⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-28 更新
Tree-based Semantic Losses: Application to Sparsely-supervised Large Multi-class Hyperspectral Segmentation
Authors:Junwen Wang, Oscar Maccormac, William Rochford, Aaron Kujawa, Jonathan Shapey, Tom Vercauteren
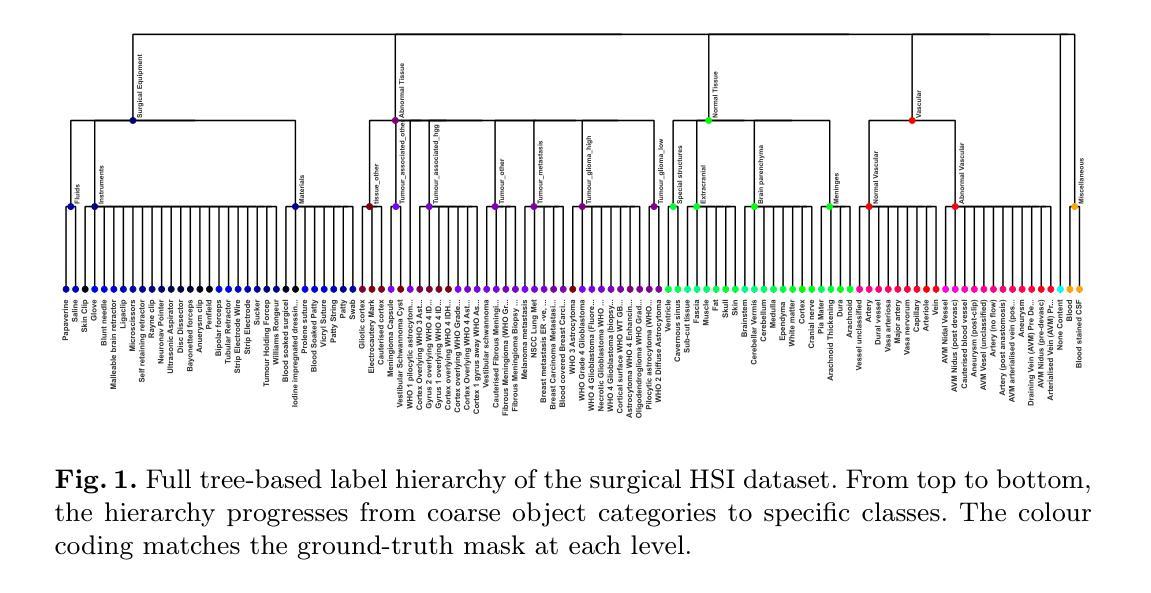
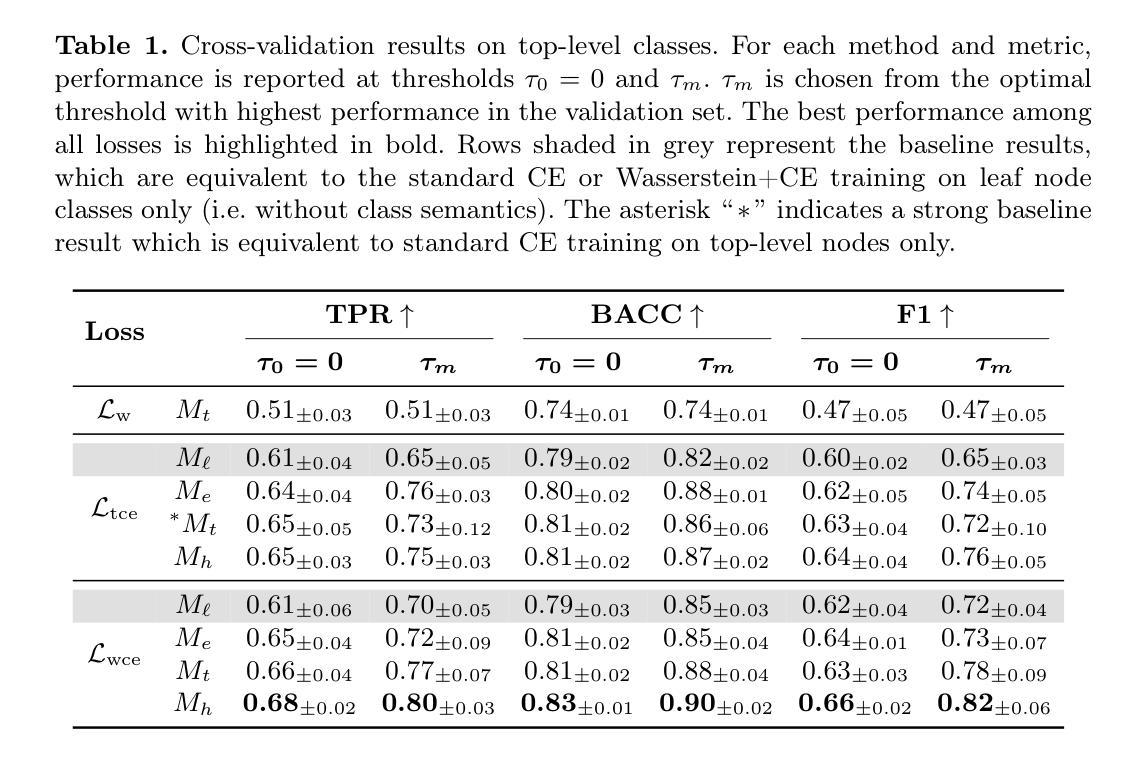
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) shows great promise for surgical applications, offering detailed insights into biological tissue differences beyond what the naked eye can perceive. Refined labelling efforts are underway to train vision systems to distinguish large numbers of subtly varying classes. However, commonly used learning methods for biomedical segmentation tasks penalise all errors equivalently and thus fail to exploit any inter-class semantics in the label space. In this work, we introduce two tree-based semantic loss functions which take advantage of a hierarchical organisation of the labels. We further incorporate our losses in a recently proposed approach for training with sparse, background-free annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method reaches state-of-the-art performance on a sparsely annotated HSI dataset comprising $107$ classes organised in a clinically-defined semantic tree structure. Furthermore, our method enables effective detection of out-of-distribution (OOD) pixels without compromising segmentation performance on in-distribution (ID) pixels.
高光谱成像(HSI)在手术应用中显示出巨大潜力,能够为肉眼无法感知的生物组织差异提供详细的见解。目前正在进行精细标注工作,以训练视觉系统区分大量细微变化的类别。然而,生物医学分割任务中常用的学习方法等价地惩罚所有错误,因此未能利用标签空间中的类间语义。在这项工作中,我们引入了两个基于树的语义损失函数,它们利用标签的层次结构。我们还将我们的损失纳入最近提出的利用稀疏、无背景注释进行训练的方法中。大量实验表明,我们在稀疏注释的HSI数据集上达到了最先进的性能,该数据集包含按临床定义的语义树结构组织的107类。此外,我们的方法能够在不影响内部分布(ID)像素分割性能的情况下,有效地检测外部分布(OOD)像素。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
高光谱成像(HSI)在手术应用中显示出巨大潜力,能够提供肉眼无法感知的生物组织差异的详细信息。为训练能够区分大量细微类别的视觉系统,正在开展精细标注工作。然而,常用的生物医学分割任务学习方法平等地惩罚所有错误,未能利用标签空间中的类间语义。本研究介绍两种基于树结构的语义损失函数,它们利用标签的层次结构。此外,将我们的损失纳入最近提出的利用稀疏、无背景注释进行训练的方法中。广泛实验表明,所提方法在多分类高光谱数据集上达到了最新性能水平,该数据集包含按临床定义的语义树结构组织的107类,且能有效检测分布外的像素,不影响分布内的像素分割性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 高光谱成像(HSI)在手术应用中有巨大潜力,能揭示肉眼无法感知的生物组织差异详细信息。
- 为训练能区分大量细微类别的视觉系统,正在进行精细标注工作。
- 常用生物医学分割任务学习方法未能利用标签空间中的类间语义。
- 本研究介绍两种基于树结构的语义损失函数,利用标签的层次结构。
- 所提方法结合了一种新的训练策略,该策略适用于稀疏、无背景注释的情况。
- 实验表明该方法在多分类高光谱数据集上达到了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

U-R-VEDA: Integrating UNET, Residual Links, Edge and Dual Attention, and Vision Transformer for Accurate Semantic Segmentation of CMRs
Authors:Racheal Mukisa, Arvind K. Bansal
Artificial intelligence, including deep learning models, will play a transformative role in automated medical image analysis for the diagnosis of cardiac disorders and their management. Automated accurate delineation of cardiac images is the first necessary initial step for the quantification and automated diagnosis of cardiac disorders. In this paper, we propose a deep learning based enhanced UNet model, U-R-Veda, which integrates convolution transformations, vision transformer, residual links, channel-attention, and spatial attention, together with edge-detection based skip-connections for an accurate fully-automated semantic segmentation of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images. The model extracts local-features and their interrelationships using a stack of combination convolution blocks, with embedded channel and spatial attention in the convolution block, and vision transformers. Deep embedding of channel and spatial attention in the convolution block identifies important features and their spatial localization. The combined edge information with channel and spatial attention as skip connection reduces information-loss during convolution transformations. The overall model significantly improves the semantic segmentation of CMR images necessary for improved medical image analysis. An algorithm for the dual attention module (channel and spatial attention) has been presented. Performance results show that U-R-Veda achieves an average accuracy of 95.2%, based on DSC metrics. The model outperforms the accuracy attained by other models, based on DSC and HD metrics, especially for the delineation of right-ventricle and left-ventricle-myocardium.
人工智能,包括深度学习模型,将在自动医疗图像分析中发挥变革性作用,用于心脏疾病的诊断和管理。自动准确描绘心脏图像是心脏疾病量化和自动诊断的第一步。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于深度学习的增强型UNet模型U-R-Veda,它结合了卷积变换、视觉转换器、残差连接、通道注意力和空间注意力,以及基于边缘检测的连接跳连,用于准确全自动地对心脏磁共振(CMR)图像进行语义分割。该模型使用堆叠的组合卷积块来提取局部特征及其相互关系,卷积块中嵌入通道注意力和空间注意力以及视觉转换器。卷积块中的通道注意力和空间注意力的深度嵌入用于识别重要特征及其空间定位。结合边缘信息与通道注意力和空间注意力作为跳跃连接,减少了卷积变换过程中的信息损失。总体而言,该模型显著提高了必要的CMR图像语义分割能力,从而改进了医疗图像分析。还介绍了双注意力模块(通道注意力和空间注意力)的算法。性能结果表明,U-R-Veda的平均准确度为95.2%,基于DSC指标。该模型的精度超过了其他模型的精度,基于DSC和HD指标,特别是在右心室和左心室心肌的描绘上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 3 figures
Summary
深度学习模型将在心脏疾病的诊断和管理工作中发挥重要作用。本研究提出了一种基于深度学习的增强型UNet模型U-R-Veda,能够自动准确地识别和分析心脏磁共振图像中的细节和区域边界,从而提升对心脏疾病的定量检测和自动化诊断能力。U-R-Veda融合了卷积变换、视觉转换器、残差连接、通道注意力和空间注意力等技术,通过边缘检测来构建跳跃连接,实现了精确的完全自动化语义分割。模型在DSC指标上达到了平均准确度为95.2%,尤其是在右心室和左心室心肌边界描绘上超过了其他模型的性能。这一研究成果对于改善医学图像处理中的心脏疾病诊断具有重大意义。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能和深度学习模型在心脏疾病的诊断和管理工作中扮演重要角色。
- 研究提出了一种新型的深度学习模型U-R-Veda,能够实现对心脏磁共振图像的准确自动语义分割。
- U-R-Veda结合了多种技术,包括卷积变换、视觉转换器、残差连接等,以提升模型的性能。
- 模型利用通道注意力和空间注意力机制来提取局部特征及其相互关系。
- U-R-Veda通过结合边缘信息以及通道和空间注意力作为跳跃连接,减少了信息损失。
- U-R-Veda模型在语义分割上的性能显著,平均准确度达到了95.2%。
点此查看论文截图

Context Aware Grounded Teacher for Source Free Object Detection
Authors:Tajamul Ashraf, Rajes Manna, Partha Sarathi Purkayastha, Tavaheed Tariq, Janibul Bashir
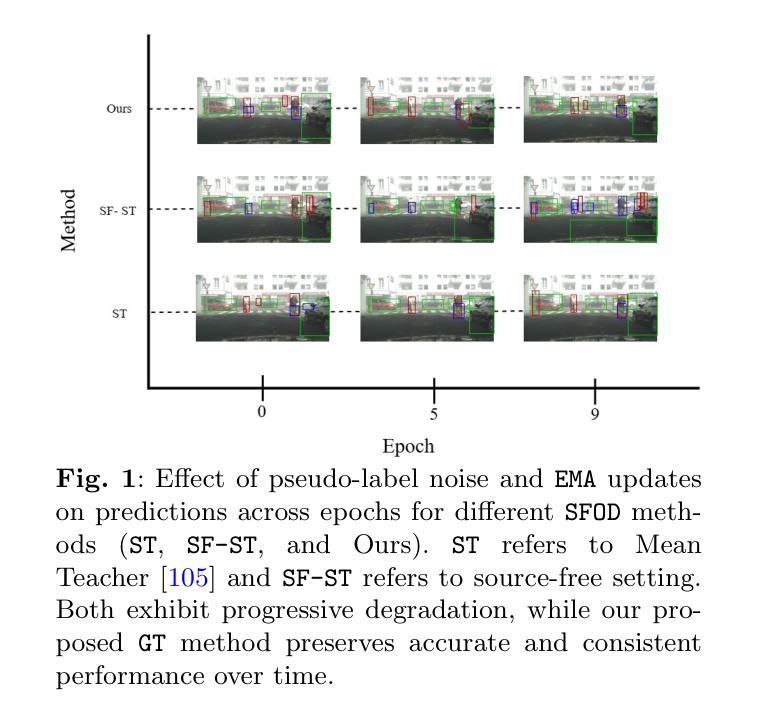
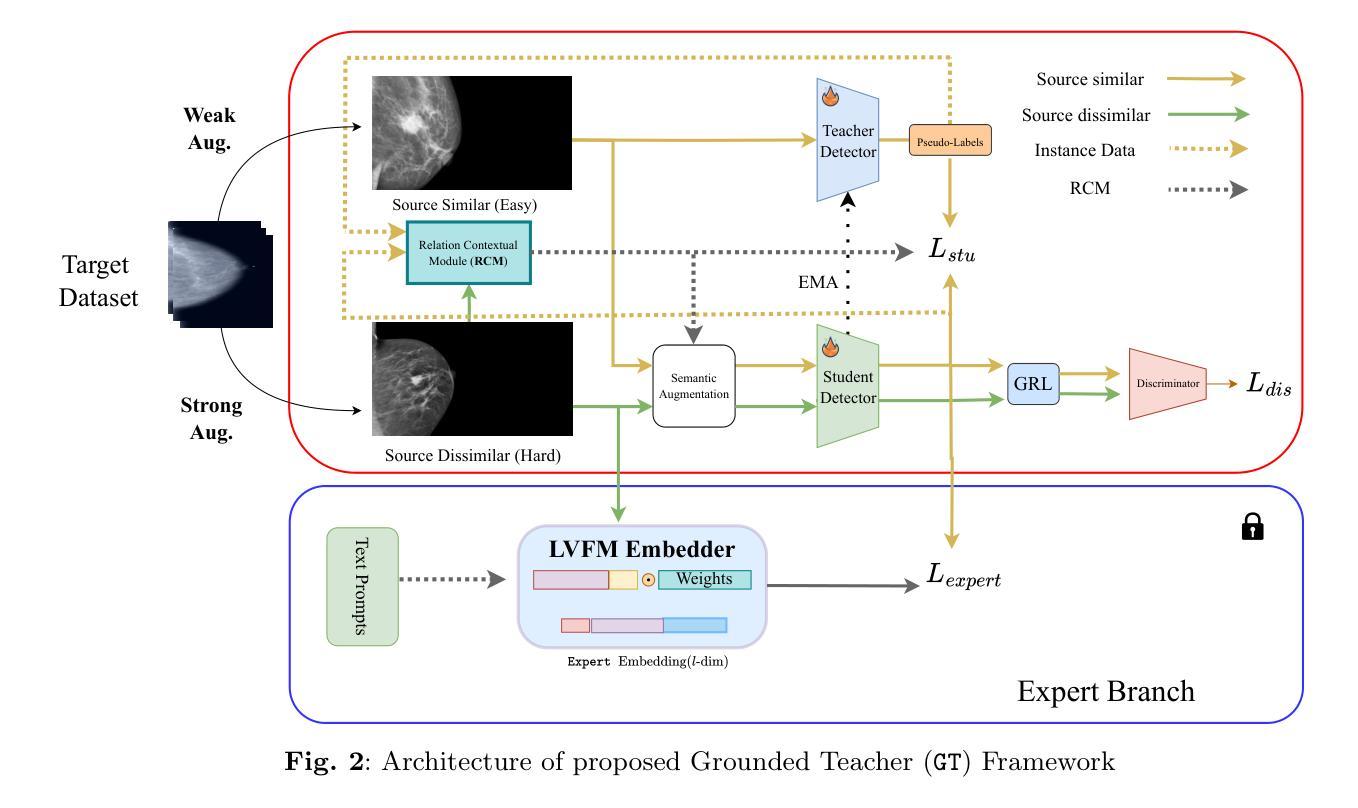
We focus on the Source Free Object Detection (SFOD) problem, when source data is unavailable during adaptation, and the model must adapt to the unlabeled target domain. In medical imaging, several approaches have leveraged a semi-supervised student-teacher architecture to bridge domain discrepancy. Context imbalance in labeled training data and significant domain shifts between domains can lead to biased teacher models that produce inaccurate pseudolabels, degrading the student model’s performance and causing a mode collapse. Class imbalance, particularly when one class significantly outnumbers another, leads to contextual bias. To tackle the problem of context bias and the significant performance drop of the student model in the SFOD setting, we introduce Grounded Teacher (GT) as a standard framework. In this study, we model contextual relationships using a dedicated relational context module and leverage it to mitigate inherent biases in the model. This approach enables us to apply augmentations to closely related classes, across and within domains, enhancing the performance of underrepresented classes while keeping the effect on dominant classes minimal. We further improve the quality of predictions by implementing an expert foundational branch to supervise the student model. We validate the effectiveness of our approach in mitigating context bias under the SFOD setting through experiments on three medical datasets supported by comprehensive ablation studies. All relevant resources, including preprocessed data, trained model weights, and code, are publicly available at this https://github.com/Tajamul21/Grounded_Teacher.
我们关注无源对象检测(SFOD)问题,即在适应过程中无法使用源数据,模型必须适应无标签的目标域。在医学成像中,一些方法已经利用半监督学生-教师架构来弥合领域差异。带有标签的训练数据中的上下文不平衡以及不同领域之间的领域漂移会导致教师模型产生偏差,从而产生不准确的伪标签,降低学生模型的性能并导致模式崩溃。类别不平衡,特别是当一个类别的数量远远超过另一个类别时,会导致上下文偏差。为了解决上下文偏差和学生在SFOD设置中的显著性能下降问题,我们引入了Grounded Teacher(GT)作为标准框架。在本研究中,我们使用专用的关系上下文模块对上下文关系进行建模,并以此来减轻模型中的固有偏差。这种方法使我们能够为密切相关类应用增强技术,跨越和内部领域,提高表现欠佳的类的性能,同时尽量减少对优势类的影响。我们进一步通过实现专家基础分支来监督学生模型,以提高预测质量。我们通过三项医学数据集的实验和综合消融研究验证了我们的方法在缓解SFOD设置下上下文偏差的有效性。所有相关资源,包括预处理数据、训练模型权重和代码,都可在https://github.com/Tajamul21/Grounded_Teacher上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在无法使用源数据进行适应时,研究聚焦于无源对象检测(SFOD)问题,模型必须适应无标签的目标域。在医学成像中,一些方法采用半监督学生-教师架构来弥合领域差异。在标签训练数据中的上下文不平衡和领域间显著转移可能导致教师模型出现偏见,产生不准确的伪标签,降低学生模型的性能并导致模式崩溃。针对这一问题,本研究引入“基础教师”(GT)作为标准框架。我们利用专门的上下文关系模块建模上下文关系,并利用它来减轻模型中的固有偏见。此方法允许我们对跨域和域内的相关类别应用增强技术,在提高表现不佳的类别的性能的同时,尽量减少对主要类别的影响。通过实施专家基础分支来监督学生模型,我们进一步提高了预测的质量。我们在三个医学数据集上进行了实验验证我们的方法对于缓解上下文偏差的有效性,并提供了相关资源,包括预处理数据、训练过的模型权重和代码,公开访问地址:https://github.com/Tajamul21/Grounded_Teacher。
Key Takeaways
- 研究聚焦于在无源数据的情况下进行对象检测(SFOD),特别是在医学成像领域。
- 上下文不平衡和领域转移可能导致教师模型的偏见和不准确的伪标签。
- 提出使用半监督学生-教师架构来应对上述问题。
- 引入“基础教师”(GT)框架作为解决方案。
- 通过专门的上下文关系模块建模上下文关系,减轻模型中的固有偏见。
- 采用增强技术改善跨域和内部类别之间的关联性。
点此查看论文截图

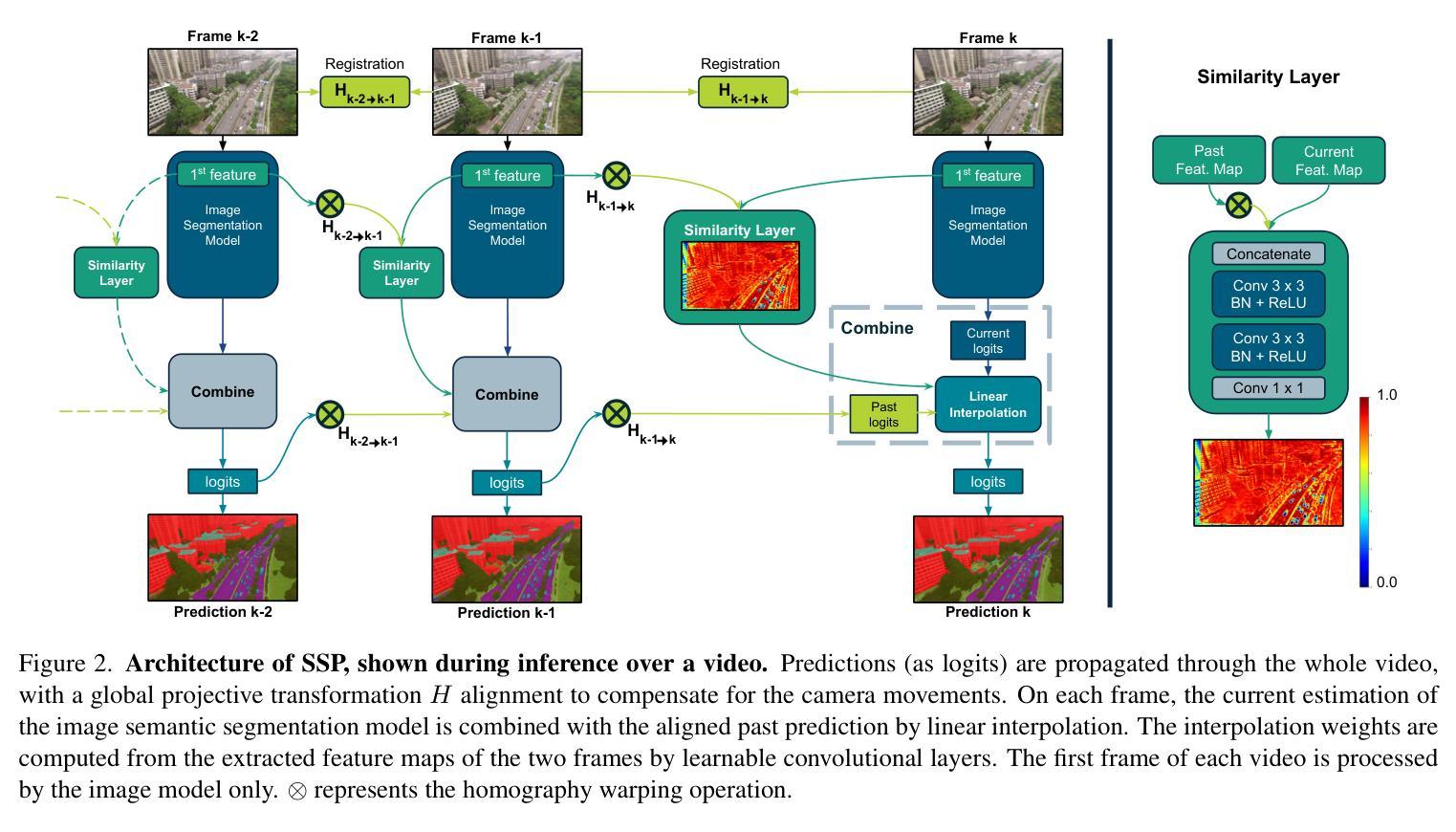
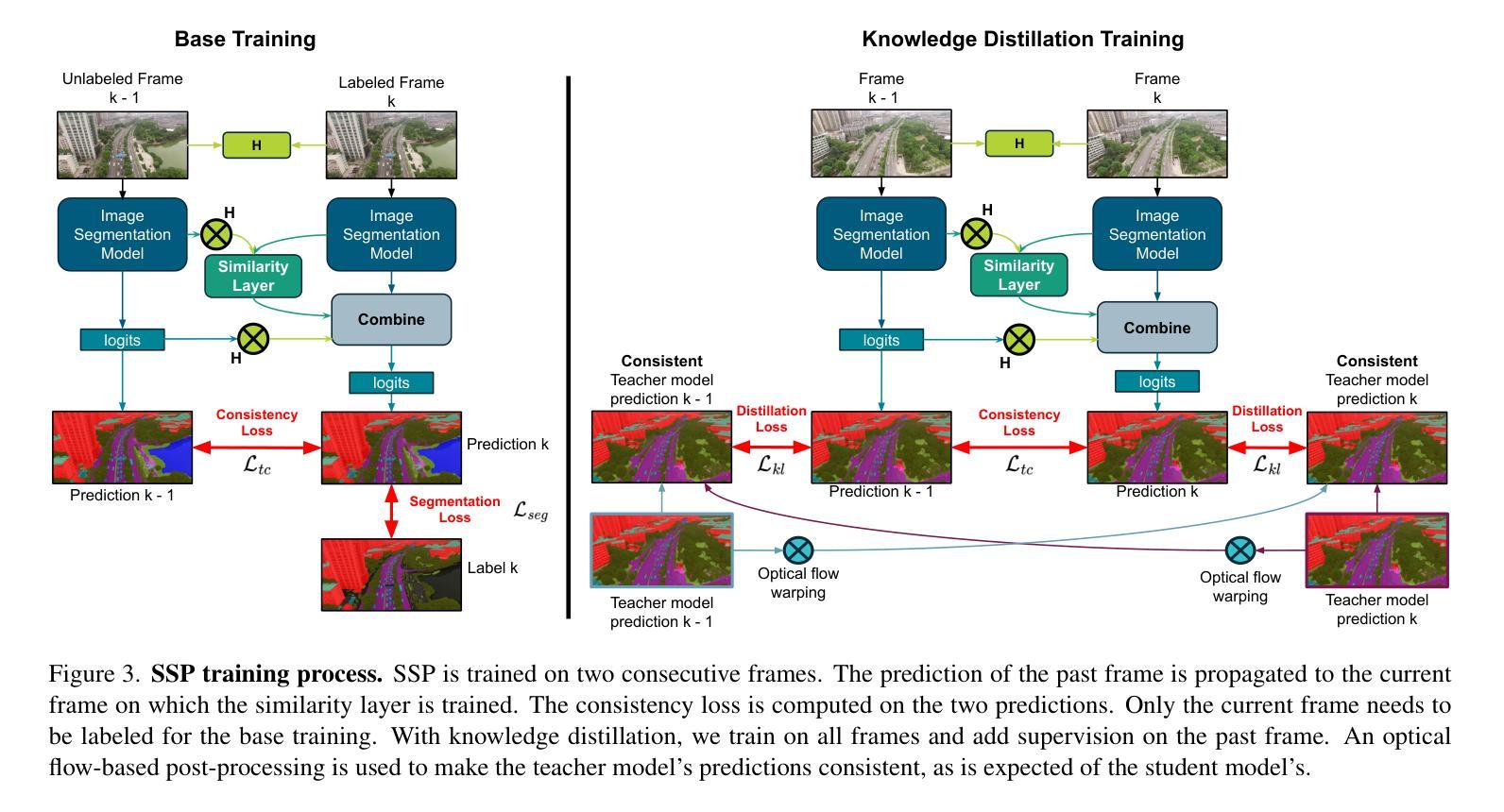
High Temporal Consistency through Semantic Similarity Propagation in Semi-Supervised Video Semantic Segmentation for Autonomous Flight
Authors:Cédric Vincent, Taehyoung Kim, Henri Meeß
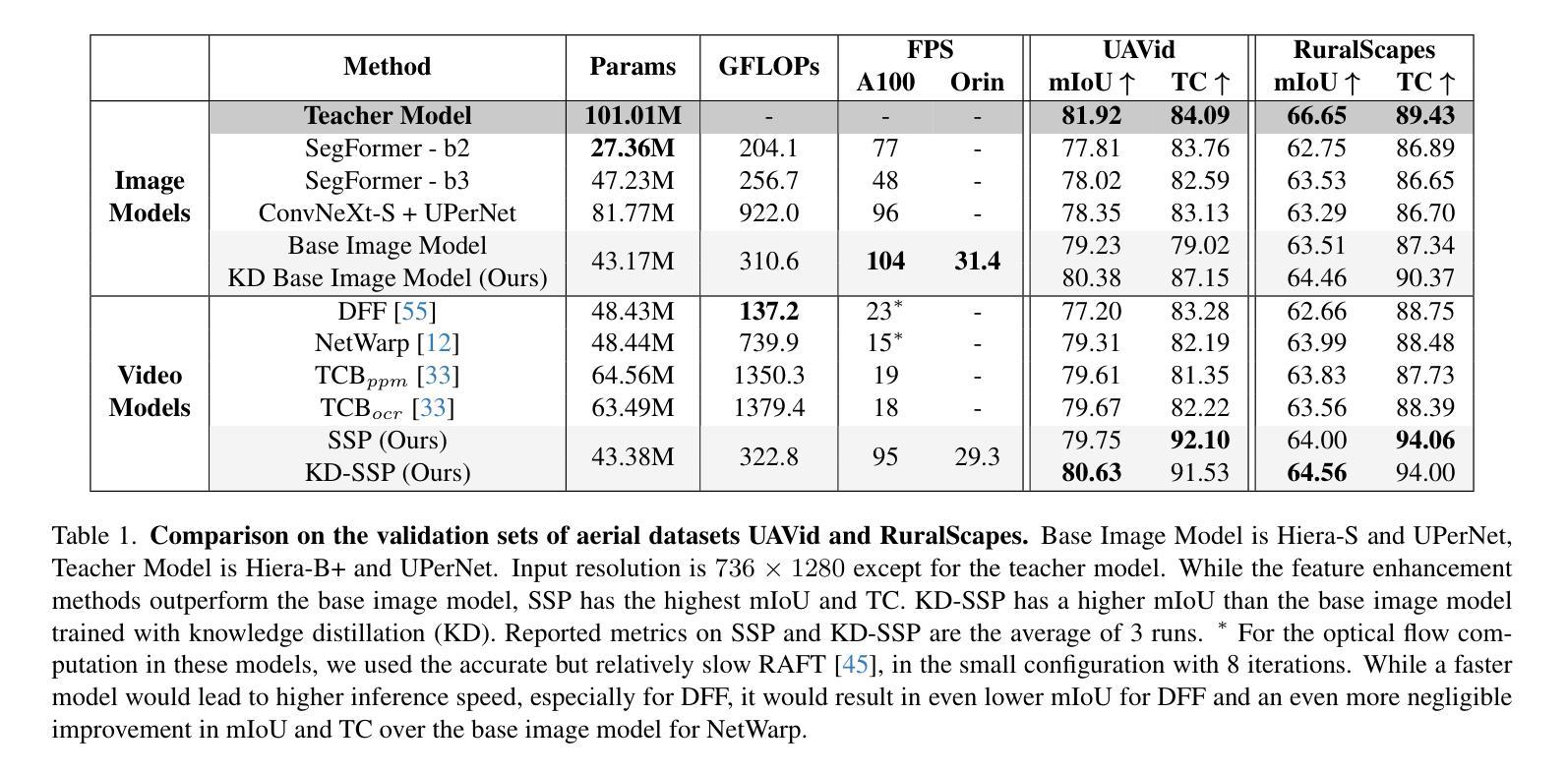
Semantic segmentation from RGB cameras is essential to the perception of autonomous flying vehicles. The stability of predictions through the captured videos is paramount to their reliability and, by extension, to the trustworthiness of the agents. In this paper, we propose a lightweight video semantic segmentation approach-suited to onboard real-time inference-achieving high temporal consistency on aerial data through Semantic Similarity Propagation across frames. SSP temporally propagates the predictions of an efficient image segmentation model with global registration alignment to compensate for camera movements. It combines the current estimation and the prior prediction with linear interpolation using weights computed from the features similarities of the two frames. Because data availability is a challenge in this domain, we propose a consistency-aware Knowledge Distillation training procedure for sparsely labeled datasets with few annotations. Using a large image segmentation model as a teacher to train the efficient SSP, we leverage the strong correlations between labeled and unlabeled frames in the same training videos to obtain high-quality supervision on all frames. KD-SSP obtains a significant temporal consistency increase over the base image segmentation model of 12.5% and 6.7% TC on UAVid and RuralScapes respectively, with higher accuracy and comparable inference speed. On these aerial datasets, KD-SSP provides a superior segmentation quality and inference speed trade-off than other video methods proposed for general applications and shows considerably higher consistency. Project page: https://github.com/FraunhoferIVI/SSP.
从RGB相机进行语义分割对自主飞行车辆的感知至关重要。通过捕获的视频进行预测的稳定性对它们的可靠性至关重要,进而影响到这些智能体的可信度。在本文中,我们提出了一种轻量级的视频语义分割方法,适用于实时在线推理,通过在帧之间进行语义相似性传播(Semantic Similarity Propagation, SSP)实现高空数据的较高时间一致性。SSP通过全局注册对齐临时传播高效图像分割模型的预测结果来补偿相机运动。它结合了当前估计和先前预测,利用两个帧的特征相似性计算得出的权重进行线性插值。由于本领域的可用数据量是一个挑战,我们针对具有少量注释的稀疏标记数据集提出了一种一致性感知的知识蒸馏训练程序。我们以大型图像分割模型作为教师来训练高效的SSP,利用同一训练视频中标记帧和无标记帧之间的强相关性来获得所有帧的高质量监督。KD-SSP相较于基础图像分割模型在UAVid和RuralScapes上分别实现了12.5%和6.7%的时间一致性增长,具有更高的准确性和相当的推理速度。在这些高空数据集中,KD-SSP相较于其他针对通用应用提出的视频方法提供了更优越的分割质量和推理速度权衡,并显示出明显更高的一致性。项目页面:https://github.com/FraunhoferIVI/SSP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
本文提出了一种轻量级的视频语义分割方法,适用于自主飞行车辆的实时感知,该方法通过对视频帧的语义相似性传播(Semantic Similarity Propagation, SSP)实现高时间一致性。该方法结合当前估计和前一个预测进行线性插值,通过计算两个帧的特征相似性的权重来实现时间上的传播。此外,针对数据可用性的挑战,本文提出了一种一致性感知的知识蒸馏训练程序,用于稀疏标注的数据集。使用大型图像分割模型作为教师进行训练,利用同一训练视频中标签帧与非标签帧之间的强相关性来获得所有高质量监督帧。与其他视频方法相比,KD-SSP在无人机和乡村景观数据集上提供了更高的分割质量和推理速度权衡,并实现了显著的时间一致性提升。
Key Takeaways
- 视频语义分割对自主飞行车辆的感知至关重要,预测的稳定性对其可靠性和信任度至关重要。
- 提出了一种轻量级的视频语义分割方法,适用于实时推理,通过语义相似性传播实现高时间一致性。
- 利用线性插值和计算帧间特征相似性权重进行时间传播。
- 针对数据可用性的挑战,提出了一种一致性感知的知识蒸馏训练程序,用于稀疏标注数据集的高质量监督。
- 利用大型图像分割模型作为教师进行训练,利用同一训练视频中标签与非标签帧之间的强相关性。
- KD-SSP在无人机和乡村景观数据集上实现了显著的时间一致性提升,与其他视频方法相比具有更高的分割质量和推理速度权衡。
点此查看论文截图


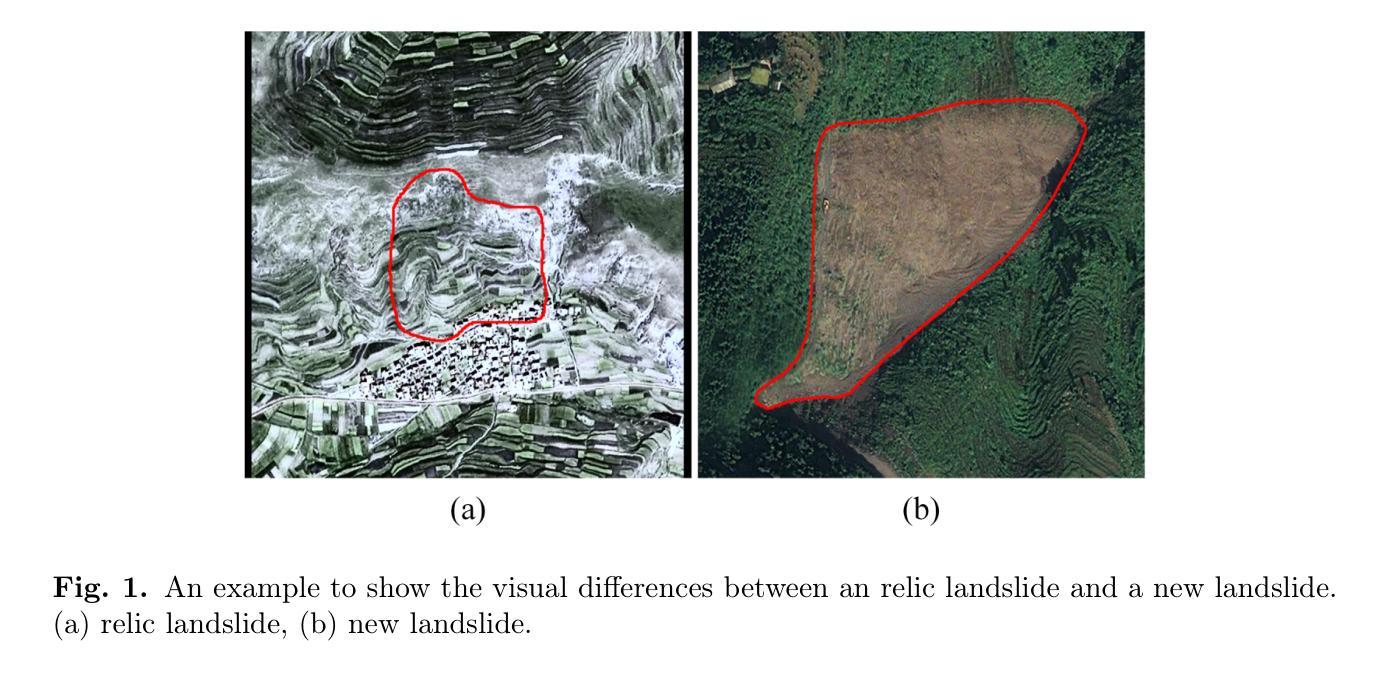
A Multi-Source Data Fusion-based Semantic Segmentation Model for Relic Landslide Detection
Authors:Yiming Zhou, Yuexing Peng, Daqing Ge, Junchuan Yu, Wei Xiang
As a natural disaster, landslide often brings tremendous losses to human lives, so it urgently demands reliable detection of landslide risks. When detecting relic landslides that present important information for landslide risk warning, problems such as visual blur and small-sized dataset cause great challenges when using remote sensing images. To extract accurate semantic features, a hyper-pixel-wise contrastive learning augmented segmentation network (HPCL-Net) is proposed, which augments the local salient feature extraction from boundaries of landslides through HPCL and fuses heterogeneous information in the semantic space from high-resolution remote sensing images and digital elevation model data. For full utilization of precious samples, a global hyper-pixel-wise sample pair queues-based contrastive learning method is developed, which includes the construction of global queues that store hyper-pixel-wise samples and the updating scheme of a momentum encoder, reliably enhancing the extraction ability of semantic features. The proposed HPCL-Net is evaluated on the Loess Plateau relic landslide dataset and experimental results verify that the proposed HPCL-Net greatly outperforms existing models, where the mIoU is increased from 0.620 to 0.651, the Landslide IoU is improved from 0.334 to 0.394 and the F1score is enhanced from 0.501 to 0.565.
作为自然灾害的一种,山体滑坡经常给人类生命带来巨大损失,因此迫切需要进行可靠的山体滑坡风险检测。在使用遥感图像检测遗迹山体滑坡(这些滑坡为滑坡风险预警提供了重要信息)时,视觉模糊和小型数据集等问题带来了很大的挑战。为了提取准确的语义特征,提出了一种超像素级对比学习增强分割网络(HPCL-Net)。该网络通过HPCL增强了从山体滑坡边界提取局部显著特征的能力,并融合了来自高分辨率遥感图像和数字高程模型数据的语义空间中的异质信息。为了充分利用珍贵样本,开发了一种基于全局超像素级样本对队列对比学习方法,包括构建存储超像素级样本的全局队列和动量编码器的更新方案,从而可靠地提高了语义特征的提取能力。在黄土高原遗迹山体滑坡数据集上对提出的HPCL-Net进行了评估,实验结果验证了HPCL-Net相较于现有模型具有显著优势,其中mIoU从0.620提高到0.651,滑坡IoU从0.334提高到0.394,F1分数从0.501提高到0.565。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于高分辨率遥感图像和数字高程模型数据,提出一种超像素级对比学习增强分割网络(HPCL-Net),用于检测滑坡遗迹。该网络通过HPCL增强局部显著特征提取,融合异质信息,解决遥感图像中的视觉模糊和小样本集问题。采用全局超像素级样本对队列对比学习方法,提高语义特征提取能力。在黄土高原滑坡遗迹数据集上的实验结果表明,HPCL-Net在mIoU、滑坡IoU和F1分数等指标上均优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- HPCL-Net网络用于检测滑坡遗迹,结合高分辨率遥感图像和数字高程模型数据。
- 采用超像素级对比学习(HPCL)以增强局部显著特征提取。
- 融合异质信息以解决遥感图像中的视觉模糊和小样本集挑战。
- 引入全局超像素级样本对队列对比学习方法,提高语义特征提取能力。
- HPCL-Net在黄土高原滑坡遗迹数据集上进行实验验证。
- HPCL-Net在mIoU、滑坡IoU和F1分数等关键指标上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图