⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
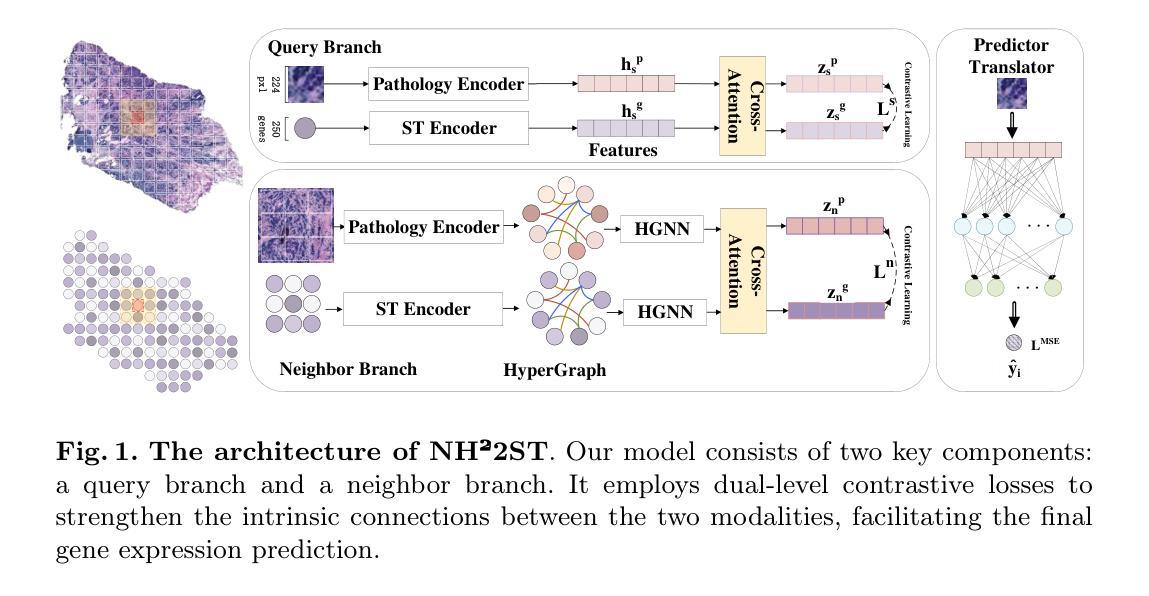
Spatially Gene Expression Prediction using Dual-Scale Contrastive Learning
Authors:Mingcheng Qu, Yuncong Wu, Donglin Di, Yue Gao, Tonghua Su, Yang Song, Lei Fan
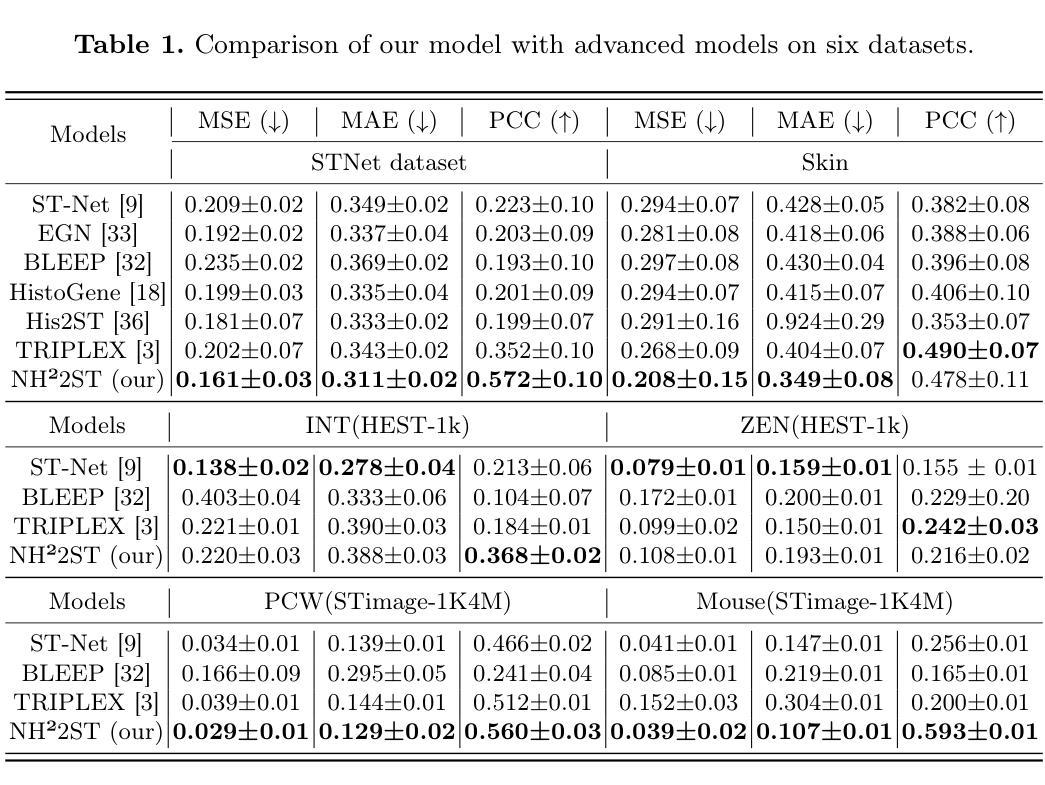
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) provides crucial insights into tissue micro-environments, but is limited to its high cost and complexity. As an alternative, predicting gene expression from pathology whole slide images (WSI) is gaining increasing attention. However, existing methods typically rely on single patches or a single pathology modality, neglecting the complex spatial and molecular interactions between target and neighboring information (e.g., gene co-expression). This leads to a failure in establishing connections among adjacent regions and capturing intricate cross-modal relationships. To address these issues, we propose NH2ST, a framework that integrates spatial context and both pathology and gene modalities for gene expression prediction. Our model comprises a query branch and a neighbor branch to process paired target patch and gene data and their neighboring regions, where cross-attention and contrastive learning are employed to capture intrinsic associations and ensure alignments between pathology and gene expression. Extensive experiments on six datasets demonstrate that our model consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving over 20% in PCC metrics. Codes are available at https://github.com/MCPathology/NH2ST
空间转录组学(ST)为组织微环境提供了关键见解,但其高昂的成本和复杂性限制了其应用。作为替代方案,从病理学全幻灯片图像(WSI)预测基因表达正引起越来越多的关注。然而,现有方法通常依赖于单个补丁或单一病理学模式,忽视了目标信息与邻近信息之间复杂的空间分子交互(例如基因共表达)。这导致了在建立相邻区域之间的联系和捕捉复杂的跨模式关系方面的失败。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了NH2ST框架,该框架融合了空间上下文以及病理学和基因模式来进行基因表达预测。我们的模型包括查询分支和邻居分支,用于处理成对的目标补丁和基因数据及其邻近区域,其中采用交叉注意力和对比学习来捕捉内在关联并确保病理与基因表达之间的对齐。在六个数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的模型始终优于现有方法,在PCC指标上达到20%以上的提升。代码可在https://github.com/MCPathology/NH2ST上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our paper has been accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
空间转录学(ST)对于研究组织微环境具有重要意义,但其高昂成本和复杂性限制了应用。因此,通过病理全切片图像预测基因表达备受关注。然而,现有方法往往依赖单一的切片或单一病理模式,忽略了目标区域与邻近信息间的复杂空间与分子交互(如基因共表达)。为解决这些问题,我们提出了NH2ST框架,它结合了空间上下文信息以及病理和基因两种模式来进行基因表达预测。该模型包含查询分支和邻近分支,用于处理目标区域和基因数据的配对以及相邻区域的信息。通过交叉注意力机制和对比学习,捕捉内在联系并确保病理与基因表达之间的对齐。在六个数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型始终优于现有方法,在PCC指标上提高了超过20%。
Key Takeaways
- 空间转录学对于研究组织微环境具有重要意义,但存在高成本和复杂性的限制。
- 通过病理全切片图像预测基因表达是一个备受关注的研究方向。
- 现有方法忽略了目标区域与邻近信息间的复杂空间与分子交互。
- NH2ST框架结合了空间上下文信息以及病理和基因两种模式进行基因表达预测。
- NH2ST模型包含查询分支和邻近分支,用于处理目标区域和基因数据的配对以及相邻区域的信息。
- NH2ST通过交叉注意力机制和对比学习来捕捉内在联系和确保病理与基因表达之间的对齐。
点此查看论文截图

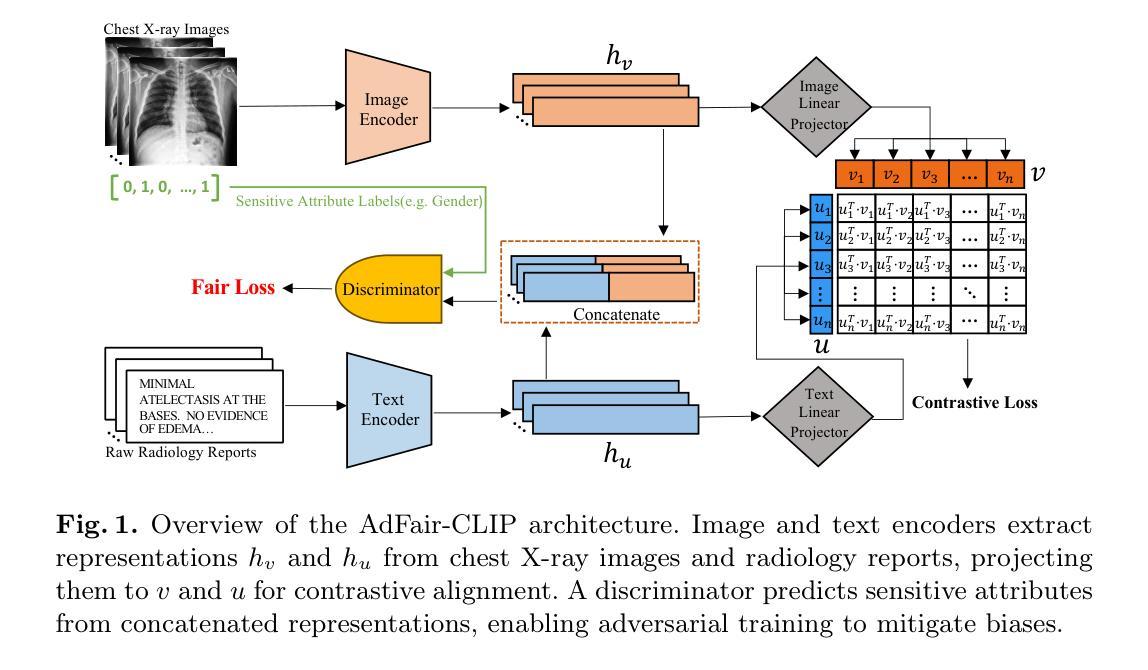
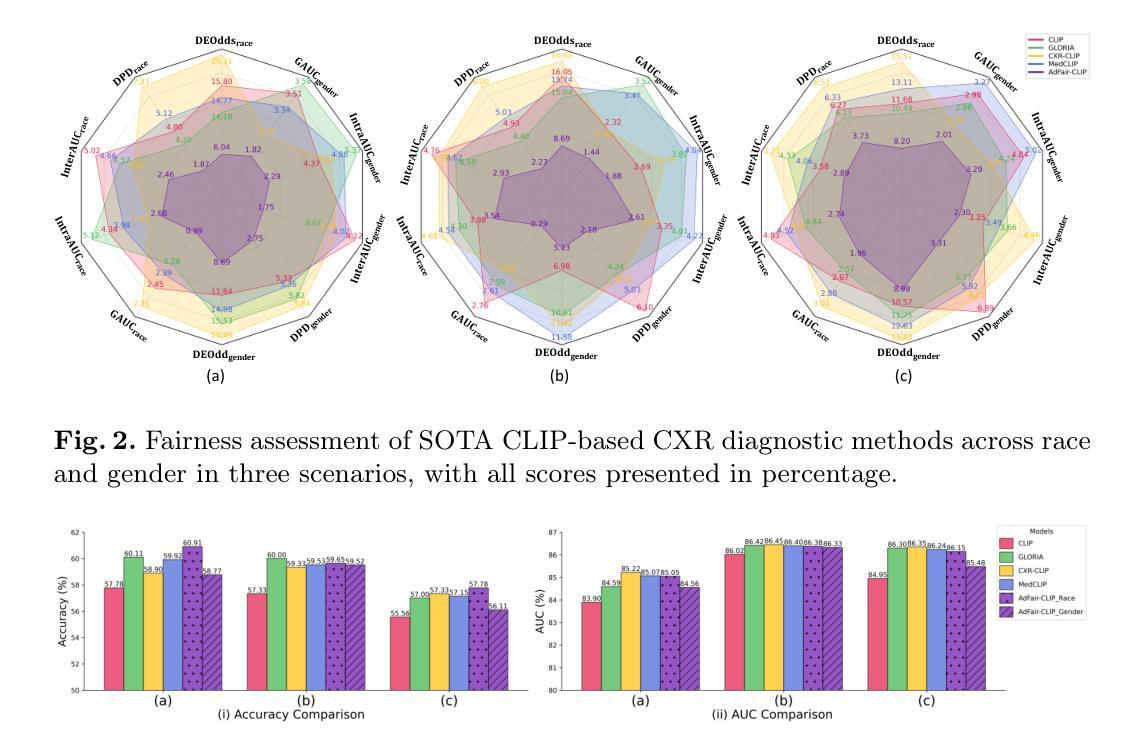
AdFair-CLIP: Adversarial Fair Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training for Chest X-rays
Authors:Chenlang Yi, Zizhan Xiong, Qi Qi, Xiyuan Wei, Girish Bathla, Ching-Long Lin, Bobak Jack Mortazavi, Tianbao Yang
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) models have demonstrated superior performance across various visual tasks including medical image classification. However, fairness concerns, including demographic biases, have received limited attention for CLIP models. This oversight leads to critical issues, particularly those related to race and gender, resulting in disparities in diagnostic outcomes and reduced reliability for underrepresented groups. To address these challenges, we introduce AdFair-CLIP, a novel framework employing adversarial feature intervention to suppress sensitive attributes, thereby mitigating spurious correlations and improving prediction fairness. We conduct comprehensive experiments on chest X-ray (CXR) datasets, and show that AdFair-CLIP significantly enhances both fairness and diagnostic accuracy, while maintaining robust generalization in zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. These results establish new benchmarks for fairness-aware learning in CLIP-based medical diagnostic models, particularly for CXR analysis.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型在包括医学图像分类在内的各种视觉任务中表现出了卓越的性能。然而,对于CLIP模型的公平性关注,包括人口统计偏见,并未得到足够的重视。这种疏忽导致了关键问题,特别是与种族和性别相关的问题,进而导致诊断结果的不公平和对代表性不足的群体的可靠性降低。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了AdFair-CLIP,这是一个采用对抗性特征干预来抑制敏感属性、从而减轻虚假关联并改善预测公平性的新型框架。我们在胸部X射线(CXR)数据集上进行了全面的实验,结果表明AdFair-CLIP在零样本和少样本场景中,显著提高了公平性和诊断准确性,同时保持了稳健的泛化能力。这些结果为CLIP基础的医学诊断模型中的公平性感知学习,特别是CXR分析,建立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This preprint has been accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型在多种视觉任务中表现优异,但在医疗图像分类等任务中存在公平性问题,特别是与种族和性别相关的挑战。为解决这一问题,提出AdFair-CLIP框架,采用对抗特征干预抑制敏感属性,减少虚假关联,提高预测公平性。在胸片X线数据集上的实验表明,AdFair-CLIP在零样本和少样本场景下,能显著提高公平性和诊断准确性,并保持稳健的泛化能力,为CLIP基医疗诊断模型的公平性认知学习树立了新标杆。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在多种视觉任务中表现优异,但在医疗图像分类等任务中存在公平性问题。
- AdFair-CLIP框架被提出来解决CLIP模型的公平性问题。
- AdFair-CLIP采用对抗特征干预来抑制敏感属性,从而减少虚假关联。
- AdFair-CLIP能提高预测公平性。
- 在胸片X线数据集上的实验表明,AdFair-CLIP在零样本和少样本场景下能显著提高公平性和诊断准确性。
- AdFair-CLIP框架的引入为CLIP基医疗诊断模型的公平性认知学习树立了新标杆。
点此查看论文截图

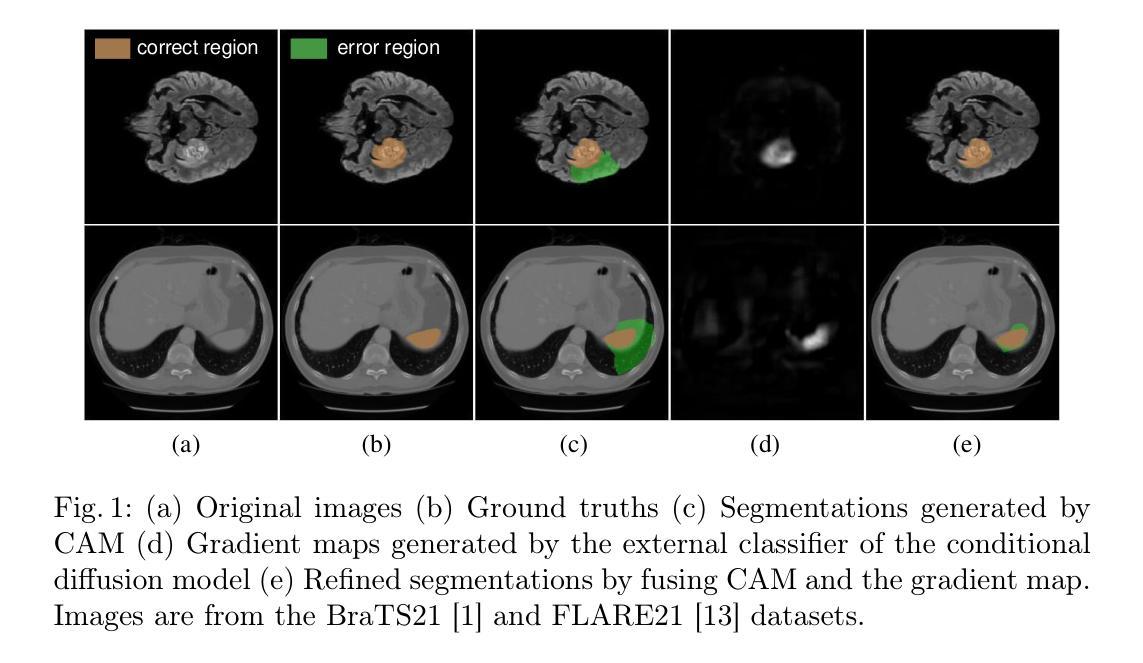
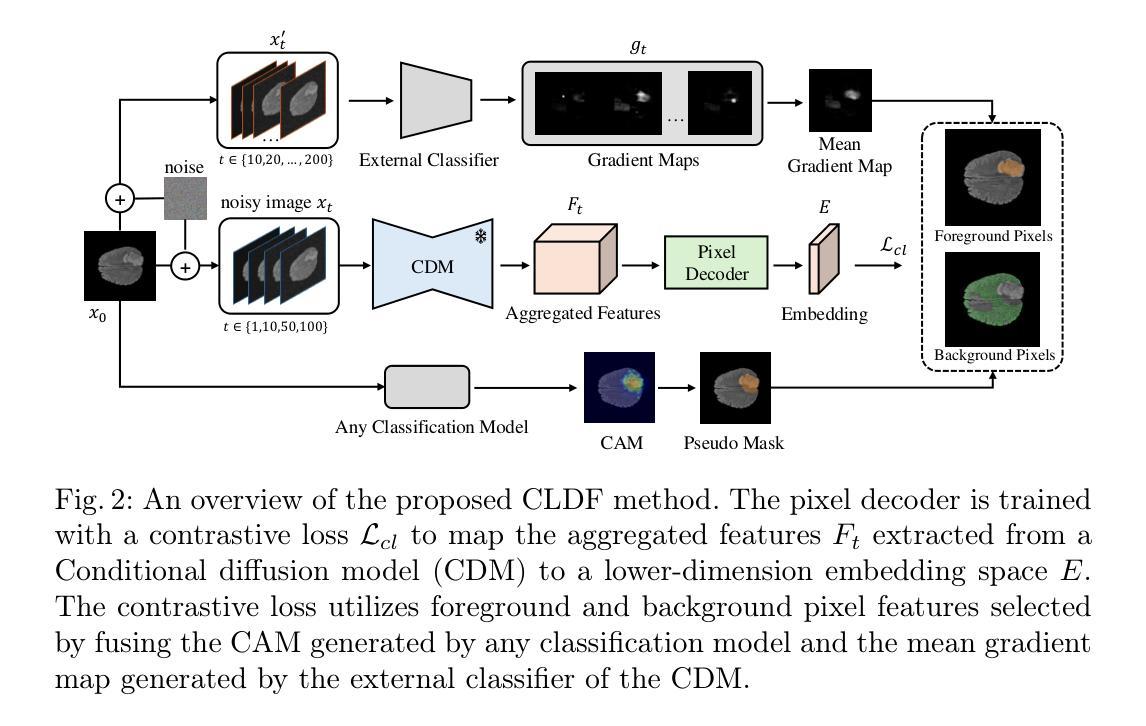
Contrastive Learning with Diffusion Features for Weakly Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Dewen Zeng, Xinrong Hu, Yu-Jen Chen, Yawen Wu, Xiaowei Xu, Yiyu Shi
Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) methods using class labels often rely on class activation maps (CAMs) to localize objects. However, traditional CAM-based methods struggle with partial activations and imprecise object boundaries due to optimization discrepancies between classification and segmentation. Recently, the conditional diffusion model (CDM) has been used as an alternative for generating segmentation masks in WSSS, leveraging its strong image generation capabilities tailored to specific class distributions. By modifying or perturbing the condition during diffusion sampling, the related objects can be highlighted in the generated images. Yet, the saliency maps generated by CDMs are prone to noise from background alterations during reverse diffusion. To alleviate the problem, we introduce Contrastive Learning with Diffusion Features (CLDF), a novel method that uses contrastive learning to train a pixel decoder to map the diffusion features from a frozen CDM to a low-dimensional embedding space for segmentation. Specifically, we integrate gradient maps generated from CDM external classifier with CAMs to identify foreground and background pixels with fewer false positives/negatives for contrastive learning, enabling robust pixel embedding learning. Experimental results on four segmentation tasks from two public medical datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing baselines.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)方法通常使用类别标签,并依赖于类别激活图(CAMs)进行对象定位。然而,传统的基于CAM的方法在部分激活和优化分类与分割之间差异导致的精确对象边界方面存在困难。最近,条件扩散模型(CDM)已被用作WSSS中生成分割掩模的替代方法,利用其针对特定类别分布的强大图像生成能力。通过在扩散采样过程中修改或扰动条件,可以在生成的图像中突出显示相关对象。然而,由CDM生成的显著性地图容易受到反向扩散过程中背景改变产生的噪声影响。为了缓解这个问题,我们引入了对比学习与扩散特征(CLDF)相结合的新方法,该方法使用对比学习训练像素解码器,将来自冻结CDM的扩散特征映射到低维嵌入空间以进行分割。具体来说,我们将由CDM外部分类器生成的梯度图与CAM相结合,以识别前景和背景像素,并减少对比学习中误报/漏报的数量,从而实现稳健的像素嵌入学习。在来自两个公共医疗数据集的四个分割任务上的实验结果表明,我们的方法显著优于现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)常使用类别标签并利用类激活图(CAMs)进行目标定位。然而,传统基于CAM的方法因分类与分割的优化差异而面临部分激活和不精确目标边界的问题。最近,条件扩散模型(CDM)被用于生成WSSS中的分割掩膜,利用其针对特定类别分布的图像生成能力。通过修改或扰动扩散采样过程中的条件,可以突出相关目标。然而,CDM生成的显著性图在反向扩散过程中易受背景变化产生的噪声影响。为解决此问题,我们提出使用对比学习训练像素解码器的方法(CLDF),将CDM的扩散特征映射到低维嵌入空间进行分割。我们整合CDM外部分类器生成的梯度图与CAMs,减少对比学习中的误报/漏报,实现稳健的像素嵌入学习。在公共医疗数据集的四个分割任务上的实验结果表明,我们的方法显著优于现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS方法常使用CAMs进行目标定位,但面临部分激活和不精确目标边界的挑战。
- CDM用于WSSS中的分割掩膜生成,具有针对特定类别分布的图像生成能力。
- CDM生成的显著性图在反向扩散过程中易受噪声影响。
- 提出CLDF方法,结合对比学习训练像素解码器,将CDM的扩散特征映射到低维嵌入空间进行分割。
- 整合梯度图和CAMs以提高对比学习的准确性,减少误报/漏报。
- CLDF方法在公共医疗数据集的四个分割任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

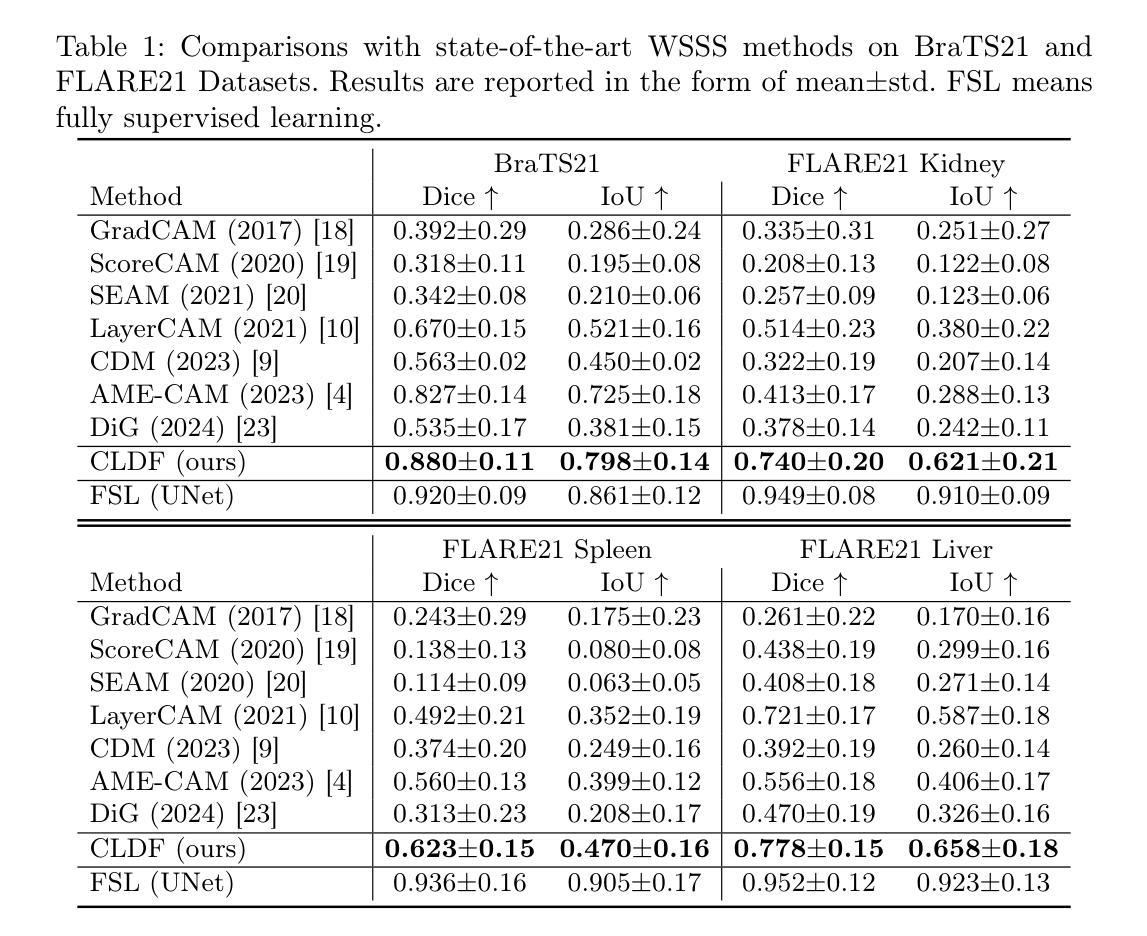
Dynamic Contrastive Learning for Hierarchical Retrieval: A Case Study of Distance-Aware Cross-View Geo-Localization
Authors:Suofei Zhang, Xinxin Wang, Xiaofu Wu, Quan Zhou, Haifeng Hu
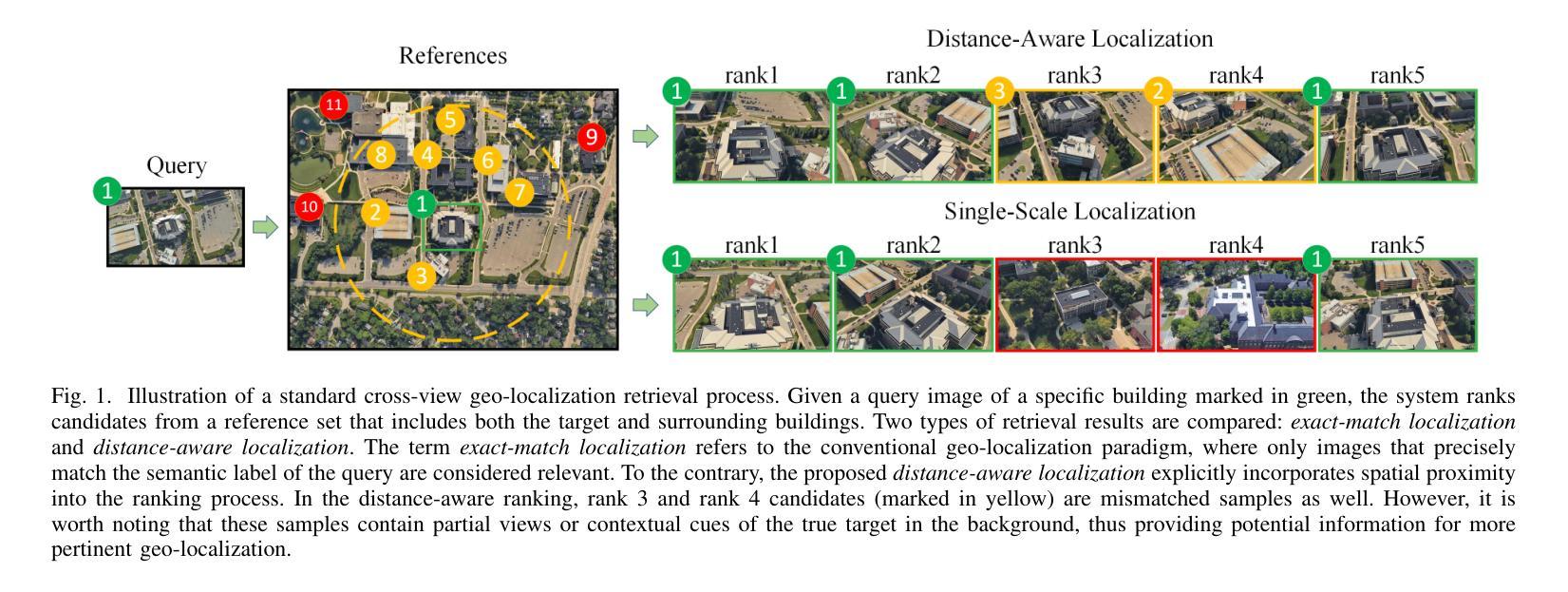
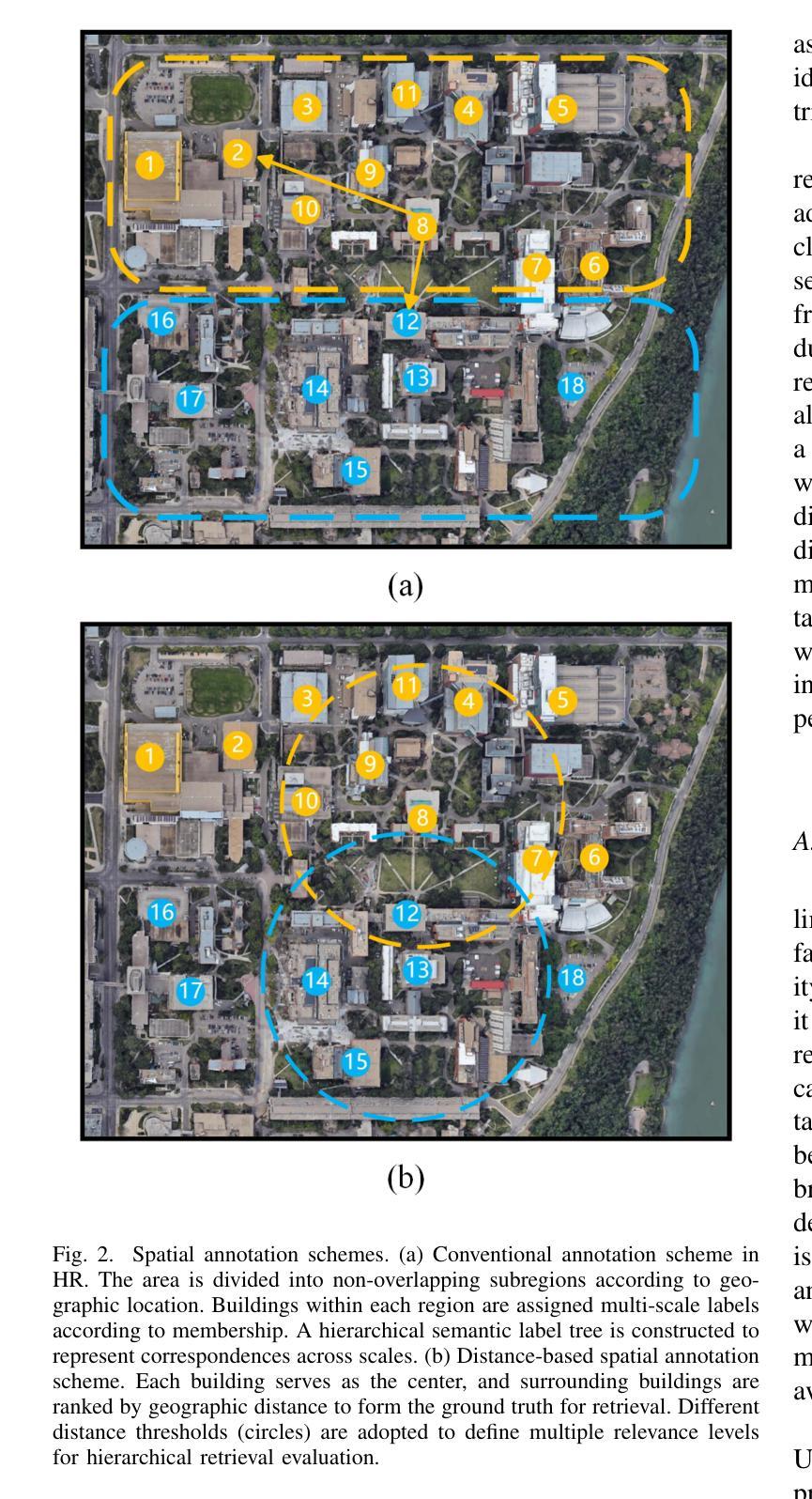
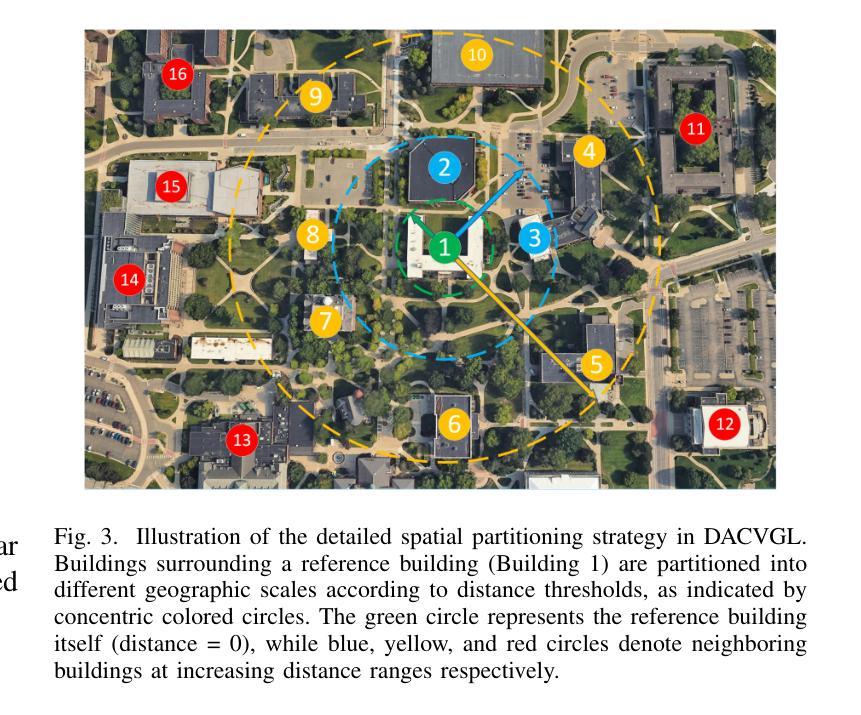
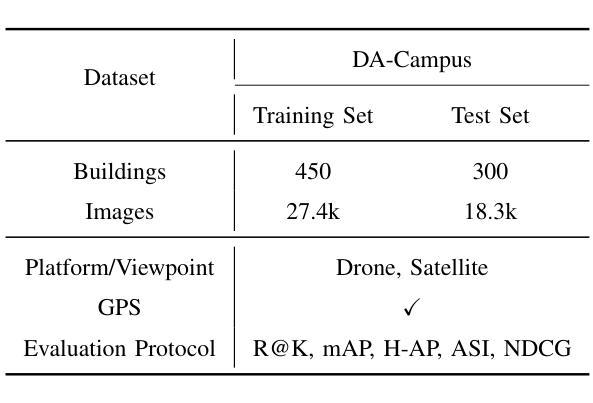
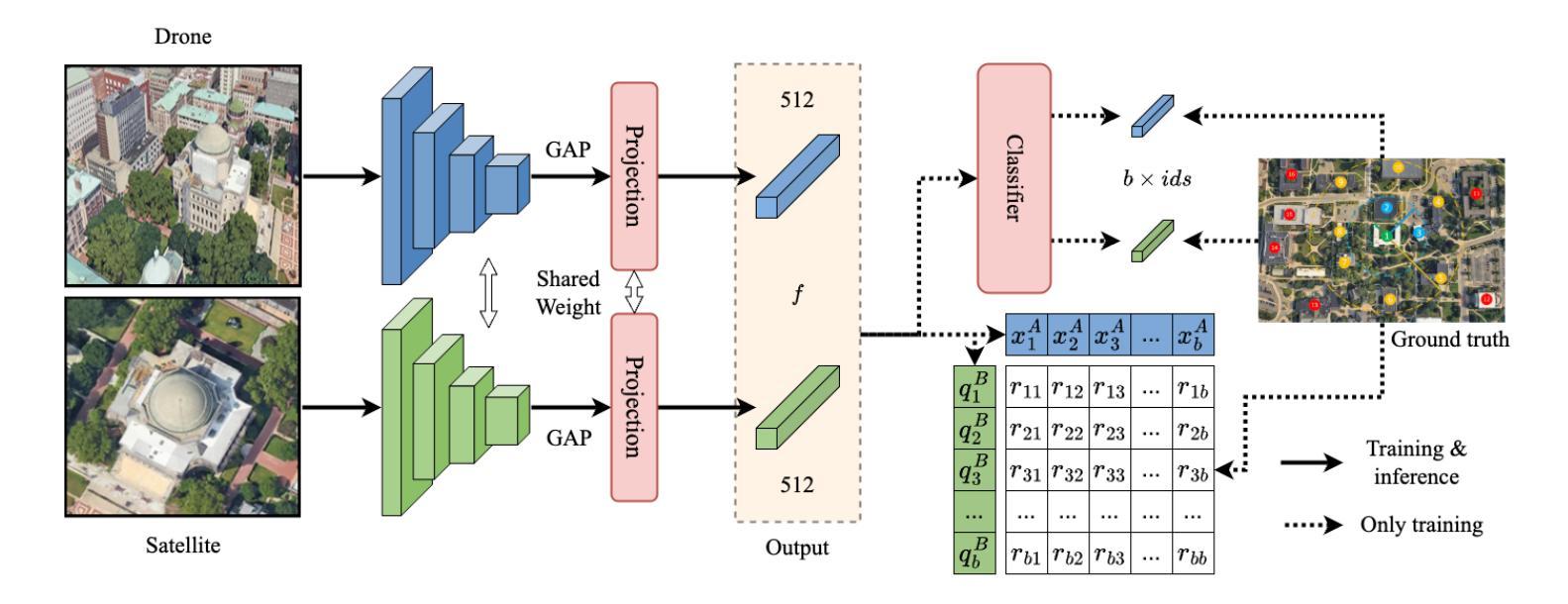
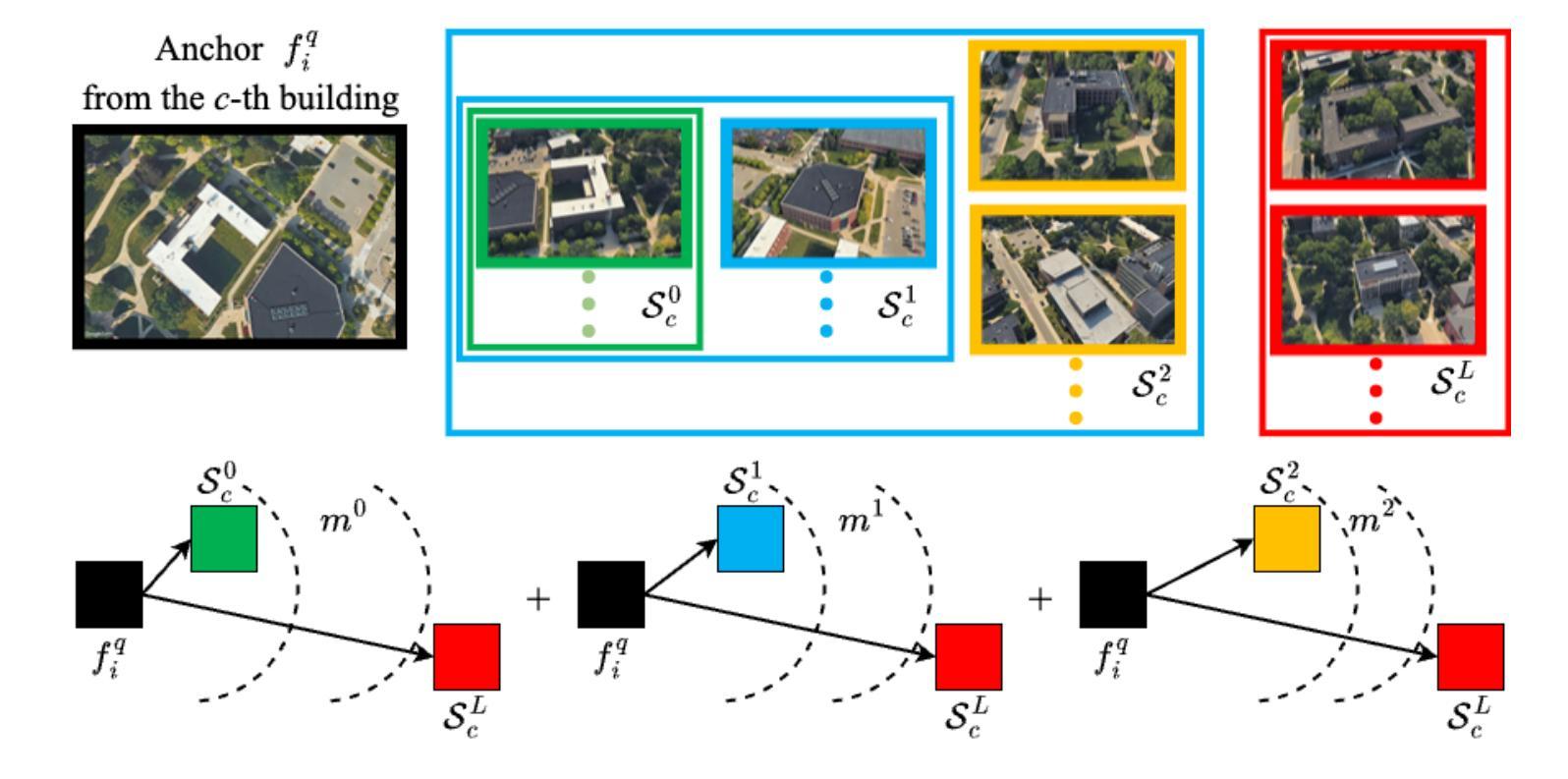
Existing deep learning-based cross-view geo-localization methods primarily focus on improving the accuracy of cross-domain image matching, rather than enabling models to comprehensively capture contextual information around the target and minimize the cost of localization errors. To support systematic research into this Distance-Aware Cross-View Geo-Localization (DACVGL) problem, we construct Distance-Aware Campus (DA-Campus), the first benchmark that pairs multi-view imagery with precise distance annotations across three spatial resolutions. Based on DA-Campus, we formulate DACVGL as a hierarchical retrieval problem across different domains. Our study further reveals that, due to the inherent complexity of spatial relationships among buildings, this problem can only be addressed via a contrastive learning paradigm, rather than conventional metric learning. To tackle this challenge, we propose Dynamic Contrastive Learning (DyCL), a novel framework that progressively aligns feature representations according to hierarchical spatial margins. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DyCL is highly complementary to existing multi-scale metric learning methods and yields substantial improvements in both hierarchical retrieval performance and overall cross-view geo-localization accuracy. Our code and benchmark are publicly available at https://github.com/anocodetest1/DyCL.
现有的基于深度学习的跨视图地理定位方法主要关注改进跨域图像匹配的准确性,而不是使模型能够全面捕获目标周围的上下文信息并最小化定位错误成本。为了支持对距离感知跨视图地理定位(DACVGL)问题的系统研究,我们构建了距离感知校园(DA-Campus),这是第一个将多视图图像与三种空间分辨率的精确距离注释配对在一起的基准测试。基于DA-Campus,我们将DACVGL制定为不同领域的分层检索问题。我们的研究进一步表明,由于建筑物之间空间关系的固有复杂性,这个问题只能通过对比学习范式来解决,而不是传统的度量学习。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了动态对比学习(DyCL)这一新颖框架,它根据分层空间边界逐步对齐特征表示。大量实验表明,DyCL与现有的多尺度度量学习方法高度互补,在分层检索性能和总体跨视图地理定位准确性方面都有显著提高。我们的代码和基准测试可在https://github.com/anocodetest1/DyCL公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文构建了一个名为DA-Campus的基准测试平台,该平台结合了多视角图像和精确的距离标注,空间分辨率各异。在此基础上,将跨视图地理定位(DACVGL)问题转化为层次检索问题。研究发现,由于建筑物之间空间关系的固有复杂性,该问题只能通过对比学习模式而非传统度量学习来解决。为此,提出了动态对比学习(DyCL)框架,该框架根据层次空间边界逐步对齐特征表示。实验表明,DyCL对现有多尺度度量学习方法具有互补性,能显著提高层次检索性能和跨视图地理定位准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Distance-Aware Cross-View Geo-Localization (DACVGL)问题,并构建了DA-Campus基准测试平台,包含多视角图像和精确距离标注。
- 将DACVGL问题转化为层次检索问题,强调在跨域图像匹配中全面捕捉目标上下文信息的重要性。
- 指出由于建筑物间空间关系的复杂性,解决DACVGL问题需要采用对比学习模式。
- 提出了Dynamic Contrastive Learning (DyCL)框架,能按层次空间边界逐步对齐特征表示。
- DyCL框架对现有多尺度度量学习方法具有互补性,能显著提高层次检索和跨视图地理定位的准确性。
- 公开了研究代码和基准测试平台,便于其他人使用和进一步的研究。
点此查看论文截图

How Semantically Informative is an Image?: Measuring the Covariance-Weighted Norm of Contrastive Learning Embeddings
Authors:Fumiya Uchiyama, Rintaro Yanagi, Shohei Taniguchi, Shota Takashiro, Masahiro Suzuki, Hirokatsu Kataoka, Yusuke Iwasawa, Yutaka Matsuo
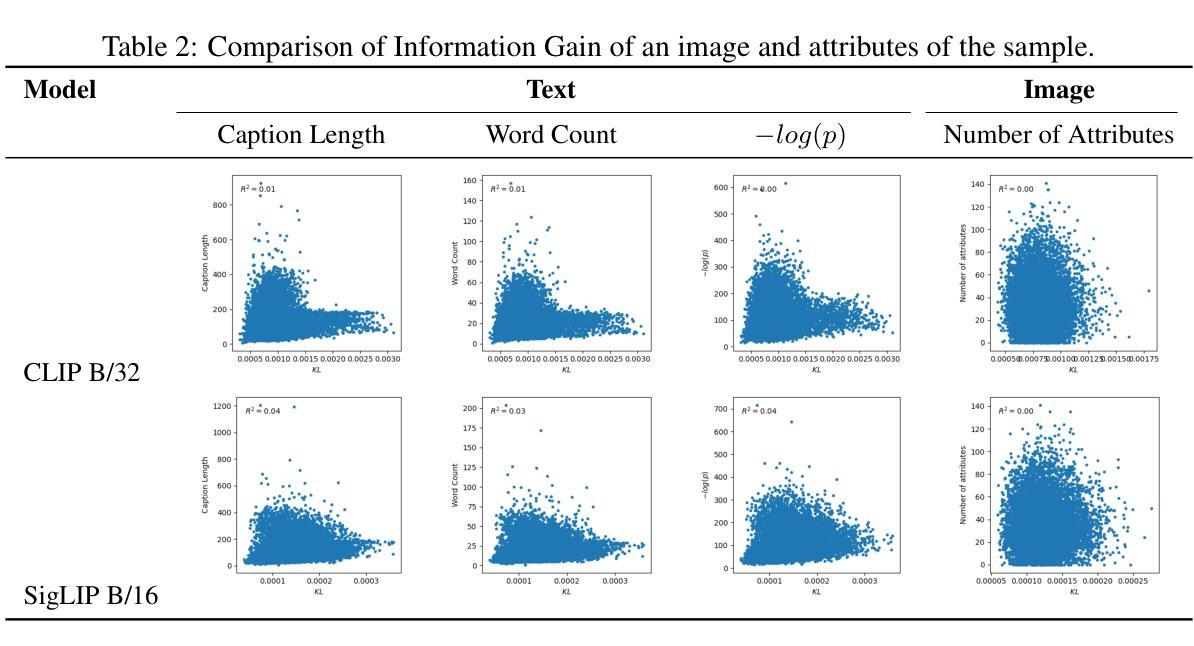
Contrastive learning has the capacity to model multimodal probability distributions by embedding and aligning visual representations with semantics from captions. This approach enables the estimation of relational semantic similarity; however, it remains unclear whether it can also represent absolute semantic informativeness. In this work, we introduce a semantic informativeness metric for an image calculated from text samples via a contrastive learning model; similarly, the informativeness of a text is calculated from image samples. We propose a redefinition of the concept of Information Gain, a concept previously explored in natural language processing, extending its application to the domains of vision and language. Our metric quantifies how conditioning on an image distorts the distribution of associated texts, and vice versa for text conditioning on image distributions. In OpenCLIP’s empirical results, we observe that images with the lowest Information Gain scores often correspond to placeholder icons such as “image not found.” Furthermore, we propose to measure a norm-based metric of the embedding to estimate the Information Gain, following the theoretical results for Skip-Gram with Negative Sampling (SGNS) word embedding. Information Gain can be measured using either CLIP or SigLIP, and the results demonstrate a strong correlation with a coefficient of determination ranging from 0.98 to 1.00. After obtaining the mean and the covariance of the sample embedding, the computational cost of this method is independent of the sample size, and it is compatible with publicly available, open-weight models.
对比学习具有通过嵌入和对齐来自字幕的语义来建模多模态概率分布的能力。这种方法能够估计关系语义相似性;然而,尚不清楚它是否能代表绝对的语义信息性。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种通过对比学习模型从文本样本计算图像语义信息性的度量标准;同样,文本的语义信息性也是从图像样本中计算得出的。我们重新定义了信息增益的概念,这是一个之前在自然语言处理中探索过的概念,将其扩展到视觉和语言领域。我们的度量标准衡量了以图像为条件时相关文本分布的扭曲程度,反之亦然。在OpenCLIP的实证结果中,我们观察到信息增益得分最低的图片通常对应于占位符图标,如“图片未找到”。此外,我们提出基于嵌入的范数度量来估计信息增益,遵循Skip-Gram负采样(SGNS)词嵌入的理论结果。信息增益可以使用CLIP或SigLIP进行测量,结果显示与从0.98到1.00的决定系数有很强的相关性。在获得样本嵌入的均值和协方差之后,该方法的计算成本独立于样本大小,并且它与公开可用的开源权重模型兼容。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了对比学习在视觉和语义融合中的潜力,并引入了一种基于对比学习的语义信息量度量方法。通过计算图像与文本样本之间的信息增益,该度量方法可以评估图像或文本所携带的语义信息量。研究结果表明,信息增益与Skip-Gram负采样词嵌入理论结果相符,并且适用于公开可用的模型。此方法计算成本低,样本嵌入的均值和协方差独立于样本大小。
Key Takeaways
- 对比学习能够建模多模态概率分布,通过嵌入和对齐视觉表示与语义字幕。
- 引入了一种基于对比学习的语义信息量度量方法,可以计算图像和文本样本之间的信息增益。
- 信息增益的概念被重新定义并扩展到视觉和语言领域。
- 图像与文本之间的信息增益度量可以评估它们所携带的语义信息量。
- 信息增益的计算基于样本嵌入的范数,与Skip-Gram负采样词嵌入理论相符。
- 信息增益的计算方法计算成本低,并且适用于公开可用的模型。
点此查看论文截图


MiCo: Multi-image Contrast for Reinforcement Visual Reasoning
Authors:Xi Chen, Mingkang Zhu, Shaoteng Liu, Xiaoyang Wu, Xiaogang Xu, Yu Liu, Xiang Bai, Hengshuang Zhao
This work explores enabling Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to link visual cues across multiple images. A straightforward solution is to adapt rule-based reinforcement learning for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). However, such methods typically rely on manually curated question-answer pairs, which can be particularly challenging when dealing with fine grained visual details and complex logic across images. Inspired by self-supervised visual representation learning, we observe that images contain inherent constraints that can serve as supervision. Based on this insight, we construct image triplets comprising two augmented views of the same image and a third, similar but distinct image. During training, the model is prompted to generate a reasoning process to compare these images (i.e., determine same or different). Then we optimize the model with rule-based reinforcement learning. Due to the high visual similarity and the presence of augmentations, the model must attend to subtle visual changes and perform logical reasoning to succeed. Experiments show that, although trained solely on visual comparison tasks, the learned reasoning ability generalizes effectively to a wide range of questions. Without relying on any human-annotated question-answer pairs, our method achieves significant improvements on multi-image reasoning benchmarks and shows strong performance on general vision tasks.
本文探讨了实现Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理,以在多张图像之间建立视觉线索的联系。一种直接的解决方案是为视觉语言模型(VLMs)使用基于规则的任务进行强化学习。然而,这种方法通常依赖于人工策划的问题答案对,当面对精细粒度的视觉细节和图像之间的复杂逻辑时,这可能会特别具有挑战性。受自我监督的视觉表示学习的启发,我们观察到图像包含可以作为监督的固有约束。基于这一见解,我们构建了包含同一张图像的两个增强视图和第三张相似但不同的图像的三重图像。在训练过程中,模型被提示生成一个推理过程来比较这些图像(即确定相同或不同)。然后我们用基于规则的任务进行强化学习来优化模型。由于高视觉相似性和增强的存在,模型必须关注微妙的视觉变化并进行逻辑推理才能成功。实验表明,尽管仅通过视觉比较任务进行训练,但所学的推理能力可以有效地推广到各种问题。我们的方法不依赖于任何人工标注的问题答案对,在跨图像推理基准测试中取得了显著的改进,并在通用视觉任务中表现出强大的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了如何通过Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理将多个图像中的视觉线索联系起来。通过自我监督的视觉表示学习,观察到图像中存在内在约束可作为监督信息。为此构建了包含两个相同图像的增强视图和一个相似但不同的图像的三重图像。训练模型时,会提示模型比较这些图像(即判断相同或不同),然后使用基于规则的强化学习进行优化。由于高视觉相似性和存在的增强,模型必须关注微妙的视觉变化并进行逻辑推理才能成功。实验表明,虽然仅通过视觉比较任务进行训练,但学到的推理能力可以有效泛化到各种问题上。并且,在不依赖任何人工标注的问题答案对的情况下,该方法在多图像推理基准测试上取得了显著改进,并在一般视觉任务上表现出强劲性能。
Key Takeaways
- 工作探索了Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理在连接多个图像视觉线索方面的应用。
- 提出使用自我监督的视觉表示学习来利用图像中的内在约束作为监督信息。
- 构建三重图像来训练模型比较并区分图像间的微妙差异。
- 使用基于规则的强化学习优化模型,使其关注视觉变化和进行逻辑推理。
- 实验表明模型在视觉比较任务上训练后,能有效泛化至多图像推理任务。
- 方法无需依赖人工标注的问题答案对,在多图像推理基准测试上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图



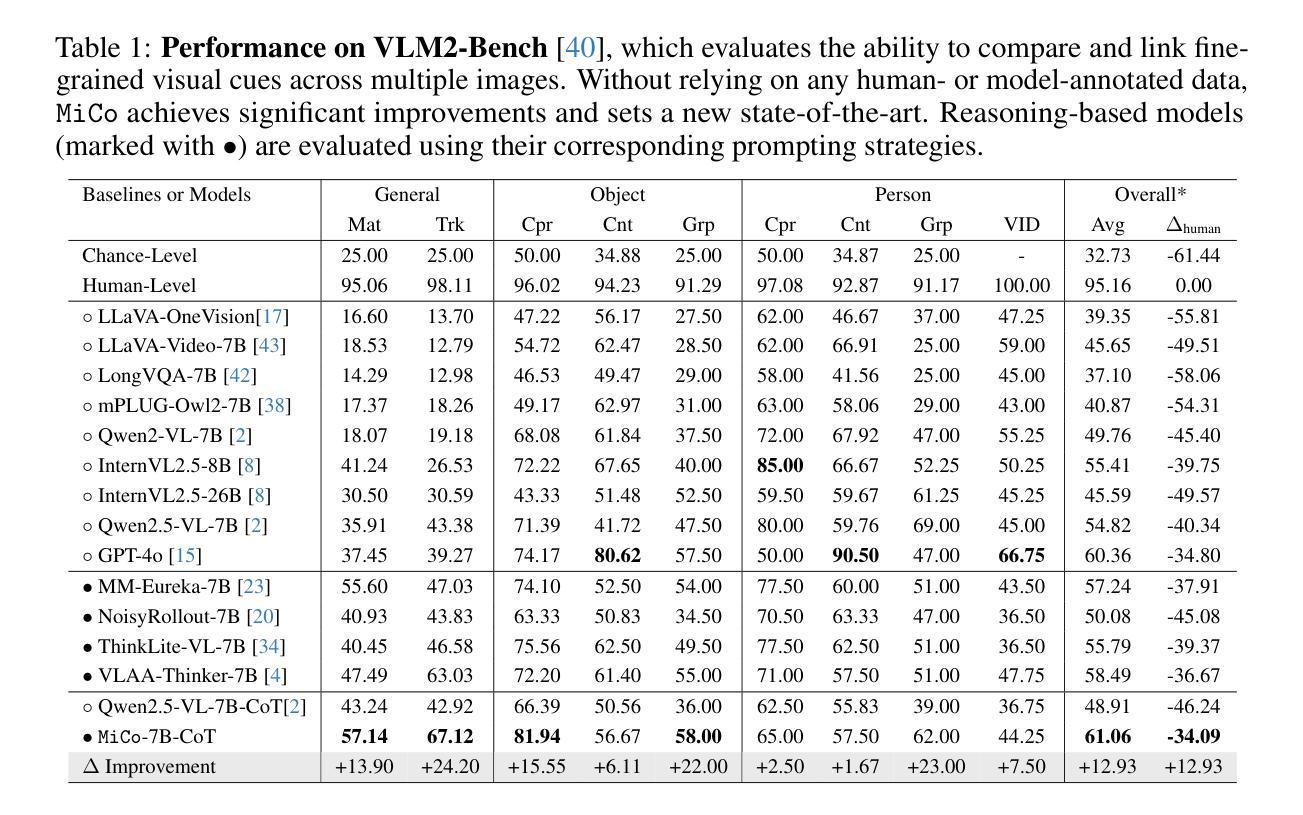
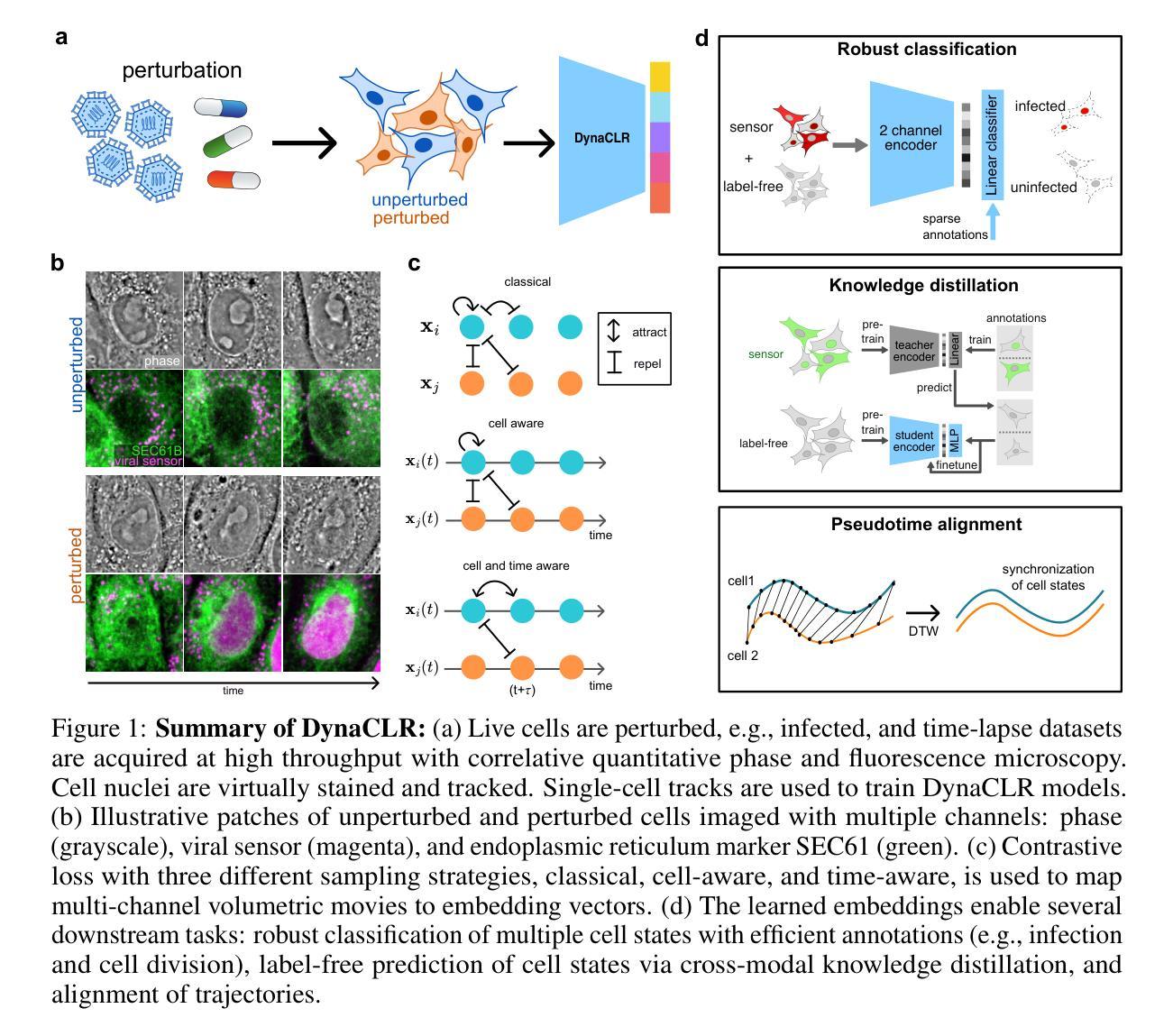
DynaCLR: Contrastive Learning of Cellular Dynamics with Temporal Regularization
Authors:Eduardo Hirata-Miyasaki, Soorya Pradeep, Ziwen Liu, Alishba Imran, Taylla Milena Theodoro, Ivan E. Ivanov, Sudip Khadka, See-Chi Lee, Michelle Grunberg, Hunter Woosley, Madhura Bhave, Carolina Arias, Shalin B. Mehta
We report DynaCLR, a self-supervised method for embedding cell and organelle Dynamics via Contrastive Learning of Representations of time-lapse images. DynaCLR integrates single-cell tracking and time-aware contrastive sampling to learn robust, temporally regularized representations of cell dynamics. DynaCLR embeddings generalize effectively to in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets, and can be used for several downstream tasks with sparse human annotations. We demonstrate efficient annotations of cell states with a human-in-the-loop using fluorescence and label-free imaging channels. DynaCLR method enables diverse downstream biological analyses: classification of cell division and infection, clustering heterogeneous cell migration patterns, cross-modal distillation of cell states from fluorescence to label-free channel, alignment of asynchronous cellular responses and broken cell tracks, and discovering organelle response due to infection. DynaCLR is a flexible method for comparative analyses of dynamic cellular responses to pharmacological, microbial, and genetic perturbations. We provide PyTorch-based implementations of the model training and inference pipeline (https://github.com/mehta-lab/viscy) and a GUI (https://github.com/czbiohub-sf/napari-iohub) for the visualization and annotation of trajectories of cells in the real space and the embedding space.
我们报告了一种名为DynaCLR的自我监督方法,该方法通过对比学习时间序列图像的表示来嵌入细胞和细胞器的动态。DynaCLR结合了单细胞追踪和时间感知对比采样,学习细胞动态稳健且时间规律化的表示。DynaCLR嵌入有效地泛化到内部分布和外部分布的数据集,并且可用于具有稀疏人工注释的多个下游任务。我们演示了使用荧光和无标记成像通道在循环中有效注释细胞状态。DynaCLR方法可用于多种下游生物学分析:细胞分裂和感染的分类,聚集异质细胞迁移模式,从荧光到无标记通道的跨模态细胞状态蒸馏,异步细胞反应的校准和断裂的细胞轨迹,以及由于感染而发现的细胞器反应。DynaCLR是一种用于比较药物学、微生物学和遗传学扰动对动态细胞反应分析的灵活方法。我们提供了基于PyTorch的模型训练和推理管道的实现(https://github.com/mehta-lab/viscy),以及一个GUI(https://github.com/czbiohub-sf/napari-iohub),用于可视化真实空间和嵌入空间中细胞的轨迹并进行注释。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 6 figures, 13 appendix figures, 5 videos (ancillary files)
Summary:
DynaCLR是一种基于对比学习的时间序列图像表示嵌入方法,用于细胞器动态的无监督学习。它通过结合单细胞追踪和时间感知对比采样,学习稳健的细胞动态表示。DynaCLR嵌入可以有效地应用于内部和外部数据集,并可在稀疏人类注释的情况下用于多种下游任务。它支持多种下游生物学分析,如细胞分裂和感染的分类、异质细胞迁移模式的聚类、从荧光到无标记成像通道的跨模态蒸馏等。DynaCLR具有灵活性,适用于动态细胞响应的药物学、微生物学和遗传学比较分析。提供了基于PyTorch的模型训练和推理管道实现以及可视化工具。
Key Takeaways:
- DynaCLR是一种自监督学习方法,用于嵌入细胞器动态的无监督学习。
- 通过结合单细胞追踪和时间感知对比采样,学习稳健的细胞动态表示。
- DynaCLR嵌入适用于内部和外部数据集,适用于多种下游任务,即使存在稀疏的人类注释也是如此。
- DynaCLR能够高效地对具有人参与的注释流程进行分类应用等多样任务包括:如分类细胞分裂和感染以及细胞的异质迁移模式的聚类。也发现能够将细分层分析延续到感染后其他机制等方面进行应用研究以及标注协同和分析上的应用方向等的深入研究。
点此查看论文截图

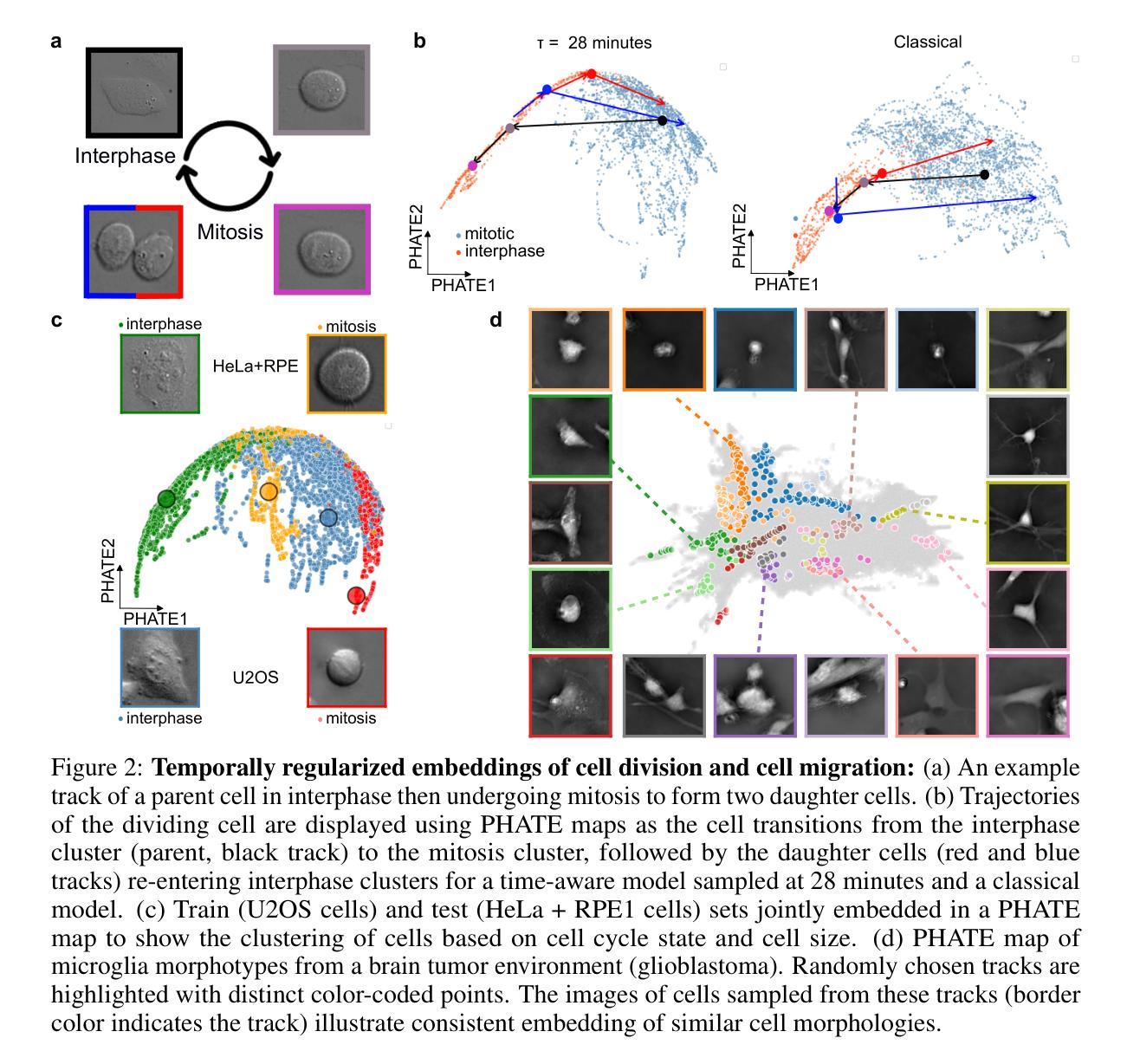
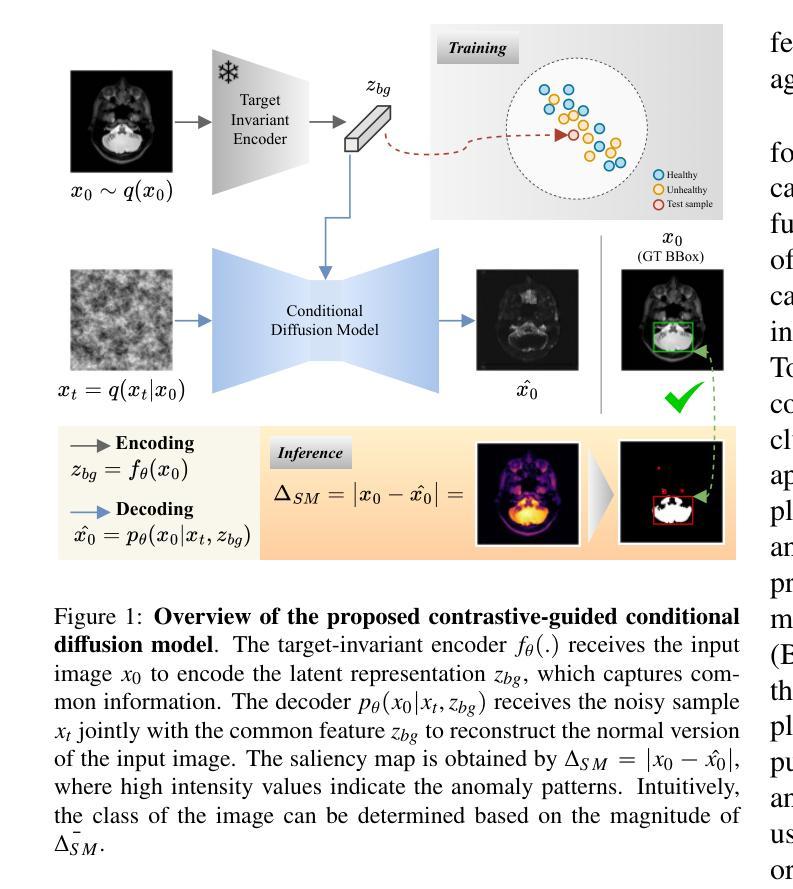
Unsupervised contrastive analysis for anomaly detection in brain MRIs via conditional diffusion models
Authors:Cristiano Patrício, Carlo Alberto Barbano, Attilio Fiandrotti, Riccardo Renzulli, Marco Grangetto, Luis F. Teixeira, João C. Neves
Contrastive Analysis (CA) detects anomalies by contrasting patterns unique to a target group (e.g., unhealthy subjects) from those in a background group (e.g., healthy subjects). In the context of brain MRIs, existing CA approaches rely on supervised contrastive learning or variational autoencoders (VAEs) using both healthy and unhealthy data, but such reliance on target samples is challenging in clinical settings. Unsupervised Anomaly Detection (UAD) offers an alternative by learning a reference representation of healthy anatomy without the need for target samples. Deviations from this reference distribution can indicate potential anomalies. In this context, diffusion models have been increasingly adopted in UAD due to their superior performance in image generation compared to VAEs. Nonetheless, precisely reconstructing the anatomy of the brain remains a challenge. In this work, we propose an unsupervised framework to improve the reconstruction quality by training a self-supervised contrastive encoder on healthy images to extract meaningful anatomical features. These features are used to condition a diffusion model to reconstruct the healthy appearance of a given image, enabling interpretable anomaly localization via pixel-wise comparison. We validate our approach through a proof-of-concept on a facial image dataset and further demonstrate its effectiveness on four brain MRI datasets, achieving state-of-the-art anomaly localization performance on the NOVA benchmark.
对比分析(CA)通过对比目标组(例如不健康主体)中独特的模式与背景组(例如健康主体)中的模式来检测异常。在脑部MRI的情境中,现有的CA方法依赖于有监督的对比学习或变分自编码器(VAEs),需要同时使用健康和不健康的数据,但在临床环境中对目标样本的依赖是一个挑战。无监督异常检测(UAD)通过学习健康组织的参考表示来提供一种替代方案,而无需使用目标样本。与此参考分布的偏差可能表明存在潜在异常。在这方面,由于其在图像生成方面的卓越性能,扩散模型在UAD中越来越被采用,相对于VAEs具有优势。然而,精确重建大脑的解剖结构仍然是一个挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出一个无监督框架,通过在有监督的对比编码器上训练健康图像来改善重建质量,从而提取有意义的解剖特征。这些特征用于调节扩散模型,以重建给定图像的健康外观,并通过像素级的比较实现可解释的异常定位。我们通过面部图像数据集的概念验证来证明我们的方法,并进一步在四个脑部MRI数据集上展示其有效性,在NOVA基准测试中实现了最先进的异常定位性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under consideration at Pattern Recognition Letters
Summary
本论文提出了一种无监督框架,通过训练自监督对比编码器提取健康图像中的有意义解剖特征,并用这些特征调节扩散模型以重建给定图像的健康外观。此方法可实现通过像素级比较进行可解释的异常定位。在面部图像数据集上的概念验证以及在四个脑MRI数据集上的有效性展示,均在NOVA基准测试上达到了最先进的异常定位性能。
Key Takeaways
- 对比分析(CA)能够通过识别目标群体(如不健康主体)与背景群体(如健康主体)之间的独特模式来检测异常。
- 在脑MRI的上下文中,现有的CA方法依赖于有监督的对比学习或变分自编码器(VAEs),需要使用健康和不健康的数据。
- 无监督异常检测(UAD)提供了一种替代方案,通过学习健康解剖的参考表示,而无需目标样本。
- 扩散模型在UAD中越来越受欢迎,其在图像生成方面的性能优于VAEs。
- 本工作提出了一种无监督框架,通过训练自监督对比编码器提取有意义解剖特征,以改善重建质量。
- 该方法使用这些特征来调节扩散模型,以重建给定图像的健康外观,通过像素级比较实现可解释的异常定位。
点此查看论文截图


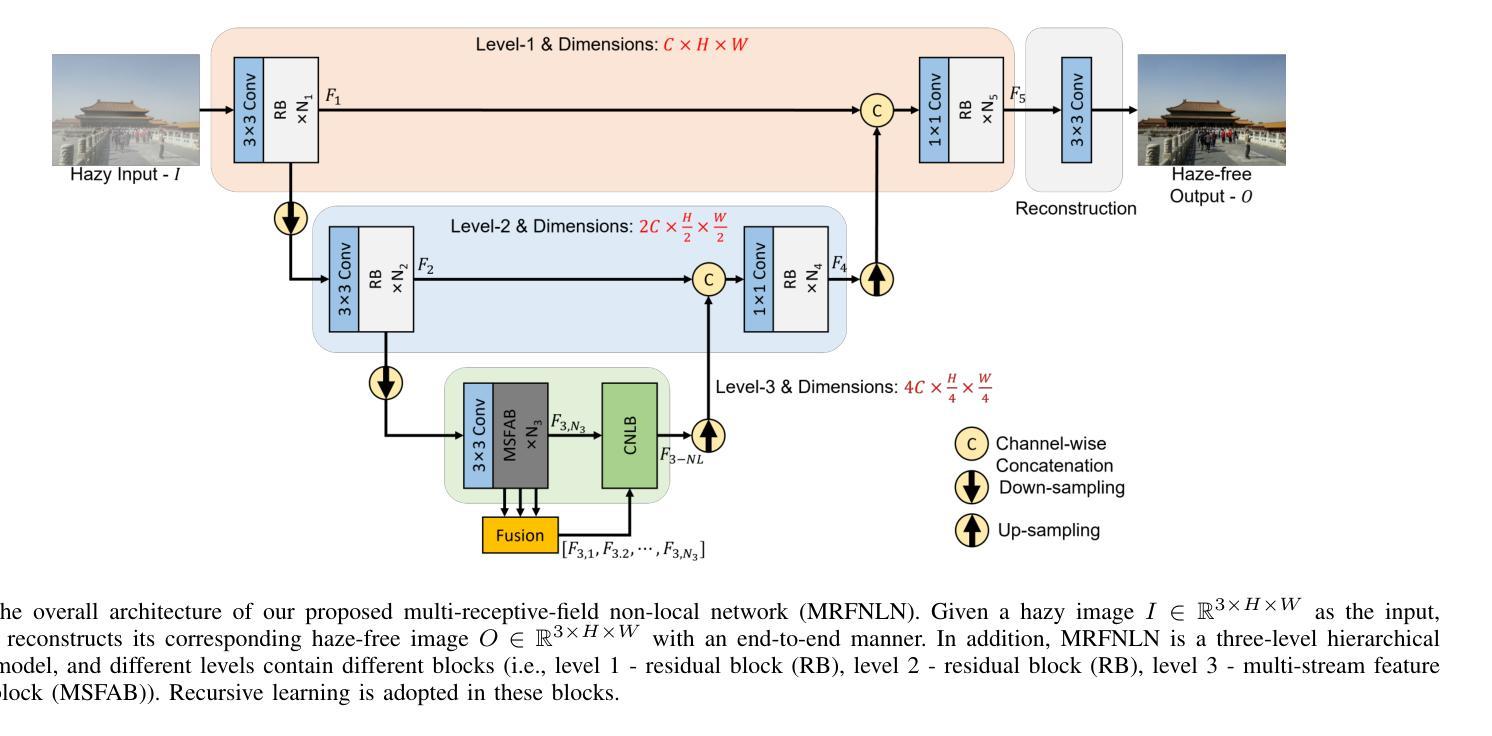
Accurate and lightweight dehazing via multi-receptive-field non-local network and novel contrastive regularization
Authors:Zewei He, Zixuan Chen, Jinlei Li, Ziqian Lu, Xuecheng Sun, Hao Luo, Zhe-Ming Lu, Evangelos K. Markakis
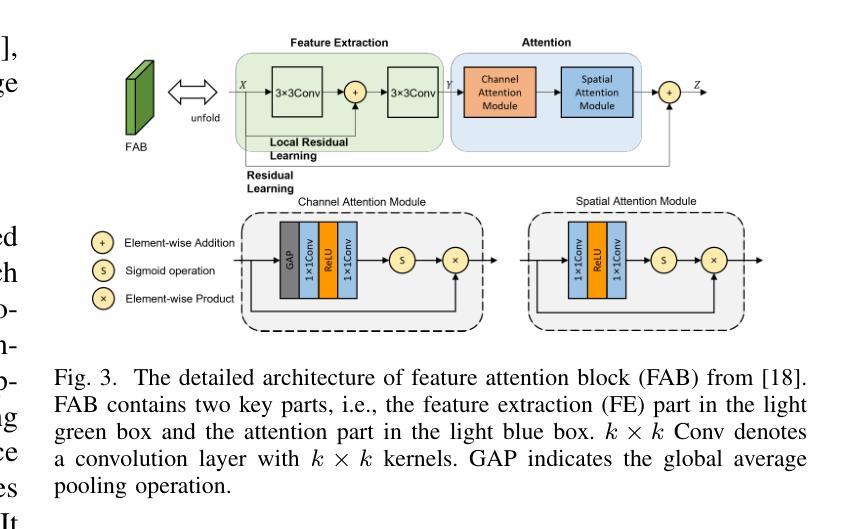
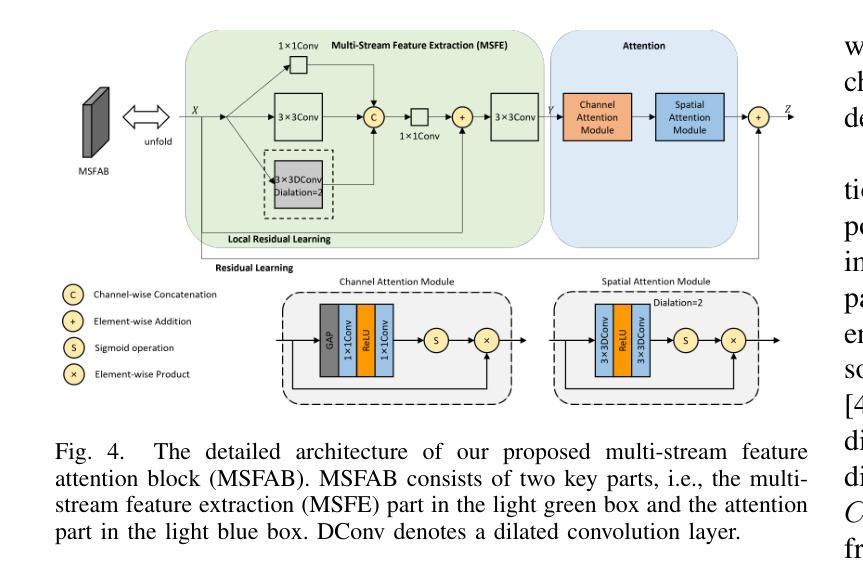
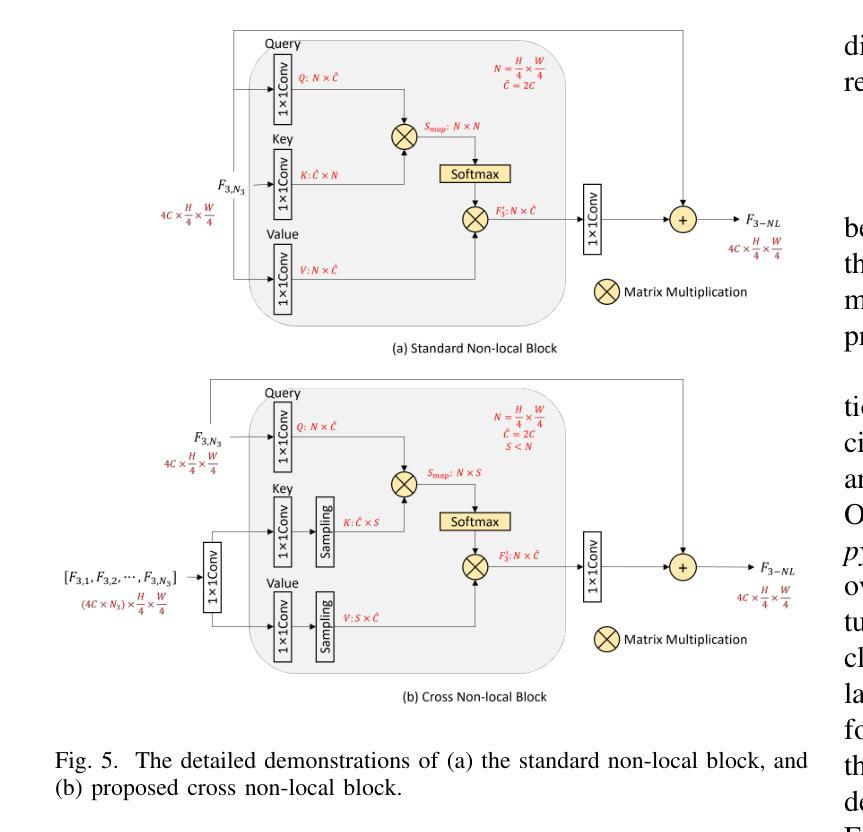
Recently, deep learning-based methods have dominated image dehazing domain. Although very competitive dehazing performance has been achieved with sophisticated models, effective solutions for extracting useful features are still under-explored. In addition, non-local network, which has made a breakthrough in many vision tasks, has not been appropriately applied to image dehazing. Thus, a multi-receptive-field non-local network (MRFNLN) consisting of the multi-stream feature attention block (MSFAB) and cross non-local block (CNLB) is presented in this paper. We start with extracting richer features for dehazing. Specifically, we design a multi-stream feature extraction (MSFE) sub-block, which contains three parallel convolutions with different receptive fields (i.e., $1\times 1$, $3\times 3$, $5\times 5$) for extracting multi-scale features. Following MSFE, we employ an attention sub-block to make the model adaptively focus on important channels/regions. The MSFE and attention sub-blocks constitute our MSFAB. Then, we design a cross non-local block (CNLB), which can capture long-range dependencies beyond the query. Instead of the same input source of query branch, the key and value branches are enhanced by fusing more preceding features. CNLB is computation-friendly by leveraging a spatial pyramid down-sampling (SPDS) strategy to reduce the computation and memory consumption without sacrificing the performance. Last but not least, a novel detail-focused contrastive regularization (DFCR) is presented by emphasizing the low-level details and ignoring the high-level semantic information in the representation space. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MRFNLN model outperforms recent state-of-the-art dehazing methods with less than 1.5 Million parameters.
最近,基于深度学习的方法在图像去雾领域占据了主导地位。尽管利用复杂模型取得了非常有竞争力的去雾性能,但提取有用特征的有效解决方案仍受到较少的探索。此外,已经在许多视觉任务中取得突破的非局部网络尚未适当地应用于图像去雾。因此,本文提出了一种多感受野非局部网络(MRFNLN),该网络由多流特征注意力块(MSFAB)和交叉非局部块(CNLB)组成。我们从提取更丰富的去雾特征开始。具体来说,我们设计了一个多流特征提取(MSFE)子块,其中包含三个具有不同感受野(即$ 1\times 1 $、$ 3\times 3 $、$ 5\times 5 $)的并行卷积,以提取多尺度特征。在MSFE之后,我们采用注意力子块使模型自适应地关注重要的通道/区域。MSFE和注意力子块构成了我们的MSFAB。然后,我们设计了一个交叉非局部块(CNLB),它能够捕捉超越查询的长程依赖关系。与查询分支的相同输入源不同,键和值分支通过融合更多的先前特征来增强。CNLB通过利用空间金字塔下采样(SPDS)策略在计算上更为友好,可以在不牺牲性能的情况下减少计算和内存消耗。最后但并非最不重要的是,提出了一种新的细节聚焦对比正则化(DFCR),它通过强调低层次细节而忽视表示空间中的高级语义信息。实验结果表明,所提出的MRFNLN模型在参数少于150万个的情况下,优于最新的先进去雾方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to the IEEE Journal for possible publication
Summary
本文提出了一种多感受野非局部网络(MRFNLN),包含多流特征注意块(MSFAB)和交叉非局部块(CNLB)。旨在图像去雾领域提取更丰富特征,通过多流特征提取子块(MSFE)获取多尺度特征,并采用注意力子块使模型自适应关注重要通道/区域。CNLB能够捕捉超出查询的长程依赖关系,并通过融合更多前期特征来提升关键值和查询分支。利用空间金字塔下采样策略,降低计算量和内存消耗而不损失性能。最后,提出了一种新的细节聚焦对比正则化(DFCR),通过强调低层次细节而忽视高层次的语义信息在表示空间内表现良好。实验结果表明,所提出的MRFNLN模型参数少于一百万五千个,但表现优于最新的去雾方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种多感受野非局部网络(MRFNLN),结合了多流特征注意块(MSFAB)和交叉非局部块(CNLB)。
- 通过多流特征提取子块(MSFE)获取多尺度特征。
- 利用注意力子块使模型能够自适应关注重要通道和区域。
- 交叉非局部块(CNLB)能捕捉超过查询的长程依赖关系。
- 采用空间金字塔下采样策略以降低计算成本和内存消耗。
- 引入细节聚焦对比正则化(DFCR),注重低层次细节的提取。
点此查看论文截图