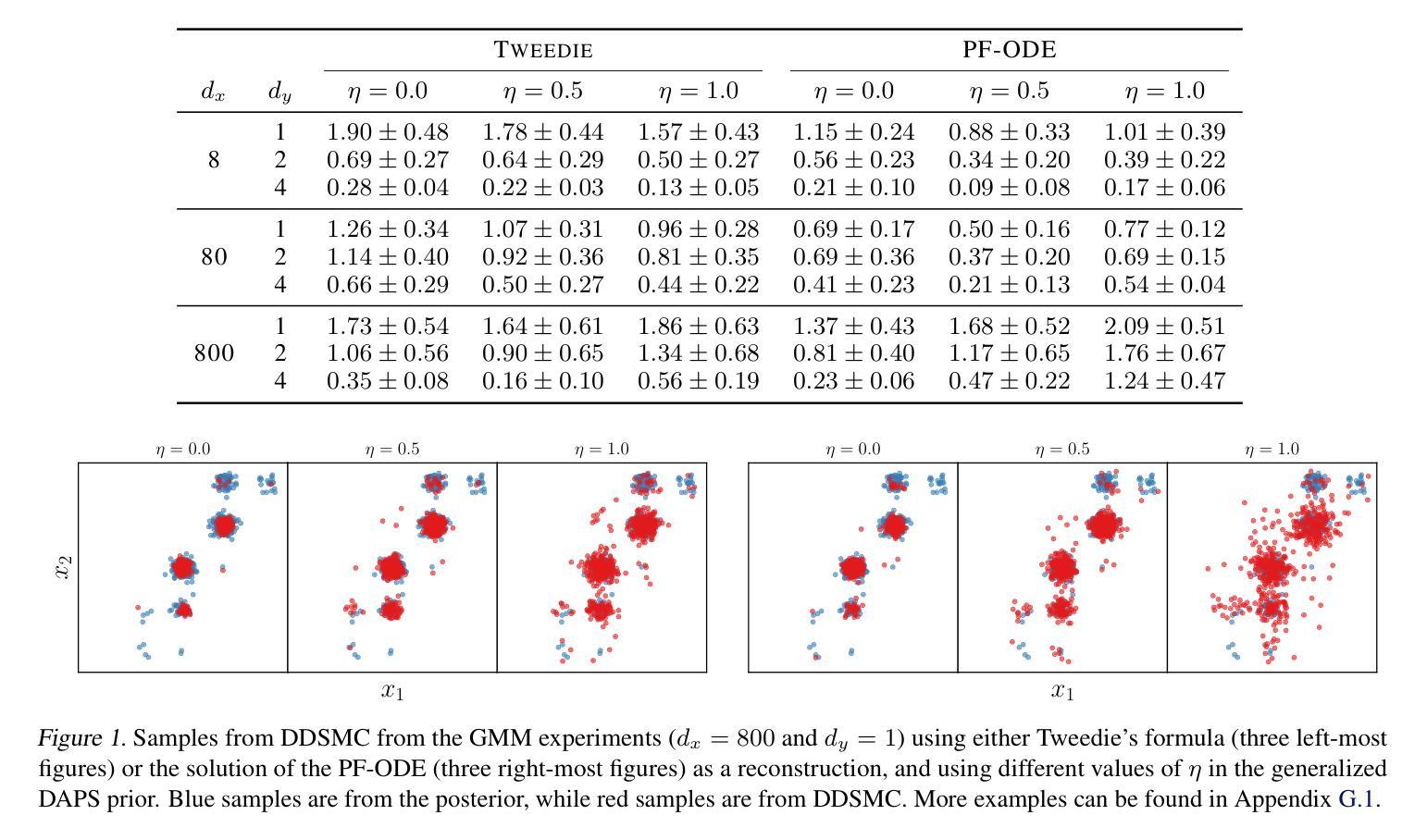
Solving Linear-Gaussian Bayesian Inverse Problems with Decoupled Diffusion Sequential Monte Carlo
Authors:Filip Ekström Kelvinius, Zheng Zhao, Fredrik Lindsten
A recent line of research has exploited pre-trained generative diffusion models as priors for solving Bayesian inverse problems. We contribute to this research direction by designing a sequential Monte Carlo method for linear-Gaussian inverse problems which builds on “decoupled diffusion”, where the generative process is designed such that larger updates to the sample are possible. The method is asymptotically exact and we demonstrate the effectiveness of our Decoupled Diffusion Sequential Monte Carlo (DDSMC) algorithm on both synthetic as well as protein and image data. Further, we demonstrate how the approach can be extended to discrete data.
最近的研究利用预训练的生成扩散模型作为解决贝叶斯反问题的先验。我们为这一研究方向设计了一种基于“解耦扩散”的线性高斯反问题的序贯蒙特卡罗方法做出贡献,其中生成过程的设计使得样本能够进行较大的更新。该方法具有渐近精确性,我们通过在合成数据以及蛋白质和图像数据上展示我们的解耦扩散序贯蒙特卡罗(DDSMC)算法的有效性来证明这一点。此外,我们还展示了如何将该方法扩展到离散数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICML 2025, to appear in PMLR 267. Code available at https://github.com/filipekstrm/ddsmc
Summary
该研究利用预训练的生成扩散模型作为先验来解决贝叶斯反问题。设计了一种基于“解耦扩散”的序贯蒙特卡洛方法,用于线性高斯反问题。生成过程的设计允许更大的样本更新。该方法在合成数据以及蛋白质和图像数据上都证明了其有效性,并展示了如何将其扩展到离散数据的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用预训练生成扩散模型作为解决贝叶斯反问题的先验。
- 设计了一种基于解耦扩散的序贯蒙特卡洛方法用于线性高斯反问题。
- 生成过程允许更大的样本更新。
- 该方法在合成数据上的有效性得到验证。
- 方法在蛋白质和图像数据上的表现得到证明。
- 该方法可以扩展到离散数据。
点此查看论文截图


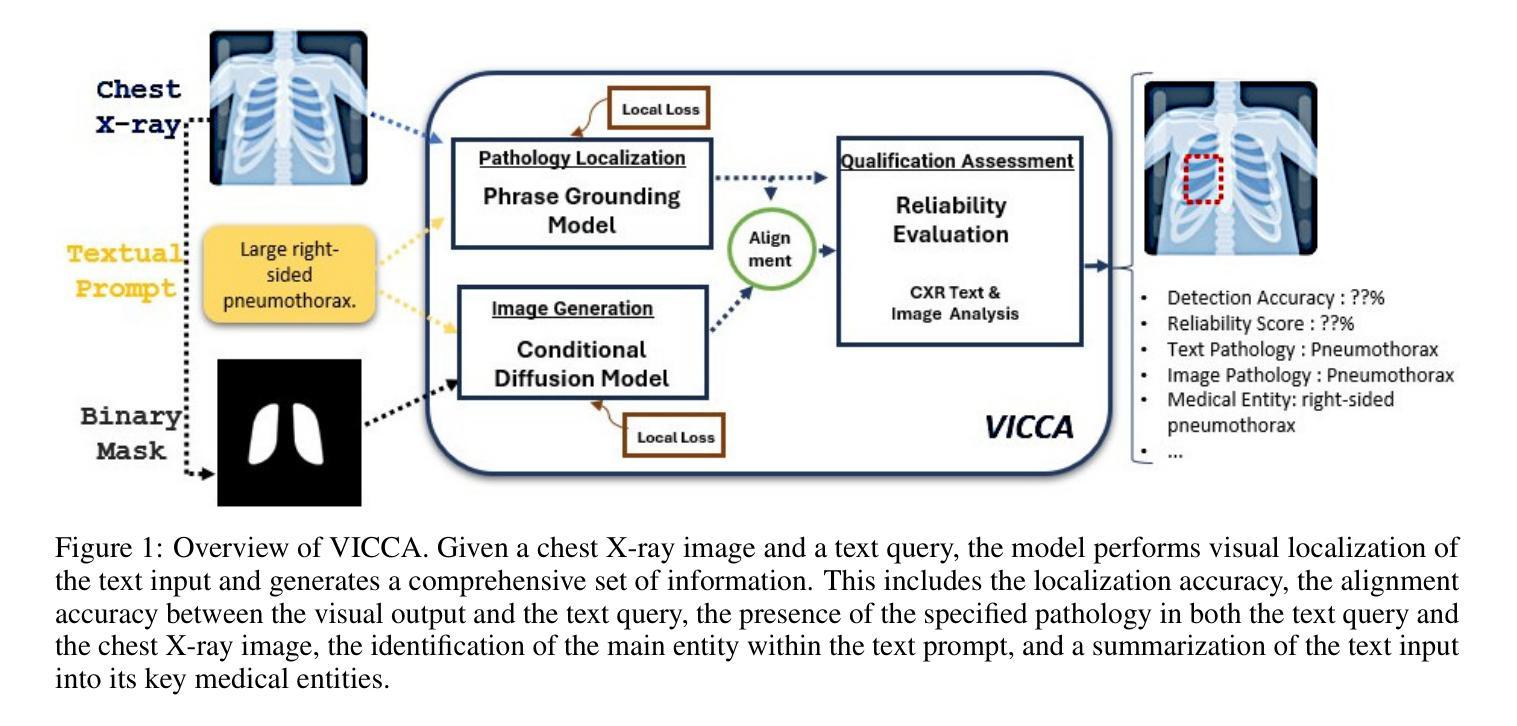
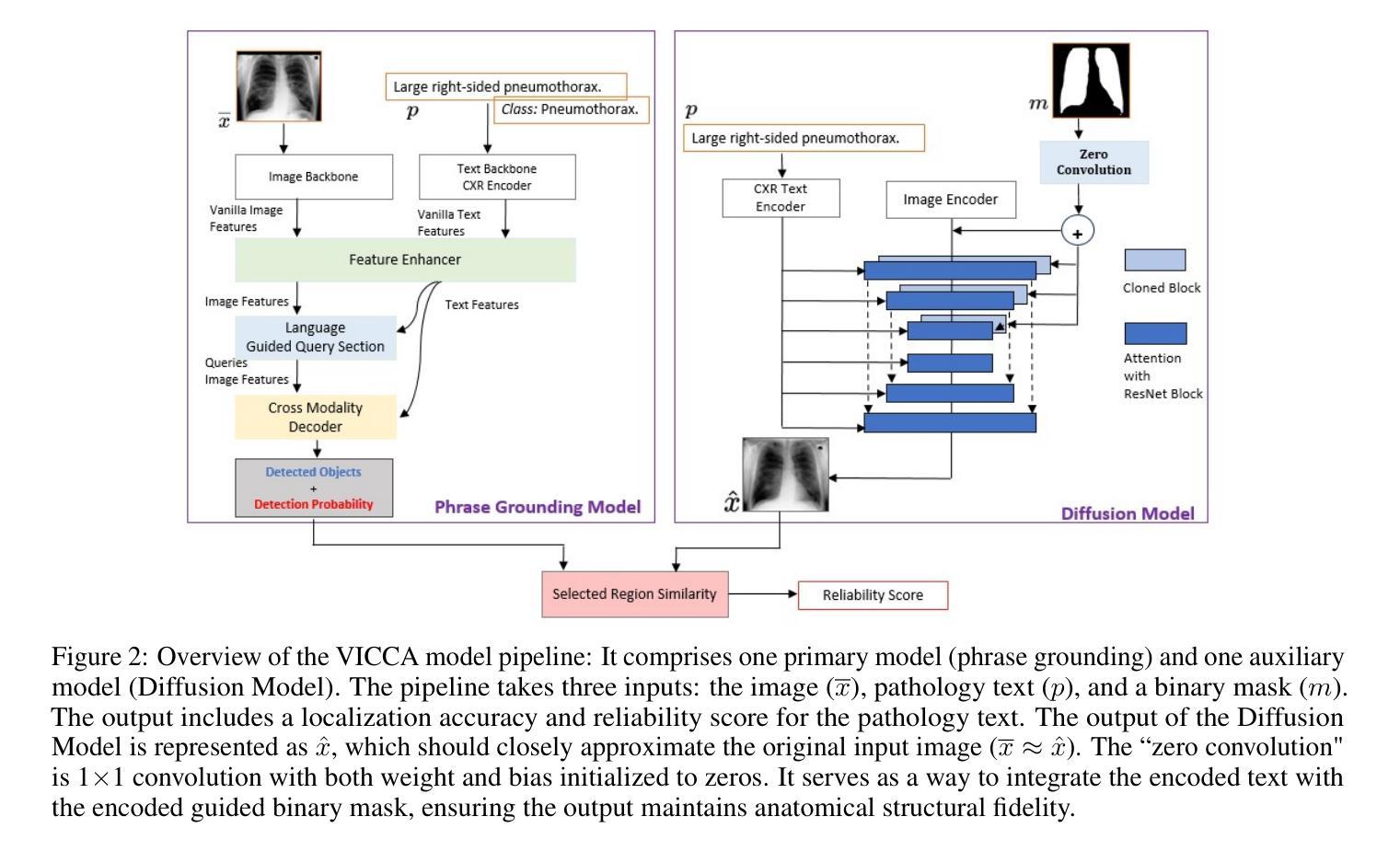
VICCA: Visual Interpretation and Comprehension of Chest X-ray Anomalies in Generated Report Without Human Feedback
Authors:Sayeh Gholipour Picha, Dawood Al Chanti, Alice Caplier
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes increasingly central to healthcare, the demand for explainable and trustworthy models is paramount. Current report generation systems for chest X-rays (CXR) often lack mechanisms for validating outputs without expert oversight, raising concerns about reliability and interpretability. To address these challenges, we propose a novel multimodal framework designed to enhance the semantic alignment and localization accuracy of AI-generated medical reports. Our framework integrates two key modules: a Phrase Grounding Model, which identifies and localizes pathologies in CXR images based on textual prompts, and a Text-to-Image Diffusion Module, which generates synthetic CXR images from prompts while preserving anatomical fidelity. By comparing features between the original and generated images, we introduce a dual-scoring system: one score quantifies localization accuracy, while the other evaluates semantic consistency. This approach significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in pathology localization and text-to-image alignment. The integration of phrase grounding with diffusion models, coupled with the dual-scoring evaluation system, provides a robust mechanism for validating report quality, paving the way for more trustworthy and transparent AI in medical imaging.
随着人工智能在医疗保健领域的作用越来越重要,对可解释性和可信度的模型需求也越来越迫切。目前用于生成胸部X光片报告的现行系统缺乏在缺乏专家监督的情况下验证输出的机制,这引发了人们对可靠性和可解释性的担忧。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的多模态框架,旨在提高人工智能生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位准确性。我们的框架集成了两个关键模块:短语定位模型能够根据文本提示识别并定位胸部X光片图像中的病理情况;文本到图像扩散模块能够根据提示生成合成胸部X光片图像,同时保留解剖结构的保真度。通过比较原始图像和生成图像的特征,我们引入了一种双重评分系统:一个评分量化定位准确性,另一个评分评估语义一致性。该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位以及文本到图像的对齐方面达到了最先进的水平。短语定位与扩散模型的集成,加上双重评分评估系统,为验证报告质量提供了稳健的机制,为医学影像领域更可靠、更透明的AI铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着人工智能在医疗保健中的核心作用日益增强,对可解释性和可靠性的模型需求变得至关重要。针对当前胸部X光报告生成系统缺乏验证机制的问题,我们提出了一种新型的多模式框架,旨在提高AI生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位准确性。该框架集成了短语定位模型和文本到图像扩散模块,通过比较原始和生成图像的特征,引入双重评分系统,分别评估定位和语义一致性。该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位和文本到图像对齐方面达到最新结果。短语定位与扩散模型的集成以及双重评分评估系统相结合,为报告质量验证提供了稳健机制,为医疗成像领域更可靠、透明的AI应用铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医疗保健领域的重要性日益增强,对可解释性和可靠性的模型需求迫切。
- 当前胸部X光报告生成系统存在缺乏验证机制的问题。
- 提出了一种新型的多模式框架,旨在提高AI生成的医疗报告的语义对齐和定位准确性。
- 框架集成了短语定位模型和文本到图像扩散模块。
- 通过比较原始和生成图像的特征,引入双重评分系统评估定位和语义一致性。
- 该方法显著优于现有方法,在病理定位和文本到图像对齐方面达到最新结果。
点此查看论文截图

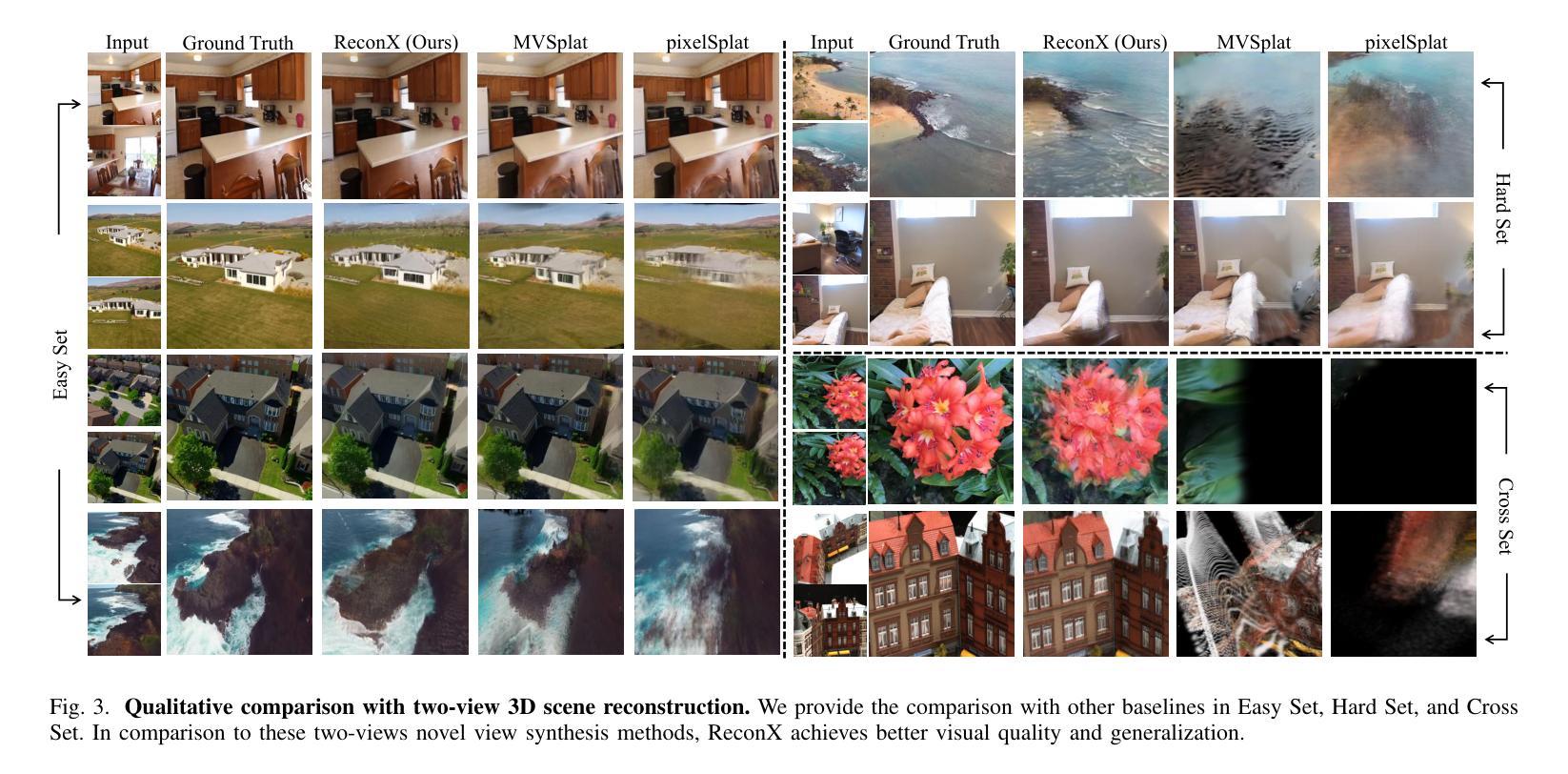
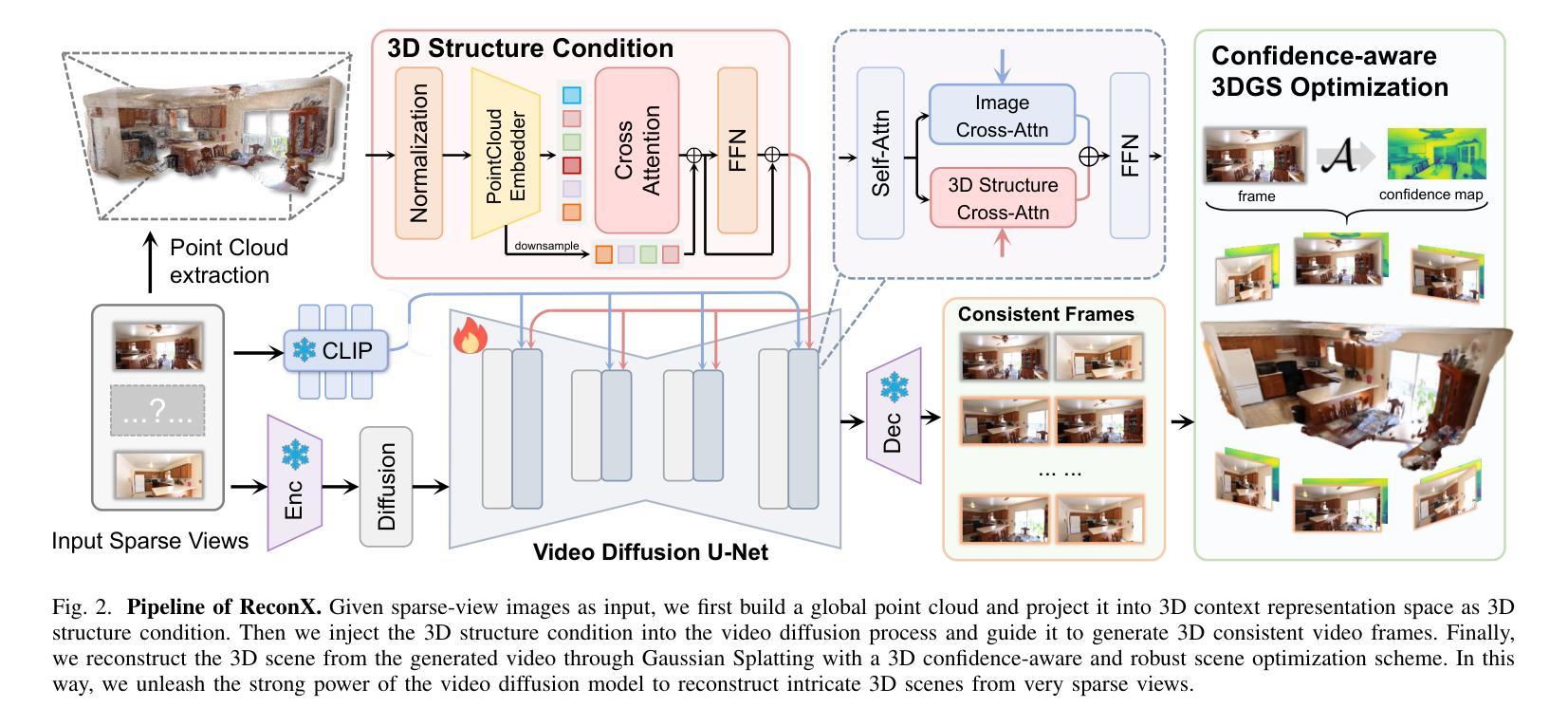
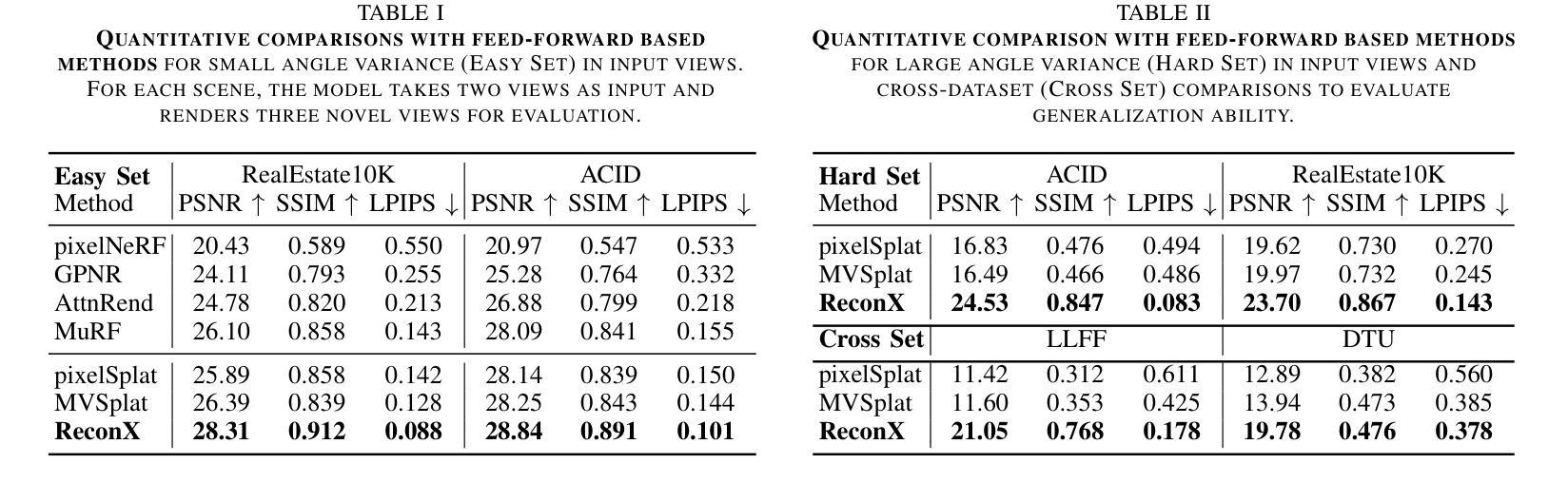
ReconX: Reconstruct Any Scene from Sparse Views with Video Diffusion Model
Authors:Fangfu Liu, Wenqiang Sun, Hanyang Wang, Yikai Wang, Haowen Sun, Junliang Ye, Jun Zhang, Yueqi Duan
Advancements in 3D scene reconstruction have transformed 2D images from the real world into 3D models, producing realistic 3D results from hundreds of input photos. Despite great success in dense-view reconstruction scenarios, rendering a detailed scene from insufficient captured views is still an ill-posed optimization problem, often resulting in artifacts and distortions in unseen areas. In this paper, we propose ReconX, a novel 3D scene reconstruction paradigm that reframes the ambiguous reconstruction challenge as a temporal generation task. The key insight is to unleash the strong generative prior of large pre-trained video diffusion models for sparse-view reconstruction. However, 3D view consistency struggles to be accurately preserved in directly generated video frames from pre-trained models. To address this, given limited input views, the proposed ReconX first constructs a global point cloud and encodes it into a contextual space as the 3D structure condition. Guided by the condition, the video diffusion model then synthesizes video frames that are both detail-preserved and exhibit a high degree of 3D consistency, ensuring the coherence of the scene from various perspectives. Finally, we recover the 3D scene from the generated video through a confidence-aware 3D Gaussian Splatting optimization scheme. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets show the superiority of our ReconX over state-of-the-art methods in terms of quality and generalizability.
随着三维场景重建技术的不断进步,能够将来自现实世界的二维图像转化为三维模型,利用数百张输入照片生成逼真的三维结果。虽然在密集视图重建场景中取得了巨大成功,但从捕获的有限视角对场景进行详细渲染仍然是一个不适定的优化问题,这常常导致未知区域出现伪影和失真。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为ReconX的新型三维场景重建方法,它将模糊的重建挑战重新定义为一种时间生成任务,其关键见解在于利用大型预训练视频扩散模型的强大生成先验来进行稀疏视图重建。然而,直接从预训练模型生成的视频帧中准确保持三维视图的一致性是一个挑战。为了解决这一问题,给定有限的输入视角,所提出的ReconX首先构建全局点云并将其编码为上下文空间作为三维结构条件。在条件的引导下,视频扩散模型随后合成的视频帧既保留了细节又表现出高度的三维一致性,从而确保了从不同角度观看场景的连贯性。最后,我们通过置信度感知的三维高斯平铺优化方案从生成的视频中恢复三维场景。在多种真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的ReconX在质量和通用性方面均优于现有先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://liuff19.github.io/ReconX
Summary
提出了一种名为ReconX的新型3D场景重建方法,将稀疏视角重建的挑战重新定位为时间生成任务,利用预训练的视频扩散模型的强大生成先验。通过构建全局点云并将其编码为三维结构条件,指导视频扩散模型合成细节丰富且高度一致的3D视频帧。采用置信度感知的三维高斯展开优化方案从生成的视频中恢复三维场景。
Key Takeaways
- ReconX将稀疏视角的3D场景重建问题重新定位为时间生成任务。
- 利用预训练的视频扩散模型的强大生成先验来解决重建问题。
- 通过构建全局点云并将其编码为三维结构条件,解决直接从预训练模型生成视频帧时出现的三维视角一致性问题。
- 合成细节丰富且高度一致的3D视频帧,确保从不同角度观看场景时的连贯性。
- 采用置信度感知的三维高斯展开优化方案从生成的视频中恢复三维场景。
- 在各种真实世界数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,ReconX在质量和泛化性方面优于现有技术。
- ReconX对于从现实世界中的二维图像创建逼真的三维模型具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图