⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-27 更新
Causal Inference for Latent Outcomes Learned with Factor Models
Authors:Jenna M. Landy, Dafne Zorzetto, Roberta De Vito, Giovanni Parmigiani
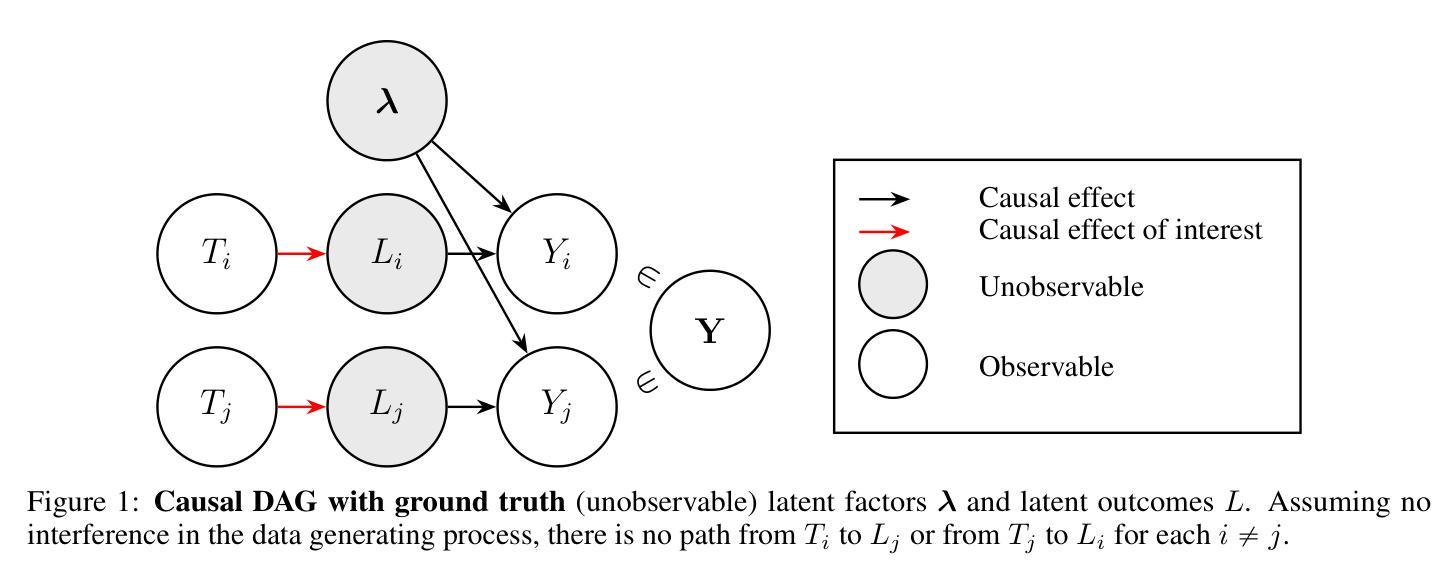
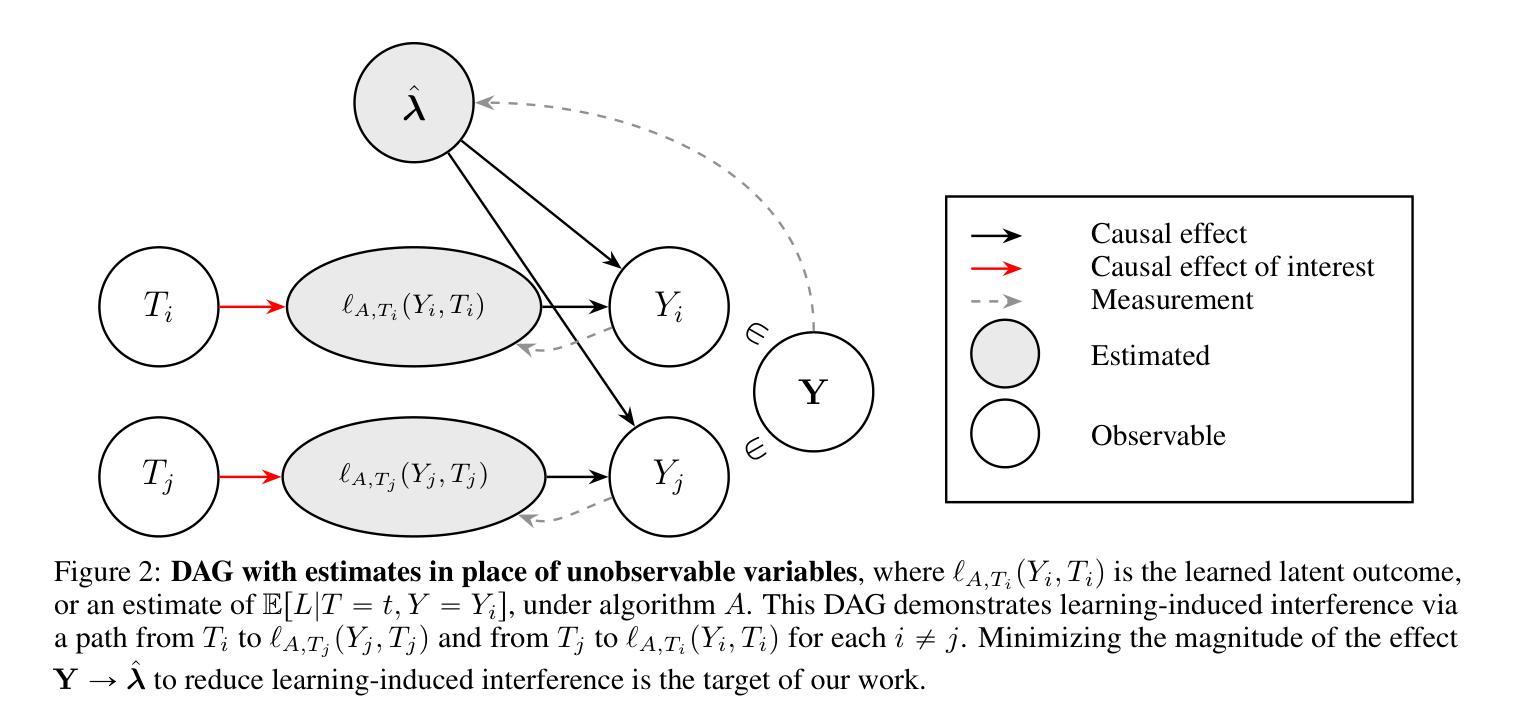
In many fields$\unicode{x2013}$including genomics, epidemiology, natural language processing, social and behavioral sciences, and economics$\unicode{x2013}$it is increasingly important to address causal questions in the context of factor models or representation learning. In this work, we investigate causal effects on $\textit{latent outcomes}$ derived from high-dimensional observed data using nonnegative matrix factorization. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to formally address causal inference in this setting. A central challenge is that estimating a latent factor model can cause an individual’s learned latent outcome to depend on other individuals’ treatments, thereby violating the standard causal inference assumption of no interference. We formalize this issue as $\textit{learning-induced interference}$ and distinguish it from interference present in a data-generating process. To address this, we propose a novel, intuitive, and theoretically grounded algorithm to estimate causal effects on latent outcomes while mitigating learning-induced interference and improving estimation efficiency. We establish theoretical guarantees for the consistency of our estimator and demonstrate its practical utility through simulation studies and an application to cancer mutational signature analysis. All baseline and proposed methods are available in our open-source R package, ${\tt causalLFO}$.
在许多领域——包括基因组学、流行病学、自然语言处理、社会行为科学和经济学——在因子模型或表示学习的背景下解决因果问题变得越来越重要。在这项工作中,我们利用非负矩阵分解法研究高维观测数据派生的潜在结果的因果关系。据我们所知,这是该领域首次正式研究因果推断。一个核心挑战在于估计潜在因子模型可能会导致个体的潜在结果与他人的处理结果之间存在依赖关系,从而违反了无干扰的标准因果推断假设。我们将这个问题形式化为“学习引起的干扰”,并将其与数据生成过程中存在的干扰区分开来。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新颖、直观且理论扎实的算法来估计潜在结果的因果关系,同时减少学习引起的干扰并提高估计效率。我们为估计器的一致性提供了理论保证,并通过模拟研究和癌症突变签名分析的应用来展示其实用性。所有基准方法和提出的方法都可在我们的开源R包${\tt causalLFO}$中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 7 figures, 1 table (+ references and supplement). For open-source R software package, see https://github.com/jennalandy/causalLFO. For all code used in the simulation studies and data application, see https://github.com/jennalandy/causalLFO_PAPER
Summary
文本探讨了在潜在结果模型中使用非负矩阵分解进行因果推断的问题。针对高维观测数据,研究如何估计潜在结果的因果效应,并首次正式解决学习引起的干扰问题。为提高估计效率,提出新的算法,理论保证估计一致性,并在模拟研究和癌症突变分析中得到验证。所有方法均可在开源R包中获得。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注于因果推断在潜在结果模型中的应用,特别是在高维观测数据的情况下。
- 提出首个解决学习引起的干扰问题的正式研究。学习干扰是指在估计潜在因子模型时,个体学习的潜在结果可能依赖于其他个体的处理结果。这种现象违反了标准因果推断假设的无干扰原则。
- 提出一种新颖、直观且理论基础的算法来解决学习干扰问题,并提高了估计效率。
- 通过模拟研究和癌症突变分析验证了算法的实际应用效果。这些实验结果表明该算法能够有效解决学习干扰问题并提高估计效率。
- 研究建立了理论保证估计一致性的理论框架。这意味着所提出的算法在理论上具有可靠性,能够准确估计潜在结果的因果效应。
- 所有方法和基线方法均可在开源R包中获得,方便其他研究者使用和扩展相关研究。该R包名为“causalLFO”。
点此查看论文截图