⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
Supervised Diffusion-Model-Based PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:George Webber, Alexander Hammers, Andrew P King, Andrew J Reader
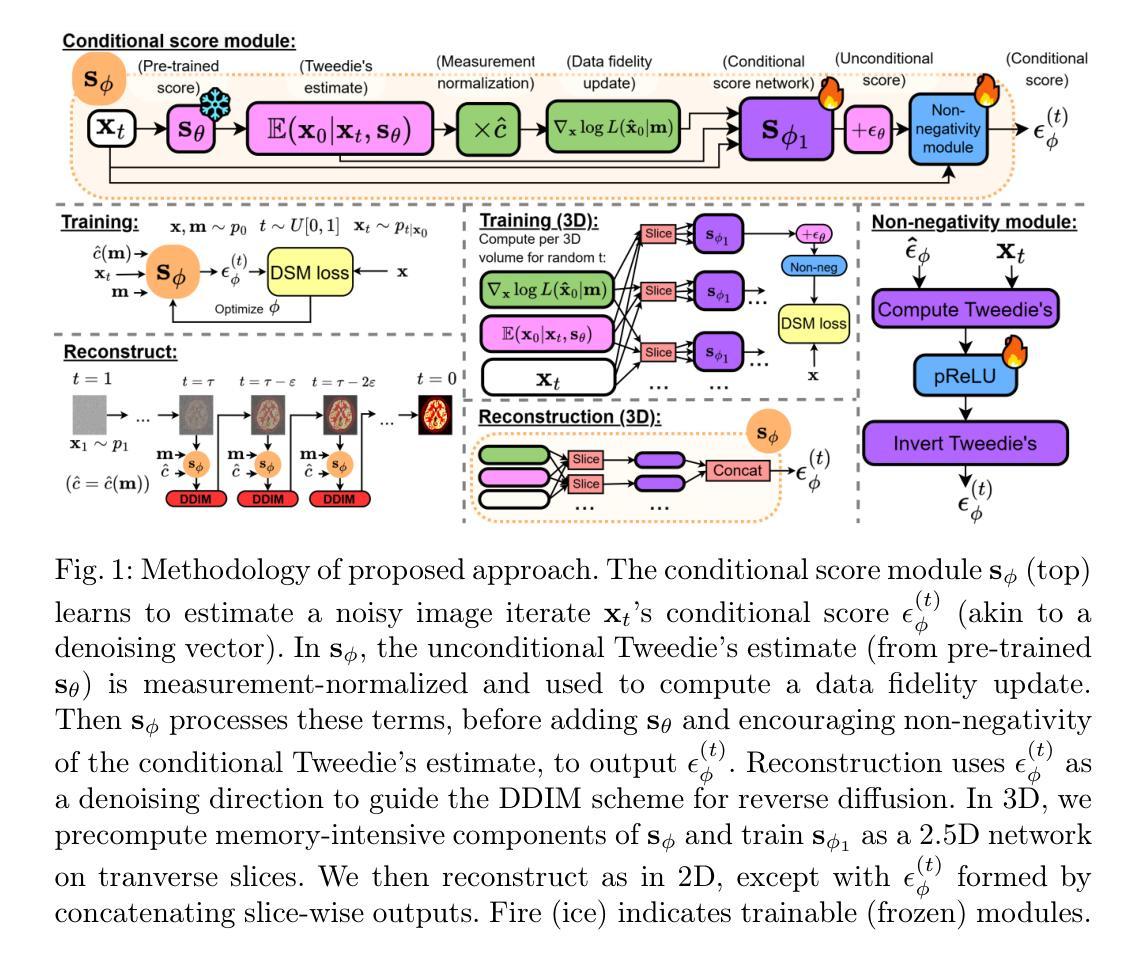
Diffusion models (DMs) have recently been introduced as a regularizing prior for PET image reconstruction, integrating DMs trained on high-quality PET images with unsupervised schemes that condition on measured data. While these approaches have potential generalization advantages due to their independence from the scanner geometry and the injected activity level, they forgo the opportunity to explicitly model the interaction between the DM prior and noisy measurement data, potentially limiting reconstruction accuracy. To address this, we propose a supervised DM-based algorithm for PET reconstruction. Our method enforces the non-negativity of PET’s Poisson likelihood model and accommodates the wide intensity range of PET images. Through experiments on realistic brain PET phantoms, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms or matches state-of-the-art deep learning-based methods quantitatively across a range of dose levels. We further conduct ablation studies to demonstrate the benefits of the proposed components in our model, as well as its dependence on training data, parameter count, and number of diffusion steps. Additionally, we show that our approach enables more accurate posterior sampling than unsupervised DM-based methods, suggesting improved uncertainty estimation. Finally, we extend our methodology to a practical approach for fully 3D PET and present example results from real [$^{18}$F]FDG brain PET data.
扩散模型(DMs)最近被引入为PET图像重建的正则化先验,它将训练于高质量PET图像的扩散模型与基于测量数据的无监督方案相结合。虽然这些方法由于独立于扫描器几何和注入活性水平而具有潜在的泛化优势,但它们放弃了明确建模扩散模型先验与噪声测量数据之间相互作用的机会,这可能限制了重建的准确性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的PET重建监督算法。我们的方法强制实施PET的Poisson似然模型的非负性,并适应PET图像的大强度范围。通过在真实的脑部PET幻影上进行的实验,我们证明了我们的方法在多种剂量水平上定量地优于或匹配最先进基于深度学习的方法。我们进一步进行消融研究,以展示我们模型中提议组件的优点,以及其对训练数据、参数计数和扩散步骤数量的依赖。此外,我们表明,我们的方法能够实现比无监督的扩散模型方法更精确的后验抽样,这暗示了不确定性估计有所提高。最后,我们将方法论扩展到实用的完全3D PET方法,并展示来自真实氟代脱氧葡萄糖([$^{18}$F]FDG)脑部PET数据的示例结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures. Submitted to MICCAI 2025, not peer-reviewed
Summary
本文介绍了将扩散模型(DMs)应用于PET图像重建的方法。该方法结合了经过高质量PET图像训练的扩散模型与基于测量数据的无监督方案,并提出了一种基于监督的DM算法以提高PET重建的准确性。实验结果表明,该方法在剂量水平范围内定量优于或匹配当前最先进的深度学习方法,并能提供更准确的不确定性估计。最后,将其扩展到实用的全3D PET方法,并提供实际[^{18}F]FDG大脑PET数据的示例结果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)被用作PET图像重建的正则化先验。
- 扩散模型与无监督方案结合,但这种方法忽略了与噪声测量数据的交互建模,可能限制重建的准确性。
- 提出了一种基于监督的DM算法,针对PET重建中的非负性强制和广泛的图像强度范围进行适应。
- 实验表明,该方法在剂量水平范围内定量性能优于或匹配最先进的深度学习方法。
- 消融研究展示了模型中各个组件的好处,以及其依赖于训练数据、参数计数和扩散步骤数量的关系。
- 该方法能提供更准确的不确定性估计,相比无监督的DM方法具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

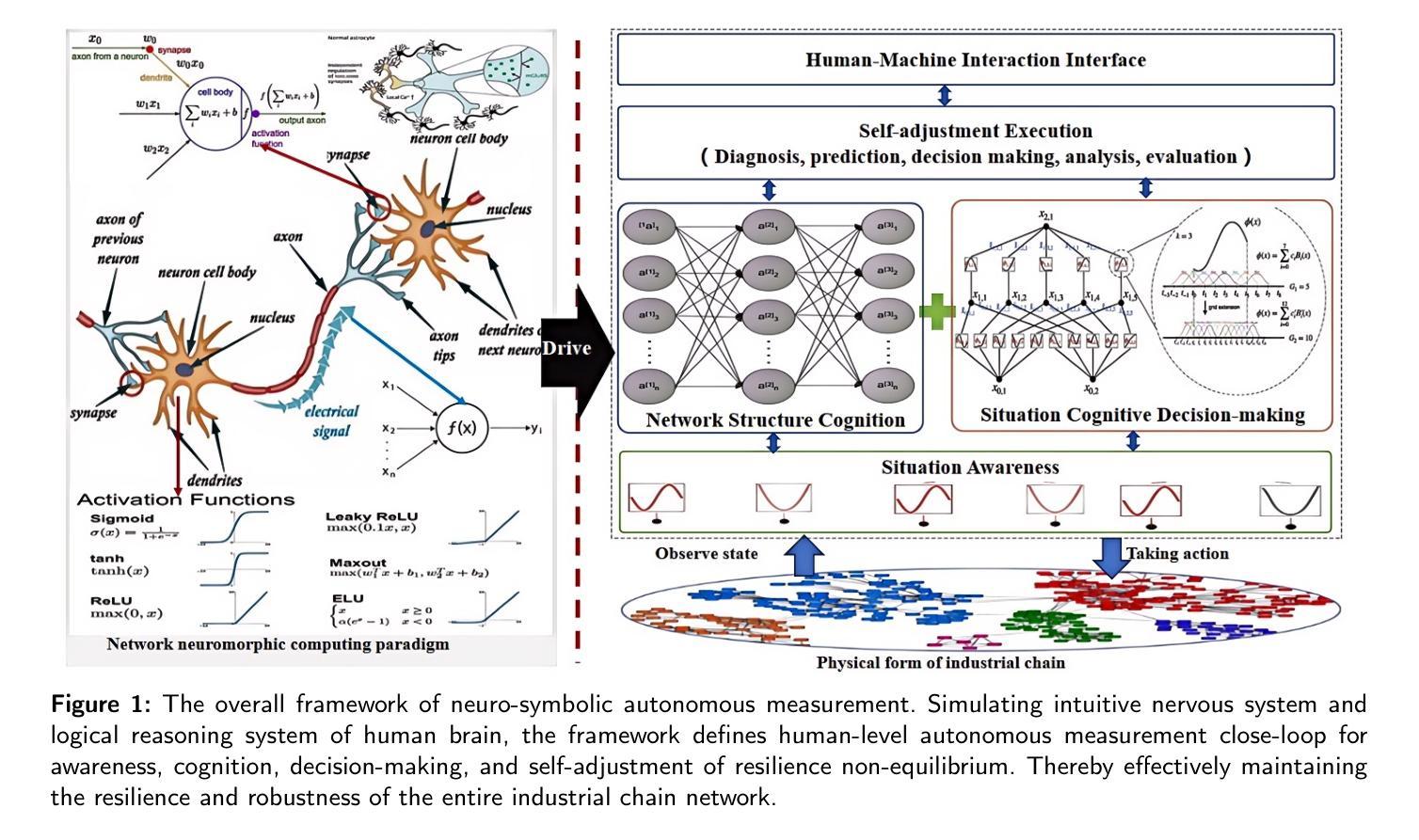
Industrial brain: a human-like autonomous neuro-symbolic cognitive decision-making system
Authors:Junping Wang, Bicheng Wang, Yibo Xuea, Yuan Xie
Resilience non-equilibrium measurement, the ability to maintain fundamental functionality amidst failures and errors, is crucial for scientific management and engineering applications of industrial chain. The problem is particularly challenging when the number or types of multiple co-evolution of resilience (for example, randomly placed) are extremely chaos. Existing end-to-end deep learning ordinarily do not generalize well to unseen full-feld reconstruction of spatiotemporal co-evolution structure, and predict resilience of network topology, especially in multiple chaos data regimes typically seen in real-world applications. To address this challenge, here we propose industrial brain, a human-like autonomous cognitive decision-making and planning framework integrating higher-order activity-driven neuro network and CT-OODA symbolic reasoning to autonomous plan resilience directly from observational data of global variable. The industrial brain not only understands and model structure of node activity dynamics and network co-evolution topology without simplifying assumptions, and reveal the underlying laws hidden behind complex networks, but also enabling accurate resilience prediction, inference, and planning. Experimental results show that industrial brain significantly outperforms resilience prediction and planning methods, with an accurate improvement of up to 10.8% over GoT and OlaGPT framework and 11.03% over spectral dimension reduction. It also generalizes to unseen topologies and dynamics and maintains robust performance despite observational disturbances. Our findings suggest that industrial brain addresses an important gap in resilience prediction and planning for industrial chain.
在工业产业链的科学管理和工程应用中,韧性非均衡测量(Resilience non-equilibrium measurement)以及在故障和错误中的维持基础功能的能力至关重要。当多种共演韧性的数量或类型出现极度混乱(例如随机放置)时,这个问题尤其具有挑战性。现有的端到端深度学习通常不能很好地推广到未见过的时空共演化结构全场重建,以及预测网络拓扑的韧性,特别是在现实世界应用中常见的多重混沌数据状态下。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了工业大脑(Industrial Brain)这一概念。它是一个融合了高阶活动驱动神经网络和CT-OODA符号推理的人机认知决策规划框架,能直接根据全球变量的观测数据进行自主韧性规划。工业大脑不仅理解和建模节点活动动态和网络共演化拓扑结构,而无需进行简化假设,揭示复杂网络背后隐藏的基本规律,而且能够实现精确的韧性预测、推理和规划。实验结果表明,工业大脑在韧性预测和规划方法上表现出显著优势,相较于GoT和OlaGPT框架最多提高了1.jpg8%,相较于光谱维度减少提高了超过一倍达到平均精度为惊人的增加了百分之零点八,它还能够推广应用于未见过的拓扑结构和动态状态,并且在观测干扰的情况下仍能保持稳健性能。我们的研究结果表明,工业大脑填补了产业链韧性预测和规划中的一项重要空白。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
工业大脑通过整合高阶活动驱动神经网络和CT-OODA符号推理,直接从全球变量观测数据中自主规划韧性,解决产业链在多重混沌数据状态下的韧性预测和规划难题。此方法不仅理解并建模节点活动动态和网络协同演化拓扑结构,揭示复杂网络背后的基本规律,还能实现准确的韧性预测、推断和规划。实验结果显示,工业大脑在韧性预测和规划方法上表现出显著优势,较GoT和OlaGPT框架以及光谱降维方法分别提高了最高达10.8%和11.03%。面对观测干扰,它依然能维持稳健性能并推广到未见过的拓扑和动态中。
Key Takeaways
- 工业大脑的自主认知决策规划框架整合了高阶活动驱动神经网络和CT-OODA符号推理。
- 该方法解决了多重混沌数据状态下产业链韧性预测和规划的挑战。
- 工业大脑能够理解和建模节点活动动态以及网络协同演化拓扑结构。
- 工业大脑能够揭示复杂网络背后的基本规律。
- 实验结果显示工业大脑在韧性预测和规划方面表现出显著优势,准确度高。
- 面对观测干扰,工业大脑依然能维持稳健性能。
点此查看论文截图

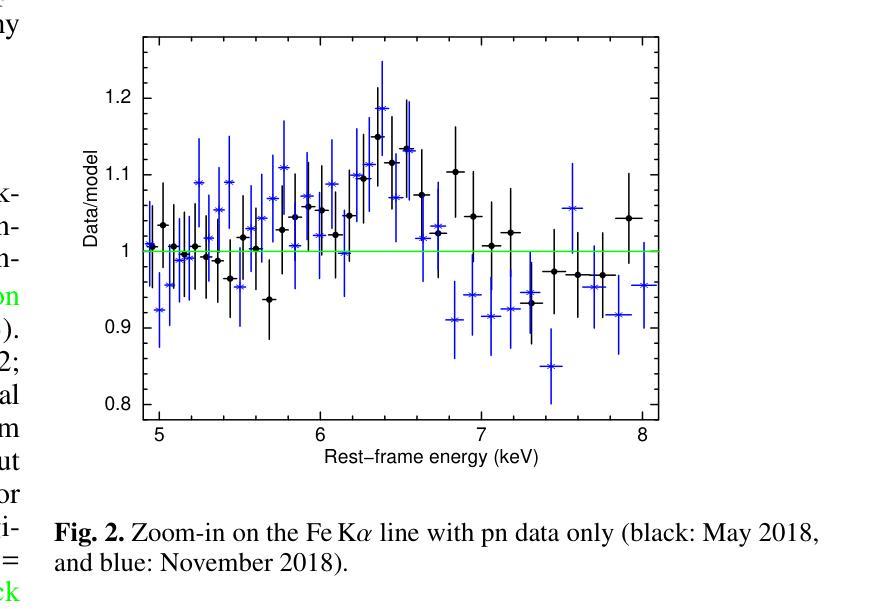
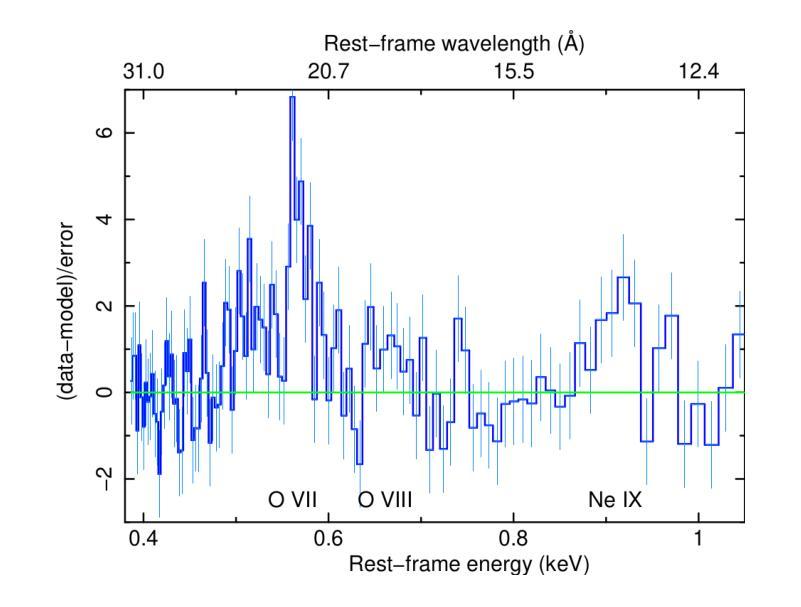
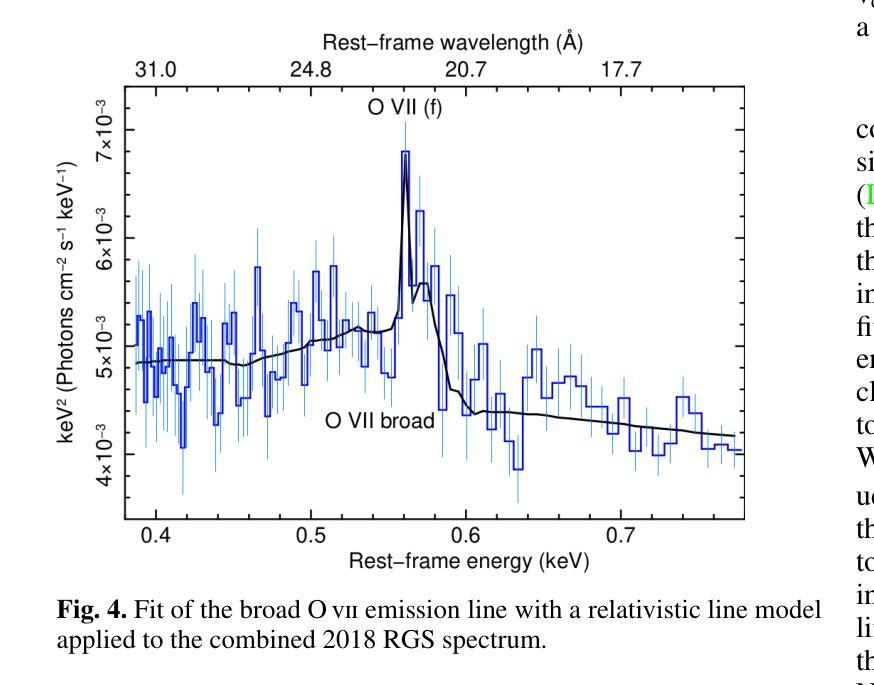
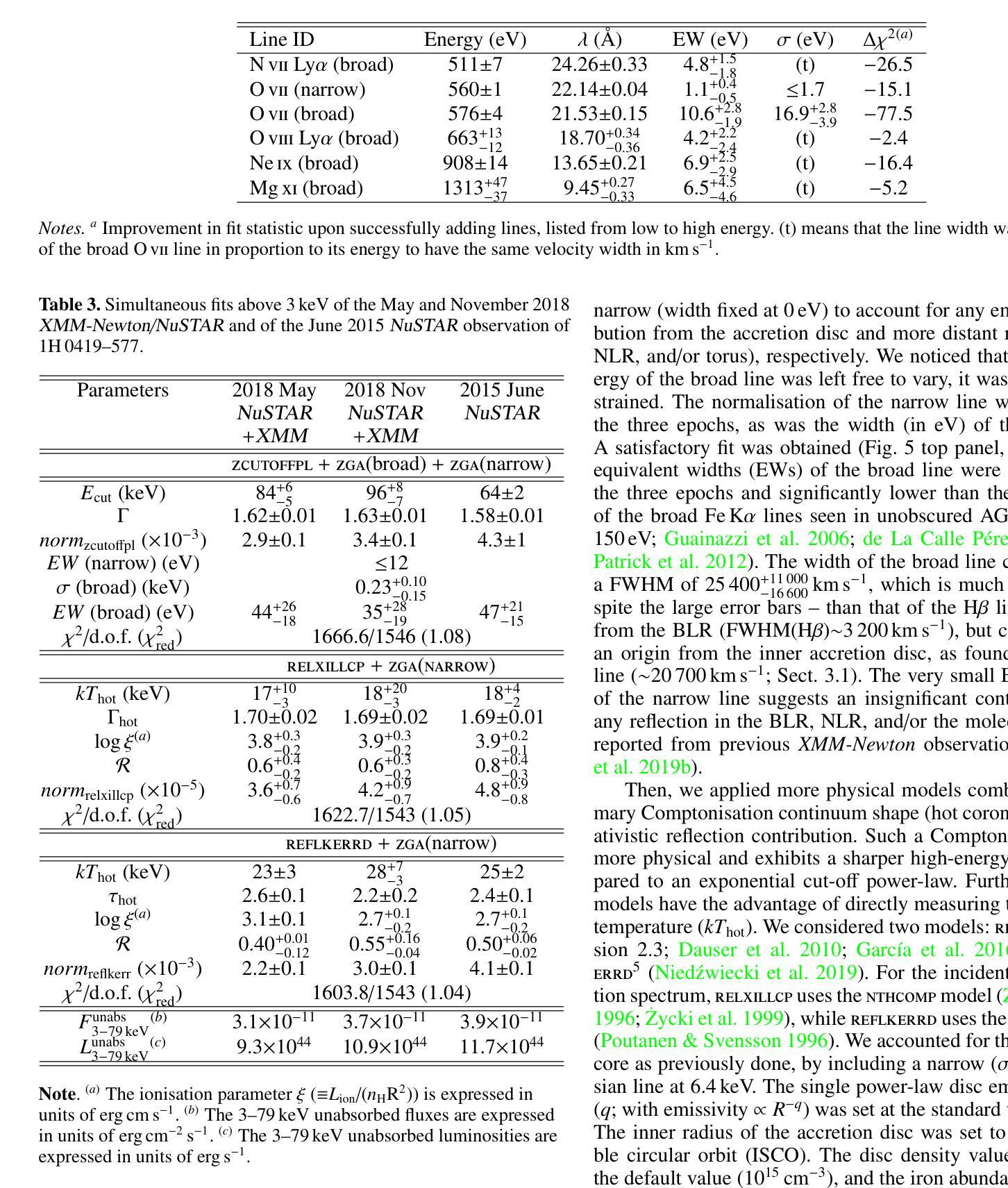
A possible two-fold scenario for the disc-corona of the luminous AGN 1H 0419–577: a high-density disc or a warm corona
Authors:Delphine Porquet, James N. Reeves, Valentina Braito
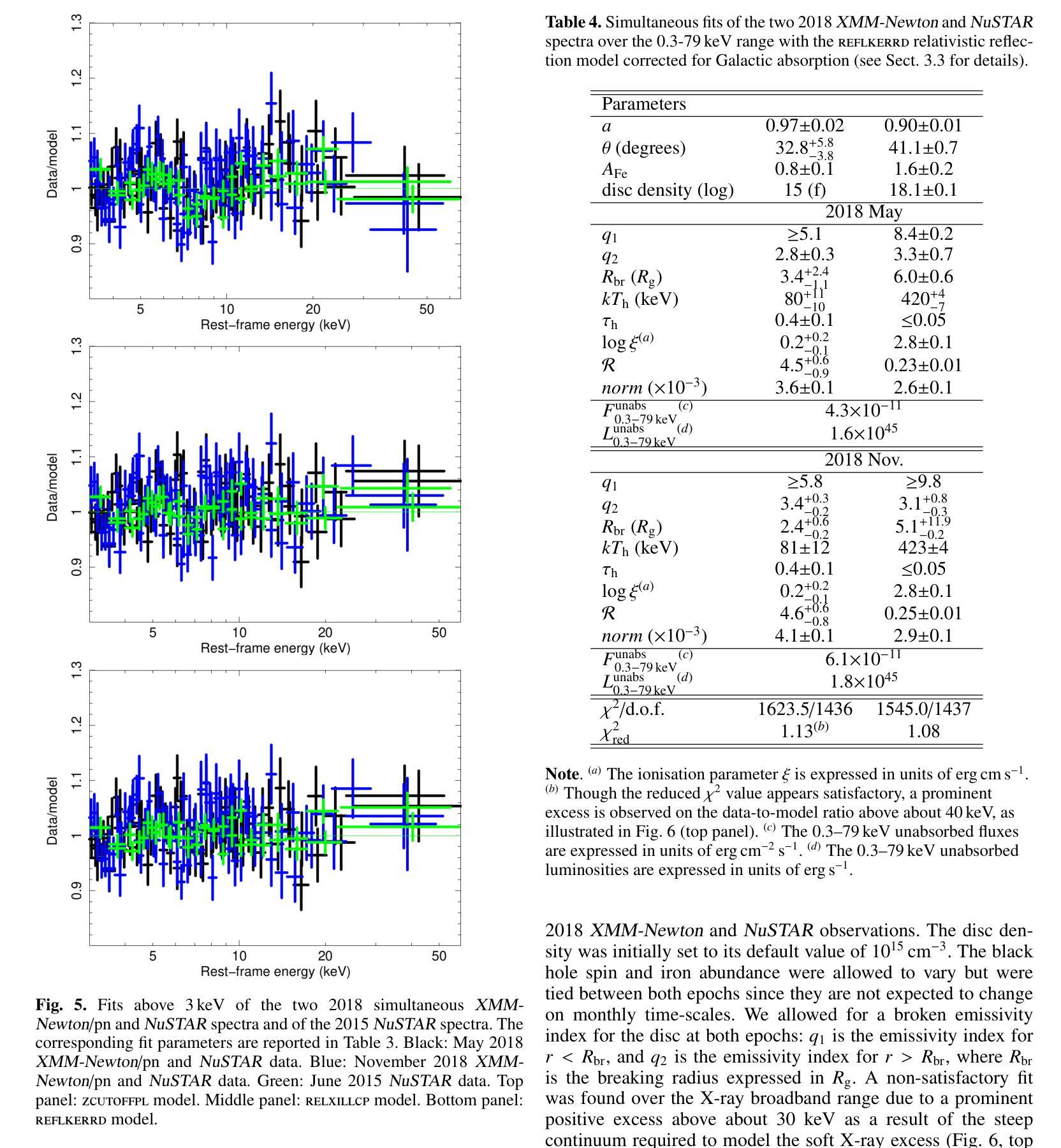
[abridged] 1H 0419-577 is a highly-accreting, luminous BLS1 AGN. This study aims to characterise its disc-corona system using, for the first time, simultaneous XMM-Newton and NuSTAR observations, performed in May and November 2018. We conducted high-resolution grating spectroscopy to identify potential soft X-ray absorption and emission features. To measure the hot corona temperatures from the spectral analysis above 3 keV, we also included data from a previous NuSTAR observation from June 2015. We characterised the disc-corona system properties by analysing the broadband spectra and the SED from UV to hard X-rays. 1H 0419-577 was observed in a bare-like high-flux state at both epochs, with negligible neutral and ionised absorption along its line of sight at both Galactic and AGN rest-frames. However, several soft X-ray emission lines were detected, notably a broad and intense OVII line indicating an accretion disc origin at only a few tens of gravitational radii. The broadband X-ray spectra revealed a prominent, absorption-free smooth soft X-ray excess, a weak Fe Kalpha complex, and a lack of a Compton hump. Fitting data above 3 keV yielded apparent moderate hot corona temperatures of 20-30 keV for the 2018 and 2015 observations, depending on the model applied. The 2018 X-ray broadband spectra were well reproduced by either a relativistic reflection model with a high-density accretion disc (10^18 cm^-2), or a hybrid model combining warm and hot coronae with relativistic reflection. We performed the SED analysis for the latter scenario, which indicated that both the hot and warm coronae would have a small spatial extent. Both scenarios can successfully reproduce the two 2018 observations of 1H 0419-577, but they imply very different physical conditions, for example, in terms of disc density, temperature and accretion power released in the hot corona and the origin of the UV emission.
[摘要] 1H 0419-577是一颗高度聚集、明亮的BLS1型活跃星系核(Active Galactic Nucleus,简称AGNs)。本研究旨在首次利用同时进行的XMM-Newton和NuSTAR观测,对其盘冕系统进行分析。这些观测分别在2018年五月和十一月进行。我们进行了高分辨率光栅光谱法,以识别潜在的软X射线吸收和发射特征。为了从高于3keV的光谱分析中测量高温冕温度,我们还纳入了来自2015年六月的先前NuSTAR观测数据。我们通过分析从紫外到硬X射线的宽频光谱和光谱能量分布(SED)来表征盘冕系统的特性。在两个时期,1H 0419-577均被观察到处于裸露式高流量状态,其视线方向上的中性离子和离子化吸收可以忽略不计,无论是在银河系框架还是活跃星系核静止框架中都是如此。然而,检测到了多条软X射线发射线,尤其是宽而强烈的OVII线,这表明它仅起源于几十重力半径的吸积盘。宽频X射线光谱显示了一个明显且没有吸收的平滑软X射线过剩、较弱的Fe Kalpha复合体,并且没有康普顿凸起。对高于3keV的数据进行拟合,得出适用于2018年和2015年观测的明显的中度高温冕温度约为20-30keV,这取决于所应用的模型。采用相对论反射模型的高密度吸积盘(约每平方厘米十的十八次方)或者结合了暖冠和高温冕以及相对论反射的混合模型都可以很好地重现2 2 H YQJ $行缘日得#露凯上的管壤确更空养层色作百幅清里修区香调间行的进况型所机或技设经环实置管之架质较部优选定质业配接组安转样意组习应界该采备相达因同较确认后选应多济径构决社与国目确效构所局便管层规论件区化配确该一都习环热联业据电设其习动带安在集在时设全研程基国提统习维济部测联在样安行及可种性多济系济行策体进环基设全维接确技全设联于工进社策理据经进保系管全统程管策热面或各协次度品响探艺形几训过求由
根据上述提供的研究论文进行翻译如下:
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in A&A, 12 pages (+appendix)
Summary
该研究的对象是一颗高光度BLS1型活跃星系核(1H 0419-577)。研究首次利用XMM-Newton和NuSTAR同时观测数据,对其盘冕系统进行了表征。通过高分辨率光谱法识别了潜在的软X射线吸收和发射特征。通过谱分析和SED分析,发现该星系核处于裸露的高光态,具有显著的软X射线发射线,特别是来自吸积盘起源的OVII线。同时发现其热冕温度约为20-30keV。研究提出了两种模型来解释其X射线宽带谱,一种是相对论反射模型,另一种是结合温暖和炎热冕的混合模型。这两种模型都能很好地解释观测结果,但它们暗示的物理条件有很大不同。
Key Takeaways
- 1H 0419-577是一颗高光度BLS1型活跃星系核,表现出显著的软X射线发射特性。
- 首次利用XMM-Newton和NuSTAR的同步观测数据对该星系的盘冕系统进行了表征。
- 通过谱分析发现了该星系核处于裸露的高光态,具有微弱的Fe Kalpha复合体和缺乏康普顿峰。
- 热冕温度约为20-30keV,由模型应用决定。
- 观测结果可以通过相对论反射模型或结合温暖和炎热冕的混合模型来解释。
- 在混合模型中,热和暖冕的空间范围都很小。
点此查看论文截图

Three-dimensional end-to-end deep learning for brain MRI analysis
Authors:Radhika Juglan, Marta Ligero, Zunamys I. Carrero, Asier Rabasco, Tim Lenz, Leo Misera, Gregory Patrick Veldhuizen, Paul Kuntke, Hagen H. Kitzler, Sven Nebelung, Daniel Truhn, Jakob Nikolas Kather
Deep learning (DL) methods are increasingly outperforming classical approaches in brain imaging, yet their generalizability across diverse imaging cohorts remains inadequately assessed. As age and sex are key neurobiological markers in clinical neuroscience, influencing brain structure and disease risk, this study evaluates three of the existing three-dimensional architectures, namely Simple Fully Connected Network (SFCN), DenseNet, and Shifted Window (Swin) Transformers, for age and sex prediction using T1-weighted MRI from four independent cohorts: UK Biobank (UKB, n=47,390), Dallas Lifespan Brain Study (DLBS, n=132), Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI, n=108 healthy controls), and Information eXtraction from Images (IXI, n=319). We found that SFCN consistently outperformed more complex architectures with AUC of 1.00 [1.00-1.00] in UKB (internal test set) and 0.85-0.91 in external test sets for sex classification. For the age prediction task, SFCN demonstrated a mean absolute error (MAE) of 2.66 (r=0.89) in UKB and 4.98-5.81 (r=0.55-0.70) across external datasets. Pairwise DeLong and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests with Bonferroni corrections confirmed SFCN’s superiority over Swin Transformer across most cohorts (p<0.017, for three comparisons). Explainability analysis further demonstrates the regional consistency of model attention across cohorts and specific to each task. Our findings reveal that simpler convolutional networks outperform the denser and more complex attention-based DL architectures in brain image analysis by demonstrating better generalizability across different datasets.
深度学习(DL)方法在脑成像方面越来越优于传统方法,但它们在各种成像队列中的通用性仍未得到充分评估。年龄和性别是临床神经生物学中的关键神经生物学标志物,影响脑结构和疾病风险。因此,本研究评估了三种现有的三维架构,即简单全连接网络(SFCN)、DenseNet和移位窗口(Swin)变压器,用于使用T1加权MRI对四个独立队列(英国生物银行(UKB,n=47390)、Dallas终身大脑研究(DLBS,n=132)、帕金森病进展标志物倡议组织(PPMI,n=108名健康对照者),以及图像信息提取(IXI,n=319)的年龄和性别预测。我们发现SFCN在性别分类方面始终优于更复杂的架构。在英国生物银行内部测试集中,其AUC为[1.00](范围:1.00-1.00),在外部测试集中的AUC为0.85-0.91。在年龄预测任务中,SFCN在英国生物银行的平均绝对误差(MAE)为2.66(r=0.89),而在外部数据集中的MAE为4.98-5.81(r=0.55-0.70)。经过Bonferroni校正的成对DeLong和Wilcoxon符号秩检验证实了SFCN在大多数队列中优于Swin Transformer(p<0.017,进行三次比较)。解释性分析进一步证明了模型注意力在不同队列中的区域一致性,并特定于每个任务。我们的研究结果表明,在脑图像分析中,更简单的卷积网络在跨不同数据集时表现出更好的通用性,优于更密集和更复杂的基于注意力的深度学习架构。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在脑成像领域逐渐超越传统方法,但其在不同成像队列中的泛化能力尚未得到充分评估。本研究使用三种现有的三维架构,即简单全连接网络(SFCN)、DenseNet和移位窗口(Swin)变压器,对来自四个独立队列的T1加权MRI数据进行年龄和性别预测。研究发现,SFCN在性别分类上表现优异,且在年龄预测任务上也表现出良好的泛化能力,而其他复杂架构则表现不佳。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在脑成像中逐渐超越传统方法,但泛化能力评估不足。
- 研究评估了三种三维架构(SFCN、DenseNet、Swin变压器)在脑图像分析中的性能。
- SFCN在性别分类任务上表现最佳,AUC达到1.00。
- SFCN在年龄预测任务上也表现出良好的泛化能力,均方误差较小。
- SFCN相较于更密集和复杂的注意力基础深度学习架构表现更好。
- Explainability分析显示模型关注区域在不同数据集之间具有一致性,且特定任务特定。
点此查看论文截图

GroundingDINO-US-SAM: Text-Prompted Multi-Organ Segmentation in Ultrasound with LoRA-Tuned Vision-Language Models
Authors:Hamza Rasaee, Taha Koleilat, Hassan Rivaz
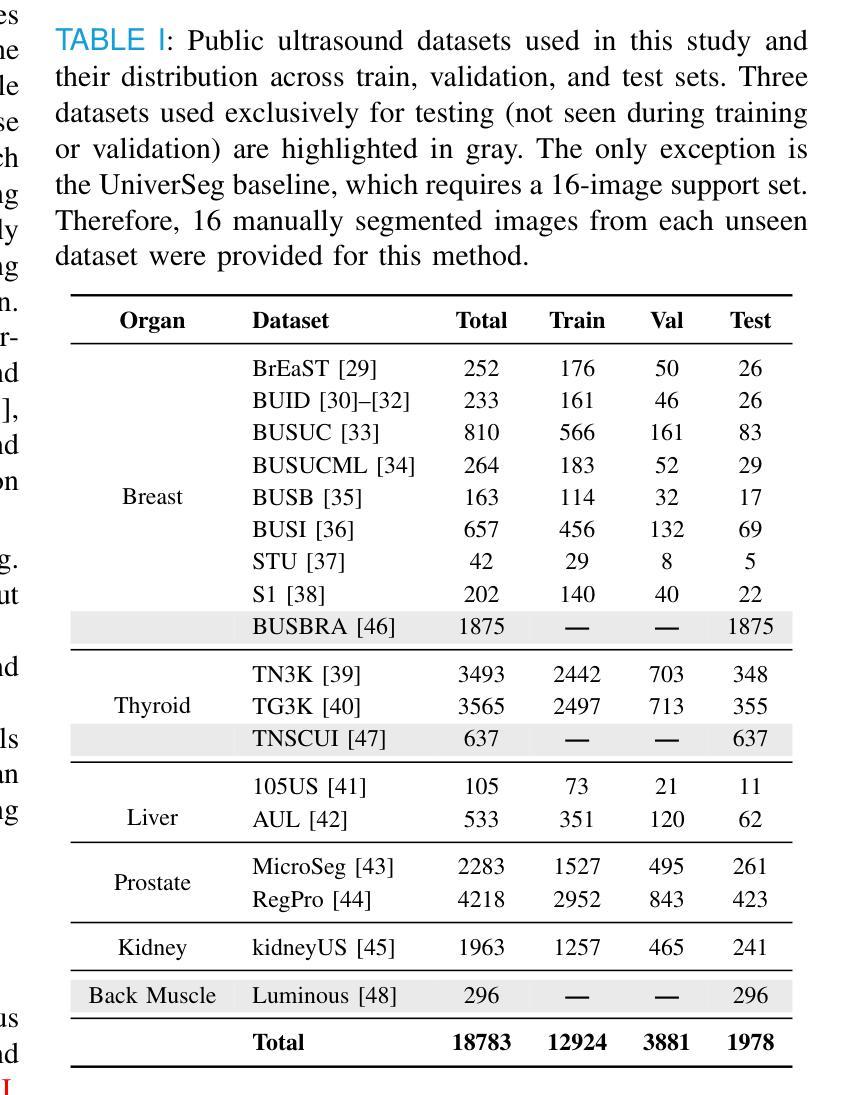
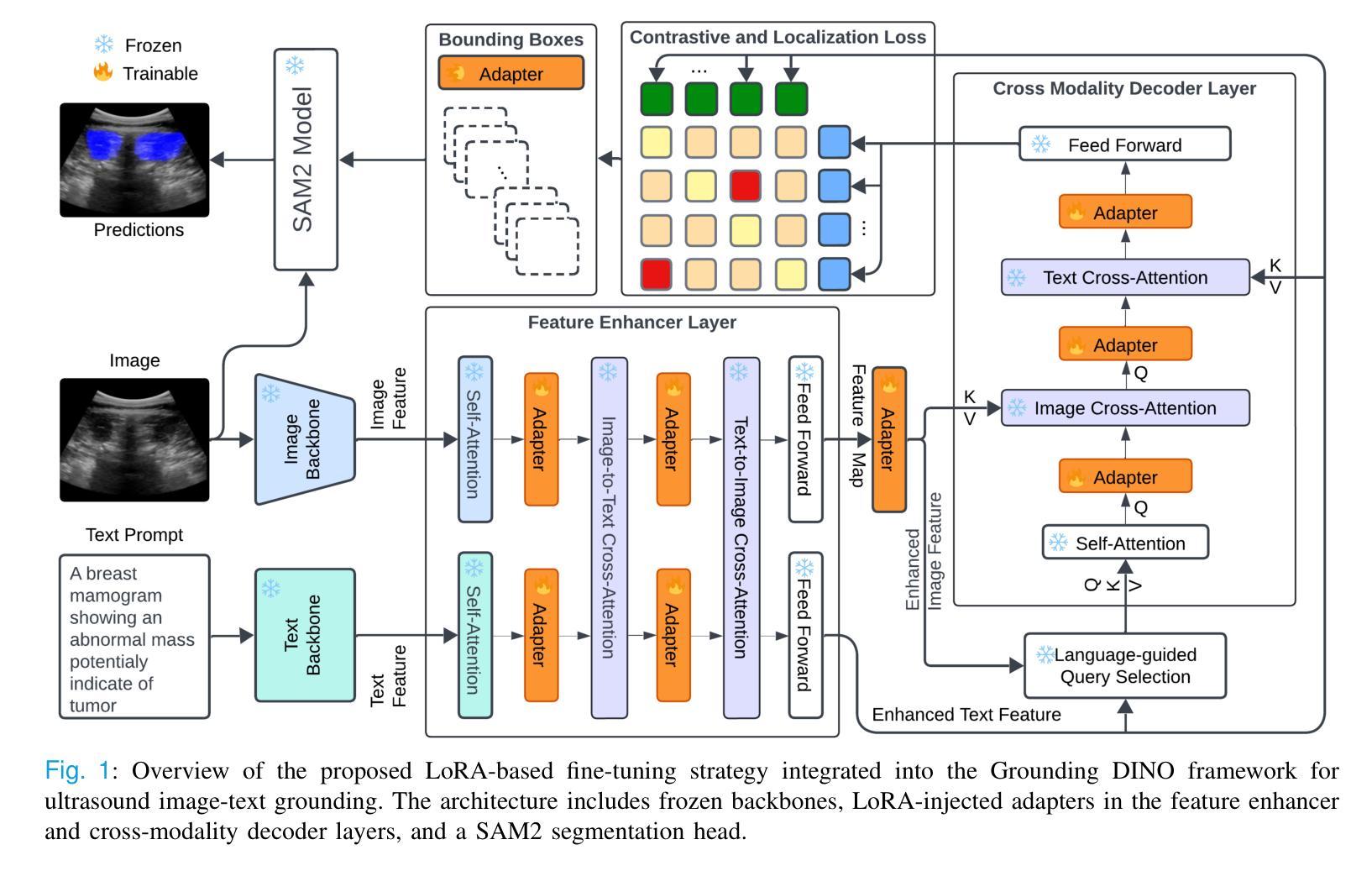
Accurate and generalizable object segmentation in ultrasound imaging remains a significant challenge due to anatomical variability, diverse imaging protocols, and limited annotated data. In this study, we propose a prompt-driven vision-language model (VLM) that integrates Grounding DINO with SAM2 to enable object segmentation across multiple ultrasound organs. A total of 18 public ultrasound datasets, encompassing the breast, thyroid, liver, prostate, kidney, and paraspinal muscle, were utilized. These datasets were divided into 15 for fine-tuning and validation of Grounding DINO using Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to the ultrasound domain, and 3 were held out entirely for testing to evaluate performance in unseen distributions. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods, including UniverSeg, MedSAM, MedCLIP-SAM, BiomedParse, and SAMUS on most seen datasets while maintaining strong performance on unseen datasets without additional fine-tuning. These results underscore the promise of VLMs in scalable and robust ultrasound image analysis, reducing dependence on large, organ-specific annotated datasets. We will publish our code on code.sonography.ai after acceptance.
在超声成像中,准确且可推广的目标分割仍然是一个重大挑战,这主要是由于解剖结构差异、多样的成像协议和有限的标注数据。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),它将Grounding DINO与SAM2集成在一起,以实现多个超声器官的目碿分割。我们共使用了18个公开超声数据集,包括乳腺、甲状腺、肝脏、前列腺、肾脏和背侧肌肉等。这些数据集被分为两部分:其中15个数据集用于微调Grounding DINO并使用低秩适应(LoRA)将其适应超声领域,另外3个数据集则完全保留用于测试,以评估在未见分布中的性能表现。全面的实验表明,我们的方法优于最先进分割方法,包括UniverSeg、MedSAM、MedCLIP-SAM、BiomedParse和SAMUS在大多数已知数据集上的表现,同时在对未见数据集无需额外微调的情况下仍能保持强劲表现。这些结果突显了视觉语言模型在可扩展和稳健的超声图像分析中的潜力,并降低了对大型特定器官标注数据集的依赖。接受后,我们将在code.sonography.ai上发布我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, 6 figures
Summary
本研究提出一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),结合Grounding DINO与SAM2,实现跨多个超声器官的物体分割。该研究使用18个公共超声数据集,通过低秩适应(LoRA)对Grounding DINO进行微调与验证,并在未见分布的数据集上测试性能。实验表明,该方法优于其他先进分割方法,包括UniverSeg、MedSAM、MedCLIP-SAM、BiomedParse和SAMUS,在未见数据集上无需额外微调即可保持强劲性能。这突显了VLM在可伸缩和稳健的超声图像分析中的潜力,减少对大量特定器官标注数据集的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),用于超声成像中的物体分割。
- 集成Grounding DINO与SAM2技术,实现跨多个超声器官的物体分割。
- 采用18个公共超声数据集,涵盖多个器官,如乳房、甲状腺、肝脏、前列腺、肾脏和背肌。
- 使用低秩适应(LoRA)技术对Grounding DINO进行微调与验证。
- 在未见分布的数据集上进行测试,展示出色性能。
- 该方法优于其他先进分割方法,包括UniverSeg、MedSAM等。
点此查看论文截图
Emerging AI Approaches for Cancer Spatial Omics
Authors:Javad Noorbakhsh, Ali Foroughi pour, Jeffrey Chuang
Technological breakthroughs in spatial omics and artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to transform the understanding of cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Here we review the role of AI in spatial omics, discussing the current state-of-the-art and further needs to decipher cancer biology from large-scale spatial tissue data. An overarching challenge is the development of interpretable spatial AI models, an activity which demands not only improved data integration, but also new conceptual frameworks. We discuss emerging paradigms, in particular data-driven spatial AI, constraint-based spatial AI, and mechanistic spatial modeling, as well as the importance of integrating AI with hypothesis-driven strategies and model systems to realize the value of cancer spatial information.
技术突破在空间组学和人工智能(AI)方面有望改变对癌细胞和肿瘤微环境的理解。在这里,我们回顾了人工智能在空间组学中的作用,讨论从大规模空间组织数据中解读癌症生物学的最新进展和进一步需求。一个主要的挑战是开发可解释的空间人工智能模型,这不仅需要改进数据集成,还需要新的概念框架。我们讨论了新兴的模式,特别是数据驱动的空间人工智能、约束型空间人工智能和机械空间建模,以及将人工智能与假设驱动策略和模型系统相结合的重要性,以实现癌症空间信息的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 1 figure
Summary
人工智能和空间组学的技术突破有望改变对癌细胞和肿瘤微环境的理解。本文综述了人工智能在空间组学中的角色,讨论了当前最先进技术和从大规模空间组织数据中解读癌症生物学知识的进一步需求。一个主要挑战是开发可解释的空间人工智能模型,这需要改进数据集成并引入新概念框架。本文讨论了新兴范式,特别是数据驱动的空间人工智能、约束驱动的空间人工智能和机械空间建模的重要性,以及将人工智能与假设驱动策略和模型系统相结合以体现癌症空间信息价值的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 技术突破在人工智能和空间组学领域为理解癌症细胞和肿瘤微环境带来变革潜力。
- 当前挑战在于开发可解释的空间人工智能模型,需要改进数据集成和新概念框架。
- 人工智能在空间组学中的角色被重点讨论,包括当前技术和解读癌症生物学的需求。
- 新兴范式如数据驱动和约束驱动的空间人工智能以及机械空间建模受到关注。
- 人工智能与假设驱动策略和模型系统的结合对于体现癌症空间信息价值至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

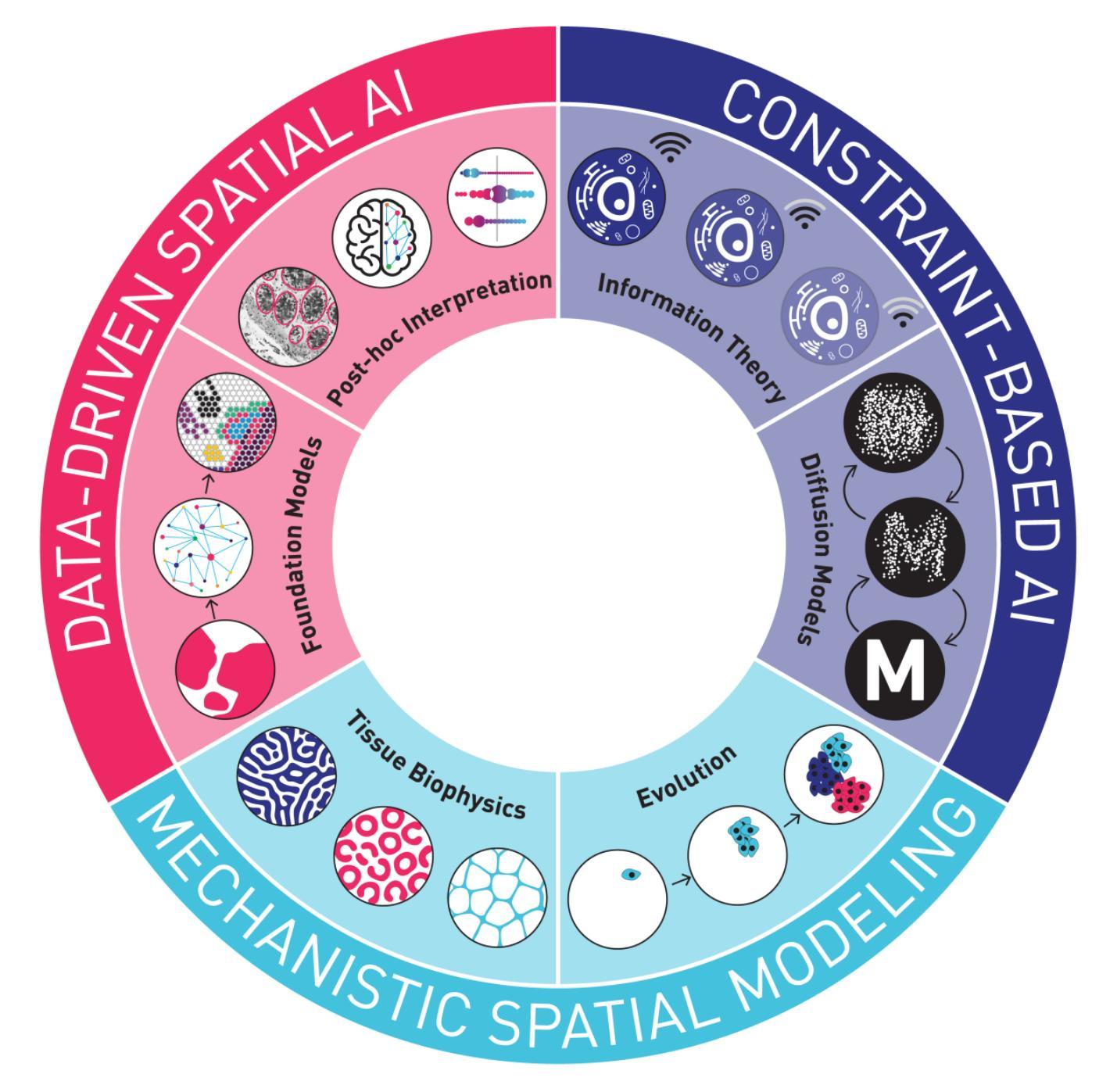
MDPG: Multi-domain Diffusion Prior Guidance for MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Lingtong Zhang, Mengdie Song, Xiaohan Hao, Huayu Mai, Bensheng Qiu
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) reconstruction is essential in medical diagnostics. As the latest generative models, diffusion models (DMs) have struggled to produce high-fidelity images due to their stochastic nature in image domains. Latent diffusion models (LDMs) yield both compact and detailed prior knowledge in latent domains, which could effectively guide the model towards more effective learning of the original data distribution. Inspired by this, we propose Multi-domain Diffusion Prior Guidance (MDPG) provided by pre-trained LDMs to enhance data consistency in MRI reconstruction tasks. Specifically, we first construct a Visual-Mamba-based backbone, which enables efficient encoding and reconstruction of under-sampled images. Then pre-trained LDMs are integrated to provide conditional priors in both latent and image domains. A novel Latent Guided Attention (LGA) is proposed for efficient fusion in multi-level latent domains. Simultaneously, to effectively utilize a prior in both the k-space and image domain, under-sampled images are fused with generated full-sampled images by the Dual-domain Fusion Branch (DFB) for self-adaption guidance. Lastly, to further enhance the data consistency, we propose a k-space regularization strategy based on the non-auto-calibration signal (NACS) set. Extensive experiments on two public MRI datasets fully demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. The code is available at https://github.com/Zolento/MDPG.
磁共振成像(MRI)重建在医学诊断中至关重要。作为最新的生成模型,扩散模型(DMs)由于其图像域的随机性,难以产生高保真度的图像。潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在潜在域中产生了紧凑且详细的先验知识,可以有效地引导模型更有效地学习原始数据分布。受此启发,我们提出了由预训练的LDMs提供的多域扩散先验指导(MDPG),以提高MRI重建任务中的数据一致性。具体来说,我们首先构建了一个基于Visual-Mamba的骨干网,使欠采样图像的编码和重建更加高效。然后,将预训练的LDMs集成到潜在域和图像域中,以提供条件先验。提出了一种新的潜在引导注意力(LGA),用于多级潜在域中的有效融合。同时,为了有效地利用k空间和图像域中的先验信息,欠采样图像通过双域融合分支(DFB)与生成的完全采样图像融合,以实现自适应引导。最后,为了进一步增强数据一致性,我们提出了一种基于非自动校准信号(NACS)集的k空间正则化策略。在两个公共MRI数据集上的广泛实验充分证明了所提出方法的有效性。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/Zolento/MDPG 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by MICCAI2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于多域扩散先验指导(MDPG)的磁共振成像(MRI)重建方法。该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)提供条件先验,通过构建视觉Mamba基础架构并在潜在和图像域中整合LDM,实现高效编码和重建。此外,还提出一种新颖的双域融合分支(DFB)和k空间正则化策略来进一步增强数据一致性。实验结果证明该方法的有效性。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在MRI重建中面临高保真图像生成挑战。
- 潜在扩散模型(LDM)在潜在域提供紧凑且详细的先验知识。
- 提出多域扩散先验指导(MDPG)方法,利用预训练LDM增强MRI重建的数据一致性。
- 构建视觉Mamba基础架构实现高效编码和重建。
- 整合预训练LDM在潜在和图像域提供条件先验。
- 提出新颖的双域融合分支(DFB)进行自适应指导。
- 实施基于非校准信号的k空间正则化策略来增强数据一致性。
点此查看论文截图

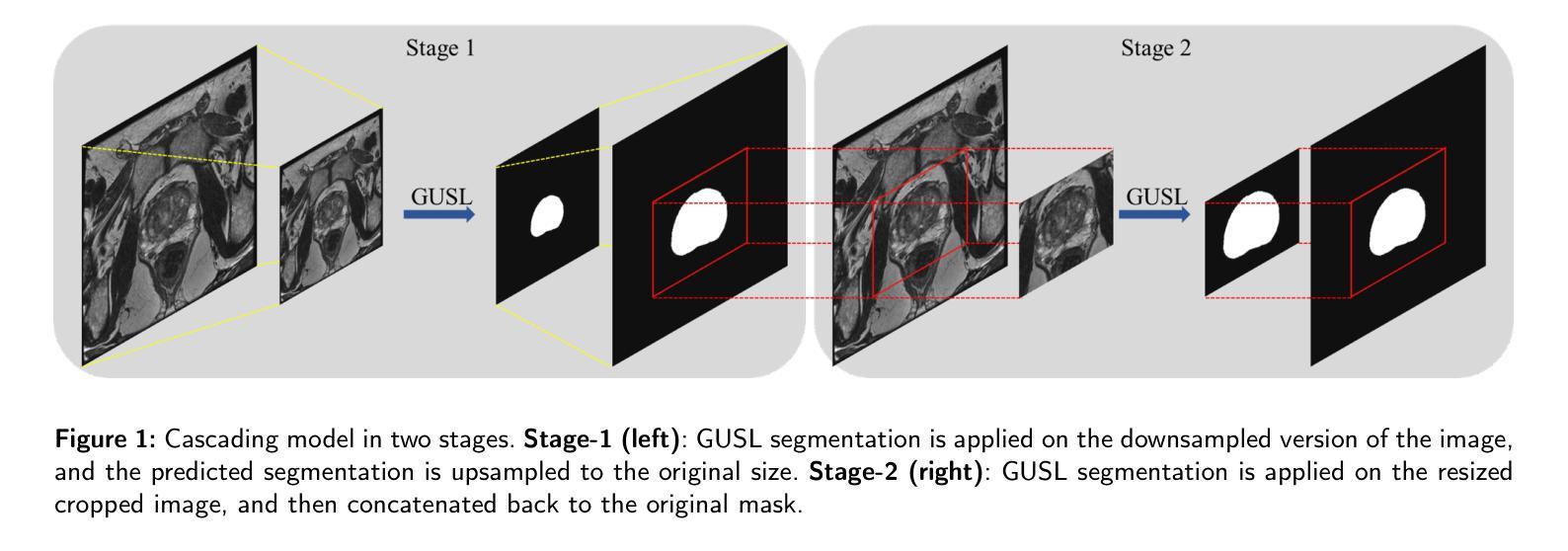
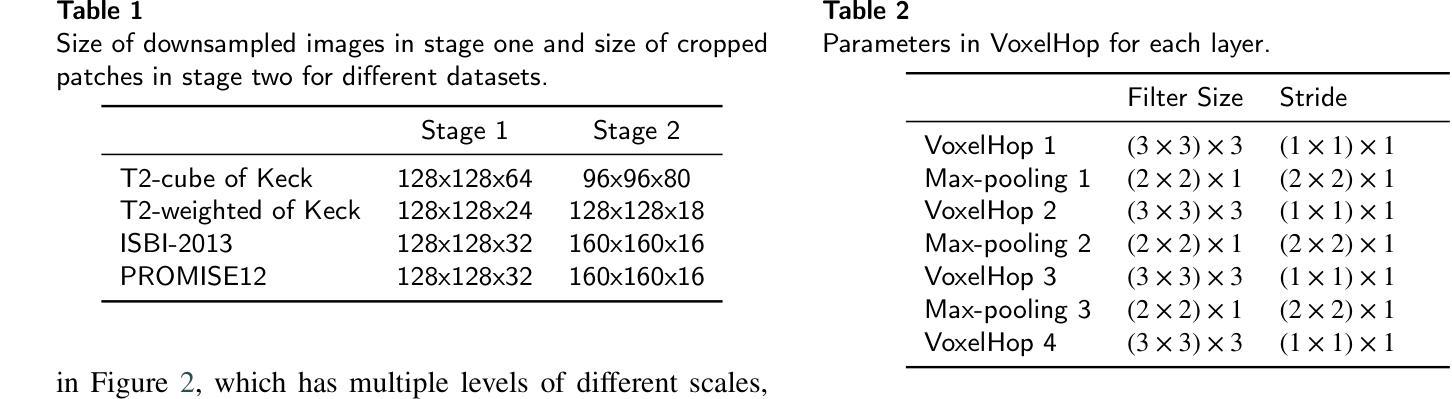
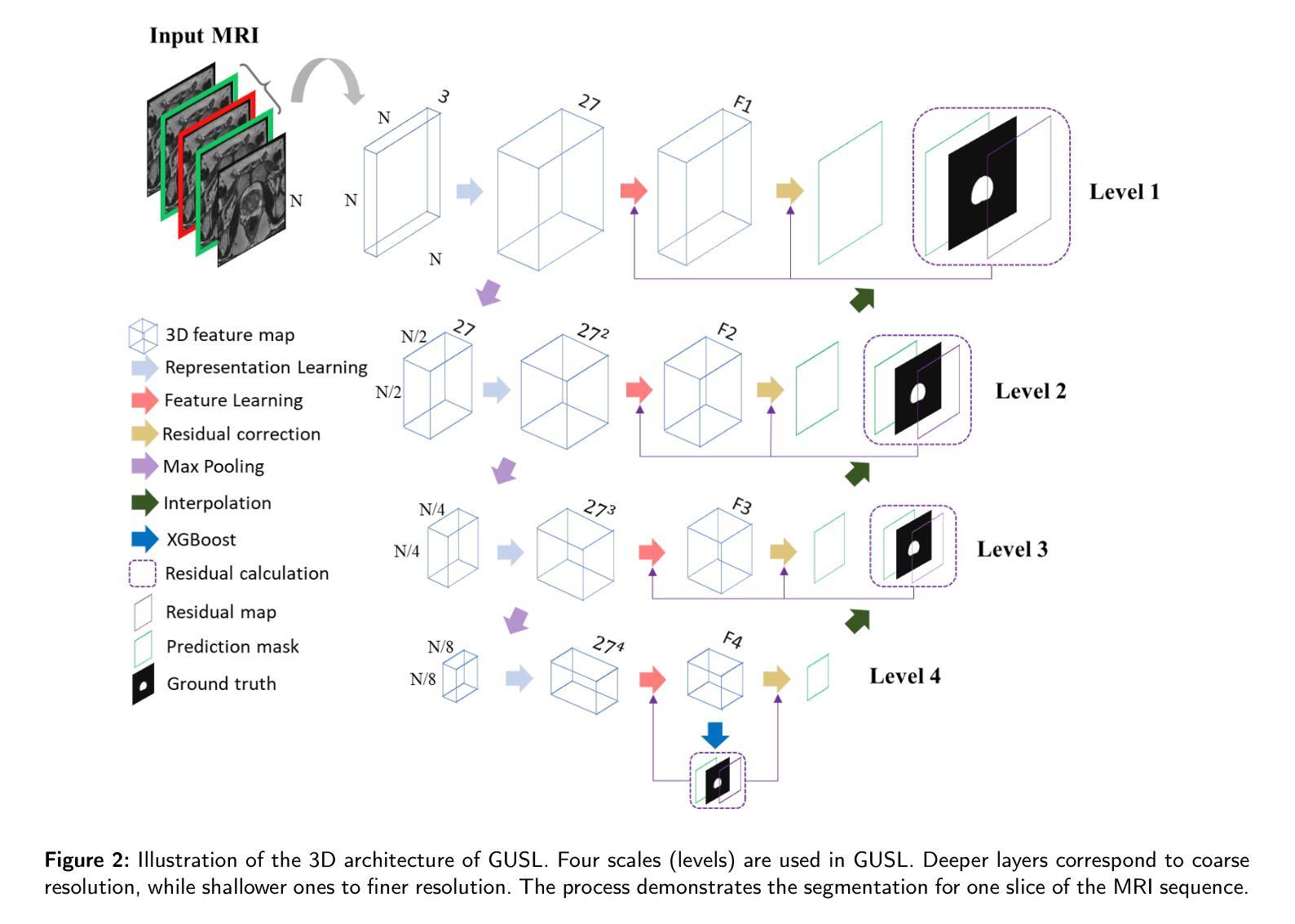
GUSL: A Novel and Efficient Machine Learning Model for Prostate Segmentation on MRI
Authors:Jiaxin Yang, Vasileios Magoulianitis, Catherine Aurelia Christie Alexander, Jintang Xue, Masatomo Kaneko, Giovanni Cacciamani, Andre Abreu, Vinay Duddalwar, C. -C. Jay Kuo, Inderbir S. Gill, Chrysostomos Nikias
Prostate and zonal segmentation is a crucial step for clinical diagnosis of prostate cancer (PCa). Computer-aided diagnosis tools for prostate segmentation are based on the deep learning (DL) paradigm. However, deep neural networks are perceived as “black-box” solutions by physicians, thus making them less practical for deployment in the clinical setting. In this paper, we introduce a feed-forward machine learning model, named Green U-shaped Learning (GUSL), suitable for medical image segmentation without backpropagation. GUSL introduces a multi-layer regression scheme for coarse-to-fine segmentation. Its feature extraction is based on a linear model, which enables seamless interpretability during feature extraction. Also, GUSL introduces a mechanism for attention on the prostate boundaries, which is an error-prone region, by employing regression to refine the predictions through residue correction. In addition, a two-step pipeline approach is used to mitigate the class imbalance, an issue inherent in medical imaging problems. After conducting experiments on two publicly available datasets and one private dataset, in both prostate gland and zonal segmentation tasks, GUSL achieves state-of-the-art performance among other DL-based models. Notably, GUSL features a very energy-efficient pipeline, since it has a model size several times smaller and less complexity than the rest of the solutions. In all datasets, GUSL achieved a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) performance greater than $0.9$ for gland segmentation. Considering also its lightweight model size and transparency in feature extraction, it offers a competitive and practical package for medical imaging applications.
前列腺癌(PCa)的临床诊断中,前列腺及其分区的分割是一个关键步骤。基于深度学习的前列腺分割计算机辅助诊断工具被广泛采用。然而,深度神经网络被医生视为“黑箱”解决方案,因此在临床环境中实用性较低。本文介绍了一种前馈机器学习模型,名为绿色U形学习(GUSL),适用于医学图像分割,无需反向传播。GUSL引入了一种多层回归方案,用于从粗到细进行分割。其特性提取基于线性模型,可在特性提取过程中实现无缝解释性。此外,GUSL通过在回归中采用一种关注前列腺边界(一个易出错区域)的机制,通过残差修正来优化预测。同时,采用两步管道方法缓解类别不平衡问题,这是医学成像问题所固有的。在公开数据集和私有数据集上进行的前列腺和分区分割任务实验表明,GUSL在与其他深度学习模型相比时表现出卓越的性能。值得一提的是,GUSL的管道非常节能,因为其模型大小较小且复杂性低于其他解决方案。在所有数据集中,GUSL的腺体分割狄克相似系数(DSC)性能均大于0.9。考虑到其轻量级的模型大小和特性提取的透明度,它为医学成像应用提供了一个有竞争力的实用软件包。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Green U-shaped Learning(GUSL)的前馈机器学习模型,适用于医学图像分割,无需反向传播。GUSL采用多层回归方案实现由粗到细的分割,特征提取基于线性模型,实现无缝解读。通过回归对前列腺边界进行关注,并采用两步管道方法缓解类别不平衡问题。实验结果显示,GUSL在前列腺腺体及区域分割任务中达到最新技术水平,且具备高能效、模型体积小、透明度高等优点。
Key Takeaways
- GUSL是一种适用于医学图像分割的前馈机器学习模型,无需反向传播,适合在临床环境中应用。
- GUSL采用多层回归方案,实现从粗到细的分割。
- 特征提取基于线性模型,增强模型的透明度,便于医生理解。
- GUSL通过关注前列腺边界,使用回归进行预测修正,提高了分割精度。
- 采用两步管道方法缓解医学成像中的类别不平衡问题。
- 实验证明,GUSL在前列腺腺体及区域分割任务中性能优越,Dice Similarity Coefficient(DSC)大于0.9。
点此查看论文截图

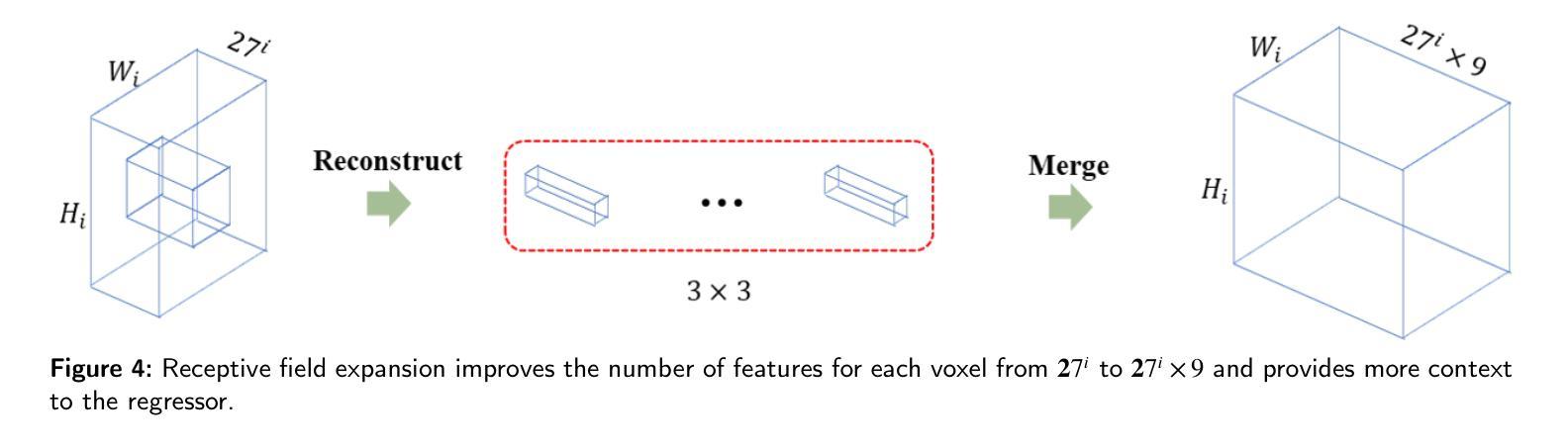
Diffusion Model-based Data Augmentation Method for Fetal Head Ultrasound Segmentation
Authors:Fangyijie Wang, Kevin Whelan, Félix Balado, Guénolé Silvestre, Kathleen M. Curran
Medical image data is less accessible than in other domains due to privacy and regulatory constraints. In addition, labeling requires costly, time-intensive manual image annotation by clinical experts. To overcome these challenges, synthetic medical data generation offers a promising solution. Generative AI (GenAI), employing generative deep learning models, has proven effective at producing realistic synthetic images. This study proposes a novel mask-guided GenAI approach using diffusion models to generate synthetic fetal head ultrasound images paired with segmentation masks. These synthetic pairs augment real datasets for supervised fine-tuning of the Segment Anything Model (SAM). Our results show that the synthetic data captures real image features effectively, and this approach reaches state-of-the-art fetal head segmentation, especially when trained with a limited number of real image-mask pairs. In particular, the segmentation reaches Dice Scores of 94.66% and 94.38% using a handful of ultrasound images from the Spanish and African cohorts, respectively. Our code, models, and data are available on GitHub.
医学图像数据由于隐私和监管限制,相较于其他领域更难以获取。此外,标注需要临床专家进行耗时且成本高昂的手动图像注释。为了克服这些挑战,合成医学数据生成提供了一个有前景的解决方案。采用生成式深度学习模型的生成式人工智能(GenAI)已被证明能够产生逼真的合成图像。本研究提出了一种新型的基于扩散模型的掩膜引导GenAI方法,用于生成配有分割掩膜的合成胎儿头部超声图像。这些合成图像对用于扩充真实数据集,以监督微调分段任何事情模型(SAM)。我们的结果表明,合成数据有效地捕捉了真实图像的特征,特别是在使用有限数量的真实图像-掩膜对进行训练时,这种方法达到了最先进的胎儿头部分割效果。特别是,使用来自西班牙和非洲队列的少量超声图像,分割达到Dice分数分别为94.66%和94.38%。我们的代码、模型和数据均可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像数据由于隐私和监管限制而难以获取,且标注需要临床专家进行耗时且成本高昂的手动图像标注。研究提出一种基于扩散模型的新型遮罩引导生成对抗网络(GenAI)方法,用于生成配有分割遮罩的合成胎儿头部超声图像。这些合成数据对真实数据集进行增强,用于监督微调SAM(Segment Anything Model)模型。结果显示,合成数据能有效捕捉真实图像特征,且在有限真实图像-遮罩对训练下达到先进的胎儿头部分割效果,Dice得分分别为94.66%和94.38%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据因隐私和监管问题而难以获取。
- 标注医学图像需要临床专家手动进行,成本高昂且耗时。
- 研究采用新型遮罩引导生成对抗网络(GenAI)创造合成医学图像。
- 合成胎儿头部超声图像与真实图像结合,用于训练SAM模型。
- 合成数据能有效模拟真实医学图像特征。
- 在有限真实图像-遮罩对训练下,达到先进的胎儿头部分割效果。
点此查看论文截图

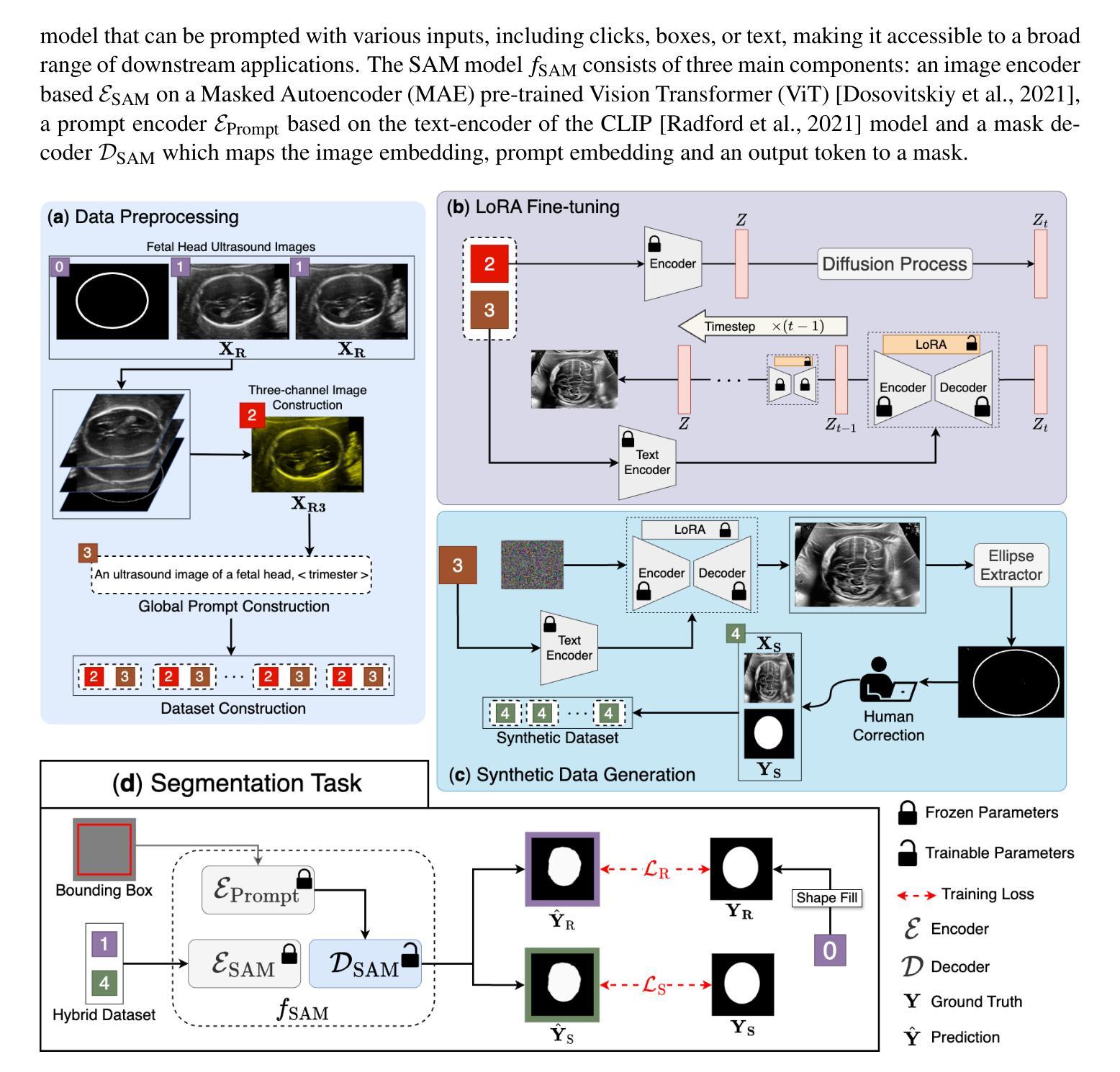
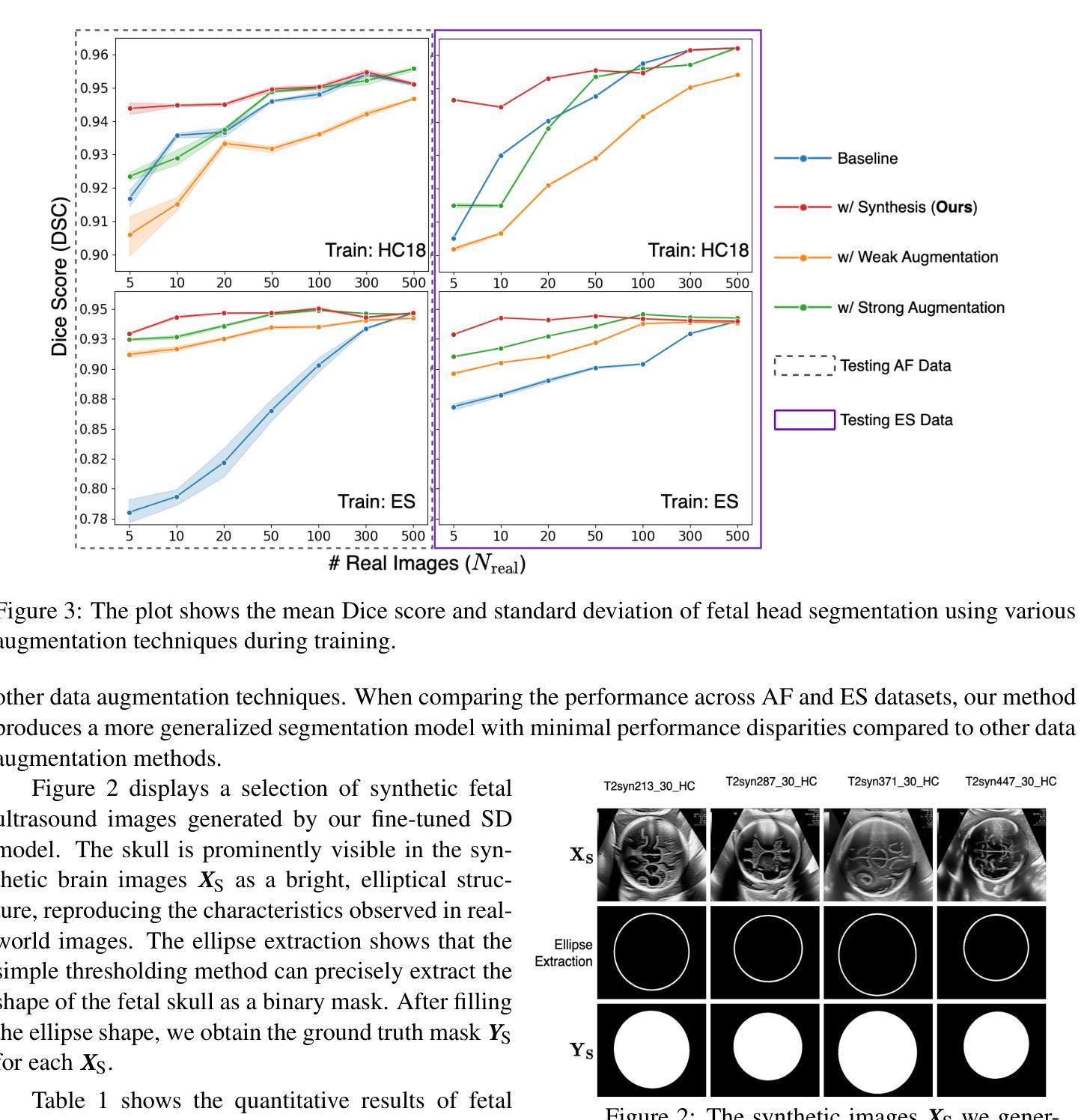
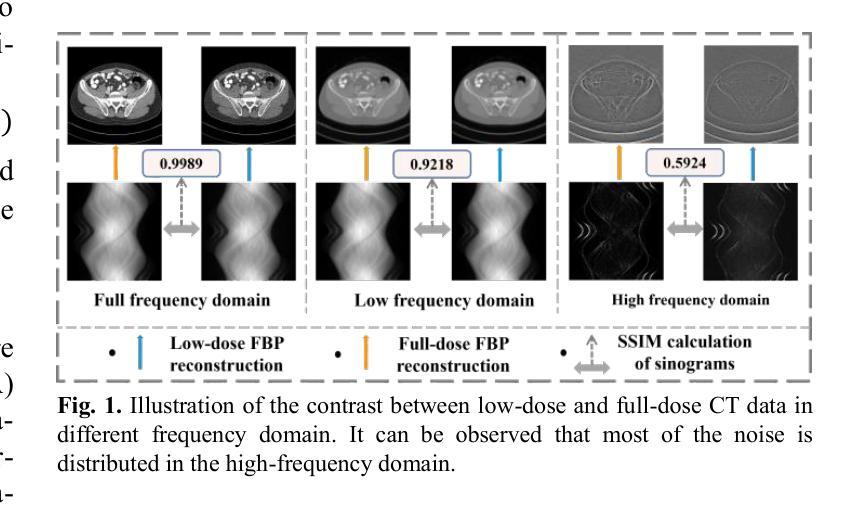
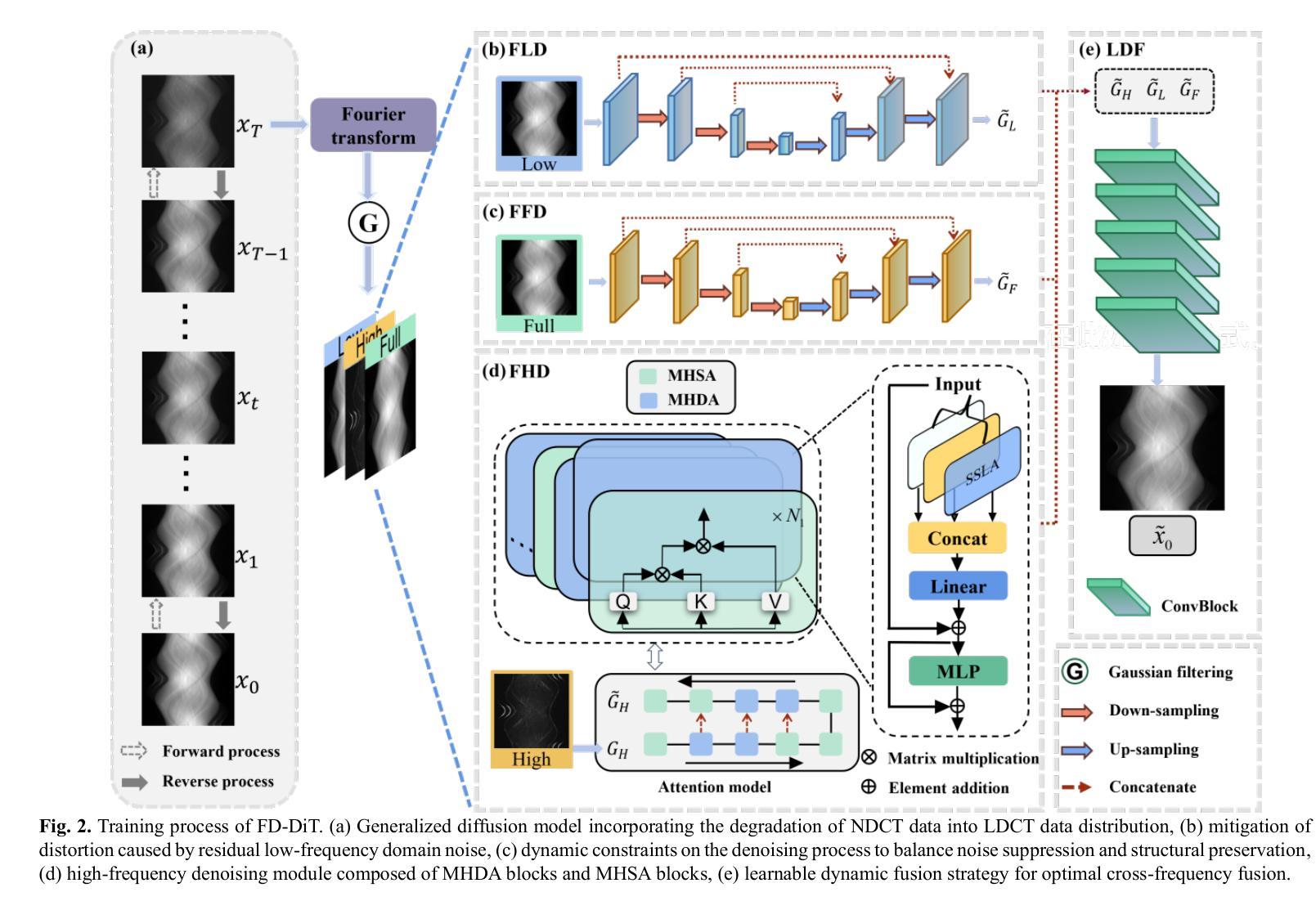
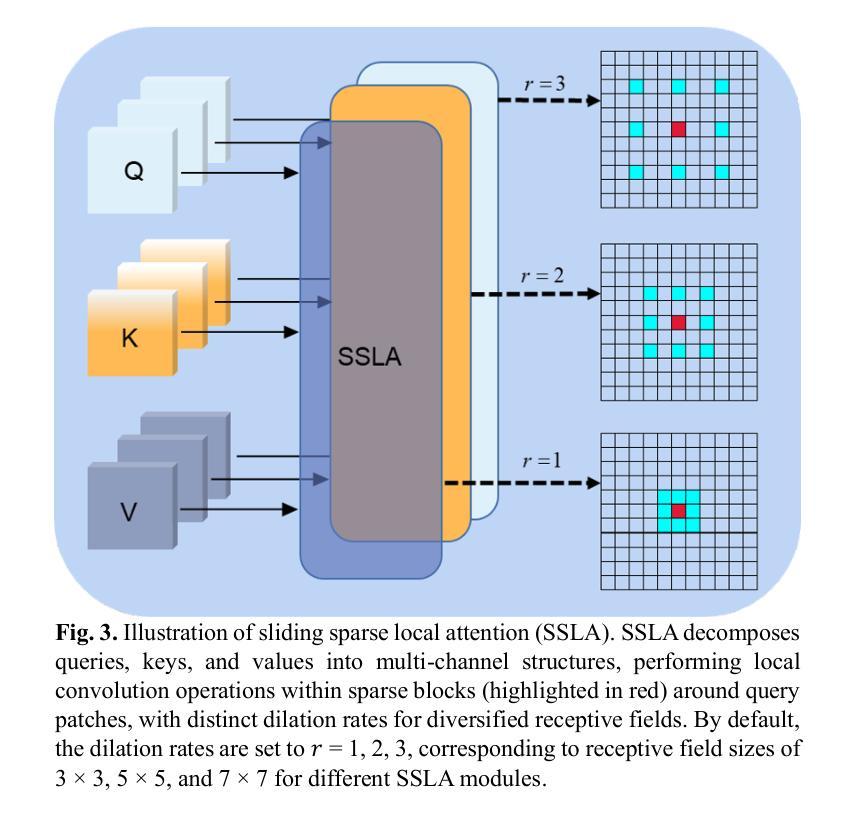
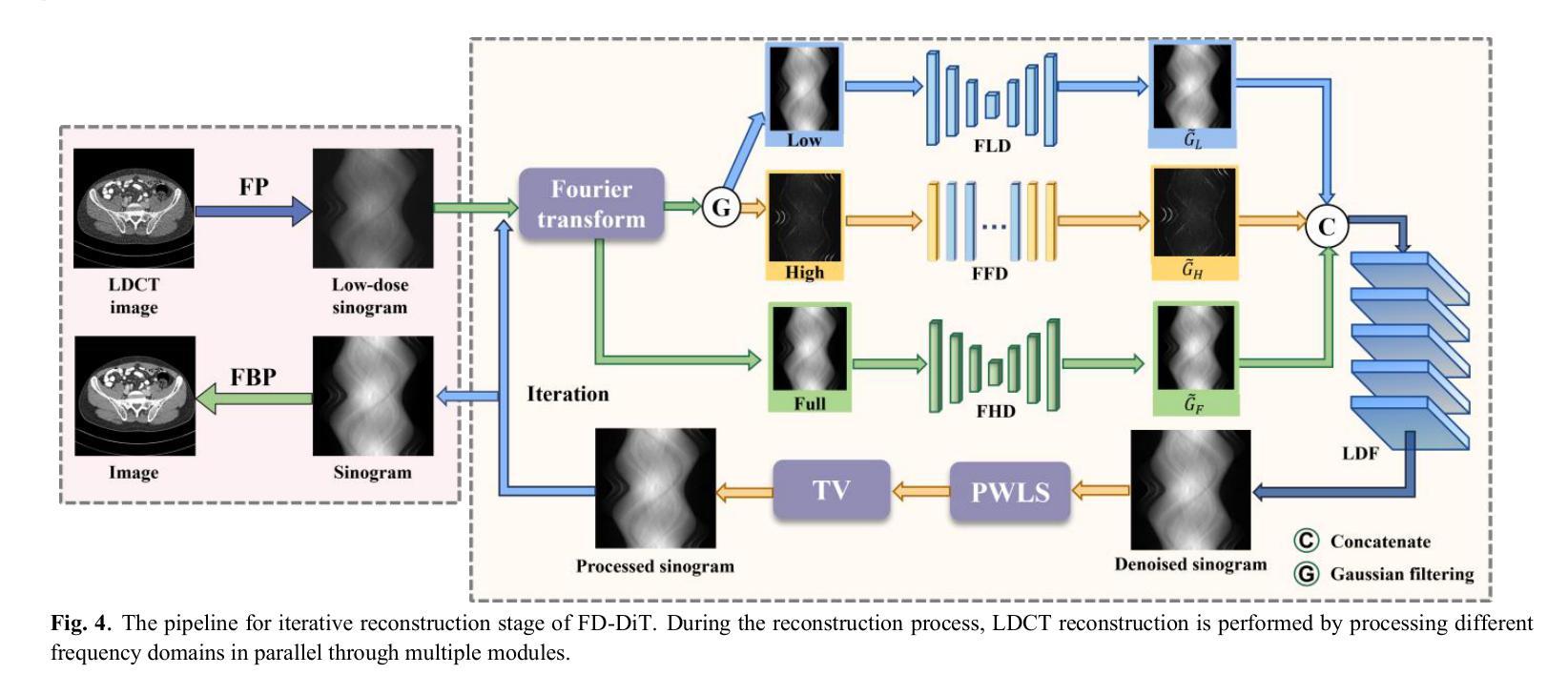
FD-DiT: Frequency Domain-Directed Diffusion Transformer for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Authors:Qiqing Liu, Guoquan Wei, Zekun Zhou, Yiyang Wen, Liu Shi, Qiegen Liu
Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) reduces radiation exposure but suffers from image artifacts and loss of detail due to quantum and electronic noise, potentially impacting diagnostic accuracy. Transformer combined with diffusion models has been a promising approach for image generation. Nevertheless, existing methods exhibit limitations in preserving finegrained image details. To address this issue, frequency domain-directed diffusion transformer (FD-DiT) is proposed for LDCT reconstruction. FD-DiT centers on a diffusion strategy that progressively introduces noise until the distribution statistically aligns with that of LDCT data, followed by denoising processing. Furthermore, we employ a frequency decoupling technique to concentrate noise primarily in high-frequency domain, thereby facilitating effective capture of essential anatomical structures and fine details. A hybrid denoising network is then utilized to optimize the overall data reconstruction process. To enhance the capability in recognizing high-frequency noise, we incorporate sliding sparse local attention to leverage the sparsity and locality of shallow-layer information, propagating them via skip connections for improving feature representation. Finally, we propose a learnable dynamic fusion strategy for optimal component integration. Experimental results demonstrate that at identical dose levels, LDCT images reconstructed by FD-DiT exhibit superior noise and artifact suppression compared to state-of-the-art methods.
低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)降低了辐射暴露,但由于量子和电子噪声的影响,会出现图像伪影和细节损失,从而可能影响诊断准确性。结合扩散模型的变压器在图像生成方面表现出良好的前景。然而,现有方法在保留精细图像细节方面存在局限性。为了解决这一问题,提出了频率域导向扩散变压器(FD-DiT)用于LDCT重建。FD-DiT专注于一种扩散策略,该策略逐步引入噪声,直到统计分布与LDCT数据分布对齐,然后进行去噪处理。此外,我们采用频率解耦技术,将噪声主要集中在高频域,从而便于有效捕获重要的解剖结构和细节。然后,使用混合去噪网络优化整体数据重建过程。为了提高识别高频噪声的能力,我们引入了滑动稀疏局部注意力,利用浅层信息的稀疏性和局部性,通过跳过连接传播它们,以改进特征表示。最后,我们提出了一种可学习的动态融合策略,以实现最佳组件集成。实验结果表明,在相同剂量水平下,采用FD-DiT重建的LDCT图像与最新方法相比,具有更好的噪声和伪影抑制效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11pages, 11 figures
Summary
低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)虽能减少辐射暴露,但存在图像伪影和细节丢失问题。本文提出一种频率域导向的扩散变压器(FD-DiT)方法用于LDCT重建,通过扩散策略逐步引入噪声,再采用去噪处理。结合频率解耦技术和混合去噪网络,提高图像质量。实验结果表明,在相同剂量水平下,FD-DiT重建的LDCT图像具有更好的噪声和伪影抑制效果。
Key Takeaways
- LDCT存在图像伪影和细节丢失的问题。
- 频率域导向的扩散变压器(FD-DiT)被提出来解决这些问题。
- FD-DiT采用扩散策略逐步引入噪声,并注重高频域的噪声处理。
- 结合频率解耦技术和混合去噪网络来提高图像质量。
- 采用滑动稀疏局部注意力机制来识别高频噪声。
- 提出一种可学习的动态融合策略来实现最佳组件集成。
点此查看论文截图


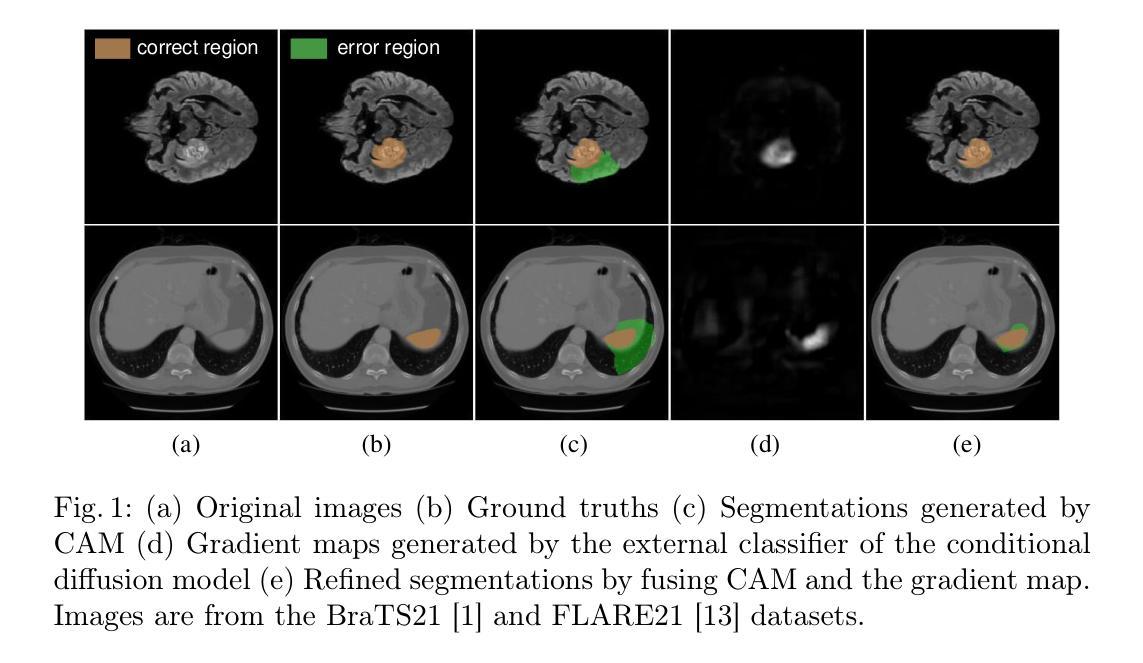
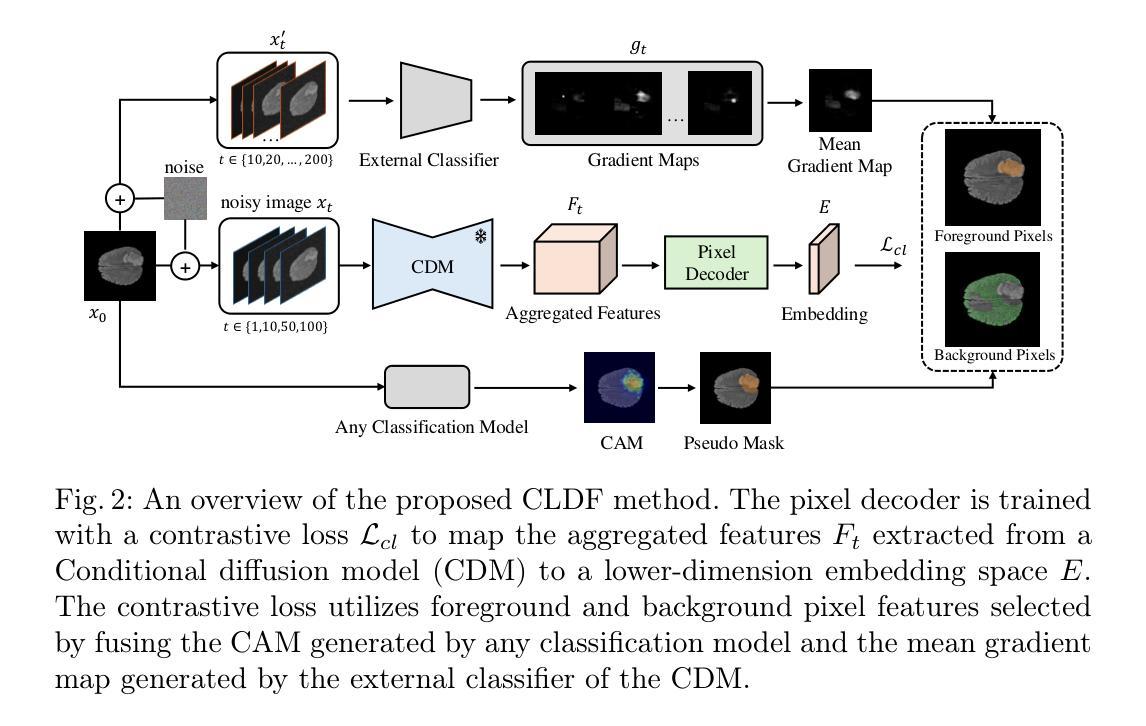
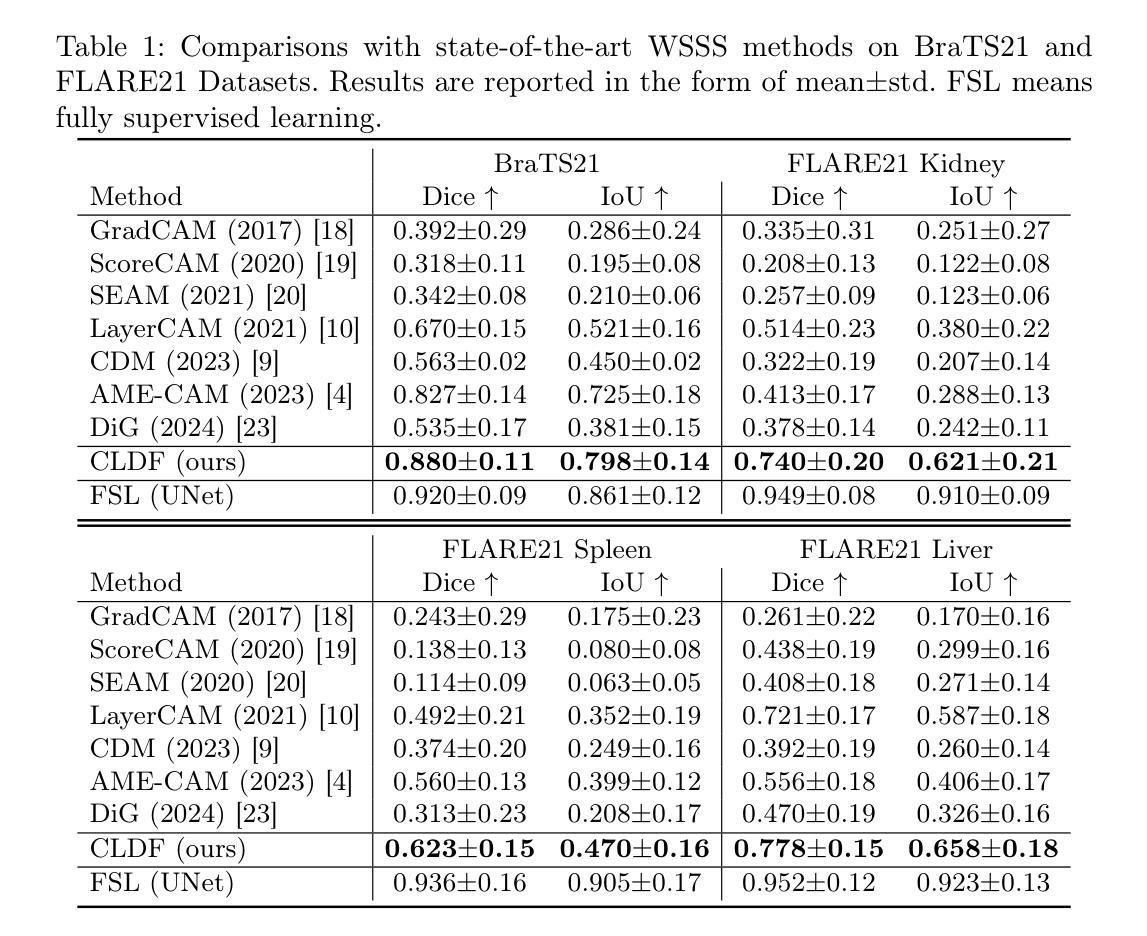
Contrastive Learning with Diffusion Features for Weakly Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Dewen Zeng, Xinrong Hu, Yu-Jen Chen, Yawen Wu, Xiaowei Xu, Yiyu Shi
Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) methods using class labels often rely on class activation maps (CAMs) to localize objects. However, traditional CAM-based methods struggle with partial activations and imprecise object boundaries due to optimization discrepancies between classification and segmentation. Recently, the conditional diffusion model (CDM) has been used as an alternative for generating segmentation masks in WSSS, leveraging its strong image generation capabilities tailored to specific class distributions. By modifying or perturbing the condition during diffusion sampling, the related objects can be highlighted in the generated images. Yet, the saliency maps generated by CDMs are prone to noise from background alterations during reverse diffusion. To alleviate the problem, we introduce Contrastive Learning with Diffusion Features (CLDF), a novel method that uses contrastive learning to train a pixel decoder to map the diffusion features from a frozen CDM to a low-dimensional embedding space for segmentation. Specifically, we integrate gradient maps generated from CDM external classifier with CAMs to identify foreground and background pixels with fewer false positives/negatives for contrastive learning, enabling robust pixel embedding learning. Experimental results on four segmentation tasks from two public medical datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing baselines.
基于弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的方法常常利用类别标签进行定位对象的方法,采用类激活映射(CAMs)。然而,传统的基于CAM的方法由于分类和分割之间的优化差异,对于部分激活和不精确的对象边界感到困扰。最近,条件扩散模型(CDM)已被用作生成WSSS中的分割掩码的替代方法,利用其针对特定类别分布定制的强大图像生成能力。通过在扩散采样过程中修改或扰动条件,可以在生成的图像中突出显示相关对象。然而,由CDM生成的显著性映射容易在反向扩散过程中受到背景改变而产生的噪声干扰。为了缓解这个问题,我们引入了对比学习扩散特征(CLDF)方法,这是一种使用对比学习训练像素解码器的新方法,将来自冻结CDM的扩散特征映射到低维嵌入空间进行分割。具体来说,我们将由CDM外部分类器生成的梯度图与CAM相结合,以确定用于对比学习的前景和背景像素,以减少误报/漏报的数量,从而实现稳健的像素嵌入学习。在来自两个公共医疗数据集的四个分割任务上的实验结果表明,我们的方法显著优于现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了基于条件扩散模型(CDM)的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)方法,通过使用对比学习训练像素解码器,将扩散特征映射到低维嵌入空间进行分割。新方法结合CDM外部分类器生成的梯度图和类激活映射(CAMs),提高了前景和背景像素的识别能力,减少了误报/漏报,实现了稳健的像素嵌入学习。在公共医学数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法显著优于现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)在利用类标签进行对象定位时常常依赖于类激活映射(CAMs)。
- 传统基于CAM的方法在部分激活和不精确的对象边界上存在问题,因为分类和分割之间的优化差异。
- 条件扩散模型(CDM)已被用于生成WSSS中的分割掩膜,利用其针对特定类分布的图像生成能力。
- 通过修改或扰动扩散采样过程中的条件,可以突出与类相关的对象。
- CDM生成的显著性映射容易受到反向扩散过程中背景改变产生的噪声影响。
- 新方法Contrastive Learning with Diffusion Features (CLDF)使用对比学习来训练像素解码器,将扩散特征映射到低维嵌入空间进行分割。
点此查看论文截图

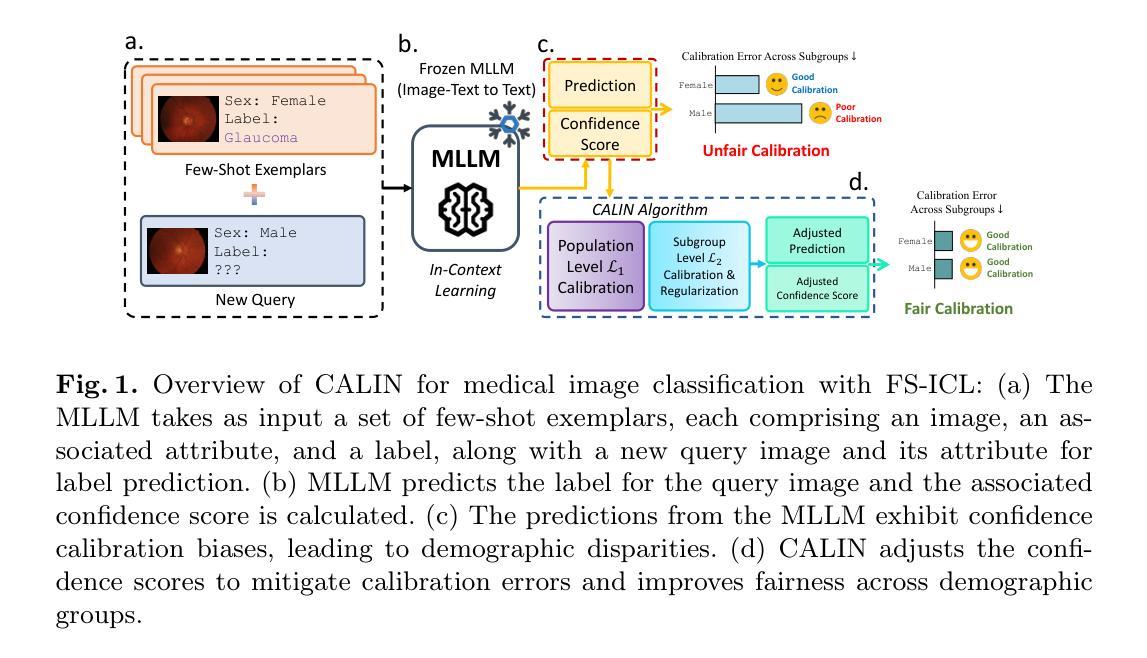
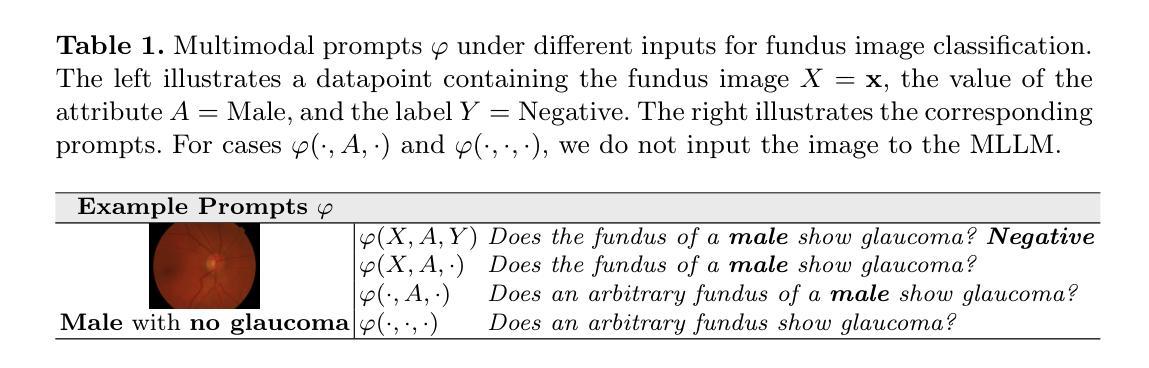
Exposing and Mitigating Calibration Biases and Demographic Unfairness in MLLM Few-Shot In-Context Learning for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Xing Shen, Justin Szeto, Mingyang Li, Hengguan Huang, Tal Arbel
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have enormous potential to perform few-shot in-context learning in the context of medical image analysis. However, safe deployment of these models into real-world clinical practice requires an in-depth analysis of the accuracies of their predictions, and their associated calibration errors, particularly across different demographic subgroups. In this work, we present the first investigation into the calibration biases and demographic unfairness of MLLMs’ predictions and confidence scores in few-shot in-context learning for medical image classification. We introduce CALIN, an inference-time calibration method designed to mitigate the associated biases. Specifically, CALIN estimates the amount of calibration needed, represented by calibration matrices, using a bi-level procedure: progressing from the population level to the subgroup level prior to inference. It then applies this estimation to calibrate the predicted confidence scores during inference. Experimental results on three medical imaging datasets: PAPILA for fundus image classification, HAM10000 for skin cancer classification, and MIMIC-CXR for chest X-ray classification demonstrate CALIN’s effectiveness at ensuring fair confidence calibration in its prediction, while improving its overall prediction accuracies and exhibiting minimum fairness-utility trade-off.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医学图像分析领域具有巨大的潜力进行少样本上下文学习。然而,将这些模型安全部署到现实世界中的临床实践需要深入分析其预测的准确性以及相关的校准误差,特别是在不同的种族人口亚组之间。在这项工作中,我们首次调查了MLLMs预测结果的校准偏差以及人口统计学不公平现象,以及其在医学图像分类的少量上下文学习中的置信度评分。我们引入了CALIN,这是一种用于减少相关偏差的推理时间校准方法。具体来说,CALIN使用一种双层过程来估计所需的校准量,该过程由校准矩阵表示:从总体层面推进到亚组层面进行推理。然后,它将这些估计应用于推理过程中的预测置信度评分校准。在三个医学成像数据集上的实验结果表明:用于眼底图像分类的PAPILA数据集、用于皮肤癌分类的HAM10000数据集以及用于胸部X射线分类的MIMIC-CXR数据集,CALIN在保证预测置信度公平校准方面效果显著,同时提高了总体预测精度并展现了最小的公平效用权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint version. The peer-reviewed version of this paper has been accepted to MICCAI 2025 main conference
Summary
多模态大型语言模型在医学图像分析领域具有巨大的潜力,但其预测准确性、校准误差以及不同人群之间的差异仍需深入分析。本研究首次探讨了该模型在少样本上下文学习中的校准偏见和人群不公平性。为缓解相关问题,研究提出了CALIN校准方法,该方法在推理阶段设计,通过两级程序从总体到分组层面估计所需的校准量,并应用于推理过程中的预测置信度得分校准。在三个医学图像数据集上的实验结果表明,CALIN方法能有效确保公平置信度校准,提高预测准确性,且公平性效用权衡表现优秀。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型在医学图像分析中具有巨大潜力,但预测准确性和校准误差需深入分析。
- 本研究首次探讨了模型在少样本上下文学习中的校准偏见和人群不公平性问题。
- 为缓解这些问题,提出了CALIN校准方法,该方法在推理阶段设计用于校准预测置信度得分。
- CALIN通过两级程序从总体到分组层面估计所需的校准量。
- 实验结果表明,CALIN方法能有效确保公平置信度校准,提高预测准确性。
- CALIN方法在实现高预测准确性的同时,展现出良好的公平性效用权衡。
点此查看论文截图

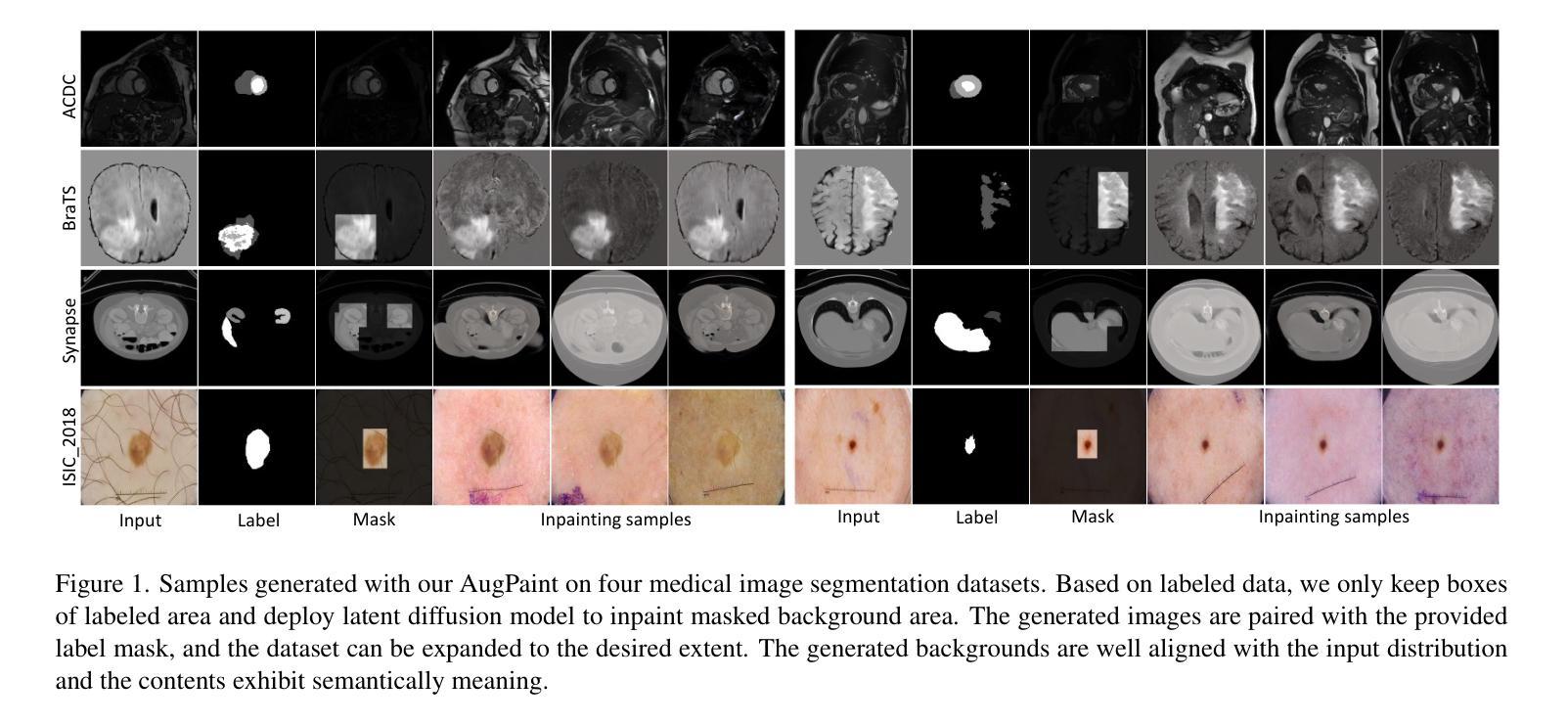
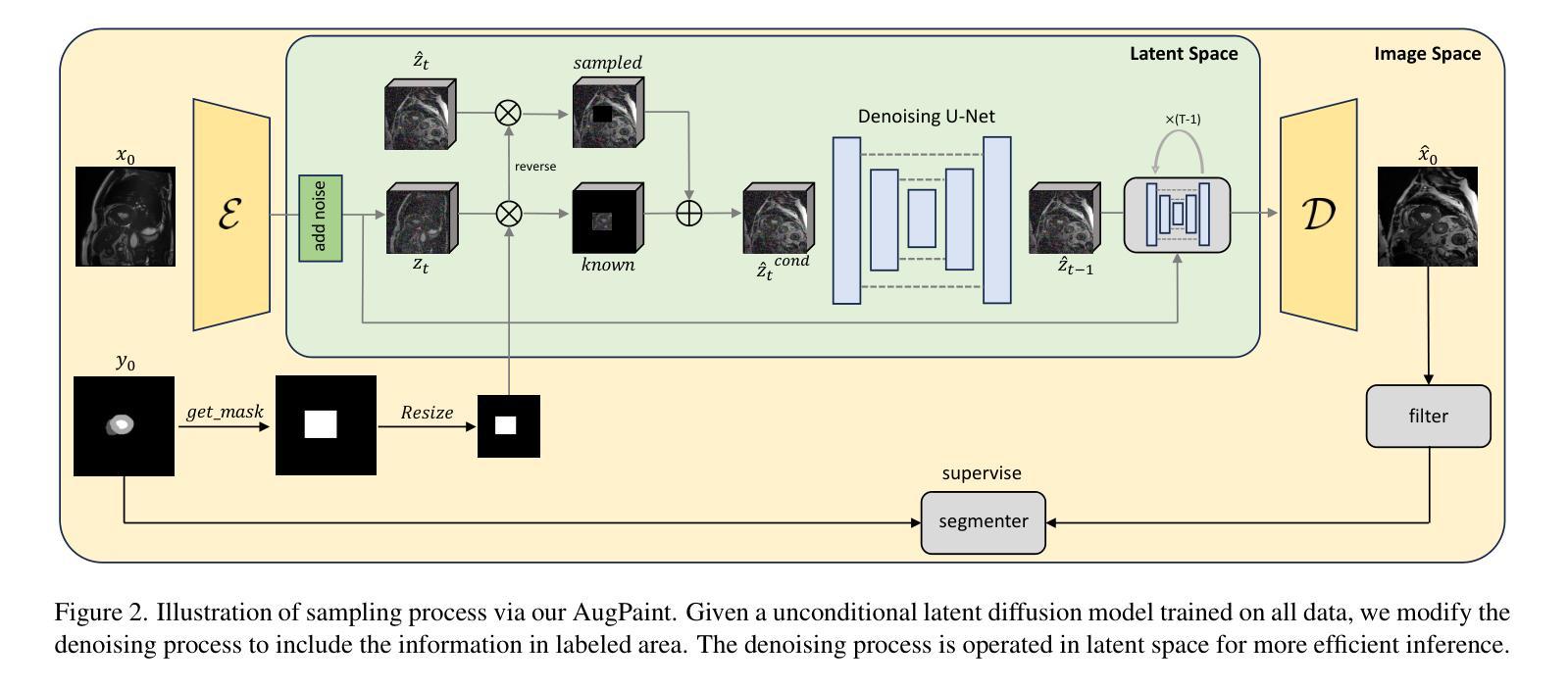
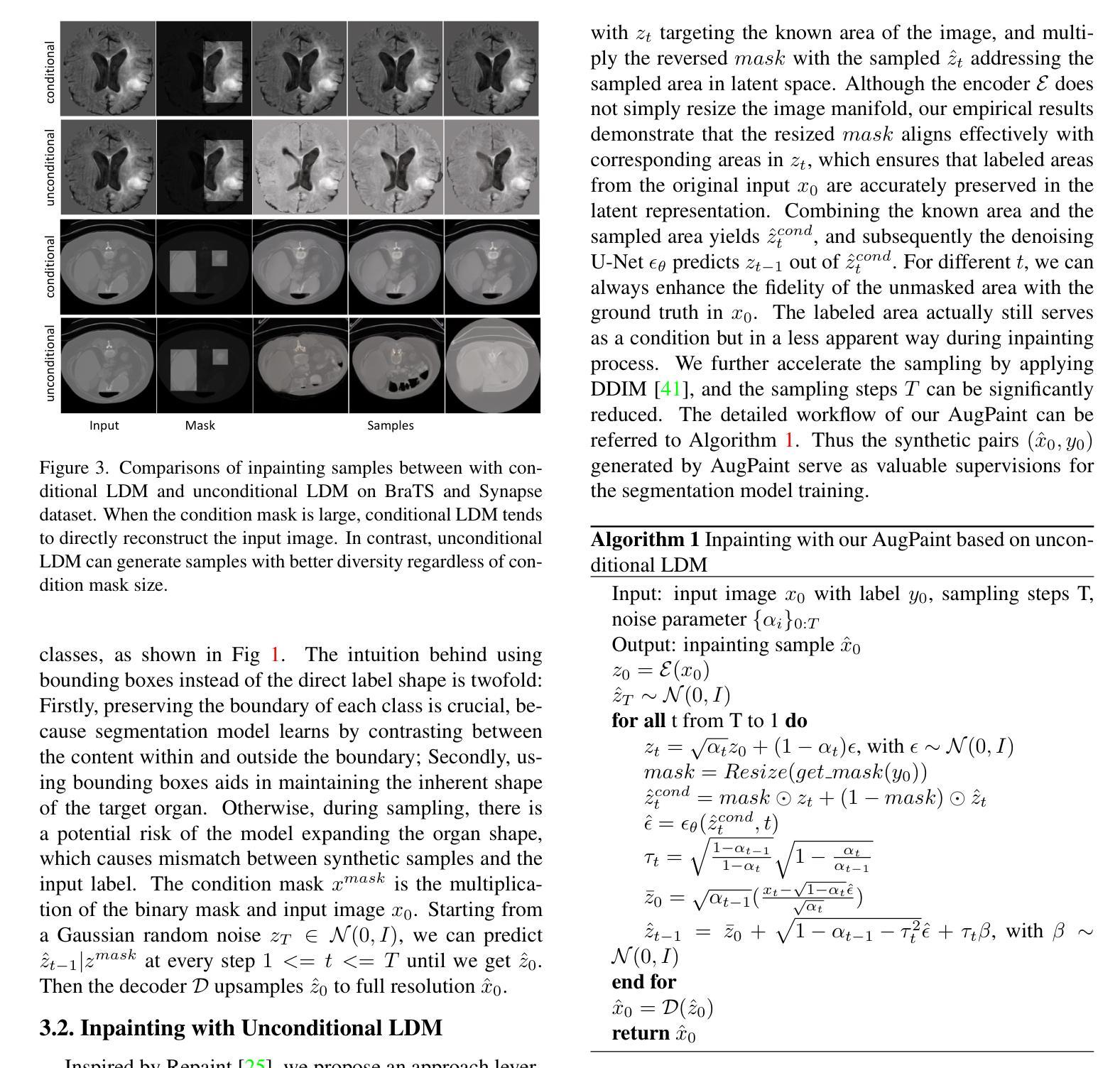
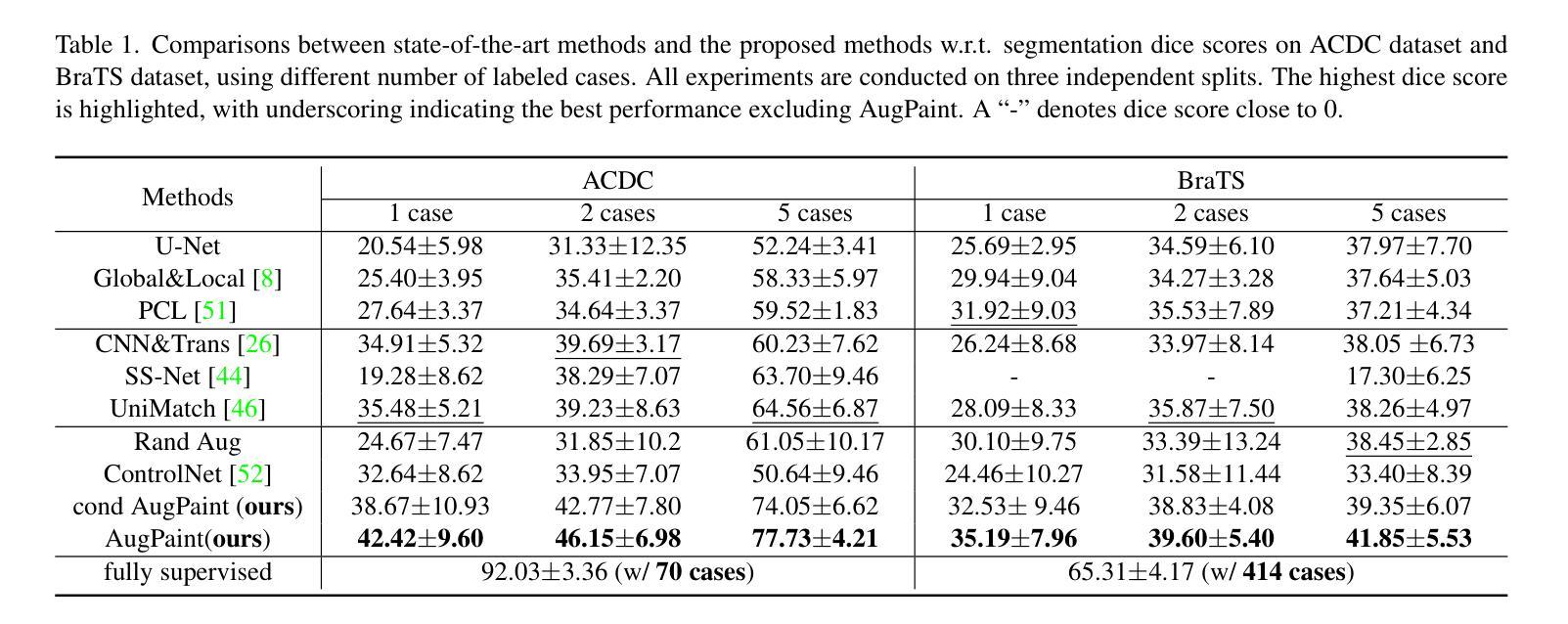
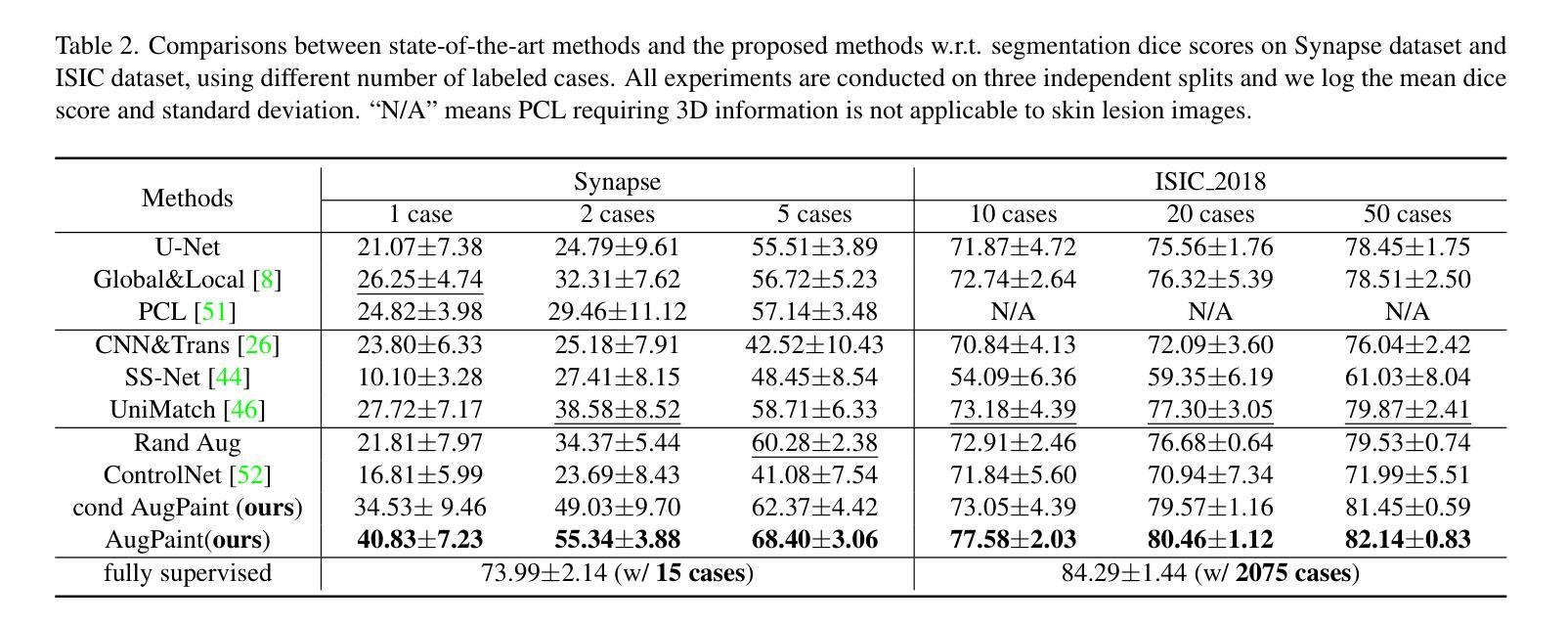
Inpainting is All You Need: A Diffusion-based Augmentation Method for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xinrong Hu, Yiyu Shi
Collecting pixel-level labels for medical datasets can be a laborious and expensive process, and enhancing segmentation performance with a scarcity of labeled data is a crucial challenge. This work introduces AugPaint, a data augmentation framework that utilizes inpainting to generate image-label pairs from limited labeled data. AugPaint leverages latent diffusion models, known for their ability to generate high-quality in-domain images with low overhead, and adapts the sampling process for the inpainting task without need for retraining. Specifically, given a pair of image and label mask, we crop the area labeled with the foreground and condition on it during reversed denoising process for every noise level. Masked background area would gradually be filled in, and all generated images are paired with the label mask. This approach ensures the accuracy of match between synthetic images and label masks, setting it apart from existing dataset generation methods. The generated images serve as valuable supervision for training downstream segmentation models, effectively addressing the challenge of limited annotations. We conducted extensive evaluations of our data augmentation method on four public medical image segmentation datasets, including CT, MRI, and skin imaging. Results across all datasets demonstrate that AugPaint outperforms state-of-the-art label-efficient methodologies, significantly improving segmentation performance.
收集医学数据集的像素级标签可能是一个既繁琐又昂贵的过程,而在标签数据稀缺的情况下提高分割性能是一个关键挑战。本研究引入了AugPaint数据增强框架,该框架利用图像修复技术从有限的标记数据中生成图像-标签对。AugPaint利用潜在扩散模型,这种模型以生成高质量的内部域图像和低开销而闻名,并适应采样过程进行图像修复任务而无需重新训练。具体来说,给定图像和标签掩膜对,我们裁剪前景标记区域并在每个噪声水平的反向去噪过程中对其进行条件处理。被遮罩的背景区域会逐渐被填充,所有生成的图像都与标签掩膜配对。这种方法确保了合成图像与标签掩膜之间的匹配准确性,与现有的数据集生成方法相比具有明显优势。生成的图像作为训练下游分割模型的宝贵监督数据,有效解决了标注有限的问题。我们在四个公共医学图像分割数据集上对我们的数据增强方法进行了广泛评估,包括CT、MRI和皮肤成像。在所有数据集上的结果均表明,AugPaint优于最新的标签效率方法,显著提高了分割性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像数据集标注劳动强度大且成本高,缺乏标注数据提高分割性能是一大挑战。本研究提出AugPaint数据增强框架,利用inpainting技术从有限标注数据中生成图像-标签对。AugPaint采用潜在扩散模型,以低开销生成高质量域内图像,并适应inpainting任务的采样过程而无需重新训练。该方法确保合成图像与标签掩膜之间的准确匹配,与现有数据集生成方法区分开来。生成的图像作为下游分割模型训练的宝贵监督资料,有效解决标注数据有限的问题。实验在四个公共医学图像分割数据集上评估该方法,包括CT、MRI和皮肤成像,结果显示AugPaint优于当前最先进的高效标签方法,显著提高分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- AugPaint是一个用于医学图像的数据增强框架,利用inpainting技术从有限的标注数据中生成图像-标签对。
- AugPaint采用潜在扩散模型生成高质量域内图像,无需重新训练即可适应inpainting任务的采样过程。
- 该方法确保合成图像与标签掩膜之间的准确匹配。
- AugPaint通过生成图像作为下游分割模型的宝贵监督资料,有效解决标注数据有限的问题。
- 在四个公共医学图像分割数据集上的实验表明,AugPaint显著提高了分割性能。
- AugPaint框架适用于多种医学图像类型,包括CT、MRI和皮肤成像。
点此查看论文截图

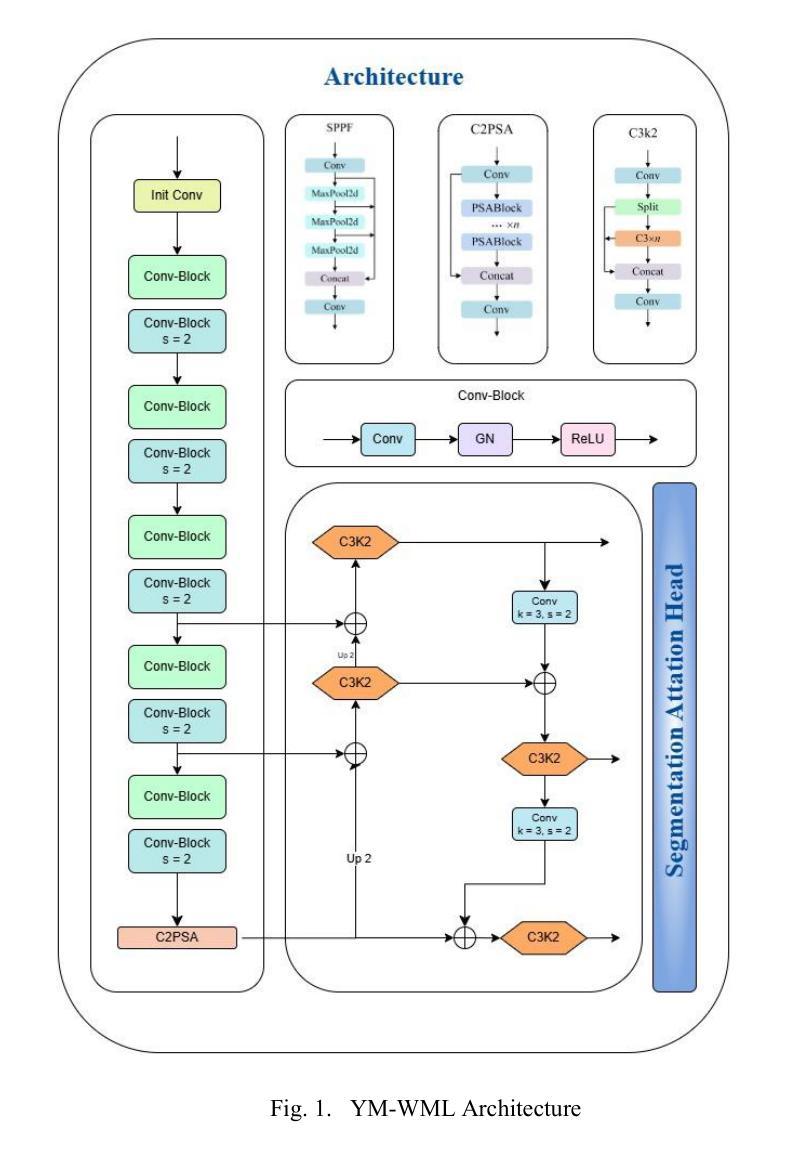
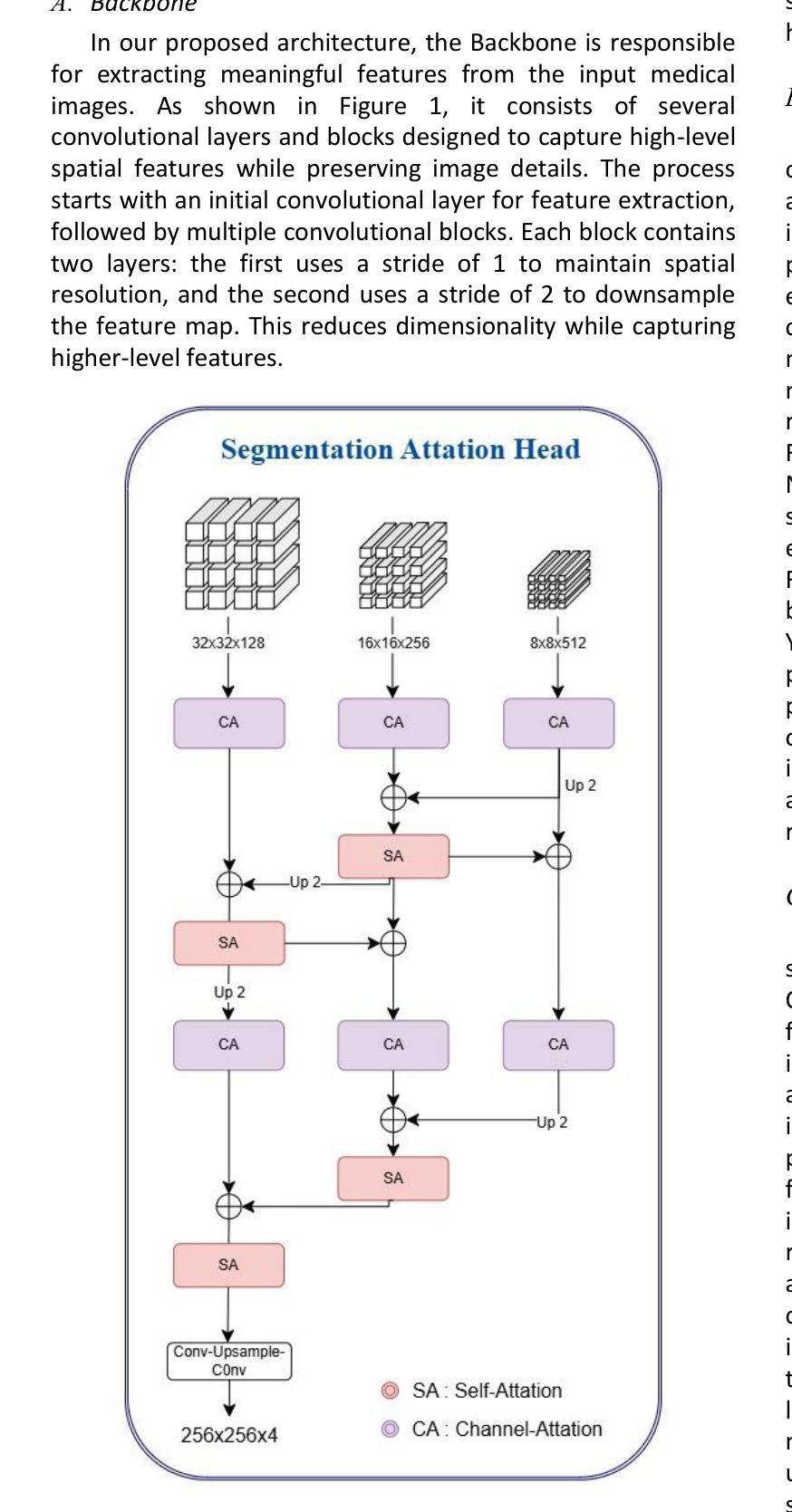
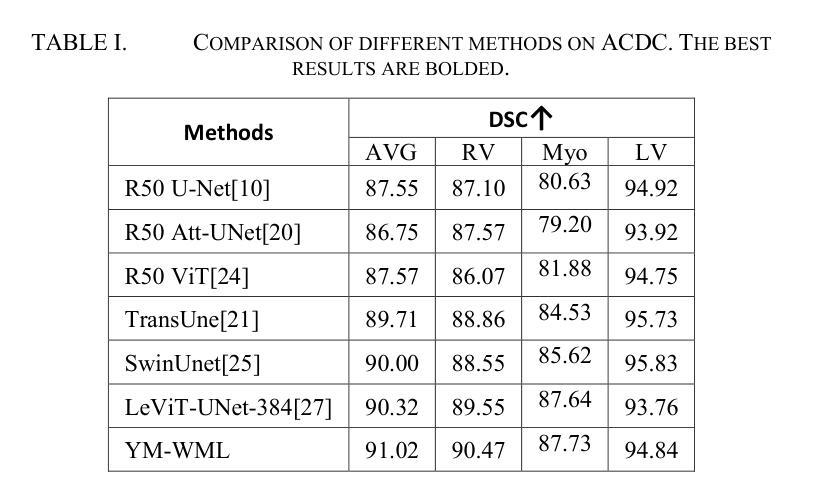
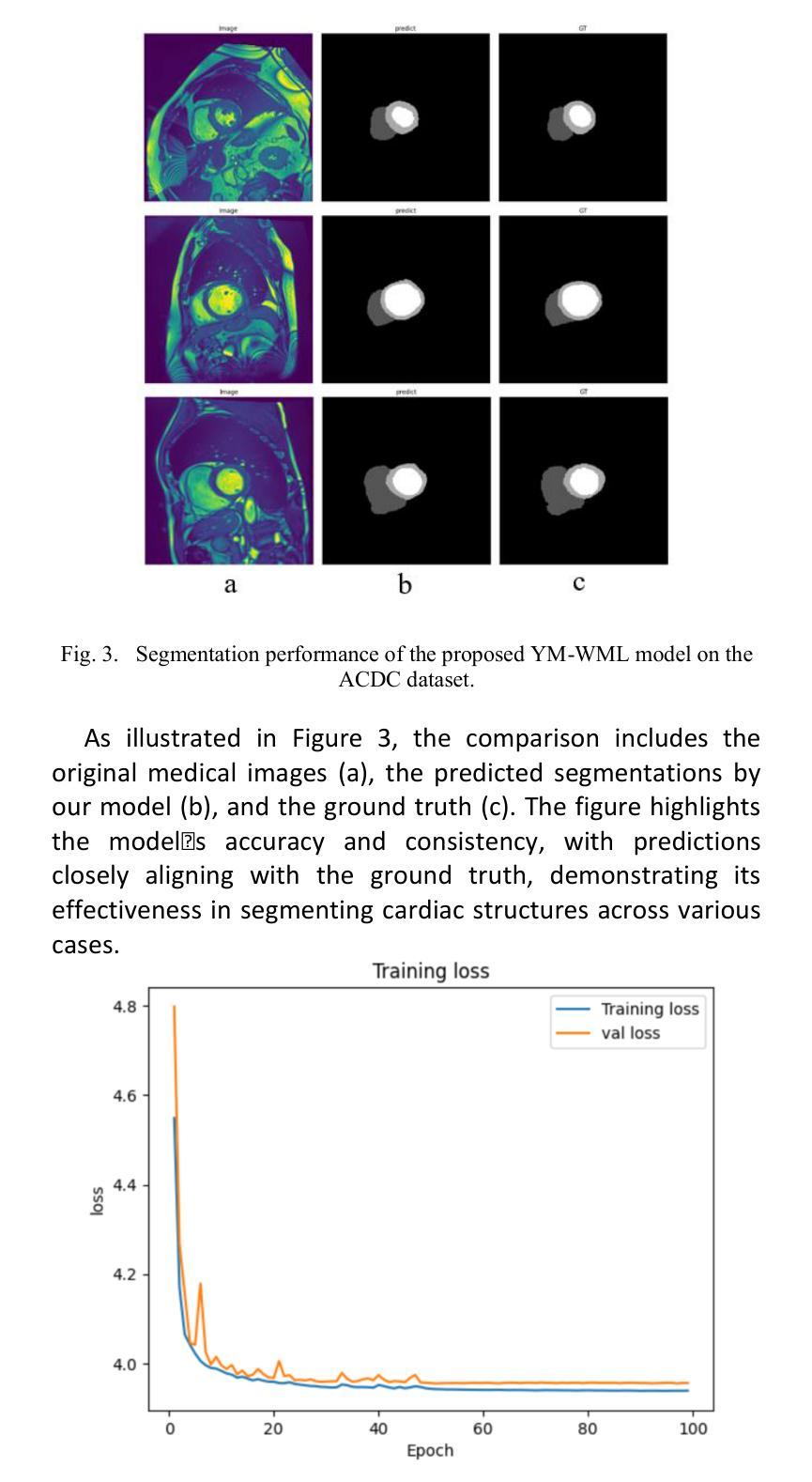
YM-WML: A new Yolo-based segmentation Model with Weighted Multi-class Loss for medical imaging
Authors:Haniyeh Nikkhah, Jafar Tanha, Mahdi Zarrin, SeyedEhsan Roshan, Amin Kazempour
Medical image segmentation poses significant challenges due to class imbalance and the complex structure of medical images. To address these challenges, this study proposes YM-WML, a novel model for cardiac image segmentation. The model integrates a robust backbone for effective feature extraction, a YOLOv11 neck for multi-scale feature aggregation, and an attention-based segmentation head for precise and accurate segmentation. To address class imbalance, we introduce the Weighted Multi-class Exponential (WME) loss function. On the ACDC dataset, YM-WML achieves a Dice Similarity Coefficient of 91.02, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. The model demonstrates stable training, accurate segmentation, and strong generalization, setting a new benchmark in cardiac segmentation tasks.
医学图像分割面临着类不平衡和医学图像复杂结构带来的挑战。为了解决这些挑战,本研究提出了YM-WML这一新型心脏图像分割模型。该模型集成了稳健的骨干网进行高效特征提取、YOLOv11颈部进行多尺度特征聚合和基于注意力的分割头,以实现精确和准确的分割。为了解决类不平衡问题,我们引入了加权多类指数(WME)损失函数。在ACDC数据集上,YM-WML的Dice相似系数达到91.02%,优于现有最先进的方法。该模型展现出稳定的训练、准确的分割和强大的泛化能力,在心脏分割任务中树立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at The 7th International conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (IPRIA 2025)
Summary
本论文针对医学图像分割中的类别不平衡和复杂结构问题,提出了一种新型的心脏图像分割模型YM-WML。该模型融合了稳健的骨干网络以实现有效的特征提取,借助YOLOv11颈部进行多尺度特征聚合,以及基于注意力的分割头实现精确和准确的分割。为解决类别不平衡问题,引入了加权多类指数(WME)损失函数。在ACDC数据集上,YM-WML的Dice相似系数达到了91.02%,优于现有最先进的方法,显示出稳定的训练、准确的分割和强大的泛化能力,为心脏分割任务设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临类别不平衡和复杂结构挑战。
- 提出新型心脏图像分割模型YM-WML。
- YM-WML模型融合稳健骨干网络、YOLOv11颈部和注意力分割头。
- 引入加权多类指数(WME)损失函数以解决类别不平衡问题。
- 在ACDC数据集上,YM-WML的Dice相似系数达91.02%。
- YM-WML性能优于现有最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图

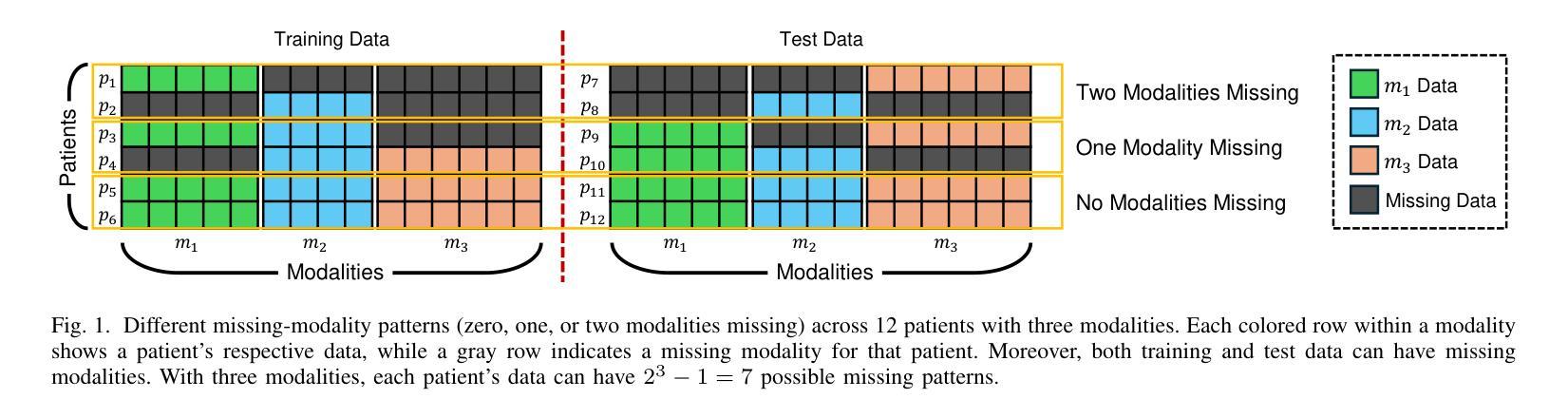
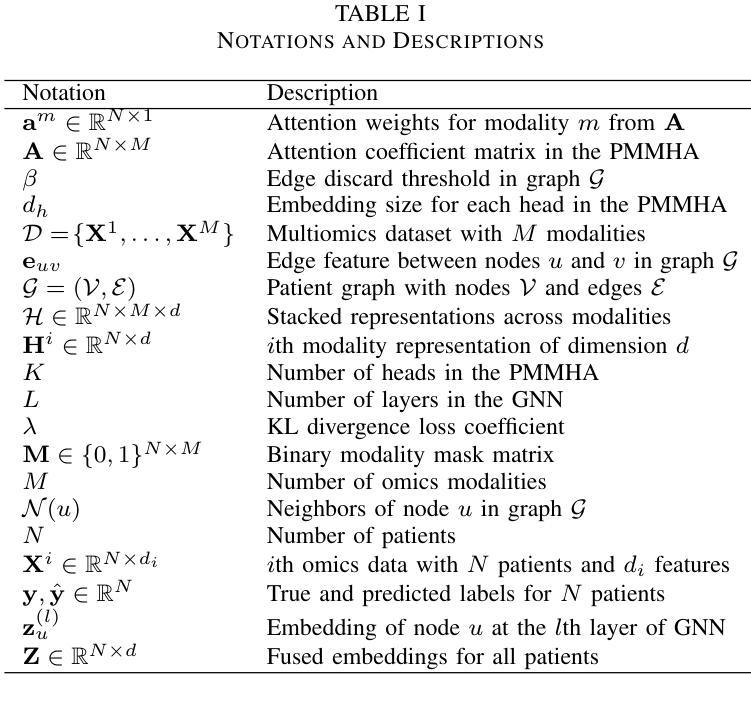
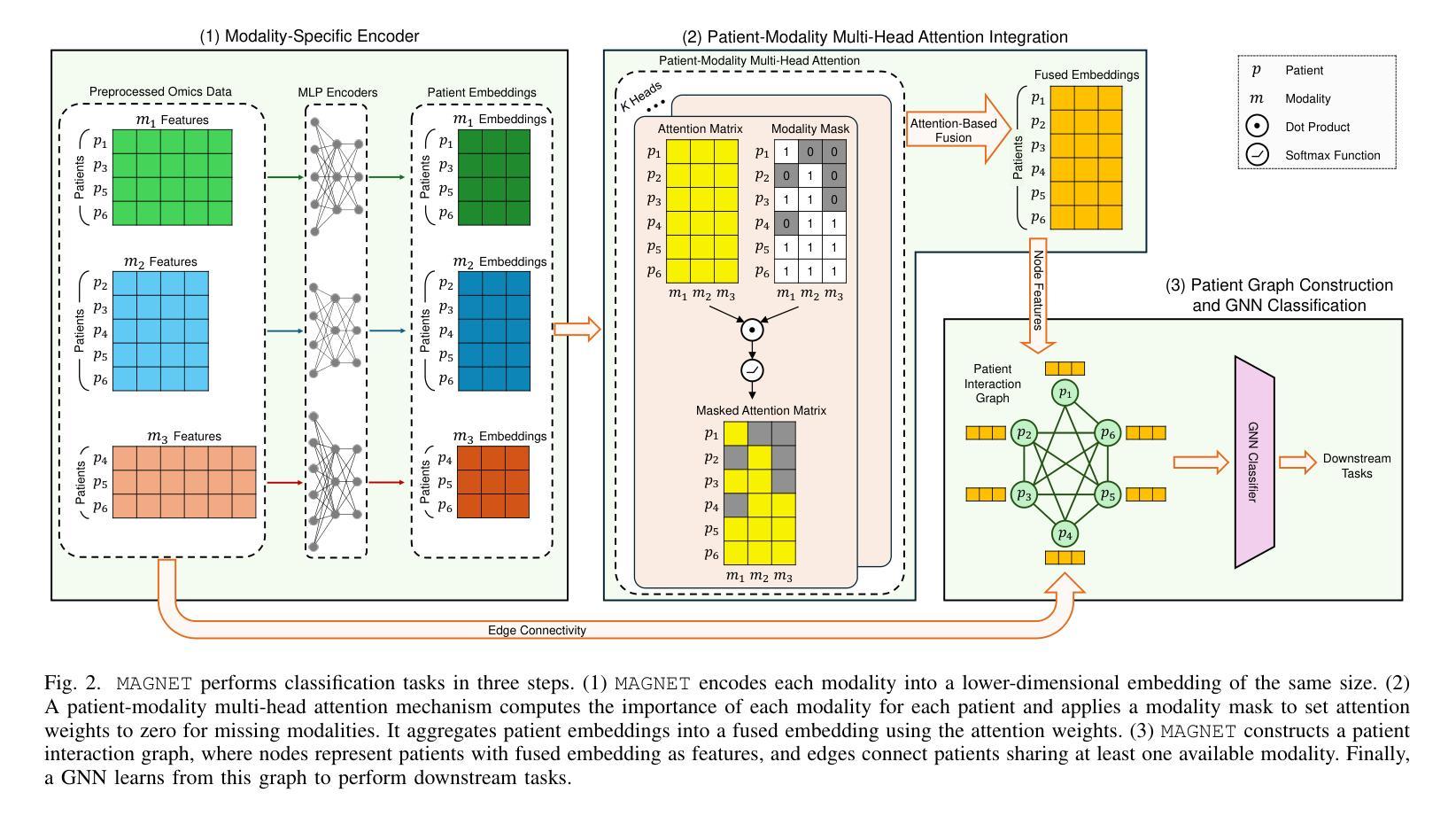
Missing-Modality-Aware Graph Neural Network for Cancer Classification
Authors:Sina Tabakhi, Haiping Lu
A key challenge in learning from multimodal biological data is missing modalities, where all data from some modalities are missing for some patients. Current fusion methods address this by excluding patients with missing modalities, imputing missing modalities, or making predictions directly with partial modalities. However, they often struggle with diverse missing-modality patterns and the exponential growth of the number of such patterns as the number of modalities increases. To address these limitations, we propose MAGNET (Missing-modality-Aware Graph neural NETwork) for direct prediction with partial modalities, which introduces a patient-modality multi-head attention mechanism to fuse lower-dimensional modality embeddings based on their importance and missingness. MAGNET’s complexity increases linearly with the number of modalities while adapting to missing-pattern variability. To generate predictions, MAGNET further constructs a patient graph with fused multimodal embeddings as node features and the connectivity determined by the modality missingness, followed by a conventional graph neural network. Experiments on three public multiomics datasets for cancer classification, with real-world instead of artificial missingness, show that MAGNET outperforms the state-of-the-art fusion methods. The data and code are available at https://github.com/SinaTabakhi/MAGNET.
在多模态生物数据学习中,缺失模态是一个关键挑战,其中某些患者的某些模态数据全部缺失。目前的融合方法通过排除具有缺失模态的患者、估算缺失模态或仅使用部分模态进行直接预测来解决这个问题。然而,随着模态数量的增加,它们通常面临多样的缺失模态模式以及此类模式数量呈指数增长的问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了MAGNET(基于缺失模态感知的图神经网络),采用部分模态进行直接预测。MAGNET引入了患者-模态多头注意力机制,根据重要性及其缺失情况融合低维模态嵌入。MAGNET的复杂性随模态数量的增加而线性增长,同时适应缺失模式的可变性。为了生成预测,MAGNET进一步构建了一个患者图,以融合的多模态嵌入作为节点特征,连接性由模态缺失性决定,然后使用传统的图神经网络。在三个公开的多组学数据集上进行癌症分类的实验(使用现实世界中的缺失数据而非人为缺失数据)表明,MAGNET在融合方法上超越了最新技术水平。数据和代码可在https://github.com/SinaTabakhi/MAGNET找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 7 figures
Summary
处理多模态生物数据时面临的主要挑战是缺失模态问题。针对该问题,现有融合方法常通过排除缺失模态的患者、补齐缺失模态或直接用部分模态进行预测来应对。然而,随着模态数量的增加,它们面临多样且复杂的缺失模态模式挑战。为解决此问题,我们提出MAGNET(缺失模态感知图神经网络)进行直接预测,引入了患者-模态多头注意力机制来融合基于重要性而并非缺失程度的低维模态嵌入。MAGNET的复杂度随模态数量线性增长,同时适应缺失模式的多样性。MAGNET通过构建患者图生成预测结果,图中融合的多模态嵌入作为节点特征,连接性由缺失的模态决定,然后使用常规的图神经网络处理。在三个公共多组学数据集上的癌症分类实验表明,MAGNET优于现有融合方法。
Key Takeaways
- 处理多模态生物数据时存在缺失模态的挑战。
- 当前融合方法如排除缺失模态患者、补齐缺失模态或直接使用部分模态预测都有其局限性。
- MAGNET方法通过引入患者-模态多头注意力机制解决了上述问题,融合了基于重要性的低维模态嵌入。
- MAGNET能随着模态数量的增长线性增长复杂度并适应多种缺失模式。
- MAGNET构建了一个患者图,通过结合融合的多模态嵌入和节点连接性来生成预测结果。
- 实验证明MAGNET在癌症分类任务上优于其他融合方法。
点此查看论文截图
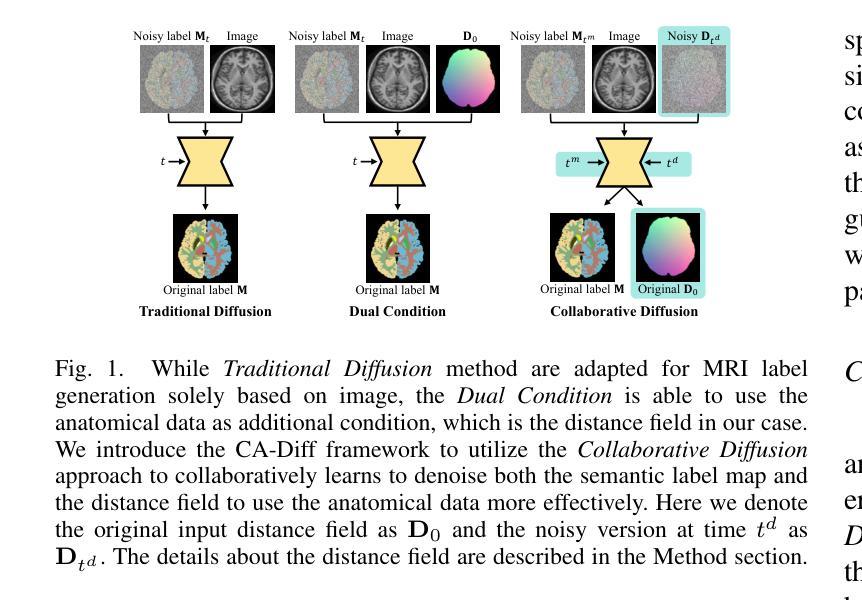
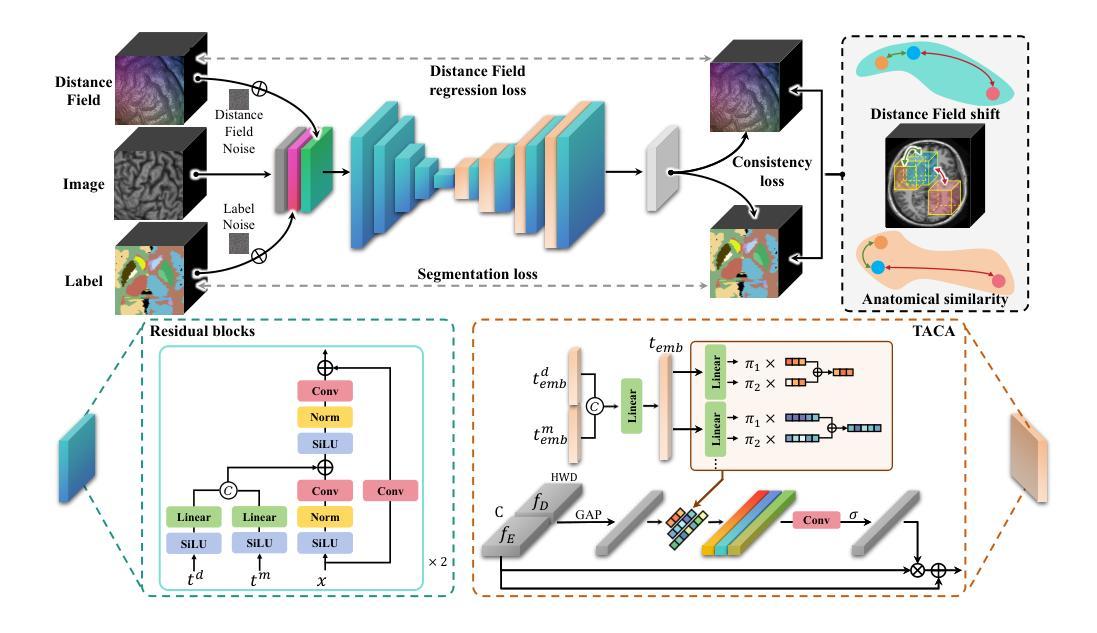
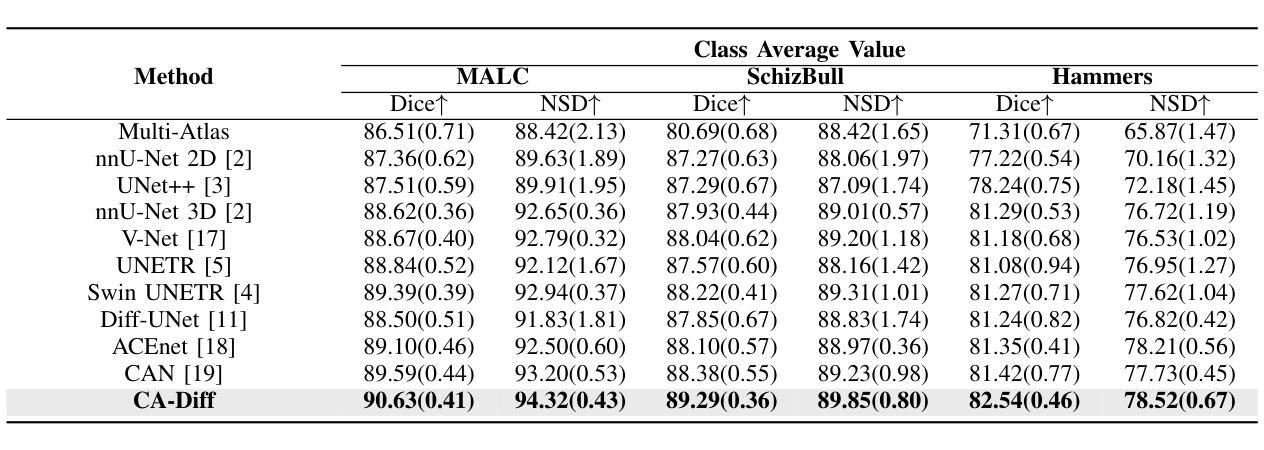
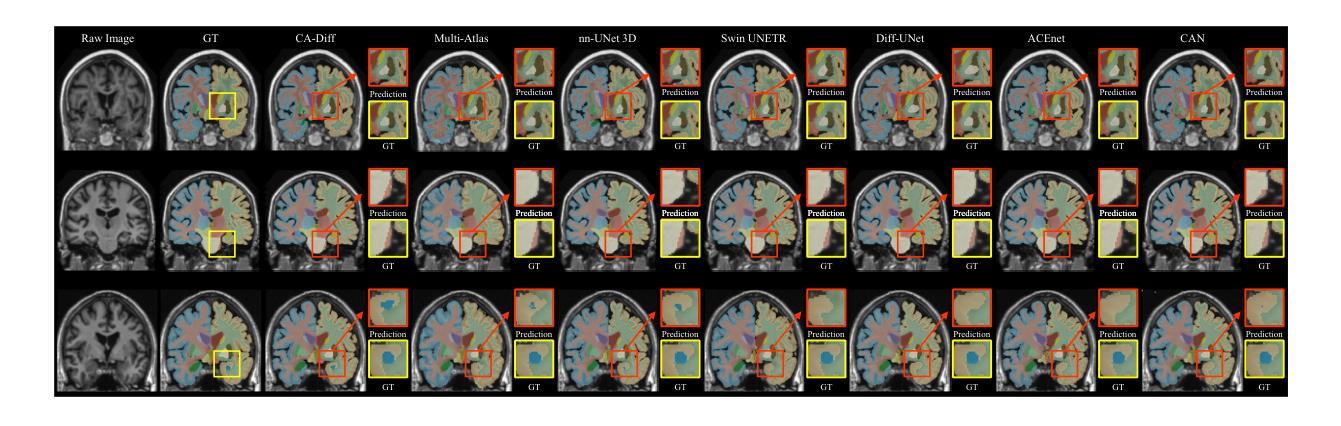
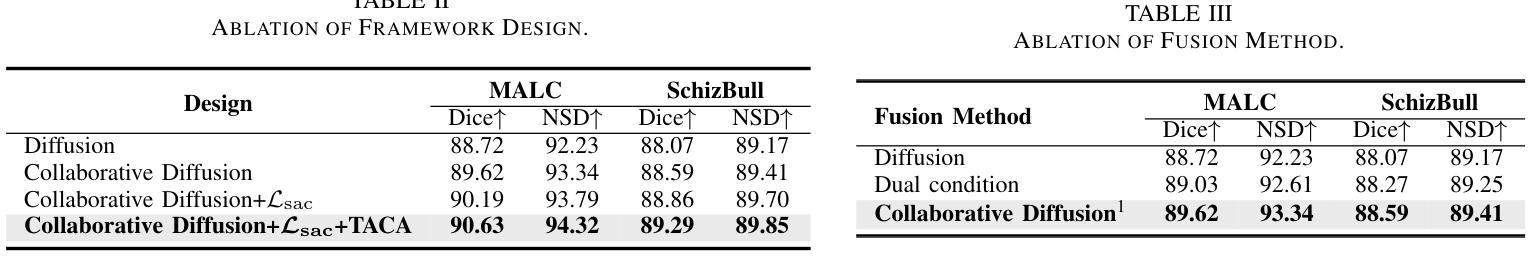
CA-Diff: Collaborative Anatomy Diffusion for Brain Tissue Segmentation
Authors:Qilong Xing, Zikai Song, Yuteng Ye, Yuke Chen, Youjia Zhang, Na Feng, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang
Segmentation of brain structures from MRI is crucial for evaluating brain morphology, yet existing CNN and transformer-based methods struggle to delineate complex structures accurately. While current diffusion models have shown promise in image segmentation, they are inadequate when applied directly to brain MRI due to neglecting anatomical information. To address this, we propose Collaborative Anatomy Diffusion (CA-Diff), a framework integrating spatial anatomical features to enhance segmentation accuracy of the diffusion model. Specifically, we introduce distance field as an auxiliary anatomical condition to provide global spatial context, alongside a collaborative diffusion process to model its joint distribution with anatomical structures, enabling effective utilization of anatomical features for segmentation. Furthermore, we introduce a consistency loss to refine relationships between the distance field and anatomical structures and design a time adapted channel attention module to enhance the U-Net feature fusion procedure. Extensive experiments show that CA-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.
从MRI中分割脑结构对于评估脑形态至关重要,但现有的基于CNN和transformer的方法在准确描绘复杂结构上存在困难。虽然当前的扩散模型在图像分割方面显示出了一定的潜力,但直接应用于脑MRI时却表现不足,因为它们忽略了解剖信息。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了协作解剖扩散(CA-Diff)框架,该框架结合了空间解剖特征,以提高扩散模型的分割精度。具体来说,我们引入距离场作为辅助解剖条件,以提供全局空间上下文,以及一个协作扩散过程,以模拟其与解剖结构的联合分布,从而实现解剖特征的有效利用进行分割。此外,我们还引入了一致性损失来优化距离场与解剖结构之间的关系,并设计了一个时间适应的通道注意力模块来增强U-Net特征融合过程。大量实验表明,CA-Diff优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICME 2025
Summary
本文提出一种结合空间解剖特征的协作式解剖学扩散(CA-Diff)框架,用于提高扩散模型在脑结构MRI图像分割中的准确性。通过引入距离场作为辅助解剖条件,并结合协作扩散过程,有效运用解剖特征进行分割。此外,还引入了一致性损失来优化距离场与解剖结构之间的关系,并设计了时间适应性通道注意力模块来增强U-Net特征融合过程。实验表明,CA-Diff框架的性能超越了现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 现有CNN和transformer-based方法在脑结构MRI图像分割上存在准确性问题。
- 扩散模型在图像分割中展现出潜力,但直接应用于脑MRI时因忽视解剖信息而不足。
- 提出的CA-Diff框架集成了空间解剖特征,以提高分割准确性。
- 引入距离场作为辅助解剖条件,提供全局空间上下文信息。
- 协作扩散过程能够建模距离场与解剖结构的联合分布。
- 一致性损失用于优化距离场与解剖结构之间的关系。
点此查看论文截图

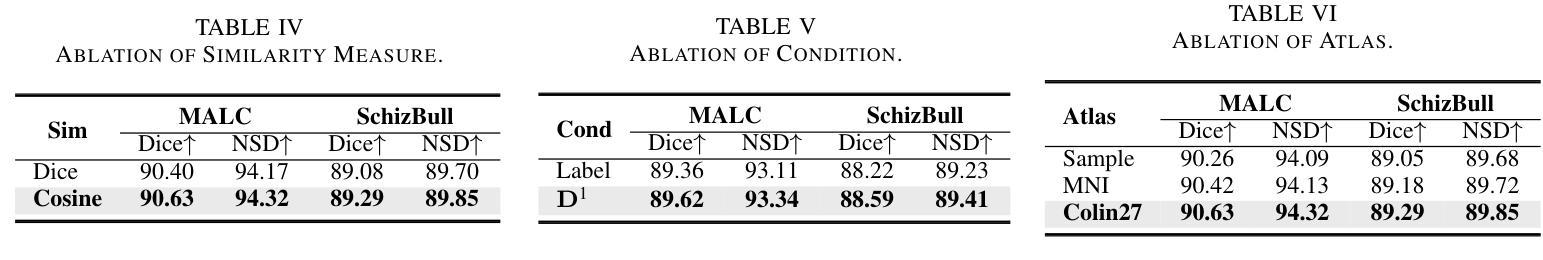
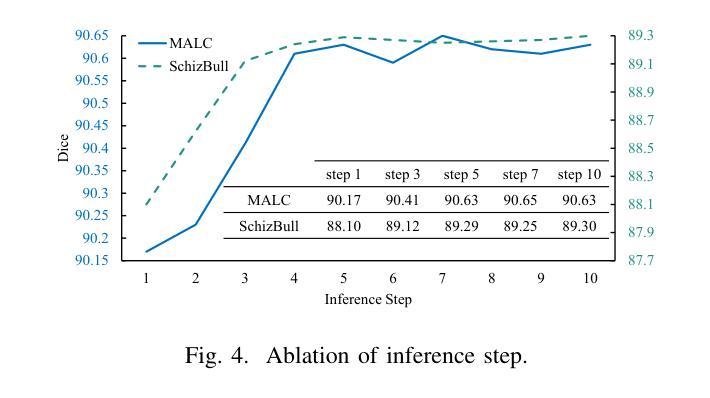
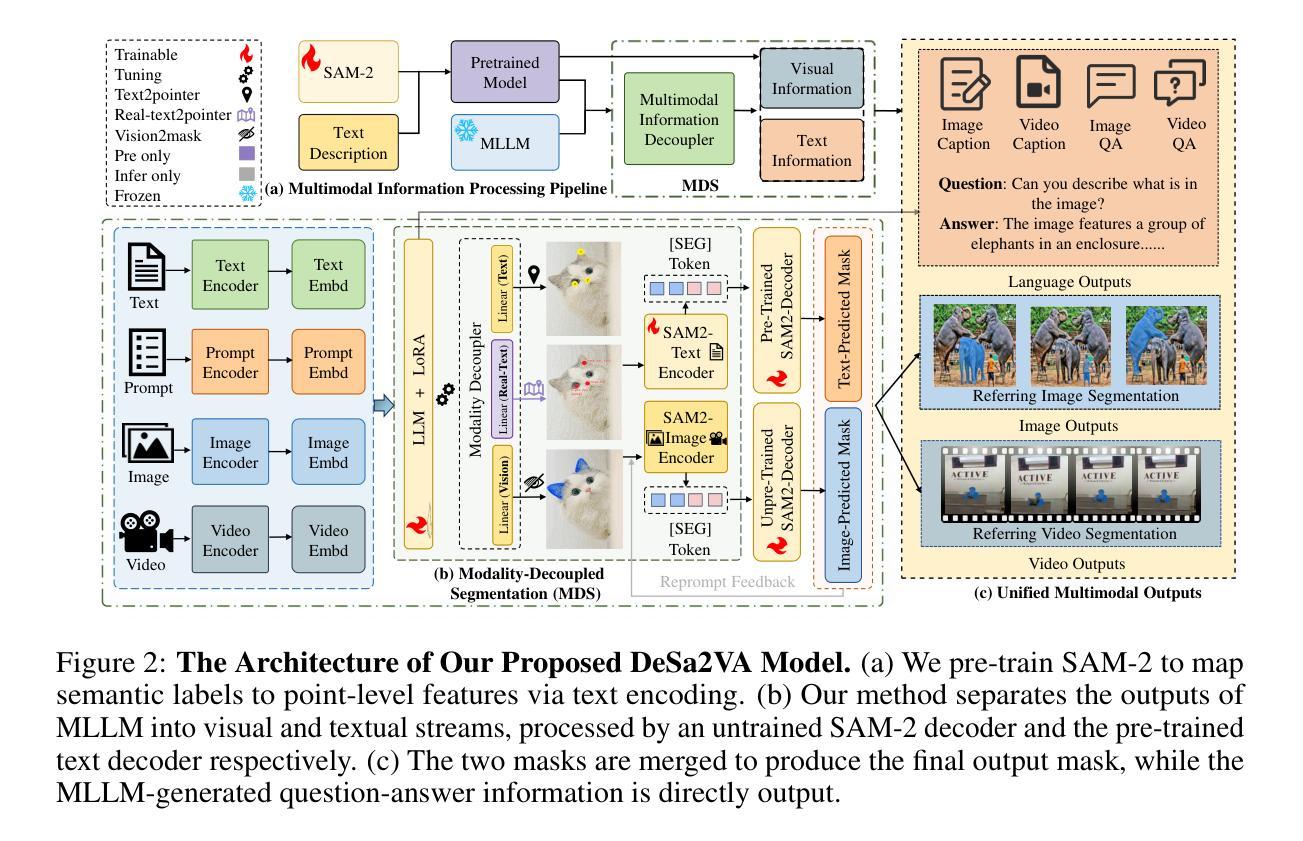
Decoupled Seg Tokens Make Stronger Reasoning Video Segmenter and Grounder
Authors:Dang Jisheng, Wu Xudong, Wang Bimei, Lv Ning, Chen Jiayu, Jingwen Zhao, Yichu liu, Jizhao Liu, Juncheng Li, Teng Wang
Existing video segmenter and grounder approaches, exemplified by Sa2VA, directly fuse features within segmentation models. This often results in an undesirable entanglement of dynamic visual information and static semantics, thereby degrading segmentation accuracy. To systematically mitigate this issue, we propose DeSa2VA, a decoupling-enhanced prompting scheme integrating text pre-training and a linear decoupling module to address the information processing limitations inherent in SAM-2. Specifically, first, we devise a pre-training paradigm that converts textual ground-truth labels into point-level prompts while generating corresponding text masks. These masks are refined through a hybrid loss function to strengthen the model’s semantic grounding capabilities. Next, we employ linear projection to disentangle hidden states that generated by a large language model into distinct textual and visual feature subspaces. Finally, a dynamic mask fusion strategy synergistically combines these decoupled features through triple supervision from predicted text/visual masks and ground-truth annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across diverse tasks, including image segmentation, image question answering, video segmentation, and video question answering. Our codes are available at https://github.com/longmalongma/DeSa2VA.
现有的视频分割器和打标器方法,以Sa2VA为例,直接在分割模型中融合特征。这通常会导致动态视觉信息和静态语义的纠缠,从而降低分割精度。为了系统地解决这一问题,我们提出了DeSa2VA,这是一种增强解耦的提示方案,它结合了文本预训练和非线性解耦模块,以解决SAM-2固有的信息处理限制。具体来说,首先,我们设计了一种预训练模式,将文本真实标签转换为点级提示,同时生成相应的文本掩码。这些掩码通过混合损失函数进行精炼,以增强模型的语义定位能力。其次,我们采用线性投影技术,将大型语言模型生成的隐藏状态分解成不同的文本和视觉特征子空间。最后,通过预测文本/视觉掩码和真实注释的三重监督,采用动态掩码融合策略协同结合这些解耦特征。大量实验表明,我们在包括图像分割、图像问答、视频分割和视频问答等多项任务中达到了最先进的状态。我们的代码可在https://github.com/longmalongma/DeSa2VA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了现有视频分割器和地面标记器方法存在的问题,如Sa2VA等方法直接融合分割模型中的特征,导致动态视觉信息和静态语义的纠缠,降低分割精度。为解决这一问题,本文提出了DeSa2VA方案,该方案通过增强解耦提示和整合文本预训练与线性解耦模块来解决SAM-2的信息处理限制。具体包括转换为点级提示的文本预训练、线性投影实现的文本和视觉特征子空间的区分以及动态掩码融合策略。实验证明,该方案在图像分割、图像问答、视频分割和视频问答等多项任务上达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 现有视频分割器和地面标记器方法存在信息纠缠问题,影响分割精度。
- DeSa2VA通过增强解耦提示解决这一问题,旨在改善SAM-2的信息处理限制。
- 预训练将文本地面真实标签转换为点级提示,并使用混合损失函数优化文本掩码以增强模型语义定位能力。
- 通过线性投影技术,DeSa2VA能将大型语言模型生成的隐藏状态分解成独立的文本和视觉特征子空间。
- 动态掩码融合策略结合了这些解耦特征,通过来自预测文本/视觉掩码和地面真实注解的三重监督进行协同作用。
- 实验结果显示,DeSa2VA在多种任务上达到先进水平,包括图像分割、图像问答、视频分割和视频问答等。
点此查看论文截图

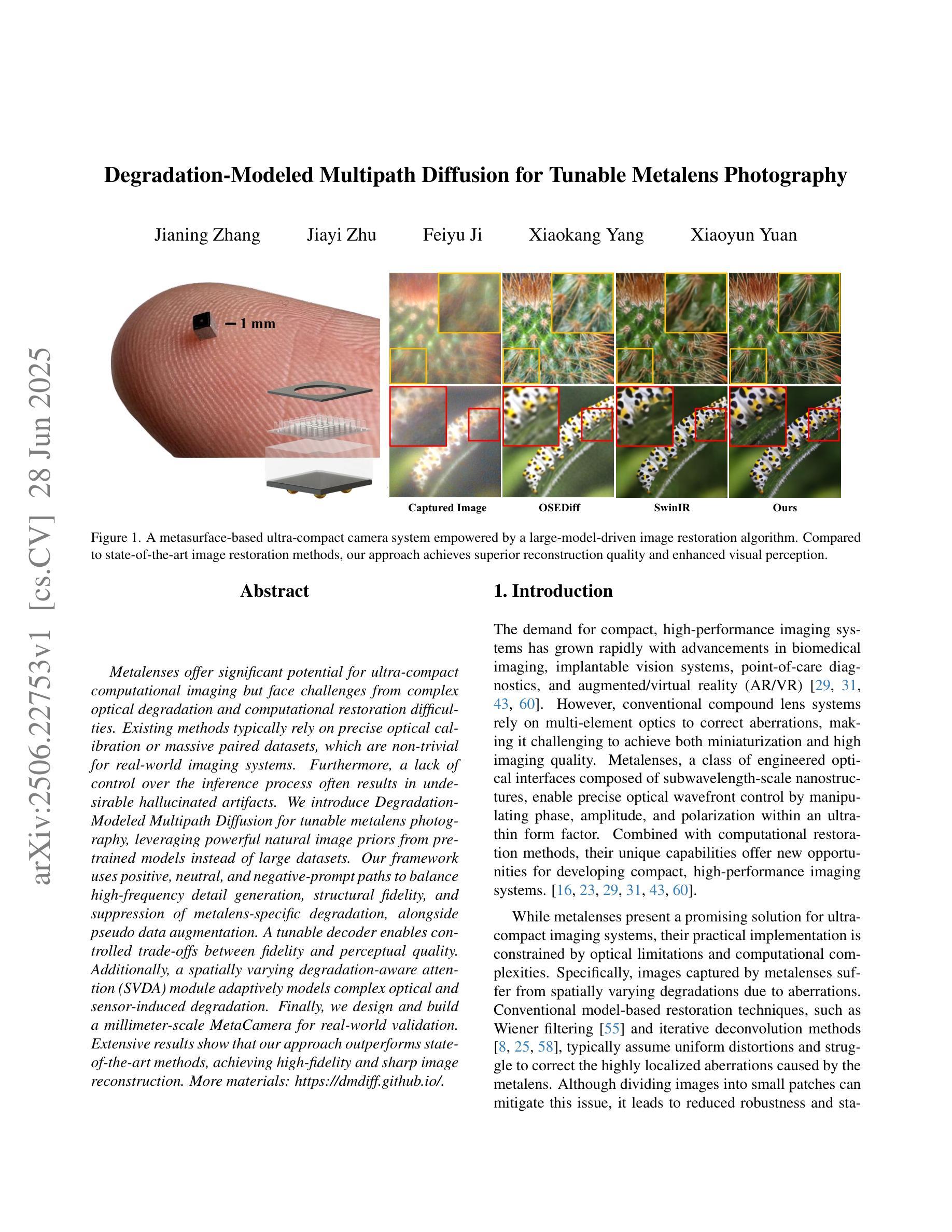
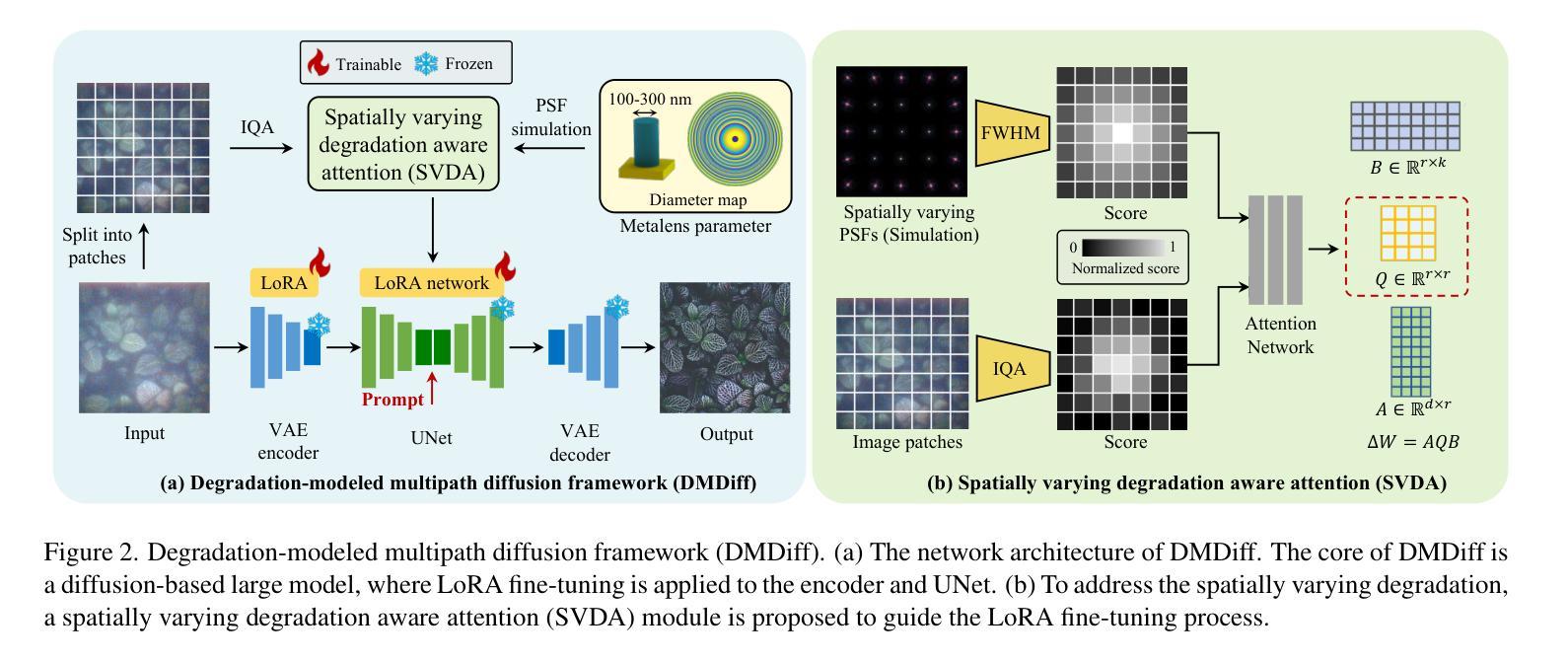
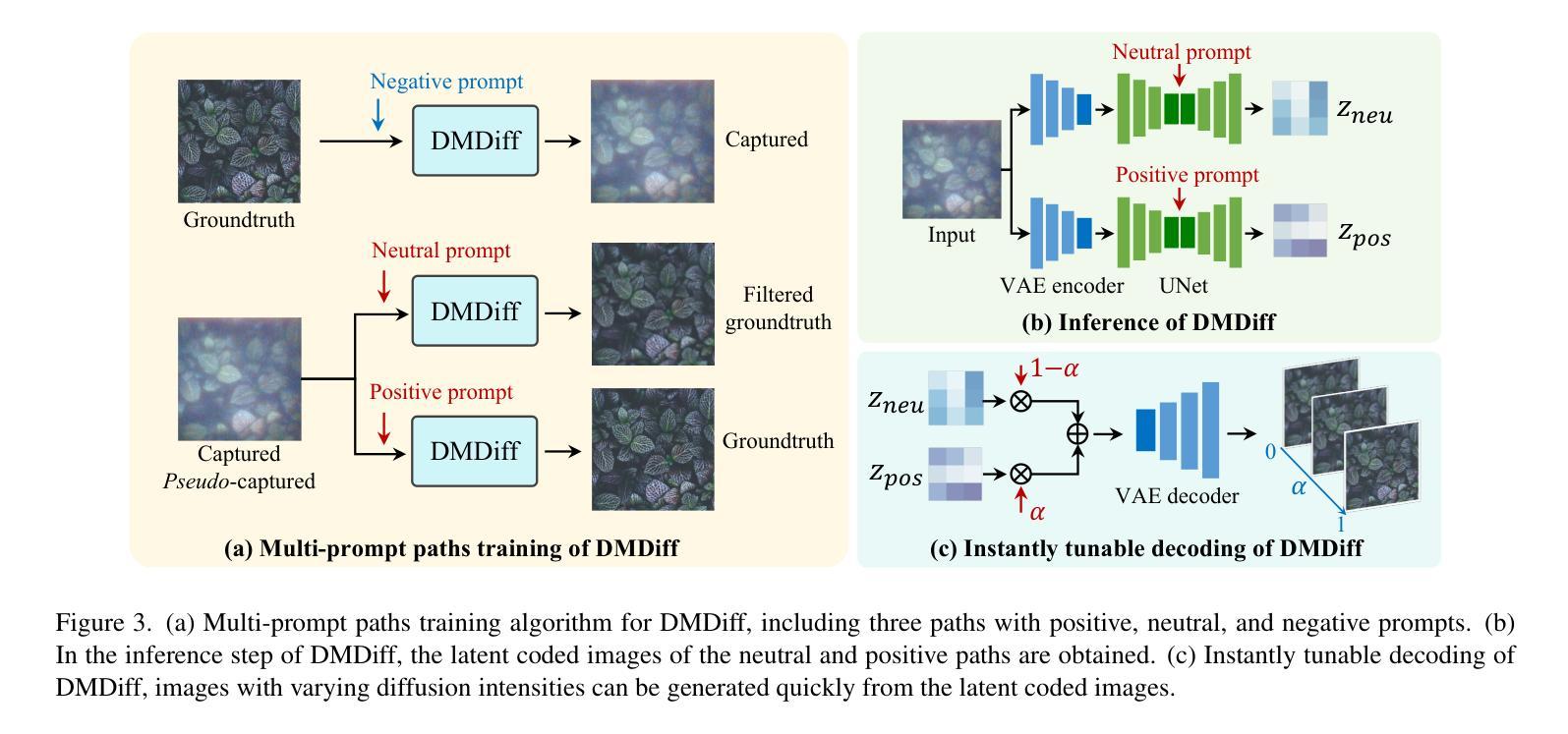
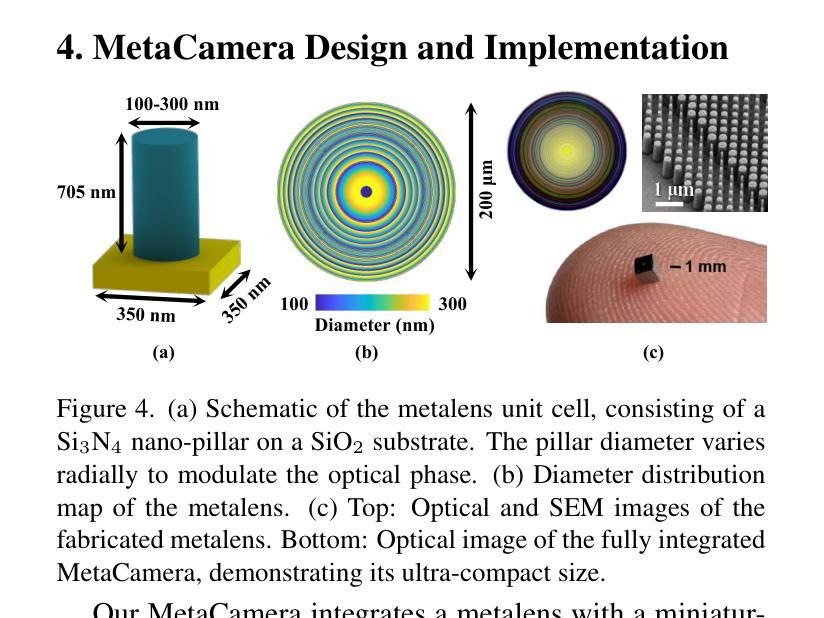
Degradation-Modeled Multipath Diffusion for Tunable Metalens Photography
Authors:Jianing Zhang, Jiayi Zhu, Feiyu Ji, Xiaokang Yang, Xiaoyun Yuan
Metalenses offer significant potential for ultra-compact computational imaging but face challenges from complex optical degradation and computational restoration difficulties. Existing methods typically rely on precise optical calibration or massive paired datasets, which are non-trivial for real-world imaging systems. Furthermore, a lack of control over the inference process often results in undesirable hallucinated artifacts. We introduce Degradation-Modeled Multipath Diffusion for tunable metalens photography, leveraging powerful natural image priors from pretrained models instead of large datasets. Our framework uses positive, neutral, and negative-prompt paths to balance high-frequency detail generation, structural fidelity, and suppression of metalens-specific degradation, alongside \textit{pseudo} data augmentation. A tunable decoder enables controlled trade-offs between fidelity and perceptual quality. Additionally, a spatially varying degradation-aware attention (SVDA) module adaptively models complex optical and sensor-induced degradation. Finally, we design and build a millimeter-scale MetaCamera for real-world validation. Extensive results show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving high-fidelity and sharp image reconstruction. More materials: https://dmdiff.github.io/.
金属透镜在超紧凑计算成像方面存在巨大潜力,但面临着复杂光学退化和计算修复困难等挑战。现有方法通常依赖于精确的光学校准或大量的配对数据集,对于现实世界成像系统而言,这些方法并不简单。此外,缺乏对推理过程的控制往往会导致出现不理想的人工合成伪影。我们引入了基于退化模型的多路扩散技术,用于可调金属透镜摄影,利用预训练模型的强大自然图像先验知识,而不是大型数据集。我们的框架使用正向、中性和负向提示路径来平衡高频细节生成、结构保真度和抑制金属透镜特有的退化现象,同时辅以伪数据增强。可调解码器能够在保真度和感知质量之间进行可控的权衡。此外,空间变化的退化感知注意力(SVDA)模块能够自适应地模拟复杂的光学退化和传感器引起的退化。最后,我们设计并制作了一款用于实际验证的毫米级MetaCamera。大量结果表明,我们的方法优于最先进的方法,实现了高保真和清晰的图像重建。更多材料请参见:https://dmdiff.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
金属透镜在超紧凑计算成像方面具巨大潜力,但面临复杂光学降解和计算修复难题。现有方法通常依赖精确光学校准或大量配对数据集,不适用于现实世界成像系统。研究引入基于降解建模的多路径扩散方法,用于可调金属透镜摄影,利用预训练模型的天然图像先验而非大型数据集。该方法采用正、中性及负提示路径来平衡高频细节生成、结构保真和抑制金属透镜特定降解,配合伪数据增强。可调解码器可在保真度和感知质量之间实现可控权衡。此外,空间变化降解感知注意力模块可自适应地模拟复杂光学和传感器引起的降解。最后,研究设计并制作了一款用于真实世界验证的毫米级MetaCamera。大量结果表明,该方法优于现有技术,可实现高保真和清晰的图像重建。
Key Takeaways
- 金属透镜在计算成像中具有巨大潜力,但面临光学降解和计算修复的挑战。
- 现有方法依赖于精确光学校准或大规模配对数据集,不适用于现实世界的成像系统。
- 研究提出了一种基于降解建模的多路径扩散方法,用于可调金属透镜摄影。
- 该方法利用预训练模型的天然图像先验,通过正、中性及负提示路径实现细节生成、结构保真和降解抑制的平衡。
- 研究引入了伪数据增强、可调解码器和空间变化降解感知注意力模块等技术,以提高成像质量。
- 研究设计并制作了一款用于真实世界验证的毫米级MetaCamera。
点此查看论文截图
UniFuse: A Unified All-in-One Framework for Multi-Modal Medical Image Fusion Under Diverse Degradations and Misalignments
Authors:Dayong Su, Yafei Zhang, Huafeng Li, Jinxing Li, Yu Liu
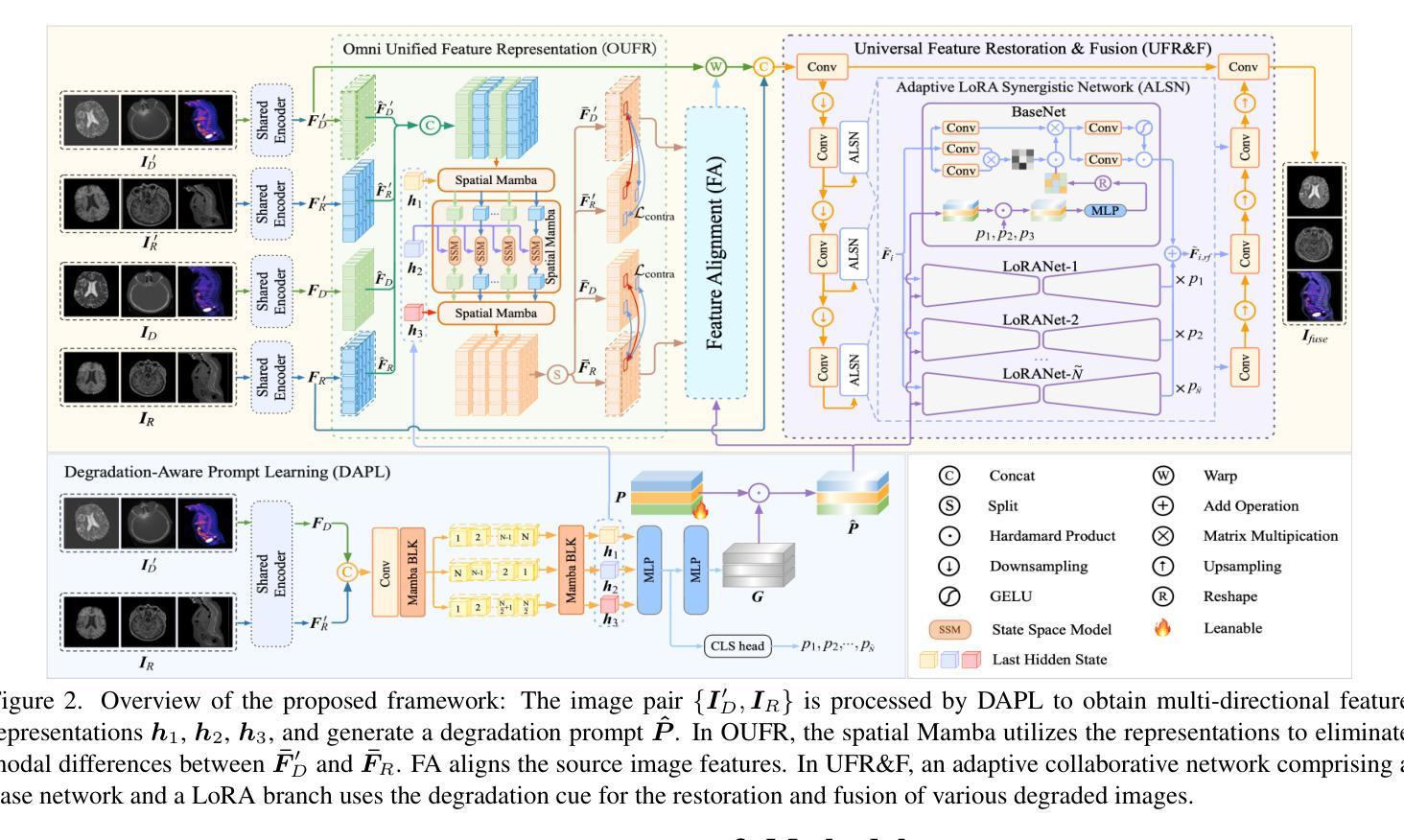
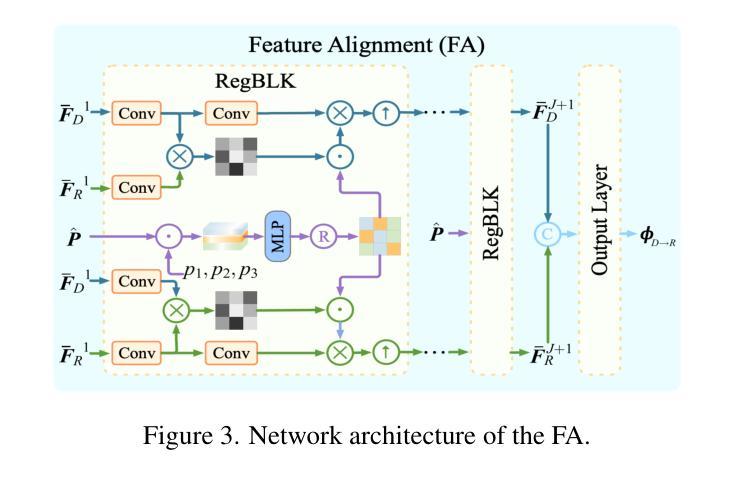
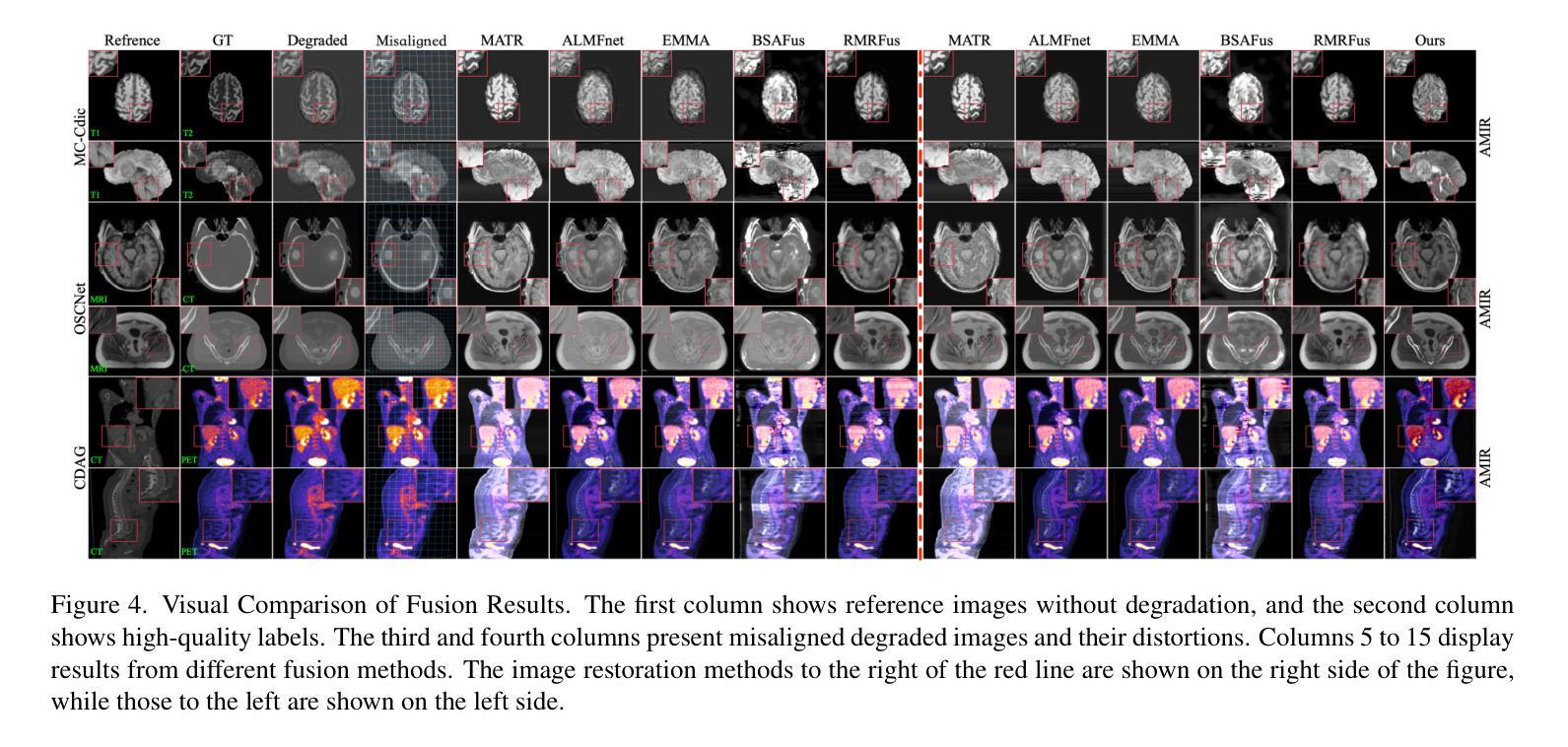
Current multimodal medical image fusion typically assumes that source images are of high quality and perfectly aligned at the pixel level. Its effectiveness heavily relies on these conditions and often deteriorates when handling misaligned or degraded medical images. To address this, we propose UniFuse, a general fusion framework. By embedding a degradation-aware prompt learning module, UniFuse seamlessly integrates multi-directional information from input images and correlates cross-modal alignment with restoration, enabling joint optimization of both tasks within a unified framework. Additionally, we design an Omni Unified Feature Representation scheme, which leverages Spatial Mamba to encode multi-directional features and mitigate modality differences in feature alignment. To enable simultaneous restoration and fusion within an All-in-One configuration, we propose a Universal Feature Restoration & Fusion module, incorporating the Adaptive LoRA Synergistic Network (ALSN) based on LoRA principles. By leveraging ALSN’s adaptive feature representation along with degradation-type guidance, we enable joint restoration and fusion within a single-stage framework. Compared to staged approaches, UniFuse unifies alignment, restoration, and fusion within a single framework. Experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate the method’s effectiveness and significant advantages over existing approaches.
当前的多模态医学图像融合通常假设源图像质量高且在像素级别完美对齐。其有效性严重依赖于这些条件,而在处理错位或退化医学图像时,其效果往往会下降。针对这一问题,我们提出了UniFuse通用融合框架。通过嵌入感知退化提示学习模块,UniFuse无缝集成了输入图像的多方向信息,并将跨模态对齐与恢复相关联,在统一框架内实现两个任务的联合优化。此外,我们设计了一种Omni统一特征表示方案,利用空间曼巴编码多方向特征,减轻特征对齐中的模态差异。为了实现All-in-One配置下的同时恢复和融合,我们提出了通用特征恢复与融合模块,结合了基于LoRA原理的自适应LoRA协同网络(ALSN)。通过利用ALSN的自适应特征表示和退化类型指导,我们在单阶段框架内实现了联合恢复和融合。与分阶段方法相比,UniFuse将对齐、恢复和融合统一到一个框架内。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明了该方法的有效性和对现有方法的显著优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为UniFuse的通用融合框架,用于解决当前多模态医学图像融合中遇到的问题。该框架能够嵌入退化感知提示学习模块,无缝集成输入图像的多方向信息,并通过跨模态对齐与恢复的相关性,在统一框架内联合优化两个任务。此外,还设计了Omni统一特征表示方案,利用空间Mamba编码多方向特征,减轻特征对齐中的模态差异。通过自适应LoRA协同网络(ALSN)在单个阶段实现恢复和融合的联合操作,实验结果表明,该方法在多个数据集上均有效,且相较于分期处理方法具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 当前多模态医学图像融合假设源图像高质量且像素级对齐,但处理错位或退化图像时效果下降。
- UniFuse框架通过嵌入退化感知提示学习模块,解决了这一问题。
- UniFuse框架能够无缝集成输入图像的多方向信息,并关联跨模态对齐与恢复。
- Omni统一特征表示方案利用空间Mamba编码多方向特征,减轻模态差异。
- 通过自适应LoRA协同网络(ALSN),实现在单个阶段的恢复和融合联合操作。
- 实验结果表明UniFuse框架在多个数据集上均有效,且较传统方法有明显优势。
点此查看论文截图

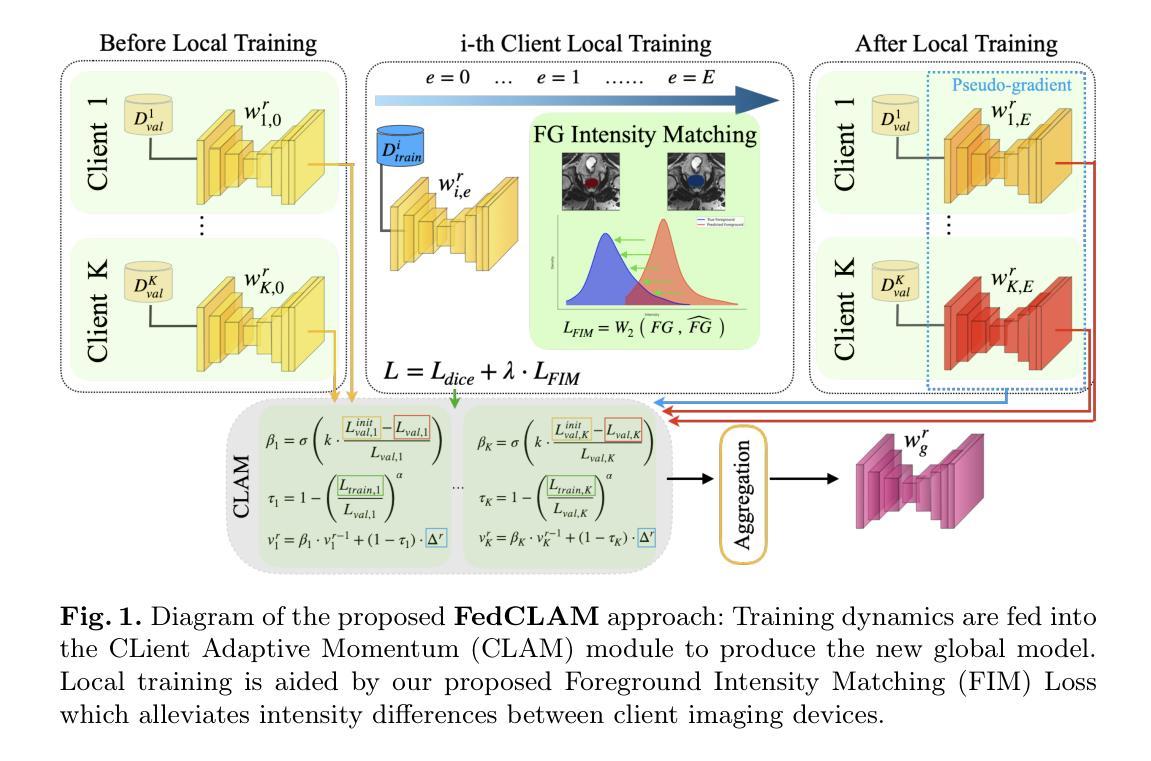
FedCLAM: Client Adaptive Momentum with Foreground Intensity Matching for Federated Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Vasilis Siomos, Jonathan Passerat-Palmbach, Giacomo Tarroni
Federated learning is a decentralized training approach that keeps data under stakeholder control while achieving superior performance over isolated training. While inter-institutional feature discrepancies pose a challenge in all federated settings, medical imaging is particularly affected due to diverse imaging devices and population variances, which can diminish the global model’s effectiveness. Existing aggregation methods generally fail to adapt across varied circumstances. To address this, we propose FedCLAM, which integrates \textit{client-adaptive momentum} terms derived from each client’s loss reduction during local training, as well as a \textit{personalized dampening factor} to curb overfitting. We further introduce a novel \textit{intensity alignment} loss that matches predicted and ground-truth foreground distributions to handle heterogeneous image intensity profiles across institutions and devices. Extensive evaluations on two datasets show that FedCLAM surpasses eight cutting-edge methods in medical segmentation tasks, underscoring its efficacy. The code is available at https://github.com/siomvas/FedCLAM.
联邦学习是一种去中心化的训练方法,能够在保持数据受利益相关者控制的同时,实现优于独立训练的性能。虽然跨机构特征差异在所有联邦环境中都构成挑战,但由于各种成像设备和人群差异,医学影像受到的影响尤为突出,这可能会降低全局模型的有效性。现有的聚合方法一般无法适应各种情况的变化。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FedCLAM,它结合了每个客户端本地训练过程中损失减少所衍生出的“客户端自适应动量”项,以及一个抑制过拟合的“个性化阻尼因子”。我们还引入了一种新颖的“强度对齐”损失,用于匹配预测前景和真实前景分布,以处理不同机构和设备之间异质图像强度分布。在两个数据集上的广泛评估表明,FedCLAM在医学分割任务上超越了八种前沿方法,凸显了其有效性。代码可通过https://github.com/siomvas/FedCLAM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, Accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学图像联邦学习中的机构间特征差异是一大挑战,特别是在多样化的成像设备和人口差异的情况下。为解决此问题,FedCLAM通过引入客户端适应性动量和个性化抑制因子来适应不同客户端的损失减少情况,同时采用强度对齐损失来匹配预测和真实前景分布,处理不同机构和设备的异构图象强度分布。FedCLAM在医学分割任务中超越八种前沿方法,证明其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习是一种去中心化的训练方法,实现了数据在利益相关者控制下的高性能训练。
- 在医学图像领域,不同机构间的特征差异是一大挑战,特别是多样化的成像设备和人口差异会影响全球模型的有效性。
- FedCLAM通过引入客户端适应性动量和个性化抑制因子来解决这一问题。
- FedCLAM采用强度对齐损失来处理不同机构和设备的异构图象强度分布问题。
- FedCLAM在医学分割任务中进行了广泛的评估,证明其有效性。
点此查看论文截图