⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-27 更新
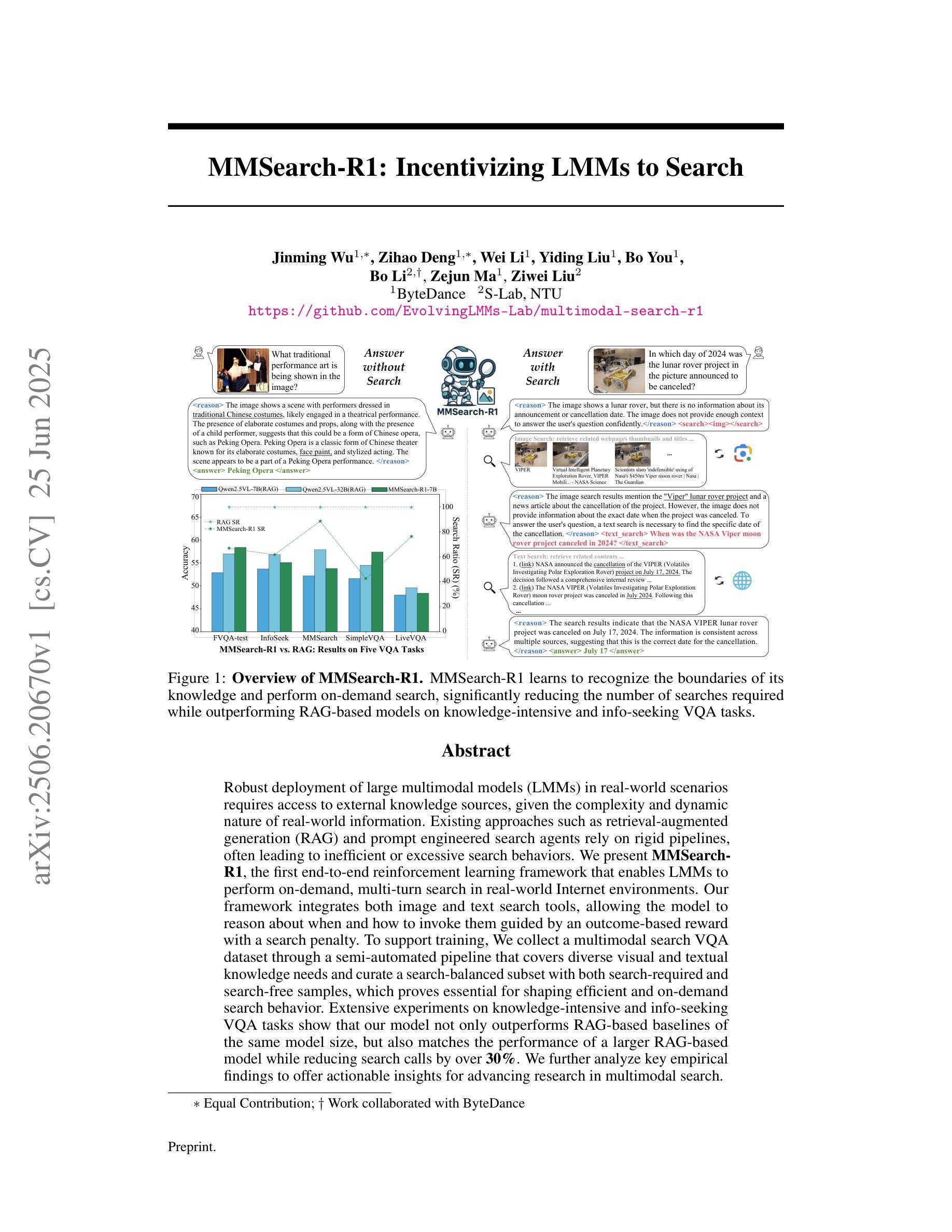
MMSearch-R1: Incentivizing LMMs to Search
Authors:Jinming Wu, Zihao Deng, Wei Li, Yiding Liu, Bo You, Bo Li, Zejun Ma, Ziwei Liu
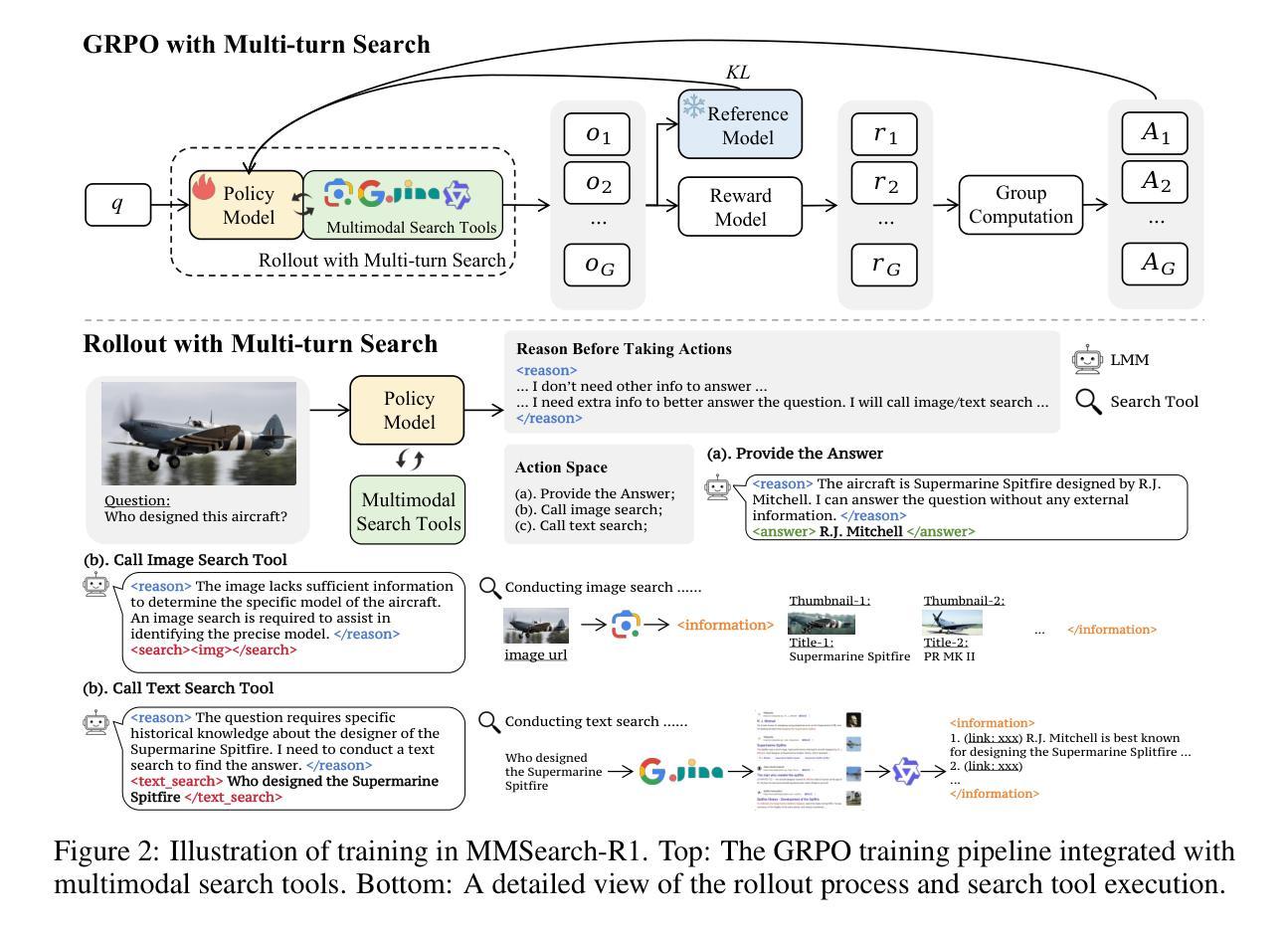
Robust deployment of large multimodal models (LMMs) in real-world scenarios requires access to external knowledge sources, given the complexity and dynamic nature of real-world information. Existing approaches such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and prompt engineered search agents rely on rigid pipelines, often leading to inefficient or excessive search behaviors. We present MMSearch-R1, the first end-to-end reinforcement learning framework that enables LMMs to perform on-demand, multi-turn search in real-world Internet environments. Our framework integrates both image and text search tools, allowing the model to reason about when and how to invoke them guided by an outcome-based reward with a search penalty. To support training, We collect a multimodal search VQA dataset through a semi-automated pipeline that covers diverse visual and textual knowledge needs and curate a search-balanced subset with both search-required and search-free samples, which proves essential for shaping efficient and on-demand search behavior. Extensive experiments on knowledge-intensive and info-seeking VQA tasks show that our model not only outperforms RAG-based baselines of the same model size, but also matches the performance of a larger RAG-based model while reducing search calls by over 30%. We further analyze key empirical findings to offer actionable insights for advancing research in multimodal search.
在真实世界场景中稳健部署大型多模态模型(LMMs)需要访问外部知识源,考虑到真实世界信息的复杂性和动态性。现有的方法如检索增强生成(RAG)和提示工程搜索代理依赖于僵化管道,通常导致低效或过度搜索行为。我们提出了MMSearch-R1,这是第一个端到端的强化学习框架,使LMMs能够在真实世界的互联网环境中进行按需多轮搜索。我们的框架集成了图像和文本搜索工具,允许模型根据以结果为基础的奖励和搜索惩罚来推理何时以及如何调用它们。为了支持训练,我们通过半自动化管道收集了一个多模态搜索VQA数据集,涵盖了多样化的视觉和文本知识需求,并筛选出一个搜索平衡的子集,其中包含搜索所需和无需搜索的样本,这对于塑造高效和按需搜索行为至关重要。在知识密集型和信息搜索VQA任务上的大量实验表明,我们的模型不仅优于基于RAG的相同模型大小的基线,而且与更大的基于RAG的模型相匹配,同时减少了超过30%的搜索调用。我们还进一步分析了关键实验结果,为推进多模态搜索研究提供了可操作的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/EvolvingLMMs-Lab/multimodal-search-r1
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于强化学习的端对端框架MMSearch-R1,用于大型多模态模型在真实互联网环境下的按需多轮搜索。框架集成了图像和文本搜索工具,通过结果导向的奖励机制和搜索惩罚来指导模型何时以及如何调用这些工具。此外,为了支持训练,本文还通过半自动化管道收集了一个多模态搜索问答数据集,并筛选出一个既包含需要搜索的样本又包含不需要搜索的样本的搜索平衡子集。实验表明,该模型不仅在知识密集型和信息搜寻问答任务上表现出优于基于RAG的基线模型的性能,而且在减少搜索调用次数方面表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型在真实场景应用需访问外部知识源,处理复杂且动态的信息。
- 现有方法如RAG和提示工程搜索代理存在效率低下或过度搜索的问题。
- MMSearch-R1是首个端到端的强化学习框架,使LMMs能在真实互联网环境中进行按需多轮搜索。
- 框架集成了图像和文本搜索工具,由结果导向的奖励和搜索惩罚机制引导模型决定何时及如何调用这些工具。
- 使用了半自动化管道收集多模态搜索问答数据集,并筛选出搜索平衡子集,对塑造高效且按需的搜索行为至关重要。
- 实验表明,MMMsearch-R1在知识密集型和信息搜寻问答任务上表现优异,相较于基线模型,不仅性能更佳,还能减少超过30%的搜索调用次数。
点此查看论文截图
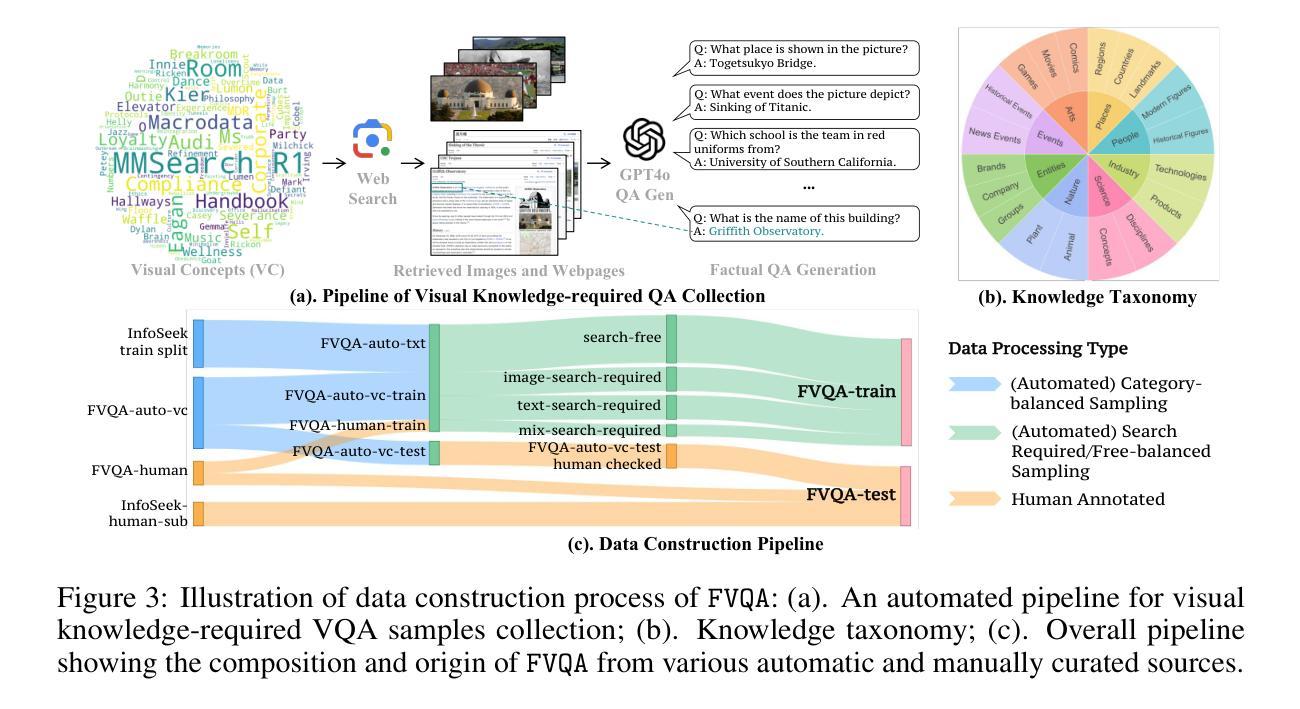
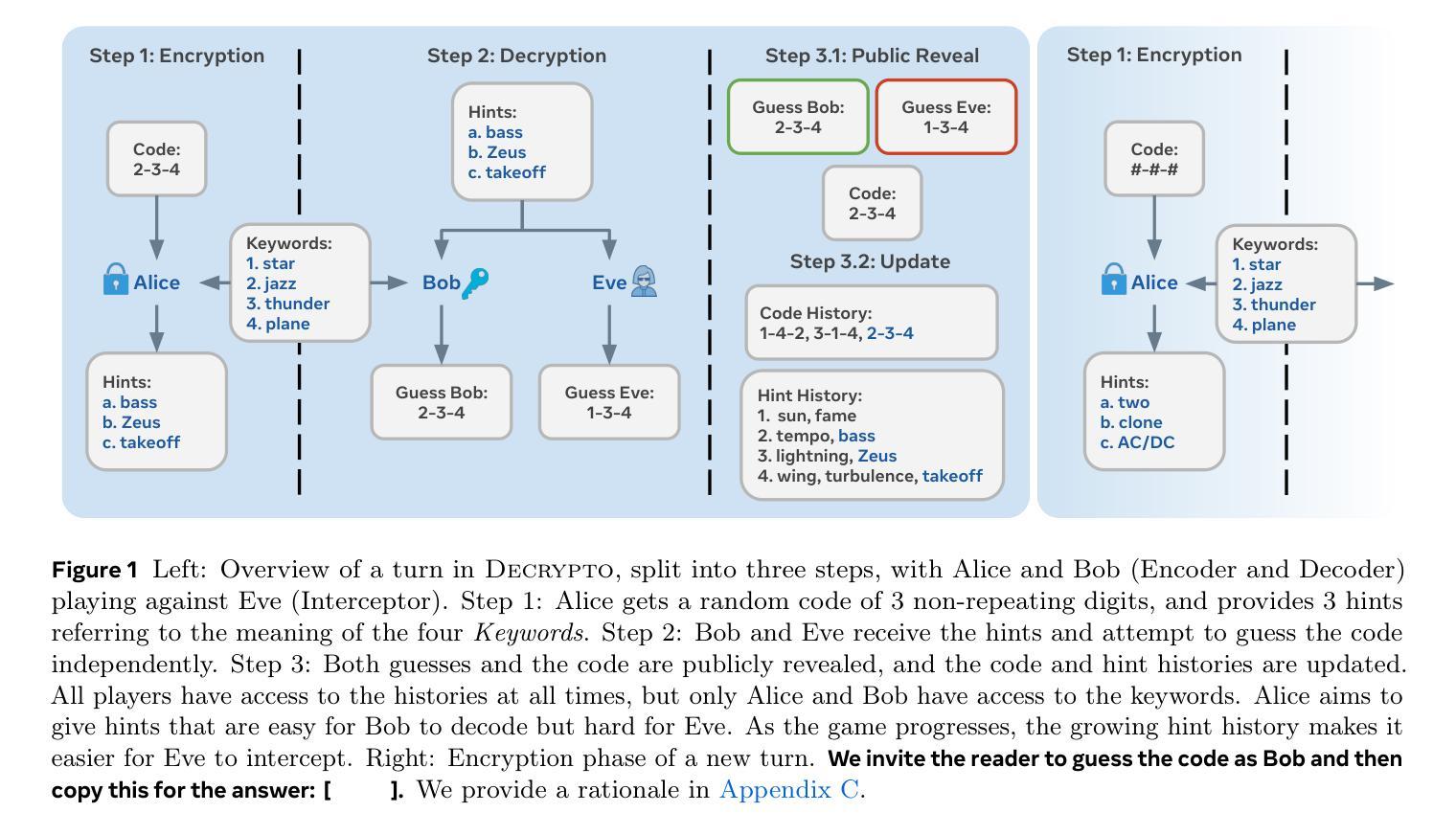
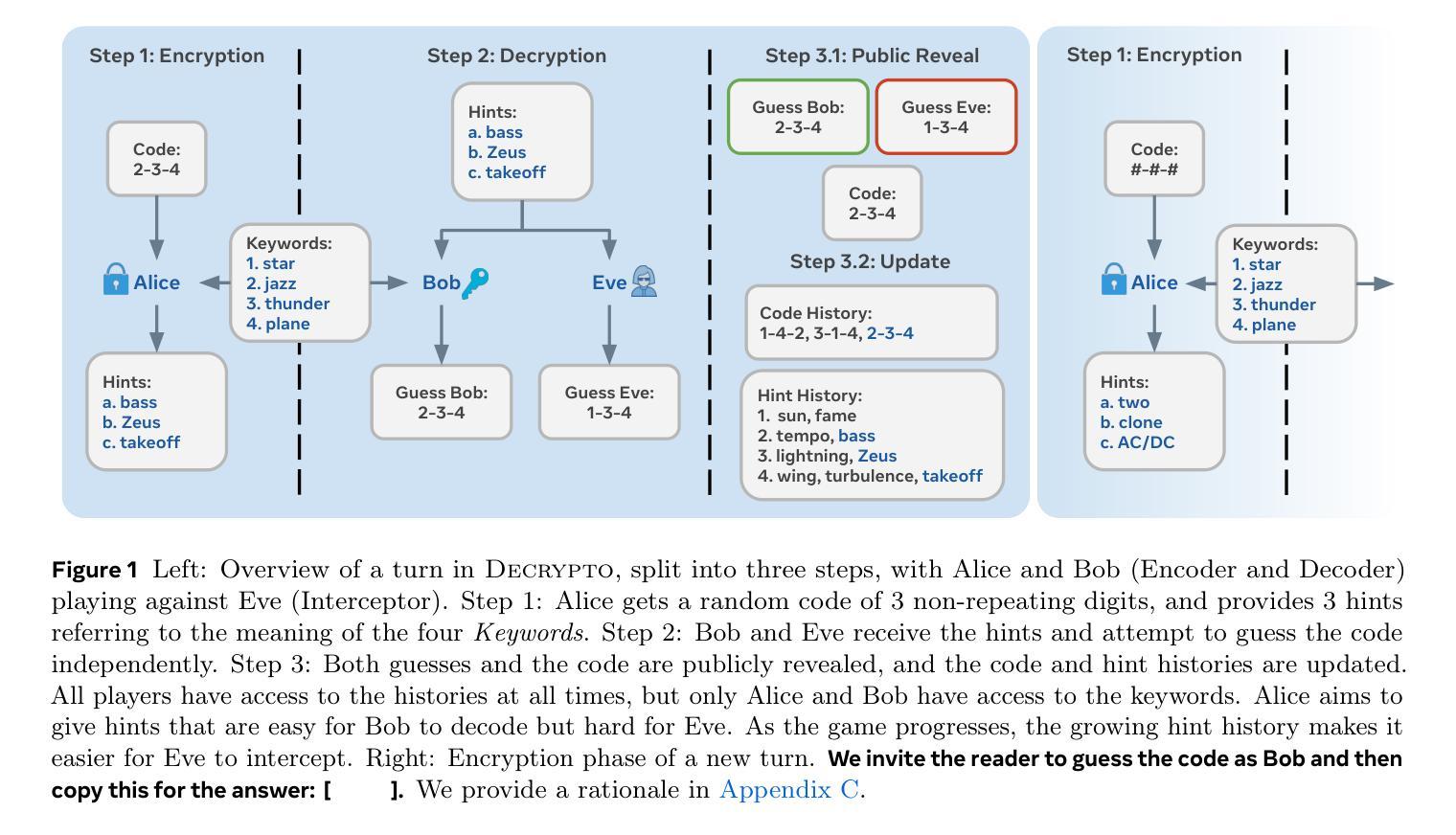
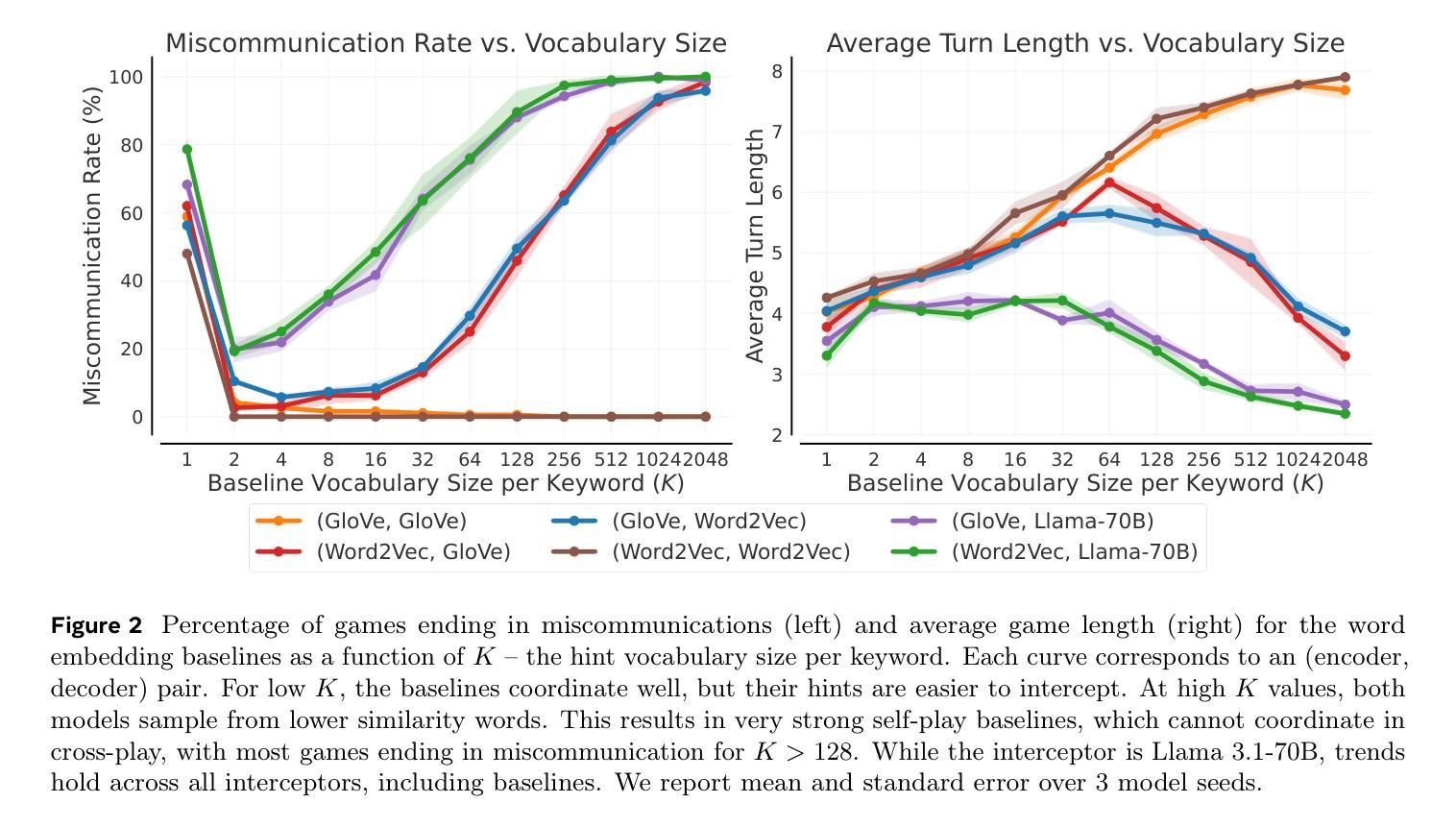
The Decrypto Benchmark for Multi-Agent Reasoning and Theory of Mind
Authors:Andrei Lupu, Timon Willi, Jakob Foerster
As Large Language Models (LLMs) gain agentic abilities, they will have to navigate complex multi-agent scenarios, interacting with human users and other agents in cooperative and competitive settings. This will require new reasoning skills, chief amongst them being theory of mind (ToM), or the ability to reason about the “mental” states of other agents. However, ToM and other multi-agent abilities in LLMs are poorly understood, since existing benchmarks suffer from narrow scope, data leakage, saturation, and lack of interactivity. We thus propose Decrypto, a game-based benchmark for multi-agent reasoning and ToM drawing inspiration from cognitive science, computational pragmatics and multi-agent reinforcement learning. It is designed to be as easy as possible in all other dimensions, eliminating confounding factors commonly found in other benchmarks. To our knowledge, it is also the first platform for designing interactive ToM experiments. We validate the benchmark design through comprehensive empirical evaluations of frontier LLMs, robustness studies, and human-AI cross-play experiments. We find that LLM game-playing abilities lag behind humans and simple word-embedding baselines. We then create variants of two classic cognitive science experiments within Decrypto to evaluate three key ToM abilities. Surprisingly, we find that state-of-the-art reasoning models are significantly worse at those tasks than their older counterparts. This demonstrates that Decrypto addresses a crucial gap in current reasoning and ToM evaluations, and paves the path towards better artificial agents.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)获得代理能力,它们将需要应对复杂的多代理场景,在合作和竞争环境中与人类用户和其他代理进行交互。这将需要新的推理能力,其中最主要的是心智理论(ToM)能力,即推理其他代理的“精神”状态的能力。然而,LLM中的心智理论和其他多代理能力尚待理解,因为现有的基准测试存在范围狭窄、数据泄露、饱和和缺乏交互性的问题。因此,我们提出了基于游戏的基准测试Decrypto,用于多代理推理和心智理论,从认知科学、计算语用学和多代理强化学习中汲取灵感。它的设计在所有其他维度上尽可能简单,消除了在其他基准测试中通常存在的混淆因素。据我们所知,它也是设计交互式心智理论实验的第一个平台。我们通过全面评估前沿的大型语言模型、稳健性研究和人机交叉实验来验证基准测试的设计。我们发现大型语言模型的游戏能力落后于人类和简单的词嵌入基线。然后我们在Decrypto中创建了两种经典认知科学实验的变体,以评估三种关键的心智理论能力。令人惊讶的是,我们发现最先进的大型语言模型在这些任务上的表现明显逊色于它们的旧版本模型。这表明Decrypto解决了当前推理和心智理论评估中的关键差距,并为更好的人工智能代理的发展铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 41 pages, 19 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在获得代理能力后将需要应对复杂的多代理场景,需要在合作和竞争环境中与人类用户和其他代理进行交互。这要求新的推理能力,其中主要是心理理论(ToM),即推理其他代理的“心理”状态的能力。然而,ToM和LLMs中的其他多代理能力尚未得到充分理解,因为现有基准测试存在范围狭窄、数据泄露、饱和和缺乏交互等问题。因此,我们提出了基于游戏的基准测试Decrypto,用于多代理推理和ToM,灵感来自认知科学、计算语用学和多代理强化学习。它是为了尽可能在其他维度上简化而设计的,消除了其他基准测试中通常存在的混淆因素。据我们所知,它也是设计交互式ToM实验的第一个平台。我们通过全面的实证评估、稳健性研究和人机交叉实验验证了基准测试设计的有效性。我们发现LLM的游戏能力落后于人类和简单的词嵌入基线。然后,我们在Decrypto内创建了两个经典认知科学实验的变种,以评估三种关键的ToM能力。令人惊讶的是,我们发现最先进的推理模型在这些任务上的表现显著不如旧模型。这表明Decrypto解决了当前推理和ToM评估中的关键差距,并为更好的人工智能代理铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在获得代理能力后面临多代理场景的复杂性,需具备新的推理能力,尤其是心理理论(ToM)。
- 现有基准测试存在缺陷,如范围狭窄、数据泄露和缺乏交互,导致对LLMs中ToM和其他多代理能力的理解不足。
- 提出了一种新的基于游戏的基准测试Decrypto,用于评估多代理推理和ToM,结合认知科学、计算语用学和强化学习。
- Decrypto设计简洁,消除了其他基准测试中的混淆因素,是首个交互式ToM实验平台。
- LLM在游戏能力方面落后于人类和词嵌入基线。
- 通过变种实验发现,最先进的推理模型在特定任务上的表现不如旧模型。
点此查看论文截图

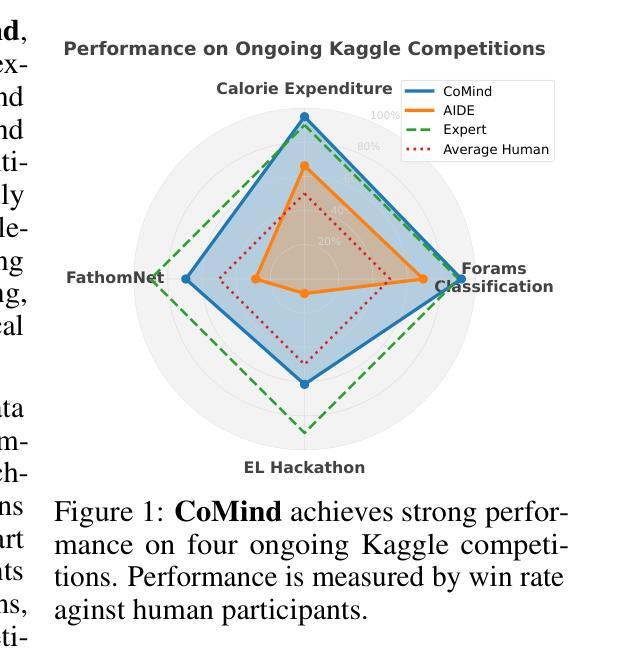
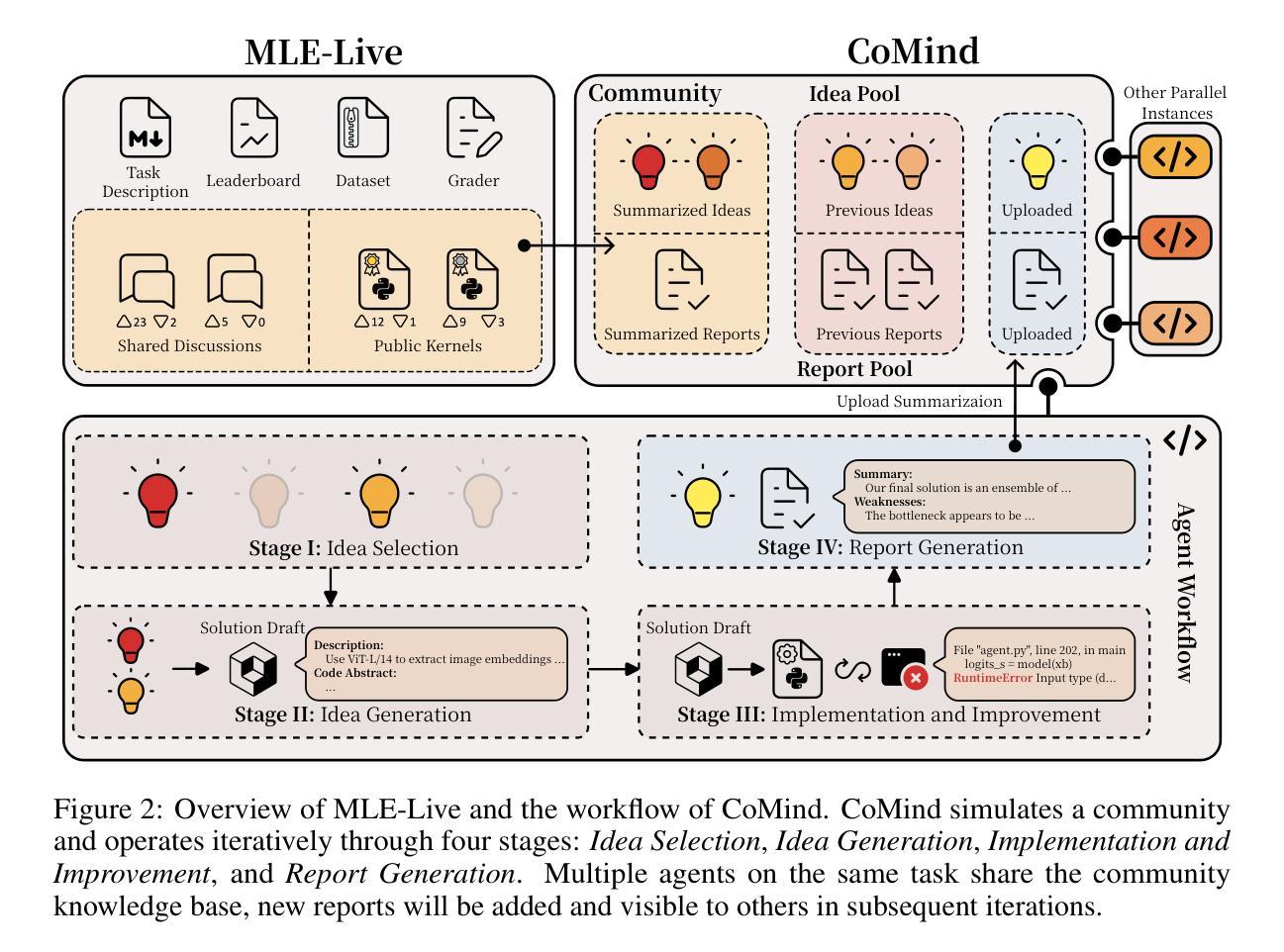
Towards Community-Driven Agents for Machine Learning Engineering
Authors:Sijie Li, Weiwei Sun, Shanda Li, Ameet Talwalkar, Yiming Yang
Large language model-based machine learning (ML) agents have shown great promise in automating ML research. However, existing agents typically operate in isolation on a given research problem, without engaging with the broader research community, where human researchers often gain insights and contribute by sharing knowledge. To bridge this gap, we introduce MLE-Live, a live evaluation framework designed to assess an agent’s ability to communicate with and leverage collective knowledge from a simulated Kaggle research community. Building on this framework, we propose CoMind, a novel agent that excels at exchanging insights and developing novel solutions within a community context. CoMind achieves state-of-the-art performance on MLE-Live and outperforms 79.2% human competitors on average across four ongoing Kaggle competitions. Our code is released at https://github.com/comind-ml/CoMind.
基于大型语言模型的机器学习(ML)代理在自动化ML研究方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,现有的代理通常在一个给定的研究问题上孤立运行,而没有与更广泛的研究社区接触,而人类研究人员往往通过分享知识获得洞察力并做出贡献。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了MLE-Live,这是一个旨在评估代理与模拟Kaggle研究社区进行交流并利用集体知识的能力的实时评估框架。在此框架的基础上,我们提出了CoMind,这是一个擅长在社区环境中交流见解并开发新解决方案的新型代理。CoMind在MLE-Live上实现了最先进的性能,并在四个正在进行的Kaggle竞赛中平均击败了79.2%的人类竞争对手。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/comind-ml/CoMind。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动化机器学习研究方面,大型语言模型驱动的机器学习(ML)代理表现出了巨大的潜力。为解决现有代理在处理特定问题时孤立运行、无法与更广泛的社区进行交流互动的问题,研究者引入了MLE-Live评估框架,旨在评估代理与模拟Kaggle研究社区进行沟通和利用集体知识的能力。基于该框架,我们提出了CoMind这一新型代理,擅长在社区环境中交流见解并开发新颖解决方案。CoMind在MLE-Live上表现卓越,并在四个持续进行的Kaggle竞赛中平均击败了79.2%的人类竞争对手。我们的代码已发布在GitHub上:https://github.com/comind-ml/CoMind。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型驱动的机器学习代理在自动化机器学习研究领域展现潜力。
- 目前存在的代理主要在孤立环境中运行,缺乏与广大研究社区的互动。
- MLE-Live评估框架旨在评估代理与模拟Kaggle研究社区交流的能力。
- CoMind是一个基于MLE-Live框架构建的新型代理,擅长在社区环境中交流和开发解决方案。
- CoMind在模拟的Kaggle竞赛环境中表现卓越,超过了大部分人类参赛者。
- CoMind已在GitHub上公开发布,以供研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图

DiffuCoder: Understanding and Improving Masked Diffusion Models for Code Generation
Authors:Shansan Gong, Ruixiang Zhang, Huangjie Zheng, Jiatao Gu, Navdeep Jaitly, Lingpeng Kong, Yizhe Zhang
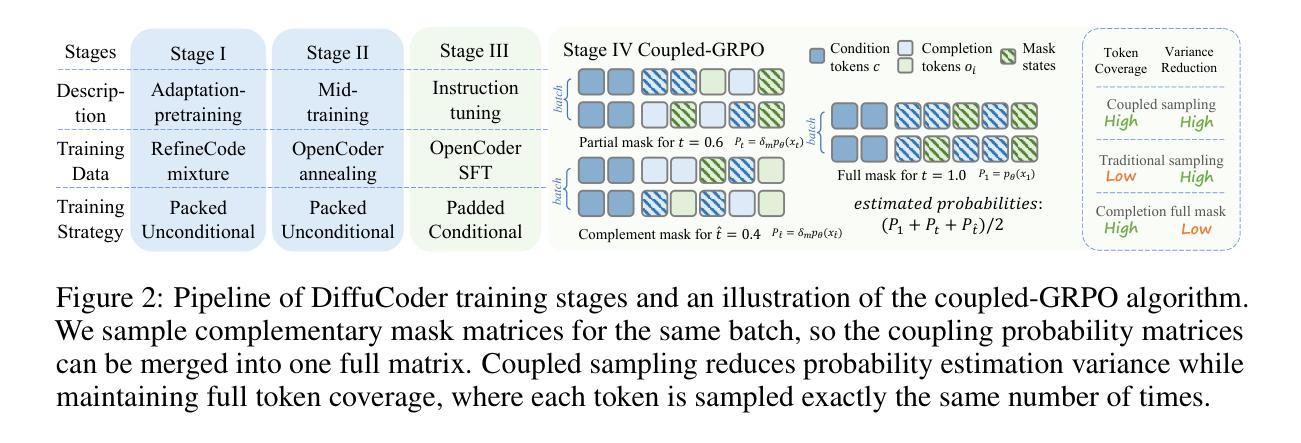
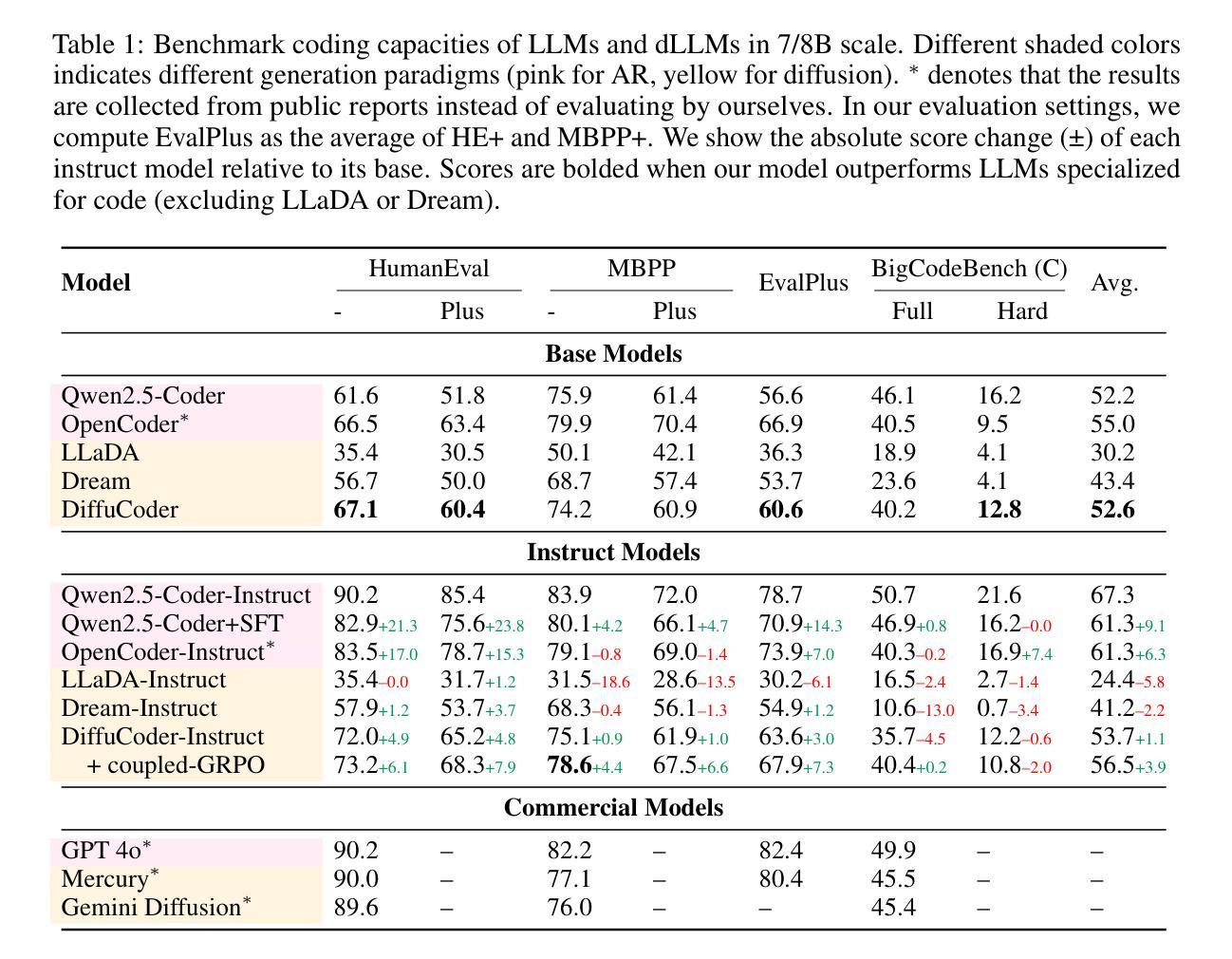
Diffusion large language models (dLLMs) are compelling alternatives to autoregressive (AR) models because their denoising models operate over the entire sequence. The global planning and iterative refinement features of dLLMs are particularly useful for code generation. However, current training and inference mechanisms for dLLMs in coding are still under-explored. To demystify the decoding behavior of dLLMs and unlock their potential for coding, we systematically investigate their denoising processes and reinforcement learning (RL) methods. We train a 7B dLLM, \textbf{DiffuCoder}, on 130B tokens of code. Using this model as a testbed, we analyze its decoding behavior, revealing how it differs from that of AR models: (1) dLLMs can decide how causal their generation should be without relying on semi-AR decoding, and (2) increasing the sampling temperature diversifies not only token choices but also their generation order. This diversity creates a rich search space for RL rollouts. For RL training, to reduce the variance of token log-likelihood estimates and maintain training efficiency, we propose \textbf{coupled-GRPO}, a novel sampling scheme that constructs complementary mask noise for completions used in training. In our experiments, coupled-GRPO significantly improves DiffuCoder’s performance on code generation benchmarks (+4.4% on EvalPlus) and reduces reliance on AR causal during decoding. Our work provides deeper insight into the machinery of dLLM generation and offers an effective, diffusion-native RL training framework. https://github.com/apple/ml-diffucoder.
扩散大型语言模型(dLLMs)是令人信服的自回归(AR)模型的替代方案,因为它们的降噪模型在整个序列上运行。dLLMs的全局规划和迭代优化功能对于代码生成特别有用。然而,目前针对编码中的dLLM的训练和推理机制仍被探索不足。为了揭示dLLMs的解码行为并解锁其在编码方面的潜力,我们系统地研究了它们的降噪过程和强化学习(RL)方法。我们在130B代码标记上训练了一个7B的dLLM,名为DiffuCoder。以此模型为测试平台,我们分析了其解码行为,揭示了其与AR模型的不同之处:(1)dLLM能够决定其生成应该如何因果关系,而无需依赖半自回归解码;(2)增加采样温度不仅使标记选择多样化,还使其生成顺序多样化。这种多样性为RL回滚创建了一个丰富的搜索空间。对于RL训练,为了减少标记对数似然估计的方差并保持训练效率,我们提出了coupled-GRPO,这是一种新的采样方案,用于构建用于训练中的完成的互补掩码噪声。在我们的实验中,coupled-GRPO显著提高了DiffuCoder在代码生成基准测试上的性能(在EvalPlus上提高了4.4%),并减少了解码过程中AR因果的依赖。我们的工作为dLLM生成机制提供了更深入的了解,并提供了一个有效的、基于扩散的RL训练框架。详情请访问:https://github.com/apple/ml-diffucoder 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
本文介绍了扩散大型语言模型(dLLMs)在代码生成方面的优势及其解码行为的研究。通过训练一个规模为7B的dLLM模型DiffuCoder,并对其进行系统分析,发现dLLMs具有全局规划和迭代优化的特点,其解码行为与自回归(AR)模型有所不同。研究还探讨了强化学习(RL)在dLLMs训练中的应用,并提出了一个新的采样方案coupled-GRPO,以提高代码生成性能并减少解码过程中对AR的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- dLLMs是代码生成领域具有吸引力的替代方案,具有全局规划和迭代优化特点。
- dLLMs的解码行为与自回归(AR)模型不同,可以决定生成的因果性,并且增加采样温度可以多样化生成顺序。
- 强化学习(RL)在dLLMs训练中起着重要作用,可以减少token log-likelihood估计的方差并保持训练效率。
- coupled-GRPO是一种新型的采样方案,为dLLMs的训练提供了一种有效的扩散原生RL训练框架。
点此查看论文截图
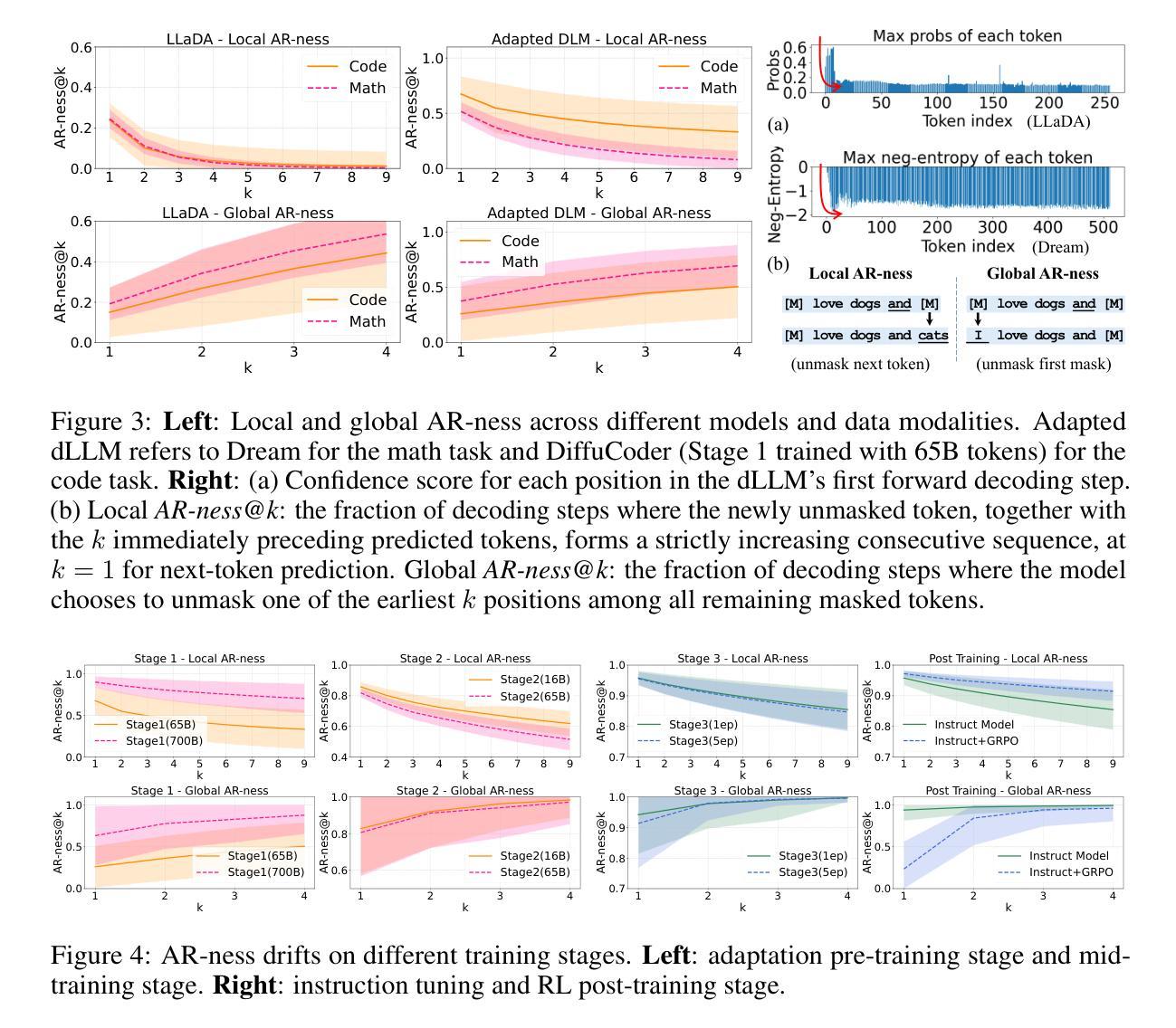
PLoP: Precise LoRA Placement for Efficient Finetuning of Large Models
Authors:Soufiane Hayou, Nikhil Ghosh, Bin Yu
Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is a widely used finetuning method for large models. Its small memory footprint allows practitioners to adapt large models to specific tasks at a fraction of the cost of full finetuning. Different modifications have been proposed to enhance its efficiency by, for example, setting the learning rate, the rank, and the initialization. Another improvement axis is adapter placement strategy: when using LoRA, practitioners usually pick module types to adapt with LoRA, such as Query and Key modules. Few works have studied the problem of adapter placement, with nonconclusive results: original LoRA paper suggested placing adapters in attention modules, while other works suggested placing them in the MLP modules. Through an intuitive theoretical analysis, we introduce PLoP (Precise LoRA Placement), a lightweight method that allows automatic identification of module types where LoRA adapters should be placed, given a pretrained model and a finetuning task. We demonstrate that PLoP consistently outperforms, and in the worst case competes, with commonly used placement strategies through comprehensive experiments on supervised finetuning and reinforcement learning for reasoning.
低秩适配(LoRA)是一种广泛应用于大型模型的微调方法。它较小的内存占用率使得实践者能够以全量微调的一小部分成本将大型模型适配到特定任务上。为了提升效率,已经提出了各种改良方法,例如设置学习率、等级和初始化等。另一个改进方向是适配器放置策略:在使用LoRA时,实践者通常会选择使用LoRA适配的模块类型,例如查询和键模块。关于适配器放置的问题研究较少,且结果尚无定论:原始LoRA论文建议在注意力模块中放置适配器,而其他研究则建议将它们放置在MLP模块中。通过直观的理论分析,我们引入了PLoP(精确LoRA放置),这是一种轻量级的方法,能够在给定预训练模型和微调任务的情况下自动识别应放置LoRA适配器的模块类型。我们通过大量的实验演示了PLoP在监督微调以及强化学习推理方面的一致优势,在最坏的情况下也能与常用放置策略相竞争。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TD,LR: A lightweight module type selection method for LoRA finetuning. PLoP gives precise placements for LoRA adapters for improved performance
Summary
LoRA(低秩适应)是一种用于大型模型的微调方法,因其较小的内存占用而备受青睐。为提高效率,人们对其进行了多种改进,如设置学习率、等级和初始化等。最近的研究关注于适配器放置策略,即选择哪些模块类型使用LoRA适配器进行适应。本文通过直观的理论分析,介绍了一种新方法PLoP(精确LoRA放置),可自动识别应放置LoRA适配器的模块类型。实验表明,PLoP在监督微调与强化学习等任务上的表现均优于常规放置策略。
Key Takeaways
- LoRA是一种用于大型模型的微调方法,具有较小的内存占用和较低的成本。
- LoRA的效率可以通过多种方式进行改进,包括设置学习率、等级和初始化等。
- 适配器放置策略是LoRA的一个重要改进方向,目前对此的研究尚少且结果非结论性。
- 原LoRA论文建议将适配器放置在注意力模块中,而其他研究则建议放置在MLP模块中。
- PLoP方法能够通过直观的理论分析,自动识别应放置LoRA适配器的模块类型。
- PLoP在监督微调与强化学习等任务上的表现均优于常规放置策略。
- PLoP的引入为大型模型的微调提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

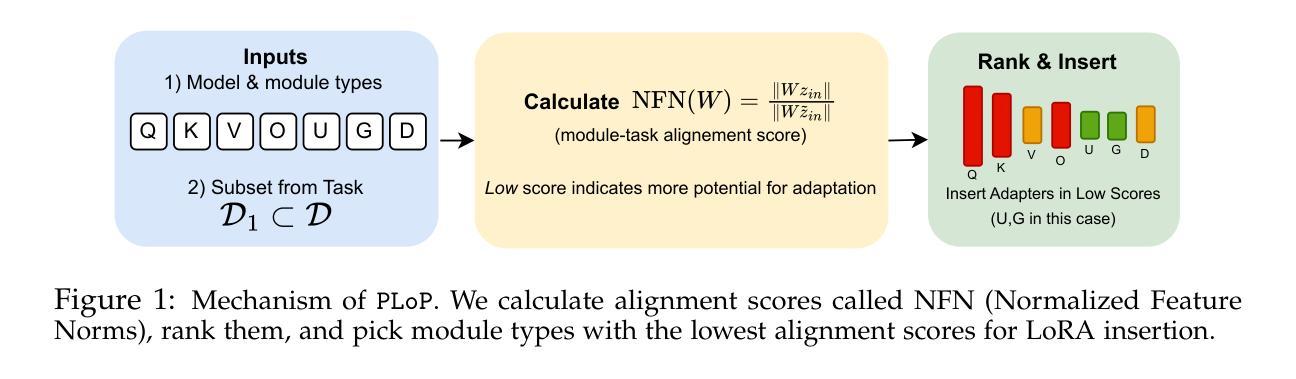
Video Perception Models for 3D Scene Synthesis
Authors:Rui Huang, Guangyao Zhai, Zuria Bauer, Marc Pollefeys, Federico Tombari, Leonidas Guibas, Gao Huang, Francis Engelmann
Traditionally, 3D scene synthesis requires expert knowledge and significant manual effort. Automating this process could greatly benefit fields such as architectural design, robotics simulation, virtual reality, and gaming. Recent approaches to 3D scene synthesis often rely on the commonsense reasoning of large language models (LLMs) or strong visual priors of modern image generation models. However, current LLMs demonstrate limited 3D spatial reasoning ability, which restricts their ability to generate realistic and coherent 3D scenes. Meanwhile, image generation-based methods often suffer from constraints in viewpoint selection and multi-view inconsistencies. In this work, we present Video Perception models for 3D Scene synthesis (VIPScene), a novel framework that exploits the encoded commonsense knowledge of the 3D physical world in video generation models to ensure coherent scene layouts and consistent object placements across views. VIPScene accepts both text and image prompts and seamlessly integrates video generation, feedforward 3D reconstruction, and open-vocabulary perception models to semantically and geometrically analyze each object in a scene. This enables flexible scene synthesis with high realism and structural consistency. For more precise analysis, we further introduce First-Person View Score (FPVScore) for coherence and plausibility evaluation, utilizing continuous first-person perspective to capitalize on the reasoning ability of multimodal large language models. Extensive experiments show that VIPScene significantly outperforms existing methods and generalizes well across diverse scenarios. The code will be released.
传统上,3D场景合成需要专业知识的大量投入和显著的手动操作。自动化这一过程可以为建筑设计、机器人仿真、虚拟现实和游戏等领域带来巨大的好处。最近的3D场景合成方法常常依赖于大型语言模型的常识推理或现代图像生成模型的强大视觉先验。然而,当前的大型语言模型表现出有限的3D空间推理能力,这限制了它们生成真实和连贯的3D场景的能力。同时,基于图像生成的方法经常受到视点选择和多视图不一致性的约束。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于3D场景合成的Video Perception模型(VIPScene),这是一个利用视频生成模型中的3D物理世界常识知识编码的新框架,以确保跨视图的连贯场景布局和一致的对象放置。VIPScene接受文本和图像提示,无缝集成视频生成、前馈3D重建和开放词汇感知模型,以语义和几何方式分析场景中的每个对象。这实现了具有高度的真实感和结构一致性的灵活场景合成。为了进行更精确的分析,我们还引入了第一人称视角评分(FPVScore)来进行连贯性和可行性评估,利用连续的第一人称视角来利用多模式大型语言模型的推理能力。大量实验表明,VIPScene显著优于现有方法,并在各种场景中具有良好的通用性。代码将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
VIPScene通过结合视频生成模型中的三维物理世界常识知识,实现了连贯的场景布局和跨视图的物体位置一致性。该方法接受文本和图像提示,无缝集成视频生成、前馈三维重建和开放词汇感知模型,实现场景的语义和几何分析。这为具有高度现实感和结构一致性的灵活场景合成提供了新的方法。
Key Takeaways
- VIPScene是一个用于三维场景合成的新型框架,能够利用视频生成模型中的三维物理世界常识知识。
- VIPScene可以接受文本和图像提示,并集成了视频生成、前馈三维重建和开放词汇感知模型。
- VIPScene能够确保场景连贯性和物体位置的一致性。
- VIPScene具备灵活的场景合成能力,具有高度的现实感和结构一致性。
- VIPScene引入第一人称视角评分(FPVScore)来评估场景合成的连贯性和可信度。
- VIPScene在实验中表现出优异的性能,显著优于现有方法,并且在各种场景下具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

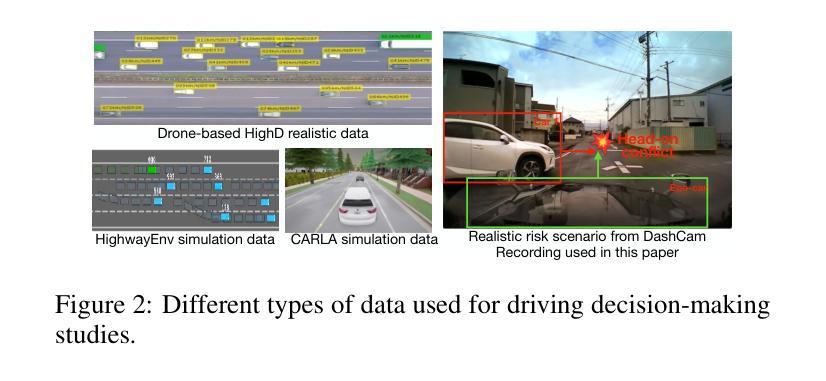
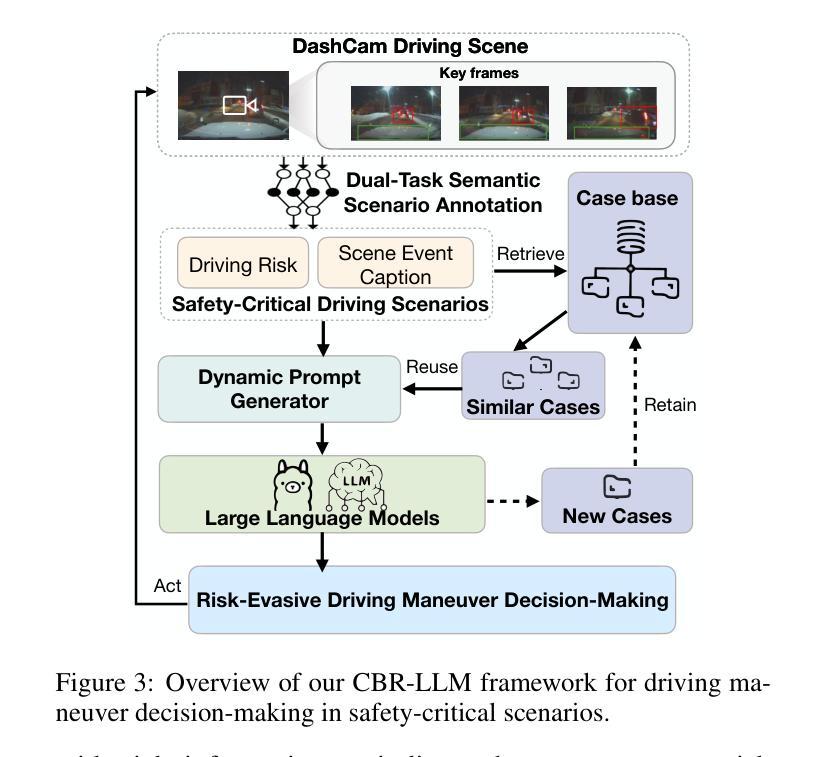
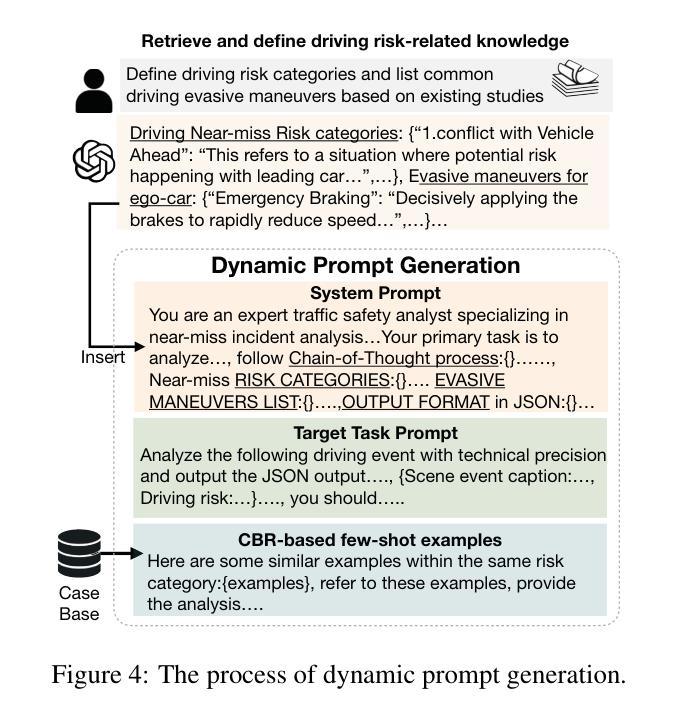
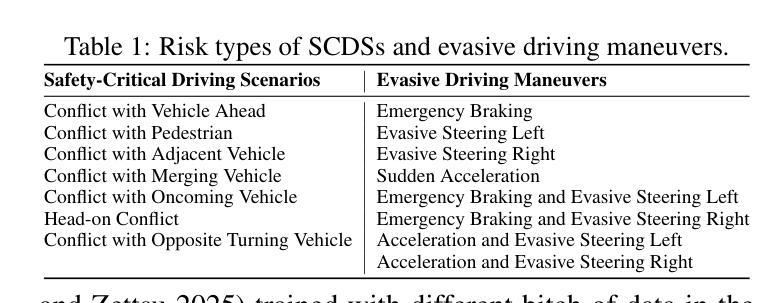
Case-based Reasoning Augmented Large Language Model Framework for Decision Making in Realistic Safety-Critical Driving Scenarios
Authors:Wenbin Gan, Minh-Son Dao, Koji Zettsu
Driving in safety-critical scenarios requires quick, context-aware decision-making grounded in both situational understanding and experiential reasoning. Large Language Models (LLMs), with their powerful general-purpose reasoning capabilities, offer a promising foundation for such decision-making. However, their direct application to autonomous driving remains limited due to challenges in domain adaptation, contextual grounding, and the lack of experiential knowledge needed to make reliable and interpretable decisions in dynamic, high-risk environments. To address this gap, this paper presents a Case-Based Reasoning Augmented Large Language Model (CBR-LLM) framework for evasive maneuver decision-making in complex risk scenarios. Our approach integrates semantic scene understanding from dashcam video inputs with the retrieval of relevant past driving cases, enabling LLMs to generate maneuver recommendations that are both context-sensitive and human-aligned. Experiments across multiple open-source LLMs show that our framework improves decision accuracy, justification quality, and alignment with human expert behavior. Risk-aware prompting strategies further enhance performance across diverse risk types, while similarity-based case retrieval consistently outperforms random sampling in guiding in-context learning. Case studies further demonstrate the framework’s robustness in challenging real-world conditions, underscoring its potential as an adaptive and trustworthy decision-support tool for intelligent driving systems.
在关键的驾驶场景中,驾驶员需要基于情境理解和经验推理的快速、灵活的决策能力。大型语言模型(LLM)以其强大的通用推理能力,为这种决策提供了有前景的基础。然而,将其直接应用于自动驾驶仍存在挑战,特别是在领域适应、上下文定位以及在动态高风险环境中做出可靠和可解释决策所需经验知识的缺乏方面。为了弥补这一差距,本文提出了一种基于案例推理的增强大型语言模型(CBR-LLM)框架,用于复杂风险场景中的规避动作决策。我们的方法结合了从行车记录仪视频输入中理解场景语义与检索相关历史驾驶案例,使LLM能够生成既敏感于上下文又与人类行为一致的机动建议。跨多个开源LLM的实验表明,我们的框架提高了决策准确性、解释质量以及与人类专家行为的契合度。风险感知提示策略进一步增强了各种风险类型的性能,而基于相似性的案例检索在指导上下文学习方面始终优于随机抽样。案例研究进一步证明了该框架在具有挑战性的现实条件下的稳健性,突显了其作为智能驾驶系统的自适应和可信赖的决策支持工具的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 10 figures, under-review conference
Summary
基于情境理解和经验推理的快速决策对于安全驾驶至关重要。大型语言模型为此类决策提供了有力支持,但在自动驾驶领域的应用仍面临域适应、上下文定位以及环境经验知识的缺乏等挑战。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于案例推理辅助的大型语言模型框架(CBR-LLM),该框架通过驾驶舱视频输入对语义场景进行理解,并检索相关驾驶案例,使语言模型能够生成既符合上下文又符合人类行为的机动建议。实验表明,该框架提高了决策准确性、解释质量和对人类专家行为的匹配度。风险感知提示策略进一步提高了各种风险类型的性能,基于相似性的案例检索在指导上下文学习方面表现优于随机抽样。案例研究证明了该框架在复杂现实条件下的稳健性,可作为智能驾驶系统的自适应和可靠决策支持工具。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在自动驾驶中的决策应用具有潜力,但需解决域适应、上下文理解和环境经验知识缺乏的问题。
- CBR-LLM框架结合了语义场景理解与相关驾驶案例检索,提高语言模型在复杂风险场景中的决策能力。
- 实验显示CBR-LLM框架能提高决策准确性、解释质量,并更贴近人类专家行为。
- 风险感知提示策略有助于提升在各种风险场景中的性能。
- 相似性基础上的案例检索在指导语言模型学习方面比随机抽样更有效。
- CBR-LLM框架在挑战现实条件下展现出稳健性,能够为智能驾驶系统提供自适应和可靠的决策支持。
点此查看论文截图


Asymmetric REINFORCE for off-Policy Reinforcement Learning: Balancing positive and negative rewards
Authors:Charles Arnal, Gaëtan Narozniak, Vivien Cabannes, Yunhao Tang, Julia Kempe, Remi Munos
Reinforcement learning (RL) is increasingly used to align large language models (LLMs). Off-policy methods offer greater implementation simplicity and data efficiency than on-policy techniques, but often result in suboptimal performance. In this work, we study the intermediate range of algorithms between off-policy RL and supervised fine-tuning by analyzing a simple off-policy REINFORCE algorithm, where the advantage is defined as $A=r-V$, with $r$ a reward and $V$ some tunable baseline. Intuitively, lowering $V$ emphasizes high-reward samples, while raising it penalizes low-reward ones more heavily. We first provide a theoretical analysis of this off-policy REINFORCE algorithm, showing that when the baseline $V$ lower-bounds the expected reward, the algorithm enjoys a policy improvement guarantee. Our analysis reveals that while on-policy updates can safely leverage both positive and negative signals, off-policy updates benefit from focusing more on positive rewards than on negative ones. We validate our findings experimentally in a controlled stochastic bandit setting and through fine-tuning state-of-the-art LLMs on reasoning tasks.
强化学习(RL)越来越多地被用于对齐大型语言模型(LLM)。相比on-policy技术,off-policy方法在实现简单性和数据效率方面提供了更大的优势,但通常会导致次优性能。在这项工作中,我们通过分析一个简单的off-policy REINFORCE算法来研究off-policy RL和受监督微调之间的算法中介范围,该算法中的优势定义为A=r-V,其中r是奖励,V是可调整的基线。直观地说,降低V会突出高奖励样本,而提高其则会更严厉地惩罚低奖励样本。我们首先对这种off-policy REINFORCE算法进行理论分析,表明当基线V预期奖励的下界时,该算法具有策略改进保证。我们的分析表明,当on-policy更新可以安全地利用正负信号时,off-policy更新更多地受益于关注正向奖励而非负向奖励。我们在受控的随机强盗环境和通过微调最新的LLM进行推理任务实验验证了我们的发现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)被越来越多地用于对齐大型语言模型(LLM)。本工作研究了介于离线策略强化学习与监督微调之间的算法,通过分析简单的离线策略REINFORCE算法的优势定义,揭示出基线值V的调整对于强化学习性能的影响。理论上分析表明,当基线值V下界预期奖励时,算法具有策略改进保证。分析还发现,相比于负向奖励,离线策略更新更侧重于正向奖励。实验验证了在受控的随机性情境以及微调状态最优的语言模型上,我们的发现均成立。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习用于对齐大型语言模型越来越普遍。
- 离线策略强化学习相较于在线策略具有实施简单和高效的数据使用效率,但性能可能不如在线策略。
- 研究集中在离线策略REINFORCE算法的优势定义上,其中优势被定义为奖励r与可调基线值V的差。
- 基线值V的调整可以影响算法性能,降低V值强调高奖励样本,提高V值则更严厉地惩罚低奖励样本。
- 理论上分析表明,当基线值V作为预期奖励的下界时,算法具有策略改进保障。
- 分析发现离线策略更新更侧重于正向奖励,而不是负向奖励。
点此查看论文截图

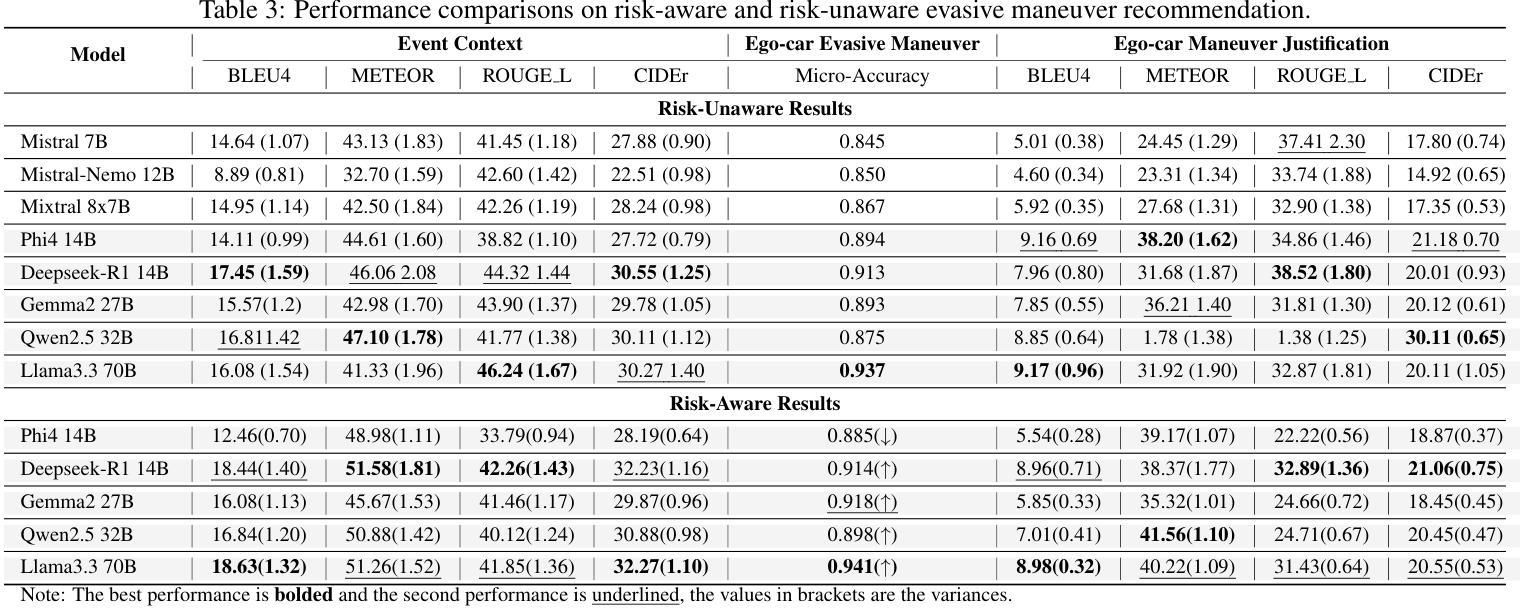
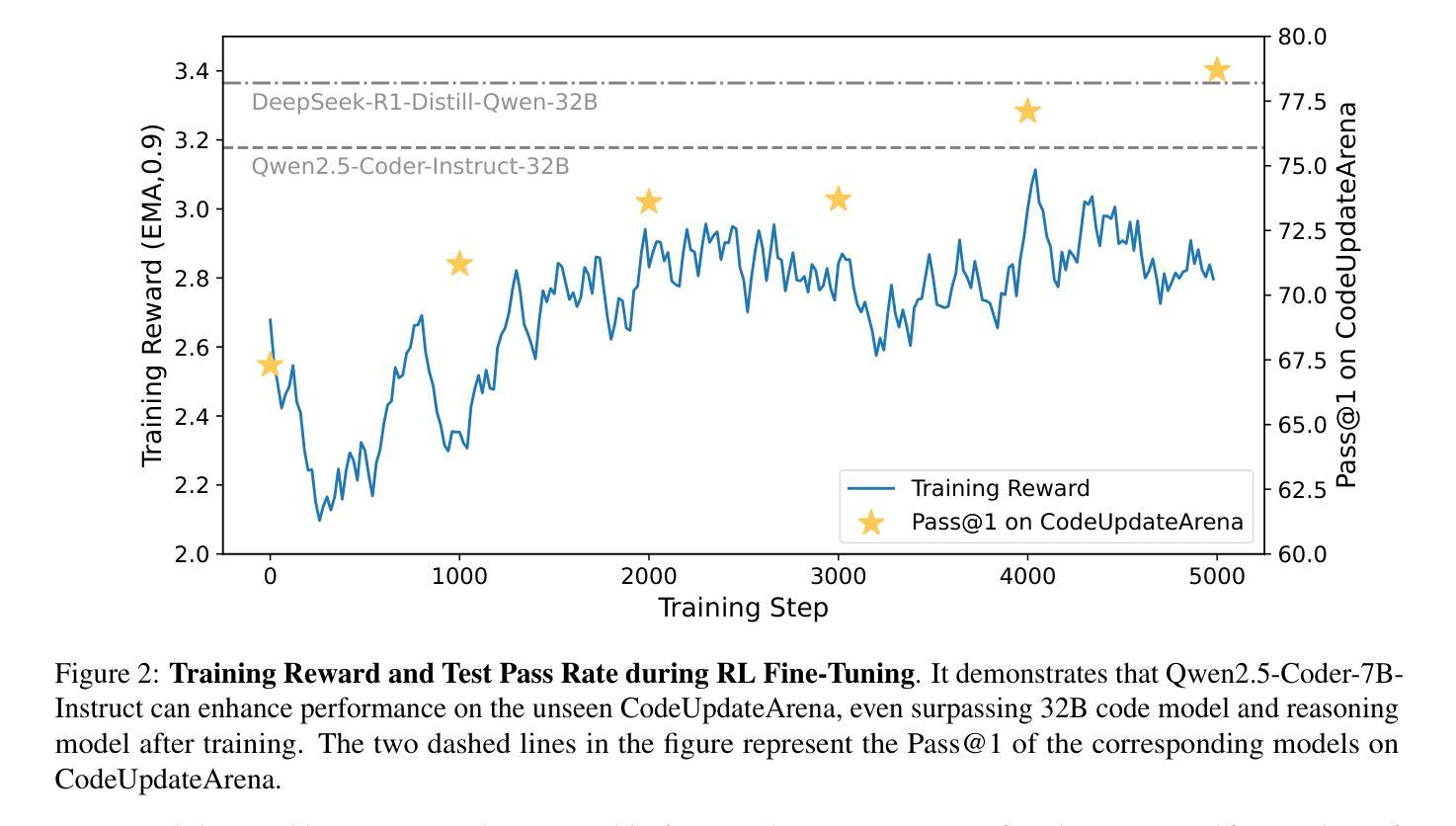
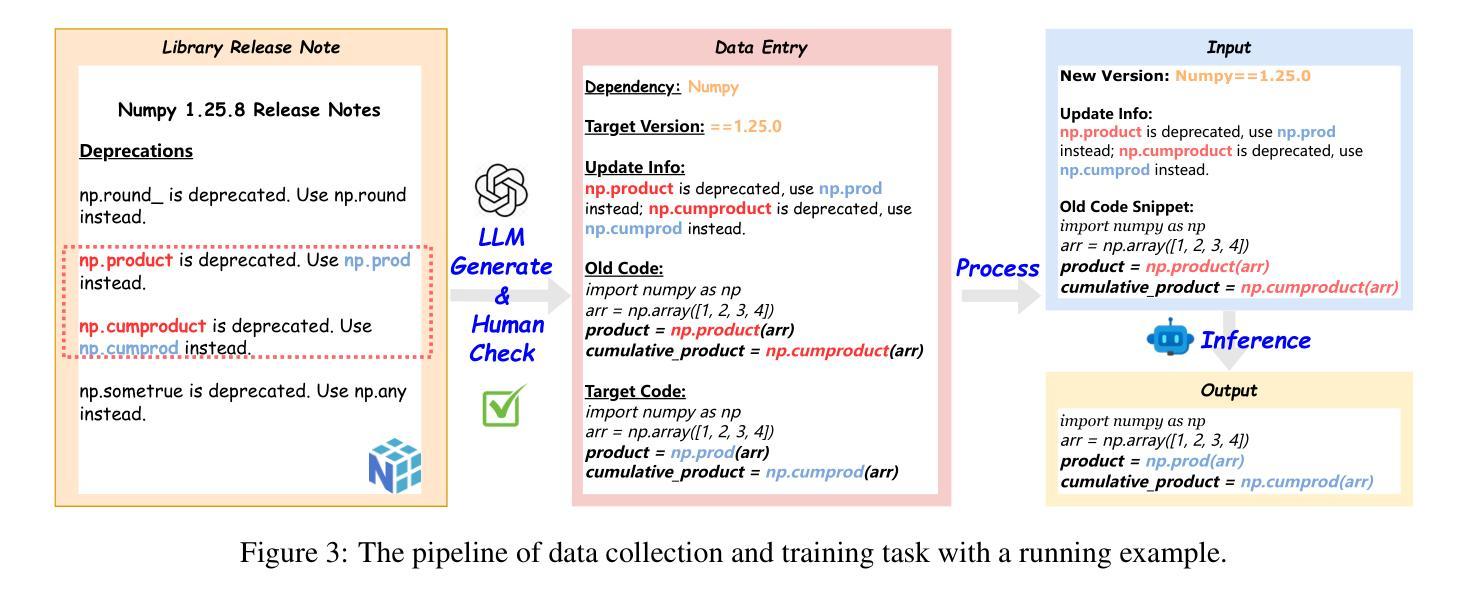
ReCode: Updating Code API Knowledge with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Haoze Wu, Yunzhi Yao, Wenhao Yu, Huajun Chen, Ningyu Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable code generation capabilities but falter when adapting to frequent updates in external library APIs. This critical limitation, stemming from reliance on outdated API knowledge from their training data, even with access to current documentation, impedes reliable code generation in dynamic environments. To tackle this issue, we propose ReCode (rule-based Reinforcement learning for Code Update), a novel framework that mimics human programmer adaptation to API changes. Specifically, we construct a dataset of approximately 2,000 data entries to train the LLMs to perform version migration based on updated information. Then, we introduce a modified string similarity metric for code evaluation as the reward for reinforcement learning. Our experiments demonstrate that ReCode substantially boosts LLMs’ code generation performance in dynamic API scenarios, especially on the unseen CodeUpdateArena task. Crucially, compared to supervised fine-tuning, ReCode has less impact on LLMs’ general code generation abilities. We apply ReCode on various LLMs and reinforcement learning algorithms (GRPO and DAPO), all achieving consistent improvements. Notably, after training, Qwen2.5-Coder-7B outperforms that of the 32B parameter code instruction-tuned model and the reasoning model with the same architecture. Code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/ReCode.
大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面表现出色,但在适应外部库API的频繁更新时却会陷入困境。这一关键局限性源于对训练数据中过时API知识的依赖,即使有访问当前文档,也阻碍了动态环境中的可靠代码生成。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了ReCode(基于规则的代码更新强化学习)这一新型框架,它模拟程序员对API变化的适应。具体来说,我们构建了大约2000个数据条目数据集,以训练LLM根据更新信息进行版本迁移。然后,我们引入了一种改进的字符串相似性度量作为代码评价的奖励,用于强化学习。我们的实验表明,ReCode在动态API场景中大幅提升了LLM的代码生成性能,特别是在未见过的CodeUpdateArena任务中。关键的是,与监督微调相比,ReCode对LLM的一般代码生成能力的影响较小。我们在各种LLM和强化学习算法(GRPO和DAPO)上应用了ReCode,均实现了持续改进。值得注意的是,经过训练后,Qwen2.5-Coder-7B的表现优于32B参数代码指令调整模型以及相同结构下的推理模型。相关代码可访问https://github.com/zjunlp/ReCode获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary:大型语言模型在代码生成方面表现出色,但在适应外部库API的频繁更新时遇到困难。为了解决这一问题,提出了一种名为ReCode的新框架,该框架通过强化学习模拟程序员对API变化的适应。实验表明,ReCode显著提高了大型语言模型在动态API场景下的代码生成性能,特别是在未见过的CodeUpdateArena任务上。此外,ReCode对大型语言模型的常规代码生成能力影响较小。不同的大型语言模型和强化学习算法在ReCode应用后均实现了一致性的改进。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在代码生成方面具有出色能力,但在动态API更新适应方面存在局限性。
- ReCode框架通过结合规则基础和强化学习来解决这一问题。
- ReCode使用自定义数据集训练大型语言模型以进行版本迁移。
- 引入修改后的字符串相似性度量作为强化学习的奖励函数,用于代码评价。
- 实验表明,ReCode显著提高了大型语言模型在动态API场景下的代码生成性能。
- ReCode对大型语言模型的常规代码生成能力影响较小。
- ReCode可应用于不同的大型语言模型和强化学习算法,实现一致性的改进。
点此查看论文截图

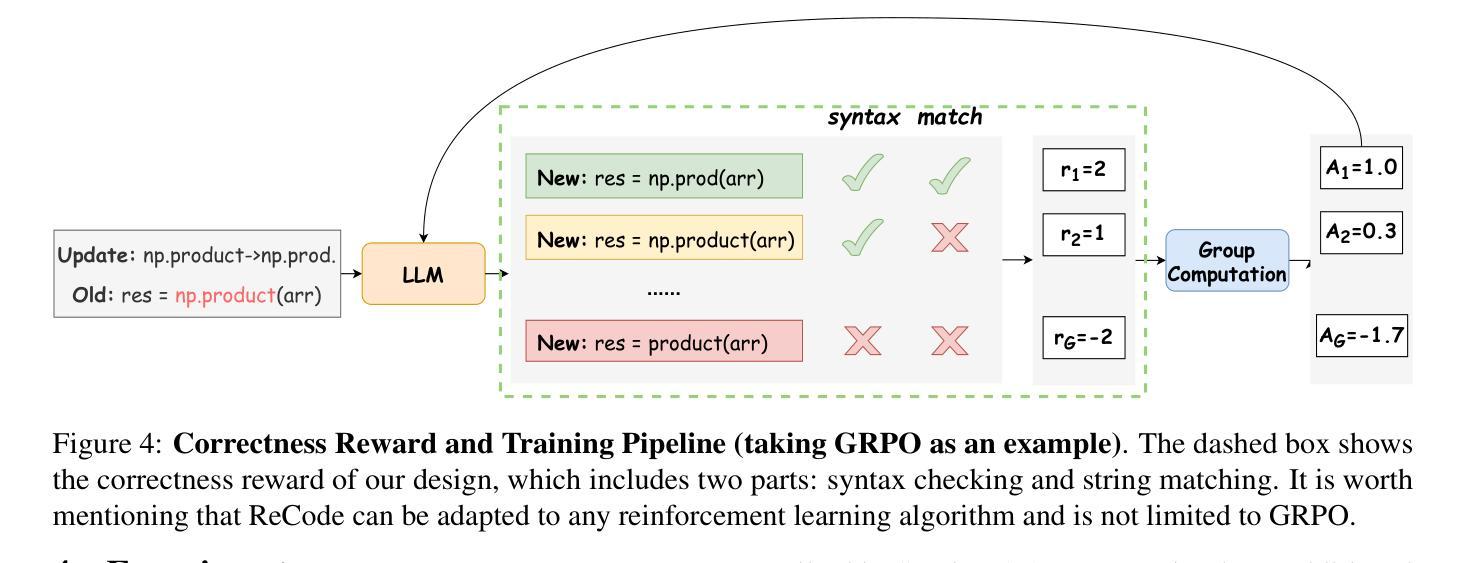
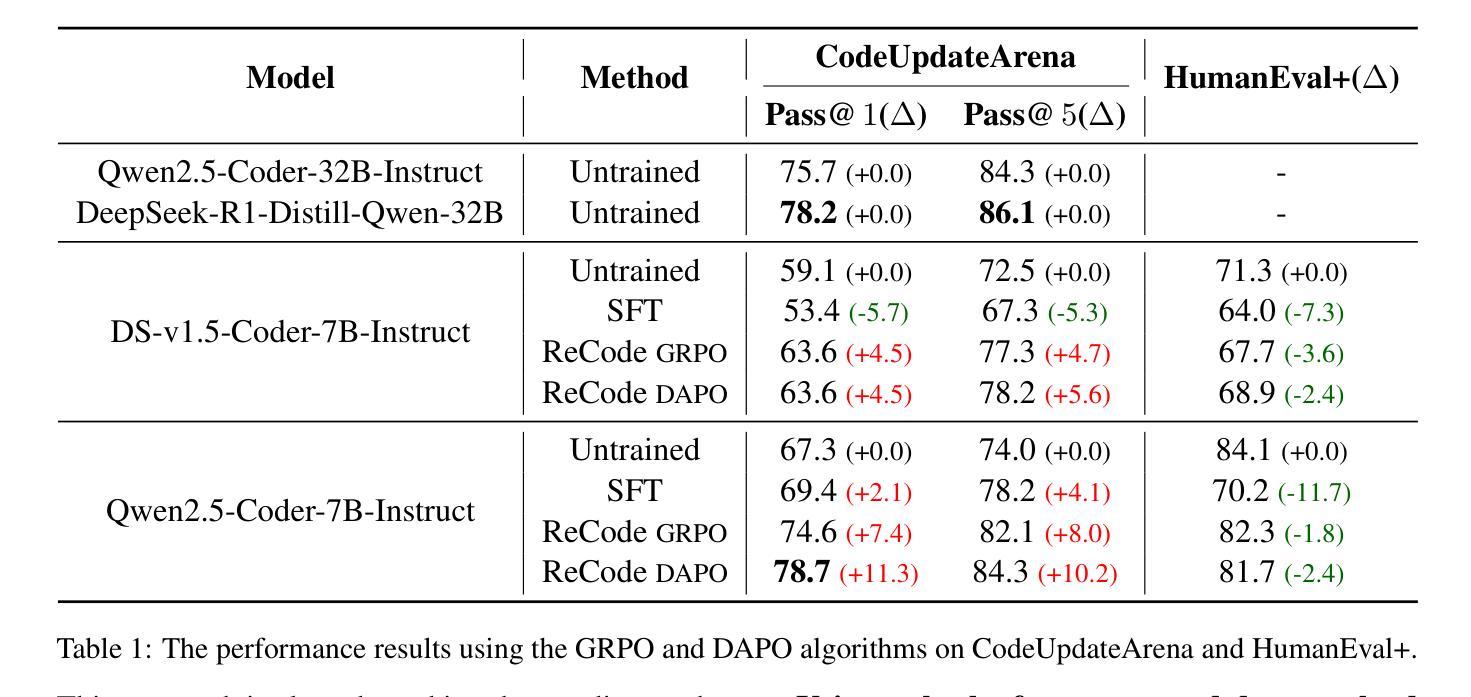
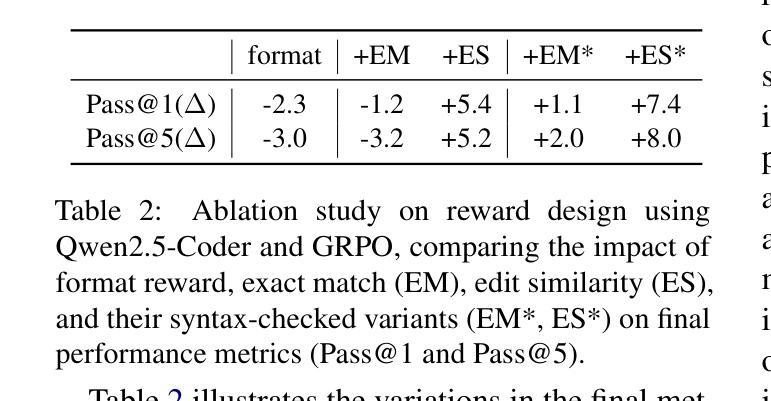
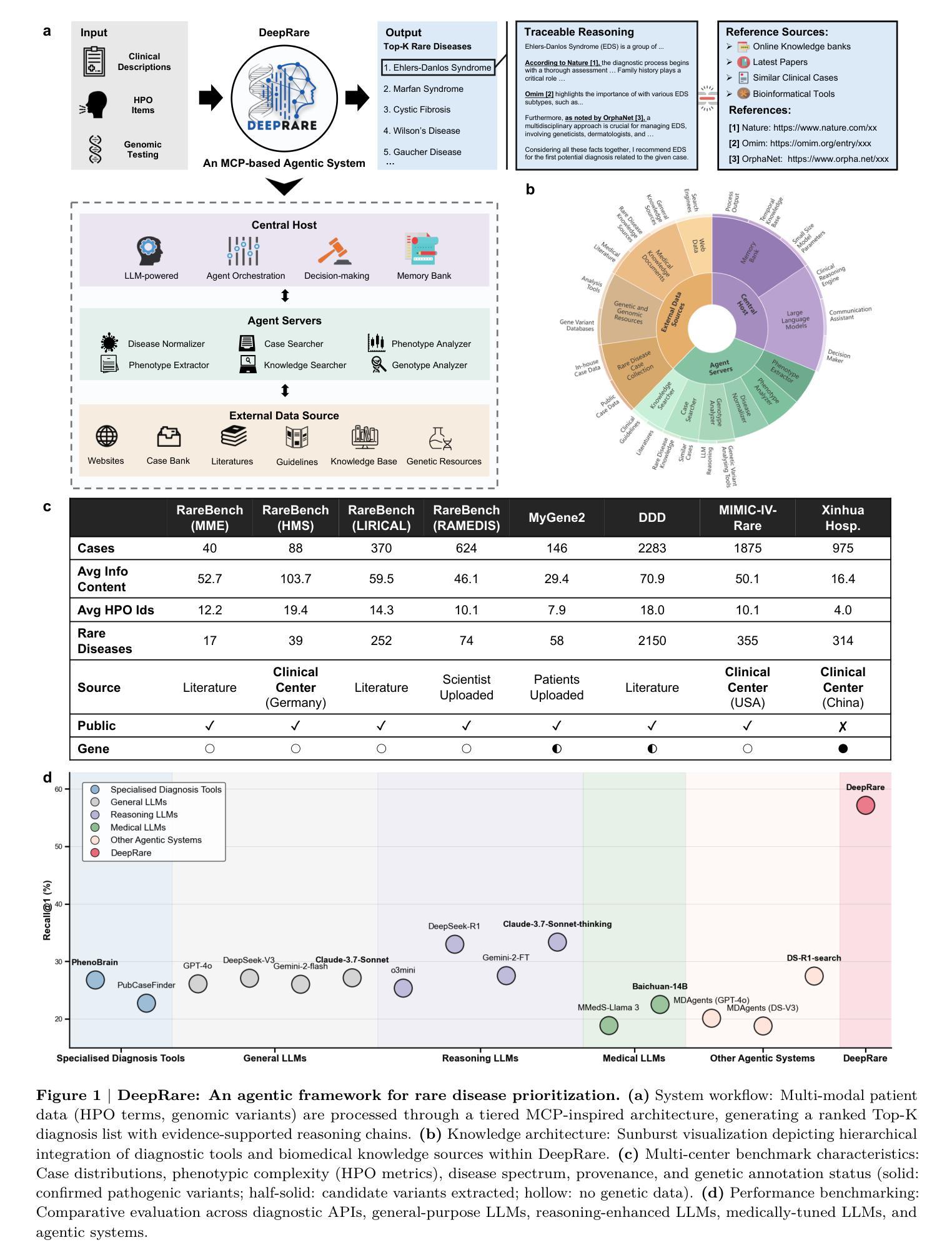
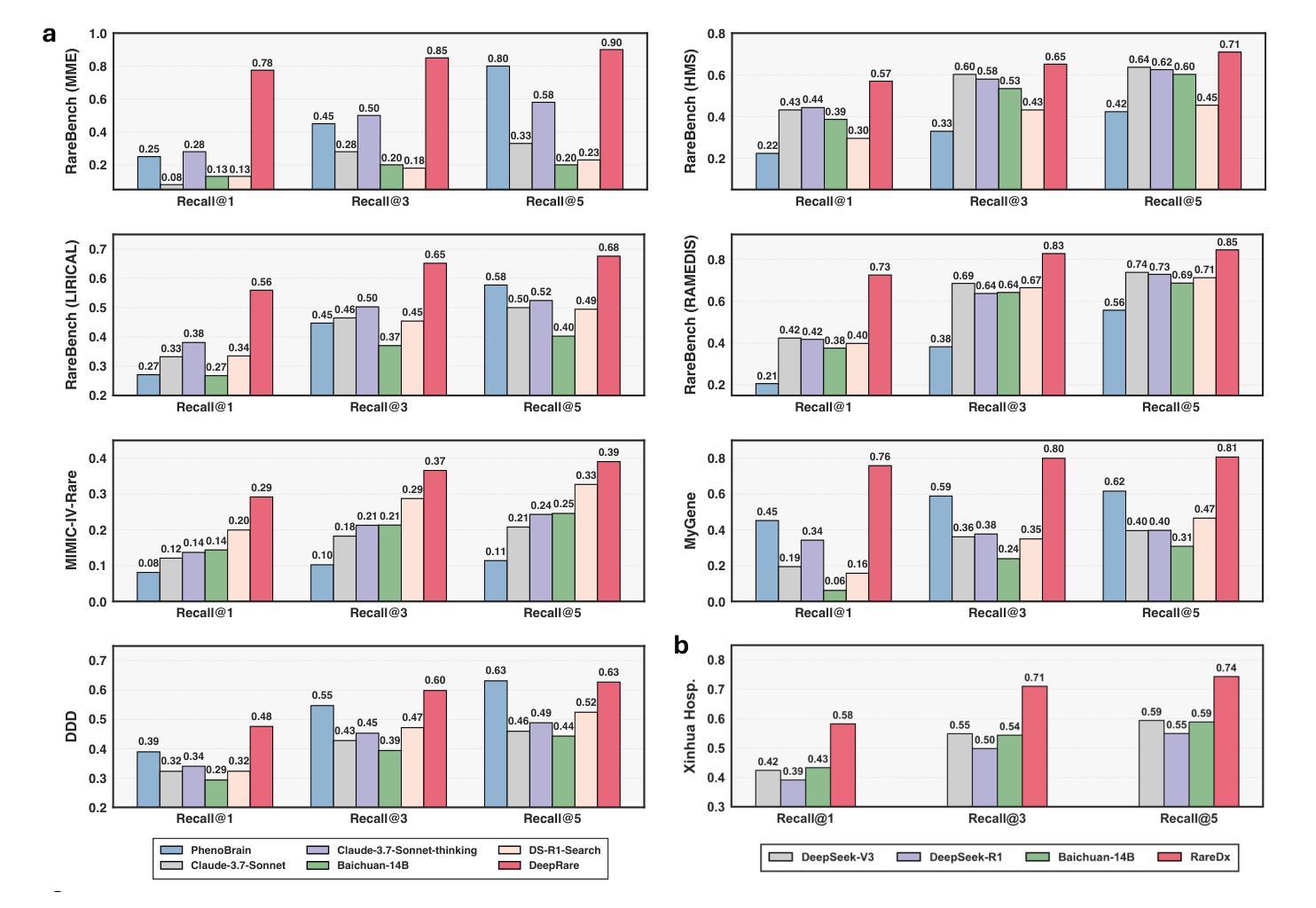
An Agentic System for Rare Disease Diagnosis with Traceable Reasoning
Authors:Weike Zhao, Chaoyi Wu, Yanjie Fan, Xiaoman Zhang, Pengcheng Qiu, Yuze Sun, Xiao Zhou, Yanfeng Wang, Ya Zhang, Yongguo Yu, Kun Sun, Weidi Xie
Rare diseases collectively affect over 300 million individuals worldwide, yet timely and accurate diagnosis remains a pervasive challenge. This is largely due to their clinical heterogeneity, low individual prevalence, and the limited familiarity most clinicians have with rare conditions. Here, we introduce DeepRare, the first rare disease diagnosis agentic system powered by a large language model (LLM), capable of processing heterogeneous clinical inputs. The system generates ranked diagnostic hypotheses for rare diseases, each accompanied by a transparent chain of reasoning that links intermediate analytic steps to verifiable medical evidence. DeepRare comprises three key components: a central host with a long-term memory module; specialized agent servers responsible for domain-specific analytical tasks integrating over 40 specialized tools and web-scale, up-to-date medical knowledge sources, ensuring access to the most current clinical information. This modular and scalable design enables complex diagnostic reasoning while maintaining traceability and adaptability. We evaluate DeepRare on eight datasets. The system demonstrates exceptional diagnostic performance among 2,919 diseases, achieving 100% accuracy for 1013 diseases. In HPO-based evaluations, DeepRare significantly outperforms other 15 methods, like traditional bioinformatics diagnostic tools, LLMs, and other agentic systems, achieving an average Recall@1 score of 57.18% and surpassing the second-best method (Reasoning LLM) by a substantial margin of 23.79 percentage points. For multi-modal input scenarios, DeepRare achieves 70.60% at Recall@1 compared to Exomiser’s 53.20% in 109 cases. Manual verification of reasoning chains by clinical experts achieves 95.40% agreements. Furthermore, the DeepRare system has been implemented as a user-friendly web application http://raredx.cn/doctor.
罕见疾病在全球范围内共同影响着超过3亿人,但及时准确的诊断仍然是一个普遍存在的挑战。这主要是由于其临床异质性、个人发病率低以及大多数临床医生对罕见疾病的不熟悉。在这里,我们推出DeepRare,这是一个由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的首个罕见疾病诊断智能系统,能够处理各种临床输入。该系统为罕见疾病生成排名诊断假设,每个假设都伴有透明的推理链,将中间分析步骤与可验证的医学证据联系起来。DeepRare包含三个关键组件:一个带有长期记忆模块的中心主机;负责特定领域分析任务的专用代理服务器,集成超过40种专业工具和最新网络规模医学知识源,确保访问最新临床信息。这种模块化且可扩展的设计在保持可追溯性和适应性的同时,实现了复杂的诊断推理。我们在八个数据集上评估了DeepRare。该系统在2919种疾病中表现出卓越的诊断性能,对1013种疾病的准确性达到100%。在基于HPO的评估中,DeepRare显著优于其他15种方法,如传统生物信息学诊断工具、大型语言模型和其他的智能系统,平均Recall@1分数达到57.18%,并大幅度超越排名第二的方法(推理大型语言模型)。对于多模式输入场景,DeepRare在Recall@1达到70.60%,相比之下Exomiser为53.20%,在109个案例中。临床专家对推理链的手动验证达到95.40%的共识。此外,DeepRare系统已作为一个用户友好的网页应用程序实现,网址为:http://raredx.cn/doctor。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
深罕病诊断系统DeepRare问世,借助大型语言模型(LLM)处理多样化临床输入,为罕见疾病生成排名诊断假设。该系统伴有透明化推理链,链接中间分析步骤与可验证医学证据。DeepRare包括三个关键组件:中央主机、专业代理服务器及医学知识源。其在八个数据集上的表现优异,在2919种疾病中准确率高达百分之百。相比其他工具,DeepRare显著提高诊断性能,平均Recall@1分数为57.18%。多模态输入场景下性能更佳,且已获得临床专家验证。
Key Takeaways:
- DeepRare是首个借助大型语言模型(LLM)进行罕见疾病诊断的系统。
- 可处理多样化的临床输入,生成排名诊断假设,并附有透明化推理链。
- 包括中央主机、专业代理服务器等三个关键组件,整合超过40种专业工具和最新医学知识源。
- 在多个数据集上表现优异,罕见疾病诊断准确率极高。
- 对比其他方法,DeepRare在诊断性能上显著提高,平均Recall@1分数领先。
- 多模态输入场景下性能优越,与Exomiser相比有较高Recall@1分数。
点此查看论文截图

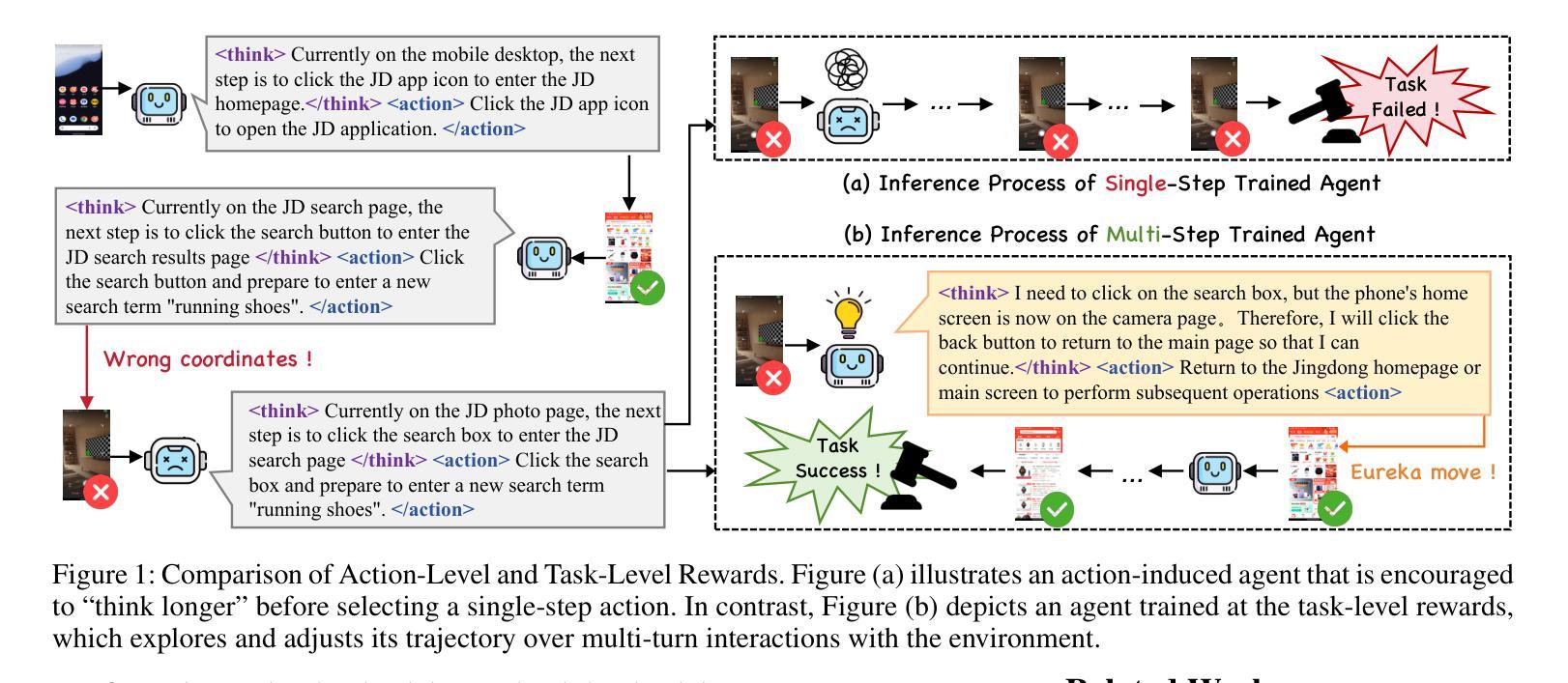
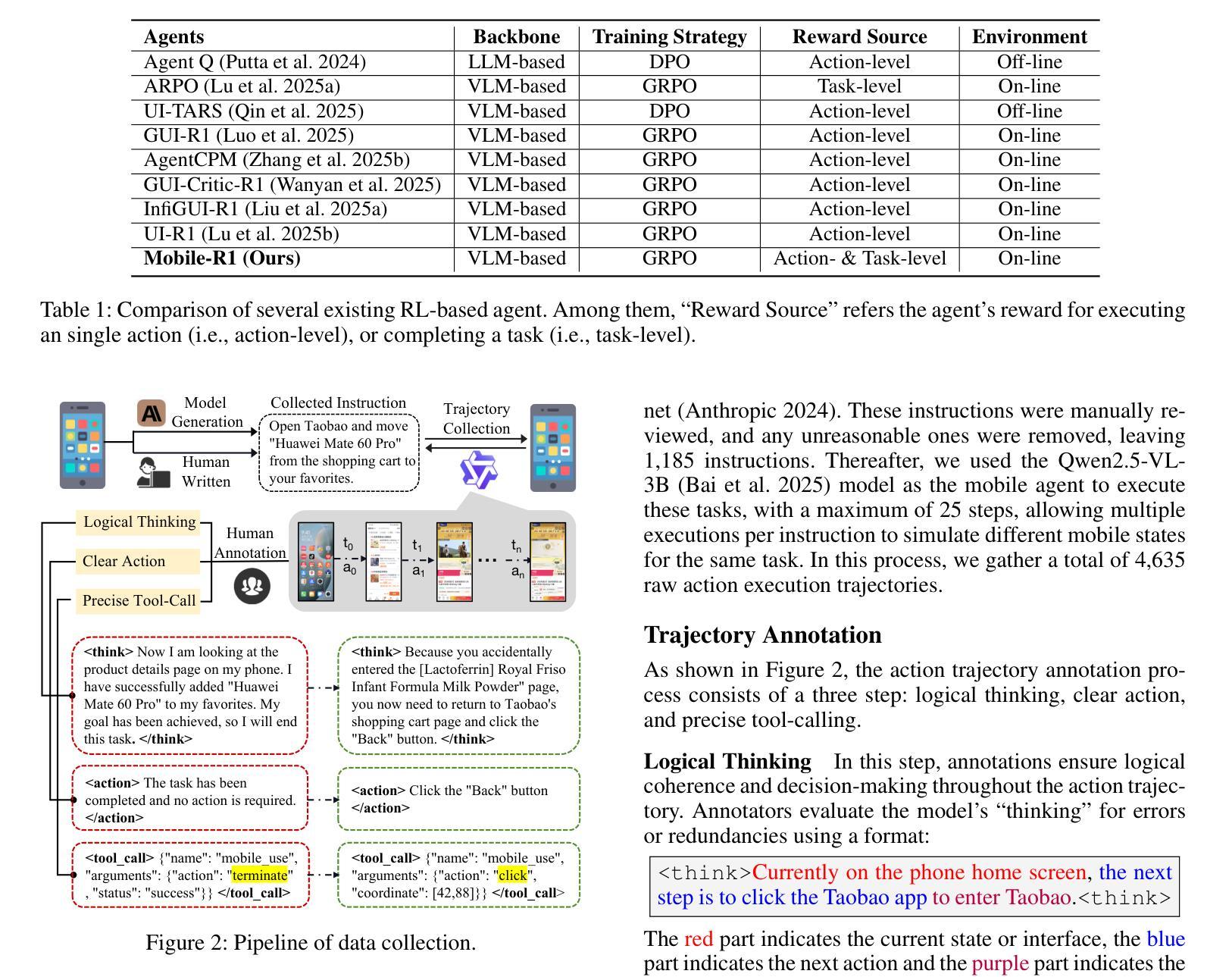
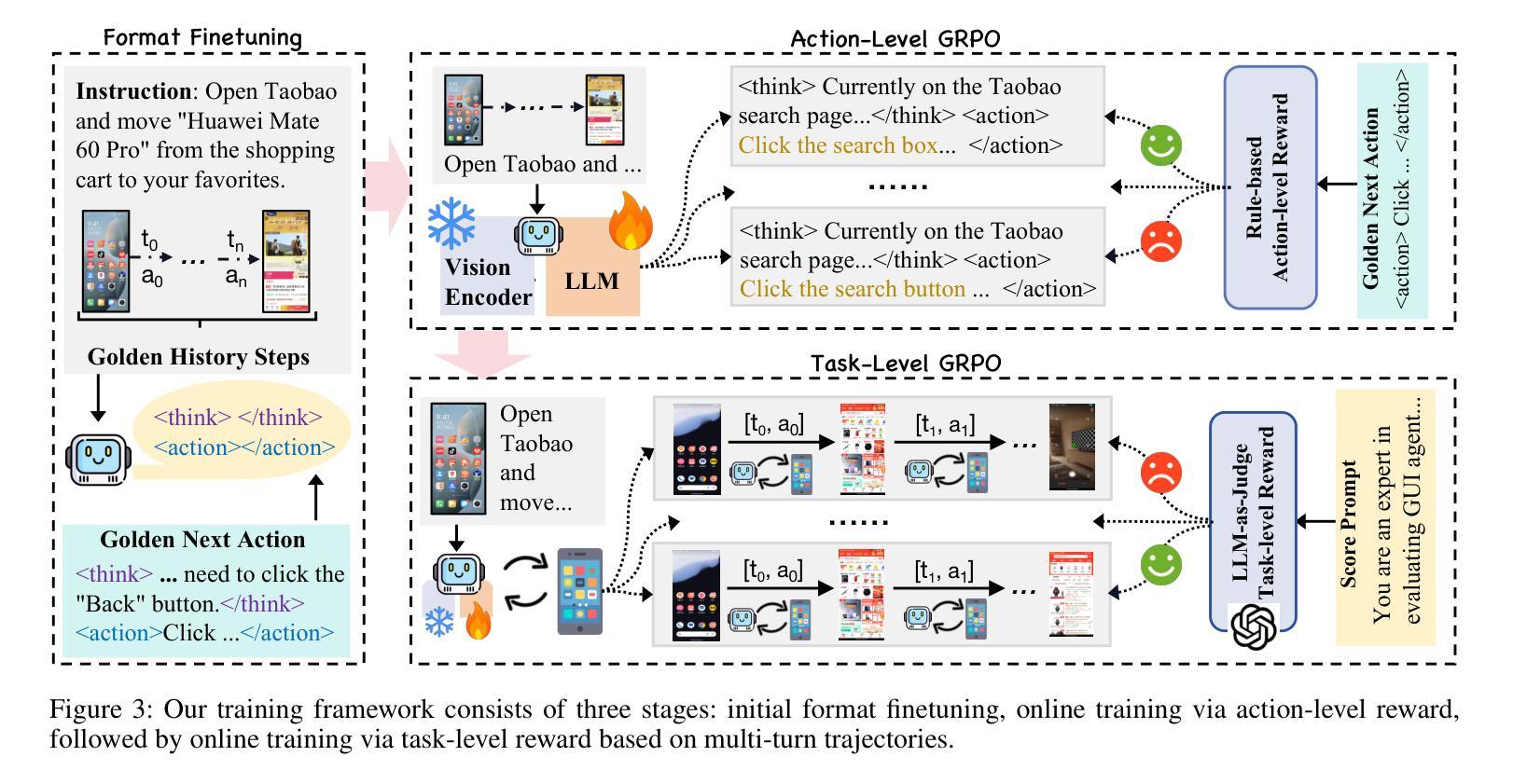
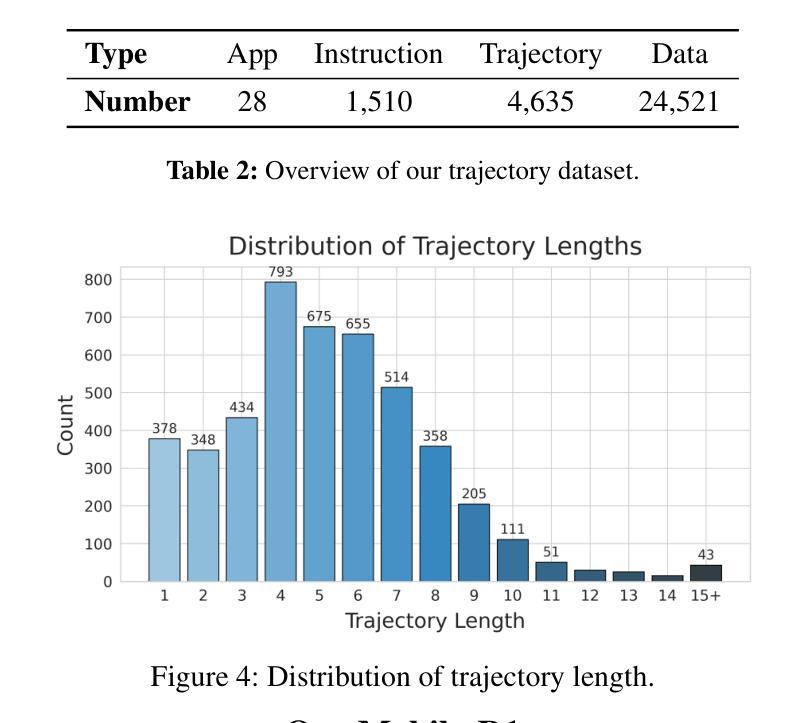
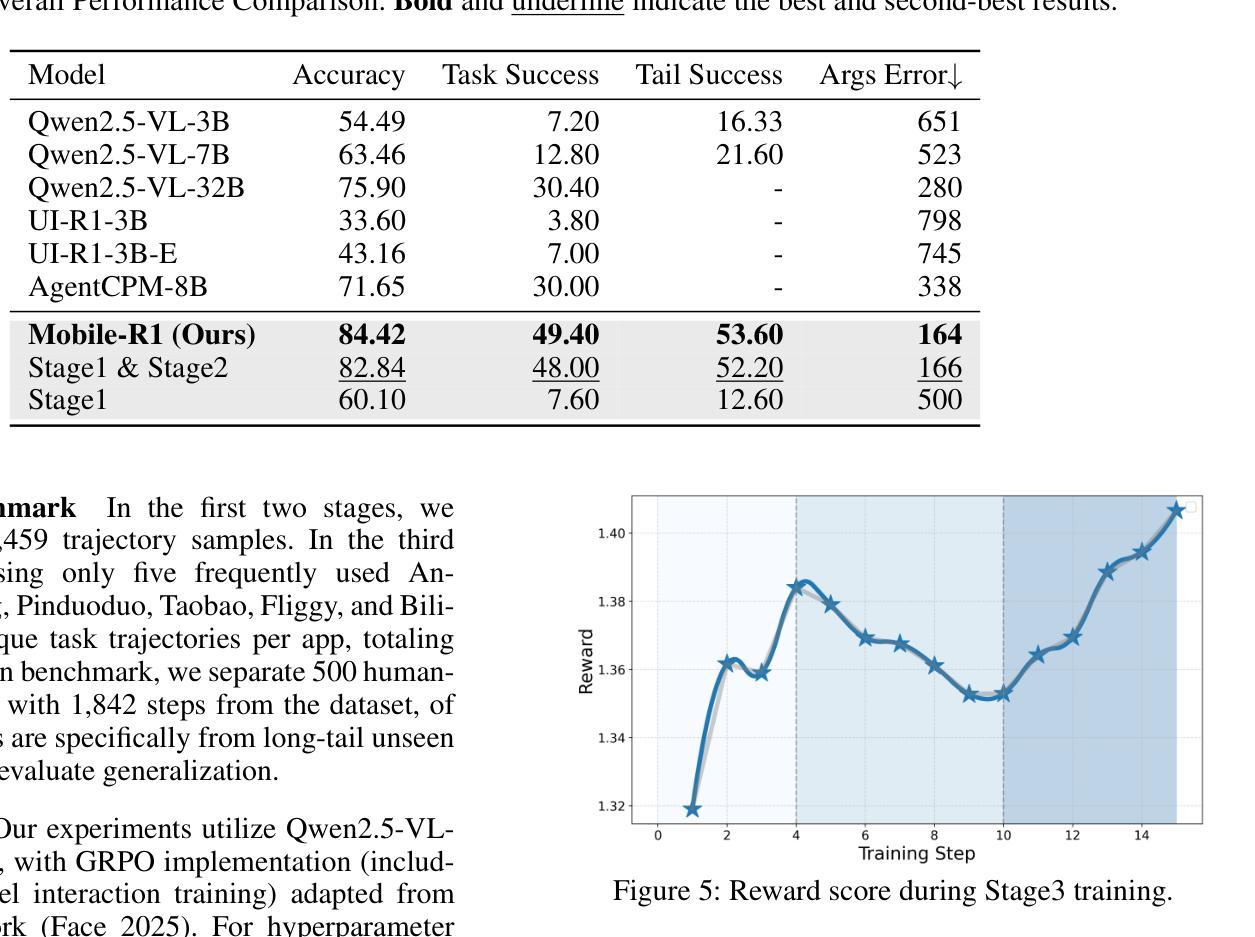
Mobile-R1: Towards Interactive Reinforcement Learning for VLM-Based Mobile Agent via Task-Level Rewards
Authors:Jihao Gu, Qihang Ai, Yingyao Wang, Pi Bu, Jingxuan Xing, Zekun Zhu, Wei Jiang, Ziming Wang, Yingxiu Zhao, Ming-Liang Zhang, Jun Song, Yuning Jiang, Bo Zheng
Vision-language model-based mobile agents have gained the ability to not only understand complex instructions and mobile screenshots, but also optimize their action outputs via thinking and reasoning, benefiting from reinforcement learning, such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). However, existing research centers on offline reinforcement learning training or online optimization using action-level rewards, which limits the agent’s dynamic interaction with the environment. This often results in agents settling into local optima, thereby weakening their ability for exploration and error action correction. To address these challenges, we introduce an approach called Mobile-R1, which employs interactive multi-turn reinforcement learning with task-level rewards for mobile agents. Our training framework consists of three stages: initial format finetuning, single-step online training via action-level reward, followed by online training via task-level reward based on multi-turn trajectories. This strategy is designed to enhance the exploration and error correction capabilities of Mobile-R1, leading to significant performance improvements. Moreover, we have collected a dataset covering 28 Chinese applications with 24,521 high-quality manual annotations and established a new benchmark with 500 trajectories. We will open source all resources, including the dataset, benchmark, model weight, and codes: https://mobile-r1.github.io/Mobile-R1/.
基于视觉语言模型的移动代理不仅获得了理解复杂指令和移动截图的能力,还通过强化学习(如群体相对策略优化(GRPO))优化了其行动输出。然而,现有研究主要关注离线强化学习训练或基于行动层面的奖励进行在线优化,这限制了代理与环境的动态交互。这通常导致代理陷入局部最优,从而削弱了它们的探索能力和错误行动纠正能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种名为Mobile-R1的方法,该方法采用交互式多回合强化学习,为移动代理提供任务级奖励。我们的训练框架包括三个阶段:初始格式微调、通过行动级奖励进行单步在线训练,然后是基于多回合轨迹的任务级奖励在线训练。该策略旨在增强Mobile-R1的探索和错误纠正能力,从而带来显著的性能改进。此外,我们收集了一个包含28个中文应用程序的数据集,包含24521个高质量的手动注释,并建立了包含500个轨迹的新基准。我们将公开所有资源,包括数据集、基准、模型权重和代码:https://mobile-r1.github.io/Mobile-R1/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 12 figures
Summary
移动智能代理通过视觉语言模型结合强化学习技术,实现了对复杂指令和移动截图的理解,并优化行动输出。然而,现有研究集中在离线强化学习训练或行动级别的在线优化上,限制了智能代理与环境的动态交互能力。为解决这一问题,我们提出Mobile-R1方法,采用多任务级别奖励的互动多回合强化学习模式进行训练。训练框架包含三个阶段:初始格式微调、通过行动级别奖励进行单步在线训练,以及基于多回合轨迹的任务级别奖励在线训练。此方法旨在提高Mobile-R1的探索和错误修正能力,实现显著的性能提升。同时,我们收集了涵盖28个中文应用程序的标注数据集并建立新基准。
Key Takeaways
- 移动智能代理能够通过视觉语言模型理解复杂指令和移动截图。
- 强化学习被用于优化移动智能代理的行动输出。
- 现有研究集中在离线强化学习训练或行动级别奖励的在线优化上,存在局限性。
- Mobile-R1方法采用多任务级别奖励的互动多回合强化学习模式训练移动智能代理。
- Mobile-R1的训练框架包括初始格式微调、单步在线训练和基于多回合轨迹的在线训练三个阶段。
- Mobile-R1旨在提高探索和错误修正能力,实现性能提升。
- 建立了一个新的基准并收集了一个涵盖多个中文应用程序的标注数据集。
点此查看论文截图

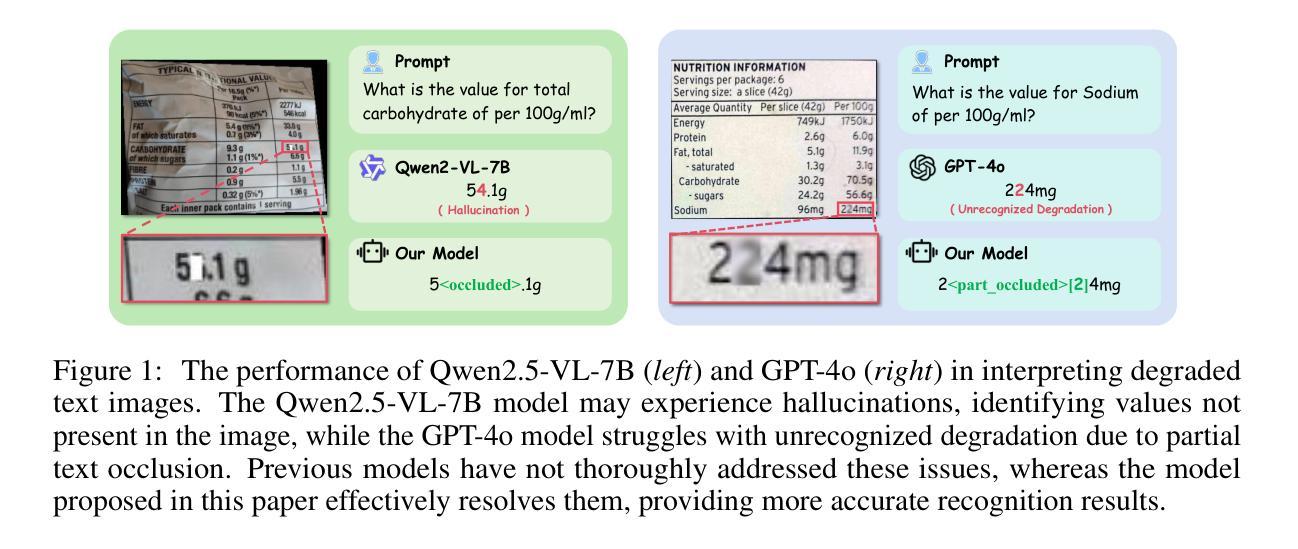
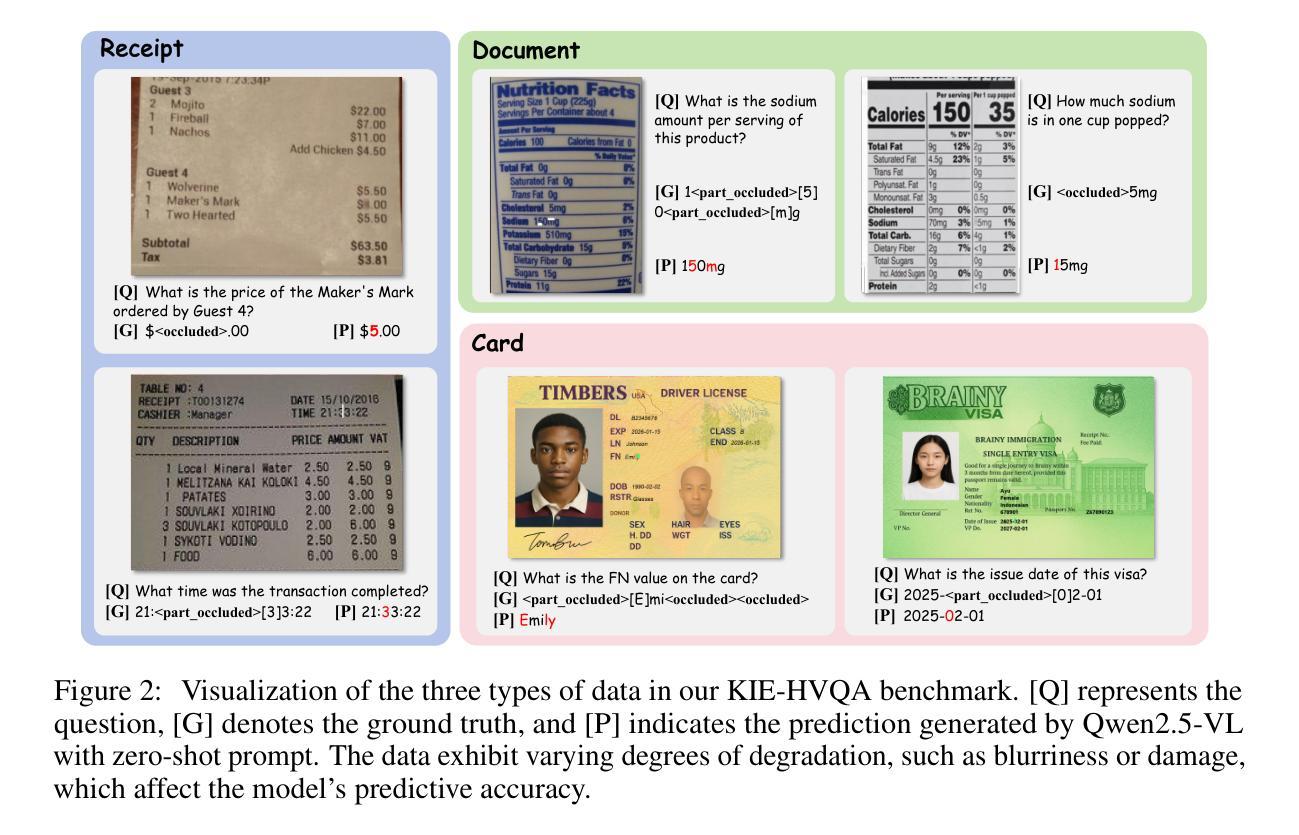
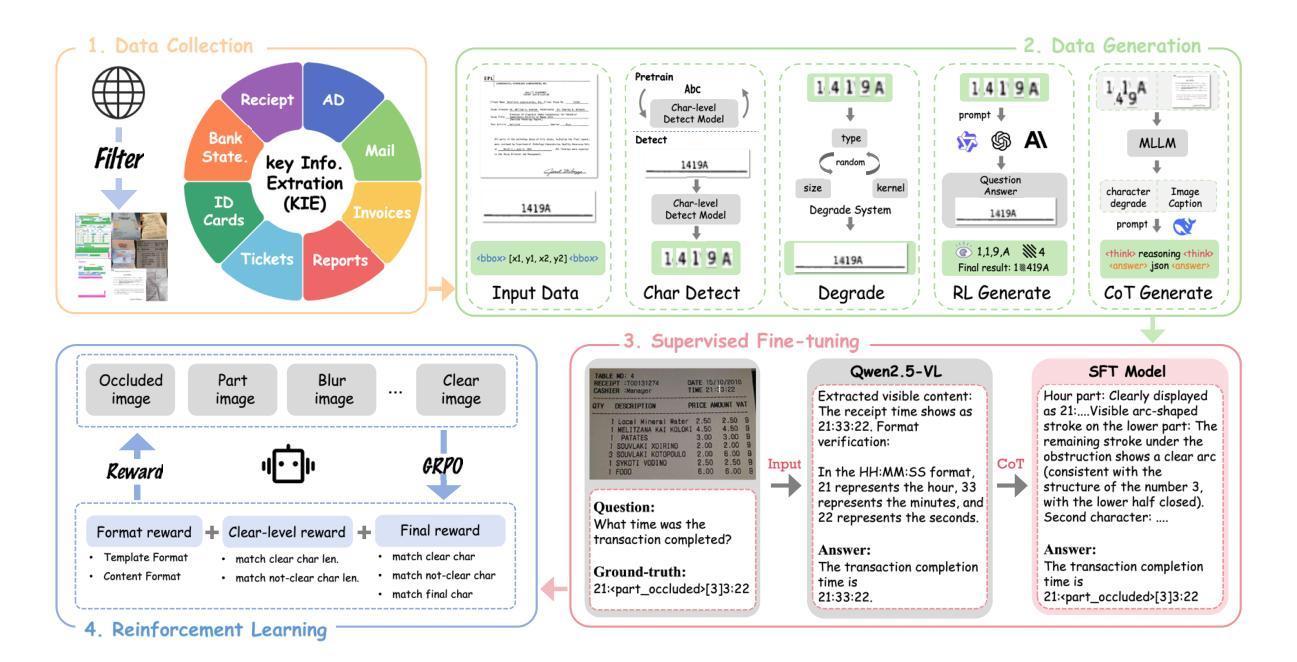
Seeing is Believing? Mitigating OCR Hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Zhentao He, Can Zhang, Ziheng Wu, Zhenghao Chen, Yufei Zhan, Yifan Li, Zhao Zhang, Xian Wang, Minghui Qiu
Recent advancements in multimodal large language models have enhanced document understanding by integrating textual and visual information. However, existing models exhibit incompleteness within their paradigm in real-world scenarios, particularly under visual degradation. In such conditions, the current response paradigm often fails to adequately perceive visual degradation and ambiguity, leading to overreliance on linguistic priors or misaligned visual-textual reasoning. This difficulty in recognizing uncertainty frequently results in the generation of hallucinatory content, especially when a precise answer is not feasible. To better demonstrate and analyze this phenomenon and problem, we propose KIE-HVQA, the first benchmark dedicated to evaluating OCR hallucination in degraded document understanding. This dataset includes test samples spanning identity cards and invoices, with simulated real-world degradations for OCR reliability. This setup allows for evaluating models’ capacity, under degraded input, to distinguish reliable visual information and answer accordingly, thereby highlighting the challenge of avoiding hallucination on uncertain data. To achieve vision-faithful reasoning and thereby avoid the aforementioned issues, we further introduce a GRPO-based framework featuring a novel reward mechanism. By incorporating a self-awareness of visual uncertainty and an analysis method that initiates refusal to answer to increase task difficulty within our supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning framework, we successfully mitigated hallucinations in ambiguous regions. Experiments on Qwen2.5-VL demonstrate that our 7B-parameter model achieves a 22% absolute improvement in hallucination-free accuracy over GPT-4o on KIE-HVQA and there is no significant performance drop in standard tasks, highlighting both effectiveness and robustness.
近年来,多模态大型语言模型的进步通过整合文本和视觉信息增强了文档理解。然而,在真实场景中,现有模型在其范式内表现出不完整性,特别是在视觉退化的情况下。在这种情况下,当前响应范式通常无法充分感知视觉退化和模糊,导致过度依赖语言先验或视觉文本推理失误。难以识别不确定性经常导致产生幻觉内容,尤其是在无法给出精确答案的情况下。为了更好地演示和分析这种现象和问题,我们提出了KIE-HVQA,这是第一个专门用于评估退化文档理解中OCR幻觉的基准测试。该数据集包含身份证和发票等测试样本,针对OCR可靠性模拟了真实世界的退化情况。此设置可以评估模型在退化输入下的能力,区分可靠视觉信息并相应地回答,从而突出避免在不确定数据上产生幻觉的挑战。为了实现忠于视觉的推理,避免上述问题,我们进一步引入了基于GRPO的框架和新型奖励机制。通过融入对视觉不确定性的自我意识以及一种分析方法拒绝回答来增加任务难度,这涵盖在我们的监督微调中以及强化学习框架内,我们成功减轻了模糊区域的幻觉现象。在Qwen2.5-VL上的实验表明,我们的7B参数模型在KIE-HVQA上相对于GPT-4o实现了无幻觉准确度的绝对提升22%,并且在标准任务中没有显著的性能下降,这突显了有效性和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型在文档理解方面的最新进展,这些模型通过整合文本和视觉信息提高了文档理解的能力。然而,现有模型在真实场景下面临不完全适应的问题,特别是在视觉退化的情况下。针对这一问题,本文提出了KIE-HVQA基准测试集,用于评估OCR幻觉在退化文档理解中的表现。同时,还介绍了一种基于GRPO的框架,通过引入新的奖励机制和自我感知视觉不确定性的分析方法来减少模糊区域的幻觉。实验结果表明,该框架在KIE-HVQA上取得了显著成效。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型通过整合文本和视觉信息提高了文档理解。
- 现有模型在视觉退化情况下存在不足,如过度依赖语言先验或视觉文本推理失调。
- KIE-HVQA基准测试集用于评估OCR幻觉在退化文档理解中的表现。
- 提出的GRPO框架通过引入新的奖励机制和自我感知视觉不确定性的分析方法,成功减少了模糊区域的幻觉。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在KIE-HVQA上较GPT-4o提高了22%的无幻觉准确率。
- 该框架在标准任务上的性能没有明显下降,证明了其有效性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

MIRAGE: A Benchmark for Multimodal Information-Seeking and Reasoning in Agricultural Expert-Guided Conversations
Authors:Vardhan Dongre, Chi Gui, Shubham Garg, Hooshang Nayyeri, Gokhan Tur, Dilek Hakkani-Tür, Vikram S. Adve
We introduce MIRAGE, a new benchmark for multimodal expert-level reasoning and decision-making in consultative interaction settings. Designed for the agriculture domain, MIRAGE captures the full complexity of expert consultations by combining natural user queries, expert-authored responses, and image-based context, offering a high-fidelity benchmark for evaluating models on grounded reasoning, clarification strategies, and long-form generation in a real-world, knowledge-intensive domain. Grounded in over 35,000 real user-expert interactions and curated through a carefully designed multi-step pipeline, MIRAGE spans diverse crop health, pest diagnosis, and crop management scenarios. The benchmark includes more than 7,000 unique biological entities, covering plant species, pests, and diseases, making it one of the most taxonomically diverse benchmarks available for vision-language models, grounded in the real world. Unlike existing benchmarks that rely on well-specified user inputs and closed-set taxonomies, MIRAGE features underspecified, context-rich scenarios with open-world settings, requiring models to infer latent knowledge gaps, handle rare entities, and either proactively guide the interaction or respond. Project Page: https://mirage-benchmark.github.io
我们推出MIRAGE,这是一个新的多模态专家级推理和决策基准,适用于咨询交互环境中的专家级推理和决策。MIRAGE专为农业领域设计,通过结合自然用户查询、专家撰写的回应和图像上下文,捕捉专家咨询的全过程复杂性,为评估模型在现实世界的知识密集型领域中的基于事实推理、澄清策略和长文本生成能力提供高保真基准。MIRAGE以超过3万5千次的真实用户与专家互动为基础,经过精心设计的多步骤流程进行筛选,涵盖了作物健康、病虫害诊断及作物管理等多种场景。该基准包含超过7千个独特的生物实体,涵盖植物种类、害虫和疾病,成为视觉语言模型中最具现实世界特征的、分类学上最多元化的基准之一。与依赖明确用户输入和封闭分类系统的现有基准不同,MIRAGE的特点是场景丰富且上下文不明确,要求模型能够推断潜在的知识空白,处理罕见实体,并能够主动引导交互或作出回应。项目页面:https://mirage-benchmark.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 66 pages, 32 figures, 23 tables
Summary
MIRAGE是一个为农业领域设计的新基准测试,用于评估多模式专家级推理和咨询交互设置中的决策能力。它结合了自然用户查询、专家撰写的回应和图像上下文,提供了一个高保真度的基准测试,用于评估模型在现实世界的复杂场景中的推理能力。该项目跨越多种作物健康、病虫害诊断和作物管理场景,并包括超过7000个独特的生物实体。其特点是情景丰富且开放世界设置,要求模型推断潜在知识空白、处理罕见实体以及主动引导交互或作出反应。更多详情可见项目页面。
Key Takeaways
- MIRAGE是一个新的基准测试,专注于农业领域的多模式专家级推理和决策能力。
- 该基准测试结合了自然用户查询、专家响应和图像上下文,模拟真实的专家咨询场景。
- MIRAGE提供了高保真度的评估环境,用于测试模型在现实世界场景中的推理能力,包括作物健康、病虫害诊断和作物管理等方面。
- 该基准测试包含超过7000个独特的生物实体,涵盖植物种类、害虫和疾病,是现有视觉语言模型中最为多样化的基准测试之一。
- MIRAGE的特点是情景丰富且开放世界设置,要求模型具备处理复杂环境和未知实体的能力。
- 模型需要能够推断潜在知识空白,处理罕见实体,并能够在交互中主动引导和作出反应。
点此查看论文截图

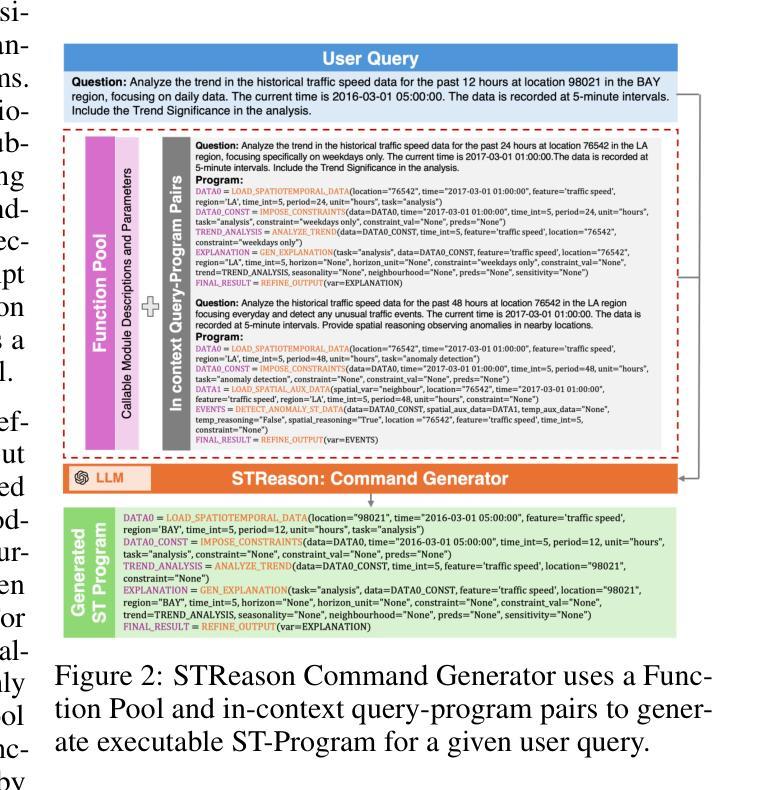
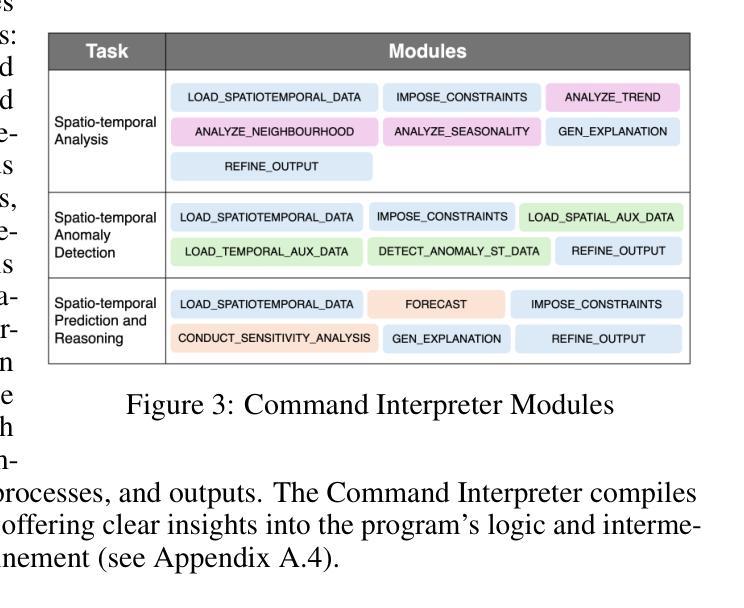
A Modular Multitask Reasoning Framework Integrating Spatio-temporal Models and LLMs
Authors:Kethmi Hirushini Hettige, Jiahao Ji, Cheng Long, Shili Xiang, Gao Cong, Jingyuan Wang
Spatio-temporal data mining plays a pivotal role in informed decision making across diverse domains. However, existing models are often restricted to narrow tasks, lacking the capacity for multi-task inference and complex long-form reasoning that require generation of in-depth, explanatory outputs. These limitations restrict their applicability to real-world, multi-faceted decision scenarios. In this work, we introduce STReason, a novel framework that integrates the reasoning strengths of large language models (LLMs) with the analytical capabilities of spatio-temporal models for multi-task inference and execution. Without requiring task-specific finetuning, STReason leverages in-context learning to decompose complex natural language queries into modular, interpretable programs, which are then systematically executed to generate both solutions and detailed rationales. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we construct a new benchmark dataset and propose a unified evaluation framework with metrics specifically designed for long-form spatio-temporal reasoning. Experimental results show that STReason significantly outperforms advanced LLM baselines across all metrics, particularly excelling in complex, reasoning-intensive spatio-temporal scenarios. Human evaluations further validate STReason’s credibility and practical utility, demonstrating its potential to reduce expert workload and broaden the applicability to real-world spatio-temporal tasks. We believe STReason provides a promising direction for developing more capable and generalizable spatio-temporal reasoning systems.
时空数据挖掘在多个领域中的决策制定中起着至关重要的作用。然而,现有模型通常仅限于狭窄的任务,缺乏多任务推理和复杂长形式推理的能力,无法生成深入的、解释性的输出。这些限制限制了它们在现实世界中多面决策场景的应用。在这项工作中,我们引入了STReason,这是一个新型框架,它将大型语言模型的推理能力与时空模型的分析能力相结合,用于多任务推理和执行。STReason不需要针对特定任务进行微调,它利用上下文学习将复杂的自然语言查询分解为模块化、可解释的程序,然后系统地执行这些程序以生成解决方案和详细的理由。为了促进严格评估,我们构建了一个新的基准数据集,并提出了一个统一的评估框架,其中设计了专门针对长形式时空推理的指标。实验结果表明,STReason在所有指标上都显著优于先进的大型语言模型基线,特别是在复杂、推理密集型的时空场景中表现尤为出色。人类评估进一步验证了STReason的可信度和实用性,表明其减少专家工作量并扩大在现实世界时空任务中的应用潜力。我们相信STReason为开发更具能力和通用性的时空推理系统提供了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时空数据挖掘在多个领域中的决策制定中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,现有模型通常局限于狭窄的任务,缺乏进行多任务推理和复杂长形式推理的能力,这要求生成深入的、解释性的输出。为了克服这些限制,本研究引入了STReason框架,该框架结合了大型语言模型的推理能力和时空模型的分析能力,用于多任务推理和执行。STReason利用上下文学习,将复杂的自然语言查询分解为模块化、可解释的程序,然后系统地执行以生成解决方案和详细的理由。实验结果表明,STReason在所有指标上都显著优于先进的大型语言模型基准测试,特别是在复杂、推理密集型的时空场景中表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 时空数据挖掘在决策制定中起关键作用,但现有模型在复杂任务中表现有限。
- STReason框架结合了大型语言模型和时空模型的能力,支持多任务推理和执行。
- STReason利用上下文学习分解自然语言查询,并系统地执行以生成解释性输出。
- STReason在复杂、推理密集型的时空场景中表现优异。
- 新构建的基准数据集和统一评估框架为长形式时空推理提供了严谨的评价方法。
- 实验结果和人类评估验证了STReason的可靠性和实用性。
点此查看论文截图


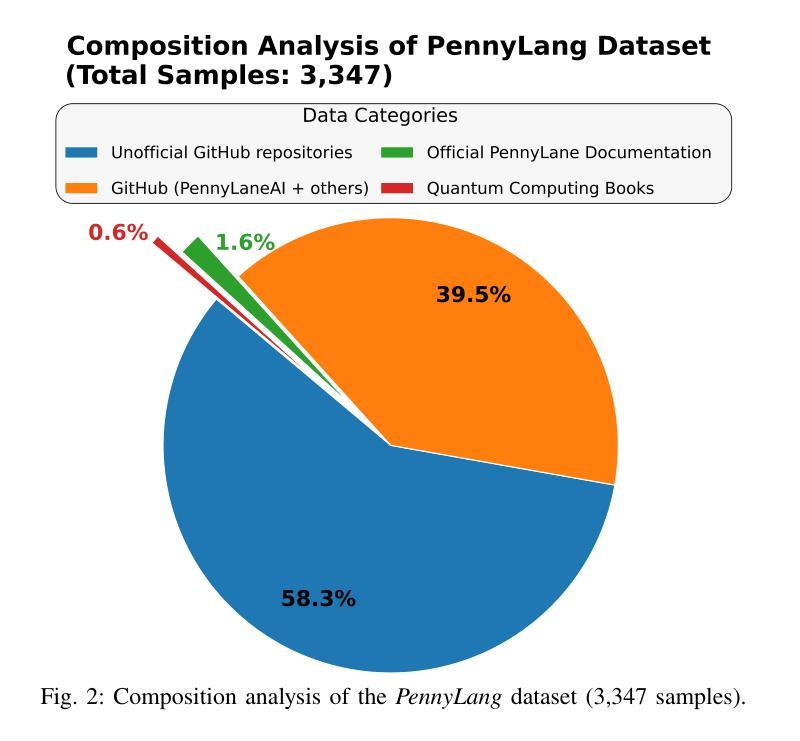
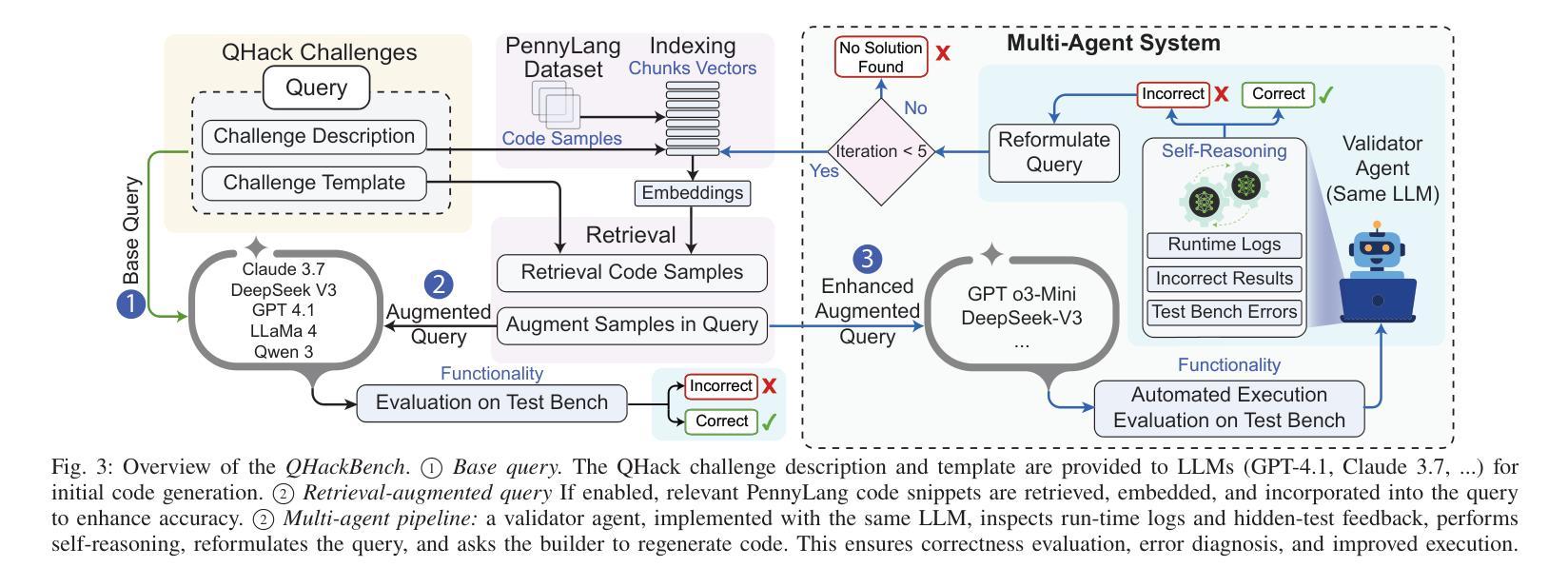
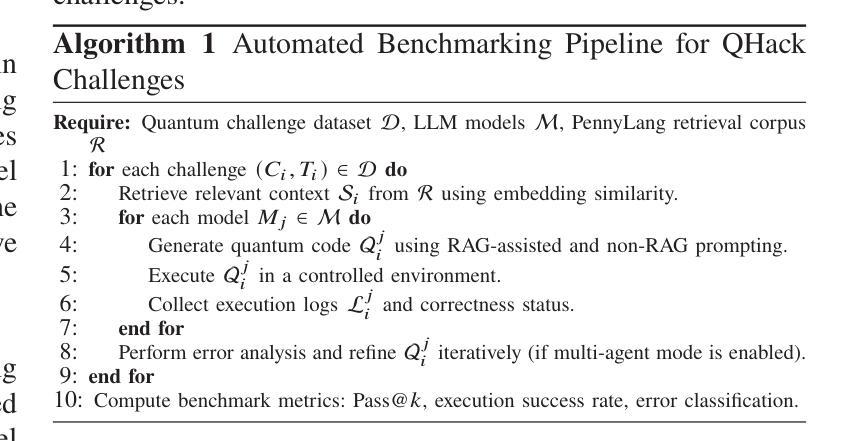
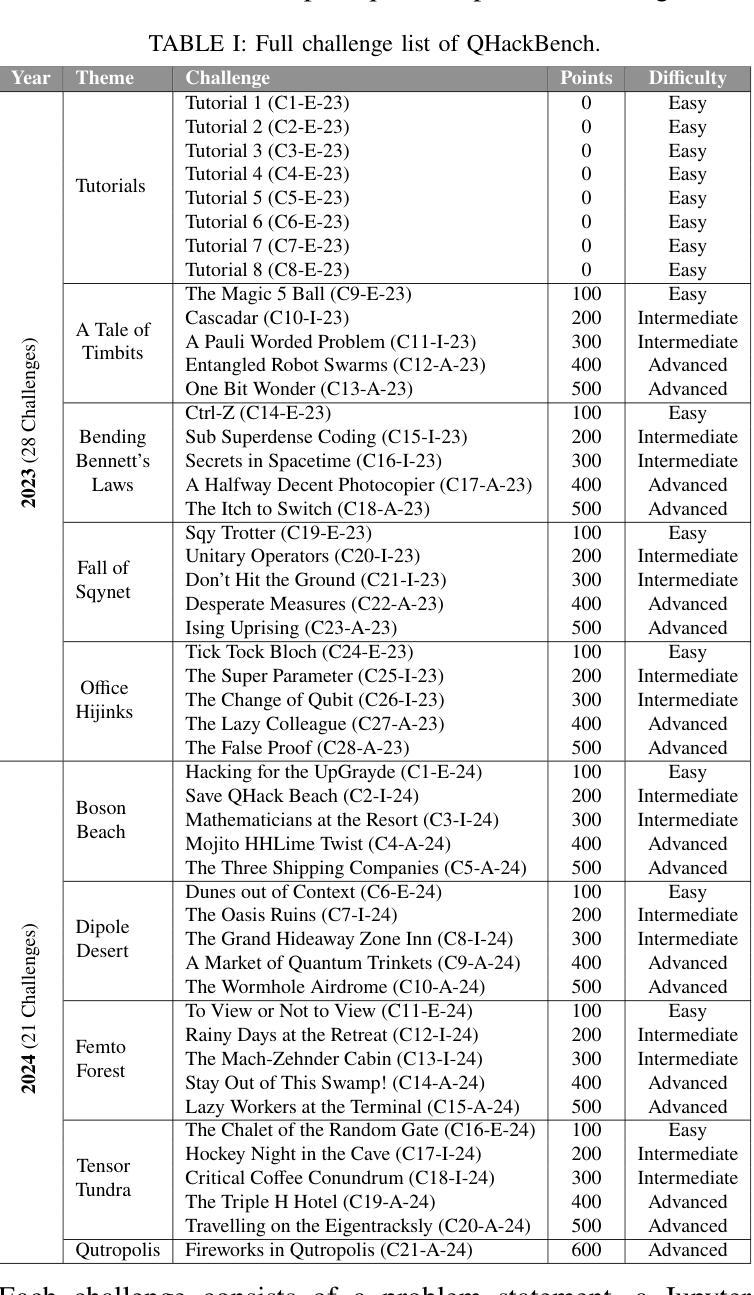
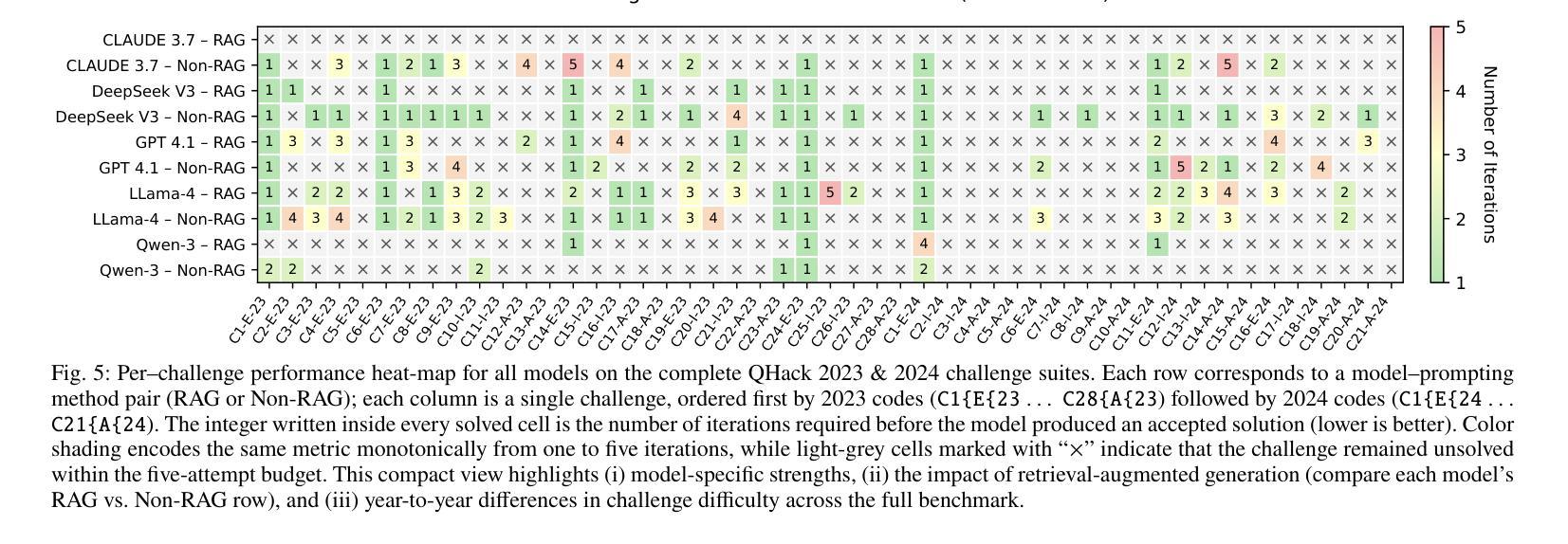
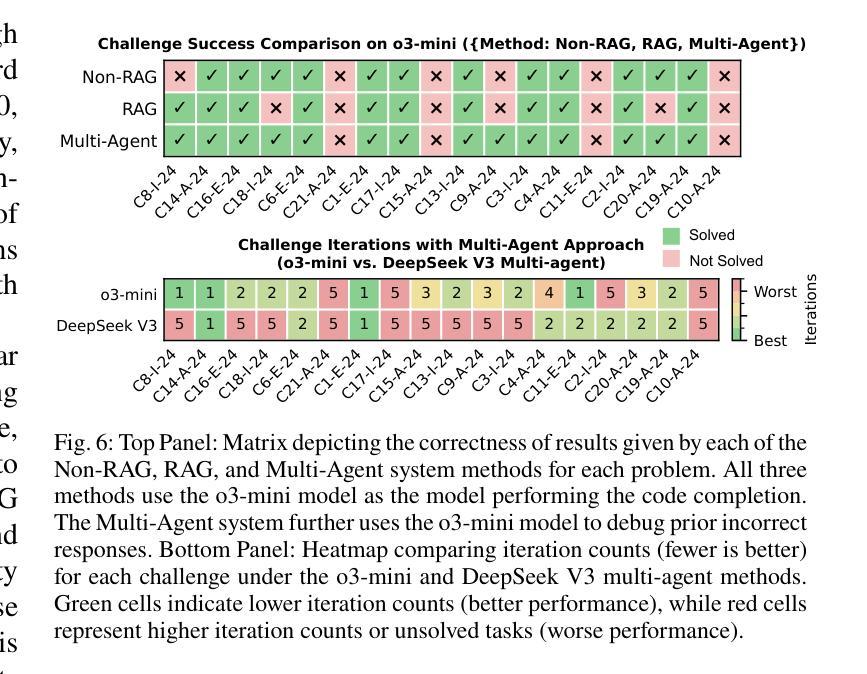
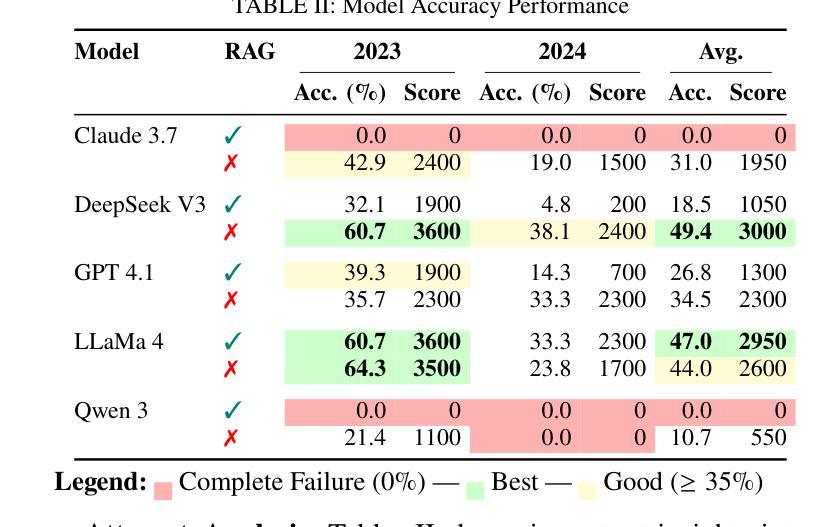
QHackBench: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Quantum Code Generation Using PennyLane Hackathon Challenges
Authors:Abdul Basit, Minghao Shao, Haider Asif, Nouhaila Innan, Muhammad Kashif, Alberto Marchisio, Muhammad Shafique
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong potential in code generation, yet their effectiveness in quantum computing remains underexplored. This paper benchmarks LLMs for PennyLane-based quantum code generation using real-world challenges from the Quantum Hackathon (QHack). We introduce QHackBench, a novel benchmark dataset derived from QHack competitions, and evaluate model performance under vanilla prompting and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Our structured evaluation framework assesses functional correctness, syntactic validity, and execution success across varying challenge difficulties. Results indicate that RAG-enhanced models, supplemented with an augmented PennyLane dataset, approximately generate similar results as the standard prompting, particularly in complex quantum algorithms. Additionally, we introduce a multi-agent evaluation pipeline that iteratively refines incorrect solutions, further enhancing execution success rates. To foster further research, we commit to publicly releasing QHackBench, along with our evaluation framework and experimental results, enabling continued advancements in AI-assisted quantum programming.
近年来,大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面展现出了强大的潜力,然而它们在量子计算中的应用仍然缺乏足够的探索。本文使用来自量子黑客马拉松(QHack)的现实挑战,对基于PennyLane的量子代码生成的LLM性能进行了基准测试。我们介绍了QHackBench,这是一个从QHack竞赛中衍生出来的新型基准数据集,并评估了标准提示和检索增强生成(RAG)下的模型性能。我们的结构化评估框架评估了不同挑战难度下的功能正确性、语法有效性和执行成功率。结果表明,通过增强PennyLane数据集增强的RAG模型在复杂量子算法方面大约生成了与标准提示相似的结果。此外,我们还引入了一个多代理评估管道,该管道可以迭代优化错误解决方案,进一步提高执行成功率。为了促进进一步研究,我们将公开发布QHackBench,以及我们的评估框架和实验结果,以促进人工智能辅助量子编程的持续发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables, submitted to QAI 2025
Summary
近期大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成方面展现出强大潜力,但在量子计算领域的应用尚待探索。本文使用来自量子黑客松(QHack)的现实挑战,对PennyLane基础的量子代码生成进行LLM基准测试。引入QHackBench基准数据集,评估了标准提示和检索增强生成(RAG)下的模型性能。通过结构化的评估框架对功能正确性、语法有效性及执行成功率在不同难度的挑战上进行了评估。结果表明,在扩充的PennyLane数据集支持下,使用RAG增强的模型能够在复杂量子算法中生成与标准提示相似的结果。此外,还引入了一种多智能体评估流程,可迭代优化错误解决方案,进一步提高执行成功率。为推进进一步研究,公开发布QHackBench基准数据集、评估框架及实验结果,推动AI辅助量子编程的持续发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在量子代码生成方面潜力巨大,但仍待探索。
- QHackBench基准数据集用于PennyLane基础的量子代码生成的LLM基准测试。
- 模型性能通过标准提示和检索增强生成(RAG)进行评估。
- 模型在功能正确性、语法有效性及执行成功率上表现良好,尤其在复杂量子算法中。
- RAG增强模型在扩充数据集支持下可生成与标准提示相似结果。
- 引入多智能体评估流程优化错误解决方案,提高执行成功率。
点此查看论文截图

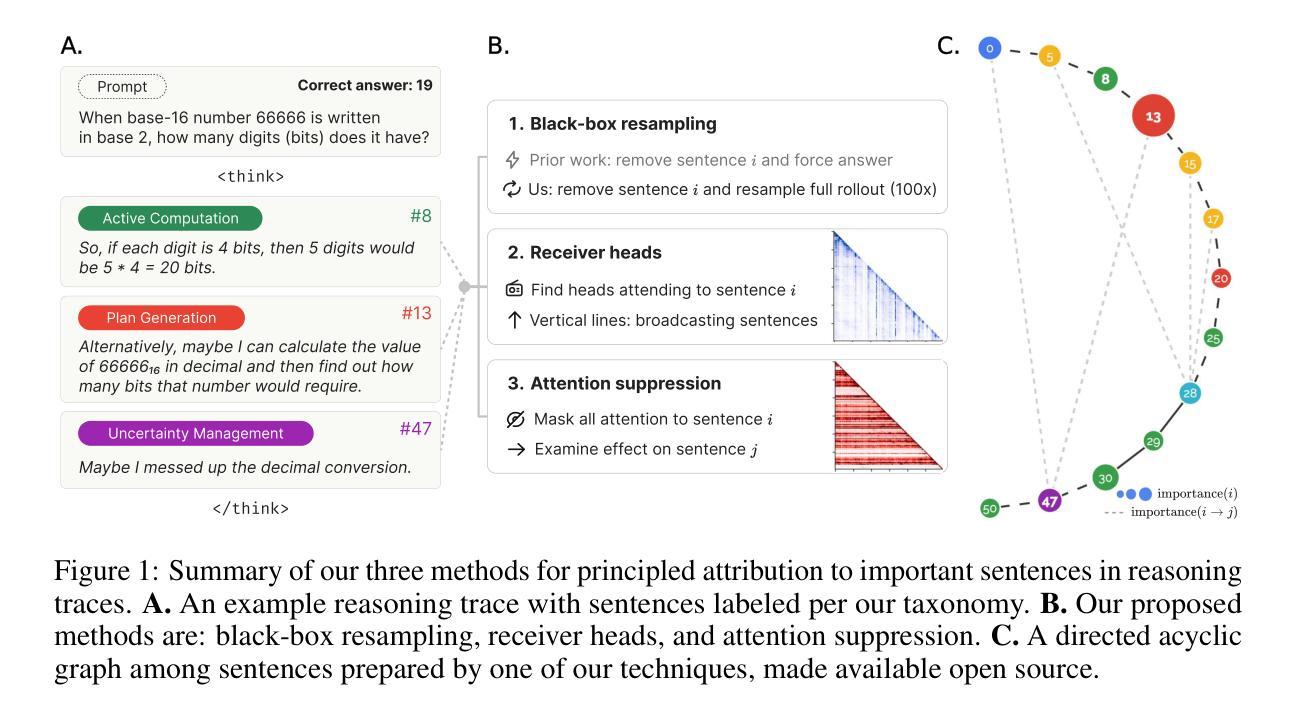
Thought Anchors: Which LLM Reasoning Steps Matter?
Authors:Paul C. Bogdan, Uzay Macar, Neel Nanda, Arthur Conmy
Reasoning large language models have recently achieved state-of-the-art performance in many fields. However, their long-form chain-of-thought reasoning creates interpretability challenges as each generated token depends on all previous ones, making the computation harder to decompose. We argue that analyzing reasoning traces at the sentence level is a promising approach to understanding reasoning processes. We present three complementary attribution methods: (1) a black-box method measuring each sentence’s counterfactual importance by comparing final answers across 100 rollouts conditioned on the model generating that sentence or one with a different meaning; (2) a white-box method of aggregating attention patterns between pairs of sentences, which identified “broadcasting” sentences that receive disproportionate attention from all future sentences via “receiver” attention heads; (3) a causal attribution method measuring logical connections between sentences by suppressing attention toward one sentence and measuring the effect on each future sentence’s tokens. Each method provides evidence for the existence of thought anchors, reasoning steps that have outsized importance and that disproportionately influence the subsequent reasoning process. These thought anchors are typically planning or backtracking sentences. We provide an open-source tool (www.thought-anchors.com) for visualizing the outputs of our methods, and present a case study showing converging patterns across methods that map how a model performs multi-step reasoning. The consistency across methods demonstrates the potential of sentence-level analysis for a deeper understanding of reasoning models.
推理大型语言模型已在许多领域取得了最先进的性能。然而,它们的长形式思维链推理带来了可解释性挑战,因为每个生成的令牌都依赖于所有先前的令牌,使得计算更难以分解。我们认为,在句子级别分析推理痕迹是理解推理过程的一种有前途的方法。我们提出了三种互补的归因方法:(1)一种黑盒方法,通过比较模型生成该句子或具有不同含义的句子的100次滚动结果中的最终答案,来衡量每个句子的反事实重要性;(2)一种白盒方法,聚合句子对之间的注意力模式,该方法确定了通过“接收者”注意力头从所有未来句子接收不成比例的注意力的“广播”句子;(3)一种因果归因方法,通过抑制对一个句子的注意力并测量对每一个未来句子的影响来衡量句子之间的逻辑联系。每种方法都证明存在思维锚点,即具有重大影响的推理步骤,这些步骤会不成比例地影响随后的推理过程。这些思维锚点通常是规划或回溯句子。我们提供了一个开源工具(www.thought-anchors.com),用于可视化我们方法的输出,并展示了一个案例研究,展示各方法之间收敛的模式,这些模式可以映射模型如何进行多步推理。各方法之间的一致性表明句子级分析在深入理解推理模型方面具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paul C. Bogdan and Uzay Macar contributed equally to this work, and their listed order was determined by coinflip. Neel Nanda and Arthur Conmy contributed equally to this work as senior authors, and their listed order was determined by coinflip
Summary
大型语言模型在多个领域取得了最先进的性能,但其长形式思维链推理带来的解释性挑战不容忽视。每个生成的标记都依赖于之前的所有标记,这使得计算难以分解。本文提出了一种有前景的方法来理解推理过程,即在句子层面分析推理痕迹。文章提出了三种互补归因方法,每种方法均支持句子在推理过程中的重要性,即思维锚的存在。本文还提供了一个开源工具,用于可视化这些方法的结果,并通过案例研究展示了这些方法如何映射模型的多步推理过程。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在多个领域表现出卓越性能,但存在解释性挑战。
- 句子层面的分析是一种理解推理过程的有前途的方法。
- 三种归因方法用于分析句子在推理中的重要性,即思维锚的存在。这些方法包括:比较句子生成的最终答案的黑箱方法;聚合句子间注意力模式的白箱方法;以及衡量句子间逻辑连接的因果归因方法。
- 开源工具可用于可视化归因方法的结果。
点此查看论文截图

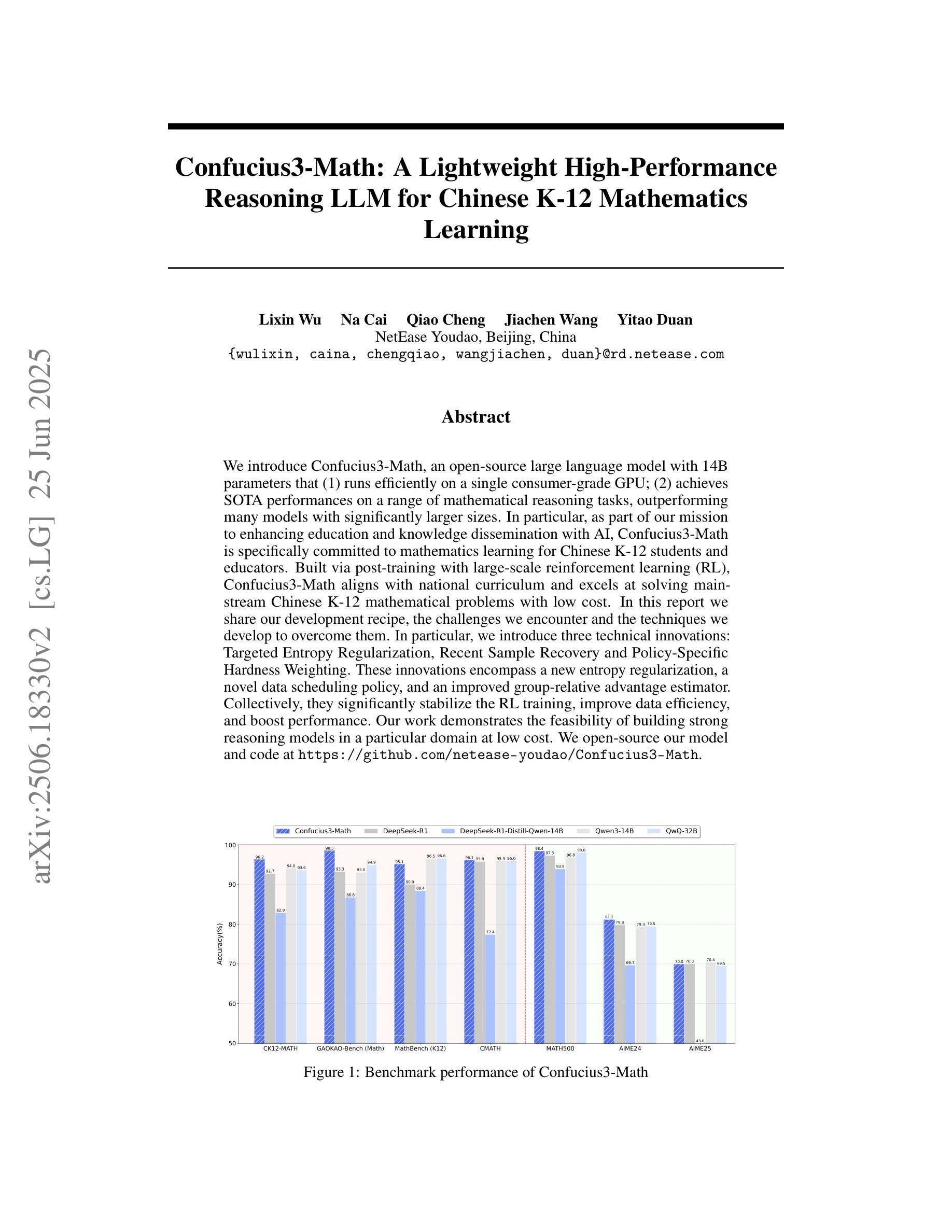
Confucius3-Math: A Lightweight High-Performance Reasoning LLM for Chinese K-12 Mathematics Learning
Authors:Lixin Wu, Na Cai, Qiao Cheng, Jiachen Wang, Yitao Duan
We introduce Confucius3-Math, an open-source large language model with 14B parameters that (1) runs efficiently on a single consumer-grade GPU; (2) achieves SOTA performances on a range of mathematical reasoning tasks, outperforming many models with significantly larger sizes. In particular, as part of our mission to enhancing education and knowledge dissemination with AI, Confucius3-Math is specifically committed to mathematics learning for Chinese K-12 students and educators. Built via post-training with large-scale reinforcement learning (RL), Confucius3-Math aligns with national curriculum and excels at solving main-stream Chinese K-12 mathematical problems with low cost. In this report we share our development recipe, the challenges we encounter and the techniques we develop to overcome them. In particular, we introduce three technical innovations: Targeted Entropy Regularization, Recent Sample Recovery and Policy-Specific Hardness Weighting. These innovations encompass a new entropy regularization, a novel data scheduling policy, and an improved group-relative advantage estimator. Collectively, they significantly stabilize the RL training, improve data efficiency, and boost performance. Our work demonstrates the feasibility of building strong reasoning models in a particular domain at low cost. We open-source our model and code at https://github.com/netease-youdao/Confucius3-Math.
我们介绍了孔子3-数学,这是一个拥有14亿参数的开源大型语言模型,它(1)在单个消费级GPU上运行高效;(2)在各种数学推理任务上达到了最先进的性能,优于许多规模更大的模型。特别是,作为我们利用人工智能增强教育和知识传播的使命的一部分,孔子3-数学致力于为中国的K-12学生和教育工作者提供数学学习支持。通过大规模强化学习(RL)进行后训练,孔子3-数学与国家课程相一致,擅长解决主流的中国K-12数学问题,成本低廉。在这份报告中,我们分享了我们的开发配方、遇到的挑战以及为克服这些挑战而开发的技术。特别是,我们介绍了三项技术创新:目标熵正则化、最近样本恢复和政策特定硬度加权。这些创新包括一种新的熵正则化、一种新的数据调度策略和改进的组相对优势估计器。它们共同显著稳定了RL训练,提高了数据效率,并提高了性能。我们的工作证明了在特定领域构建强大的推理模型的可行性,并且成本低廉。我们在https://github.com/netease-youdao/Confucius3-Math上公开了我们的模型和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对中文基础教育领域的数学问题,提出了一种新的大型语言模型Confucius3-Math。此模型参数达到十四亿规模,能在单一消费级GPU上高效运行,并在一系列数学推理任务上取得了卓越表现。通过大规模强化学习进行训练,与国家政策一致并能低成本地解决主流中小学数学问题。我们分享了这个模型的发展过程及所采用的创新方法。开源此模型和代码于公众视野,希望能助力教育普及和知识传播。
Key Takeaways
- Confucius3-Math是一个针对中文基础教育领域的大型语言模型,旨在解决数学学习问题。
- 模型具备优异性能和高效率,能够在单个消费级GPU上运行。在多个数学推理任务上表现突出,超越许多更大规模的模型。
- 模型通过大规模强化学习进行训练,与国家课程大纲相符,擅长解决主流中小学数学问题。
点此查看论文截图
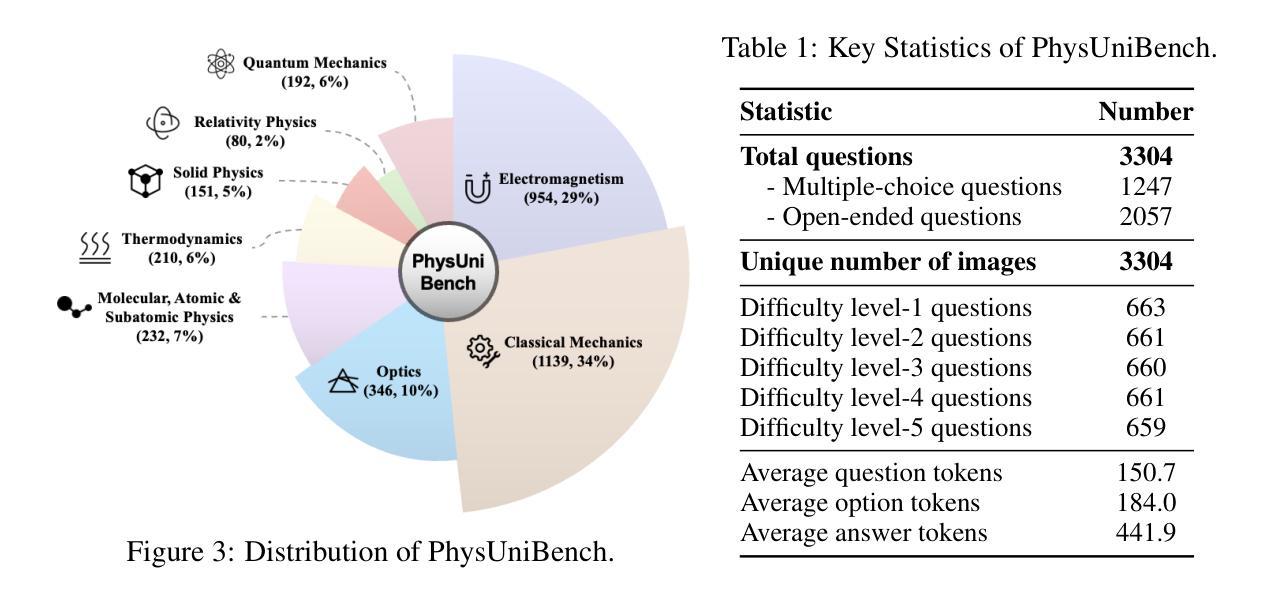
PhysUniBench: An Undergraduate-Level Physics Reasoning Benchmark for Multimodal Models
Authors:Lintao Wang, Encheng Su, Jiaqi Liu, Pengze Li, Peng Xia, Jiabei Xiao, Wenlong Zhang, Xinnan Dai, Xi Chen, Yuan Meng, Mingyu Ding, Lei Bai, Wanli Ouyang, Shixiang Tang, Aoran Wang, Xinzhu Ma
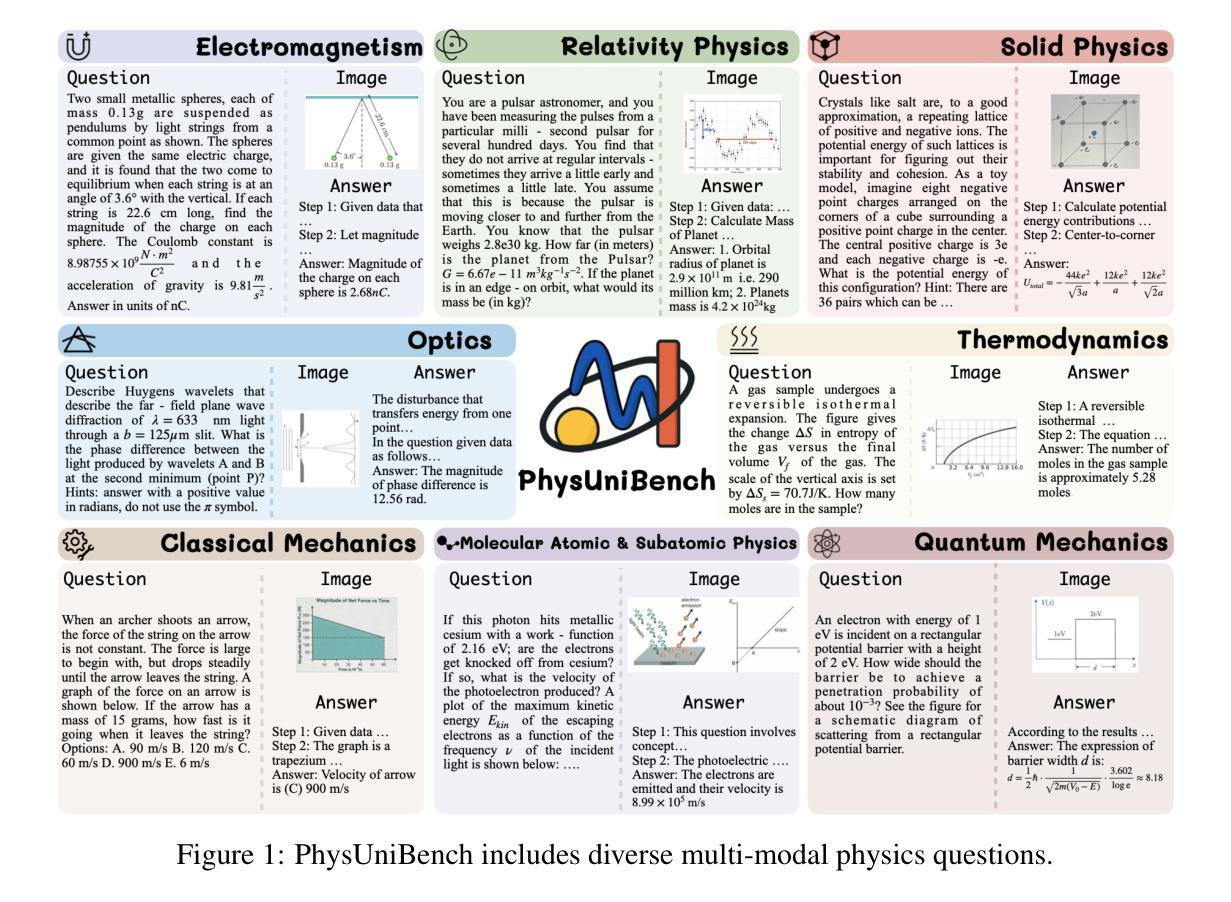
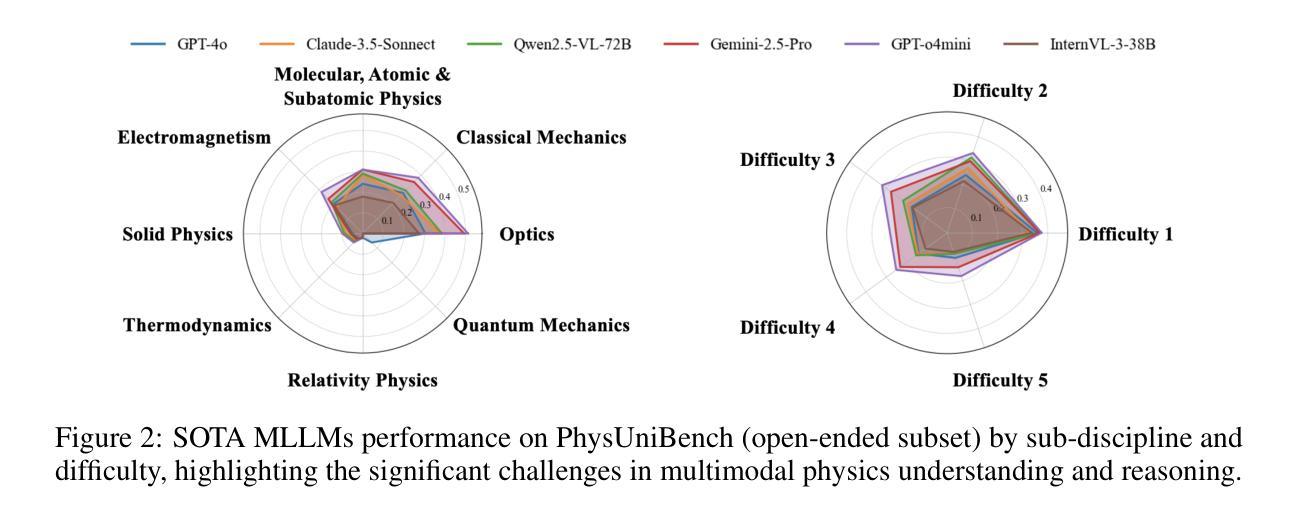
Physics problem-solving is a challenging domain for large AI models, requiring integration of conceptual understanding, mathematical reasoning, and interpretation of physical diagrams. Current evaluation methodologies show notable limitations in capturing the breadth and complexity of undergraduate-level physics, underscoring the need for more rigorous assessments. To this end, we present PhysUniBench, a large-scale multimodal benchmark designed to evaluate and improve the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) specifically on undergraduate-level physics problems. PhysUniBench consists of 3,304 physics questions spanning 8 major sub-disciplines of physics, each accompanied by one visual diagrams. The benchmark includes both open-ended and multiple-choice questions, systematically curated and difficulty-rated through an iterative model-in-the-loop process. The benchmark’s construction involved a rigorous multi-stage process, including multiple roll-outs, expert-level evaluation, automated filtering of easily solved problems, and a nuanced difficulty grading system with five levels. Through extensive experiments, we observe that current state-of-the-art models encounter substantial challenges in physics reasoning. For example, GPT-4o mini achieves only about 34.2% accuracy in the proposed PhysUniBench. These results highlight that current MLLMs struggle with advanced physics reasoning, especially on multi-step problems and those requiring precise diagram interpretation. By providing a broad and rigorous assessment tool, PhysUniBench aims to drive progress in AI for Science, encouraging the development of models with stronger physical reasoning, problem-solving skills, and multimodal understanding. The benchmark and evaluation scripts are available at https://prismax-team.github.io/PhysUniBenchmark/.
物理问题解决是一个对大型AI模型具有挑战性的领域,它要求整合概念理解、数学推理和物理图表解释。现有的评估方法在计算本科生水平的物理知识的广度和复杂性方面存在明显的局限性,这强调了需要进行更严格评估的必要性。为此,我们推出了PhysUniBench,这是一个大规模的多模式基准测试,旨在评估和提高多模式大型语言模型(MLLMs)在本科生水平物理问题上的推理能力。PhysUniBench包含3304个物理问题,涵盖物理学的8个主要子学科,每个问题都配有一个视觉图表。该基准测试包括开放问题和多项选择题,通过循环模型过程进行系统的整理和难度评级。基准测试的构建涉及一个严格的多阶段过程,包括多次推出、专家级评估、自动过滤容易解决的问题,以及一个五级精细的难度分级系统。通过广泛的实验,我们发现最先进的模型在物理推理方面遇到了很大的挑战。例如,GPT-4o mini在提出的PhysUniBench上仅达到约34.2%的准确率。这些结果强调,当前的大型语言模型在高级物理推理方面遇到困难,尤其是在多步骤问题和需要精确图表解释的问题方面。通过提供广泛而严格的评估工具,PhysUniBench旨在推动人工智能科学的发展,鼓励开发具有更强物理推理能力、问题解决能力和多模式理解能力的模型。基准测试和评估脚本可在链接地址找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为PhysUniBench的大规模多模式基准测试,旨在评估和改进大型语言模型在本科物理学问题上的推理能力。该基准测试包含3304个物理学问题,涵盖物理学的8个主要子学科,每个问题都配备了一个视觉图表。通过广泛的实验观察,发现当前最先进的模型在物理推理方面遇到较大挑战。PhysUniBench的推出旨在为人工智能科学领域的发展提供推动力,鼓励开发具有更强物理推理、问题解决能力和多模式理解能力的模型。
Key Takeaways
- Physics problem-solving is challenging for large AI models, requiring integration of conceptual understanding, mathematical reasoning, and diagram interpretation.
- 当前评估方法在捕捉本科物理学广度与复杂性方面存在局限。
- 推出PhysUniBench基准测试,包含3304个物理学问题,涉及8个主要物理子学科。
- 该基准测试包含开放问题和选择题,通过模型循环过程中的迭代进行系统性筛选和难度评级。
- 基准测试的构建涉及多阶段过程,包括多次滚动发布、专家评估、自动过滤易解决问题和细致的难度分级系统。
- 广泛实验表明,当前最先进的模型在物理推理方面面临挑战,如GPT-4o mini在PhysUniBench上的准确率仅为34.2%。
点此查看论文截图

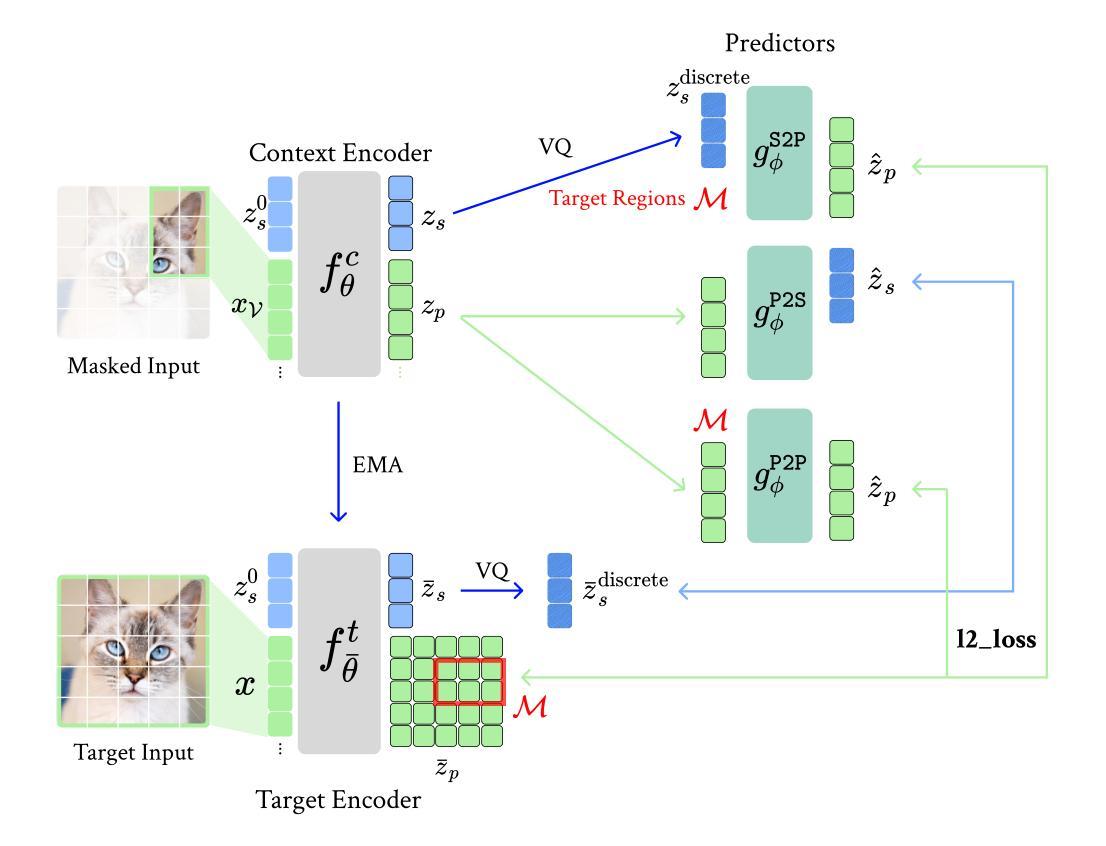
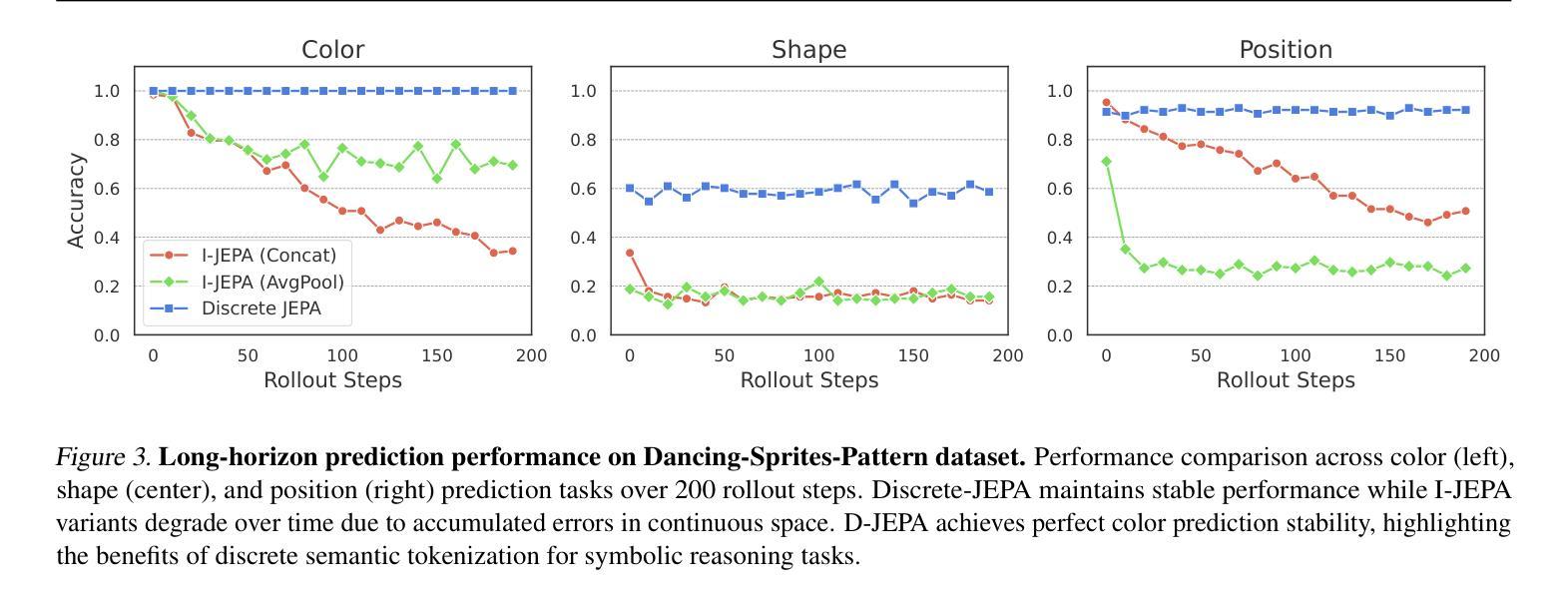
Discrete JEPA: Learning Discrete Token Representations without Reconstruction
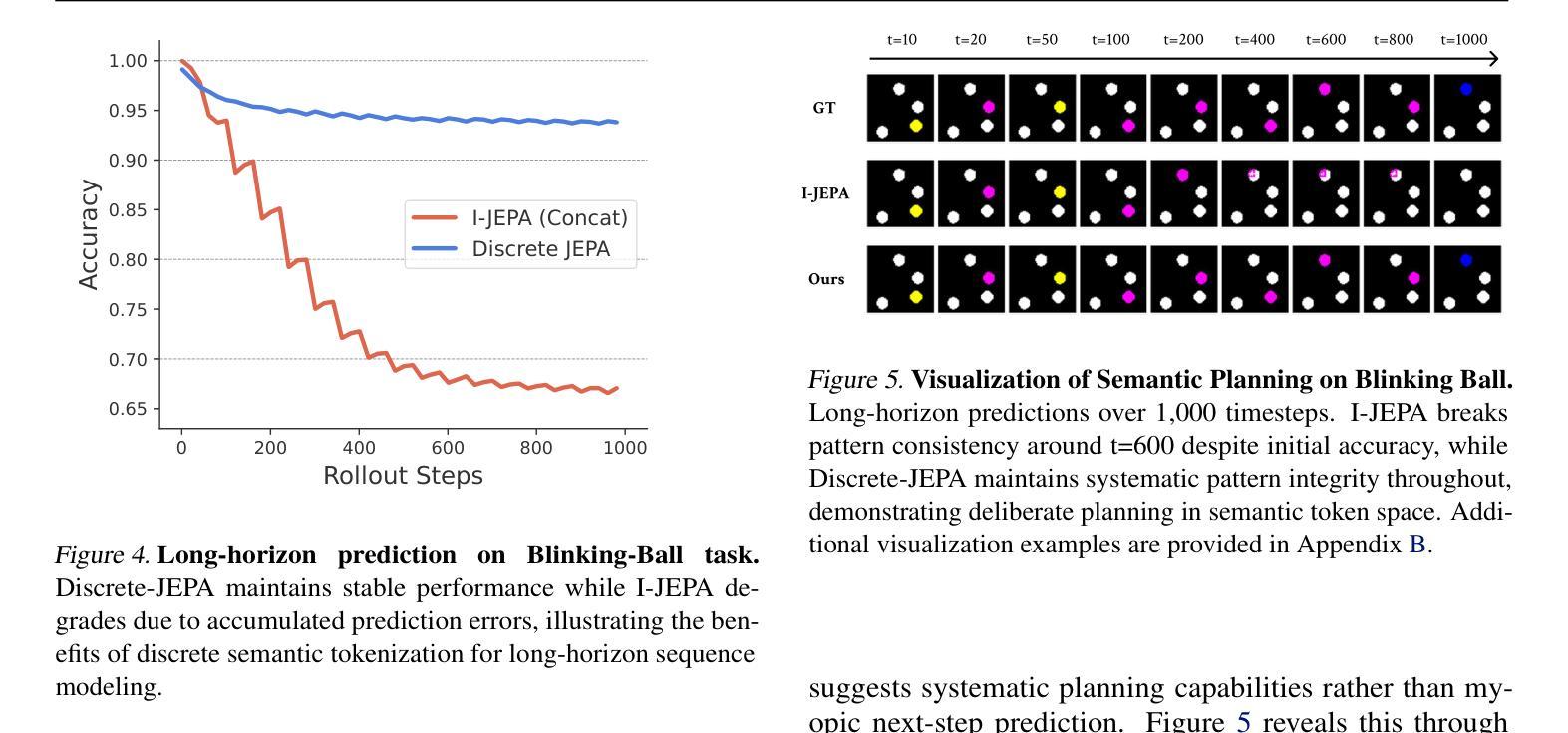
Authors:Junyeob Baek, Hosung Lee, Christopher Hoang, Mengye Ren, Sungjin Ahn
The cornerstone of cognitive intelligence lies in extracting hidden patterns from observations and leveraging these principles to systematically predict future outcomes. However, current image tokenization methods demonstrate significant limitations in tasks requiring symbolic abstraction and logical reasoning capabilities essential for systematic inference. To address this challenge, we propose Discrete-JEPA, extending the latent predictive coding framework with semantic tokenization and novel complementary objectives to create robust tokenization for symbolic reasoning tasks. Discrete-JEPA dramatically outperforms baselines on visual symbolic prediction tasks, while striking visual evidence reveals the spontaneous emergence of deliberate systematic patterns within the learned semantic token space. Though an initial model, our approach promises a significant impact for advancing Symbolic world modeling and planning capabilities in artificial intelligence systems.
认知智能的核心在于从观察中提取隐藏的模式,并利用这些原理系统地预测未来结果。然而,当前的图像令牌化方法在需要象征性抽象和逻辑推理能力的任务中显示出重大局限性,这对于系统推理至关重要。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了Discrete-JEPA,它在潜在预测编码框架的基础上,通过语义令牌化和新型互补目标,为符号推理任务创建了稳健的令牌化。Discrete-JEPA在视觉符号预测任务上的表现远超基线,而有力的视觉证据表明,在所学的语义令牌空间内出现了自发系统的模式。尽管这是一个初步模型,但我们的方法为推进人工智能系统中的符号世界建模和规划能力带来了重大影响的承诺。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:认知智能的核心在于从观察中提取隐藏模式,并利用这些原则系统地预测未来结果。然而,当前图像令牌化方法在需要符号抽象和逻辑推理能力的任务中表现出显著局限性,这对于系统推理至关重要。为解决这一挑战,我们提出了Discrete-JEPA,它通过语义令牌化和新的补充目标扩展潜在预测编码框架,为符号推理任务创建稳健的令牌化。Discrete-JEPA在视觉符号预测任务上显著优于基准测试,而有力的视觉证据表明,在学习的语义令牌空间内出现了自发系统的模式。尽管是一个初步模型,但我们的方法为推进人工智能系统中的符号世界建模和规划能力产生了重大影响。
Key Takeaways:
- 认知智能的核心是提取隐藏模式并进行预测。
- 当前图像令牌化方法在符号抽象和逻辑推理任务中存在局限性。
- Discrete-JEPA通过语义令牌化和补充目标扩展潜在预测编码框架。
- Discrete-JEPA在视觉符号预测任务上表现优异。
- 学习的语义令牌空间内出现了自发系统的模式。
- Discrete-JEPA对推进人工智能的符号世界建模有影响。
点此查看论文截图

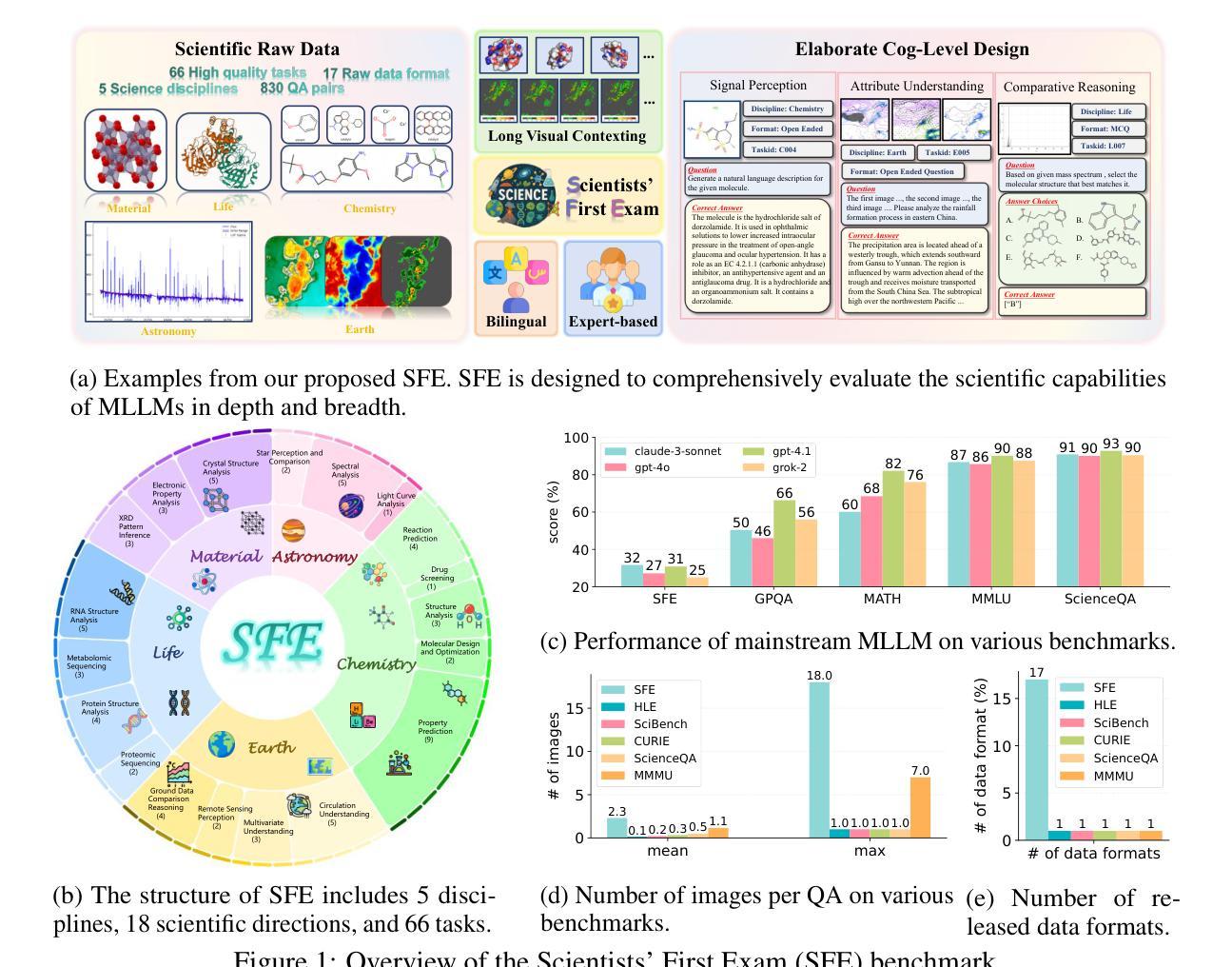
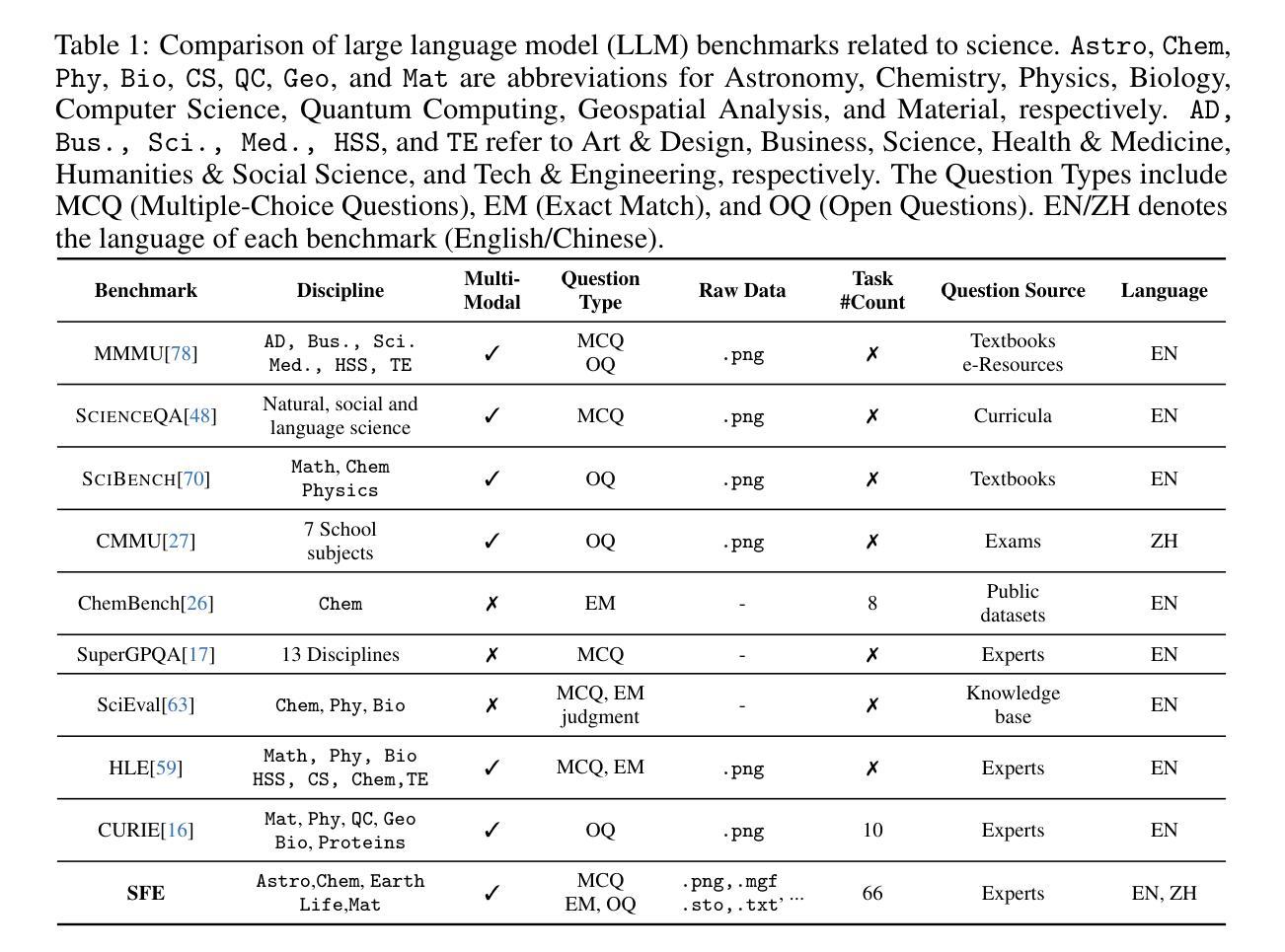
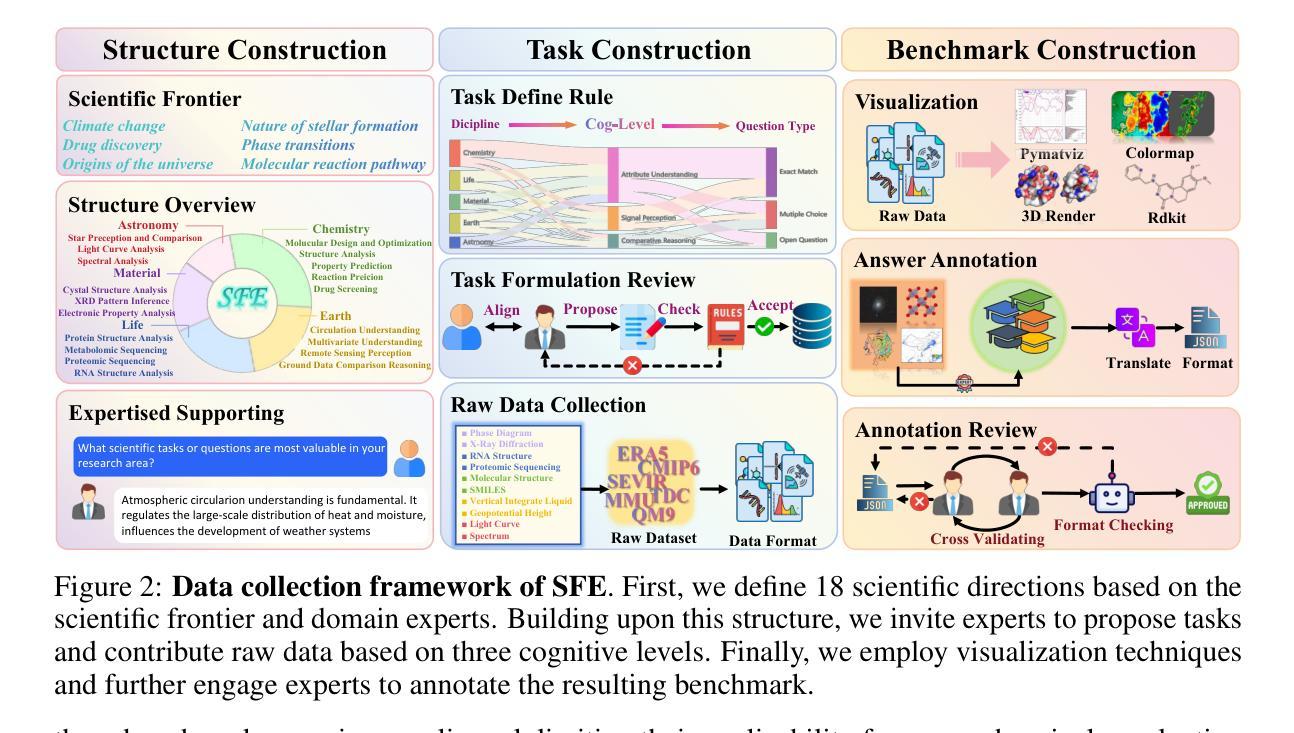
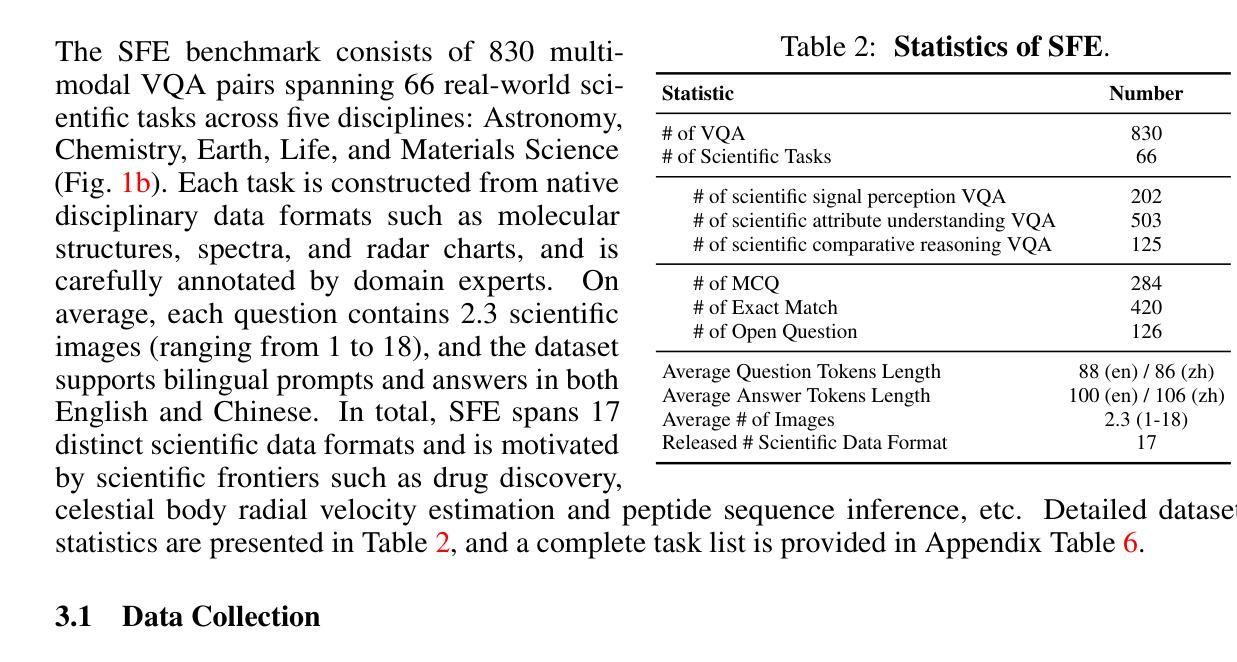
Scientists’ First Exam: Probing Cognitive Abilities of MLLM via Perception, Understanding, and Reasoning
Authors:Yuhao Zhou, Yiheng Wang, Xuming He, Ruoyao Xiao, Zhiwei Li, Qiantai Feng, Zijie Guo, Yuejin Yang, Hao Wu, Wenxuan Huang, Jiaqi Wei, Dan Si, Xiuqi Yao, Jia Bu, Haiwen Huang, Tianfan Fu, Shixiang Tang, Ben Fei, Dongzhan Zhou, Fenghua Ling, Yan Lu, Siqi Sun, Chenhui Li, Guanjie Zheng, Jiancheng Lv, Wenlong Zhang, Lei Bai
Scientific discoveries increasingly rely on complex multimodal reasoning based on information-intensive scientific data and domain-specific expertise. Empowered by expert-level scientific benchmarks, scientific Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) hold the potential to significantly enhance this discovery process in realistic workflows. However, current scientific benchmarks mostly focus on evaluating the knowledge understanding capabilities of MLLMs, leading to an inadequate assessment of their perception and reasoning abilities. To address this gap, we present the Scientists’ First Exam (SFE) benchmark, designed to evaluate the scientific cognitive capacities of MLLMs through three interconnected levels: scientific signal perception, scientific attribute understanding, scientific comparative reasoning. Specifically, SFE comprises 830 expert-verified VQA pairs across three question types, spanning 66 multimodal tasks across five high-value disciplines. Extensive experiments reveal that current state-of-the-art GPT-o3 and InternVL-3 achieve only 34.08% and 26.52% on SFE, highlighting significant room for MLLMs to improve in scientific realms. We hope the insights obtained in SFE will facilitate further developments in AI-enhanced scientific discoveries.
科学发现越来越依赖于基于信息密集的科学数据和特定领域专业知识进行复杂的多模式推理。得益于专家级的科学基准测试,科学多模式大型语言模型(MLLMs)在真实的工作流程中有潜力显著增强这一发现过程。然而,当前的科学基准测试主要集中在评估MLLMs的知识理解能力上,导致对其感知和推理能力的评估不足。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了科学家第一次考试(SFE)基准测试,旨在通过三个相互关联的水平来评估MLLMs的科学认知能力:科学信号感知、科学属性理解、科学比较推理。具体来说,SFE包含830个专家验证过的问答对,涉及三种问题类型,涵盖五个高价值学科的66个多模式任务。大量实验表明,目前最先进的GPT-o3和InternVL-3在SFE上的表现仅为34.08%和26.52%,这表明MLLMs在科学领域仍有很大的改进空间。我们希望从SFE中获得的认识能够促进人工智能增强科学发现的进一步发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 82 pages
Summary
基于信息密集型科学数据和领域特定专业知识,科学发现越来越依赖于复杂的跨模态推理。科学跨模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)借助专家级科学基准,具有增强现实工作流程中的发现过程的潜力。然而,当前的科学基准主要侧重于评估MLLMs的知识理解能力,导致对其感知和推理能力的评估不足。为解决这一空白,我们提出了科学家第一次考试(SFE)基准,旨在通过三个相互联系的水平评估MLLMs的科学认知能力:科学信号感知、科学属性理解、科学比较推理。SFE包含830个专家验证的问答对,涵盖三种问题类型和66个跨模态任务,涉及五个高价值学科。实验表明,当前最先进的GPT-o3和InternVL-3在SFE上的表现仅为34.08%和26.52%,这突显出MLLMs在科学领域有巨大的改进空间。我们希望通过SFE获得的见解能促进AI增强科学发现的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- 科学发现现在依赖于复杂的跨模态推理和信息密集型数据。
- 科学跨模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)有潜力改善科学发现过程。
- 当前的科学评估基准主要关注MLLMs的知识理解能力,忽视了其感知和推理能力。
- 科学家第一次考试(SFE)基准旨在全面评估MLLMs的科学认知能力,包括科学信号感知、科学属性理解和科学比较推理。
- SFE包含专家验证的问答对,涵盖多种问题类型和跨模态任务,涉及多个学科。
- 最先进的MLLMs在SFE上的表现不佳,显示其在科学领域的巨大改进空间。
点此查看论文截图