⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-28 更新
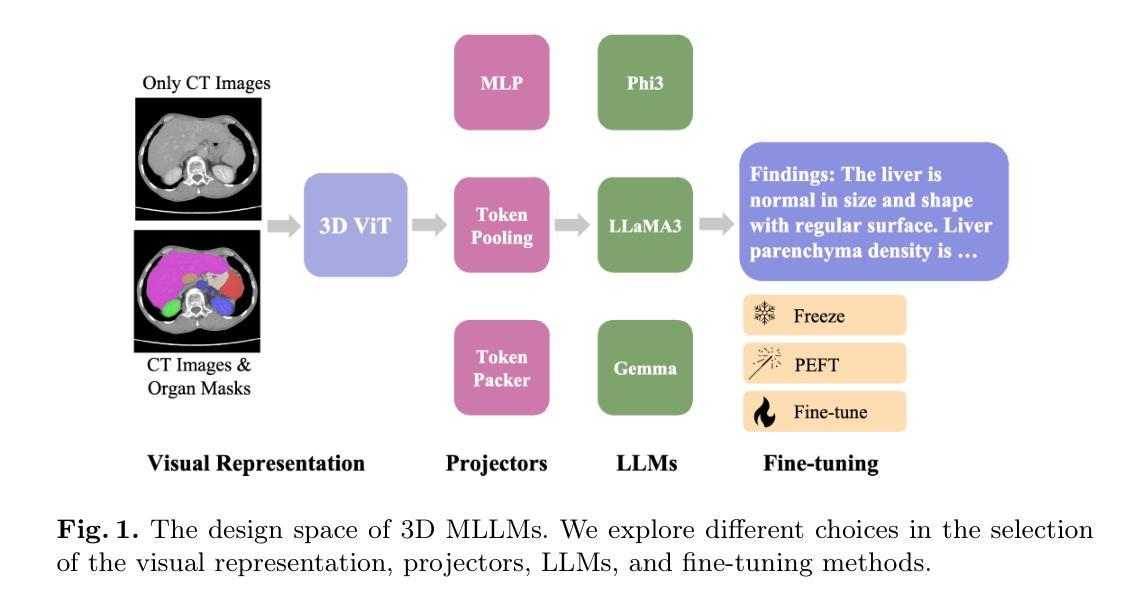
Exploring the Design Space of 3D MLLMs for CT Report Generation
Authors:Mohammed Baharoon, Jun Ma, Congyu Fang, Augustin Toma, Bo Wang
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have emerged as a promising way to automate Radiology Report Generation (RRG). In this work, we systematically investigate the design space of 3D MLLMs, including visual input representation, projectors, Large Language Models (LLMs), and fine-tuning techniques for 3D CT report generation. We also introduce two knowledge-based report augmentation methods that improve performance on the GREEN score by up to 10%, achieving the 2nd place on the MICCAI 2024 AMOS-MM challenge. Our results on the 1,687 cases from the AMOS-MM dataset show that RRG is largely independent of the size of LLM under the same training protocol. We also show that larger volume size does not always improve performance if the original ViT was pre-trained on a smaller volume size. Lastly, we show that using a segmentation mask along with the CT volume improves performance. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/bowang-lab/AMOS-MM-Solution
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)作为一种有前景的方法,已经出现在自动放射学报告生成(RRG)中。在这项工作中,我们系统地研究了3DMLLMs的设计空间,包括视觉输入表示、投影仪、大型语言模型(LLMs)和用于3D计算机断层扫描(CT)报告生成的微调技术。我们还介绍了两种基于知识的报告增强方法,这些方法在GREEN评分上的性能提高了高达10%,并在MICCAI 2024 AMOS-MM挑战中获得了第二名。我们在AMOS-MM数据集上的1687个案例结果表明,在同一训练协议下,RRG在很大程度上独立于LLM的大小。我们还表明,如果原始ViT是在较小的体积上预训练的,那么较大的体积大小并不一定总能提高性能。最后,我们表明,使用分段掩膜与CT体积一起可以提高性能。代码可在https://github.com/bowang-lab/AMOS-MM-Solution公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了利用多模态大型语言模型自动化生成放射学报告的方法。文章系统地探讨了三维多模态大型语言模型的设计空间,包括视觉输入表示、投影器、大型语言模型和针对三维CT报告生成的微调技术。此外,还介绍了两种基于知识的报告增强方法,提高了GREEN指标的评分,并在MICCAI 2024 AMOS-MM挑战赛中荣获第二名。在AMOS-MM数据集上,结果显示报告生成在很大程度上独立于同一训练协议下的语言模型大小,并且更大的体积大小并不总是能提高性能,如果原始ViT是在较小的体积大小上进行预训练的。最后,使用分段掩码与CT体积相结合可以提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型在放射学报告生成中展现出潜力。
- 研究了三维多模态大型语言模型的设计空间,包括视觉输入、投影器、大型语言模型和微调技术。
- 引入两种知识增强报告方法,提高性能并在竞赛中取得第二名。
- 报告生成对语言模型大小相对独立,在同一训练协议下。
- 更大的体积大小不一定能提高性能,若预训练时的体积较小。
- 结合分段掩码与CT体积使用能提高报告生成的性能。
点此查看论文截图

HyperSORT: Self-Organising Robust Training with hyper-networks
Authors:Samuel Joutard, Marijn Stollenga, Marc Balle Sanchez, Mohammad Farid Azampour, Raphael Prevost
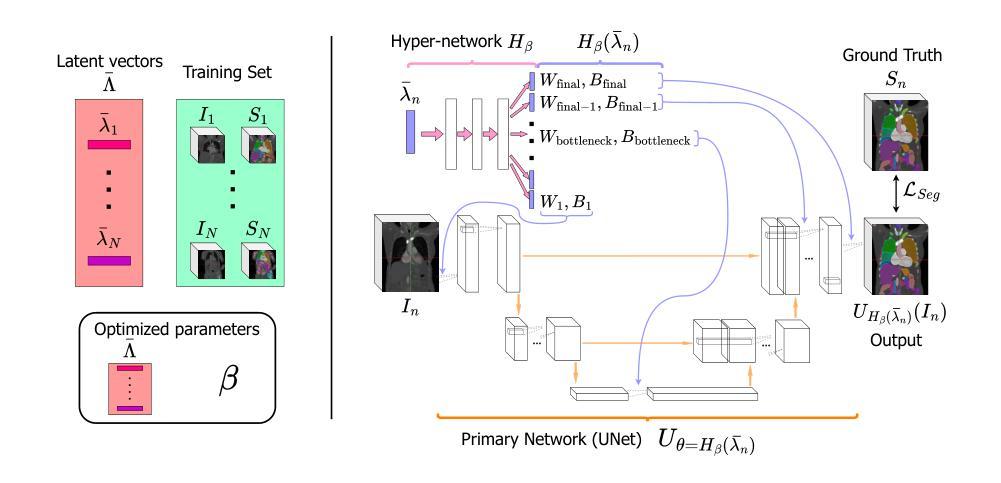
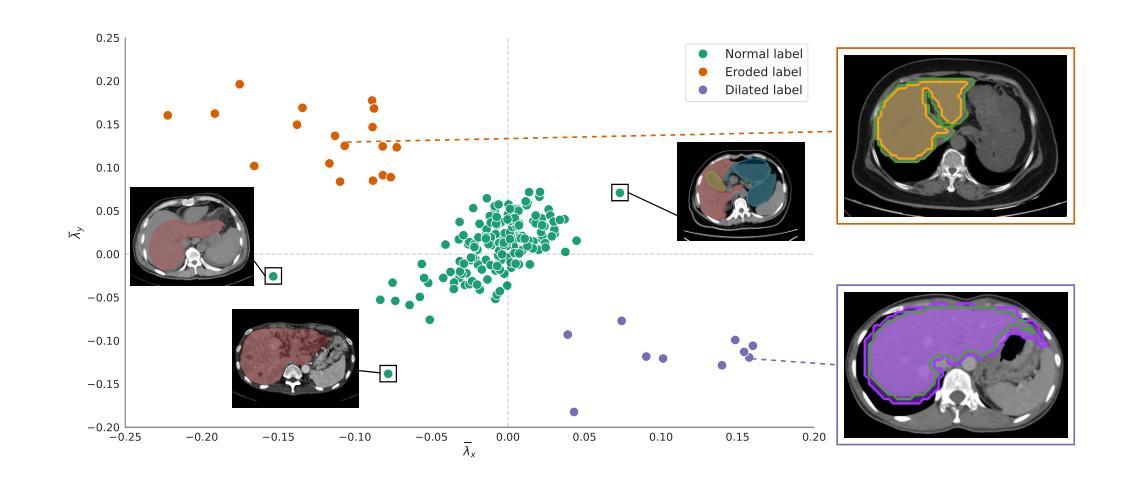
Medical imaging datasets often contain heterogeneous biases ranging from erroneous labels to inconsistent labeling styles. Such biases can negatively impact deep segmentation networks performance. Yet, the identification and characterization of such biases is a particularly tedious and challenging task. In this paper, we introduce HyperSORT, a framework using a hyper-network predicting UNets’ parameters from latent vectors representing both the image and annotation variability. The hyper-network parameters and the latent vector collection corresponding to each data sample from the training set are jointly learned. Hence, instead of optimizing a single neural network to fit a dataset, HyperSORT learns a complex distribution of UNet parameters where low density areas can capture noise-specific patterns while larger modes robustly segment organs in differentiated but meaningful manners. We validate our method on two 3D abdominal CT public datasets: first a synthetically perturbed version of the AMOS dataset, and TotalSegmentator, a large scale dataset containing real unknown biases and errors. Our experiments show that HyperSORT creates a structured mapping of the dataset allowing the identification of relevant systematic biases and erroneous samples. Latent space clusters yield UNet parameters performing the segmentation task in accordance with the underlying learned systematic bias. The code and our analysis of the TotalSegmentator dataset are made available: https://github.com/ImFusionGmbH/HyperSORT
医学图像数据集常常包含从错误标签到标注风格不一致等各种异质偏见。这些偏见可能会对深度分割网络性能产生负面影响。然而,识别和描述这些偏见是一项特别繁琐且具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们介绍了HyperSORT,这是一个使用超网络预测UNet参数的框架,该参数从代表图像和注释可变性的潜在向量中提取。超网络参数和与训练集中每个数据样本对应的潜在向量集合是联合学习的。因此,HyperSORT不是优化单个神经网络以适应数据集,而是学习UNet参数的复杂分布,其中低密度区域可以捕获噪声特定模式,而较大的模式则以有区别但有意义的方式稳健地分割器官。我们在两个三维腹部CT公共数据集上验证了我们的方法:首先是AMOS数据集的合成扰动版本,以及包含真实未知偏见和错误的TotalSegmentator大规模数据集。我们的实验表明,HyperSORT创建了一个结构化数据集映射,从而能够识别相关的系统性偏见和错误样本。潜在空间聚类产生UNet参数,根据学到的系统性偏见执行分割任务。我们的代码和对TotalSegmentator数据集的分析已提供:https://github.com/ImFusionGmbH/HyperSORT
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为HyperSORT的框架,它通过超网络预测UNet参数,这些参数从代表图像和注释可变性的潜在向量中派生出来。该框架能联合学习超网络参数和对应训练集中每个数据样本的潜在向量集合。HyperSORT能在数据集上学习一个复杂的UNet参数分布,其中低密度区域可以捕捉噪声特定模式,而较大的模式能以有意义的方式稳健地分割器官。实验表明,HyperSORT能够创建数据集的结构映射,以识别相关的系统性偏见和错误样本。
Key Takeaways
- HyperSORT框架利用超网络预测UNet参数,这些参数从图像和注释可变性的潜在向量中生成。
- 该框架联合学习超网络参数和每个训练数据样本的潜在向量集合。
- HyperSORT学习一个复杂的UNet参数分布,以适应数据集,其中低密度区域和较大的模式分别用于捕捉噪声特定模式和稳健地分割器官。
- HyperSORT能创建数据集的结构映射,以识别相关的系统性偏见和错误样本。
- 通过潜在空间聚类,HyperSORT可以根据学到的系统性偏见进行分割任务。
- HyperSORT在合成干扰的AMOS数据集和包含真实未知偏见和错误的TotalSegmentator数据集上进行了验证。
- HyperSORT的代码和对TotalSegmentator数据集的分析已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

Robust Deep Learning for Myocardial Scar Segmentation in Cardiac MRI with Noisy Labels
Authors:Aida Moafi, Danial Moafi, Evgeny M. Mirkes, Gerry P. McCann, Abbas S. Alatrany, Jayanth R. Arnold, Mostafa Mehdipour Ghazi
The accurate segmentation of myocardial scars from cardiac MRI is essential for clinical assessment and treatment planning. In this study, we propose a robust deep-learning pipeline for fully automated myocardial scar detection and segmentation by fine-tuning state-of-the-art models. The method explicitly addresses challenges of label noise from semi-automatic annotations, data heterogeneity, and class imbalance through the use of Kullback-Leibler loss and extensive data augmentation. We evaluate the model’s performance on both acute and chronic cases and demonstrate its ability to produce accurate and smooth segmentations despite noisy labels. In particular, our approach outperforms state-of-the-art models like nnU-Net and shows strong generalizability in an out-of-distribution test set, highlighting its robustness across various imaging conditions and clinical tasks. These results establish a reliable foundation for automated myocardial scar quantification and support the broader clinical adoption of deep learning in cardiac imaging.
心脏磁共振成像中心肌瘢痕的精确分割对临床评估和治疗计划至关重要。在本研究中,我们提出了一种稳健的深度学习流水线,通过微调最先进模型实现全自动心肌瘢痕检测和分割。该方法通过采用Kullback-Leibler损失和广泛的数据增强,明确解决了来自半自动注释的标签噪声、数据异质性和类别不平衡等挑战。我们对模型在急性和慢性病例上的表现进行了评估,证明了其在标签噪声的情况下仍能产生准确、平滑分割的能力。尤其值得一提的是,我们的方法优于最先进模型(如nnU-Net),并且在离分布测试集上表现出很强的泛化能力,凸显了其在各种成像条件和临床任务中的稳健性。这些结果为自动心肌瘢痕量化奠定了基础,并支持深度学习在心脏成像中的更广泛临床应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
本研究提出一种基于深度学习的全自动心肌瘢痕检测和分割方法,通过微调先进技术模型来解决标签噪声、数据异质性和类别不平衡等挑战。模型性能在急性和慢性病例中均得到评估,表现出准确平滑的分割能力,尽管标签存在噪声。该研究的方法在nnU-Net等最新模型的基础上表现更优秀,并且在离分布测试集中展现出强大的泛化能力,支持其在不同成像条件和临床任务中的广泛应用。这些结果为自动心肌瘢痕量化奠定了基础,支持深度学习在心脏成像中的临床广泛应用。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出一种全自动心肌瘢痕检测和分割的深度学习管道方法。
- 方法通过微调先进技术模型解决标签噪声、数据异质性和类别不平衡等挑战。
- 模型评估表明其在急性和慢性病例中具有准确和光滑的分割能力。
- 该方法优于现有最新模型,如nnU-Net。
- 模型在外部测试集中展现出强大的泛化能力,适用于不同成像条件和临床任务。
- 研究结果支持自动心肌瘢痕量化的应用。
点此查看论文截图

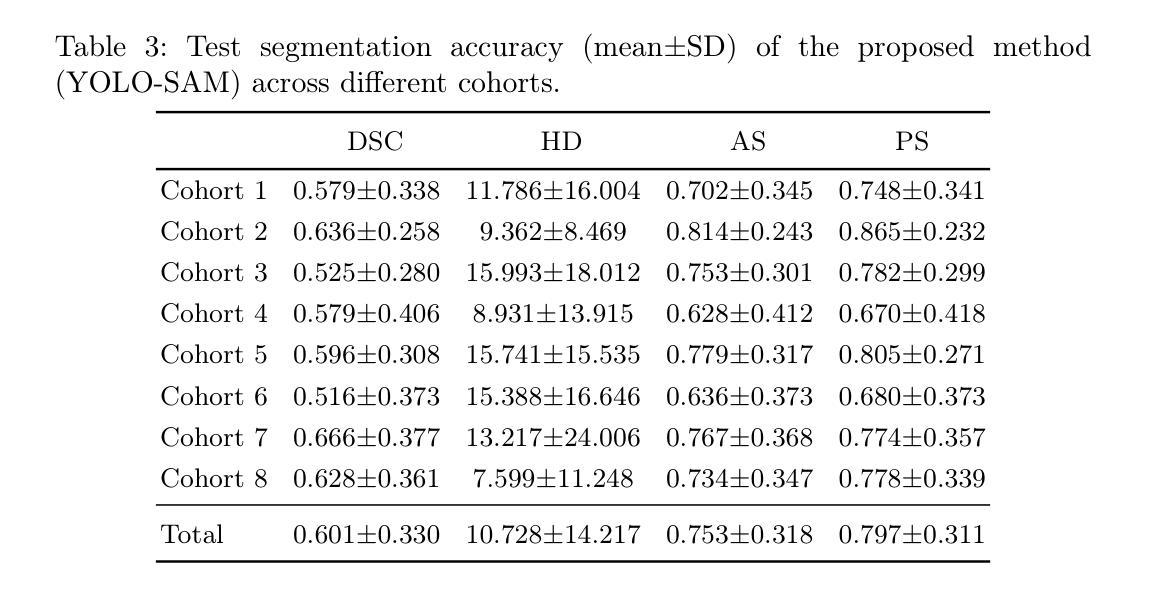
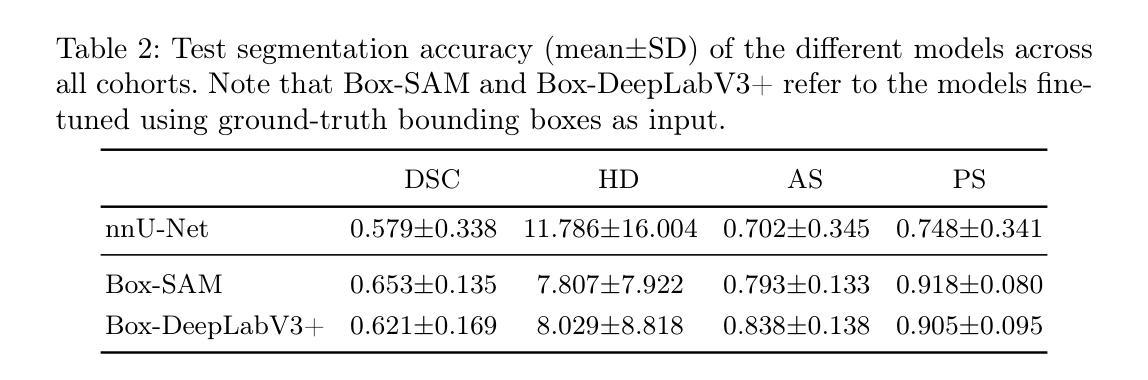
Detection of Breast Cancer Lumpectomy Margin with SAM-incorporated Forward-Forward Contrastive Learning
Authors:Tyler Ward, Xiaoqin Wang, Braxton McFarland, Md Atik Ahamed, Sahar Nozad, Talal Arshad, Hafsa Nebbache, Jin Chen, Abdullah Imran
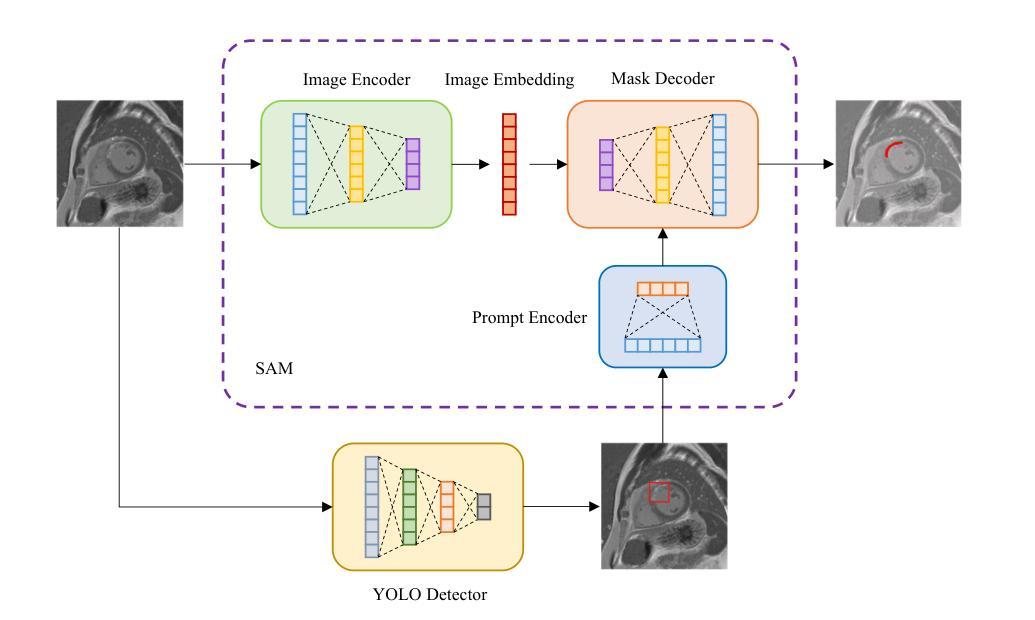
Complete removal of cancer tumors with a negative specimen margin during lumpectomy is essential in reducing breast cancer recurrence. However, 2D specimen radiography (SR), the current method used to assess intraoperative specimen margin status, has limited accuracy, resulting in nearly a quarter of patients requiring additional surgery. To address this, we propose a novel deep learning framework combining the Segment Anything Model (SAM) with Forward-Forward Contrastive Learning (FFCL), a pre-training strategy leveraging both local and global contrastive learning for patch-level classification of SR images. After annotating SR images with regions of known maligancy, non-malignant tissue, and pathology-confirmed margins, we pre-train a ResNet-18 backbone with FFCL to classify margin status, then reconstruct coarse binary masks to prompt SAM for refined tumor margin segmentation. Our approach achieved an AUC of 0.8455 for margin classification and segmented margins with a 27.4% improvement in Dice similarity over baseline models, while reducing inference time to 47 milliseconds per image. These results demonstrate that FFCL-SAM significantly enhances both the speed and accuracy of intraoperative margin assessment, with strong potential to reduce re-excision rates and improve surgical outcomes in breast cancer treatment. Our code is available at https://github.com/tbwa233/FFCL-SAM/.
在保乳手术中,完全移除癌症肿瘤并带有阴性标本边缘是降低乳腺癌复发的关键。然而,目前用于评估术中标本边缘状态的二维标本放射线照相术(SR)的准确度有限,导致近四分之一的患者需要接受额外手术。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的深度学习框架,该框架结合了Segment Anything Model(SAM)和Forward-Forward Contrastive Learning(FFCL)。FFCL是一种预训练策略,利用局部和全局对比学习对SR图像进行补丁级别的分类。在对SR图像进行已知恶性区域、非恶性组织和经病理证实的边缘标注后,我们使用FFCL预训练一个ResNet-18骨干网来分类边缘状态,然后重建粗糙的二值掩膜来提示SAM进行精细的肿瘤边缘分割。我们的方法在边缘分类方面达到了0.8455的AUC,在边缘分割方面相较于基准模型在Dice相似度上提高了27.4%,同时减少了每幅图像的推理时间至47毫秒。这些结果表明,FFCL-SAM显著提高了术中边缘评估的速度和准确度,具有强大的潜力来降低再切除率并改善乳腺癌治疗的手术效果。我们的代码可在https://github.com/tbwa233/FFCL-SAM/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 7 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文强调了在乳腺癌保乳手术中完全去除肿瘤、确保负性标本边缘的重要性,以降低癌症复发的风险。然而,现有的二维标本放射线检测(SR)在评估标本边缘状态时的准确度有限,约四分之一的患者需要再次手术。为此,我们提出一种结合Segment Anything Model(SAM)与Forward-Forward Contrastive Learning(FFCL)的深度学习框架。通过标注SR图像中的已知恶性区域、非恶性组织和经病理证实的边缘,我们利用FFCL进行边缘状态分类的预训练,然后重建粗二进制掩膜以引导SAM进行更精细的肿瘤边缘分割。该方法在边缘分类方面取得了0.8455的AUC值,相较于基线模型,Dice相似度提高了27.4%,且每张图像的推理时间缩短至47毫秒。这表明FFCL-SAM能显著提高术中边缘评估的速度和准确度,具有降低再切除率、改善乳腺癌治疗手术效果的重要潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 完全移除癌症肿瘤并确证负性标本边缘对降低乳腺癌复发至关重要。
- 当前使用的二维标本放射线检测(SR)方法存在准确度问题,约四分之一的患者需接受再次手术。
- 提出的深度学习框架结合了Segment Anything Model(SAM)与Forward-Forward Contrastive Learning(FFCL)。
- 通过标注SR图像并预训练模型进行边缘状态分类,实现了较高的分类准确度。
- 使用重建的粗二进制掩膜引导SAM进行更精细的肿瘤边缘分割,提高了分割效果。
- FFCL-SAM方法提高了术中边缘评估的速度和准确度。
点此查看论文截图

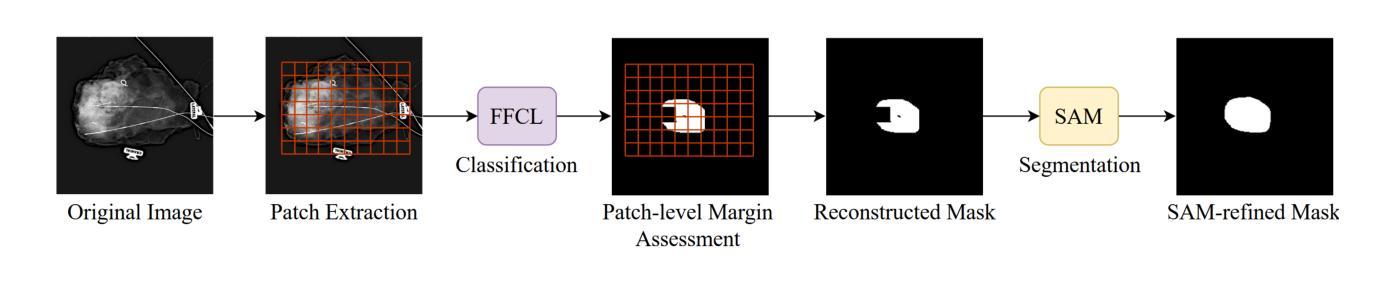
Segment Anything in Pathology Images with Natural Language
Authors:Zhixuan Chen, Junlin Hou, Liqi Lin, Yihui Wang, Yequan Bie, Xi Wang, Yanning Zhou, Ronald Cheong Kin Chan, Hao Chen
Pathology image segmentation is crucial in computational pathology for analyzing histological features relevant to cancer diagnosis and prognosis. However, current methods face major challenges in clinical applications due to limited annotated data and restricted category definitions. To address these limitations, we propose PathSegmentor, the first text-prompted segmentation foundation model designed specifically for pathology images. We also introduce PathSeg , the largest and most comprehensive dataset for pathology segmentation, built from 17 public sources and containing 275k image-mask-label triples across 160 diverse categories. With PathSegmentor, users can perform semantic segmentation using natural language prompts, eliminating the need for laborious spatial inputs such as points or boxes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PathSegmentor outperforms specialized models with higher accuracy and broader applicability, while maintaining a compact architecture. It significantly surpasses existing spatial- and text-prompted models by 0.145 and 0.429 in overall Dice scores, respectively, showing strong robustness in segmenting complex structures and generalizing to external datasets. Moreover, PathSegmentor’s outputs enhance the interpretability of diagnostic models through feature importance estimation and imaging biomarker discovery, offering pathologists evidence-based support for clinical decision-making. This work advances the development of explainable AI in precision oncology.
病理学图像分割在计算病理学中对分析癌症诊断和治疗相关的组织学特征至关重要。然而,由于标注数据有限和类别定义受限,当前方法在临床应用中面临重大挑战。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了PathSegmentor,这是首个专为病理学图像设计的文本提示分割基础模型。我们还介绍了PathSeg,这是最大的综合性病理学分割数据集,由17个公开来源构建,包含跨越160个不同类别的27.5万张图像-掩膜-标签三元组。通过PathSegmentor,用户可以使用自然语言提示进行语义分割,无需繁琐的空间输入,如点或框。大量实验表明,PathSegmentor在准确度和适用性方面超越了专业模型,同时保持了紧凑的架构。在总体Dice得分上,它与现有的空间提示模型和文本提示模型相比,分别高出0.145和0.429,在分割复杂结构和适应外部数据集方面表现出强大的稳健性。此外,PathSegmentor的输出通过特征重要性评估和成像生物标志物发现,增强了诊断模型的可解释性,为病理学家提供基于证据的支持,有助于临床决策。这项工作推动了精准肿瘤学中可解释人工智能的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了病理图像分割在计算病理学中的重要性,并指出了当前方法在临床应用中的局限性。为解决这些问题,提出了一种名为PathSegmentor的文本提示分割基础模型,并引入了规模最大的病理分割数据集PathSeg。PathSegmentor允许用户通过自然语言提示进行语义分割,无需繁琐的空间输入。实验证明,PathSegmentor在准确性和适用性方面超越了专业模型,同时在总体Dice得分上分别比现有的空间提示和文本提示模型高出0.145和0.429。此外,PathSegmentor的输出增强了诊断模型的解释性,为病理医师提供基于证据的支持,有助于临床决策。
Key Takeaways
- 病理图像分割在计算病理学中对癌症诊断和治疗反应评估的组织学特征分析至关重要。
- 当前病理图像分割方法在临床应用中面临有限标注数据和类别定义限制的挑战。
- PathSegmentor是首个针对病理图像设计的文本提示分割基础模型,简化了复杂的空间输入需求。
- PathSeg数据集是规模最大的病理分割数据集,包含来自17个公共来源的27.5万张图像-掩膜-标签三元组,涉及160多个类别。
- PathSegmentor在总体Dice得分上显著超越了现有的空间提示和文本提示模型。
- PathSegmentor的输出增强了诊断模型的解释性,有助于病理医师进行临床决策。
点此查看论文截图

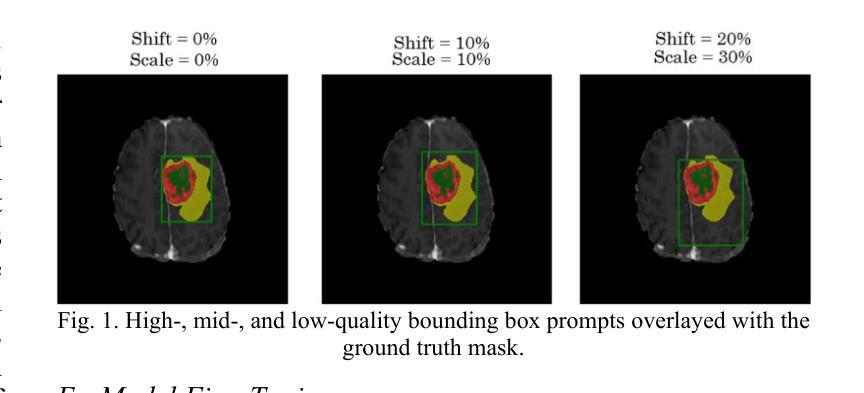
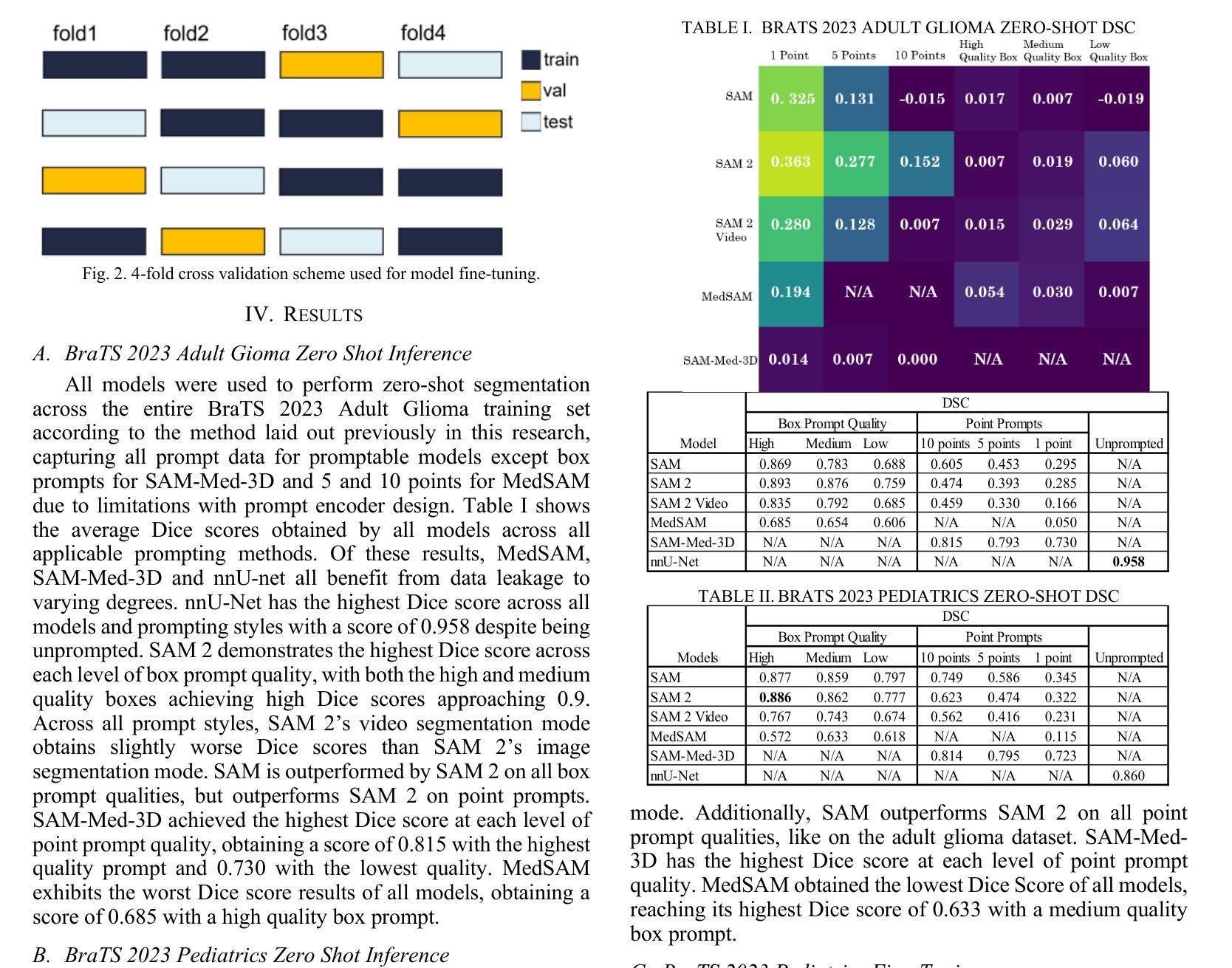
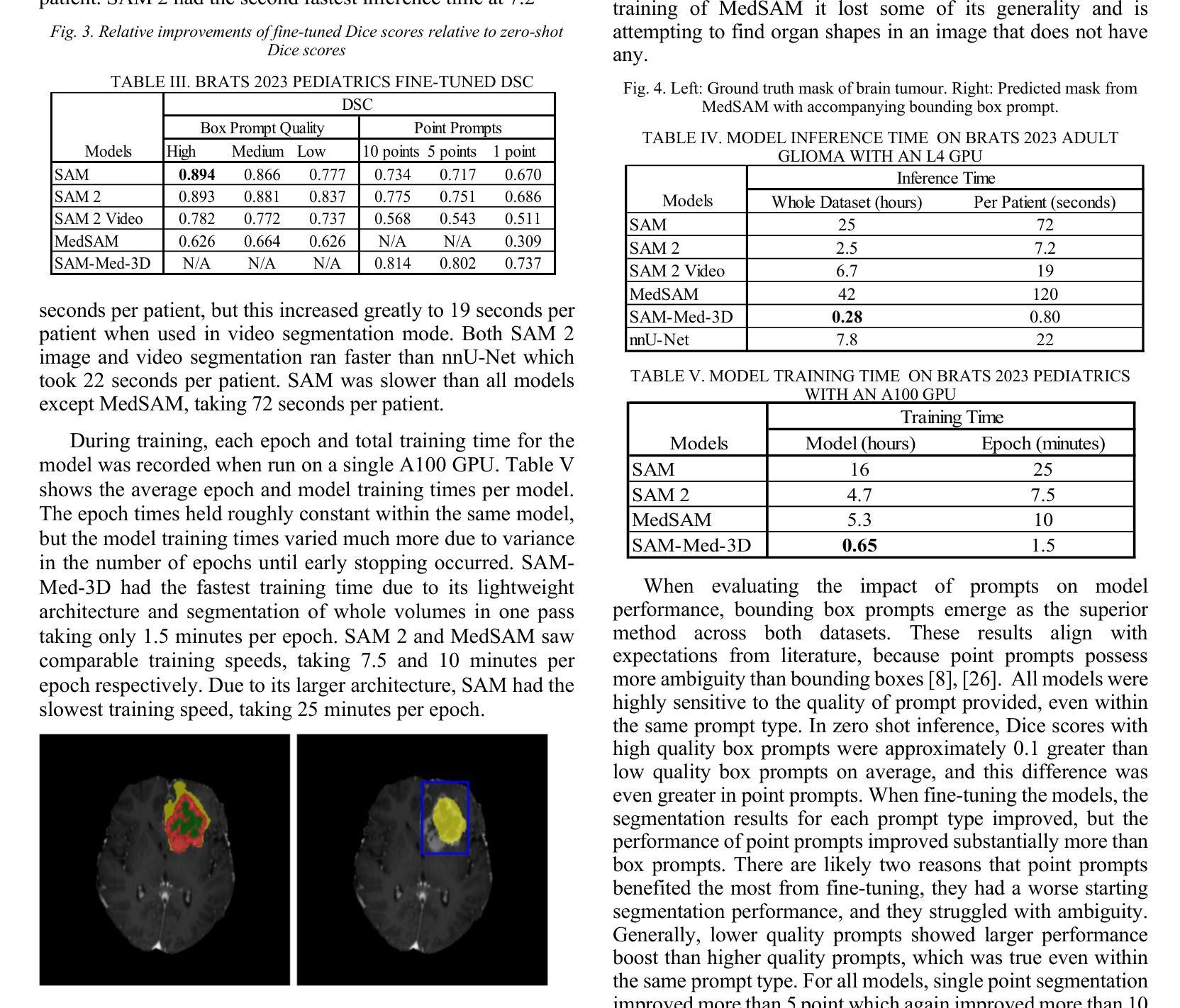
AI-Driven MRI-based Brain Tumour Segmentation Benchmarking
Authors:Connor Ludwig, Khashayar Namdar, Farzad Khalvati
Medical image segmentation has greatly aided medical diagnosis, with U-Net based architectures and nnU-Net providing state-of-the-art performance. There have been numerous general promptable models and medical variations introduced in recent years, but there is currently a lack of evaluation and comparison of these models across a variety of prompt qualities on a common medical dataset. This research uses Segment Anything Model (SAM), Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2), MedSAM, SAM-Med-3D, and nnU-Net to obtain zero-shot inference on the BraTS 2023 adult glioma and pediatrics dataset across multiple prompt qualities for both points and bounding boxes. Several of these models exhibit promising Dice scores, particularly SAM and SAM 2 achieving scores of up to 0.894 and 0.893, respectively when given extremely accurate bounding box prompts which exceeds nnU-Net’s segmentation performance. However, nnU-Net remains the dominant medical image segmentation network due to the impracticality of providing highly accurate prompts to the models. The model and prompt evaluation, as well as the comparison, are extended through fine-tuning SAM, SAM 2, MedSAM, and SAM-Med-3D on the pediatrics dataset. The improvements in point prompt performance after fine-tuning are substantial and show promise for future investigation, but are unable to achieve better segmentation than bounding boxes or nnU-Net.
医学图像分割已经极大地辅助了医学诊断,基于U-Net的架构和nnU-Net提供了最先进的性能。近年来已经出现了许多通用提示模型和医疗变体,但在一个公共医学数据集上,关于这些模型在各种提示质量方面的评估与比较仍然缺乏。本研究使用Segment Anything Model(SAM)、Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2)、MedSAM、SAM-Med-3D和nnU-Net,在BraTS 2023成人胶质瘤和儿科数据集上,通过多种提示质量获得零射击推断点和边界框。其中一些模型表现出有希望的Dice得分,特别是SAM和SAM 2在给出了极其准确的边界框提示时,分别达到了0.894和0.893的分数,超过了nnU-Net的分割性能。然而,由于向模型提供高度准确提示的不切实际性,nnU-Net仍然是主导的医疗图像分割网络。通过对SAM、SAM 2、MedSAM和SAM-Med-3D在儿科数据集上进行微调,模型和提示的评估以及比较得到了扩展。微调后点提示性能的改进是巨大的,显示出未来研究的希望,但无法实现在边界框或nnU-Net上的更好分割效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了医学图像分割在医疗诊断中的应用,并比较了多种模型(包括U-Net、SAM、SAM 2、MedSAM、SAM-Med-3D等)在BraTS 2023成人胶质瘤和儿科数据集上的表现。研究发现,在某些条件下,SAM和SAM 2的Dice得分高于nnU-Net,但在提供高度准确的提示方面,nnU-Net仍是主导的医疗图像分割网络。通过微调模型,点提示性能得到显著改善,但无法实现比边界框或nnU-Net更好的分割效果。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割对医疗诊断有重要作用,多种模型如U-Net、SAM系列等在BraTS数据集上得到应用。
- SAM和SAM 2在某些条件下表现出较高的Dice得分,但在提供高度准确的提示方面,nnU-Net仍是主导的医疗图像分割网络。
- 点提示在微调后性能显著改善,但无法实现比边界框或nnU-Net更好的分割效果。
- 目前缺乏对各种模型在不同提示质量下的评估和比较。
点此查看论文截图

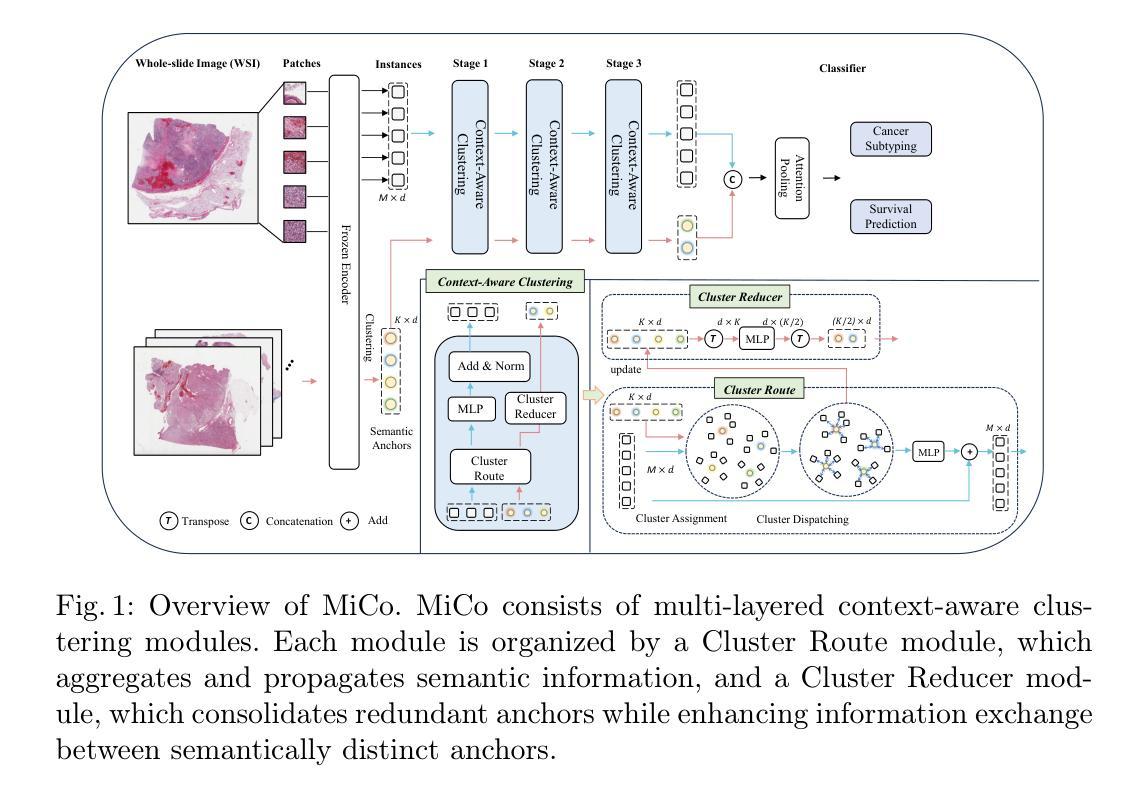
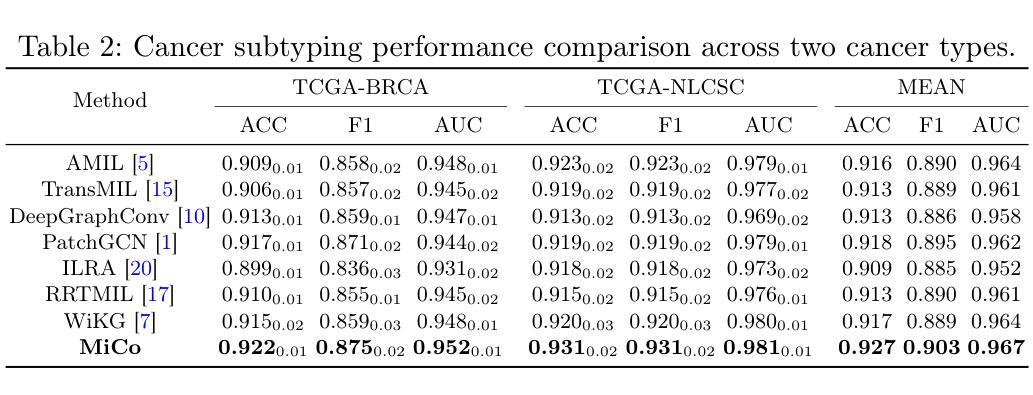
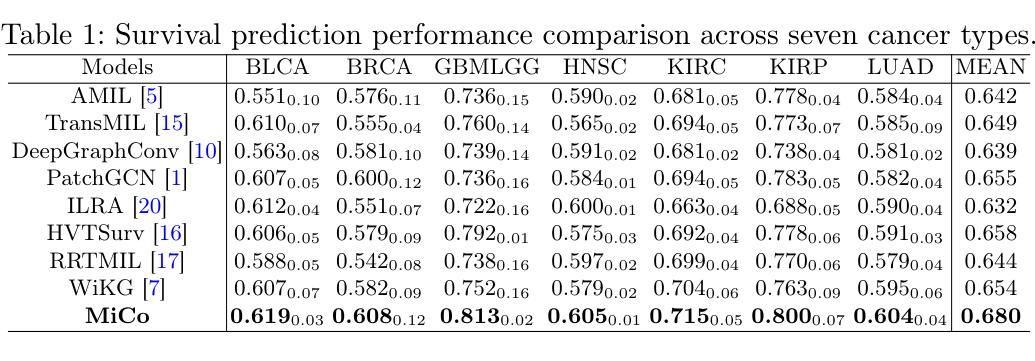
MiCo: Multiple Instance Learning with Context-Aware Clustering for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Junjian Li, Hulin Kuang, Jin Liu, Hailin Yue, Mengshen He, Jianxin Wang
Multiple instance learning (MIL) has shown significant promise in histopathology whole slide image (WSI) analysis for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. However, the inherent spatial heterogeneity of WSIs presents critical challenges, as morphologically similar tissue types are often dispersed across distant anatomical regions. Conventional MIL methods struggle to model these scattered tissue distributions and capture cross-regional spatial interactions effectively. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Multiple instance learning framework with Context-Aware Clustering (MiCo), designed to enhance cross-regional intra-tissue correlations and strengthen inter-tissue semantic associations in WSIs. MiCo begins by clustering instances to distill discriminative morphological patterns, with cluster centroids serving as semantic anchors. To enhance cross-regional intra-tissue correlations, MiCo employs a Cluster Route module, which dynamically links instances of the same tissue type across distant regions via feature similarity. These semantic anchors act as contextual hubs, propagating semantic relationships to refine instance-level representations. To eliminate semantic fragmentation and strengthen inter-tissue semantic associations, MiCo integrates a Cluster Reducer module, which consolidates redundant anchors while enhancing information exchange between distinct semantic groups. Extensive experiments on two challenging tasks across nine large-scale public cancer datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of MiCo, showcasing its superiority over state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/junjianli106/MiCo.
多实例学习(MIL)在病理学全切片图像(WSI)分析中显示出巨大的潜力,对于癌症的诊断和预后具有重要的应用价值。然而,WSI固有的空间异质性带来了重大挑战,因为形态相似的组织类型通常分布在遥远的解剖区域。传统的MIL方法难以对这些分散的组织分布进行建模,并有效地捕获跨区域的空间交互。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种具有上下文感知聚类的多实例学习框架(MiCo),旨在增强跨区域的组织内相关性和加强WSI中的组织间语义关联。MiCo首先通过聚类实例来提炼判别性形态模式,以聚类中心作为语义锚点。为了增强跨区域的组织内相关性,MiCo采用了一个聚类路径模块,该模块通过特征相似性动态链接同一组织类型的实例,这些实例位于不同的区域。这些语义锚点作为上下文中心,传播语义关系以优化实例级的表示。为了消除语义碎片并加强组织间的语义关联,MiCo集成了一个聚类缩减模块,该模块巩固了冗余的锚点,同时增强了不同语义组之间的信息交换。在两个具有挑战性的任务上进行的广泛实验,涉及九个大规模公共癌症数据集,证明了MiCo的有效性,展示了其优于最先进的方法。代码可在https://github.com/junjianli106/MiCo上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于多实例学习框架的上下文感知聚类方法(MiCo),用于增强全视野图像(WSI)分析中跨区域的内部组织关联性和组织间语义关联。MiCo通过聚类实例来提取判别形态模式,并以聚类中心点作为语义锚点。通过动态链接同一组织类型的实例,MiCo增强了跨区域的内部组织关联性;同时整合Cluster Reducer模块,巩固冗余锚点并强化不同语义组之间的信息交流。在多个大型公共癌症数据集上的实验表明,MiCo方法效果显著,优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- MiCo是一种基于多实例学习框架的方法,用于解决全视野图像分析中的空间异质性挑战。
- MiCo通过上下文感知聚类增强跨区域的内部组织关联性。
- 聚类中心点作为语义锚点,帮助识别和组织形态模式。
- MiCo采用Cluster Route模块,通过特征相似性动态链接同一组织类型的实例。
- Cluster Reducer模块用于巩固冗余锚点并强化不同语义组之间的信息交流。
- MiCo在多个大型公共癌症数据集上的实验表现出优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Simultaneous Segmentation of Ventricles and Normal/Abnormal White Matter Hyperintensities in Clinical MRI using Deep Learning
Authors:Mahdi Bashiri Bawil, Mousa Shamsi, Abolhassan Shakeri Bavil
Multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis and monitoring rely heavily on accurate assessment of brain MRI biomarkers, particularly white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) and ventricular changes. Current segmentation approaches suffer from several limitations: they typically segment these structures independently despite their pathophysiological relationship, struggle to differentiate between normal and pathological hyperintensities, and are poorly optimized for anisotropic clinical MRI data. We propose a novel 2D pix2pix-based deep learning framework for simultaneous segmentation of ventricles and WMHs with the unique capability to distinguish between normal periventricular hyperintensities and pathological MS lesions. Our method was developed and validated on FLAIR MRI scans from 300 MS patients. Compared to established methods (SynthSeg, Atlas Matching, BIANCA, LST-LPA, LST-LGA, and WMH-SynthSeg), our approach achieved superior performance for both ventricle segmentation (Dice: 0.801+/-0.025, HD95: 18.46+/-7.1mm) and WMH segmentation (Dice: 0.624+/-0.061, precision: 0.755+/-0.161). Furthermore, our method successfully differentiated between normal and abnormal hyperintensities with a Dice coefficient of 0.647. Notably, our approach demonstrated exceptional computational efficiency, completing end-to-end processing in approximately 4 seconds per case, up to 36 times faster than baseline methods, while maintaining minimal resource requirements. This combination of improved accuracy, clinically relevant differentiation capability, and computational efficiency addresses critical limitations in current neuroimaging analysis, potentially enabling integration into routine clinical workflows and enhancing MS diagnosis and monitoring.
多发性硬化症(MS)的诊断和监测严重依赖于对大脑MRI生物标志物的准确评估,特别是脑白质高信号(WMHs)和脑室变化。当前的分割方法存在几个局限性:它们通常独立地分割这些结构,尽管存在病理生理关系;难以区分正常和病理性高信号;对于各向异性的临床MRI数据优化不足。我们提出了一种新型的基于二维pix2pix的深度学习框架,可以同时分割脑室和WMHs,具有区分正常脑室周围高信号和病理性MS病变的独特能力。我们的方法在来自300名MS患者的FLAIR MRI扫描上进行了开发和验证。与现有方法(SynthSeg、Atlas Matching、BIANCA、LST-LPA、LST-LGA和WMH-SynthSeg)相比,我们的方法在脑室分割(Dice:0.801+/-0.025,HD95:18.46+/-7.1mm)和WMH分割(Dice:0.624+/-0.061,精确度:0.755+/-0.161)方面表现出卓越的性能。此外,我们的方法成功地区分了正常和异常的高信号,Dice系数为0.647。值得注意的是,我们的方法在计算效率方面表现出色,每例病例的端到端处理时间约为4秒,比基线方法快36倍,同时保持最低的资源需求。这种集提高准确性、具有临床意义的鉴别能力和计算效率于一体的方法,解决了当前神经影像分析的关键局限性,有望融入常规临床工作流程,提高MS的诊断和监测水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 43 pages, 11 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的二维pix2pix框架,可同时分割脑室和脑白质高信号区(WMHs),并区分正常与病理性MS病变。在300名MS患者的FLAIR MRI扫描上验证,该方法的性能优于现有方法,计算效率高,为MS诊断和监测提供了重要改进。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种新型的基于深度学习的pix2pix框架,能同时分割脑室和WMHs。
- 该方法可以区分正常和病理性的MS病变。
- 方法在300名MS患者的FLAIR MRI扫描上进行了开发和验证。
- 相比现有方法,所提方法在脑室和WMHs分割上表现出卓越性能。
- 该方法具有高效的计算能力,能在约4秒内完成案例的端到端处理,比基线方法快36倍。
点此查看论文截图

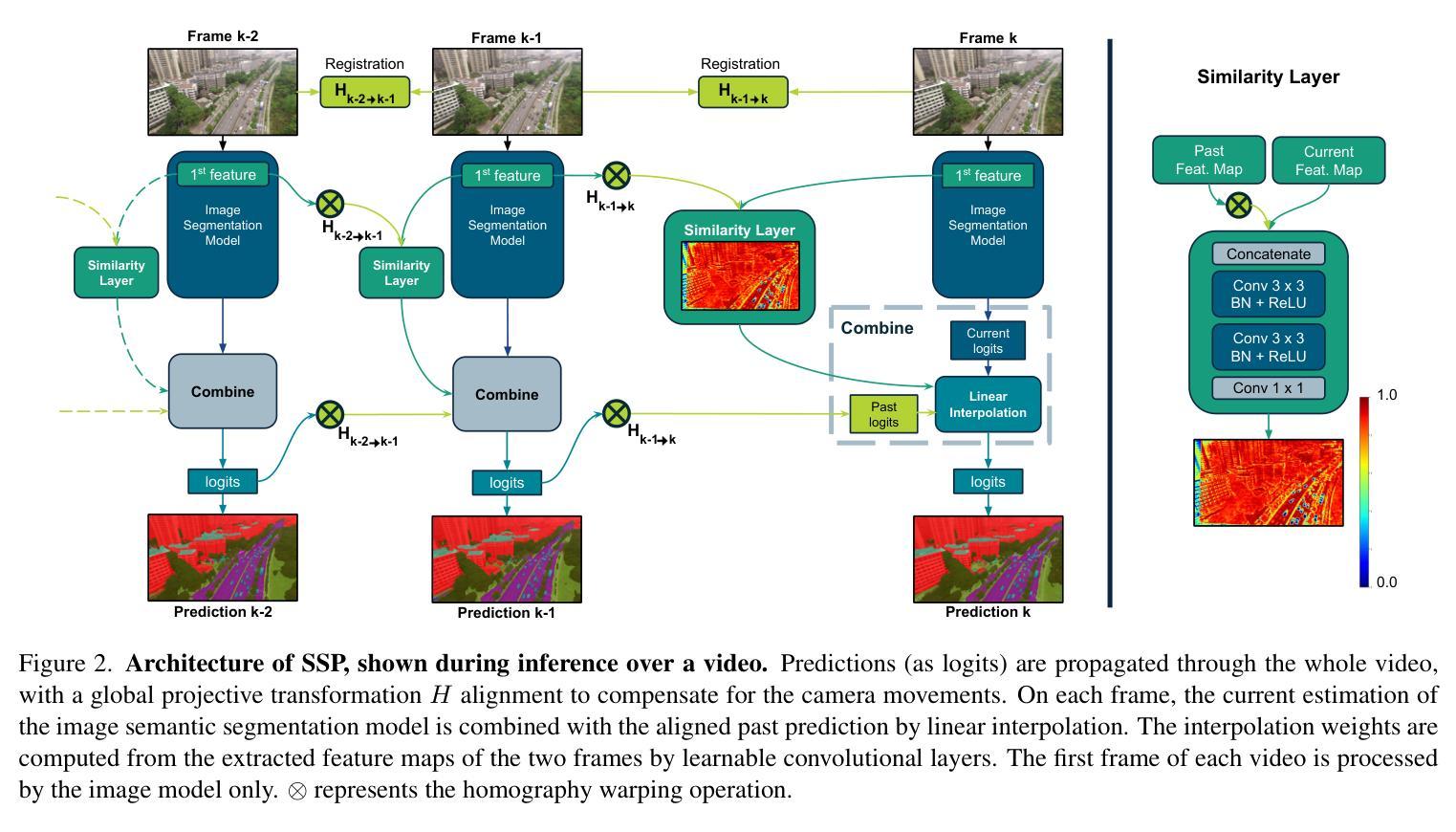
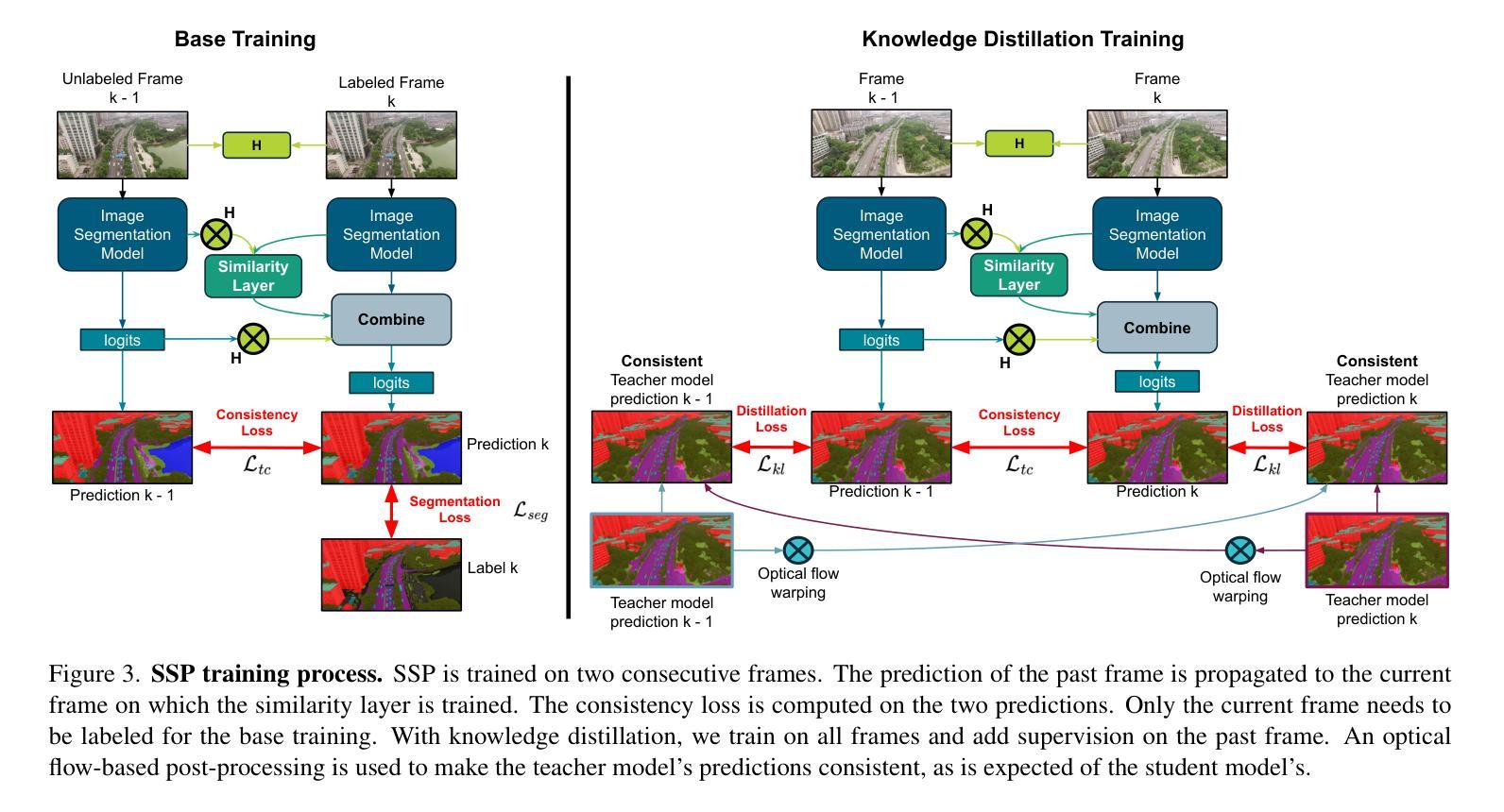
High Temporal Consistency through Semantic Similarity Propagation in Semi-Supervised Video Semantic Segmentation for Autonomous Flight
Authors:Cédric Vincent, Taehyoung Kim, Henri Meeß
Semantic segmentation from RGB cameras is essential to the perception of autonomous flying vehicles. The stability of predictions through the captured videos is paramount to their reliability and, by extension, to the trustworthiness of the agents. In this paper, we propose a lightweight video semantic segmentation approach-suited to onboard real-time inference-achieving high temporal consistency on aerial data through Semantic Similarity Propagation across frames. SSP temporally propagates the predictions of an efficient image segmentation model with global registration alignment to compensate for camera movements. It combines the current estimation and the prior prediction with linear interpolation using weights computed from the features similarities of the two frames. Because data availability is a challenge in this domain, we propose a consistency-aware Knowledge Distillation training procedure for sparsely labeled datasets with few annotations. Using a large image segmentation model as a teacher to train the efficient SSP, we leverage the strong correlations between labeled and unlabeled frames in the same training videos to obtain high-quality supervision on all frames. KD-SSP obtains a significant temporal consistency increase over the base image segmentation model of 12.5% and 6.7% TC on UAVid and RuralScapes respectively, with higher accuracy and comparable inference speed. On these aerial datasets, KD-SSP provides a superior segmentation quality and inference speed trade-off than other video methods proposed for general applications and shows considerably higher consistency. Project page: https://github.com/FraunhoferIVI/SSP.
从RGB相机进行语义分割对自主飞行车辆的感知至关重要。通过拍摄视频进行预测的稳定性对其可靠性至关重要,并且由此可以扩展到智能体的可信度。在本文中,我们提出了一种轻量级的视频语义分割方法,该方法适合在车载实时推理中使用,通过在帧之间传播语义相似性来实现高空数据的高时间一致性。SSP通过全局注册对齐临时传播高效图像分割模型的预测,以补偿相机移动。它结合当前估计和先前预测,利用两个帧的特征相似性计算的权重进行线性插值。由于本领域的数据可用性是一个挑战,我们针对少量标注的数据集提出了一种一致性感知的知识蒸馏训练程序。我们利用大型图像分割模型作为教师来训练高效的SSP,并充分利用同一训练视频中标注和未标注帧之间的强相关性,对所有帧进行高质量监督。KD-SSP在UAVid和RuralScapes上相较于基础图像分割模型分别实现了12.5%和6.7%的时间一致性增长,具有更高的准确性和相当的推理速度。在这些航空数据集中,KD-SSP相较于其他为通用应用提出的视频方法提供了更优越的分割质量和推理速度之间的权衡,并显示出明显更高的一致性。项目页面:https://github.com/FraunhoferIVI/SSP 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
本文提出了一种轻量级的视频语义分割方法,适用于自主飞行车辆的实时推理。该方法通过语义相似性传播(SSP)技术实现了高时空一致性,在航拍数据上具有良好的表现。同时,为了提高在数据稀缺环境下的模型性能,研究提出了一种一致性感知的知识蒸馏训练程序。项目页面:链接。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割对于自主飞行车辆的感知至关重要,预测的稳定性对于其可靠性和信任度至关重要。
- 提出了一种轻量级的视频语义分割方法,适合实时推理应用,能在航拍数据上实现高时空一致性。
- 利用语义相似性传播(SSP)技术结合全局注册对齐来补偿摄像头移动,通过线性插值将当前估计与先前预测结合起来。
- 在数据稀缺的情况下,提出一致性感知的知识蒸馏训练程序,使用大型图像分割模型作为教师模型进行训练。
- 该方法通过利用有标签和无标签帧之间的强相关性,对所有帧进行高质量监督。
- 与基础图像分割模型相比,KD-SSP在UAVid和RuralScapes数据集上实现了显著的时空一致性提升。
点此查看论文截图


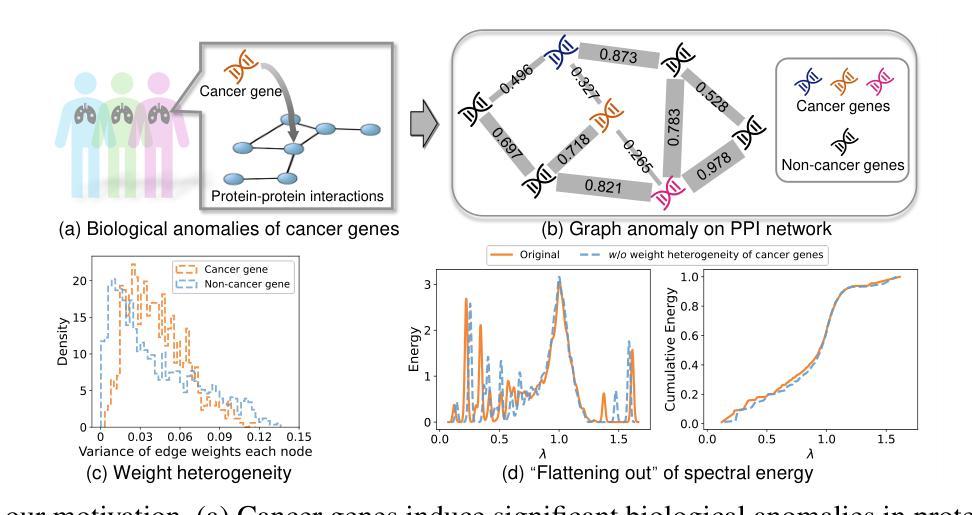
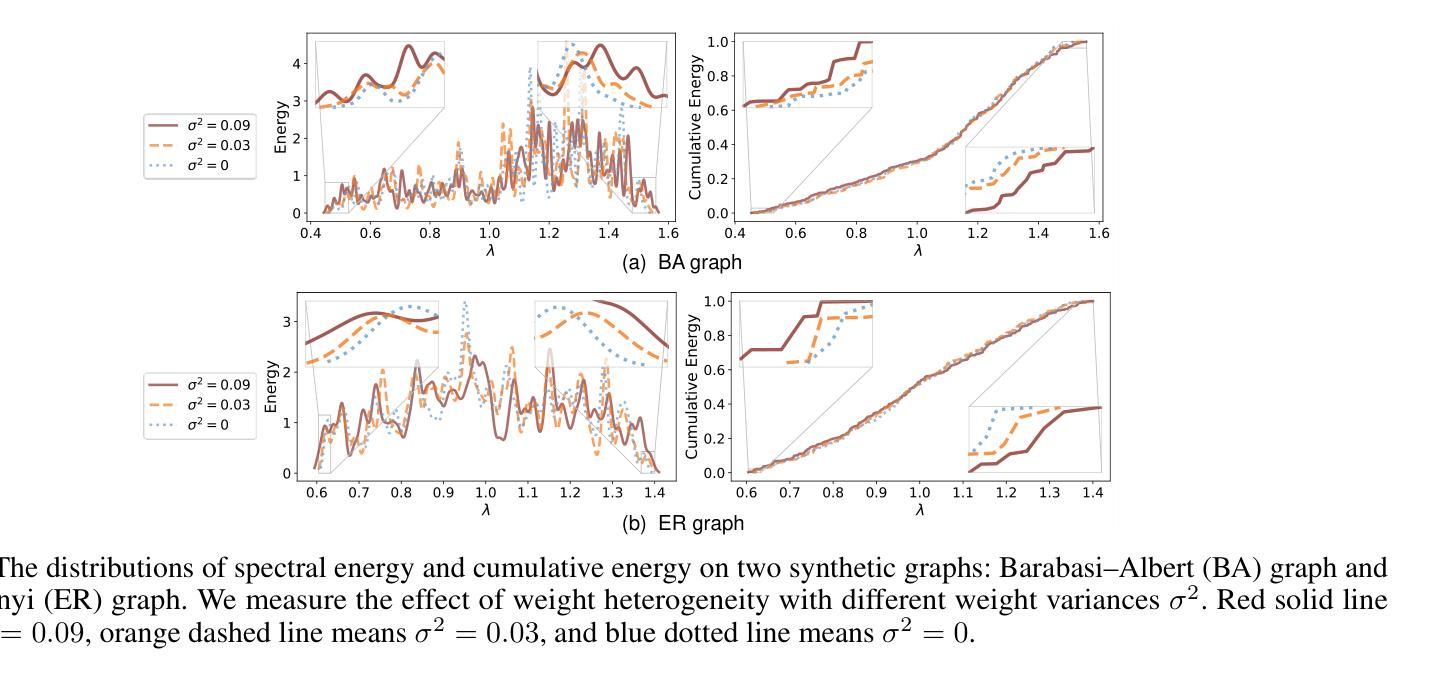
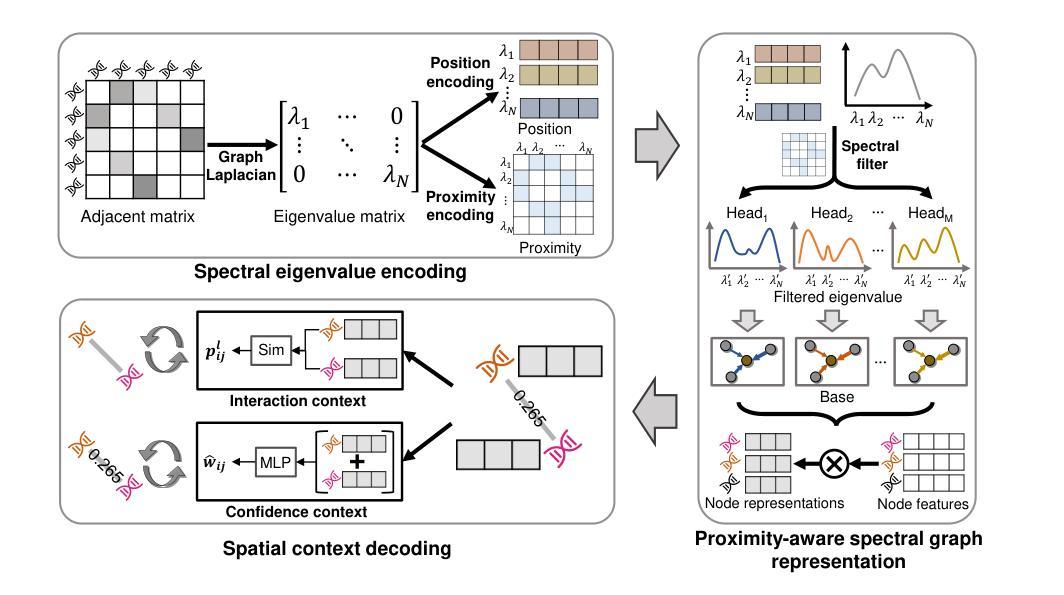
Rethinking Cancer Gene Identification through Graph Anomaly Analysis
Authors:Yilong Zang, Lingfei Ren, Yue Li, Zhikang Wang, David Antony Selby, Zheng Wang, Sebastian Josef Vollmer, Hongzhi Yin, Jiangning Song, Junhang Wu
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown promise in integrating protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks for identifying cancer genes in recent studies. However, due to the insufficient modeling of the biological information in PPI networks, more faithfully depiction of complex protein interaction patterns for cancer genes within the graph structure remains largely unexplored. This study takes a pioneering step toward bridging biological anomalies in protein interactions caused by cancer genes to statistical graph anomaly. We find a unique graph anomaly exhibited by cancer genes, namely weight heterogeneity, which manifests as significantly higher variance in edge weights of cancer gene nodes within the graph. Additionally, from the spectral perspective, we demonstrate that the weight heterogeneity could lead to the “flattening out” of spectral energy, with a concentration towards the extremes of the spectrum. Building on these insights, we propose the HIerarchical-Perspective Graph Neural Network (HIPGNN) that not only determines spectral energy distribution variations on the spectral perspective, but also perceives detailed protein interaction context on the spatial perspective. Extensive experiments are conducted on two reprocessed datasets STRINGdb and CPDB, and the experimental results demonstrate the superiority of HIPGNN.
图神经网络(GNNs)在整合蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络以识别癌症基因方面显示出潜力。然而,由于PPI网络中生物信息建模的不足,对于图形结构内癌症基因的复杂蛋白质相互作用模式的更忠实描述仍然未得到充分探索。本研究迈出了将蛋白质相互作用中的生物异常与统计图异常联系起来的第一步。我们发现癌症基因表现出一种独特的图形异常,即权重异质性,它表现为图形内癌症基因节点的边权重方差显著较高。此外,从光谱角度,我们证明了权重异质性可能导致光谱能量的“平坦化”,并集中在光谱的极端部分。基于这些见解,我们提出了分层透视图神经网络(HIPGNN),它不仅从光谱角度确定光谱能量分布的变化,而且在空间角度上感知详细的蛋白质相互作用上下文。在重新处理过的STRINGdb和CPDB两个数据集上进行了大量实验,实验结果证明了HIPGNN的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探索了图神经网络在癌症基因蛋白质交互网络中的应用,并发现癌症基因在图中表现出独特的权重异质性特征。提出一种层次视角图神经网络(HIPGNN),能同时从光谱和空间角度感知蛋白质交互上下文,并通过实验验证了其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 图神经网络在整合癌症基因蛋白质交互网络方面展现出潜力。
- 癌症基因在图中表现出独特的权重异质性特征。
- 权重异质性会导致光谱能量的“扁平化”,并向光谱极端集中。
- 层次视角图神经网络(HIPGNN)能同时从光谱和空间角度处理数据。
- HIPGNN能确定光谱能量的分布变化,并感知蛋白质交互的详细上下文。
- 在两个重新处理的数据集STRINGdb和CPDB上进行了广泛实验。
点此查看论文截图

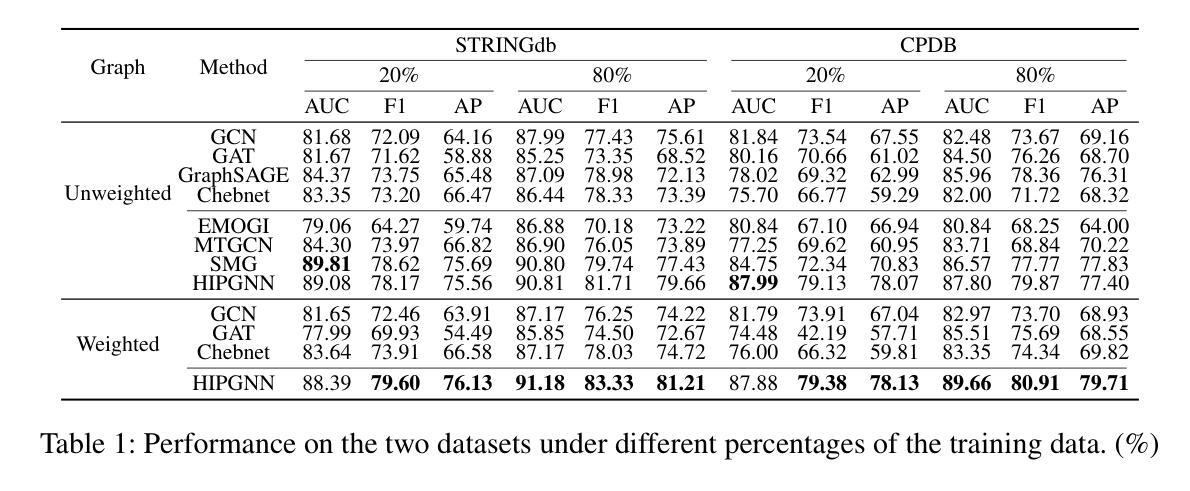
MvKeTR: Chest CT Report Generation with Multi-View Perception and Knowledge Enhancement
Authors:Xiwei Deng, Xianchun He, Jianfeng Bao, Yudan Zhou, Shuhui Cai, Congbo Cai, Zhong Chen
CT report generation (CTRG) aims to automatically generate diagnostic reports for 3D volumes, relieving clinicians’ workload and improving patient care. Despite clinical value, existing works fail to effectively incorporate diagnostic information from multiple anatomical views and lack related clinical expertise essential for accurate and reliable diagnosis. To resolve these limitations, we propose a novel Multi-view perception Knowledge-enhanced TansfoRmer (MvKeTR) to mimic the diagnostic workflow of clinicians. Just as radiologists first examine CT scans from multiple planes, a Multi-View Perception Aggregator (MVPA) with view-aware attention is proposed to synthesize diagnostic information from multiple anatomical views effectively. Then, inspired by how radiologists further refer to relevant clinical records to guide diagnostic decision-making, a Cross-Modal Knowledge Enhancer (CMKE) is devised to retrieve the most similar reports based on the query volume to incorporate domain knowledge into the diagnosis procedure. Furthermore, instead of traditional MLPs, we employ Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) as the fundamental building blocks of both modules, which exhibit superior parameter efficiency and reduced spectral bias to better capture high-frequency components critical for CT interpretation while mitigating overfitting. Extensive experiments on the public CTRG-Chest-548 K dataset demonstrate that our method outpaces prior state-of-the-art (SOTA) models across almost all metrics. The code is available at https://github.com/xiweideng/MvKeTR.
CT报告生成(CTRG)旨在自动为三维体积生成诊断报告,减轻临床医生的工作量,提高患者护理的质量。尽管具有临床价值,但现有工作未能有效地结合多个解剖视角的诊断信息,并缺乏准确可靠诊断所需的相关临床经验。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的多视角感知知识增强转换器(MvKeTR)来模拟临床医生的诊断工作流程。就像放射科医生首先会从多个平面检查CT扫描一样,我们提出了一个具有视图感知注意力的多视图感知聚合器(MVPA),以有效地合成多个解剖视角的诊断信息。接着,受放射科医生如何进一步参考相关病历以指导诊断决策过程的启发,我们设计了一个跨模态知识增强器(CMKE),以根据查询体积检索最相似的报告,将领域知识融入诊断过程。此外,与传统的多层感知器不同,我们采用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)作为两个模块的基本构建块,它们在参数效率方面表现出优势,并降低了光谱偏差,以更好地捕捉对CT解释至关重要的高频成分,同时减轻过拟合。在公共CTRG-Chest-548K数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在几乎所有指标上都超过了最新的先进技术模型。代码可在https://github.com/xiweideng/MvKeTR上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MvKeTR的多视角感知知识增强转换器,旨在模仿医生的诊断流程,自动生成三维体积的诊断报告。通过使用多视角感知聚合器和跨模态知识增强器,该方法能有效融合多视角诊断信息并融入领域知识,提高诊断的准确性和可靠性。采用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络作为模块的基本构建块,以提高参数效率和降低光谱偏差,更好地捕捉CT解读中的高频成分。在公共CTRG-Chest-548K数据集上的实验表明,该方法在几乎所有指标上都超过了现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- CT报告生成(CTRG)旨在自动为3D体积生成诊断报告,减轻医生工作量,提高患者护理质量。
- 现有方法未能有效融合多视角诊断信息,缺乏临床专业知识,影响诊断和可靠性。
- MvKeTR模型通过模仿医生诊断流程,使用多视角感知聚合器和跨模态知识增强器解决这些问题。
- 多视角感知聚合器(MVPA)具有视图感知注意力机制,能有效合成多视角诊断信息。
- 跨模态知识增强器(CMKE)通过检索最相似的报告,将领域知识融入诊断过程。
- 采用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)作为模块基本构建块,提高参数效率和降低光谱偏差,更好地捕捉CT解读高频成分。
- 在公共数据集上的实验表明,MvKeTR模型在各项指标上超越现有先进技术。
点此查看论文截图

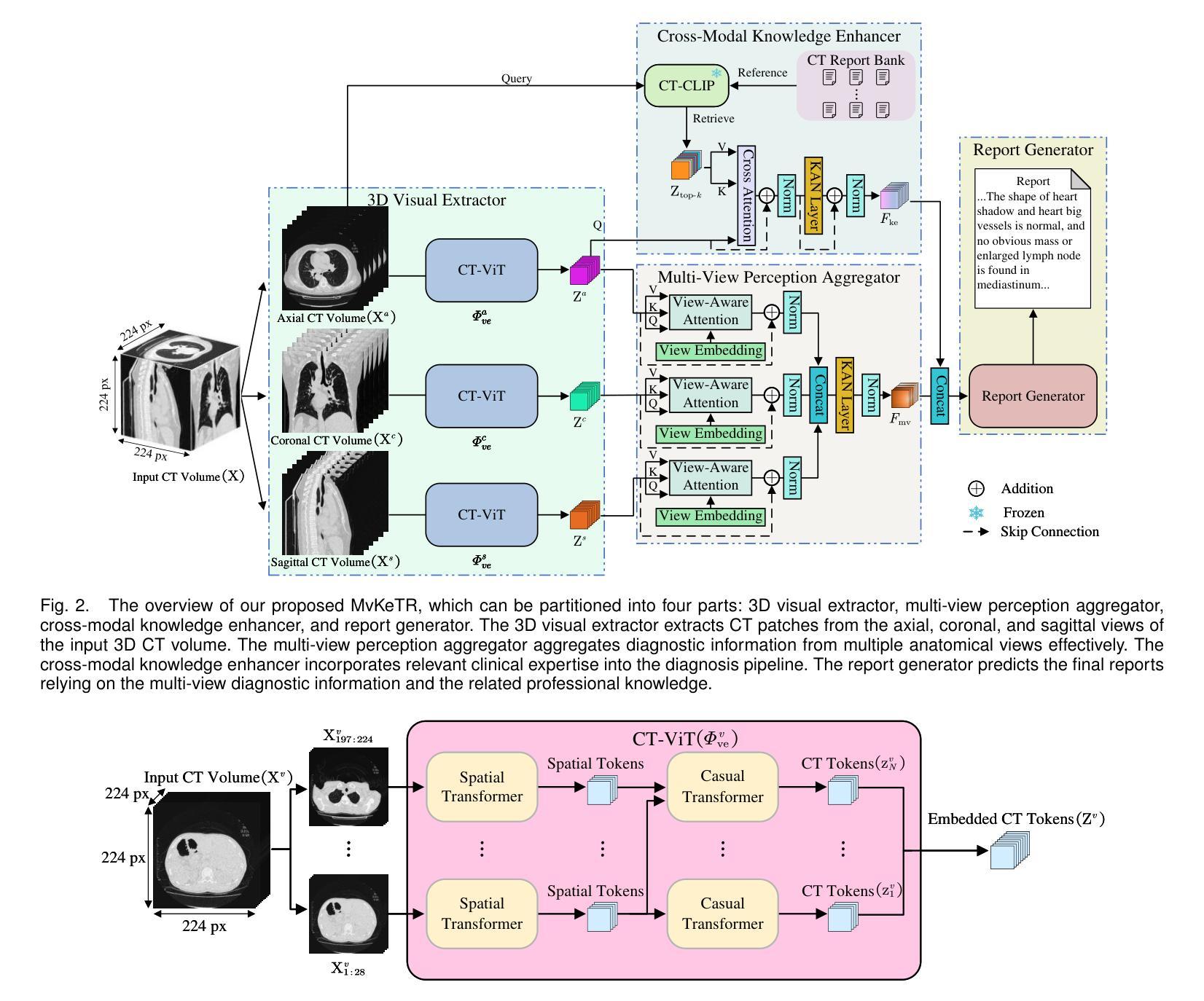
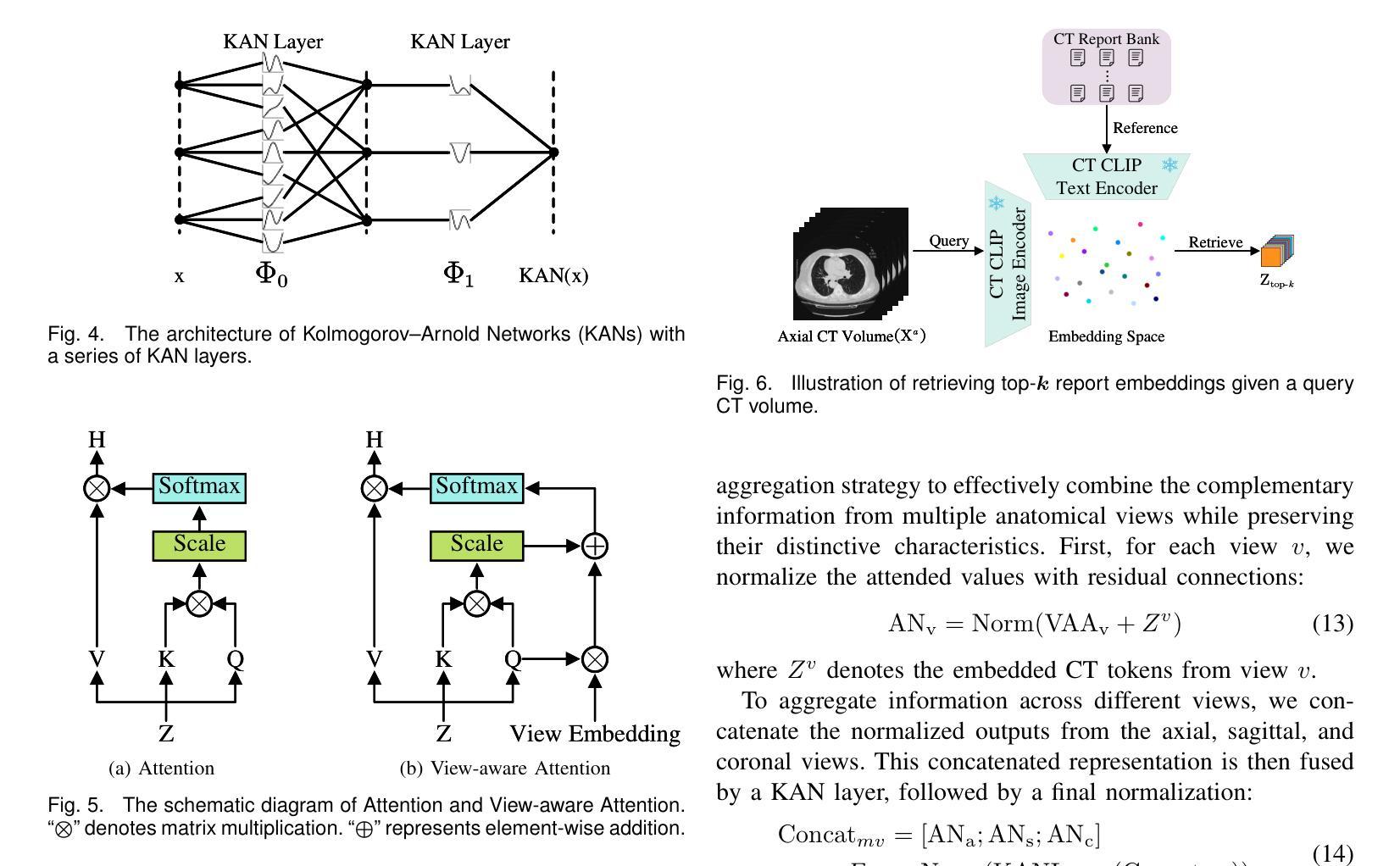
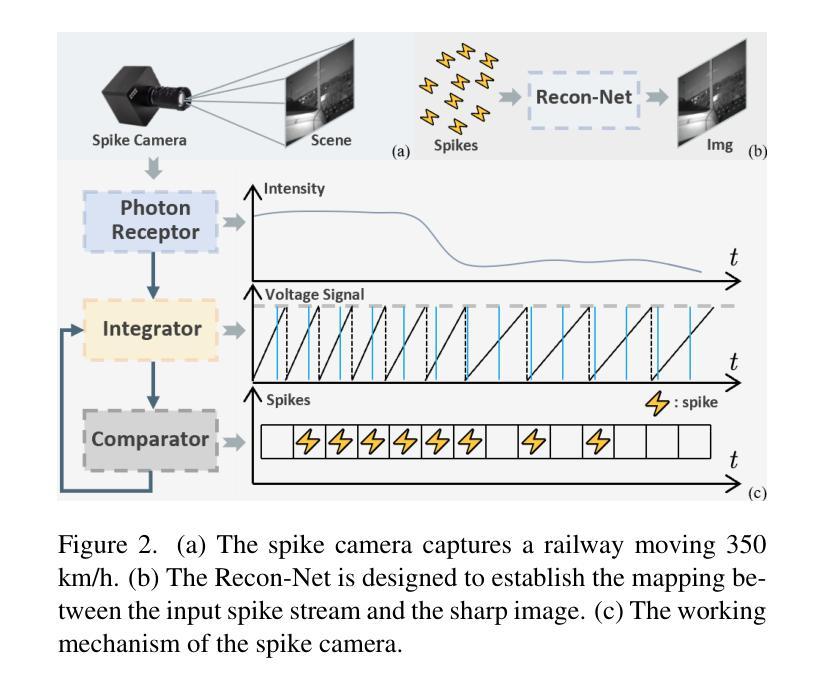
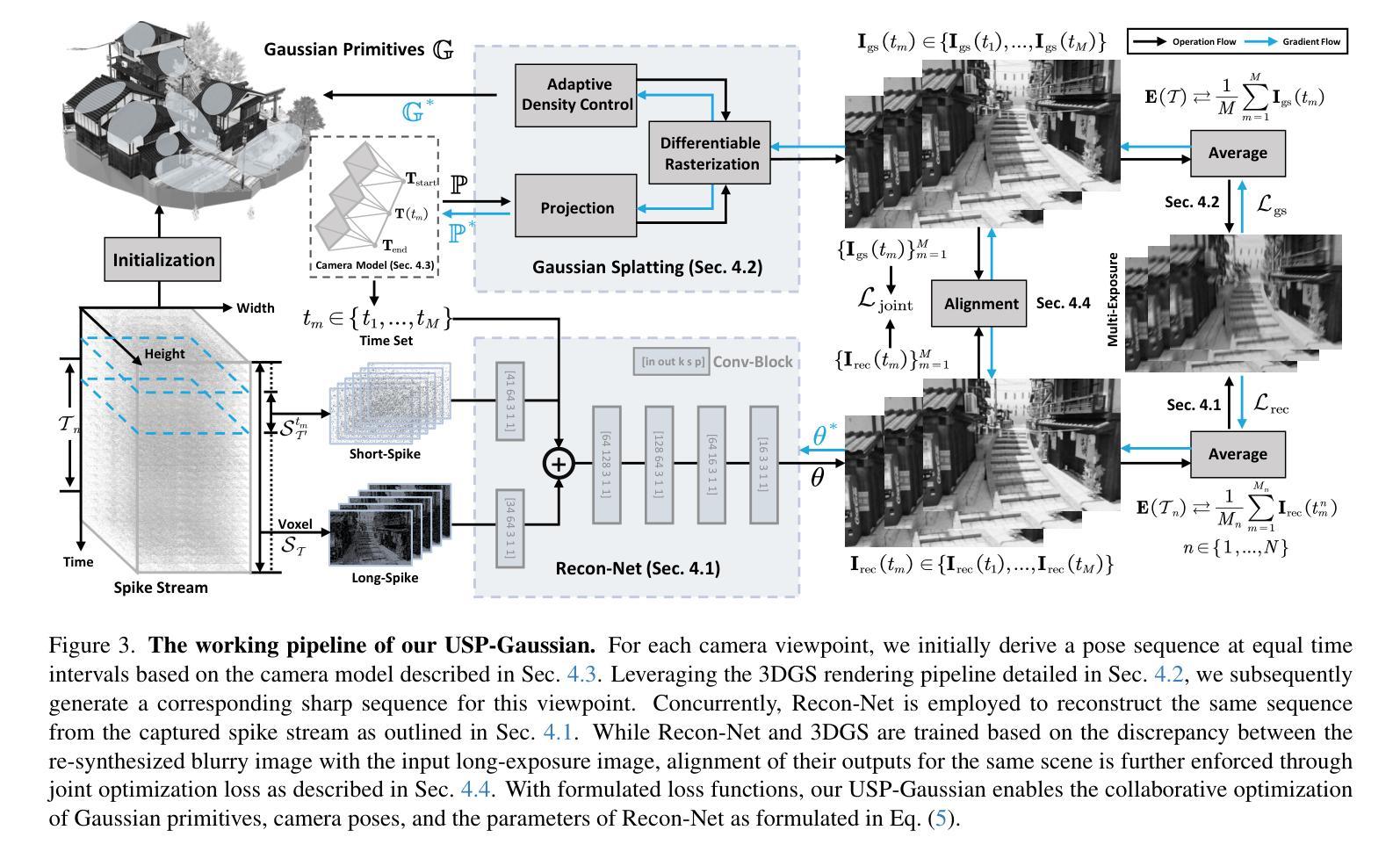
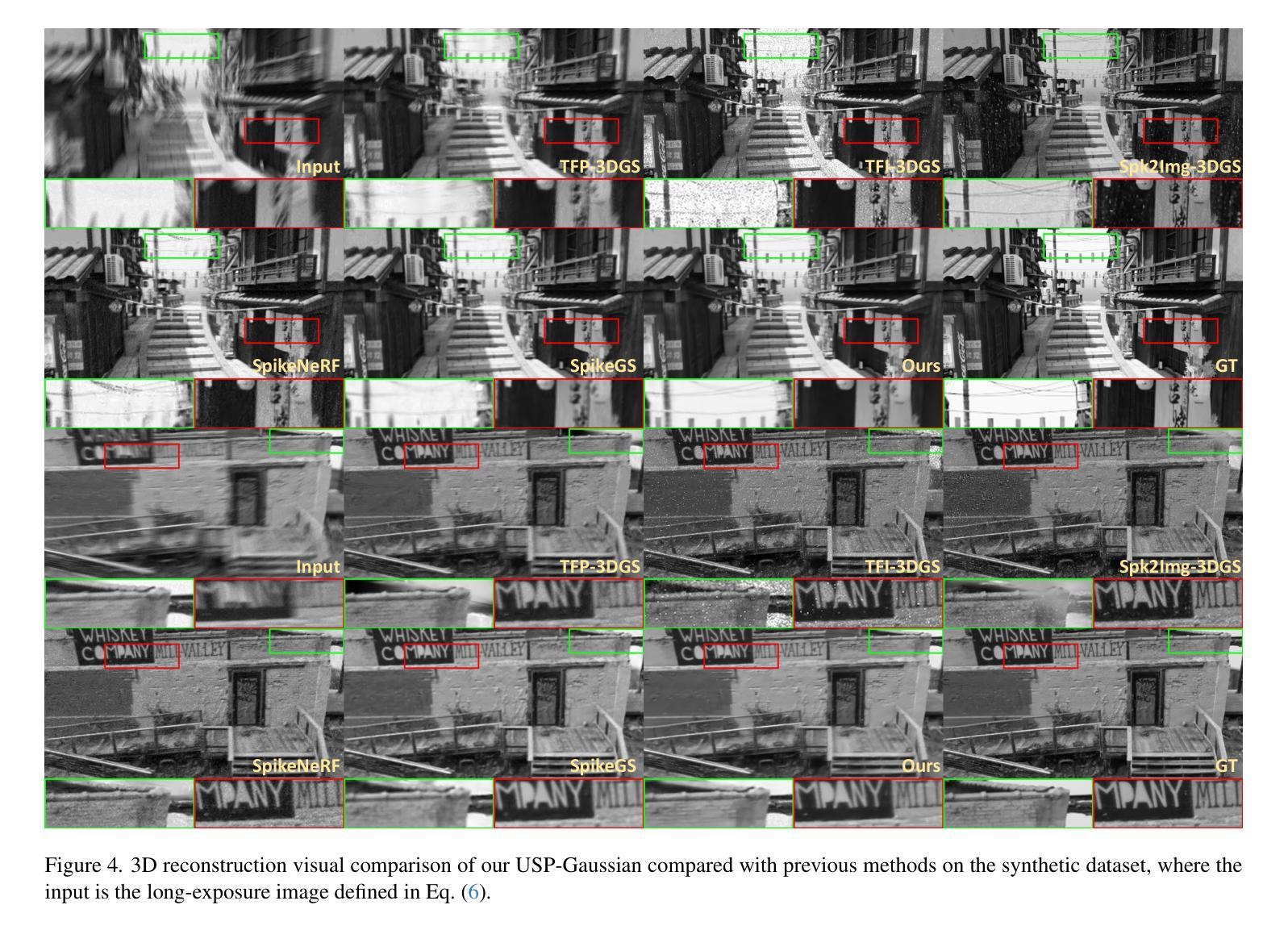
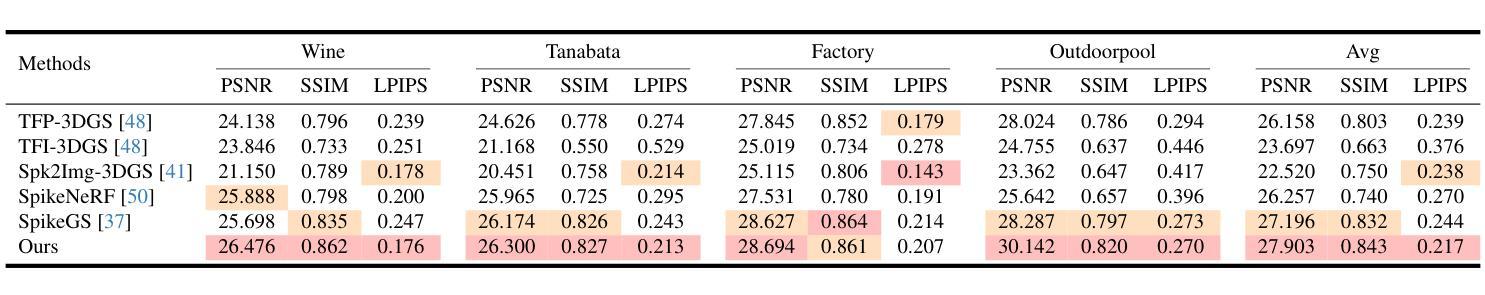
USP-Gaussian: Unifying Spike-based Image Reconstruction, Pose Correction and Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Kang Chen, Jiyuan Zhang, Zecheng Hao, Yajing Zheng, Tiejun Huang, Zhaofei Yu
Spike cameras, as an innovative neuromorphic camera that captures scenes with the 0-1 bit stream at 40 kHz, are increasingly employed for the 3D reconstruction task via Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) or 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Previous spike-based 3D reconstruction approaches often employ a casecased pipeline: starting with high-quality image reconstruction from spike streams based on established spike-to-image reconstruction algorithms, then progressing to camera pose estimation and 3D reconstruction. However, this cascaded approach suffers from substantial cumulative errors, where quality limitations of initial image reconstructions negatively impact pose estimation, ultimately degrading the fidelity of the 3D reconstruction. To address these issues, we propose a synergistic optimization framework, \textbf{USP-Gaussian}, that unifies spike-based image reconstruction, pose correction, and Gaussian splatting into an end-to-end framework. Leveraging the multi-view consistency afforded by 3DGS and the motion capture capability of the spike camera, our framework enables a joint iterative optimization that seamlessly integrates information between the spike-to-image network and 3DGS. Experiments on synthetic datasets with accurate poses demonstrate that our method surpasses previous approaches by effectively eliminating cascading errors. Moreover, we integrate pose optimization to achieve robust 3D reconstruction in real-world scenarios with inaccurate initial poses, outperforming alternative methods by effectively reducing noise and preserving fine texture details. Our code, data and trained models will be available at https://github.com/chenkang455/USP-Gaussian.
神经形态相机(Spike cameras)是一种创新型的神经形态摄像头,能够以每秒40千赫的速度捕捉场景的零到一比特流。它们正越来越多地被用于通过神经网络辐射场(NeRF)或三维高斯涂鸦(3DGS)执行三维重建任务。以前基于脉冲的三维重建方法通常采用级联管道:首先使用基于现有脉冲到图像重建算法的脉冲流高质量图像重建,然后进行相机姿态估计和三维重建。然而,这种级联方法存在大量累积误差问题,初始图像重建的质量限制会对姿态估计产生负面影响,最终降低三维重建的保真度。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种协同优化框架USP-Gaussian,该框架将基于脉冲的图像重建、姿态校正和高斯涂鸦统一到一个端到端的框架中。利用三维高斯涂鸦的多视角一致性以及脉冲相机的运动捕捉能力,我们的框架能够实现联合迭代优化,无缝集成脉冲到图像网络和三维高斯涂鸦之间的信息。在具有准确姿态的合成数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法通过有效消除级联误差超越了以前的方法。此外,我们集成了姿态优化以实现鲁棒的三维重建,在具有不准确初始姿态的现实世界场景中表现优异,通过有效降低噪声并保留精细纹理细节而优于其他方法。我们的代码、数据和训练模型将在https://github.com/chenkang455/USP-Gaussian上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯扩展(3DGS)技术的脉冲相机3D重建新方法——USP-Gaussian协同优化框架。针对传统脉冲相机三维重建过程中的级联误差问题,USP-Gaussian实现了脉冲相机图像重建、姿态校正和高斯扩展的端到端集成优化,提高了重建精度和鲁棒性。通过利用多视角一致性和脉冲相机的运动捕捉能力,USP-Gaussian在合成数据集和真实世界场景中均展现出优异的性能表现。代码和模型已公开于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键要点总结:
- Spike相机通过捕捉场景中的0-1位流实现场景重建,频率高达40 kHz。
- 传统脉冲相机三维重建方法采用级联处理流程,存在累积误差问题。
- USP-Gaussian框架通过整合脉冲相机图像重建、姿态校正和高斯扩展技术,实现了端到端的协同优化。
- 多视角一致性和脉冲相机的运动捕捉能力为USP-Gaussian提供了强大支持。
- USP-Gaussian在合成数据集上的实验验证了其消除级联误差的能力。
- 在真实世界场景中,USP-Gaussian通过集成姿态优化实现了稳健的3D重建,有效减少噪声并保留精细纹理细节。
点此查看论文截图
Visual Prompt Engineering for Vision Language Models in Radiology
Authors:Stefan Denner, Markus Bujotzek, Dimitrios Bounias, David Zimmerer, Raphael Stock, Klaus Maier-Hein
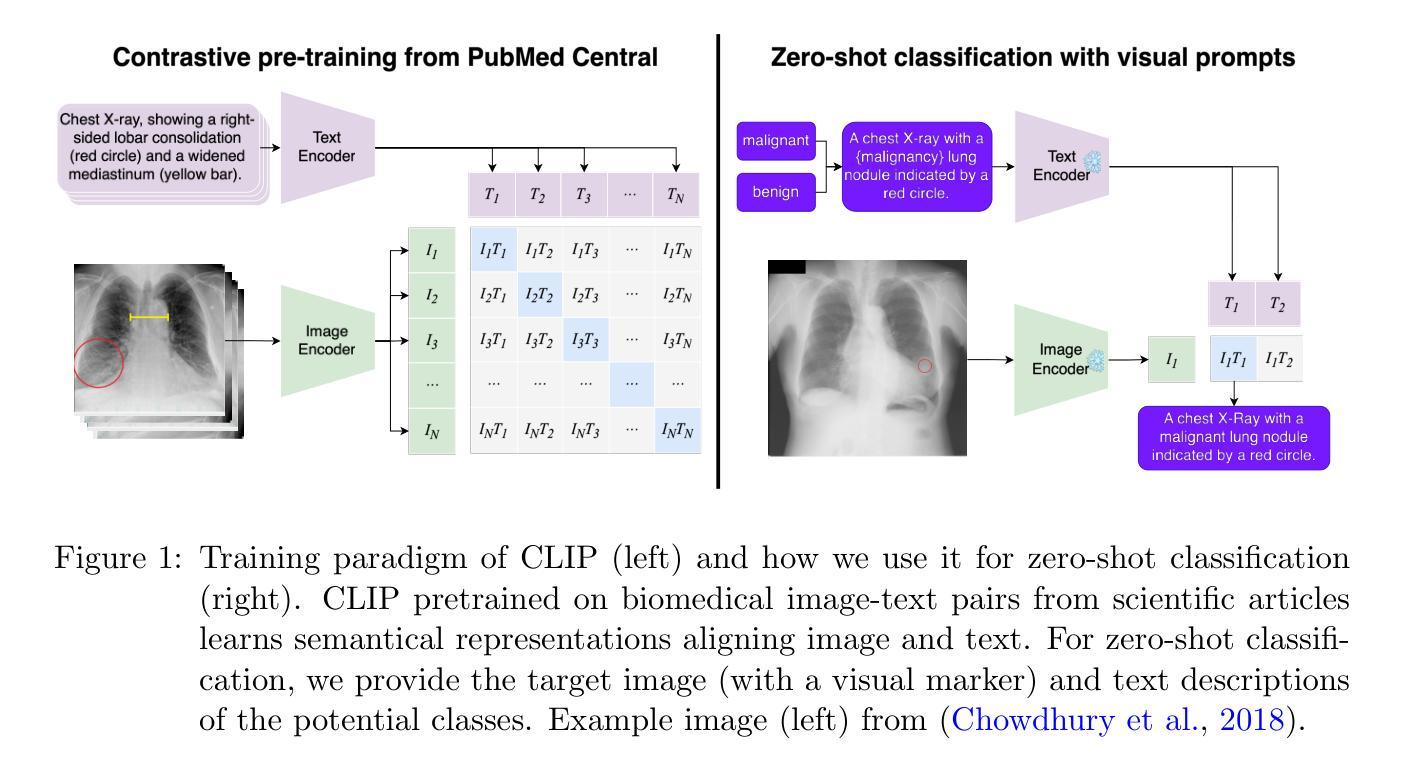
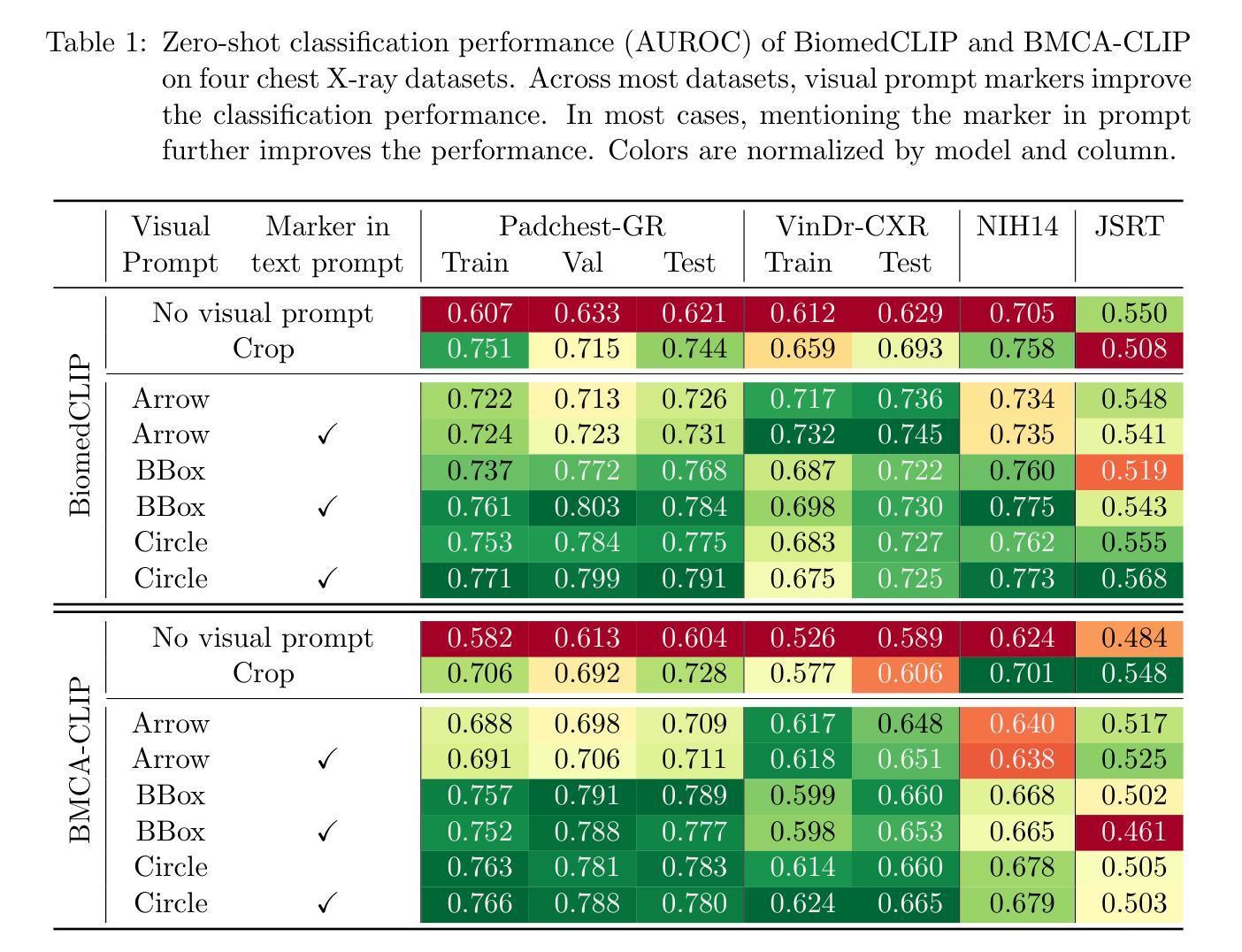
Medical image classification plays a crucial role in clinical decision-making, yet most models are constrained to a fixed set of predefined classes, limiting their adaptability to new conditions. Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) offers a promising solution by enabling zero-shot classification through multimodal large-scale pretraining. However, while CLIP effectively captures global image content, radiology requires a more localized focus on specific pathology regions to enhance both interpretability and diagnostic accuracy. To address this, we explore the potential of incorporating visual cues into zero-shot classification, embedding visual markers, such as arrows, bounding boxes, and circles, directly into radiological images to guide model attention. Evaluating across four public chest X-ray datasets, we demonstrate that visual markers improve AUROC by up to 0.185, highlighting their effectiveness in enhancing classification performance. Furthermore, attention map analysis confirms that visual cues help models focus on clinically relevant areas, leading to more interpretable predictions.To support further research, we use public datasets and provide our codebase and preprocessing pipeline under https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/VPE-in-Radiology, serving as a reference point for future work on localized classification in medical imaging.
医学图像分类在临床决策中起着至关重要的作用,然而大多数模型都局限于一组预定义的类别,限制了它们对新条件的适应性。对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)通过多模式大规模预训练提供了零样本分类的有前途的解决方案。然而,虽然CLIP能够有效地捕获全局图像内容,但放射学需要更侧重于特定的病理区域,以提高可解释性和诊断准确性。为了解决这一问题,我们探索将视觉线索融入零样本分类的潜力,直接在放射图像中嵌入视觉标记,如箭头、边界框和圆圈,以引导模型注意力。在四个公共胸部X射线数据集上的评估表明,视觉标记提高了AUROC值达0.185,证明了它们在提高分类性能方面的有效性。此外,注意力图分析证实,视觉线索有助于模型关注临床相关区域,从而做出更可预测的解释。为了支持进一步研究,我们使用公共数据集,并在https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/VPE-in-Radiology上提供我们的代码库和预处理管道,作为未来医学成像中局部化分类研究的一个参考点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ECCV 2024 Workshop on Emergent Visual Abilities and Limits of Foundation Models & Medical Imaging with Deep Learning 2025
Summary
医学图像分类在临床决策中至关重要,但大多数模型受限于固定的预定义类别,难以适应新情况。对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)通过多模态大规模预训练实现零样本分类,为解决此问题提供了希望。然而,CLIP虽然能捕捉图像全局内容,但放射学需要更专注于特定病理区域以提高解释和诊断准确性。本研究探索将视觉线索融入零样本分类的潜力,通过在放射图像中嵌入视觉标记(如箭头、边界框和圆圈)来引导模型注意力。在四个公共胸部X射线数据集上的评估表明,视觉标记提高了AUROC达0.185,验证了其在提高分类性能方面的有效性。此外,注意力图分析证实视觉线索有助于模型关注临床相关区域,产生更可解释的预测。相关代码和预处理管道可通过链接https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/VPE-in-Radiology获取,为医学成像中的局部化分类提供未来研究的参考点。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类在临床决策中具有重要作用,但模型受限于预定义类别,需要提高适应性。
- 对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)提供零样本分类解决方案,但全局分类在放射学中需更关注特定区域。
- 融入视觉线索(如箭头、边界框和圆圈)可有效提高模型在医学图像上的分类性能。
- 在四个公共胸部X射线数据集上的评估显示,使用视觉标记提高了AUROC值。
- 注意力图分析证实视觉线索有助于模型关注临床相关区域,提升预测的可解释性。
- 研究者提供了代码库和预处理管道,便于未来对医学成像局部化分类的研究。
点此查看论文截图

FusionSAM: Visual Multi-Modal Learning with Segment Anything
Authors:Daixun Li, Weiying Xie, Mingxiang Cao, Yunke Wang, Yusi Zhang, Leyuan Fang, Yunsong Li, Chang Xu
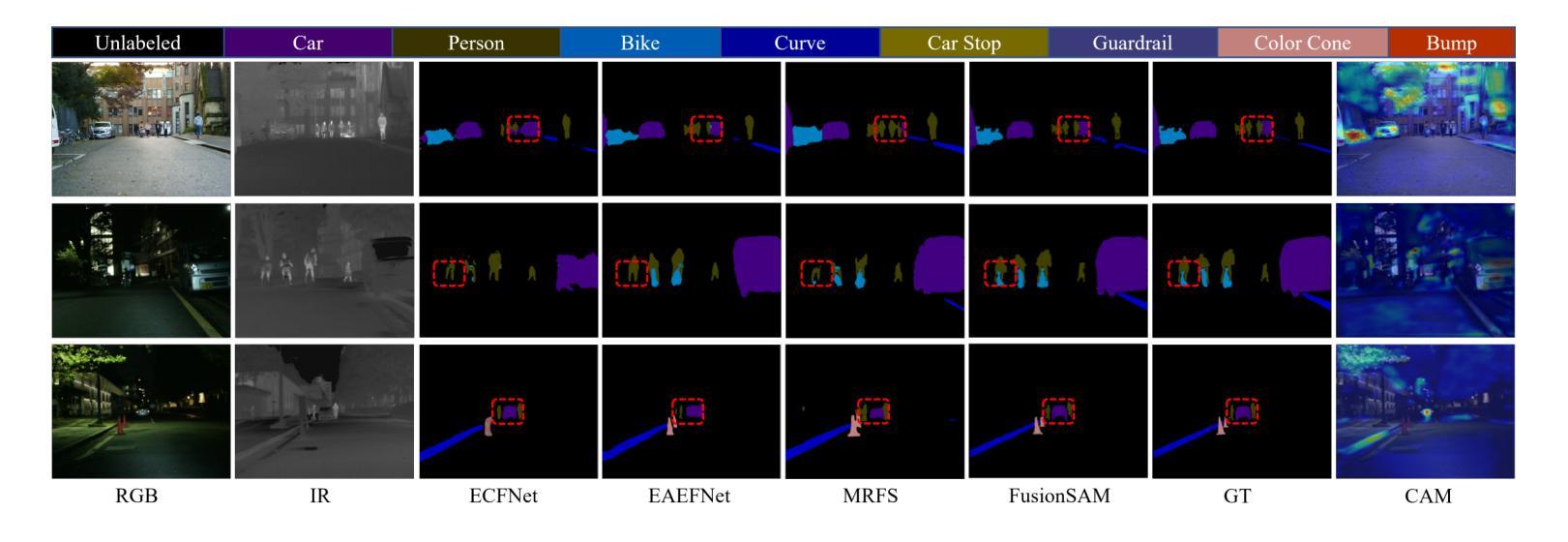
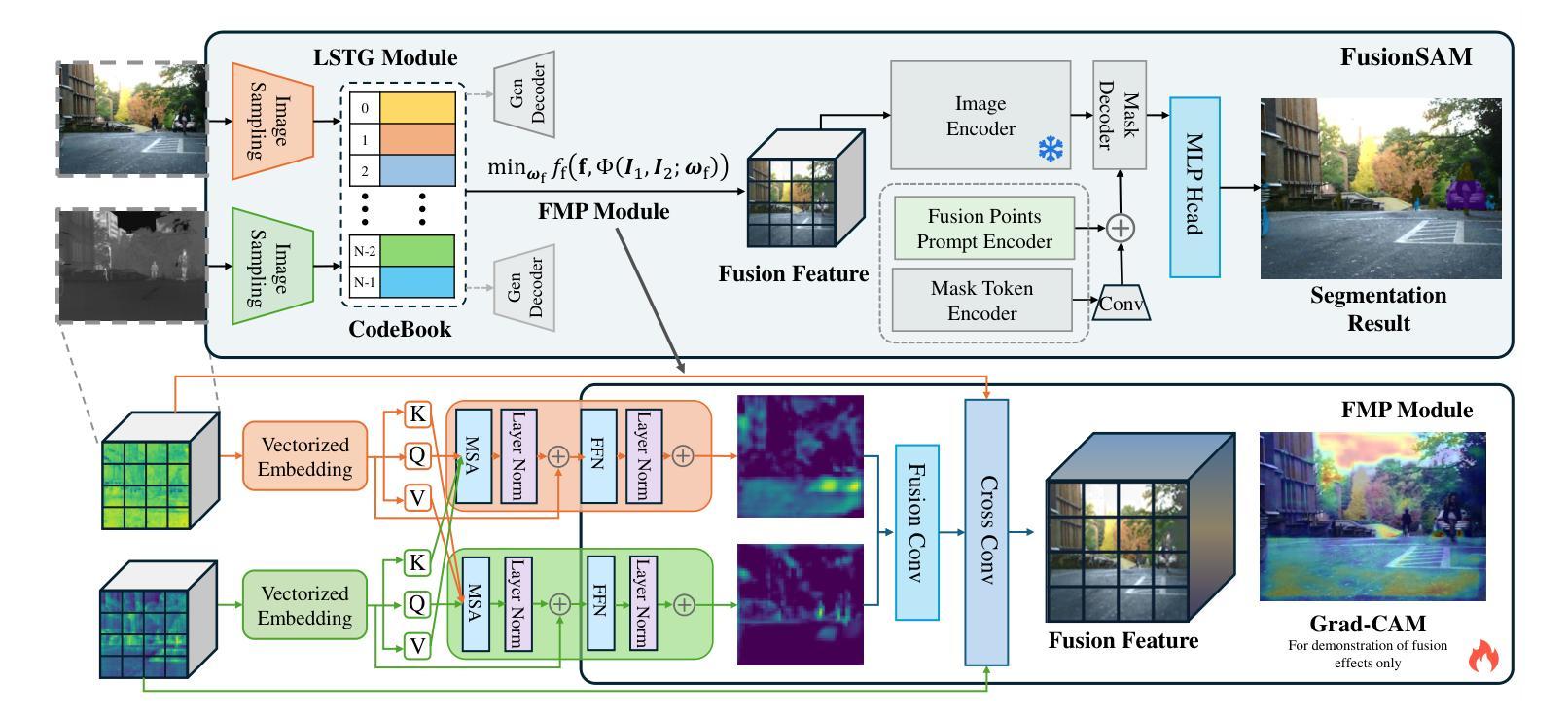
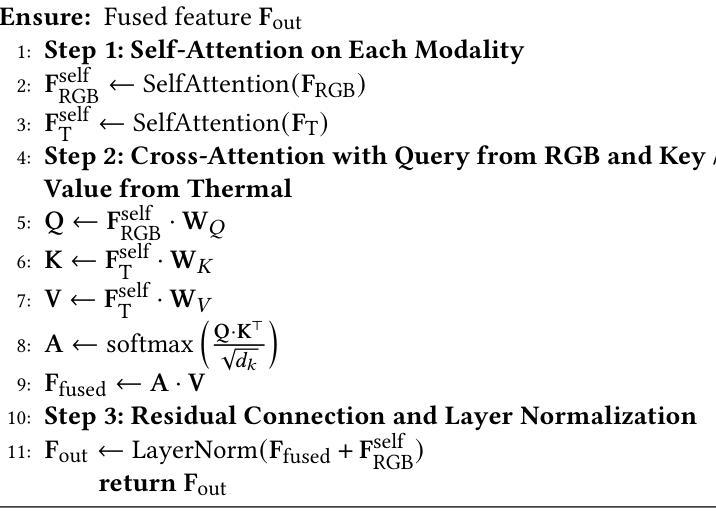
Multimodal image fusion and semantic segmentation are critical for autonomous driving. Despite advancements, current models often struggle with segmenting densely packed elements due to a lack of comprehensive fusion features for guidance during training. While the Segment Anything Model (SAM) allows precise control during fine-tuning through its flexible prompting encoder, its potential remains largely unexplored in the context of multimodal segmentation for natural images. In this paper, we introduce SAM into multimodal image segmentation for the first time, proposing a novel framework that combines Latent Space Token Generation (LSTG) and Fusion Mask Prompting (FMP) modules. This approach transforms the training methodology for multimodal segmentation from a traditional black-box approach to a controllable, prompt-based mechanism. Specifically, we obtain latent space features for both modalities through vector quantization and embed them into a cross-attention-based inter-domain fusion module to establish long-range dependencies between modalities. We then use these comprehensive fusion features as prompts to guide precise pixel-level segmentation. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms SAM and SAM2 in multimodal autonomous driving scenarios, achieving an average improvement of 4.1$%$ over the state-of-the-art method in segmentation mIoU, and the performance is also optimized in other multi-modal visual scenes.
多模态图像融合和语义分割对于自动驾驶至关重要。尽管有所进展,但当前模型在分割密集元素时经常遇到困难,因为在训练过程中缺乏全面的融合特征作为指导。虽然Segment Anything Model(SAM)通过其灵活的提示编码器允许微调过程中的精确控制,但在自然图像的多模态分割背景下,其在该领域的潜力尚未得到广泛探索。在本文中,我们首次将SAM引入多模态图像分割,提出了一种结合潜在空间令牌生成(Latent Space Token Generation,LSTG)和融合掩码提示(Fusion Mask Prompting,FMP)模块的新型框架。该方法将多模态分割的训练方法从传统黑箱方法转变为可控的基于提示的机制。具体来说,我们通过向量量化获得两种模态的潜在空间特征,并将其嵌入基于交叉注意力的跨域融合模块中,以在模态之间建立远程依赖关系。然后,我们将这些全面的融合特征作为提示来指导精确的像素级分割。在多个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在多种模态的自动驾驶场景中显著优于SAM和SAM2,在分割mIoU方面比最新技术平均提高了4.1%,并且在其他多模态视觉场景中的性能也得到了优化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文将Segment Anything Model(SAM)引入多模态图像分割中,提出了一种新的结合Latent Space Token Generation(LSTG)和Fusion Mask Prompting(FMP)模块的方法。该方法通过向量量化和跨域融合模块,获得两种模态的潜在空间特征,建立模态间的长程依赖关系,并利用这些综合融合特征作为提示来指导精确的像素级分割。在多个公共数据集上的实验表明,该方法在多模态自动驾驶场景中的表现显著优于SAM和SAM2,在分割mIoU上平均提高了4.1%,并且在其他多模态视觉场景中的性能也得到了优化。
Key Takeaways
- 本文首次将Segment Anything Model (SAM) 引入多模态图像分割领域。
- 提出了一种结合Latent Space Token Generation (LSTG) 和Fusion Mask Prompting (FMP) 模块的新框架。
- 通过向量量化和跨域融合模块,获得两种模态的潜在空间特征。
- 建立模态间的长程依赖关系,并利用综合融合特征作为提示,指导精确的像素级分割。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验表明,该方法在多模态自动驾驶场景中的表现优于SAM和SAM2。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法在分割mIoU上平均提高了4.1%。
点此查看论文截图


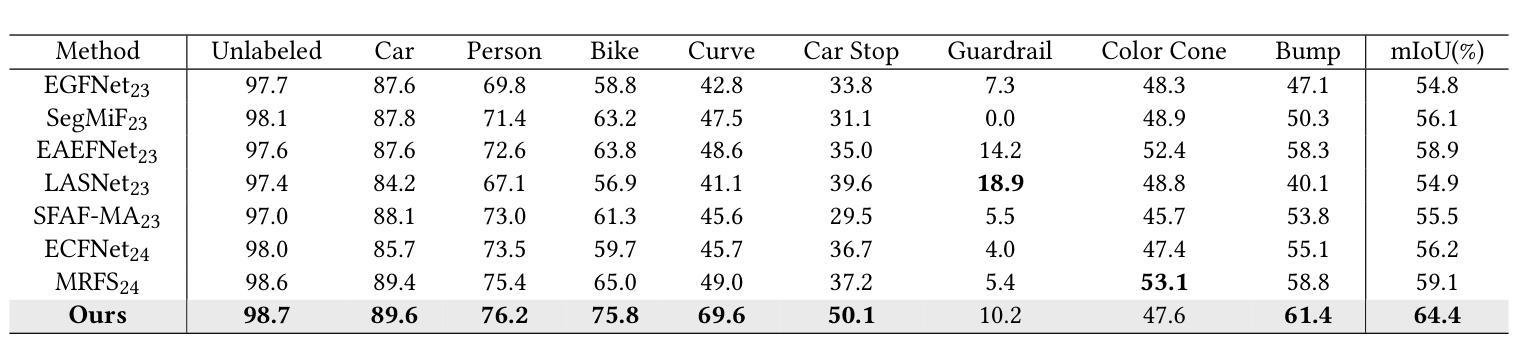
Improved Baselines with Synchronized Encoding for Universal Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Sihan Yang, Jiadong Feng, Xuande Mi, Haixia Bi, Hai Zhang, Jian Sun
Large foundation models, known for their strong zero-shot generalization capabilities, can be applied to a wide range of downstream tasks. However, developing foundation models for medical image segmentation poses a significant challenge due to the domain gap between natural and medical images. While fine-tuning techniques based on the Segment Anything Model (SAM) have been explored, they primarily focus on scaling up data or refining inference strategies without incorporating domain-specific architectural designs, limiting their zero-shot performance. To optimize segmentation performance under standard inference settings and provide a strong baseline for future research, we introduce SyncSAM, which employs a synchronized dual-branch encoder that integrates convolution and Transformer features in a synchronized manner to enhance medical image encoding, and a multi-scale dual-branch decoder to preserve image details. SyncSAM is trained on two of the largest medical image segmentation datasets, SA-Med2D-20M and IMed-361M, resulting in a series of pre-trained models for universal medical image segmentation. Experimental results demonstrate that SyncSAM not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on test sets but also exhibits strong zero-shot capabilities on unseen datasets. Code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/Hhankyangg/SyncSAM.
大型基础模型以其强大的零样本泛化能力而广泛应用于各种下游任务。然而,由于自然图像与医学图像领域之间的差距,开发用于医学图像分割的基础模型是一个巨大的挑战。虽然基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的微调技术已经被探索,但它们主要集中在扩大数据或改进推理策略上,而没有融入领域特定的架构设计,从而限制了其零样本性能。为了优化标准推理设置下的分割性能,并为未来的研究提供强大的基线,我们引入了SyncSAM。SyncSAM采用同步双分支编码器,以同步的方式融合卷积和Transformer特征,以增强医学图像编码;并采用多尺度双分支解码器,以保留图像细节。SyncSAM在两大医学图像分割数据集SA-Med2D-20M和IMed-361M上进行训练,生成了一系列用于通用医学图像分割的预训练模型。实验结果表明,SyncSAM不仅在测试集上达到了最先进的性能,而且在未见数据集上表现出了强大的零样本能力。相关代码和检查点可访问https://github.com/Hhankyangg/SyncSAM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型通用模型具有良好的零样本泛化能力,可应用于多种下游任务。然而,将其应用于医学图像分割时面临域差距问题。基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的微调技术虽然已被探索,但它们主要关注扩大数据规模或优化推理策略,未融入特定领域的架构设计,从而限制了零样本性能。为在标准推理设置下优化分割性能并为未来研究提供强劲基准线,我们推出SyncSAM,采用同步双分支编码器,融合卷积和Transformer特征,强化医学图像编码;以及多尺度双分支解码器,保留图像细节。SyncSAM在两大医学图像分割数据集SA-Med2D-20M和IMed-361M上进行训练,生成一系列用于通用医学图像分割的预训练模型。实验结果证明SyncSAM不仅在测试集上达到领先水平,而且在未见数据集上展现出强大的零样本能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型通用模型在医学图像分割上应用时存在域差距问题。
- 基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的微调技术虽有所探索,但缺乏特定领域的架构设计,限制了零样本性能。
- SyncSAM通过同步双分支编码器融合卷积和Transformer特征,强化医学图像编码。
- SyncSAM采用多尺度双分支解码器以保留图像细节。
- SyncSAM在SA-Med2D-20M和IMed-361M两个大型医学图像分割数据集上进行训练。
- SyncSAM实现医学图像分割的领先水平,并在未见数据集上展现出强大的零样本能力。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Dynamic CT Image Reconstruction with Neural Fields and Optical Flow
Authors:Pablo Arratia, Matthias Ehrhardt, Lisa Kreusser
In this paper, we investigate image reconstruction for dynamic Computed Tomography. The motion of the target with respect to the measurement acquisition rate leads to highly resolved in time but highly undersampled in space measurements. Such problems pose a major challenge: not accounting for the dynamics of the process leads to a poor reconstruction with non-realistic motion. Variational approaches that penalize time evolution have been proposed to relate subsequent frames and improve image quality based on classical grid-based discretizations. Neural fields have emerged as a novel way to parameterize the quantity of interest using a neural network with a low-dimensional input, benefiting from being lightweight, continuous, and biased towards smooth representations. The latter property has been exploited when solving dynamic inverse problems with neural fields by minimizing a data-fidelity term only. We investigate and show the benefits of introducing explicit motion regularizers for dynamic inverse problems based on partial differential equations, namely, the optical flow equation, for the optimization of neural fields. We compare it against its unregularized counterpart and show the improvements in the reconstruction. We also compare neural fields against a grid-based solver and show that the former outperforms the latter in terms of PSNR in this task.
本文研究了动态计算机断层扫描的图像重建。目标相对于测量采集率的运动导致在时间上的分辨率很高,但在空间上的测量严重不足。这样的问题带来了很大的挑战:不考虑过程的动态性会导致重建质量不佳和出现非现实的运动。基于经典网格离散化的方法已经提出了对时间演化进行惩罚的变分方法,以关联后续帧并提高图像质量。神经场作为一种新的方法已经崭露头角,利用低维输入的神经网络对感兴趣的量进行参数化,得益于其轻便、连续以及偏向平滑表示的特性。在解决动态逆问题时,我们已经利用了后者的属性,通过仅最小化数据保真项来利用神经场。我们研究和展示了引入基于偏微分方程的显式运动正则化器对于动态逆问题的优化好处,特别是针对光流方程优化神经场。我们将其与未正则化的方法进行比较,并展示了重建质量的改进。此外,我们还比较了神经场和基于网格的求解器,并证明在此任务中,神经场在峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面表现优于基于网格的求解器。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了动态计算机断层扫描的图像重建问题。目标运动与测量采集率的相对关系导致在时间上的分辨率高而在空间上的采样不足。忽略过程的动态性会导致重建质量差,出现非现实运动。研究人员提出了基于变分的方法,通过惩罚时间演化来关联后续帧并基于经典网格离散化提高图像质量。神经网络场作为一种新的参数化方法出现,使用低维输入参数化感兴趣的量,其优势在于轻量化、连续性和偏向平滑表示。本研究探索并展示了为动态反问题引入基于偏微分方程的显式运动正则化器的优势,特别是使用光流方程优化神经网络场。与未正则化的方法相比,本研究显示重建质量有所提高。此外,将神经网络场与网格求解器进行比较,结果显示神经网络场在此任务中的峰值信噪比表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 本文研究了动态计算机断层扫描中的图像重建问题,特别关注了目标运动与测量采集率之间的关系。
- 忽略过程的动态性在图像重建中会导致质量下降和非现实运动的出现。
- 基于变分的方法被提出,通过关联后续帧和基于网格的离散化来提高图像质量。
- 神经网络场作为一种新的参数化方法出现,具有轻量化、连续性和偏向平滑表示的优势。
- 引入基于偏微分方程的显式运动正则化器对于优化神经网络场解决动态反问题有益。
- 与未正则化的方法相比,引入光流方程正则化器的图像重建质量有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

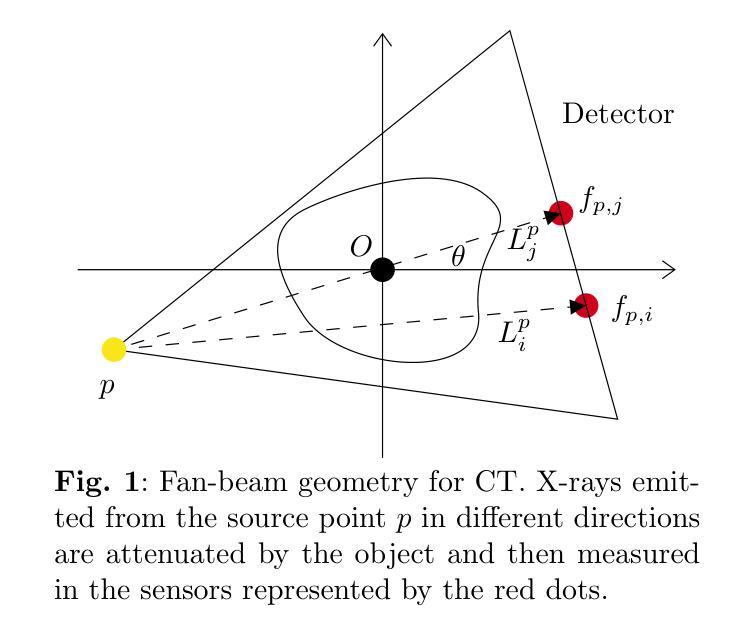
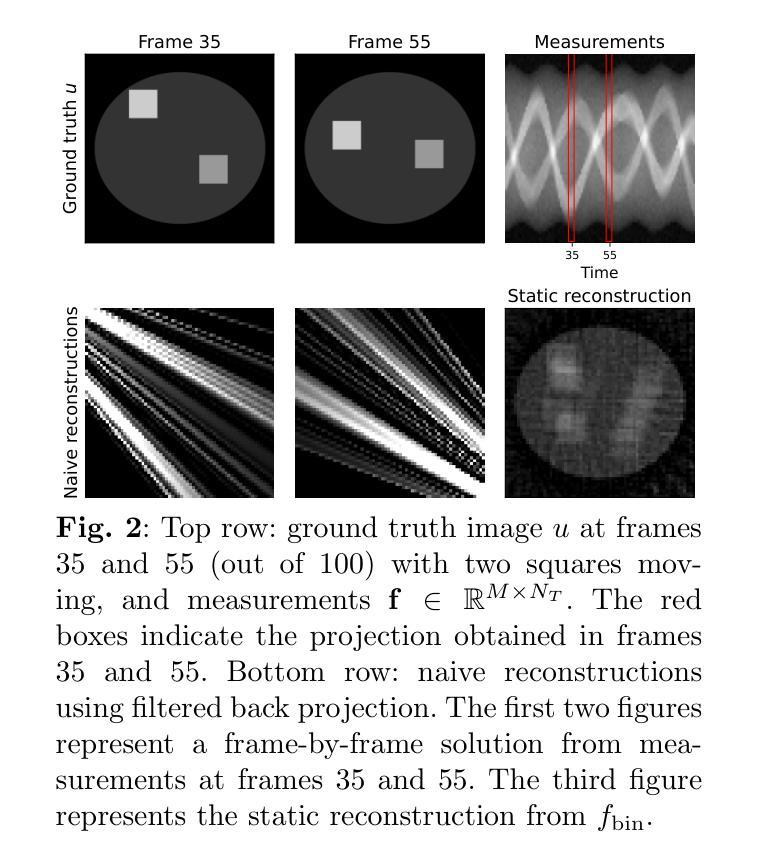
IgCONDA-PET: Weakly-Supervised PET Anomaly Detection using Implicitly-Guided Attention-Conditional Counterfactual Diffusion Modeling – a Multi-Center, Multi-Cancer, and Multi-Tracer Study
Authors:Shadab Ahamed, Arman Rahmim
Minimizing the need for pixel-level annotated data to train PET lesion detection and segmentation networks is highly desired and can be transformative, given time and cost constraints associated with expert annotations. Current unsupervised or weakly-supervised anomaly detection methods rely on autoencoder or generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained only on healthy data. While these approaches reduce annotation dependency, GAN-based methods are notably more challenging to train than non-GAN alternatives (such as autoencoders) due to issues such as the simultaneous optimization of two competing networks, mode collapse, and training instability. In this paper, we present the weakly-supervised $\textbf{I}$mplicitly-$\textbf{g}$uided $\textbf{CO}$u$\textbf{N}$terfactual diffusion model for $\textbf{D}$etecting $\textbf{A}$nomalies in $\textbf{PET}$ images (IgCONDA-PET). The solution is developed and validated using PET scans from six retrospective cohorts consisting of a total of 2652 cases (multi-cancer, multi-tracer) containing both local and public datasets (spanning multiple centers). The training is conditioned on image class labels (healthy vs. unhealthy) via attention modules, and we employ implicit diffusion guidance. We perform counterfactual generation which facilitates “unhealthy-to-healthy” domain translation by generating a synthetic, healthy version of an unhealthy input image, enabling the detection of anomalies through the calculated differences. The performance of our method was compared against several other deep learning based weakly-supervised or unsupervised methods as well as traditional methods like 41% SUV$_\text{max}$ thresholding. We also highlight the importance of incorporating attention modules in our network for the detection of small anomalies. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git.
在 PET 病变检测和分割网络训练中,最小化对像素级标注数据的需求是非常理想且具有变革性的,因为这样可以节省时间和成本,避免昂贵的专家标注。当前的无监督或弱监督异常检测方法依赖于仅使用健康数据训练的自动编码器或生成对抗网络(GANs)。虽然这些方法减少了标注依赖,但基于 GAN 的方法由于其固有的复杂性(如两个竞争网络的同步优化、模式崩溃和训练不稳定等)相较于非 GAN 替代方案(如自动编码器)的训练更具挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了弱监督隐导PET异常检测对比扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)。该解决方案是使用来自六个回顾性队列的 PET 扫描开发并验证的,包括总共 2652 例多癌症、多示踪剂病例,包含本地和公开数据集(涵盖多个中心)。训练是通过图像类别标签(健康与否)通过注意力模块进行的,我们采用了隐式扩散指导。我们执行了反事实生成,通过生成不健康输入图像的合成健康版本,促进了“不健康到健康”的域转换,并通过计算差异进行异常检测。我们的方法与基于深度学习的其他弱监督或无监督方法以及传统的如使用 41% SUVmax 值阈值的方法进行了比较。我们还强调了在网络中融入注意力模块以检测小异常的重要性。代码可在 https://github.com/ahxmeds/IgCONDA-PET.git 上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 48 pages, 13 figures, 4 tables
摘要
本研究提出一种用于PET图像异常检测的弱监督隐式引导扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)。该模型利用PET扫描数据开发并验证,通过注意力模块以图像类别标签(健康与非健康)为条件进行训练,采用隐式扩散引导并生成反事实数据,实现非健康图像向健康图像的转换,以检测异常。与多种深度学习的弱监督或无监督方法以及传统的SUVmax阈值方法相比,该方法性能优异。公开的代码可供研究使用。该方法的亮点在于注意力模块的使用,对于检测小型异常具有重要意义。
关键见解
- 提出了一种基于弱监督的隐式引导扩散模型(IgCONDA-PET)用于PET图像异常检测。
- 该模型通过注意力模块以图像类别标签为条件进行训练,提高了检测的准确性。
- 采用了隐式扩散引导和反事实生成,实现了非健康图像向健康图像的转换,有助于异常检测。
- 模型性能优于多种深度学习的弱监督或无监督方法以及传统的SUVmax阈值方法。
- 公开的代码为研究者提供了便利。
- 注意力模块的使用对于检测小型异常具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

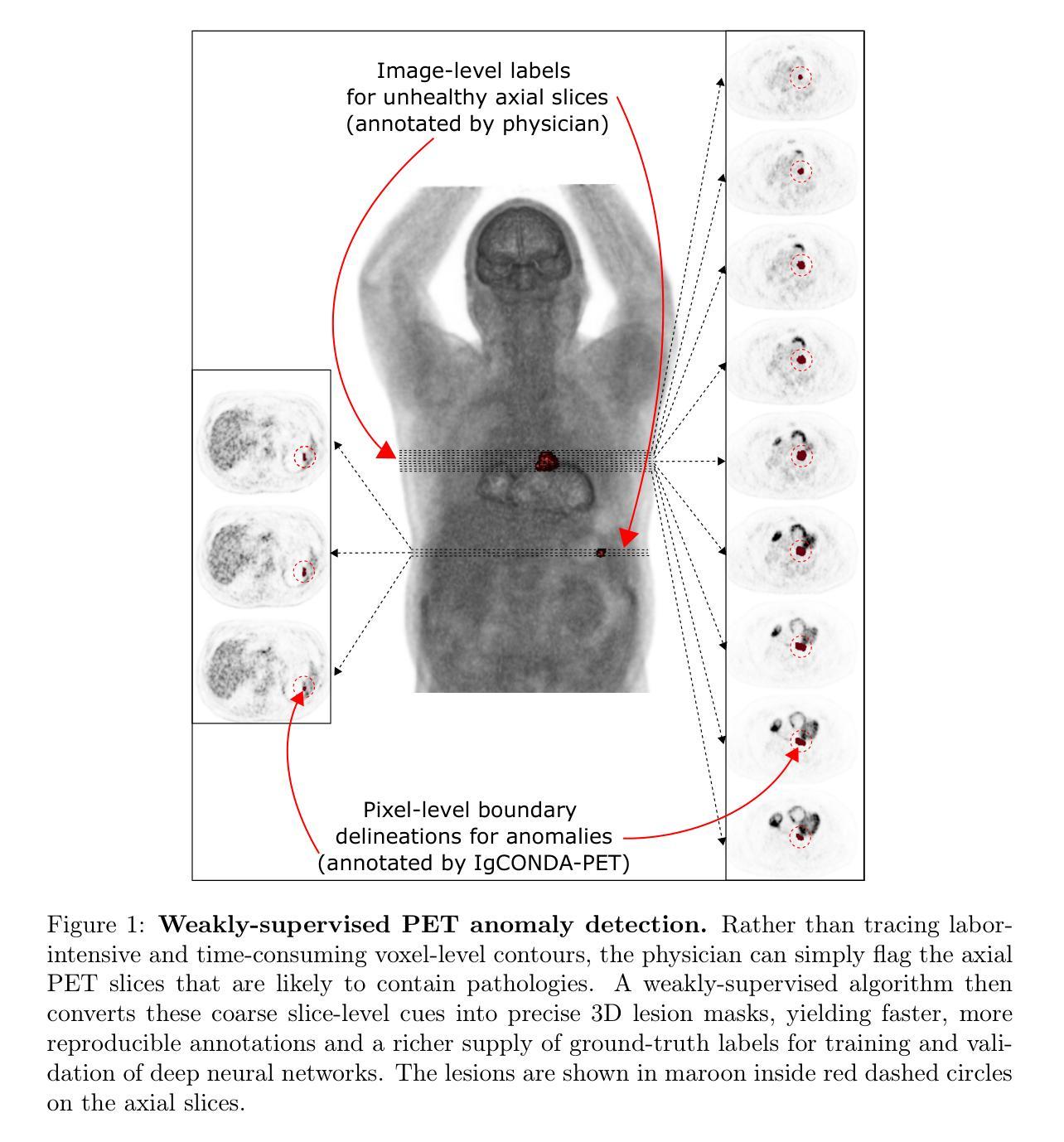
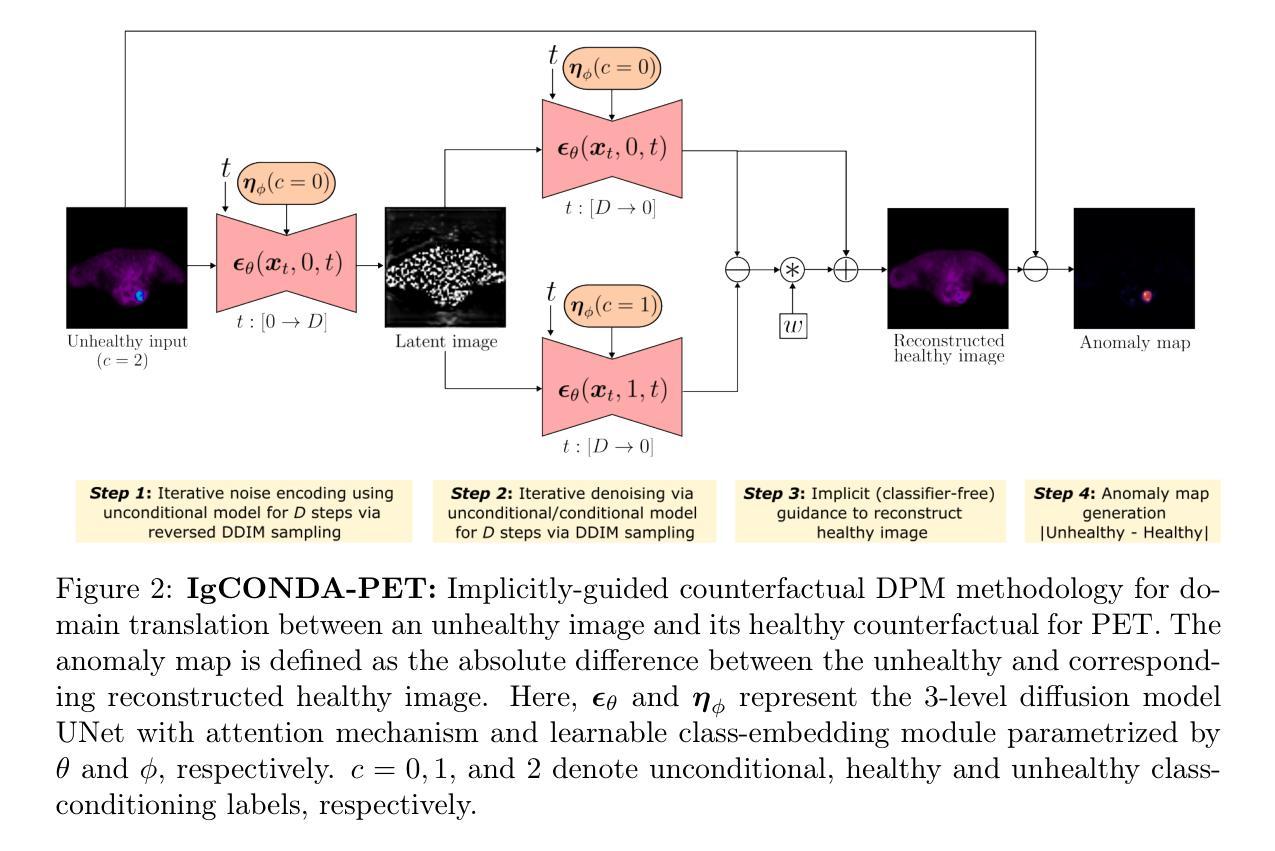
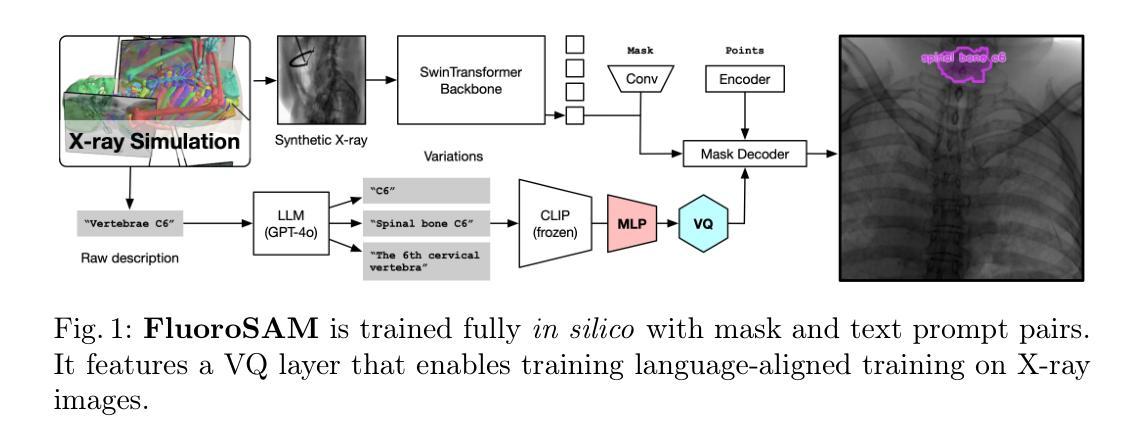
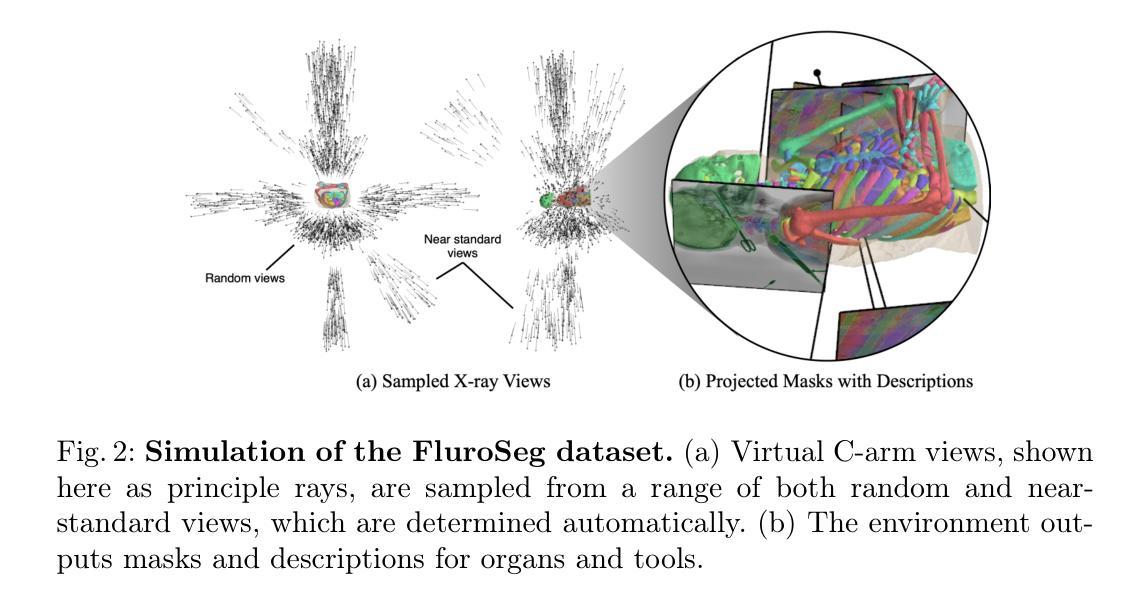
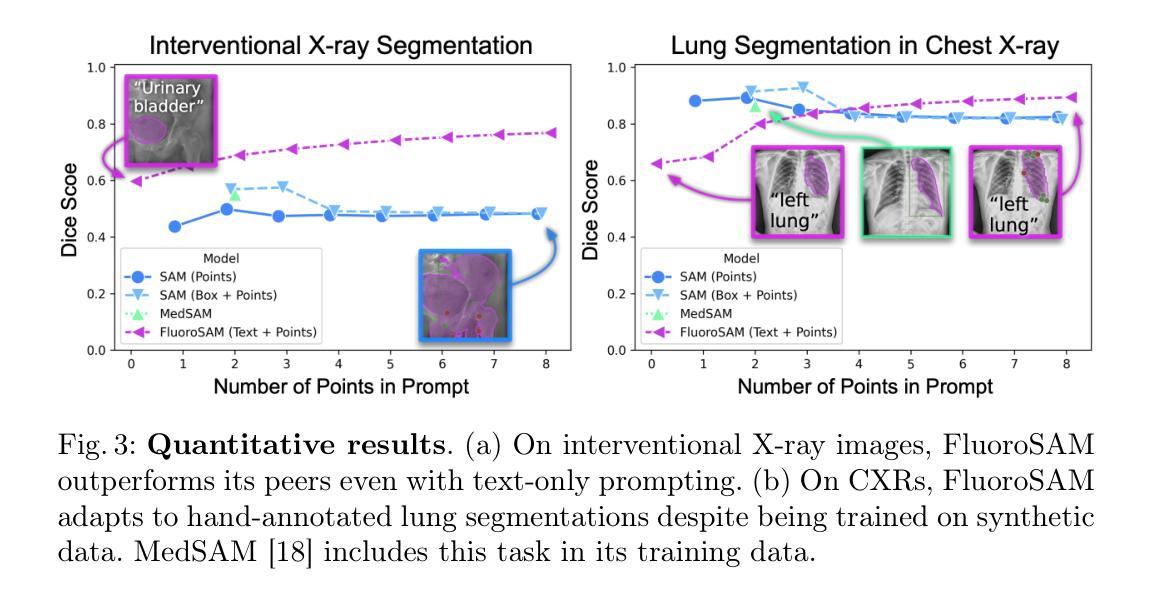
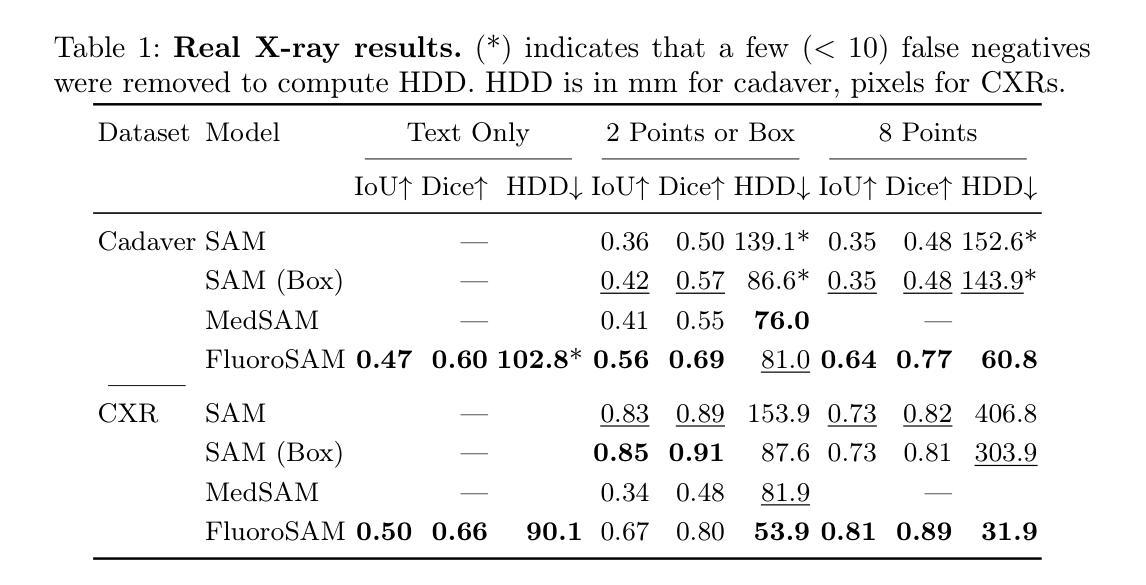
FluoroSAM: A Language-promptable Foundation Model for Flexible X-ray Image Segmentation
Authors:Benjamin D. Killeen, Liam J. Wang, Blanca Inigo, Han Zhang, Mehran Armand, Russell H. Taylor, Greg Osgood, Mathias Unberath
Language promptable X-ray image segmentation would enable greater flexibility for human-in-the-loop workflows in diagnostic and interventional precision medicine. Prior efforts have contributed task-specific models capable of solving problems within a narrow scope, but expanding to broader use requires additional data, annotations, and training time. Recently, language-aligned foundation models (LFMs) – machine learning models trained on large amounts of highly variable image and text data thus enabling broad applicability – have emerged as promising tools for automated image analysis. Existing foundation models for medical image analysis focus on scenarios and modalities where large, richly annotated datasets are available. However, the X-ray imaging modality features highly variable image appearance and applications, from diagnostic chest X-rays to interventional fluoroscopy, with varying availability of data. To pave the way toward an LFM for comprehensive and language-aligned analysis of arbitrary medical X-ray images, we introduce FluoroSAM, a language-promptable variant of the Segment Anything Model, trained from scratch on 3M synthetic X-ray images from a wide variety of human anatomies, imaging geometries, and viewing angles. These include pseudo-ground truth masks for 128 organ types and 464 tools with associated text descriptions. FluoroSAM is capable of segmenting myriad anatomical structures and tools based on natural language prompts, thanks to the novel incorporation of vector quantization (VQ) of text embeddings in the training process. We demonstrate FluoroSAM’s performance quantitatively on real X-ray images and showcase on several applications how FluoroSAM is a key enabler for rich human-machine interaction in the X-ray image acquisition and analysis context. Code is available at https://github.com/arcadelab/fluorosam.
语言提示型X射线图像分割将在诊断和介入精准医学的人类闭环工作流程中提供更灵活的解决方案。之前的努力已经贡献了一些针对特定任务的模型,这些模型能够在狭窄范围内解决问题,但要扩展到更广泛的应用则需要更多的数据、注释和训练时间。最近,语言对齐基础模型(LFMs)——在大量高度可变的图像和文本数据上进行训练的机器学习模型,能够实现广泛的适用性——已成为自动化图像分析的很有前途的工具。现有的医学图像分析基础模型侧重于大型丰富注释数据集可用的场景和模式。然而,X射线成像模式具有高度可变的图像外观和应用场景,从诊断胸部X射线到介入荧光镜检查,数据可用性各不相同。为了建立一种用于任意医学X射线图像的综合和语言对齐分析的基础模型,我们引入了FluoroSAM,这是一个语言提示型的分段任何东西模型(Segment Anything Model)变种,从头开始训练,使用了来自各种人类解剖学、成像几何和视角的300万合成X射线图像。这些包括用于128种器官类型和464种工具相关的文本描述的伪真实掩模。由于训练过程中文本嵌入的向量量化(VQ)的新颖结合,FluoroSAM能够基于自然语言提示对多种解剖结构和工具进行分割。我们在真实X射线图像上定量展示了FluoroSAM的性能,并在几个应用场景中展示了FluoroSAM如何在X射线图像采集和分析环境中实现丰富的人机交互的关键功能。代码可在https://github.com/arcadelab/fluorosam找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语言提示型X射线图像分割技术为诊断与介入精准医疗中的人机协作流程带来了更大的灵活性。现有任务特定模型只能在狭窄范围内解决问题,要扩大应用范围需增加数据、标注和训练时间。新兴的语言对齐基础模型(LFMs)具备处理大量多变图像和文本数据的能力,为医学图像分析提供了广阔适用的工具。针对医学X射线成像模态高度多变的特点,推出FluoroSAM模型,这是一种语言提示型的基础模型变体,可在广泛的医学X射线图像上进行语言对齐分析。FluoroSAM通过训练获得对多种人体结构、成像几何和视角的300万合成X射线图像的认识,并融入文本嵌入的向量量化(VQ)新方法。它能根据自然语言提示对多种解剖结构和工具进行分割,并在多个应用中展示了其在丰富人机交互中的关键作用。
Key Takeaways
- 语言提示型X射线图像分割技术提高了诊断与介入医疗中的人机协作流程的灵活性。
- 现有任务特定模型在解决医学图像分析问题时存在局限性,需要扩大应用范围。
- 语言对齐基础模型(LFMs)具备处理大量多变图像和文本数据的能力,为医学图像分析提供广泛适用的工具。
- FluoroSAM是一种语言提示型基础模型变体,能在广泛的医学X射线图像上进行语言对齐分析。
- FluoroSAM通过训练获得对多种人体结构、成像几何和视角的X射线图像的认识。
- FluoroSAM融入文本嵌入的向量量化(VQ)新方法,能够根据自然语言提示对多种解剖结构和工具进行分割。
点此查看论文截图

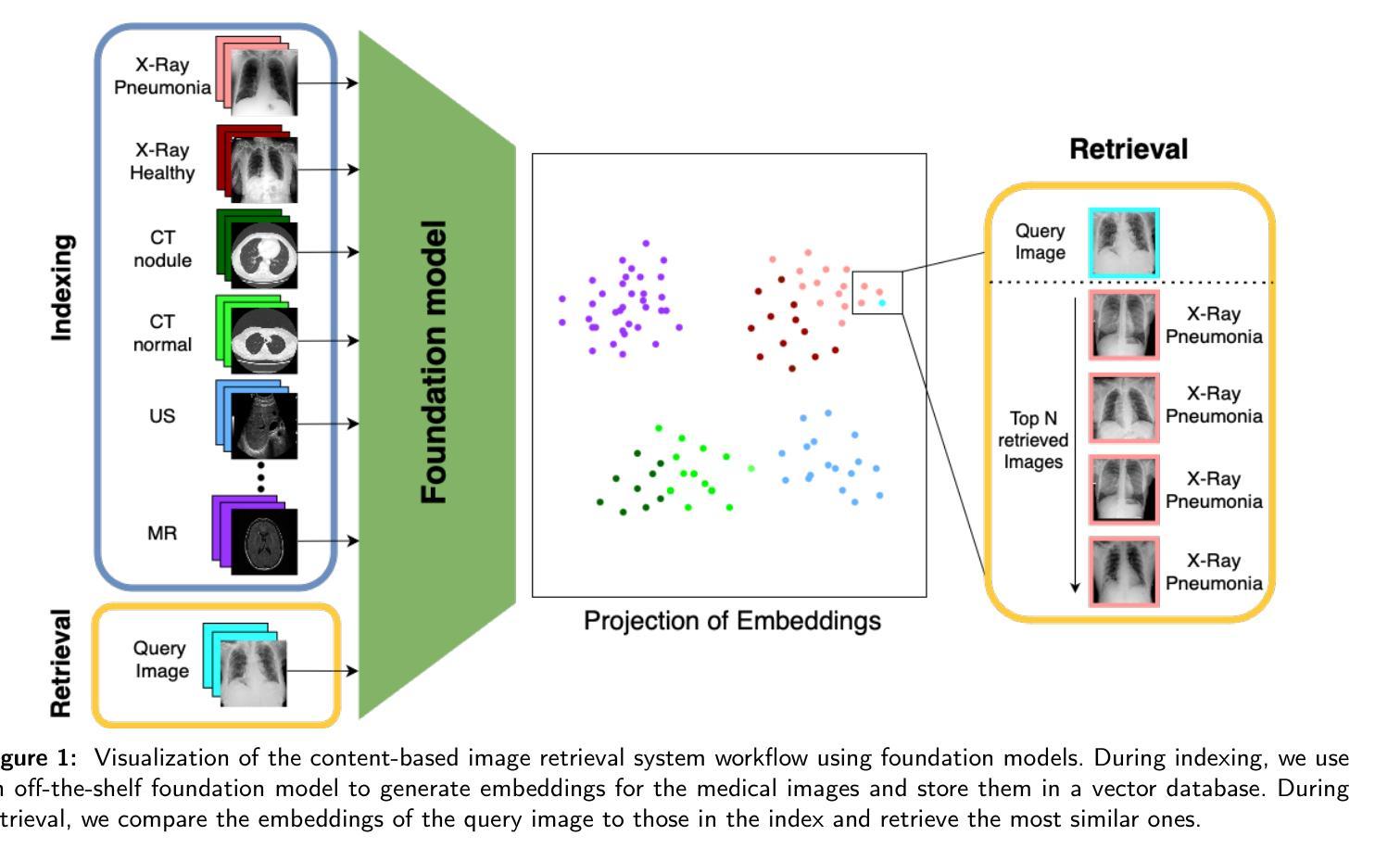
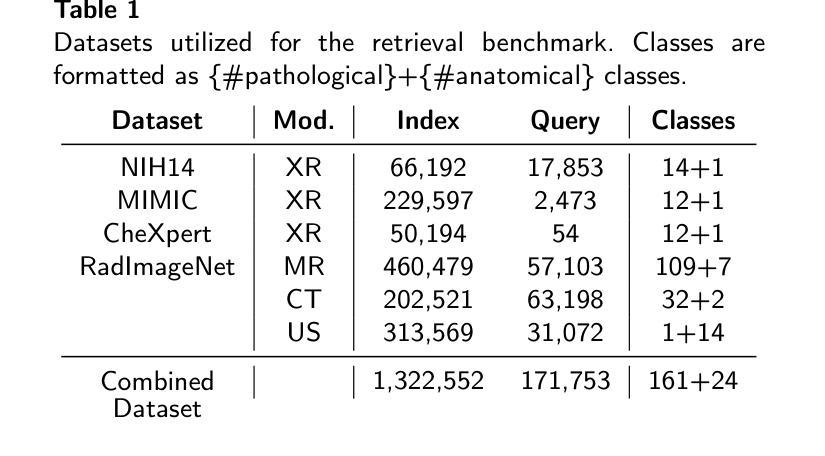
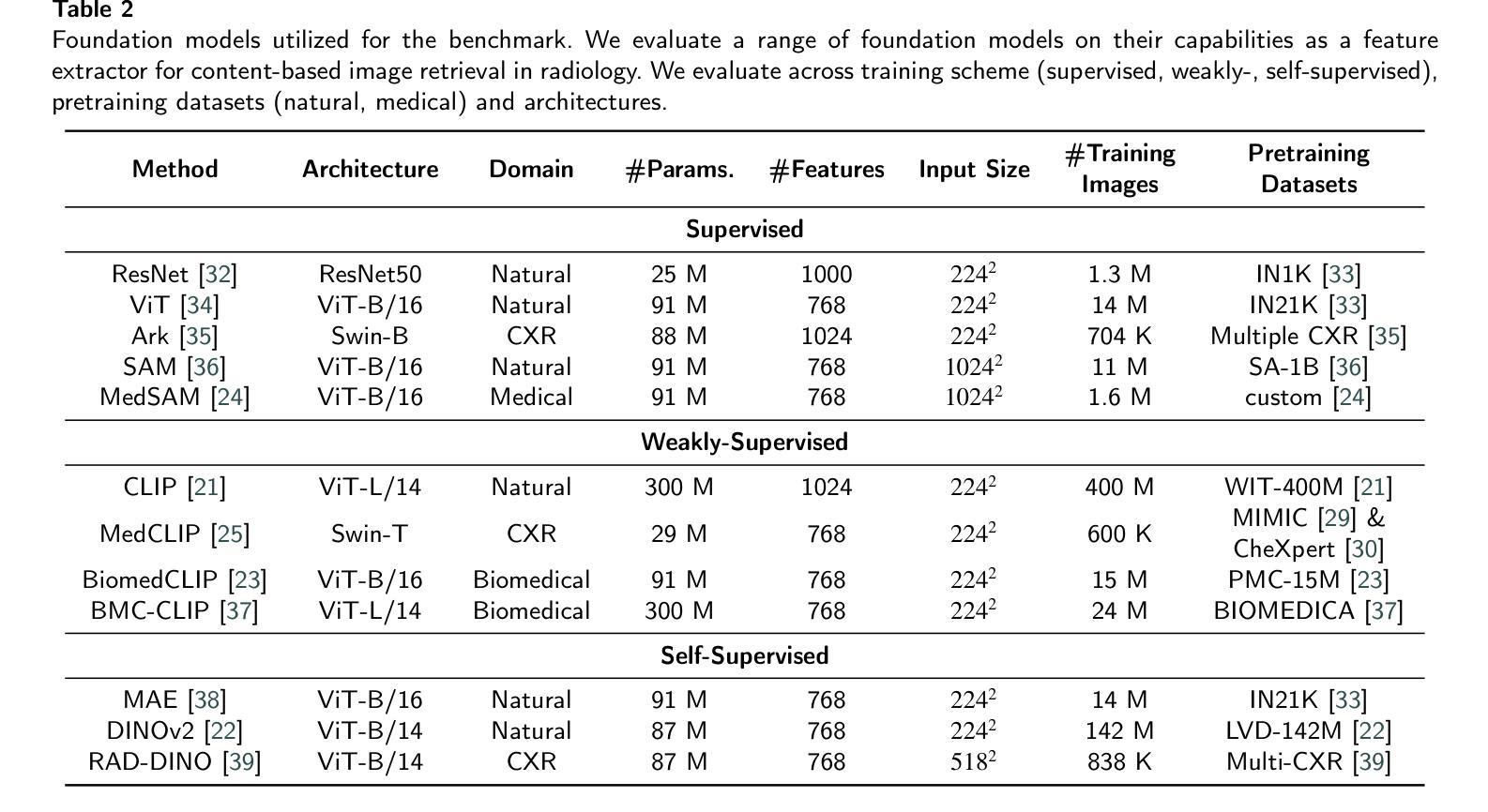
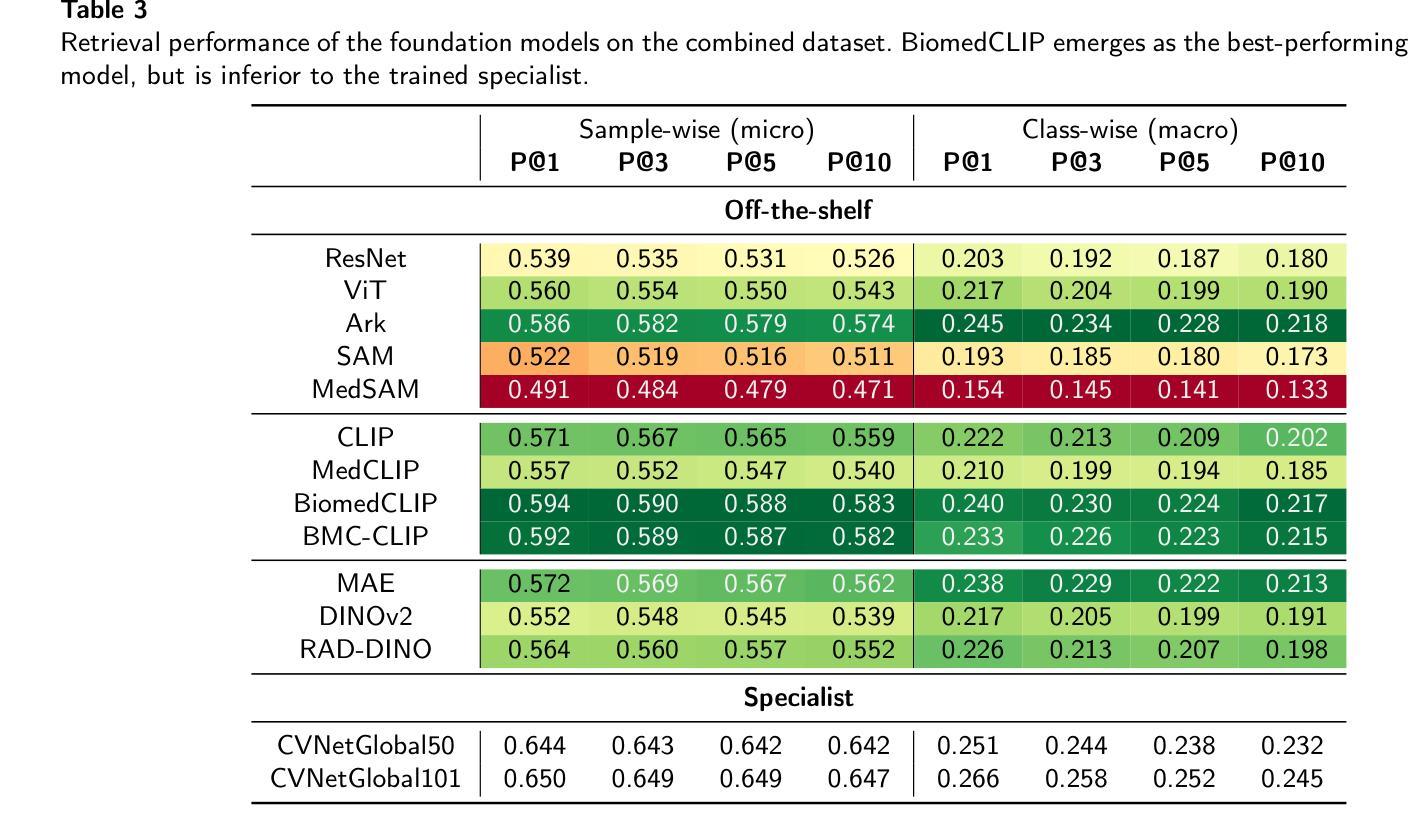
Leveraging Foundation Models for Content-Based Image Retrieval in Radiology
Authors:Stefan Denner, David Zimmerer, Dimitrios Bounias, Markus Bujotzek, Shuhan Xiao, Raphael Stock, Lisa Kausch, Philipp Schader, Tobias Penzkofer, Paul F. Jäger, Klaus Maier-Hein
Content-based image retrieval (CBIR) has the potential to significantly improve diagnostic aid and medical research in radiology. However, current CBIR systems face limitations due to their specialization to certain pathologies, limiting their utility. On the other hand, several vision foundation models have been shown to produce general-purpose visual features. Therefore, in this work, we propose using vision foundation models as powerful and versatile off-the-shelf feature extractors for content-based image retrieval. Our contributions include: (1) benchmarking a diverse set of vision foundation models on an extensive dataset comprising 1.6 million 2D radiological images across four modalities and 161 pathologies; (2) identifying weakly-supervised models, particularly BiomedCLIP, as highly effective, achieving a achieving a P@1 of up to 0.594 (P@3: 0.590, P@5: 0.588, P@10: 0.583), comparable to specialized CBIR systems but without additional training; (3) conducting an in-depth analysis of the impact of index size on retrieval performance; (4) evaluating the quality of embedding spaces generated by different models; and (5) investigating specific challenges associated with retrieving anatomical versus pathological structures. Despite these challenges, our research underscores the vast potential of foundation models for CBIR in radiology, proposing a shift towards versatile, general-purpose medical image retrieval systems that do not require specific tuning. Our code, dataset splits and embeddings are publicly available under https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/foundation-models-for-cbmir.
基于内容的图像检索(CBIR)在放射科的诊断和医疗研究方面有着巨大的潜力。然而,当前的CBIR系统因专门处理特定病理而受到局限,导致其实用性受限。另一方面,一些视觉基础模型已被证明可以产生通用视觉特征。因此,在这项工作中,我们提出利用视觉基础模型作为强大的通用即插即用特征提取器,用于基于内容的图像检索。我们的贡献包括:(1)在包含160万张跨越四种模态和161种病理的2D放射图像的大规模数据集上,对一系列多样化的视觉基础模型进行基准测试;(2)发现弱监督模型,特别是BiomedCLIP,表现出高度有效性,无需额外训练即可实现高达0.594的P@1(P@3:0.590,P@5:0.588,P@10:0.583),与专用CBIR系统的性能相当;(3)深入分析索引大小对检索性能的影响;(4)评估不同模型生成的嵌入空间的质量;(5)研究在检索解剖结构与病理结构时面临的特定挑战。尽管存在这些挑战,我们的研究强调了基础模型在放射科CBIR中的巨大潜力,提出了向通用医疗图像检索系统的转变,这些系统不需要特定调整即可适应多种用途。我们的代码、数据集分割和嵌入可在https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/foundation-models-for-cbmir上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于内容的图像检索(CBIR)在放射学诊断辅助和医学研究中的应用潜力。针对当前CBIR系统专业化导致的局限性,提出使用通用视觉基础模型作为功能强大且通用的离线特征提取器,用于基于内容的图像检索。通过广泛的实验验证,发现弱监督模型,特别是BiomedCLIP,在大型数据集上表现出优异的性能,无需额外训练即可与专业化CBIR系统相媲美。研究强调了基础模型在放射学CBIR中的巨大潜力,提倡开发通用、多用途的医学图像检索系统。
Key Takeaways
- 内容基于图像的检索(CBIR)在放射学中有改进诊断和医学研究的潜力。
- 当前CBIR系统因专业化而对某些病理的局限性。
- 提议使用视觉基础模型作为强大的通用特征提取器,用于CBIR。
- 在包含161种病理的1.6百万张2D放射图像的大规模数据集上,对多种视觉基础模型进行了基准测试。
- 弱监督模型,特别是BiomedCLIP,表现出高效果,无需额外训练即可与专业化CBIR系统竞争。
- 研究发现基础模型在放射学CBIR中的巨大潜力,鼓励开发通用、多用途的医学图像检索系统。
点此查看论文截图