⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-27 更新
BEVPlace++: Fast, Robust, and Lightweight LiDAR Global Localization for Unmanned Ground Vehicles
Authors:Lun Luo, Si-Yuan Cao, Xiaorui Li, Jintao Xu, Rui Ai, Zhu Yu, Xieyuanli Chen
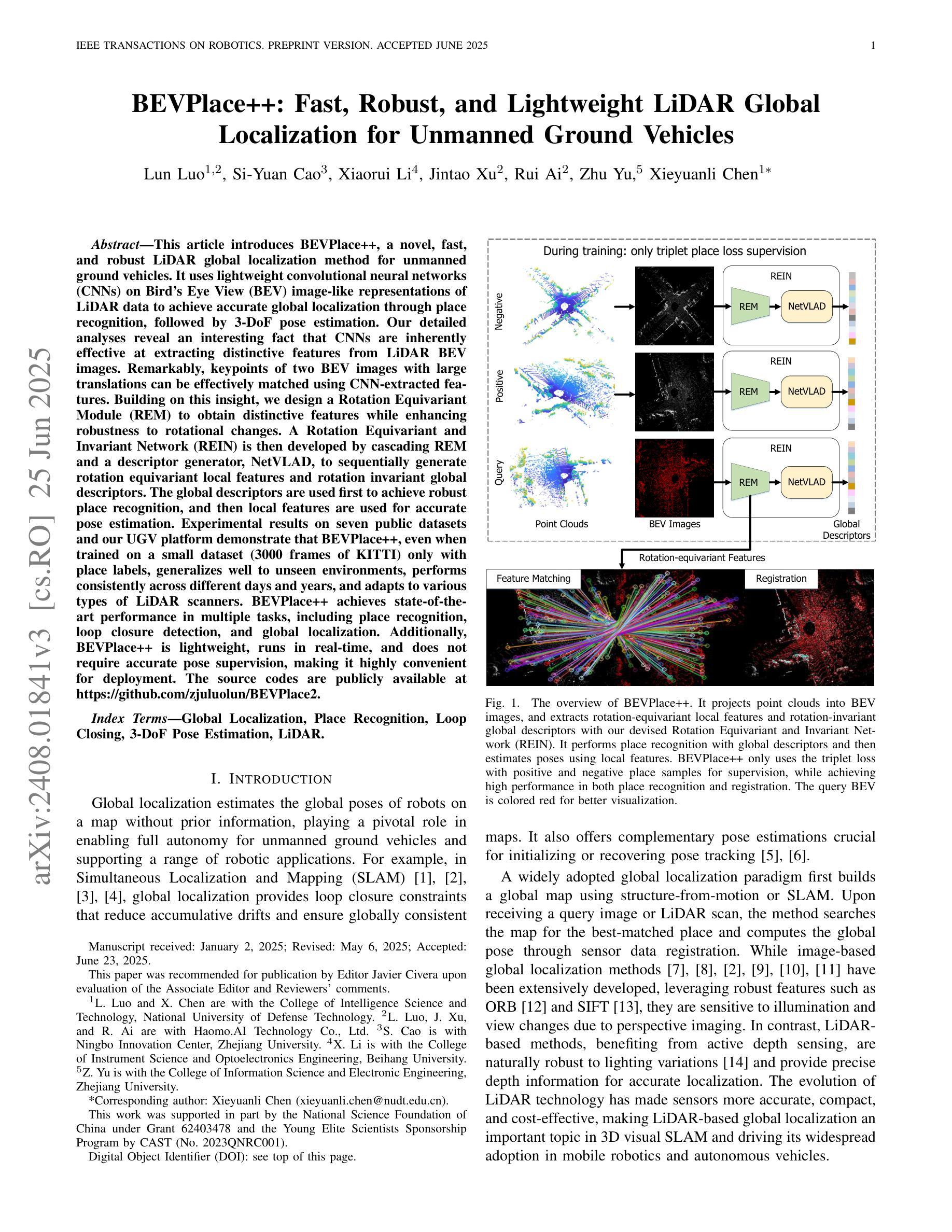
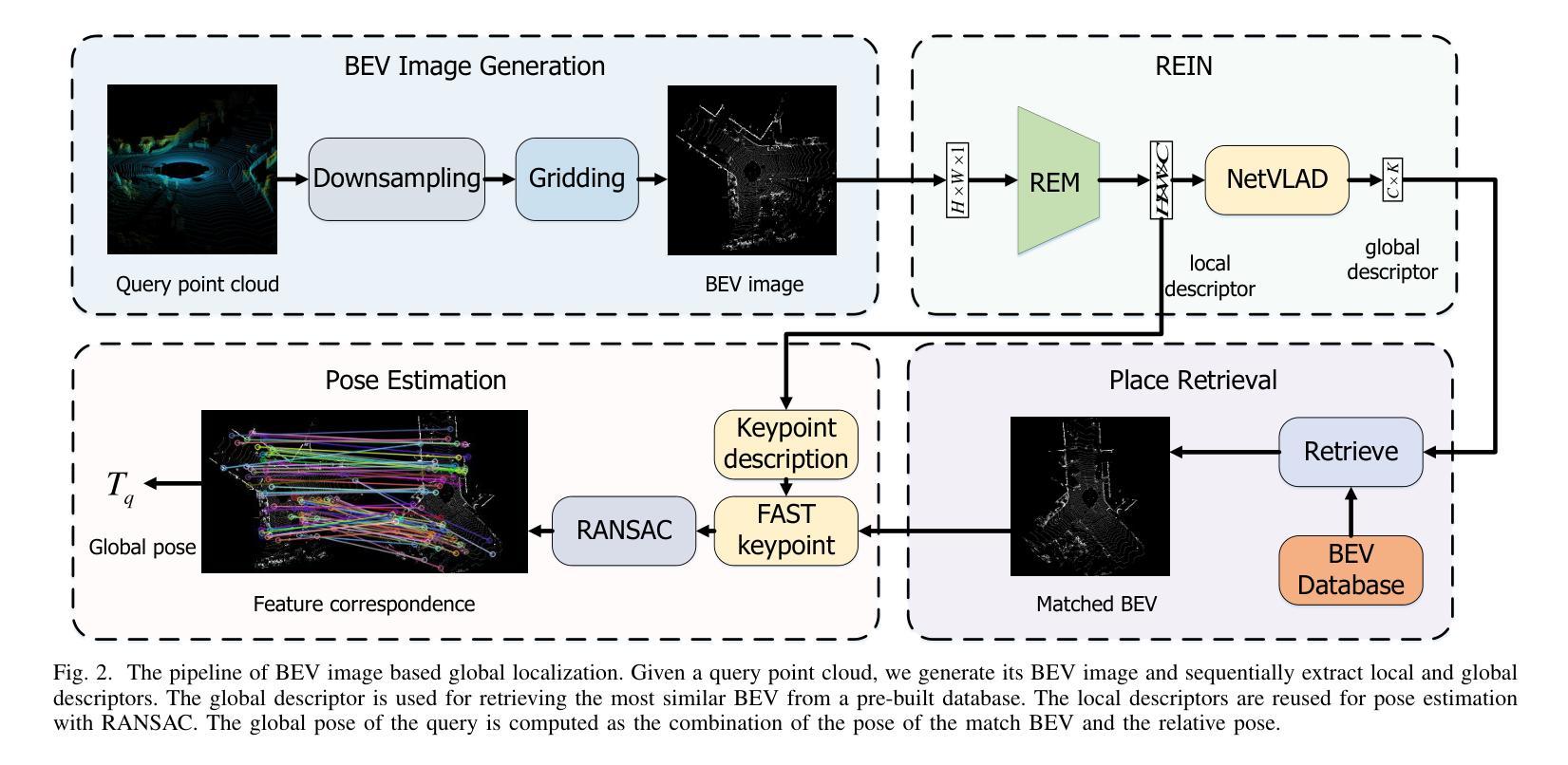
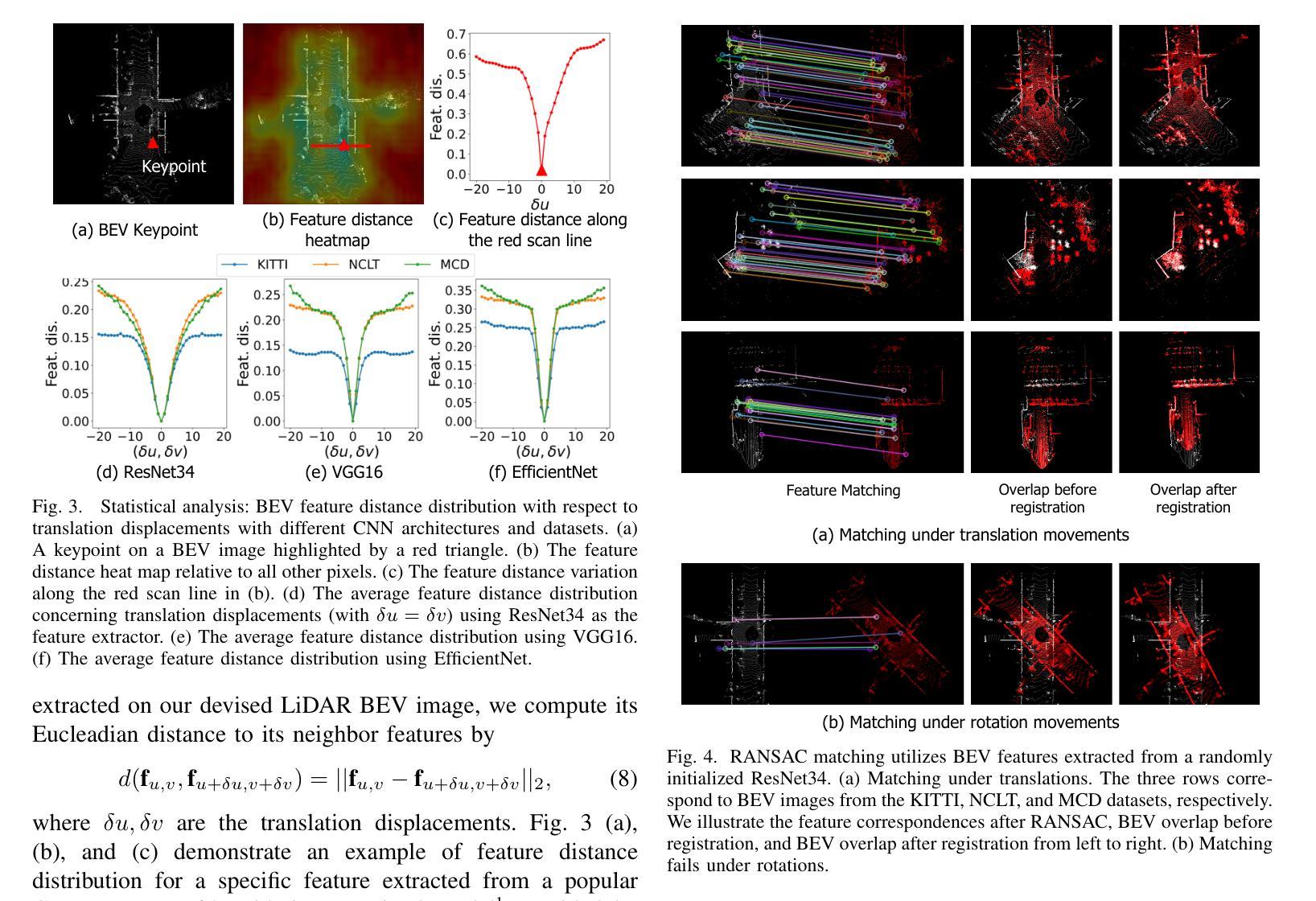
This article introduces BEVPlace++, a novel, fast, and robust LiDAR global localization method for unmanned ground vehicles. It uses lightweight convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on Bird’s Eye View (BEV) image-like representations of LiDAR data to achieve accurate global localization through place recognition, followed by 3-DoF pose estimation. Our detailed analyses reveal an interesting fact that CNNs are inherently effective at extracting distinctive features from LiDAR BEV images. Remarkably, keypoints of two BEV images with large translations can be effectively matched using CNN-extracted features. Building on this insight, we design a Rotation Equivariant Module (REM) to obtain distinctive features while enhancing robustness to rotational changes. A Rotation Equivariant and Invariant Network (REIN) is then developed by cascading REM and a descriptor generator, NetVLAD, to sequentially generate rotation equivariant local features and rotation invariant global descriptors. The global descriptors are used first to achieve robust place recognition, and then local features are used for accurate pose estimation. \revise{Experimental results on seven public datasets and our UGV platform demonstrate that BEVPlace++, even when trained on a small dataset (3000 frames of KITTI) only with place labels, generalizes well to unseen environments, performs consistently across different days and years, and adapts to various types of LiDAR scanners.} BEVPlace++ achieves state-of-the-art performance in multiple tasks, including place recognition, loop closure detection, and global localization. Additionally, BEVPlace++ is lightweight, runs in real-time, and does not require accurate pose supervision, making it highly convenient for deployment. \revise{The source codes are publicly available at https://github.com/zjuluolun/BEVPlace2.
本文介绍了BEVPlace++,这是一种针对无人驾驶地面车辆的新型快速鲁棒的激光雷达全局定位方法。它使用轻型卷积神经网络(CNN),在激光雷达数据的鸟瞰图像表示上实现准确的全局定位,包括通过地点识别以及随后的3自由度姿态估计。我们的深入分析揭示了一个有趣的事实,即CNN从本质上擅长从激光雷达鸟瞰图像中提取特征。值得注意的是,即使在大范围平移的情况下,两个鸟瞰图像的关键点也可以有效地通过CNN提取的特征进行匹配。基于这一见解,我们设计了一个旋转等价模块(REM)来提取特征,同时提高其对旋转变化的鲁棒性。然后,通过级联REM和描述符生成器NetVLAD,开发了一个旋转等价和不变网络(REIN),以生成旋转等价的局部特征和旋转不变的全局描述符。首先使用全局描述符实现稳健的地点识别,然后使用局部特征进行精确的姿态估计。实验结果表明,在七个公共数据集和我们自身的无人地面车辆平台上,即使在只使用标有地点的小数据集(KITTI的3000帧)进行训练的情况下,BEVPlace++也能很好地适应未见过的环境,在不同的日子和年份之间表现一致,并适应各种类型的激光雷达扫描仪。BEVPlace++在多个任务上实现了最先进的性能,包括地点识别、闭环检测和全局定位。此外,BEVPlace++具有轻量级、实时运行的特点,并且不需要精确的姿态监督,因此部署起来非常方便。相关源代码可在https://github.com/zjuluolun/BEVPlace2公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Robotics
Summary
本文介绍了BEVPlace++,这是一种针对无人驾驶地面车辆的新型快速稳健的LiDAR全局定位方法。它利用轻量级卷积神经网络(CNNs)在鸟瞰图(BEV)图像表示形式的LiDAR数据上,通过场所识别实现准确全局定位,然后进行3自由度姿态估计。文章详细分析了CNN从LiDAR BEV图像中提取特征的有效性,并设计了旋转等价模块(REM)以增强对旋转变化的稳健性。通过串联REM和描述符生成器NetVLAD,开发出旋转等价和不变网络(REIN),依次生成旋转等价局部特征和旋转不变全局描述符。全局描述符用于实现稳健的场所识别,而局部特征用于精确姿态估计。实验结果表明,BEVPlace++在多个任务上实现了一流性能,包括场所识别、闭环检测和全局定位。此外,它具有实时运行能力且无需精确姿态监督,便于部署。
Key Takeaways
- BEVPlace++是一种针对无人驾驶地面车辆的新型LiDAR全局定位方法,融合了深度学习技术与传统的定位策略。
- 使用轻量级CNN处理鸟瞰视图数据来实现全球定位以及三维姿态估算。
- CNN能够从LiDAR BEV图像中提取显著特征,并且在存在较大平移的情况下仍能有效匹配关键点。
- 设计了旋转等价模块(REM)以提高系统对旋转变化的鲁棒性。
- 通过实验验证了BEVPlace++的优越性,在多个数据集和UGV平台上的实验表明,它在不同的环境和不同类型的LiDAR扫描仪下均具有良好的泛化能力和适应性。
- BEVPlace++具有实时性能,且部署方便,无需精确的姿态监督。
点此查看论文截图