⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
GroundingDINO-US-SAM: Text-Prompted Multi-Organ Segmentation in Ultrasound with LoRA-Tuned Vision-Language Models
Authors:Hamza Rasaee, Taha Koleilat, Hassan Rivaz
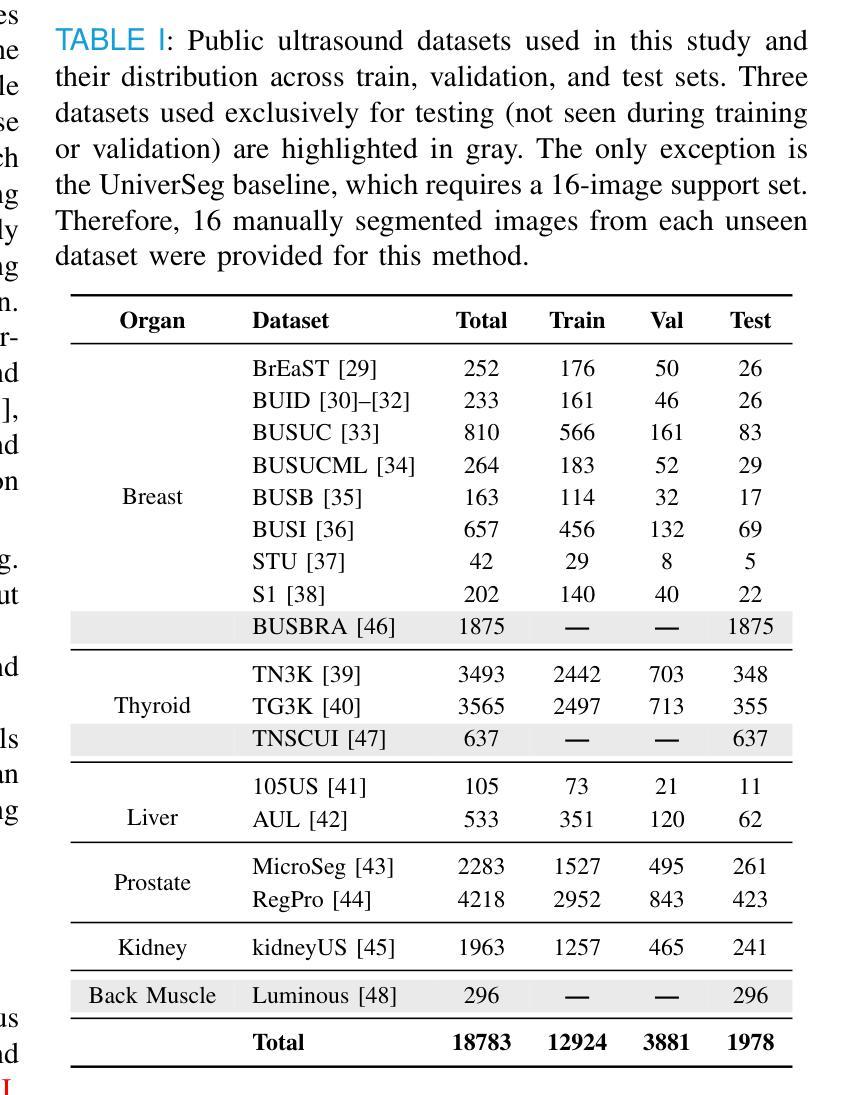
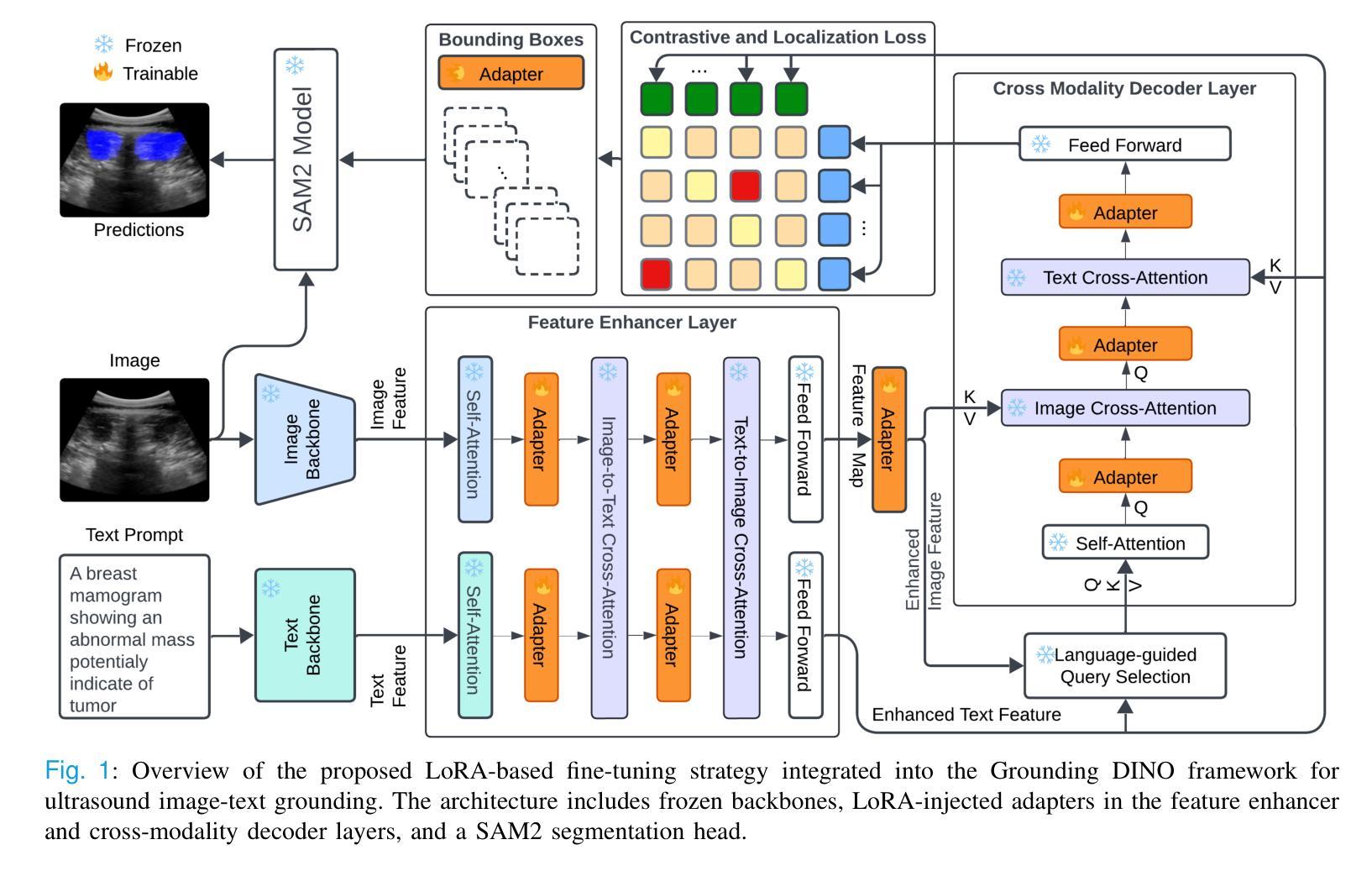
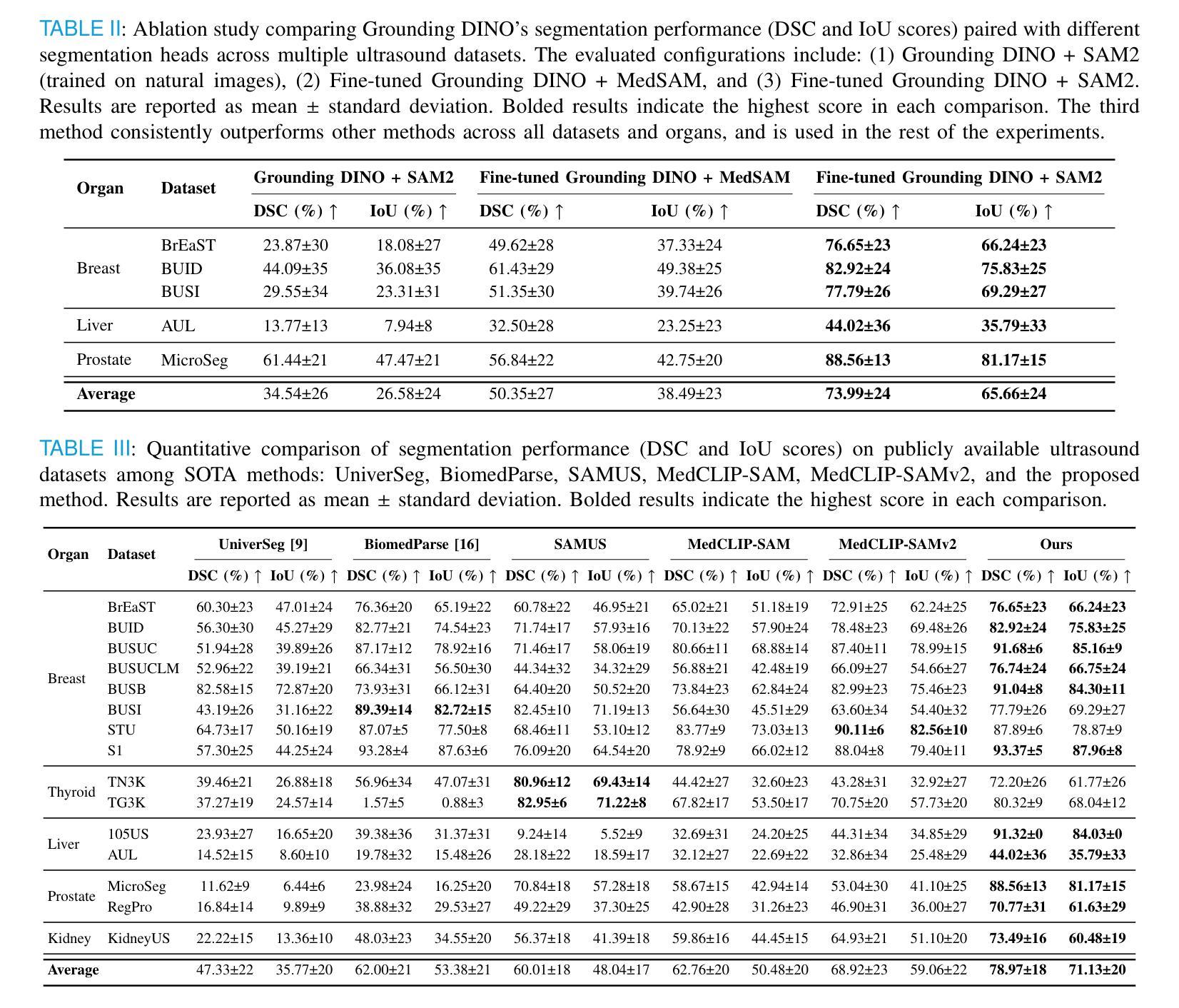
Accurate and generalizable object segmentation in ultrasound imaging remains a significant challenge due to anatomical variability, diverse imaging protocols, and limited annotated data. In this study, we propose a prompt-driven vision-language model (VLM) that integrates Grounding DINO with SAM2 to enable object segmentation across multiple ultrasound organs. A total of 18 public ultrasound datasets, encompassing the breast, thyroid, liver, prostate, kidney, and paraspinal muscle, were utilized. These datasets were divided into 15 for fine-tuning and validation of Grounding DINO using Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to the ultrasound domain, and 3 were held out entirely for testing to evaluate performance in unseen distributions. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods, including UniverSeg, MedSAM, MedCLIP-SAM, BiomedParse, and SAMUS on most seen datasets while maintaining strong performance on unseen datasets without additional fine-tuning. These results underscore the promise of VLMs in scalable and robust ultrasound image analysis, reducing dependence on large, organ-specific annotated datasets. We will publish our code on code.sonography.ai after acceptance.
在超声成像中,实现准确且普遍适用的目标分割仍然是一个巨大的挑战,这主要是由于解剖结构的变异性、成像协议的多样性和标注数据的有限性。本研究提出了一种基于提示的视觉语言模型(VLM),该模型集成了Grounding DINO与SAM2,可在多个超声器官上实现目标分割。我们共使用了包含乳房、甲状腺、肝脏、前列腺、肾脏和背伸肌群的公开超声数据集共十八份样本,用于调整和完善针对超声领域的Grounding DINO的低阶适应性(LoRA),并提供三份独立样本作为测试集评估模型在未可见分布上的性能。全面实验证明,与最新流行的其他分割方法相比,我们的方法表现出更高的性能,包括在大多数可见数据集上的UniverSeg、MedSAM、MedCLIP-SAM、BiomedParse和SAMUS等。同时,在未进行额外微调的情况下,我们的模型在未可见数据集上保持了强大的性能。这些结果突显了视觉语言模型在可扩展和稳健的超声图像分析中的潜力,减少了我们对大型特定器官标注数据集的依赖。在论文被接受后,我们将在code.sonography.ai上发布我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, 6 figures
Summary
该研究表明,超声成像中的目标分割仍然存在挑战,该研究提出了一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),整合Grounding DINO与SAM2进行多器官超声的目标分割。研究使用了涵盖多个器官的公共超声数据集,并通过实验验证了该方法在未见分布数据上的性能表现优于其他先进的分割方法。这为超声图像分析中大规模应用视觉语言模型提供了希望,并降低了对大量特定器官标注数据集的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 研究指出了超声成像中准确且可推广的目标分割所面临的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),整合Grounding DINO与SAM2用于超声图像的目标分割。
- 该方法采用了多器官数据,并通过Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA)进行微调验证。
- 研究使用公开数据集进行实验验证,涉及多个器官如乳腺、甲状腺等。
- 方法在大多数已知数据集上的表现优于其他先进分割方法。
- 在未见数据集上无需额外微调也能保持强劲表现。
点此查看论文截图