⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-28 更新
Deception Detection in Dyadic Exchanges Using Multimodal Machine Learning: A Study on a Swedish Cohort
Authors:Franco Rugolon, Thomas Jack Samuels, Stephan Hau, Lennart Högman
This study investigates the efficacy of using multimodal machine learning techniques to detect deception in dyadic interactions, focusing on the integration of data from both the deceiver and the deceived. We compare early and late fusion approaches, utilizing audio and video data - specifically, Action Units and gaze information - across all possible combinations of modalities and participants. Our dataset, newly collected from Swedish native speakers engaged in truth or lie scenarios on emotionally relevant topics, serves as the basis for our analysis. The results demonstrate that incorporating both speech and facial information yields superior performance compared to single-modality approaches. Moreover, including data from both participants significantly enhances deception detection accuracy, with the best performance (71%) achieved using a late fusion strategy applied to both modalities and participants. These findings align with psychological theories suggesting differential control of facial and vocal expressions during initial interactions. As the first study of its kind on a Scandinavian cohort, this research lays the groundwork for future investigations into dyadic interactions, particularly within psychotherapy settings.
本研究旨在探讨在多模态机器学习中使用技术检测二元互动中的欺骗行为的效力,重点关注欺骗者和受骗者数据的整合。我们对比了早期和后期的融合方法,使用了音频和视频数据——特别是面部动作单元和目光信息——涵盖了所有可能的模态和参与者的组合。我们的数据集是从瑞典本土参与者中收集的,他们参与了关于情绪相关话题的真实或谎言场景,构成了我们分析的基础。结果表明,与单模态方法相比,同时利用语音和面部信息可获得更好的性能。此外,同时包括两位参与者的数据可以显著提高检测欺骗的准确性,采用应用于两种模态和两位参与者的后期融合策略时,表现最佳(准确率为71%)。这些发现符合心理学理论,即面部表情和声音控制的初次互动存在差异。作为斯堪的纳维亚人群的首项研究,该研究为二元互动的进一步研究奠定了基础,特别是在心理治疗环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 40 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables. To be submitted in Behavior Research Methods
Summary
本研究利用多模态机器学习技术检测双人互动中的欺骗行为,重点研究欺骗者和受骗者数据的整合。研究对比了早期和晚期融合方法,使用了音频和视频数据——特别是动作单元和目光信息——涵盖了所有可能的模态和参与者组合。研究基于瑞典母语者在新收集的、真实或谎言场景中关于情感相关话题的数据进行分析。结果表明,与单模态方法相比,结合语音和面部信息表现更优。同时,包含双方参与者的数据能显著提高欺骗检测的准确性,采用双模态和双方参与者的晚期融合策略时表现最佳(准确率为71%)。这些发现与心理学理论相符,该理论表明在初次互动中面部和语音表达的控制存在差异。作为斯堪的纳维亚人群的首项研究,该研究为二人互动的未来研究,特别是心理治疗设置中的研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用多模态机器学习技术检测双人互动中的欺骗行为。
- 采用了早期和晚期融合方法,考虑了音频和视频数据的所有可能组合。
- 数据集来自瑞典母语者在真实或谎言场景中关于情感相关话题的新收集数据。
- 结合语音和面部信息比单模态方法表现更优。
- 包括双方参与者的数据能显著提高欺骗检测的准确性。
- 最佳表现(准确率为71%)是通过双模态和双方参与者的晚期融合策略实现的。
点此查看论文截图

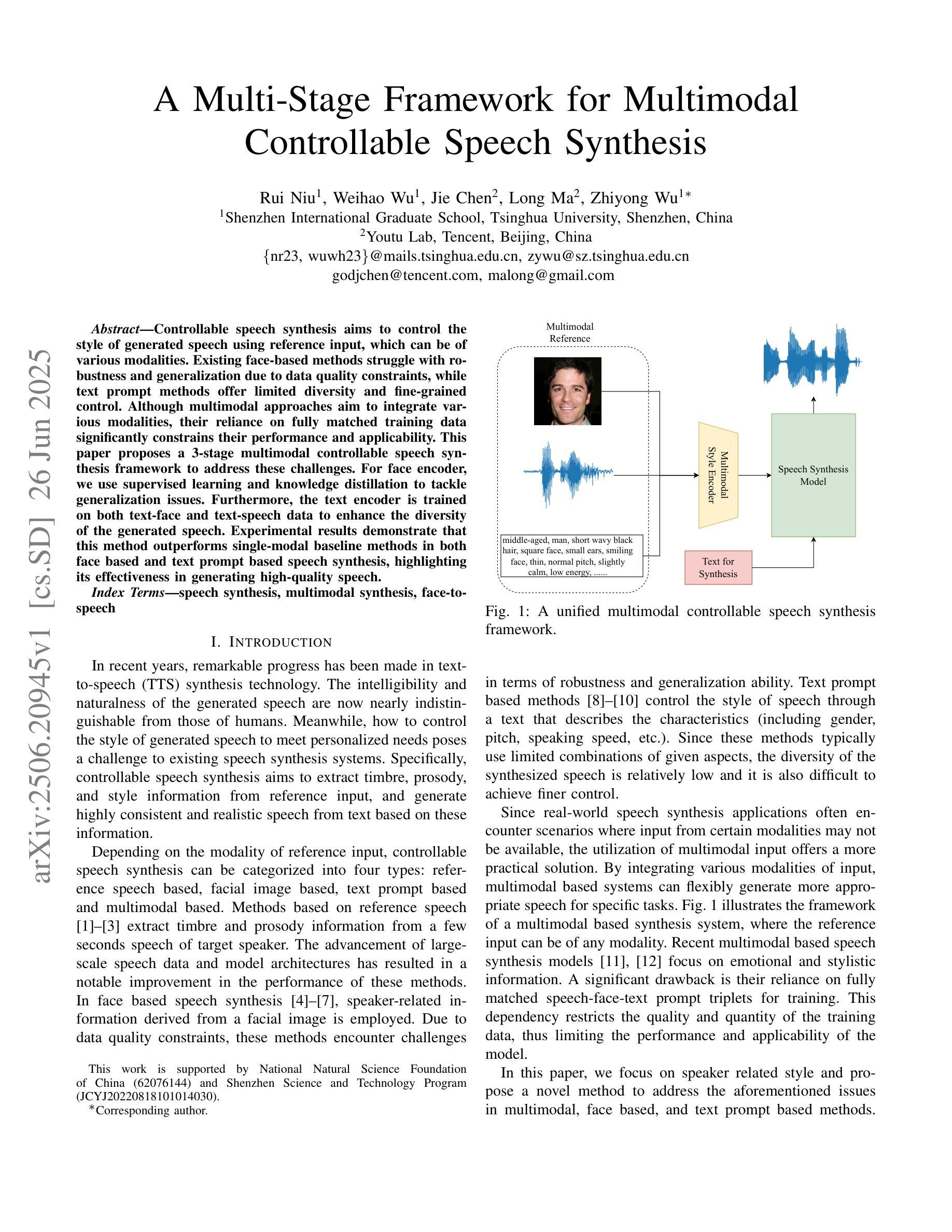
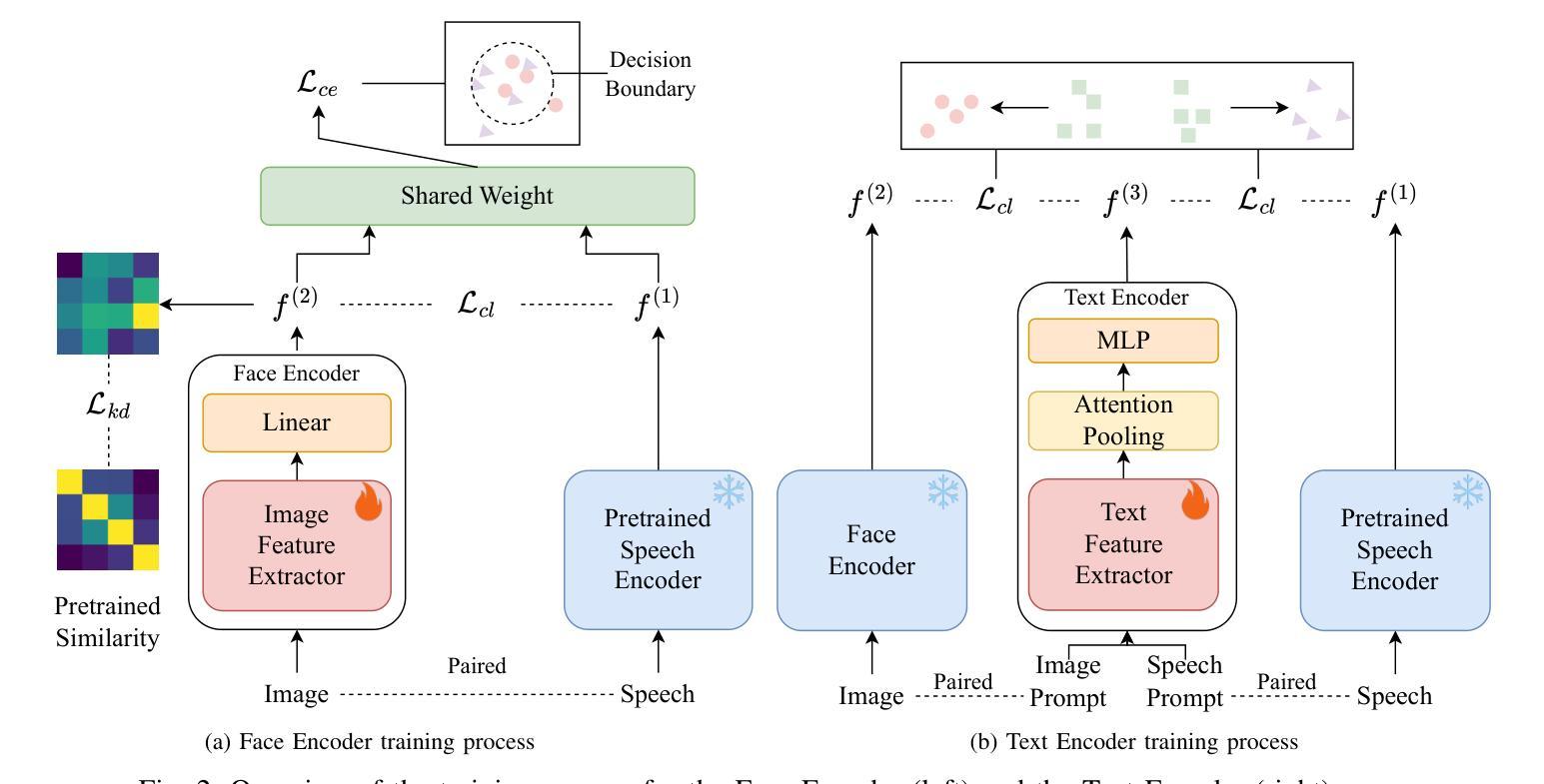
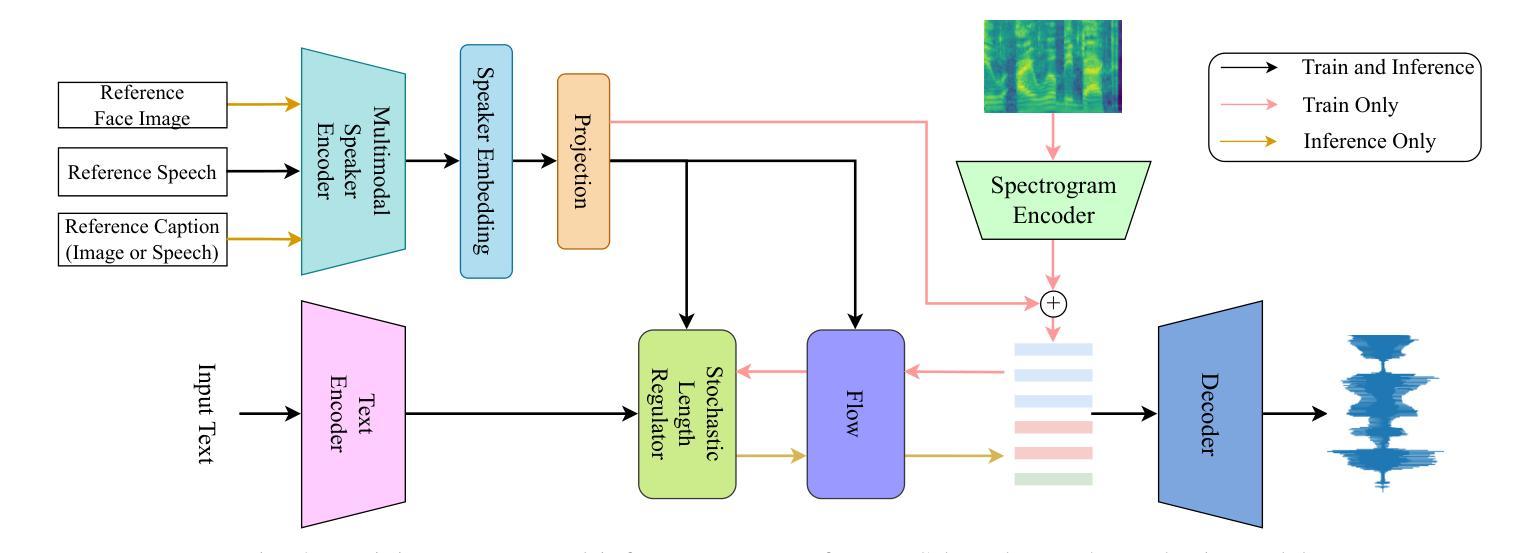
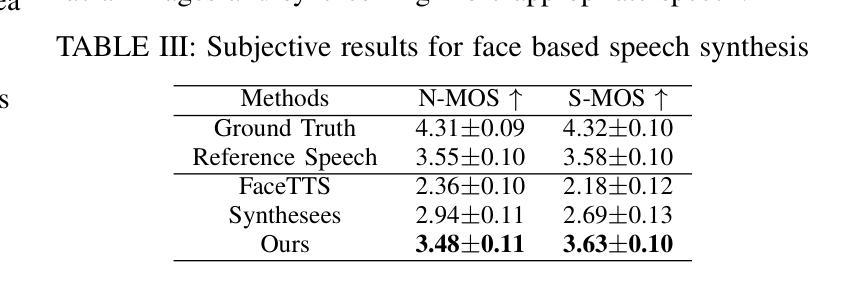
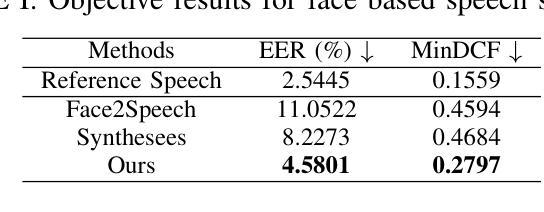
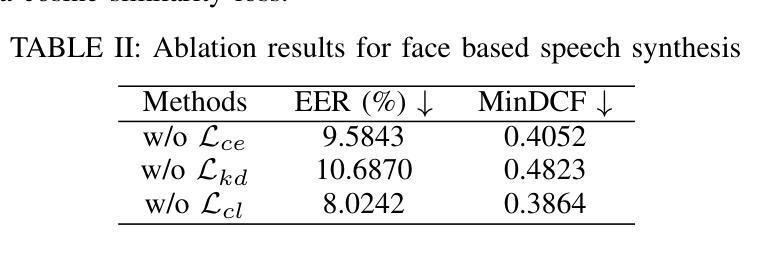
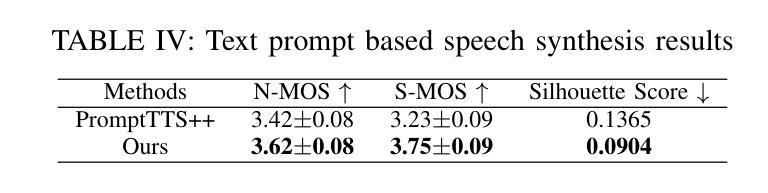
A Multi-Stage Framework for Multimodal Controllable Speech Synthesis
Authors:Rui Niu, Weihao Wu, Jie Chen, Long Ma, Zhiyong Wu
Controllable speech synthesis aims to control the style of generated speech using reference input, which can be of various modalities. Existing face-based methods struggle with robustness and generalization due to data quality constraints, while text prompt methods offer limited diversity and fine-grained control. Although multimodal approaches aim to integrate various modalities, their reliance on fully matched training data significantly constrains their performance and applicability. This paper proposes a 3-stage multimodal controllable speech synthesis framework to address these challenges. For face encoder, we use supervised learning and knowledge distillation to tackle generalization issues. Furthermore, the text encoder is trained on both text-face and text-speech data to enhance the diversity of the generated speech. Experimental results demonstrate that this method outperforms single-modal baseline methods in both face based and text prompt based speech synthesis, highlighting its effectiveness in generating high-quality speech.
可控语音合成的目标是使用各种模态的参考输入来控制生成语音的风格。基于面部的方法由于数据质量约束而面临鲁棒性和泛化能力的问题,而基于文本提示的方法则提供有限的多样性和精细控制。尽管多模态方法旨在整合各种模态,但它们对完全匹配的培训数据的依赖严重限制了其性能和适用性。针对这些挑战,本文提出了一个3阶段的多模态可控语音合成框架。对于面部编码器,我们使用有监督学习和知识蒸馏来解决泛化问题。此外,文本编码器在文本-面部和文本-语音数据上进行训练,以增强生成语音的多样性。实验结果表明,该方法在基于面部和基于文本提示的语音合成方面优于单模态基线方法,突出了其在生成高质量语音方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME2025
Summary
本文提出了一种三阶段的多模态可控语音合成框架,旨在解决现有方法在面对不同模态参考输入时的局限性。通过采用监督学习和知识蒸馏技术,提高了面部编码器的泛化能力;同时,对文本编码器进行文本-面部和文本-语音数据的训练,增强了生成语音的多样性。实验结果表明,该方法在面部和文本提示的语音合成方面优于单模态基准方法,能够有效生成高质量的语音。
Key Takeaways
- 现有可控语音合成方法面临挑战:面部方法受限于数据质量,文本提示方法缺乏多样性和精细控制,多模态方法依赖完全匹配的训练数据。
- 本文提出一种三阶段的多模态可控语音合成框架,旨在解决这些问题。
- 框架中采用监督学习和知识蒸馏技术提高面部编码器的泛化能力。
- 文本编码器经过文本-面部和文本-语音数据的训练,增强了生成语音的多样性。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在面部和文本提示的语音合成方面优于单模态方法。
- 该方法能够生成高质量的语音。
点此查看论文截图
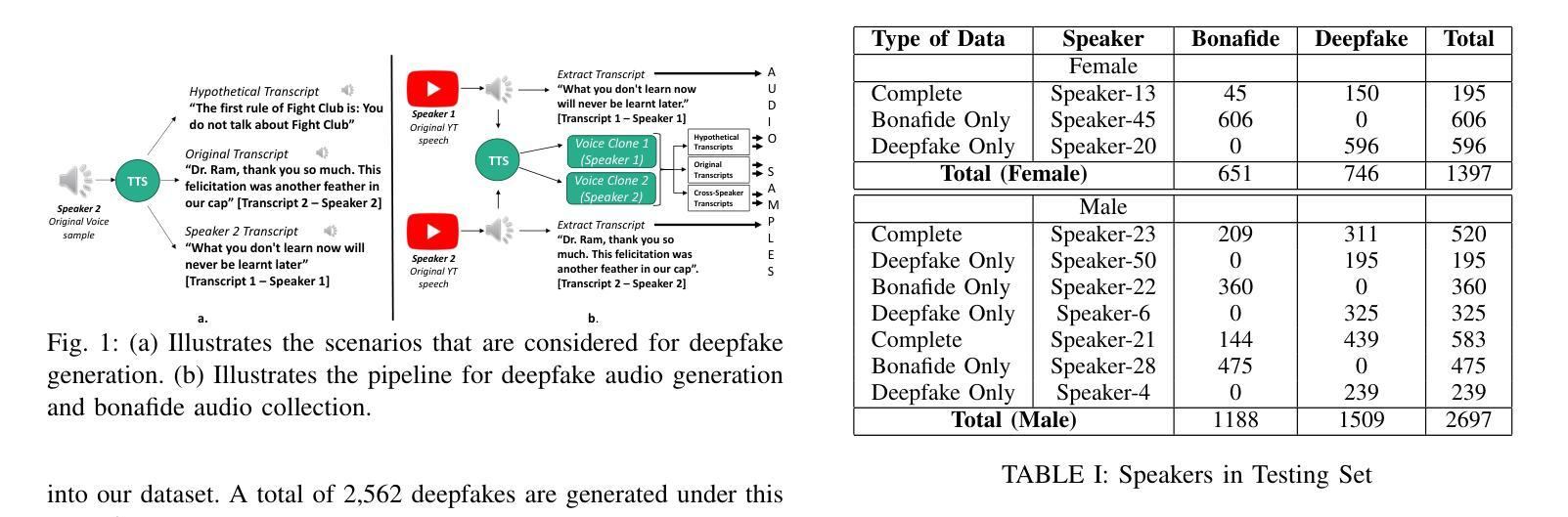
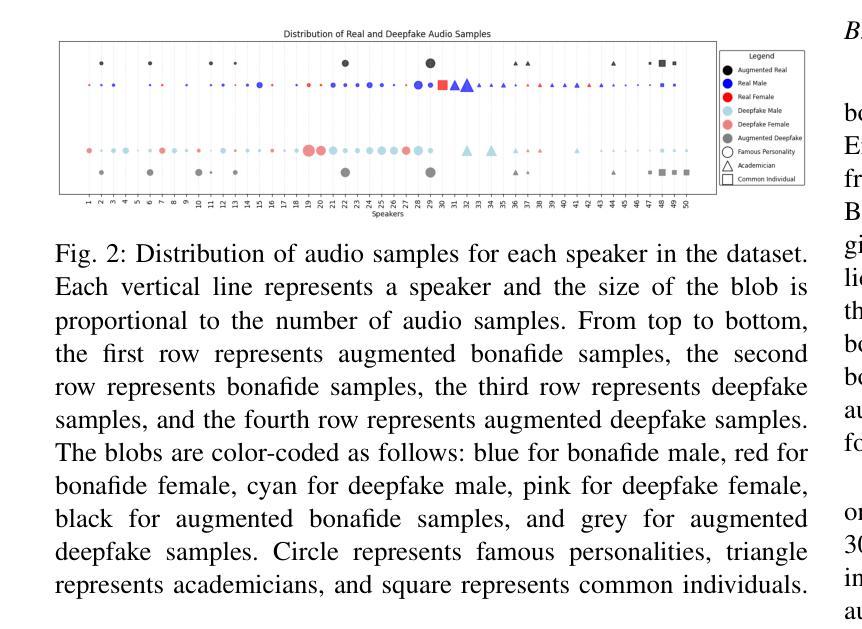
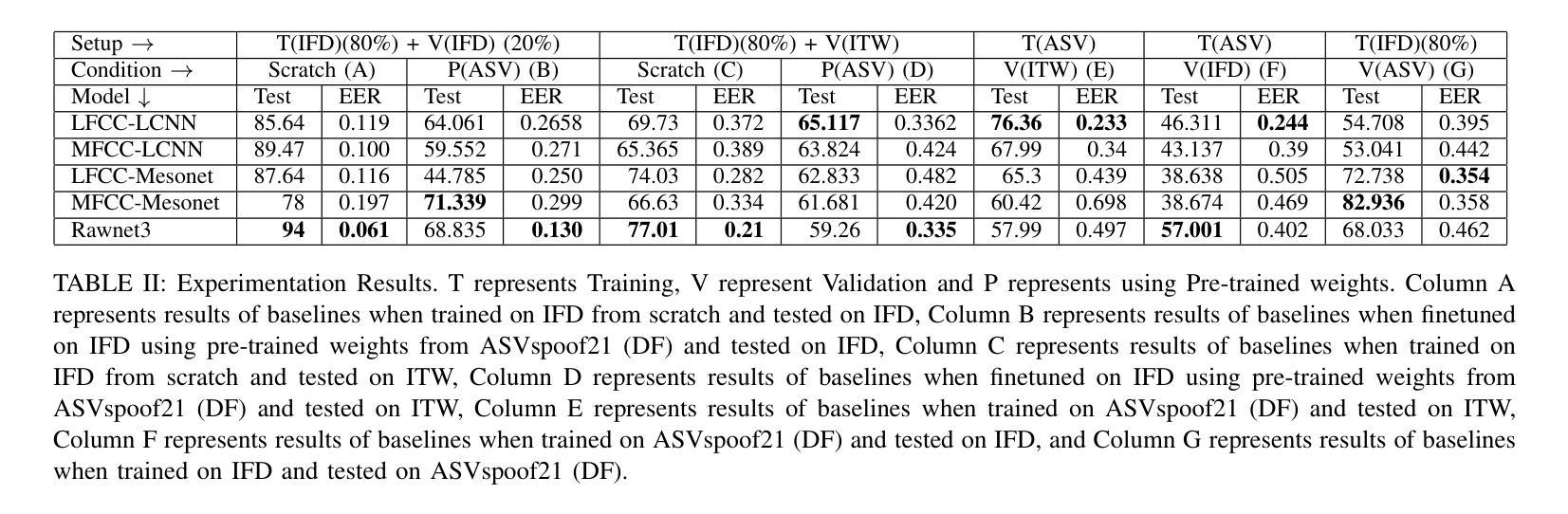
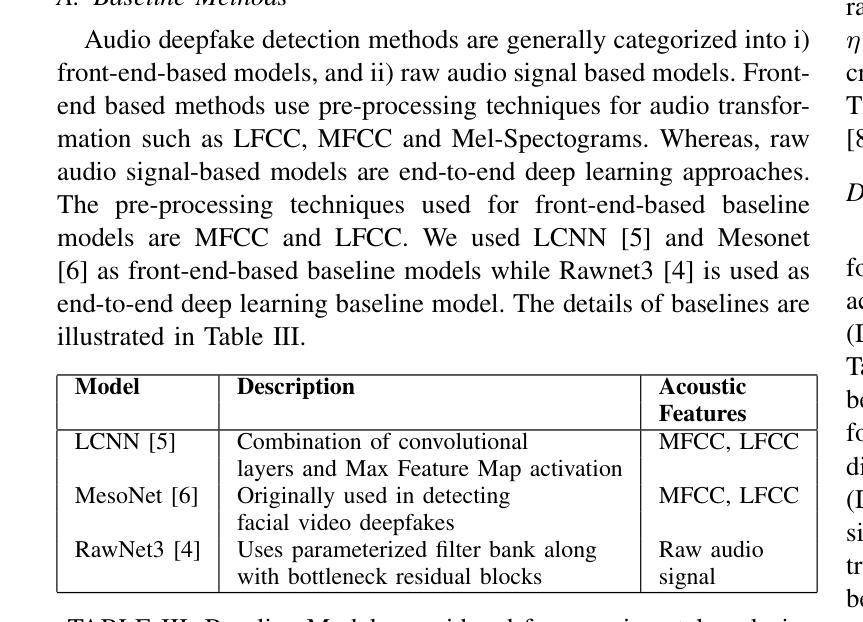
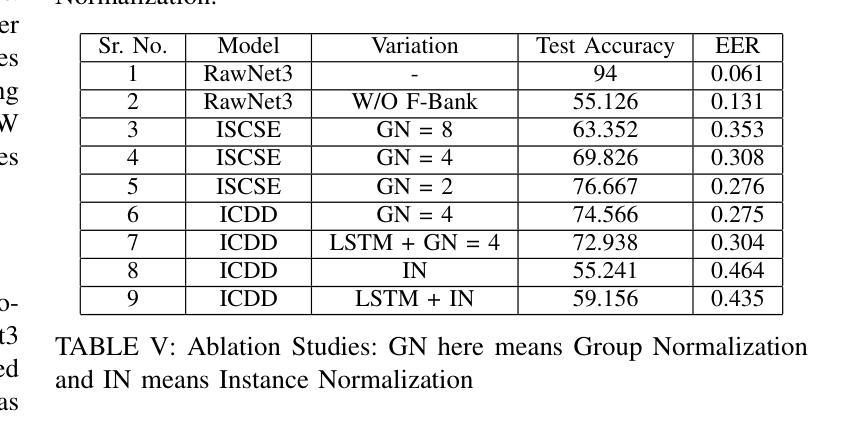
IndieFake Dataset: A Benchmark Dataset for Audio Deepfake Detection
Authors:Abhay Kumar, Kunal Verma, Omkar More
Advancements in audio deepfake technology offers benefits like AI assistants, better accessibility for speech impairments, and enhanced entertainment. However, it also poses significant risks to security, privacy, and trust in digital communications. Detecting and mitigating these threats requires comprehensive datasets. Existing datasets lack diverse ethnic accents, making them inadequate for many real-world scenarios. Consequently, models trained on these datasets struggle to detect audio deepfakes in diverse linguistic and cultural contexts such as in South-Asian countries. Ironically, there is a stark lack of South-Asian speaker samples in the existing datasets despite constituting a quarter of the worlds population. This work introduces the IndieFake Dataset (IFD), featuring 27.17 hours of bonafide and deepfake audio from 50 English speaking Indian speakers. IFD offers balanced data distribution and includes speaker-level characterization, absent in datasets like ASVspoof21 (DF). We evaluated various baselines on IFD against existing ASVspoof21 (DF) and In-The-Wild (ITW) datasets. IFD outperforms ASVspoof21 (DF) and proves to be more challenging compared to benchmark ITW dataset. The complete dataset, along with documentation and sample reference clips, is publicly accessible for research use on project website.
音频深度伪造技术的进展为我们带来了人工智能助手、更好的语音障碍可访问性以及娱乐体验等方面的好处。然而,它也带来了对安全、隐私和数字通信中的信任的重大风险。检测和缓解这些威胁需要综合数据集。现有数据集缺乏多样化的民族口音,使得它们在许多真实场景中表现不足。因此,在这些数据集上训练的模型在多元化的语言和文化背景下,如南亚国家,检测音频深度伪造时面临困难。具有讽刺意味的是,尽管南亚人口占世界四分之一,但现有数据集中严重缺乏南亚人的语音样本。这项工作引入了IndieFake数据集(IFD),包含来自50名英语印度发言人的真实和深度伪造音频共27.17小时。IFD提供了平衡的数据分布,并包括未在ASVspoof21(DF)等数据集出现的发言人级别表征。我们在IFD上评估了基线相对于现有的ASVspoof21(DF)和野外(ITW)数据集的表现。IFD表现优于ASVspoof21(DF),并证明与基准ITW数据集相比更具挑战性。完整的数据集,以及文档和样本参考剪辑,可在项目网站上公开访问以供研究使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Website: https://indie-fake-dataset.netlify.app/
Summary:音频深度伪造技术带来的进展带来了AI助手、更好的语音障碍可及性和增强的娱乐等优势。但同时也带来了严重的安全、隐私和信任风险。检测并缓解这些威胁需要全面的数据集。现有数据集缺乏种族口音多样性,无法适应现实世界的许多场景。因此,在这些数据集上训练的模型在检测具有多样语言和文化背景的音频深度伪造时遇到困难,例如在南亚国家。本工作推出了IndieFake数据集(IFD),包含来自50名印度英语发言人的共27.17小时的真正和深度伪造音频样本。IFD提供平衡的数据分布,包括未出现在其他数据集(如ASVspoof21)中的发言人级别特征。在与其他数据集(如ASVspoof21和In-The-Wild)的基线评估中,IFD表现出卓越性能,证明其更具挑战性。整个数据集及其文档和样本参考片段可在项目网站上公开获取供研究使用。
Key Takeaways:
- 音频深度伪造技术既有优势也有风险,如AI助手等好处以及安全威胁。
- 检测音频深度伪造威胁需要全面的数据集。现有数据集缺乏种族口音多样性,导致模型在多样语言和文化背景下表现不佳。
- 缺乏南亚口音样本的数据集成为现有数据集的缺陷,尽管南亚人口占全球四分之一。
- 新推出的IndieFake数据集(IFD)包括平衡分布的发音清晰的深度伪造音频样本和不同说话人的特征分布。
- 与其他数据集相比,IFD表现出卓越性能,证明了其有效性并展示了更大的挑战性。
- IFD公开供研究使用,包括完整的文档和样本参考片段。
点此查看论文截图

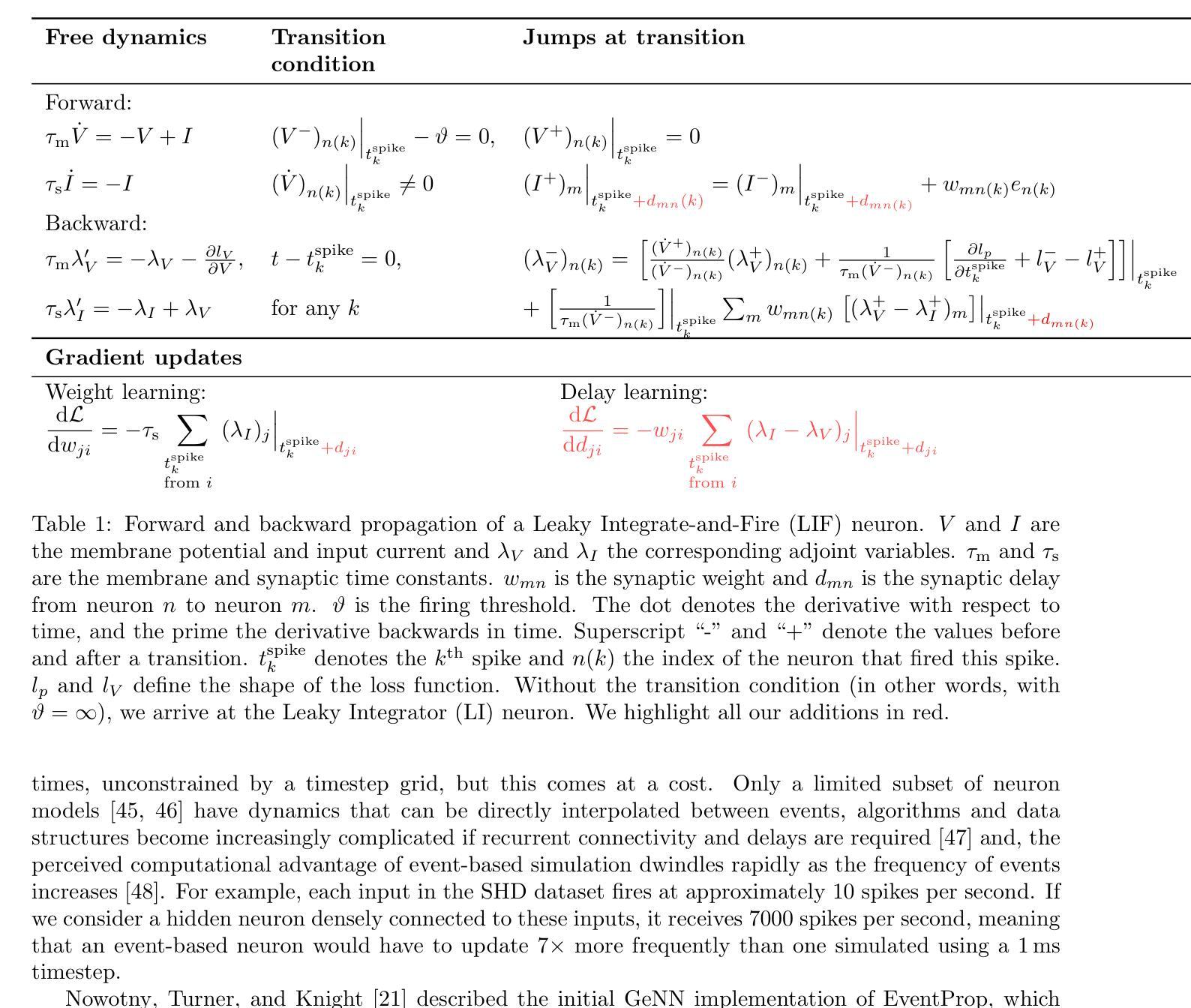
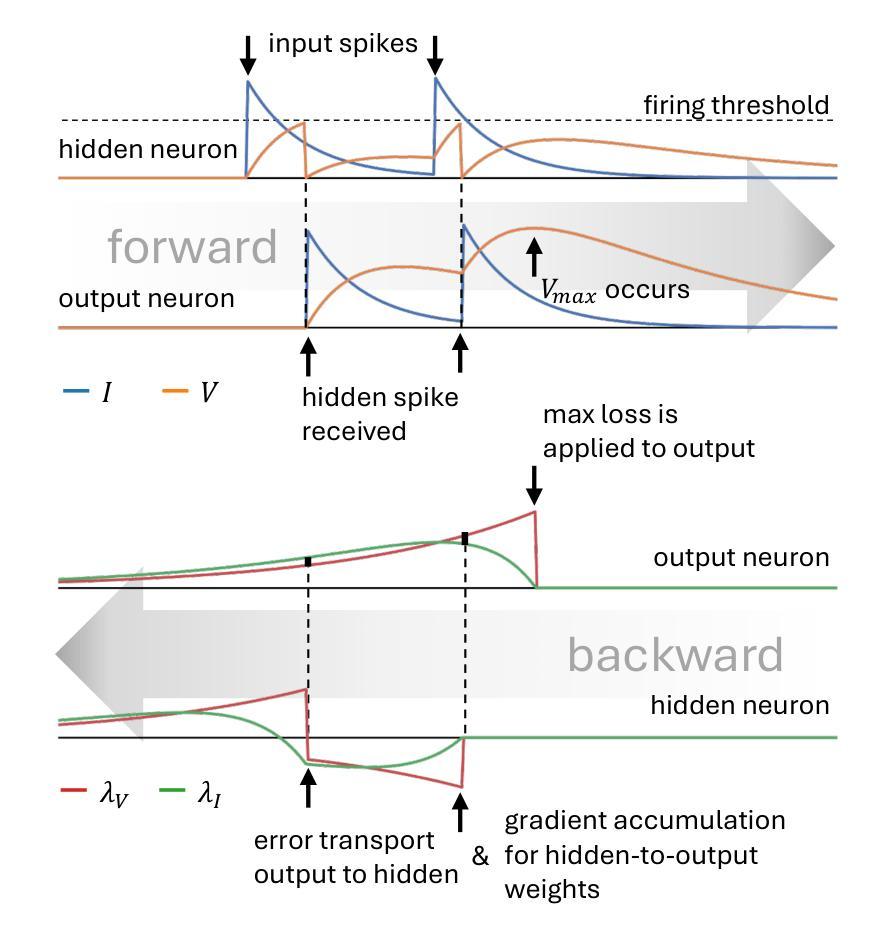
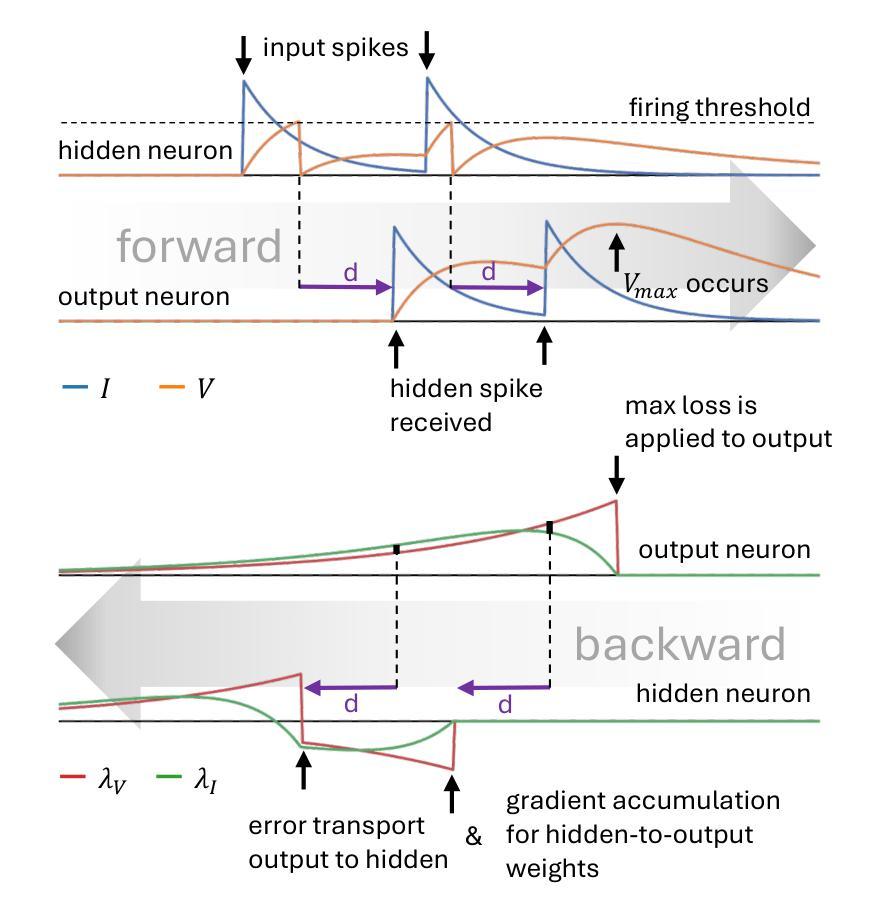
Efficient Event-based Delay Learning in Spiking Neural Networks
Authors:Balázs Mészáros, James C. Knight, Thomas Nowotny
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) compute using sparse communication and are attracting increased attention as a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional Artificial Neural Networks~(ANNs). While standard ANNs are stateless, spiking neurons are stateful and hence intrinsically recurrent, making them well-suited for spatio-temporal tasks. However, the duration of this intrinsic memory is limited by synaptic and membrane time constants. Delays are a powerful additional mechanism and, in this paper, we propose a novel event-based training method for SNNs with delays, grounded in the EventProp formalism which enables the calculation of exact gradients with respect to weights and delays. Our method supports multiple spikes per neuron and, to the best of our knowledge, is the first delay learning algorithm to be applied to recurrent SNNs. We evaluate our method on a simple sequence detection task, as well as the Yin-Yang, Spiking Heidelberg Digits, Spiking Speech Commands and Braille letter reading datasets, demonstrating that our algorithm can optimise delays from suboptimal initial conditions and enhance classification accuracy compared to architectures without delays. We also find that recurrent delays are particularly beneficial in small networks. Finally, we show that our approach uses less than half the memory of the current state-of-the-art delay-learning method and is up to 26x faster.
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)通过稀疏通信进行计算,并作为传统人工神经网络(ANNs)的能效更高的替代方案而越来越受到关注。虽然标准ANNs是无状态的,但脉冲神经元是有状态的,因此本质上是递归的,非常适合用于时空任务。然而,这种内在记忆的持续时间受到突触和膜时间常数的限制。延迟是一种强大的附加机制,本文中,我们提出了一种基于延迟的SNNs的新型事件驱动训练方法,该方法基于EventProp形式主义,能够计算关于权重和延迟的确切梯度。我们的方法支持每个神经元的多个脉冲,据我们所知,它是第一个应用于递归SNNs的延迟学习算法。我们在简单的序列检测任务以及阴阳、脉冲海德堡数字、脉冲语音命令和盲文字母阅读数据集上评估了我们的方法,结果表明,我们的算法可以从不佳的初始条件优化延迟,并在没有延迟的架构的基础上提高分类精度。我们还发现,在小型网络中,递归延迟特别有益。最后,我们证明我们的方法使用的内存不到当前最先进的延迟学习方法的一半,并且速度最快可提高26倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)通过稀疏通信进行计算,作为一种更节能的人工智能神经网络(ANNs)替代方案而备受关注。与传统无状态的ANNs不同,脉冲神经元具有状态性,因此适合处理时空任务。然而,其固有记忆持续时间受限于突触和膜时间常数。本文提出一种基于事件的新型训练法,适用于具有延迟的SNNs,基于EventProp形式化计算权重和延迟的确切梯度。该方法支持每个神经元的多次脉冲,据我们所知,是首个应用于递归SNNs的延迟学习算法。评估显示,该方法能在简单序列检测任务以及Yin-Yang、Spiking Heidelberg Digits等数据集上优化延迟并提高分类精度。此外,递归延迟对小网络特别有益。最后,我们的方法使用的内存不到当前最先进的延迟学习方法的一半,速度最快可达其26倍。
Key Takeaways
- 脉冲神经网络(SNNs)作为一种更节能的神经网络形式正受到关注,它们通过稀疏通信进行计算。
- 与传统无状态的ANNs不同,脉冲神经元具有状态性,更适合处理时空任务。
- 本文提出了一种基于事件的新型训练法,适用于具有延迟的SNNs,可以计算权重和延迟的确切梯度。
- 该方法支持每个神经元的多次脉冲,是首个应用于递归SNNs的延迟学习算法。
- 方法在多个数据集上的评估表明,该算法能优化延迟并提高分类精度。
- 递归延迟对小网络特别有益。
点此查看论文截图