⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-28 更新
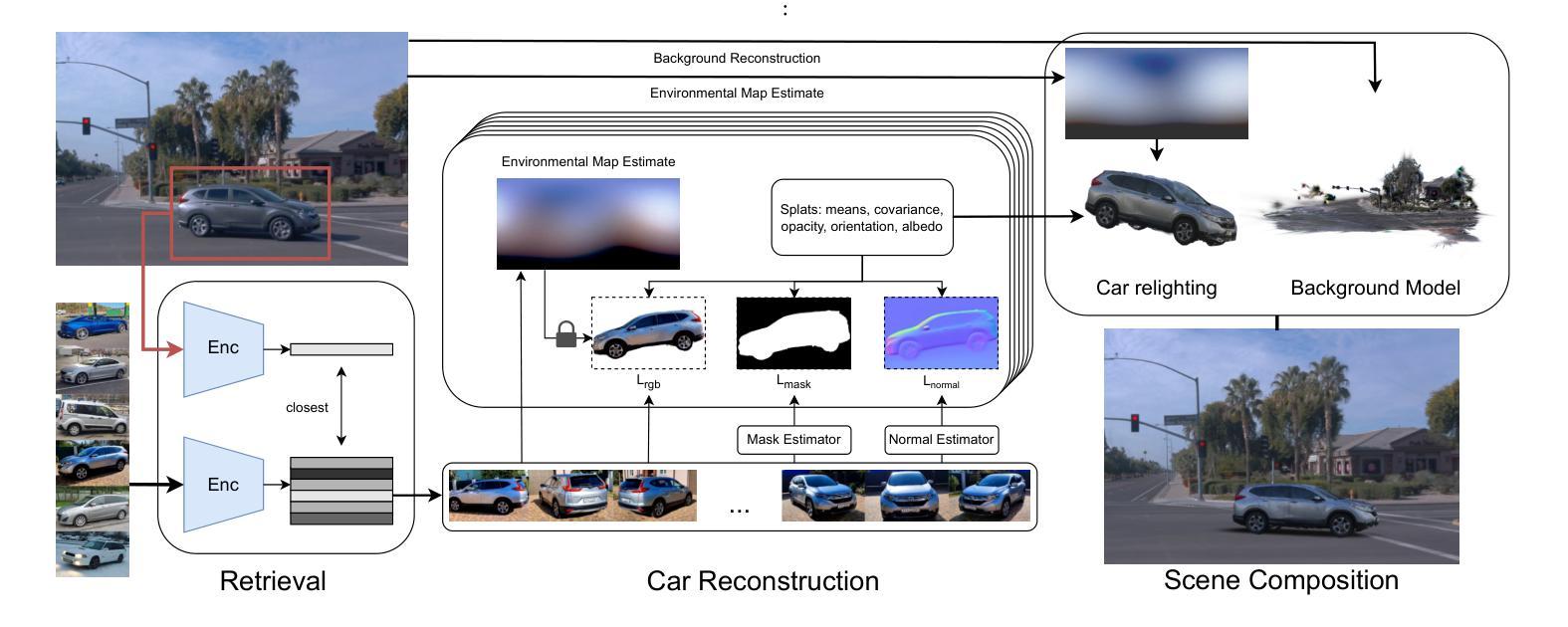
MADrive: Memory-Augmented Driving Scene Modeling
Authors:Polina Karpikova, Daniil Selikhanovych, Kirill Struminsky, Ruslan Musaev, Maria Golitsyna, Dmitry Baranchuk
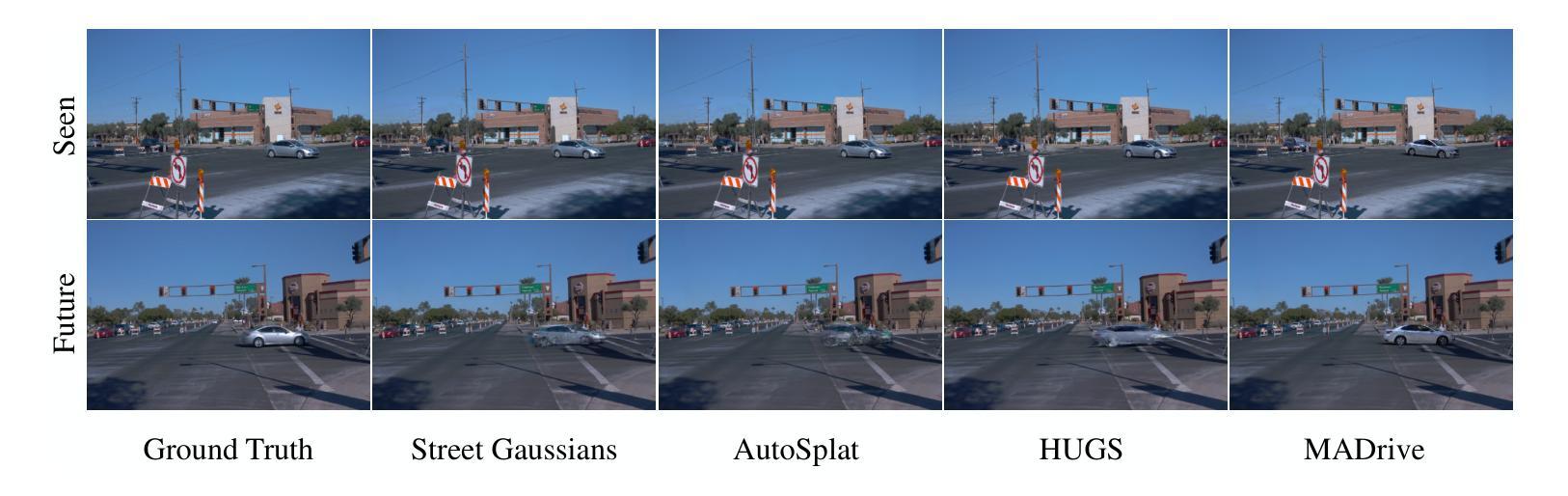
Recent advances in scene reconstruction have pushed toward highly realistic modeling of autonomous driving (AD) environments using 3D Gaussian splatting. However, the resulting reconstructions remain closely tied to the original observations and struggle to support photorealistic synthesis of significantly altered or novel driving scenarios. This work introduces MADrive, a memory-augmented reconstruction framework designed to extend the capabilities of existing scene reconstruction methods by replacing observed vehicles with visually similar 3D assets retrieved from a large-scale external memory bank. Specifically, we release MAD-Cars, a curated dataset of ${\sim}70$K 360{\deg} car videos captured in the wild and present a retrieval module that finds the most similar car instances in the memory bank, reconstructs the corresponding 3D assets from video, and integrates them into the target scene through orientation alignment and relighting. The resulting replacements provide complete multi-view representations of vehicles in the scene, enabling photorealistic synthesis of substantially altered configurations, as demonstrated in our experiments. Project page: https://yandex-research.github.io/madrive/
近期场景重建技术的进展推动了使用3D高斯喷绘进行自动驾驶(AD)环境的高度现实建模。然而,所得的重建结果仍然与原始观察紧密相关,并且在支持大幅更改或新型驾驶场景的逼真合成方面存在困难。本研究引入了MADrive,这是一个增强型重建框架,旨在通过替换观察到的车辆为从大规模外部存储器检索的视觉相似的3D资产来扩展现有场景重建方法的能力。具体来说,我们发布了MAD-Cars,这是一个中国野生的约7万辆车的全方位视频数据集,并展示了一个检索模块,该模块可在内存库中找到最相似的车辆实例,从视频中重建相应的3D资产并将其融入目标场景,实现方向对齐和重新照明。由此产生的替换为场景中的车辆提供了完整的多视角表示,从而实现了大幅更改配置的逼真合成,正如我们的实验所示。项目页面:https://yandex-research.github.io/madrive/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,基于三维高斯贴图技术的场景重建在模拟自动驾驶环境方面取得了进展,但现有技术受限于观测数据,难以生成逼真的虚拟驾驶场景。为解决此问题,本文提出了一个名为MADrive的记忆增强重建框架,用于改进现有场景重建方法。该框架通过从大规模外部记忆库中检索与观测车辆相似的三维资产替换观测车辆。为此,本文发布了MAD-Cars数据集,包含约7万段野外采集的360度汽车视频。检索模块能够在记忆库中找到最相似的车辆实例,重建相应的三维资产,并通过方向对齐和重新照明将其集成到目标场景中。此举实现了车辆的全方位表示,并能生成大幅修改的驾驶场景配置,如实验所示。项目页面:https://yandex-research.github.io/madrive/。
Key Takeaways
- 当前场景重建技术在模拟自动驾驶环境方面存在局限性,难以生成逼真的虚拟驾驶场景。
- MADrive框架旨在改进现有技术,通过替换观测车辆来扩展场景重建能力。
- 使用从大规模外部记忆库中检索的三维资产替换观测车辆的方法被介绍。
- 发布了包含野外采集的360度汽车视频数据集MAD-Cars。
- 检索模块能够在记忆库中找到最相似的车辆实例并进行重建。
- 通过方向对齐和重新照明技术将重建的三维资产集成到目标场景中。
点此查看论文截图


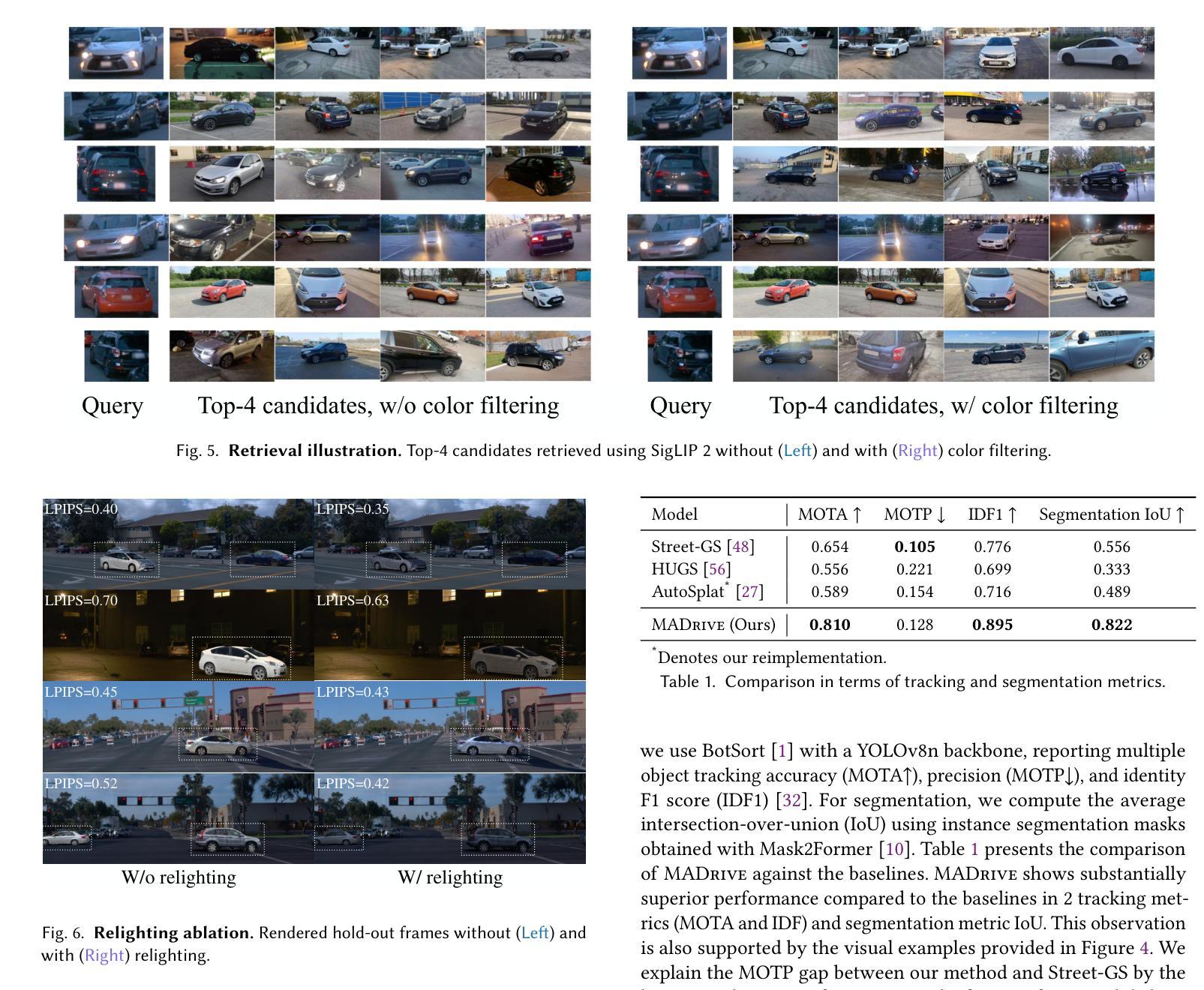
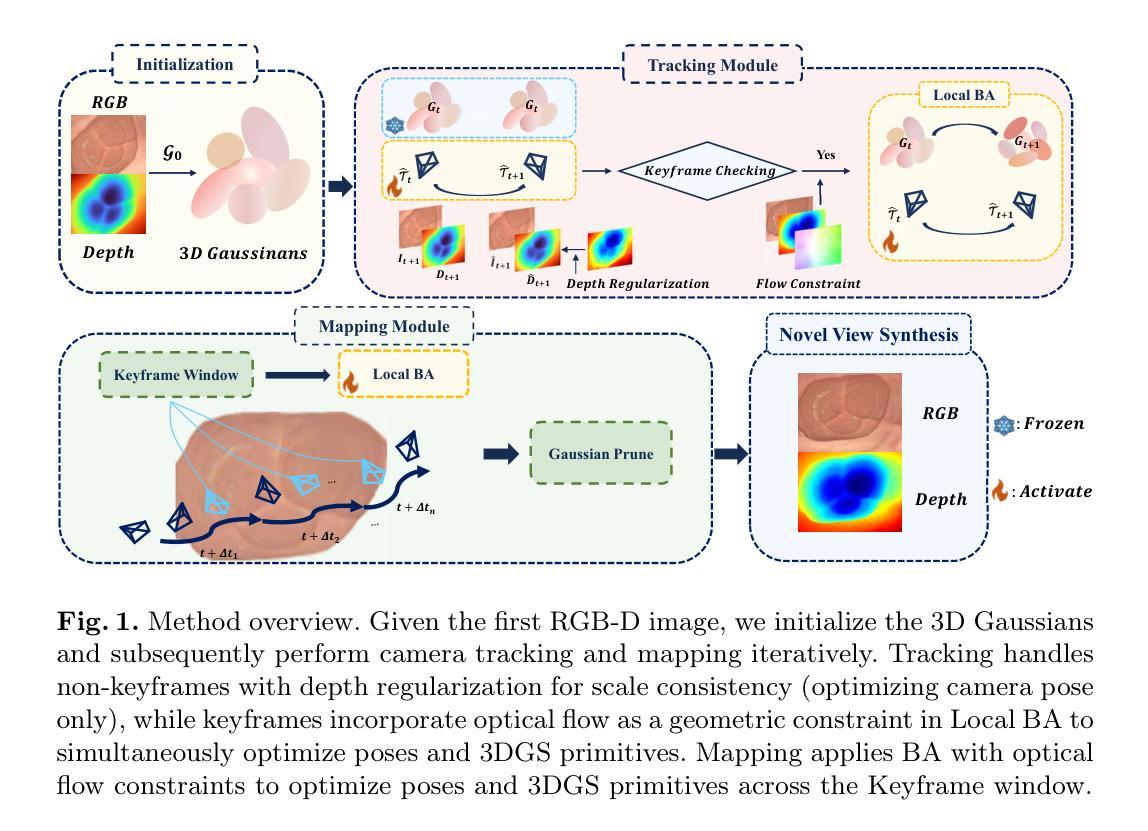
EndoFlow-SLAM: Real-Time Endoscopic SLAM with Flow-Constrained Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Taoyu Wu, Yiyi Miao, Zhuoxiao Li, Haocheng Zhao, Kang Dang, Jionglong Su, Limin Yu, Haoang Li
Efficient three-dimensional reconstruction and real-time visualization are critical in surgical scenarios such as endoscopy. In recent years, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated remarkable performance in efficient 3D reconstruction and rendering. Most 3DGS-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods only rely on the appearance constraints for optimizing both 3DGS and camera poses. However, in endoscopic scenarios, the challenges include photometric inconsistencies caused by non-Lambertian surfaces and dynamic motion from breathing affects the performance of SLAM systems. To address these issues, we additionally introduce optical flow loss as a geometric constraint, which effectively constrains both the 3D structure of the scene and the camera motion. Furthermore, we propose a depth regularisation strategy to mitigate the problem of photometric inconsistencies and ensure the validity of 3DGS depth rendering in endoscopic scenes. In addition, to improve scene representation in the SLAM system, we improve the 3DGS refinement strategy by focusing on viewpoints corresponding to Keyframes with suboptimal rendering quality frames, achieving better rendering results. Extensive experiments on the C3VD static dataset and the StereoMIS dynamic dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis and pose estimation, exhibiting high performance in both static and dynamic surgical scenes. The source code will be publicly available upon paper acceptance.
在手术场景(如内窥镜手术)中,高效的三维重建和实时可视化至关重要。近年来,三维高斯斑点(3DGS)在高效的三维重建和渲染方面表现出了卓越的性能。大多数基于3DGS的同步定位和地图构建(SLAM)方法仅依赖外观约束来优化3DGS和相机姿态。然而,在内窥镜场景中,非朗伯表面引起的光度不一致以及呼吸动态运动影响了SLAM系统的性能。为了解决这些问题,我们额外引入了光流损失作为几何约束,有效地约束了场景的三维结构和相机运动。此外,我们提出了一种深度正则化策略,以缓解光度不一致的问题,并确保在内窥镜场景中3DGS深度渲染的有效性。为了改善SLAM系统中的场景表示,我们改进了3DGS细化策略,重点关注与关键帧相对应的观点,这些关键帧具有次优渲染质量帧,从而实现更好的渲染结果。在C3VD静态数据集和StereoMIS动态数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在新型视图合成和姿态估计方面优于现有先进技术,在静态和动态手术场景中均表现出高性能。论文被接受后,源代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在手术场景(如内窥镜)中,高效的三维重建和实时可视化至关重要。采用3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)技术可以实现高效的三维重建和渲染。针对内窥镜场景中面临的挑战,如非Lambertian表面引起的光度不一致性和动态运动(如呼吸)对SLAM系统性能的影响,本文引入了光学流损失作为几何约束,并提出深度正则化策略来缓解光度不一致性问题,确保3DGS深度渲染在内窥镜场景中的有效性。此外,通过改进3DGS优化策略,关注对应于关键帧的视点,提高了场景表示和渲染质量。在C3VD静态数据集和StereoMIS动态数据集上的实验表明,该方法在新型视图合成和姿态估计方面优于现有最先进的方法,在静态和动态手术场景中均表现出高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)在内窥镜手术场景中表现突出,用于高效的三维重建和渲染。
- 内窥镜场景中的挑战包括光度不一致性和动态运动对SLAM系统性能的影响。
- 引入光学流损失作为几何约束,有效约束场景的三维结构和相机运动。
- 提出深度正则化策略,确保3DGS深度渲染在内窥镜场景中的有效性,缓解光度不一致性问题。
- 通过改进3DGS优化策略,关注关键帧的视点,提高场景表示和渲染质量。
- 在C3VD静态数据集和StereoMIS动态数据集上的实验表明,该方法在视图合成和姿态估计方面超越现有技术。
- 源码将在论文被接受后公开。
点此查看论文截图

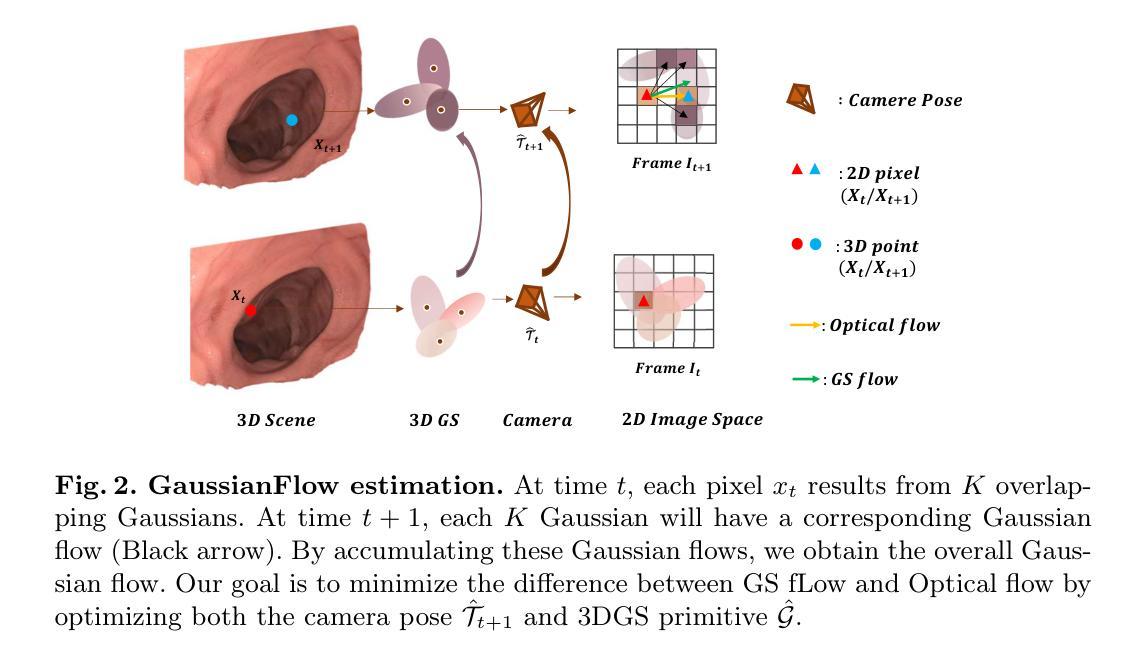
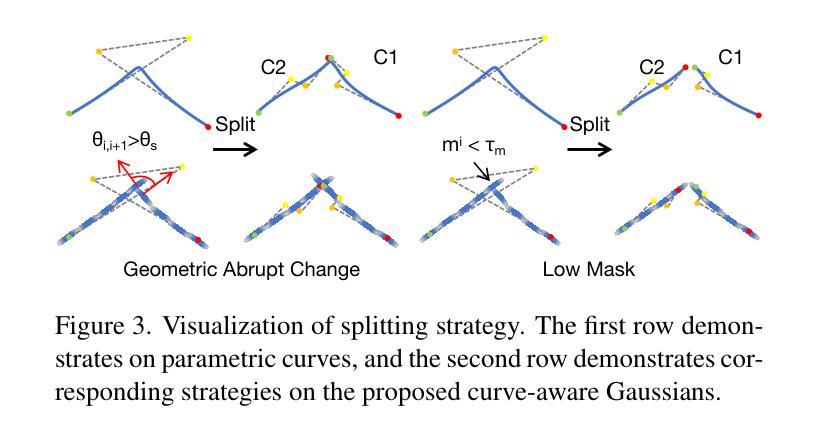
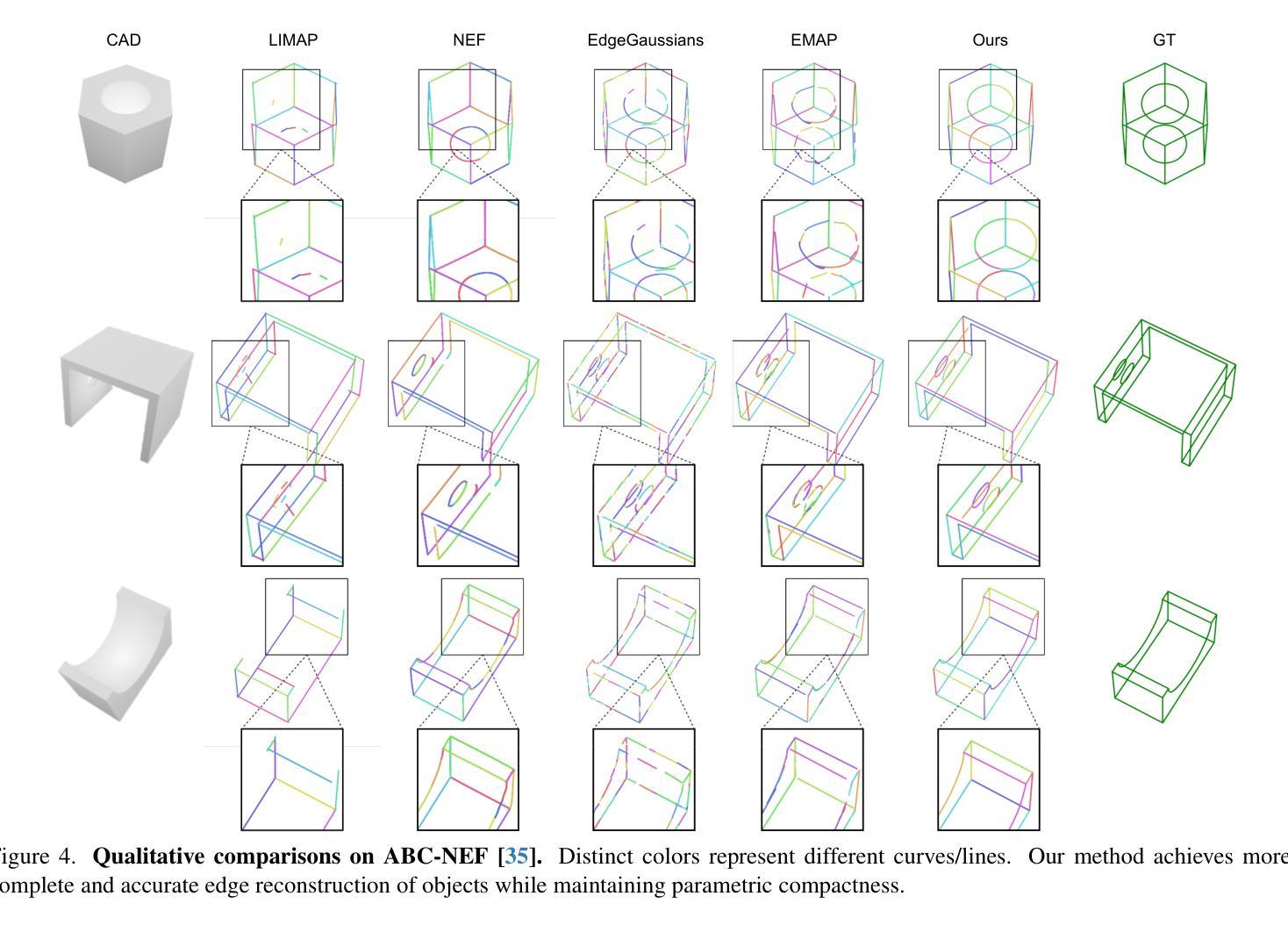
Curve-Aware Gaussian Splatting for 3D Parametric Curve Reconstruction
Authors:Zhirui Gao. Renjiao Yi, Yaqiao Dai, Xuening Zhu, Wei Chen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
This paper presents an end-to-end framework for reconstructing 3D parametric curves directly from multi-view edge maps. Contrasting with existing two-stage methods that follow a sequential ``edge point cloud reconstruction and parametric curve fitting’’ pipeline, our one-stage approach optimizes 3D parametric curves directly from 2D edge maps, eliminating error accumulation caused by the inherent optimization gap between disconnected stages. However, parametric curves inherently lack suitability for rendering-based multi-view optimization, necessitating a complementary representation that preserves their geometric properties while enabling differentiable rendering. We propose a novel bi-directional coupling mechanism between parametric curves and edge-oriented Gaussian components. This tight correspondence formulates a curve-aware Gaussian representation, \textbf{CurveGaussian}, that enables differentiable rendering of 3D curves, allowing direct optimization guided by multi-view evidence. Furthermore, we introduce a dynamically adaptive topology optimization framework during training to refine curve structures through linearization, merging, splitting, and pruning operations. Comprehensive evaluations on the ABC dataset and real-world benchmarks demonstrate our one-stage method’s superiority over two-stage alternatives, particularly in producing cleaner and more robust reconstructions. Additionally, by directly optimizing parametric curves, our method significantly reduces the parameter count during training, achieving both higher efficiency and superior performance compared to existing approaches.
本文提出了一种端到端的框架,可直接从多视角边缘地图重建3D参数曲线。与现有的两阶段方法(遵循“边缘点云重建和参数曲线拟合”的流水线)形成对比,我们的单阶段方法直接从二维边缘地图优化三维参数曲线,消除了由于不同阶段之间固有的优化间隔所导致的误差累积。然而,参数曲线在基于渲染的多视角优化中固有的不适性要求有一种互补的表示形式,能够保留其几何属性并实现可微分渲染。我们提出了参数曲线和边缘方向高斯组件之间的新型双向耦合机制。这种紧密对应关系形成了一种曲线感知的高斯表示形式——CurveGaussian,它能够实现三维曲线的可微分渲染,允许由多视角证据直接引导优化。此外,我们在训练过程中引入了一种动态自适应拓扑优化框架,通过线性化、合并、拆分和修剪操作来优化曲线结构。在ABC数据集和现实世界基准测试上的综合评估表明,我们的单阶段方法在清洁度和稳健性方面优于两阶段替代方案,特别是在重建方面。此外,通过直接优化参数曲线,我们的方法在训练过程中显著减少了参数计数,与现有方法相比,既提高了效率又提高了性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/zhirui-gao/Curve-Gaussian Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
该论文提出了一种端到端的框架,直接从多视角边缘图重建3D参数曲线。与现有的两阶段方法不同,该方法采用一站式优化,消除了因阶段间优化差距导致的误差累积。为解决参数曲线不适合基于渲染的多视角优化问题,论文提出了参数曲线与边缘定向高斯组件之间的双向耦合机制,形成了一种曲线感知的高斯表示方法CurveGaussian,实现了3D曲线的可微渲染,可直接由多视角证据进行优化。此外,论文还引入了动态自适应拓扑优化框架,在训练过程中通过线性化、合并、分割和修剪操作细化曲线结构。在ABC数据集和真实世界基准测试上的综合评估表明,该方法在一站式重建中优于两阶段替代方案,特别是在产生更干净、更稳健的重建结果方面。同时,该方法通过直接优化参数曲线,降低了训练时的参数计数,提高了效率并提升了性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种端到端的框架,用于直接从多视角边缘图重建3D参数曲线。
- 与传统的两阶段方法相比,该方法采用一站式优化,减少了误差累积。
- 为了解决参数曲线不适合多视角优化的问题,论文提出了CurveGaussian表示方法,实现了3D曲线的可微渲染。
- 该方法通过引入动态自适应拓扑优化框架,可以在训练过程中细化曲线结构。
- 在ABC数据集和真实世界基准测试上,该方法的性能优于其他方法。
- 该方法通过直接优化参数曲线,提高了重建效率和性能。
点此查看论文截图

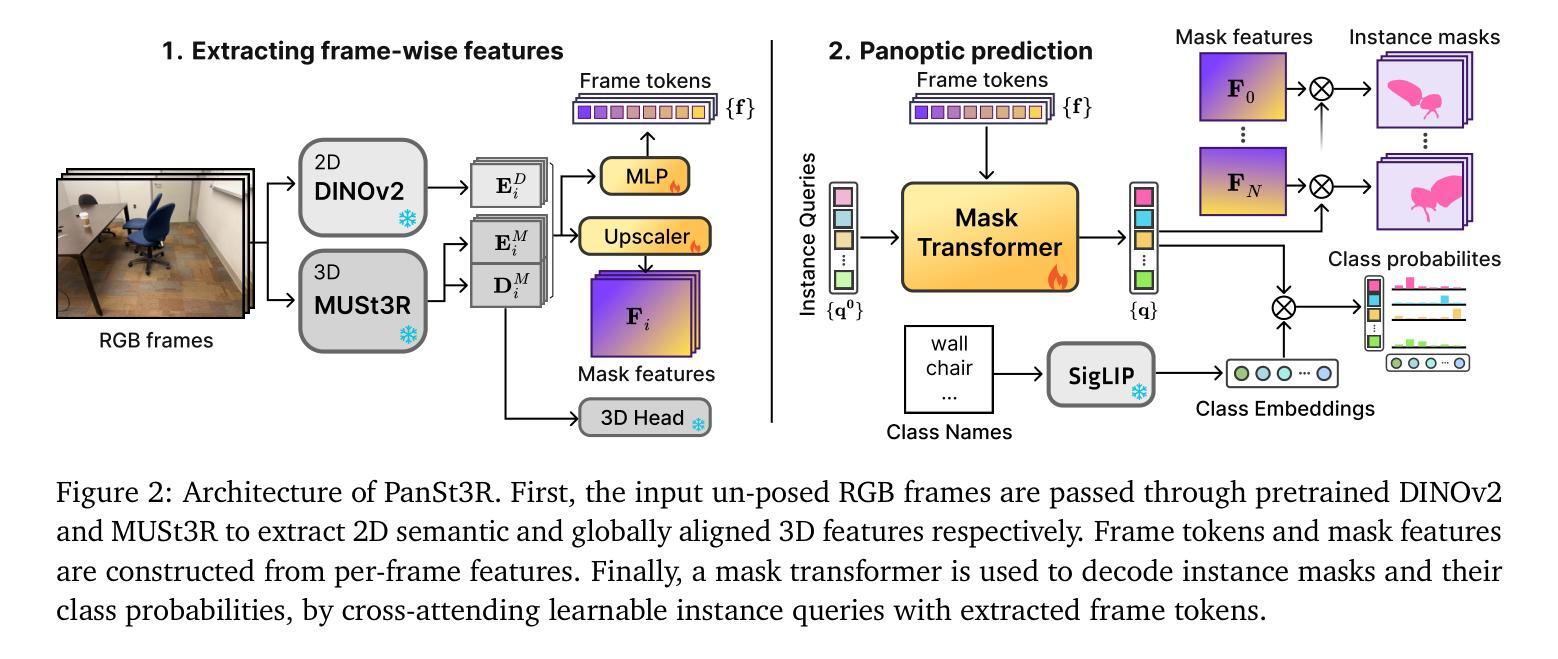
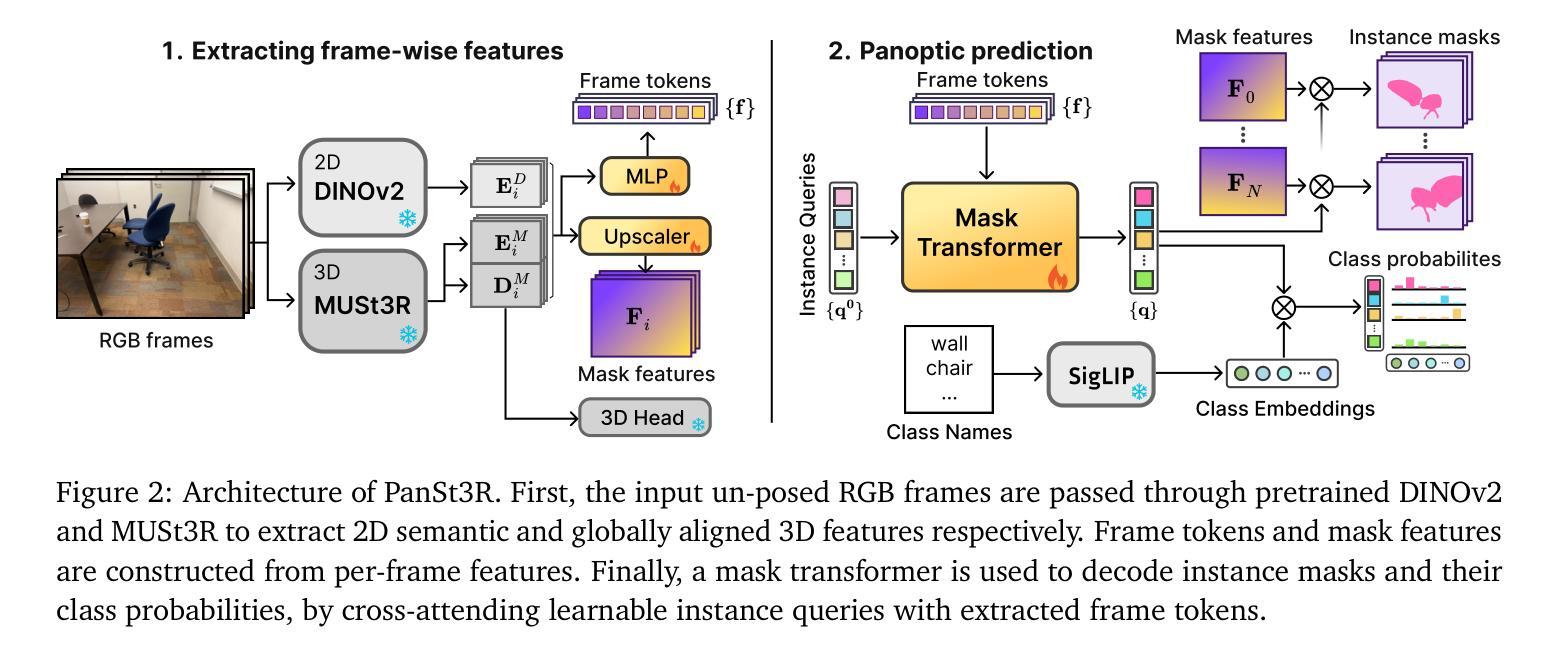
PanSt3R: Multi-view Consistent Panoptic Segmentation
Authors:Lojze Zust, Yohann Cabon, Juliette Marrie, Leonid Antsfeld, Boris Chidlovskii, Jerome Revaud, Gabriela Csurka
Panoptic segmentation of 3D scenes, involving the segmentation and classification of object instances in a dense 3D reconstruction of a scene, is a challenging problem, especially when relying solely on unposed 2D images. Existing approaches typically leverage off-the-shelf models to extract per-frame 2D panoptic segmentations, before optimizing an implicit geometric representation (often based on NeRF) to integrate and fuse the 2D predictions. We argue that relying on 2D panoptic segmentation for a problem inherently 3D and multi-view is likely suboptimal as it fails to leverage the full potential of spatial relationships across views. In addition to requiring camera parameters, these approaches also necessitate computationally expensive test-time optimization for each scene. Instead, in this work, we propose a unified and integrated approach PanSt3R, which eliminates the need for test-time optimization by jointly predicting 3D geometry and multi-view panoptic segmentation in a single forward pass. Our approach builds upon recent advances in 3D reconstruction, specifically upon MUSt3R, a scalable multi-view version of DUSt3R, and enhances it with semantic awareness and multi-view panoptic segmentation capabilities. We additionally revisit the standard post-processing mask merging procedure and introduce a more principled approach for multi-view segmentation. We also introduce a simple method for generating novel-view predictions based on the predictions of PanSt3R and vanilla 3DGS. Overall, the proposed PanSt3R is conceptually simple, yet fast and scalable, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on several benchmarks, while being orders of magnitude faster than existing methods.
对三维场景的全景分割(Panoptic segmentation)是一个具有挑战性的问题,它涉及到在场景密集的三维重建中对对象实例进行分割和分类。尤其是当仅依赖于无姿态的二维图像时更是如此。现有方法通常利用现成的模型提取每帧的二维全景分割,然后优化隐式几何表示(通常基于NeRF)来集成和融合二维预测结果。我们认为,依赖二维全景分割来解决一个本质上是三维和多视角的问题可能是次优的,因为它未能充分利用不同视角之间的空间关系的潜力。此外,这些方法不仅需要相机参数,还需要对每个场景进行昂贵的测试时间优化。相反,在这项工作中,我们提出了一种统一和集成的PanSt3R方法,通过一次前向传播联合预测三维几何和多视角全景分割,从而消除了对测试时间优化的需求。我们的方法建立在最近的3D重建进展之上,特别是可伸缩的多视角版本MUSt3R,通过语义意识和多视角全景分割能力对其进行增强。我们还重新访问了标准的后处理掩膜合并过程,并引入了一种更严谨的多视角分割方法。此外,我们还提出了一种基于PanSt3R和基本的3DGS预测生成新颖视角预测的简单方法。总的来说,所提出的PanSt3R在概念上简单、快速且可扩展,在多个基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,同时比现有方法快几个数量级。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary
提出了一种名为PanSt3R的统一方法,用于在单个前向传递中联合预测3D几何和全景分割,无需测试时优化。该方法基于最近的3D重建技术MUSt3R,增强了语义感知和多视角全景分割能力。通过简化标准的后处理遮罩合并过程,引入更有原则的多视角分割方法,并基于PanSt3R和基本的3DGS生成新视角预测。该方法概念简单,速度快,可扩展性强,在多个基准测试中达到最佳性能,并且计算速度比现有方法快几个数量级。
Key Takeaways
- Panoptic segmentation of 3D scenes is challenging, especially when relying on unposed 2D images.
- Existing methods leverage off-the-shelf models to extract 2D panoptic segmentations and then integrate them with implicit geometric representations.
- These methods require camera parameters and computationally expensive test-time optimization for each scene.
- PanSt3R is a unified approach that eliminates the need for test-time optimization by jointly predicting 3D geometry and multi-view panoptic segmentation in a single forward pass.
- PanSt3R builds upon recent advances in 3D reconstruction, specifically MUSt3R, and enhances it with semantic awareness and multi-view panoptic segmentation capabilities.
- PanSt3R introduces a more principled approach for multi-view segmentation and generates novel-view predictions based on the predictions of PanSt3R and basic 3DGS.
点此查看论文截图

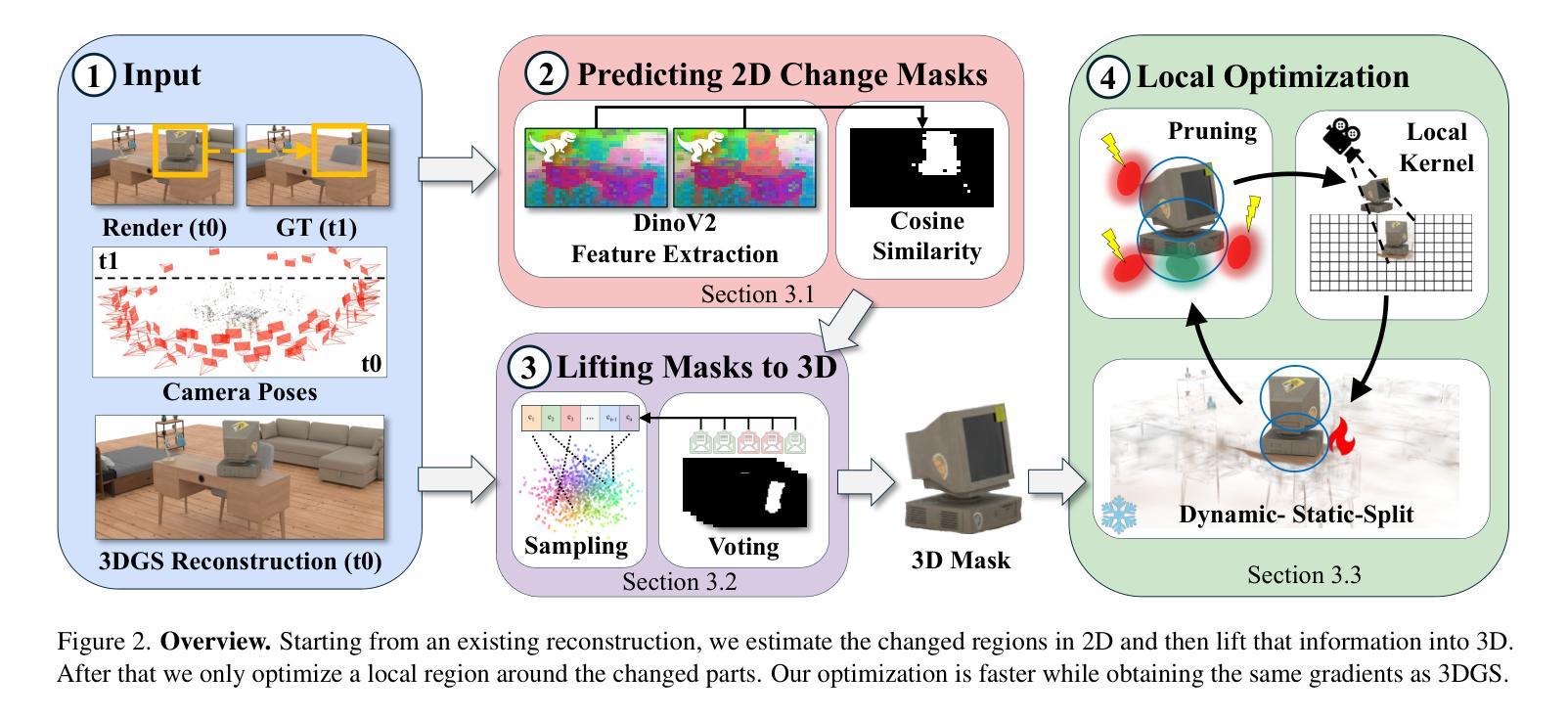
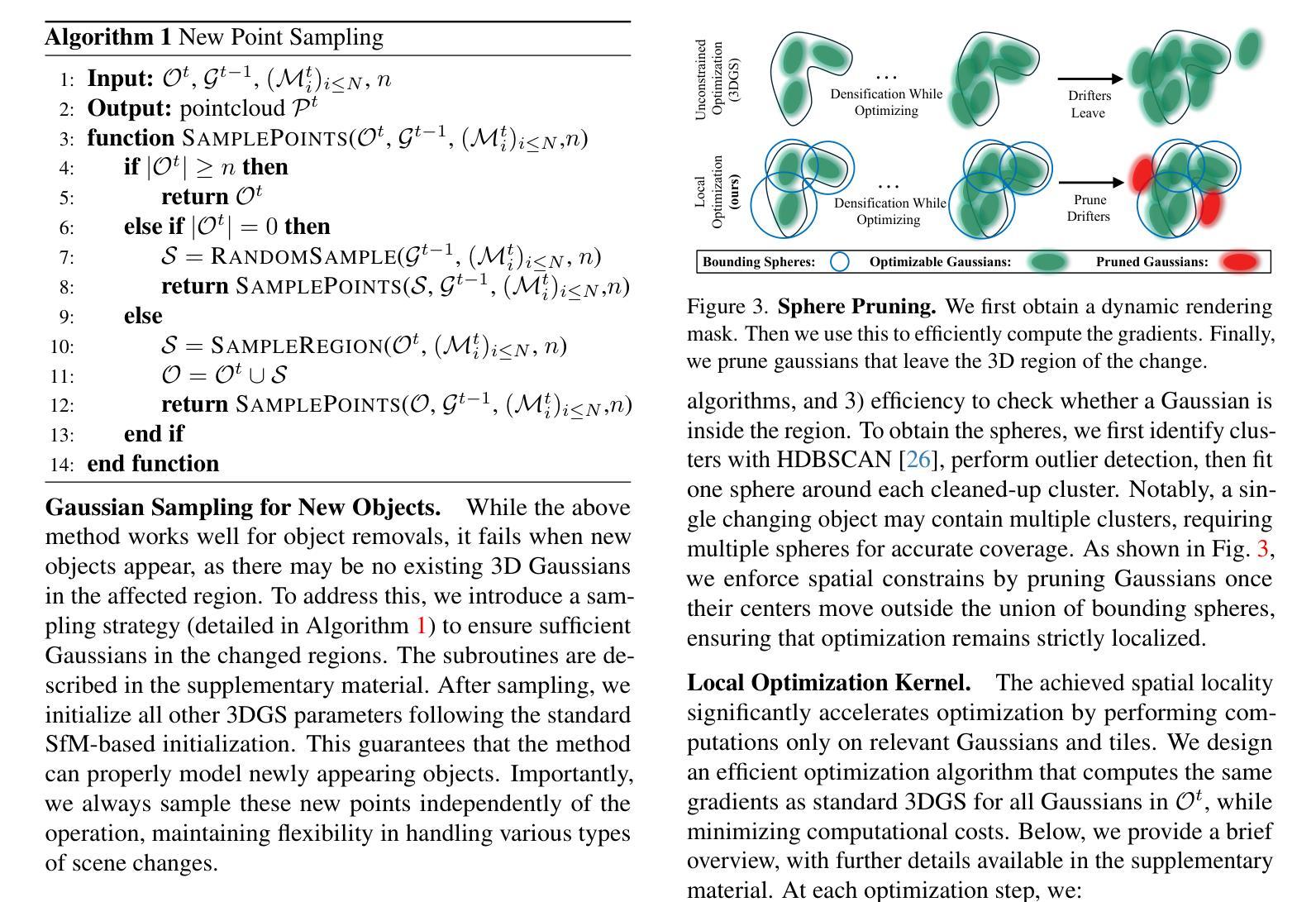
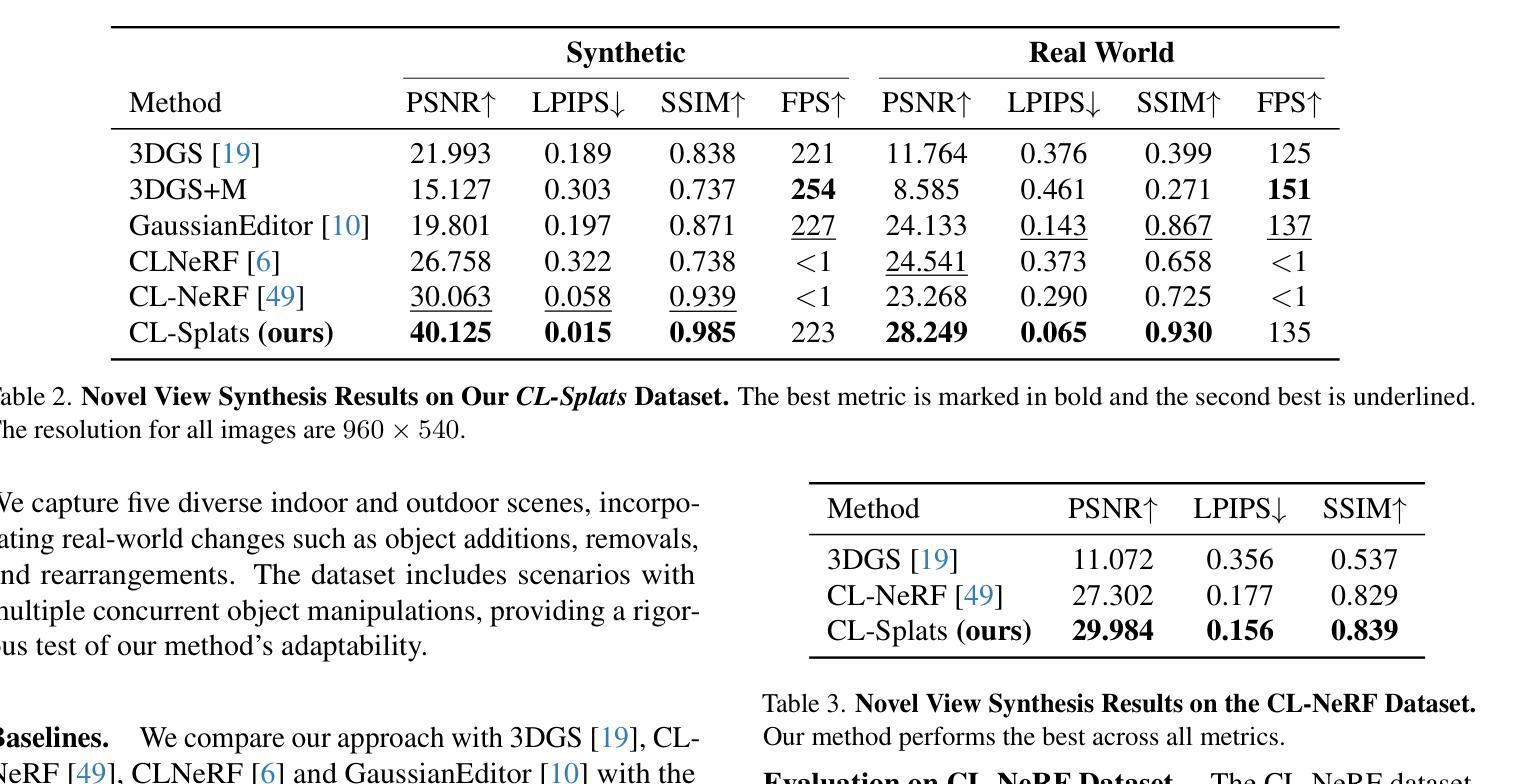
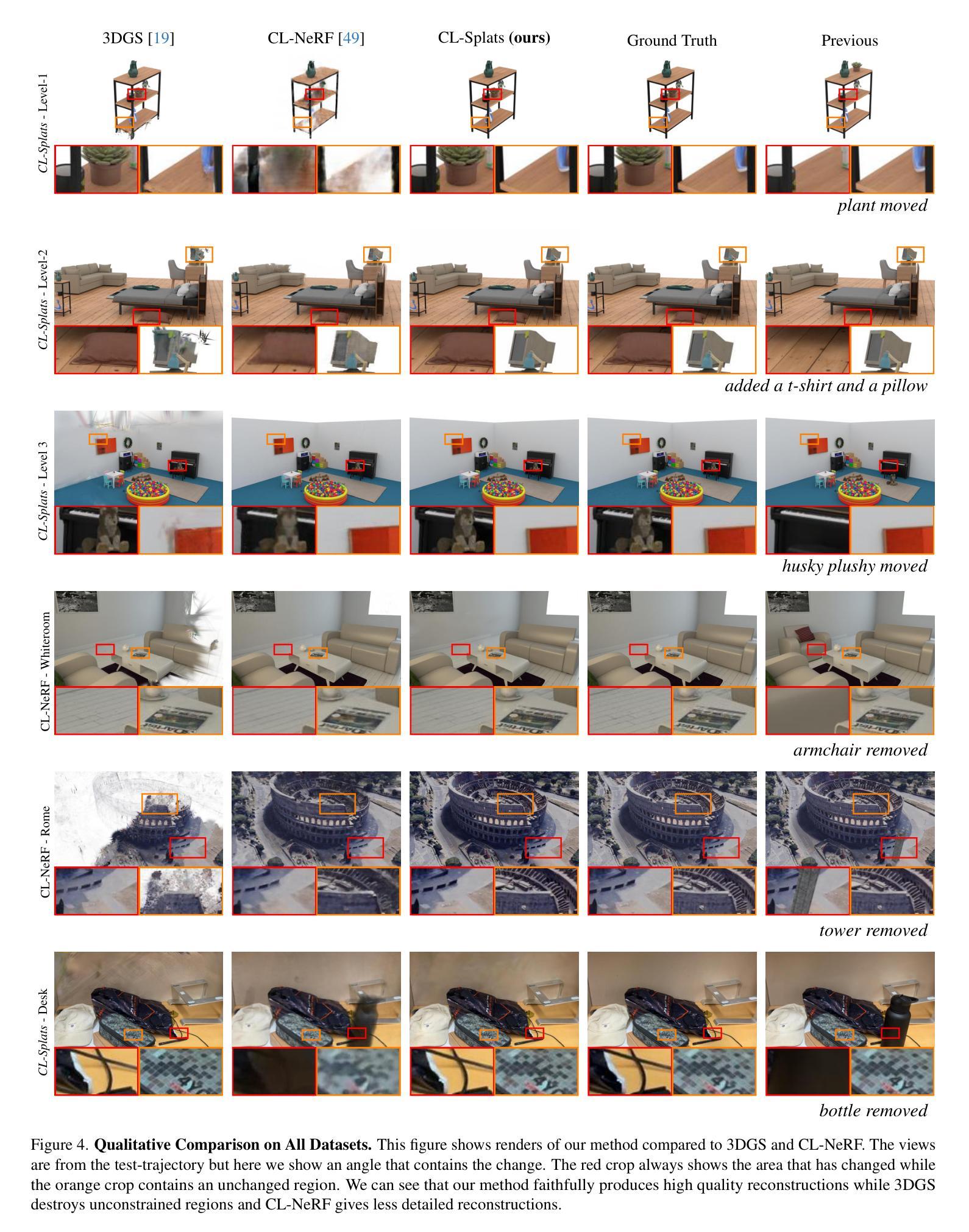
CL-Splats: Continual Learning of Gaussian Splatting with Local Optimization
Authors:Jan Ackermann, Jonas Kulhanek, Shengqu Cai, Haofei Xu, Marc Pollefeys, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas Guibas, Songyou Peng
In dynamic 3D environments, accurately updating scene representations over time is crucial for applications in robotics, mixed reality, and embodied AI. As scenes evolve, efficient methods to incorporate changes are needed to maintain up-to-date, high-quality reconstructions without the computational overhead of re-optimizing the entire scene. This paper introduces CL-Splats, which incrementally updates Gaussian splatting-based 3D representations from sparse scene captures. CL-Splats integrates a robust change-detection module that segments updated and static components within the scene, enabling focused, local optimization that avoids unnecessary re-computation. Moreover, CL-Splats supports storing and recovering previous scene states, facilitating temporal segmentation and new scene-analysis applications. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that CL-Splats achieves efficient updates with improved reconstruction quality over the state-of-the-art. This establishes a robust foundation for future real-time adaptation in 3D scene reconstruction tasks.
在动态3D环境中,随着时间的推移准确更新场景表示为机器人技术、混合现实和实体人工智能的应用至关重要。随着场景的发展,需要有效的方法来融入变化,以维持最新、高质量的重构,而无需对整个场景进行重新优化的计算开销。本文介绍了CL-Splats,它基于高斯splat方法逐步更新稀疏场景捕获的3D表示。CL-Splats集成了一个稳健的变化检测模块,该模块可以在场景中分割出更新的和静态的组件,从而实现有针对性的局部优化,避免了不必要的重新计算。此外,CL-Splats支持存储和恢复之前的场景状态,便于进行时间分割和新的场景分析应用。我们的广泛实验表明,CL-Splats实现了高效的更新,在重建质量上超过了最新技术。这为未来3D场景重建任务的实时适应奠定了坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025, Project Page: https://cl-splats.github.io
Summary
这篇论文介绍了CL-Splats技术,该技术能够动态地更新三维场景表示。它通过增量更新基于高斯喷溅的3D表示,实现稀疏场景的捕捉。CL-Splats集成了一个稳健的变化检测模块,能够分割场景中的更新和静态组件,实现局部优化,避免不必要的重新计算。此外,CL-Splats支持存储和恢复之前的场景状态,促进时间分割和新的场景分析应用。实验证明,CL-Splats在更新效率和重建质量方面优于现有技术,为未来的实时适应三维重建任务奠定了坚实的基础。
Key Takeaways
- CL-Splats技术能够动态更新三维场景表示,适用于机器人、混合现实和实体人工智能等领域。
- 通过增量更新基于高斯喷溅的3D表示,实现从稀疏场景中捕捉信息。
- 引入变化检测模块,有效分割场景中的更新和静态部分,实现局部优化,避免不必要的重新计算。
- 支持存储和恢复之前的场景状态,有助于实现时间分割和新的场景分析应用。
- CL-Splats实验证明其在更新效率和重建质量方面的优越性。
- CL-Splats技术为实时适应三维重建任务提供了坚实的基础。
点此查看论文截图


User-in-the-Loop View Sampling with Error Peaking Visualization
Authors:Ayaka Yasunaga, Hideo Saito, Shohei Mori
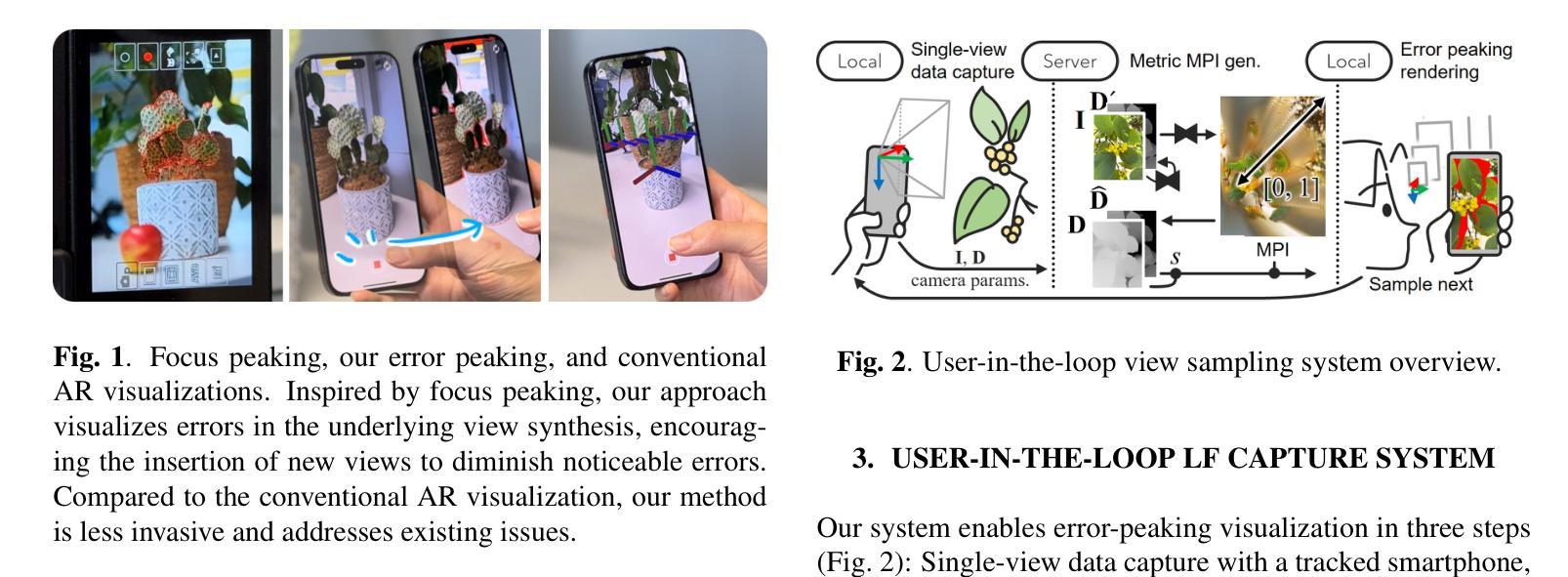
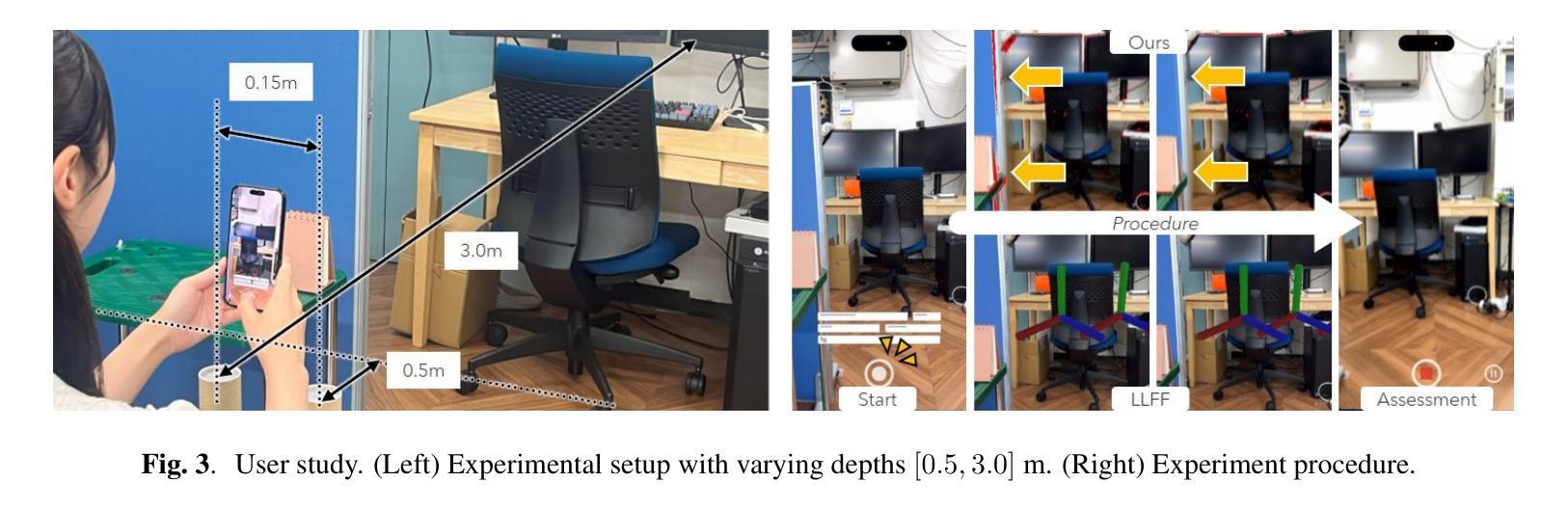
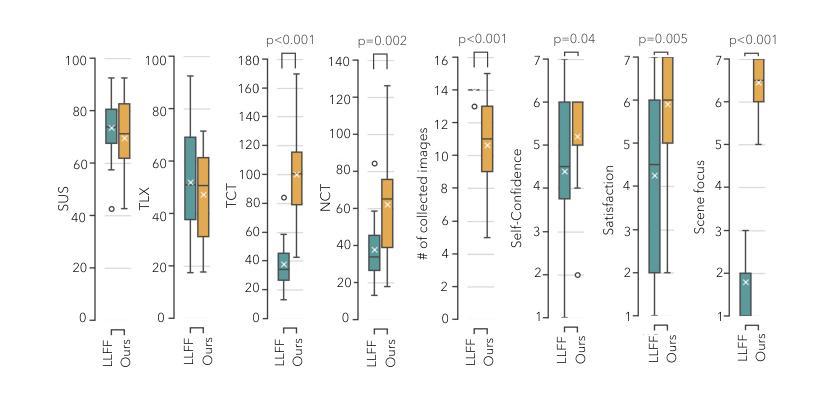
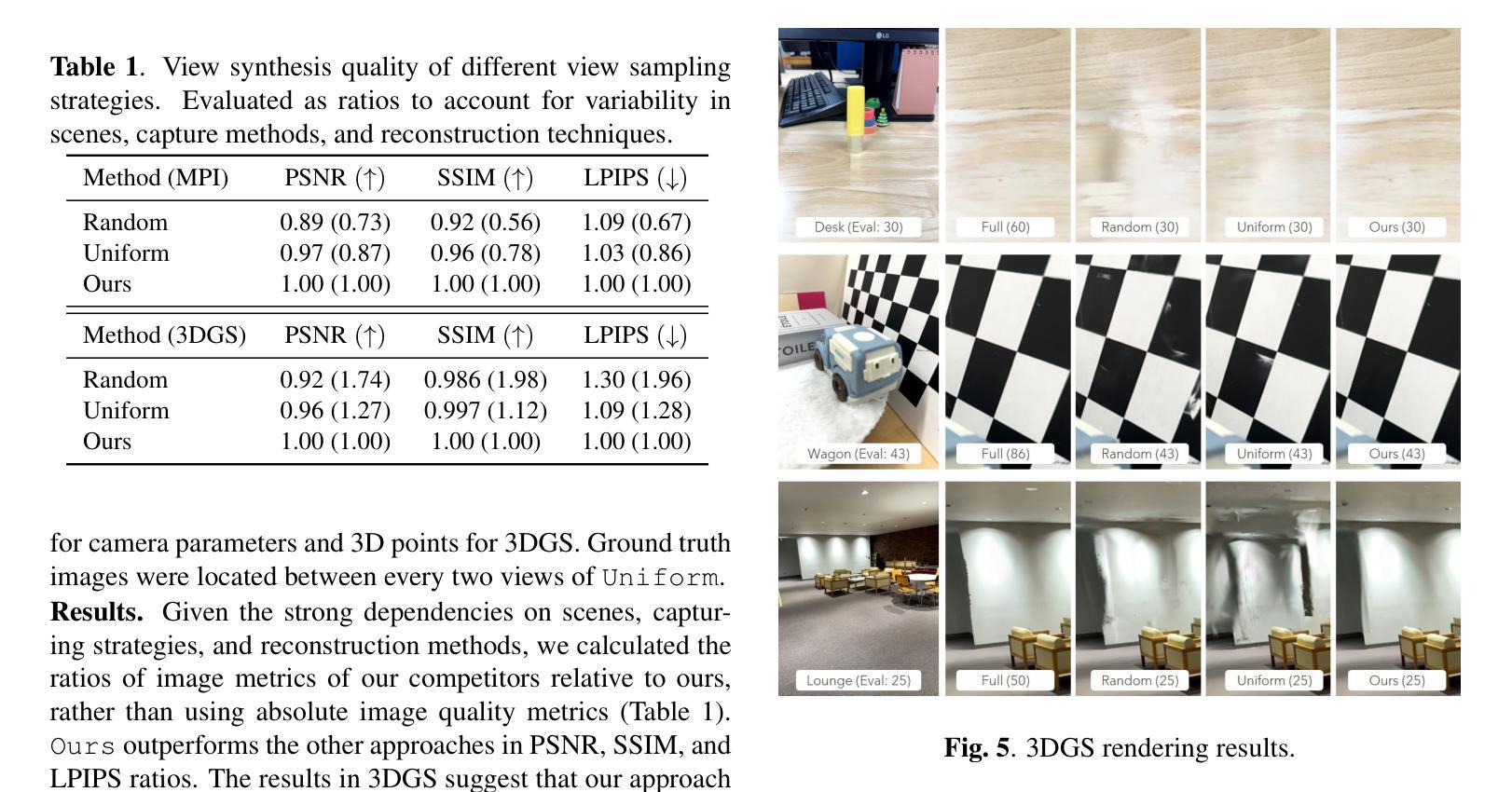
Augmented reality (AR) provides ways to visualize missing view samples for novel view synthesis. Existing approaches present 3D annotations for new view samples and task users with taking images by aligning the AR display. This data collection task is known to be mentally demanding and limits capture areas to pre-defined small areas due to the ideal but restrictive underlying sampling theory. To free users from 3D annotations and limited scene exploration, we propose using locally reconstructed light fields and visualizing errors to be removed by inserting new views. Our results show that the error-peaking visualization is less invasive, reduces disappointment in final results, and is satisfactory with fewer view samples in our mobile view synthesis system. We also show that our approach can contribute to recent radiance field reconstruction for larger scenes, such as 3D Gaussian splatting.
增强现实(AR)提供了可视化缺失视图样本以合成新视图的方法。现有方法为新视图样本提供三维注释,并要求用户通过调整AR显示屏来拍摄图像。众所周知,此数据采集任务要求较高的脑力负担,而且由于理想但限制性的底层采样理论,捕获区域仅限于预先定义的小区域。为了使用户摆脱三维注释和场景探索的限制,我们提出使用局部重建的光场并通过可视化错误来消除通过插入新视图产生的错误。我们的结果表明,误差峰值可视化具有较小的侵入性,减少了最终结果的失望感,在我们的移动视图合成系统中具有较少的视图样本时就能令人满意。我们还表明,我们的方法可以支持对更大的场景进行近期的辐射场重建,例如用于高斯二维卷积贴片纹理技术的渲染过程的升级版算法——“高斯辐板化”(Gaussian Splatting)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ICIP 2025, Project Page: https://mediated-reality.github.io/projects/yasunaga_icip25/
Summary
文章讨论了使用增强现实技术为新型视角合成提供可视化缺失视角样本的方法。现有方法需要用户进行繁琐的3D标注并采集图像,任务量大且受限于预先设定的区域。为解决这些问题,该文提出了基于局部重建光场并可视化误差来添加新视角的方法。这种方法具有较低的侵犯性,减少了最终结果的失望感,并在移动视角合成系统中使用较少的视角样本即可达到满意的效果。此外,该文也表明该方法有助于对大场景进行辐射场重建,如3D高斯板绘。
Key Takeaways
- AR技术用于新型视角合成中的可视化缺失视角样本。
- 现有方法依赖用户进行繁琐的3D标注和图像采集,任务量大并受限于预定义区域。
- 提出基于局部重建光场的方法,无需用户进行3D标注,并能在移动视角合成系统中实现满意的效果。
- 通过可视化误差来添加新视角,降低侵犯性并减少最终结果的失望感。
- 该方法有助于对大场景进行辐射场重建,如使用3D高斯板绘技术。
- 该方法能够在较少的视角样本下实现满意的效果。
点此查看论文截图

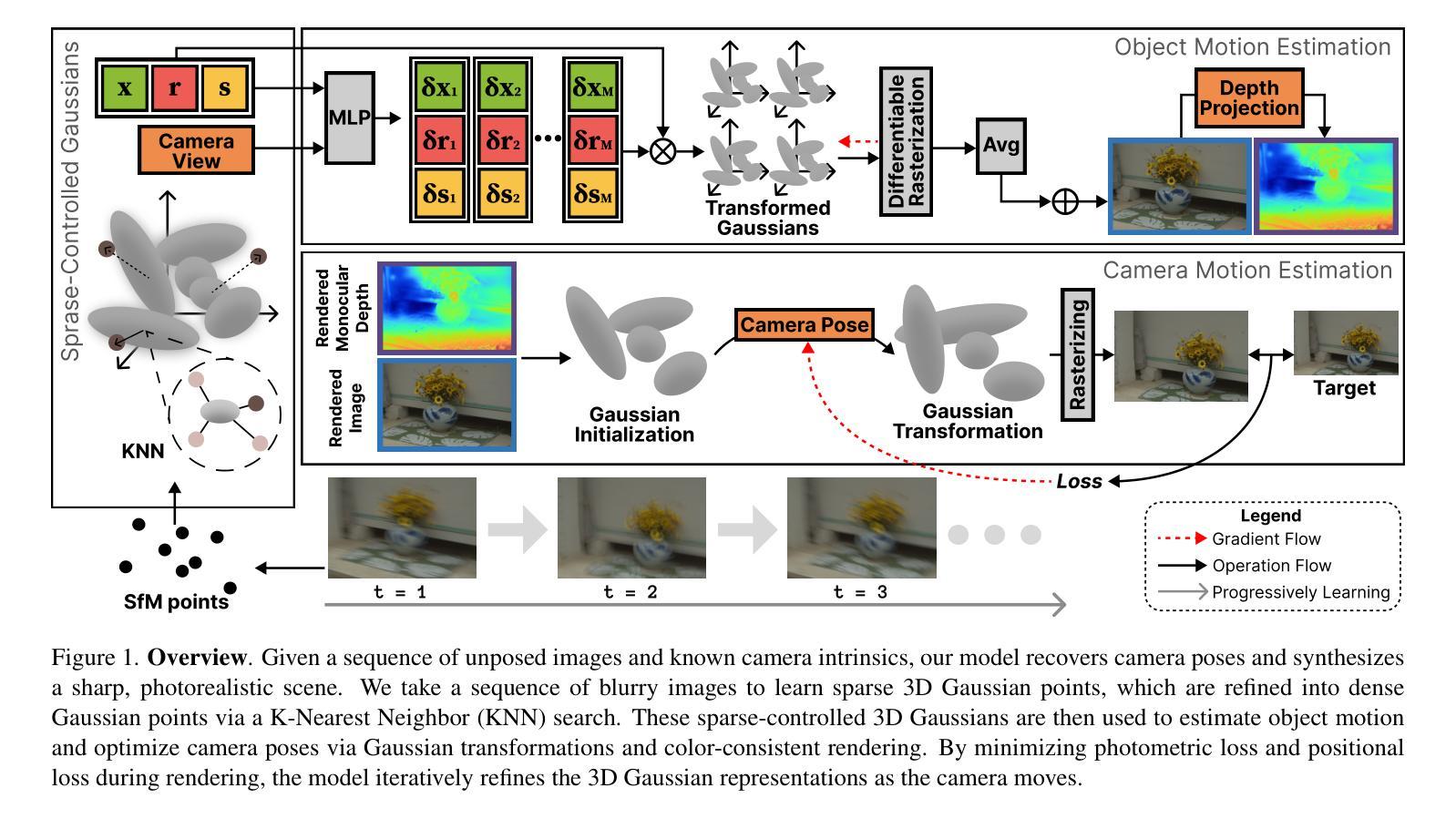
DBMovi-GS: Dynamic View Synthesis from Blurry Monocular Video via Sparse-Controlled Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yeon-Ji Song, Jaein Kim, Byung-Ju Kim, Byoung-Tak Zhang
Novel view synthesis is a task of generating scenes from unseen perspectives; however, synthesizing dynamic scenes from blurry monocular videos remains an unresolved challenge that has yet to be effectively addressed. Existing novel view synthesis methods are often constrained by their reliance on high-resolution images or strong assumptions about static geometry and rigid scene priors. Consequently, their approaches lack robustness in real-world environments with dynamic object and camera motion, leading to instability and degraded visual fidelity. To address this, we propose Motion-aware Dynamic View Synthesis from Blurry Monocular Video via Sparse-Controlled Gaussian Splatting (DBMovi-GS), a method designed for dynamic view synthesis from blurry monocular videos. Our model generates dense 3D Gaussians, restoring sharpness from blurry videos and reconstructing detailed 3D geometry of the scene affected by dynamic motion variations. Our model achieves robust performance in novel view synthesis under dynamic blurry scenes and sets a new benchmark in realistic novel view synthesis for blurry monocular video inputs.
场景的新视角合成是一项从未见过的视角生成场景的任务;然而,从模糊的单目视频中合成动态场景仍然是一个尚未有效解决的挑战。现有的新视角合成方法通常受限于对高分辨率图像的依赖或对静态几何和刚性场景先验的强烈假设。因此,他们在现实世界环境中,面对动态物体和相机运动时,缺乏稳健性,导致不稳定和视觉保真度下降。为了解决这一问题,我们提出一种基于稀疏控制的高斯拼贴法(DBMovi-GS)的动态模糊视频中的动态视角合成方法。该方法旨在从模糊的单目视频中实现动态视角合成。我们的模型生成密集的3D高斯,从模糊的视频中恢复清晰度,并重建受动态运动变化影响的场景的详细3D几何形状。我们的模型在动态模糊场景下的新视角合成中实现了稳健的性能表现,并为模糊单目视频输入的真实新视角合成设定了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPRW 2025, Neural Fields Beyond Conventional Cameras
Summary
该文探讨了从模糊的单目视频中合成动态场景的新视角挑战。现有方法依赖于高分辨率图像或静态几何的强假设,难以应对真实世界中的动态对象和相机运动,导致不稳定和视觉保真度降低。为此,提出了基于稀疏控制高斯点绘技术的Motion-aware Dynamic View Synthesis from Blurry Monocular Video(DBMovi-GS)方法。该方法能够生成密集的三维高斯,从模糊视频中恢复清晰度,并重建受动态运动变化影响的场景的详细三维几何。该方法在模糊动态场景下的新视角合成中实现了稳健性能,为模糊单目视频输入的真实新视角合成树立了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 文章介绍了从模糊的单目视频中合成动态场景的新视角的挑战性。
- 现有方法在处理动态场景时存在局限性,特别是在处理模糊视频时。
- 现有方法依赖于高分辨率图像或静态场景的假设,导致在真实环境中的性能不稳定。
- 文章提出了一种名为DBMovi-GS的新方法,用于从模糊的单目视频中合成动态场景。
- DBMovi-GS方法通过生成密集的三维高斯来恢复视频的清晰度。
- DBMovi-GS方法可以重建受动态运动变化影响的场景的详细三维几何。
点此查看论文截图

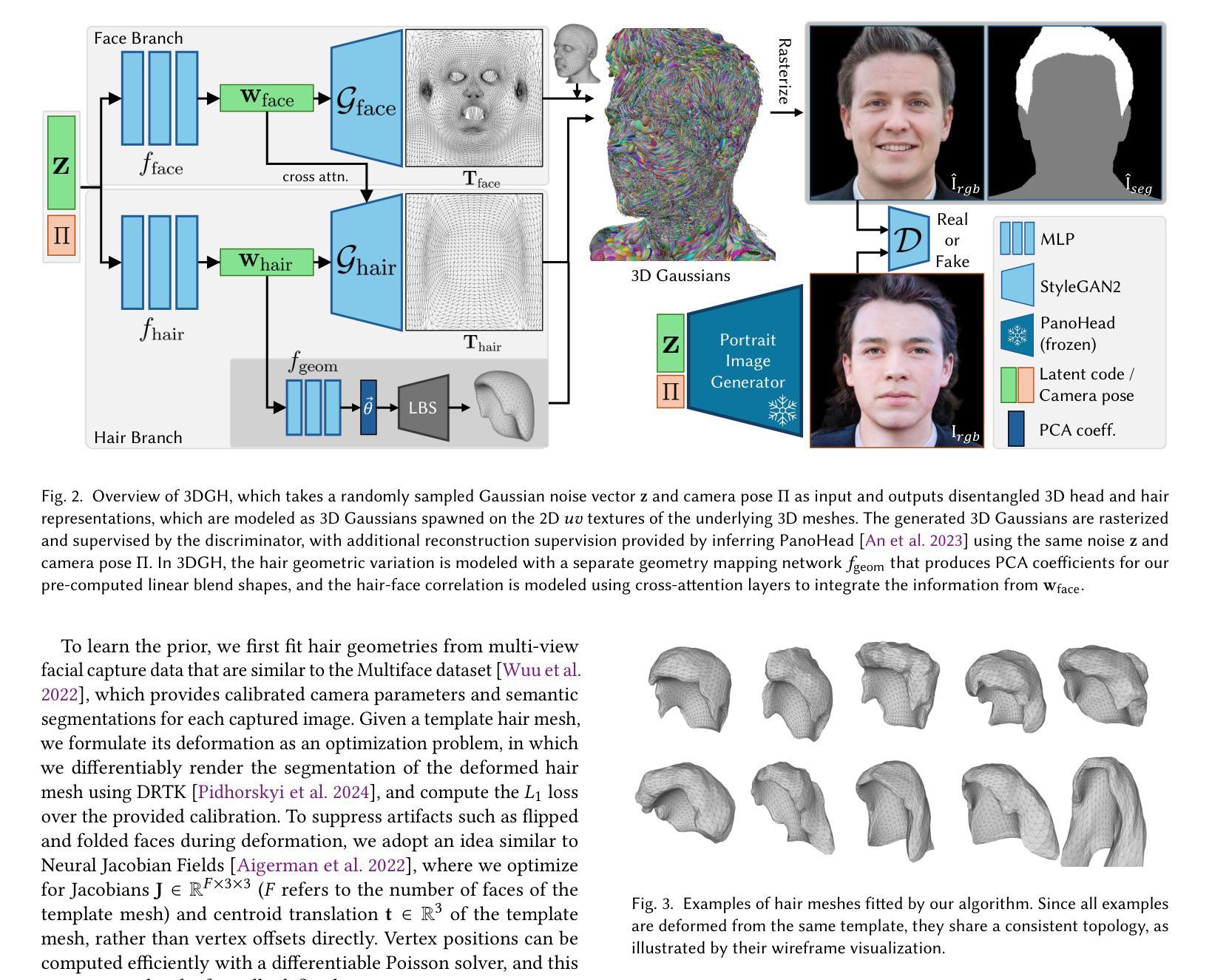
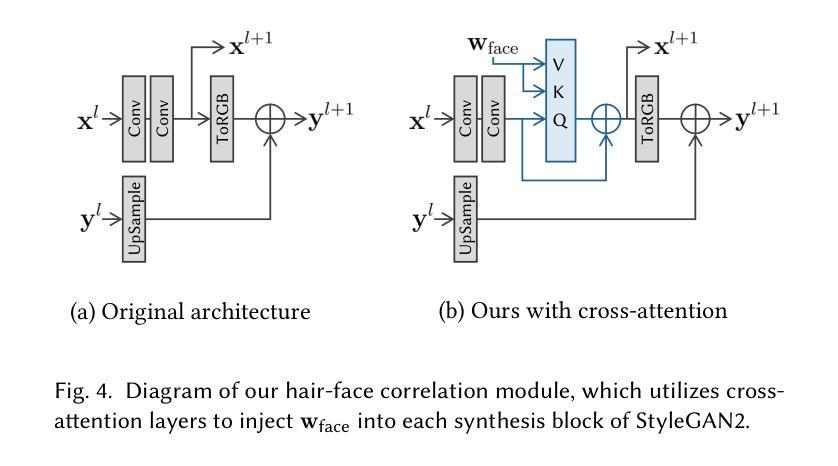
3DGH: 3D Head Generation with Composable Hair and Face
Authors:Chengan He, Junxuan Li, Tobias Kirschstein, Artem Sevastopolsky, Shunsuke Saito, Qingyang Tan, Javier Romero, Chen Cao, Holly Rushmeier, Giljoo Nam
We present 3DGH, an unconditional generative model for 3D human heads with composable hair and face components. Unlike previous work that entangles the modeling of hair and face, we propose to separate them using a novel data representation with template-based 3D Gaussian Splatting, in which deformable hair geometry is introduced to capture the geometric variations across different hairstyles. Based on this data representation, we design a 3D GAN-based architecture with dual generators and employ a cross-attention mechanism to model the inherent correlation between hair and face. The model is trained on synthetic renderings using carefully designed objectives to stabilize training and facilitate hair-face separation. We conduct extensive experiments to validate the design choice of 3DGH, and evaluate it both qualitatively and quantitatively by comparing with several state-of-the-art 3D GAN methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in unconditional full-head image synthesis and composable 3D hairstyle editing. More details will be available on our project page: https://c-he.github.io/projects/3dgh/.
我们提出了3DGH,这是一种用于3D人头部的无条件生成模型,具有可组合的头发和面部组件。与之前的将头发和脸部建模纠缠在一起的工作不同,我们提出了一种使用基于模板的3D高斯喷涂的新型数据表示来分离它们的方法,其中引入了可变形头发几何来捕获不同发型之间的几何变化。基于这种数据表示,我们设计了一种基于3D GAN的架构,具有双生成器,并采用交叉注意力机制来建模头发和脸部之间的内在关联。该模型在合成渲染图像上进行训练,使用精心设计的目标来稳定训练和促进头发与脸部的分离。我们进行了大量实验来验证3DGH的设计选择,并通过与几种最先进的3D GAN方法进行比较,从定性和定量两个方面对其进行了评估,证明了它在无条件全头图像合成和可编辑的3D发型编辑方面的有效性。更多详细信息将公布在我们的项目页面:https://c-he.github.io/projects/3dgh/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to SIGGRAPH 2025. Project page: https://c-he.github.io/projects/3dgh/
Summary
本文介绍了名为3DGH的无条件生成模型,用于生成具有可组合头发和面部分量的3D人头。该研究提出了一种基于模板的3D高斯喷涂新技术表示法,将头发和面部的建模分开,解决了以往工作中头发和面部建模纠缠的问题。基于此数据表示,研究设计了基于3D GAN的架构,采用双生成器,并运用跨注意力机制来模拟头发和面部之间的内在关联。该模型在合成渲染上进行训练,采用精心设计的目标来稳定训练并促进头发与面部的分离。实验验证表明,相比于其他先进的3D GAN方法,该模型在无条件的全头图像合成和可编辑的3D发型上具有显著效果。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGH是一个无条件生成模型,用于生成具有可组合头发和面部分量的3D人头图像。
- 研究提出了一种新的基于模板的3D高斯喷涂数据表示法,实现了头发和面部的分离建模。
- 基于该数据表示法,设计了基于3D GAN的架构,包含双生成器,并运用跨注意力机制模拟头发和面部之间的关联。
- 模型在合成渲染上进行训练,采用精心设计的目标以稳定训练过程并促进头发与面部的分离。
- 通过广泛实验验证了模型设计选择的有效性。
- 与其他先进的3D GAN方法相比,该模型在无条件的全头图像合成上表现出显著效果。
点此查看论文截图

2D Triangle Splatting for Direct Differentiable Mesh Training
Authors:Kaifeng Sheng, Zheng Zhou, Yingliang Peng, Qianwei Wang
Differentiable rendering with 3D Gaussian primitives has emerged as a powerful method for reconstructing high-fidelity 3D scenes from multi-view images. While it offers improvements over NeRF-based methods, this representation still encounters challenges with rendering speed and advanced rendering effects, such as relighting and shadow rendering, compared to mesh-based models. In this paper, we propose 2D Triangle Splatting (2DTS), a novel method that replaces 3D Gaussian primitives with 2D triangle facelets. This representation naturally forms a discrete mesh-like structure while retaining the benefits of continuous volumetric modeling. By incorporating a compactness parameter into the triangle primitives, we enable direct training of photorealistic meshes. Our experimental results demonstrate that our triangle-based method, in its vanilla version (without compactness tuning), achieves higher fidelity compared to state-of-the-art Gaussian-based methods. Furthermore, our approach produces reconstructed meshes with superior visual quality compared to existing mesh reconstruction methods. Please visit our project page at https://gaoderender.github.io/triangle-splatting.
使用3D高斯原语的可微渲染已经成为从多视角图像重建高保真3D场景的一种强大方法。虽然它在NeRF(神经网络辐射场表示)方法的基础上有所改进,但与基于网格的模型相比,这种表示形式在渲染速度和高级渲染效果(如重新照明和阴影渲染)方面仍然面临挑战。在本文中,我们提出了二维三角剖分(2DTS),这是一种用二维三角形小平面替换3D高斯原语的新方法。这种表示形式保留了连续体积建模的优点,同时自然地形成了离散网格状结构。通过将紧凑参数引入到三角形原语中,我们实现了对真实感网格的直接训练。我们的实验结果表明,我们的基于三角形的方法在原始版本(无紧凑度调整)上实现了与最新高斯方法相比更高的保真度。此外,我们的方法生成的重建网格在视觉质量方面优于现有的网格重建方法。请访问我们的项目页面:https://gaoderender.github.io/triangle-splatting了解更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures
摘要
基于3D高斯原始数据的可微分渲染方法,已从多视角图像重建高保真3D场景方面展现出强大能力。尽管相较于NeRF的方法有所提升,但这种表示在渲染速度和高级渲染效果方面仍面临挑战,如与基于网格的模型相比的重新照明和阴影渲染等。本文提出一种新型方法——二维三角贴片(2DTS),以二维三角形面片取代3D高斯原始数据。这种表示法自然形成离散网格状结构,同时保留连续体积建模的优点。通过将紧凑参数融入三角形原始数据中,我们实现了对真实感网格的直接训练。实验结果表明,我们的基于三角形的方法在基础版本(无紧凑度调整)上实现了与最新高斯方法相比更高的保真度。此外,我们的方法生成的重建网格在视觉质量上优于现有的网格重建方法。更多详情,请访问我们的项目页面:网站链接。
要点
- 基于3D高斯原始数据的可微分渲染方法能够从多视角图像重建高保真3D场景。
- 与NeRF方法相比,该表示方法在渲染速度和高级渲染效果方面仍有挑战。
- 论文提出了二维三角贴片(2DTS)方法,以二维三角形面片作为新的表示方式。
- 这种新表示方法结合离散网格状结构和连续体积建模的优点。
- 通过引入紧凑参数到三角形原始数据中,可直接训练真实感网格。
- 实验显示,基于三角形的方法在保真度和视觉质量上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图




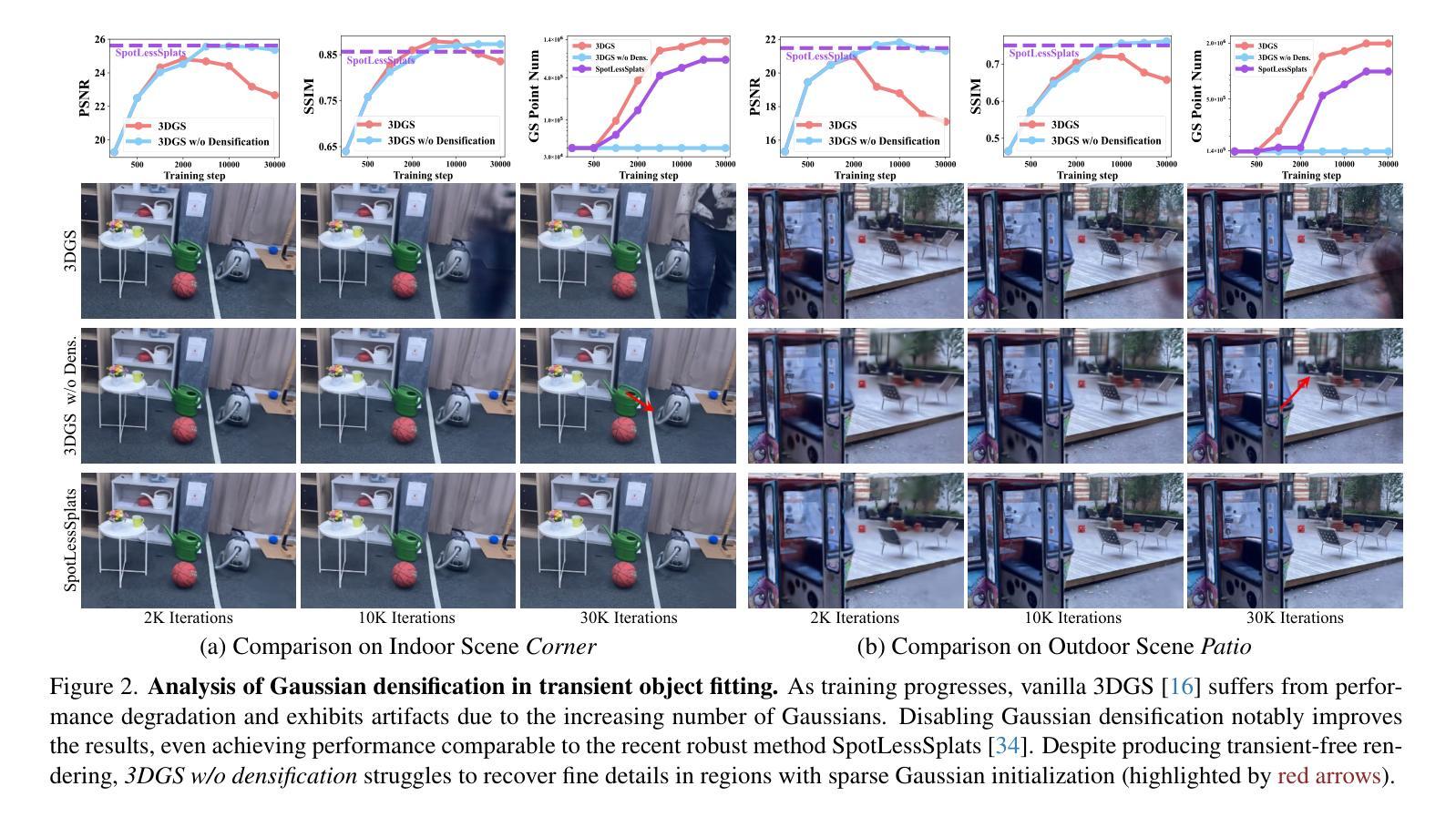
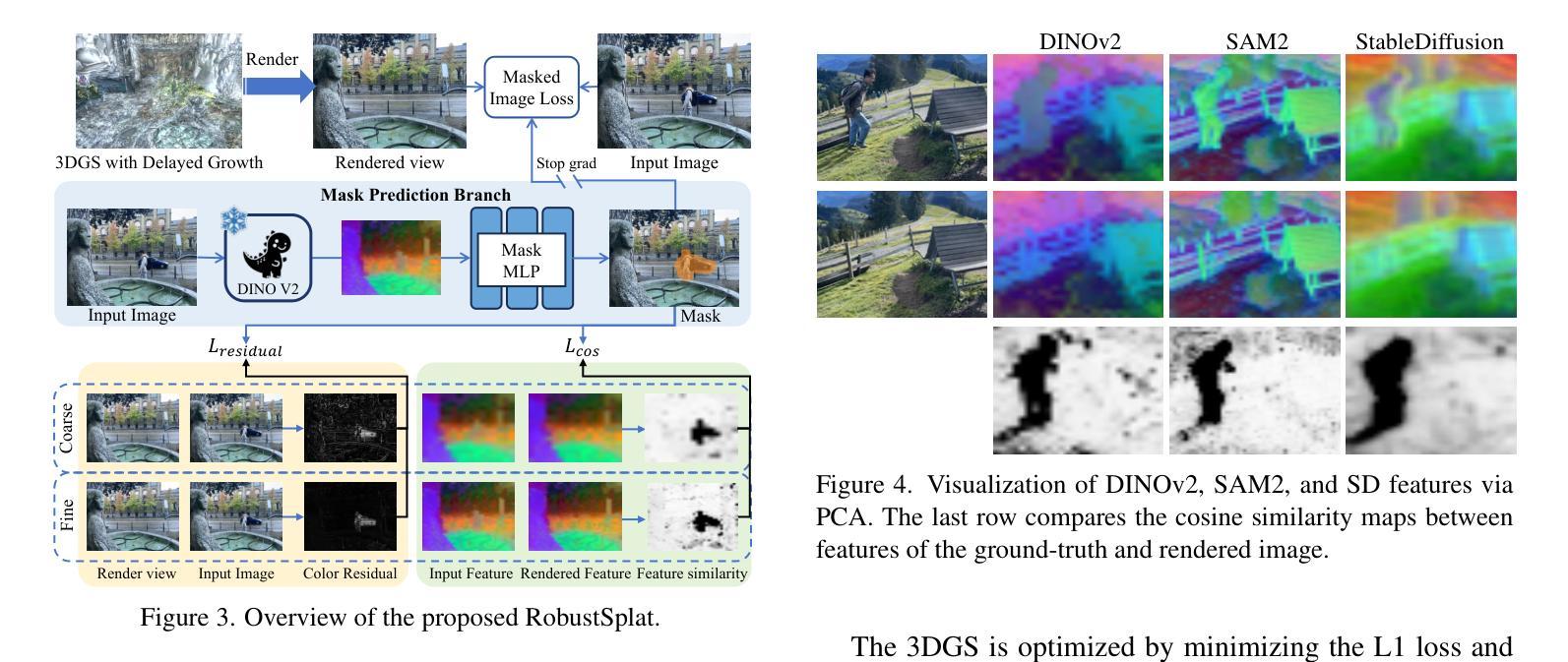
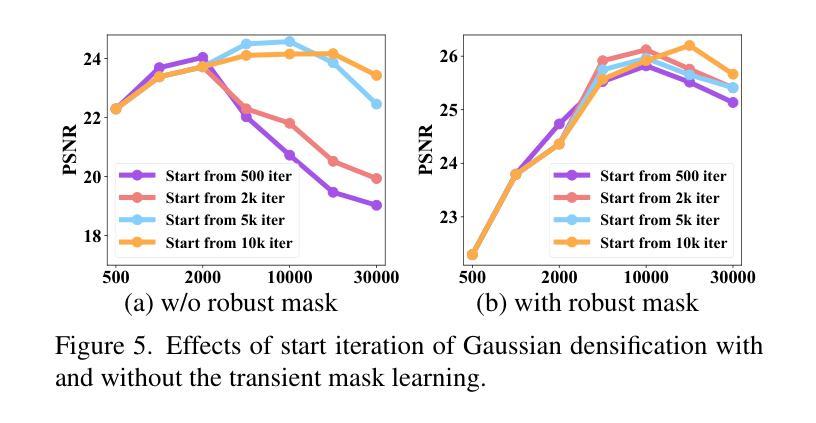
RobustSplat: Decoupling Densification and Dynamics for Transient-Free 3DGS
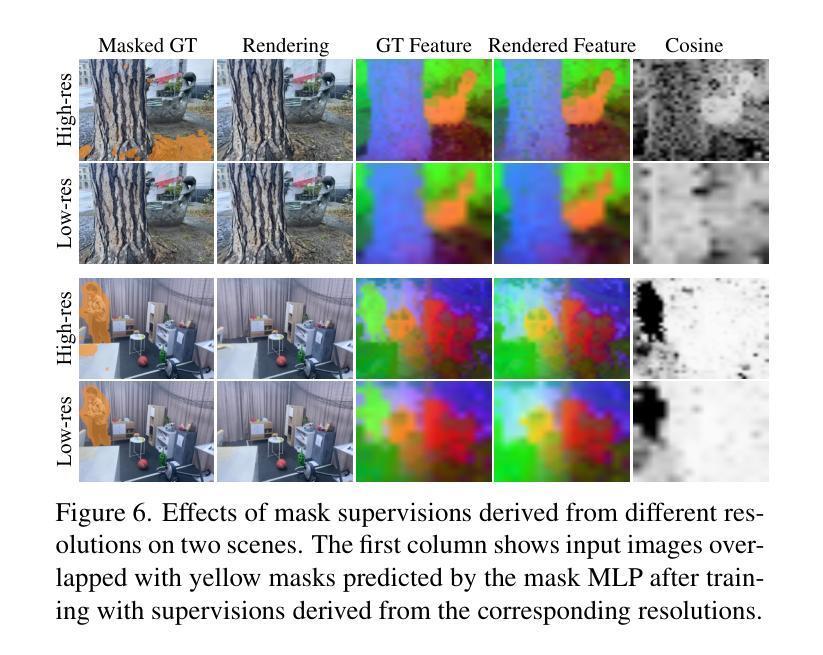
Authors:Chuanyu Fu, Yuqi Zhang, Kunbin Yao, Guanying Chen, Yuan Xiong, Chuan Huang, Shuguang Cui, Xiaochun Cao
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention for its real-time, photo-realistic rendering in novel-view synthesis and 3D modeling. However, existing methods struggle with accurately modeling scenes affected by transient objects, leading to artifacts in the rendered images. We identify that the Gaussian densification process, while enhancing scene detail capture, unintentionally contributes to these artifacts by growing additional Gaussians that model transient disturbances. To address this, we propose RobustSplat, a robust solution based on two critical designs. First, we introduce a delayed Gaussian growth strategy that prioritizes optimizing static scene structure before allowing Gaussian splitting/cloning, mitigating overfitting to transient objects in early optimization. Second, we design a scale-cascaded mask bootstrapping approach that first leverages lower-resolution feature similarity supervision for reliable initial transient mask estimation, taking advantage of its stronger semantic consistency and robustness to noise, and then progresses to high-resolution supervision to achieve more precise mask prediction. Extensive experiments on multiple challenging datasets show that our method outperforms existing methods, clearly demonstrating the robustness and effectiveness of our method. Our project page is https://fcyycf.github.io/RobustSplat/.
三维高斯融合(3DGS)因其在新视角合成和三维建模中的实时逼真渲染而受到广泛关注。然而,现有方法在模拟受瞬态物体影响的场景时遇到了困难,导致渲染图像出现伪影。我们发现高斯密集化过程在增强场景细节捕捉的同时,也无意中通过生成额外的模拟瞬态干扰的高斯函数,导致伪影的出现。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了RobustSplat,这是一个基于两种关键设计的稳健解决方案。首先,我们引入了一种延迟高斯增长策略,该策略优先优化静态场景结构,然后再进行高斯分裂或克隆,从而减轻早期优化中对瞬态物体的过度拟合。其次,我们设计了一种级联掩码引导方法,首先利用低分辨率特征相似性监督进行可靠的初始瞬态掩码估计,利用其在语义一致性方面具有较强的噪声稳健性,然后再转向高分辨率监督,以实现更精确的掩码预测。在多个具有挑战性的数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,这充分证明了我们的方法的稳健性和有效性。我们的项目页面是:[https://fcyycf.github.io/RobustSplat/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page: https://fcyycf.github.io/RobustSplat/
Summary
3DGS技术在实时渲染和3D建模中备受关注,但在处理受瞬态对象影响场景时存在缺陷,导致渲染图像出现伪影。RobustSplat方法通过引入延迟高斯增长策略和尺度级联掩码引导策略来解决这一问题,提高了场景建模的鲁棒性和准确性。该方法在多个数据集上的实验表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在实时渲染和3D建模中具有显著优势,但在处理受瞬态对象影响场景时存在挑战。
- 现有方法在处理受瞬态对象影响场景时,可能导致渲染图像出现伪影。
- RobustSplat方法引入延迟高斯增长策略,优先优化静态场景结构,避免早期优化中对瞬态对象的过度拟合。
- 该方法采用尺度级联掩码引导策略,利用低分辨率特征相似性监督进行可靠的初始瞬态掩码估计,再过渡到高分辨率监督,实现更精确的掩码预测。
- RobustSplat方法提高了场景建模的鲁棒性和准确性,通过多个数据集的实验验证。
- 该方法的实现细节和更多实验结果可在项目页面查看。
点此查看论文截图


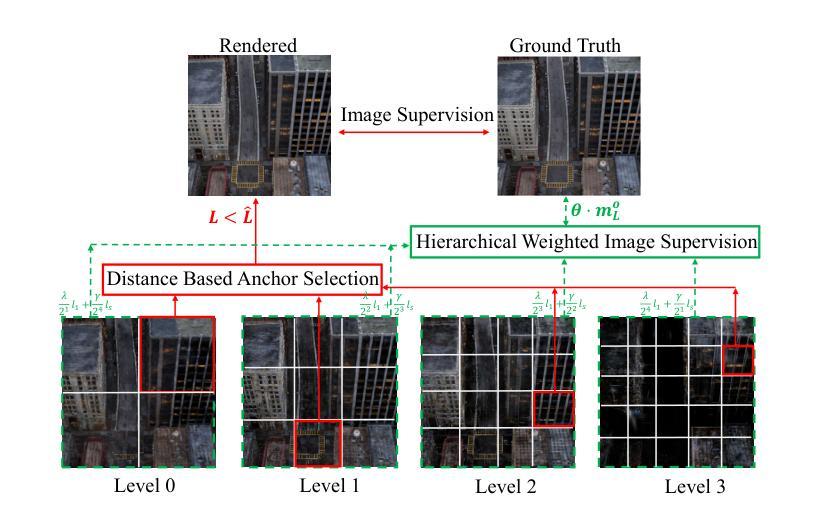
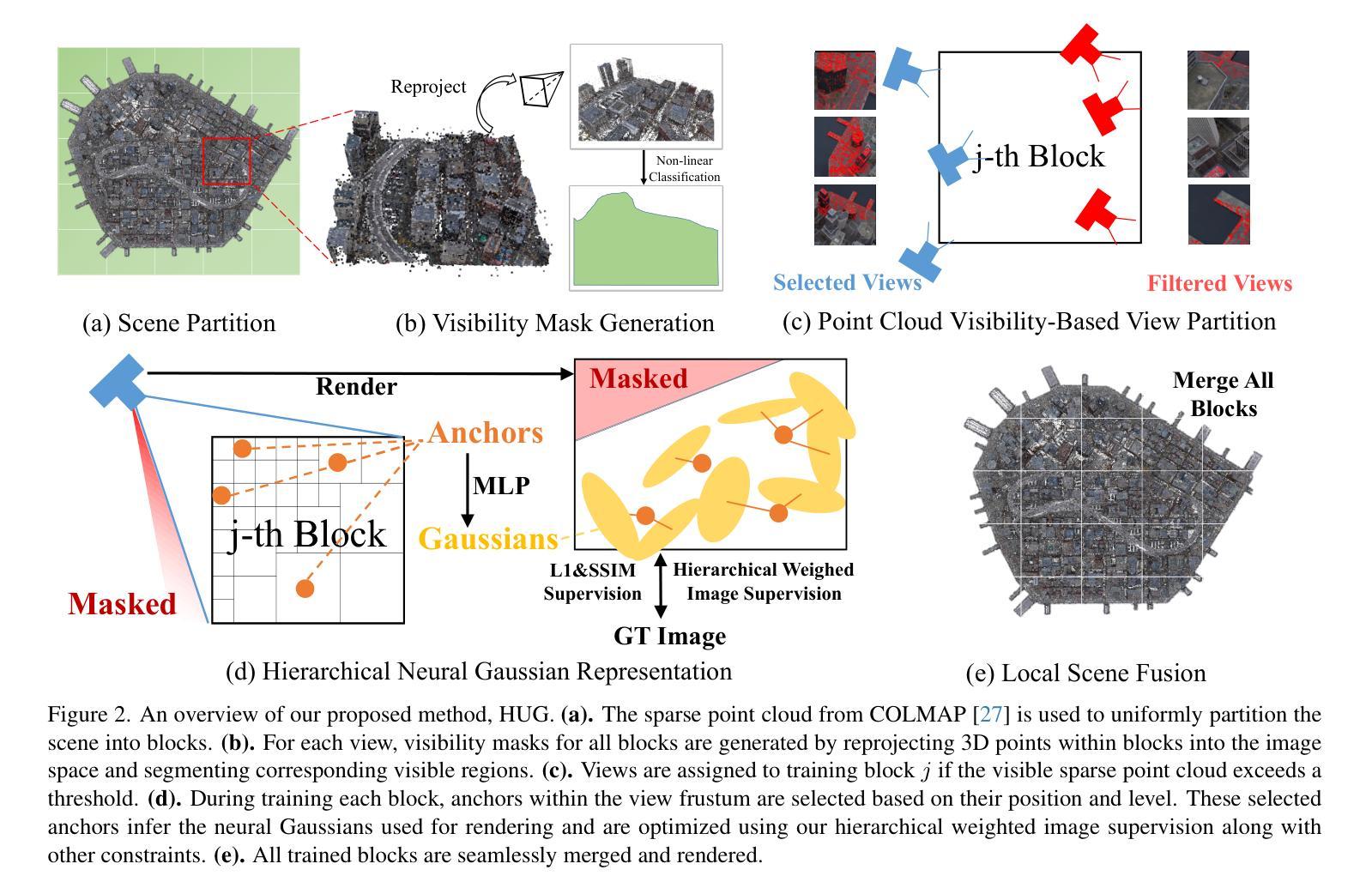
HUG: Hierarchical Urban Gaussian Splatting with Block-Based Reconstruction for Large-Scale Aerial Scenes
Authors:Mai Su, Zhongtao Wang, Huishan Au, Yilong Li, Xizhe Cao, Chengwei Pan, Yisong Chen, Guoping Wang
3DGS is an emerging and increasingly popular technology in the field of novel view synthesis. Its highly realistic rendering quality and real-time rendering capabilities make it promising for various applications. However, when applied to large-scale aerial urban scenes, 3DGS methods suffer from issues such as excessive memory consumption, slow training times, prolonged partitioning processes, and significant degradation in rendering quality due to the increased data volume. To tackle these challenges, we introduce \textbf{HUG}, a novel approach that enhances data partitioning and reconstruction quality by leveraging a hierarchical neural Gaussian representation. We first propose a visibility-based data partitioning method that is simple yet highly efficient, significantly outperforming existing methods in speed. Then, we introduce a novel hierarchical weighted training approach, combined with other optimization strategies, to substantially improve reconstruction quality. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on one synthetic dataset and four real-world datasets.
3DGS是新型视图合成领域的新兴且越来越受欢迎的技术。其高度逼真的渲染质量和实时渲染能力使其在多种应用中具有广阔前景。然而,当应用于大规模空中城市场景时,3DGS方法面临内存消耗过大、训练时间过长、分区过程延长以及由于数据量增加导致渲染质量显著下降等问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了名为“HUG”的新方法,该方法通过利用分层神经高斯表示来提高数据分区和重建质量。我们首先提出了一种基于可见性的数据分区方法,该方法简单高效,在速度上大大优于现有方法。然后,我们引入了一种新的分层加权训练方法,结合其他优化策略,以显著提高重建质量。我们的方法在1个合成数据集和4个真实世界数据集上达到了最新水平的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF An improved version has recently been accepted to ICCV, manuscript, not camera-ready
Summary
本文介绍了三维图形合成(3DGS)技术在大型空中城市场景的应用挑战和应对方法。现有技术存在内存消耗大、训练时间长、数据分割效率低以及渲染质量差等问题。为了克服这些难题,提出一种名为HUG的新方法,利用层次性神经高斯表示法优化数据分割和重建质量。此方法基于可见性进行高效数据分割,并提出一种新颖的层次加权训练方法和其他优化策略,以提高重建质量。在合成数据集和四个真实数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法达到业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在大型空中城市场景应用面临挑战,如内存消耗大、训练时间长等。
- 提出一种名为HUG的新方法,通过层次性神经高斯表示法优化数据分割和重建过程。
- HUG方法基于可见性进行高效数据分割,显著提高了数据分割的速度。
- 引入了一种新颖的层次加权训练方法和其他优化策略,旨在提高重建质量。
- HUG方法在合成数据集和四个真实数据集上的表现达到业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图


InfiniCube: Unbounded and Controllable Dynamic 3D Driving Scene Generation with World-Guided Video Models
Authors:Yifan Lu, Xuanchi Ren, Jiawei Yang, Tianchang Shen, Zhangjie Wu, Jun Gao, Yue Wang, Siheng Chen, Mike Chen, Sanja Fidler, Jiahui Huang
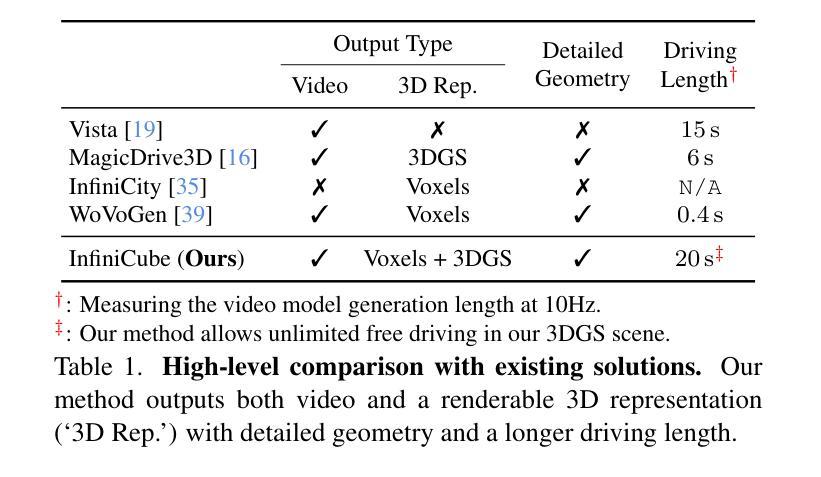
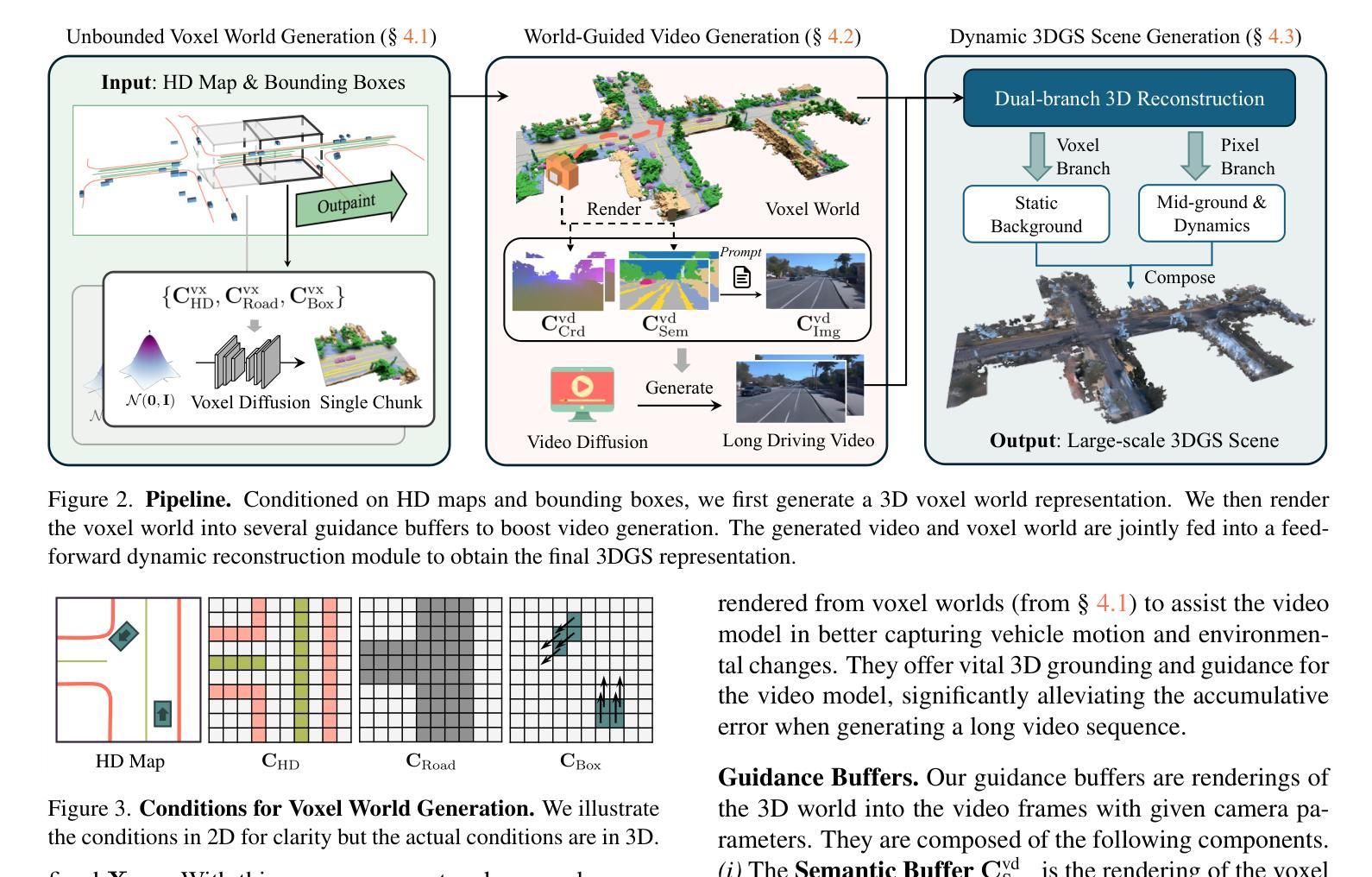
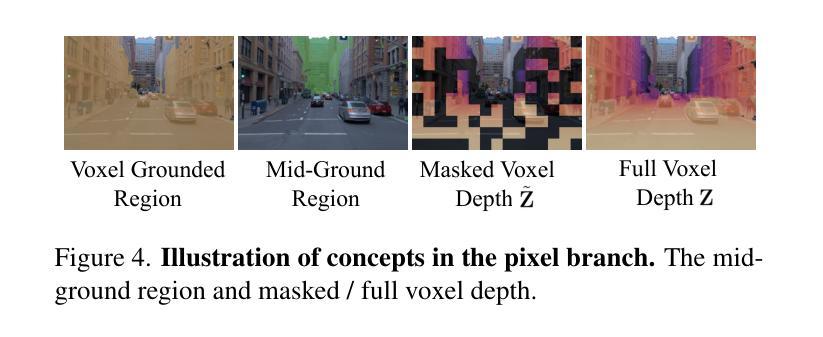
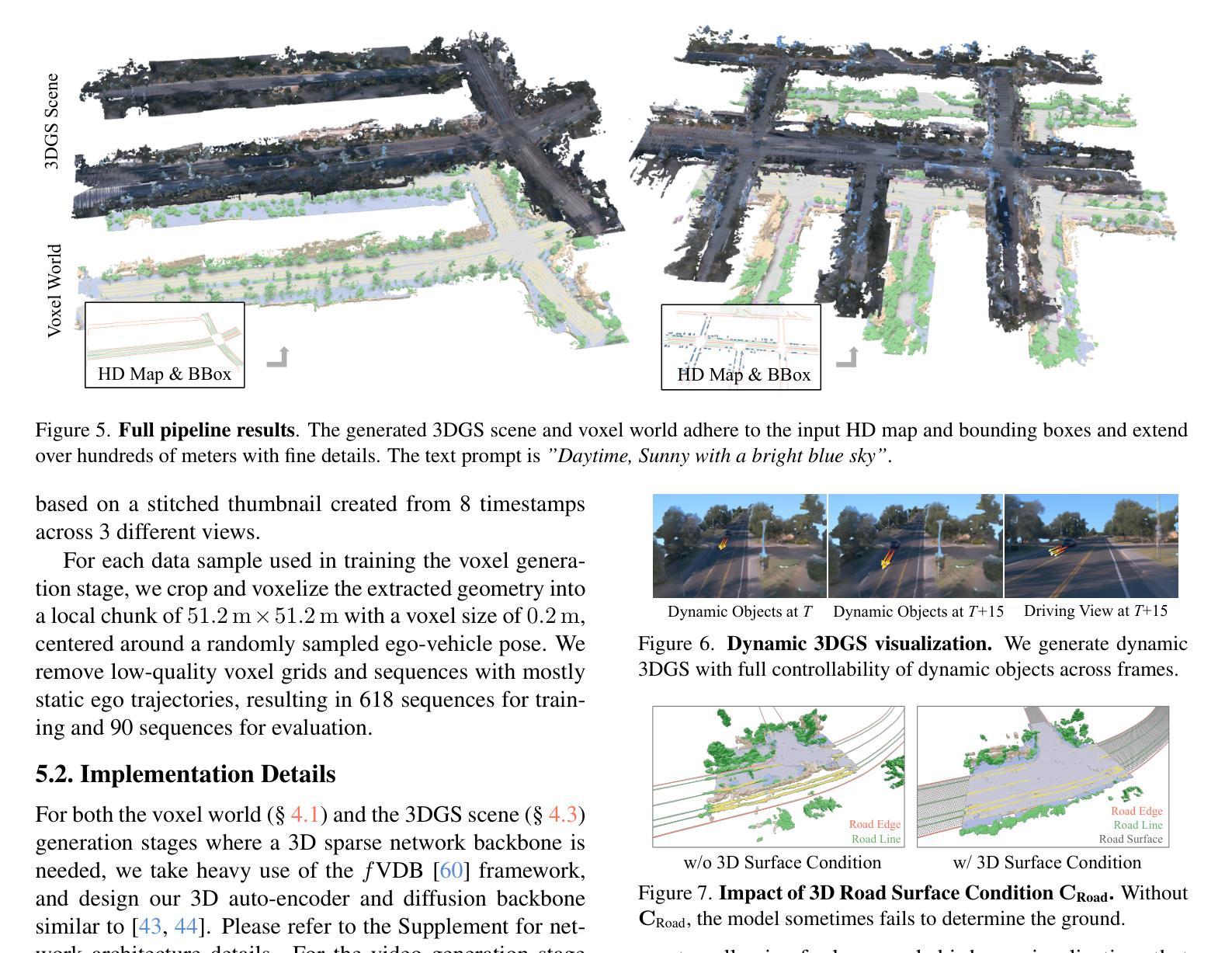
We present InfiniCube, a scalable method for generating unbounded dynamic 3D driving scenes with high fidelity and controllability. Previous methods for scene generation either suffer from limited scales or lack geometric and appearance consistency along generated sequences. In contrast, we leverage the recent advancements in scalable 3D representation and video models to achieve large dynamic scene generation that allows flexible controls through HD maps, vehicle bounding boxes, and text descriptions. First, we construct a map-conditioned sparse-voxel-based 3D generative model to unleash its power for unbounded voxel world generation. Then, we re-purpose a video model and ground it on the voxel world through a set of carefully designed pixel-aligned guidance buffers, synthesizing a consistent appearance. Finally, we propose a fast feed-forward approach that employs both voxel and pixel branches to lift the dynamic videos to dynamic 3D Gaussians with controllable objects. Our method can generate controllable and realistic 3D driving scenes, and extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and superiority of our model.
我们介绍了InfiniCube,这是一种可生成无界限动态3D驾驶场景的高保真和可控性强的可扩展方法。之前的场景生成方法要么规模有限,要么在生成序列中缺乏几何和外观的一致性。与之相比,我们利用最新的可扩展3D表示和视频模型的技术进步,实现大型动态场景生成,通过高清地图、车辆边界框和文本描述实现灵活控制。首先,我们构建了一个以地图为条件的稀疏体素基3D生成模型,以释放其在无界限体素世界生成方面的潜力。然后,我们重新定位了一个视频模型,并通过一系列精心设计的像素对齐引导缓冲区将其建立在体素世界上,从而合成一致的外观。最后,我们提出了一种快速前馈方法,该方法结合了体素和像素分支,将动态视频提升到具有可控对象的动态3D高斯模型。我们的方法可以生成可控且逼真的3D驾驶场景,大量实验验证了我们的模型的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/infinicube/
Summary
本文介绍了InfiniCube,一种用于生成无界动态3D驾驶场景的可扩展方法。该方法借助最新的可扩展3D表示和视频模型技术,实现了大规模动态场景生成,可通过高清地图、车辆边界框和文本描述进行灵活控制。该方法包括构建基于地图条件的稀疏体素3D生成模型、重新设计视频模型以在体素世界上进行渲染,并提出一种快速前馈方法,将动态视频提升到可控制的动态3D高斯场景。该方法能生成可控且逼真的3D驾驶场景,并通过大量实验验证了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- InfiniCube是一种用于生成无界动态3D驾驶场景的方法。
- 该方法结合最新的可扩展3D表示和视频模型技术。
- 通过高清地图、车辆边界框和文本描述实现灵活控制场景生成。
- 采用基于地图条件的稀疏体素3D生成模型。
- 重新设计视频模型以在体素世界上进行渲染,确保场景的一致性。
- 提出一种快速前馈方法,将动态视频转化为可控制的动态3D高斯场景。
点此查看论文截图